Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Write-once" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cache coherency protocol literature, Write-Once was the first MESI protocol defined. It has the optimization of executing write-through on the first write and a write-back on all subsequent writes, reducing the overall bus traffic in consecutive writes to the computer memory. It was first described by James R. Goodman in (1983). Cache coherence protocols are an important issue in Symmetric multiprocessing systems, where each CPU maintains a cache of the memory.
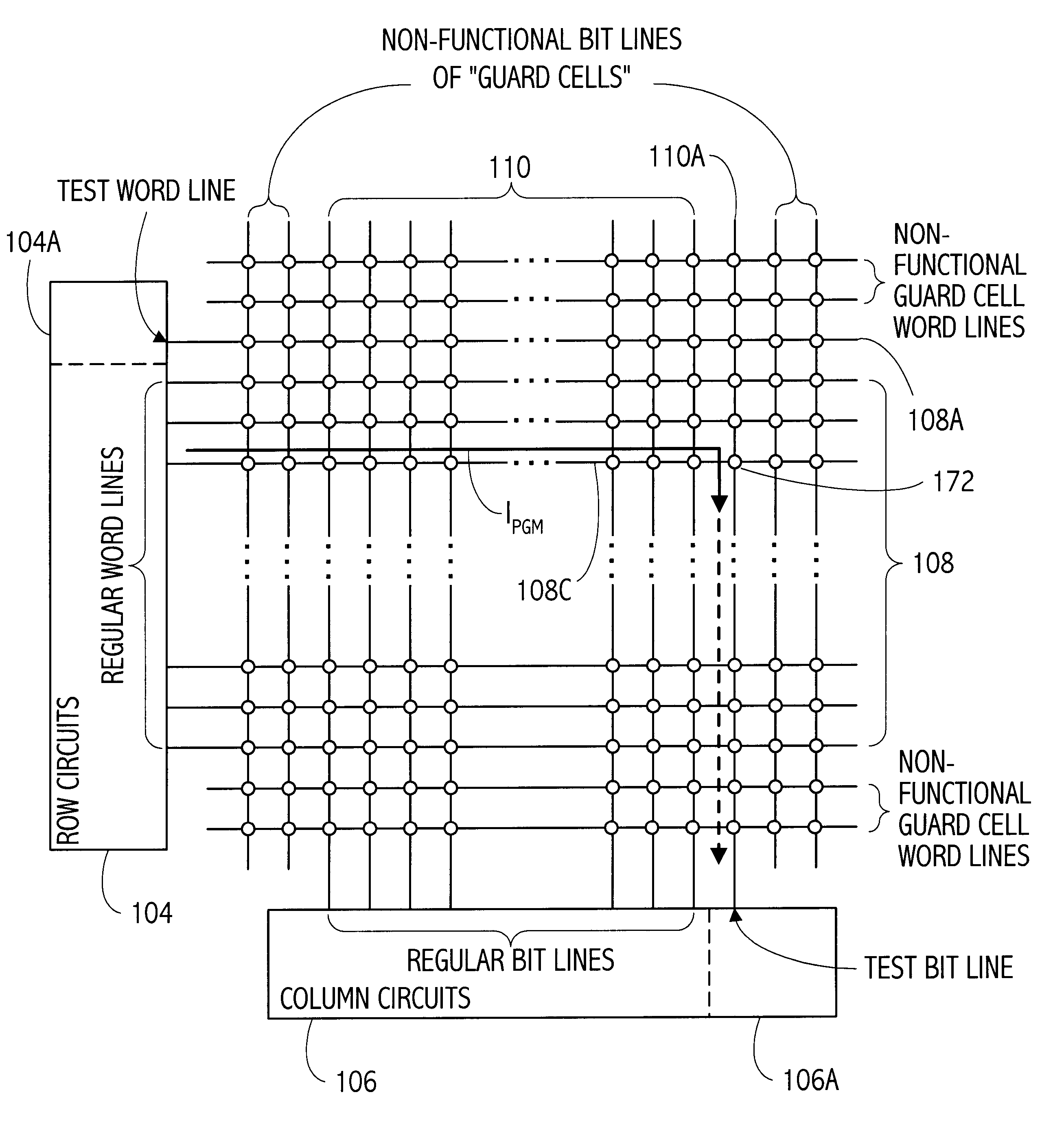
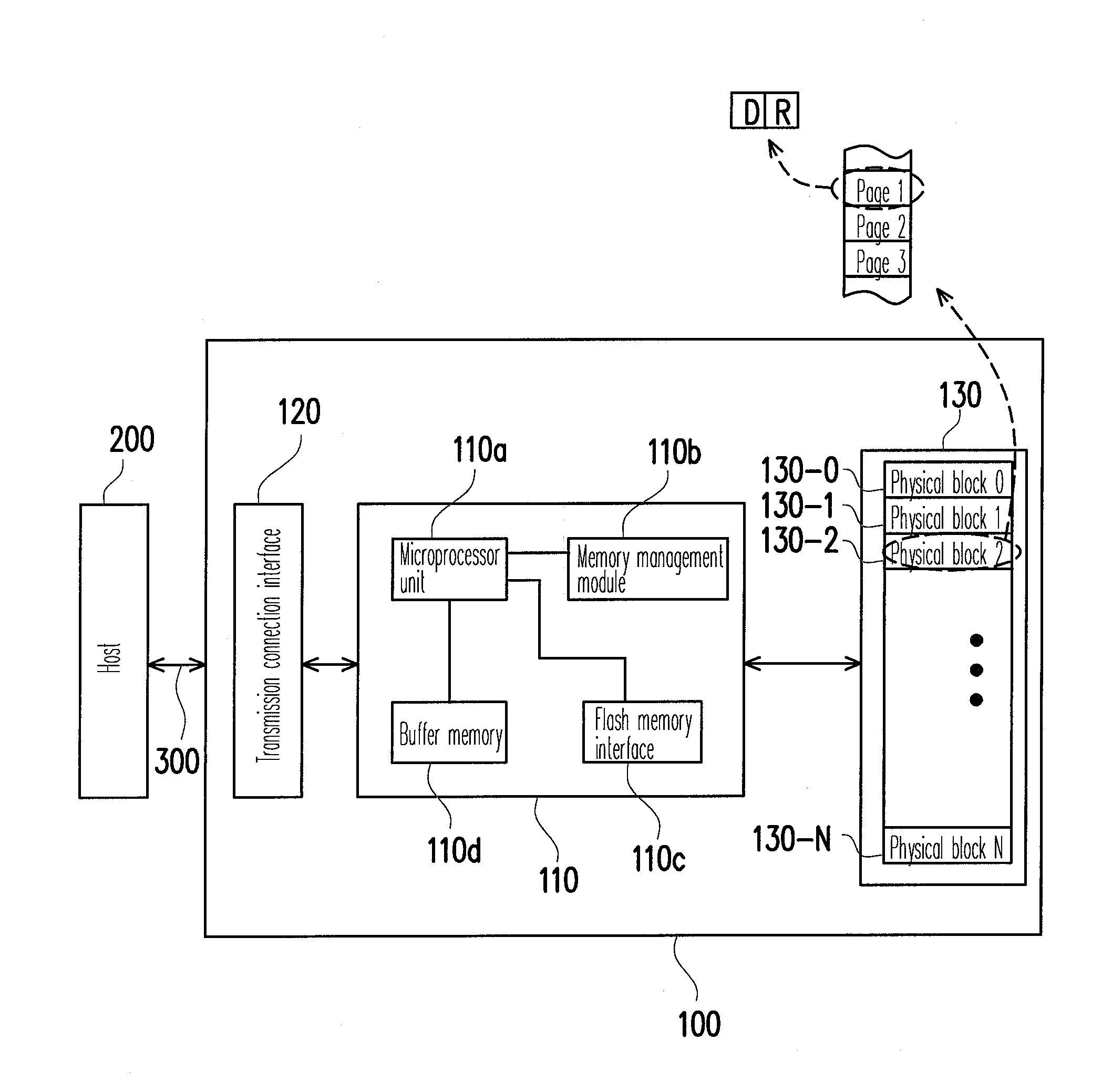
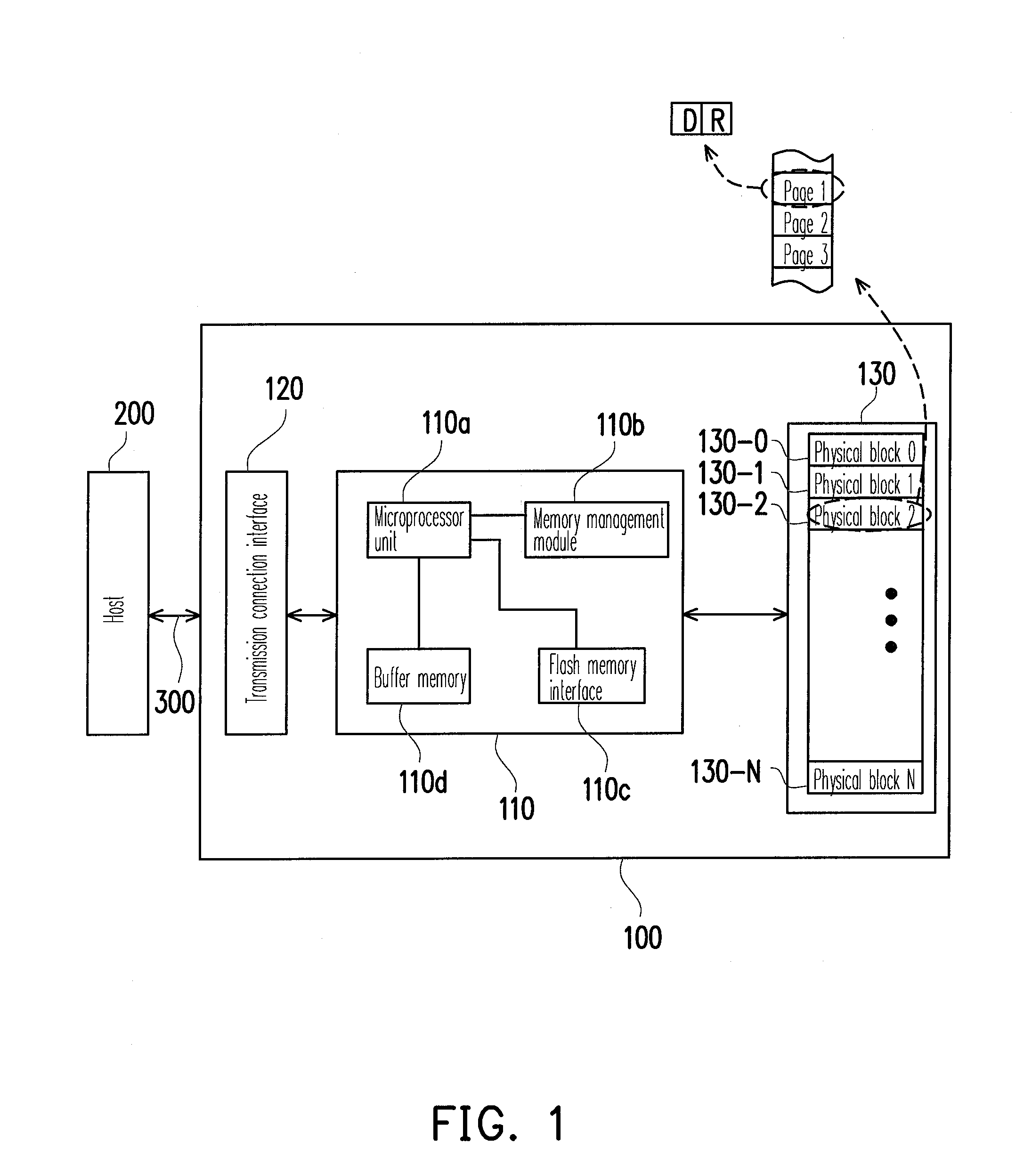
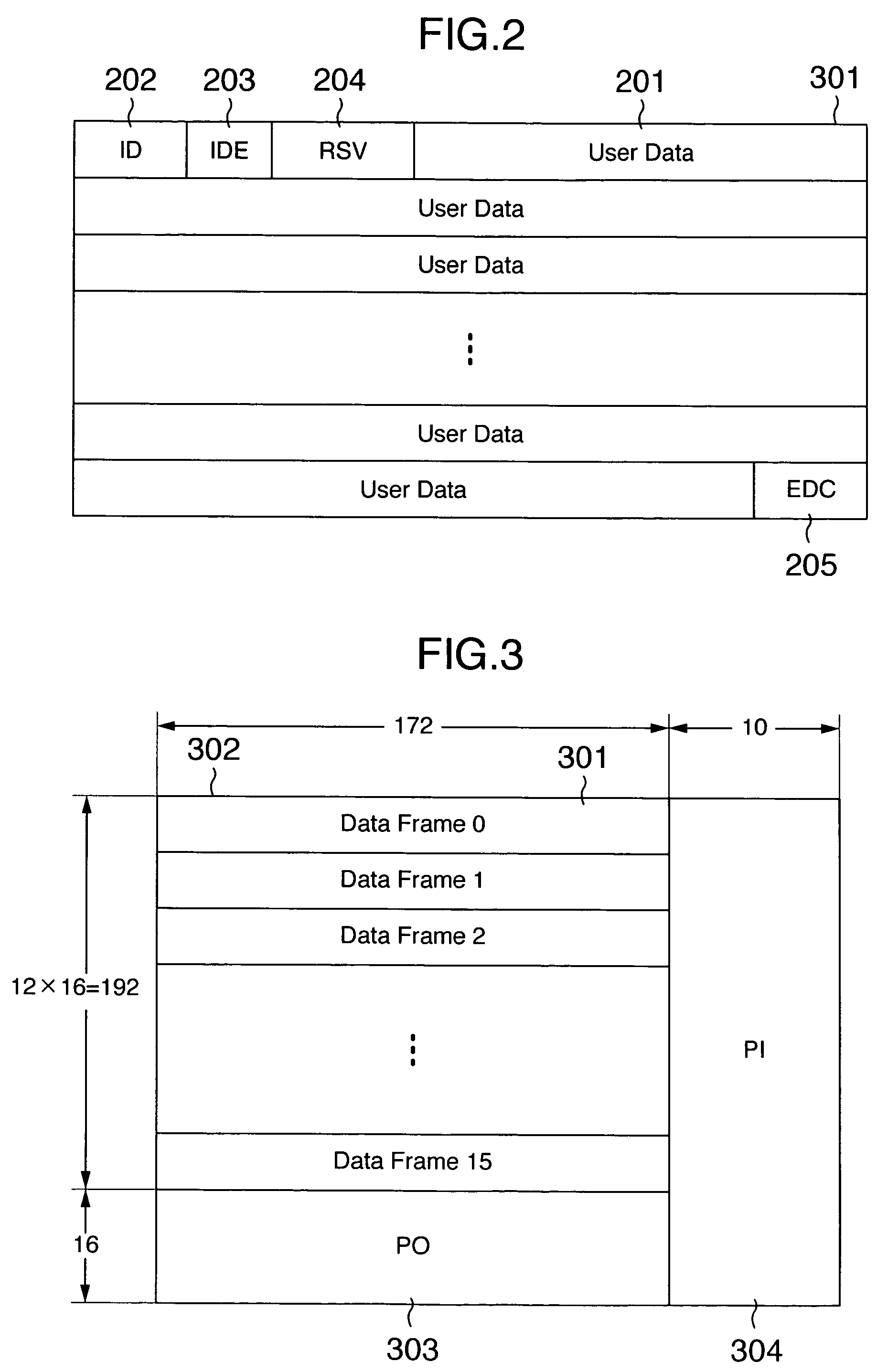
Memory array organization and related test method particularly well suited for integrated circuits having write-once memory arrays
In a preferred integrated circuit embodiment, a write-once memory array includes at least one test bit line which provides a respective test memory cell at the far end of each respective word line relative to its word line driver, and further includes at least one test word line which provides a respective test memory cell at the far end of each respective bit line relative to its bit line driver. An intra-layer short between word lines may be detected, such as during manufacturing testing, by biasing adjacent word lines to different voltages and detecting whether any leakage current flowing from one to another exceeds that normally accounted for by the memory cells and other known circuits. Intra-layer bit line shorts and inter-layer word line and bit line shorts may also be similarly detected. An "open" in a word line or bit line may be detected by trying to program the test memory cell at the far end of each such word line or bit line. If successfully programmed, the continuity of each word line and bit line is assured, and the programming circuitry for each word line and bit line is also known to be functional.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
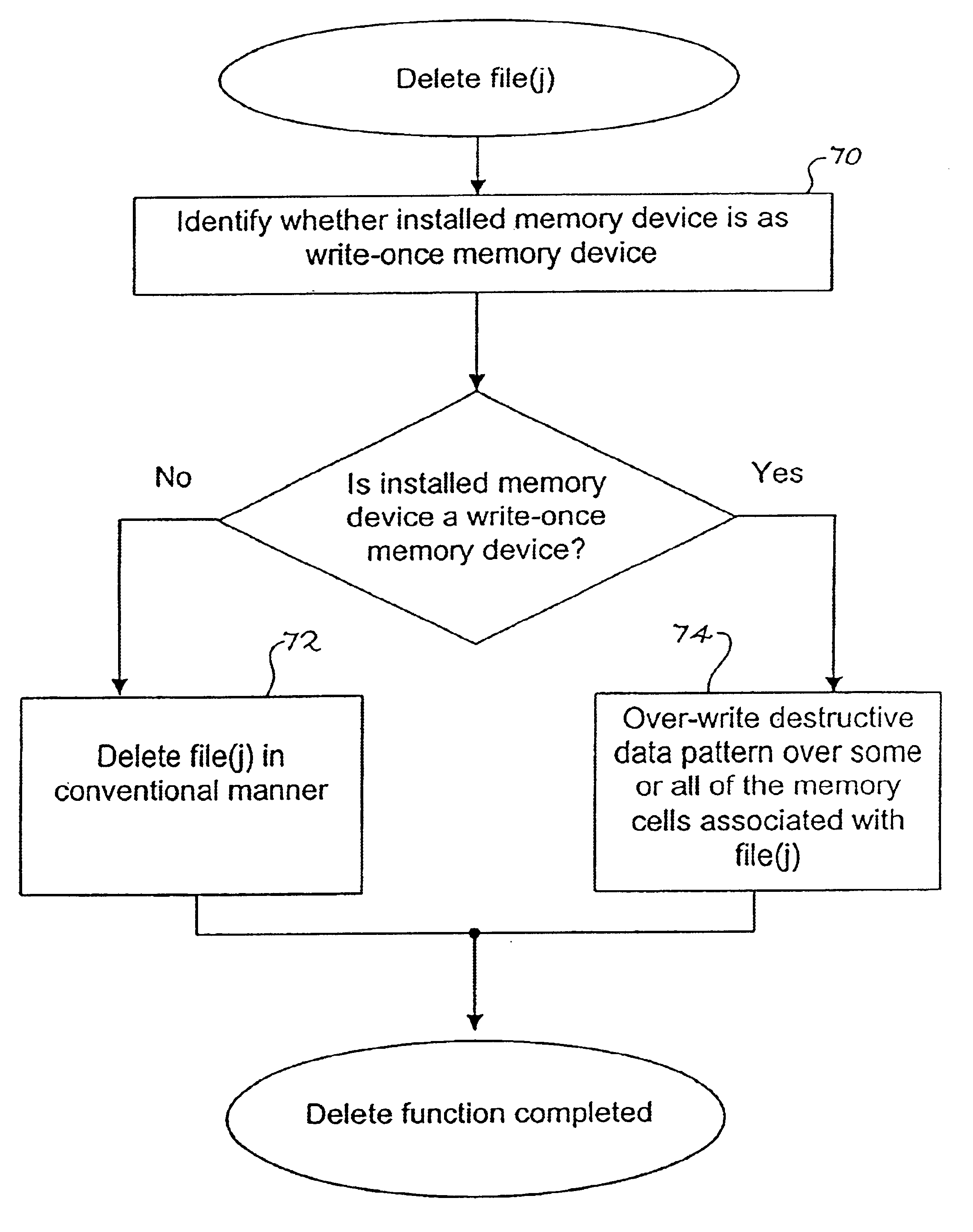
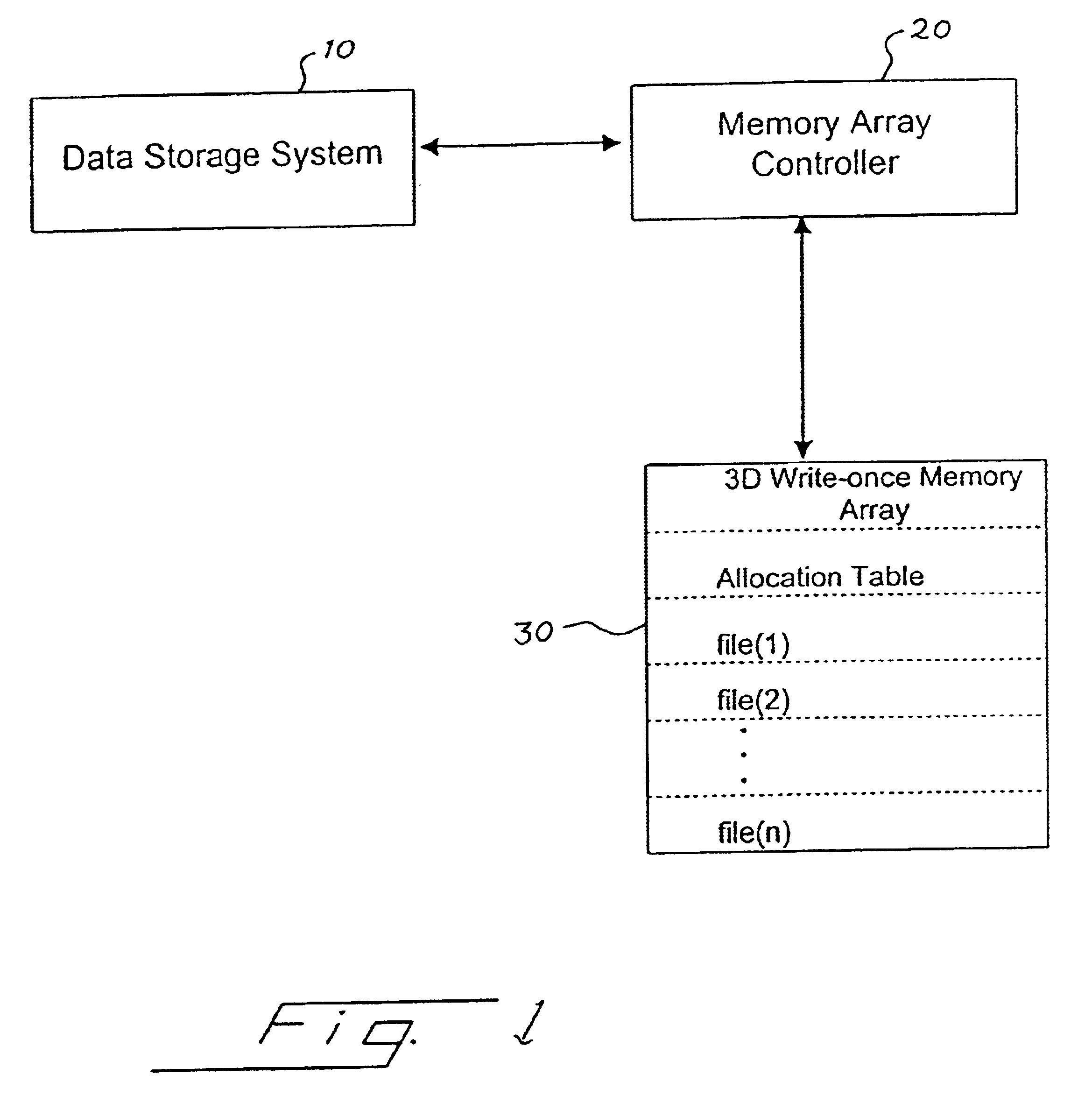
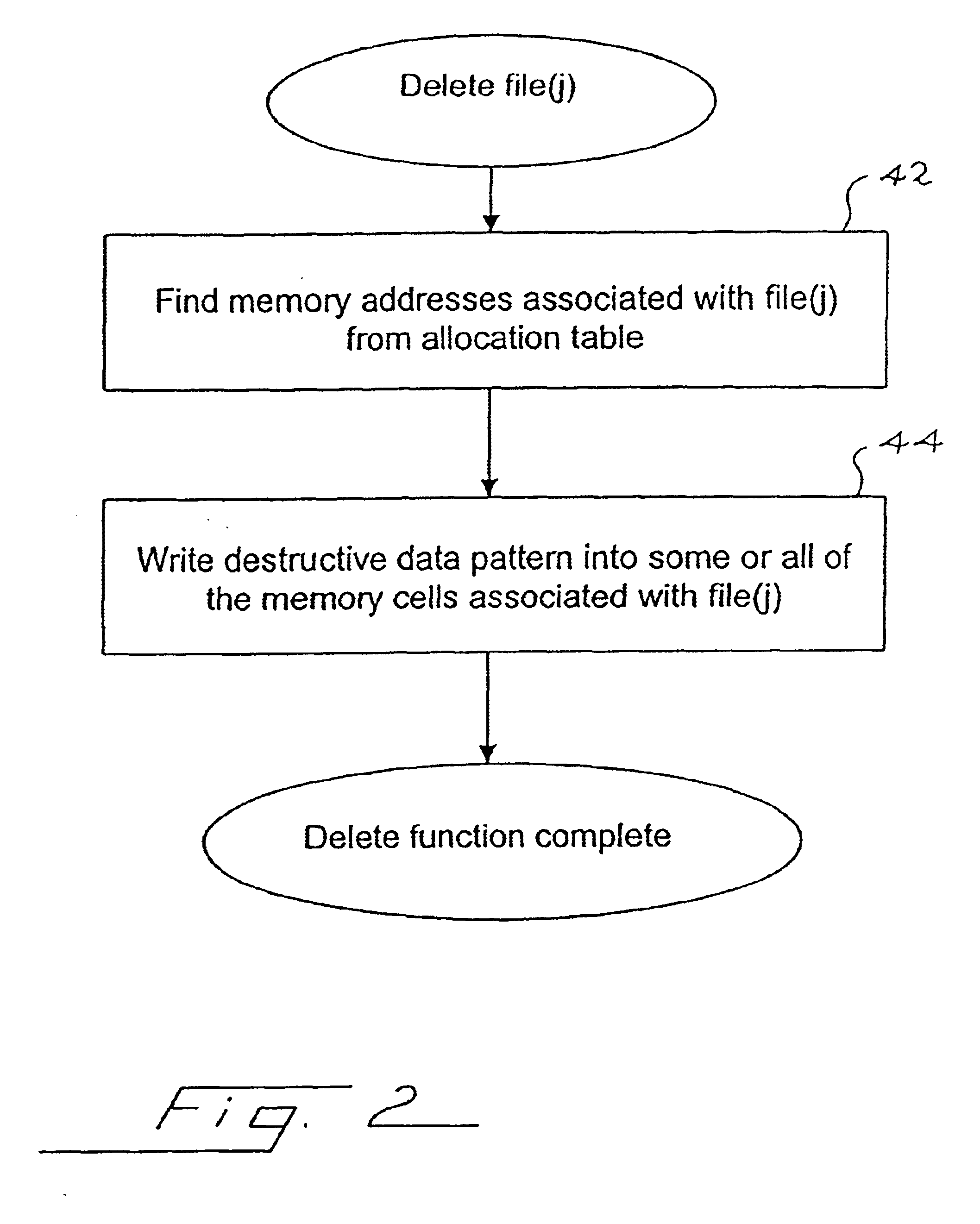
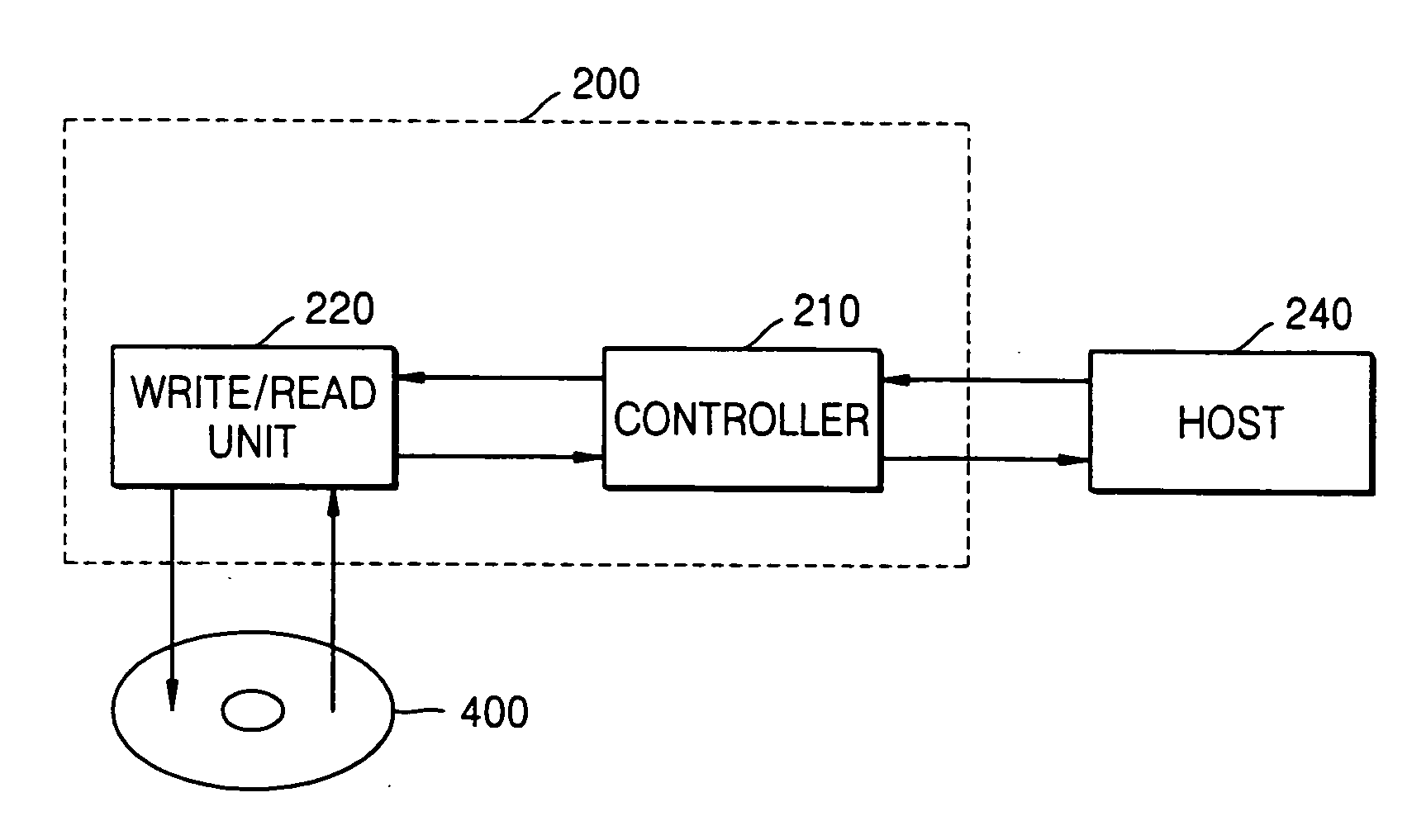
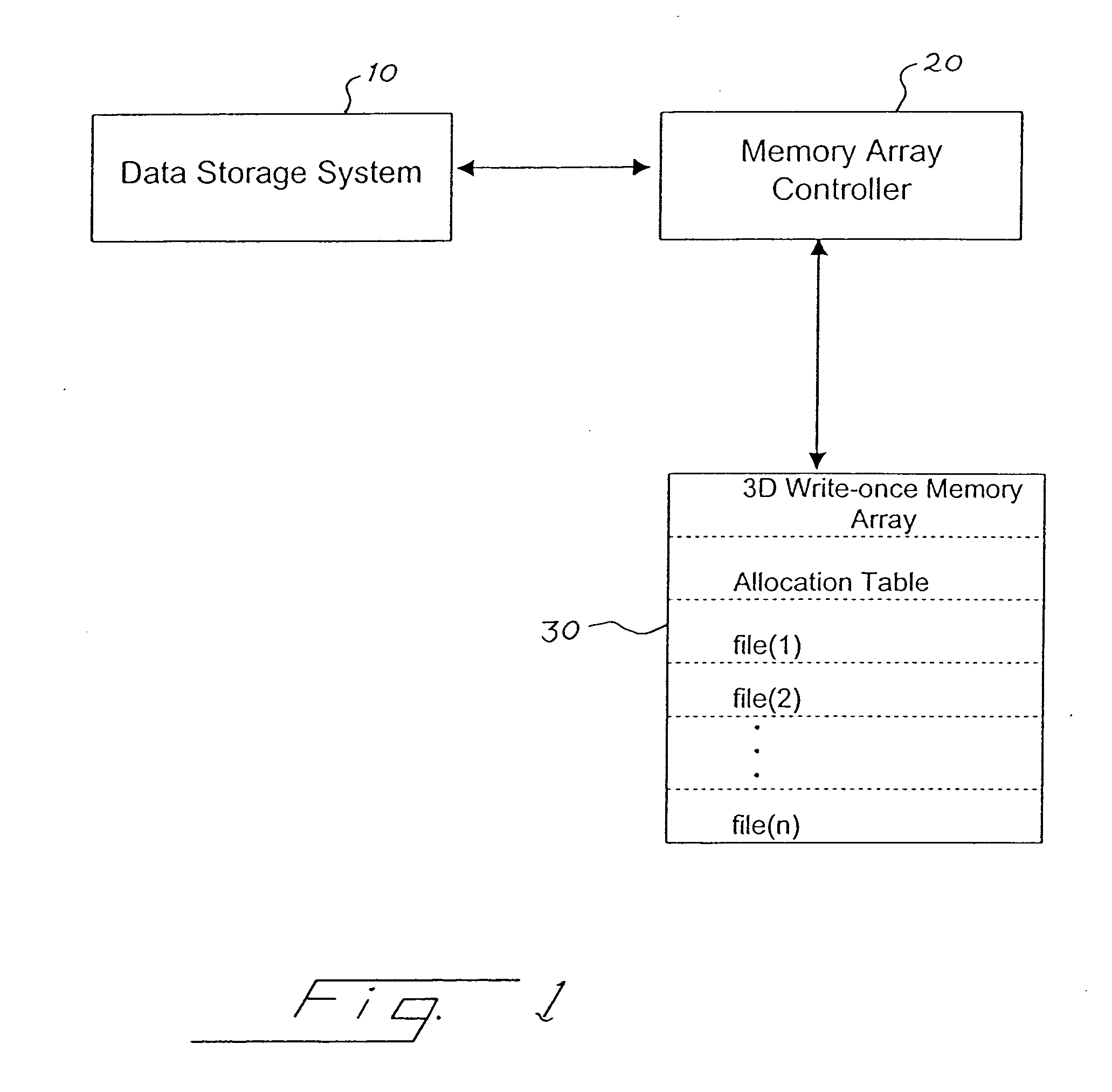
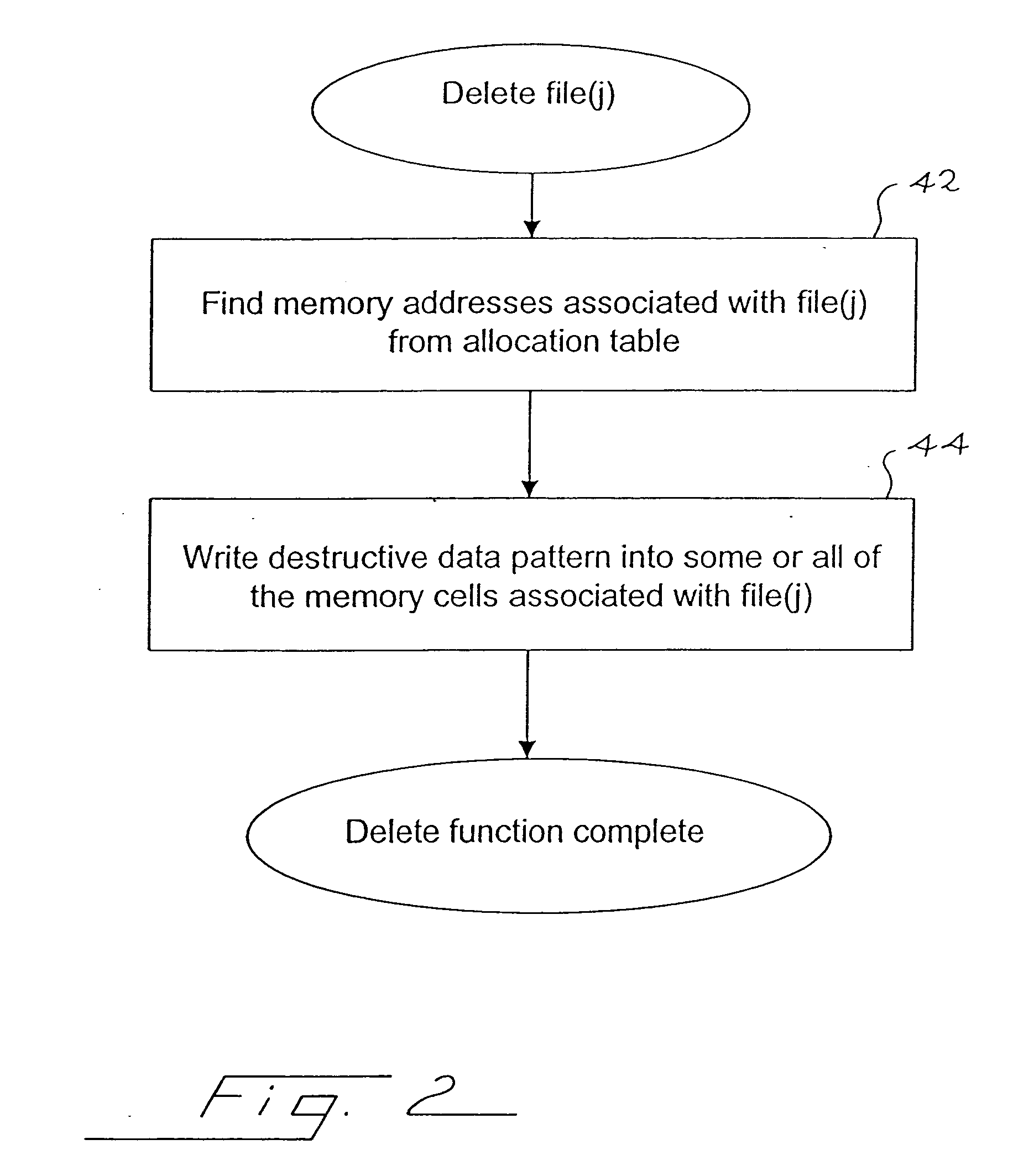
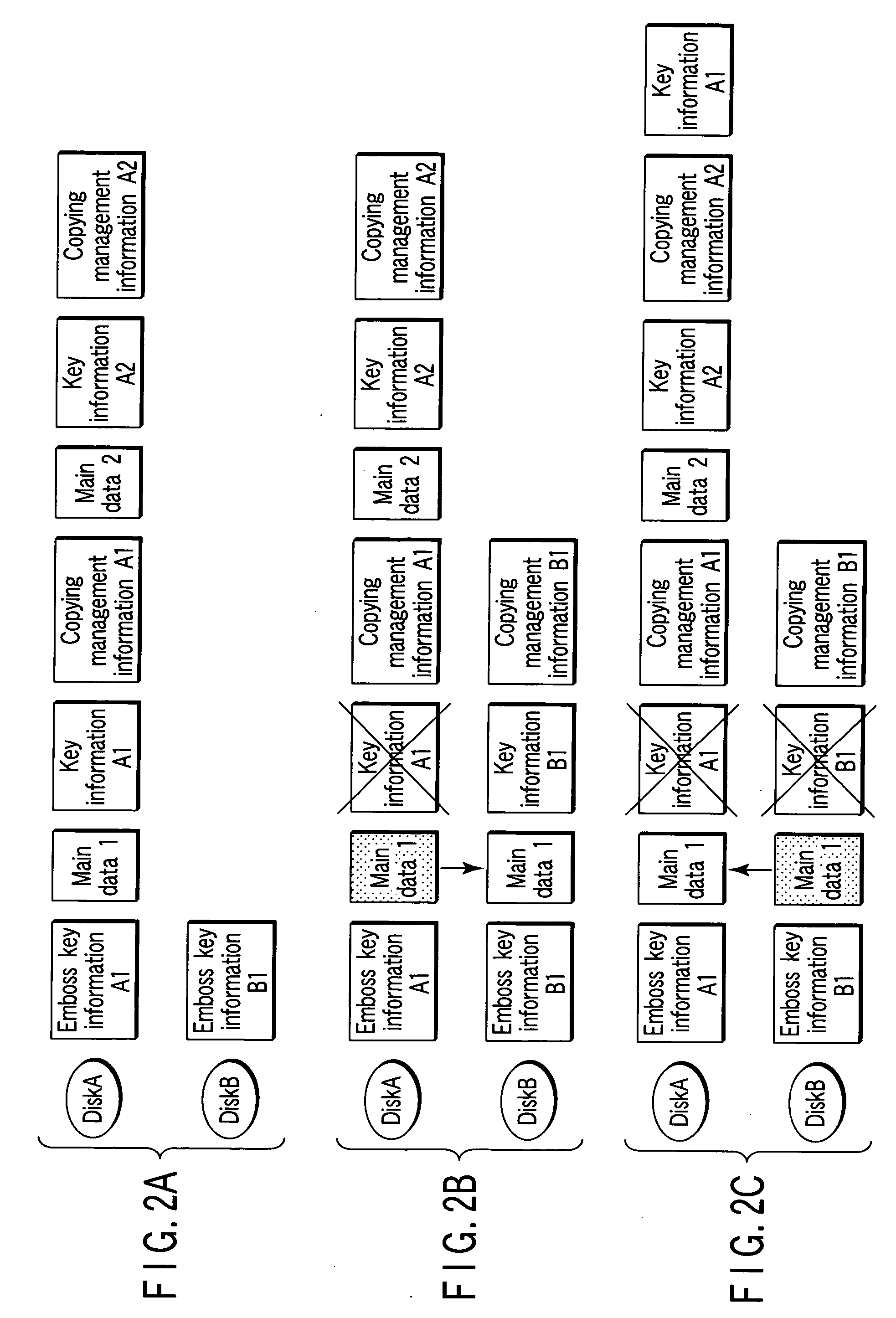
Method for deleting stored digital data from write-once memory device
InactiveUS6658438B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDigital dataDigital storage
A digital storage system is coupled to a write-once memory array. File delete commands are implemented by over-writing a destructive digital pattern to at least a portion of the memory cells associated with the file to be deleted. One disclosed system alters the manner in which a file delete command is implemented, depending upon whether the file is stored in a write-once memory or in a re-writable memory.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
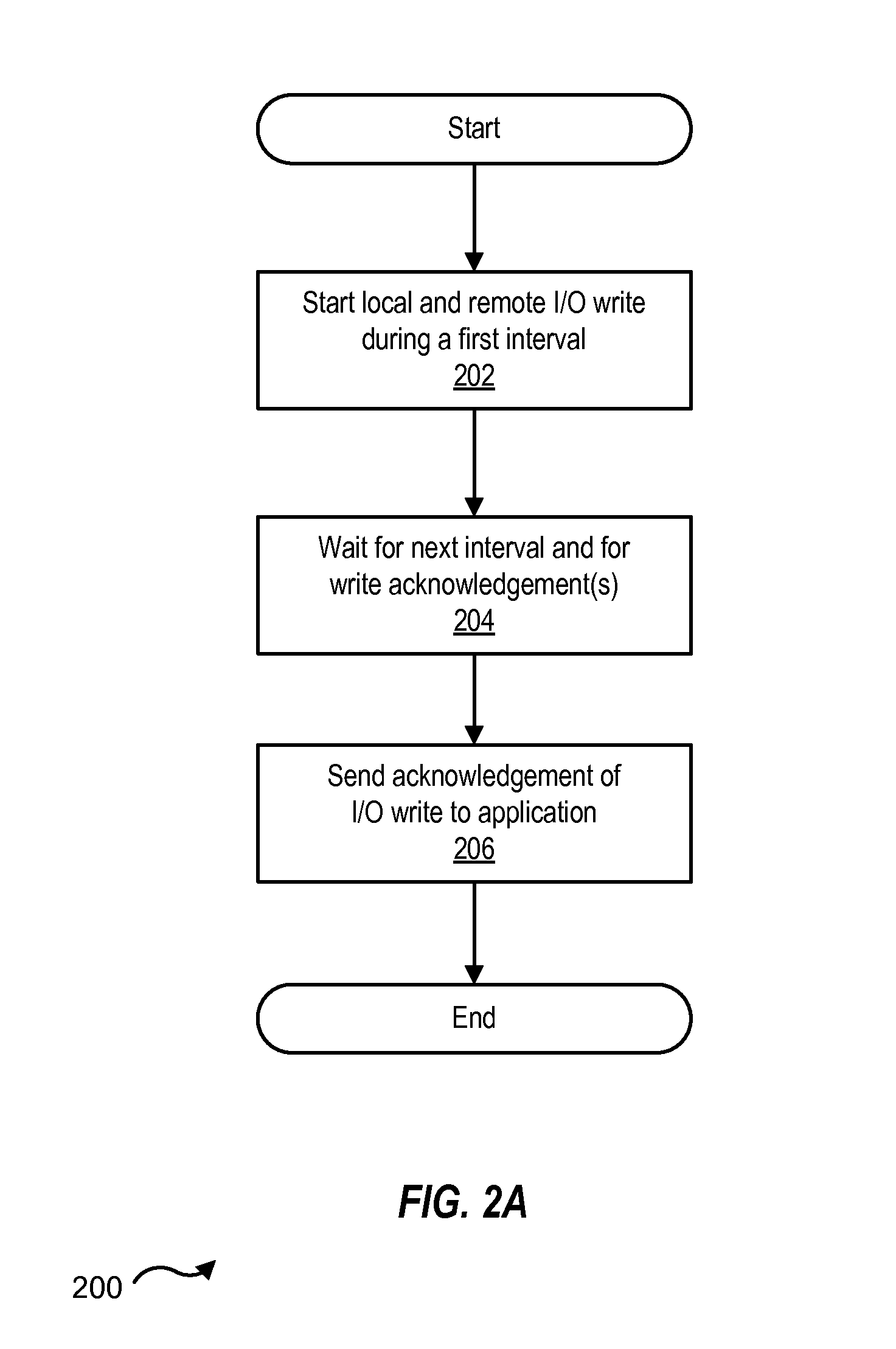
Interval-controlled replication
InactiveUS20130226870A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionComputer scienceOperating system
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Data writing method for flash memory and storage system and controller using the same
ActiveUS20090307413A1Prevented incorrect dataGuaranteed accuracyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti-level cellNand flash memory
A data writing method for a multi-level cell (MLC) NAND flash memory and a storage system and a controller using the same are provided. The flash memory includes a plurality of blocks. Each of the blocks includes a plurality of page addresses. The page addresses are categorized into a plurality of upper page addresses and a plurality of lower page addresses. The writing speed of the lower page addresses is faster than that of the upper page addresses. The data writing method includes receiving a writing command and data and writing the data into a page address. The page address is skipped when it is an upper page address and a corresponding lower page address stores a valid data written by a previous writing command. Thereby, the accuracy of the data written by the previous writing command is ensured when a programming error occurs to the flash memory.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
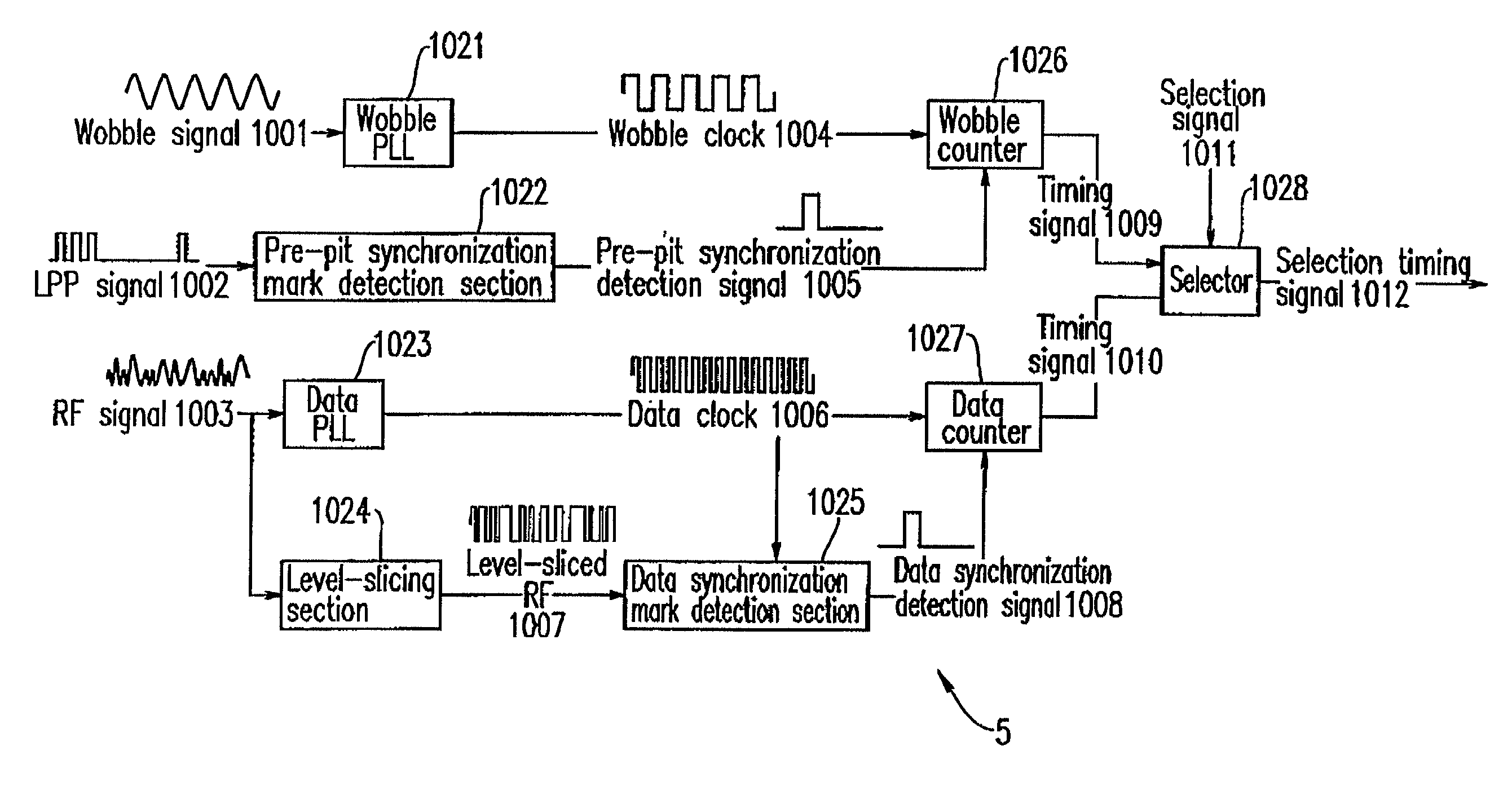
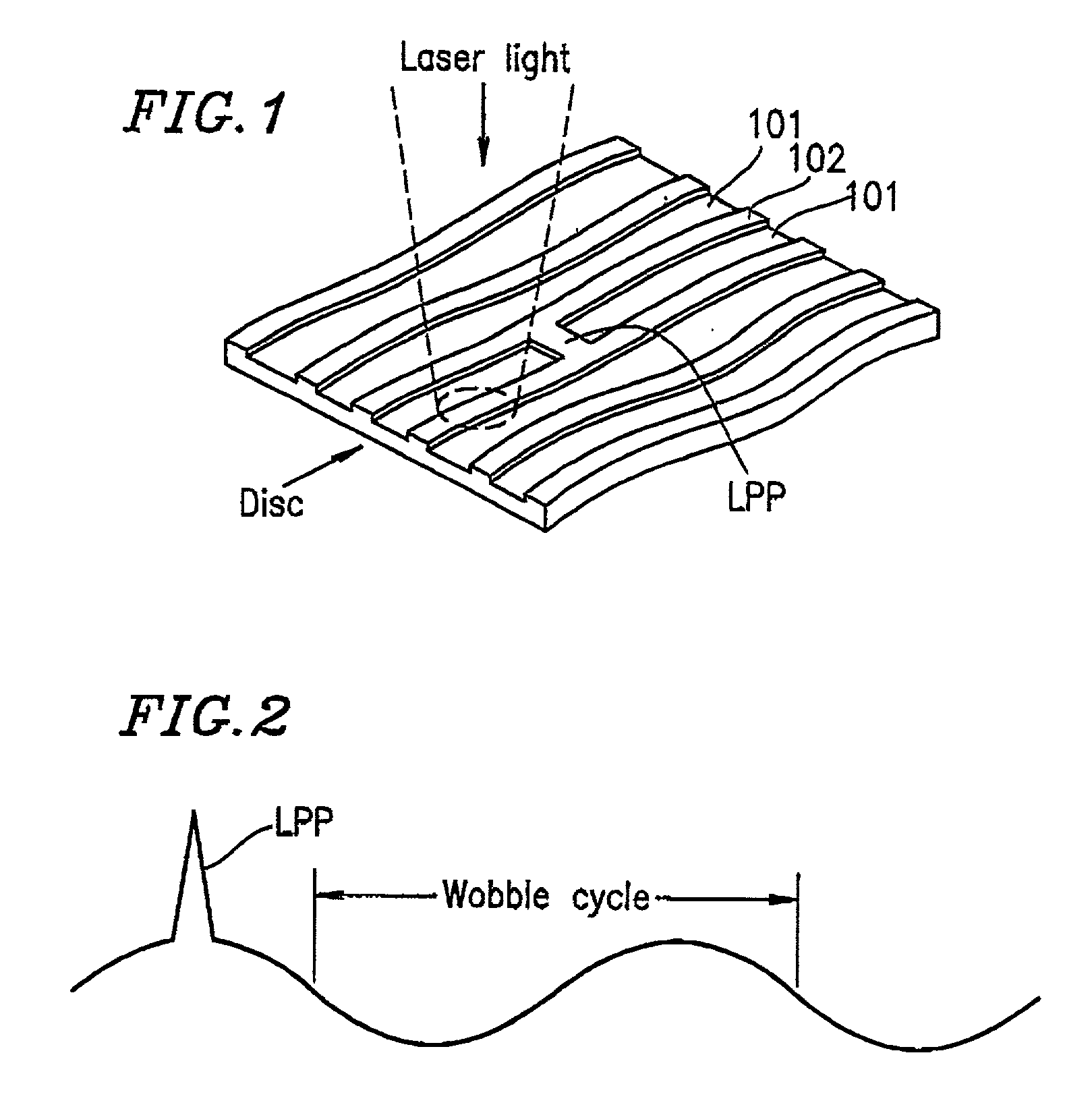
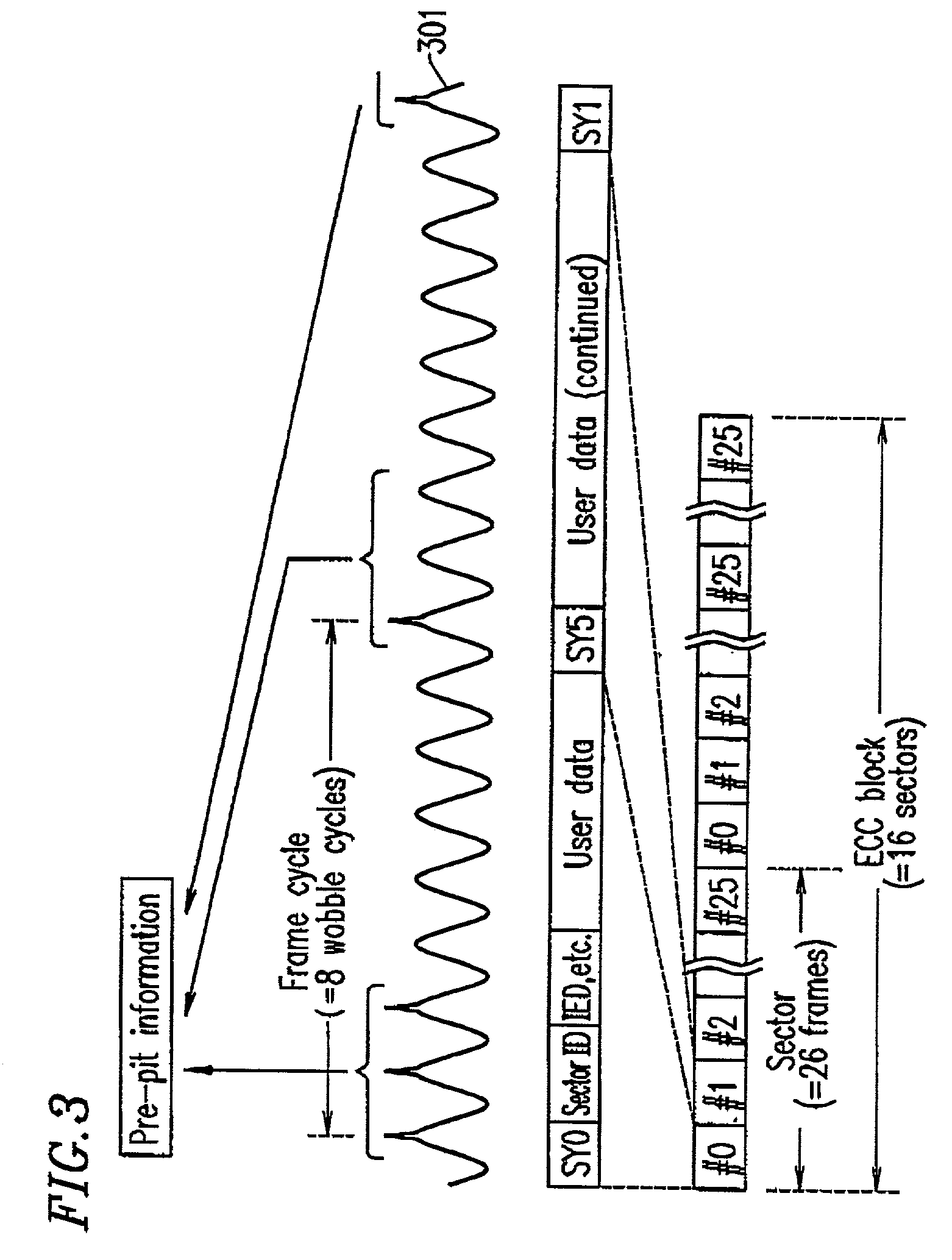
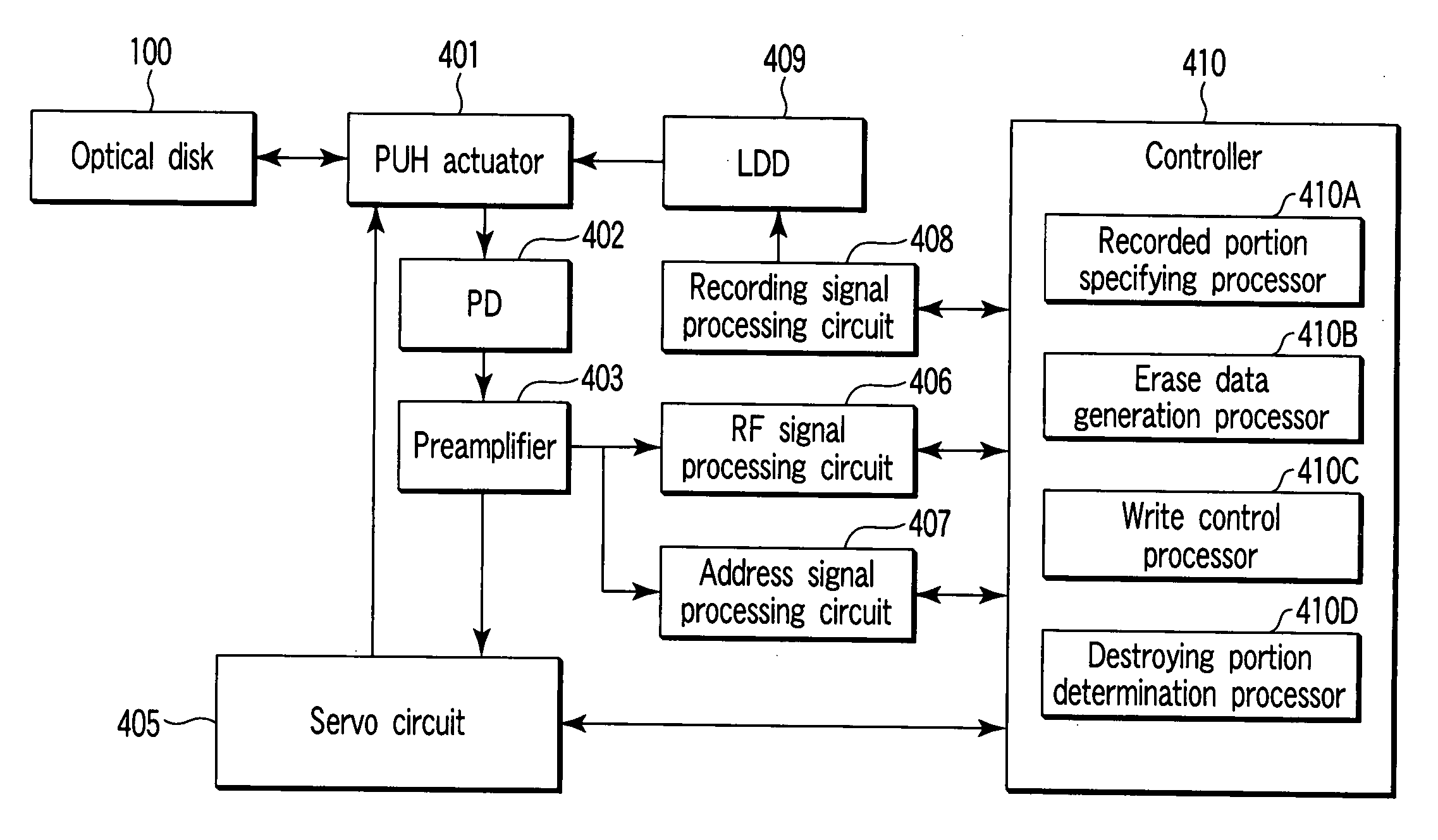
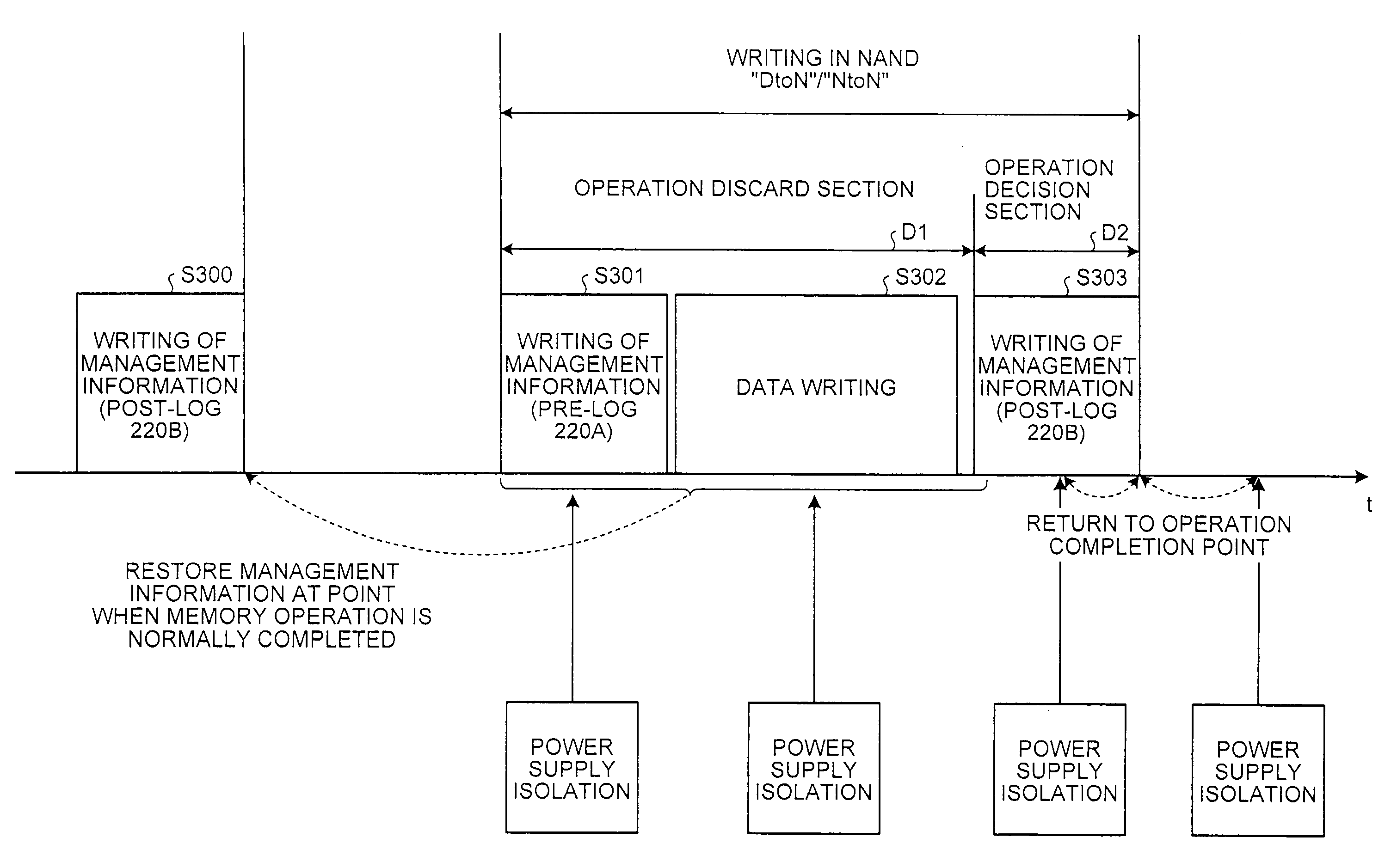
Recording apparatus and method, and reproduction apparatus and method for recording data to or reproducing data from a write once type information recording medium, and write once type information recording medium
ActiveUS7023775B2Improve reliabilityHighly reliable RMDTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersRecord statusWrite-once
A recording method for recording, on a write once type information recording medium, management information representing a recording state of the write once type information recording medium is provided. The information recording medium includes data including a first synchronization signal. The information recording medium has a second synchronization signal pre-recorded by cutting. The recording method includes the steps of (a) performing a recording operation for recording the management information at a predetermined position of the information recording medium based on the first synchronization signal; (b) determining whether the recording operation in step (a) is normally terminated or not; and (c) when the recording operation in step (a) is not normally terminated, performing a recording operation for recording the management information at the predetermined position of the information recording medium based on the second synchronization signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
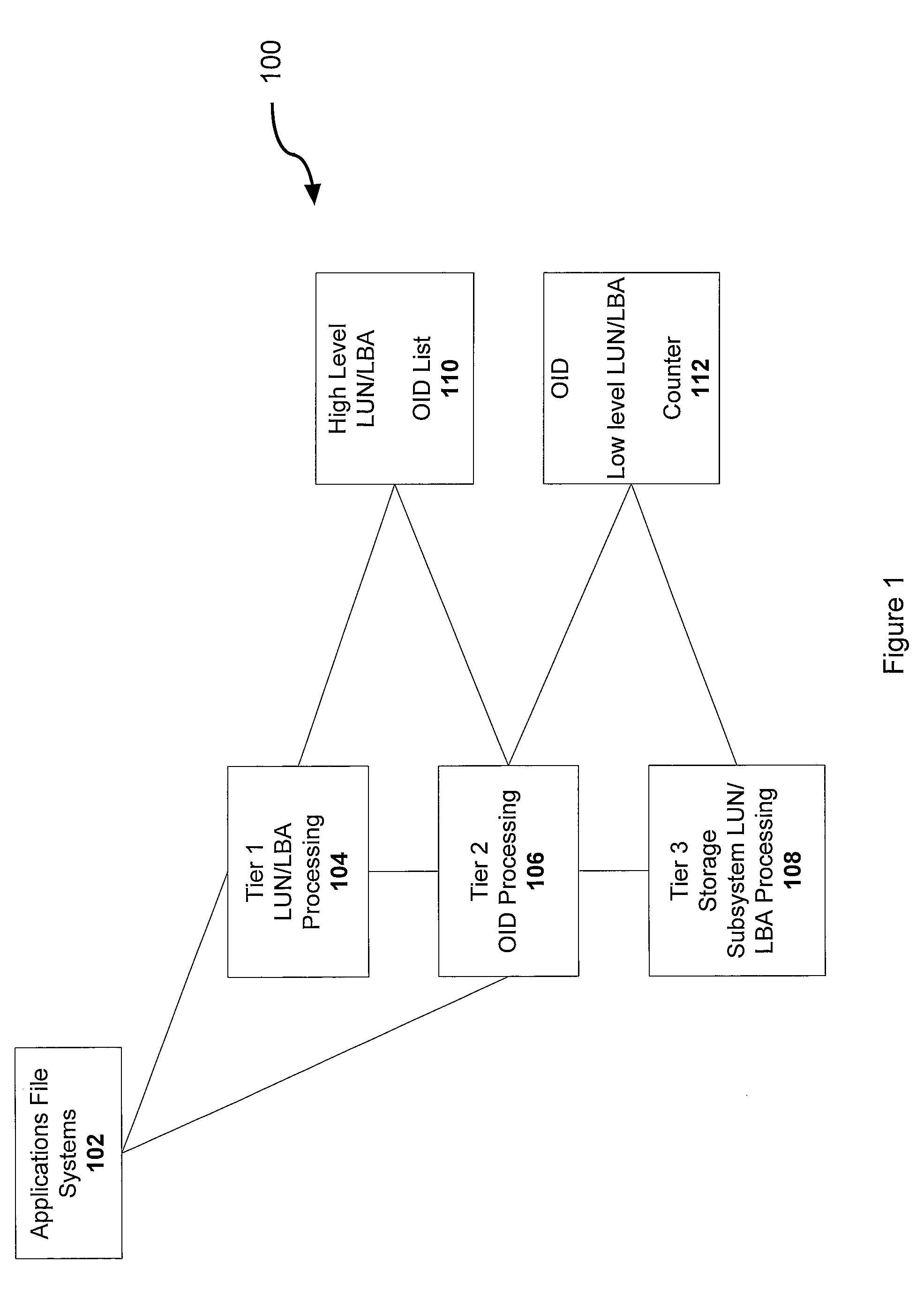
Flexible LUN/LBA interface for content addressable reference storage
InactiveUS7096342B2Facilitate writing and retrievalEasy to writeInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsApplication softwareComputer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
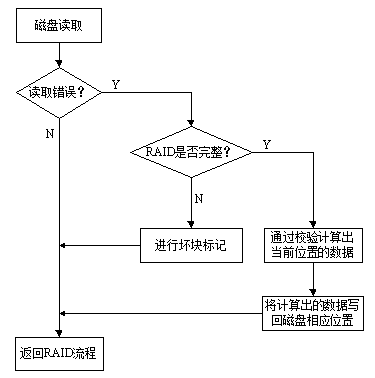
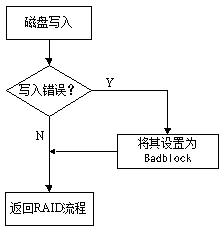
Fault-tolerance method for high-reliability disk array
ActiveCN103309775AReduce the frequency of cullingExtended service lifeRedundant hardware error correctionOccurrence dataDisk array
The invention discloses a fault-tolerance method for a high-reliability disk array. The fault-tolerance method comprises the following steps: when a data write error occurs, confirming storage space of a disk in which data with the write error is, and carrying out bad block marking on the storage space; when a data read error occurs, judging if the disk array is complete, if so, working out current position data by checking, writing the data in a corresponding position of the disk, and otherwise, carrying out bad block marking on the storage space with the data read error; and when a next write operation is carried out, carrying out the write operation on the storage space subjected to bad block marking, if the storage space is successfully written and the subsequent read operation is also successful, removing a bad block mark of the storage space, and on the contrary, remaining the bad block mark. According to the fault-tolerance method, the technical problems that only bad block information of read-write errors is recorded and bad blocks are not repaired in a disk array system and the disk array system is limited by a fault-tolerance range in the prior art are solved; and the fault-tolerance method is in particular suitable for occasions with low data accuracy requirements.
Owner:SUZHOU KEDA TECH
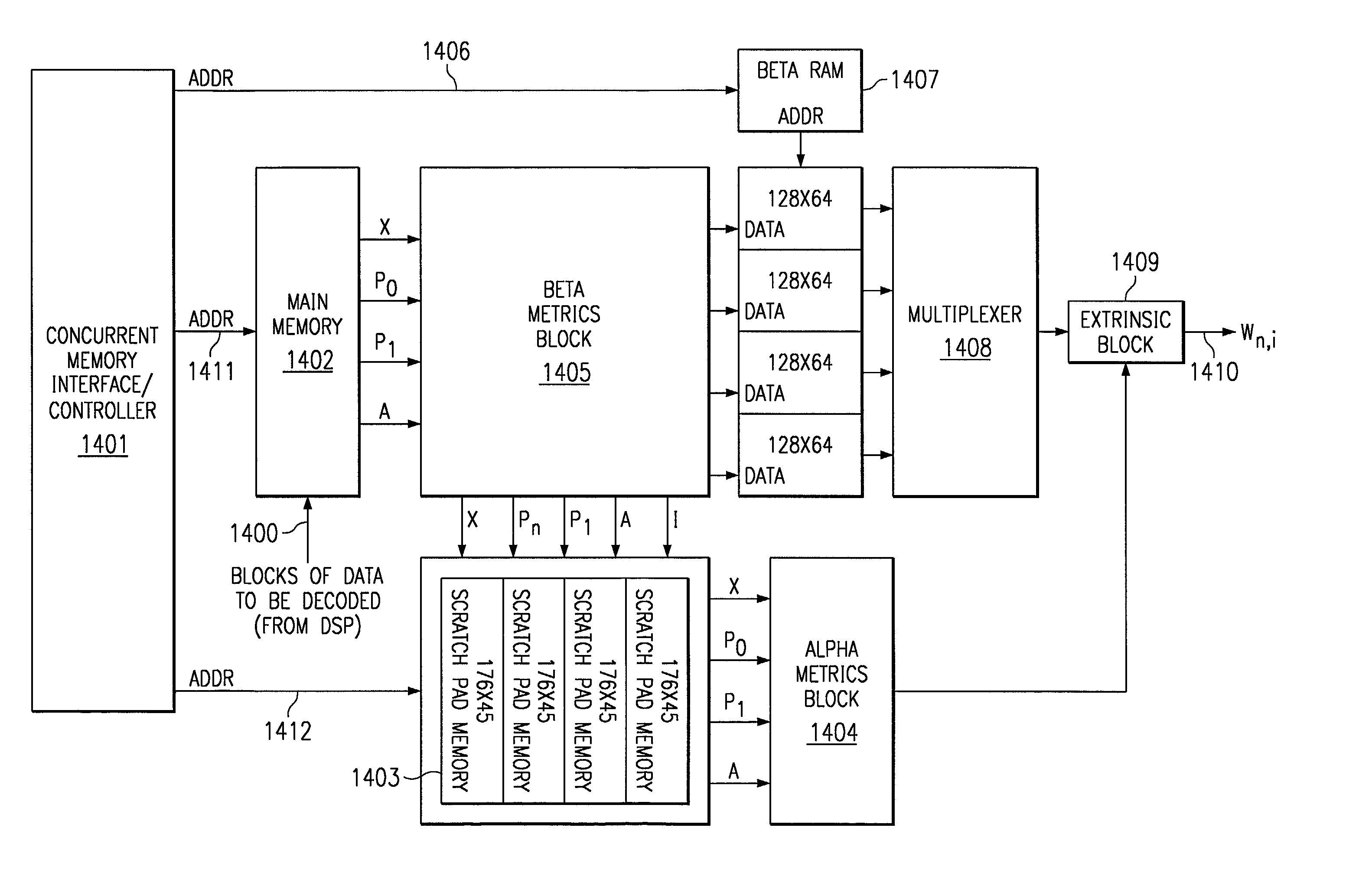
Concurrent memory control for turbo decoders
InactiveUS6993704B2Data representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesComputer architectureScratchpad memory
The concurrent memory control turbo decoder solution of this invention uses a single port main memory and a simplified scratch memory. This approach uses an interleaved forward-reverse addressing which greatly relieves the amount of memory required. This approach is in marked contrast to conventional turbo decoders which employ either a dual port main memory or a single port main memory in conjunction with a complex ping-ponged scratch memory. In the system of this invention, during each cycle accomplishes one read and one write operation in the scratch memories. If a particular location in memory, has been read, then that location is free. The next write cycle can use that location to store its data. Similarly a simplified beta RAM is implemented using a unique addressing scheme which also obviates the need for a complex ping-ponged beta RAM.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
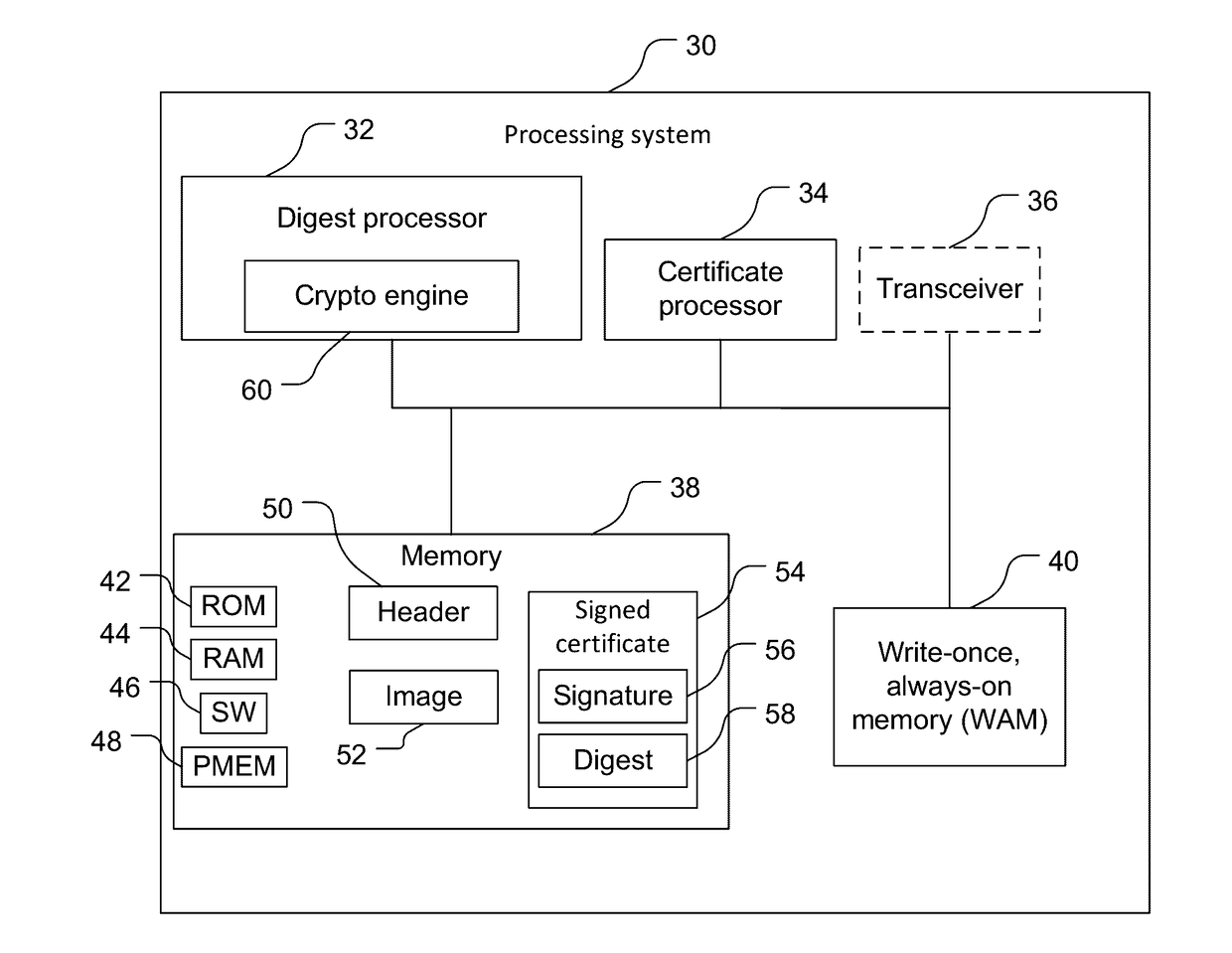
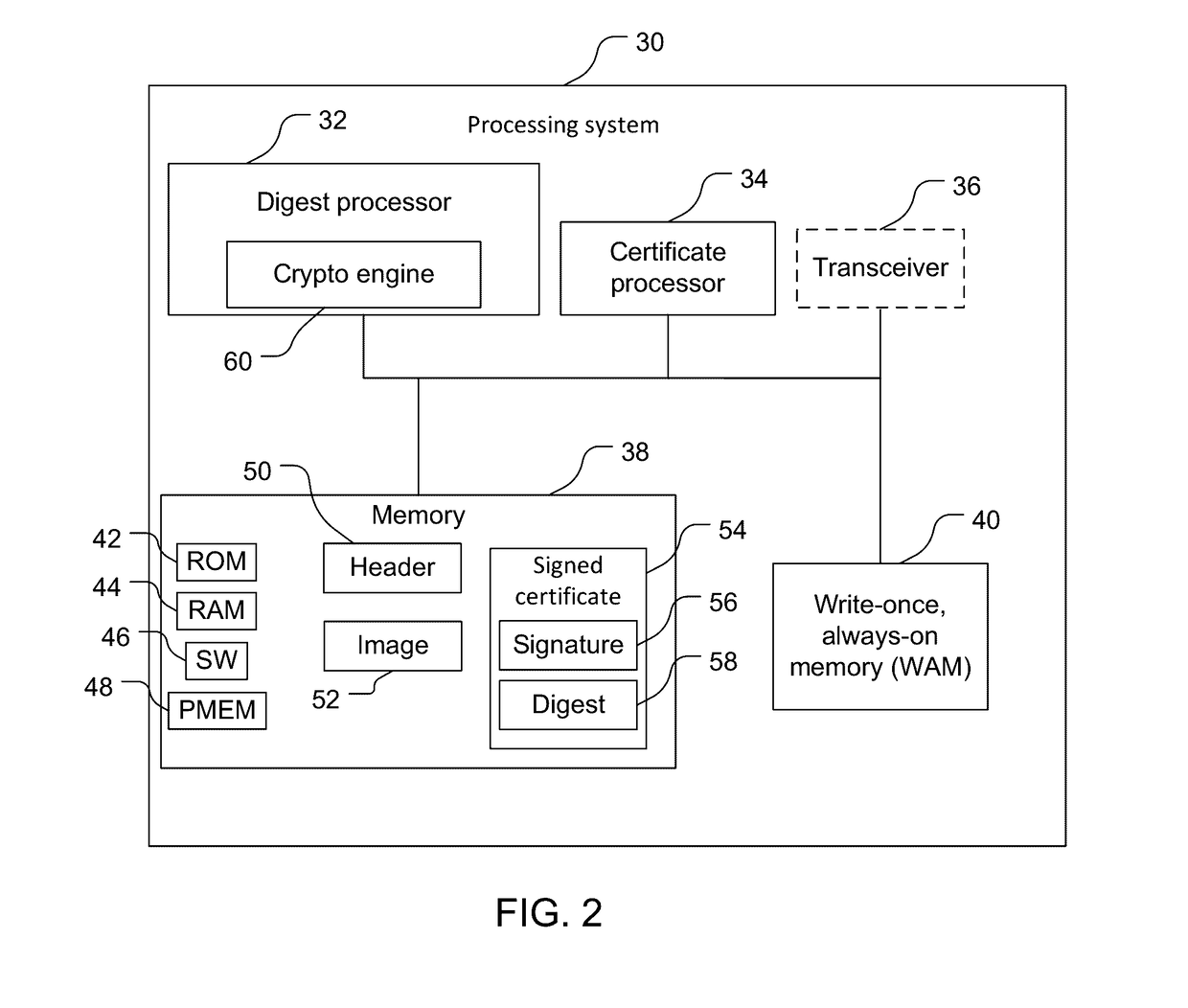
Secure boot devices, systems, & methods
ActiveUS20170093582A1User identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionWrite-onceOperating system
A secure boot method includes: obtaining a certificate digest at a digest processor from a write-once, always-on memory; calculating a flash digest using the digest processor by cryptographically processing a sensitive information image; and comparing, using the digest processor, the flash digest with the certificate digest.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
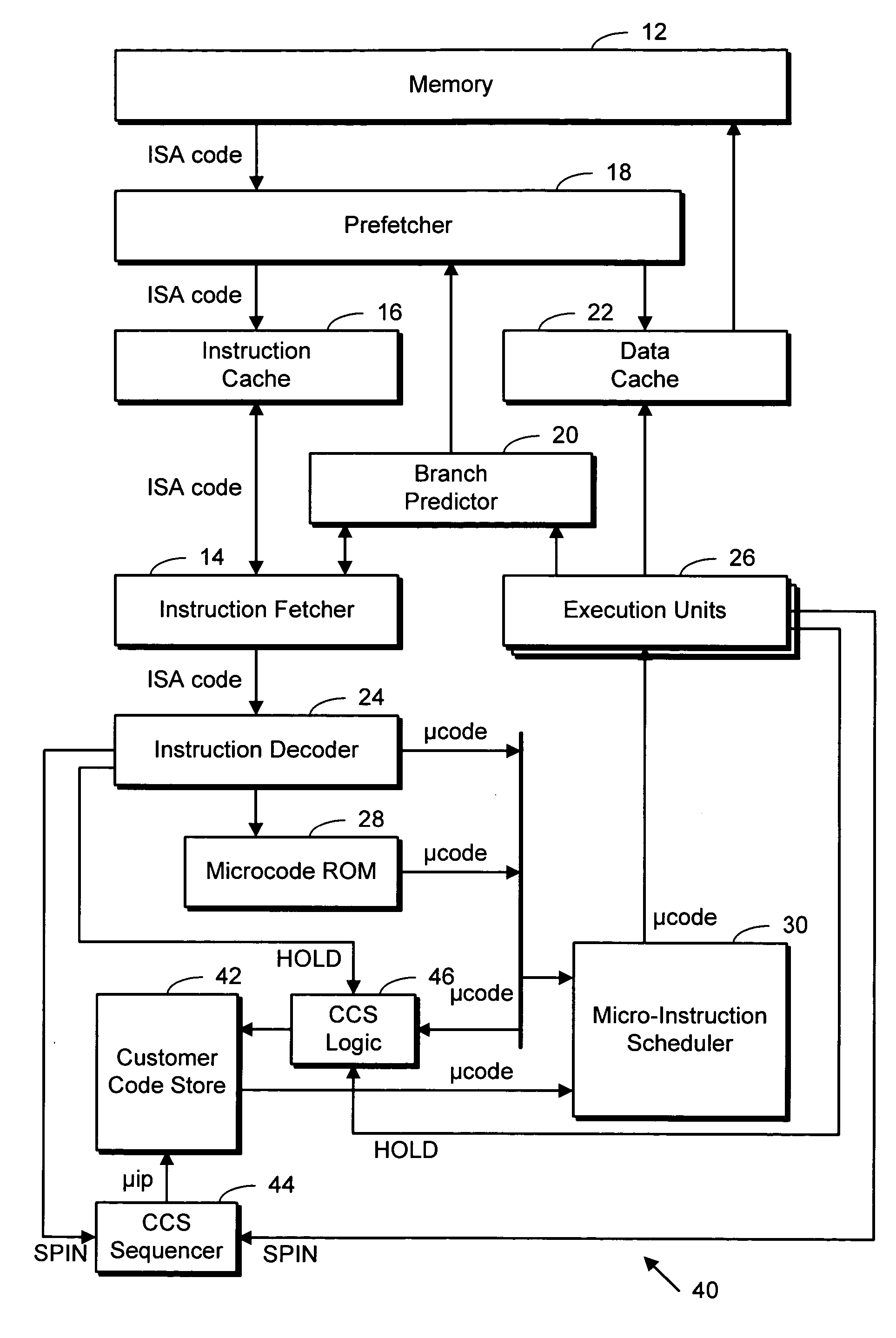
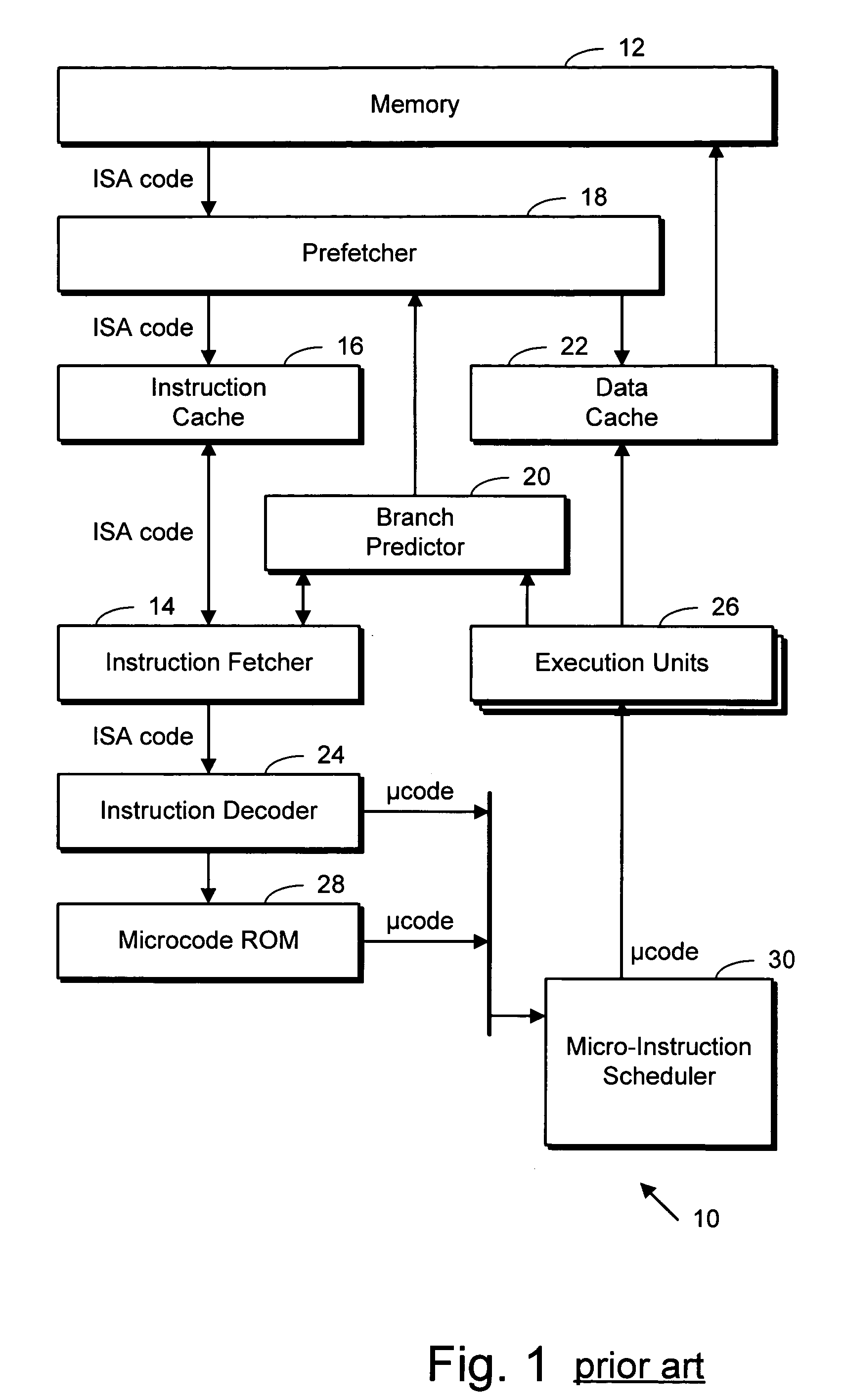
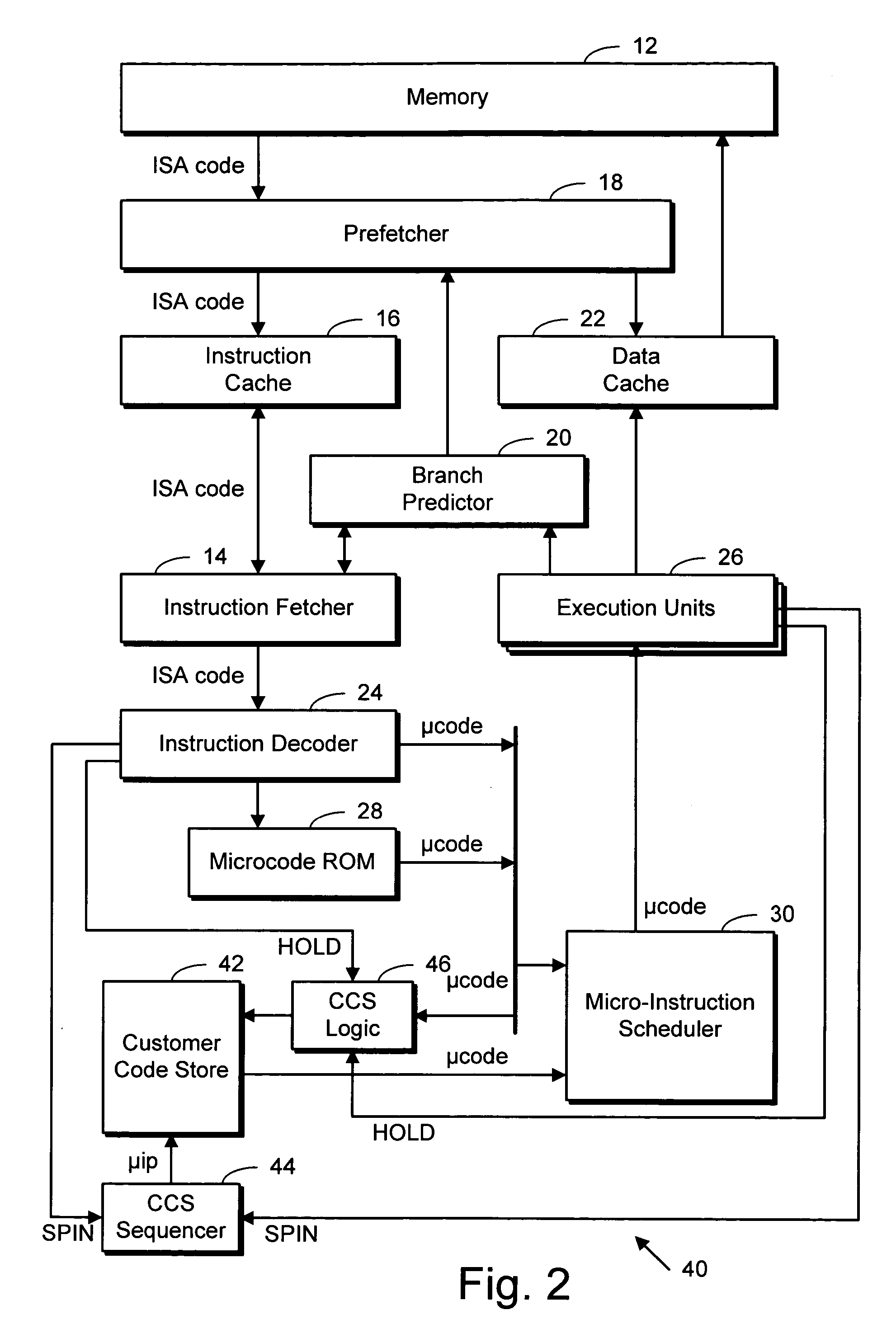
Microprocessor with customer code store
InactiveUS20060015707A1Runtime instruction translationDigital computer detailsParallel computingMicroprocessor
A microprocessor including memory storage into which ISA customer code routines can be stored after having been decoded into their machine-native microinstructions. The customer code store is not subject to eviction and the like, as a cache memory would be. ISA level code can specify a routine for storage into the customer code store, at a time prior to its execution. The customer code store thus serves as a write-once execute-many library of pre-decoded routines which ISA level applications can subsequently use, permitting a system manufacturer to create a highly customized and optimized system.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Data processing apparatus, data processing system, and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS20110271121A1Accurate readingDisabling correct readingUnauthorized memory use protectionRecord information storageData processing systemWrite-once
A data processing apparatus acquires content, generates an encryption key by using an initial value written in an unwritten memory block in a write-once recording medium, encrypts the content by using the encryption key, and writes to the write-once recording medium the encrypted content and an address table for identifying the memory block storing the initial value used for generating the encryption key.
Owner:CANON KK
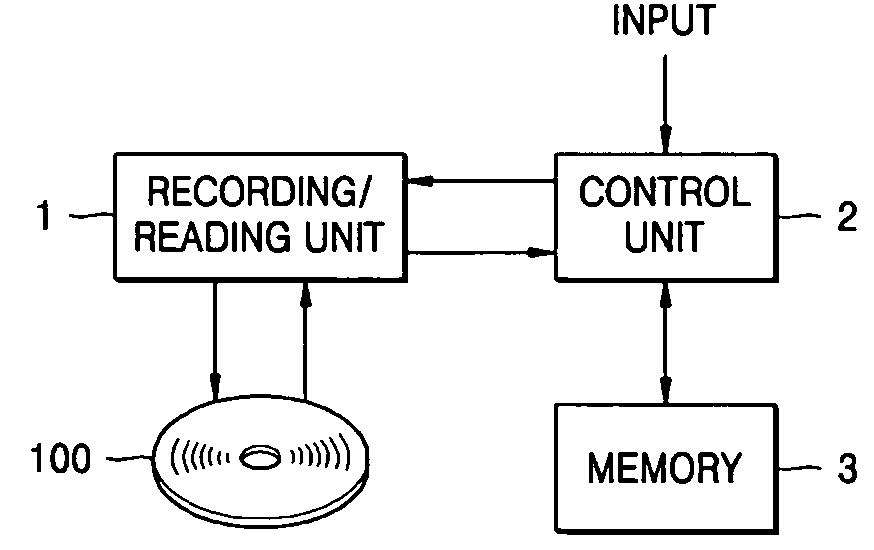
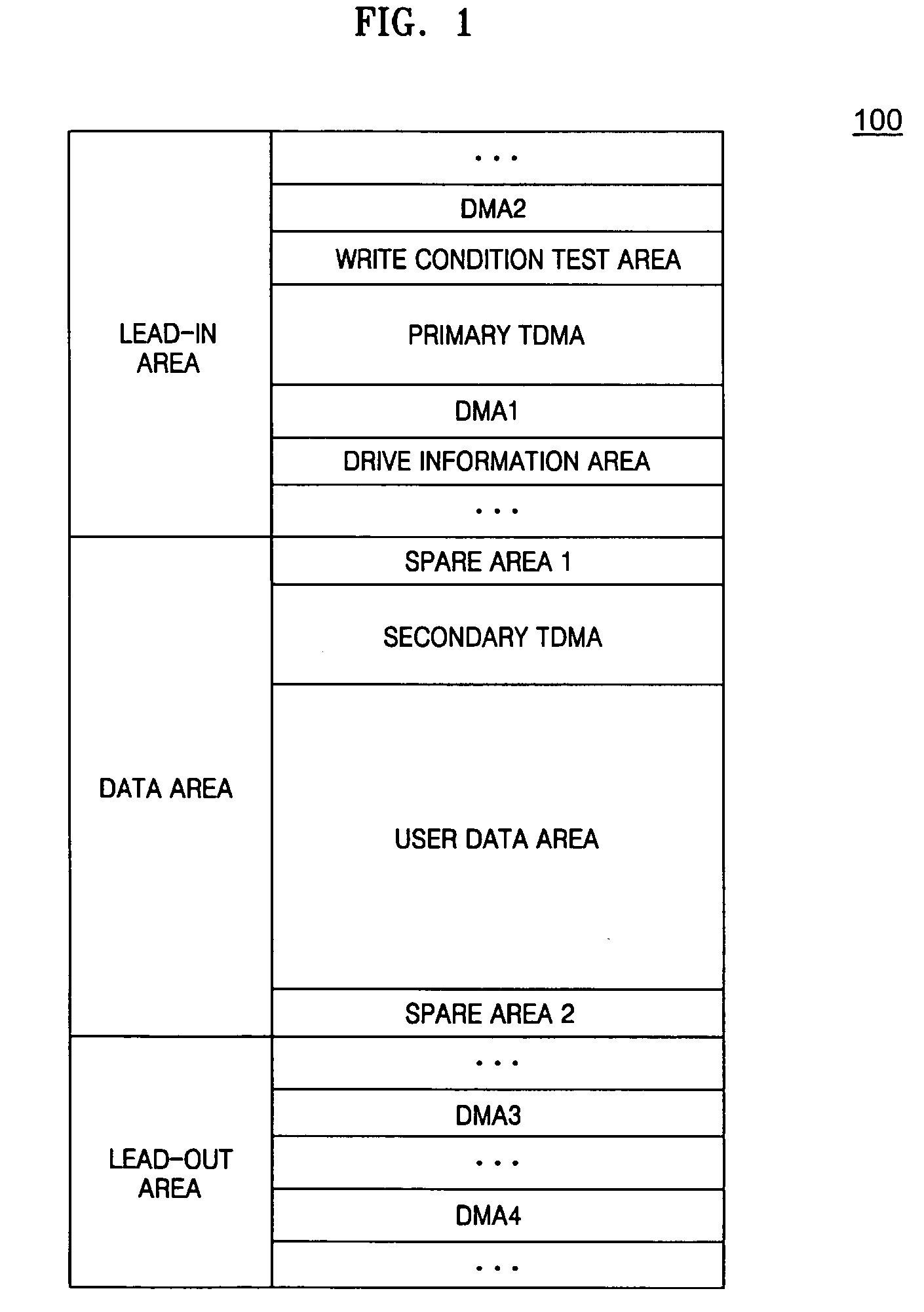
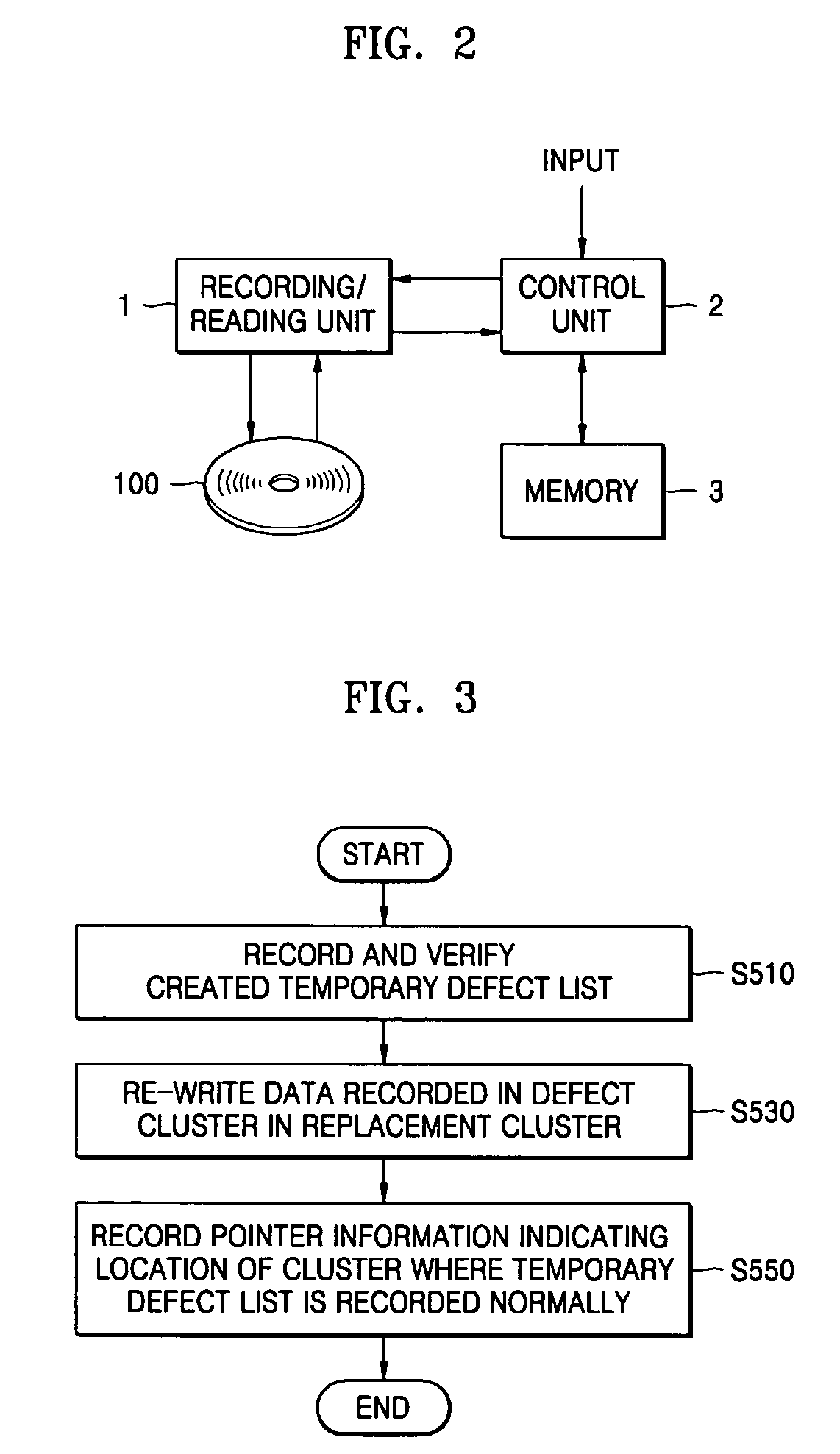
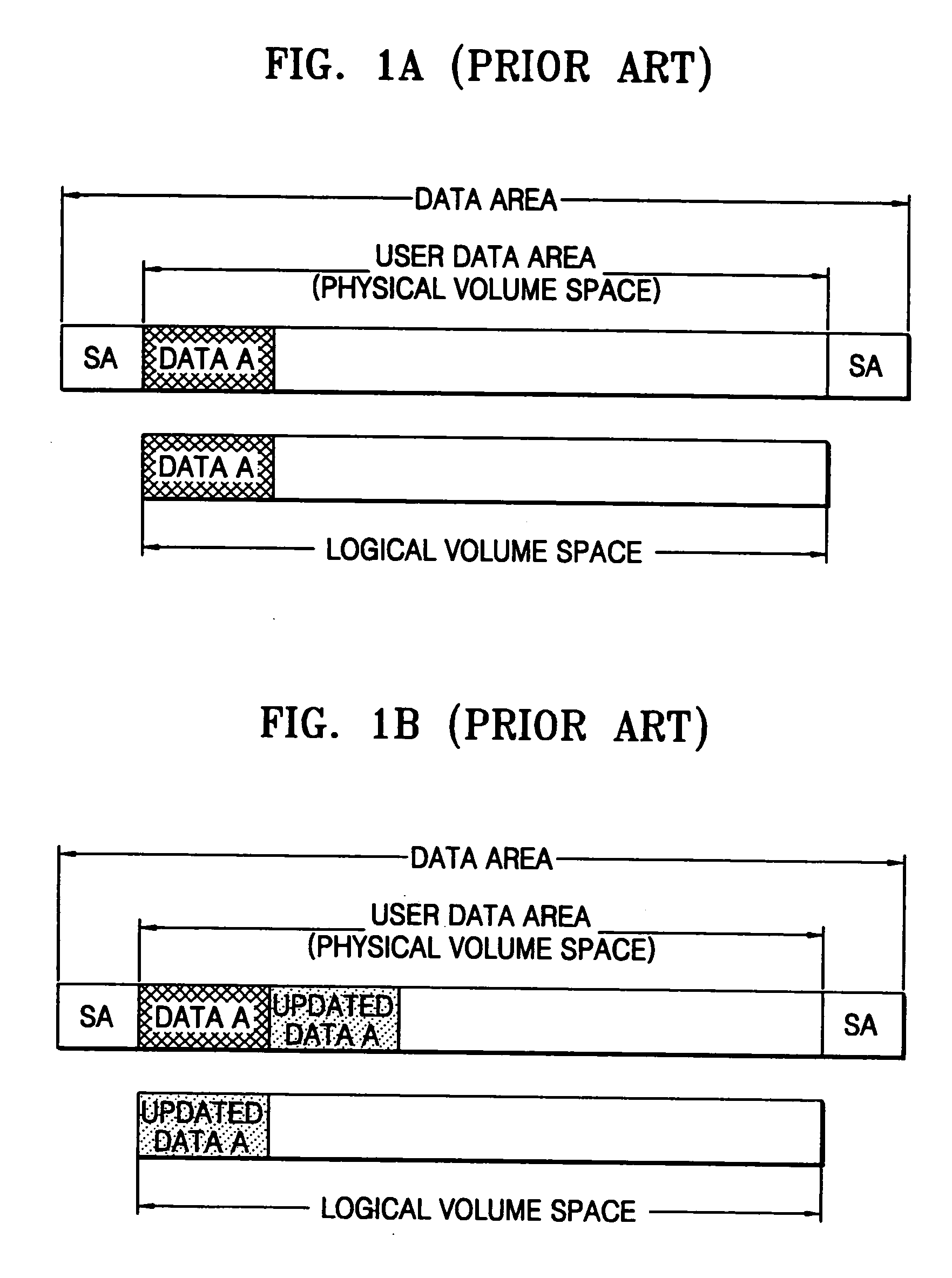
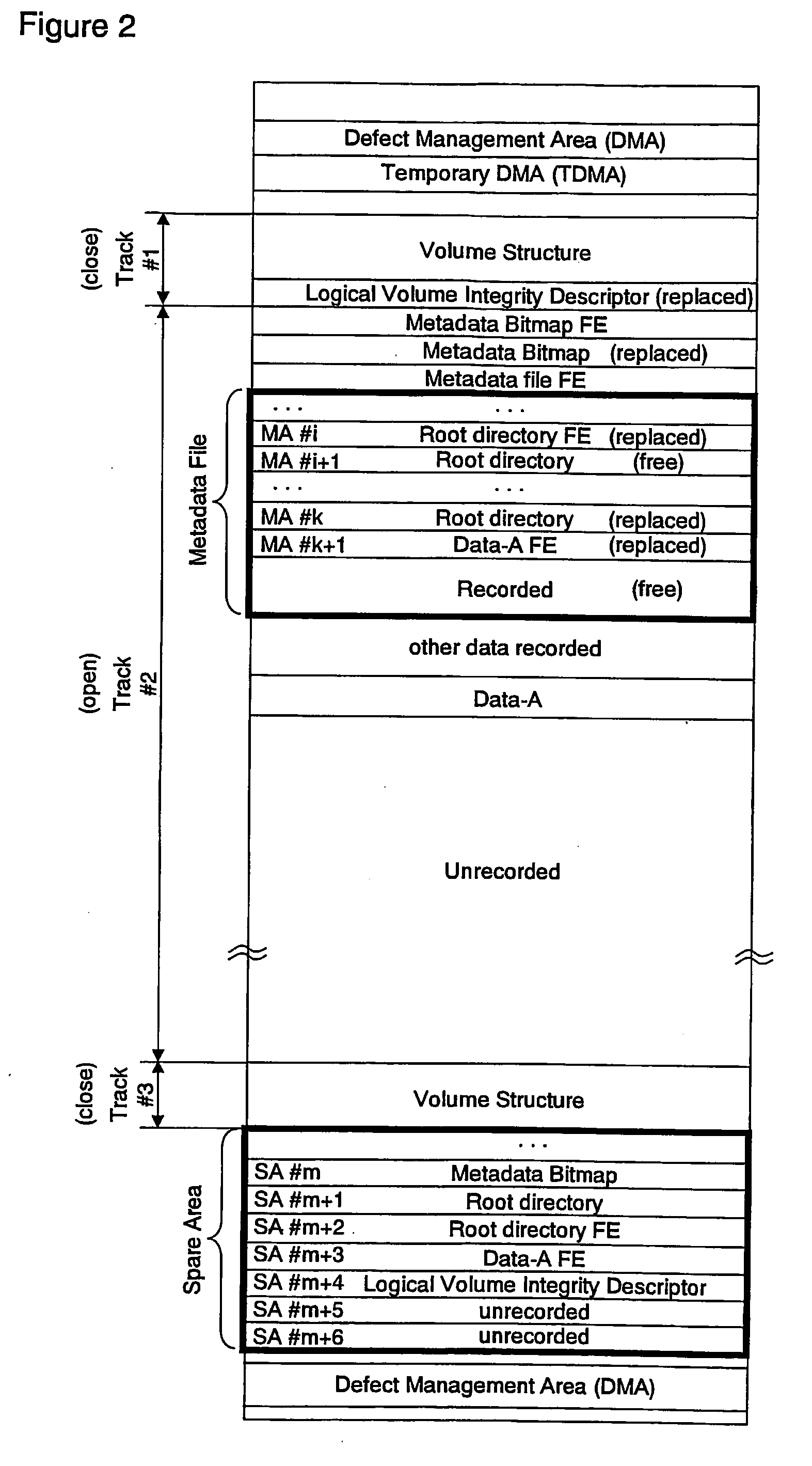
Method of recording temporary defect list on write-once recording medium, method of reproducing the temporary defect list, recording and/or reproducing apparatus, and the write-once recording medium
ActiveUS20050002294A1Improve reliabilityImprove area utilizationRecording verificationError preventionComputer hardwareRecording media
A method of recording a temporary defect list on a write-once recording medium, a method of reproducing the temporary defect list, an apparatus for recording and / or reproducing the temporary defect list, and the write-once recording medium. The method of recording a temporary defect list for defect management on a write-once recording medium includes recording the temporary defect list, which is created while data is recorded on the write-once recording medium, in at least one cluster of the write-once recording medium, and verifying if a defect is generated in the at least one cluster. Then, the method includes re-recording data originally recorded in a defective cluster in another cluster, and recording pointer information, which indicates a location of the at least one cluster where the temporary defect list is recorded, on the write-once recording medium.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information storage medium, recording/reproducing apparatus and recording/reproducing method
InactiveUS20060026455A1Increase of data reproduction efficiencyData augmentationRecording verificationError detection/correctionComputer hardwareOriginal data
A write once information storage medium having original data, replacement data, updated data and management information recorded thereon and an apparatus for and a method of recording and managing the data and the management information. The management information includes a defect address, a replacement address and state information for distinguishing whether data at the replacement address replaces a defect encountered in the original data, a defect encountered in recording replacement data, or a defect encountered during updating of data by logical overwrite (LOW). Accordingly, by using state information to discriminate between replacement by LOW, replacement by defect during LOW and replacement by defect without LOW, data reproduction efficiency is increased in a system in which both replacement by LOW and replacement by defect are implemented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of recording and/or reproducing temporary defect list, recording and/or reproducing apparatus, and write-once recording medium
ActiveCN1705986AReliable recordReliable reproductionBio-organic fraction processingDrying solid materials with heatComputer hardwareRecording media
A method of recording a temporary defect list on a write-once recording medium, a method of reproducing the temporary defect list, an apparatus for recording and / or reproducing the temporary defect list, and the write-once recording medium. The method of recording a temporary defect list for defect management on a write-once recording medium includes recording the temporary defect list, which is created while data is recorded on the write-once recording medium, in at least one cluster of the write-once recording medium, and verifying if a defect is generated in the at least one cluster. Then, the method includes re-recording data originally recorded in a defective cluster in another cluster, and recording pointer information, which indicates a location of the at least one cluster where the temporary defect list is recorded, on the write-once recording medium.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for deleting stored digital data from write-once memory device
InactiveUS20040098416A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDigital dataMemory cell
A digital storage system is coupled to a write-once memory array. File delete commands are implemented by over-writing a destructive digital pattern to at least a portion of the memory cells associated with the file to be deleted. One disclosed system alters the manner in which a file delete command is implemented, depending upon whether the file is stored in a write-once memory or in a re-writable memory.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Pseudo-overwriting data on write-once discs
A file system which is enabled to use a Metadata Partition instead of VAT for write-once discs, is provided by a pseudo-overwrite method. On applying this invention to a drive apparatus which supports pseudo-overwrite media, the file system distinguishes data to overwrite from data to append. When the data is newly written to a logical sector, the drive apparatus writes the data to a physical sector to which the logical sector corresponds. When the logical sector is overwritten the data is written to another unrecorded physical sector in the volume space, and remapping information that specifies the original address, and the remapping address are stored in the remapping table.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
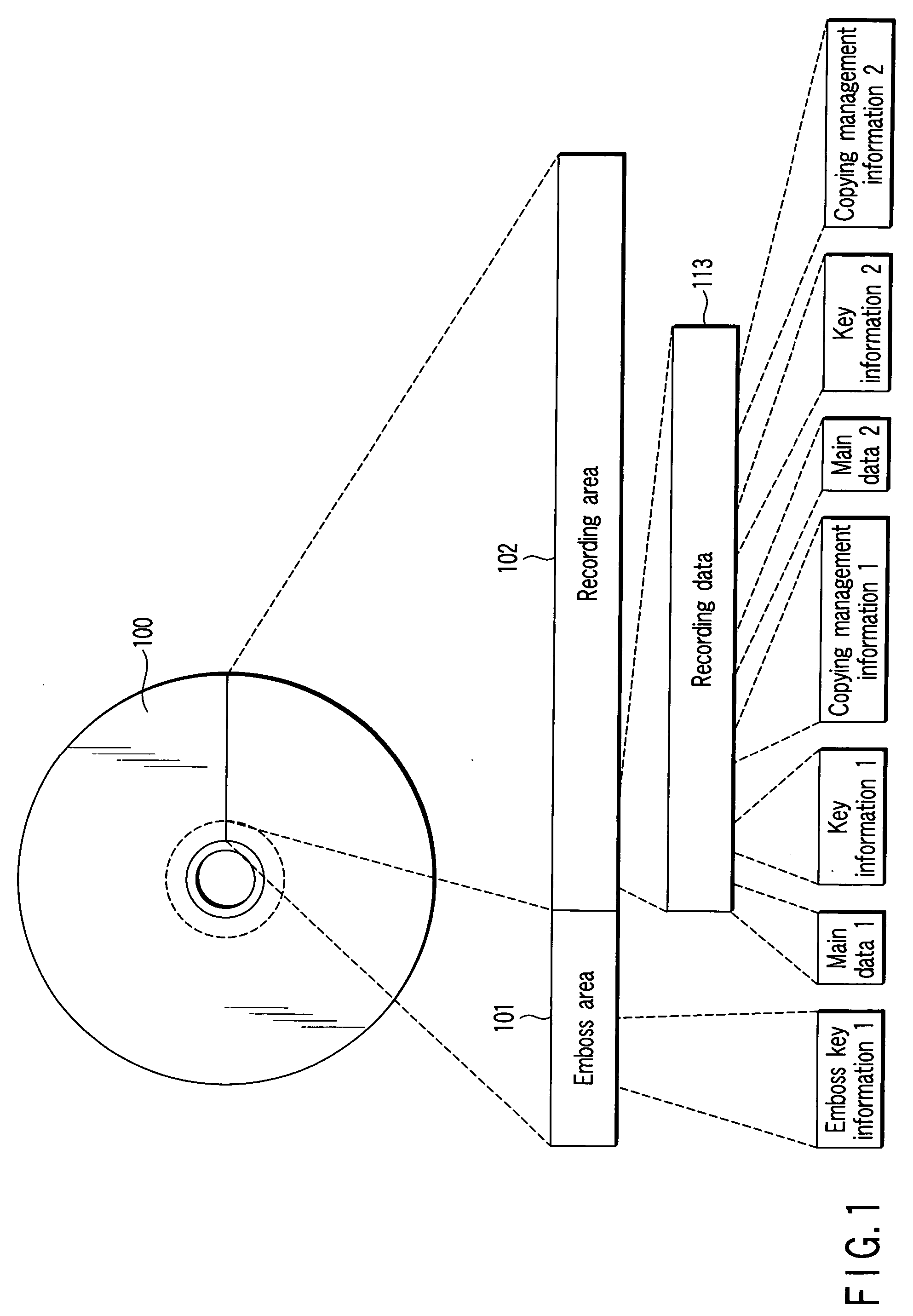
Information recording medium, information recording/reproducing apparatus and information management method
InactiveUS20060023596A1Improve practicalityEnhanced informationCombination recordingTelevision system detailsComputer hardwareFrequency of occurrence
There is provided an information management apparatus which can make it impossible to read out data recorded on a write-once type recordable optical disk as required and the usefulness thereof is enhanced. When recorded data is destroyed on the write-once type recordable optical disk, data modulated by a modulation system of the same run length restriction as run length restriction of a modulation system used for recording data is overwritten and recorded, data is overwritten and recorded by use of patterns in which the frequency of occurrence of spaces of the longest code is higher than the frequency of occurrence of the modulation system used for recording data, or data is overwritten and recorded by use of successive patterns of the shortest code in the run length restriction of the modulation system used for recording data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Write once type recording medium, recorder and recording method for write once recording medium, reproducer and reproducing method for write once recording medium, computer program for record or reproduction control, and data structure
InactiveUS20060187811A1Accurate recordEfficient and maximum useCombination recordingInformation arrangementComputer hardwareComputer program
A write-once-type recording medium (100) on which record data can be recorded only once, provided with: a data area (108) to record therein the record data; and a shared area (104, 105) to temporarily record therein evacuation data which is record data to be recorded or already recorded at a position of a defect in the data area and defect management information (120) including an evacuation source address of the evacuation data.
Owner:KODA TAKESHI +2
Data Recording/Reproduction for Write-Once Discs
The recording method of the present invention includes the steps of: receiving a write instruction which specifies at least a logical sector in which data is to be written; determining whether the logical sector corresponds to a recorded physical sector or an unrecorded physical sector; when it is determined that the logical sector corresponds to an unrecorded physical sector, writing the data into the unrecorded physical sector, determining whether a verification of the data which has been written into a physical sector is successful, if the verification of the data that has been written is not successful, writing the data into an unrecorded physical sector, generating a remapping table including remapping information which remaps an original address of the physical sector corresponding to the logical sector to a remapping address of the selected physical sector, and writing the remapping table on the write-once disc.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
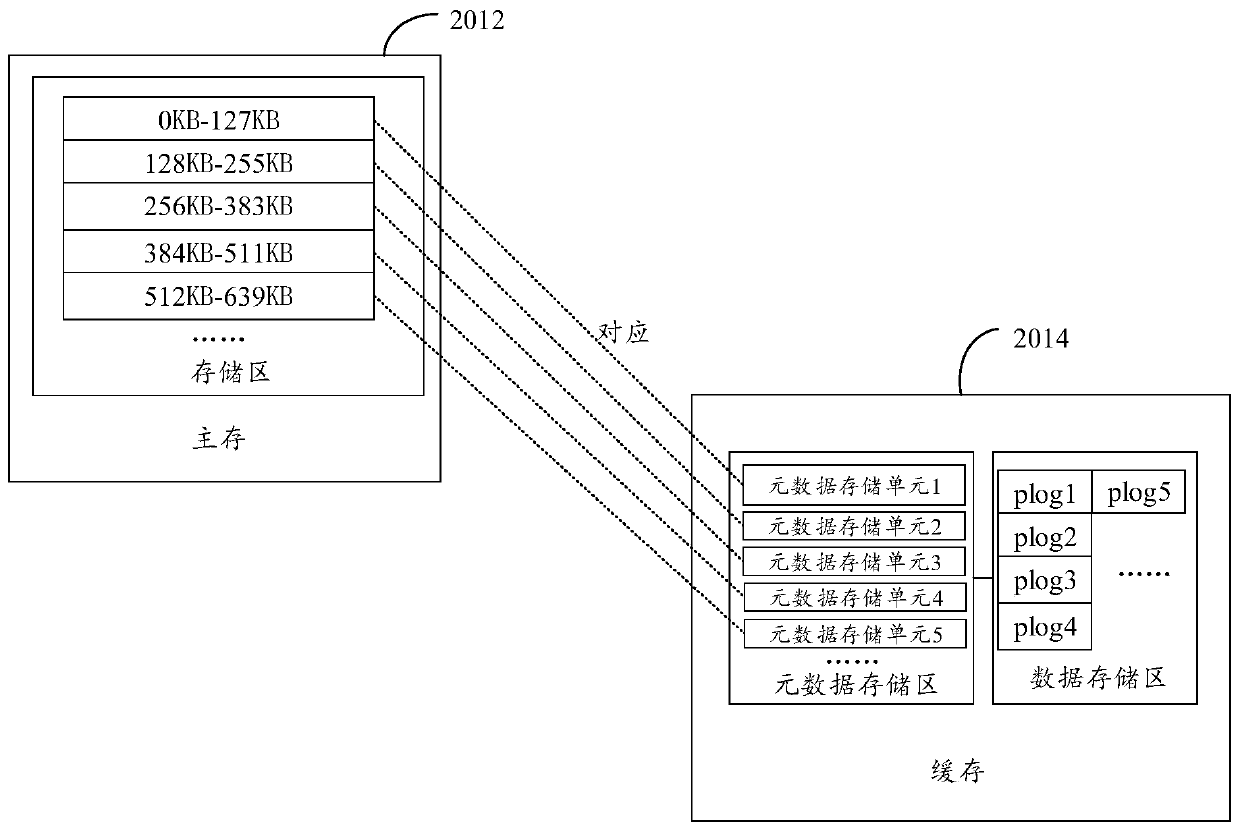
Metadata management method and device
ActiveCN110727403AInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMetadata managementEngineering
The invention discloses a metadata management method and device, relates to the technical field of data storage, and the metadata management method and device are helpful for reducing read amplification and saving cache resources. The method comprises the steps of receiving a write request, wherein the write request comprises first data and a first logic address range; wherein the first logic address range is an address range of a storage space used for storing the first data in the main memory; determining a first address in a cache according to the write request, and writing the first data into a first data storage unit indicated by the first address; wherein the first address comprises an identifier of the first data storage unit, an initial storage position of the first data in the first data storage unit and the length of the first data; generating metadata of the first data and writing the metadata into a target metadata storage unit; wherein the preset logic address range corresponding to the target metadata storage unit comprises a first logic address range; establishing a sequential relationship between the metadata of the first data and the write-in time of the target metadata; wherein the target metadata is the metadata written into the target metadata storage unit last time.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Data access method and device, client and storage medium
ActiveCN113515531AStrong consistencyGuaranteed high performance requirementsDatabase updatingDatabase distribution/replicationData packData access
The invention relates to the field of distributed storage, and provides a data access method and device, a client and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining to-be-written data, wherein the to-be-written data comprises a plurality of target data blocks organized by erasure codes, each target data block needs to be written into each storage node, each storage node comprises old data written last time; sending a write request to each storage node, so that each storage node writes the corresponding target data block based on the respective received write request and feeds back a write response message to the client; and if the number of the target storage nodes feeding back the write response message of successful writing is greater than a preset number, sending deletion commands to the target storage nodes according to the number of the target storage nodes, so that the target storage nodes delete respective old data according to the respective received deletion commands. According to the method, the high consistency of data writing can be ensured, and the requirement of high performance can also be ensured.
Owner:重庆紫光华山智安科技有限公司
Memory system
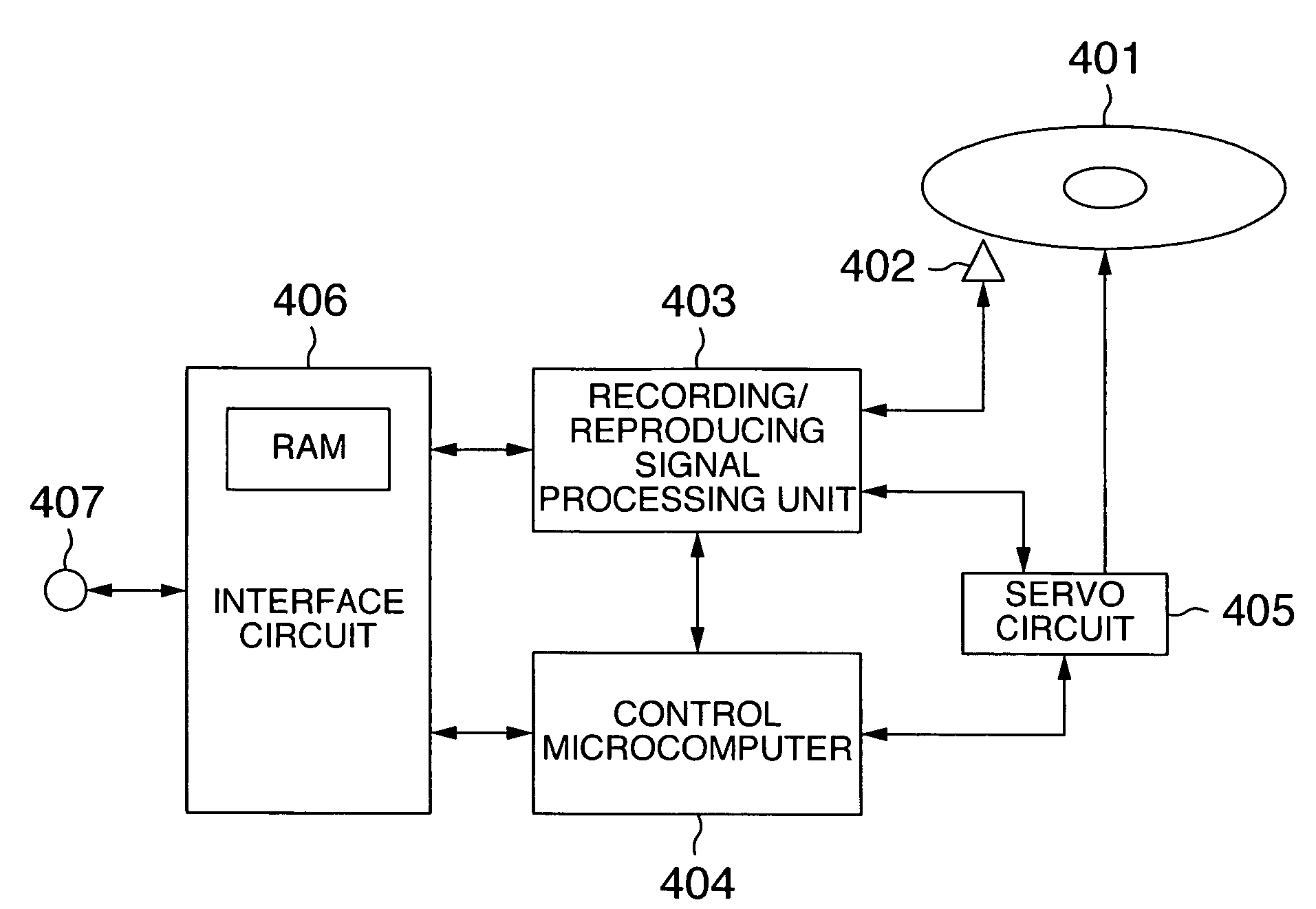
ActiveUS20110185108A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionMain processing unitData transmission
A memory system includes a volatile first storing unit, a nonvolatile second storing unit in which a plurality of memory cells that can store multi-value data are arranged, the memory cells having a plurality of pages, and a controller that performs data transfer between a host apparatus and the second storing unit via the first storing unit. The controller includes a save processing unit that backs up, when, before data is written in the second storing unit in a write-once manner, data is written in a lower order page of a memory cell same as that of a page in which the data is written, the data of the lower order page and a broken-information-restoration processing unit that restores, when the data in the lower order page is broken, the broken data using the backed-up data.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
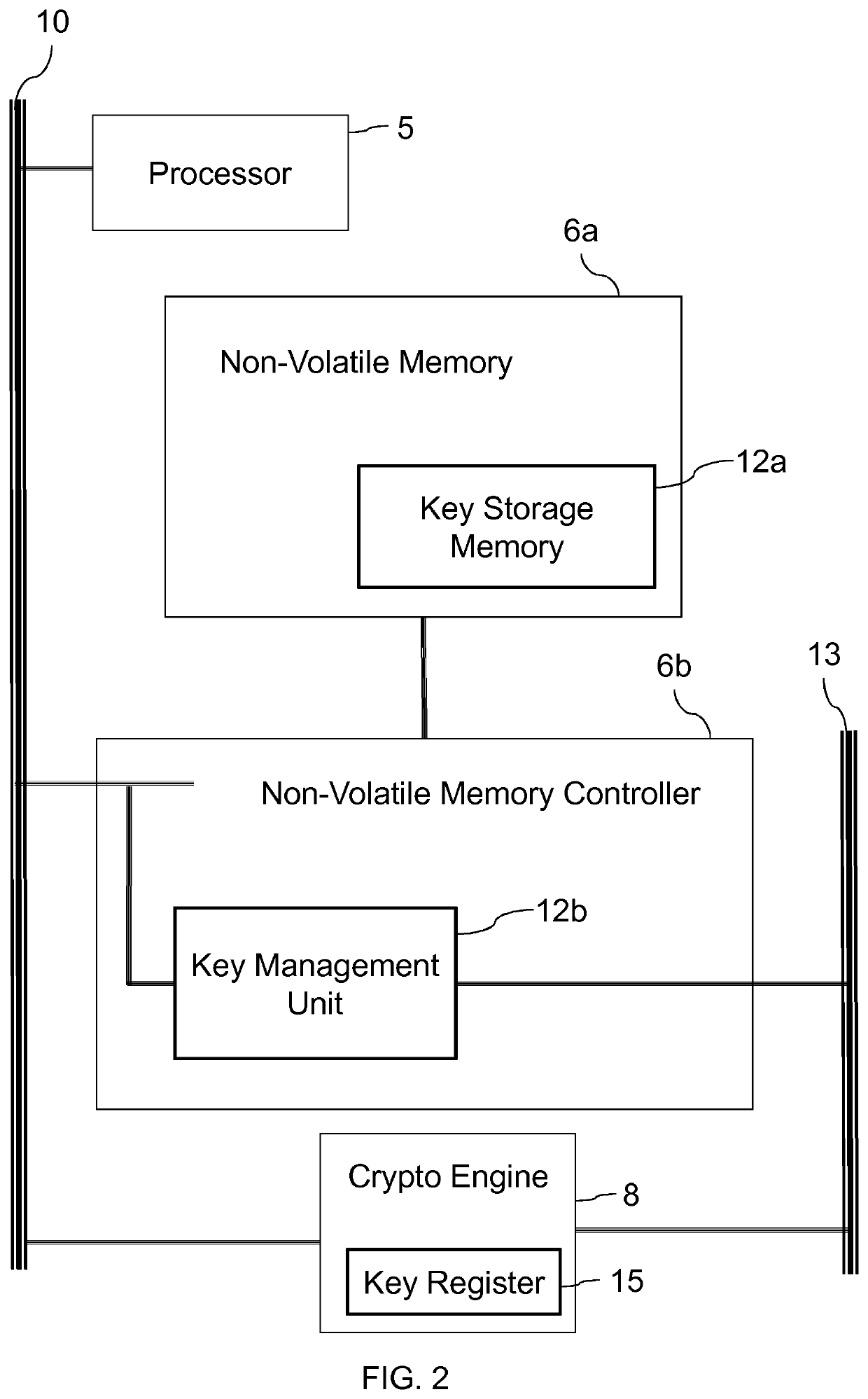
Cryptographic key distribution
ActiveUS20210240870A1Avoid modificationIncrease flexibilityDigital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionComputer hardwareMemory address
An integrated-circuit device comprises a processor, a hardware key-storage system, and a key bus. The hardware key-storage system comprises a non-volatile key storage memory, which includes a key register, for storing a cryptographic key, and an address register, for storing a destination memory address for the cryptographic key. The hardware key-storage system further comprises output logic for sending the cryptographic key over the key bus to the destination memory address, and write-once logic for preventing an address being written to the address register unless the address register is in an erased state.
Owner:NORDIC SEMICONDUCTOR
Write-once-type recording medium, recording apparatus and method for write-once-type recording medium, reproducing apparatus and method for write-once-type recording medium, computer program for recording or reproduction control, and data structure
InactiveUS20070174359A1Efficient and maximum useAccurate recordInformation arrangementRecord information storageComputer hardwareSoftware engineering
A write-once-type recording medium (100) on which record data can be recorded only once, provided with: a data area (108) to record therein the record data; and a shared area (104, 105) to temporarily record therein evacuation data which is record data to be recorded or already recorded at a position of a defect in the data area and defect management information (120) including an evacuation source address of the evacuation data.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Data backup method and system based on continuous data protection (CDP) protocol
PendingCN113608925AImplement backupResolve inconsistenciesRedundant operation error correctionSoftware engineeringWrite-once
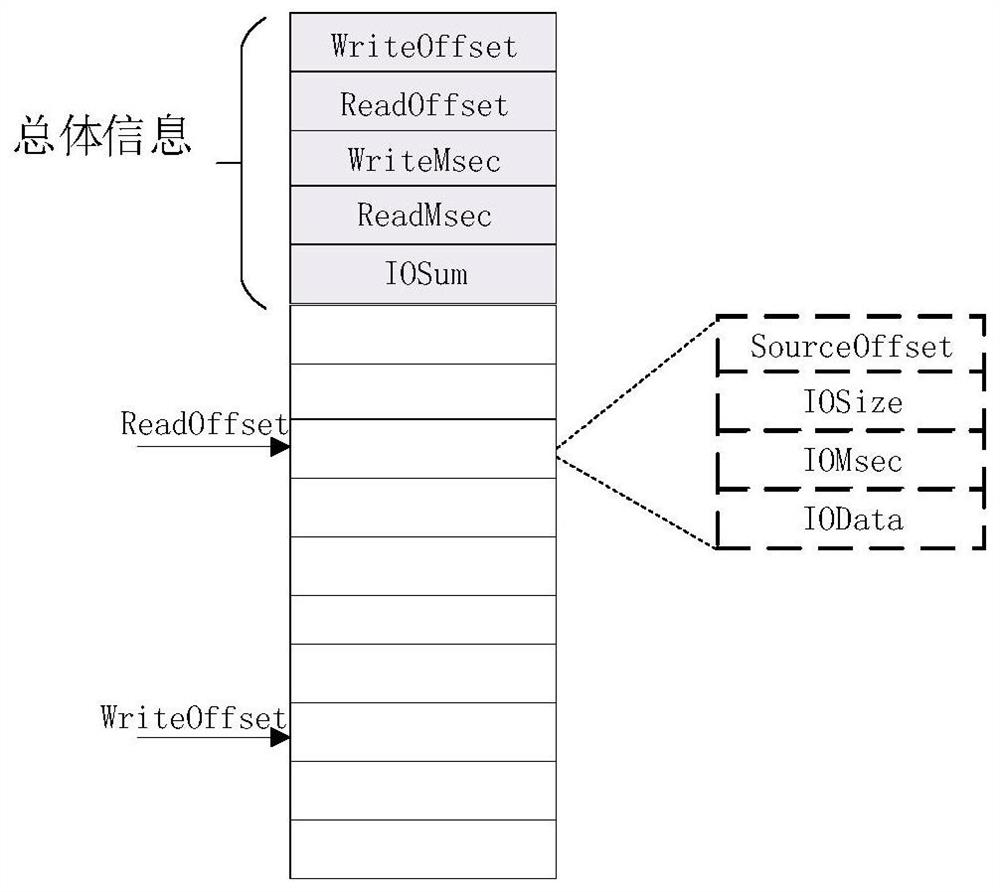
The invention relates to the technical field of data backup, and provides a data backup method and system based on a continuous data protection (CDP) protocol, and the method comprises the steps that a connection with a shared memory is built when IO is written, and obtaining a WriteOffset and a ReadOffset ; whether the shared memory is fully written once or not is judged; if yes, the difference value between the WriteOffset and the ReadOffset is compared, basic data information is obtained and written into the address position of the WriteOffset, and otherwise, basic data information of IO to be written is obtained and written into the address position of the WriteOffset; after IO writing is completed, IO is controlled to be written into the standby storage device, data backup is achieved. It can be guaranteed that the IO writing performance of the virtual machine is not affected during CDP backup, and the problem of IO data inconsistency caused by abnormal power failure can be avoided.
Owner:济南浪潮数据技术有限公司
Write once type recording medium, recording device and recording method for write once type recording medium, and reproduction device and reproduction method for write once type recording medium
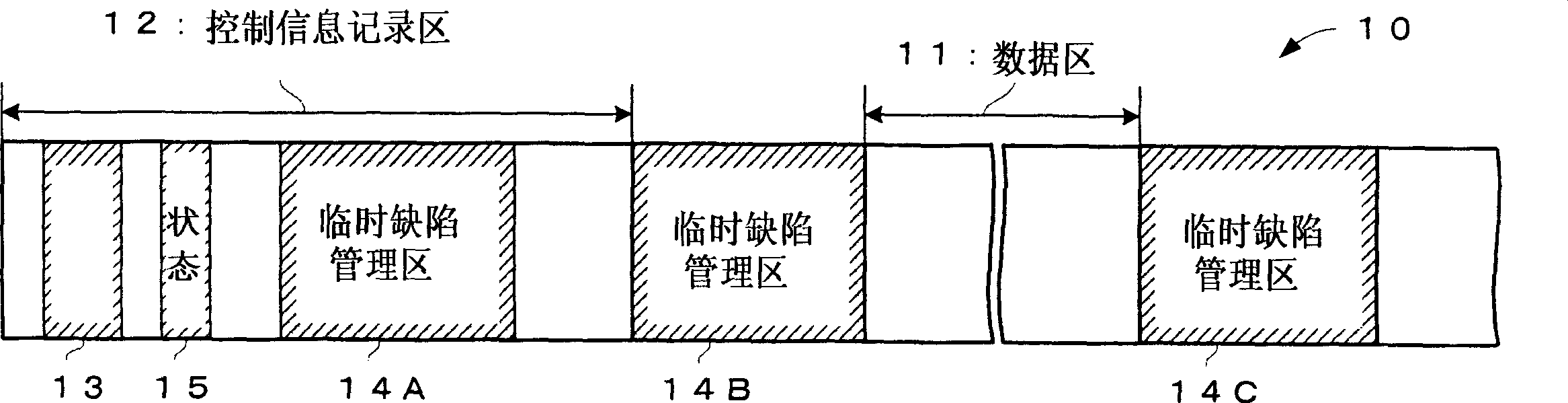
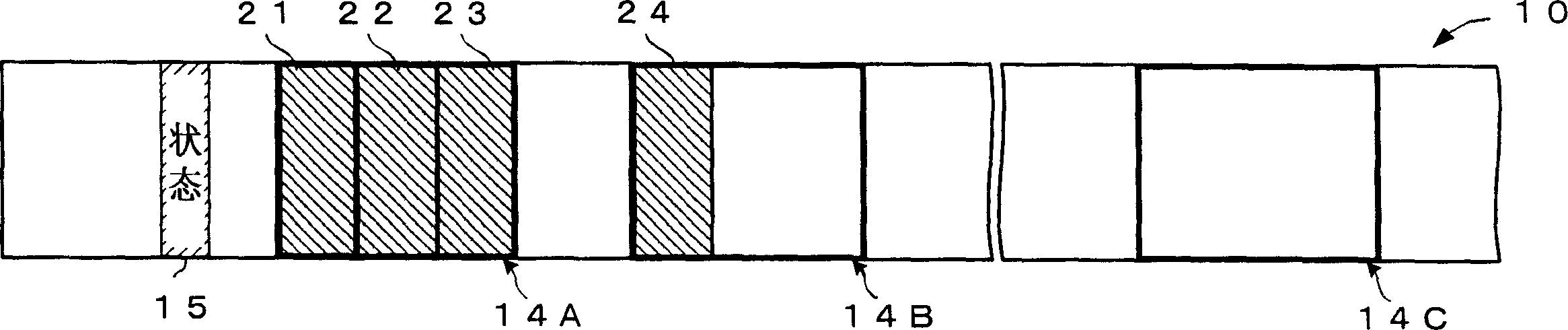
On a write-once-type recording medium 10, there are provided: a definite defect management area 13 to definitely record therein defect management information; and a plurality of temporary defect management areas 14A, 14B, and 14C to temporarily record therein the defect management information. If the recording medium 10 is not yet finalized, every time the defect management information is updated, the updated defect management information is recorded into any one of the plurality of temporary defect management areas. Moreover, a status information recording area 15 is provided on the recording medium 10, and status information for indicating the temporary defect management area in which there is the defect management information recorded at last is recorded into the status information recording area 15. By referring to the status information, it is possible to quickly specify the defect management information recorded at last.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Recording method and optical disk recording device
InactiveUS7571361B2Improve Optical ReliabilityImprove reliabilityCombination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareOptical disc
A recording method and a recording apparatus capable of optimally arranging data on a write-once type optical disc. In a write-once type optical disc recording method with respect to a disc having a read-in, a user area, and a read-out by employing defect management information, the user area is divided into 3, or more pieces of R-zones; at least 2 recordable R-zones having recordable areas are present. When an unrecordable R-zone having no recordable area is present on the read-in side rather than two, or more pieces of the R-zones among the R-zones having the recordable areas, a linear replacement destination of a logical overwriting is determined to such an R-zone other than an R-zone having a recordable area, which is located adjacent to the unrecordable R-zone.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP +1
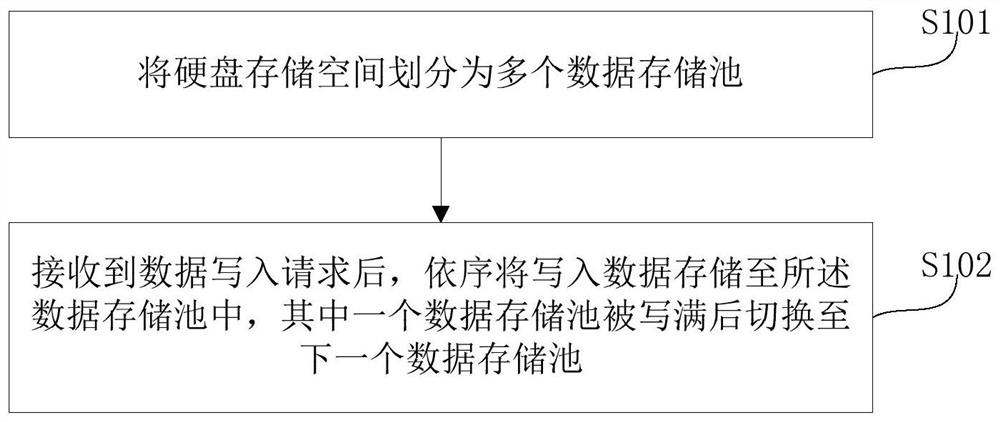
Read-write method for third-generation gene sequencing data and distributed file system
InactiveCN113192558AGuaranteed read performanceLow real-time requirementsDatabase distribution/replicationProteomicsDistributed File SystemParallel computing
The invention provides a third-generation gene sequencing data read-write method and a distributed file system. The method comprises the steps that a hard disk storage space is divided into a plurality of data storage pools, and after a data write-in request is received, write-in data are sequentially stored in the data storage pools, and after one data storage pool is fully written, the system is switched to the next data storage pool. According to the scheme, the characteristics that the gene sequencing application data is written once, only data can be read and cannot be modified subsequently, meanwhile, data writing is asynchronously carried out, and the real-time requirement is not high are utilized; and on the basis, through the scheme in the embodiment of the invention, the reading performance of the gene sequencing application data can be at least guaranteed.
Owner:北京自由猫科技有限公司 +1
Quality of service dirty line tracking
Systems, apparatuses, and methods for generating a measurement of write memory bandwidth are disclosed. A control unit monitors writes to a cache hierarchy. If a write to a cache line is a first time that the cache line is being modified since entering the cache hierarchy, then the control unit increments a write memory bandwidth counter. Otherwise, if the write is to a cache line that has already been modified since entering the cache hierarchy, then the write memory bandwidth counter is not incremented. The first write to a cache line is a proxy for write memory bandwidth since this will eventually cause a write to memory. The control unit uses the value of the write memory bandwidth counter to generate a measurement of the write memory bandwidth. Also, the control unit can maintain multiple counters for different thread classes to calculate the write memory bandwidth per thread class.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
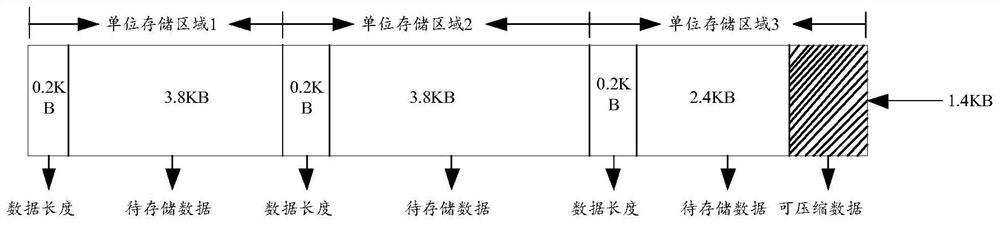
Data storage method and device
ActiveCN113176859AAvoid duplicate writingNo write amplificationInput/output to record carriersWrite amplificationEngineering
The invention provides a data storage method and device, and relates to a data storage technology. The data storage method includes: writing the to-be-stored data into at least one unit storage area by taking the initial address of the next unit storage area adjacent to the unit storage area in which the data is written last time as an initial storage address; filling compressible data in the unit storage area in which the to-be-stored data is written and the residual storage space exists; and finally, taking data in each unit storage area in the at least one unit storage area as unit read-write data, writing each unit read-write data into a physical address space of the solid state disk from the logic address space, wherein each unit read-write data located in the physical address space is in a compressed state. Only the to-be-stored data is occupied in the physical address space of the solid state disk, and write amplification of the data is not caused, so that the erasing times of the solid state disk can reach the preset threshold value later, and the service life of the solid state disk is prolonged.
Owner:锐掣(杭州)科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com