Hydrometallurgical process and method for recovering metals
A technology of metals and valuable metals, applied in the direction of rare earth metal fluorides, chemical instruments and methods, rare earth metal compounds, etc., to reduce the cost of reactants and transportation requirements, reduce the demand for fresh water, and reduce operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
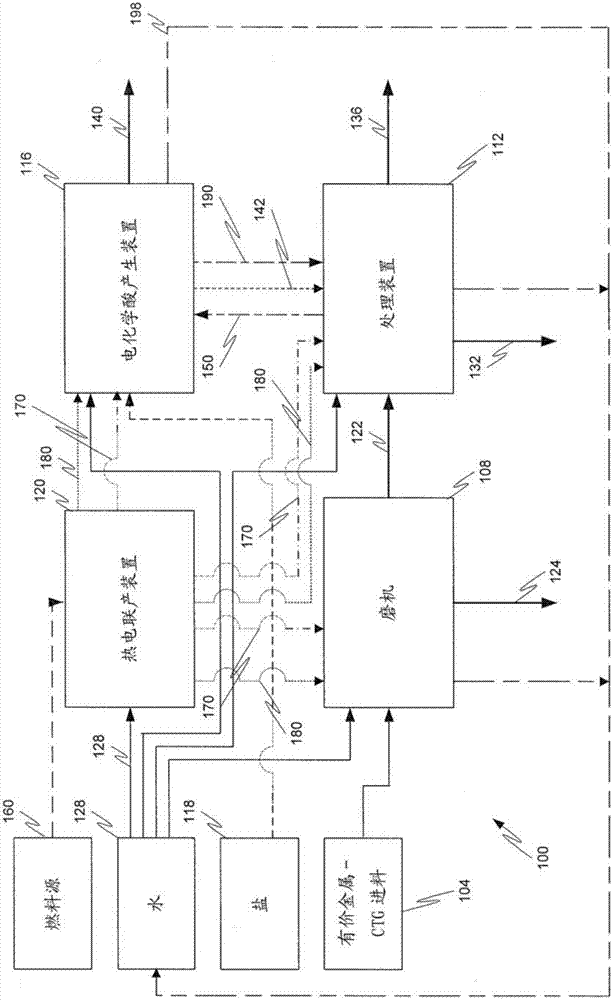
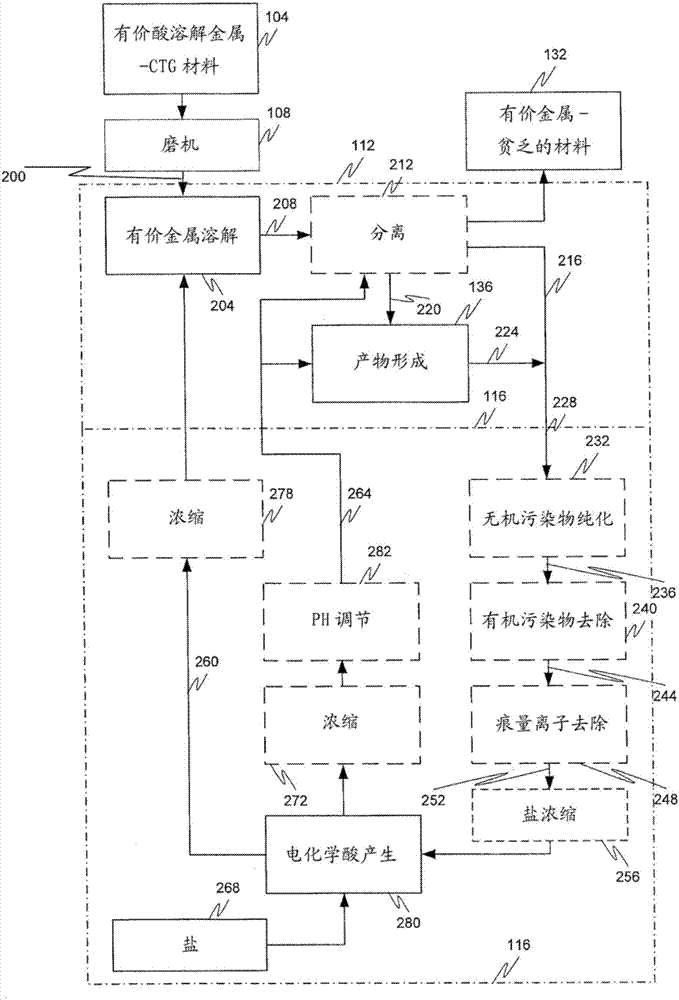
[0141] 1. A method comprising:
[0142] (a) contacting the metal value-containing material with an acidic leach solution to form a rich leachate comprising dissolved metal values;
[0143] (b) recovering said dissolved metal value to form a metal value product and a by-product brine solution from the reaction of an acid component of said leach solution with a base;
[0144] (c) converting said by-product brine solution to said acid component and said base by at least one of a chlor-alkali and a bipolar membrane electrodialysis cell;
[0145] (d) recycling the acid component to step (a) as part of the acid leach solution; and
[0146] (e) recycling the base to at least one of steps (a) and (b).
[0147] 2. The method of item 1, wherein at least a majority of said by-product brine solution is converted to said acid component and base, and wherein at least a majority of said acid component and base are recycled.
[0148] 3. The method of item 1, wherein the valuable metal is a...
Embodiment A
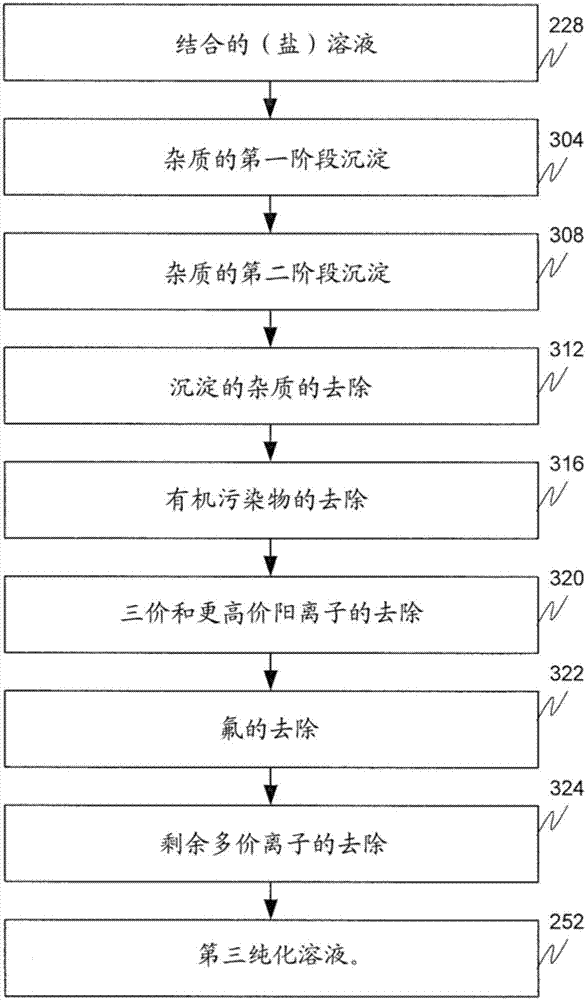
[0242] Example A is the determination of a multi-stage precipitation and ion exchange process for the removal of divalent and trivalent cations prior to salt splitting treatment. Figure 4 and Figure 5 The reduction of divalent alkaline earth metal (especially magnesium, calcium, strontium and barium) and trivalent (lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium and iron) cations after each precipitation and ion exchange stage are shown, respectively.
[0243] M1 is the first precipitation stage ( image 3 ), wherein a salt solution having a pH of about pH 7 (e.g., the by-product salt solution 224, the metal value-depleted salt solution 216, or a combination thereof (combined solution 228) as described above) contacts a Sodium carbonate solution at a pH of about pH 9.5 to form a metal carbonate slurry. Sodium carbonate was dissolved in water with stirring to form the sodium carbonate solution. The metal carbonate slurry has metal carbonate precipitates dispersed in b...
Embodiment B
[0249] Embodiment B is trivalent cation in chelating ion exchange resin ( image 3 Determination of load capacity on IX1) in. The chelating ion exchange resin evaluated was an iminodiacetoxy resin sold under the trademark Amberlite IRC-748i by Rohm & Haas. The trivalent cation is lanthanum. By adding about 400 mg of lanthanum oxide (La 2 o 3 ) was dissolved in hydrochloric acid (about 3.7 ml of 2N HCl) to obtain a pH of about pH 4, about 50 g / L NaCl and 83 mg / L lanthanum (as LaCl 3 ) of the lanthanum feed solution. After dissolving the lanthanum oxide, about 200 grams of NaCl was added, the pH was adjusted to about pH 4 with 1 N NaOH and deionized water was added to give a final volume of about 4 liters. The column was packed with Amberlite IRC-748i. The lanthanum feed solution was passed through the packed column at a rate of about 2.05 mL / min at about 21 degrees Celsius (see Image 6 ). The maximum trivalent cation capacity of the iminodiacetoxy resin was determined ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com