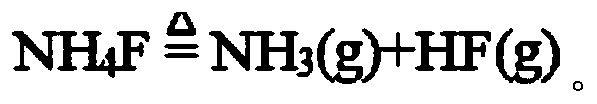Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135results about "Rare earth metal fluorides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of Preparing Nano-Structured Material(s) and Uses Thereof
The present invention provides a method of preparing at least one nano-structured material of formula M1M2Xn comprising the step of treating: at least one compound having the formula [CX3(CX2)n(CH2)mCOO]pM1; and at least one compound having the formula [CX3(CX2)n(CH2)mCOO]pM2; wherein each X is the same or different and is selected from the group consisting of: halogens, O, S, Se, Te, N, P and As; each n is the same or different and is 0≦n≦10; each m is the same or different and is 0≦m≦10; each p is the same or different and is 1≦p≦5; each M1 is the same or different and is selected from the group consisting of: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra and NH4; each M2 is the same or different and is a metal ion. The present invention also provides uses of the nano-structured material prepared according to the method of the present invention.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
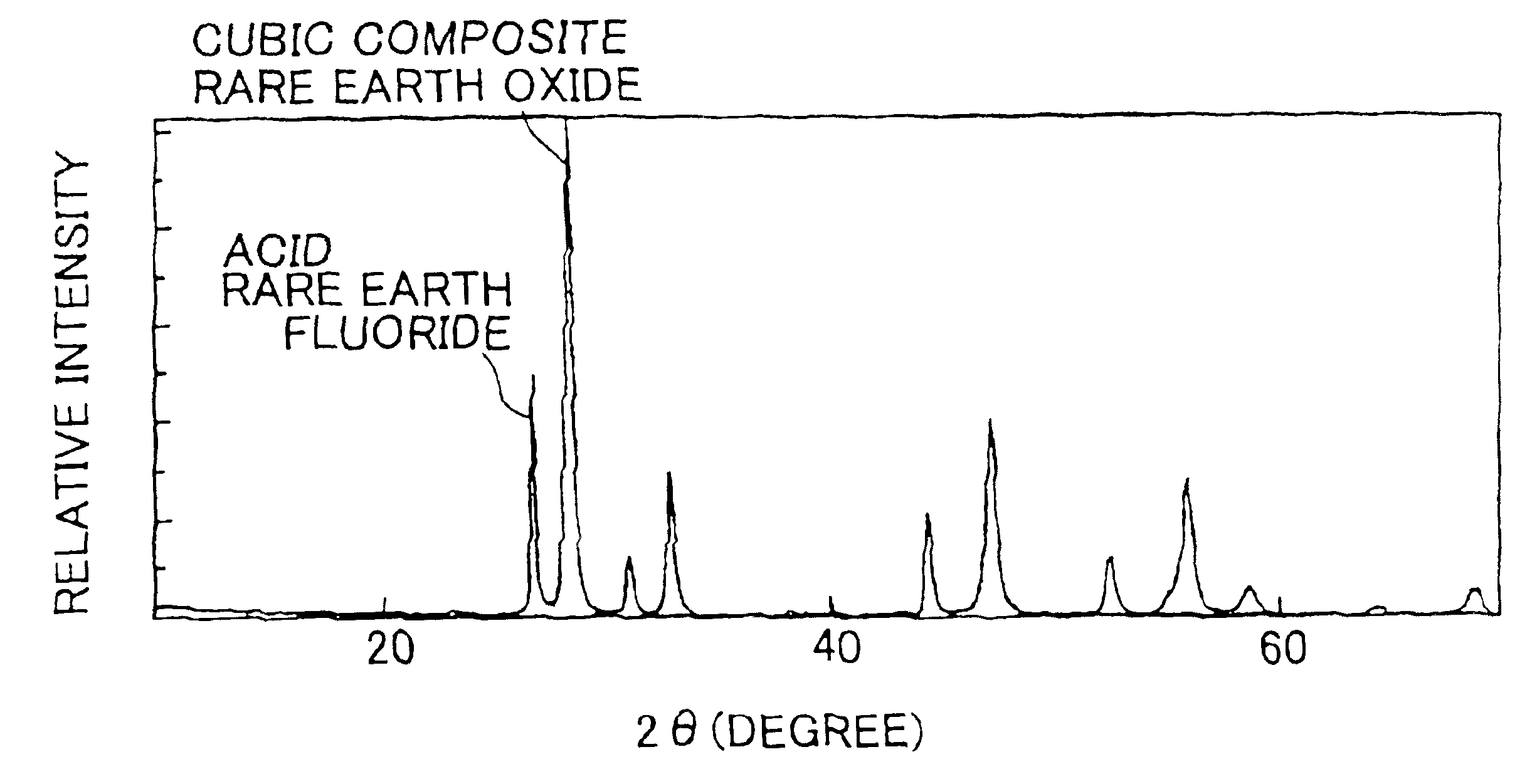
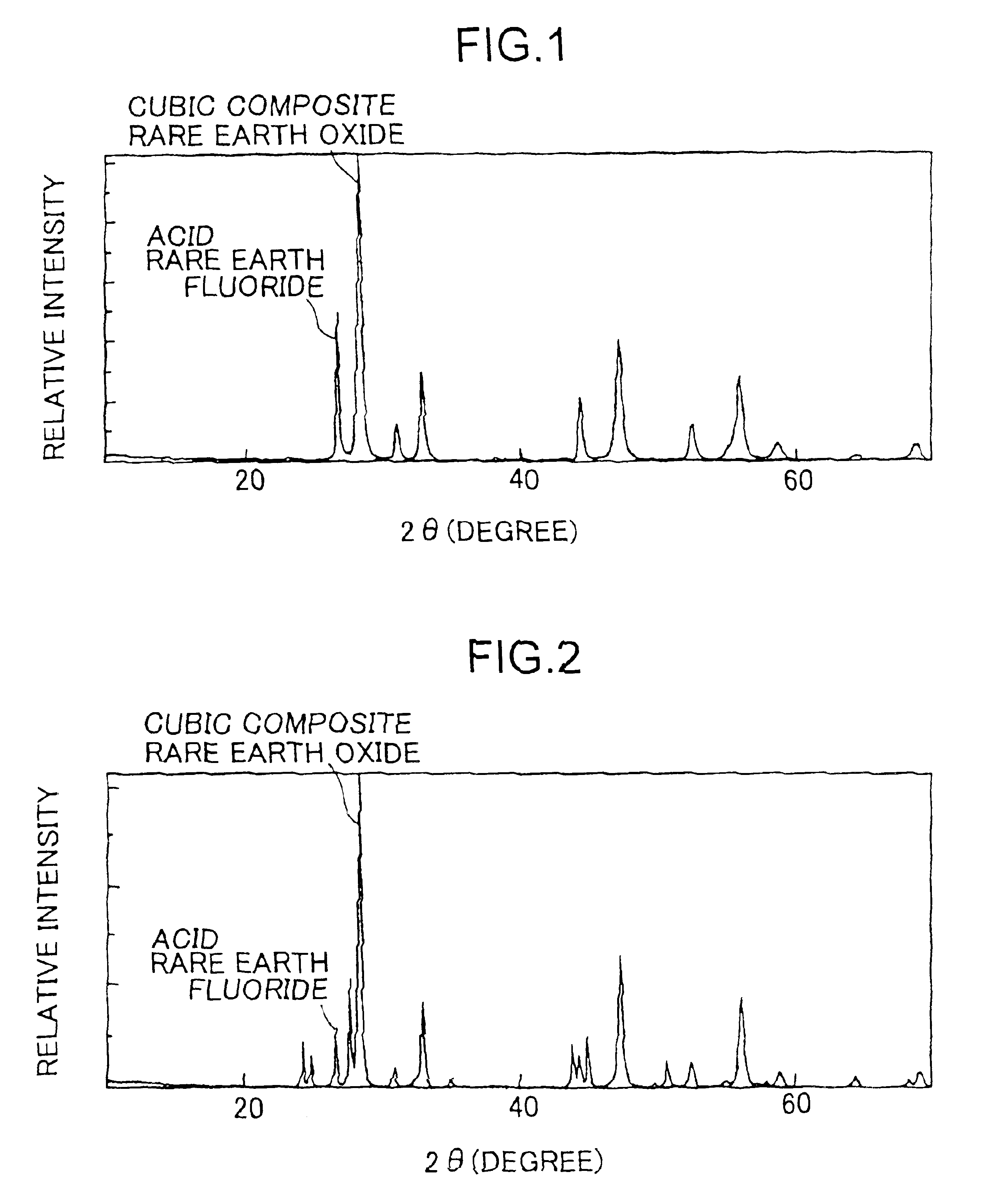
Thermal spray material
ActiveUS20150111037A1Various disadvantageImprove stabilityMolten spray coatingSynthetic resin layered productsThermal sprayingRare earth
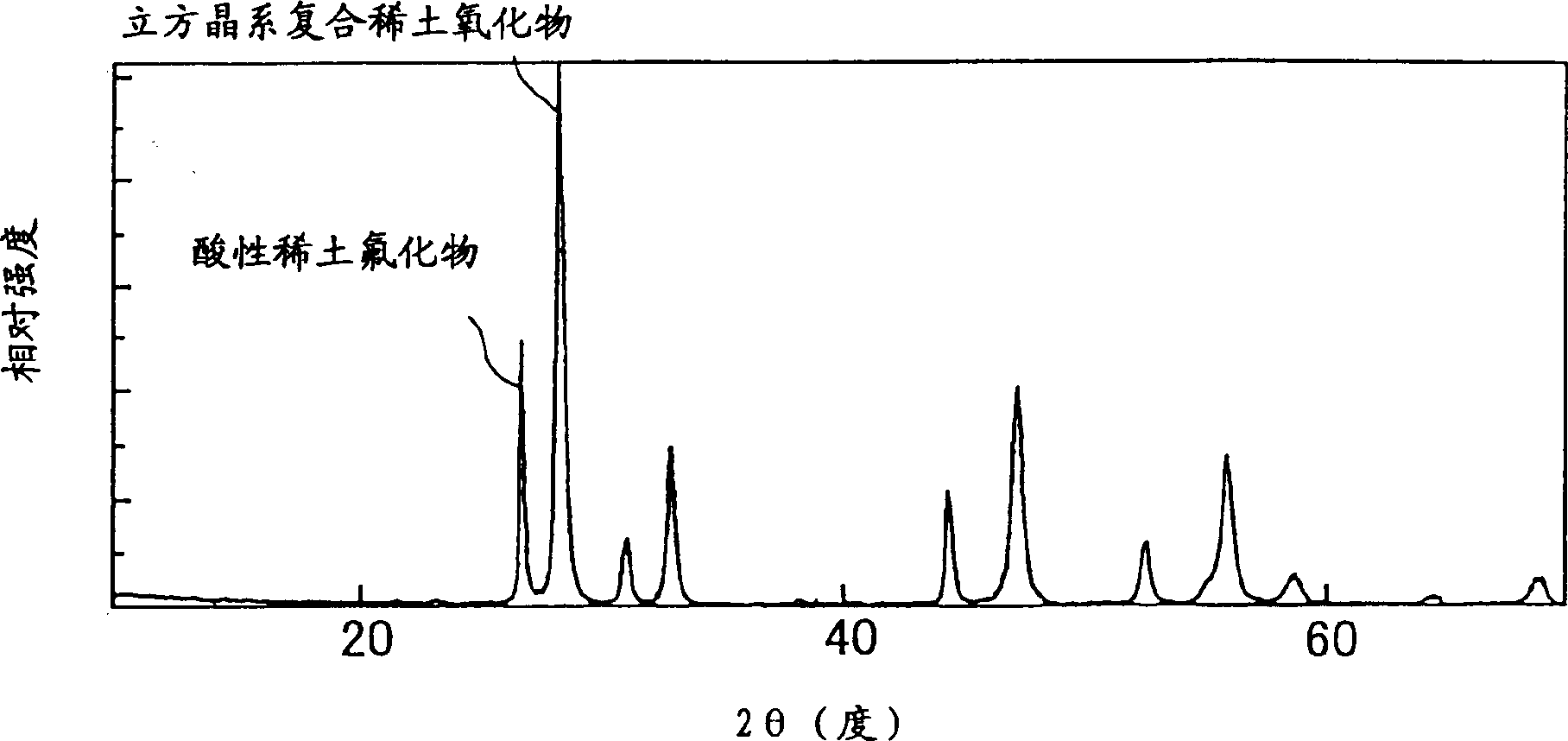
A thermal spray material comprising granules containing a rare earth oxyfluoride has a particle diameter of 1 to 150 μm at a cumulative volume of 50 vol % before ultrasonic dispersion and 10 μm or smaller after ultrasonic dispersion at 300 W for 15 minutes as determined by laser diffraction / scattering particle size distribution analysis. The particle diameter after ultrasonic dispersion is one-third or less of that before ultrasonic dispersion. The thermal spray material has an average aspect ratio of 2.0 or lower and a compressibility of 30% or less. When the granules further contain a rare earth fluoride, upon being analyzed by X-ray diffractometry using Cu-Kα or Cu-Kα1 radiation, S1 / S2 is preferably ≧0.10. S1=intensity of the maximum peak assigned to the rare earth oxyfluoride. S2=intensity of the maximum peak assigned to the rare earth fluoride, both observed in a 2θ angle range of 20° to 40°.
Owner:NIPPON YTTRIUM
Fine particles containing rare earth element and fluorescent probe using the same
InactiveUS20050014283A1Small particle sizeEasy to getChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceGlass/slag layered productsRare-earth elementFluorescence
A main object of the present invention is to provide: fine particles whose excitation light is not the one such as UV light or the like which has negative effects on a subject to be analyzed, emit light stably, and has excellent light emitting efficiency, and a fluorescent probe labeled with the fine particles. In order to achieve the aforementioned object, the present invention provides a fluorescent probe comprising: fine particles containing a rare earth element characterized in that they are excited by light having a wavelength in a range of 500 nm to 2000 nm and thereby emit up-conversion emission; and a specific binding substance which binds to the fine particles containing a rare earth element.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Hydrometallurgical process and method for recovering metals
InactiveCN102939397AReduce demandAvoid demandCerium oxides/hydroxidesEnergy inputMineral processingMetal
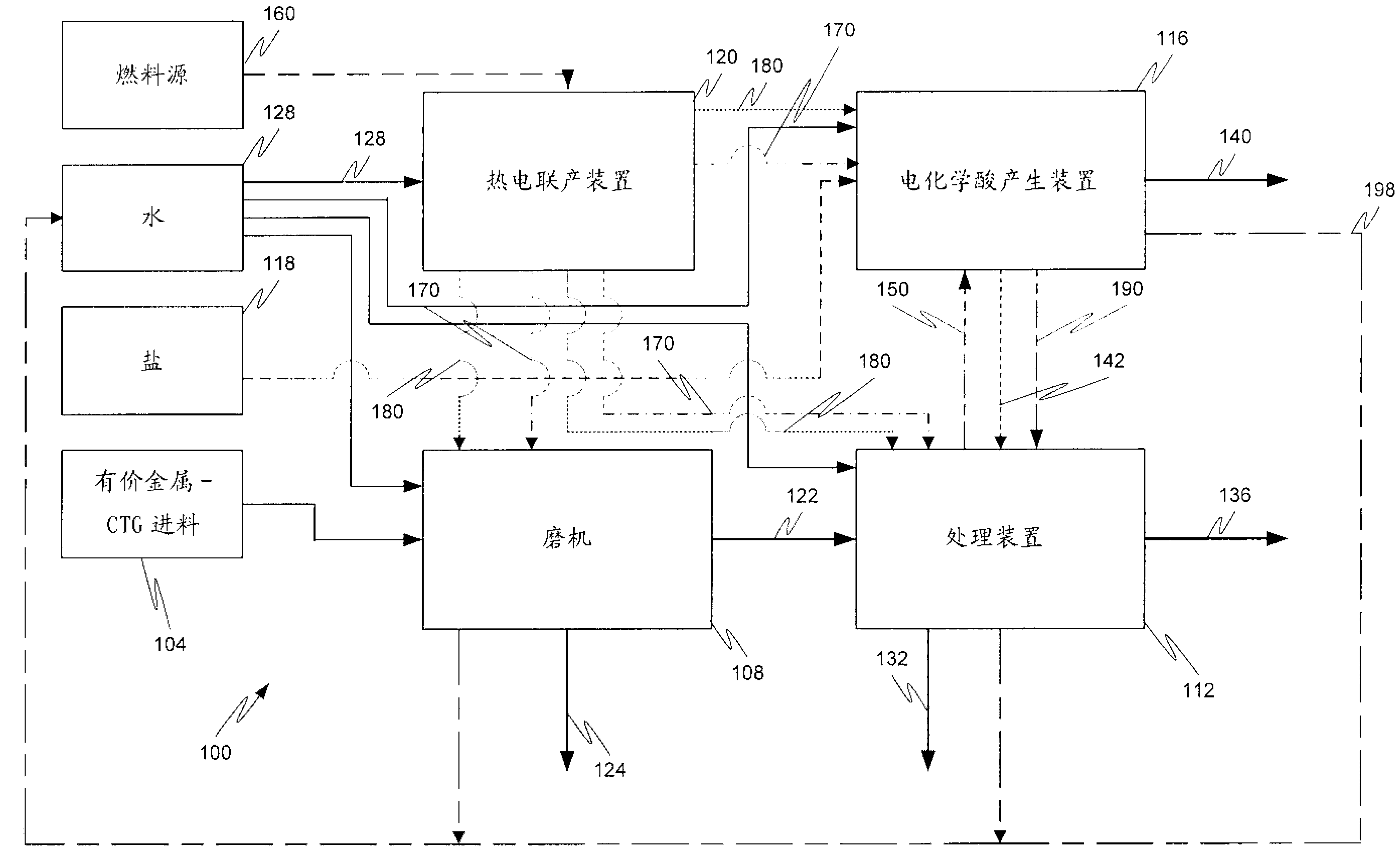
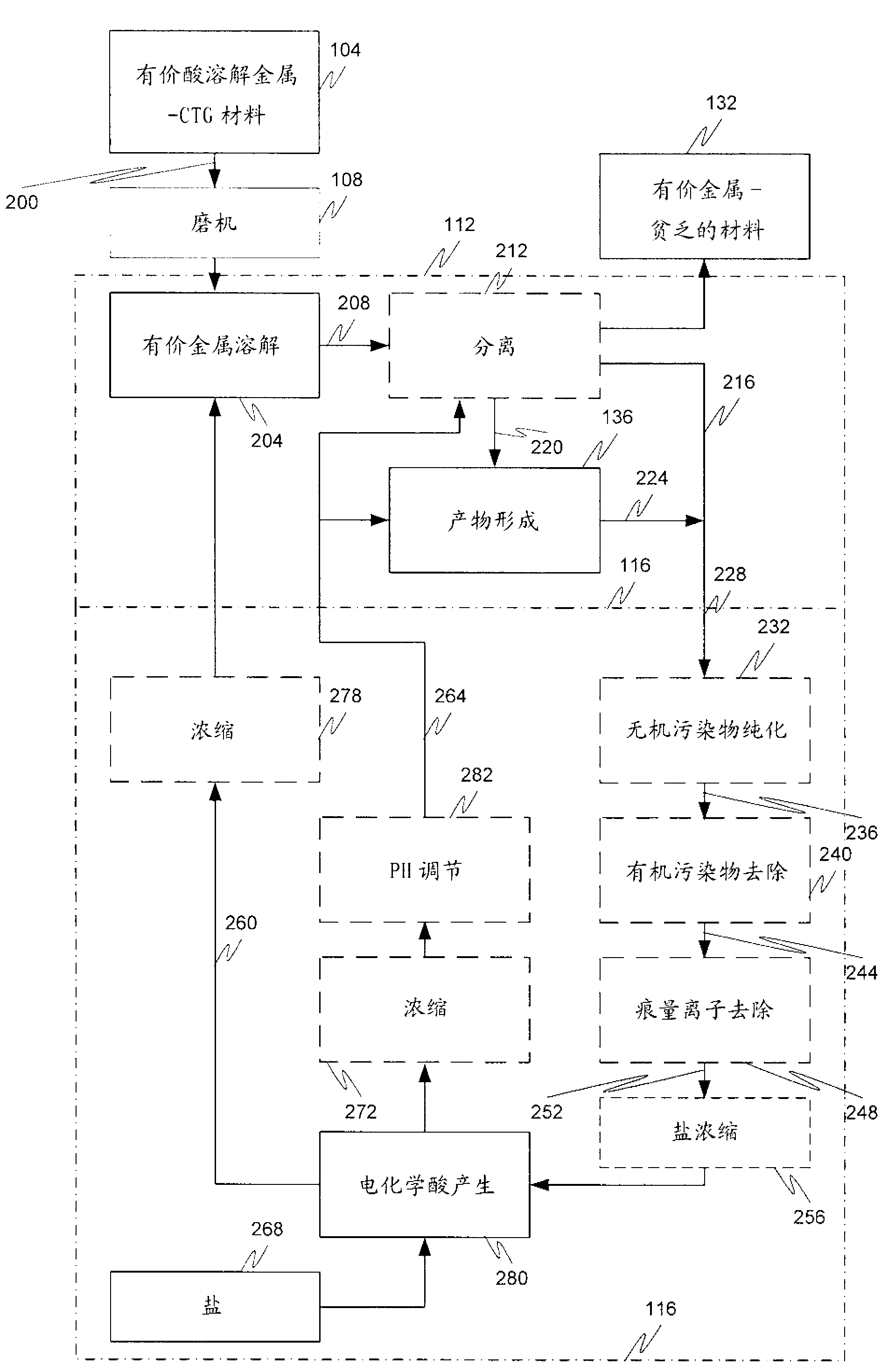
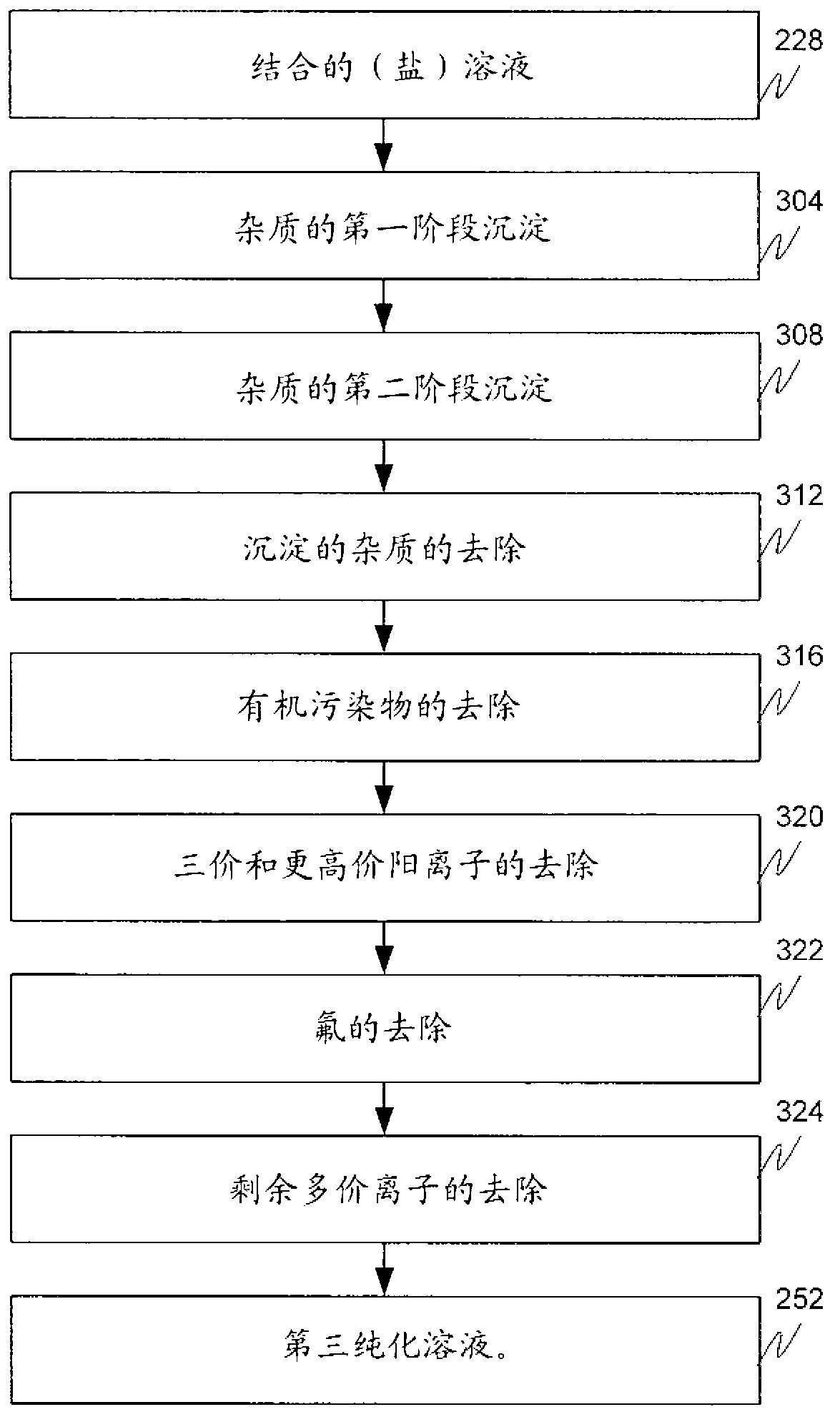
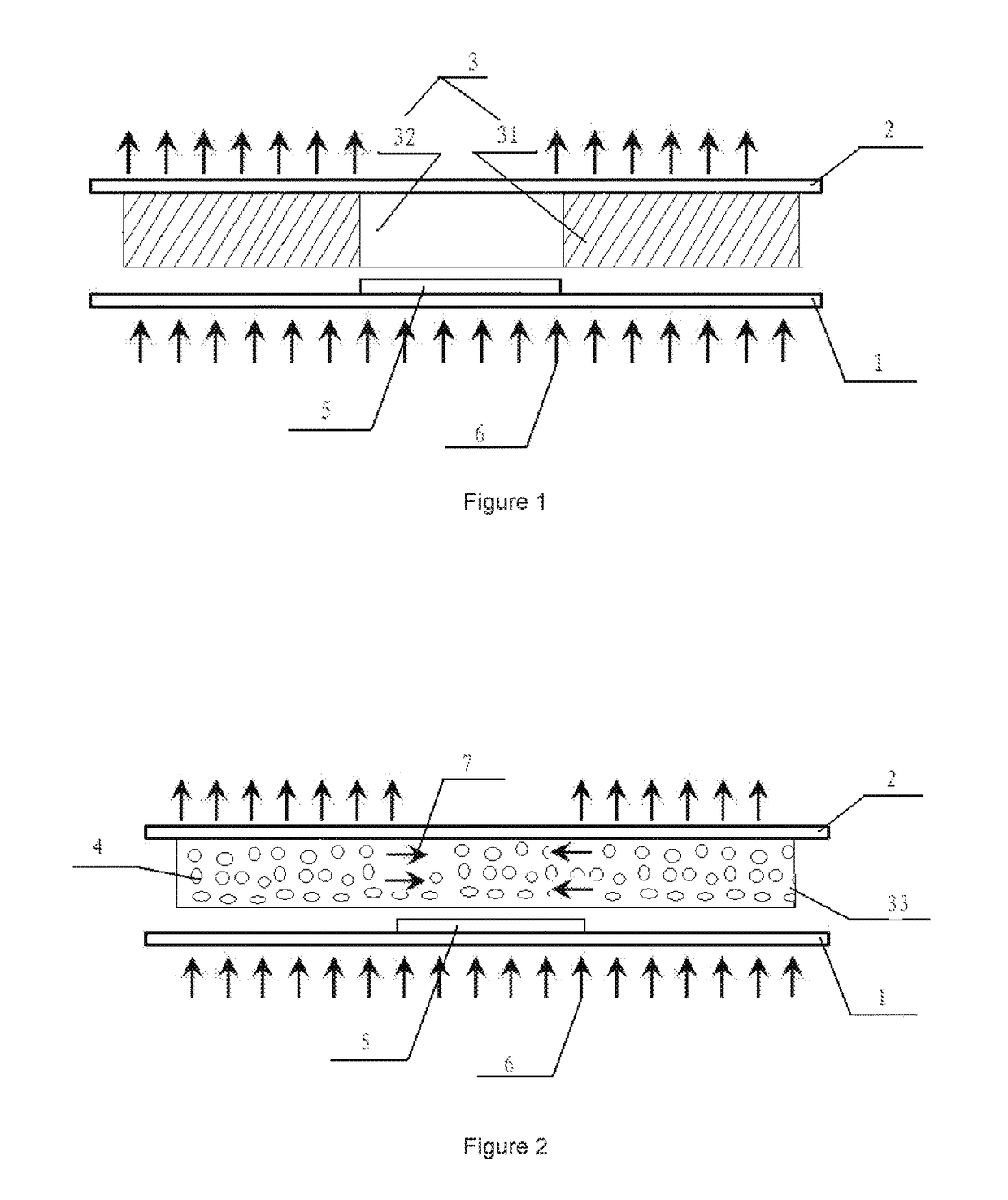
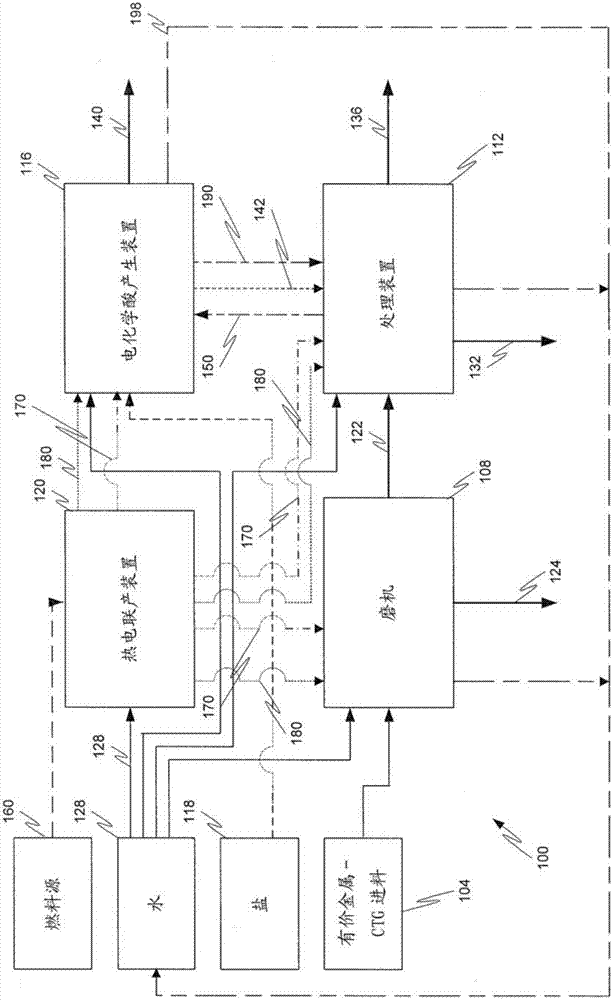
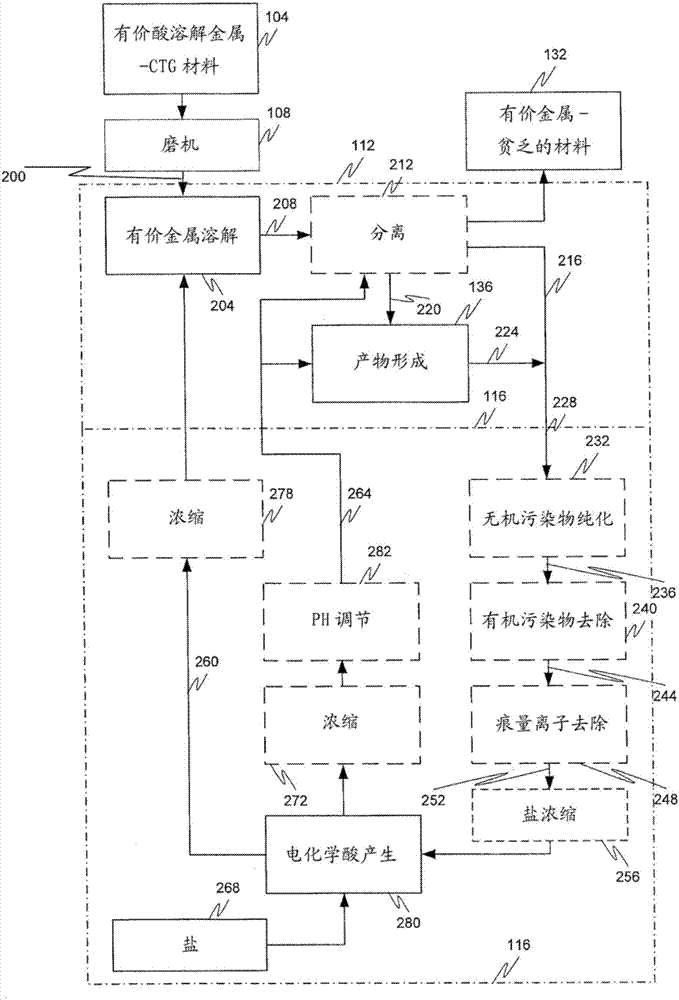
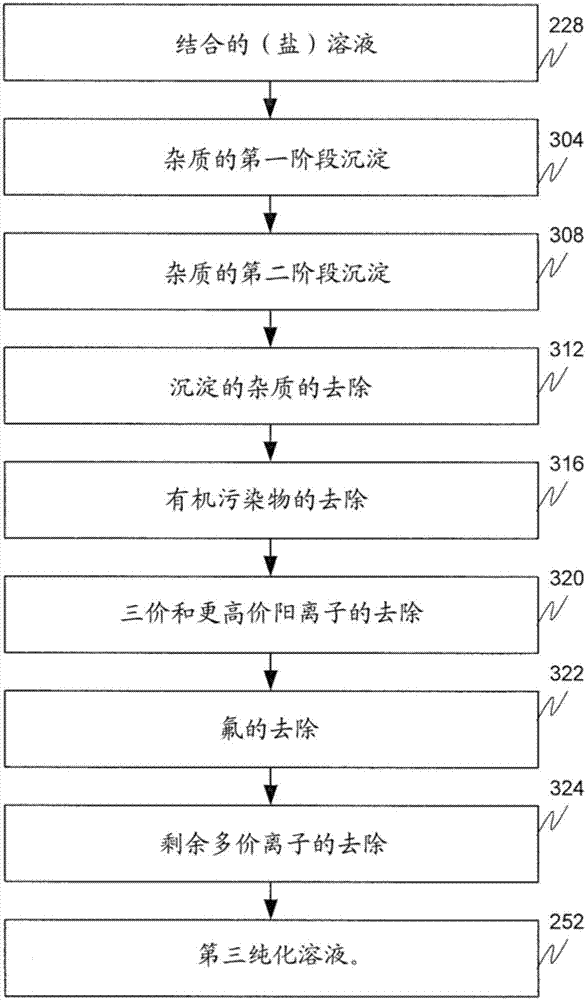
A mineral processing facility is provided that includes a cogen plant to provide electrical energy and waste heat to the facility and an electrochemical acid generation plant to generate, from a salt, a mineral acid for use in recovering valuable metals.
Owner:MOLYCORP MINERALS
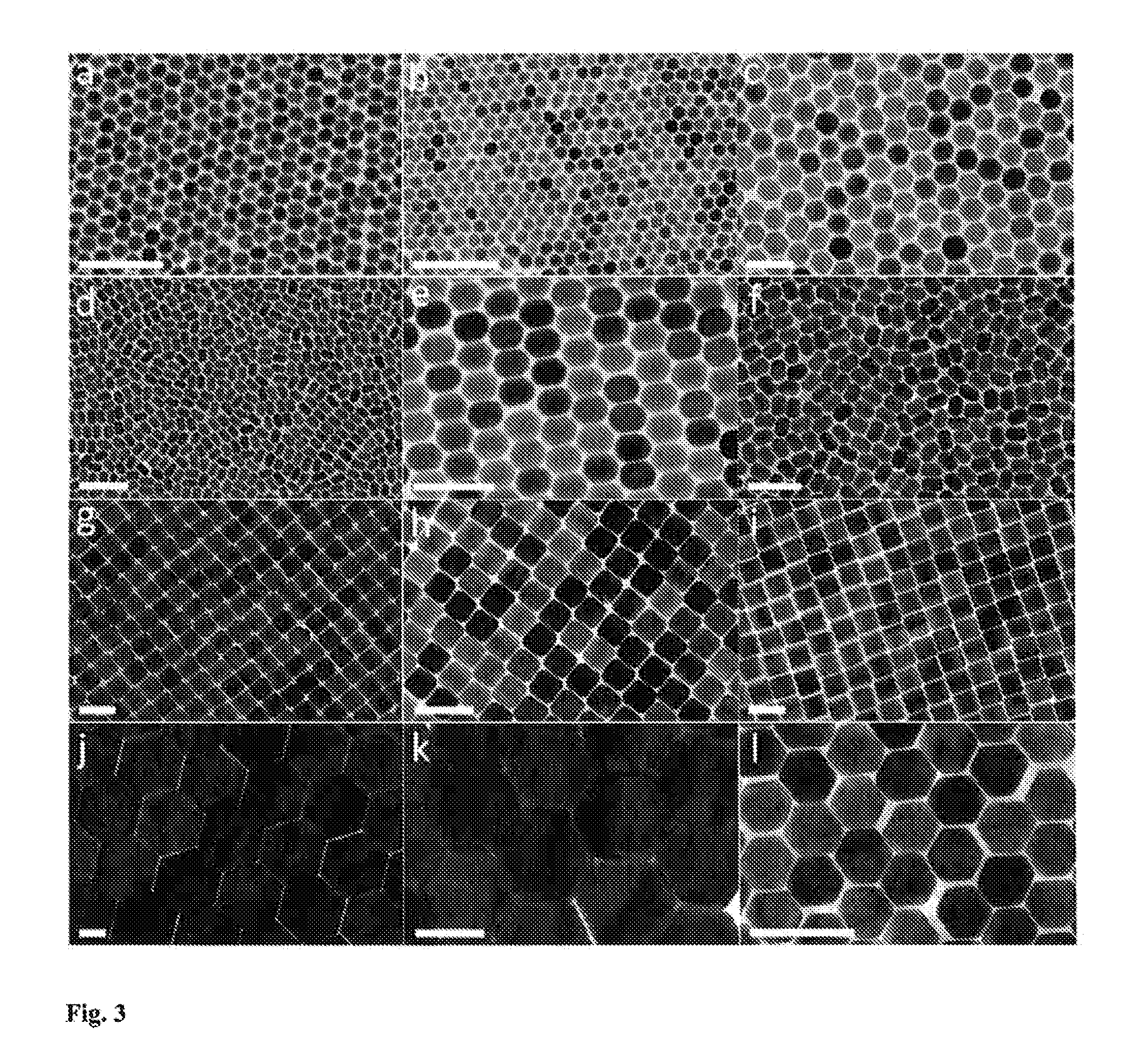
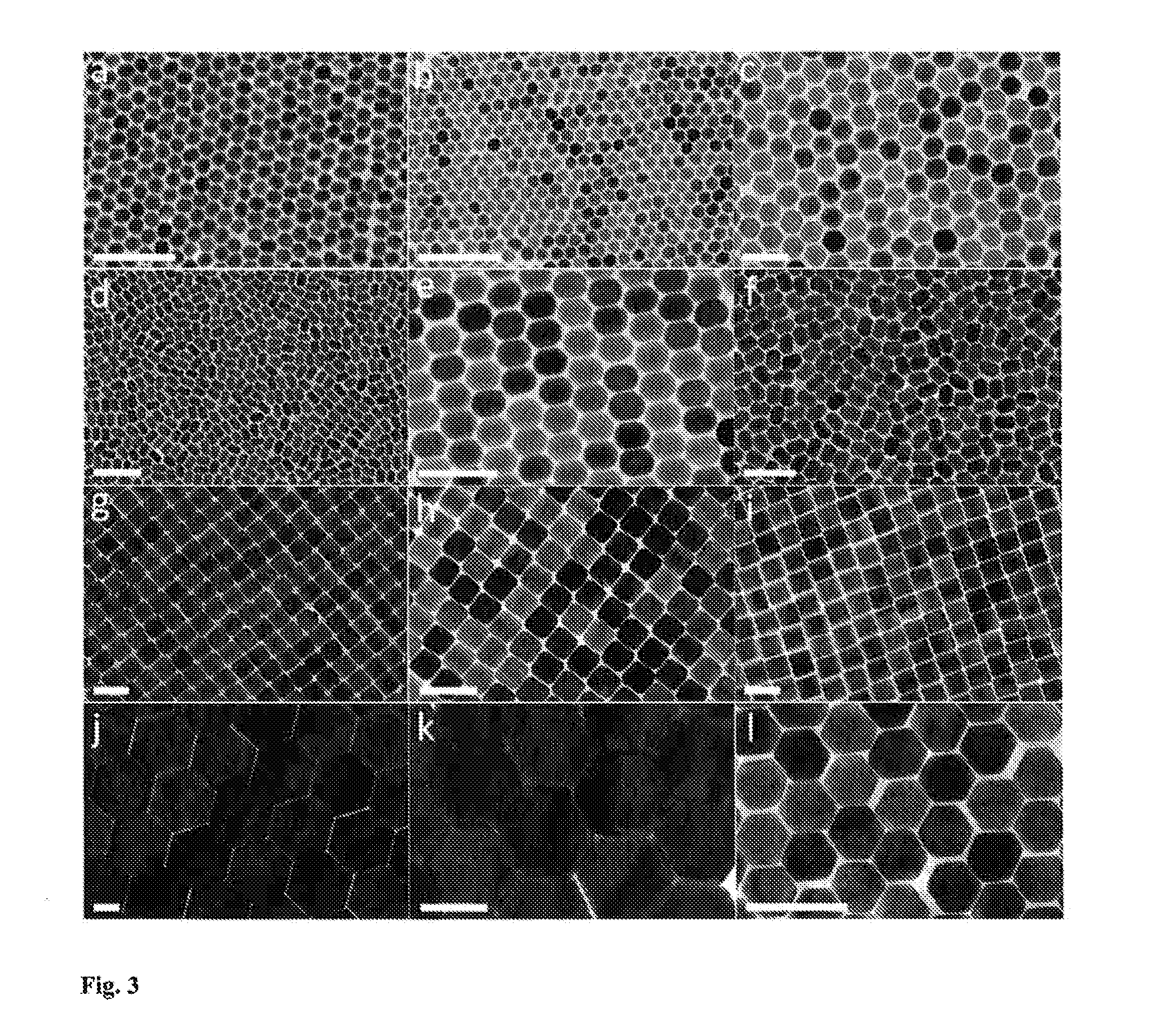
Morphologically and size uniform monodisperse particles and their shape-directed self-assembly
ActiveUS9181477B2Increase in sizeQuench reactionMaterial nanotechnologyFrom normal temperature solutionsRare earthLanthanide
Monodisperse particles having: a single pure crystalline phase of a rare earth-containing lattice, a uniform three-dimensional size, and a uniform polyhedral morphology are disclosed. Due to their uniform size and shape, the monodisperse particles self assemble into superlattices. The particles may be luminescent particles such as down-converting phosphor particles and up-converting phosphors. The monodisperse particles of the invention have a rare earth-containing lattice which in one embodiment may be an yttrium-containing lattice or in another may be a lanthanide-containing lattice. The monodisperse particles may have different optical properties based on their composition, their size, and / or their morphology (or shape). Also disclosed is a combination of at least two types of monodisperse particles, where each type is a plurality of monodisperse particles having a single pure crystalline phase of a rare earth-containing lattice, a uniform three-dimensional size, and a uniform polyhedral morphology; and where the types of monodisperse particles differ from one another by composition, by size, or by morphology. In a preferred embodiment, the types of monodisperse particles have the same composition but different morphologies. Methods of making and methods of using the monodisperse particles are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Thermal spray material, thermal spray coating and thermal spray coated article
ActiveUS20160326059A1Improve corrosion resistanceHigh porosityMolten spray coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare-earth elementPorosity
This invention provides a thermal spray material capable of forming a thermal spray coating excellent in plasma erosion resistance as well as in properties such as porosity and hardness. The thermal spray material comprises a rare earth element oxyhalide (RE-O-X) which comprises a rare earth element (RE), oxygen (O) and a halogen atom (X) as its elemental constituents. The thermal spray material has an X-ray diffraction pattern that shows a main peak intensity IA corresponding to the rare earth element oxyhalide, a main peak intensity IB corresponding to a rare earth element oxide and a main peak intensity IC corresponding to a rare earth element halide, satisfying a relationship [(IB+IC) / IA]<0.02.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Thermal spray material, thermal spray coating and thermal spray coated article
ActiveUS20160326058A1Improve corrosion resistanceIncrease resistanceMolten spray coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare-earth elementPorosity
This invention provides a thermal spray material capable of forming a thermal spray coating excellent in plasma erosion resistance as well as in properties such as porosity and hardness. The thermal spray material comprises a rare earth element oxyhalide (RE-O—X) which comprises a rare earth element (RE), oxygen (O) and a halogen atom (X) as its elemental constituents. The rare earth element oxyhalide has a halogen to rare earth element molar ratio (X / RE) of 1.1 or greater.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Cerium-based abrasive, production process thereof
InactiveUS6986798B2High quality polishingSmall surface roughnessRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesPigmenting treatmentRare-earth elementCerium
A mixed light rare earth compound which has been obtained by chemically removing medium-to-heavy rare earth elements, Nd and impurities other than rare earth elements from an ore containing rare earth elements is fired at 500 to 1100° C. to yield a mixed rare earth oxide. A cerium-based rare earth fluoride is added to the mixed rare earth oxide to obtain a mixture. The mixture is subjected to wet-pulverization, drying, firing, disintegration and classification to thereby yield a cerium-containing abrasive.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Frame sealing glue combination, display panel, preparation method of display panel and display device
The invention provides a frame sealing glue combination, a display panel, a preparation method of the display panel and a display device in order to solve the problems that because incident light cannot irradiate frame sealing glue of the portion, shielded by metal wires, of a display panel in the prior art, the frame sealing glue is not totally cured, the frame sealing glue which is not totally cured will contaminate liquid crystals on the periphery of the frame sealing glue which is not totally cured, the periphery is bad, and line residual images are caused. Due to the fact that the frame sealing glue combination comprises optical wave conversion materials which can convert incident light into curing light making the frame sealing glue cured, the frame sealing glue which is not irradiated by the incident light can also be cured by the light obtained after conversion of the optical wave conversion materials, and therefore the problems that in the pre-curing process, because the frame sealing glue is not totally cured, liquid crystal contamination is caused, the periphery is bad, and line residual images are caused are avoided.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Method for making colloidal nanocrystals
ActiveUS20080247932A1Good size controlNarrow size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyFluoride preparationOrganic solventEmulsion
A method for making colloidal nanocrystals includes the following steps: dissolving a nanocrystal powder in an organic solvent, and achieving a solution A of a concentration of 1-30 mg / ml; dissolving a surfactant in water, and achieving a solution B of a concentration of 0.002-0.05 mmol / ml; mixing the solution A and the solution B in a volume ratio of 1: (5-30), and achieving a mixture; stirring and emulsifying the mixture, until an emulsion C is achieved; removing the organic solvent from the emulsion C, and achieving a deposit; then washing the deposit with deionized water, and achieving colloidal nanocrystals. The present method for making colloidal nanocrystals is economical and timesaving, and has a low toxicity associated therewith. Thus, the method is suitable for industrial mass production. The colloidal nanocrystals made by the present method have a readily controllable size, a narrow size distribution, and good configuration.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Rare earth fluoride spray powder and rare earth fluoride-sprayed article
InactiveUS20130122283A1Speed up the flowLow yieldRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMolten spray coatingRare-earth elementHalogen
A powder comprising rare earth element fluoride particles having an aspect ratio of up to 2, an average particle size of 10-100 m, a bulk density of 0.8-1.5 g / cm3, and a carbon content of 0.1-0.5 wt % is amenable to atmospheric plasma spraying. An article obtained by spraying the rare earth fluoride spray powder to a substrate undergoes few partial color changes and performs well even when used in a halogen gas plasma.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Morphologically and size uniform monodisperse particles and their shape-directed self-assembly
ActiveUS20130302358A1Increase in sizeQuench reactionMaterial nanotechnologyRare earth metal sulfidesOptical propertyPhosphor
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
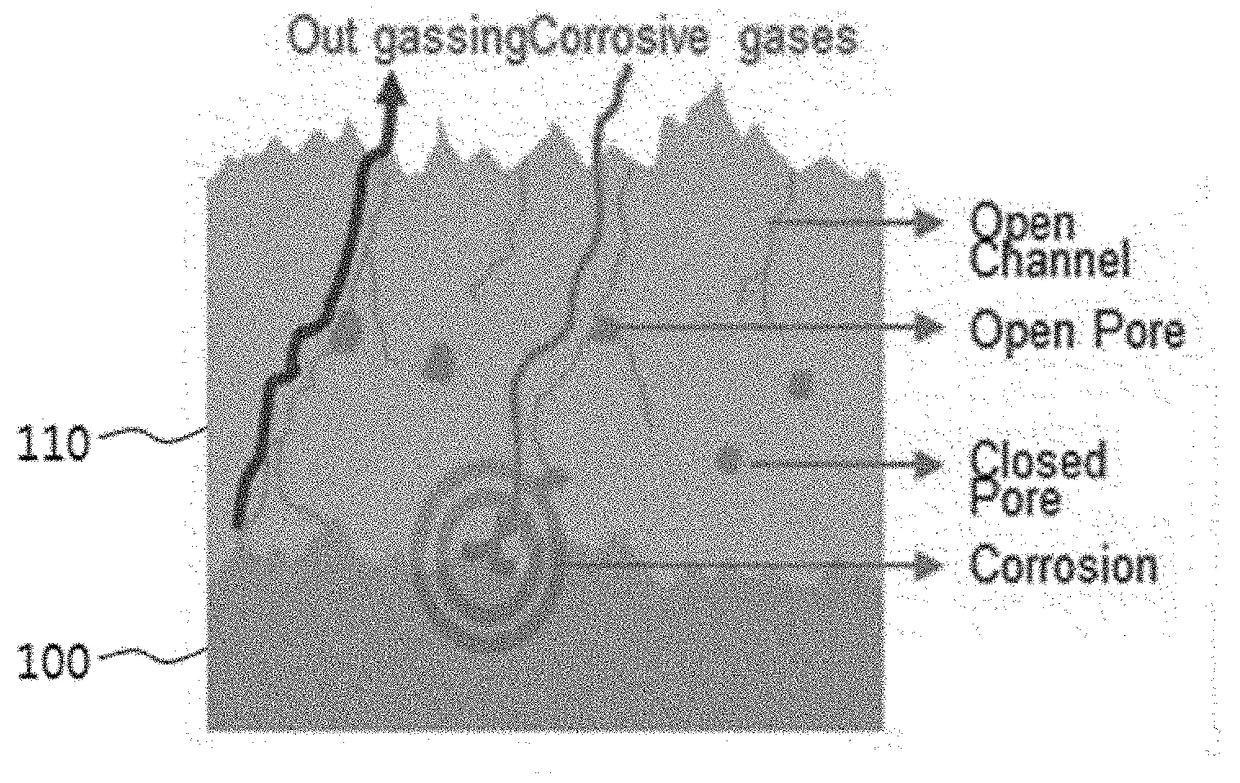
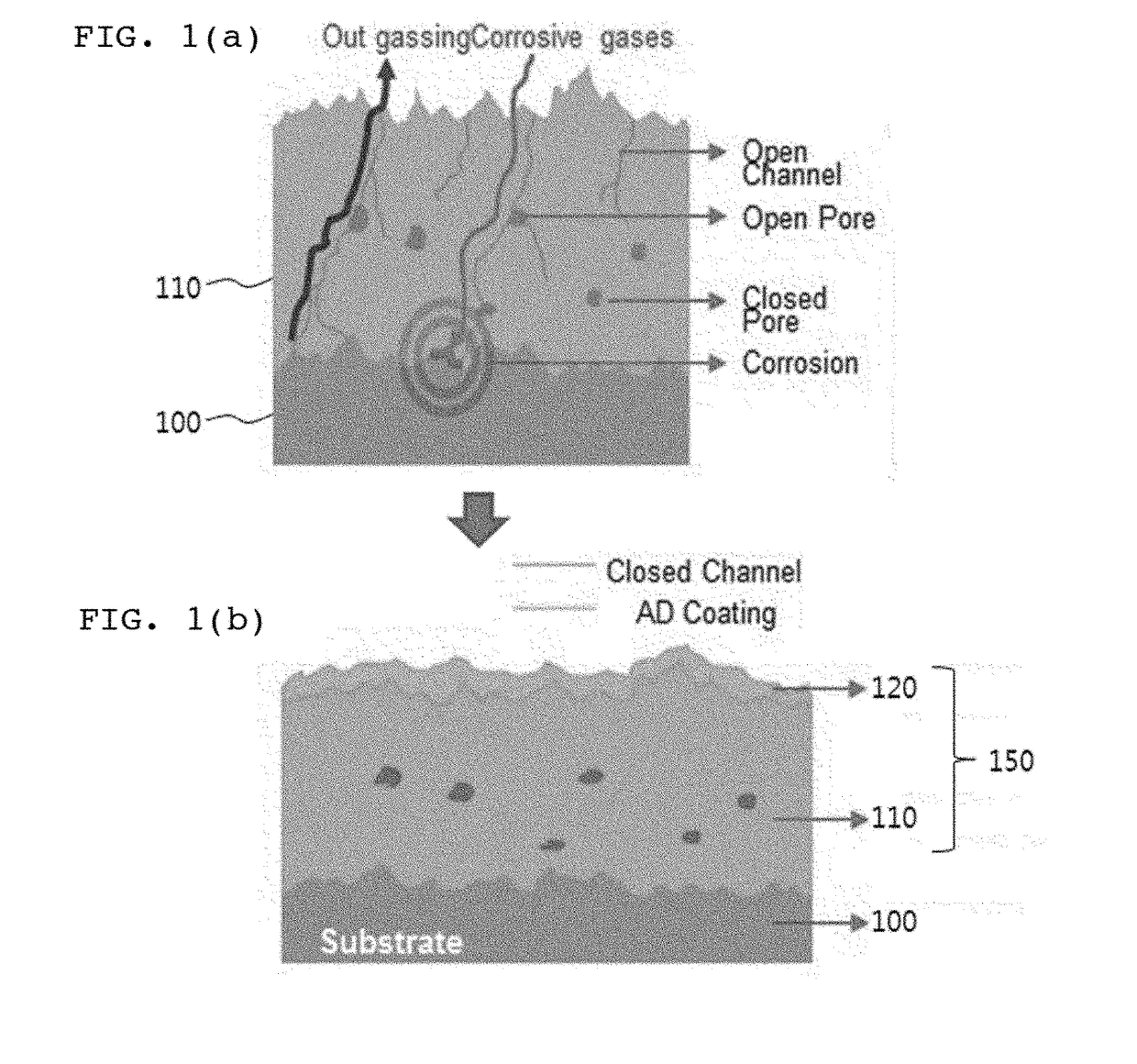
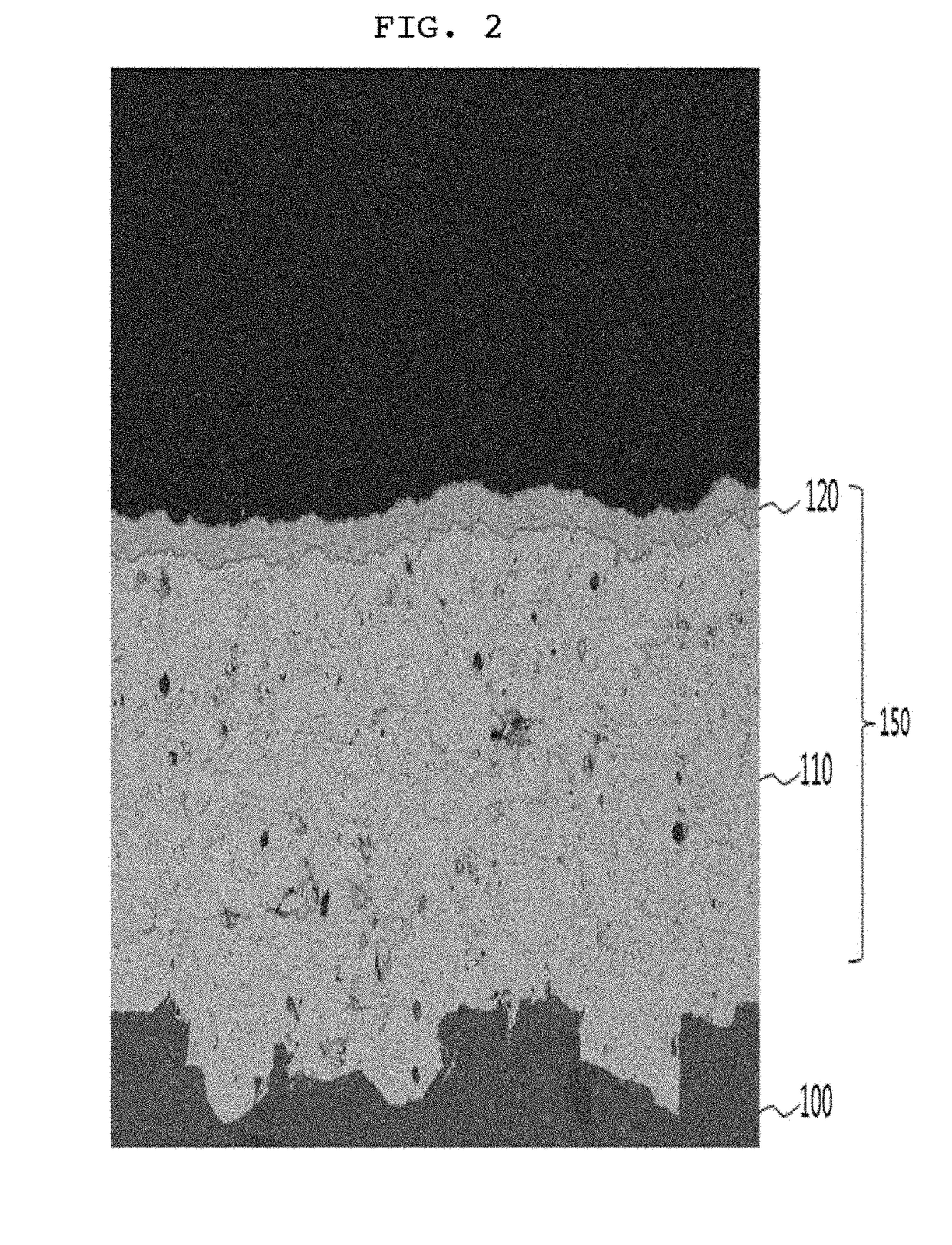
Plasma resistant coating film and fabricating method thereof
InactiveUS20180135157A1Increase resistanceStable physical propertiesMolten spray coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal sprayingRare earth metal compounds
The present disclosure relates to a plasma resistant coating film and a fabricating method thereof, more particularly a plasma resistant coating film and a fabricating method thereof which can secure chemical resistance by means of, after thermally spraying the first rare earth metal compound, double sealing through aerosol deposition and hydration, thereby minimizing open channels and open pores in the coating layer and plasma corrosion resistance by means of the dense rare earth metal compound coating film.
Owner:KOMICO
Sealant composition, display panel and method for manufacturing the same and display device
The present invention provides a sealant composition, a display panel and a method for manufacturing the same and a display device. For the sealant composition, the display panel and the display device provided in the present invention, the issues such as contamination of liquid crystal, peripheral defects and line residual image due to the incomplete curing of the sealant are prevented because the sealant composition comprises light converting material which could convert the incident light into the light for curing the sealant, and thus the sealant which cannot be irradiated directly by the incident light also could be cured by the converted light obtained from the light converting material.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Hydrometallurgical process and method for recovering metals
The invention relates to a hydrometallurgical process and a method for recovering metals. The mineral processing facility is provided that includes a cogen plant to provide electrical energy and waste heat to the facility and an electrochemical acid generation plant to generate, from a salt, a mineral acid for use in recovering valuable metals.
Owner:MOLYCORP MINERALS
Lanthanide fluoride two-dimensional porous nanosheet as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108358233AFewer post-processing stepsAvoid pollutionMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesSodium acetateLanthanide
The invention provides a preparation method of a lanthanide fluoride two-dimensional porous nanosheet, and belongs to the field of novel materials. The method comprises the following steps: mixing water-soluble lanthanide metal salt with a sodium acetate aqueous solution in a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain a mixed solution; adding the aqueous solution of fluorine-containing salts to the mixed solution for precipitation reaction to obtain the lanthanide fluoride two-dimensional porous nanosheet. Additional surfactants or template agents are not needed to be added in the preparation process, pollution of the surfactants on the surface of a preparation material is prevented, the complicated template agent post-treatment step is reduced, large-scale production can be performed, and one-step large-scale preparation of the lanthanide fluoride two-dimensional porous nanosheet constructed by nanoparticles is realized; other organic solvents are not needed, and environmental pollution caused bythe preparation process is prevented.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Fine particles containing rare earth element and fluorescent probe using the same
InactiveUS20080292520A1Insufficient stabilityEnhanced glowIndividual molecule manipulationBiological testingRare-earth elementFluorescence
A main object of the present invention is to provide: fine particles whose excitation light is not the one such as UV light or the like which has negative effects on a subject to be analyzed, emit light stably, and has excellent light emitting efficiency, and a fluorescent probe labeled with the fine particles.In order to achieve the aforementioned object, the present invention provides a fluorescent probe comprising: fine particles containing a rare earth element characterized in that they are excited by light having a wavelength in a range of 500 nm to 2000 nm and thereby emit up-conversion emission; and a specific binding substance which binds to the fine particles containing a rare earth element.
Owner:MATSUURA DAISUKE +1
Devices for charge-titrating particle assembly, and methods of using the devices
ActiveUS9981240B1Polycrystalline material growthSequential/parallel process reactionsNanoparticlePh control
Methods to fabricate tightly packed arrays of nanoparticles are disclosed, without relying on organic ligands or a substrate. In some variations, a method of assembling particles into an array comprises dispersing particles in a liquid solution; introducing a triggerable pH-control substance capable of generating an acid or a base; and triggering the pH-control substance to generate an acid or a base within the liquid solution, thereby titrating the pH. During pH titration, the particle-surface charge magnitude is reduced, causing the particles to assemble into a particle array. Other variations provide a device for assembling particles into particle arrays, comprising a droplet-generating microfluidic region; a first-fluid inlet port; a second-fluid inlet port; a reaction microfluidic region, disposed in fluid communication with the droplet-generating microfluidic region; and a trigger source configured to trigger generation of an acid or a base from at least one pH-control substance contained within the reaction microfluidic region.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method for recovering rare earth fluoride from electrode scrap reclaimed material and slag of rare earth
ActiveCN106044833AConvenient and effective purificationSave resourcesRare earth metal fluoridesAnode effectSlag
The invention discloses a method for recovering rare earth fluoride from an electrode scrap reclaimed material and slag of rare earth. The electrode scrap reclaimed material and the slag of the rare earth are taken as raw materials, the massive raw materials are sieved, non-rare-earth impurity blocks are removed, and the materials are subjected to sieving, ball milling and magnetic separation; the materials with most iron removed after magnetic separation are mixed with lithium fluoride; the mixture is heated to be melted until a melted liquid reaches a sufficient liquid level; the melted liquid is stirred and subjected to slag removal through filtering; a filtrate after slag removal is subjected to electrolytic impurity removal, slag is fished after an anode effect occurs in electrolysis, and a supernatant is subjected to cyclic electrolysis; the obtained supernatant is detected and is weighed and packaged after reaching the standard, and the final recovery product is obtained. Rare earth fluoride can be extracted conveniently and effectively from the electrode scrap reclaimed material and the slag of the rare earth, resources are saved, pollution is reduced, and the method has the characteristics of simple process and low cost.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Preparation method of water-phase cerium fluoride microparticle and application thereof
InactiveCN106865594AImprove photocatalytic reactivityPromote growthWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsNitrateHexafluorotitanic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of a water-phase cerium fluoride microparticle and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of photocatalysis. The preparation method has the advantages that by using ceric ammonium nitrate or cerous nitrate as a cerium source, and using ammonium hexafluorotitanate or ammonium fluoride as a fluorine source, the water-phase cerium fluoride microparticle with good dispersivity is prepared by a simpler and mild preparation technology; the good phtocatalysis property is realized under the visible light condition, and the application field of cerium fluoride is widened.
Owner:KAIFENG UNIV
Process for purifying a fluorine compound
InactiveUS20100099931A1Improve responseEasy to separatePhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesFluoride preparationCarbonyl fluorideOxygen compound
Provided is a process for purifying a fluorine compound capable of yielding a highly pure fluorine compound by removing at least oxygen from a fluorine compound containing an oxygen compound as an impurity. In a process according to the present invention for purifying a fluorine compound, the following is brought into contact with the fluorine compound, which contains an oxygen compound as an impurity, thereby removing at least oxygen: carbonyl fluoride in an amount of a 0.1-fold equivalent or more and a 100-fold equivalent or less of oxygen atoms in the fluorine compound.
Owner:STELLA CHEMIFA CORP
Method for preparing rare earth fluoride by using fluorinated ionic liquid
ActiveCN114074951AAvoid dangerHigh purityRare earth metal compounds preparation/treatmentRare earth metal fluoridesPtru catalystActive agent
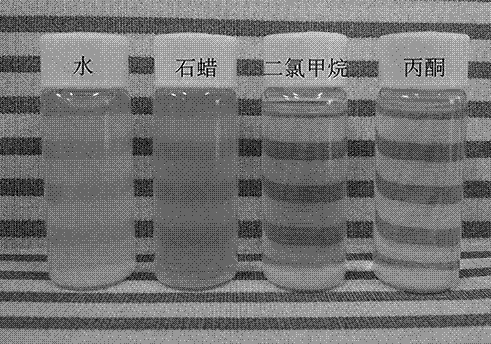
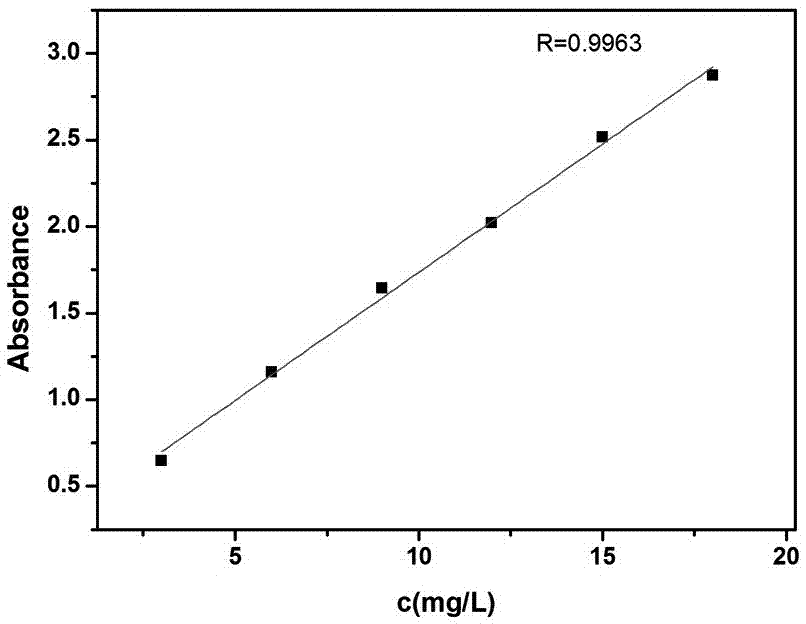
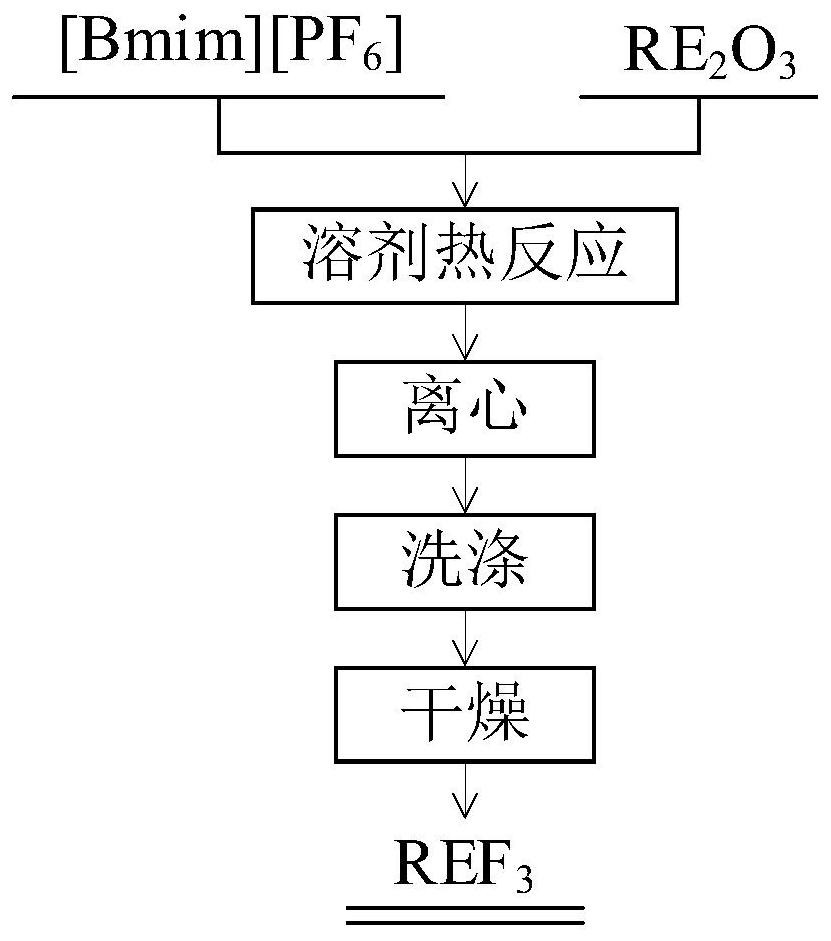
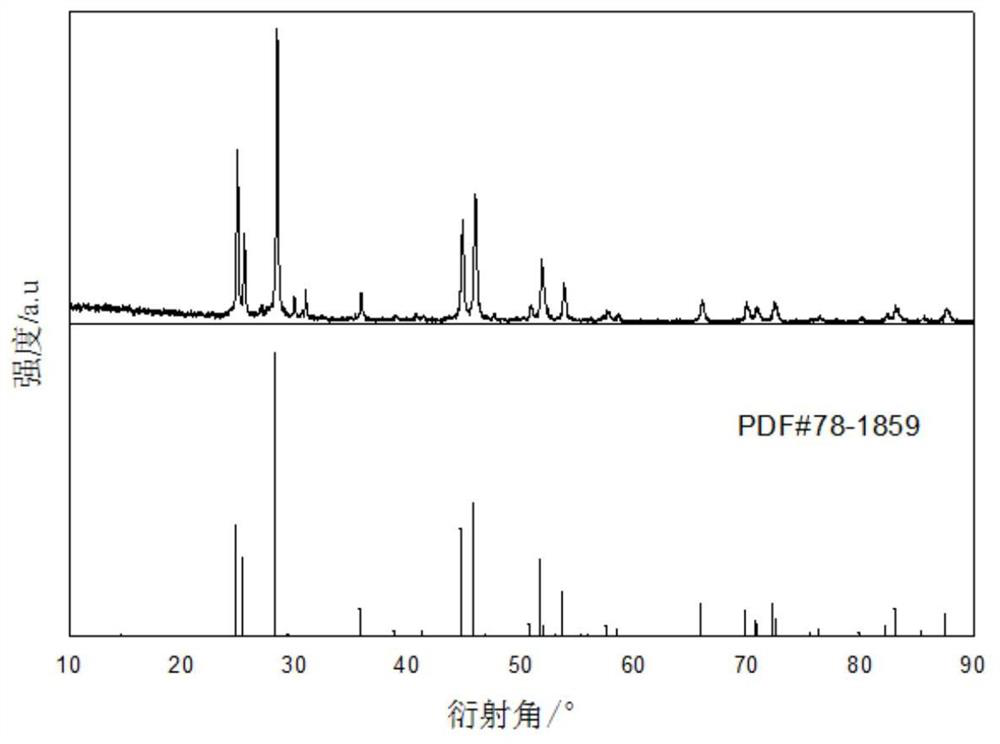
The invention discloses a method for preparing rare earth fluoride by using fluorinated ionic liquid. The rare earth fluoride is represented by a chemical formula REF3, wherein RE is selected from at least one of La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Y and Sc. A fluorinated ionic liquid and rare earth oxides are used as raw materials, the rare earth oxides are directly converted into rare earth fluoride through a solvothermal method, and the reaction can be carried out under a relatively low-temperature condition, so that a certain danger caused by fluorine gas generated at a high temperature is avoided; and meanwhile, the preparation method of the rare earth fluoride provided by the invention is mild in reaction condition, and the rare earth fluoride can be obtained without adding any surfactant, catalyst or template, so that the purity and the yield of the rare earth fluoride are greatly improved. The oxygen content of the rare earth fluoride prepared through the method is lower than 100 ppm, and the rare earth fluoride can be widely used for preparing rare earth fluoride single crystals, low-oxygen metal gadolinium and fluorescent matrix materials.
Owner:XIAMEN INST OF RARE EARTH MATERIALS
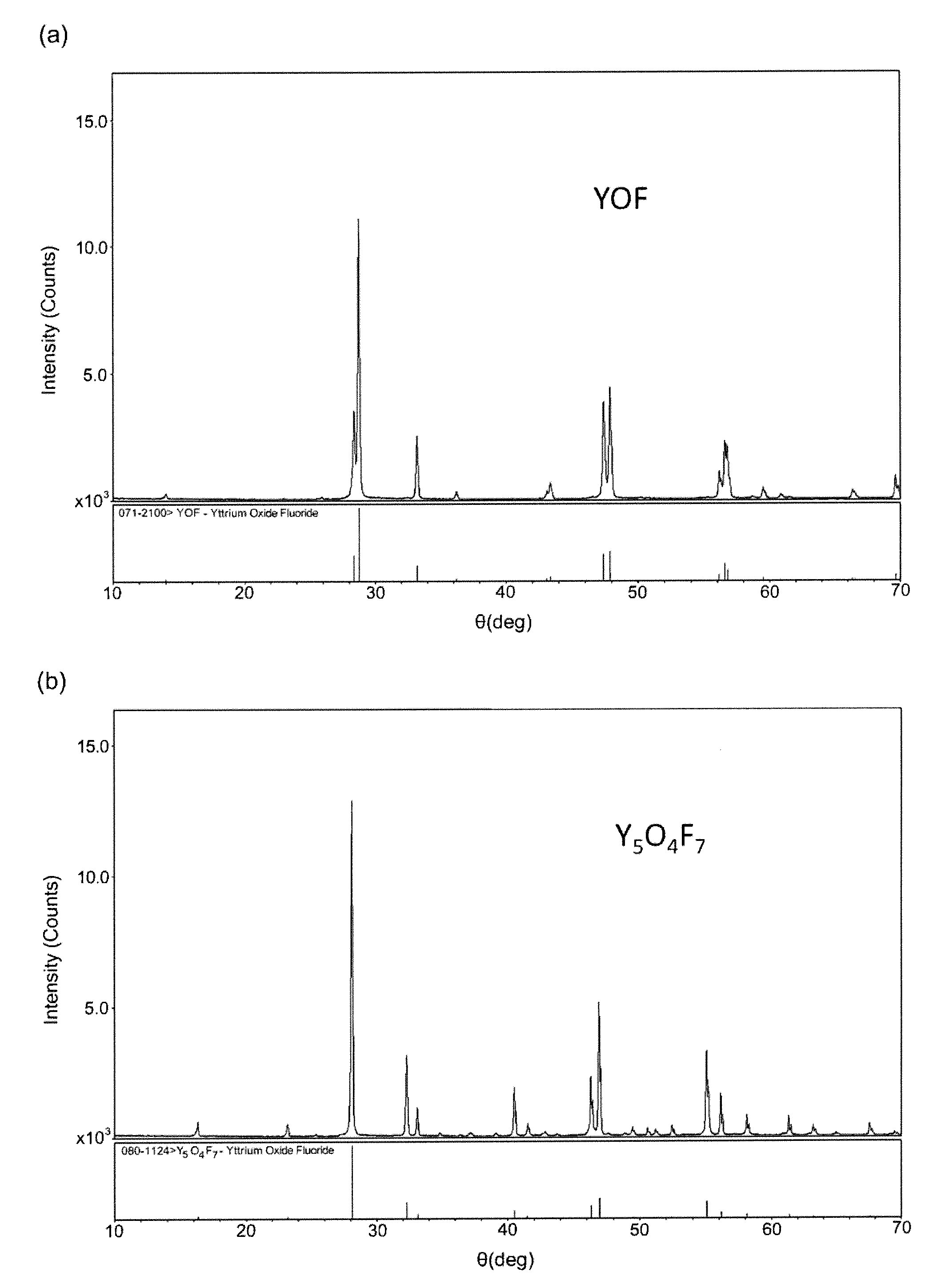
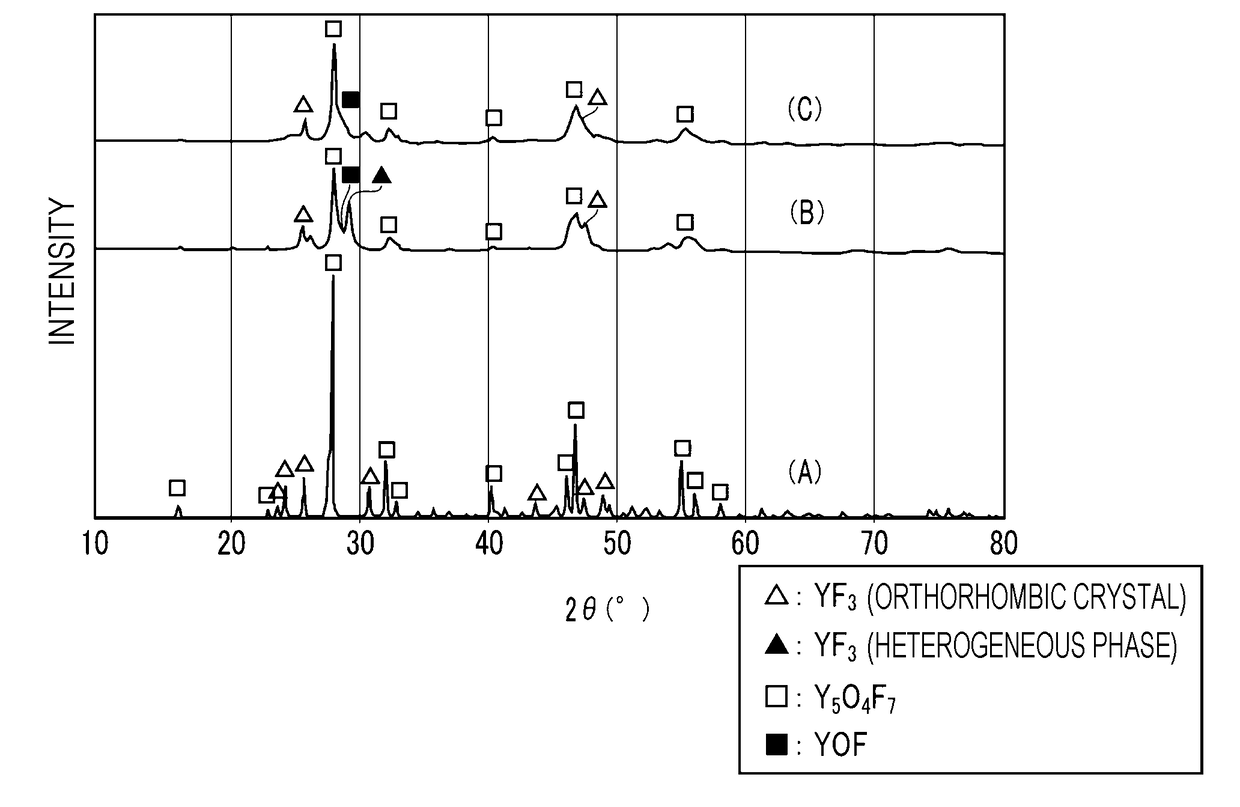
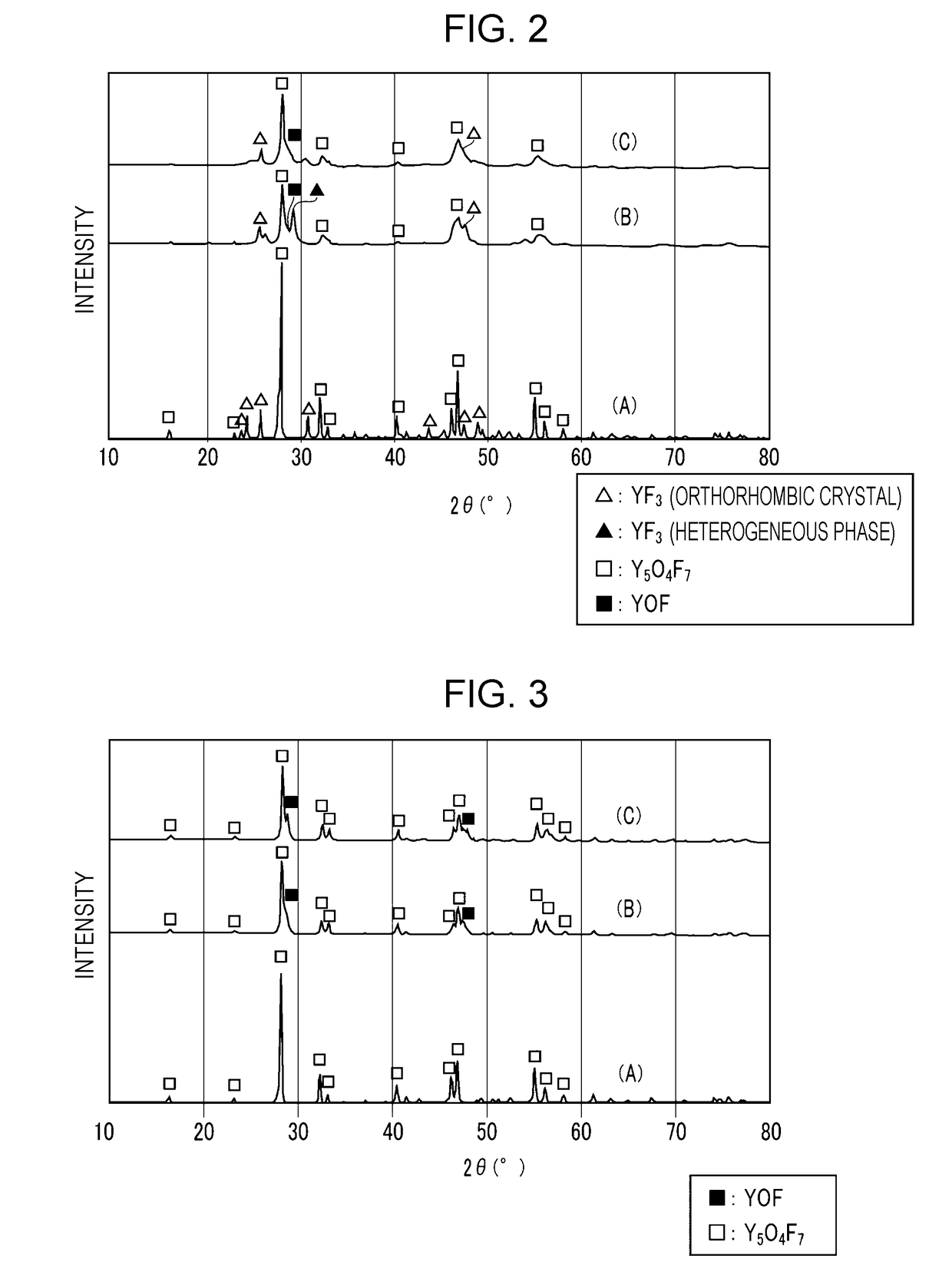
Yttrium oxyfluoride sprayed coating and method for producing the same, and sprayed member
ActiveUS20170370007A1Inhibits the formation of cracksIncrease heatMolten spray coatingYittrium oxides/hydroxidesDiffractometerX-ray
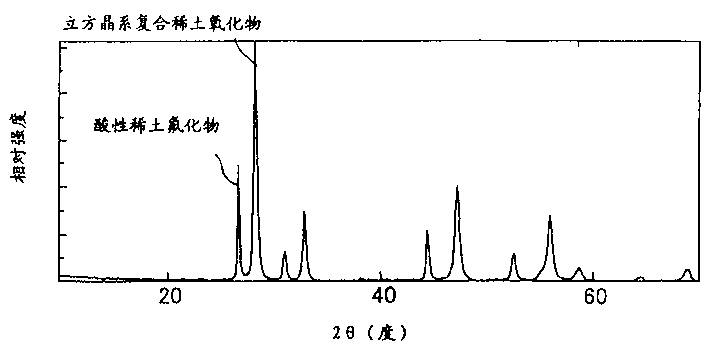
An yttrium oxyfluoride sprayed coating contains Y5O4F7 as a main component. In the yttrium oxyfluoride sprayed coating, when the total intensity of all peaks attributable to yttrium oxyfluoride in a diffraction spectrum obtained by X-ray diffractometry is assumed to be 100, the total intensity of all peaks attributable to yttrium fluoride and yttrium oxide is less than 10. Furthermore, in an yttrium oxyfluoride-containing sprayed coating, when the total intensity of all peaks attributable to yttrium oxyfluoride and yttrium fluoride in a diffraction spectrum obtained by X-ray diffractometry is assumed to be 100, the total intensity of all peaks attributable to yttrium oxide is less than 1.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Preparation method of rare earth fluoride
InactiveCN111115677ALess corrosiveAchieve the purpose of separationRare earth metal fluoridesHydrogen fluorideProcess engineering
The invention provides a preparation method of rare earth fluoride, and belongs to the technical field of chemical salt preparation. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps:mixing rare earth carbonate and ammonium fluoride, then carrying out a fluorination reaction, and performing heating to remove residual ammonium fluoride to obtain rare earth fluoride, wherein the molar ratio of the rare earth carbonate to the ammonium fluoride is 1:(6-18). According to the method provided by the invention, rare earth carbonate and ammonium fluoride are used as raw materials, thepreparation process is divided into a fluorination process and an impurity removal process, rare earth carbonate is firstly fluorinated by utilizing ammonium fluoride, and then the characteristic that the decomposition temperature of the ammonium fluoride is relatively low is utilized, so that the residual ammonium fluoride is heated to be decomposed into gaseous substances to volatilize, and theaim of separating impurities from a product is further achieved. Compared with the existing dry process, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the temperature required by the fluorination reaction is greatly reduced, the corrosivity of ammonium fluoride is lower than that of hydrogen fluoride, the manufacturing cost of used equipment is low, the ammonium fluoride decomposition product is easy to recycle, and the production cost is low.
Owner:GANZHOU NONFERROUS METALLURGICAL RES INST
Cerium-based abrasive and production process thereof
InactiveCN1478135AGood polishing speedRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesOther chemical processesRare-earth elementCerium
A mixed light rare earth compound which has been obtained by chemically removing medium-to-heavy rare earth elements, Nd and impurities other than rare earth elements from an ore containing rare earth elements is fired at 500 to 1100 DEG C. to yield a mixed rare earth oxide. A cerium-based rare earth oxy-fluoride is added to the mixed rare earth oxide to obtain a mixture. The mixture is subjected to wet-pulverization, drying, firing, disintegration and classification to thereby yield a cerium-containing abrasive.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Method for promoting rare earth carbonate to be converted into rare earth fluoride and recovering ammonia water
ActiveCN111204791AImprove conversion rateRare earth metal fluoridesAmmonia preparation/separationEnvironmental engineeringFluoride
The invention discloses a method for promoting rare earth carbonate to be converted into rare earth fluoride and recovering ammonia water, which comprises the following steps: heating a mixed solutionof a fluorine-ammonia composite fluorinating agent and rare earth carbonate, blowing the mixed solution by using gas, and absorbing ammonia gas in tail gas by using water, wherein the fluorine-ammonia composite fluorinating agent is a mixed solution of a fluorine-containing inorganic matter and ammonia water, and the pH value of the fluorine-ammonia composite fluorinating agent is greater than orequal to 6. According to the method, rare earth carbonate can be almost completely converted into rare earth fluoride, the conversion rate of fluorine is high, and meanwhile ammonia water can be recycled.
Owner:BAOTOU RES INST OF RARE EARTHS +1
Para-aminobenzoic acid sensitized terbium doped laf3 nanoparticles for detection of explosive nitro compounds
ActiveUS20170225963A1Remarkable enhancement in luminescence intensityNanosensorsInvestigating pH valueNitro compoundBenzoic acid
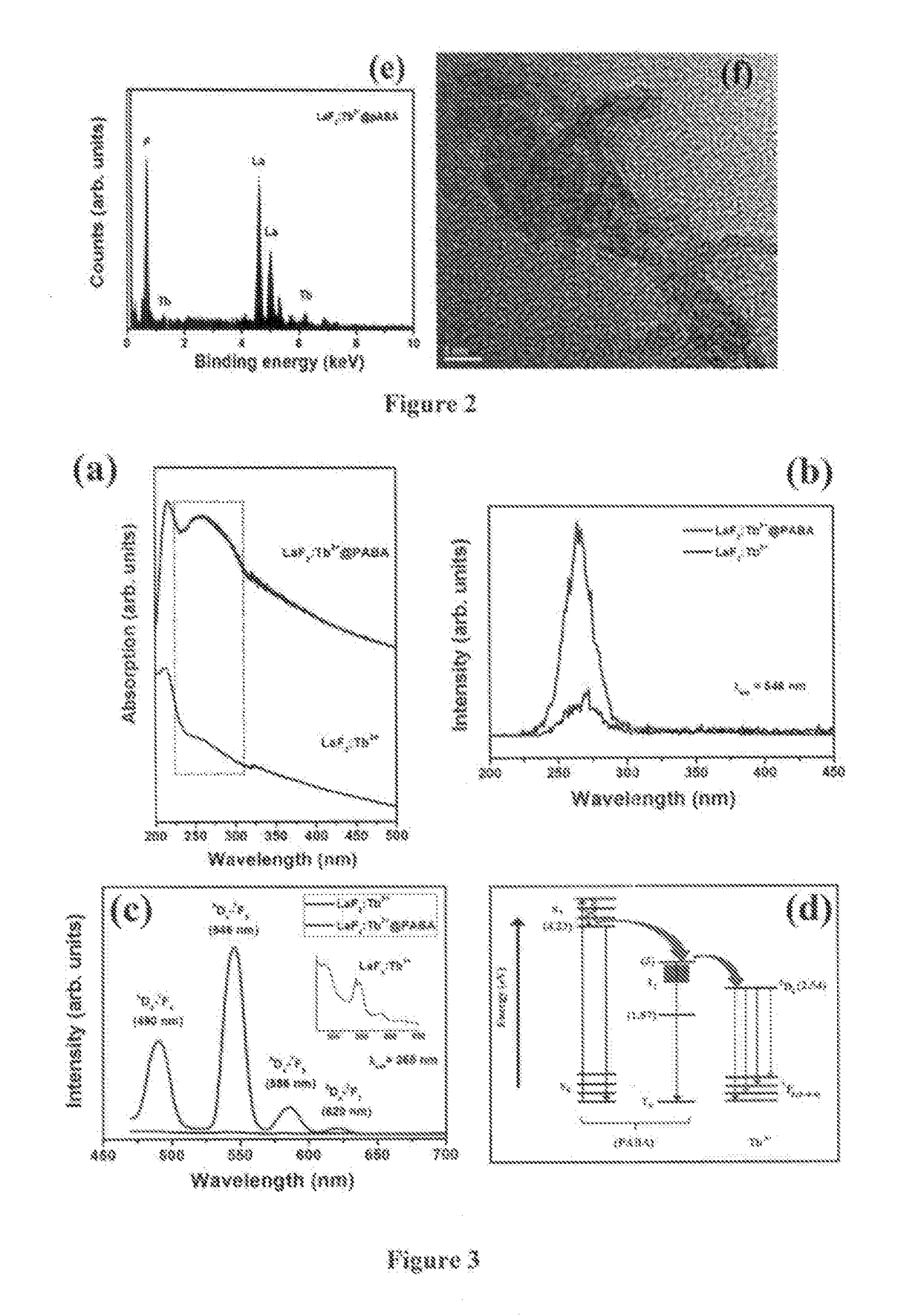
The patent relates to para amino benzoic acid (pABA) sensitized terbium (Tb3+) doped spherical LaF3 nanoparticles used for detection of nitro group containing compounds using the terbium (Tb3+) doped spherical LaF3 nanoparticles sensitized by para amino benzoic acid (pABA).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Rare earth fluoride spray powder and rare earth fluoride-sprayed article
ActiveUS20150225832A1Rare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMolten spray coatingRare-earth elementHalogen
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for purifying fluorine compound
InactiveCN101558008AImprove responseEasy to separateAmino compound purification/separationPhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesCarbonyl fluorideOxygen compound
Provided is a process for purifying a fluorine compound capable of yielding a highly pure fluorine compound by removing at least oxygen from a fluorine compound containing an oxygen compound as an impurity. In a process according to the present invention for purifying a fluorine compound, the following is brought into contact with the fluorine compound, which contains an oxygen compound as an impurity, thereby removing at least oxygen: carbonyl fluoride in an amount of a 0.1-fold equivalent or more and a 100-fold equivalent or less of oxygen atoms in the fluorine compound.
Owner:STELLA CHEMIFA CORP
Preparation method of rare earth fluoride
PendingCN111392760AHigh viscosityWon't happenRare earth metal fluoridesHydrogen fluorideRare-earth element
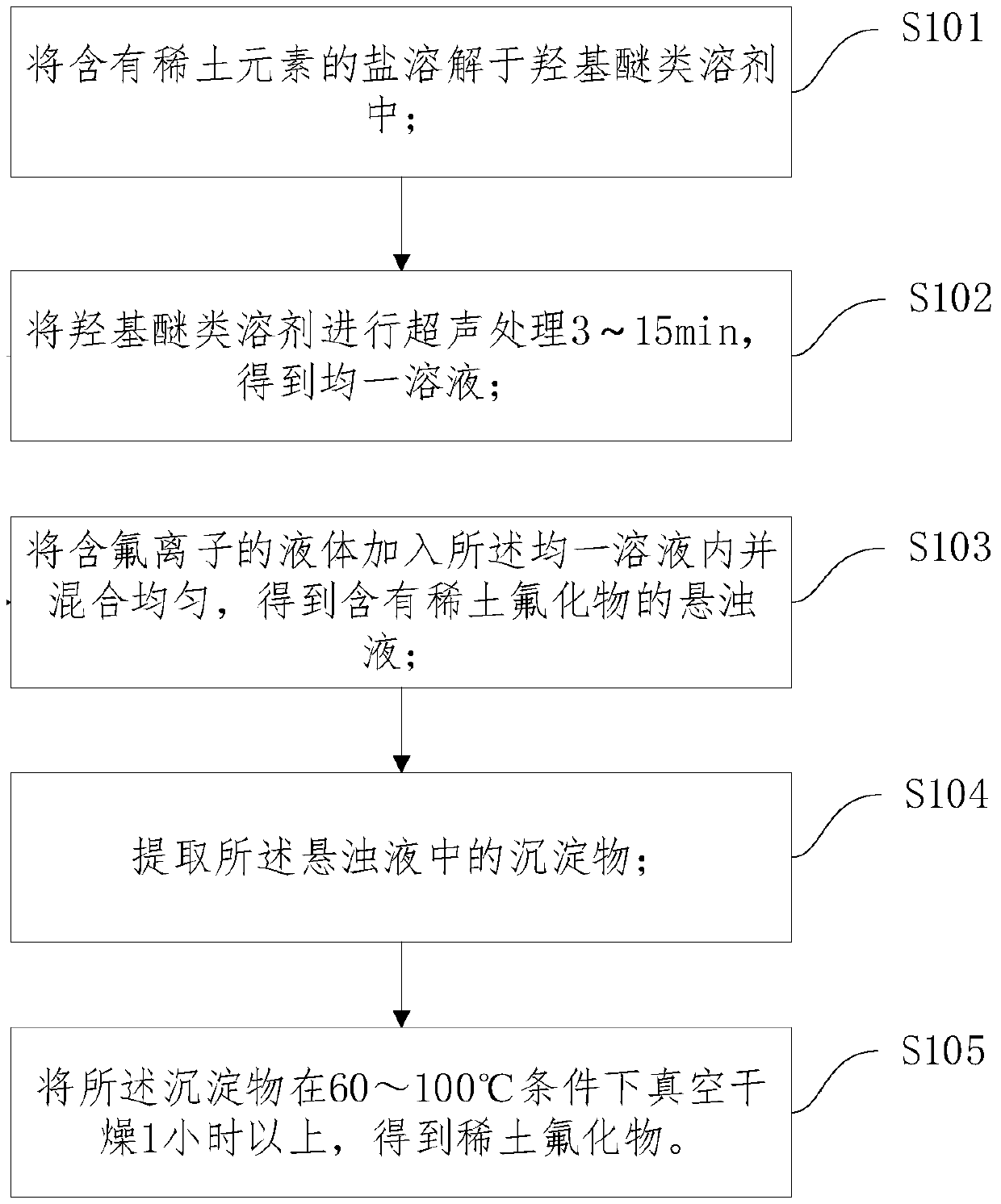
The invention discloses a preparation method of rare earth fluoride. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving salt containing rare earth elements into a hydroxyl ether solvent;carrying out ultrasonic treatment for 3-15 minutes to obtain a uniform solution; adding liquid containing fluorine ions into the uniform solution and uniformly mixing to obtain turbid liquid containing rare earth fluoride; extracting precipitate in the turbid liquid; and vacuum-drying the precipitate at the temperature of 60-100 DEG C for 1 h or longer to obtain rare earth fluoride, wherein the water oxygen content of the rare earth fluoride is smaller than 100ppm. According to the preparation method of the rare earth fluoride provided by the embodiment of the invention, the salt containing rare earth elements is dissolved in the hydroxyl ether solvent, the viscosity of the hydroxyl ether solvent is relatively high, the rare earth fluoride is prepared in a high-viscosity environment, thereaction environment is liquid, the reaction selectivity is relatively high, and the reaction is complete. Moreover, the whole process is carried out in liquid, hydrogen fluoride is not needed, no tail gas is generated, and the reaction process is energy-saving and environment-friendly. No water is contained in the whole reaction process, and the water oxygen content of the product is low.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com