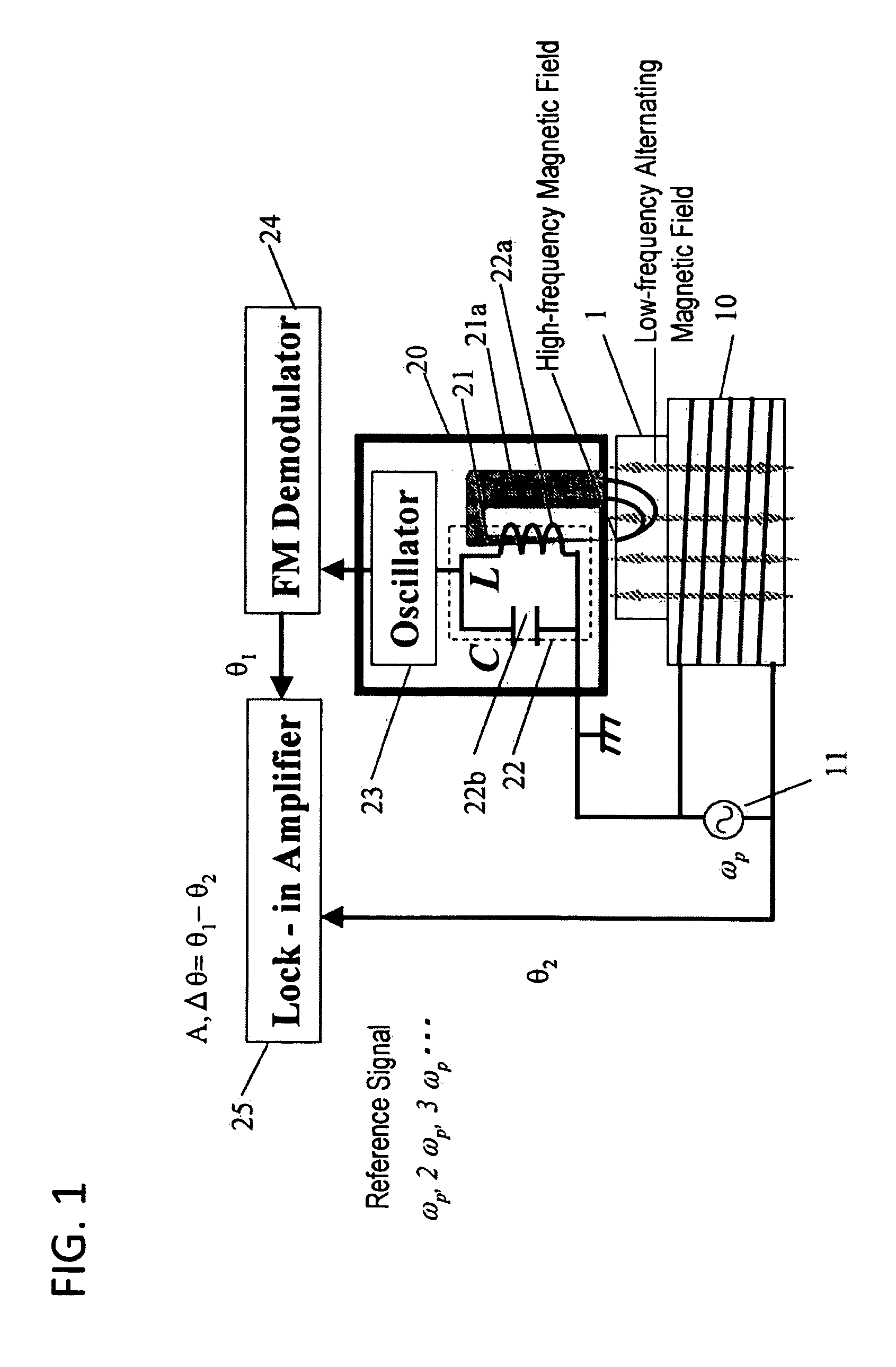
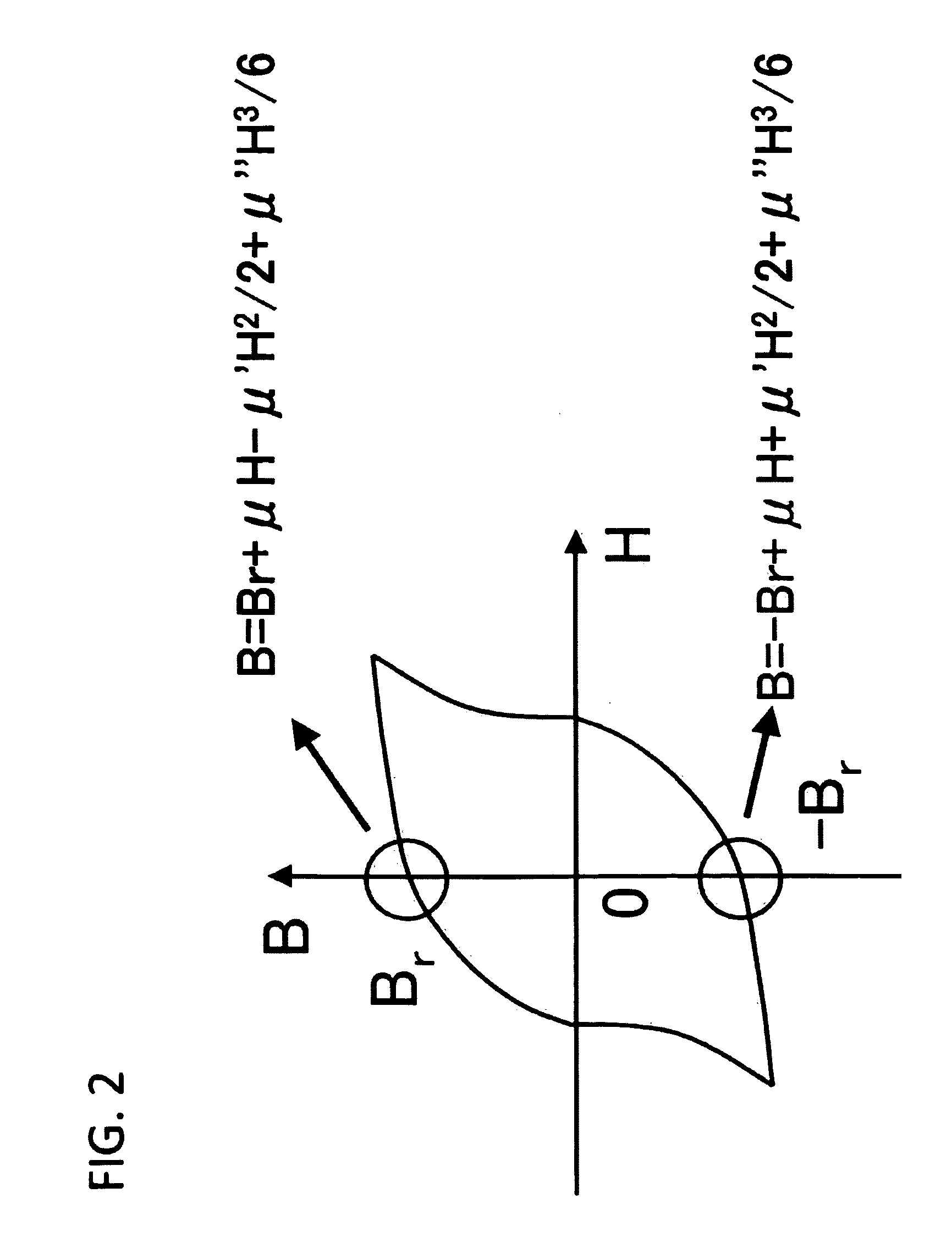
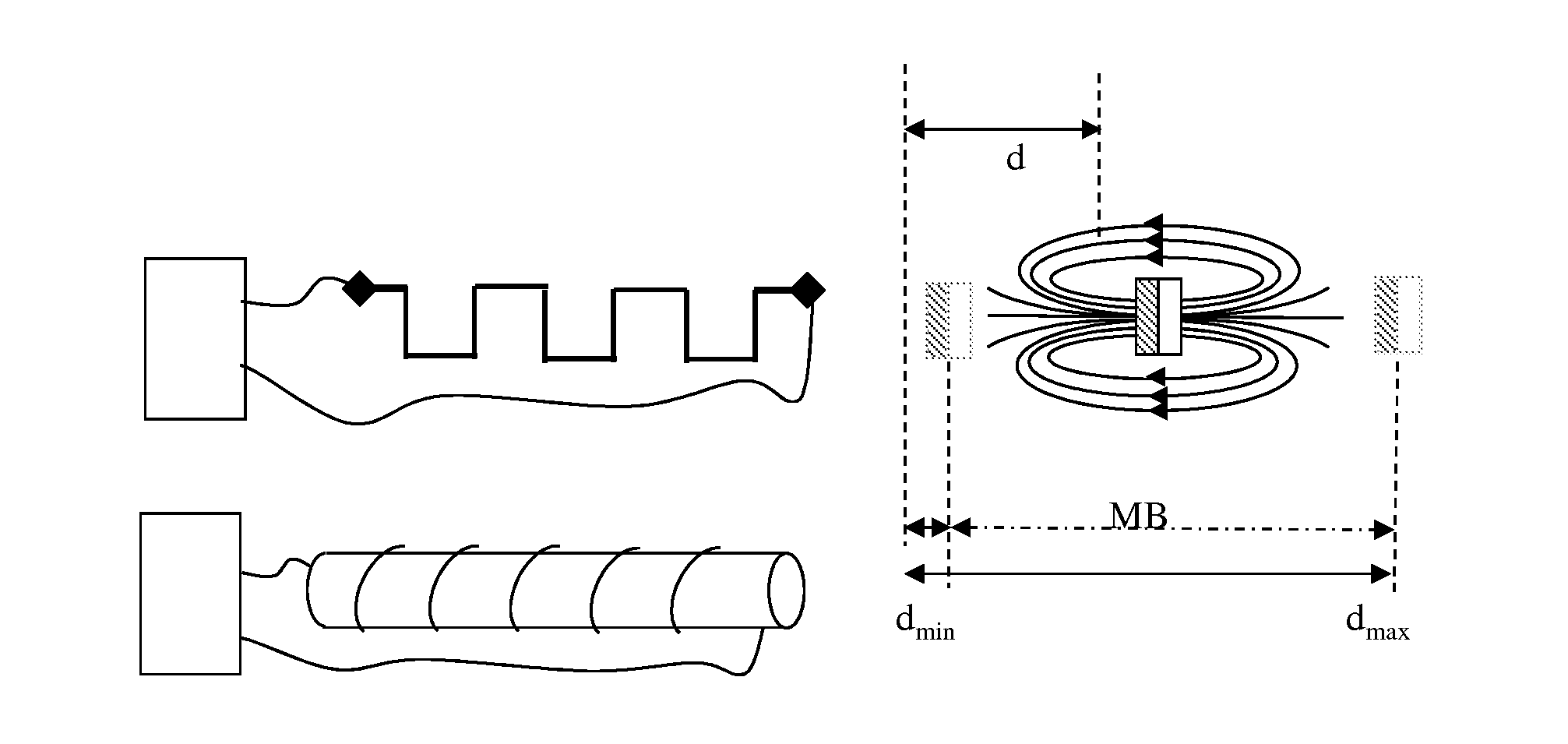
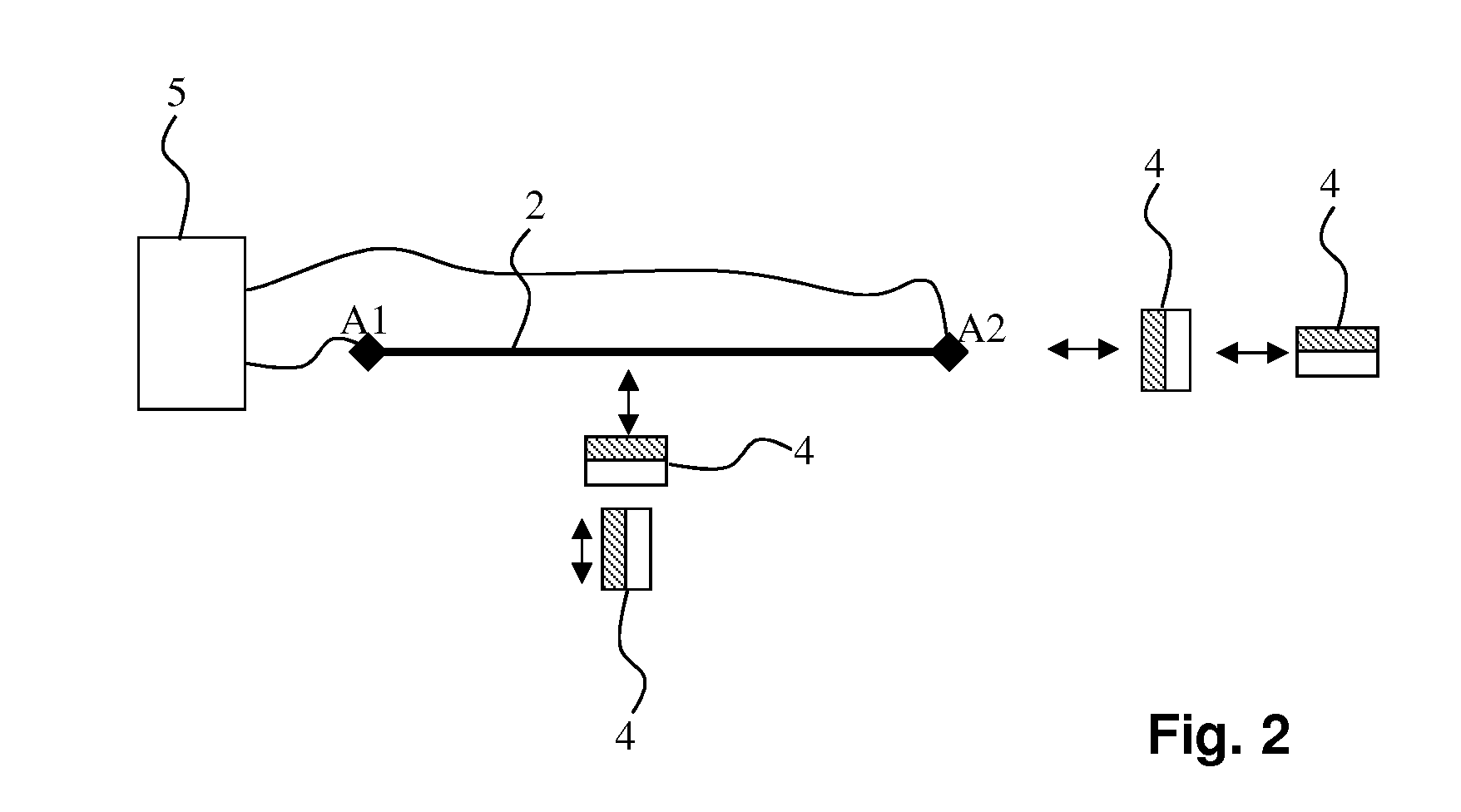
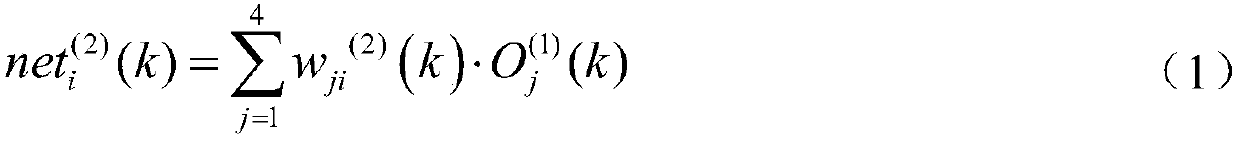Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
175results about "Permeability measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
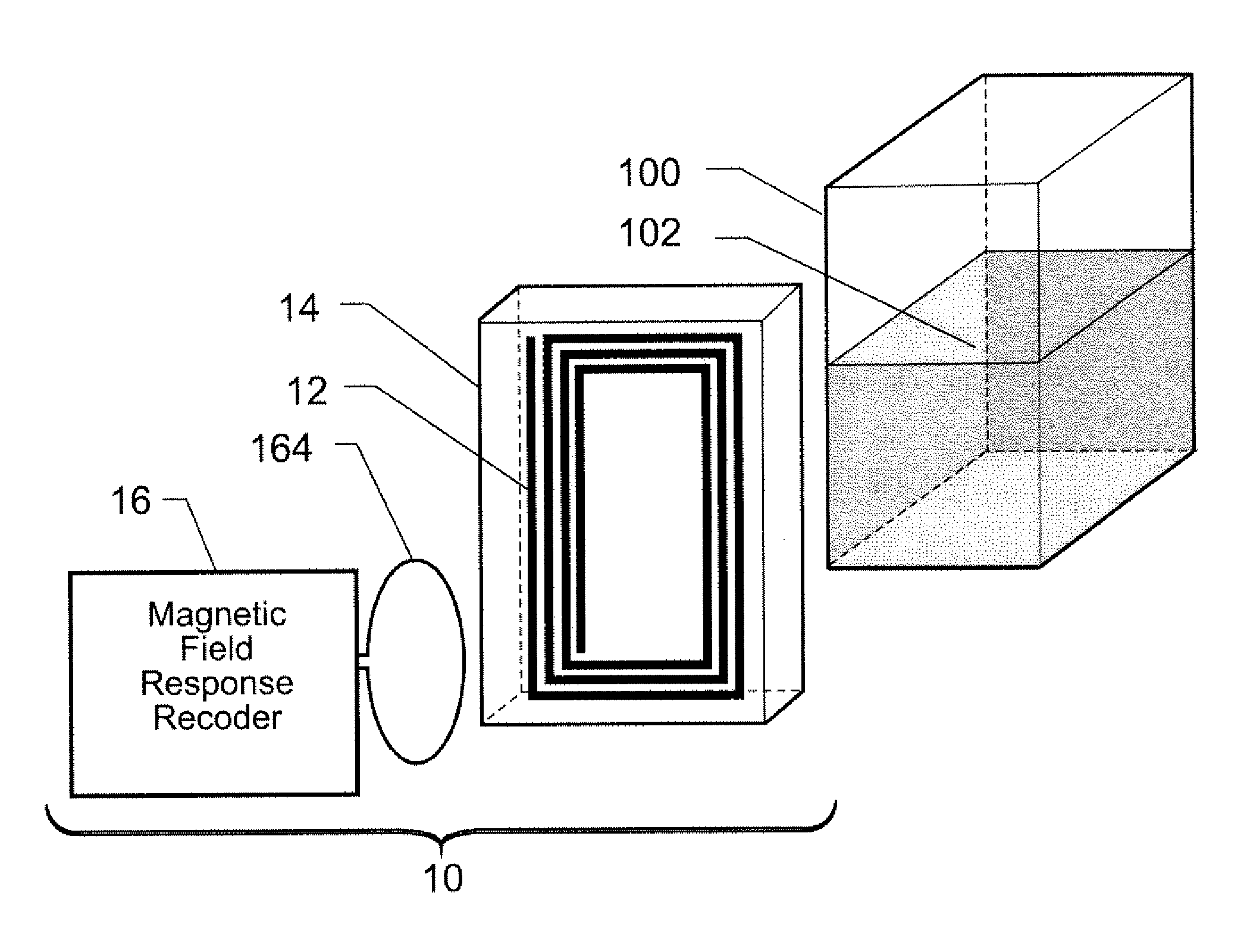
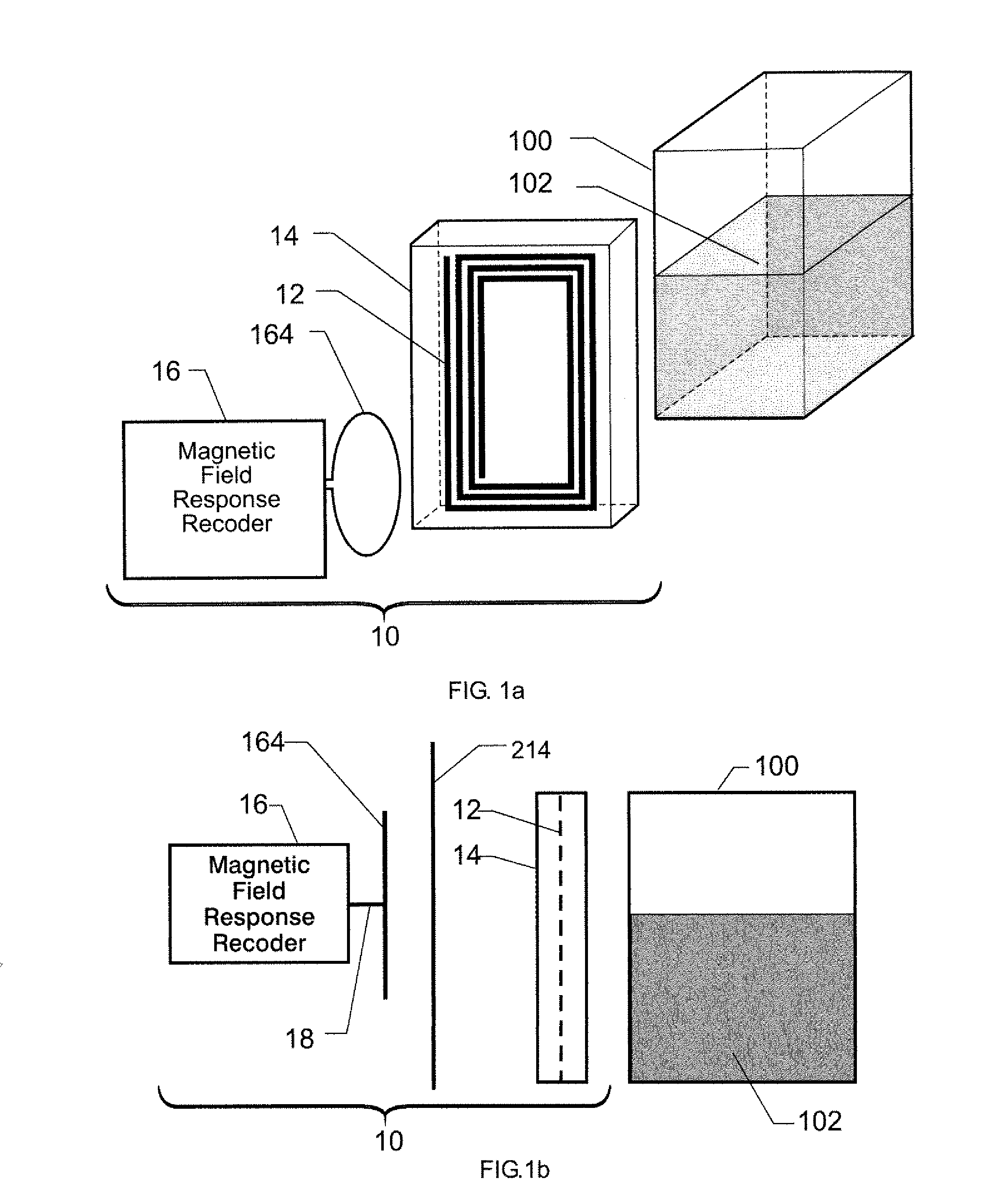
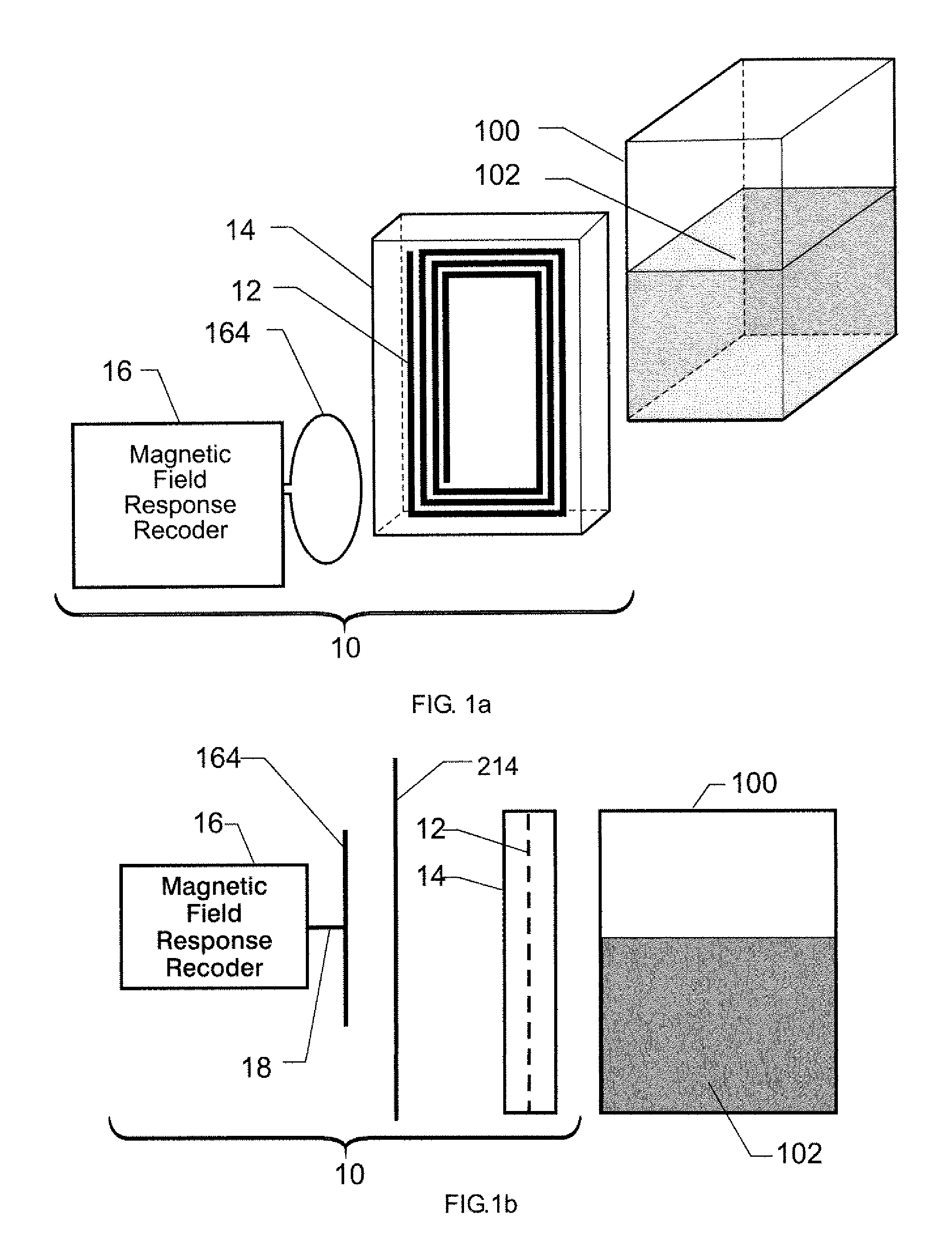
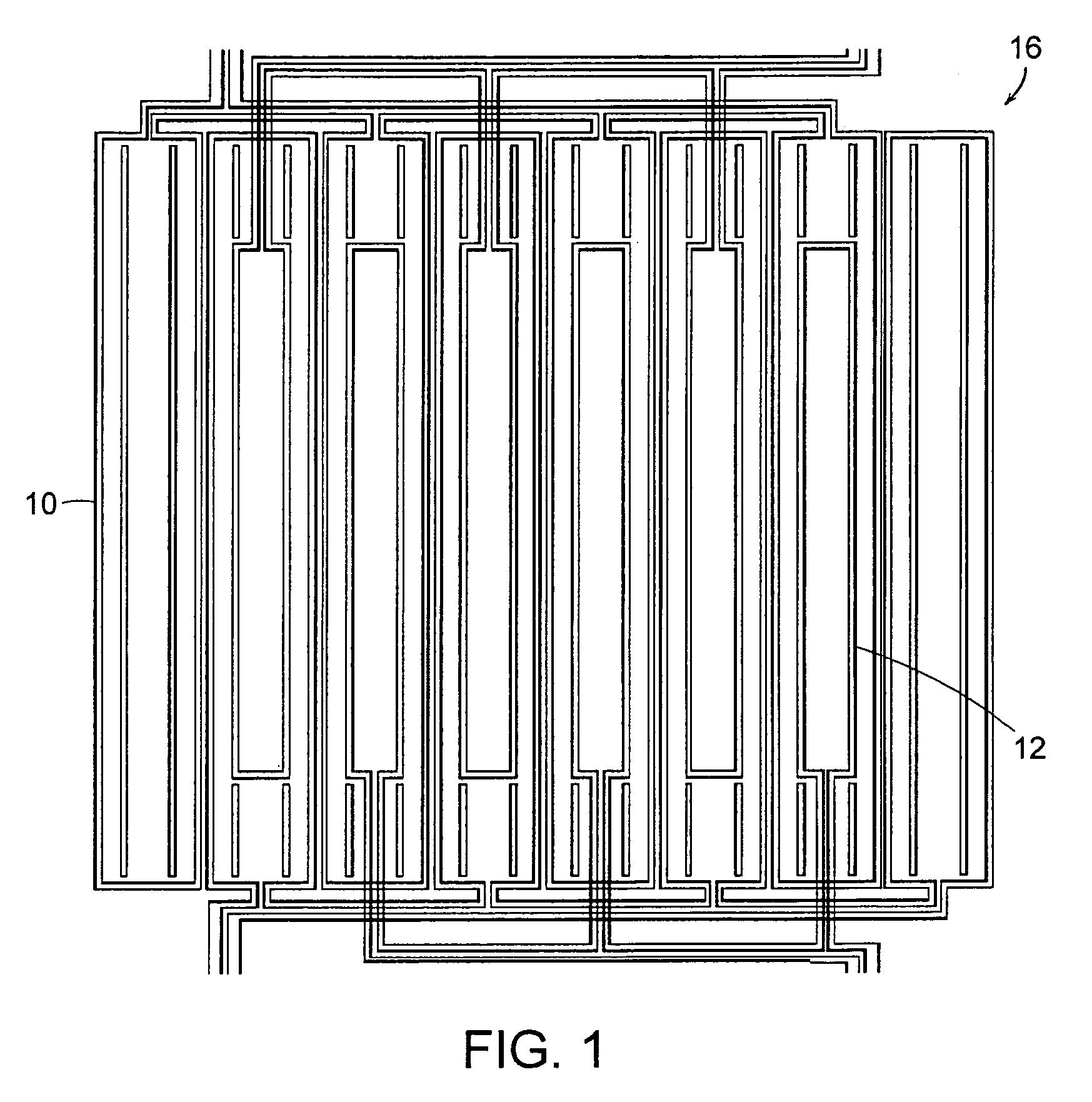
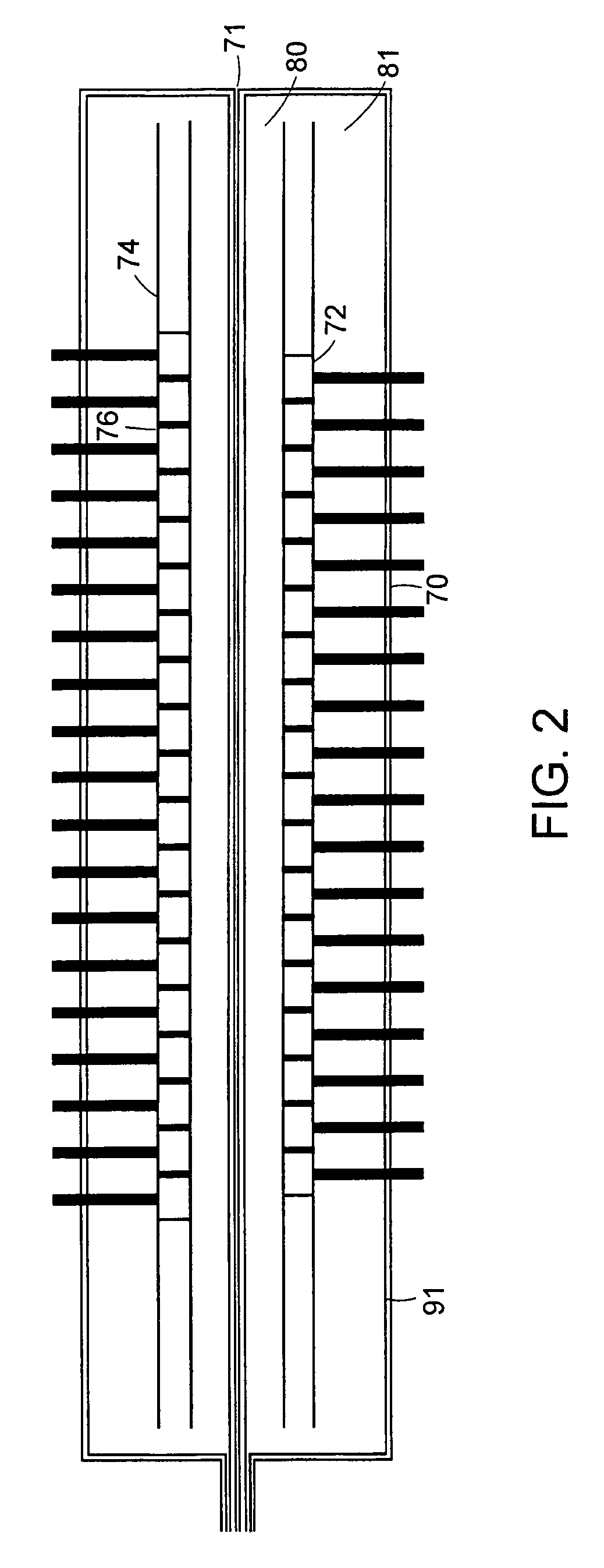
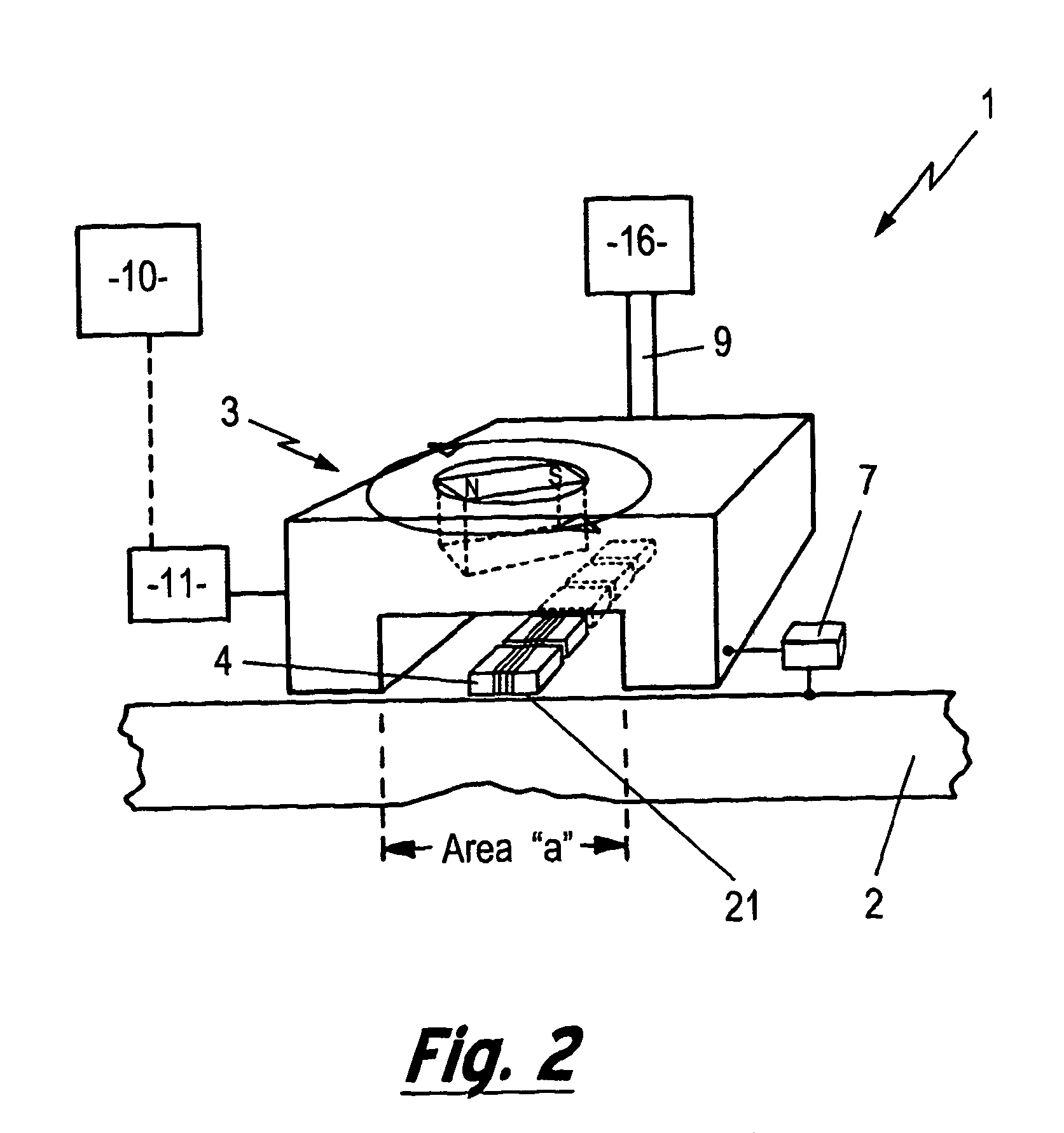
Wireless Sensing System for Non-Invasive Monitoring of Attributes of Contents in a Container
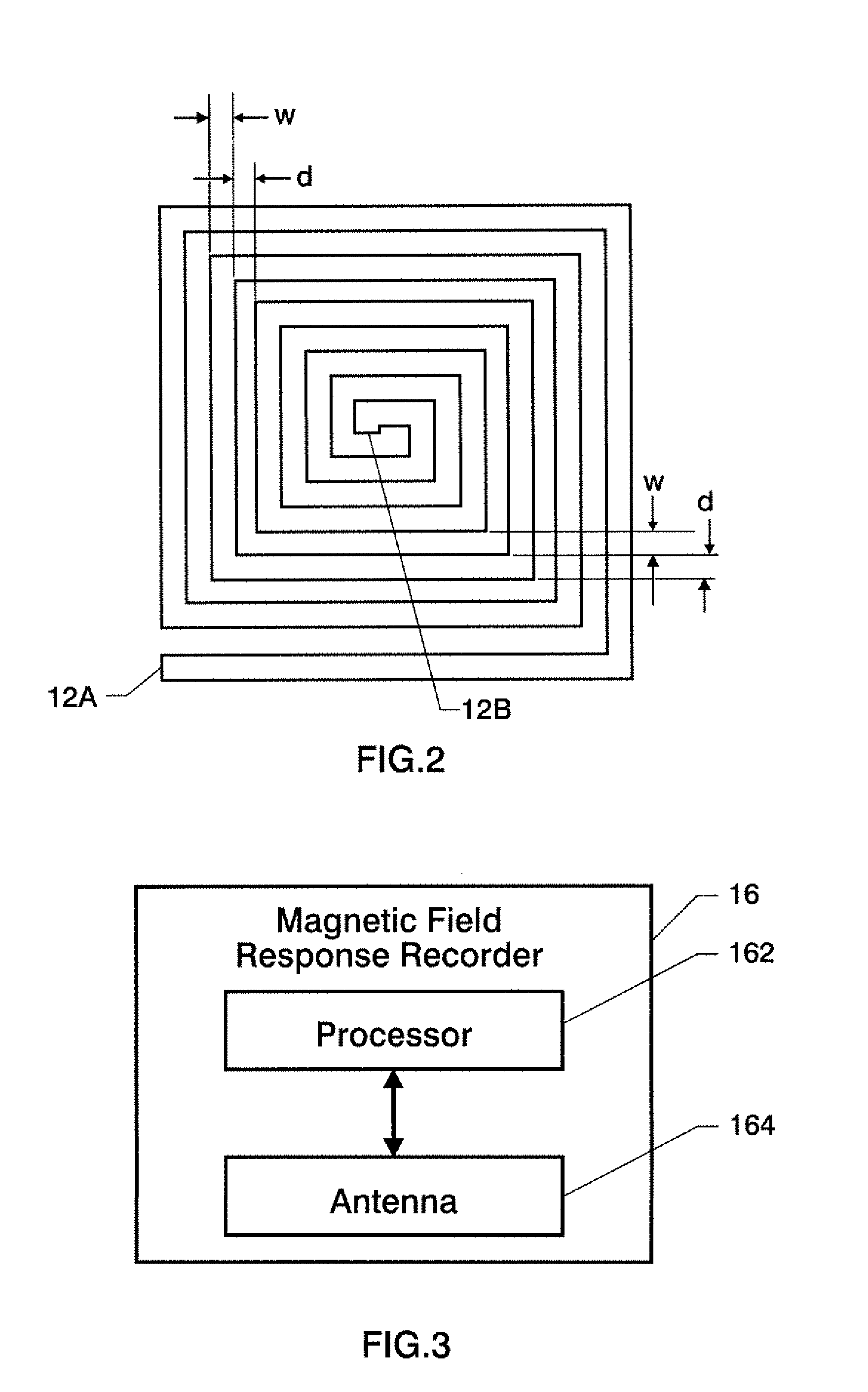
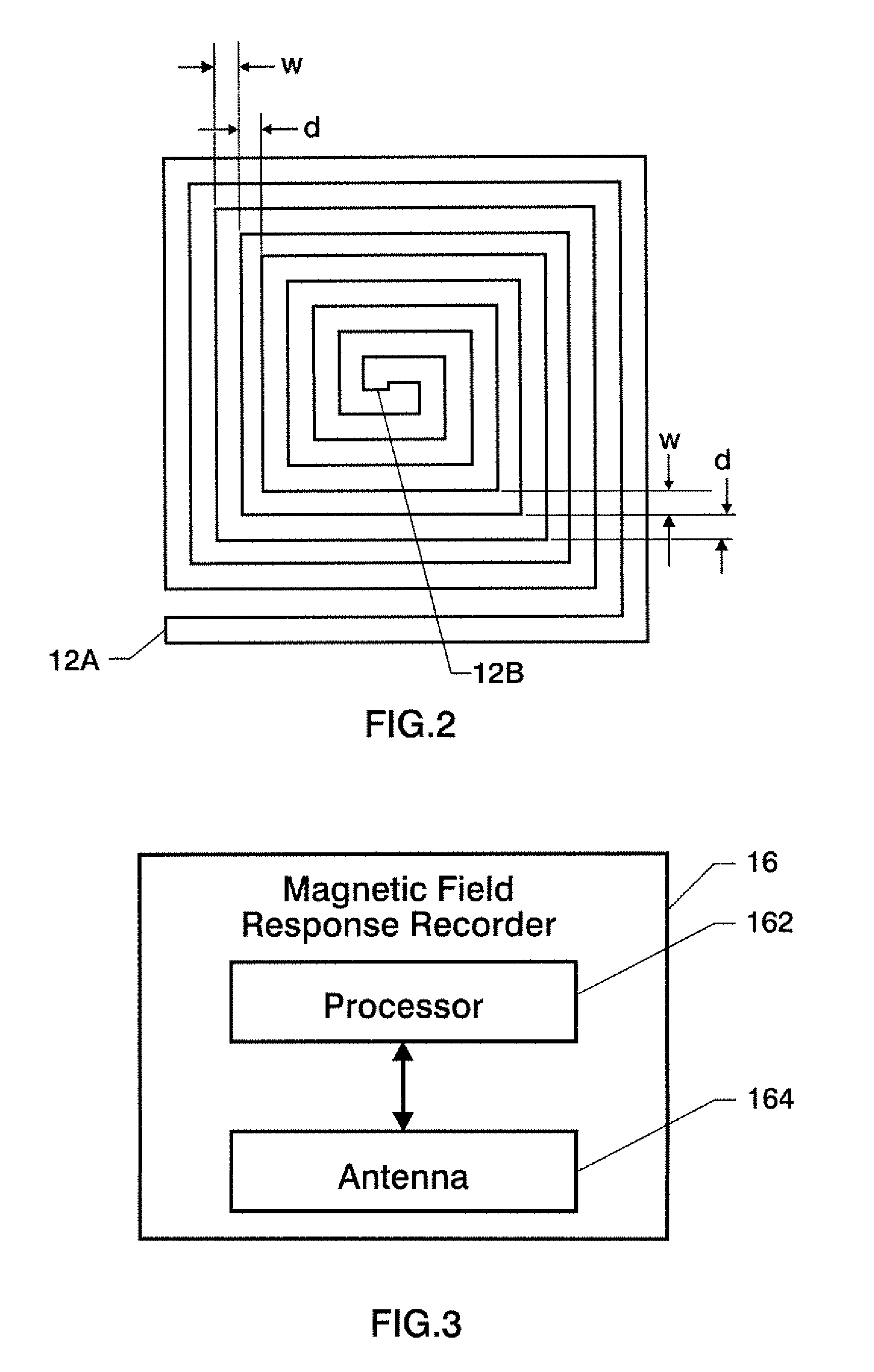
A wireless sensing system monitors the level, temperature, magnetic permeability and electrical dielectric constant of a non-gaseous material in a container. An open-circuit electrical conductor is shaped to form a two-dimensional geometric pattern that can store and transfer electrical and magnetic energy. The conductor resonates in the presence of a time-varying magnetic field to generate a harmonic response. The conductor is mounted in an environmentally-sealed housing. A magnetic field response recorder wirelessly transmits the time-varying magnetic field to power the conductor, and wirelessly detects the harmonic response that is an indication of at least one of level of the material in the container, temperature of the material in the container, magnetic permeability of the material in the container, and dielectric constant of the material in the container.
Owner:NASA
Wireless sensing system for non-invasive monitoring of attributes of contents in a container
A wireless sensing system monitors the level, temperature, magnetic permeability and electrical dielectric constant of a non-gaseous material in a container. An open-circuit electrical conductor is shaped to form a two-dimensional geometric pattern that can store and transfer electrical and magnetic energy. The conductor resonates in the presence of a time-varying magnetic field to generate a harmonic response. The conductor is mounted in an environmentally-sealed housing. A magnetic field response recorder wirelessly transmits the time-varying magnetic field to power the conductor, and wirelessly detects the harmonic response that is an indication of at least one of level of the material in the container, temperature of the material in the container, magnetic permeability of the material in the container, and dielectric constant of the material in the container.
Owner:NASA
Electromagnet inspection apparatus and method
ActiveUS20120306483A1Less sensitiveEfficient detectionPermeability measurementsUsing electrical meansPartial saturationComputer module
A method and apparatus for the inspection of electrically conductive components is described. The described apparatus comprises a sensor module having a magnetiser unit suitable for generating a variable DC magnetic field within the test component and an eddy current probe. The variable DC magnetic field and eddy current probe are configured to perform a partial saturation eddy current test upon the test component. The eddy current probe further comprises a magnetic field sensor that provides a means for measuring the permeability within the test component. Employing the magnetic field sensor provides apparatus that is more accurate and flexible in its modes of operation since such sensors provide a means for the actual permeability of a material being tested to be measured. The described methods and apparatus find particular application in the inspection of tubular components used in the oil and gas exploration and production industries.
Owner:SONOMATIC
Remote environment inspection apparatus and method
ActiveUS20130127452A1Magnetic field strength can be changedLess sensitivePermeability measurementsUsing electrical meansNon destructivePartial saturation
An inspection tool for the non-destructive testing of a test component made of an electrically conductive material is described. The inspection tool employs movably mounted permanent magnets, which provides a means for generating a variable DC magnetic field within the test component, and eddy current probes so as to provide a means for performing a partial saturation eddy current test upon the test component. The eddy current probe preferably comprises an integrated magnetic field sensor which increases the accuracy and flexibility of the modes of operation of the described apparatus and methods. The described apparatus and methods are particularly suited for the inspection of tubular components that are often remotely located within the oil and gas exploration and production industries.
Owner:SONOMATIC
Method and Apparatus for Magnetic Response Imaging
InactiveUS20130187641A1Easy to detect and measureEffectively and economicallyWeather/light/corrosion resistancePermeability measurementsEngineeringMagnetic response
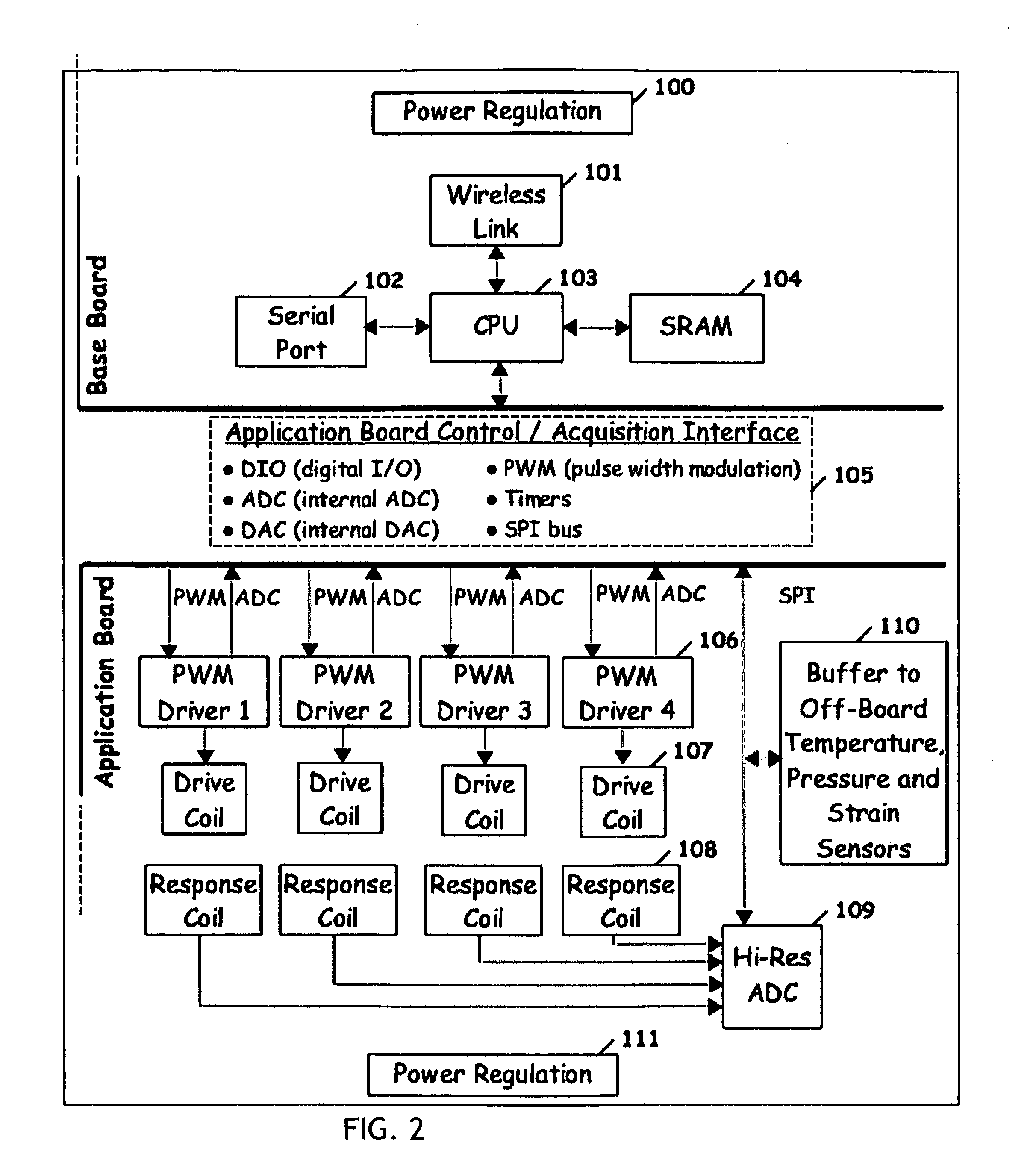
A method for identifying, measuring, and monitoring metal loss through corrosion ferromagnetic piping includes drive coils secured to the pipe and driven to emit a magnetic field which is transmitted through the object by magnetic domains in the object. Response coils detect the magnetic domains and generate a response signal. Response coils may be saddle or loop coils, or printed coils on flexible substrates that are applied to conform to the pipe peripheral surface. The system operates reiteratively over an extended period of time to detect loss of magnetic domains which is an important indicator of corrosion and deterioration of the object.
Owner:SINGER JEROME R
Paramagnetic particle detection
InactiveUS20010050555A1High sensitivityAccurately determinePermeability measurementsBiological testingHemt circuitsCondensed matter physics
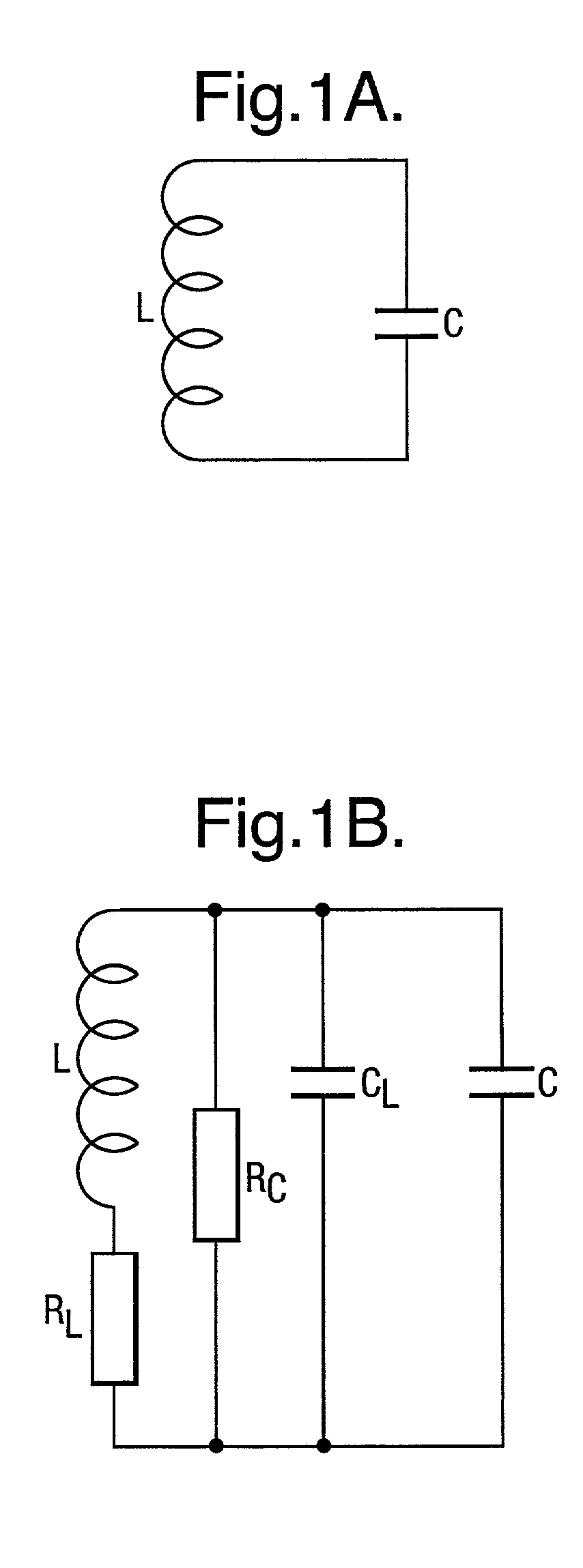
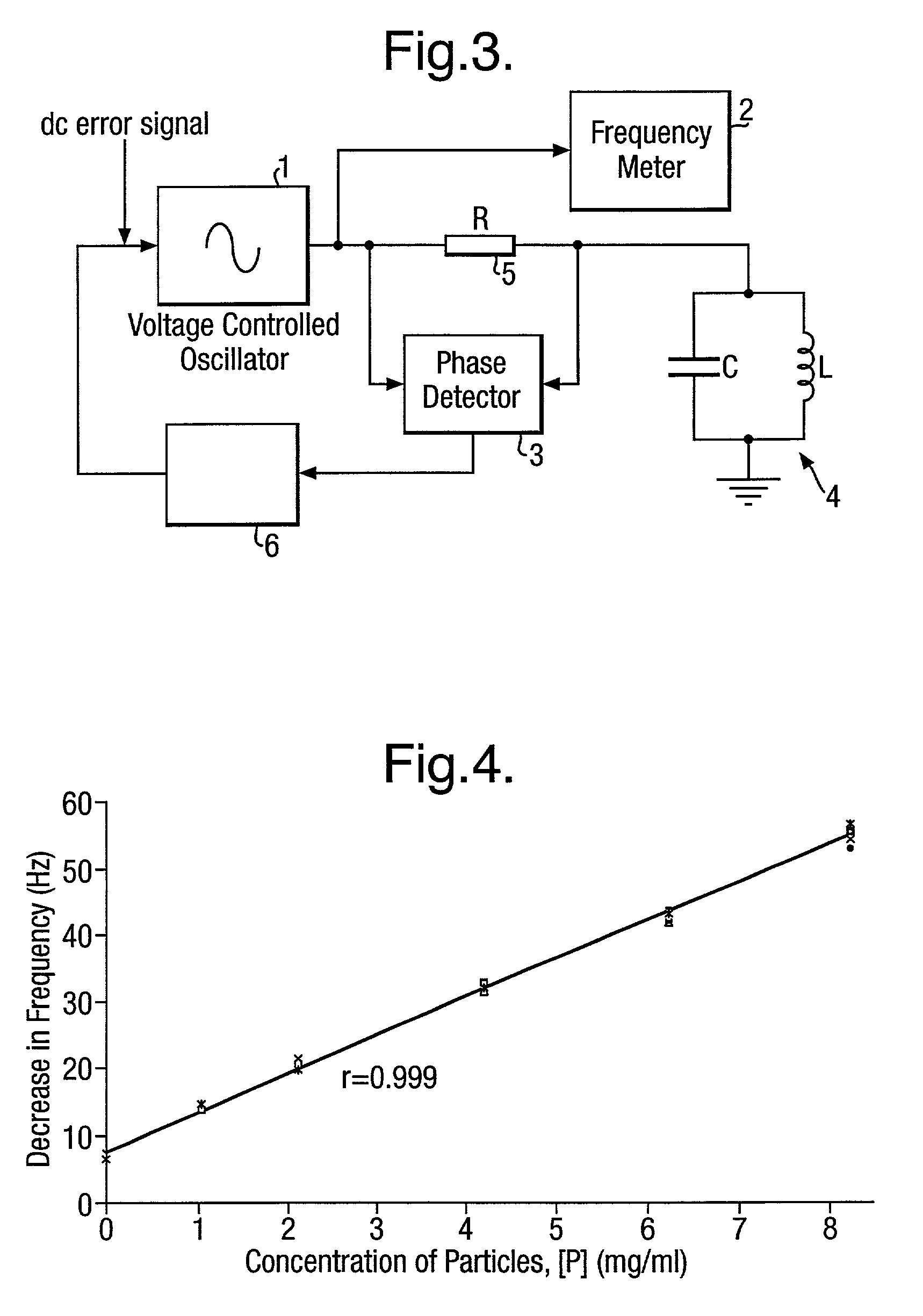
A method of determining the number of magnetic particles within a sample using a tuned circuit having a capacitor and a coil. The method comprises: a. determining the difference in the resonant frequency of the tuned circuit when the sample is exposed to a magnetic field generated by the coil and when the sample is not exposed to the magnetic field generated by the coil; and b. using the difference in the resonant frequency to determine the number of magnetic particles within the sample.
Owner:RANDOX LAB LTD
Process control and damage monitoring
InactiveUS7095224B2Promote accurate modelingImprove ObservabilityTesting/calibration apparatusPermeability measurementsSensor arraySingle element
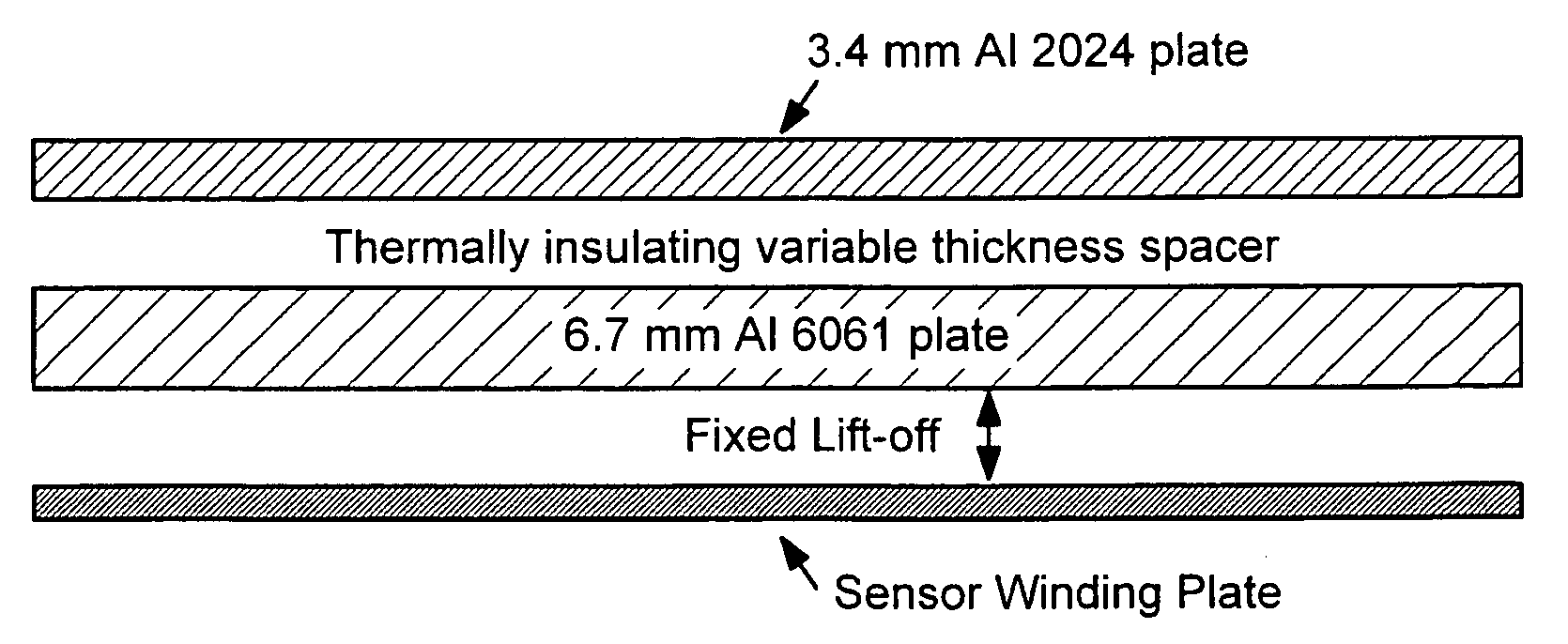
A process control method is described which uses measurements from magnetic field sensors to monitor the condition of material, such as from a heat treatment process. The sensors can be single element sensors or sensor arrays, can be used to periodically inspect selected locations, mounted to the test material, or scanned over the test material to generate two-dimensional images of the material properties. The sensors can be exposed to the same process conditions as the material, such as elevated temperatures, or the shielding layers can be placed between the test material and the sensors to reduce sensor exposure to the processing conditions. Additional property measurements, such as sensor lift-off, can be used to ensure proper sensors operation.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
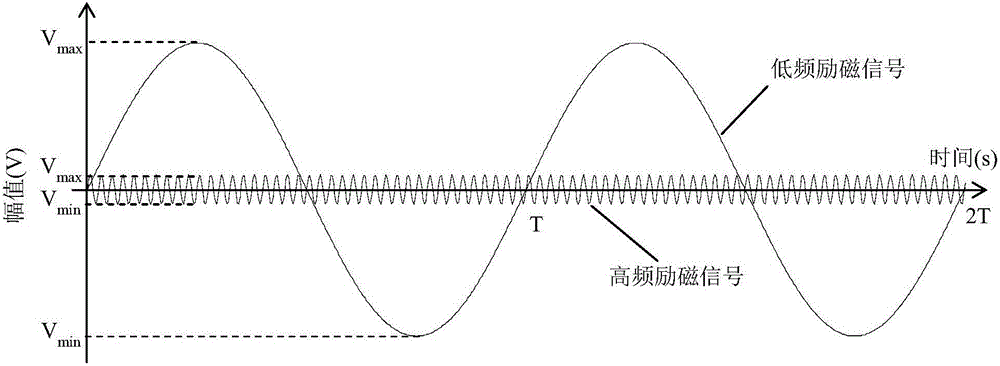
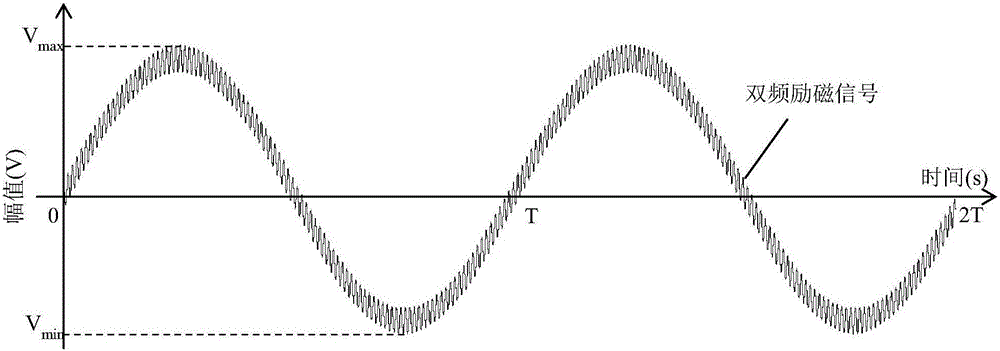
Common source double-frequency excitation type multifunctional micro-magnetic signal synchronous detection method
ActiveCN105911489ARealize synchronized measurementsImprove detection efficiencyPermeability measurementsHysteresis curve measurementsMagnetic field magnitudeMagnetic signal
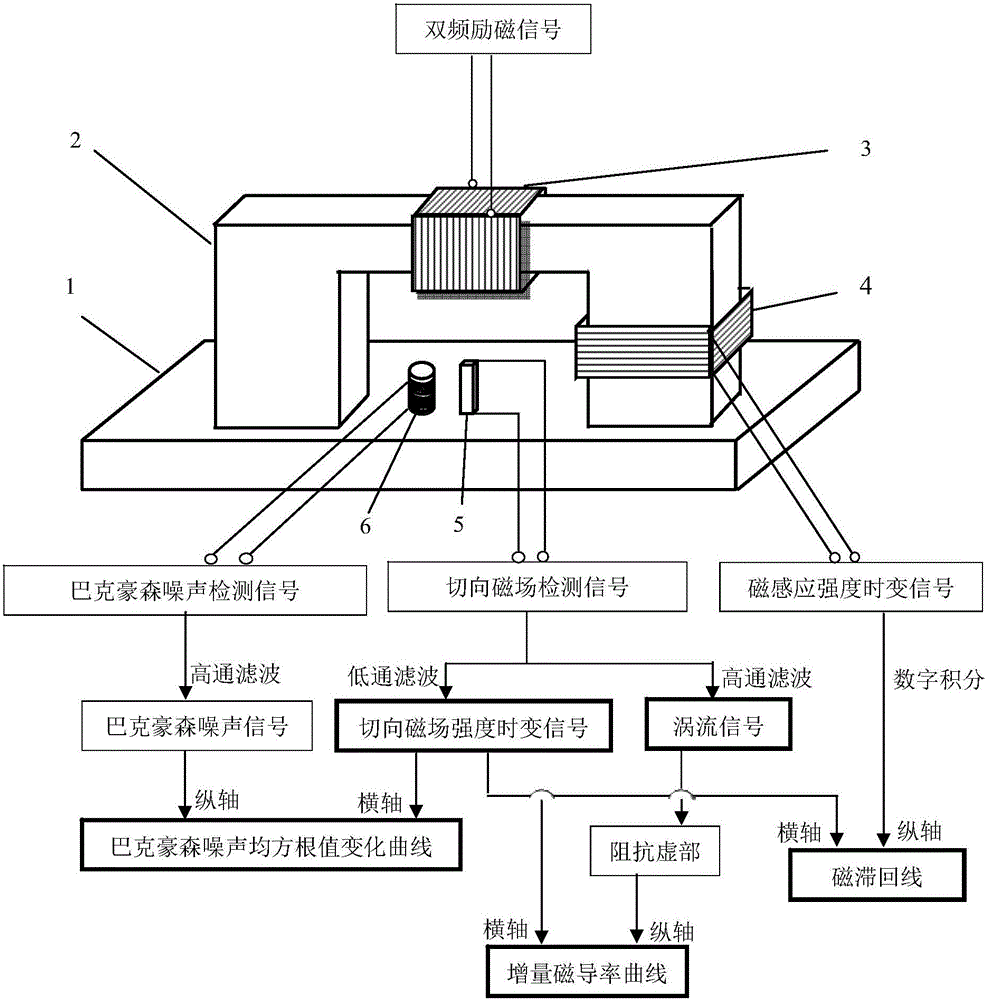
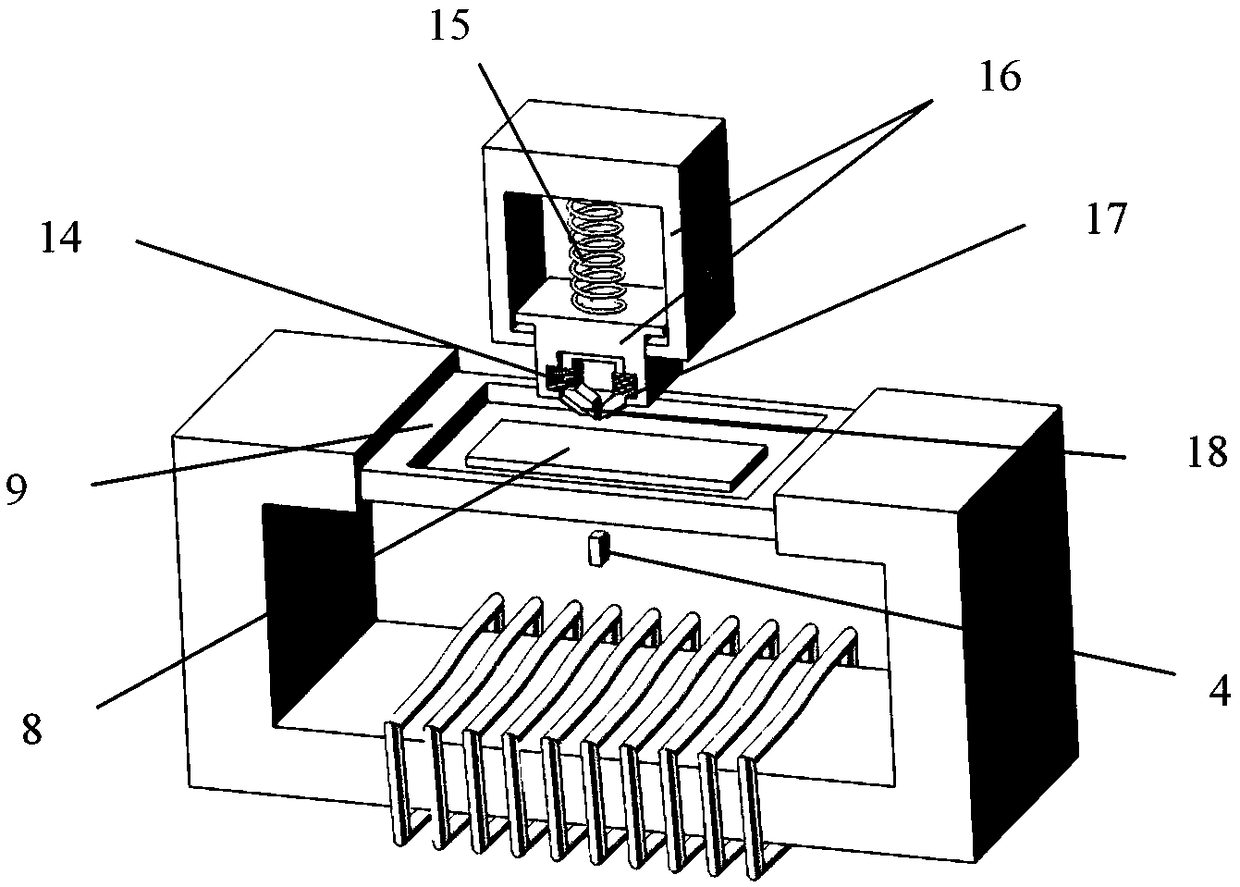
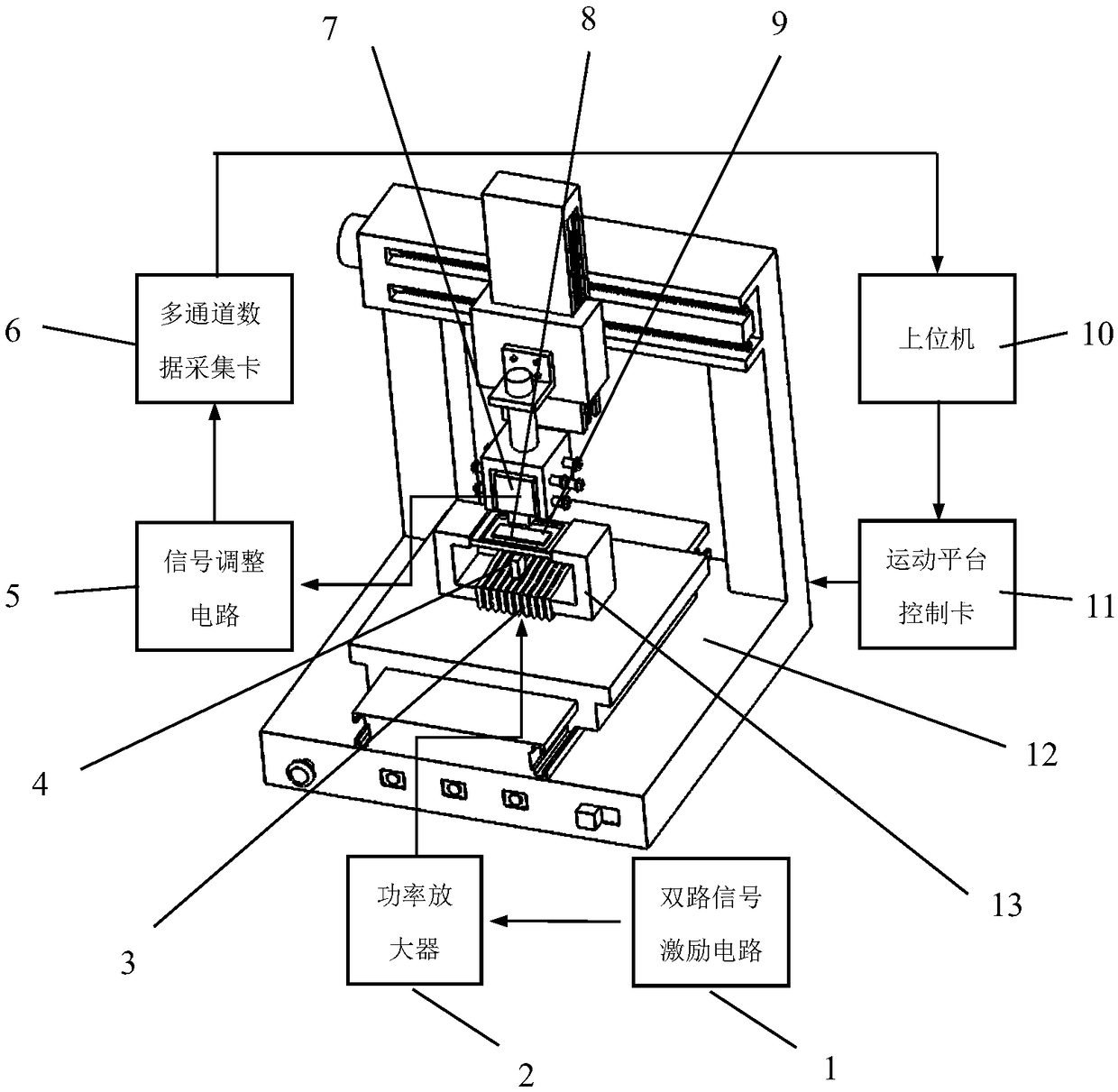
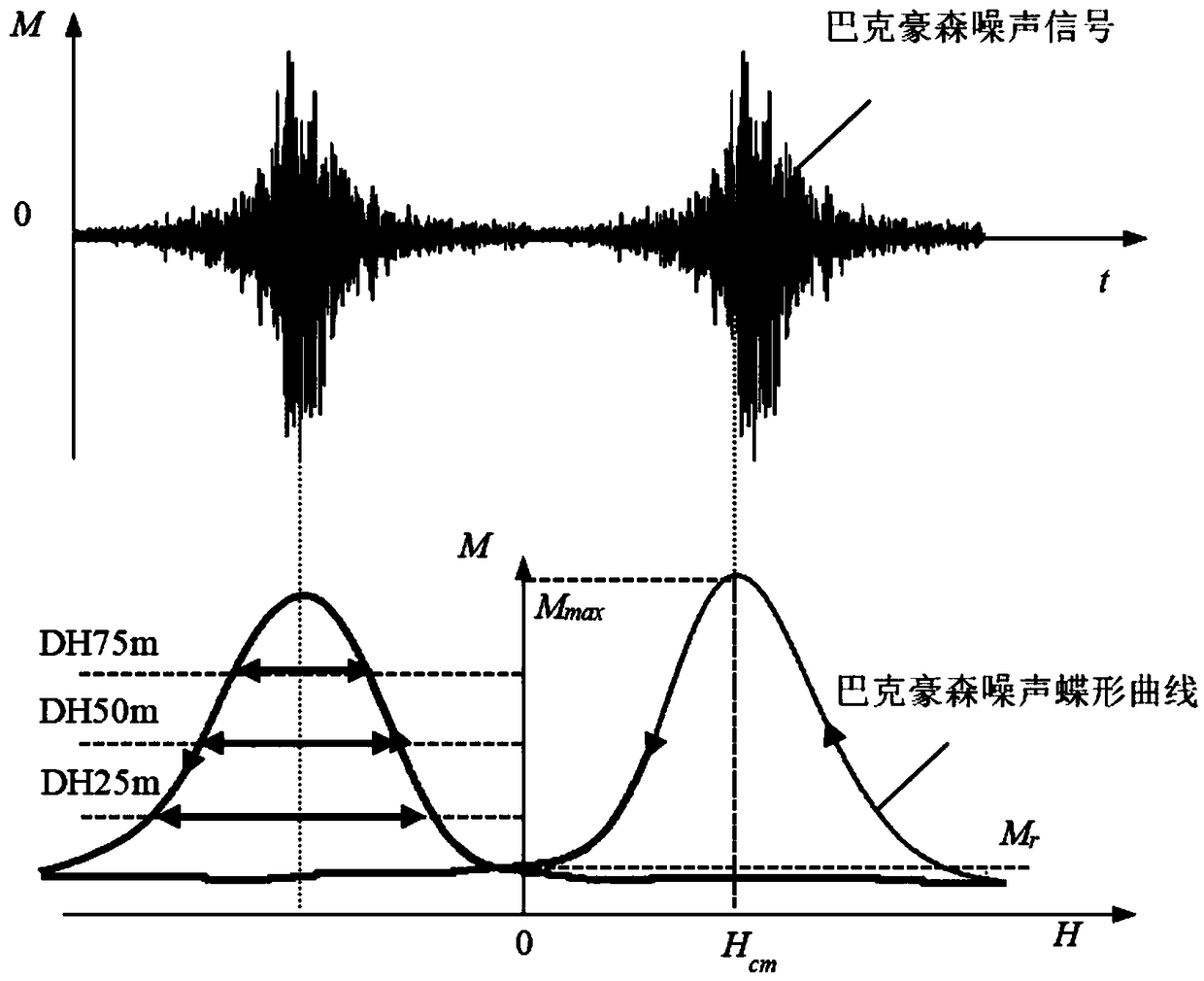
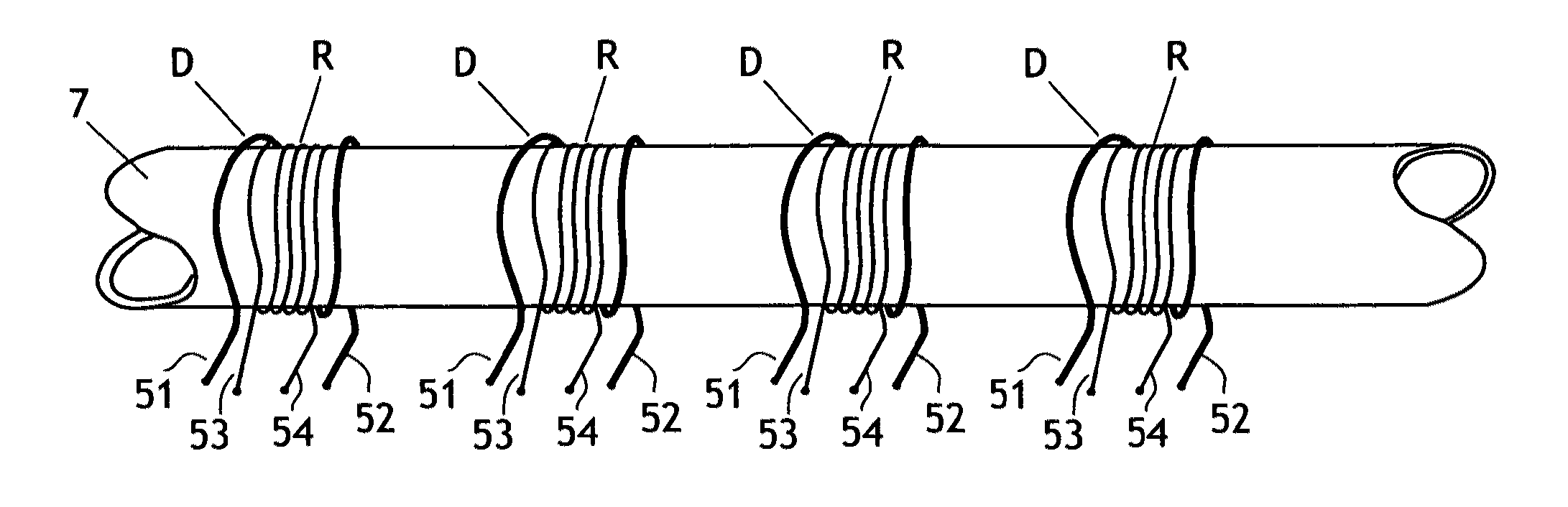
A common source double-frequency excitation type multifunctional micro-magnetic signal synchronous detection method is disclosed and belongs to the technical field of micro-magnetic nondestructive testing. Via use of the common source double-frequency excitation type multifunctional micro-magnetic signal synchronous detection method, five types of typical micro-magnetic detection parameters can be obtained synchronously, and detecting efficiency can be greatly improved. A standard micro-magnetic probe comprises an excitation magnetic circuit consisting of a magnetic core and an excitation wire coil, an induction wire coil wounded around the magnetic core, a Hall element used for detecting surface tangential magnetic field change of a ferromagnetic component being detected, and a Barkhausen noise detection wire coil. Sine wave superposed signals having a low frequency less than 100 Hz and a high frequency greater than 1k Hz that matche with an amplitude ration are used as excitation signals, and the excitation signals are sent into the excitation wire coil of the standard micro-magnetic probe so as to magnetize the ferromagnetic component being detected. The induction wire coil, the Hall element and the Barkhausen noise detection wire coil are respectively used for synchronously picking characteristic signals such as magnetic induction intensity time-varying signals, tangential magnetic field detection signals and Barkhausen noise detection signals; magnetic hysteresis loops, tangential magnetic field intensity time-varying signals, Barkhausen noise, eddy current impedance and incremental magnetic permeability can be quickly detected.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for Measuring Magnetic Permeability and Reference Sample Used in the Latter
InactiveUS20090102458A1Precise positioningStay in shapePermeability measurementsElectrical measurementsCapacitanceReference sample
The invention relates to a method for measuring the magnetic permeability of a magnetic material by measuring the magnetic interaction of an electromagnetic field with this material by using a measuring device including a measuring cell connected through a microwave frequency cable (13) to a vector network analyser (12), said method comprising steps for gauging / calibrating said measuring device, for determining corrective coefficients to be applied to the measurements obtained by means of this device, for verifying the non-drift of this device, these steps being carried out with the help of a reference sample, wherein a reference sample is used, comprising at least one inclusion which enables creation, in a given volume, of a local artificial permeability, each inclusion being achieved by combining at least one inductive component possibly associated with a combination of at last one capacitive and / or resistive and / or active component, the frequency response of the electromagnetic properties of each volume being adjusted by the value and the assembly architecture of the components.The invention also relates to such a reference sample.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Device and method for measuring electromagnetic parameter of material in microwave heating process
ActiveCN108828380AEasy to measureAccurate measurementDielectric property measurementsPermeability measurementsMicrowaveEngineering
The invention relates to a device and method for measuring the electromagnetic parameter of a material in a microwave heating process. According to the device and method, a waveguide switch is adoptedto realize the controllability of the separation of a microwave heating system from an electromagnetic parameter measuring system; a microwave heating process and a microwave heating process are alternately performed so as to measure the electromagnetic parameter of the material during the entire microwave heating process. The device and method of the invention are simple and highly feasible. With the device and method adopted, a foundation can be laid for the analysis and adjustment of the microwave heating process of the material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Micro-magnetic Detecting Method and Micro-magnetic Detecting Device
ActiveUS20170176391A1Improve performance and adaptabilityImprove detection efficiencyPermeability measurementsAc/pulses peak value measurementsLinear relationshipLinearity
A micro-magnetic detecting method includes the steps of: detecting a magnetic induction intensity along a first direction on a surface of a detected object to generate a detection signal, determining whether an amplitude of the detection signal is an anomalous value at a first position of the surface of the detected object, wherein the anomalous value is a value which is inconsistent with a linear value of the detection signal at the first position, and the linear value is a value that satisfies a linear relationship of the detection signal, and determining there is a defect at the first position of the detected object in case that the amplitude of the detection signal is the anomalous value. Accordingly, it detects the magnetic induction intensity on the surface of the detected object so as to detect its surface and internal defects when it remains in its original status.
Owner:NINGBO YINZHOU CITAI ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Microstrip nanometer film microwave electromagnetic parameter testing apparatus
InactiveCN106018973ANo damageSimple and fast operationDielectric property measurementsPermeability measurementsMicrowaveCoaxial cable
The invention provides a microstrip nanometer film microwave electromagnetic parameter testing apparatus, which belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic parameter testing. The apparatus is provided with a microstrip clamp, a microwave vector network analyzer, a GPIB data acquisition card, and a computer. The microstrip clamp is composed of an L-shaped base, an upper conduction band, an adjustable short circuit piece, an SMA connector, a shield cover and a fixed platform. One end of the L-shaped base is provided with a circular hole; the other a step. The two ends of the adjustable short circuit piece are provided with grooves. The SMA connector is mounted on the L-shaped base and is connected to the coaxial cable of the microwave vector network analyzer; a nanometer film sample is placed at the center position of the input end and the adjustable short circuit piece. The microstrip clamp is fixed on the fixed platform, and the four corners of the fixed platform are equipped with height adjustable supporting rods. The fixed platform is evenly engraved with a set of horizontal lines marked with scales. Two spring clamp sheets are locked on the fixed platform and are placed on the end face and the face of the microstrip clamp respectively. The apparatus can achieve precise measurement, cause no damage and is convenient to operate.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Microwave sensor for synchronously measuring dielectric constant and magnetic conductivity of magnetic medium material
ActiveCN110133375AOvercoming only a single measurement of dielectric constantOvercoming the disadvantages of magnetic permeabilityResistance/reactance/impedencePermeability measurementsElectrical field strengthMagnetic media
The invention discloses a microwave sensor for synchronously measuring a dielectric constant and magnetic conductivity of a magnetic medium material. The microwave sensor comprises two microstrip linestructures, a medium layer, a metal sheet and two slotted metal CSRR (complementary split-ring resonator) structures from a top layer to a bottom layer. Each slotted metal CSRR structure is composedof an inner slot ring and an outer slot ring, wherein each of the inner slot ring and the outer slot ring is provided with an opening, and facing directions of the openings are identical; two oppositeright angles of the opening of the inner slot ring and two opposite right angles of the opening of the outer slot ring are all folded inwards in an alignment mode, and the opening of the outer slot ring extends towards the inside and outside of the outer slot ring to form channels; the part between the channels of the opening of the outer slot ring is a region with maximum magnetic field intensity, and the region is used to contain a to-be-detected sample for measuring the magnetic conductivity of the sample; and the part between the channels, where the two inwards-folded right angles of theinner slot ring and the two inwards-folded right angles of the outer slot ring are connected, is a region with maximum electric field intensity, and the region is used to contain the to-be-detected sample for measuring the dielectric constant of the sample. According to the microwave sensor, the form of a differential structure is adopted, differential measurement can be performed on the dielectric constant and the magnetic conductivity, and the influence of environment factors is eliminated by the adoption of a relative measurement mode.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Electromagnet inspection apparatus with a movable magnet and method for non-destructive testing of electrically conductive test components
ActiveUS9285345B2Less sensitiveEfficient detectionPermeability measurementsUsing electrical meansNon destructivePartial saturation
An inspection tool for the non-destructive testing of a test component made of an electrically conductive material is described. The inspection tool employs movably mounted permanent magnets, which provides a means for generating a variable DC magnetic field within the test component, and eddy current probes so as to provide a means for performing a partial saturation eddy current test upon the test component. The eddy current probe preferably comprises an integrated magnetic field sensor which increases the accuracy and flexibility of the modes of operation of the described apparatus and methods. The described apparatus and methods are particularly suited for the inspection of tubular components that are often remotely located within the oil and gas exploration and production industries.
Owner:SONOMATIC
Sensors
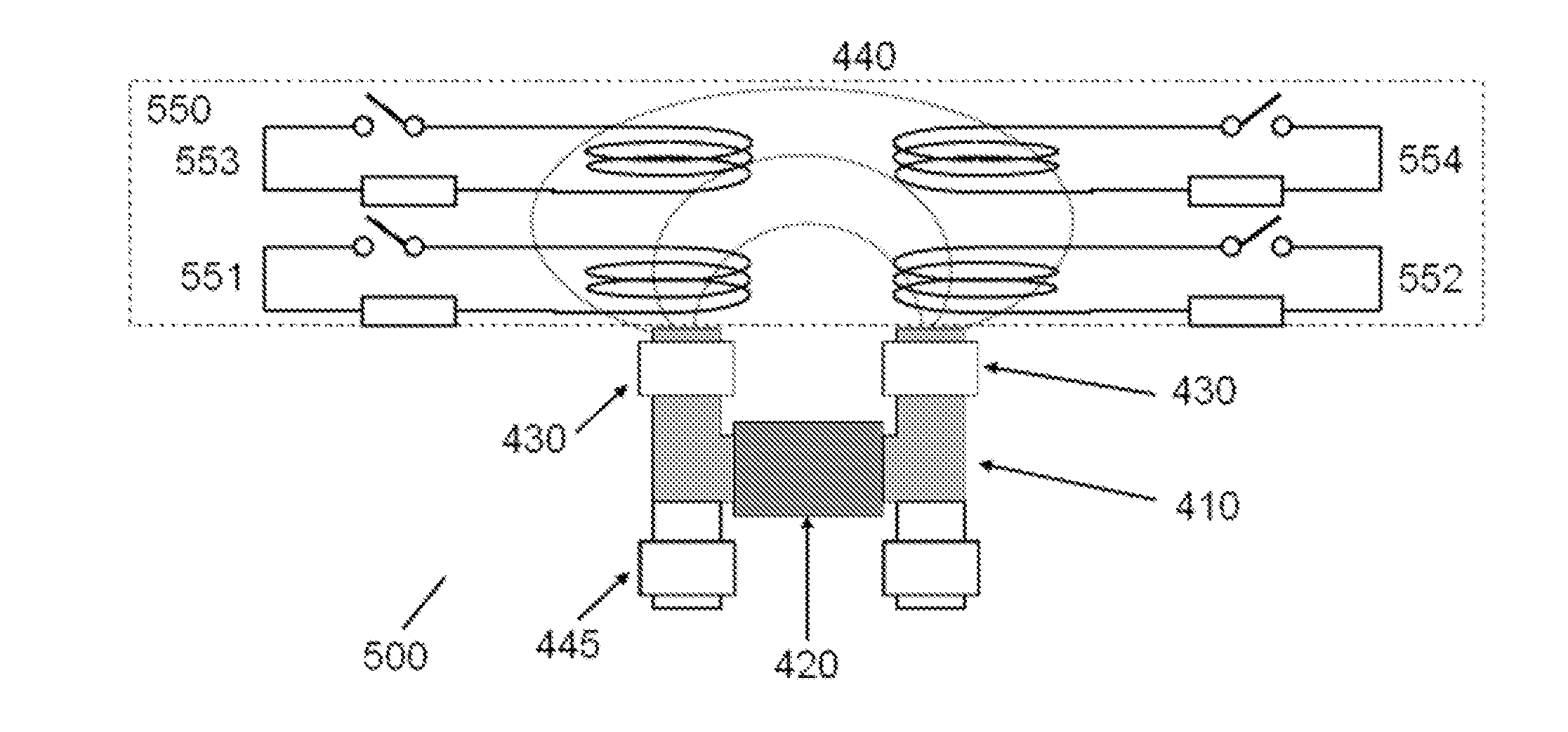
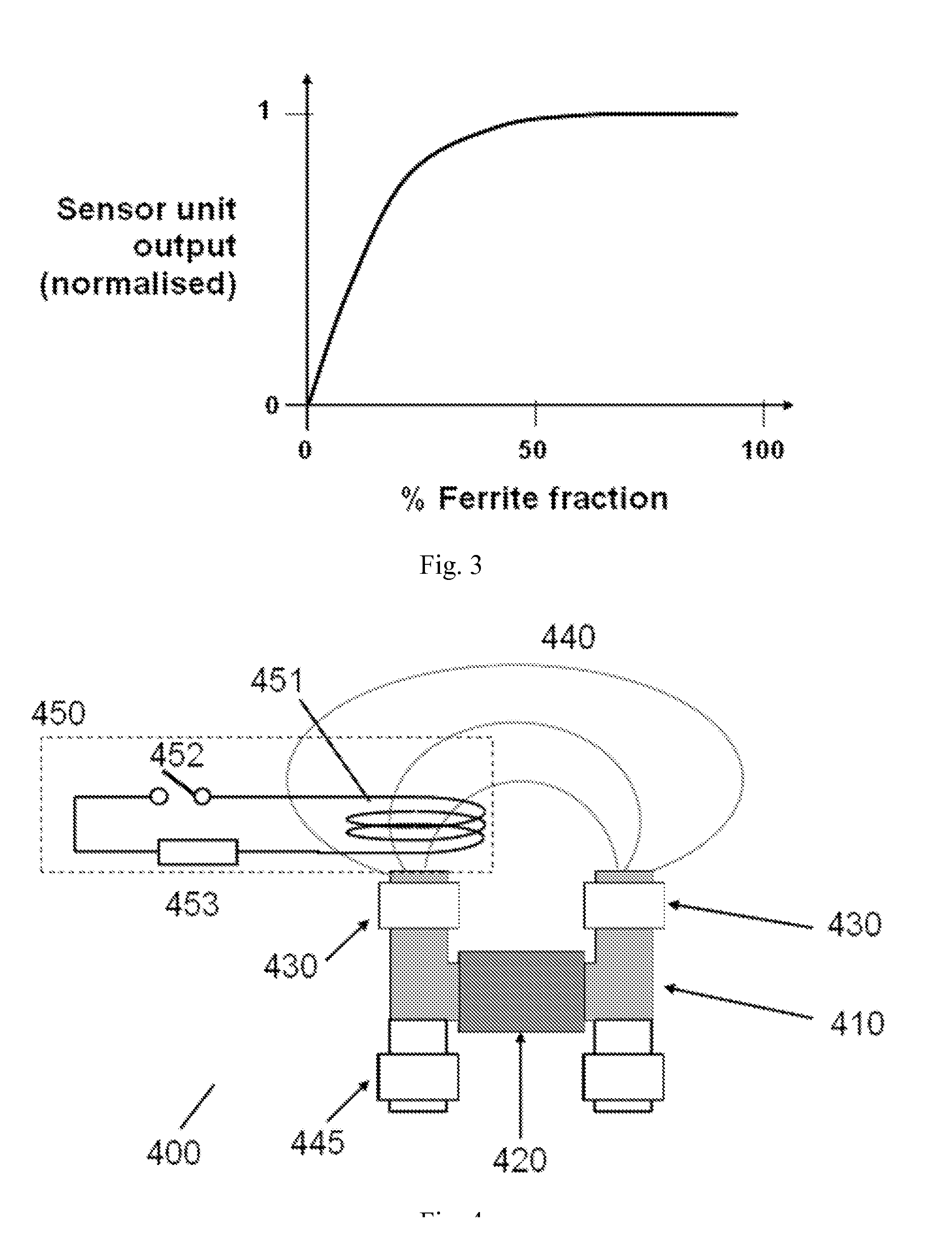
ActiveUS20140049251A1Permeability measurementsTemperature control devicePower flowElectromagnetic shielding
Embodiments of the present invention provide an electromagnetic sensor (400) for detecting a microstructure of a metal target, comprising: a magnetic device (410, 420) for providing an excitation magnetic field; a magnetometer (430) for detecting a resultant magnetic field induced in a metal target; and a calibration circuit (450, 551, 552, 553, 554) for generating a calibration magnetic field for calibrating the electromagnetic sensor, wherein the calibration reference magnetic field is generated by an electrical current induced in the calibration circuit by the excitation magnetic field.
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
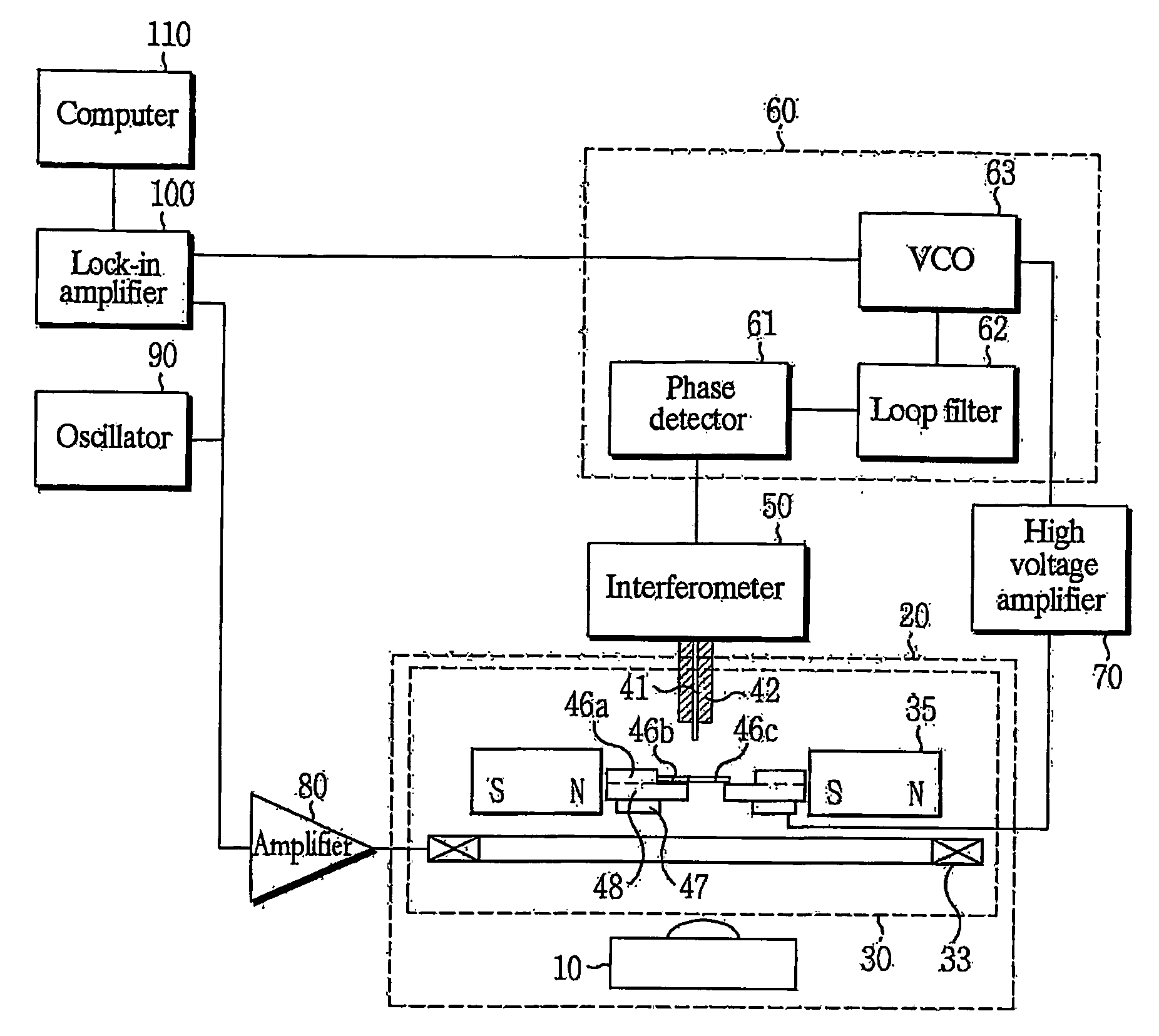
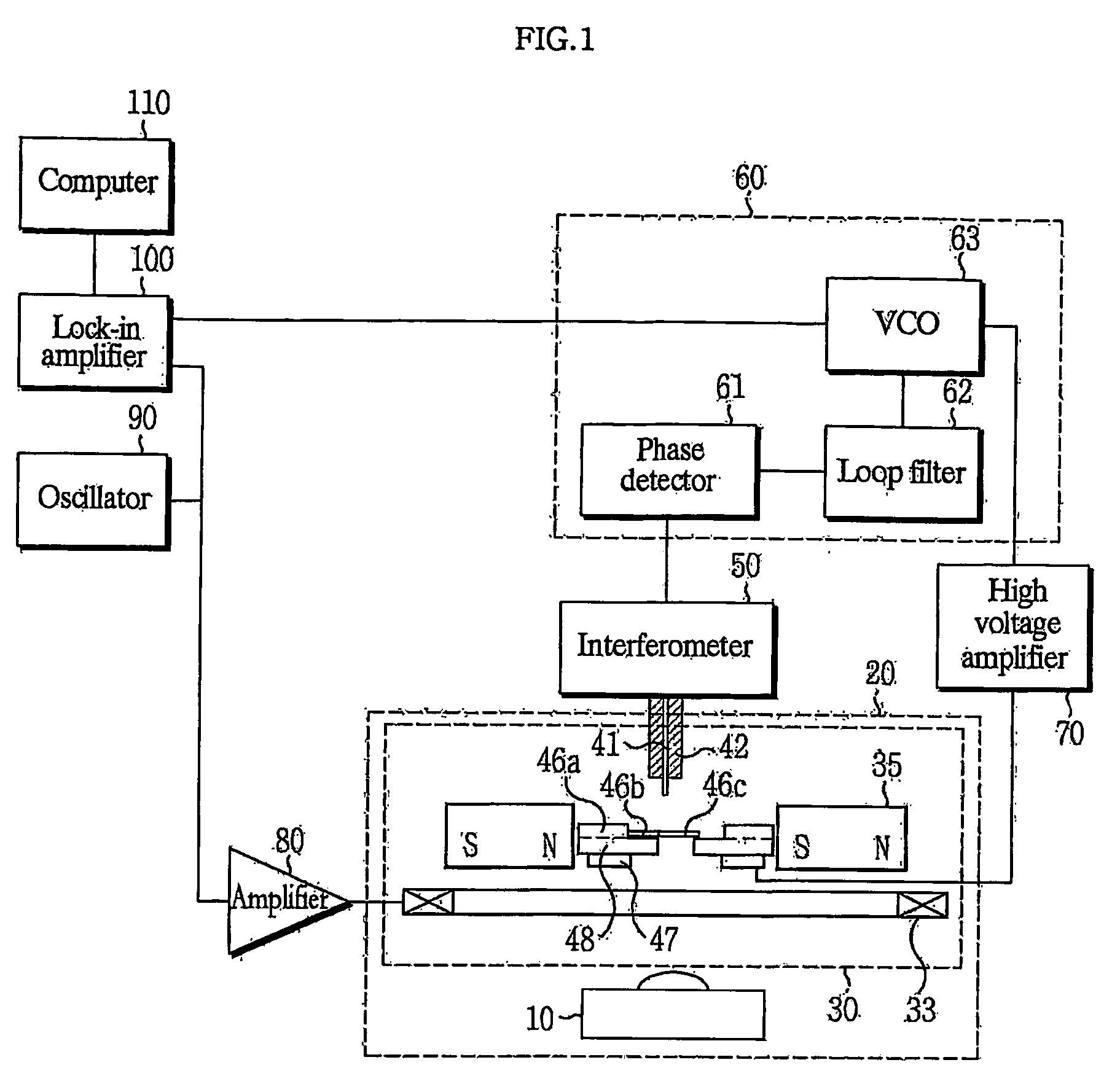
Permeability measurement apparatus
InactiveUS20080169805A1High sensitivitySuppression of Leakage FluxPermeability measurementsMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMeasurement deviceCoil inductance
A permeability measurement apparatus includes a magnetic field generation means applying an alternating magnetic field having a predetermined frequency to a magnetic substance to be measured; a probe needle placed in proximity or in contact to a microscopic area of the magnetic substance to be measured to which the alternating magnetic field is applied; a resonator including a coil wound on the probe needle, and generating a magnetic field having a resonant frequency higher than the frequency of the alternating magnetic field applied on the microscopic area having the probe needle in proximity or in contact thereto, and having an inductance of the coil varied as permeability in the microscopic area varies; and a measurement means measuring the permeability of the microscopic area of the magnetic substance to be measured based on the variation of the resonant frequency of the resonator according to the variation of the coil inductance.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Method and apparatus for sensing magnetic fields
InactiveUS20130141081A1Reduce penetrationEffective wire cross-section increasesPermeability measurementsUsing electrical meansElectrical impedanceElectron
A method for detecting magnetic fields, particularly for detecting the position of objects with a preferably oblong, soft-magnetic element, which is connected to electronics, with via the electronics the impedance of the soft-magnetic material is measured, characterized in that a magnetic field is used in which by the position of an object which is located in an arrangement with the soft-magnetic material the magnetic field develops at the location of the soft-magnetic material, with the magnetic permeability μ of the soft-magnetic material adjusting, depending on the magnetic field and thus the position of the object. A respective device serves for applying the method according to the invention.
Owner:MICRO EPSILON MESSTECHNIK GMBH & CO KG
High-resolution Barkhausen noise and incremental permeability scanning imaging system
InactiveCN109407018AEnabling imaging of magnetic propertiesImprove spatial resolutionPermeability measurementsApparatus for force/torque/work measurementFerromagnetismMagnetic signal
The present invention discloses a high-resolution Barkhausen noise and incremental permeability scanning imaging system. An upper computer controls a multi-functional electromagnetic detection deviceto perform detection of feature magnetic signals such as localization Barkhausen noise, the eddy and the incremental permeability for a ferromagnetic block or magnetic film materials, software in theupper computer can extract at least 14 items of magnetic parameters from the detected feature magnetic signals; a triaxial movement platform is employed to carry a magnetic head in the electromagneticdetection device to perform plane scanning of the ferromagnetic block or the magnetic film materials to obtain a magnetic parameter space distribution imaging result; and the air gap width of a tailend of a magnetic core employed by the magnetic head is changed about 0.2-10[Mu]m, and the lateral resolution of the magnetic head can be regulated in the range of 10-100 [Mu]m. The distribution stateof a plurality of magnetic parameters at the surface of a testpiece is measured to achieve magnetic property imaging so as to reflect the distribution state of the microstructures and the residual stresses in the materials.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for magnetic response imaging
InactiveUS20120126798A1Measurement stabilityDetect small levelWeather/light/corrosion resistancePermeability measurementsEngineeringMagnetic response
An apparatus and method for identifying, measuring, and monitoring metal loss through corrosion or other deleterious factors in ferromagnetic piping and ferromagnetic objects. Drive coils secured to the object are driven to emit a magnetic field which is transmitted through the object by magnetic domains in the object. Response coils detect the magnetic domains and generate a response signal. The drive and response signals can penetrate insulating materials and non-ferromagnetic metallic coverings of the piping and vessels. The system operates reiteratively over an extended period of time, e.g., months or years, to detect loss of magnetic domains which is an important indicator of corrosion and deterioration of the object.
Owner:4D IMAGING
Sensor used for magnetic conductivity measurement and measurement method thereof
InactiveCN107085191AEasy to fixPromote structural optimizationPermeability measurementsAudio power amplifierExcitation current
The invention provides a sensor used for magnetic conductivity measurement. The sensor comprises a four-tap solenoid coil. Four taps are led out of the solenoid coil from the top to the bottom in turn. The first tap of the four taps is connected with an excitation current source which is connected with the ground. The fourth tap is connected with the ground potential of the excitation current source so as to form a current loop. The second tap and the third tap are connected with the input end of an instrument amplifier to acquire differential voltage and connected with a voltage measurement module. The invention also provides a measurement method using the sensor used for magnetic conductivity measurement. The effects of the sensor used for magnetic conductivity measurement are that the four-tap solenoid sensor is simple and feasible and can directly measure the magnetic conductivity of particle / powder material without preparing a magnetic core of the specific shape in advance; the physical model of the sensor is clear, and the relational expression between the induction value and the measured medium magnetic conductivity can be determined by the analytic formula so that structural optimization and parameter correction are facilitated; and the middle tap performs measurement so that the influence of the edge effect of the two ends of the solenoid can be avoided and the more accurate measurement result can be acquired.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Magneto resistance sensor-based magnetic conductivity electromagnetic tomography system
InactiveCN107526048AHigh sensitivityImprove reliabilityPermeability measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesSignal conditioningElectromagnetic shielding
The invention relates to a magneto resistance sensor-based magnetic conductivity electromagnetic tomography system. An electromagnetic imaging sensor is adopted as the sensor of the magneto resistance sensor-based magnetic permeability tomography system; the electromagnetic imaging sensor comprises M excitation coils, N pairs of magneto resistance sensors and an electromagnetic shielding layer, wherein the excitation coils and the magneto resistance sensors are arranged in the electromagnetic shielding layer; each excitation coil is provided with a separate excitation channel; the excitation coils are arranged on the same section outside a cylindrical object field region; the magneto resistance sensor pairs are also arranged on the same section; the excitation coils and the magneto resistance sensors are arranged on different circles; and each pair of magneto resistance sensors is located inside a certain excitation coil. Under the control of a control module, an excitation signal generation and power amplification unit generates excitation signals with different amplitudes and frequencies; the excitation signals are connected onto the designated excitation coils through a multi-channel gating switch; signals outputted by the magneto resistance sensors pass through the gating switch and are transmitted to the control module through a signal conditioning and acquisition unit; the control module demodulates the signals; and the demodulate signals are transmitted to an upper computer through a communication module.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
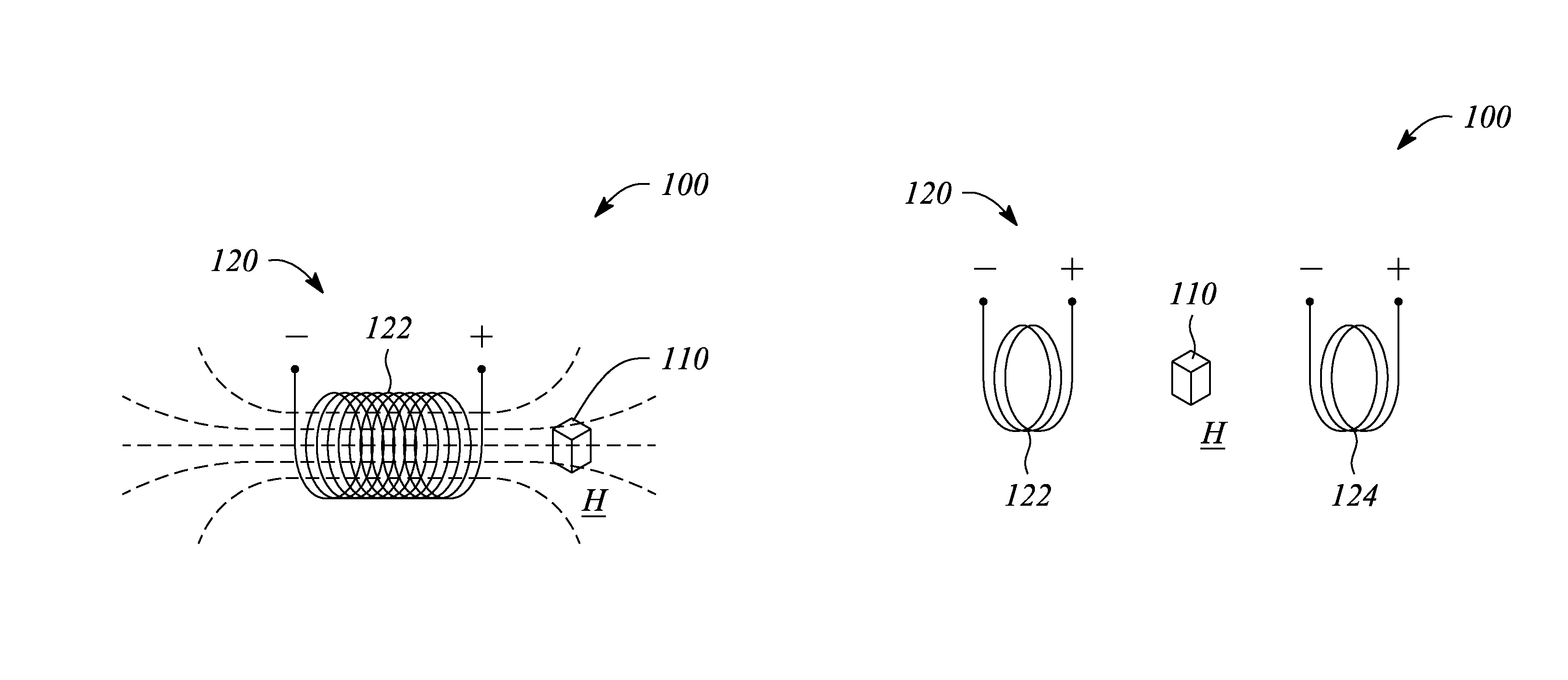
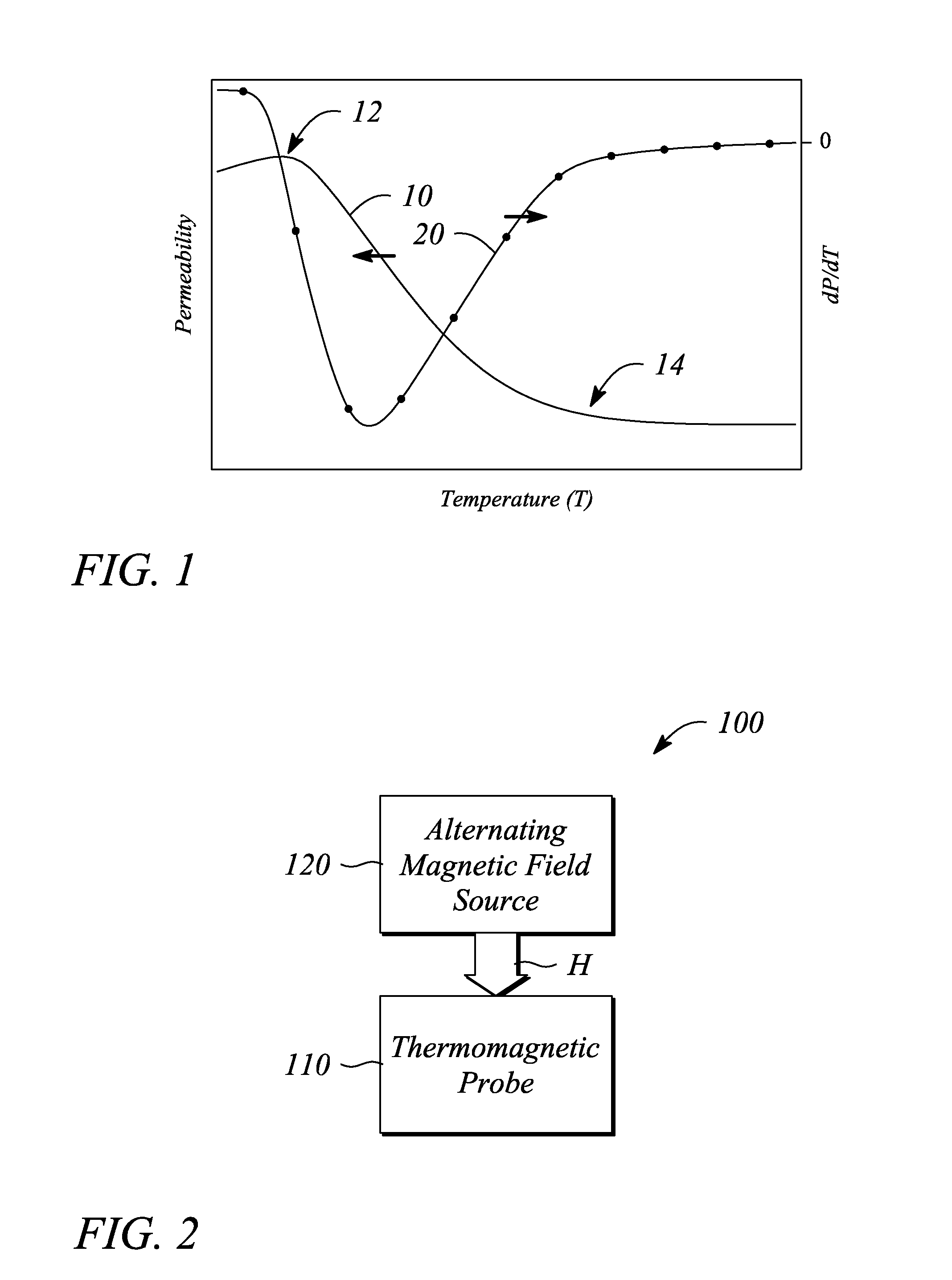
Thermomagnetic temperature sensing
ActiveUS9417292B1Decreasing temperature-dependent magnetic permeability valuePermeability measurementsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsPermeability measurementsCurie temperature
A thermomagnetic sensor includes a thermomagnetic probe that includes a ferromagnetic material having a temperature-dependent magnetic permeability characterized by a maximum magnetic permeability value at a temperature below a Curie temperature of the ferromagnetic material. The thermomagnetic sensor further includes an alternating magnetic field source to produce an alternating magnetic field in a vicinity of the thermomagnetic probe to facilitate a measurement of the temperature-dependent magnetic permeability as function of temperature remotely using a thermomagnetic effect. A predetermined relationship between the temperature-dependent magnetic permeability and temperature in a range between the maximum magnetic permeability value and the Curie temperature provides a measurement of a temperature local to the thermomagnetic probe. A battery-temperature measurement system includes the thermomagnetic probe in a battery, a magnetic field coil to apply the alternating magnetic field, and a magnetic permeability measurement apparatus to measure the temperature-dependent magnetic permeability.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method for determining the permeability of a magnetic material by coaxial line perturbation
The process determines the permeability of the magnetic material by disturbance of a hyper frequency coaxial line. In the process, a sample of the material is formed and placed in a hyper frequency coaxial line. The reflection and / or transmission of a hyper frequency electromagnetic wave on and / or through this coaxial line is measured and the result of this measurement is used to deduce the magnetic permeability of the material. The fractional volume of magnetic material in the sample compared with the volume of the disturbed coaxial line is less than 1%.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
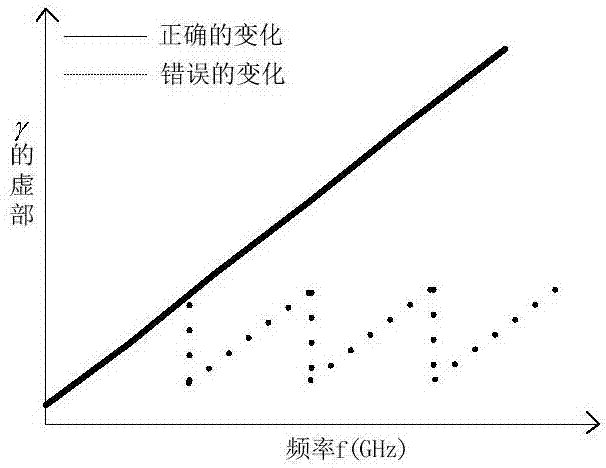
Metamaterial electromagnetic parameter inversion method based on improved K-K algorithm
ActiveCN106980095ASolve the multi-value problemImprove test accuracyDielectric property measurementsPermeability measurementsComputer scienceInversion methods
The invention discloses a metamaterial electromagnetic parameter inversion method based on an improved K-K (Kramers-Kronig) algorithm and belongs to the technical field of testing. The method solves the multi valuedness of a metamaterial electromagnetic parameter inversion process relative to a group delay method and an imaginary part compensation method, does not need to estimate the n value of a test starting frequency point or carry out complex data processing, and is high in test precision.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Microwave sensor for measuring dielectric constant and magnetic conductivity of magnetic medium material
ActiveCN110133376AImproving Impedance MatchingStrong bondageResistance/reactance/impedencePermeability measurementsDielectricElectrical field strength
The invention discloses a microwave sensor for measuring a dielectric constant and magnetic conductivity of a magnetic medium material. The microwave sensor comprises a microstrip line structure, a medium layer, a metal sheet and a slotted metal CSRR (complementary split-ring resonator) structure from a top layer to a bottom layer. The slotted metal CSRR structure is composed of an inner slot ringand an outer slot ring, wherein each of the inner slot ring and the outer slot ring is provided with an opening, and facing directions of the openings are identical; two opposite right angles of theopening of the inner slot ring and two opposite right angles of the opening of the outer slot ring are all folded inwards in an alignment mode, and the opening of the outer slot ring extends towards the inside and outside of the outer slot ring to form channels; the part between the channels of the opening of the outer slot ring is a region with maximum magnetic field intensity, and the region isused to contain a to-be-detected sample for measuring the magnetic conductivity of the sample; and the part between the channels, where the two inwards-folded right angles of the inner slot ring and the two inwards-folded right angles of the outer slot ring are connected, is a region with maximum electric field intensity, and the region is used to contain the to-be-detected sample for measuring the dielectric constant of the sample. According to the microwave sensor, the dielectric constant and the magnetic conductivity can be measured simultaneously in different regions of the same sensor, the sensor has extremely high sensitivity and Q value, and the accuracy of measurement is guaranteed.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Electromagnet inspection apparatus and method
ActiveUS20130234701A2Less sensitiveEfficient detectionPermeability measurementsUsing electrical meansMeasurement testPartial saturation
Owner:SONOMATIC
Method for detecting complex permittivity of nano film by virtue of multifunctional rectangular cavity perturbation method
InactiveCN109212322AWide detection rangeImprove applicabilityDielectric property measurementsPermeability measurementsCoaxial cableMicrowave
A method for detecting complex permittivity of a nano film by virtue of a multifunctional rectangular cavity perturbation method relates to the field of detection of material performance parameters. The nano film chip-type material measuring device contains a rectangular cavity sensor, a microwave vector network analyzer, an input coaxial cable, an output coaxial cable, a GPIB data acquisition card and a computer. The method provided by the invention can detect complex permittivity (permittivity and a dielectric loss coefficient) of a pure dielectric material, complex permeability (permeability and a magnetic loss coefficient) of a pure magnetic material and complex permittivity (permittivity, a dielectric loss coefficient, permeability and a magnetic loss coefficient) of a mixed dielectric material, has multiple functions and multiple modes and is high in accuracy and easy in experimental operation.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Ultra sensitive in-situ magnetometer system
InactiveUS20070007956A1High densityPermeability measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsUltra-high vacuumUltra sensitive
The present invention relates to an ultra sensitive in-situ magnetometer system, and more particularly to an ultra sensitive in-situ magnetometer system that can in-situ monitor a magnetic moment of a magnetic thin film with sub-monolayer precision while depositing and growing the magnetic thin film in an ultra high vacuum (UHV) chamber.
Owner:POSSIBLE ENERGY
Metal detector sensor head
InactiveUS20110234214A1High sensitivityReduce inductionMagnetisation measurementsPermeability measurementsEddy currentConductive materials
A metal detector includes means for reducing the induction of eddy currents in conductive elements of a sensor head. The aim of this invention is to remove the effect of small pieces of conductive material, located within or close to the sensor head, being seen as sought targets as the sensor head is moved over magnetic matrix. The means is to surround the conductive material with material with high magnetic permeability and low losses in a time-varying magnetic field, say low-loss ferrite. This will prevent the reflected field from illuminating the conductive material so eddy currents are not generated.
Owner:MINELAB ELECTRONICS
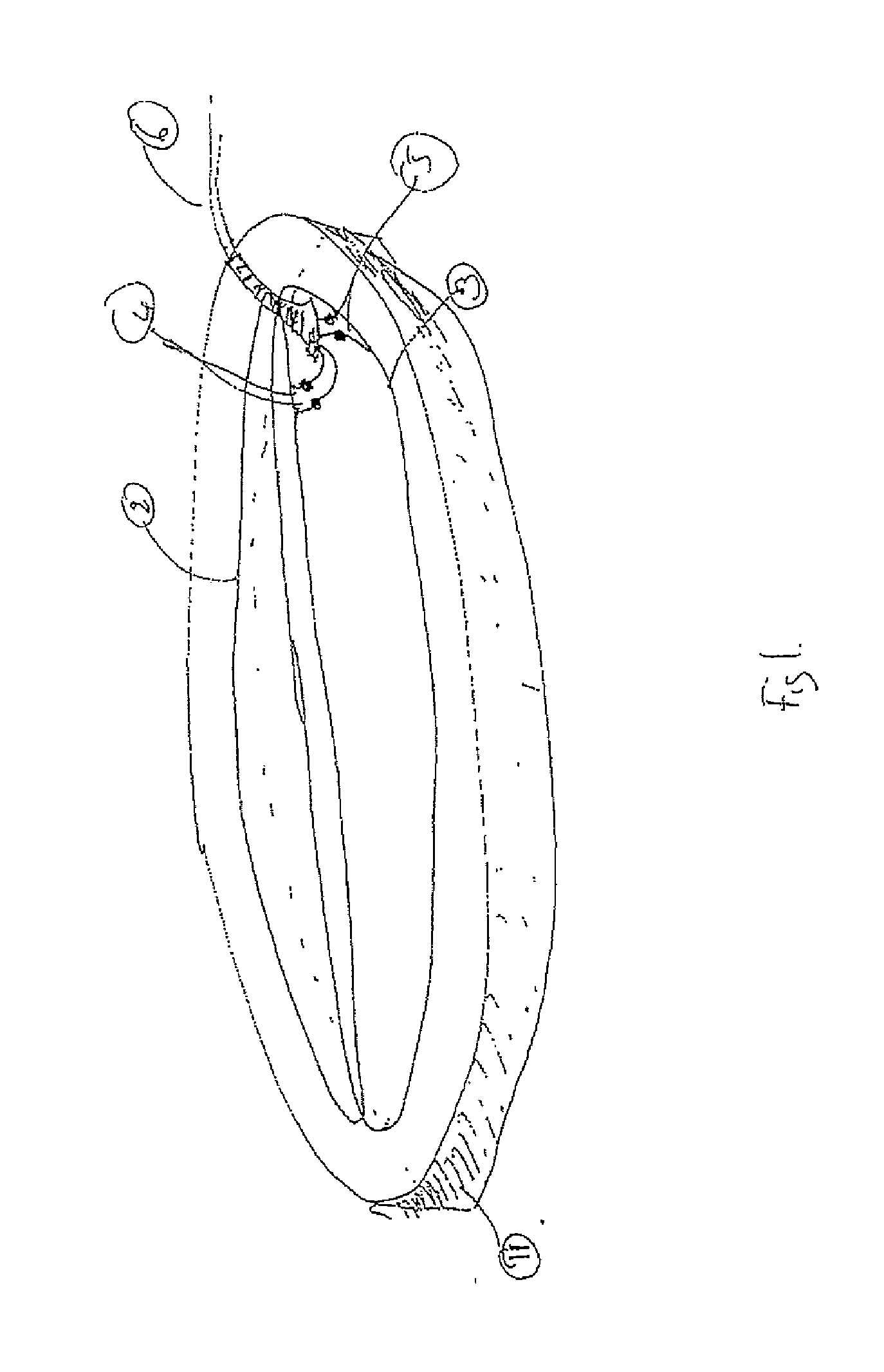
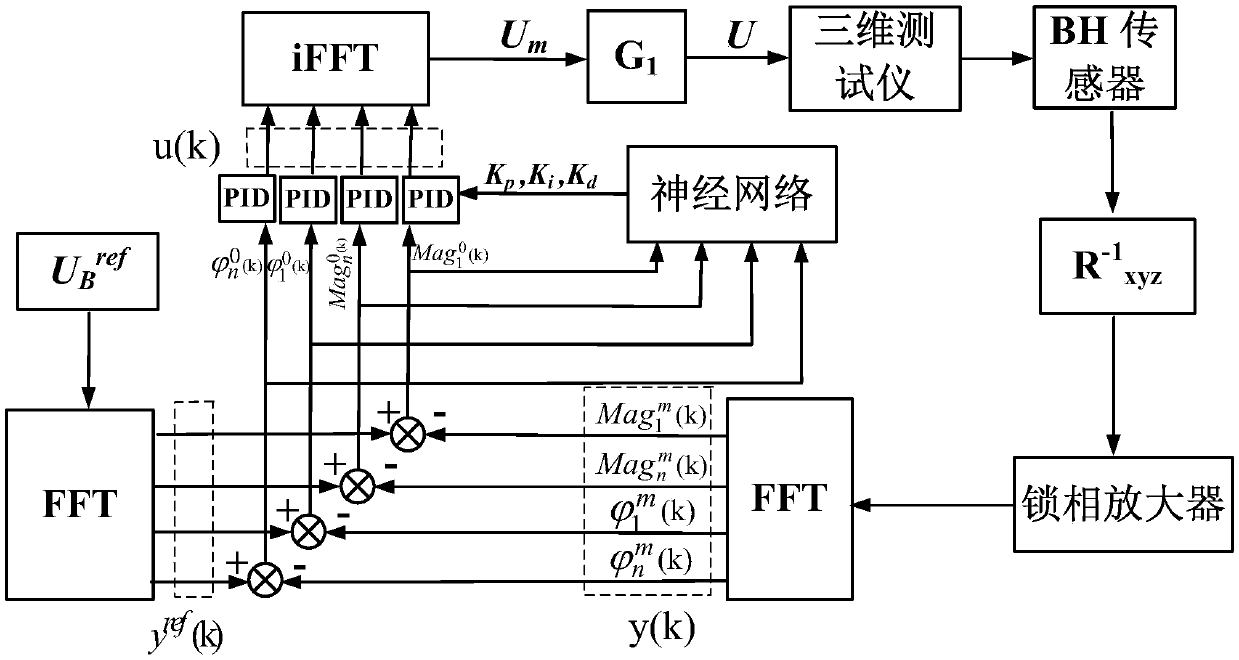
Phase angle amplitude PID adaptive method based on BP neural network for three-dimensional magnetic property measurement
ActiveCN109034390AStrong weak signal acquisition capabilityImprove signal-to-noise ratioPermeability measurementsHysteresis curve measurementsClosed loopAdaptive method
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Popular searches
Lubrication indication devices Level indicators by physical variable measurement Electric/magnetic roughness/irregularity measurements Magnetostrictive property measurements Electrical/magnetic solid deformation measurement Particle suspension analysis Immunoassays Electric testing/monitoring Speed measurement using gyroscopic effects Electrical/magnetic thickness measurements
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com