Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
354results about "Accessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted use" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
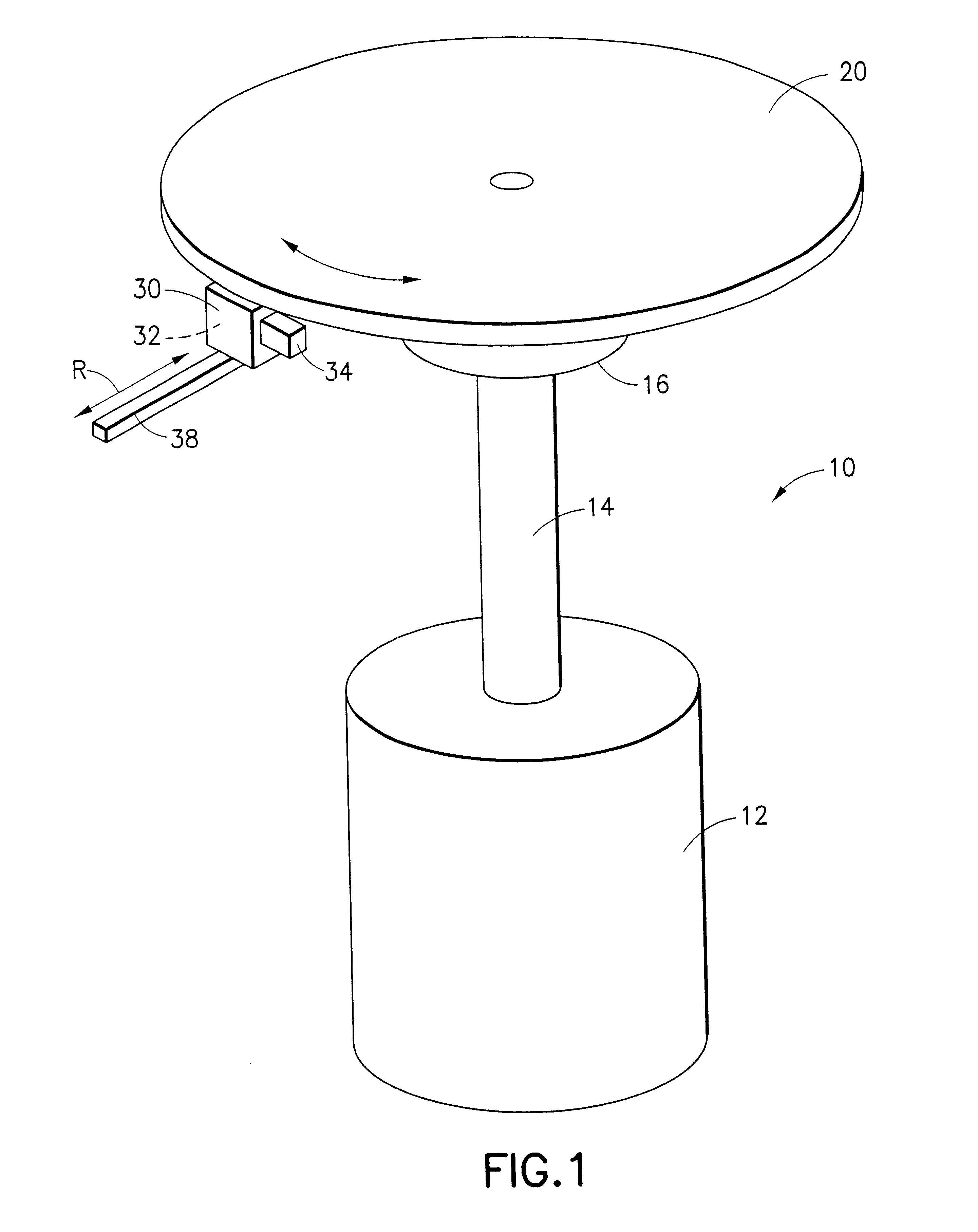
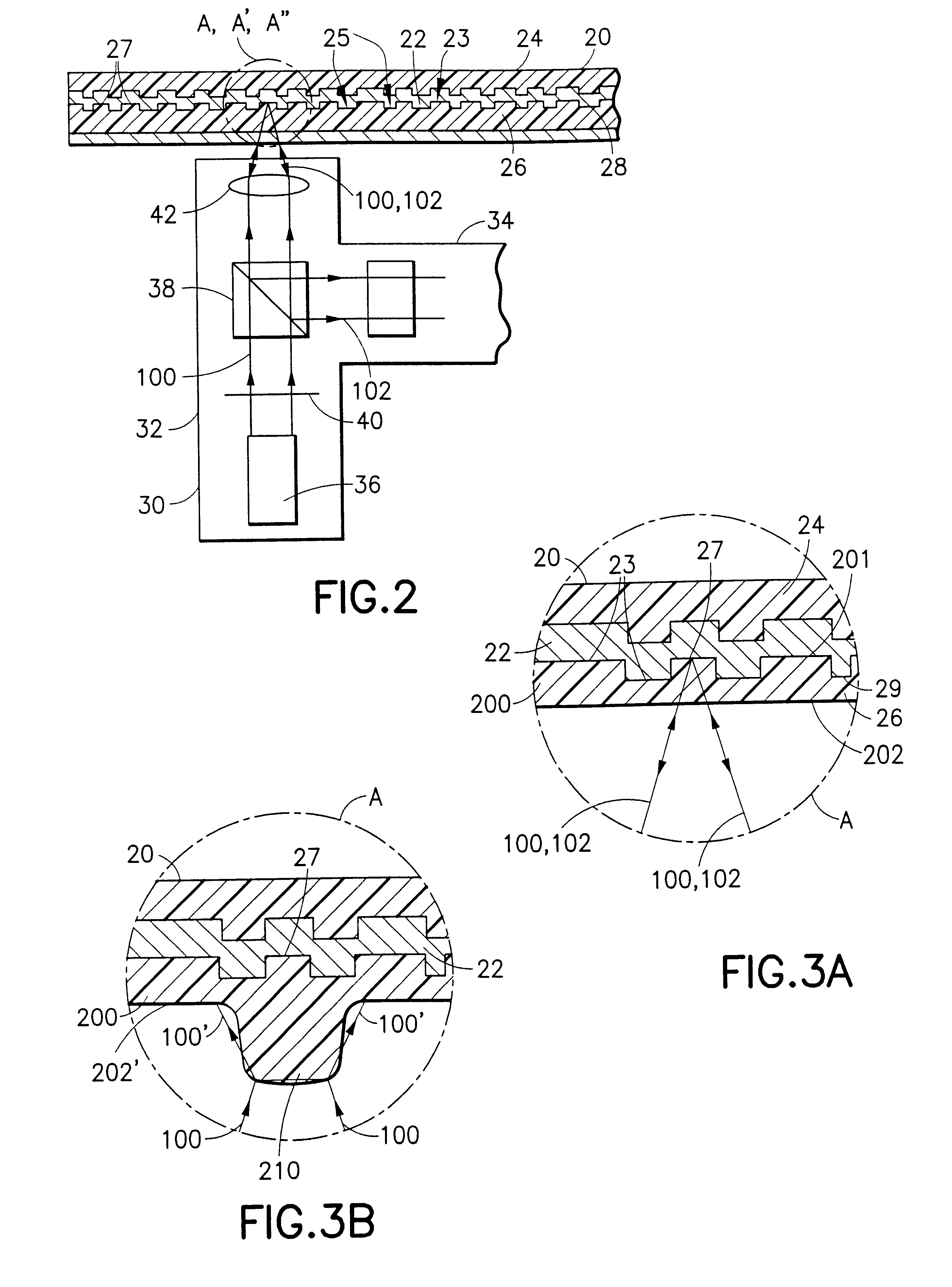
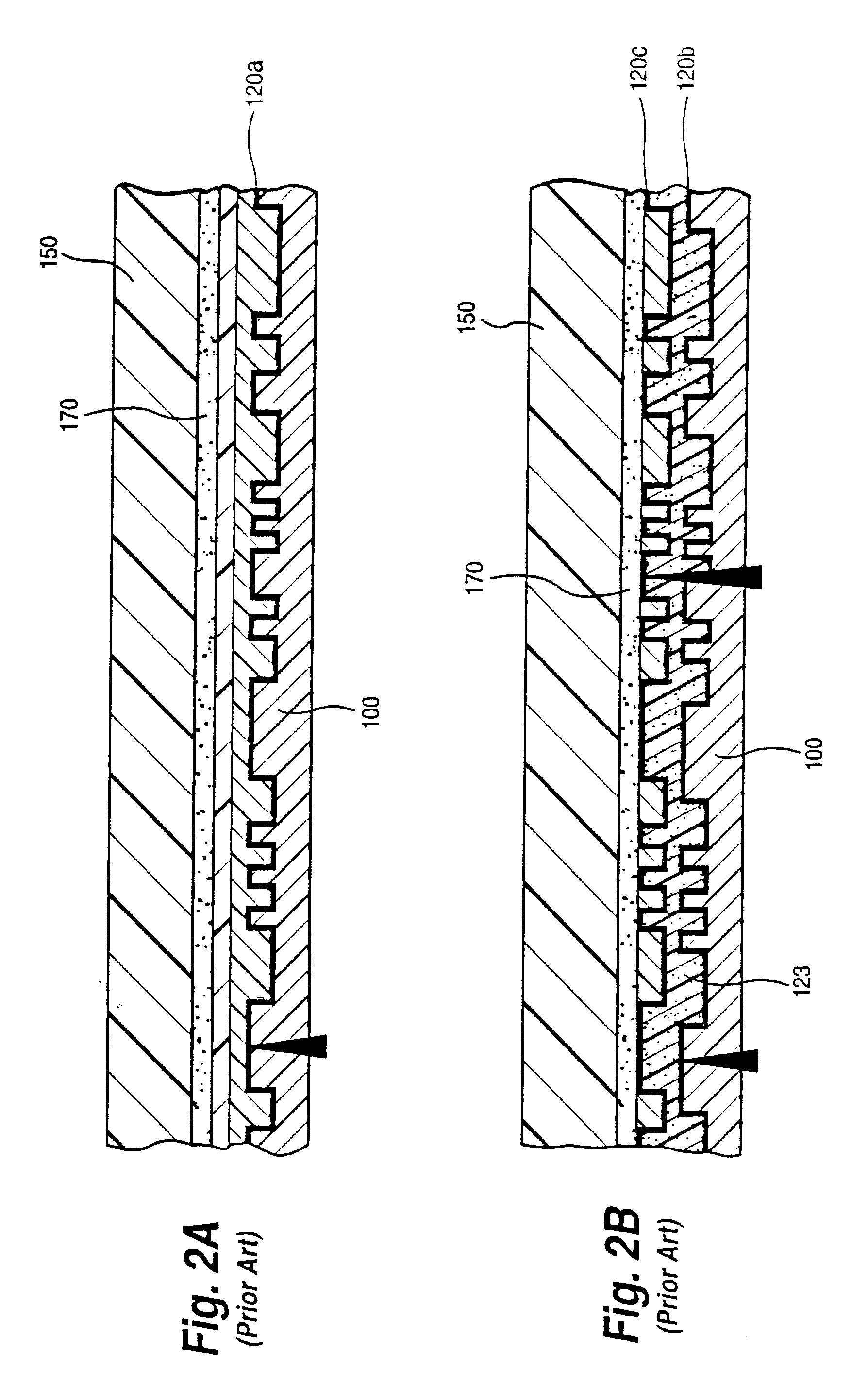
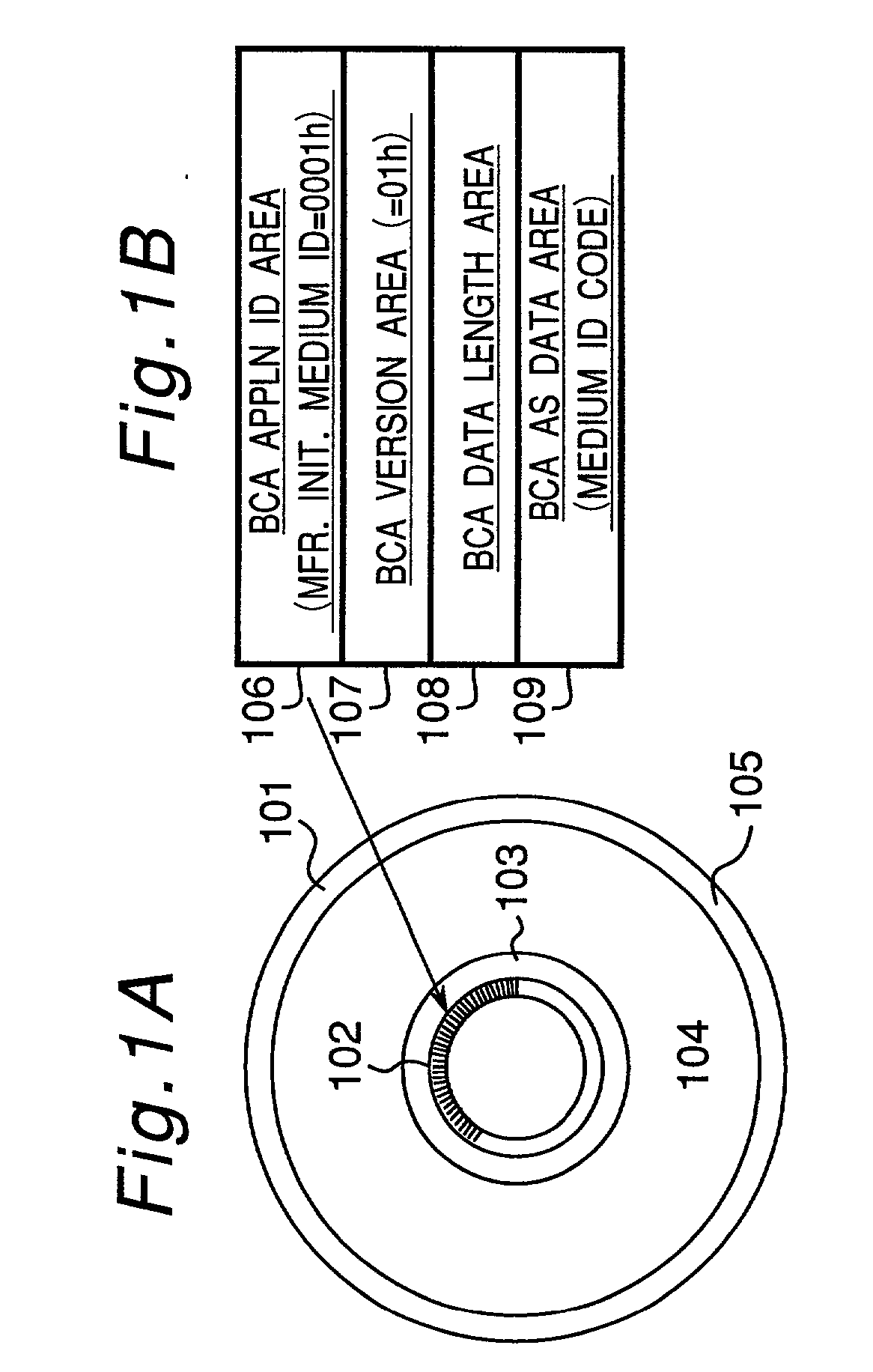
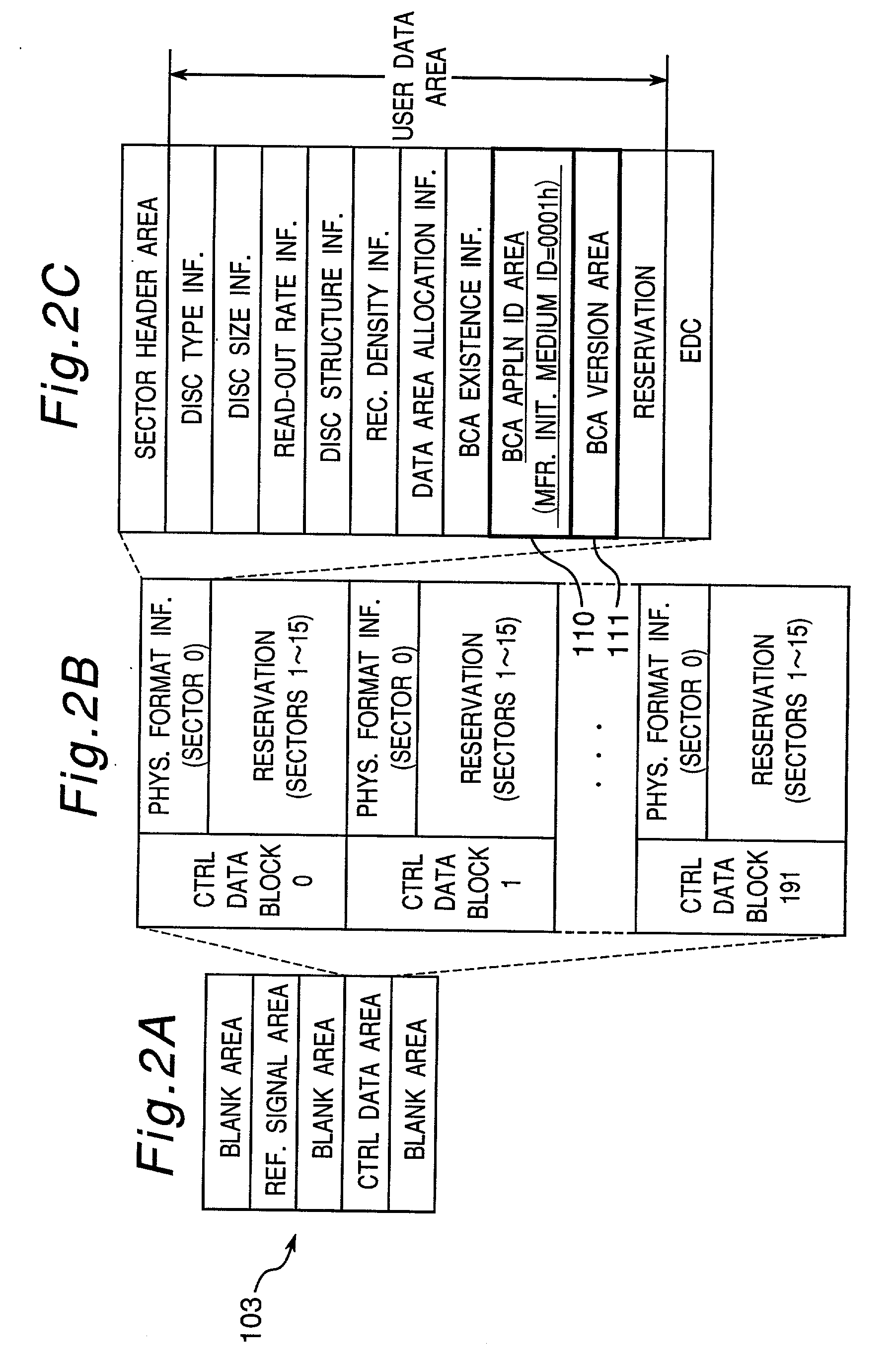
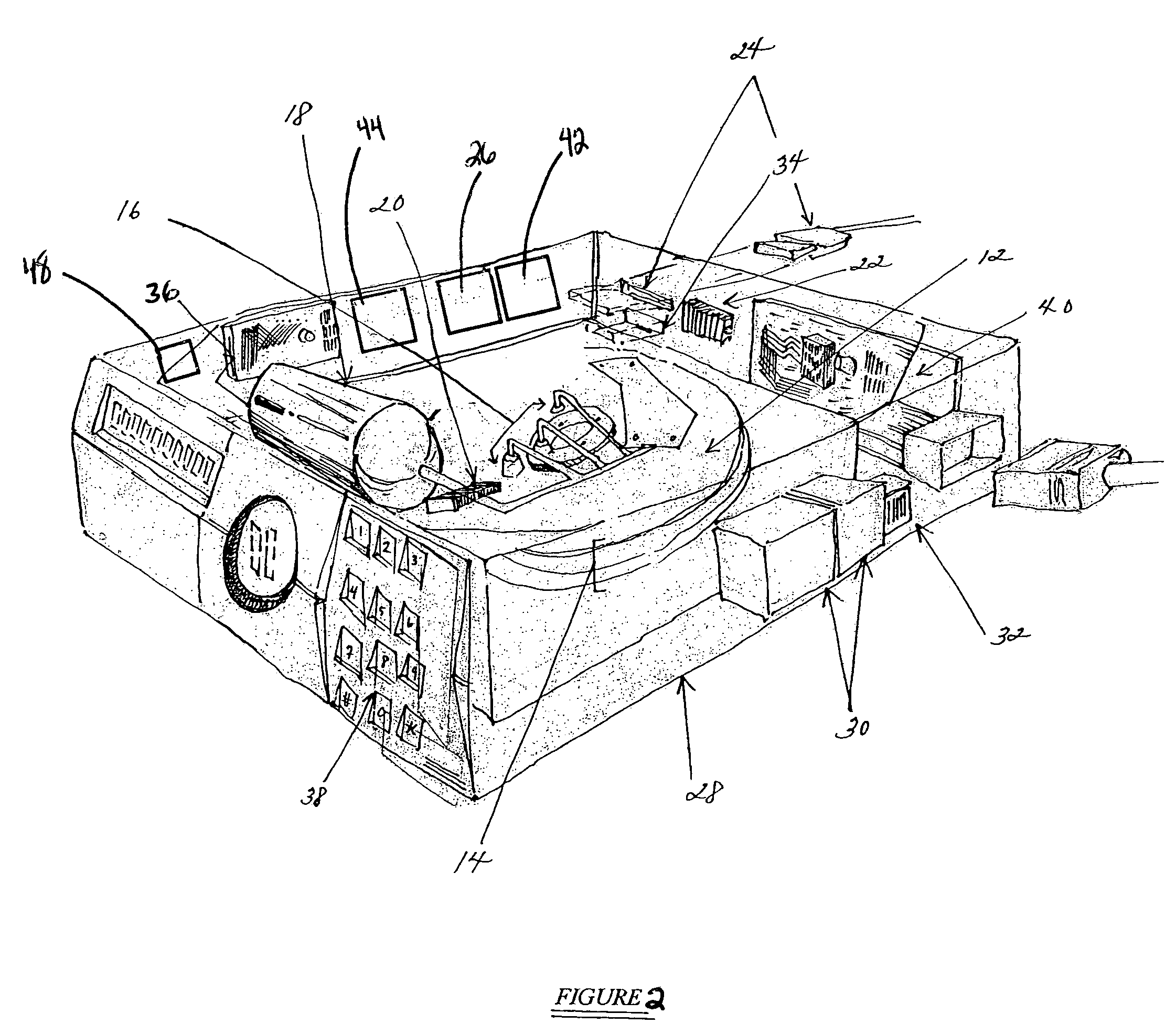
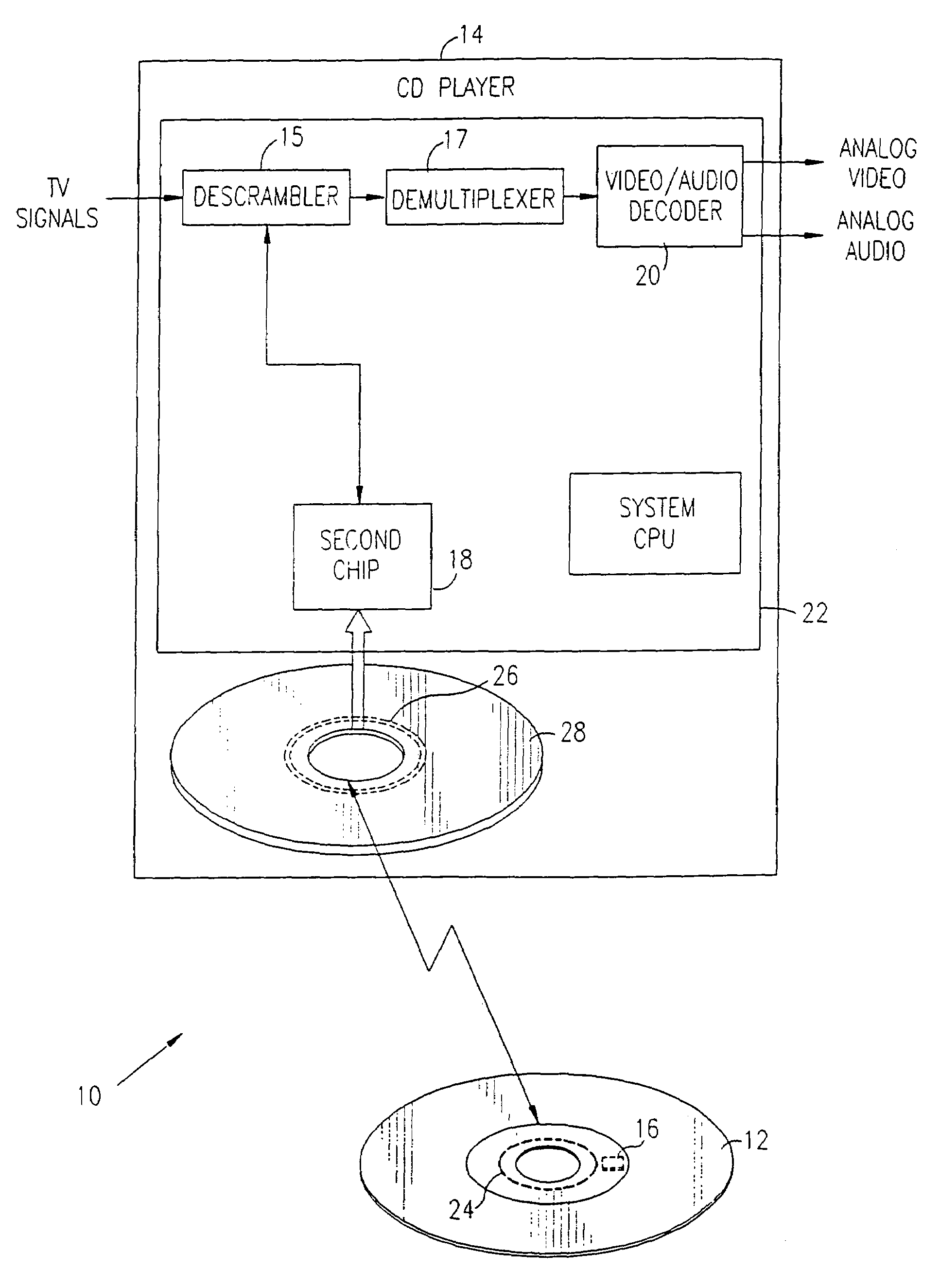
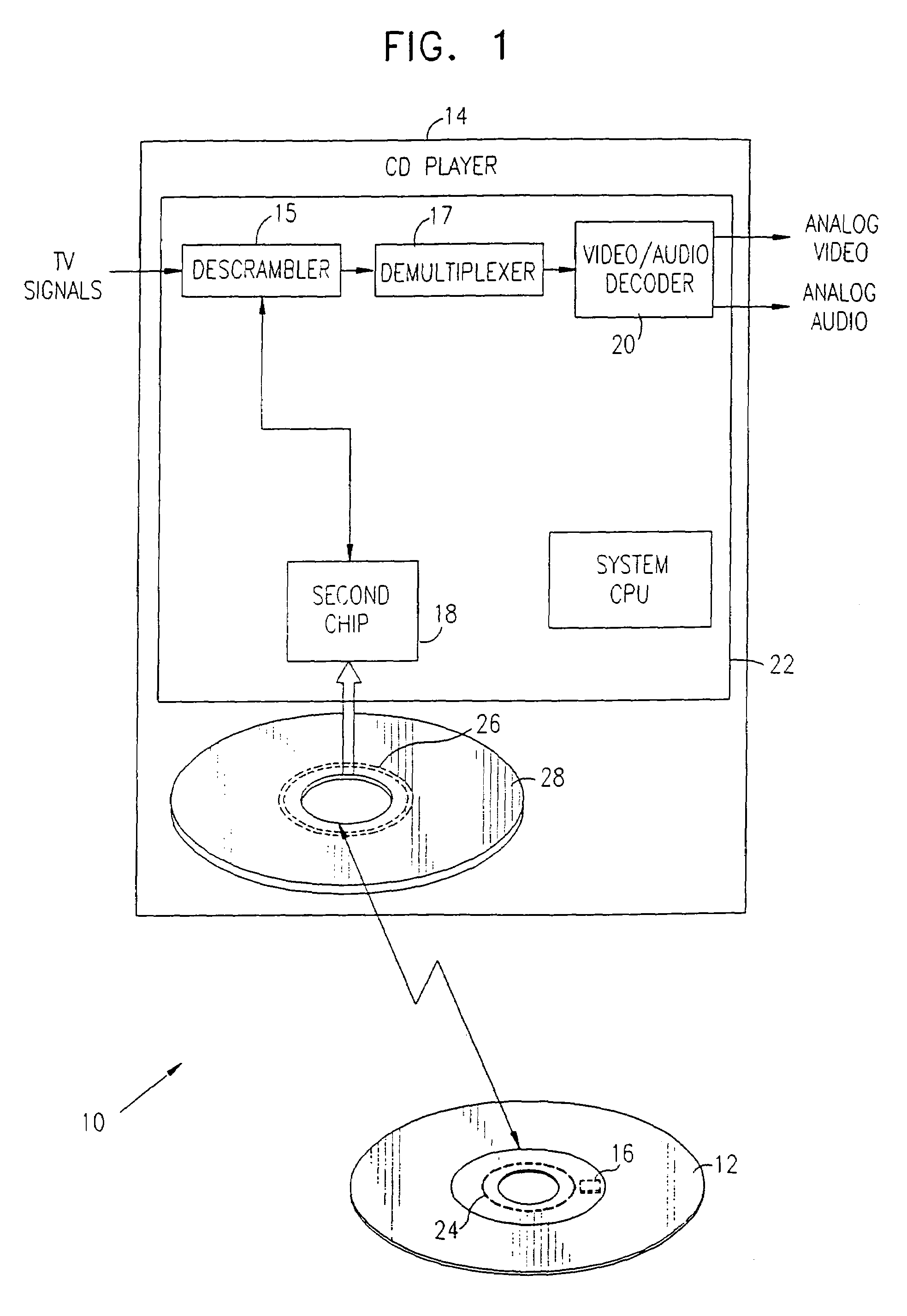
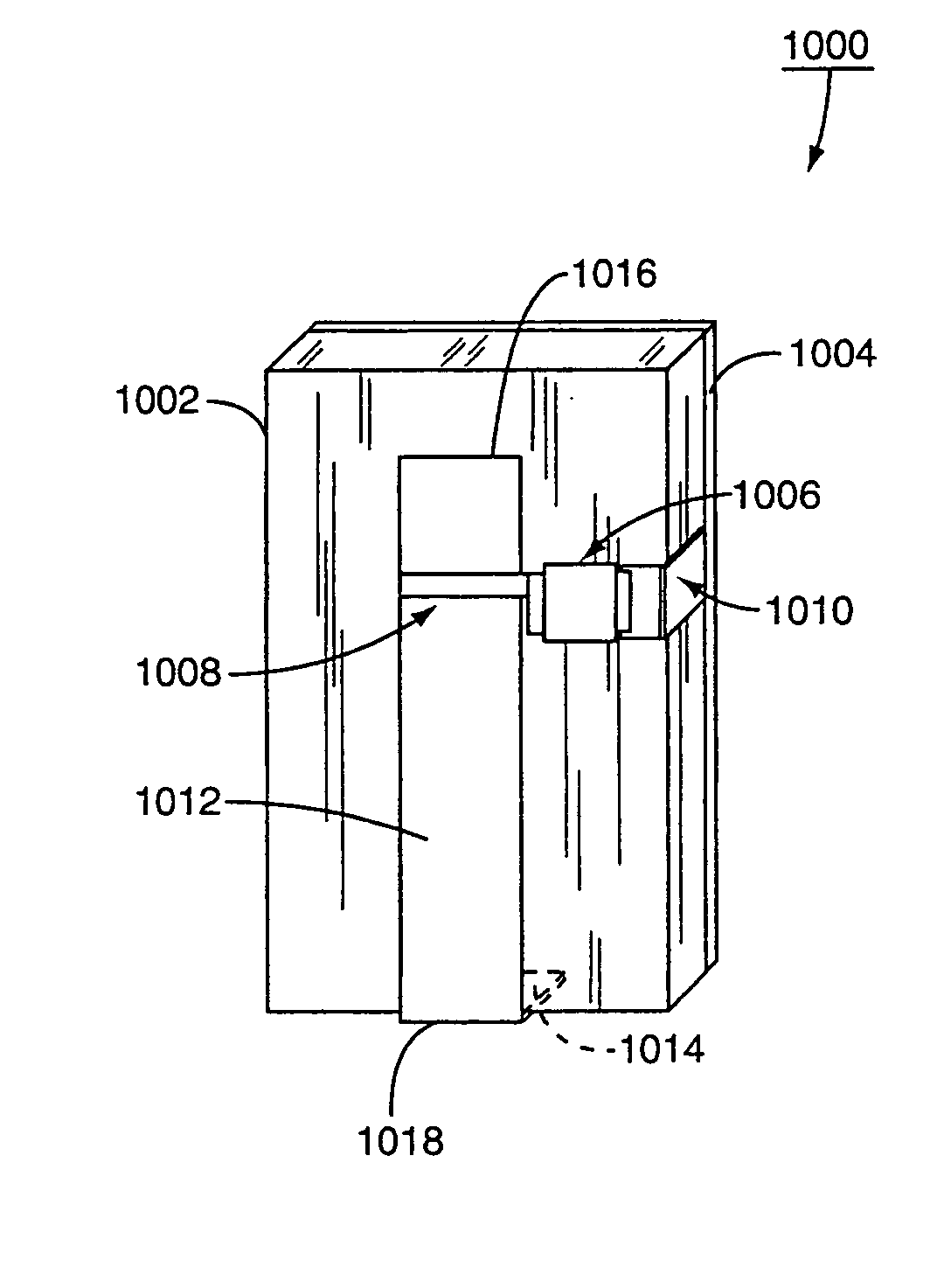
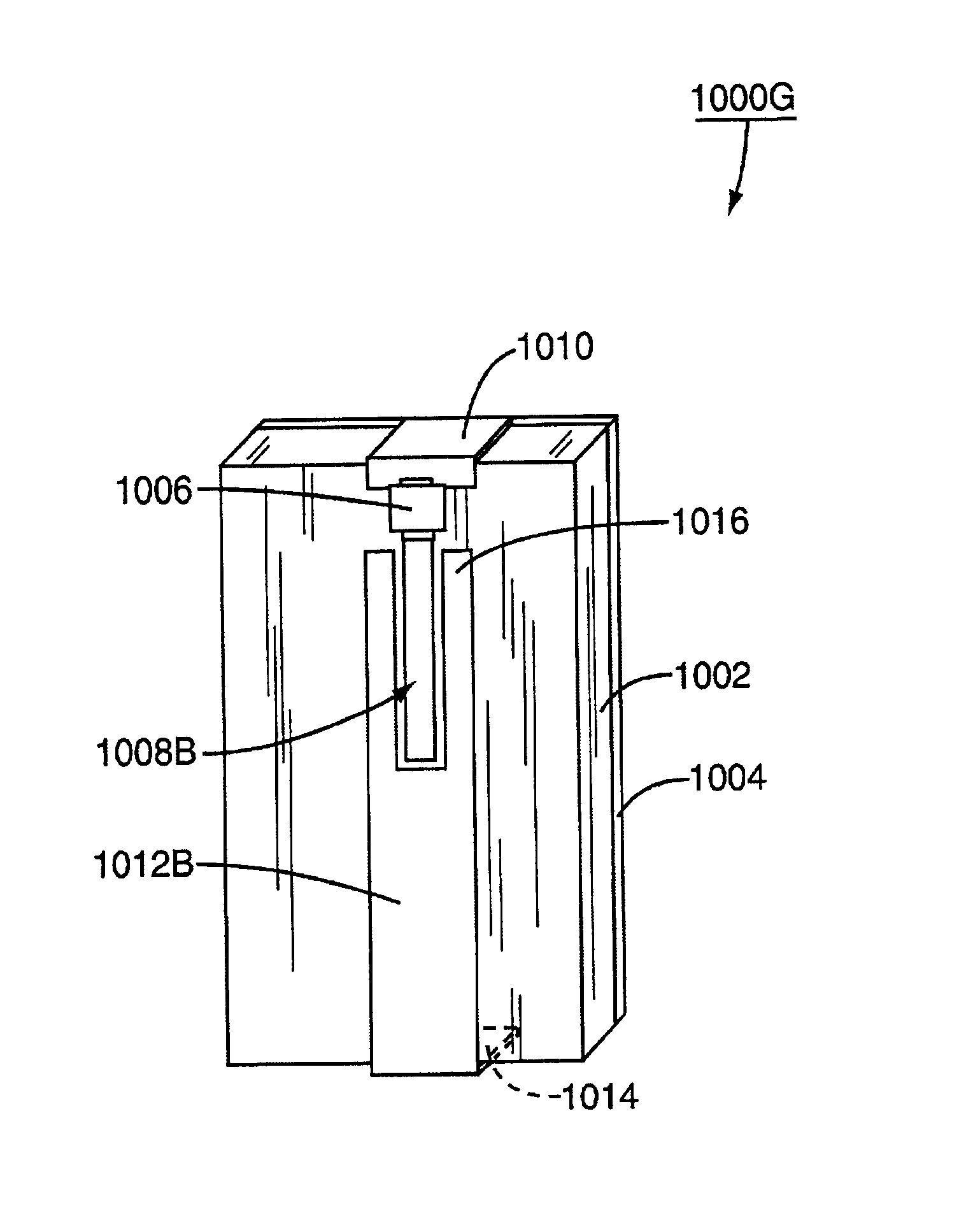
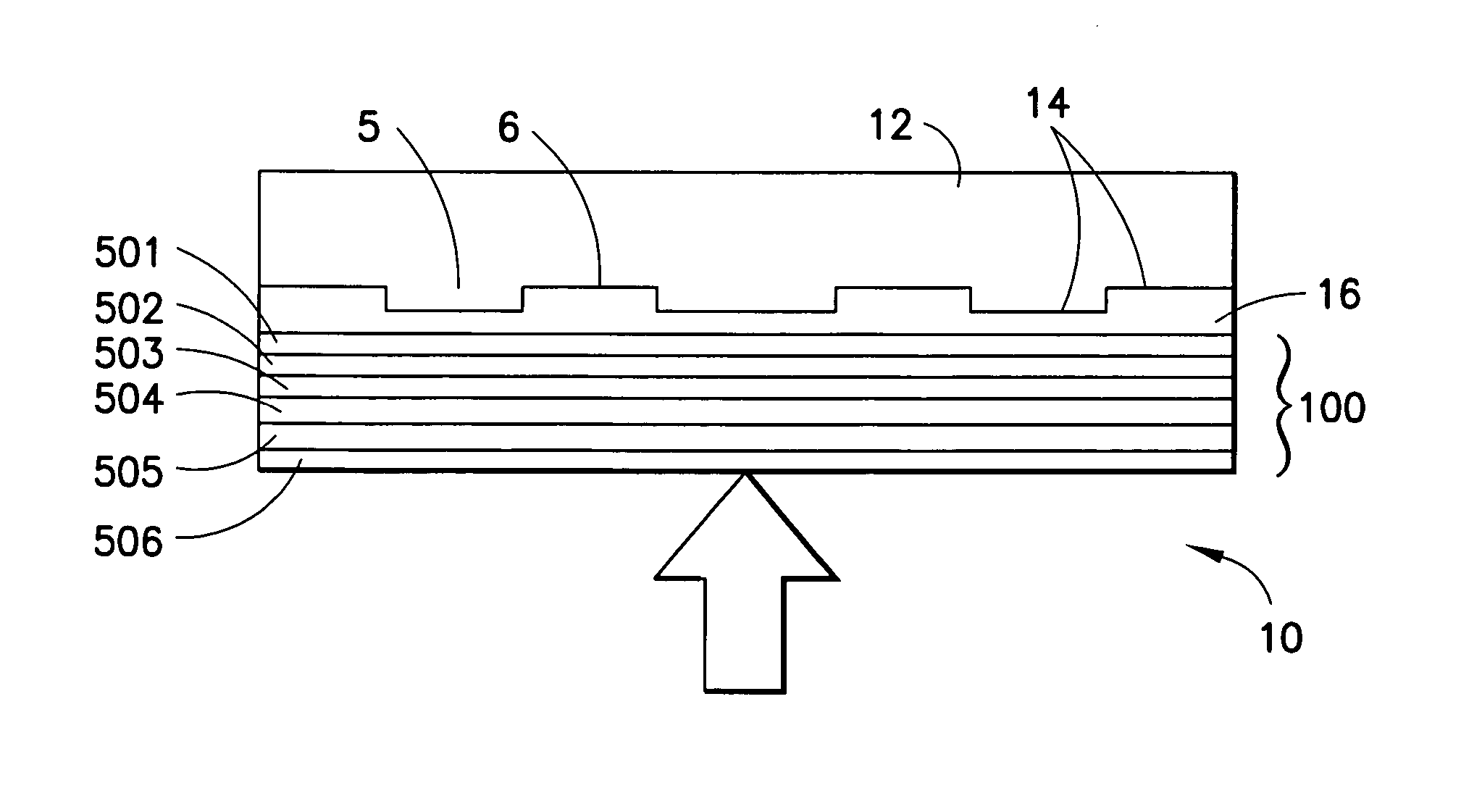
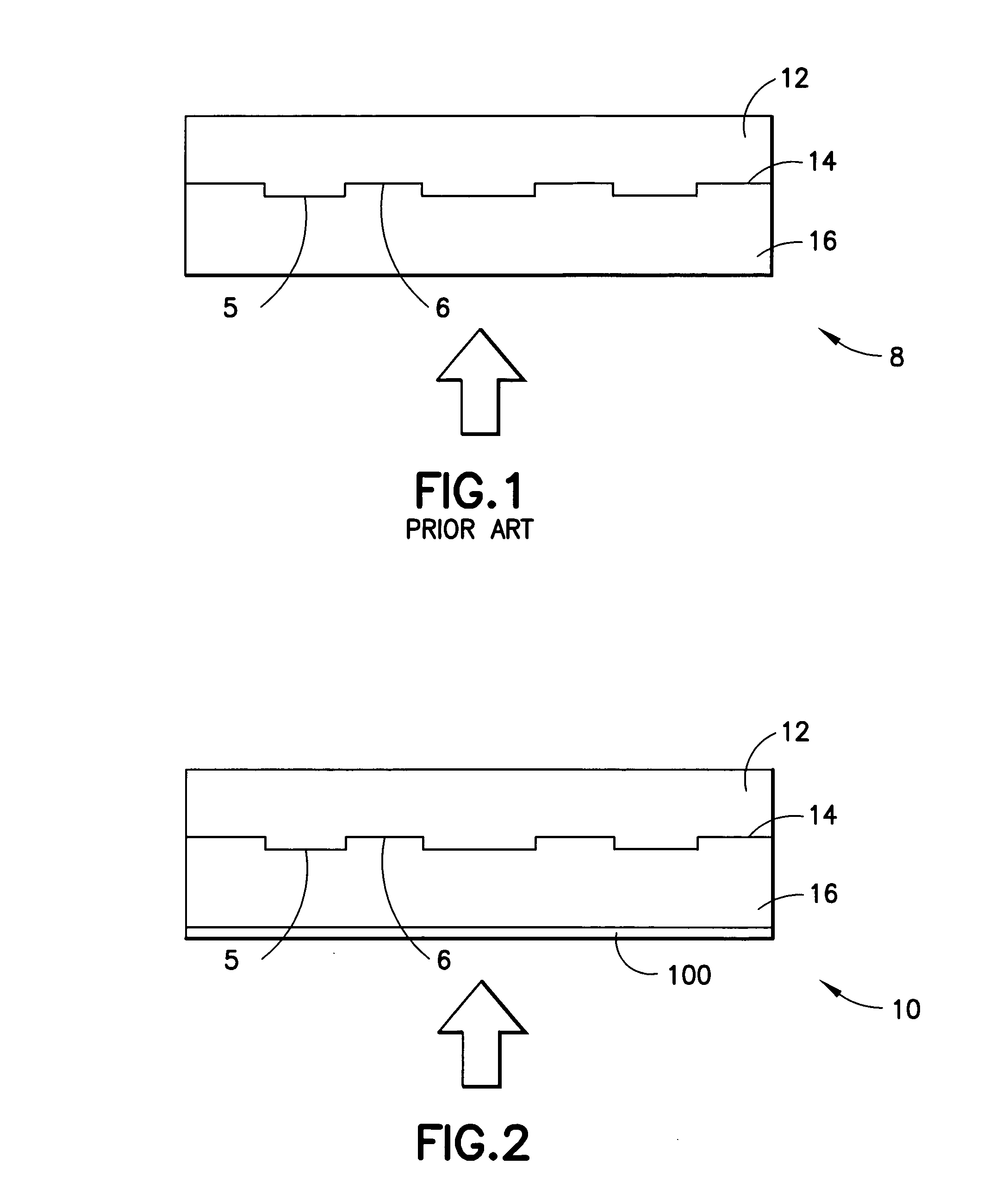
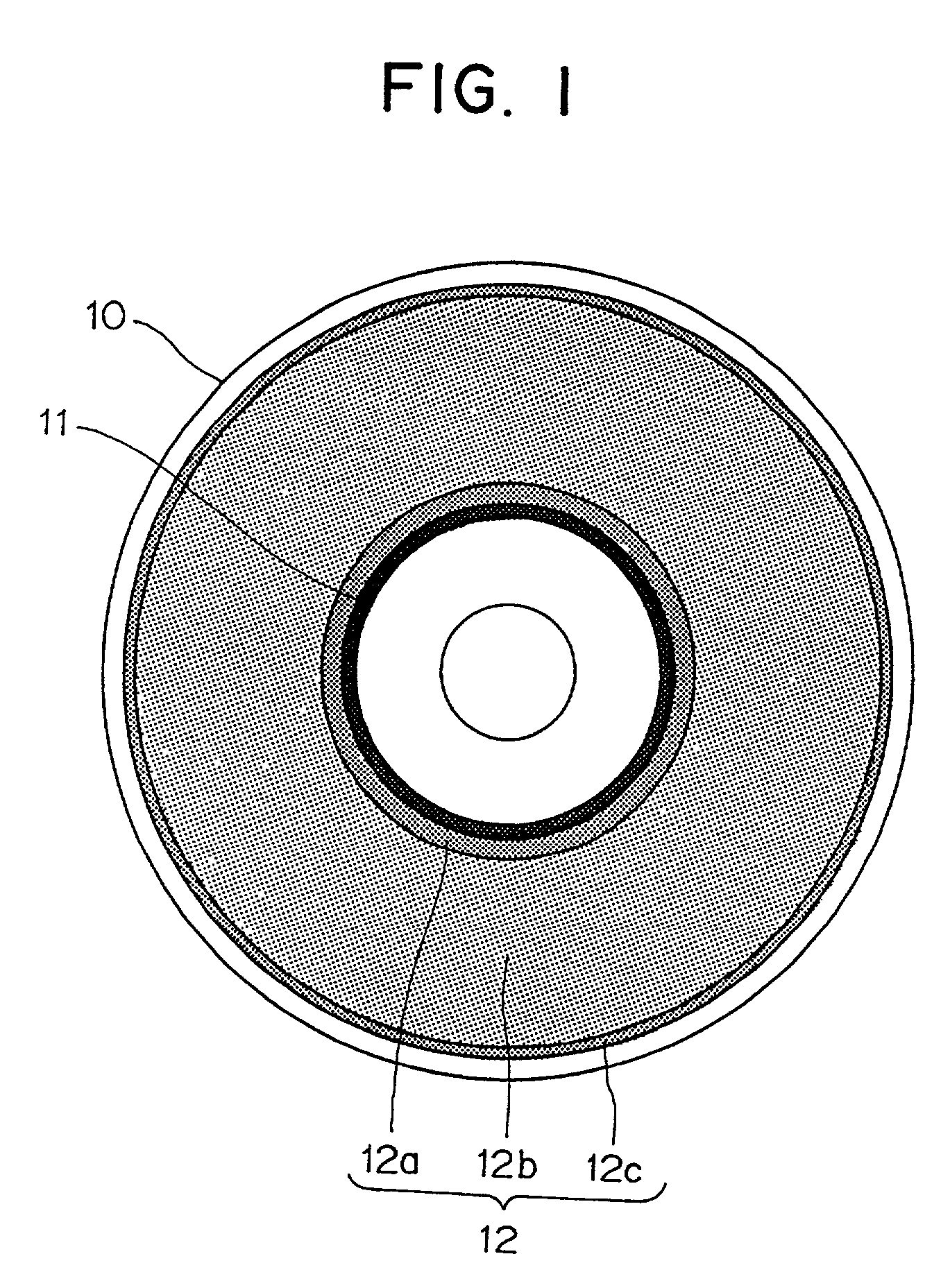
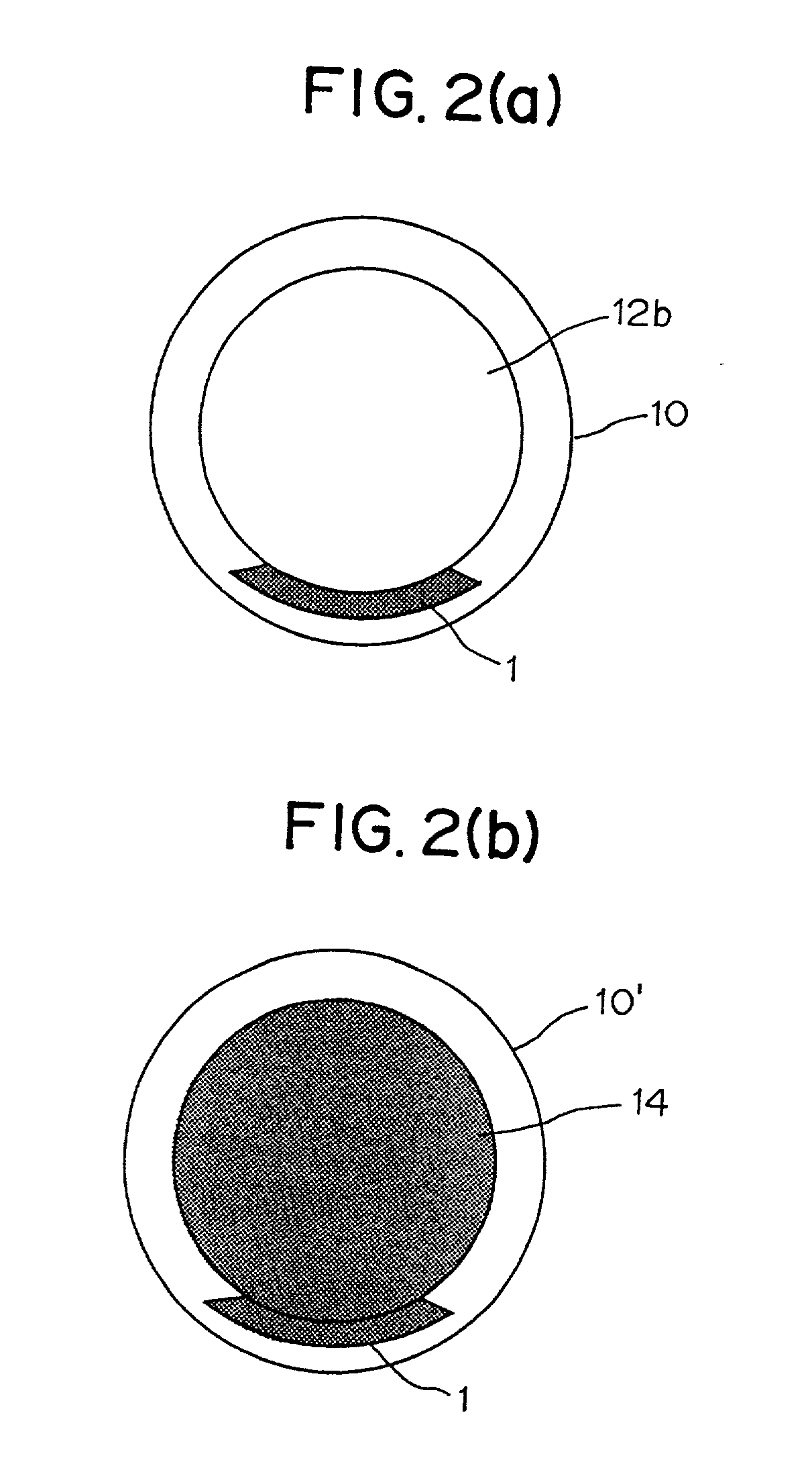
Optical disk, optical disk recording and reproducing apparatus, method for recording, reproducing and deleting data on optical disk, and information processing system
InactiveUS6938162B1Prevent unjust digital copyingImprove reliabilityAccessories for auxillary signalsAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useInformation processingHandling system
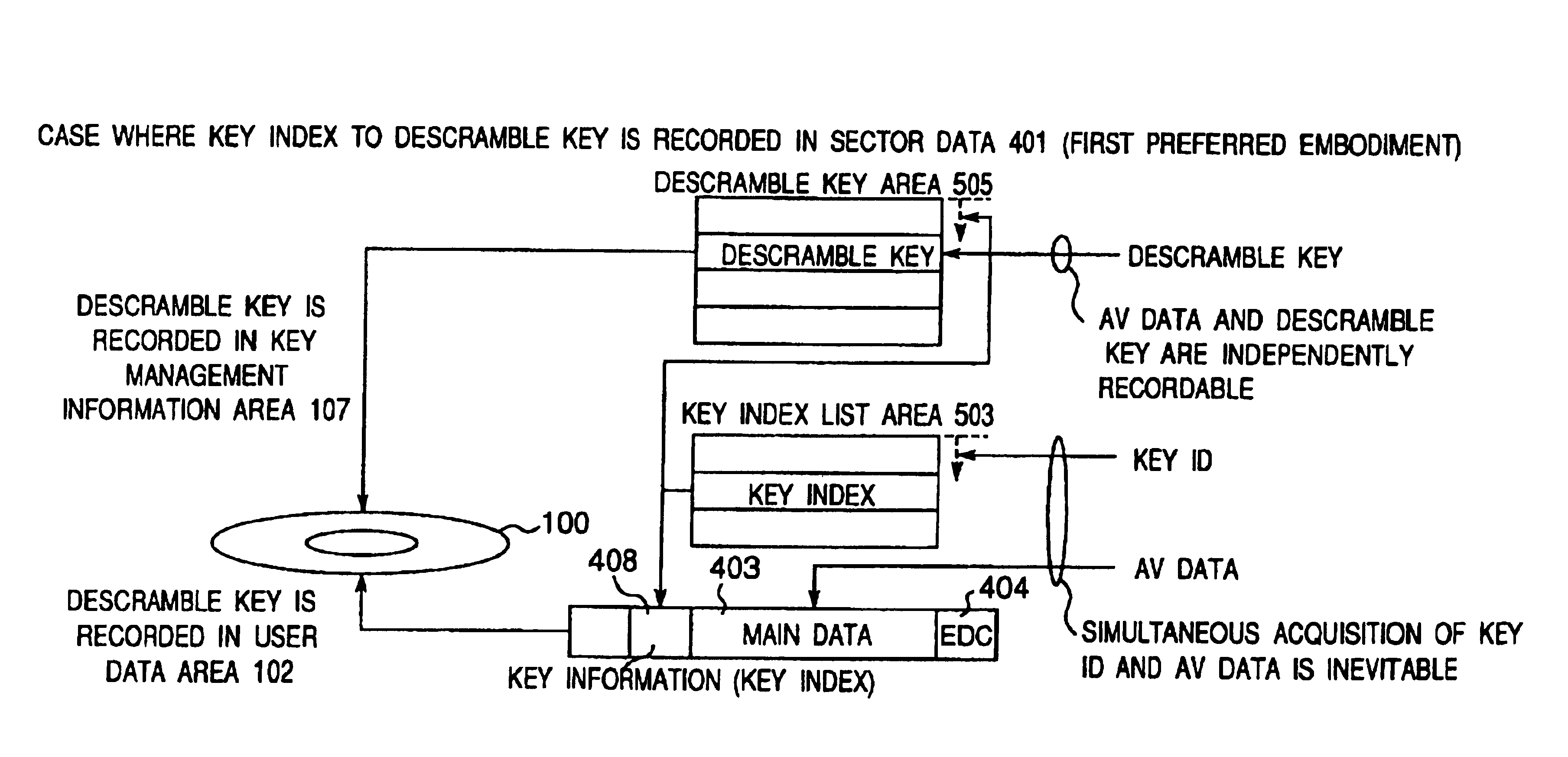
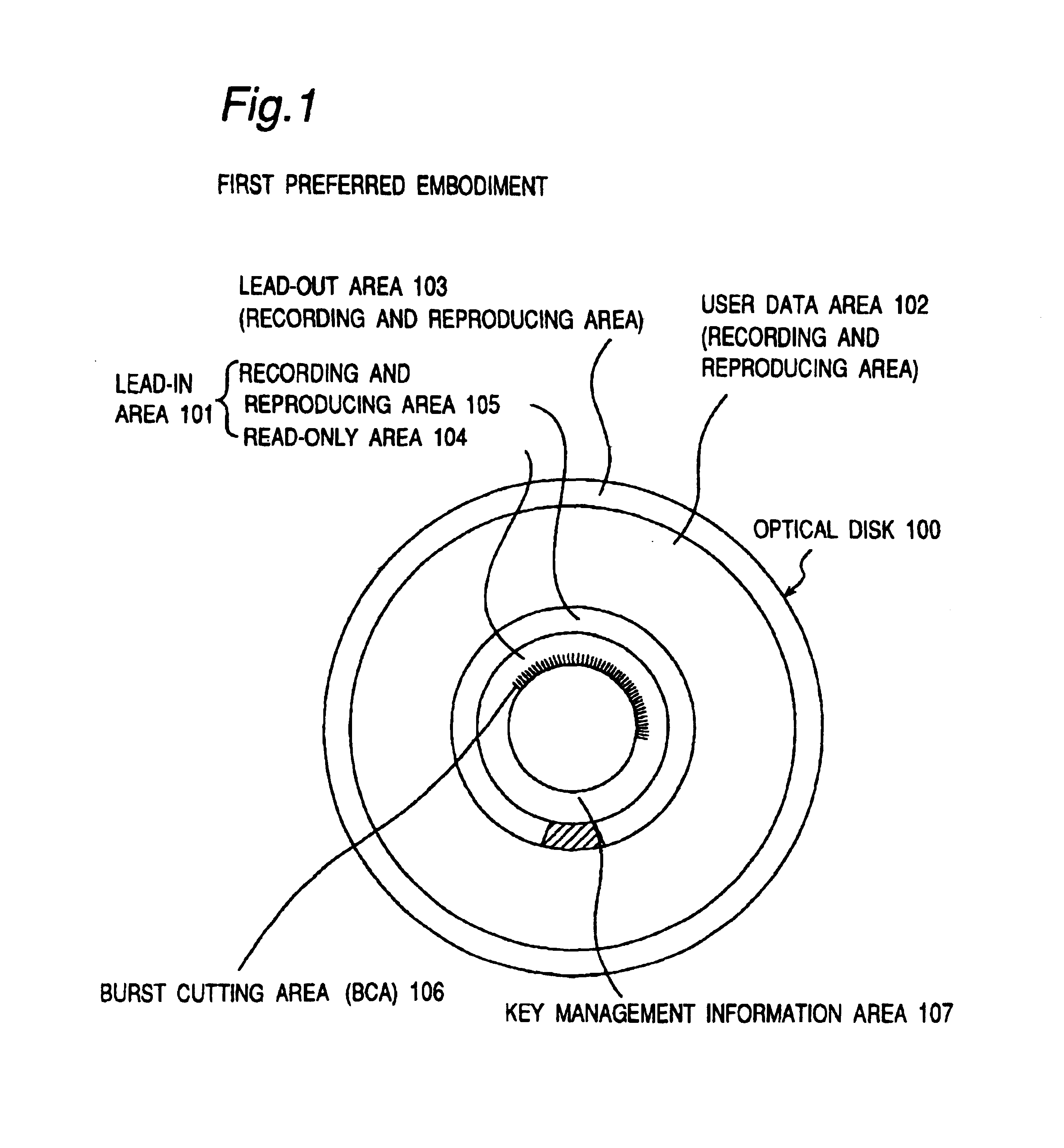
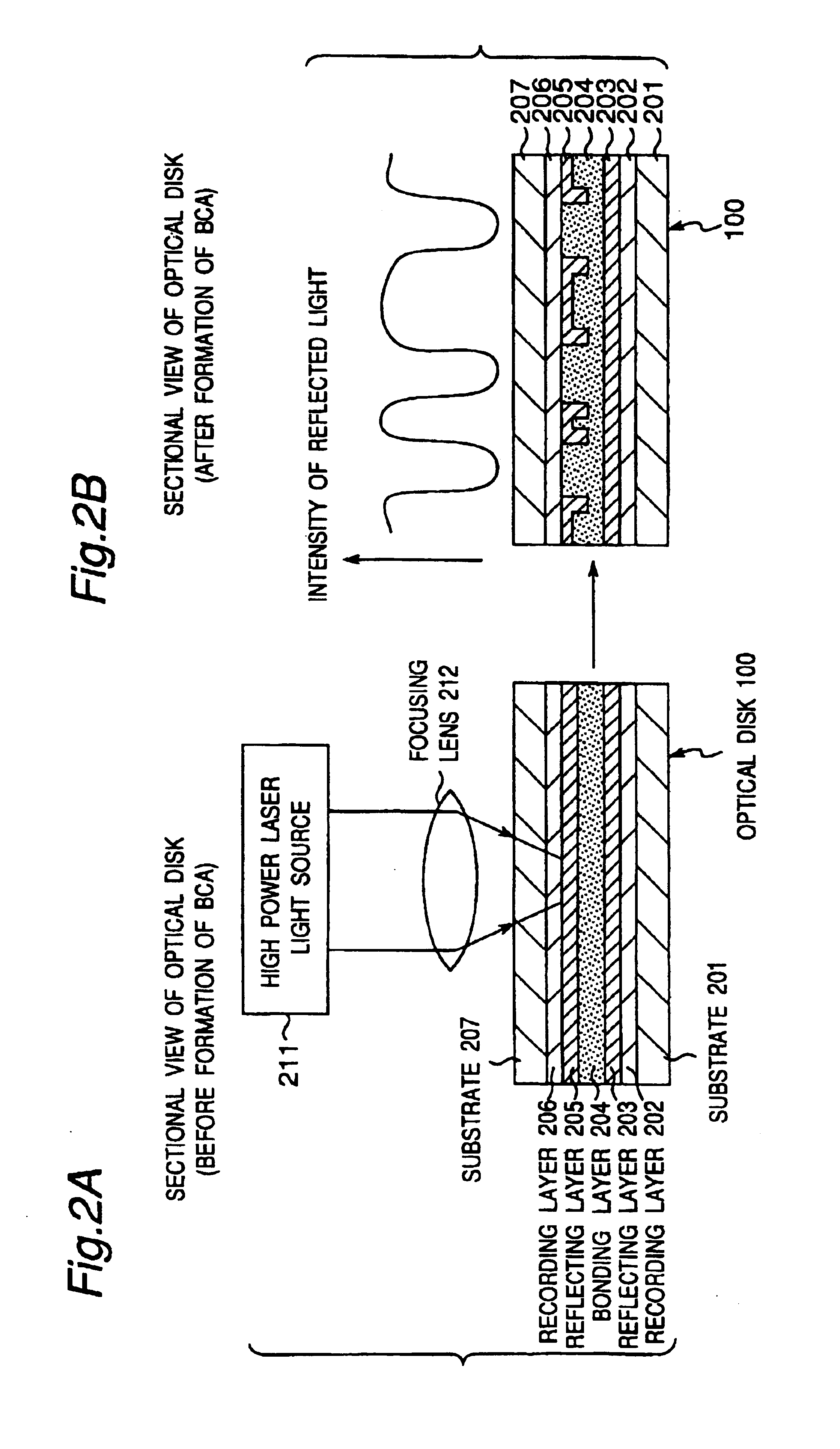
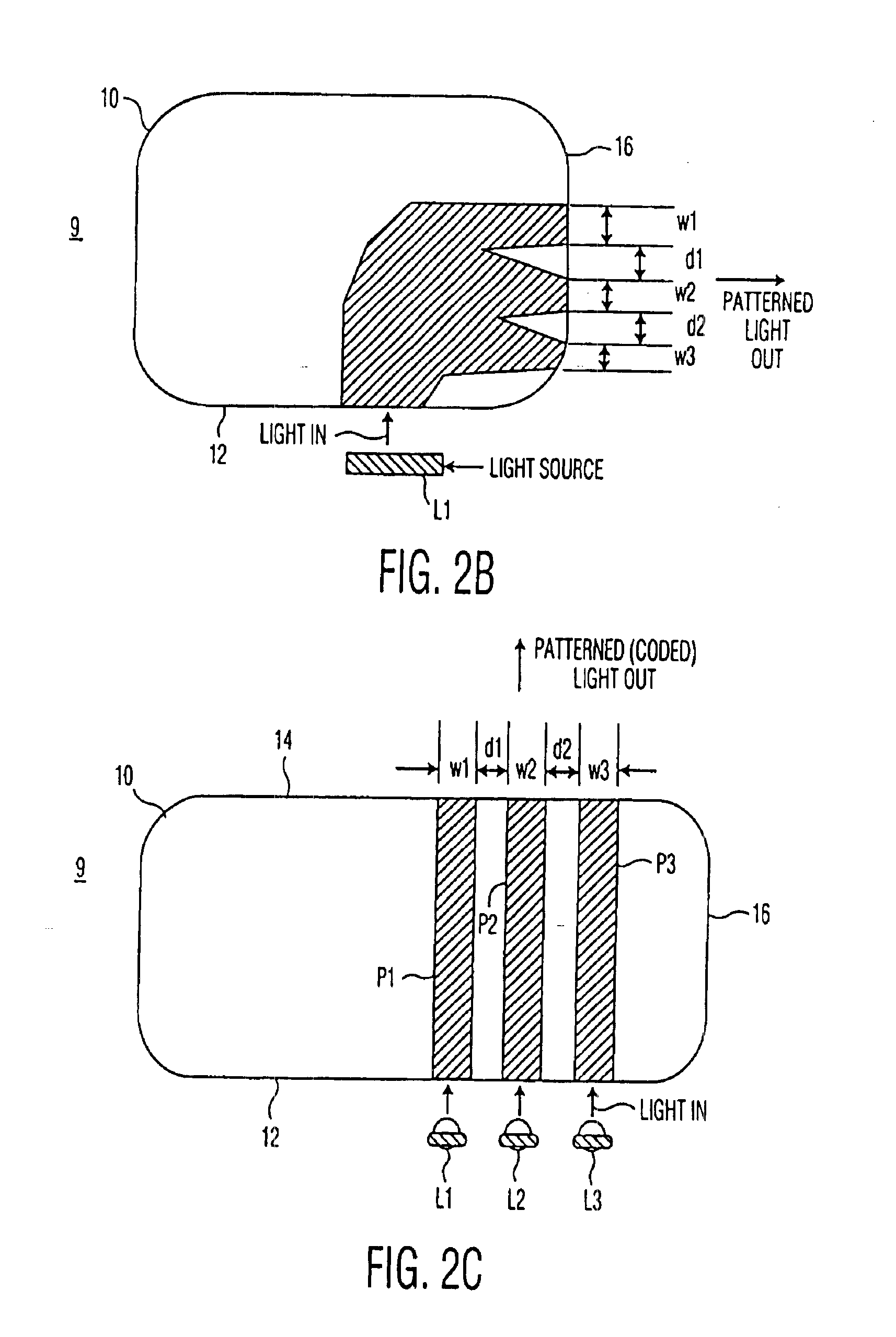
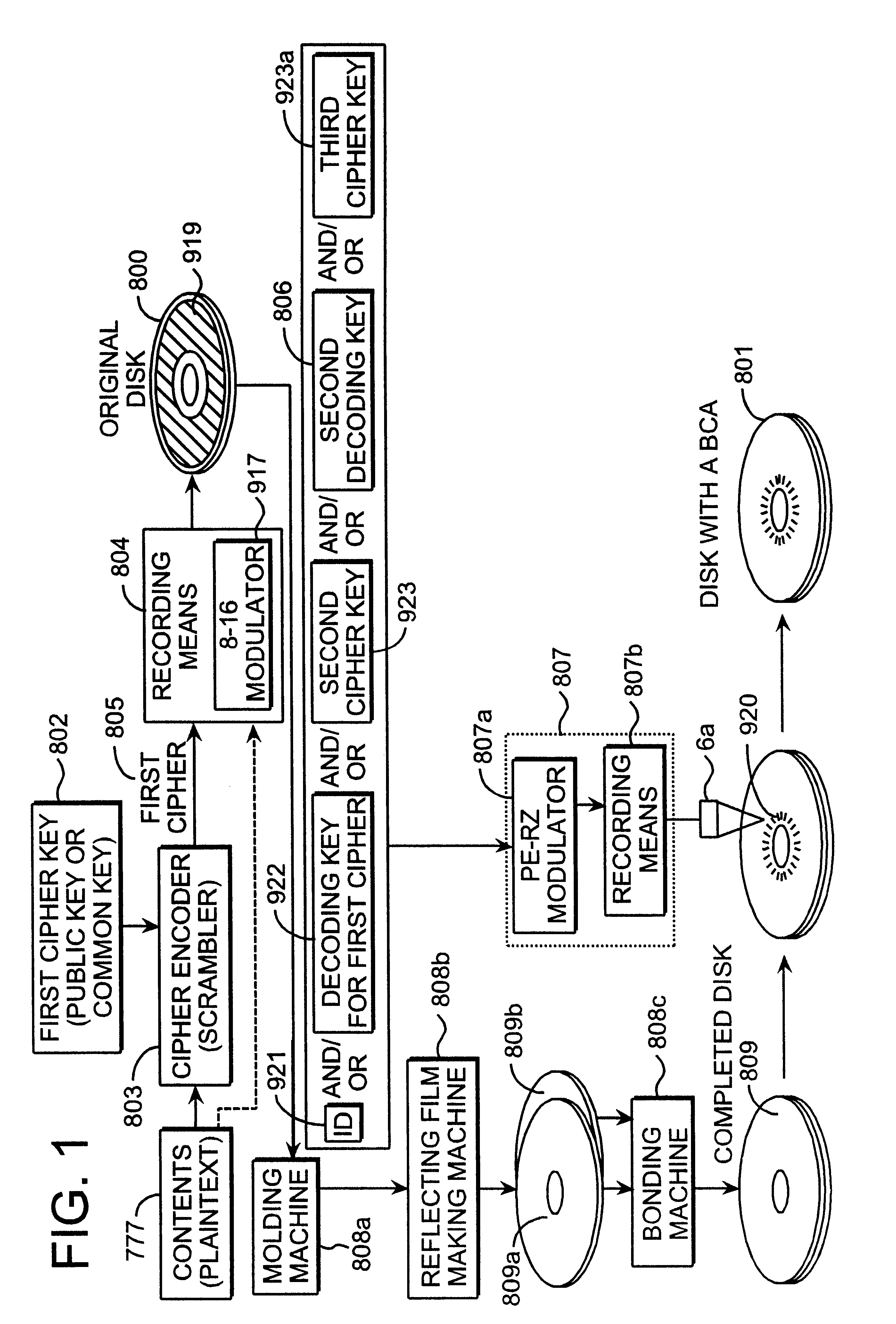
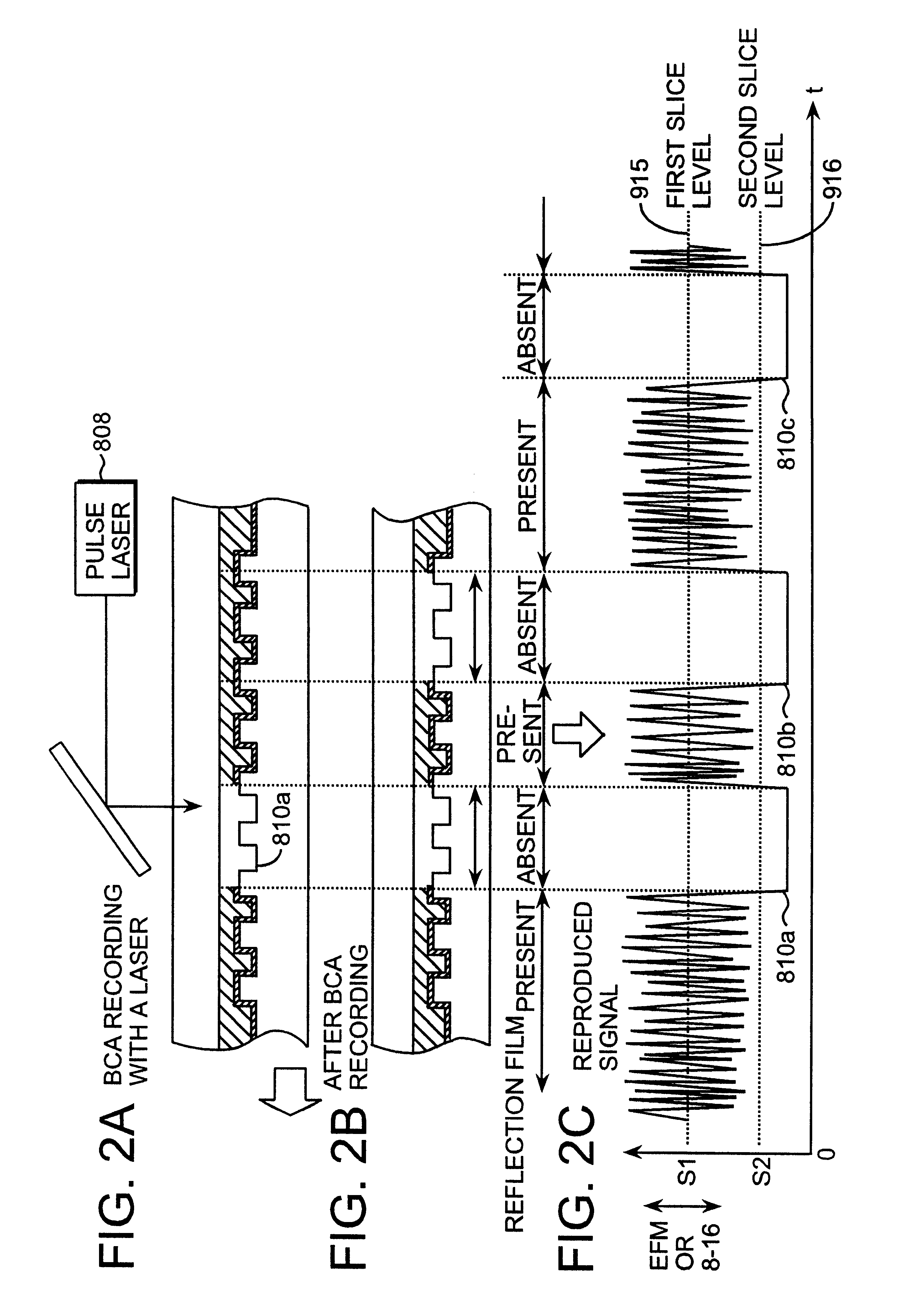
A recording type optical disk on which data is recordable includes a data recording and reproducing area for recording data therein and reproducing data therefrom, and a read-only disk identification information area for recording disk identification information for identifying the optical disk therein. In the optical disk, the disk identification information is formed by removing a reflection film that is formed on the optical disk in a strip shape. The disk identification information includes an inherent disk identifier for each optical disk, and the data recording and reproducing area includes an area for recording encrypted data therein. The encrypted data is encrypted by using information including the disk identification information for identifying the optical disk as a key.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS6338933B1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationAtmospheric air
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Method and apparatus for impeding the counterfeiting of discs
InactiveUS6902111B2Not be readily accessedIncrease probabilityAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useRecord information storageDigital videoCompact disc
One aspect of the invention includes one or more security devices embedded on one of the two surfaces, or between the two surfaces, of a compact disc (CD) or digital video disc (DVD) to impede the counterfeiting of the disc. The security devices may be, for example, holograms, optically variable devices (OVD) or RFID chips. CD / DVD is an authorized (non-pirated) version of a manufacturer's product. A system embodying the invention includes a player / reader which contains means for sensing selected characteristics of the security devices embedded on or within a CD / DVD and which is programmed to ascertain that the CD / DVD is in fact a valid document. Another aspect of the invention may include encrypting apparatus for reading / sensing selected characteristics of security device(s) and for annotating the disc and / or the security device(s) with corresponding information. Still another aspect includes a player / reader which is programmed to sense selected characteristics of security device(s) and / or to read information written back onto the disc and / or on the security device and to compare the information to ascertain the validity of the disc.
Owner:HAN WENYU +1
Method of authenticating articles, authenticatable polymers, and authenticatable articles
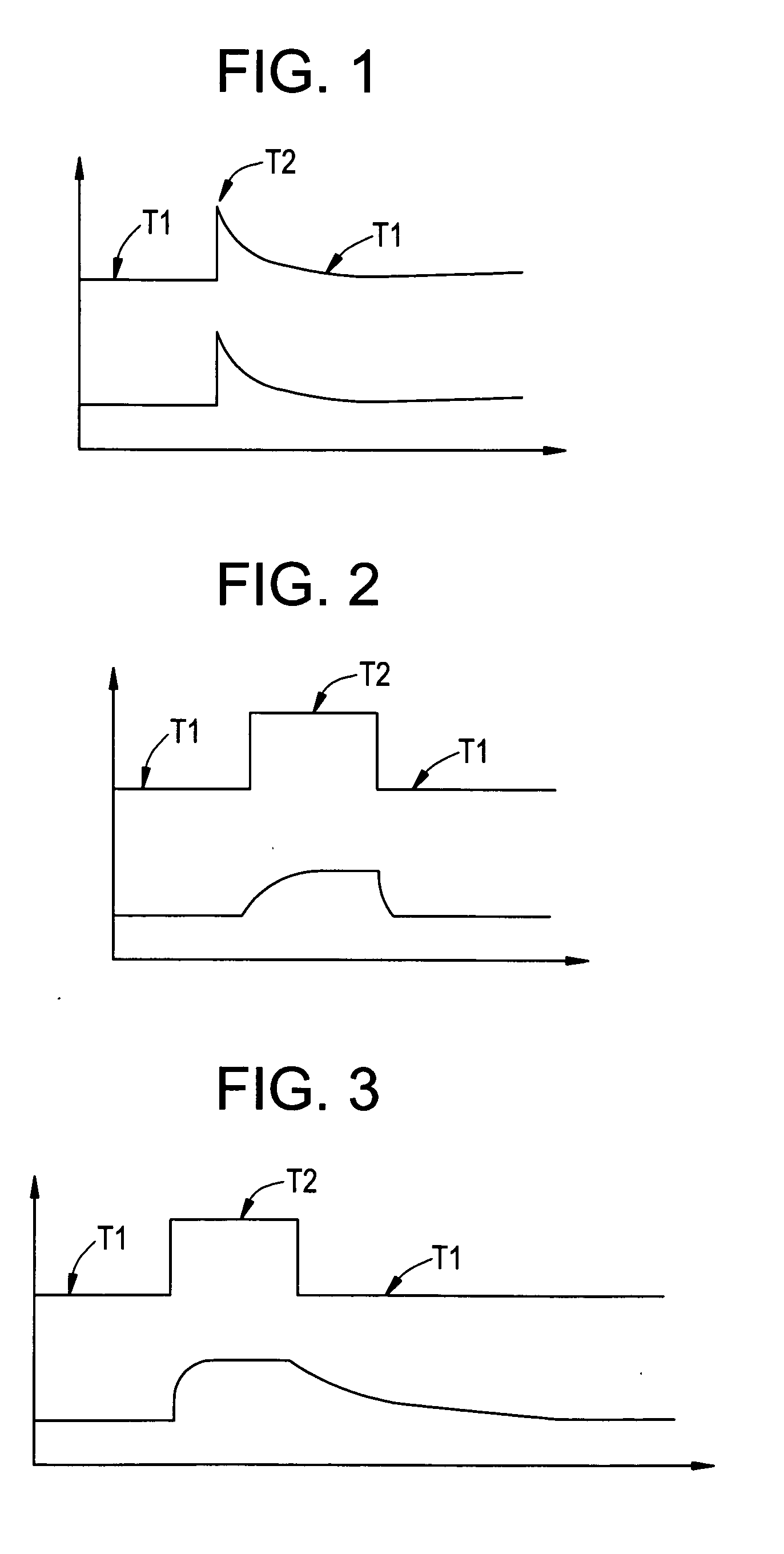
Disclosed is a method for authenticating that an article is an authenticatable article. The method uses an optical tester, the optical tester comprising an electromagnetic radiation source and a detector. The authenticatable article comprises a heat responsive compound having a temperature dependent optical interaction with the electromagnetic radiation source in the presence of a heat stimulus to produce a heat induced electromagnetic radiation signature. The method comprises placing a test portion of the article in interaction with the electromagnetic radiation source of the optical tester, creating a heated portion by exposing the test portion of the article to a heat stimulus sufficient to raise the temperature of the test portion from a temperature T1 to a temperature T2, measuring the heat induced electromagnetic radiation signature of the heated portion with the detector, and authenticating that the article is an authenticatable article if the heat induced electromagnetic radiation signature is present.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
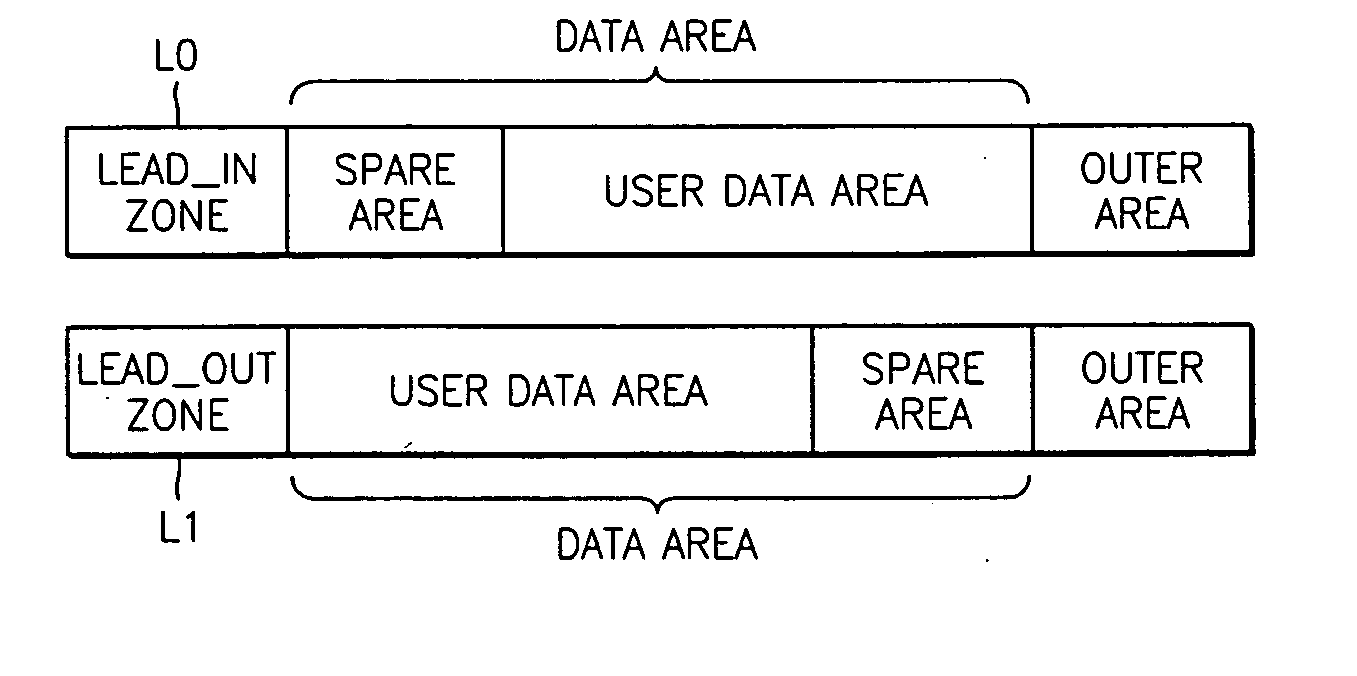
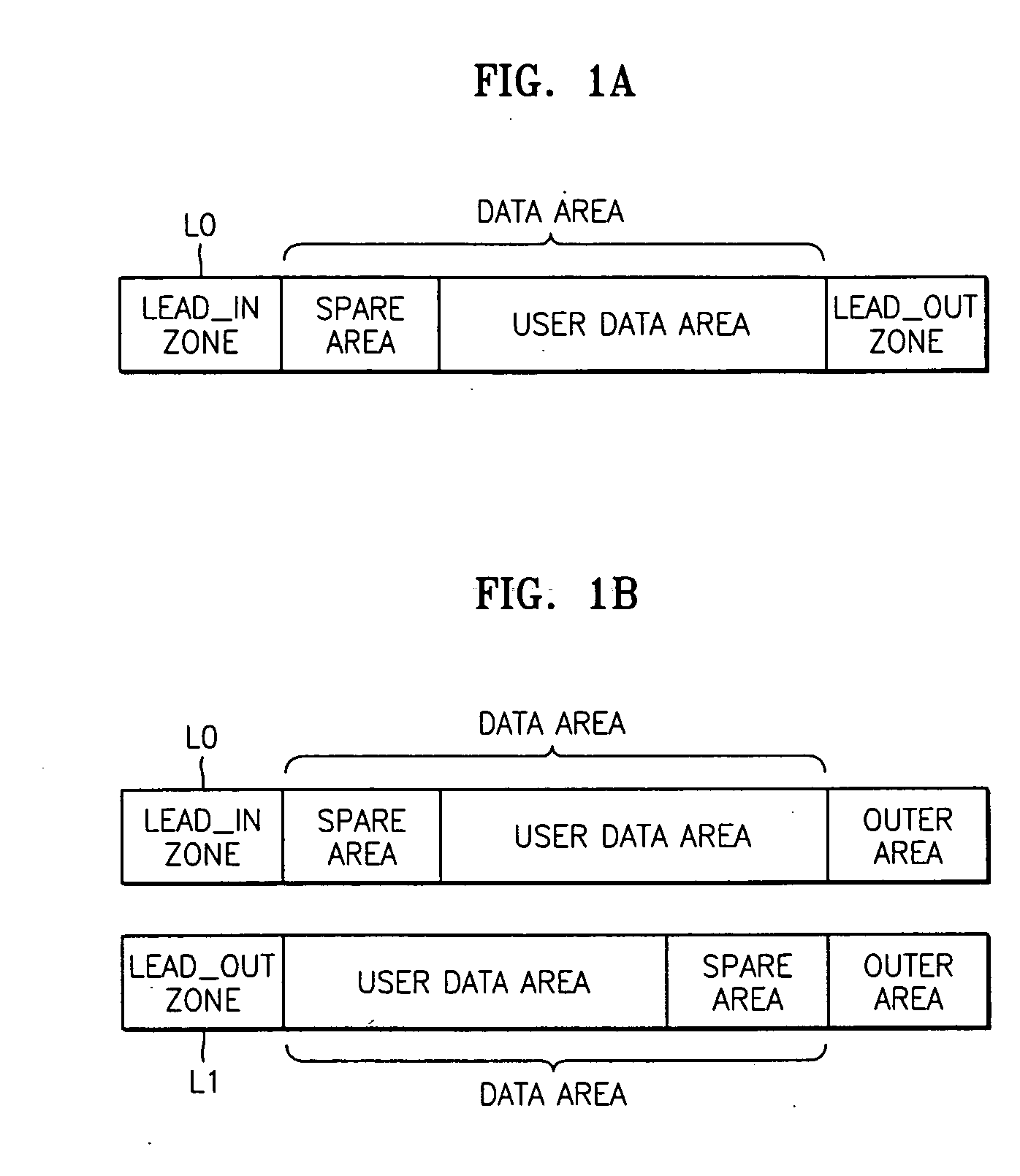
Write once disc allowing management of data area, method of managing the data area, and apparatus and method for reproducing data from write once disc
ActiveUS20040179458A1Accessories for auxillary signalsFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardware
A write once disc allowing management of a data area, a method of managing the data area of the write once disc, an apparatus recording data on the write once disc, an apparatus and method of reproducing data from a write once disc. The write once disc, includes a lead-in zone, a data area, and a lead-out zone. The write once disc includes a predetermined area storing area allocation information which indicates whether at least one section of the data area is allocated for disc defect management. In the disc and method, area allocation information specifying a structure of the data area is recorded on the disc, thus allowing a recording / reproducing apparatus to recognize the data area structure. Therefore, allocating areas, such as a spare area, for disc defect management other than an area for storing user data, to the data area is possible. The allocation of the areas for disc defect management to the data area enables effective use of the write once disc.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Limited use DVD-video disc
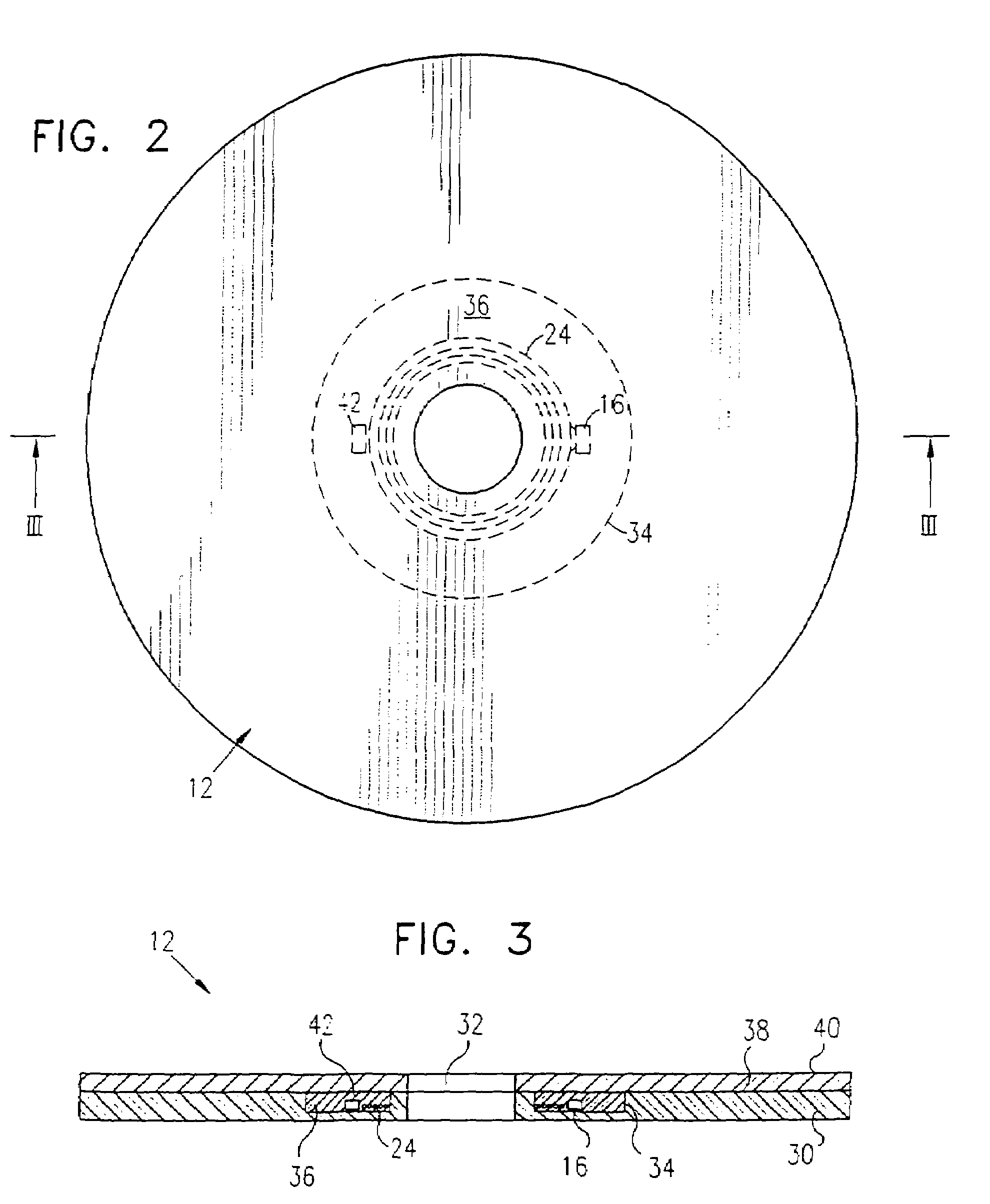
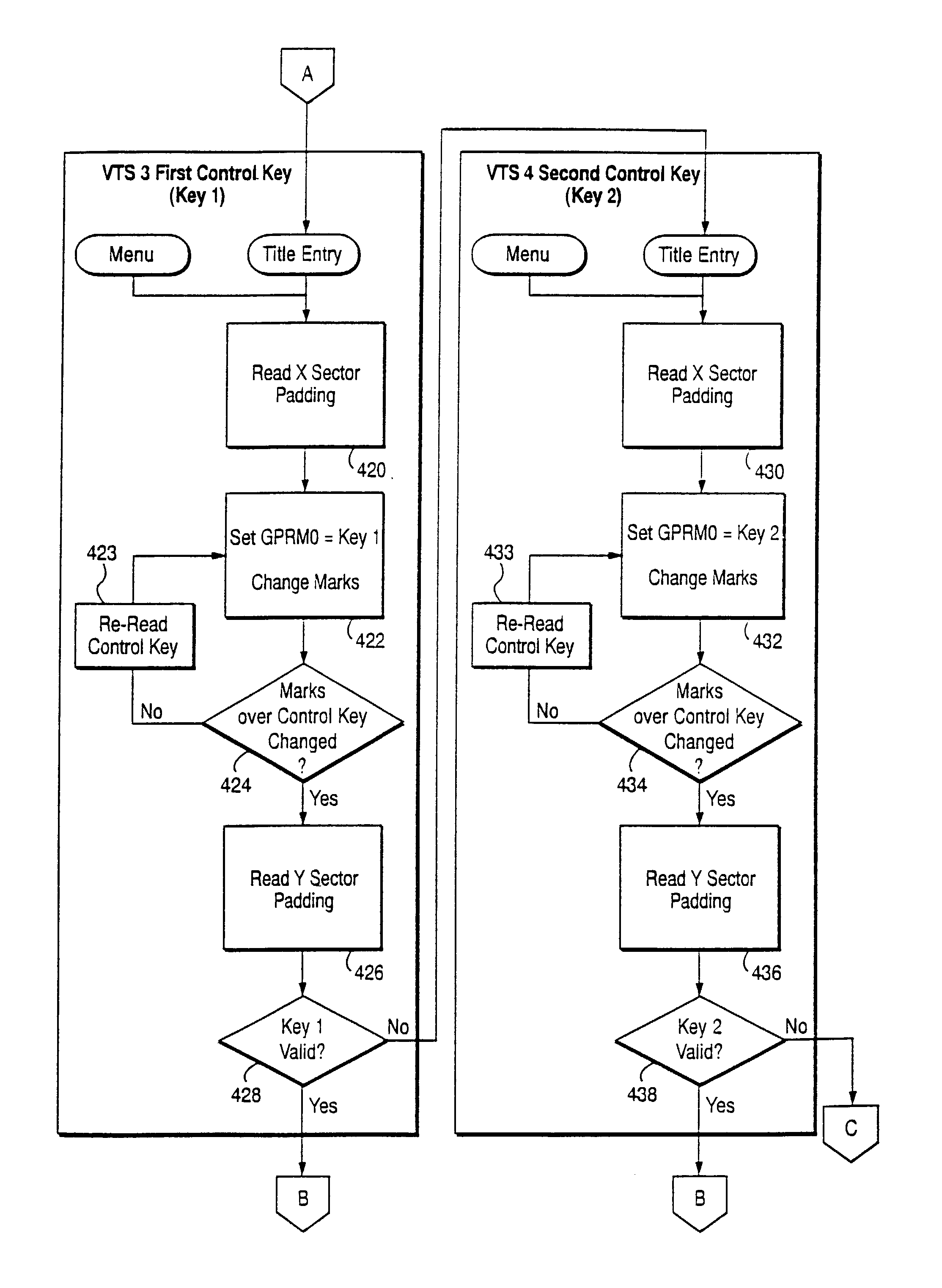
InactiveUS20030081521A1Efficient interfaceCombination recordingAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useOptical propertyTime segment
A limited-use Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) includes a storage layer for storing content data and control key data. At least one mark of photosensitive dye is disposed on the disc exterior to the storage layer and over at least a portion of the control key data. In one embodiment, the mark is initially transparent to allow a DVD player to read the control key data. The mark changes from clear to become opaque when it is exposed to DVD reader laser light for a cumulative period of time. This change in the optical property of the mark and the configuration of the control key data prevents further reading of the content data after predetermined reading and playback usage of at least some of the content data is permitted. In another embodiment, the mark is initially opaque to initially prevent the successful reading of the control key data, and permanently changes to transparent when exposed to DVD reader laser light for a cumulative period of time.
Owner:NOW SHOWING ENTERTAINMENT
Motion picture anti-piracy coding
ActiveUS7206409B2Increase awarenessEasy to detectTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsComputer graphics (images)
Owner:TECHNICOLOR INC +1
Information recording disc and information reproducing system
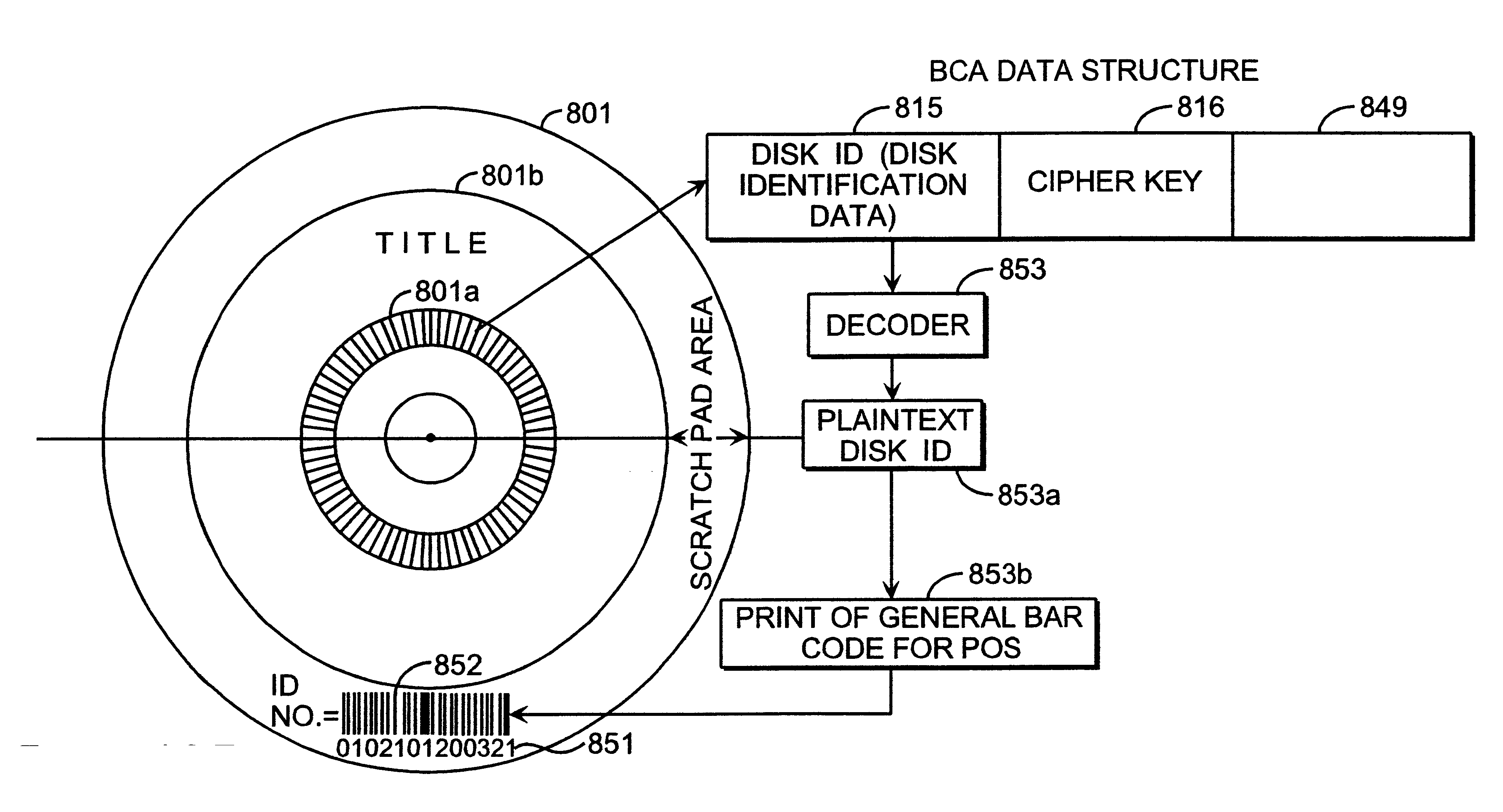
InactiveUS20010007545A1Method securityAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useRecord information storageControl dataApplication specific
An information recording disc having a burst cutting area (BCA) for recording control information for a reproducing apparatus by removing a reflective layer of the disc in a striped shape and a data recording area for recording user data, wherein the burst cutting area includes at least one BCA control information area and the BCA control information area comprises: an application identifier area for identifying applications of control data; a data length area for indicating data length of the control data; and an application specific data area for recording the control data, and an information reproducing drive for reproducing data from the information recording disc.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Media drive with a luminescence detector and methods of detecting an authentic article
InactiveUS20060041898A1Paper-money testing devicesPhotomechanical apparatusComputer scienceLuminescent material
A media drive is disclosed. In one embodiment, a media drive can comprise: a disk holder, a drive laser, a disk reader, and a luminescence detector. The disk holder can be capable of applying a rotational force to a media disk. The drive laser is disposed so that light from the laser will be incident on the media disk when it is disposed in the disk holder. The disk reader is disposed to receive data from the media disk. A method for authenticating a media disk is also disclosed. The method can comprises: disposing the article in a reader, illuminating at least a portion of the article with the information reader, monitoring a luminescence emission of the illuminated article, and determining if the luminescence emission is consistent with an authentic article. If a luminescent material is present, the information reader excites the luminescent material to create a luminescence emission.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Dead on demand disk technology
InactiveUS7099110B2Avoid retrievingApparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionMagnetic mediaData storing
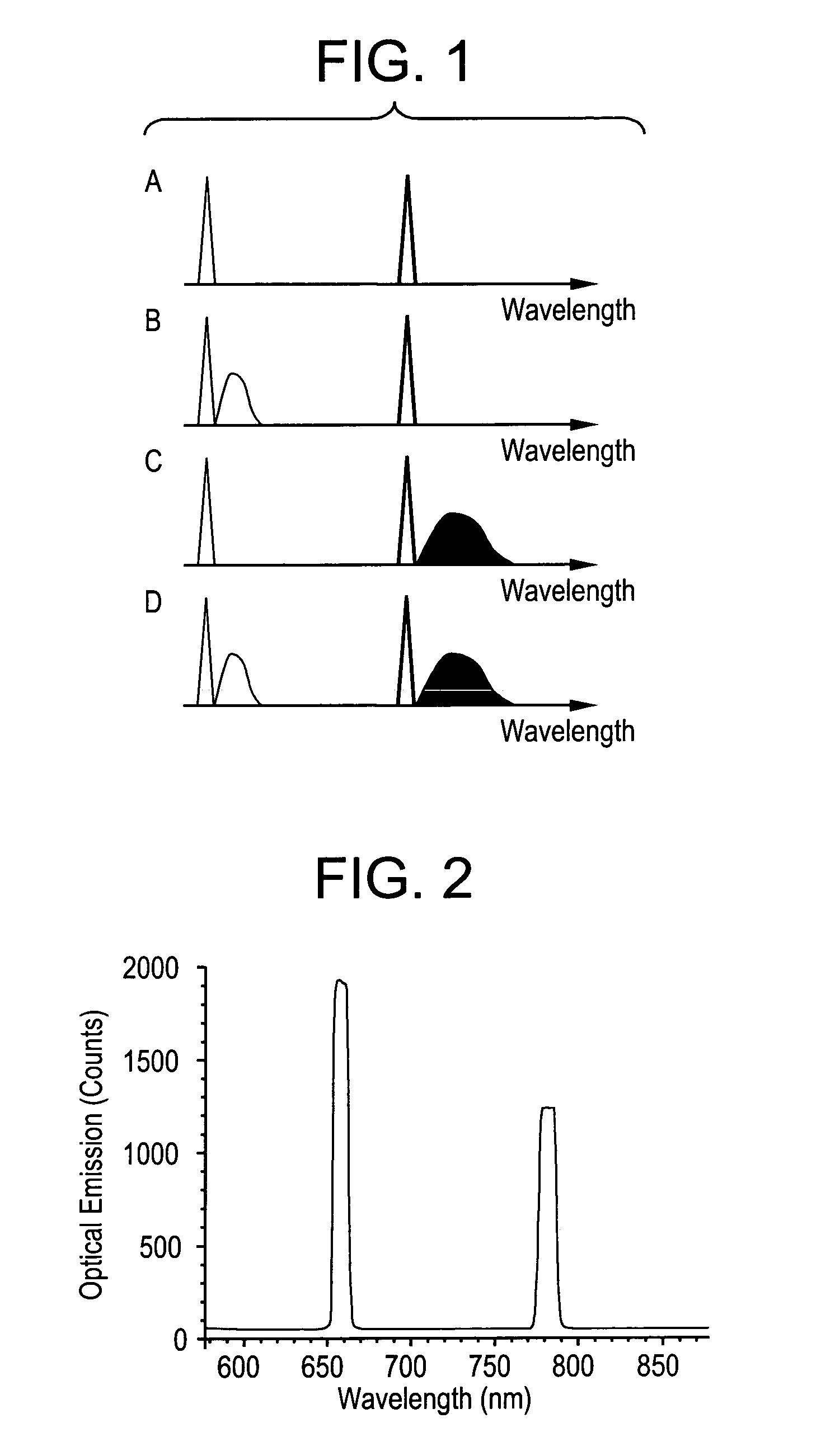
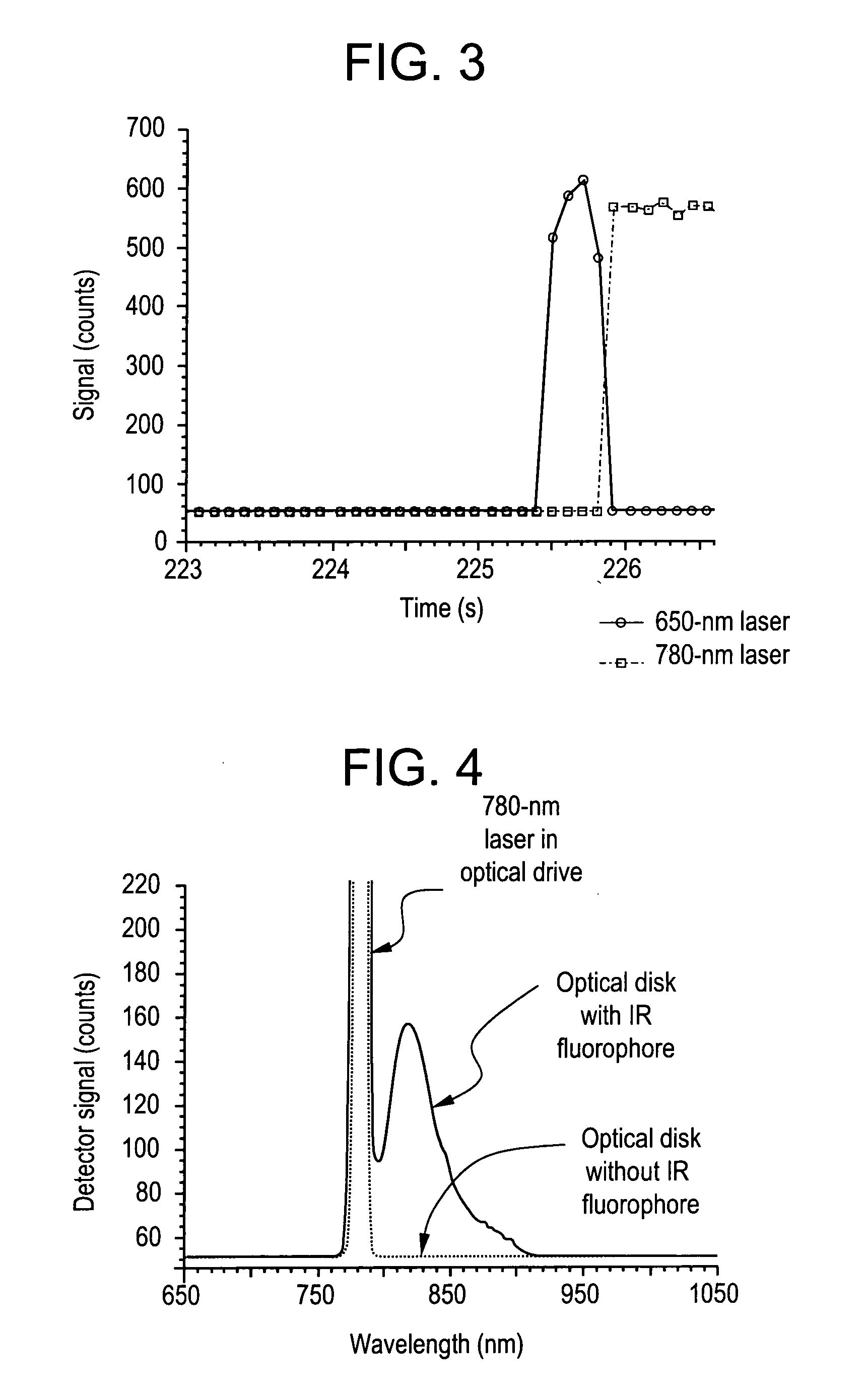
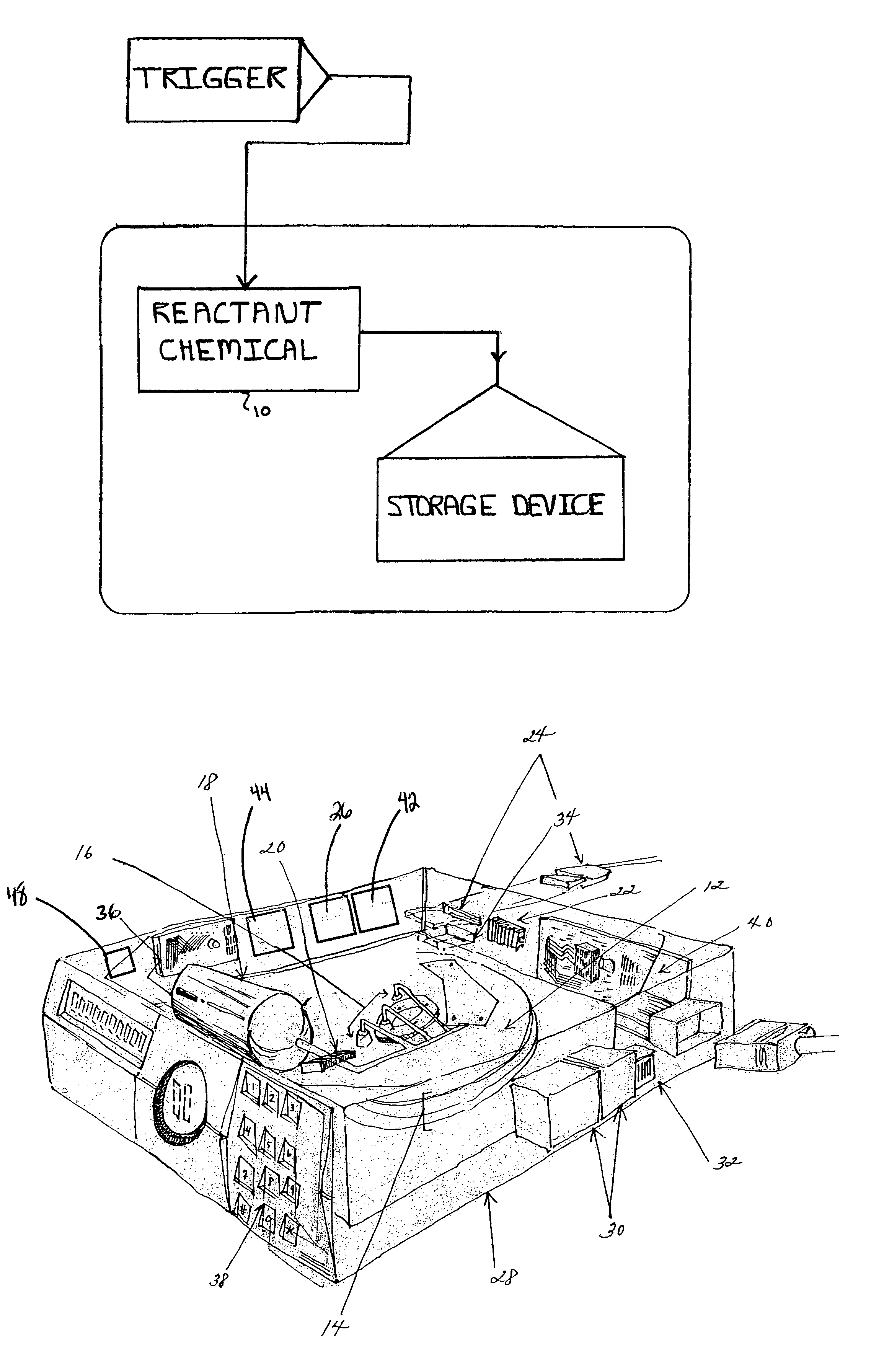
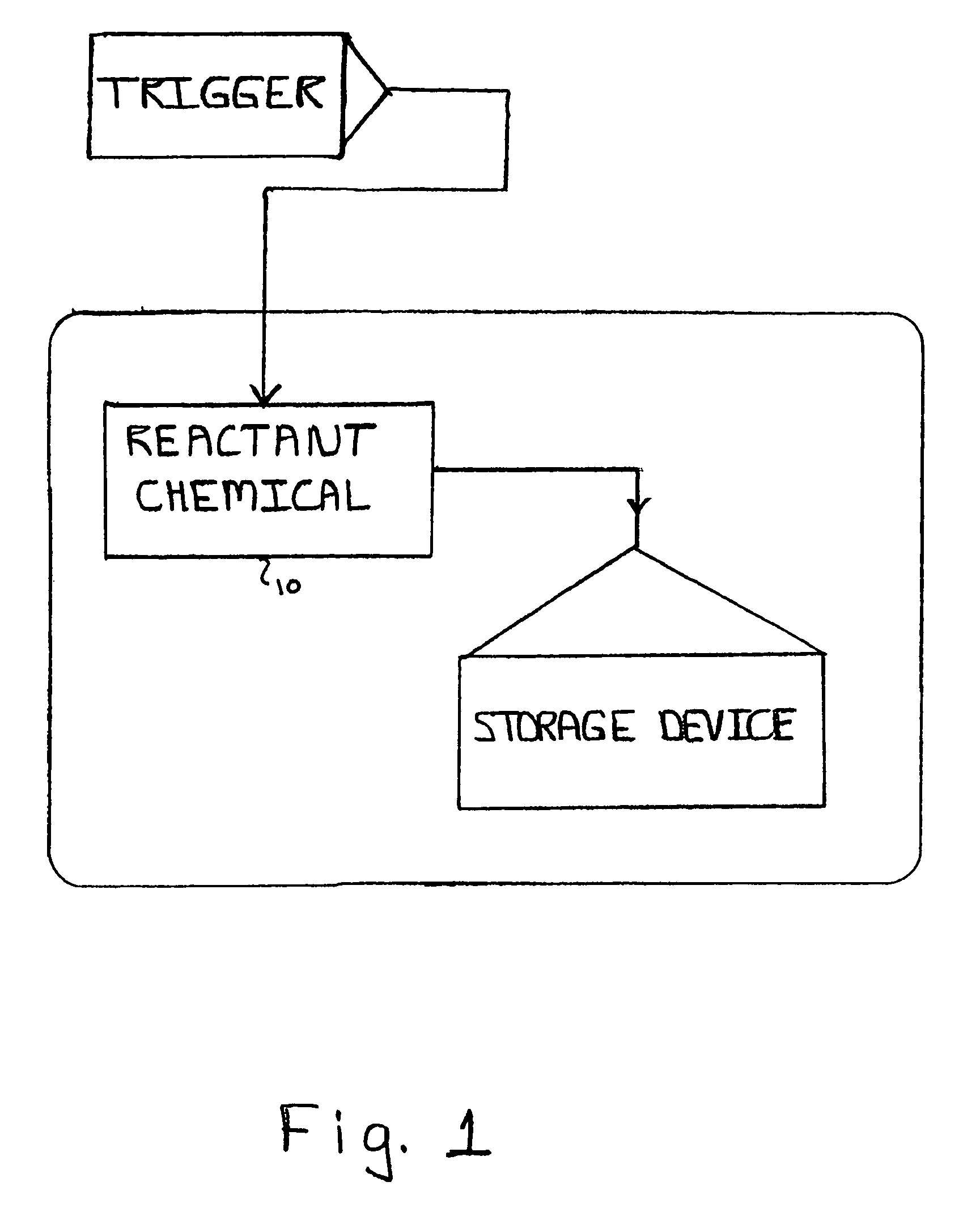
The present invention relates to a system and method for permanently and generally instantaneously destroying at least the data contained on magnetic data storage media upon the occurrence of certain events. Unauthorized access to data stored on magnetic media is prevented by destruction of the media with a reactant chemical. This approach may be initiated as a response to tampering or intentionally by using any one of several triggering interfaces described herein. Destruction of the media is quick and permanent, rendering the data unrecoverable even to aggressive recovery procedures.
Owner:ENSCONCE DATA TECH
Pseudo-reflective read inhibitor for optical storage media
InactiveUS6839316B2Low costChange is minimalCombination recordingLayered productsOptical reflectionTime function
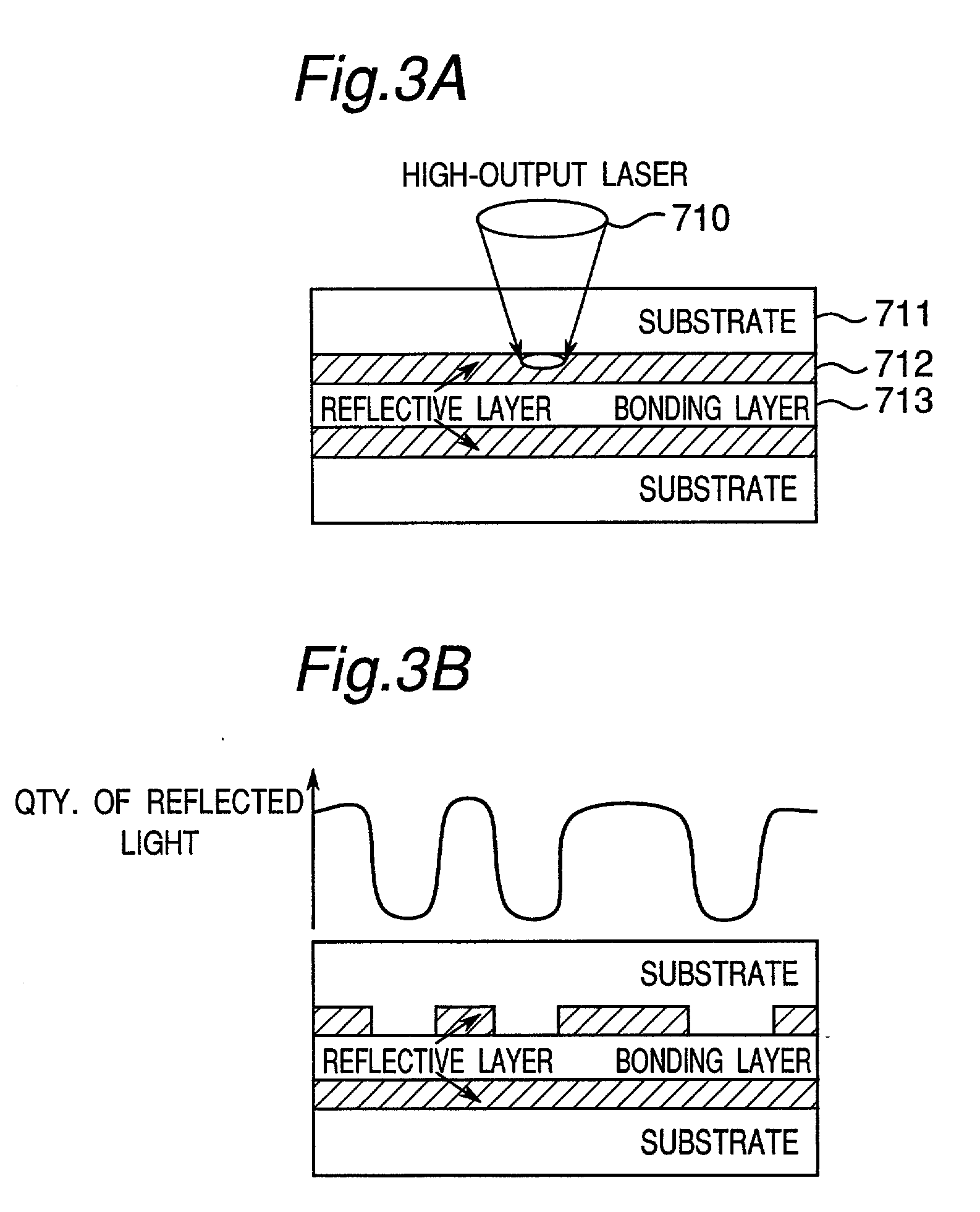
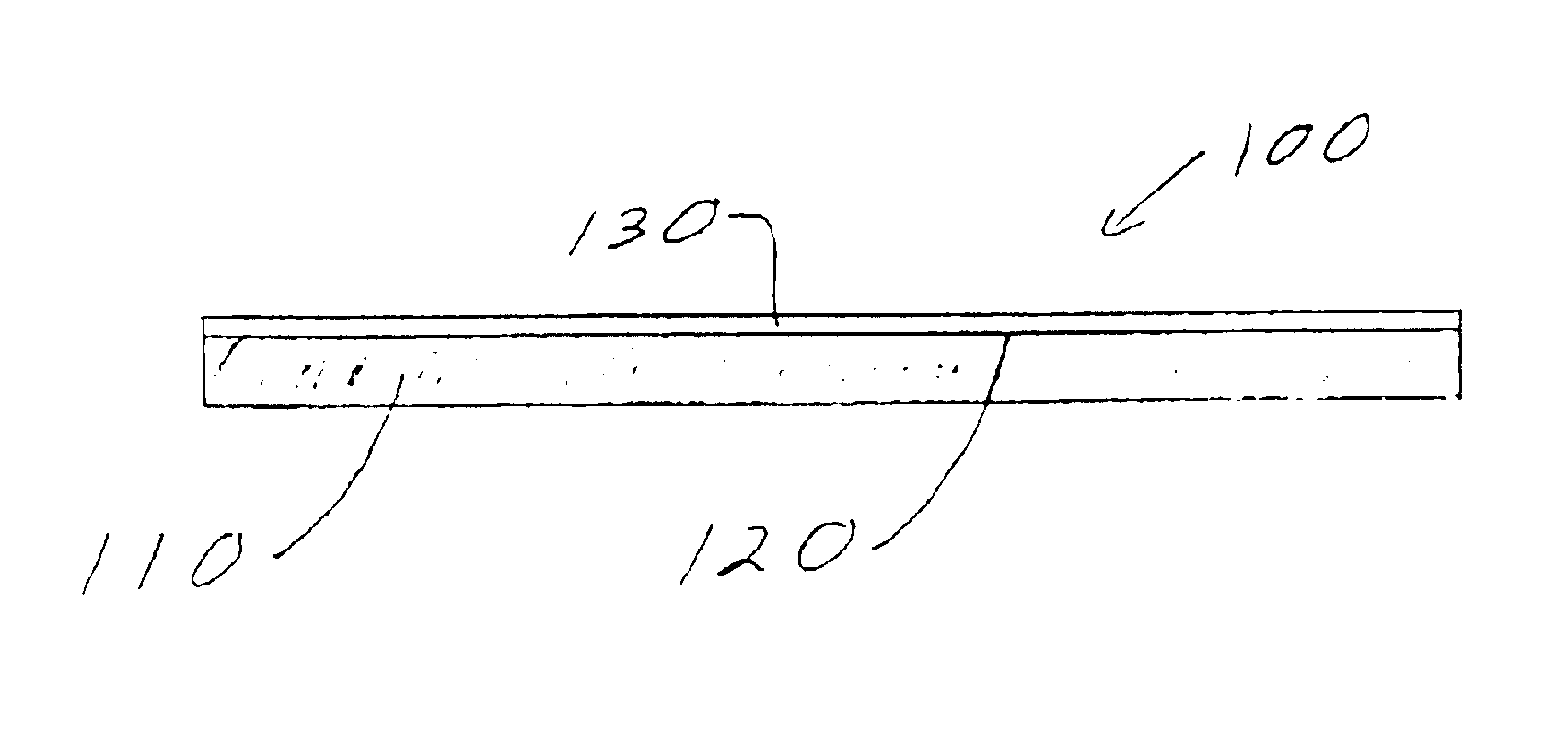
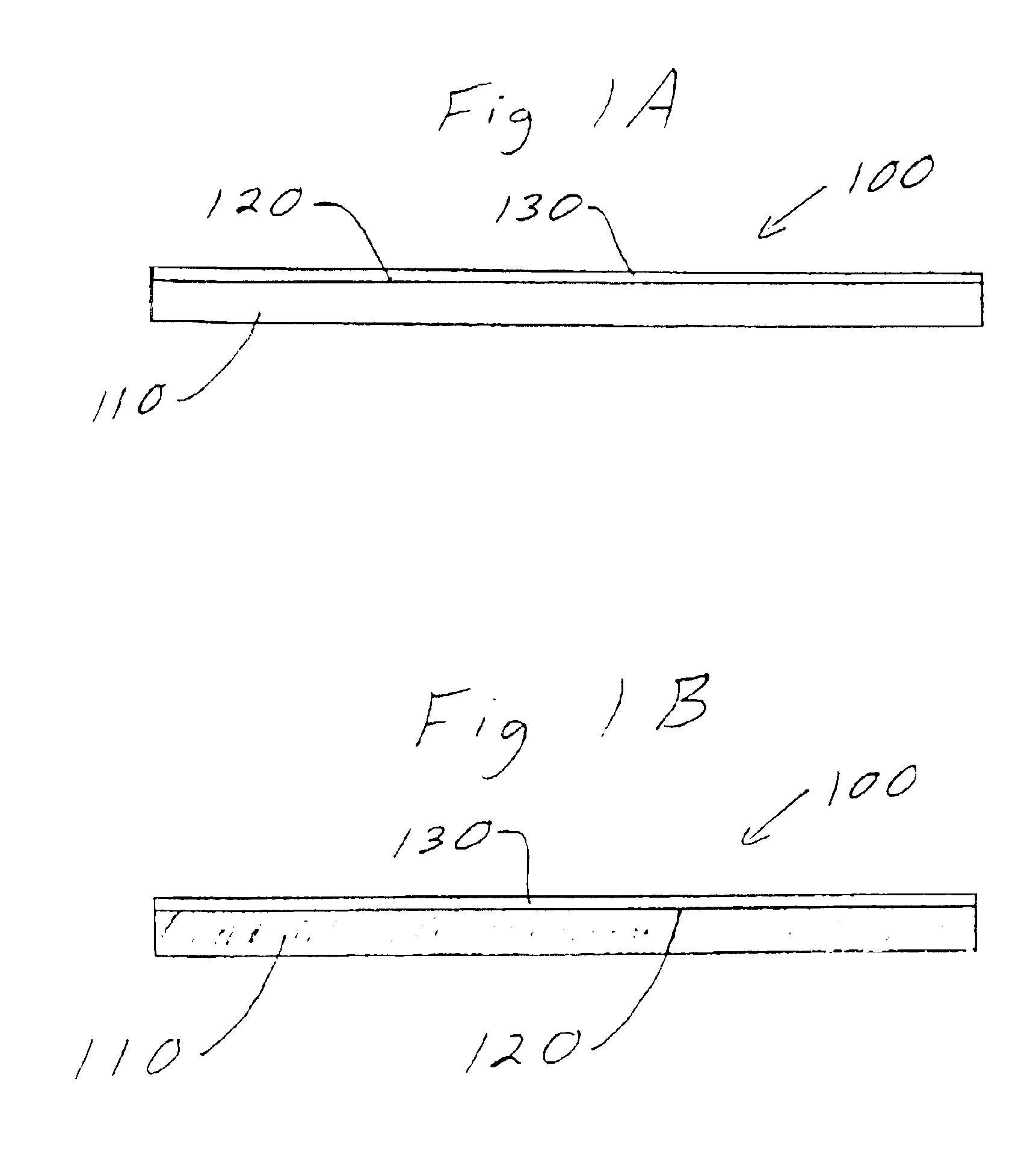
System and methods are described for inhibiting the readability of an optical media due to changes in a pseudo-reflective material that composes the optical media after the optical media has been exposed to air for a predetermined time. An optical media includes a data encoded component. At least a fraction of the data encoded component transforms from a substantially optically reflective state to a substantially optically non-reflective state as at-least-in-part a function of time from an initializing event. The systems and methods provide advantages because of low cost, limited content lifetime, avoidance of rental returns and minimum changes to existing manufacturing processes.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS20020076647A1Increase scatteringReduce the ratioPhotography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationSinglet oxygen
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Limited play optical devices with interstitial reactive layer and methods of making same
InactiveUS7177261B2Change is minimalDifficult to defeatLayered productsMechanical record carriersLight beamReactive material
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Limited play data storage media and method for limiting access to data thereon
InactiveUS20030002431A1Improve reflectivityGuaranteed playabilityPhotography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical storageEngineering
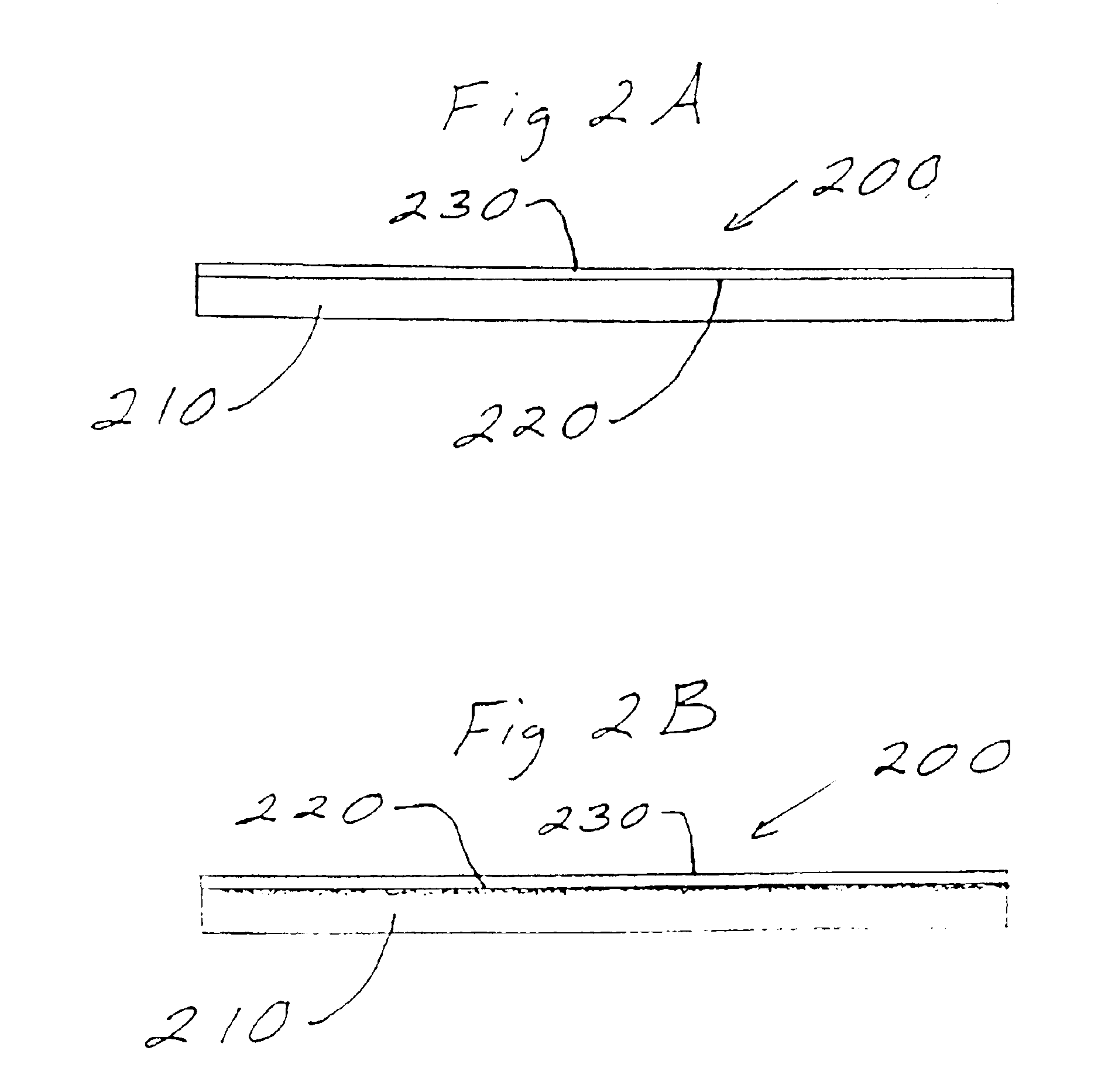
The present disclosure relates to a limited play optical storage media and a method for limiting access to data thereon. This storage media comprises: an optically transparent substrate; a reflective layer; a data storage layer disposed between said substrate and said reflective layer; an oxygen penetrable UV coating disposed on a side of said substrate opposite said data storage layer; and a reactive layer disposed between said UV coating and said substrate, said reactive layer having an initial percent reflectivity of about 50% or greater and a subsequent percent reflectivity of about 45% or less.
Owner:NBCUNIVERSAL
Method of authenticating polymers, authenticatable polymers, methods of making authenticatable polymers and authenticatable articles, and articles made there from
In one embodiment, a method for authenticating that a test polymer is an authenticatable polymer is disclosed wherein the authenticatable polymer comprises a substrate polymer and a thermochromic compound, the thermochromic compound having a first signal at a first temperature and at an authenticating wavelength, and a second signal at an authenticating temperature and the authenticating wavelength, the first and second signals being different, and the authenticating temperature being greater than the first temperature, the method comprising subjecting the test polymer to a stimulus sufficient to raise a portion of the test polymer to the authenticating temperature to create a heated portion, determining a test signal of the heated portion of the test polymer at the authenticating wavelength, and authenticating that the test polymer is an authenticatable polymer if the test signal is the same as an authenticating signal of the authenticatable polymer.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Directory read inhibitor for optical storage media
InactiveUS6838144B2Low costChange is minimalLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusOptical reflectionTime function
Systems and methods are described for inhibiting the readability of an optical media due to changes in a pseudo-reflective material that composes the optical media after the optical media has been exposed to air for a predetermined time. An optical media includes a data encoded component. At least a fraction of the data encoded component transforms from a substantially optically reflective state to a substantially optically non-reflective state as at-least-in-part a function of time from an initializing event. The systems and methods provide advantages because of low cost, limited content lifetime, avoidance of rental returns and minimum changes to existing manufacturing processes.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
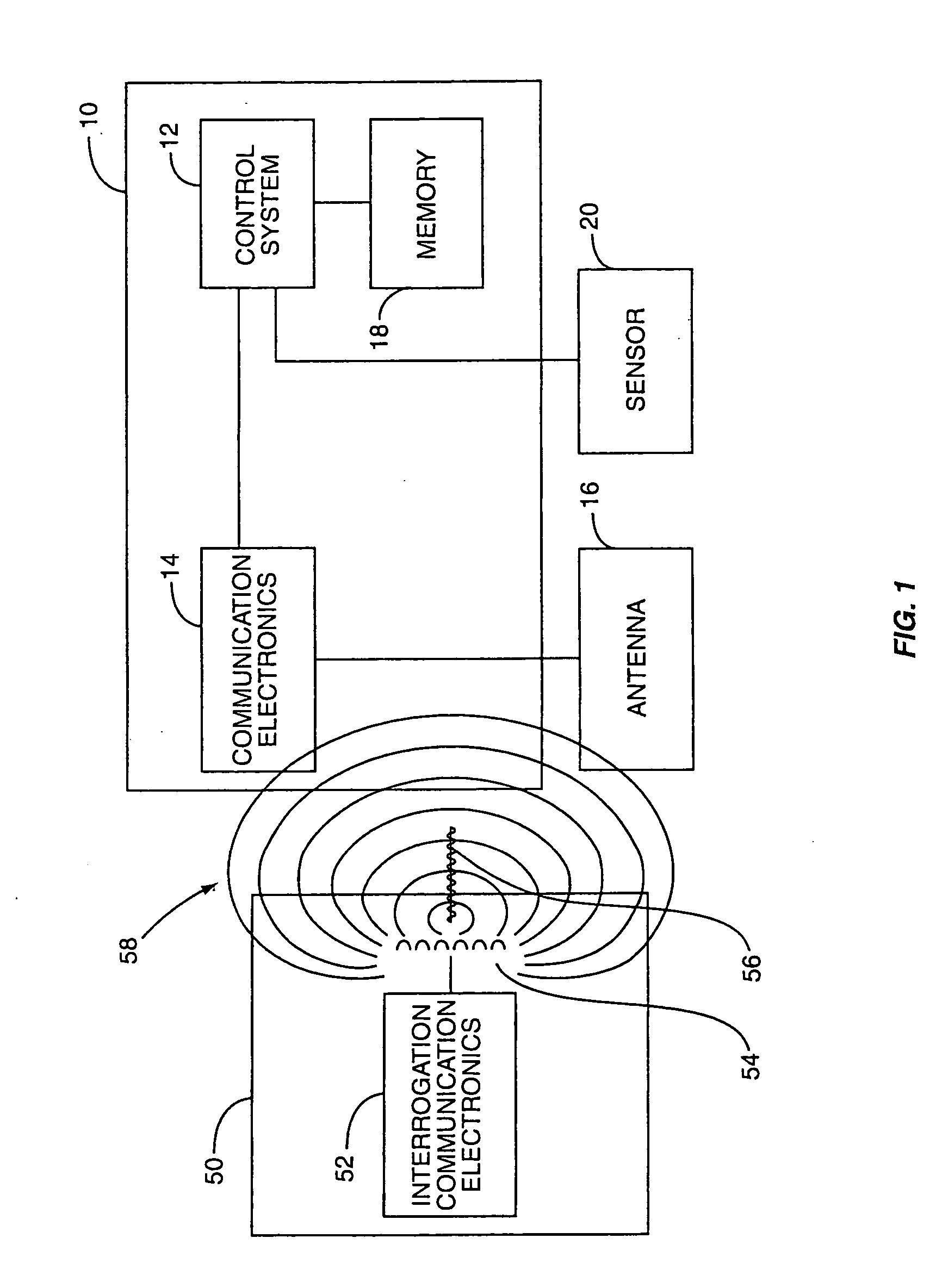
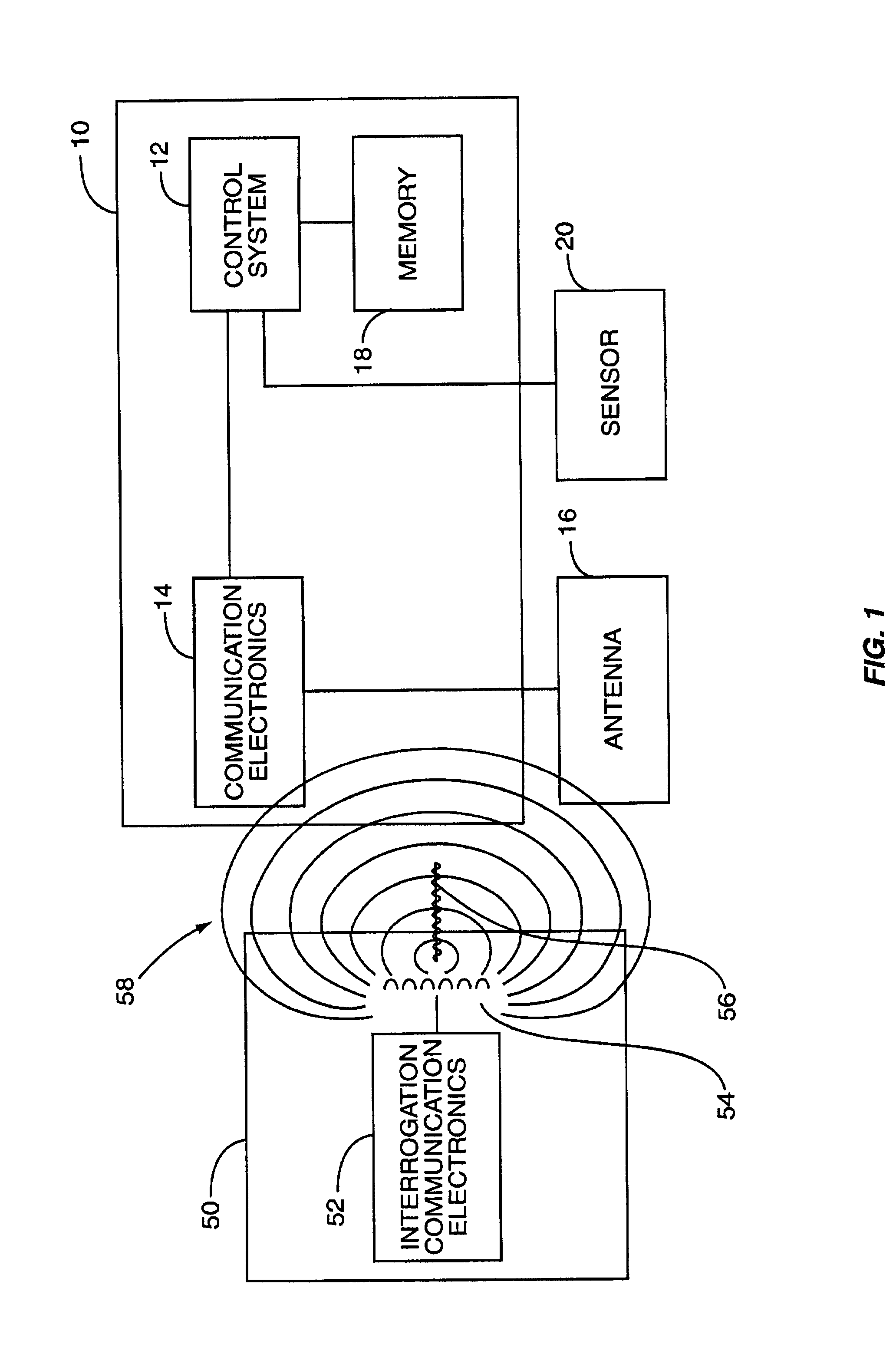
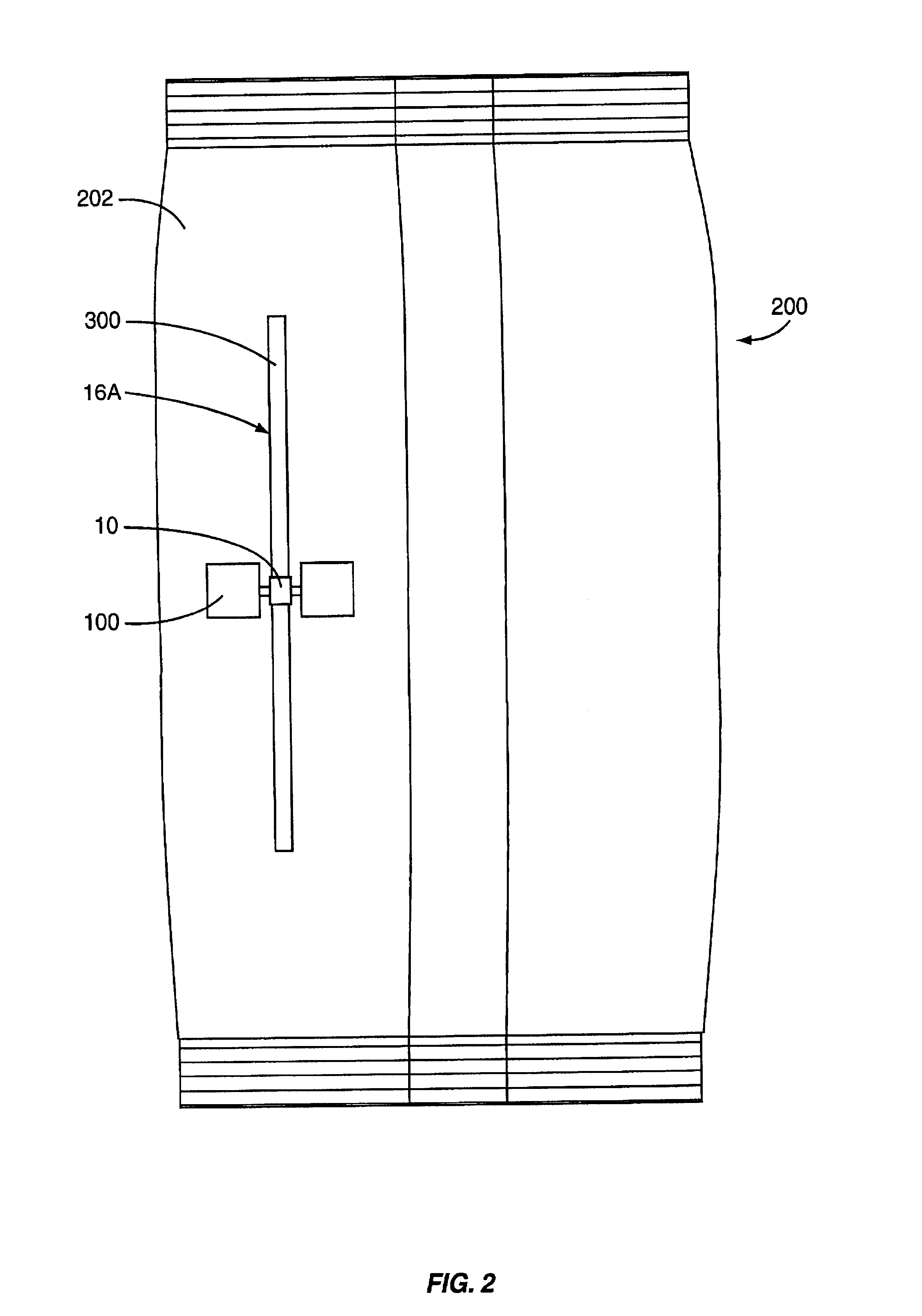
Wireless communication device and method
InactiveUS20020126057A1Antenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsCircularly polarized antennaAssembly line
The invention relates to a wireless communication device that is capable of communicating using a pole antenna in a first mode and a slot antenna in a second mode. The wireless communication device contains at least one conductive tab that provide an antenna. The tab(s) form a pole antenna, and the tabs may also be attached across a slot to form a slot antenna. The wireless communication device can communicate at different frequencies using the pole antenna in a first mode and the slot antenna in a second mode. The tab(s) may be attached across a slot created in a package to form a slot antenna, or the tab(s) may be attached to a slot that is created as part of the wireless communication device to form a slot antenna. The tab(s) and / or the slot may also contain an adhesive material to attach the wireless communication device to a package, container or other material. More than one slot may be provided to form a circularly polarized antenna. The wireless communication device can be placed inside a conductive package using a slot antenna to provide unshielded communications. The wireless communication device can be further adapted to detect when the package is opened and to communicate such information. The wireless communication devices can be printed or placed on a carrier or support, such as film, to be stamped onto packages in a manufacturing facility and / or assembly line. The carrier may be a conductive material in which tabs are formed as part of the carrier before the wireless communication device is attached.
Owner:TERRESTRIAL COMMS LLC
Storage media access control method and system
InactiveUS20050050343A1Limit installationAvoid accessUser identity/authority verificationAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useMedia access controlOptical medium
A method and apparatus for controlling access to a storage medium, such as an optically readable medium. Light sensitive or other materials that are adapted to change state and affect reading of a storage medium are used to control access to data that may be stored on optical medium and / or to control use of the medium.
Owner:SELINFREUND RICHARD H +4
Combination mastered and writeable medium and use in electronic internet appliance
InactiveUS6980652B1Avoid viewingDisc-shaped record carriersAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useHyperlinkIntellectual property
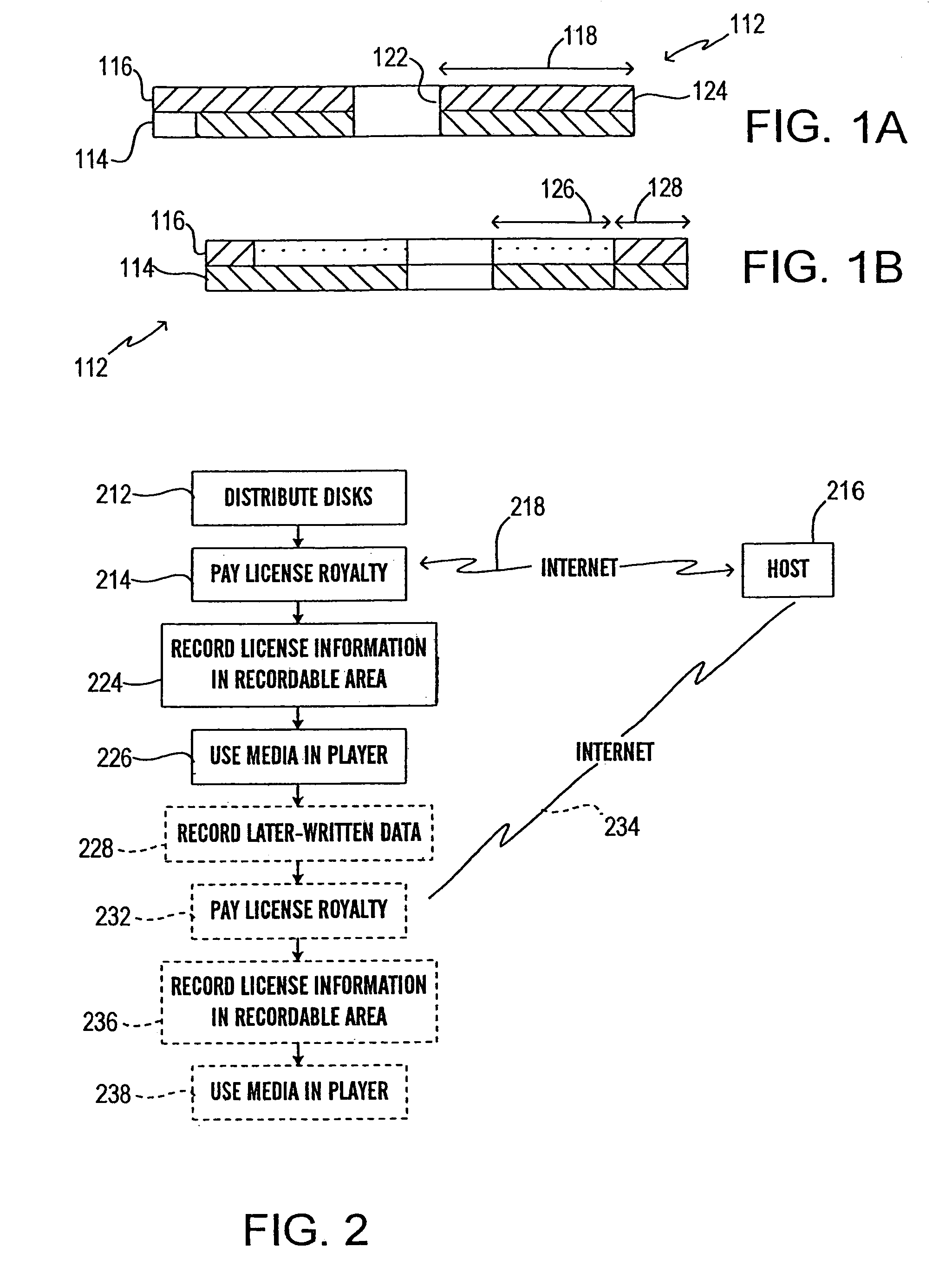
An optical medium uses a single structure or format (such as identical materials, layers and the like) for both a region for holding mastered data and a writeable area. In one aspect, a writeable region of a medium with mastered content is used in connection with paying, collecting or accounting for usage or royalties for proprietary intellectual property embodied in or associated with the content. In one embodiment, the (preferably write-once) writeable area can be used for storing later-written information such as annotations, highlighting, reordering, remixing, modifications, supplements, collections, additions, bookmarks, cross references, hypertext or hyperlinks and the like. Preferably, annotations and similar materials can be associated, by the user, with particular portions or content of the mastered data.
Owner:DATAPLAY
Limited play data storage media and method for limiting access to data thereon
InactiveUS6733950B2Reducing percent reflectivityReduce the amount requiredPhotography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsEngineeringOptical storage
The present disclosure relates to a limited play optical storage media and a method for limiting access to data thereon. This storage media comprises: an optically transparent substrate; a reflective layer; a data storage layer disposed between said substrate and said reflective layer; an oxygen penetrable UV coating disposed on a side of said substrate opposite said data storage layer; and a reactive layer disposed between said UV coating and said substrate, wherein said optical storage media has an initial percent reflectivity of about 50% or greater and a subsequent percent reflectivity of about 45% or less.
Owner:NBCUNIVERSAL
Protection of data on media recording disks
InactiveUS7031470B1Level of securitySimple methodTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareSoftware
This invention discloses a secure recording medium having at least one of audio, video and software content, comprising a plurality of media recording disks (DVD's) with a disk security chip embedded in each the DVD, each the disk chip comprising a security key, wherein at least two of the DVD's have different disk security keys.A method for protecting access to content recorded on a media recording disk (DVD) is also disclosed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Limited use DVD-video disc
InactiveUS7127066B2Efficient interfaceAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useRecord information storageOptical propertyEngineering
A limited-use Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) includes a storage layer for storing content data and control key data. At least one mark of photosensitive dye is disposed on the disc exterior to the storage layer and over at least a portion of the control key data. In one embodiment, the mark is initially transparent to allow a DVD player to read the control key data. The mark changes from clear to become opaque when it is exposed to DVD reader laser light for a cumulative period of time. This change in the optical property of the mark and the configuration of the control key data prevents further reading of the content data after predetermined reading and playback usage of at least some of the content data is permitted. In another embodiment, the mark is initially opaque to initially prevent the successful reading of the control key data, and permanently changes to transparent when exposed to DVD reader laser light for a cumulative period of time.
Owner:NOW SHOWING ENTERTAINMENT
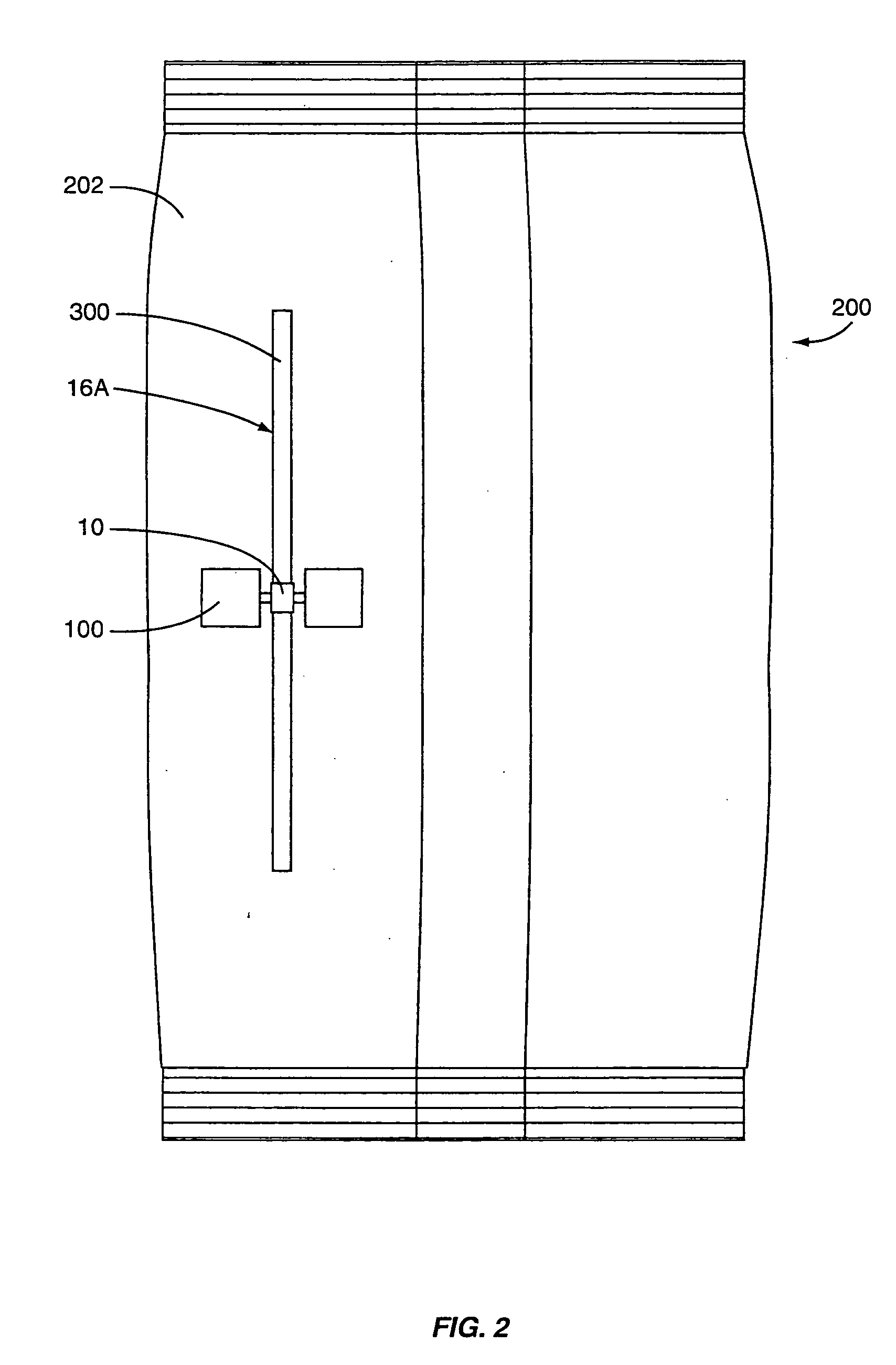
Grounded antenna for a wireless communication device and method
InactiveUS20050275591A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsGround planeImpedance matching
A wireless communication device includes an antenna for wireless communication with a remote interrogator. Several embodiments are disclosed to increase the options available to designers of wireless communication devices. In some embodiments, the antenna is a quarter wavelength long with one end of the antenna being grounded to provide desired impedance matching characteristics. The position of the ground plane relative to the antenna is also varied between embodiments. The connection from a wireless communication chip to the antenna is also varied between embodiments to provide alternate structures.
Owner:TERRESTRIAL COMMS LLC
Grounded antenna for a wireless communication device and method
InactiveUS7098850B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsImpedance matchingGround plane
A wireless communication device includes an antenna for wireless communication with a remote interrogator. Several embodiments are disclosed to increase the options available to designers of wireless communication devices. In some embodiments, the antenna is a quarter wavelength long with one end of the antenna being grounded to provide desired impedance matching characteristics. The position of the ground plane relative to the antenna is also varied between embodiments. The connection from a wireless communication chip to the antenna is also varied between embodiments to provide alternate structures.
Owner:TERRESTRIAL COMMS LLC
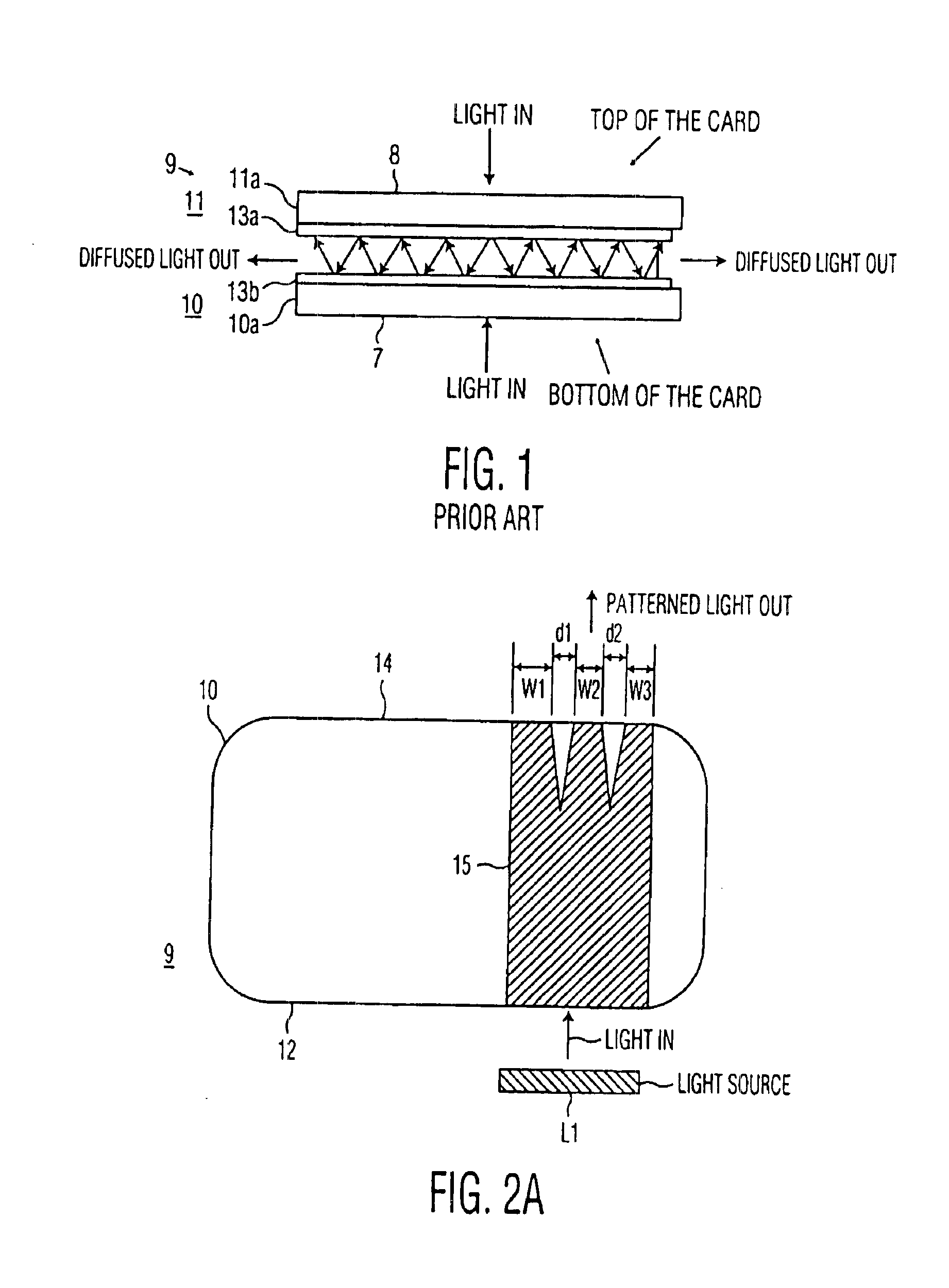
System for applying markings to optical media
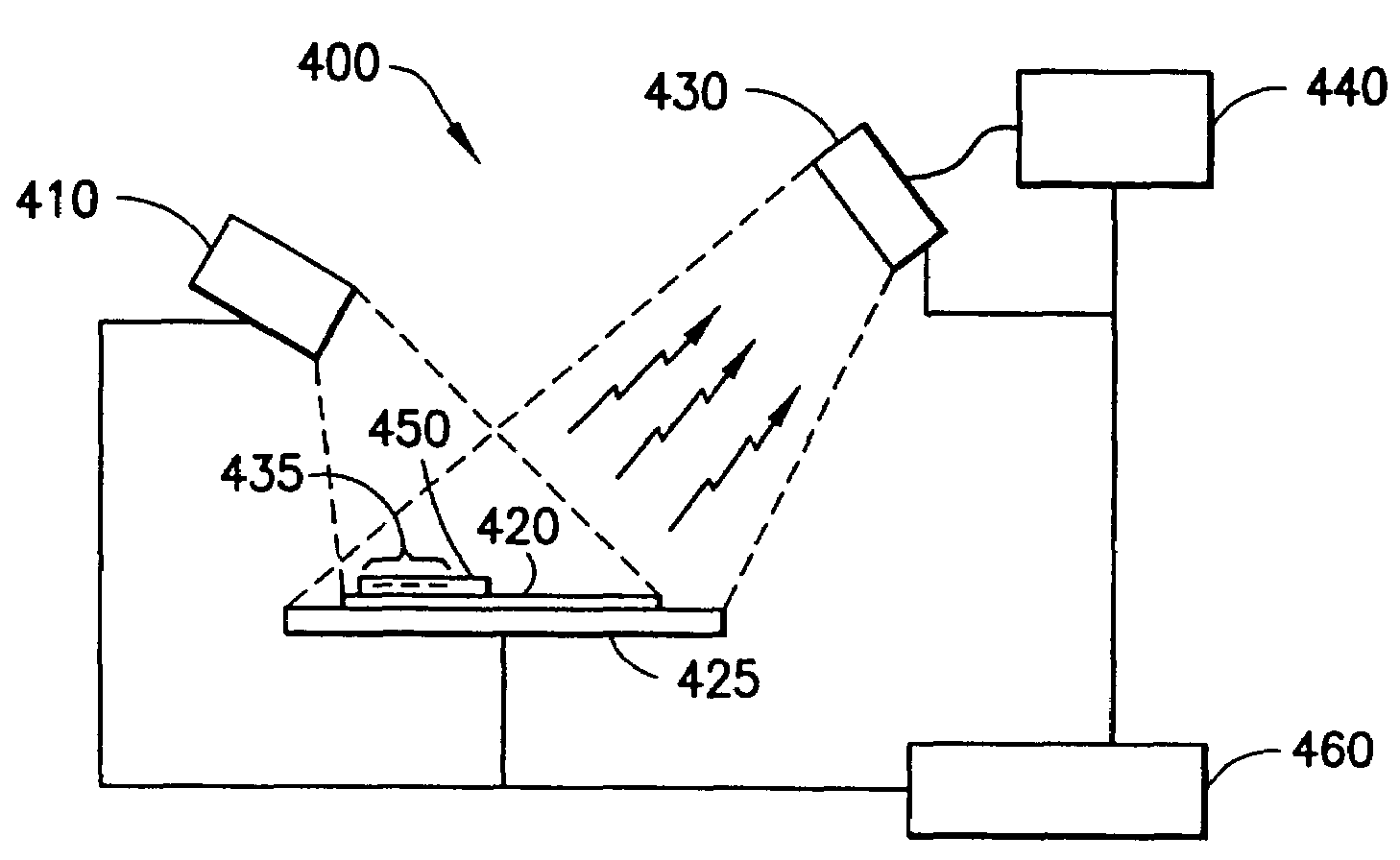
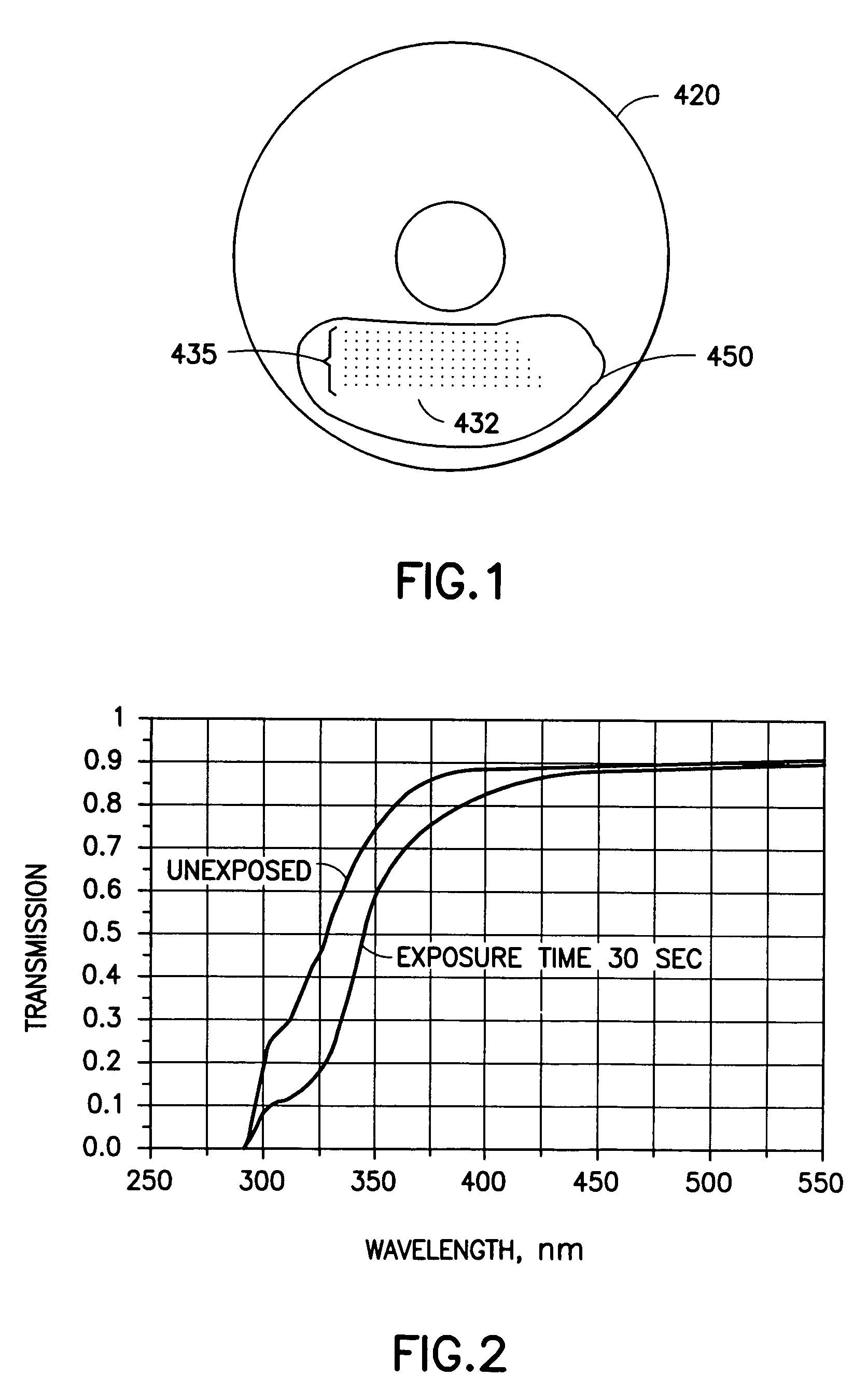
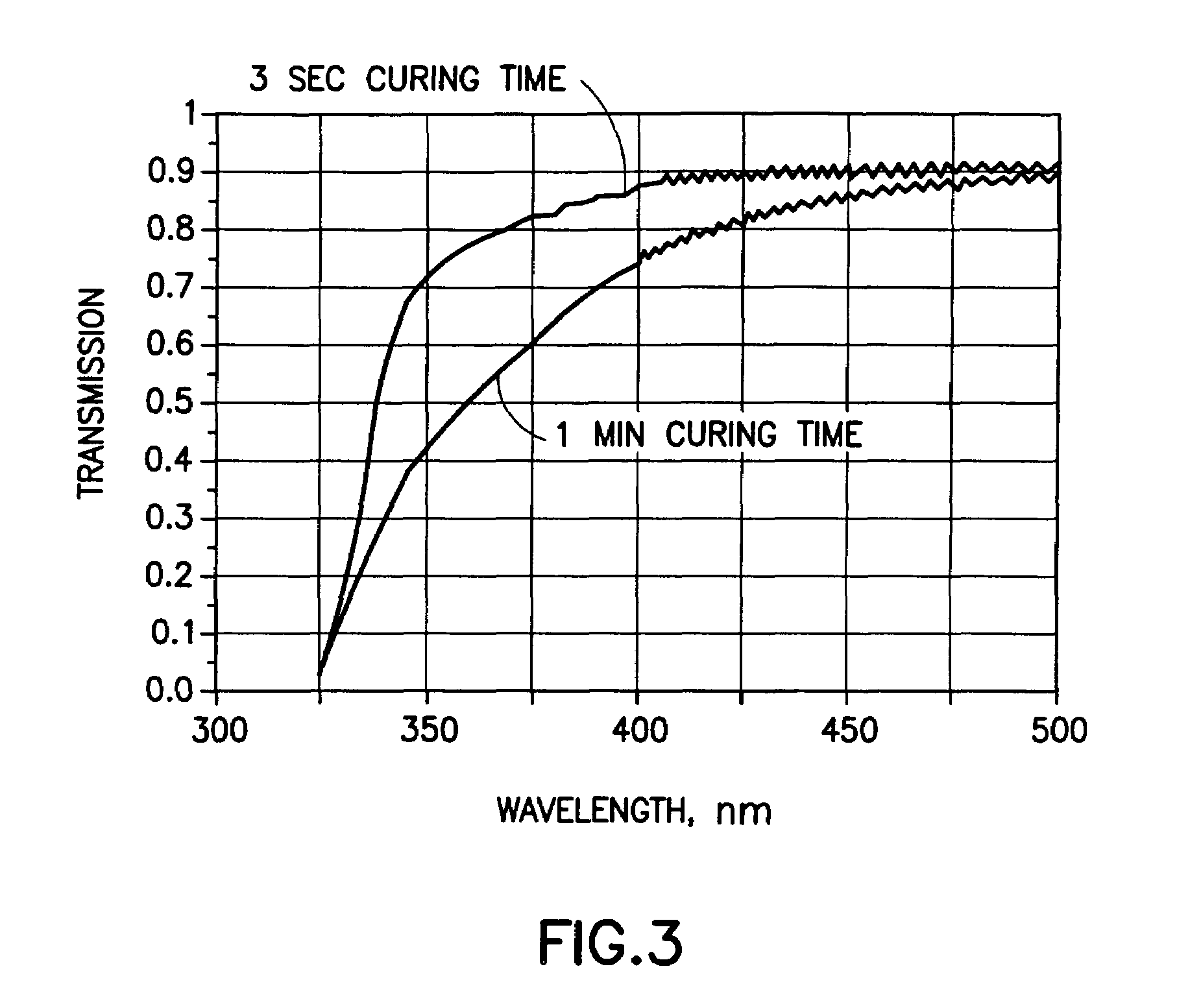
Disclosed herein is a system for recording a marking in the readout area of an optical media, wherein the marking does not interfere, or substantially interfere, with the readout of data from the optical media. The system disclosed herein is supportive of commercial production requirements. Markings may contain content as desired by the user of the system, including text, graphics, or other items. The marking is formed in a photosensitive coating that is applied to the optical media, and then cured with a first light. A second light, having a substantially separate band of wavelengths from the first light, is used to image a marking into the coating. The coating is robust to many external influences, such as ambient environmental conditions, and physical wear.
Owner:SPECTRA SYST CORP
Apparatus and method for recording data onto a predetermined recording medium
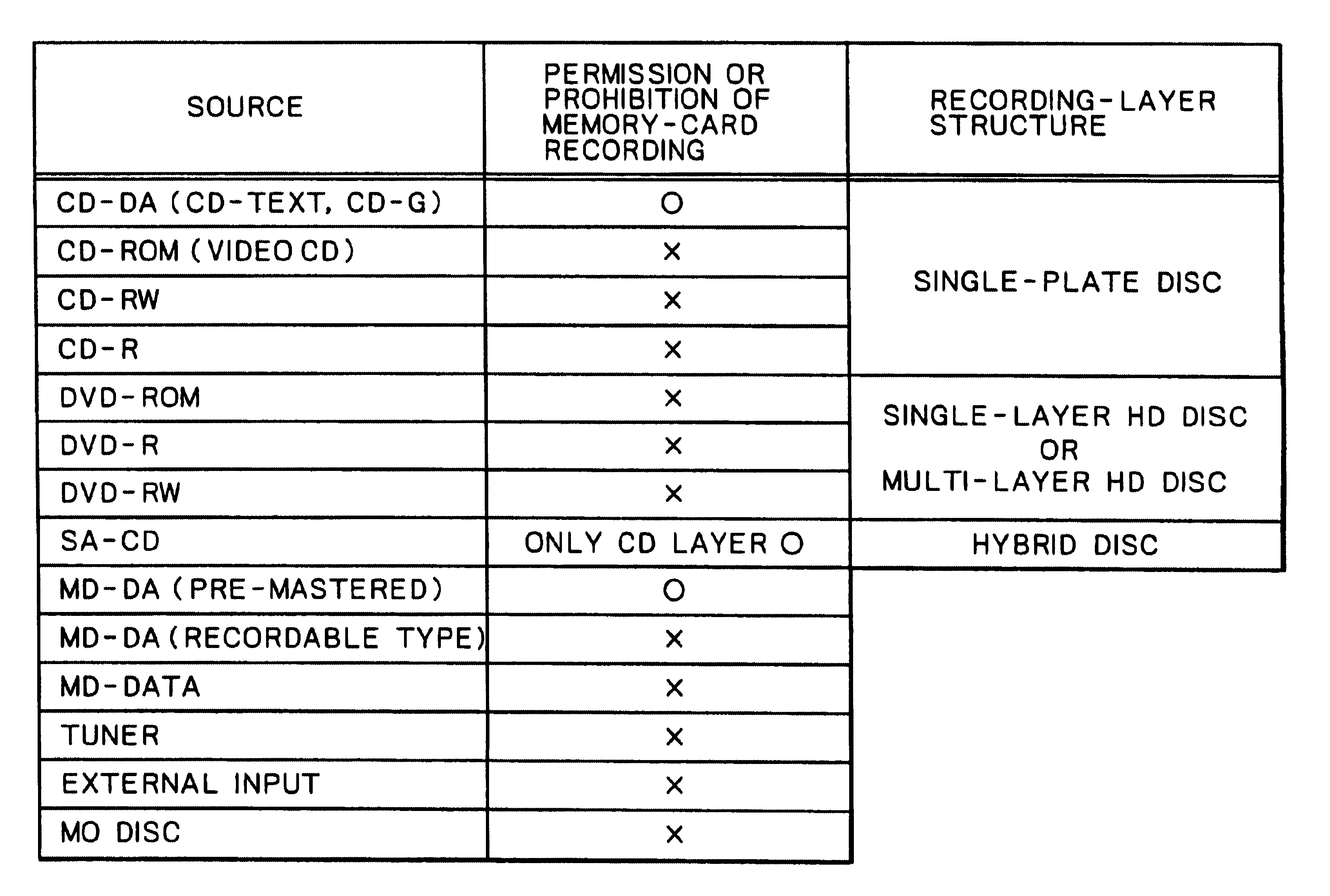
In an operation to record information played back from a first recording medium into a second recording medium, control is executed to permit or prohibit the operation to record (dub or copy) the information into the second recording medium on the basis of a judgment as to whether the first recording medium is a recording medium that is permitted to be dubbed or prohibited from being dubbed. The control can be executed to permit or prohibit the operation to copy the information in accordance with the type of the first recording medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
Marking articles using a covert digitally watermarked image
ActiveUS7184569B2Accessories for auxillary signalsUser identity/authority verificationFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
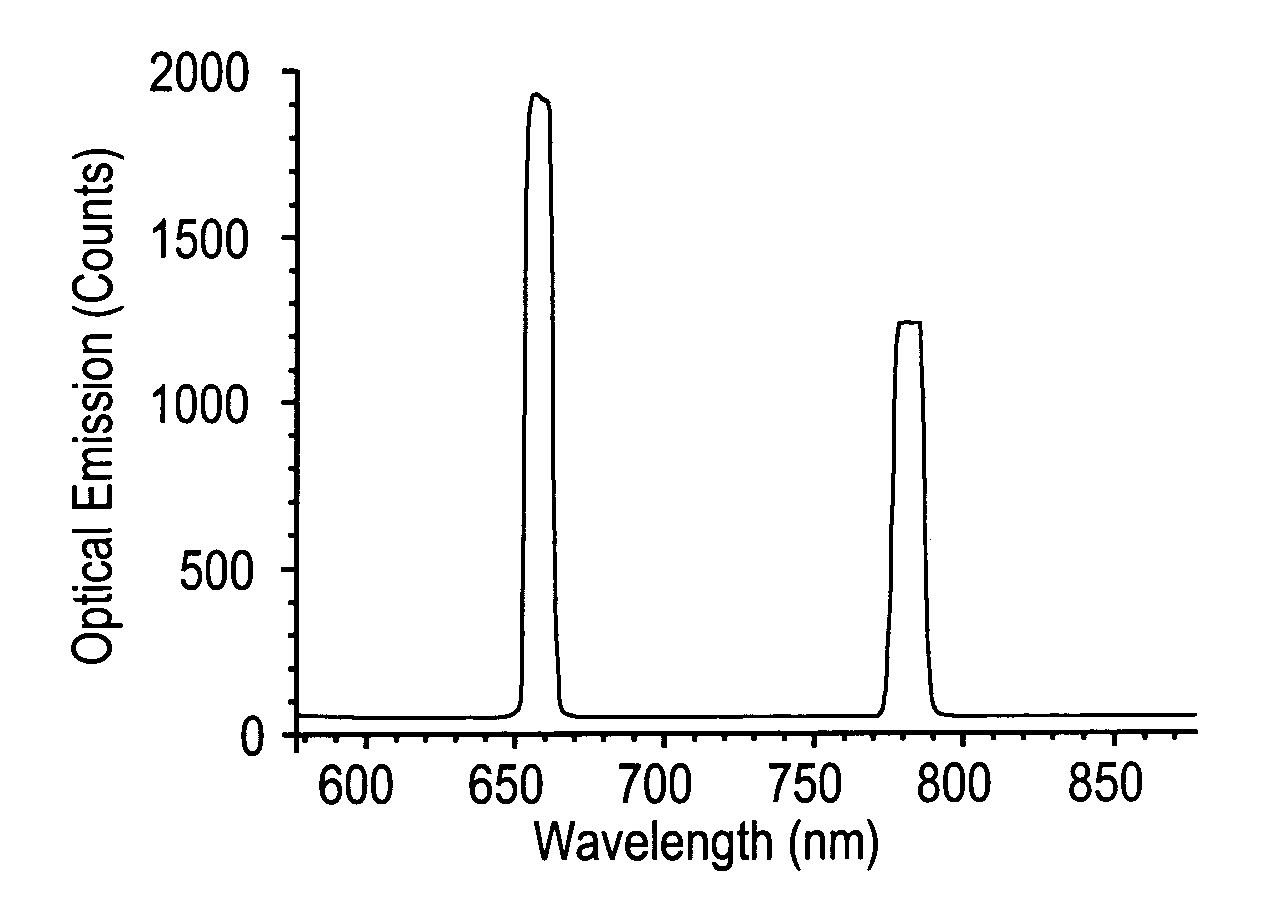
A marking system that includes forming at least one marking in or on an article, wherein the image formed is not visible to the unaided human observer, and further contains at least one digital watermark. The digitally watermarked image comprises emissive and photoabsorptive portions. The digitally watermarked image is applied using a substance reactive to a predetermined excitation source, and exposure to ultraviolet light. Other traditional techniques, such as printing with fluorescent inks may be used in combination. The digitally watermarked image is subsequently observable upon exposure to the predetermined excitation source. The digitally watermarked image may be observed and decoded by appropriately configured detection systems, wherein the information obtained may be used for purposes including, but not limited to, authentication and security of the article or information contained within the article.
Owner:SPECTRA SYST CORP
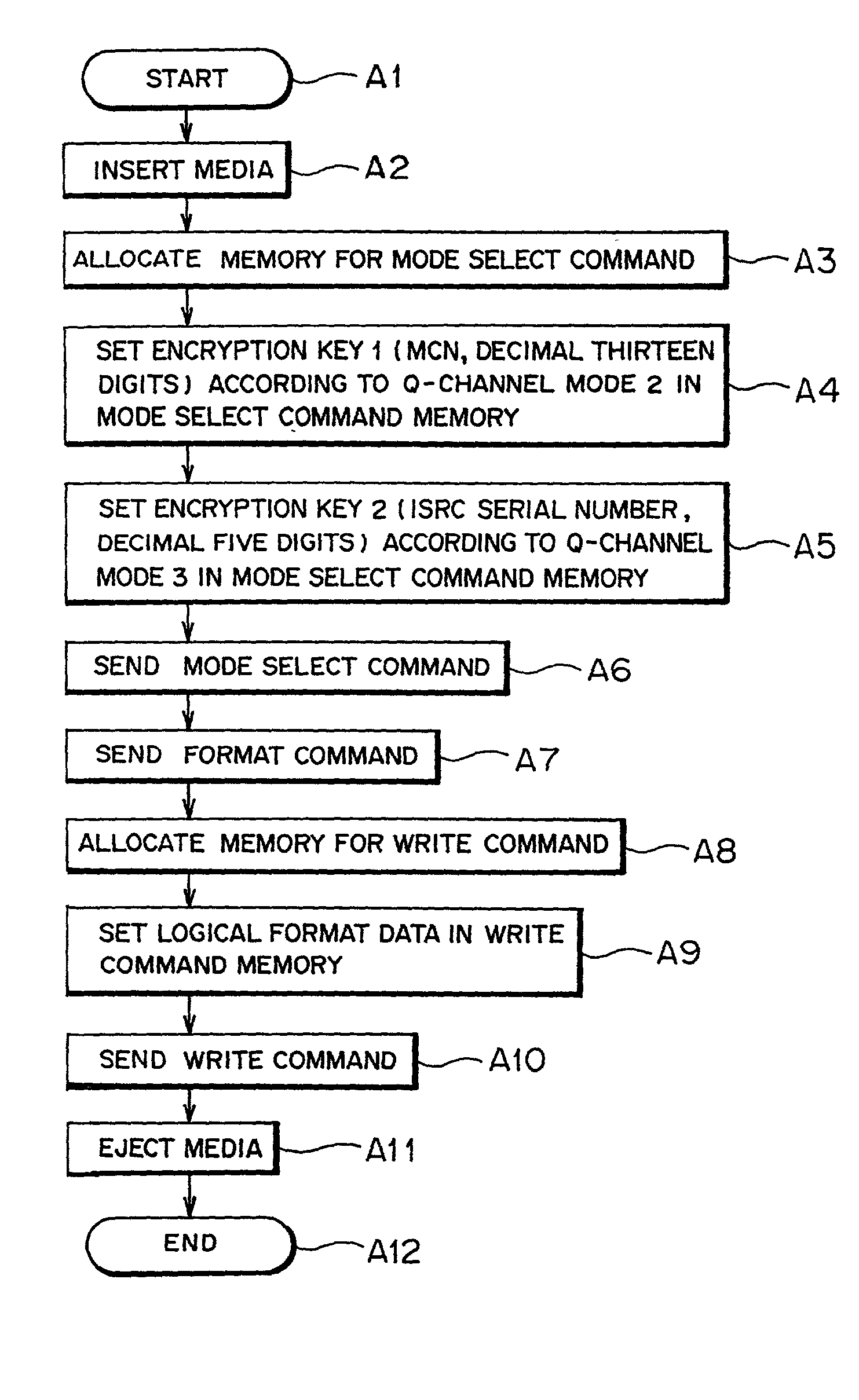
Recording medium, initialize method for recording medium, method for encryption on recording medium, encryption equipment, decryption equipment, and audio/visual/data equipment
InactiveUS20020080960A1Improve the immunityInformation arrangementAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useRecordable CDAudio frequency
A predetermined initialization is made on a CD-R disc or a CD-RW disc using an existing formatting method to a specific disc on which recorded are a media number forming an encryption key based on a combination of a decimal six-digit disc ID, a decimal thirteen-digit MCN and a decimal five-digit ISRC serial number and encrypted data obtained by the encryption using this media number. This allows a user to make the copy of copyrighted data such as music, movie and computer program data only once, but inhibits the secondary copy from this copy disc to another disc, which achieves the protection of the copyrighted data.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION
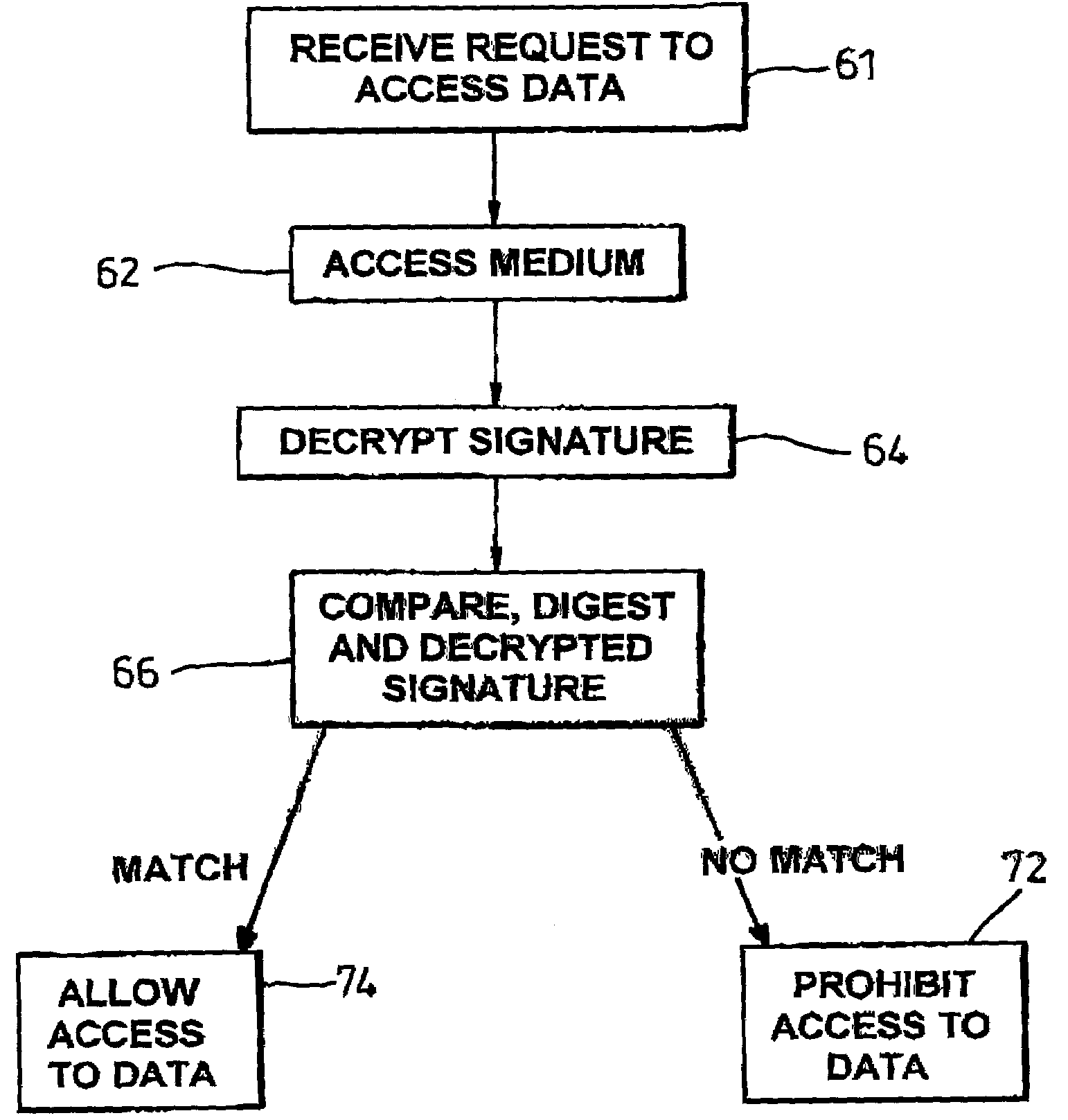
Data authentication
ActiveUS7194636B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureData content
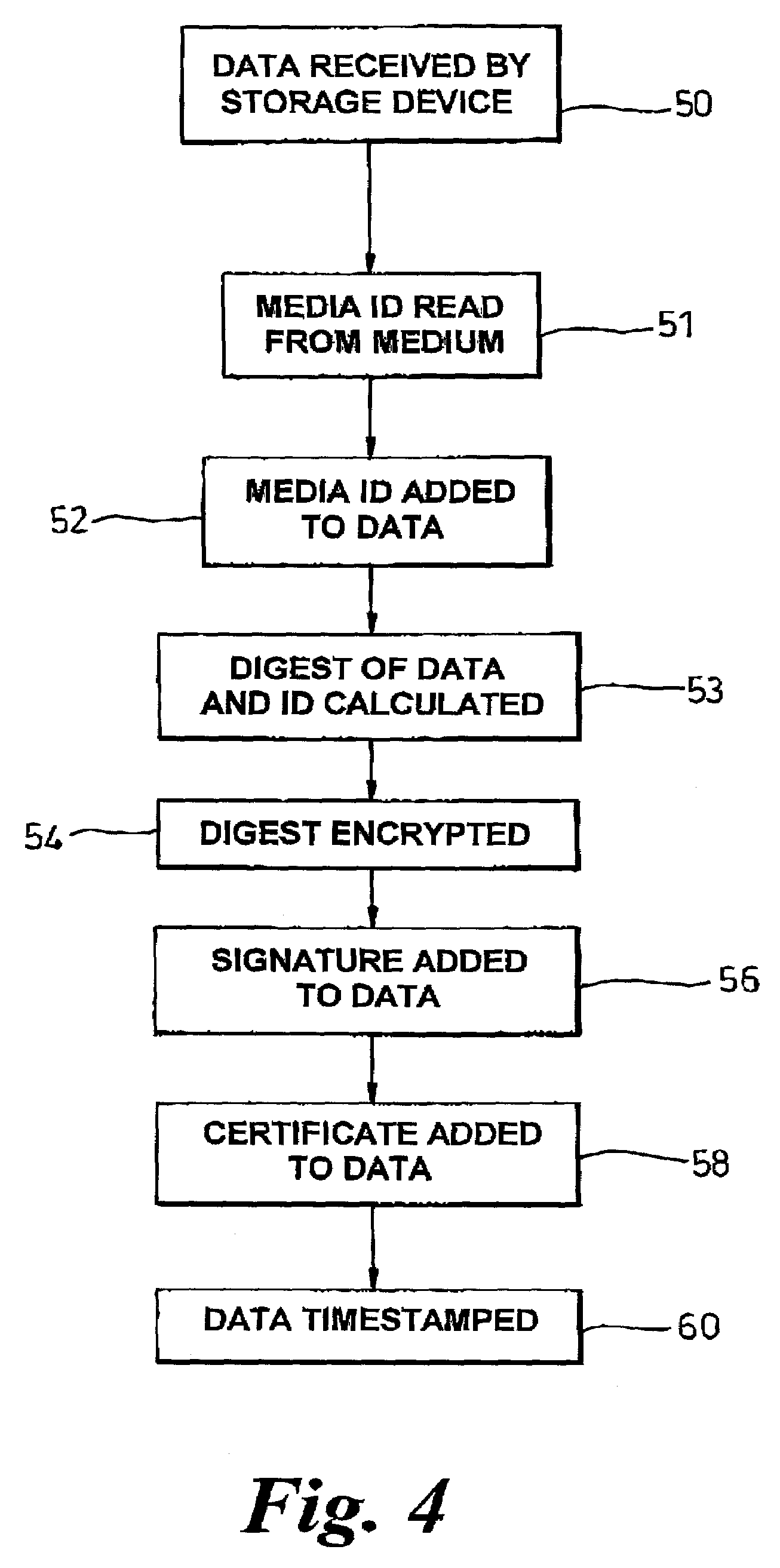
A storage medium carrying data content has an electronically readable modification-resistant identifier for distinguishing that medium from other storage media. The medium stores a digital signature associated with a data content portion carried by the storage medium. The identifier read from the storage medium generates the digital signature. The identifier and digital signature enable verification of storage of the data content on an authorised storage medium in an authorised manner.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
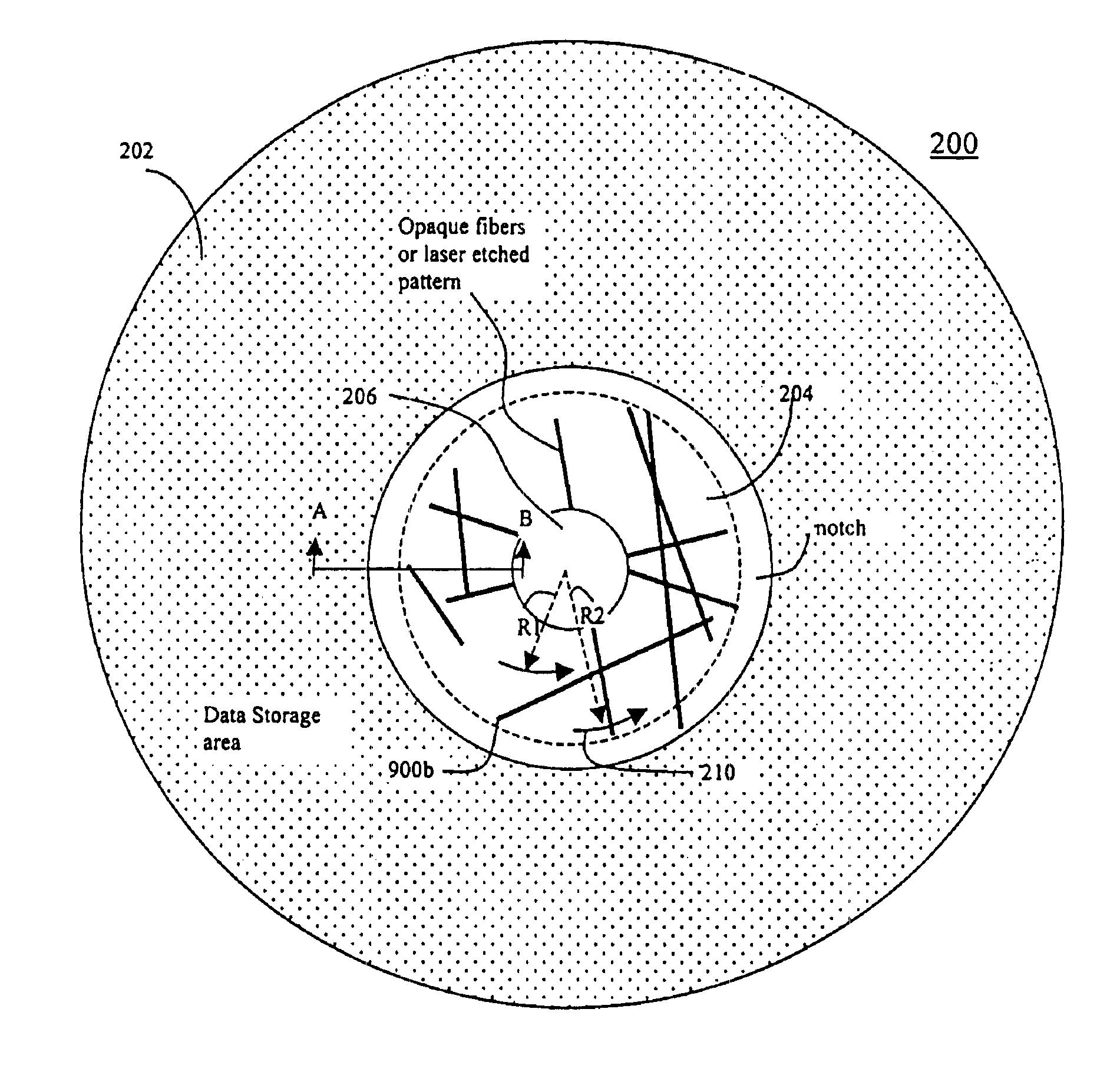
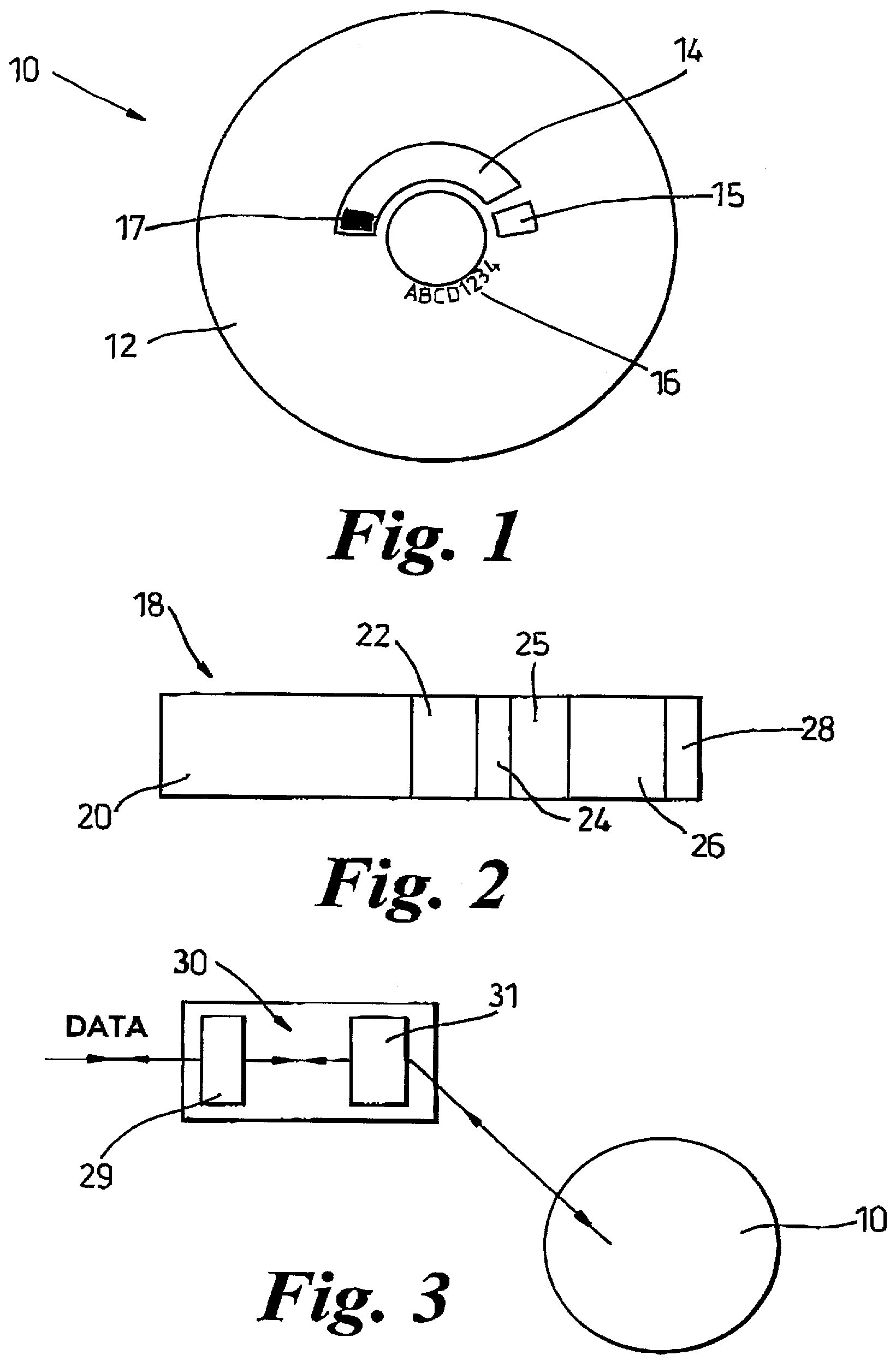
Recordable optical disk including an auxiliary information presence indicator
InactiveUS6885629B2Copyright protectionPrevent the software from being illegally installedAccessories for auxillary signalsDigital data processing detailsRecordable compact discComputer science
An optical disk having a first recording area for recording information; and a second recording area having auxiliary information including disk identification information unique to that optical disk recorded therein, wherein the second recording area including circumferentially arranged multiple stripe patterns each strip extending along a radius of the disk; and indicator indicating the presence of auxiliary information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com