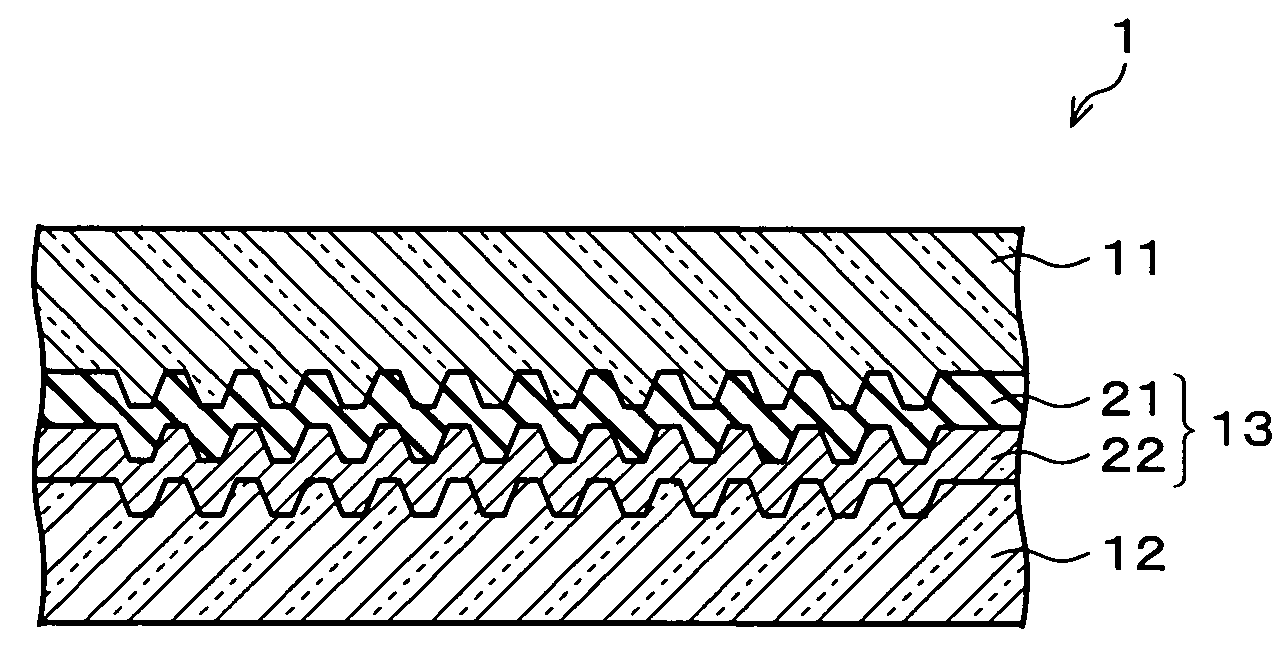
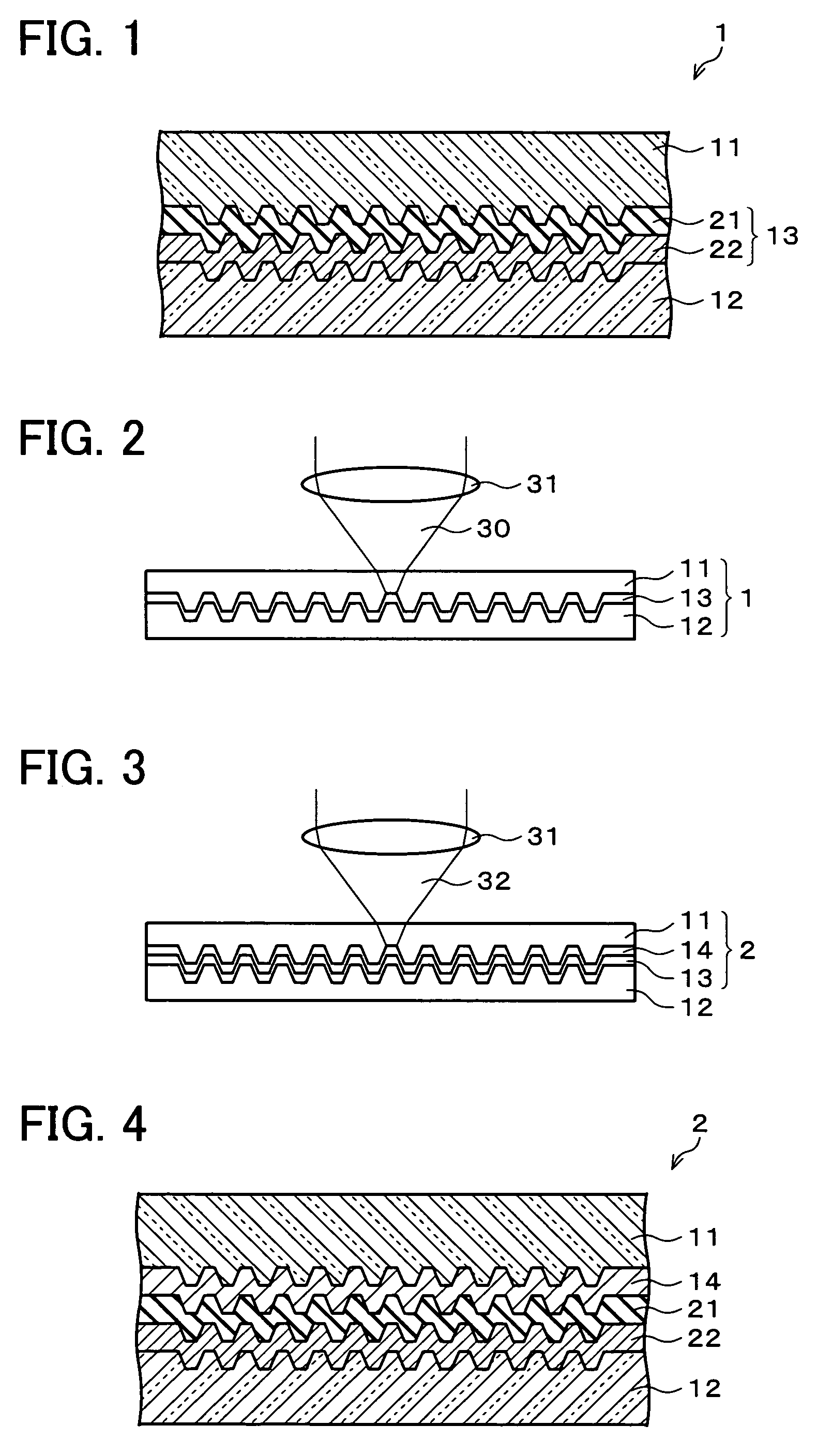
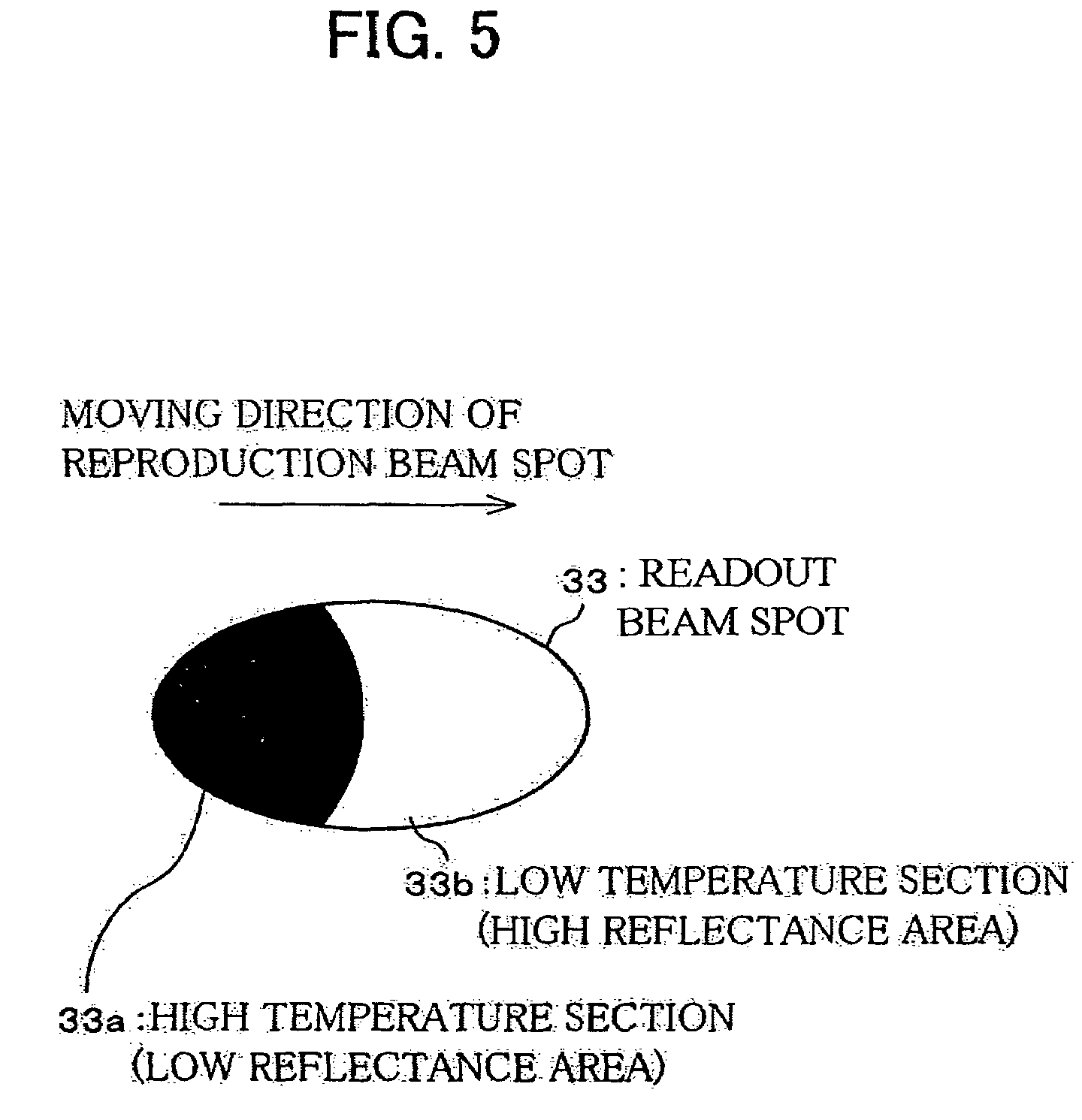
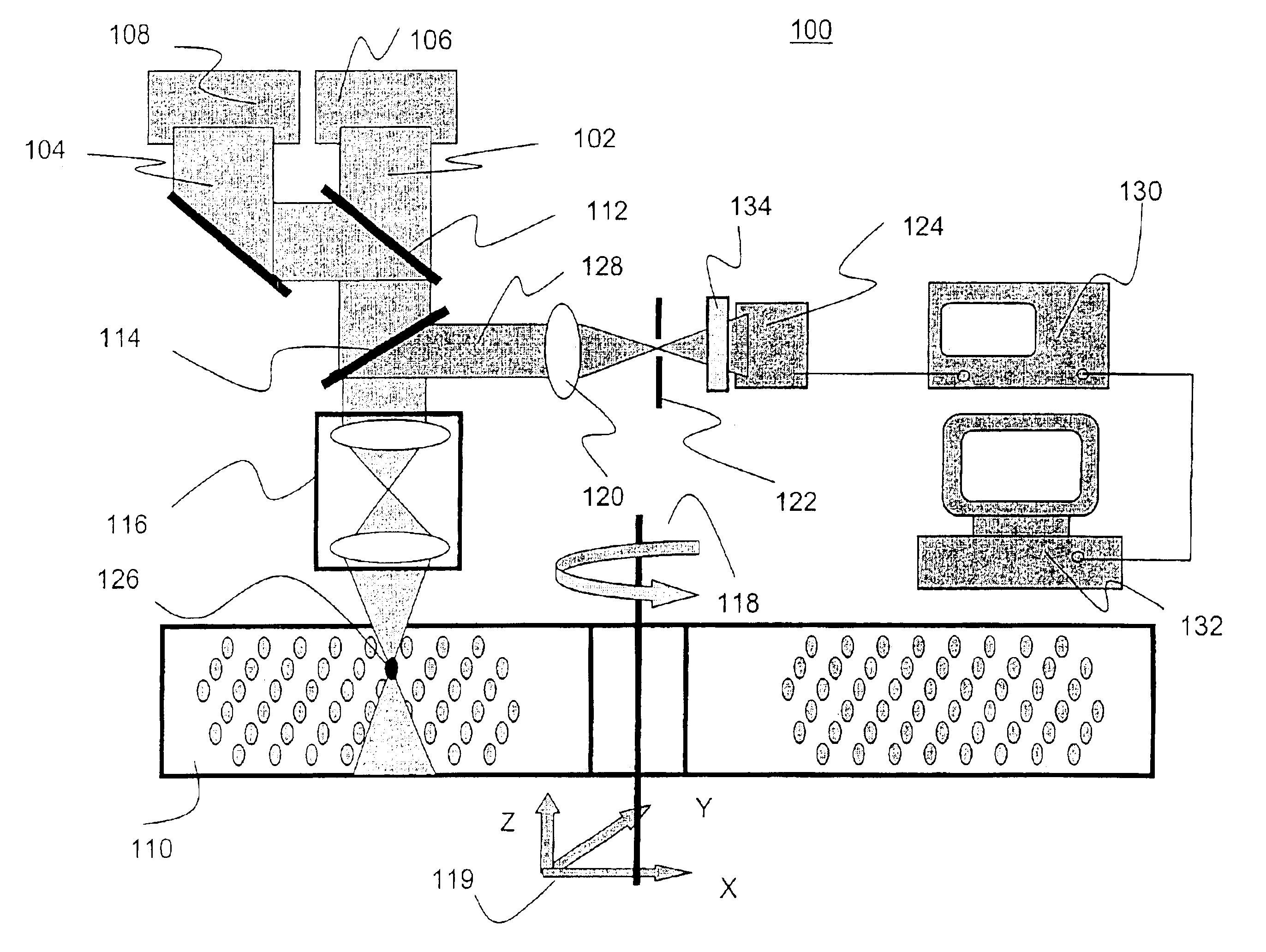
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104results about "Reproducing involving reflectivity/absorption/color-change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
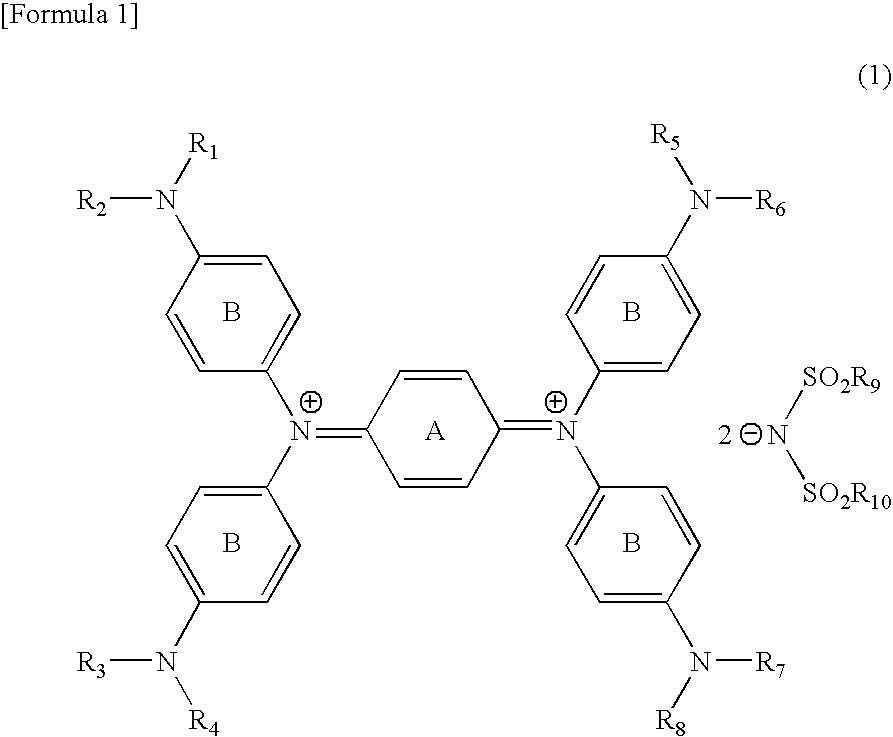
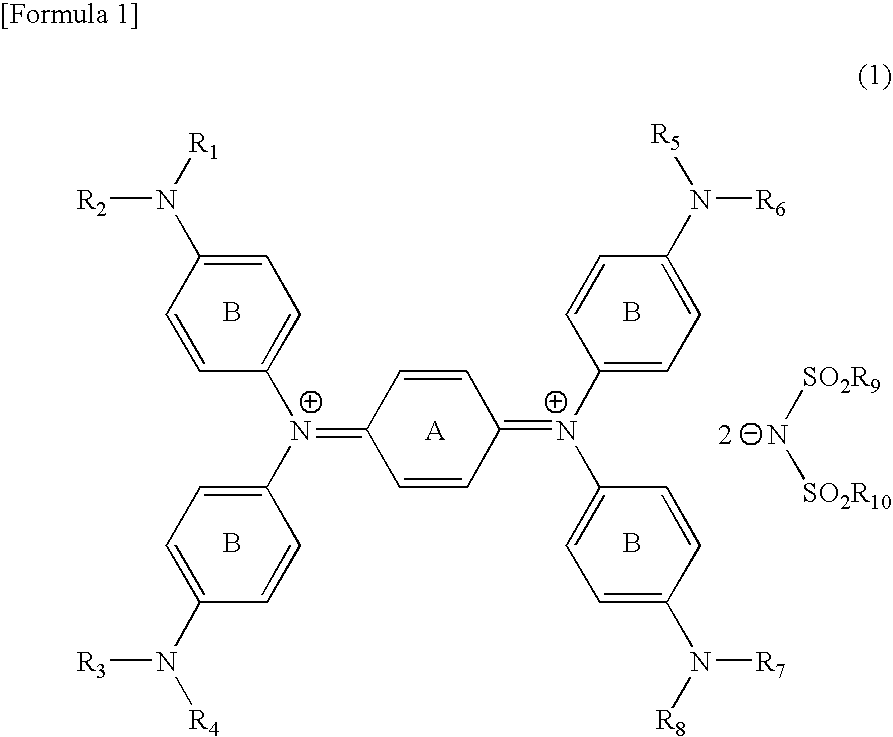
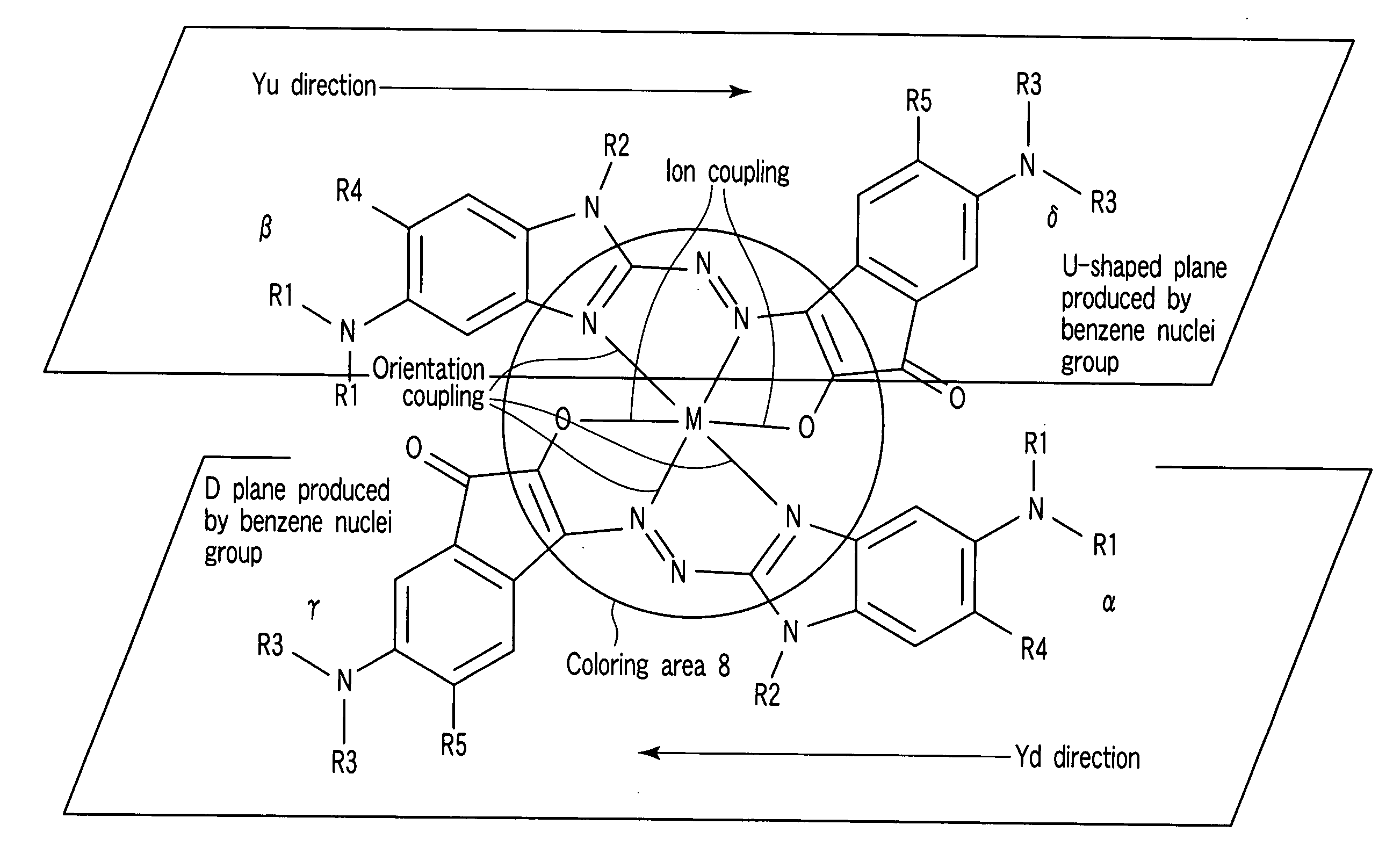
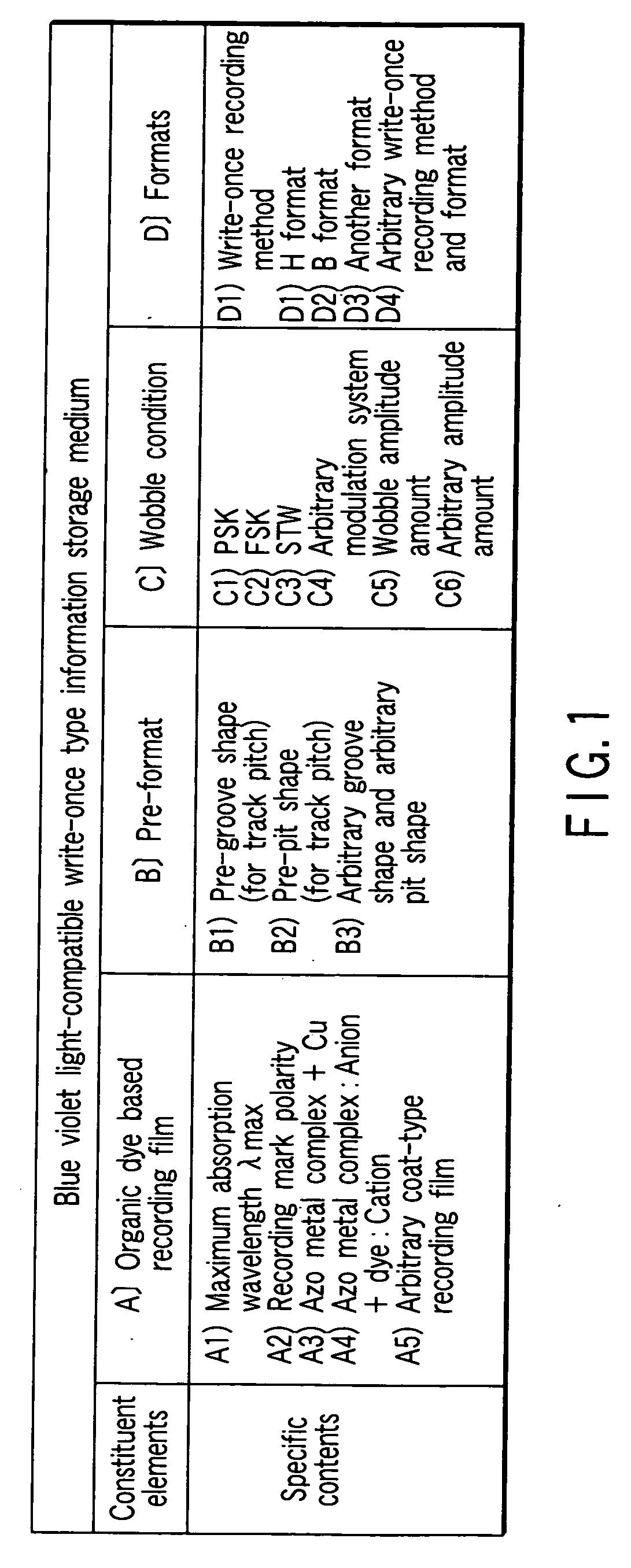
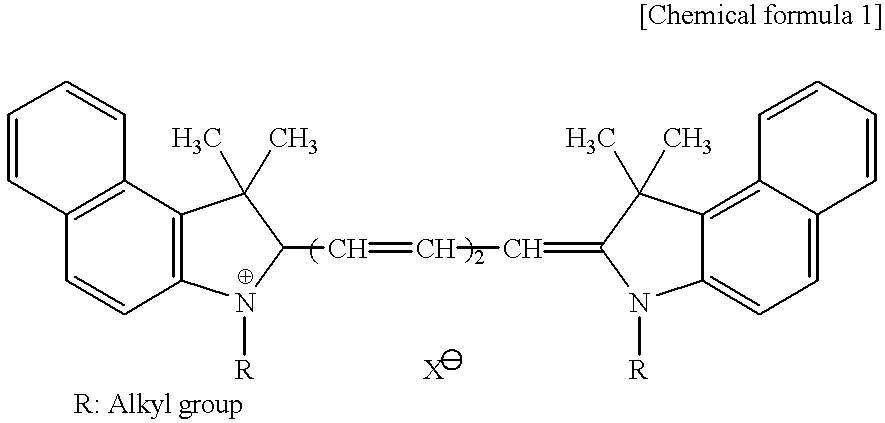
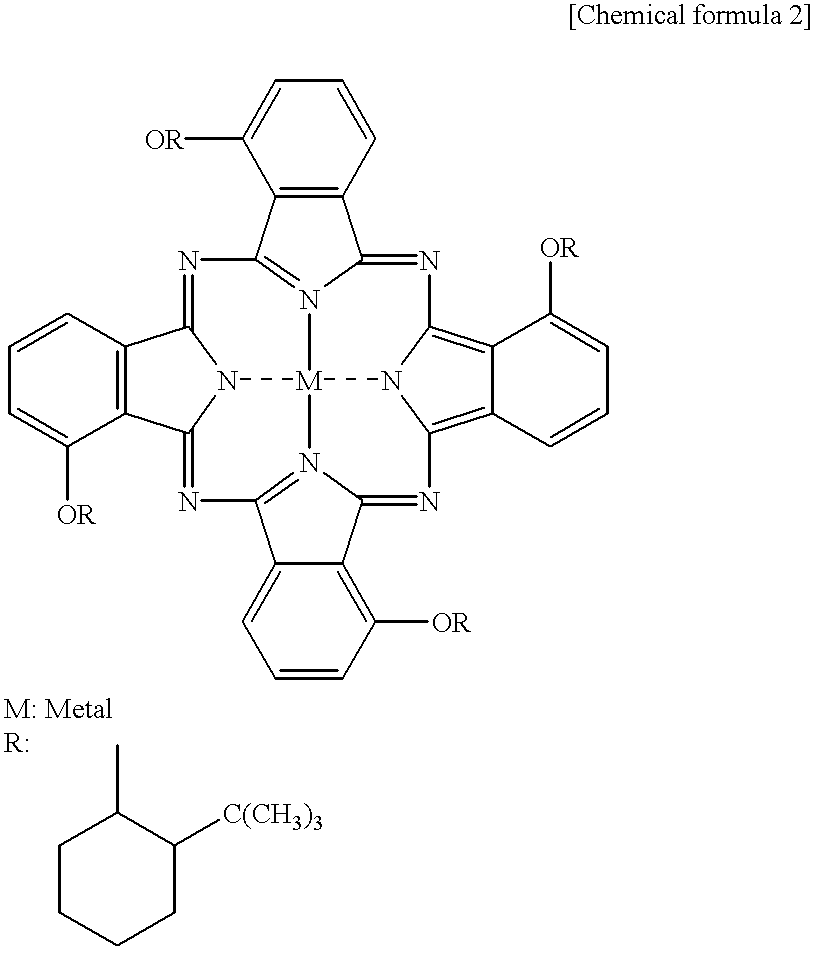
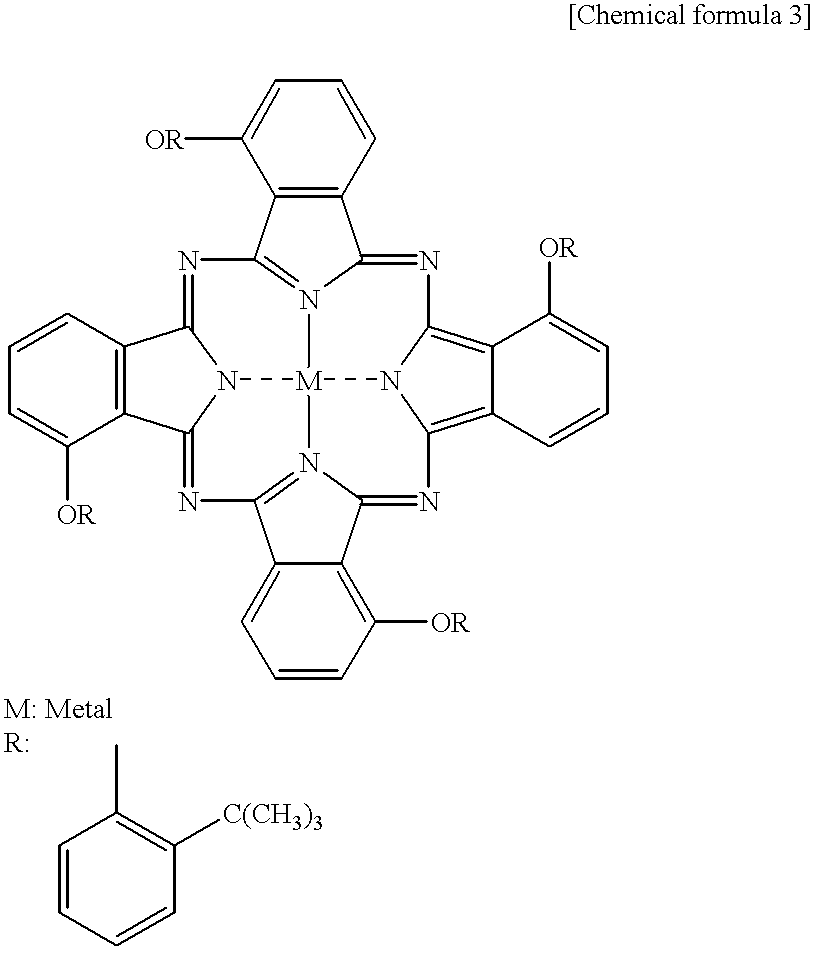
Diimmonium compound and use thereof
InactiveUS20050148786A1High visible light transmittanceHigh light transmittanceOrganic chemistryPhotomechanical apparatusInfraredAmmonium compounds
To provide a near-IR absorption compound free from antimony or arsenic and excellent in stability, especially, in heat resistance, light fastness, and moisture-and-heat resistance and also an IR absorption filter, an optical information recording medium, and a resin composition excellent in durability by using the near-IR absorption compound. The near-IR absorption compound is a diimmonium compound having the following structure and the resin composition contains the diimmonium compound: (wherein R1 to R8 independently denote hydrogen atom or an optionally substituted aliphatic hydrocarbon group; R9 and R10 independently denote an aliphatic hydrocarbon group optionally containing a halogen atom; and rings A and B may further have substituent groups.).
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
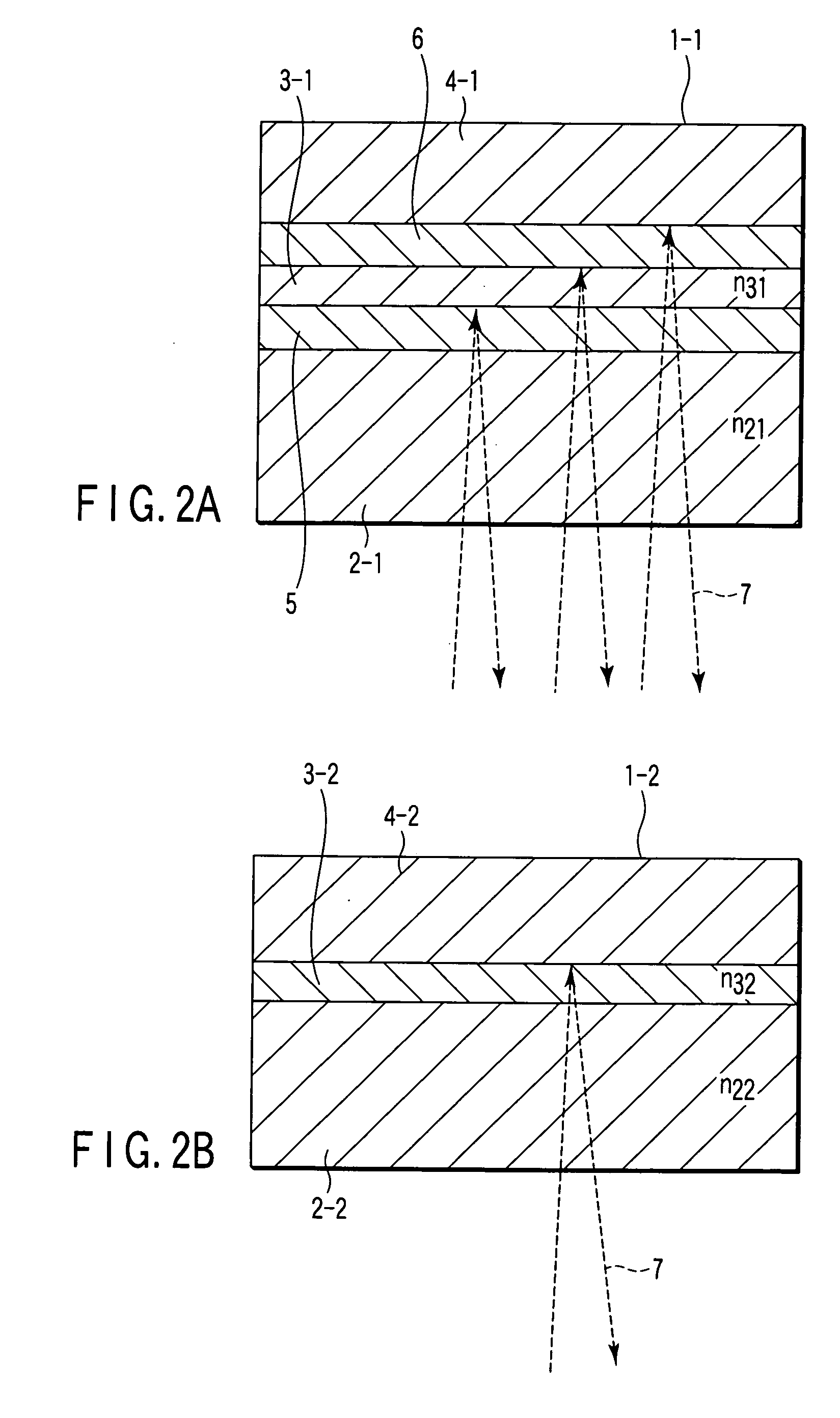
Optical information medium having high resolution beyond a diffraction limit and reading method
InactiveUS6965556B1Minimize dependenciesHigh resolutionNanoinformaticsMechanical record carriersRefractive indexLength wave
In an optical information medium having an information bearing surface having projections and depressions and / or capable of forming recorded marks, a functional layer is added. The information borne on the information bearing surface can be read by using reading light of a wavelength longer than 4NA·PL wherein PL is the minimum size of the projections and depressions or the recorded marks and NA is the numerical aperture of a reading optical system, setting the power of the reading light within such a range that the functional layer does not change its complex index of refraction, and irradiating the reading light to the information bearing surface constructed by the functional layer or to the information bearing surface through the functional layer or to the functional layer through the information bearing surface. The medium enables reading at a high resolution beyond the diffraction limit.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information medium and reading method
InactiveUS20050237912A1Minimize dependenciesHigh resolutionNanoinformaticsMechanical record carriersRefractive indexLength wave
In an optical information medium having an information bearing surface having projections and depressions and / or capable of forming recorded marks, a functional layer is added. The information borne on the information bearing surface can be read by using reading light of a wavelength longer than 4NA·PL wherein PL is the minimum size of the projections and depressions or the recorded marks and NA is the numerical aperture of a reading optical system, setting the power of the reading light within such a range that the functional layer does not change its complex index of refraction, and irradiating the reading light to the information bearing surface constructed by the functional layer or to the information bearing surface through the functional layer or to the functional layer through the information bearing surface. The medium enables reading at a high resolution beyond the diffraction limit.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Multi-layer optical recording media and system for recording and reproducing information data
InactiveUS6498775B1Precise alignmentOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageEngineeringOptical recording
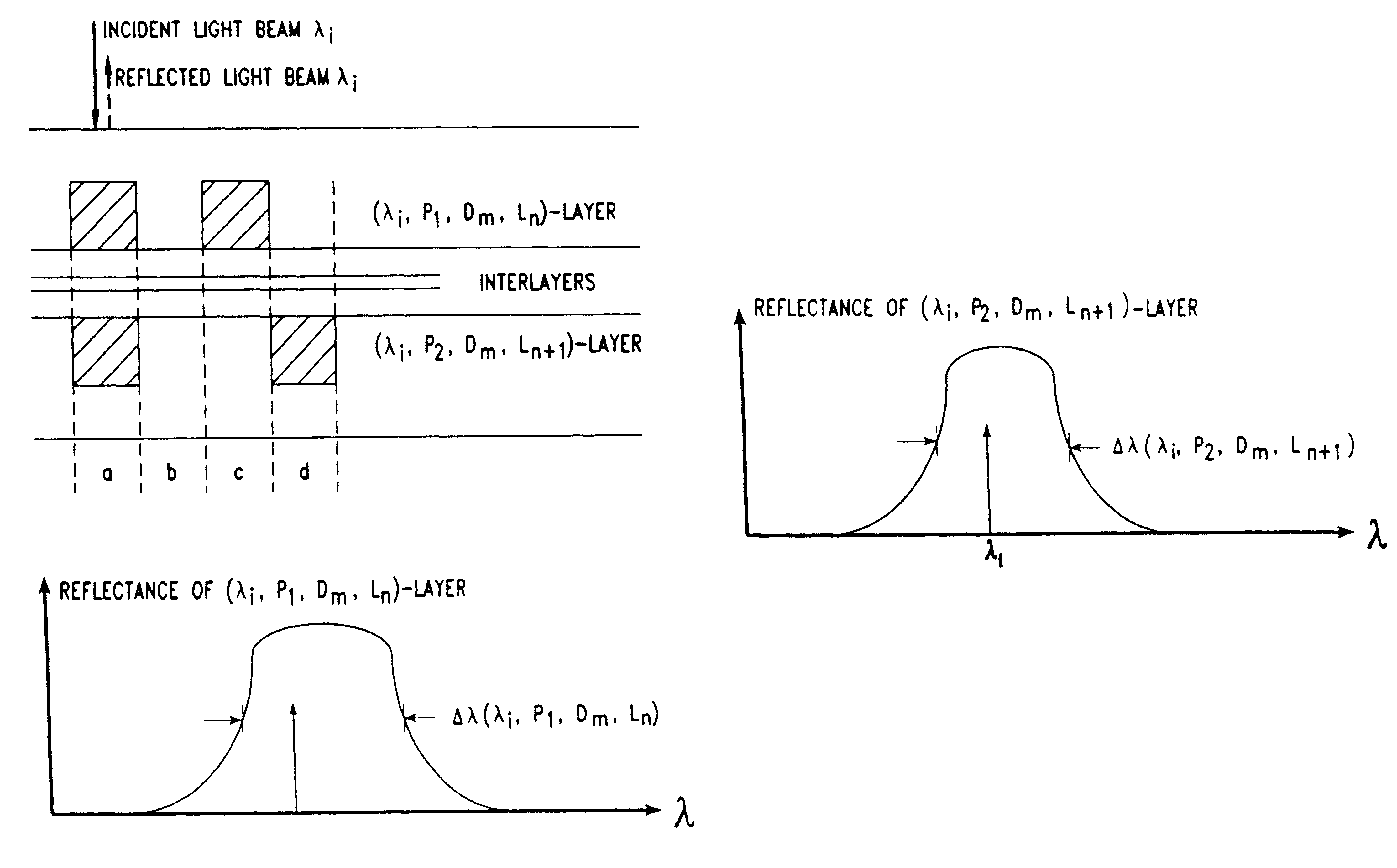
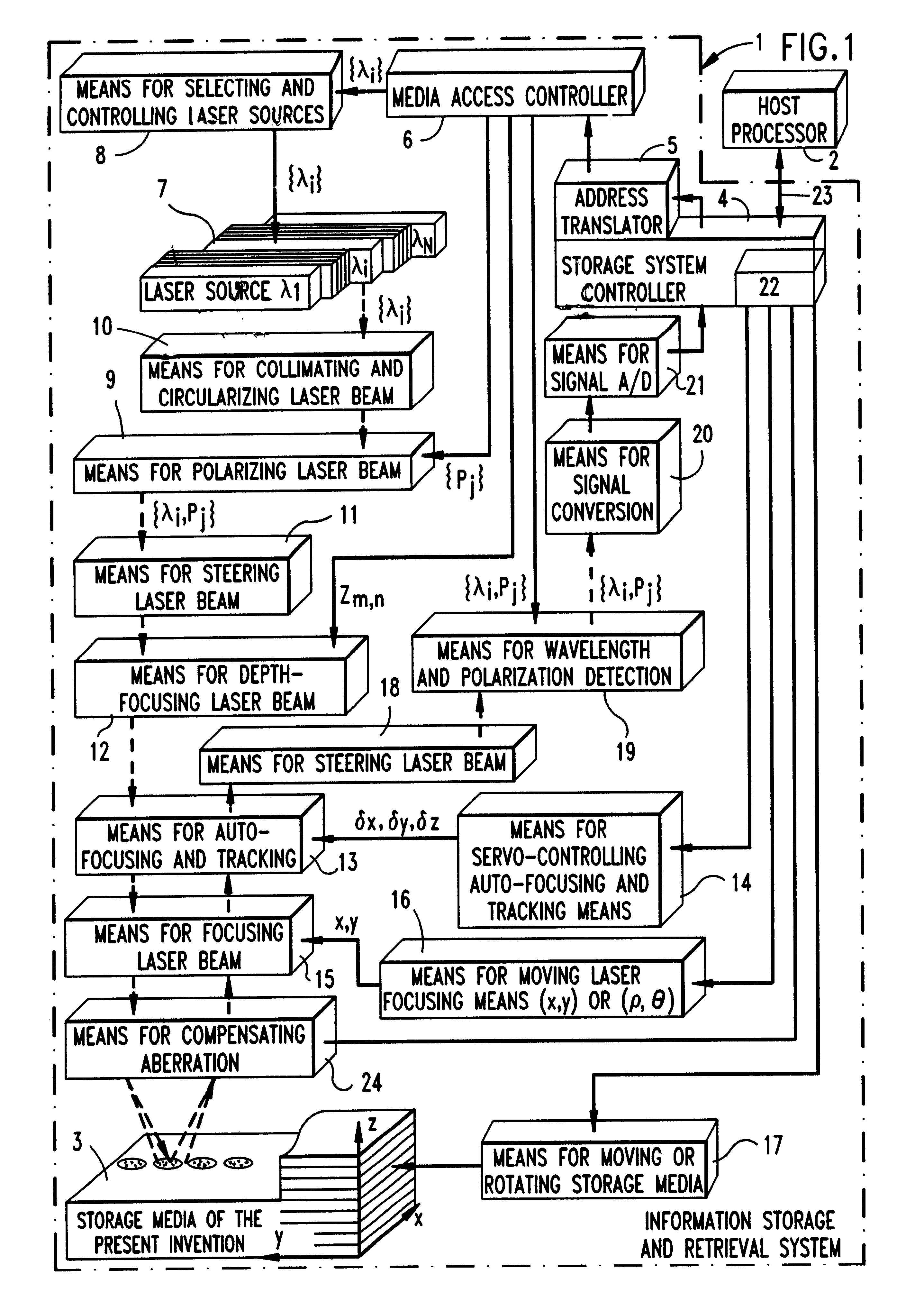
Disclosed is a novel multi-layered optical recording media and system for recording and reproducing information data. The multi-layered topical recording media has M information storage decks, and each information storage deck has N information storage layers, and each information storage layer has a pair of information storage structures. Each paired information storage structure has a characteristic wavelength and polarization state, and from which recorded information can be read by a laser beam having similar wavelength and polarization-state characteristics. In the illustrative embodiment, the multi-layered optical recording media of the present invention has MxNx2 information storage layers which can be read using only N laser lines (i.e. spectral components), thereby providing a 2M-fold increase in information storage capacity over prior art systems. The information storage and retrieval system of the present invention is completely backward compatible to allow for the reading of conventional CD-ROM devices.
Owner:REVEO
Pseudo-reflective read inhibitor for optical storage media
InactiveUS6839316B2Low costChange is minimalCombination recordingLayered productsOptical reflectionTime function
System and methods are described for inhibiting the readability of an optical media due to changes in a pseudo-reflective material that composes the optical media after the optical media has been exposed to air for a predetermined time. An optical media includes a data encoded component. At least a fraction of the data encoded component transforms from a substantially optically reflective state to a substantially optically non-reflective state as at-least-in-part a function of time from an initializing event. The systems and methods provide advantages because of low cost, limited content lifetime, avoidance of rental returns and minimum changes to existing manufacturing processes.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS20060210925A1High densityHigh speed recordingRecording strategiesRadiation applicationsSubstrate deformationComputer science
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium using a recording material which has a low to high characteristic that a light reflectivity in a recording mark increases with respect to a non-recording area and which has a recording characteristic in accordance with a principle of recording without substrate deformation, wherein the recording material includes at least an organic metal complex, and wherein the organic metal complex includes a center metal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
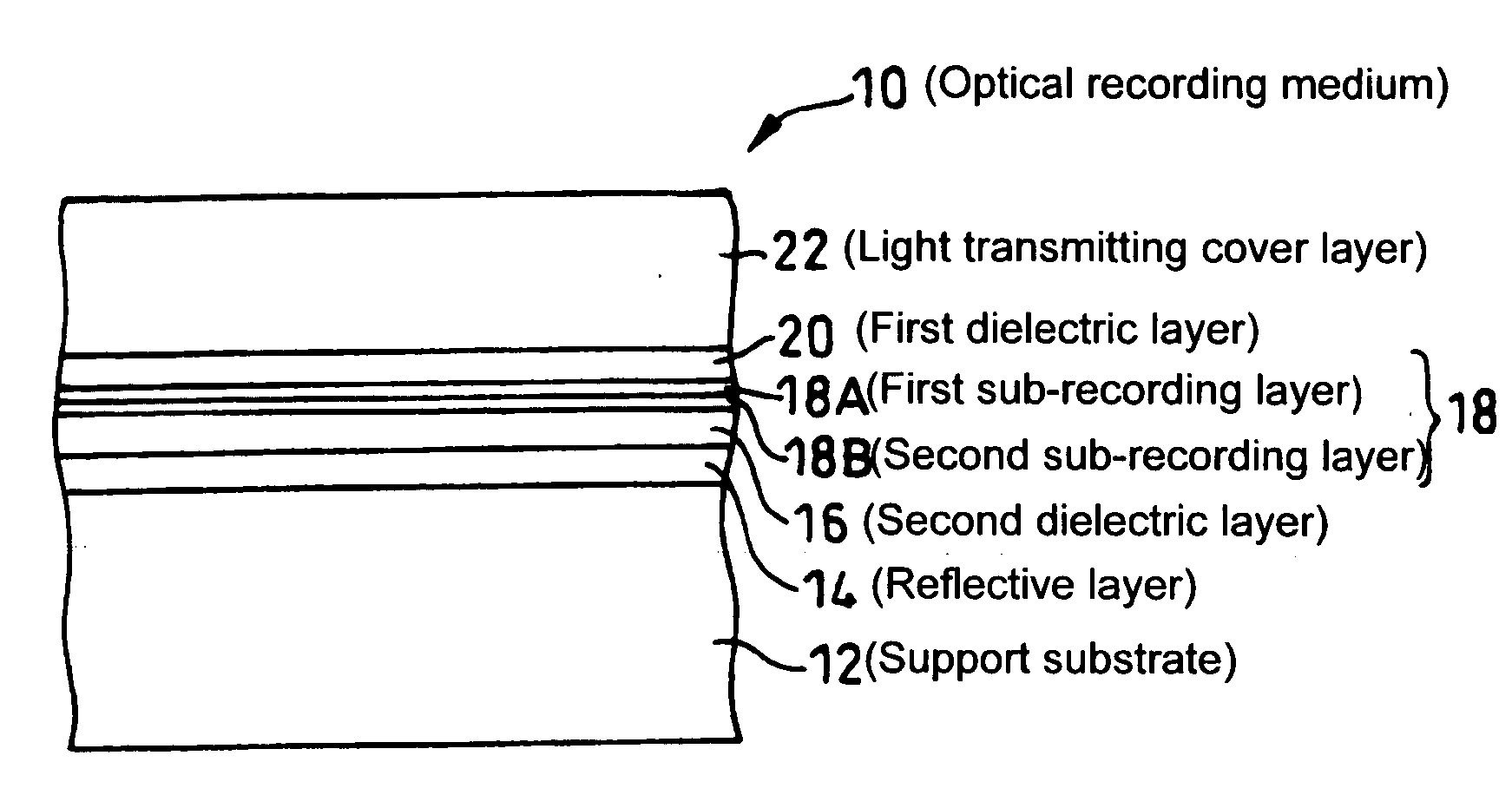
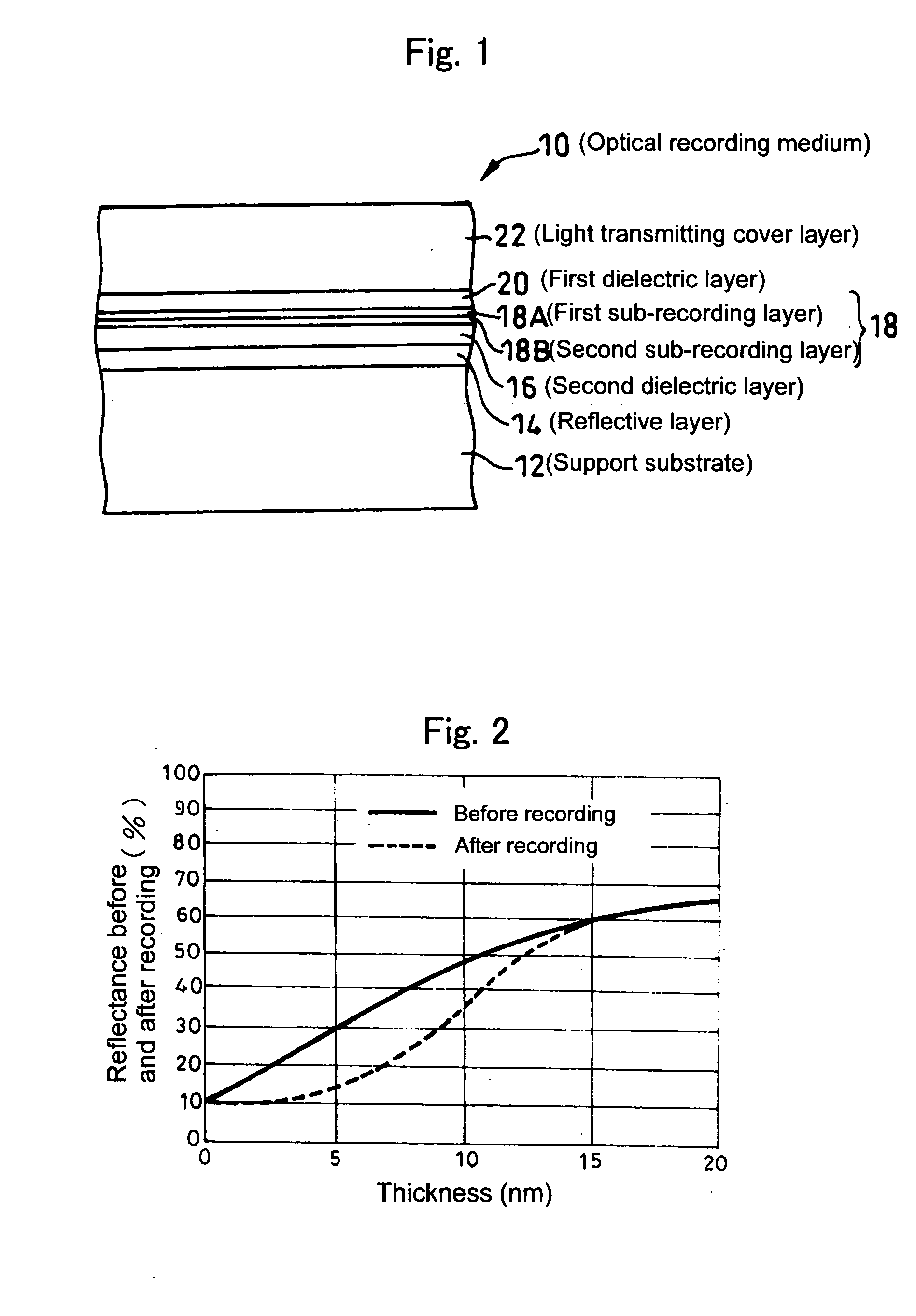
Method of regulating reflectance of worm type optical recording medium and worm type optical recording medium
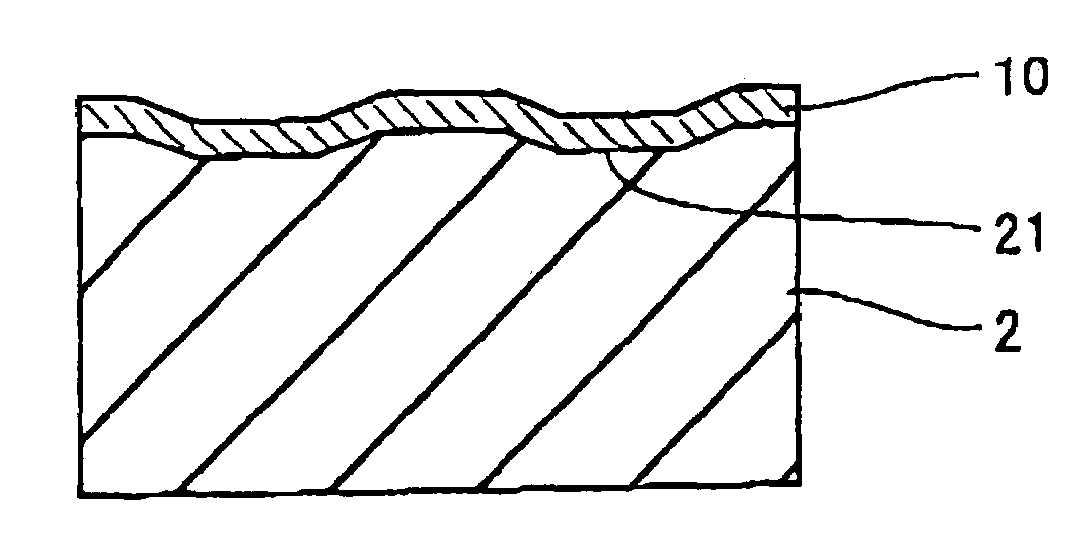
InactiveUS20050081230A1Easily and reliably maintaining compatibilityHigh-speed, high density write-onceLayered productsRecord information storageOptical recordingLength wave
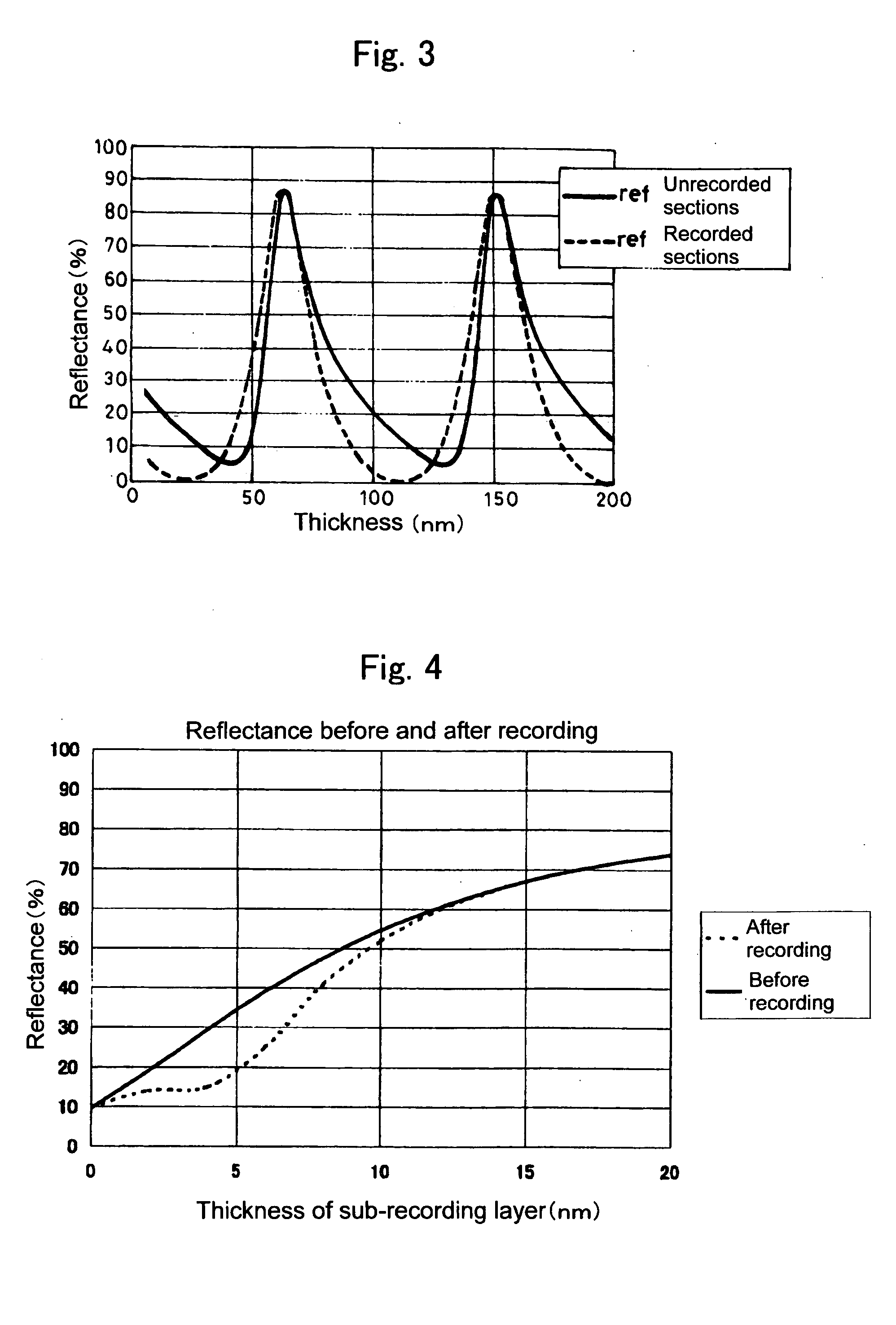
The reflectance of an optical recording medium for which high speed recording using a laser beam with blue wavelength or a shorter wavelength than blue light is possible is adjusted to a predetermined value of no more than 60%. A recording layer 18 of a high-speed write-once type optical recording medium 10 is formed by laminating first and second sub-recording layers 18A, 18B, each of which contains one type of different metal as a primary component. When laser beam of a blue wavelength is irradiated onto the recording layer 18, the irradiation causes the primary component metals contained within each of the first and second sub-recording layers 18A, 18B to diffuse and mix, and this mixing forms a recording mark with an irreversibly changed reflectance. The recording layer 18 is sandwiched between first and second dielectric layers 20, 16, and by adjusting the material and the thickness of the recording layer 18 and the first and second dielectric layers 20, 16, the reflectance of the unrecorded sections can be adjusted to a value within a range from 5% to 60%.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording medium using scattering bodies to enhance modulation
InactiveUS6848115B2Convenient ArrangementLight generatedLayered productsNanoinformaticsScattering effectOptical recording
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Circularly Polarized Light-Emitting Nanoparticle
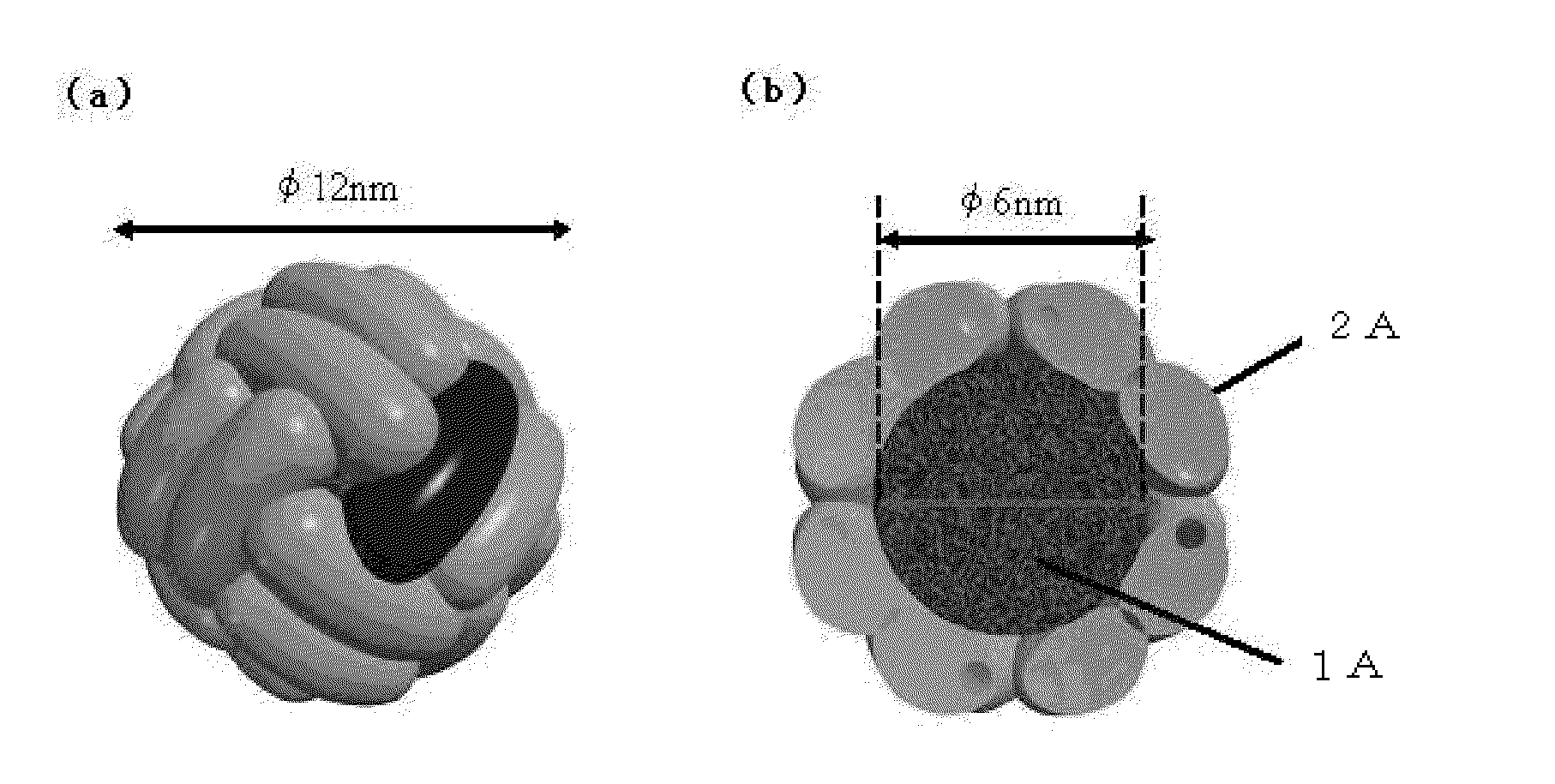
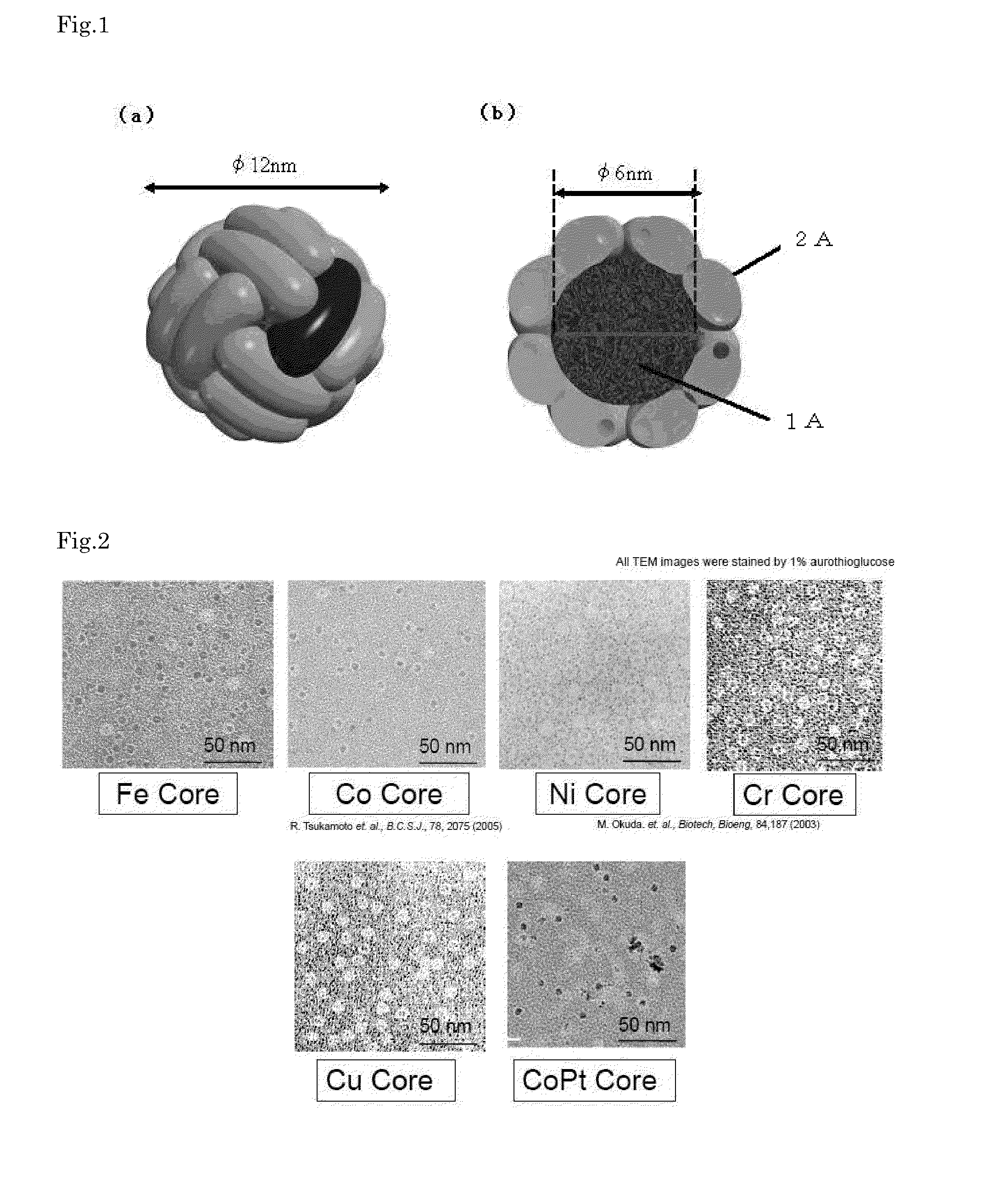
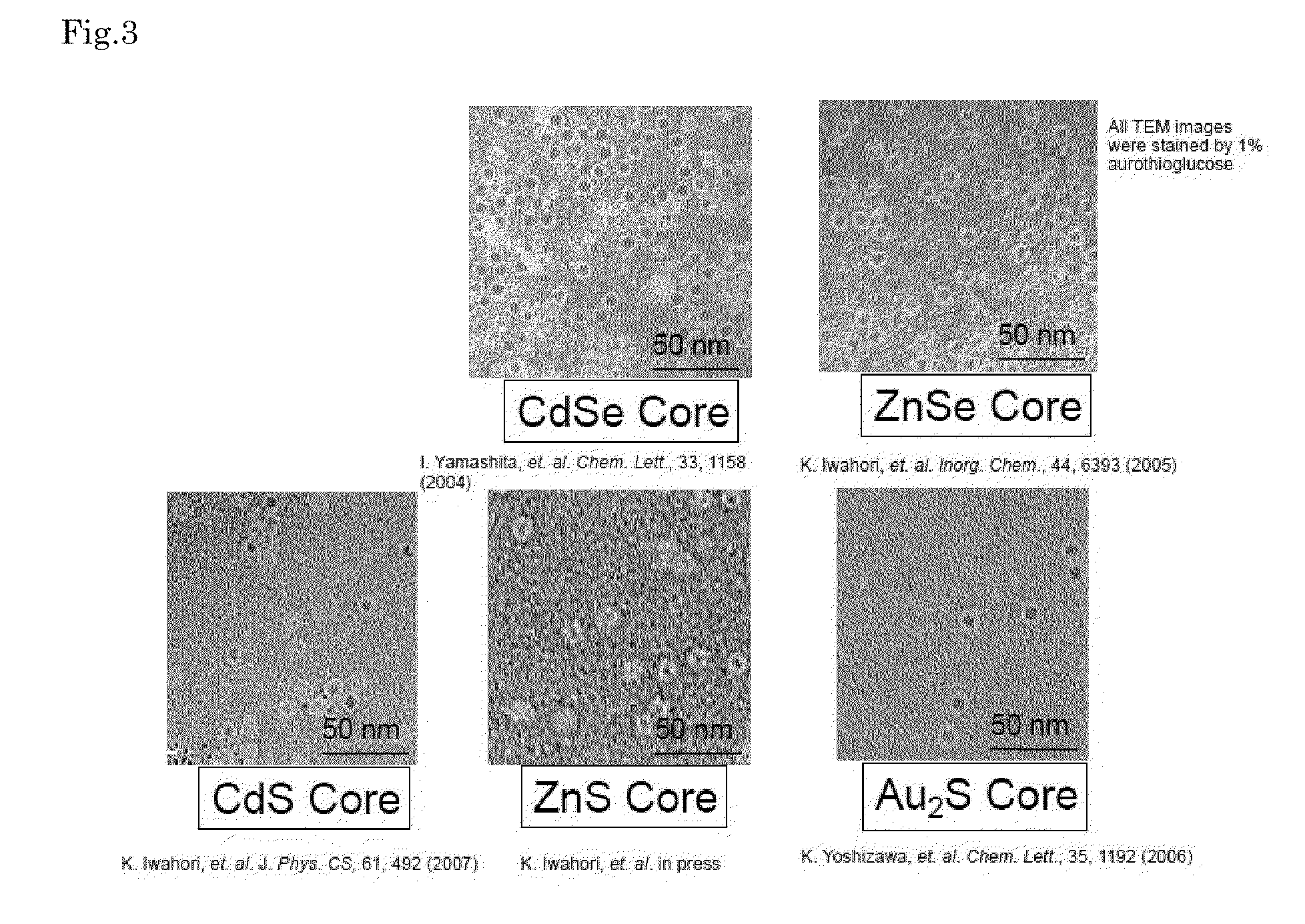
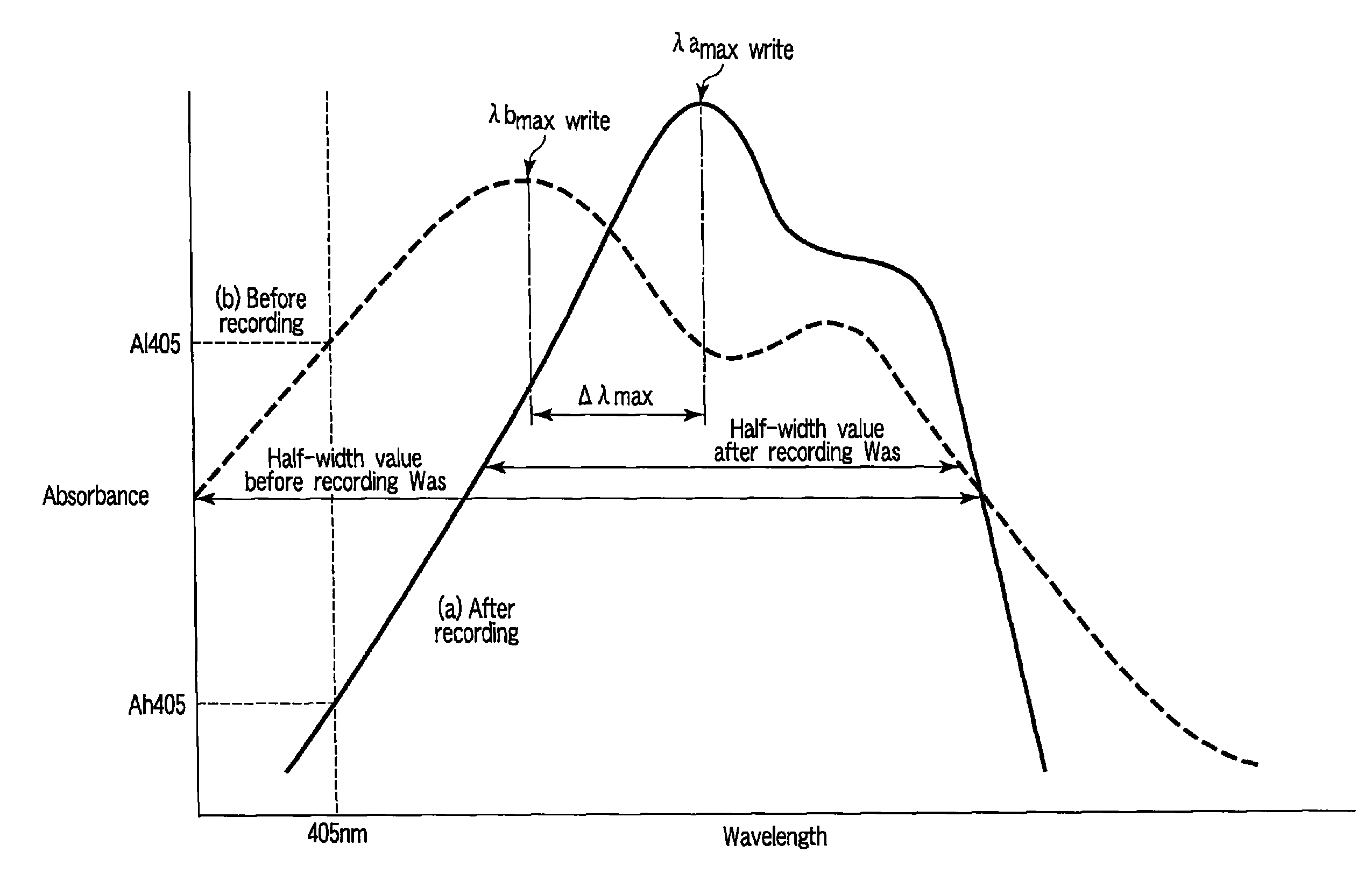
Provided is a compound semiconductor nanoparticle that exhibits circularly polarized luminescence characteristics. CdS prepared inside a core of ferritin, which is a cage-like protein, exhibits a high circularly polarized luminescence (CPL). A wavelength of the circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) can be controlled by laser irradiation, thereby enabling utilization of the compound semiconductor nanoparticle in the field of bionanotechnology, for example, in creating a WORM (Write-Once Read-Many times) memory. As the cage-like protein, which is a protein with a cavity formed therein, a protein belonging to the ferritin protein family, such as apoferritin, or a recombinant thereof can be used.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS7960093B2High densityHigh sensitivityRecording strategiesRadiation applicationsSubstrate deformationComputer science
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium using a recording material which has a low to high characteristic that a light reflectivity in a recording mark increases with respect to a non-recording area and which has a recording characteristic in accordance with a principle of recording without substrate deformation, wherein the recording material includes at least an organic metal complex, and wherein the organic metal complex includes a center metal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multi-layer optical recording media and method for recording and reproducing information using the same
InactiveUS6094410AEasy and inexpensive way to upgrade the information storage and reading capabilitiesPrecise alignmentOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical storageLength wave
Disclosed is a novel optical information storage media having M information storage decks. Each information storage deck has N information storage layers, and each information storage layer has a pair of information storage structures. Each paired information storage structure has a characteristic wavelength and polarization state, and from which recorded information can be read by a laser beam having similar wavelength and polarization-state characteristics. A novel system is provided for reading the optical information storage media of the present invention. In the illustrative embodiment, an optical storage device of the present invention having MxNx2 information storage layers can be read using only N laser lines (i.e. spectral components), thereby providing a 2M-fold increase in information storage capacity over prior art systems. The information storage and retrieval system of the present invention is completely backward compatible to allow for the reading of conventional CD-ROM devices. Various techniques are disclosed for manufacturing and reading the optical storage devices of the present invention.
Owner:REVEO
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
InactiveUS20050089799A1Good weather resistanceImprove featuresRadiation applicationsOptical overwritingWeather resistanceOptoelectronics
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Device and method for optical data storage having multiple optical states
InactiveUS6115344APhotography auxillary processesMechanical record carriersPolymer substrateOptical storage
PCT No. PCT / NO96 / 00125 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 20, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 20, 1997 PCT Filed May 22, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 37888 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 28, 1996The optical storage device and method includes a fluorescent layer arranged on a substrate and having a surface. The fluorescent layer is composed of fluorescent dye molecules embedded in a transparent polymeric base material. A group of data-carrying structures are arranged in the fluorescent layer. Each of the data-carrying structures has more than two optical states represented by a specific degree of quenching of fluorescence emitted from the data-carrying structure when irradiated with a fluorescence exciting radiation.
Owner:THIN FILM ELECTRONICS ASA +1
Optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20050058028A1Reduce polarization noiseReducing polarization noiseOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical depthLength wave
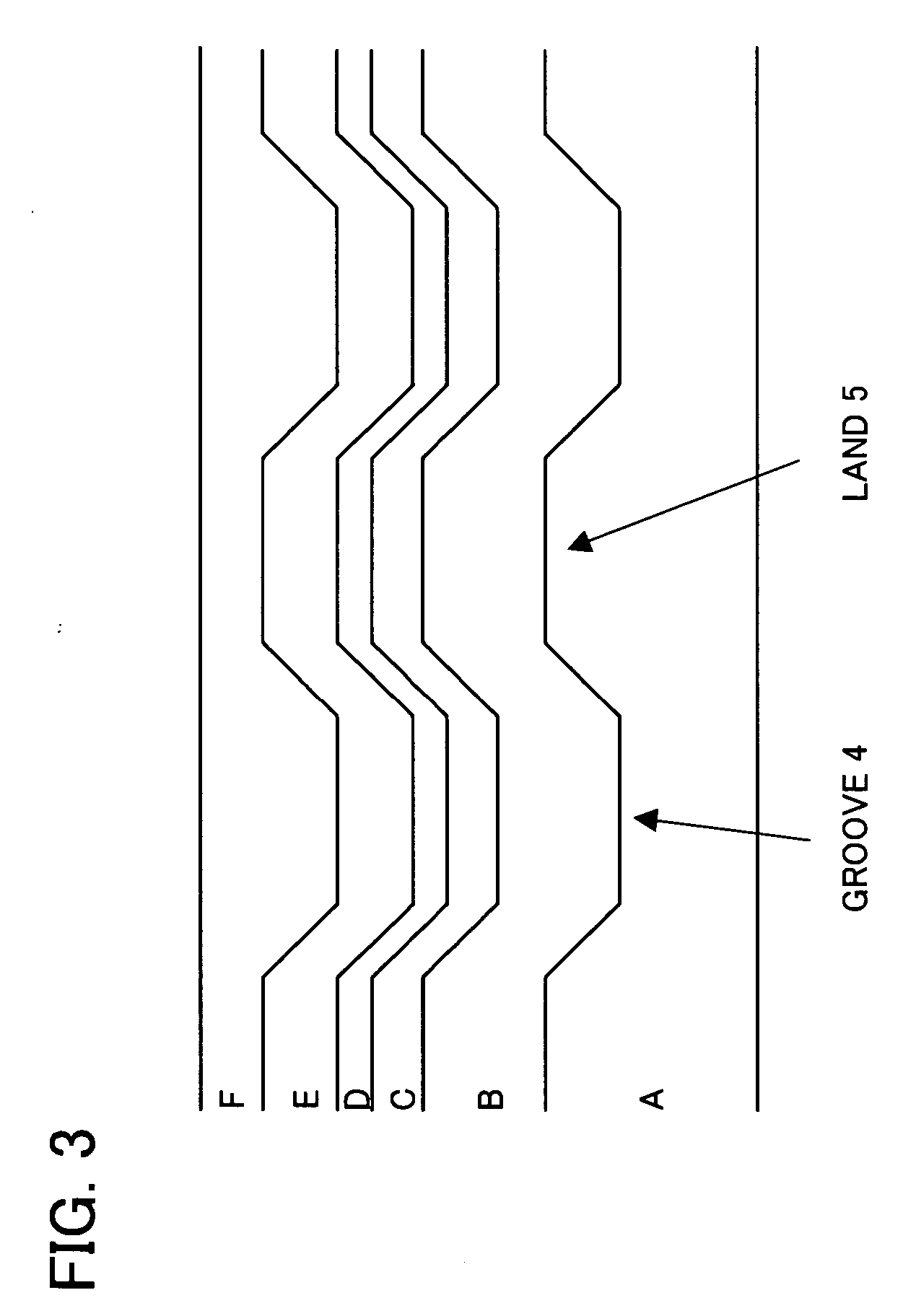
An optical information recording medium can reproduce stably RAM information during concurrent reading out of ROM-RAM information. The optical information recording medium comprises a substrate having a ROM area where phase pits to be ROM data are formed, and a magneto-optical recording film for recording RAM data, formed on an area corresponding to the ROM area of the substrate and, in the ROM area, the degree of modulation in the user area is at least 10-37% and, preferably, the degree of modulation of the phase pits in the user area is 15-25%. As an aspect, the optical depth of the phase pits is approximately λ / 8-λ / 10 (λ is the wavelength of the laser used for recording / reproducing).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
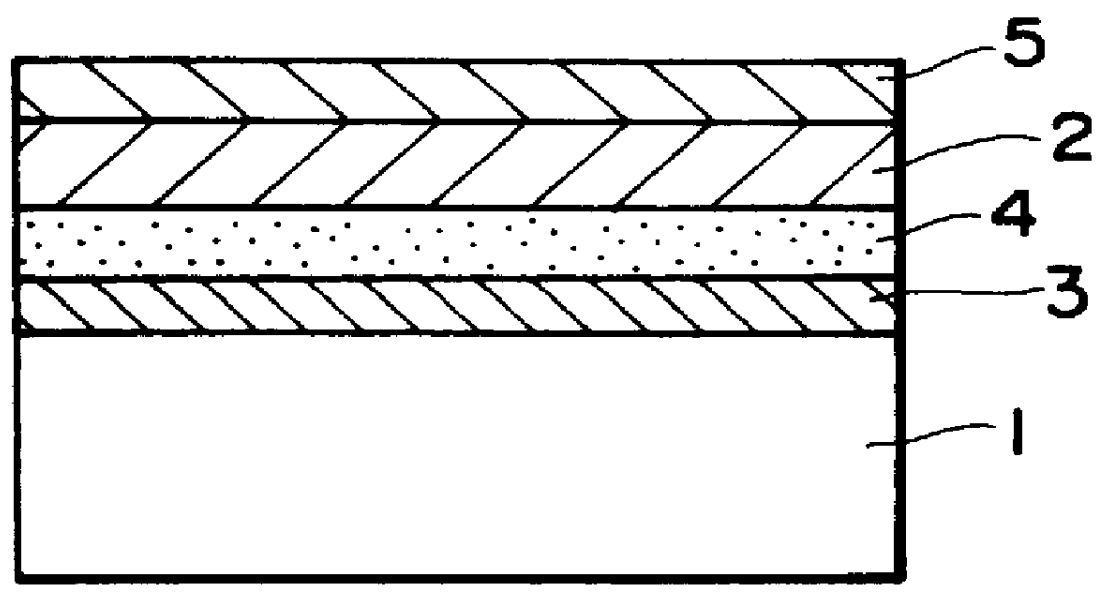
Phase-Change Type Optical Recording Medium and Reproduction Method and Apparatus for Such a Recording Medium
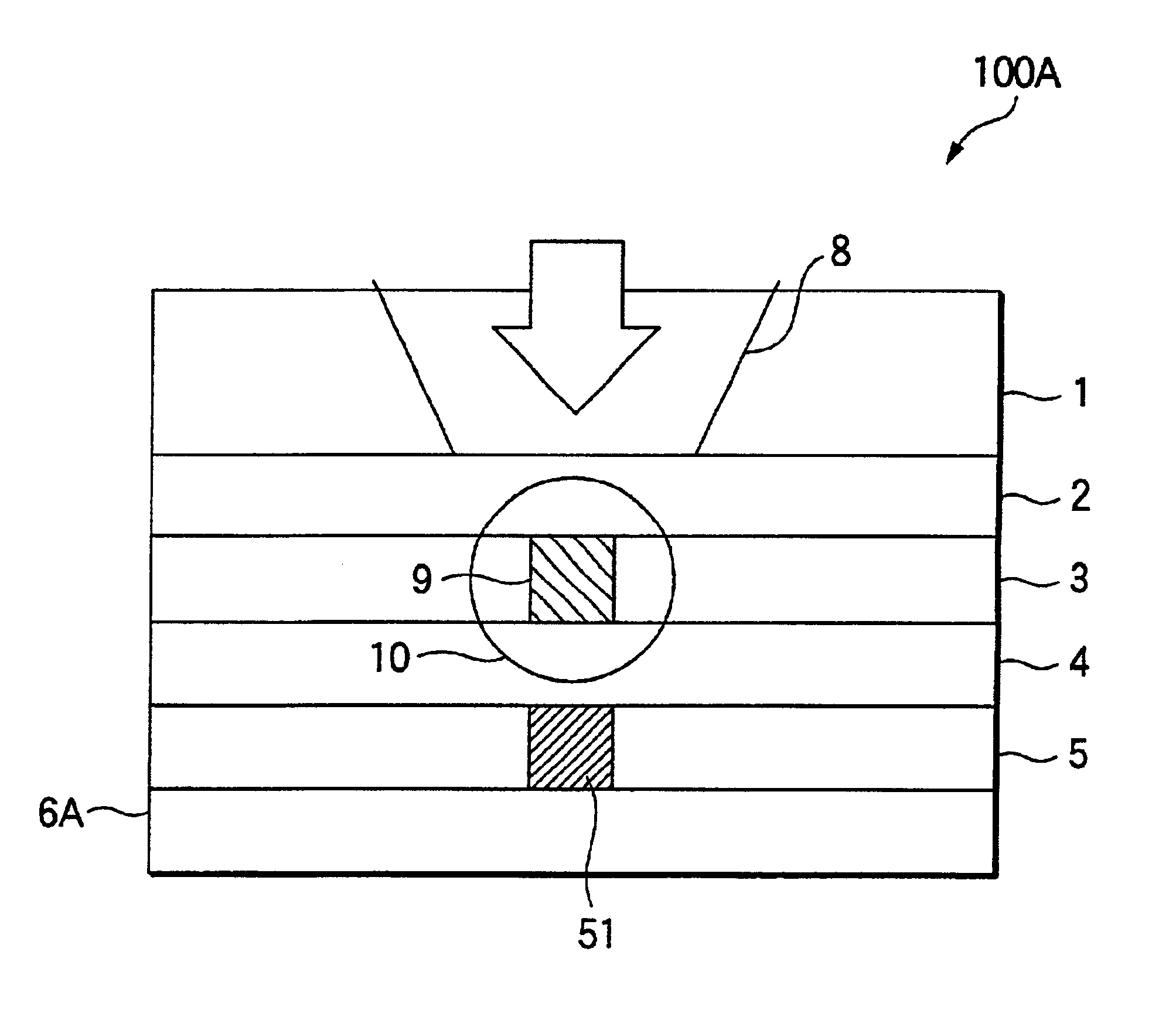
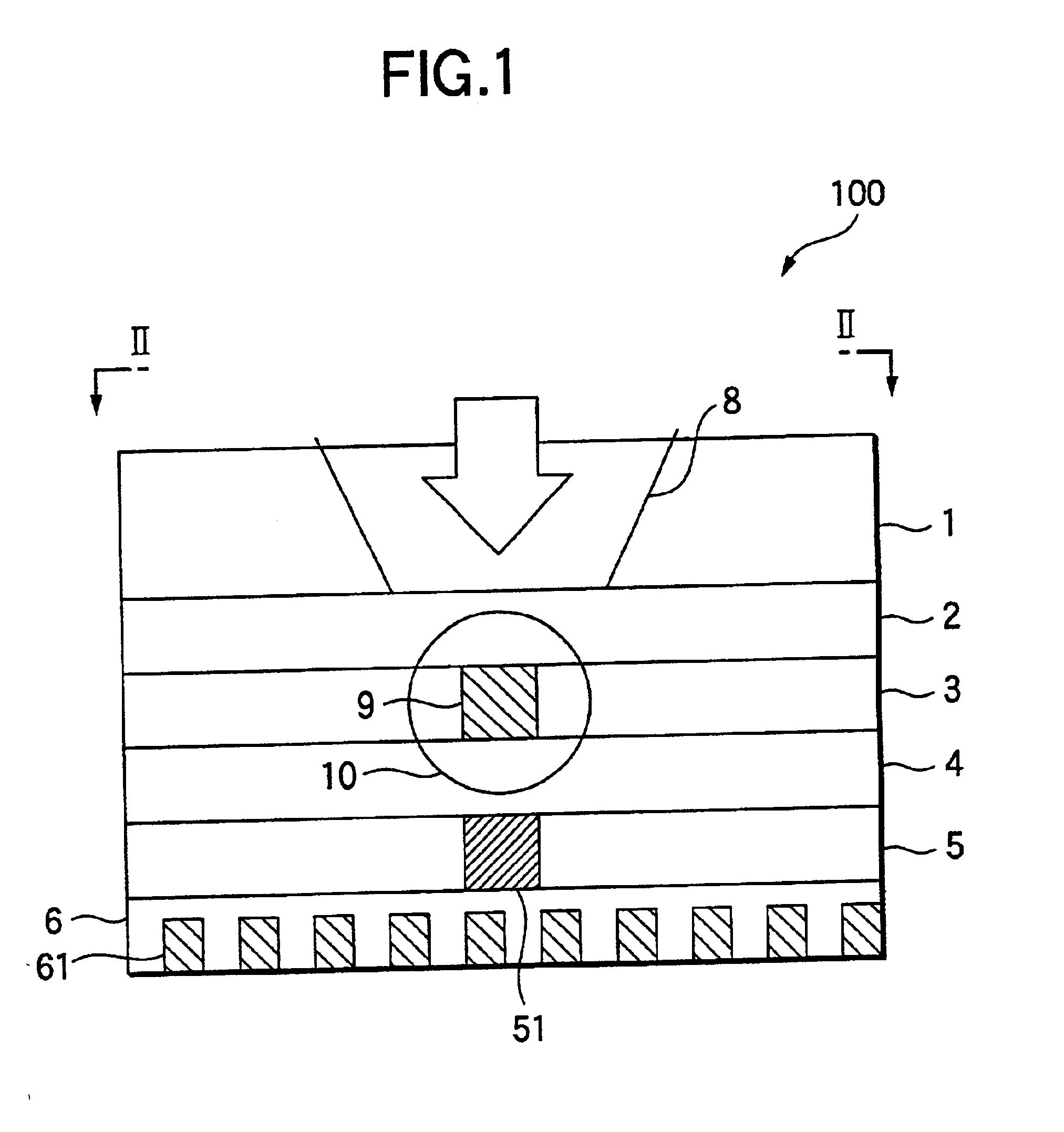
ActiveUS20070237062A1Easy to performPromote reproductionCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsLower limitAlloy
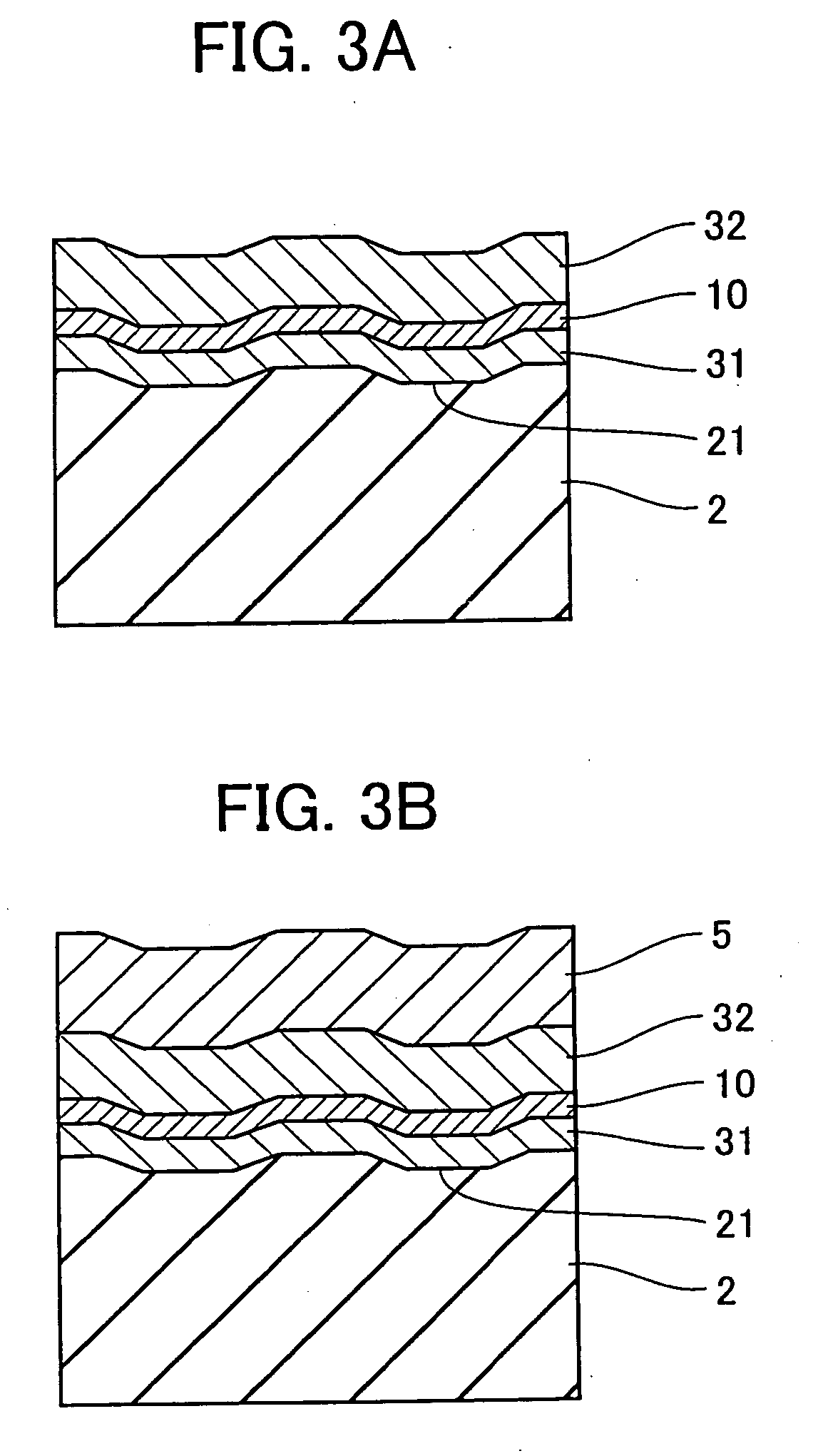
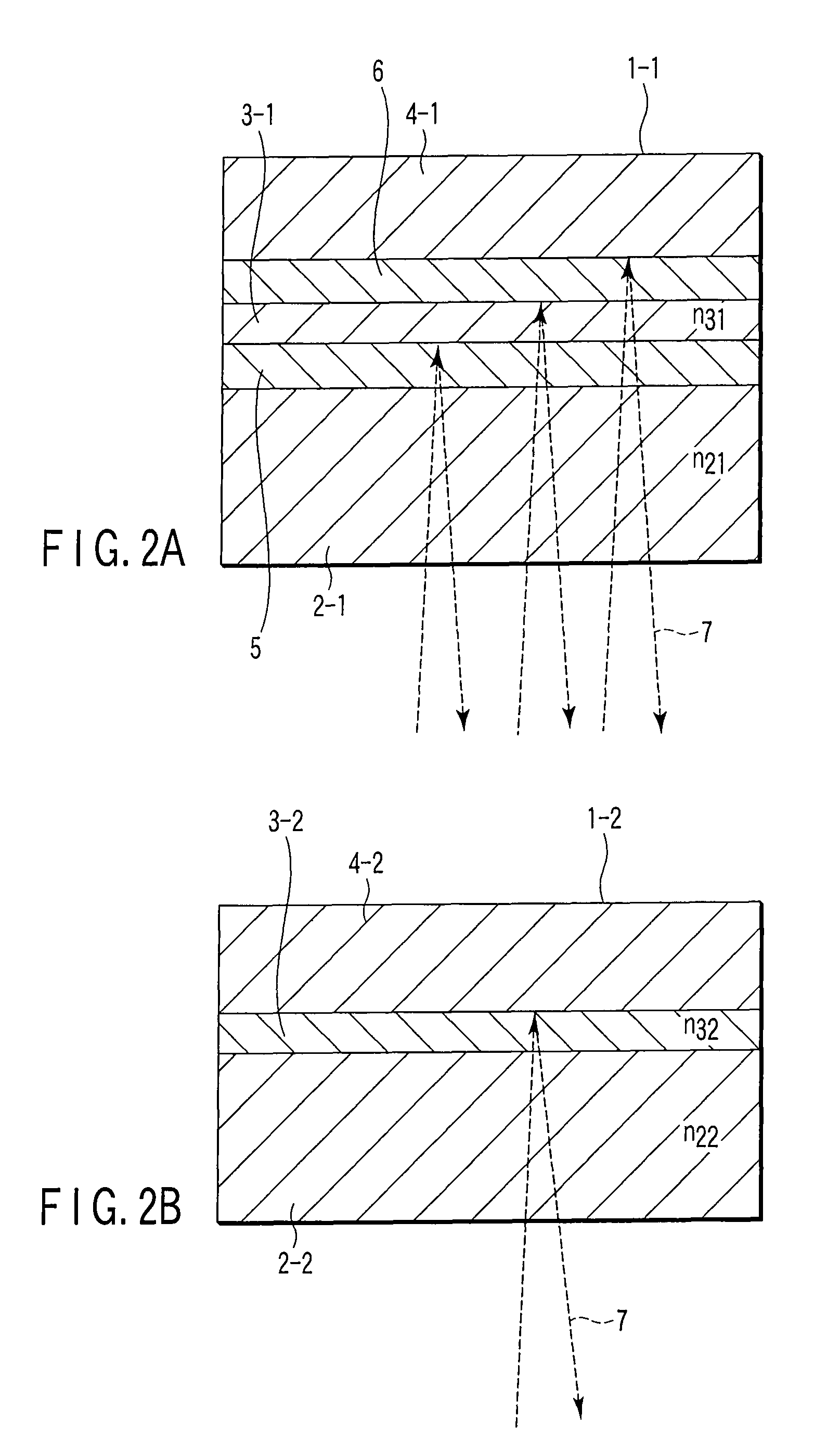
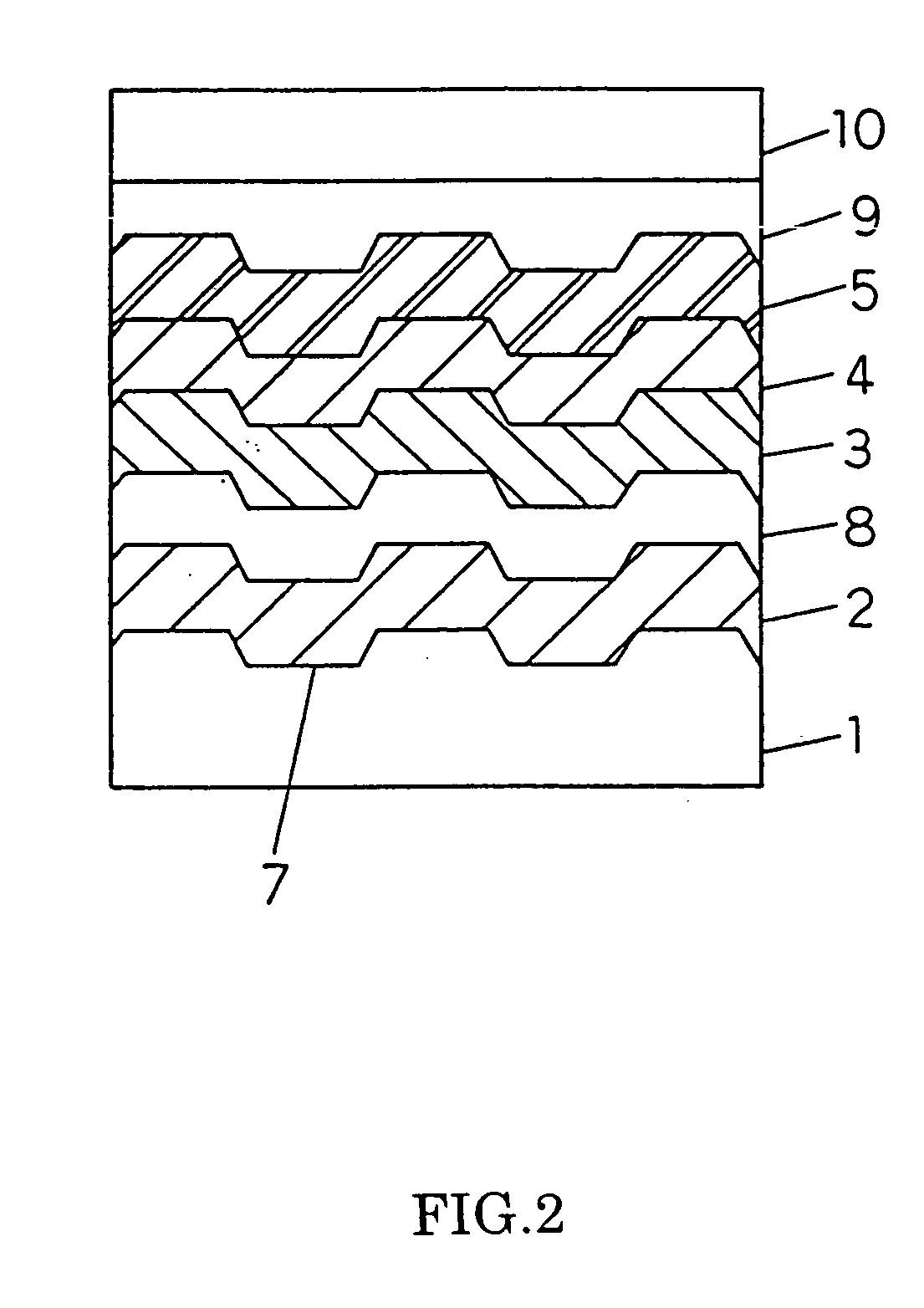
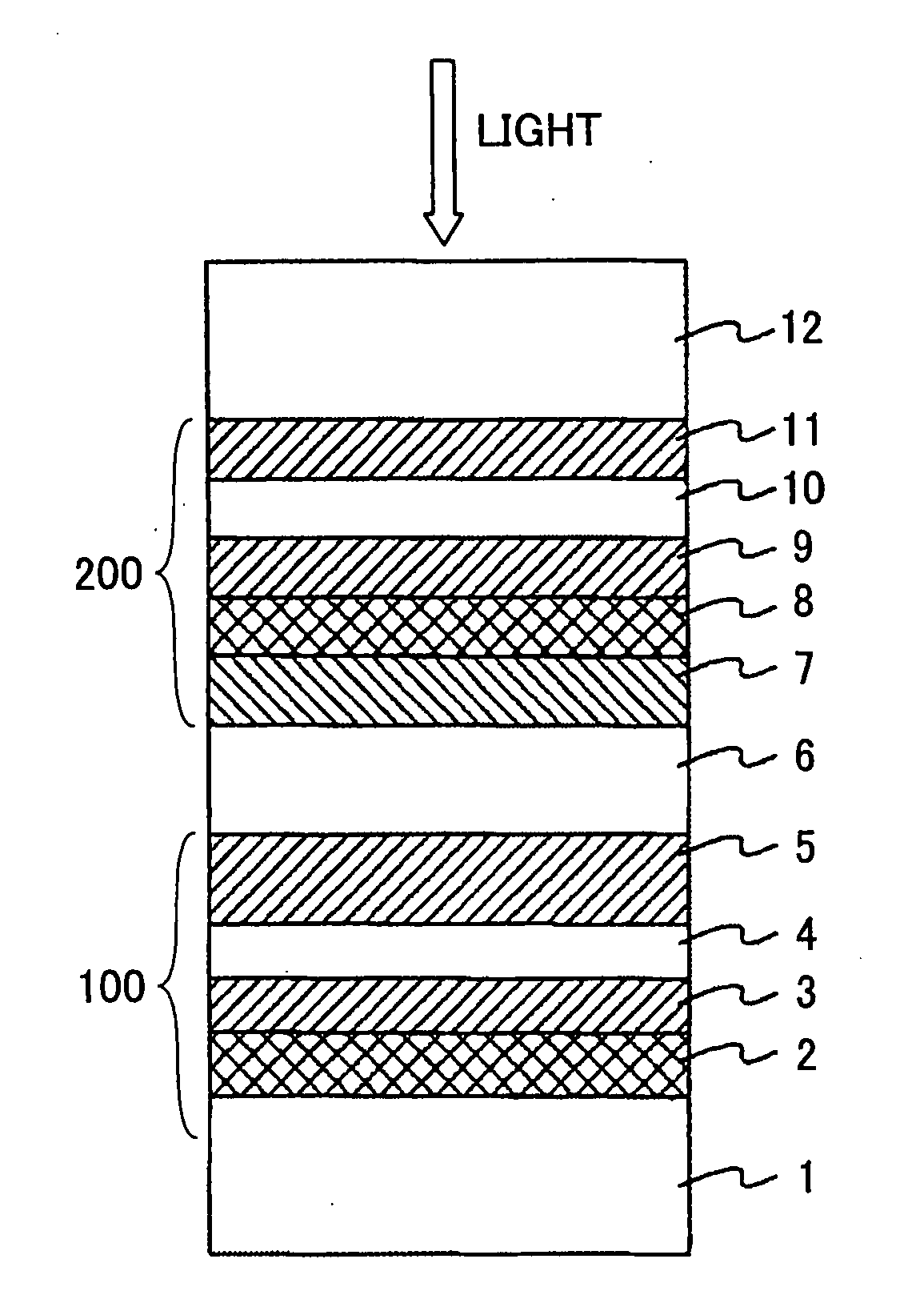
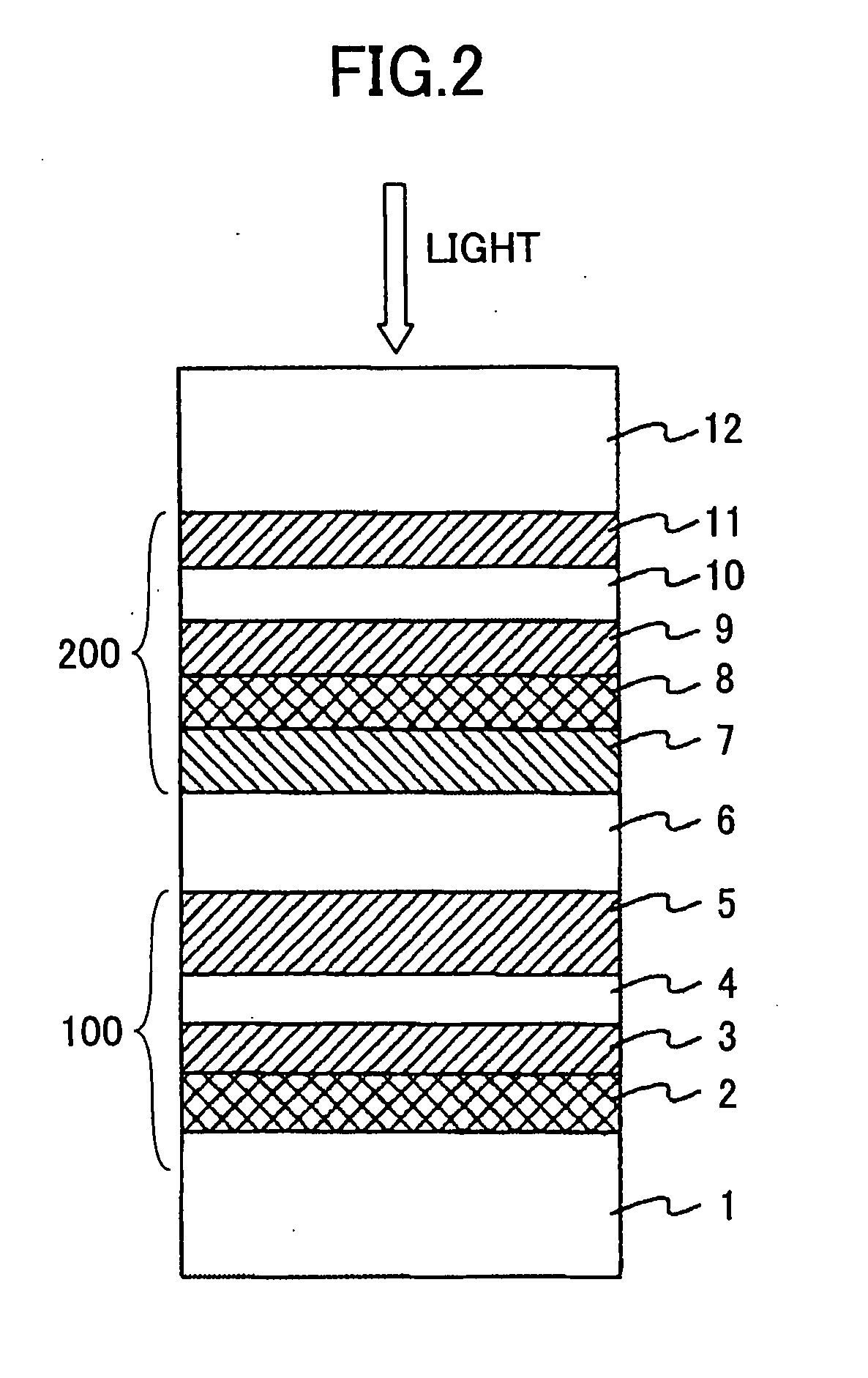
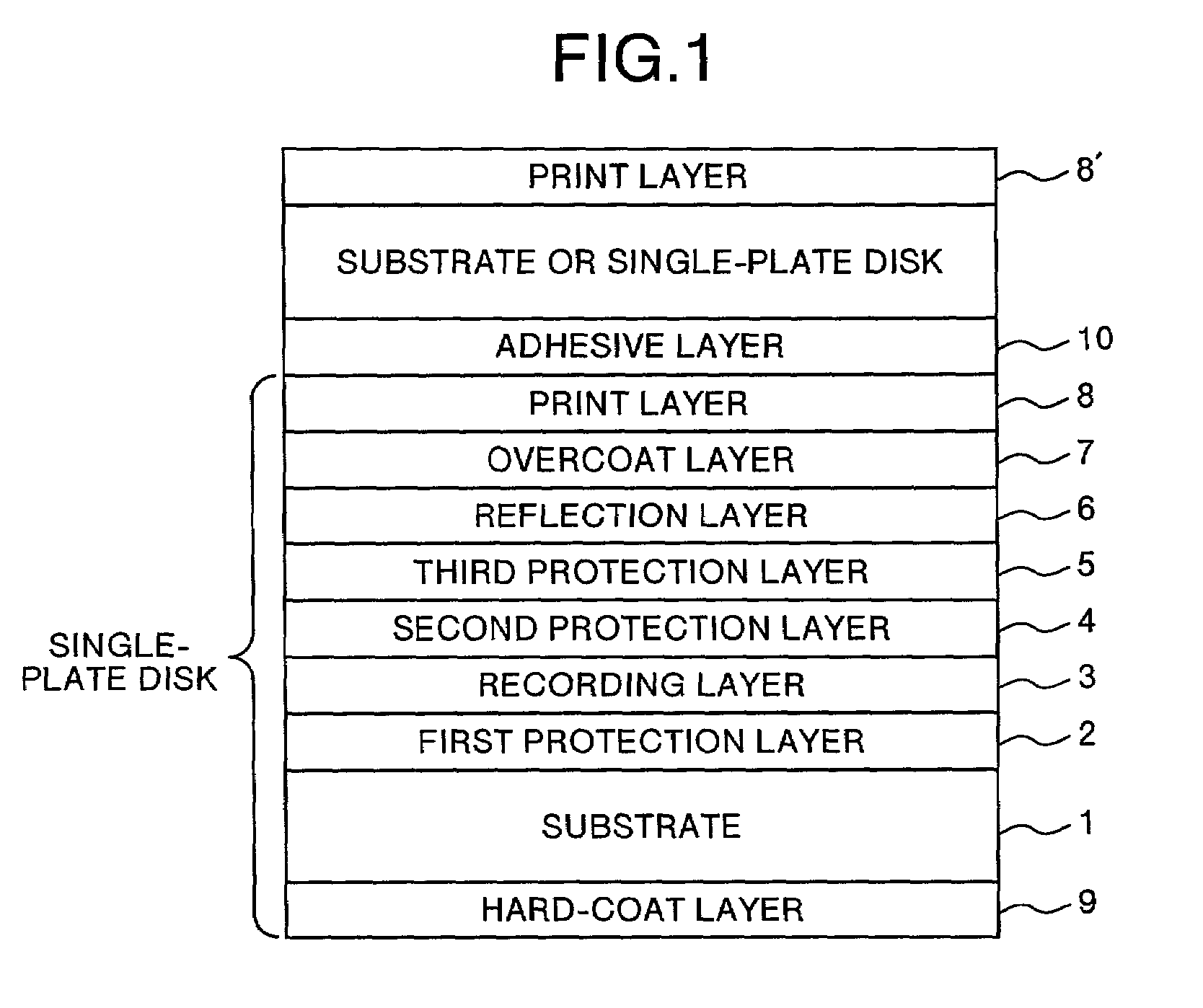
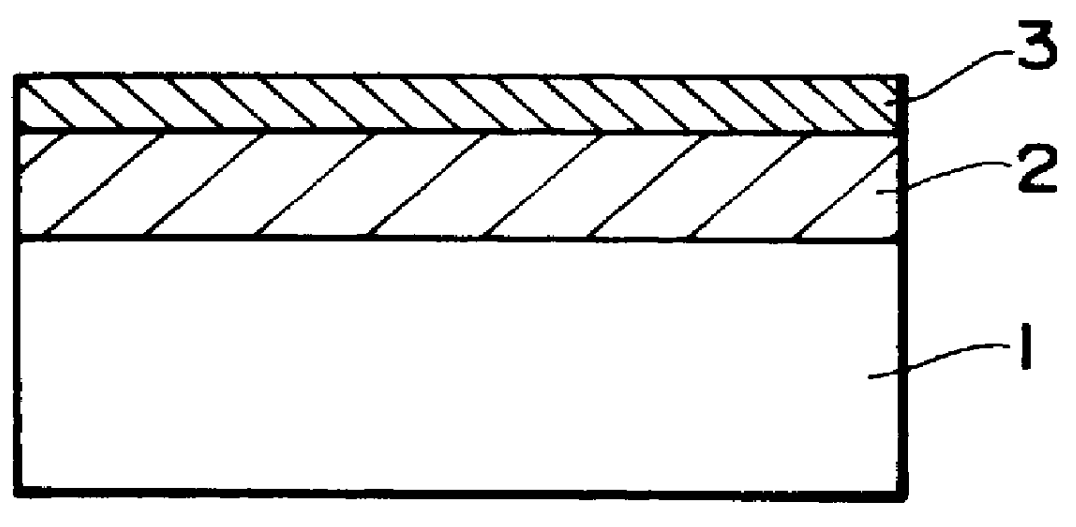
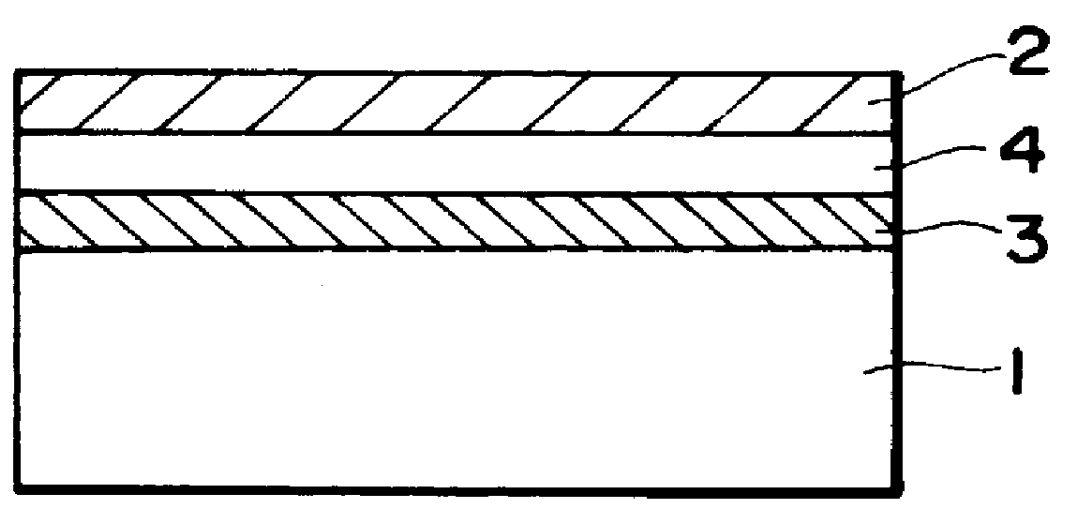
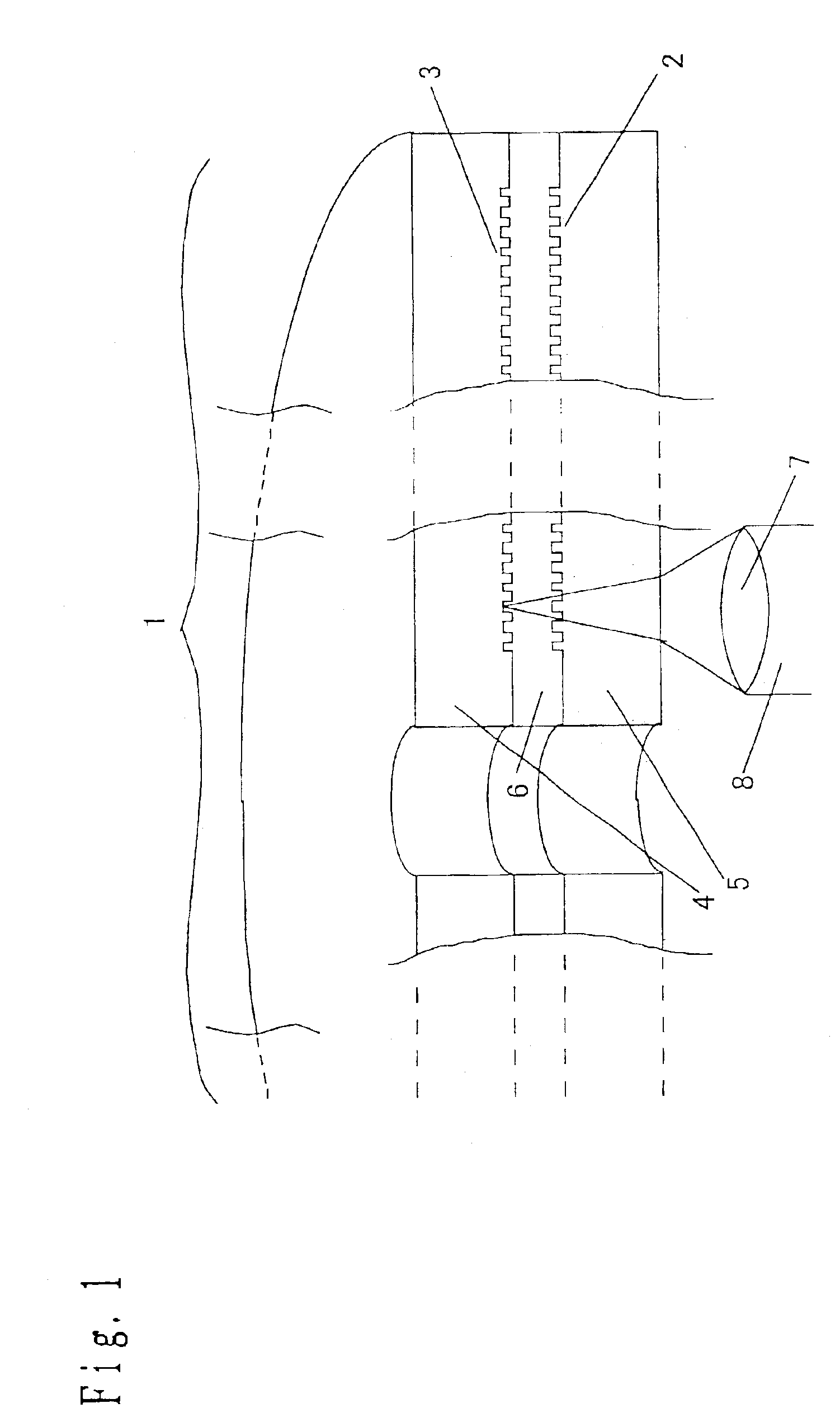
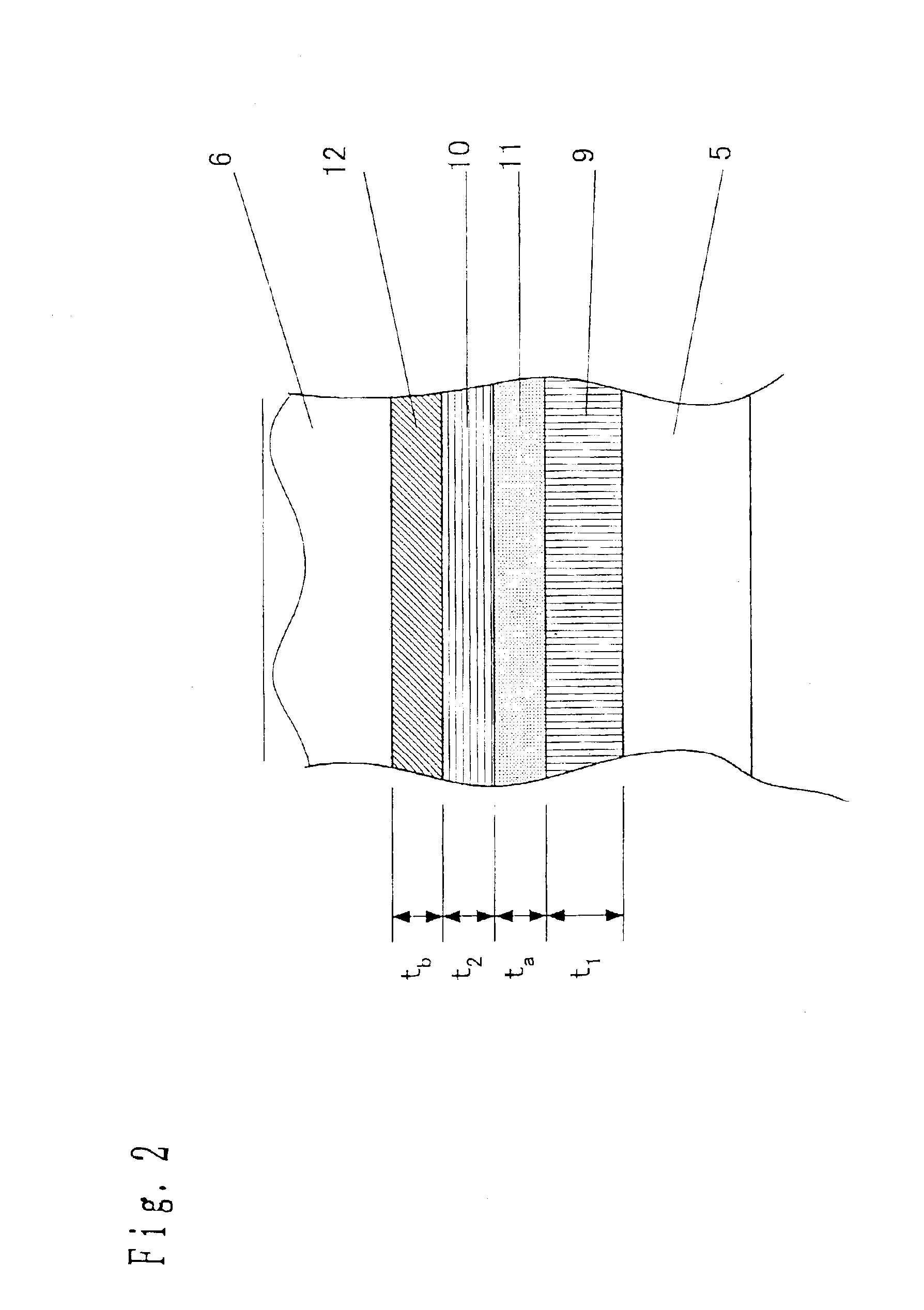
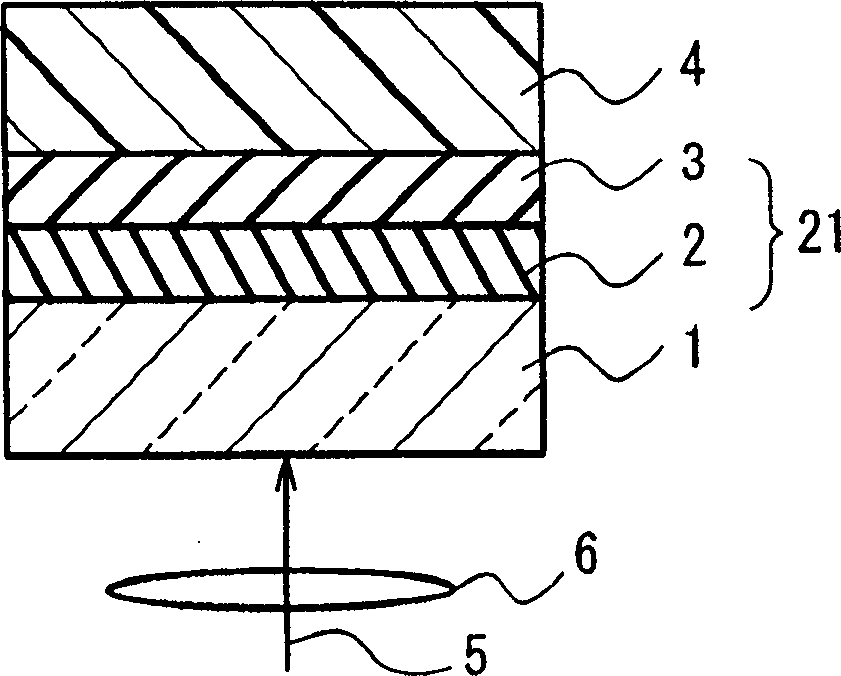
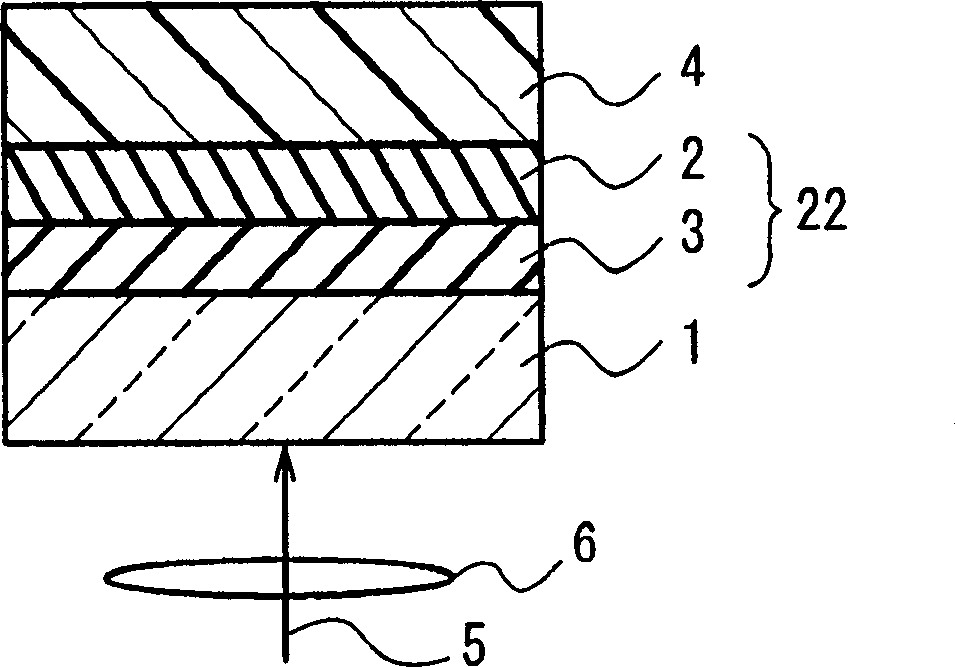
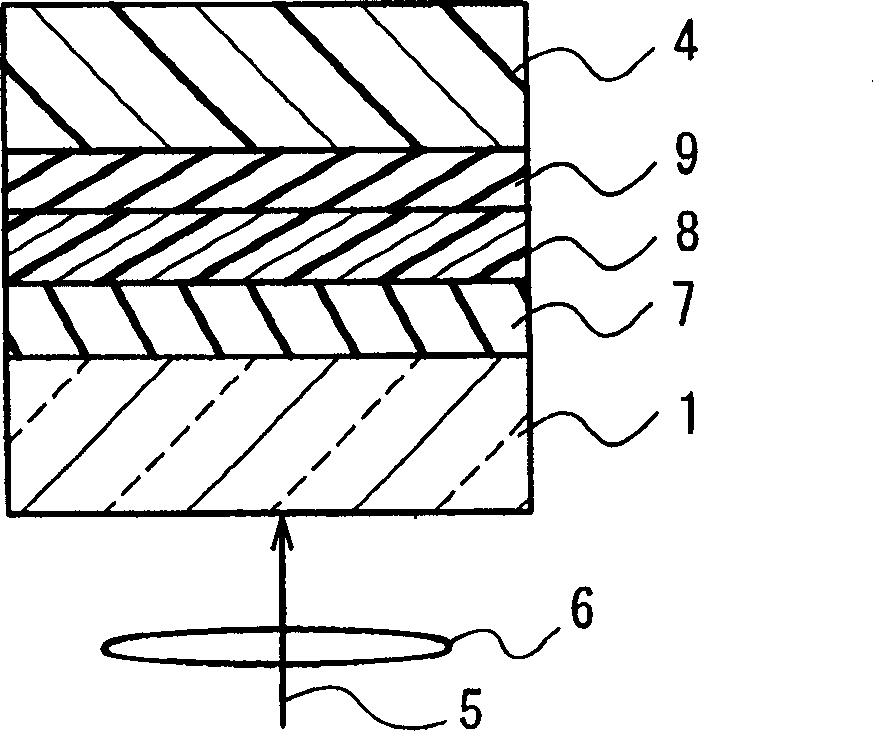
A dual-layer structure phase-change type optical recording medium includes a substrate (1), a reflective layer (2), a first protective layer (3), a first recording layer (4), a second protective layer (5), a resin intermediate layer (6), a third protective layer (7), a heat release layer (8) made of Cu or a Cu alloy, a fourth protective layer (9), a second recording layer (10), a fifth protective layer (11) and a cover substrate (12). A product of a reflectance of a high-reflection part and a modulation after recording is a value equal to or higher than a lower limit value for reproduction.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical information recording medium, method of manufacturing the optical information recording medium, and method of and apparatus for recording/reproducing optical information
InactiveUS7507523B2Sufficient capabilityImprove stabilityRadiation applicationsLayered productsPhase changeRecording layer
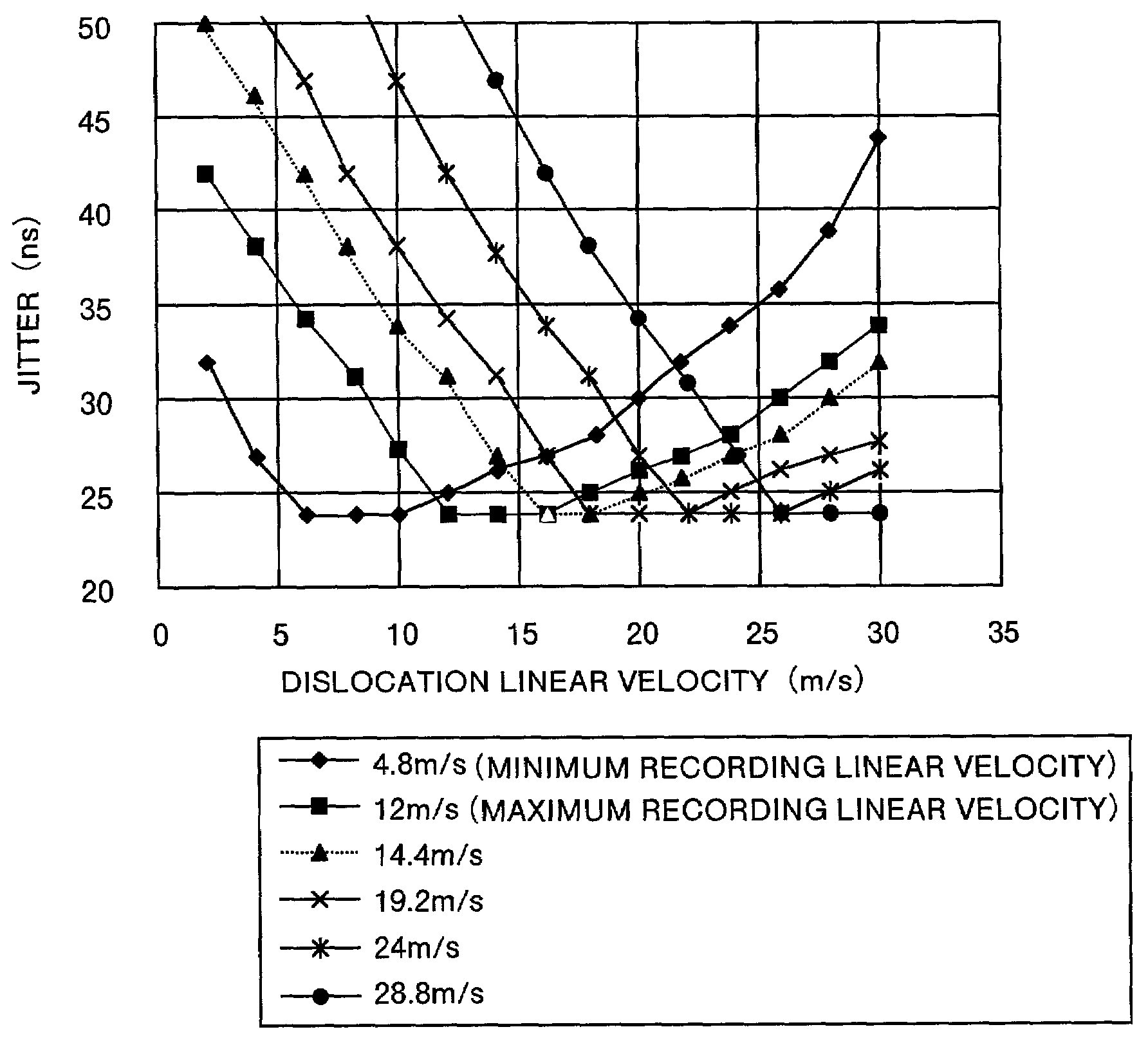
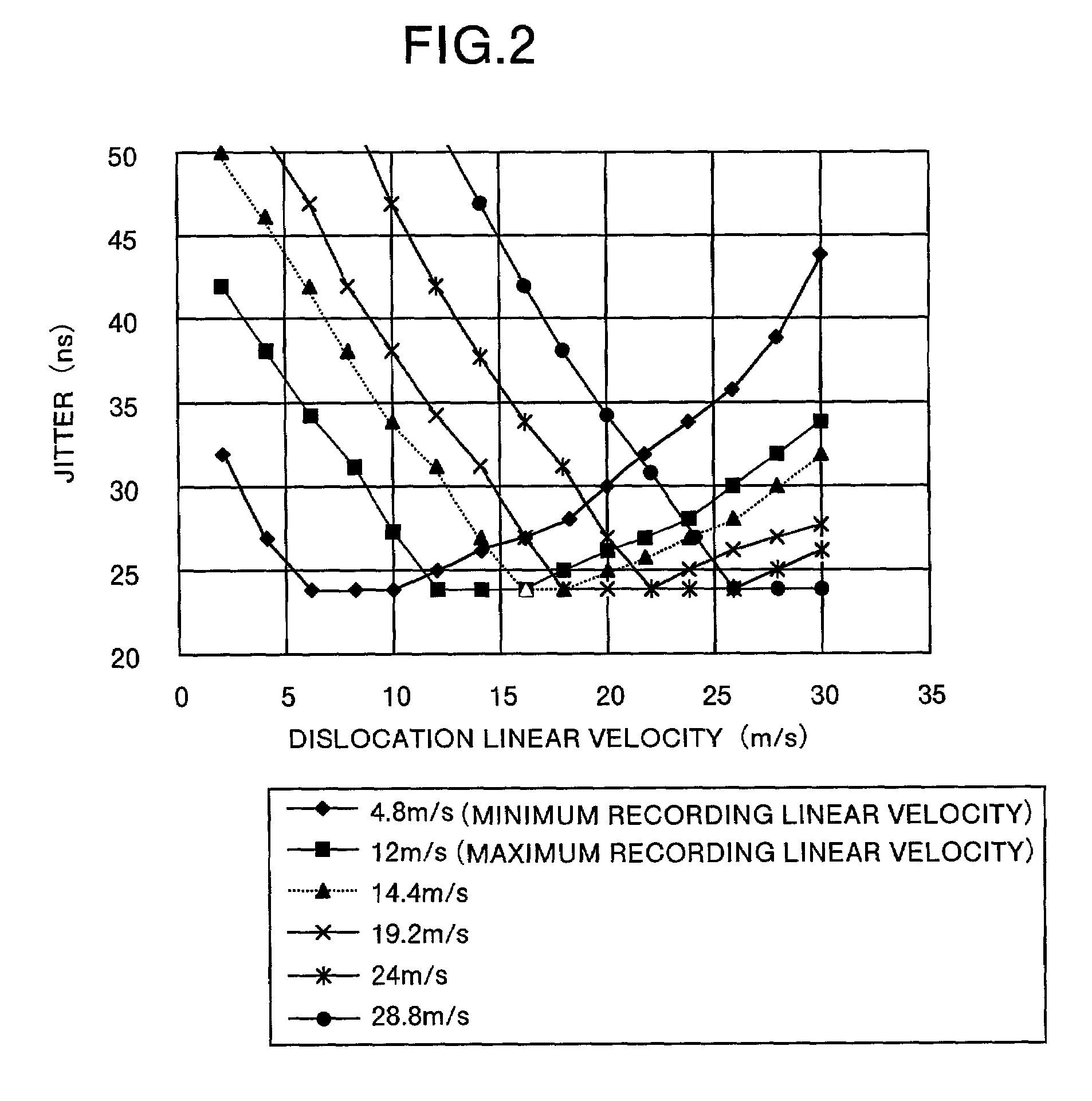
An optical information recording medium is provided. This medium at least stores information that indicates a maximum recording linear velocity Vh. The medium comprises a substrate having a concentric circular guide groove. This guide grove has land portions and groves portions. At least a phase change type recording layer is formed on the substrate. The recording layer has such a composition and thickness that a dislocation linear velocity V satisfies the relation V≧Vh×0.85.
Owner:RICOH KK
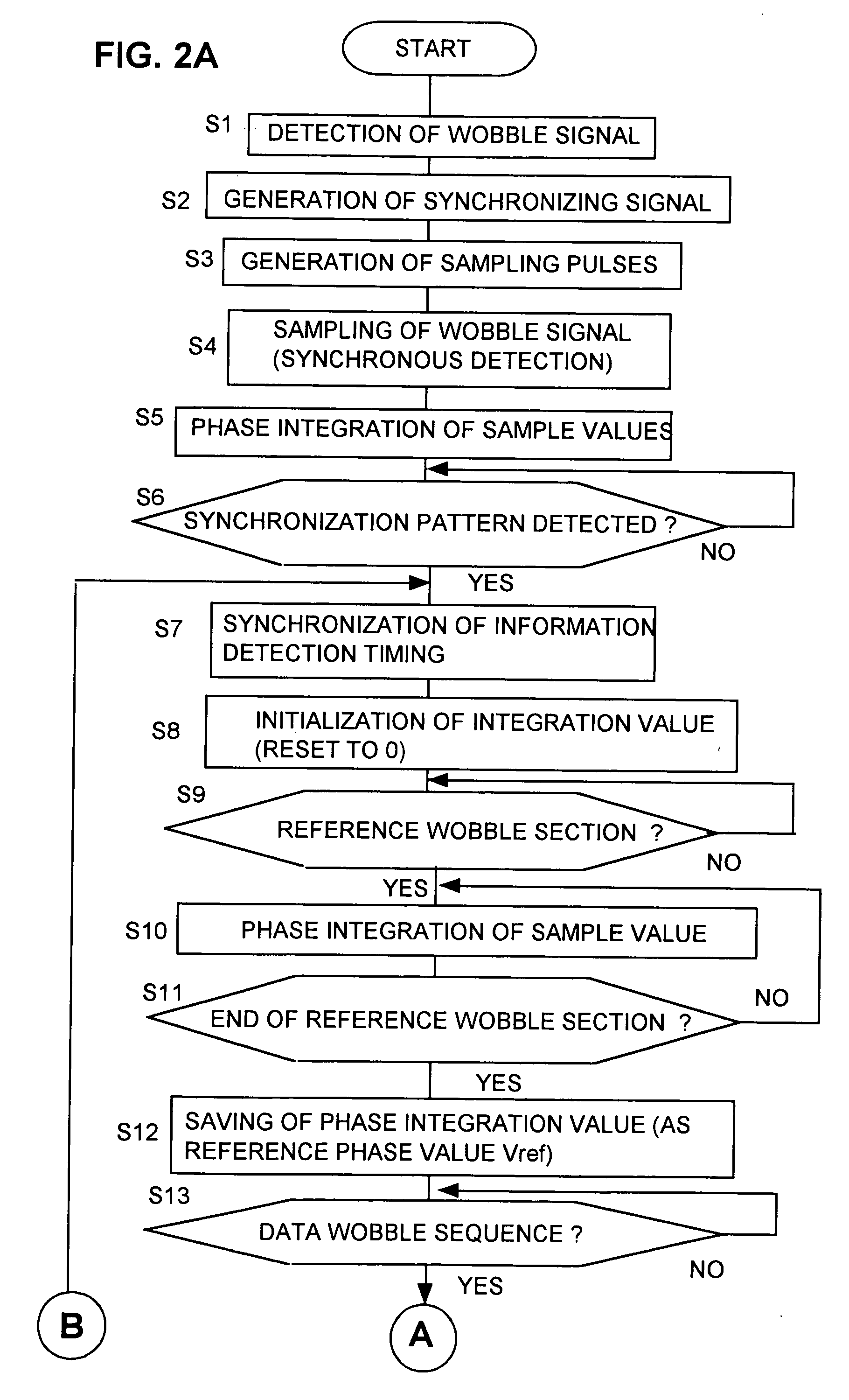
Wobble information detection method and wobble information detection apparatus for optical recording medium
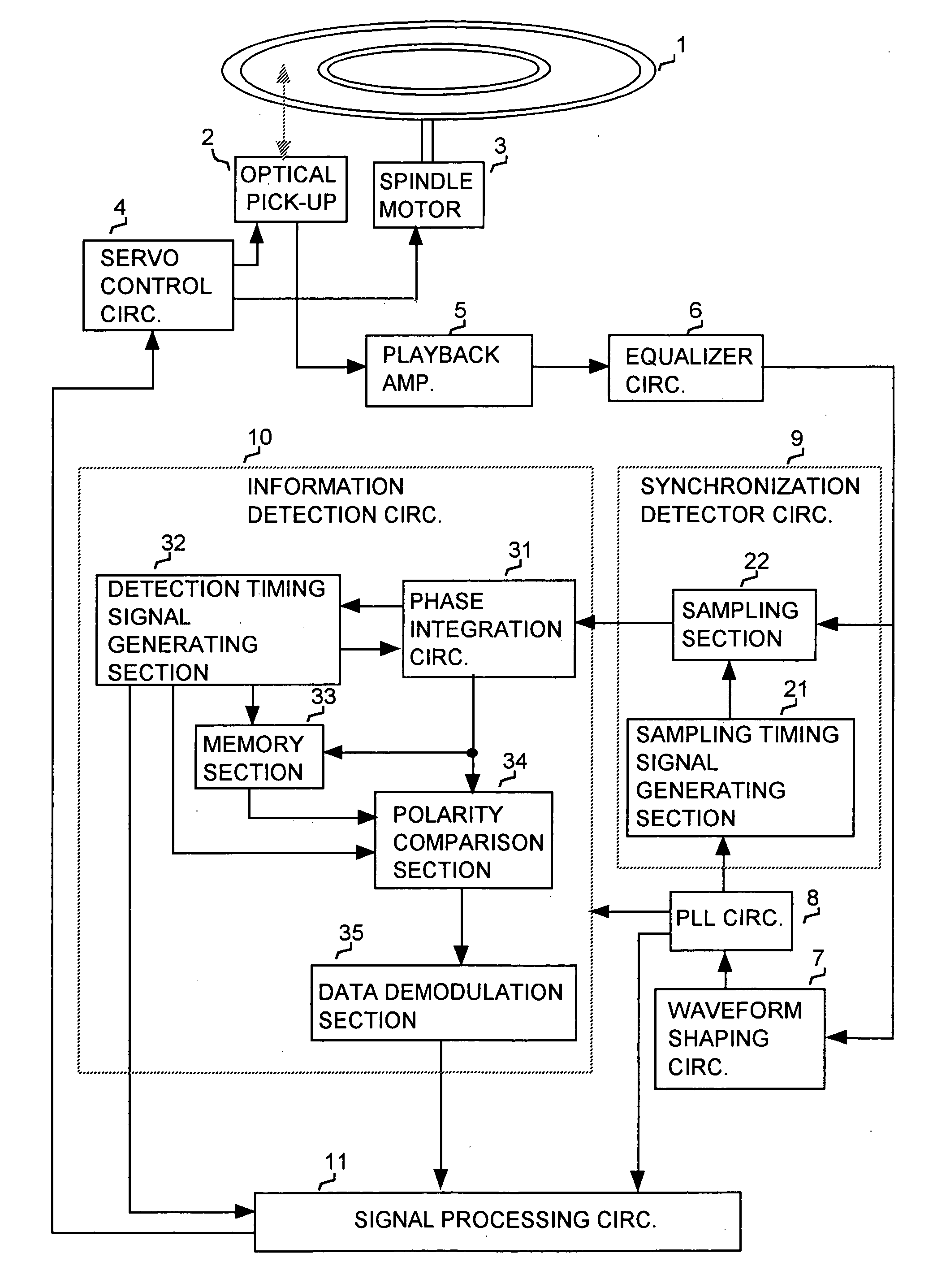
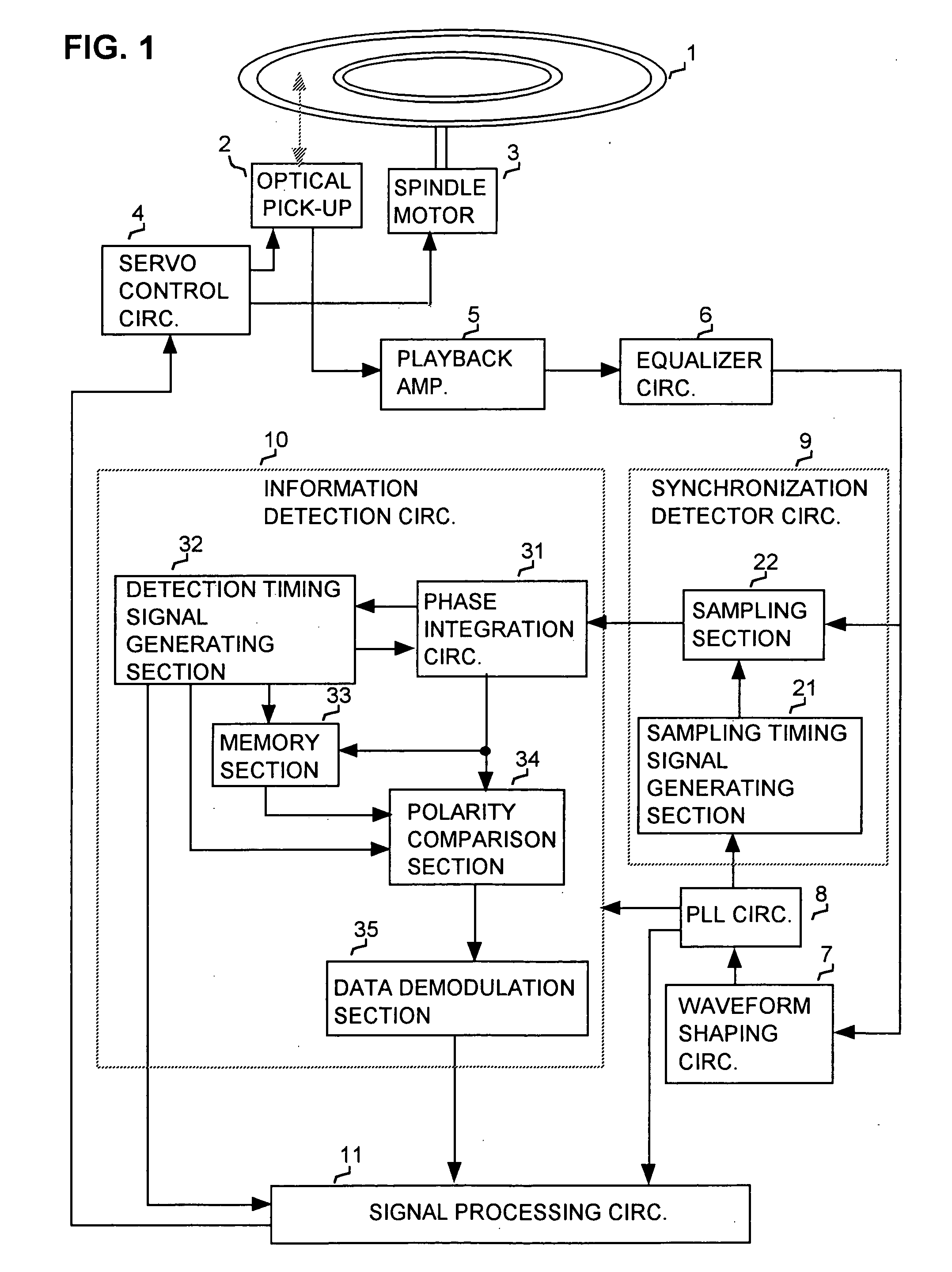
InactiveUS20040202079A1Television system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersElectrical polaritySynchronous detection
A method and apparatus for detecting information recorded as a phase-modulated wobble along a track of an optical disk, whereby a reference phase section is recorded with wobble having a predetermined reference phase and whereby respective polarities of phase integration values obtained by synchronous detection of phase-modulated unit sections following the reference phase section, in a playback wobble signal, are compared with the polarity of a reference phase integration value obtained for the reference phase section, to thereby detect respective bit states expressed by the phase-modulated unit sections.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
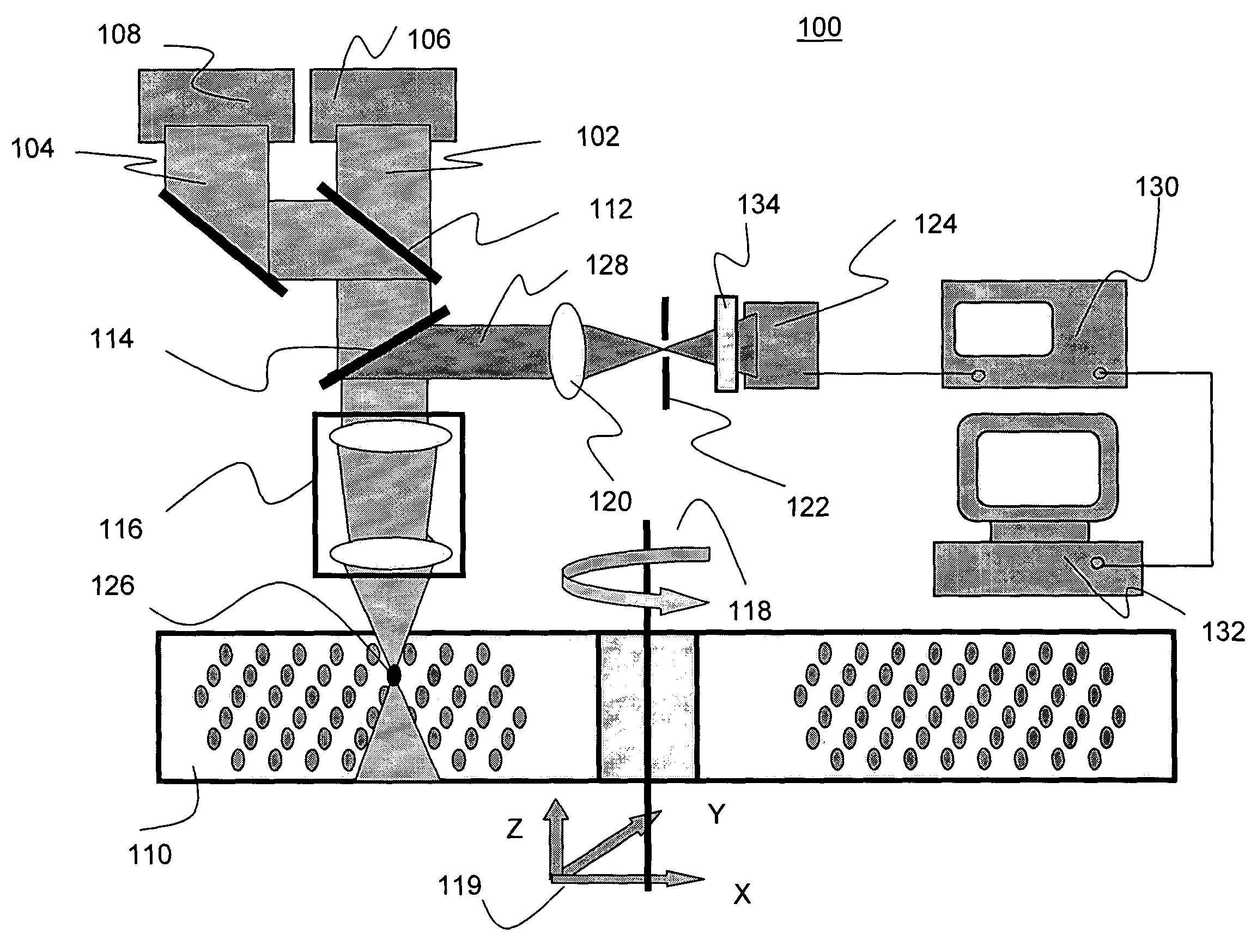
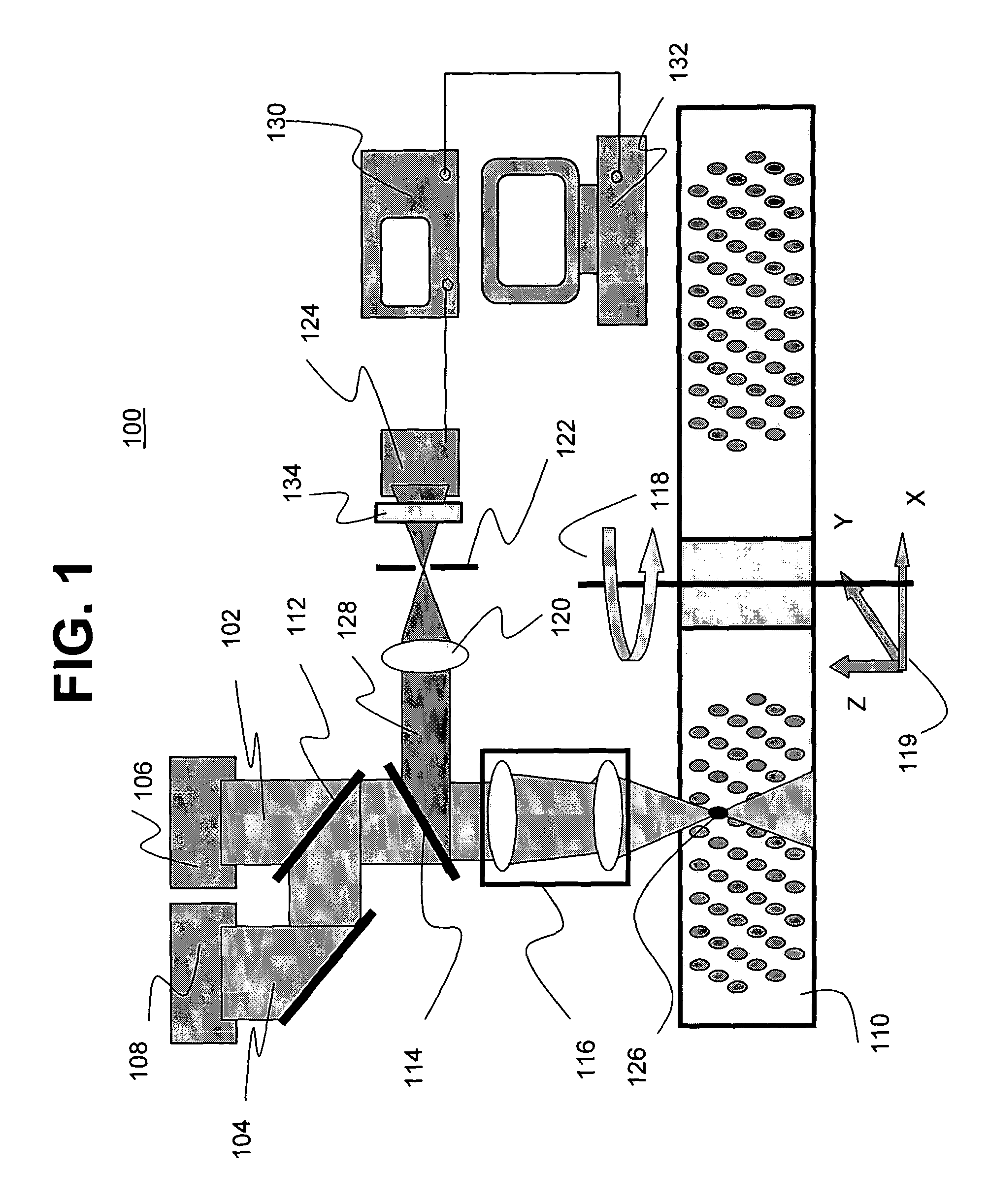
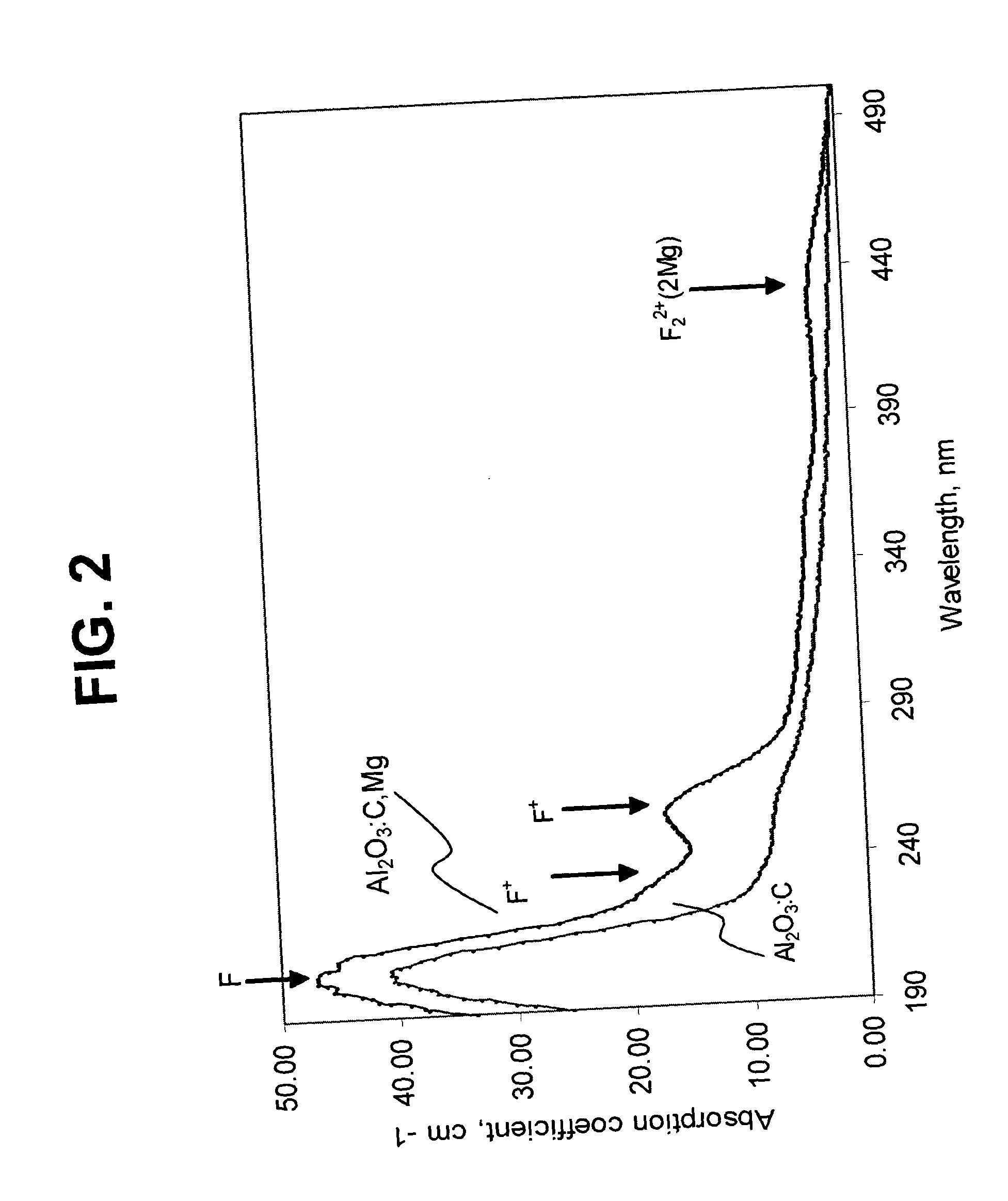
Bit-wise optical data storage utilizing aluminum oxide single crystal medium
ActiveUS20050078591A1Fast electronic processingFast processingFilamentary/web record carriersNanoinformaticsNon destructiveTwo-photon absorption
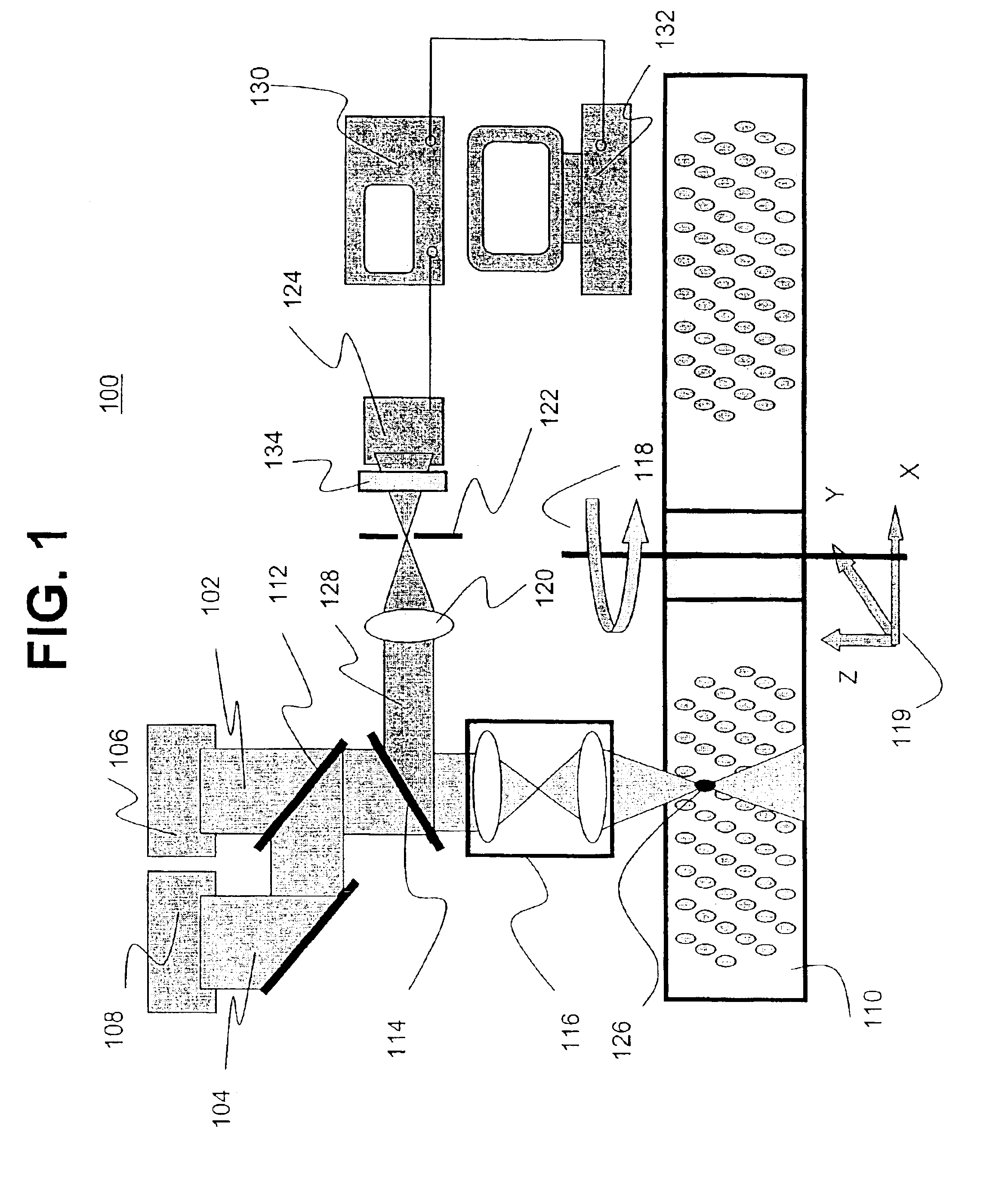
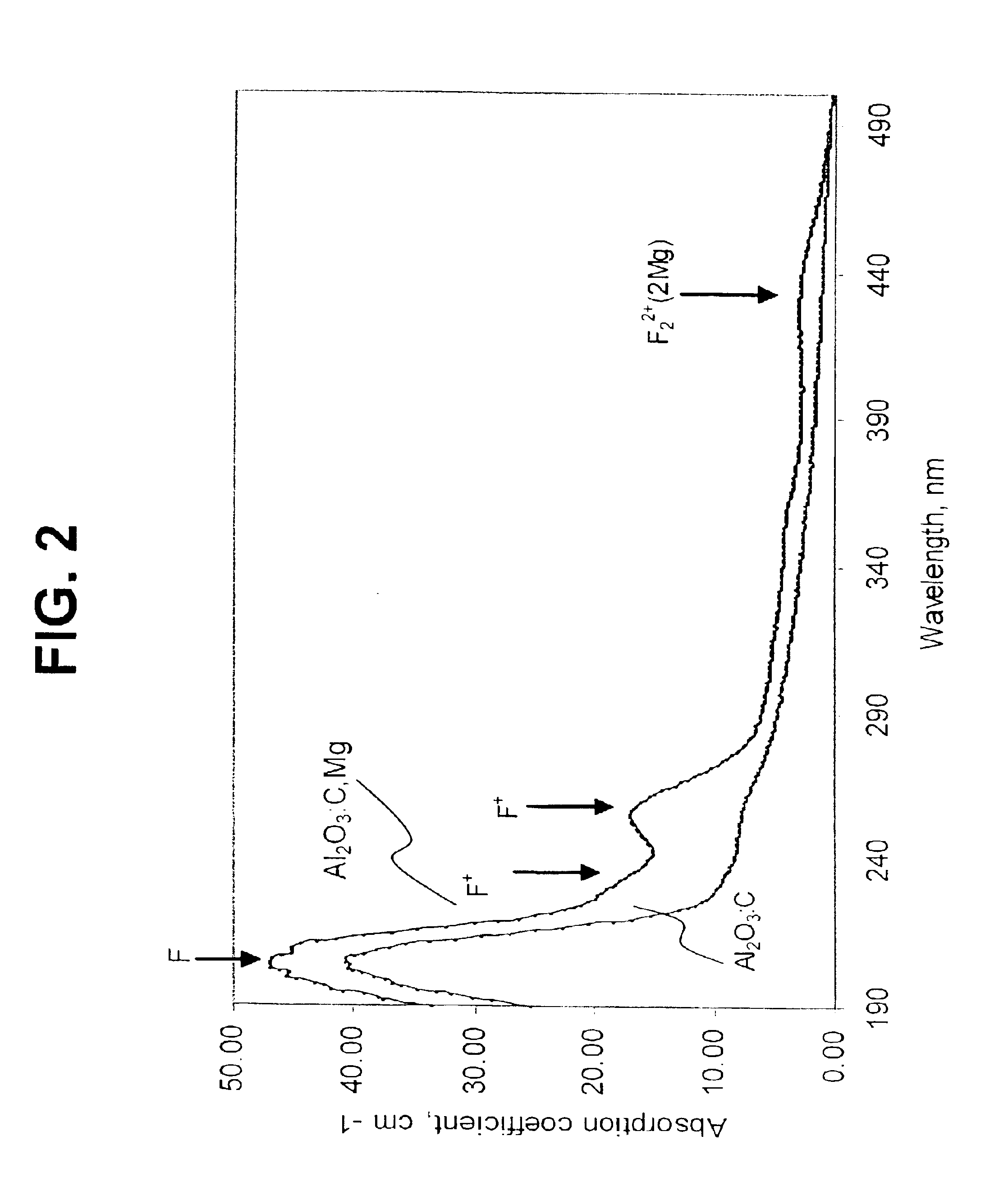
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for writing information to, reading information from, and erasing information on a luminescent data storage medium comprising Al2O3. The method includes writing and erasing of the information using photoionization via sequential two-photon absorption and non-destructive reading the information using one-photon absorption and confocal fluorescent detection. The apparatuses for writing and reading the information incorporate confocal detection and spherical aberration correction for multilayer volumetric fluorescent data storage. The methods also allow multilevel recording and readout of information for increased storage capacity.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS6808778B2High sensitive recordingImprove recording densityLayered productsOptical beam sourcesIncrease sizeGlass transition point
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optically anisotropic recording medium and method of recording and erasing information using the same
InactiveUS6090508AHigh densityIncrease speedLiquid crystal compositionsPhotography auxillary processesRecording layerRecording media
An optically anisotropic recording medium and a method of recording and erasing method using the recording medium are disclosed, which comprises the steps of applying heat or light to the recording medium which comprises a recording layer made of optically anisotropic organic thin-film-shaped crystals to raise the temperature of an organic material or which comprises the optically anisotropic organic thin-film-shaped crystals to a recording temperature at which the crystals are fused, performing partial changing of the crystalline state of the crystals by rapidly cooling the recording layer, thereby recording information in the recording layer; and heating the recording layer to an erasing temperature which is lower than the recording temperature, at which the crystals are not fused, but the molecules thereof can be thermally moved.
Owner:RICOH KK
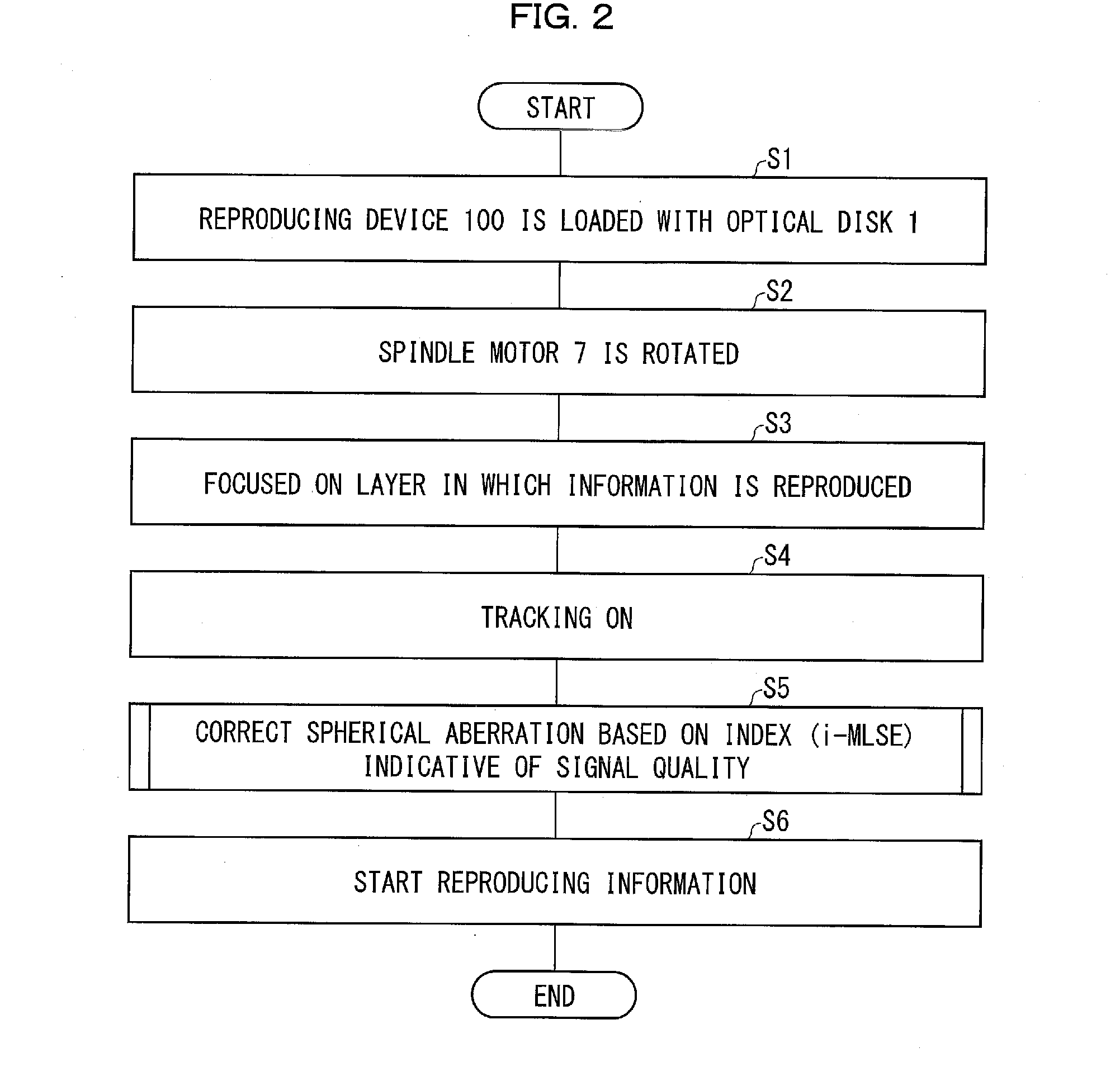
Reproducing device
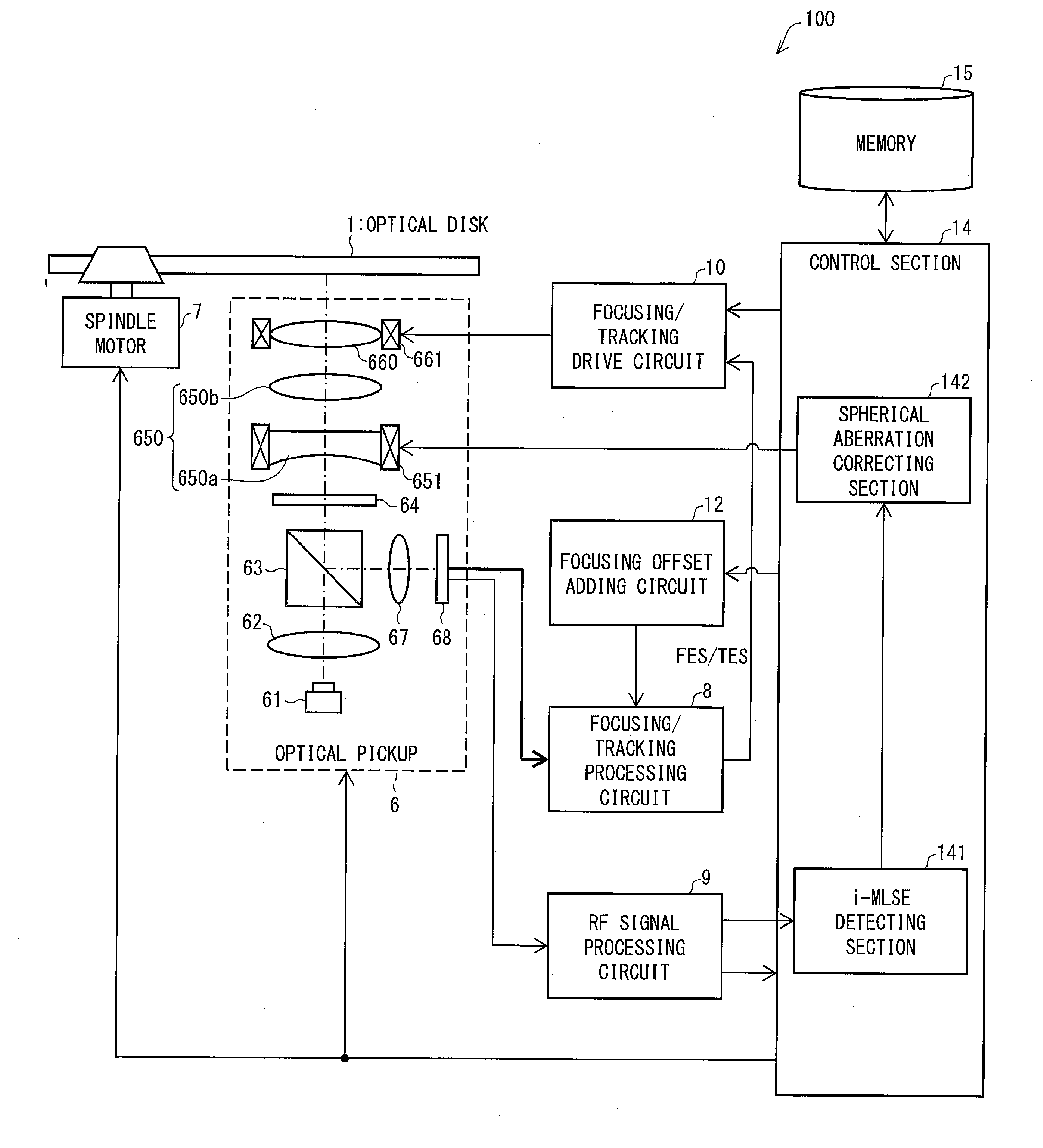
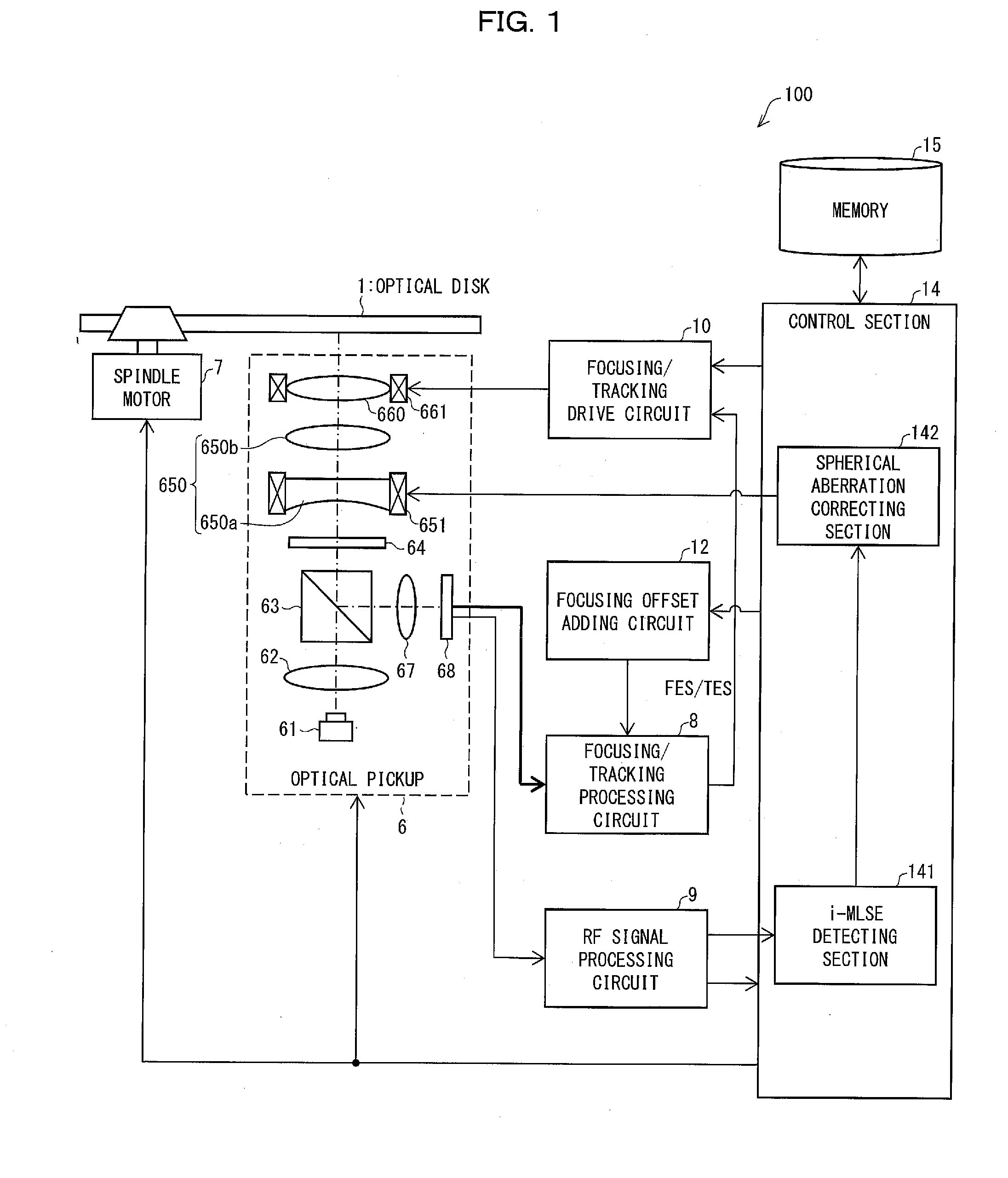
ActiveUS20160155469A1Exact reproductionCombination recordingRecord information storageOptical pickupSignal quality
A reproducing device (100) includes (i) an optical pickup (6) for irradiating, with reproduction light, an optical disk (1) which is a super-resolution medium, (ii) an RF signal processing circuit (9) for converting, into a reproduction signal, light which reflected off optical disk (1), (iii) an i-MLSE detecting section (141) for evaluating quality of the reproduction signal, and (iv) a spherical aberration correcting section (142) for correcting a spherical aberration by using a result of evaluation of the quality of the reproduction signal.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Optical information recording medium, and information recording method and information reproducing method using the same
InactiveUS20060262711A1Good reproducibilityImprove recording densityRecording strategiesRecord information storageHigh densityOptical property
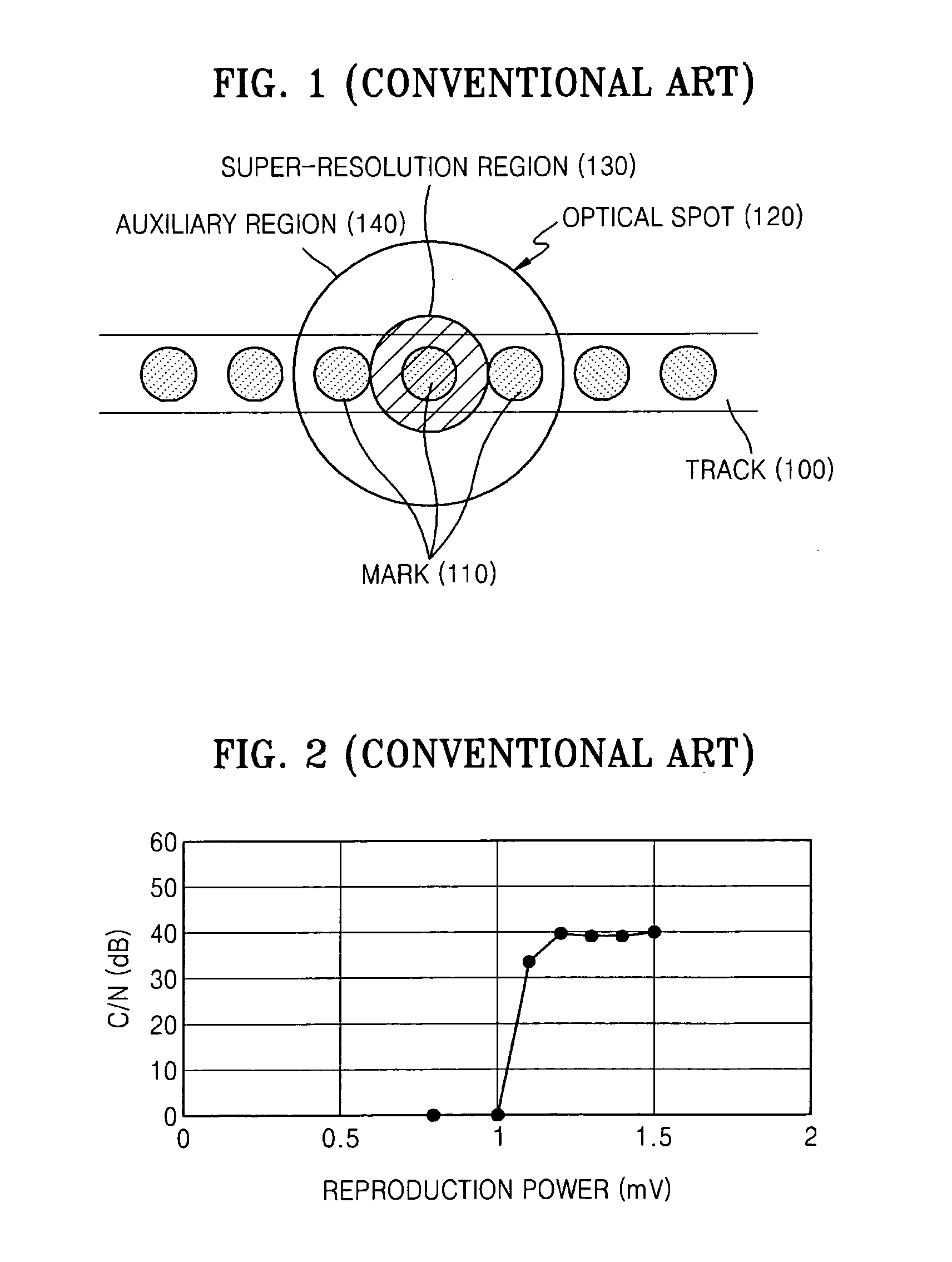
An optical disk medium in which high density recording / reproducing is possible, an information recording method and an information reproducing method using it are provided. A pit composed of a phase change material and a recording film different from it are provided on an optical disk. The phase change pit has a pattern of a single frequency. A mark having a size on the same level as the phase change pit can be formed by melting a single phase change pit while recording and controlling the optical absorbance and the temperature of the recording film at the region. A single phase change pit is molten while reproducing. Since the optical characteristics of the molten region are different from the optical characteristics of other regions, only data at the molten region can be reproduced by a super-resolution effect.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical information recording medium, producing method thereof and method of recording/erasing/reproducing information
InactiveUS7037413B1Improve cycle performanceImprove performanceRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingWeather resistanceRecording layer
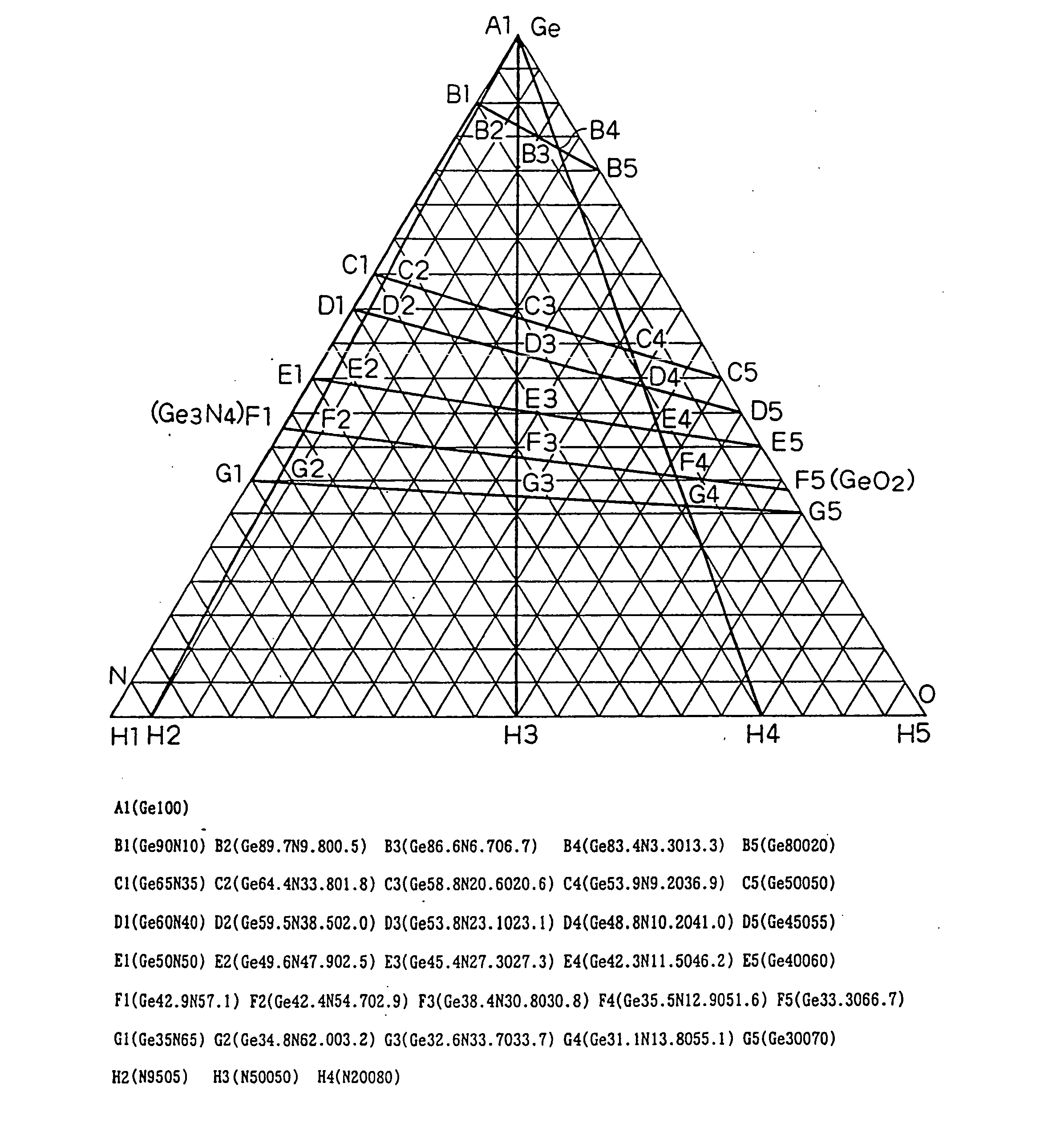
The present invention provides an optical information medium having excellent weather resistance and repeating characteristics. The optical information medium has a barrier layer between a protective layer and a recording layer. The barrier layer includes GeN or GeON, and at least one element selected from the group consisting of Al, B, Ba, Bi, C, Ca, Ce, Cr, Dy, Eu, Ga, H, In, K, La, Mn, N, Nb, Ni, Pb, Pd, S, Si, Sb, Sn, Ta, Te, Ti, V, W, Yb, Zn and Zr.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical information recording medium, optical measuring method and optical information recording/reproducing method
An optical information recording medium having two or more information layers, wherein the irradiation of either the information layer with a laser beam converging thereon causes information signals to be recorded or reproduced; the nearer positioned information layer than the farthest information layer as viewed from the incidence side of the laser beam has a recording layer varying between two optically detectable states, and0≦|Tc−Ta| / Tc≦0.1where Tc is the transmittance of the nearer positioned information layer when the recording layer is in state (a) and Ta, the transmittance, when it is in state (b). This makes possible accurate accurately recording and reproduction of information onto and out of the farther information layer irrespective of whether or not any information is recorded on the nearer information layer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Super-resolution information recording medium, recording/reproducing apparatus, and recording/reproducing method
InactiveUS20070030776A1Good recording/reproductionImprove featuresFilamentary/web record carriersRecording involving bubble/bump formingComputer hardwareOptical property
A super-resolution information recording medium, a recording / reproducing apparatus, and a recording / reproducing method uses an information recording medium provides a super-resolution effect by fluid bubbles. The fluid bubbles are formed in at least a portion of the medium by a light beam radiated to reproduce a signal from the information recording medium. Accordingly, the super-resolution information recording medium has improved optical characteristics, so that better recording / reproduction is possible.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Optical recording medium
InactiveUS20020034604A1High sensitive recordingImprove recording densityLayered productsOptical beam sourcesIncrease sizeGlass transition point
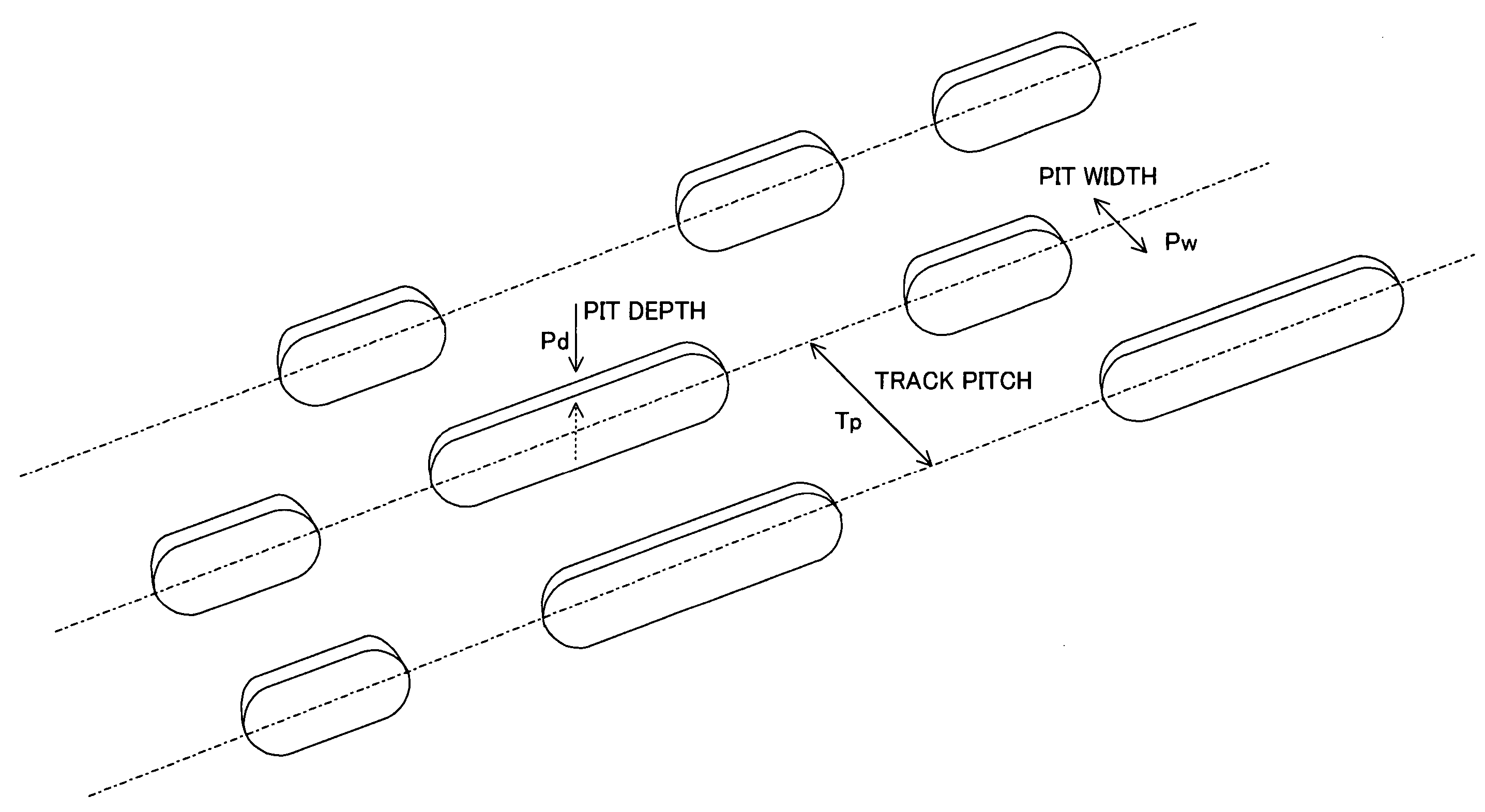
An optical recording medium is provided with a recording layer and a reflecting film on an optically transparent substrate. The principal component of the recording layer is a dye. Virtual recording cells are assumed within grooves on the recording layer and recording marks with five different levels or more of increasing size are formed on each of the virtual recording cells by modulating the irradiation time of the laser beam in five levels or more in correspondence to the information to be recorded. The reflectance of the virtual recording cells modulates in many levels and the reflection level of the reading laser beam during regeneration is changed in five levels or more. The optically transparent substrate is made of a plastic with a glass transition point (Tg) of 160° C. or less. The reflecting film is a metal with a coefficient of thermal conductivity of 300 k / W.m-1.K-1 or more and a film thickness of 50 nm or more.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium, recording and reproduction methods using the same, optical information recording device, and optical information reproduction device
InactiveUS7436755B2Securely and accurately record informationHigh densityCombination recordingLayered productsHigh densityLight beam
An optical information recording medium includes a substrate formed in a concave-convex state by providing pits or grooves corresponding to recorded information, used for optically reproducing the information by irradiation of a light beam, and may also include a recording layer. The optical information recording medium includes a temperature responsive layer whose reflectance and / or transmittance for the light beam changes with a change in temperature caused by the irradiation of a light beam. With such an arrangement, the present invention provides an optical information recording medium enabling secure and highly accurate reproduction of information recorded with high density, and the recording and reproduction methods thereof.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for thermally erasing information stored in an aluminum oxide data storage medium
InactiveUS6950382B2Fast electronic processingFast processingNanoinformaticsBy pulling from meltTwo-photon absorptionNon destructive
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for writing information to, reading information from, and erasing information on a luminescent data storage medium comprising Al2O3. The method includes writing and erasing of the information using photoionization via sequential two-photon absorption and non-destructive reading the information using fluorescent detection. The apparatuses for writing and reading the information incorporate confocal detection and spherical aberration correction for multilayer volumetric fluorescent data storage. The methods also allow multilevel recording and readout of information for increased storage capacity.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
Pseudo-reflective read inhibitor for optical storage media
InactiveUS20050213435A1Reduce readabilityReduce capacityCombination recordingAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useOptical reflectionOptical storage
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Optical information recording medium and its manufacturing method, recording and playback method and device
InactiveCN1479287AEasy to recordImprove featuresRecord information storageRecording involving phase-change effectsInformation layerHigh density
An optical information recording medium comprises a transparent substrate 1 on which an information layer 21 is disposed, the information layer 21 comprising a recording layer 3 and a dielectric layer 2, and the recording layer 3 containing Te, O and M (wherein M is one or more elements selected from Al, Si, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ga, Ge, Zr, Nb, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, In, Sn, Sb, Hf, Ta, W, Re, Os, Ir, Pt, Au and Bi), wherein a content ratio of 0-atom in the recording layer ranges from 25 atomic percent to 60 atomic percent, and a content ratio of M-atom therein ranges from 1 atomic percent to 35 atomic percent, and a refractive index n of the dielectric layer 2 is not less than 1.5 . Accordingly, a write-once optical information recording medium, from which excellent recording reproduction characteristics with a high C / N ratio can be obtained even for recording and reproduction of high density information using a violet laser beam, is provided as well as a manufacturing method, a recording and reproduction method and a recording / reproduction device for the same.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Popular searches
Recording involving reflectivity/absorption/color-change Indamines/indophenols Reproducing involving reflectivity/absorption/color-change Record carrier materials Optical record carrier manufacture Optical elements Record carriers manufacture Arrangement for discrete information storage Systems characterised by carrier shape Adhesives
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com