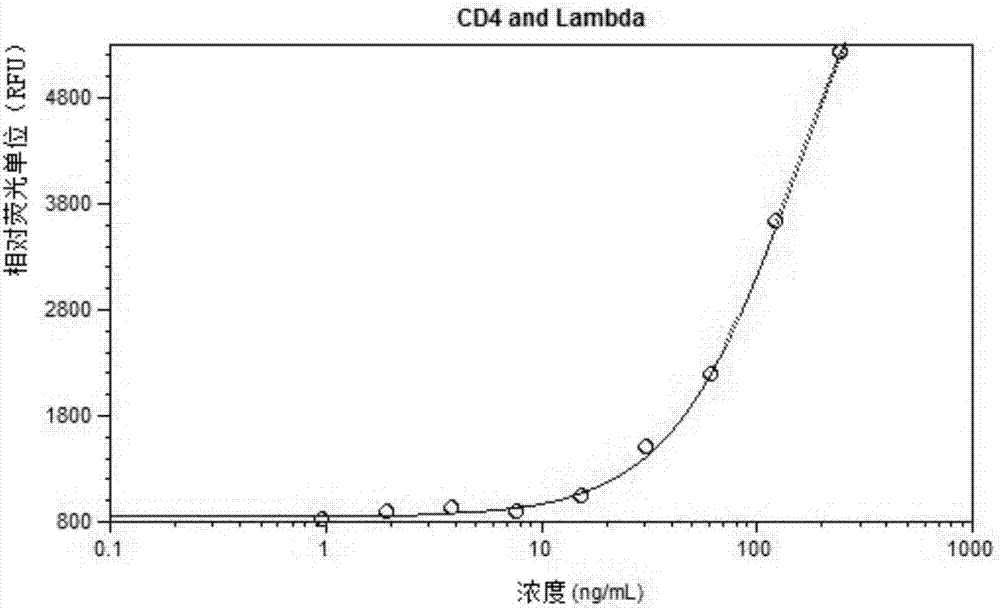
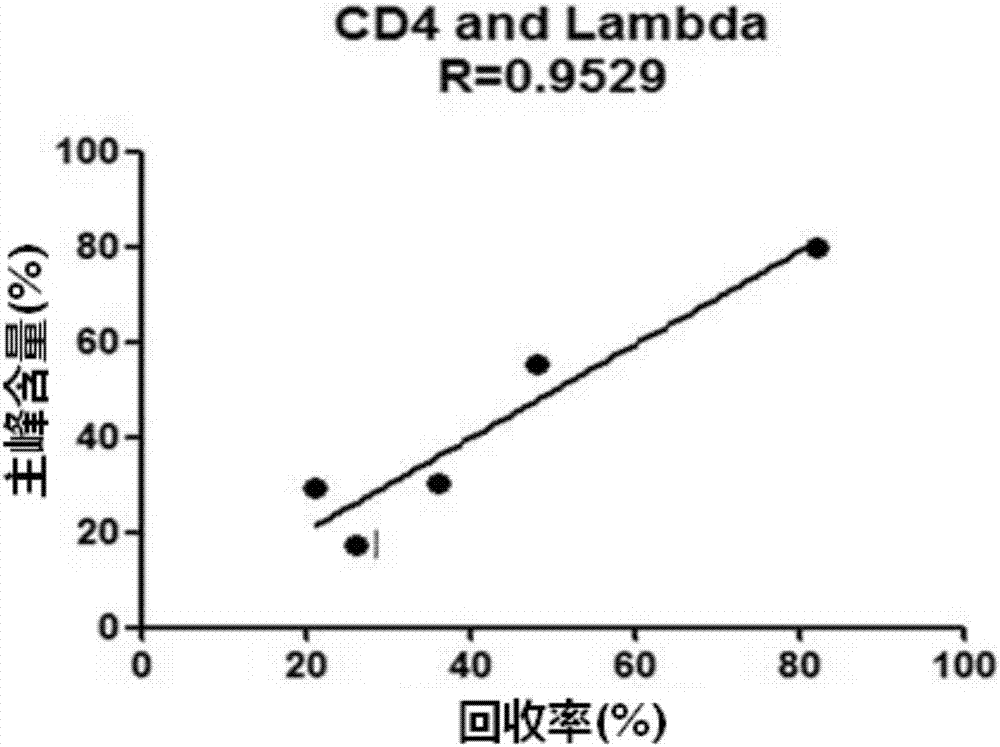
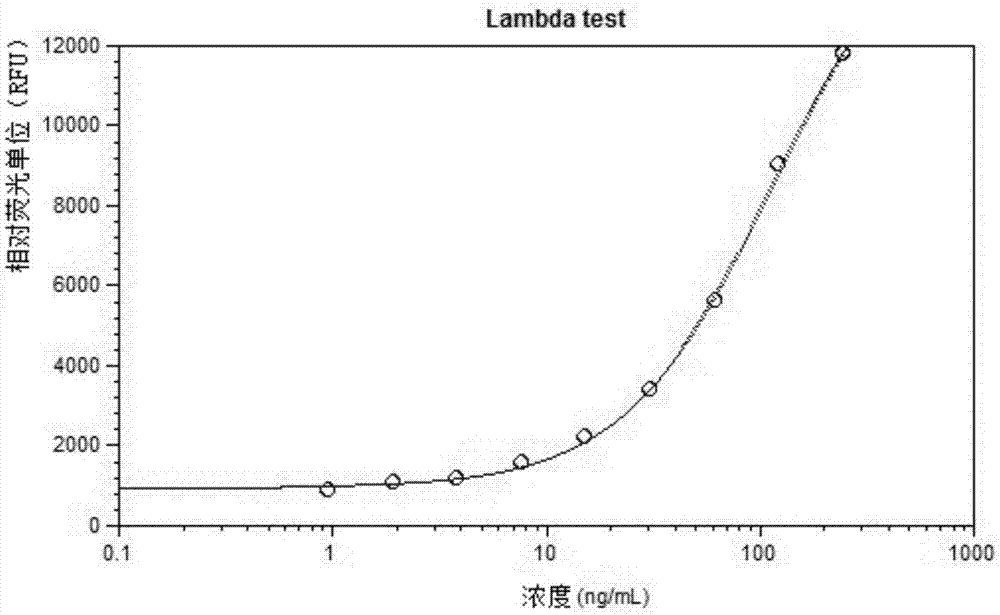
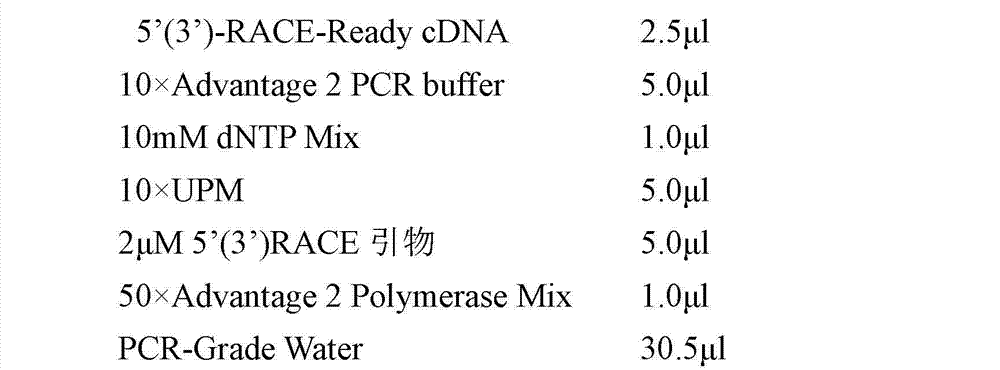
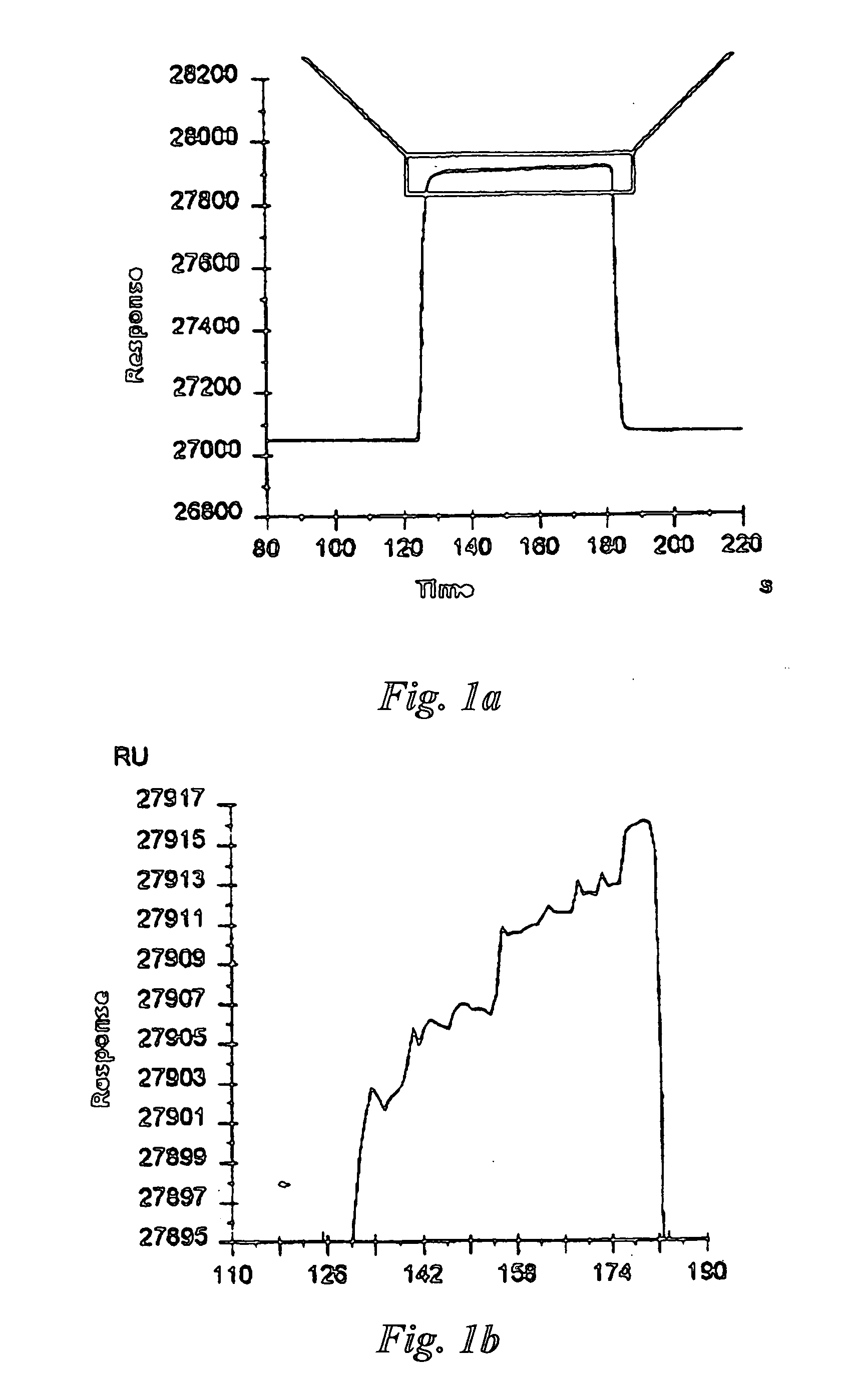
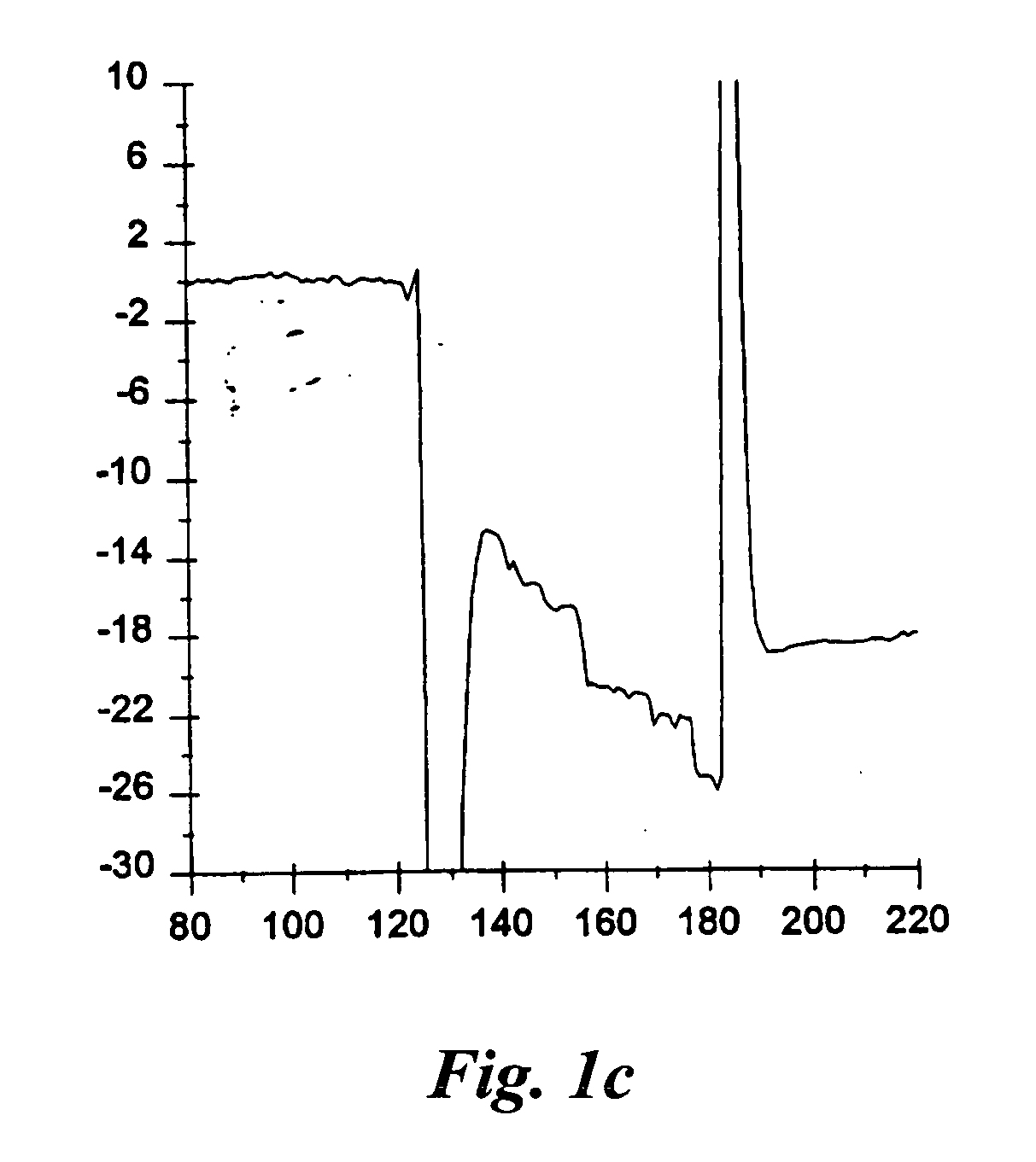
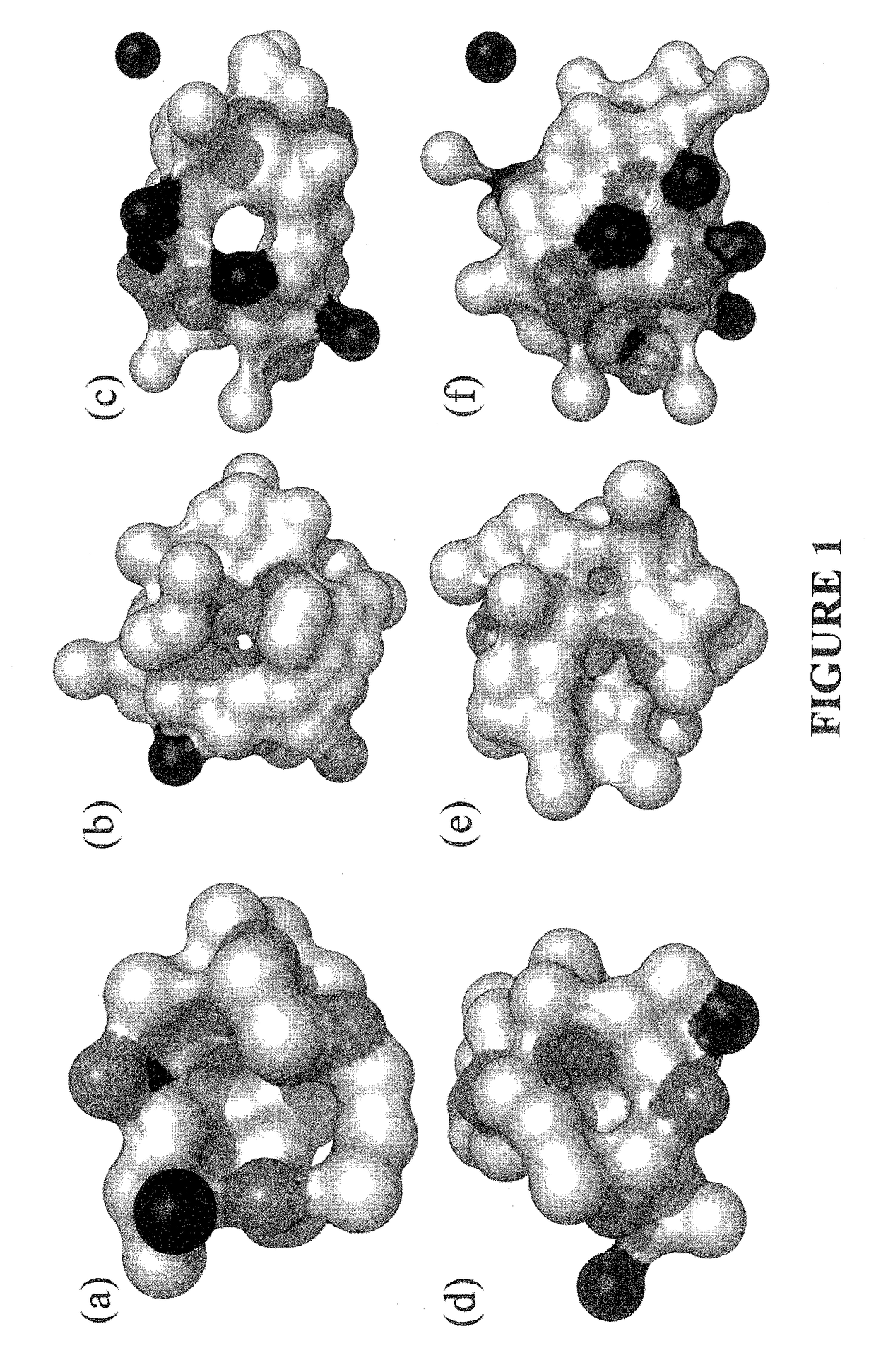
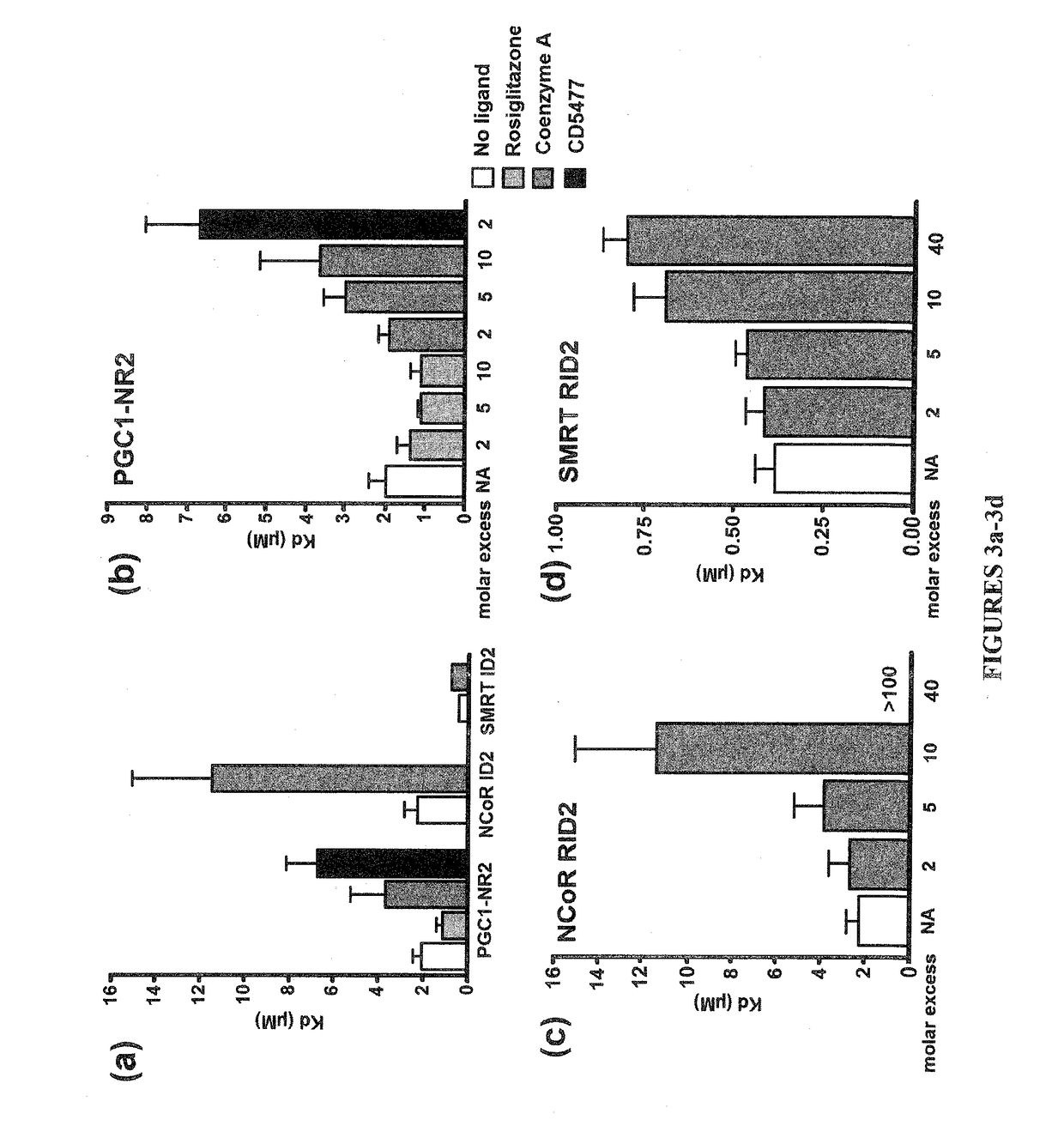
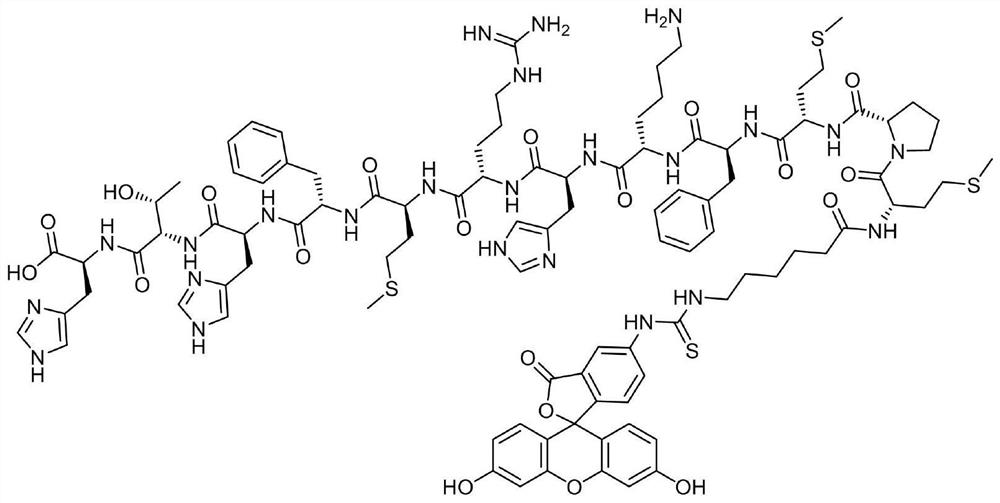
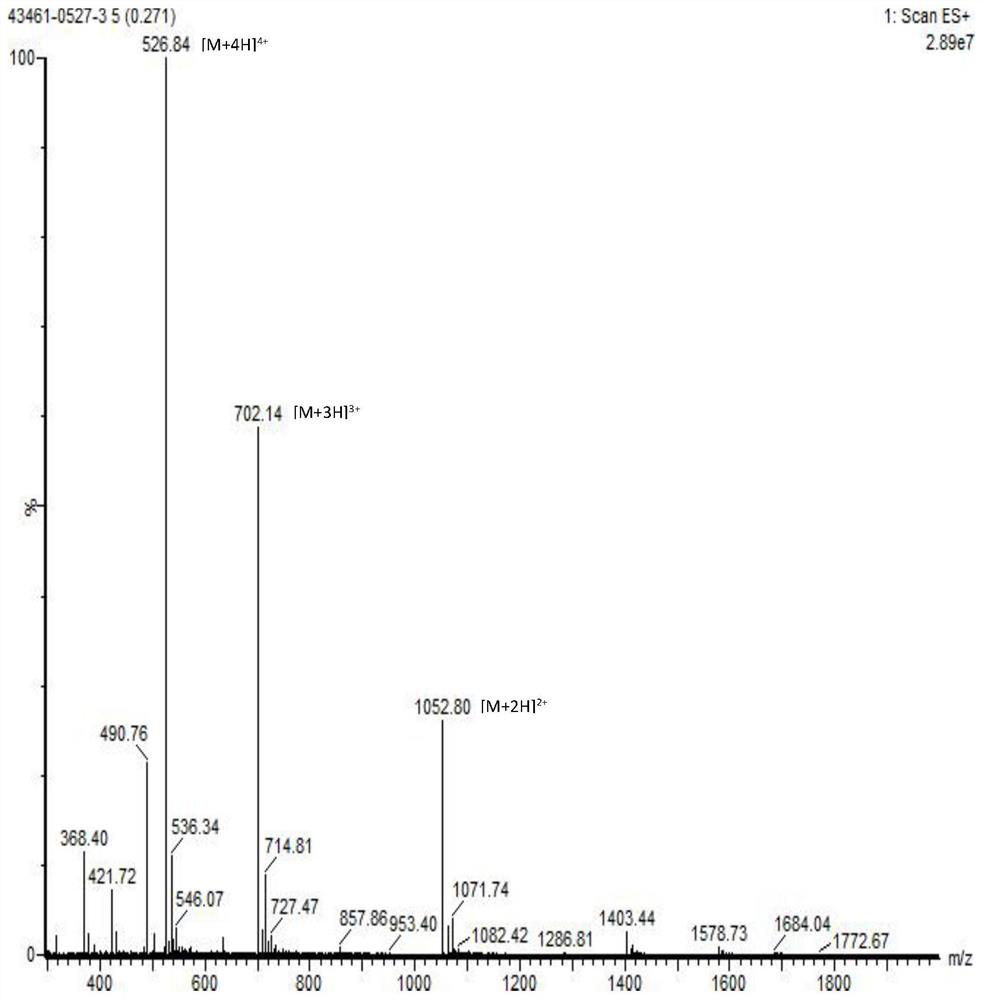
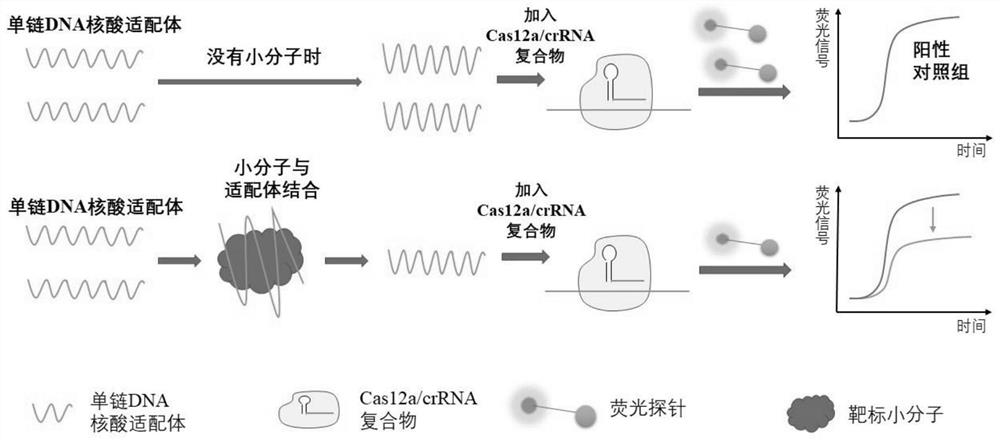
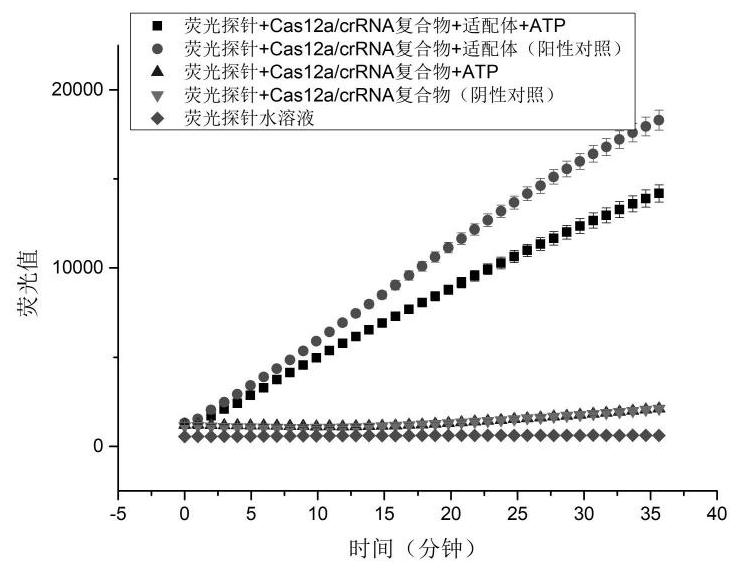
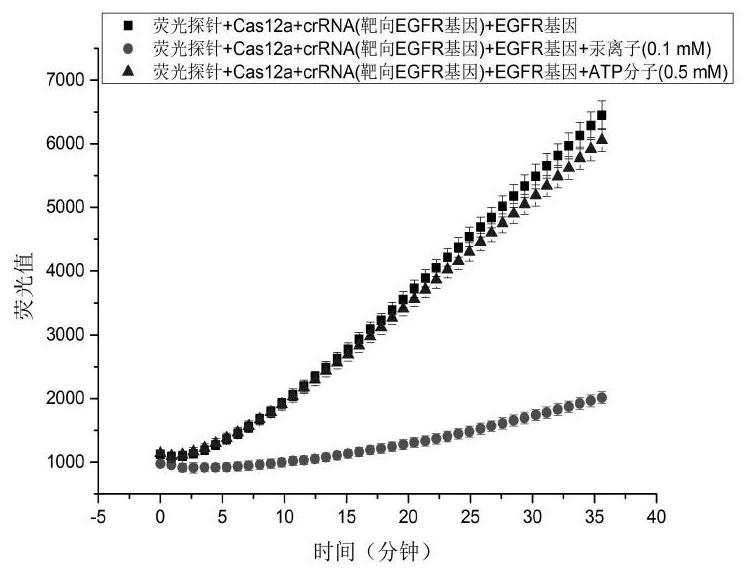
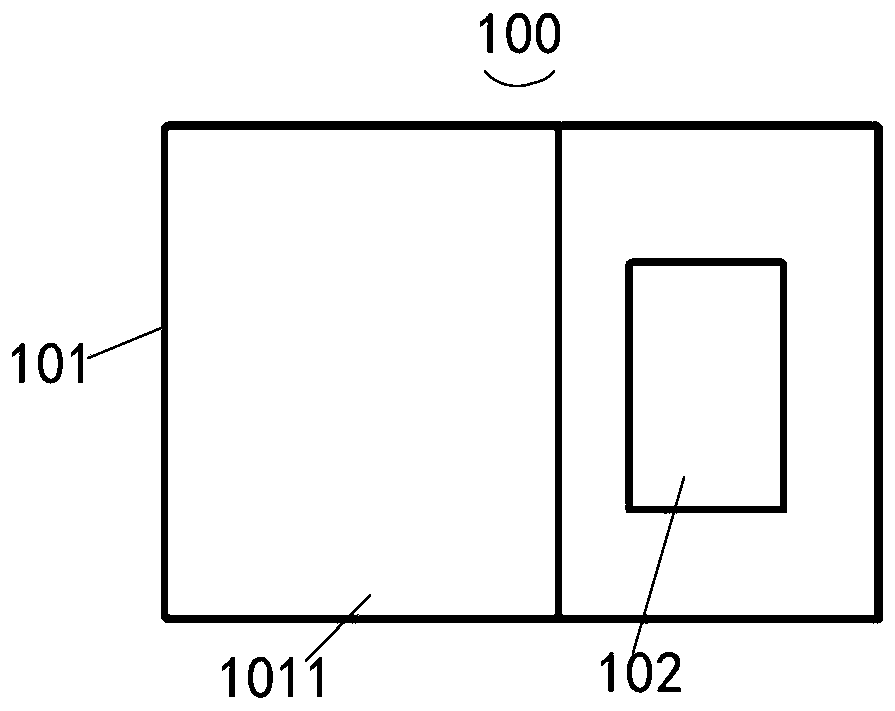
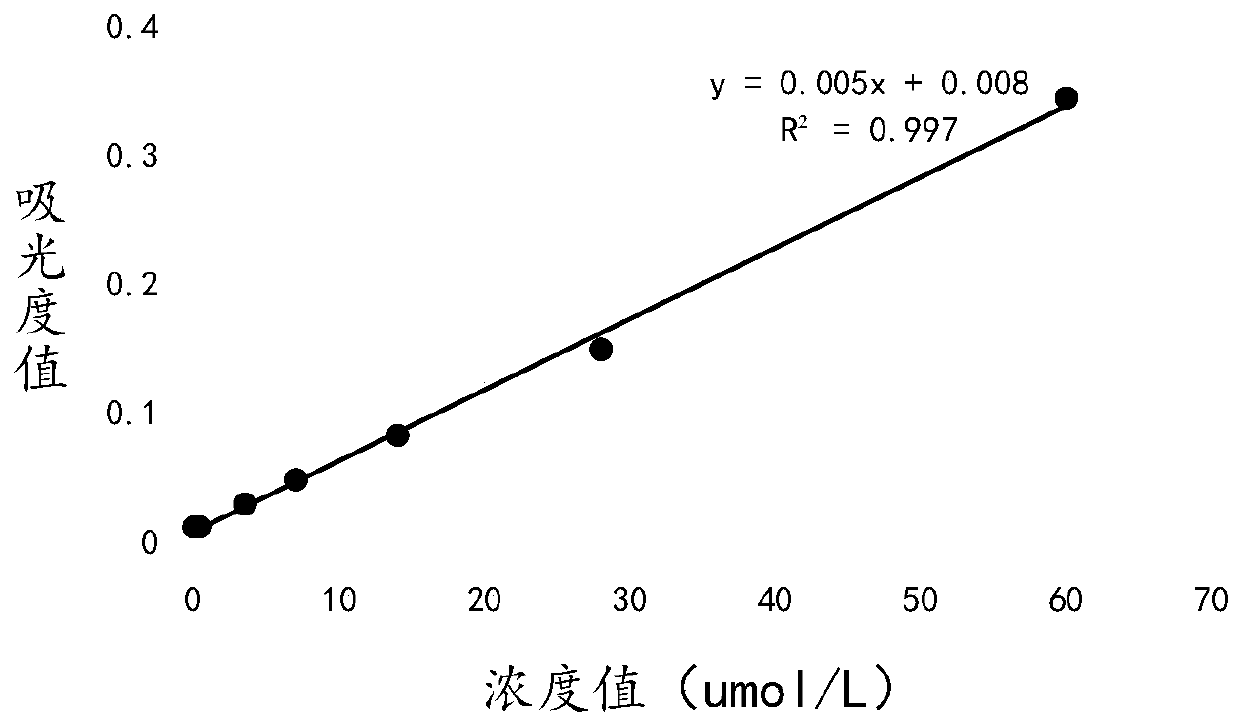
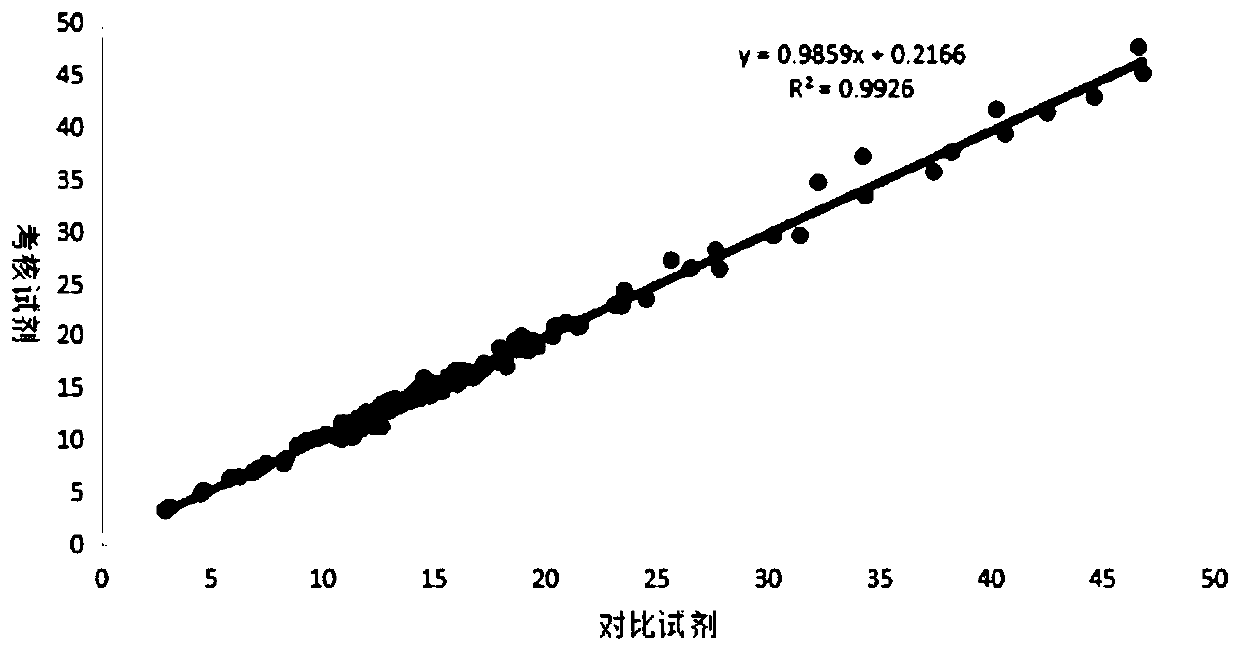
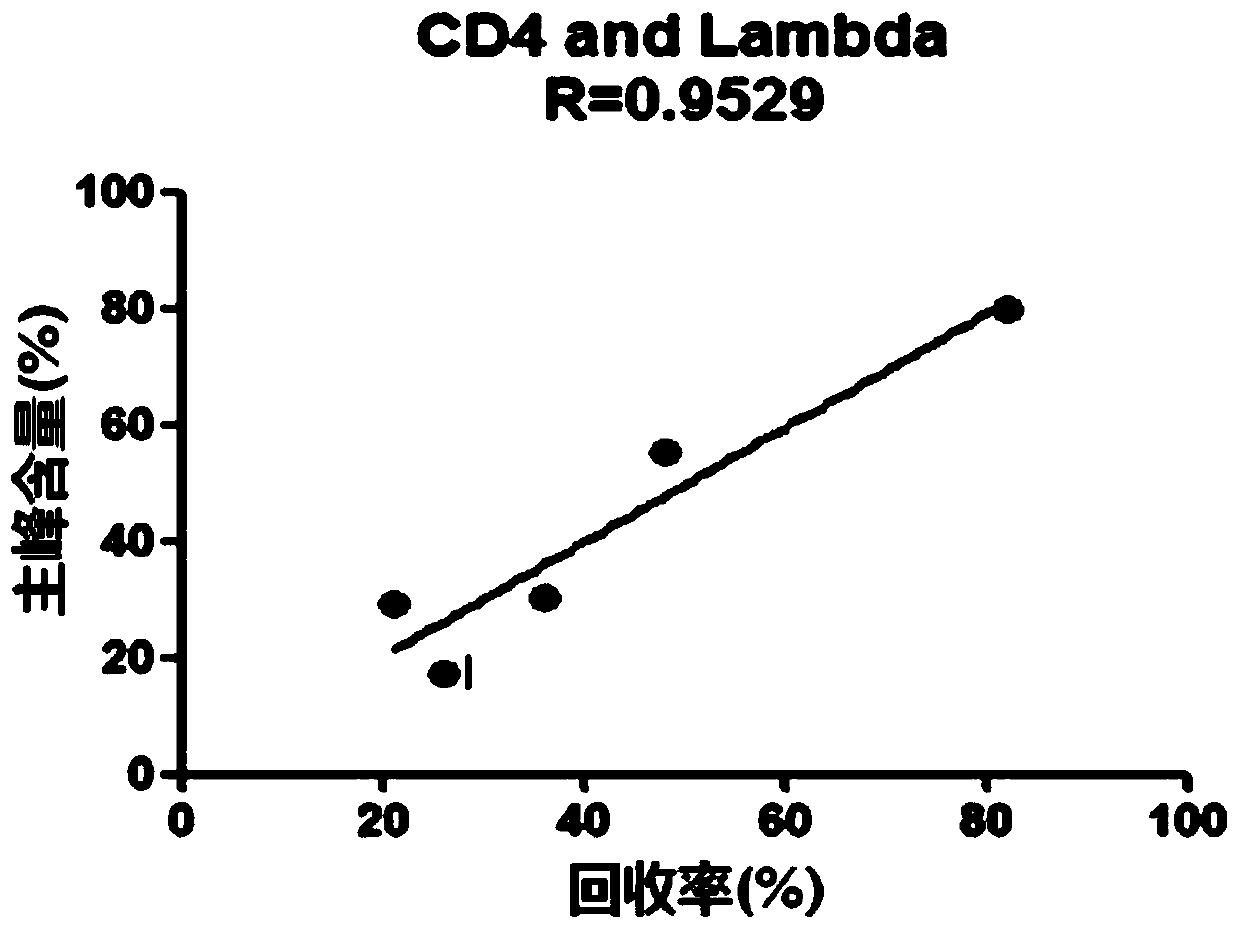
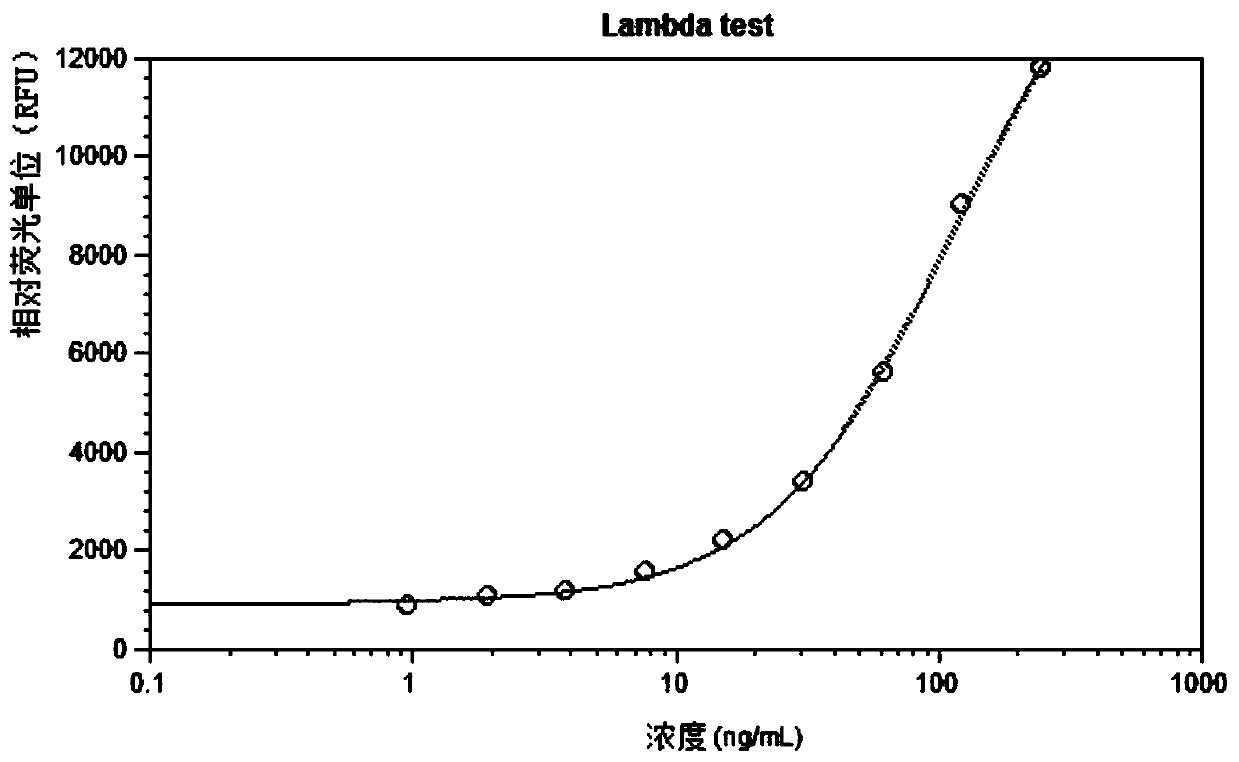
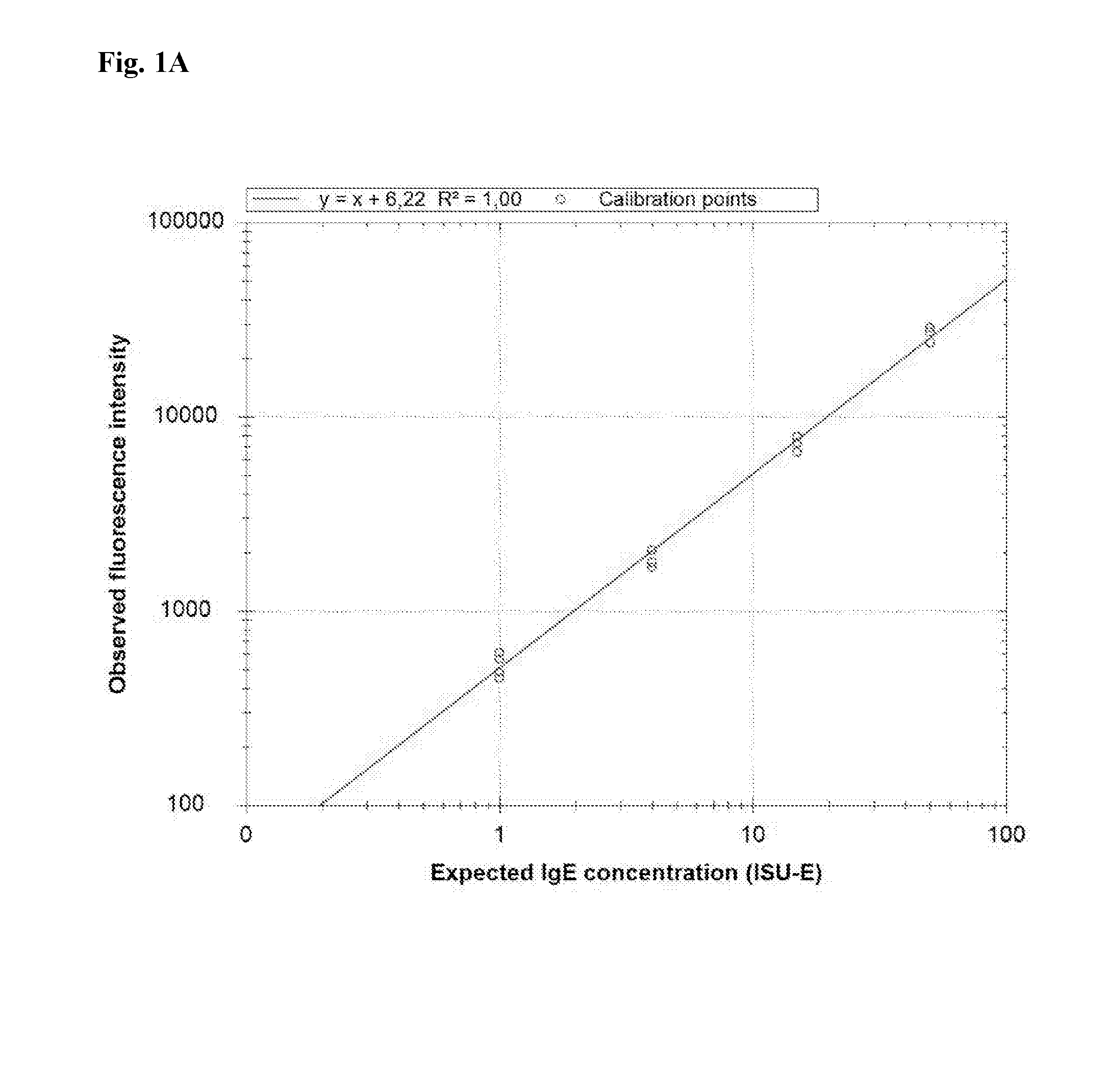
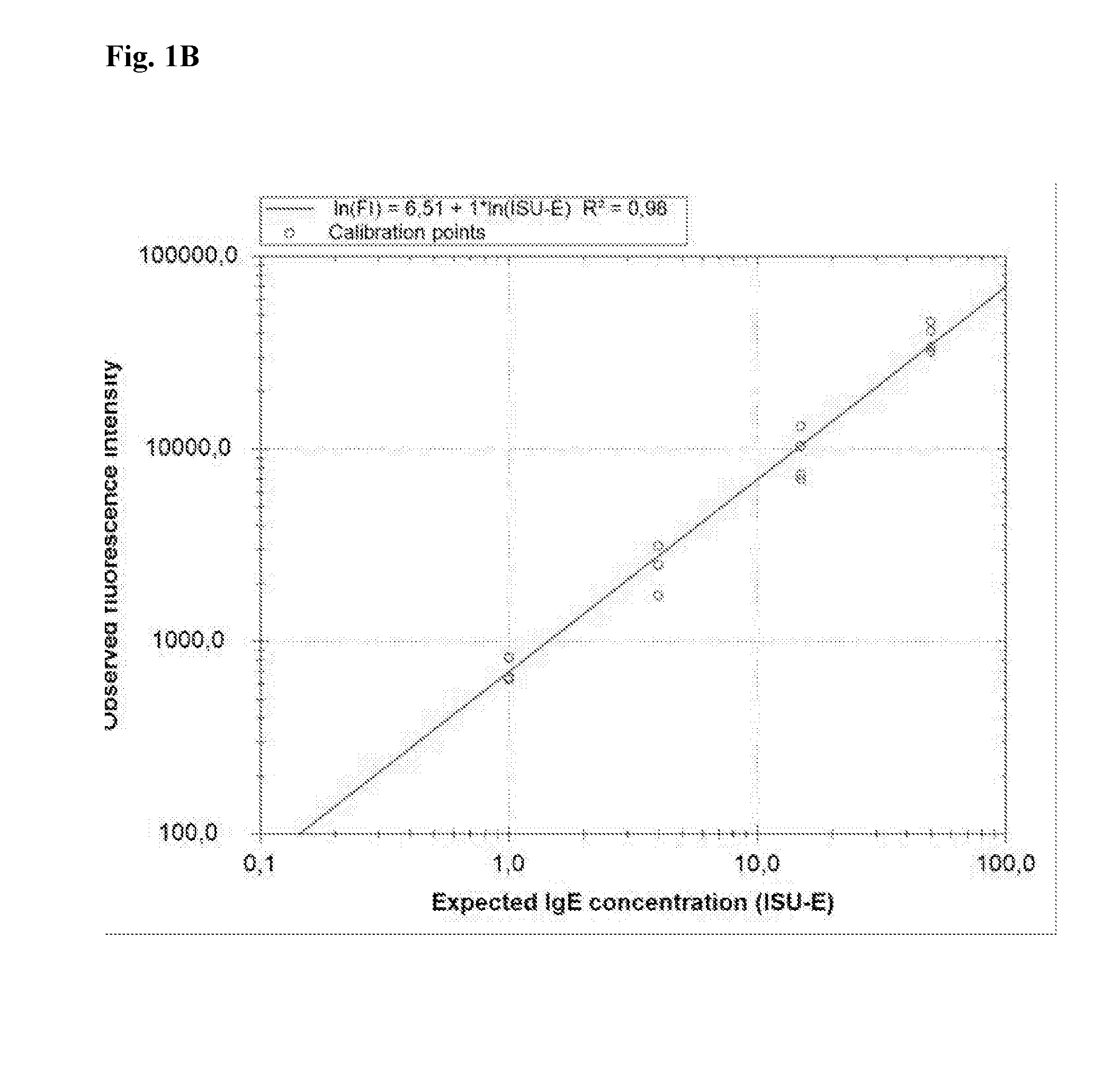
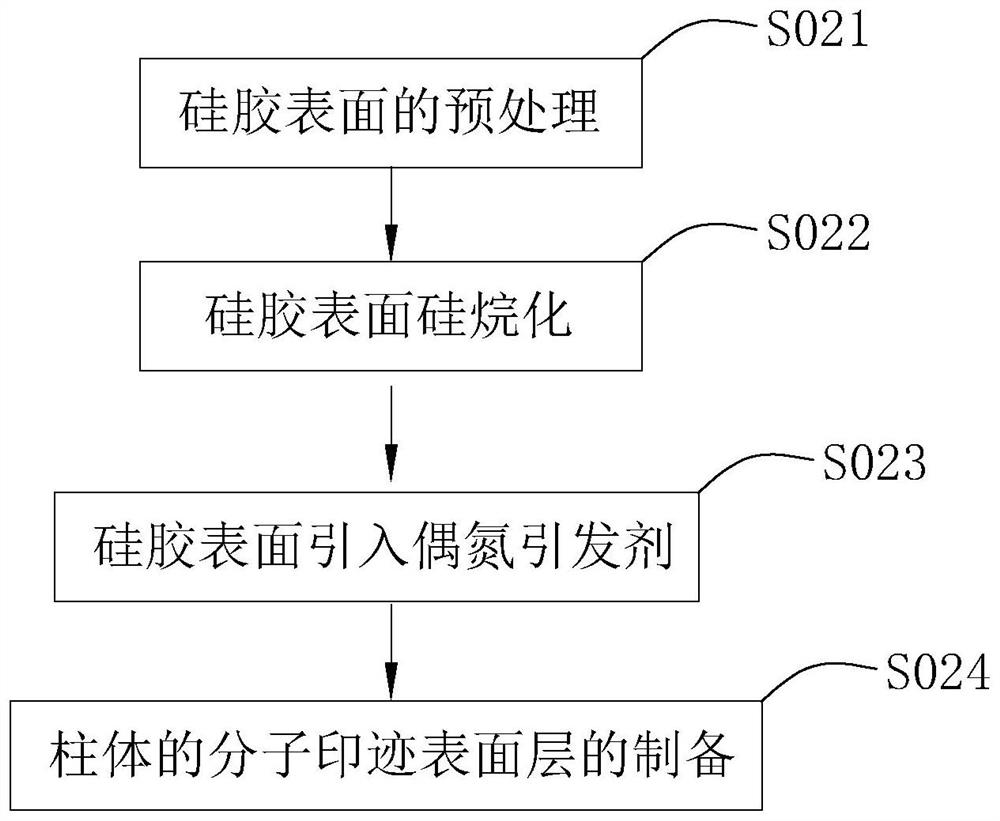
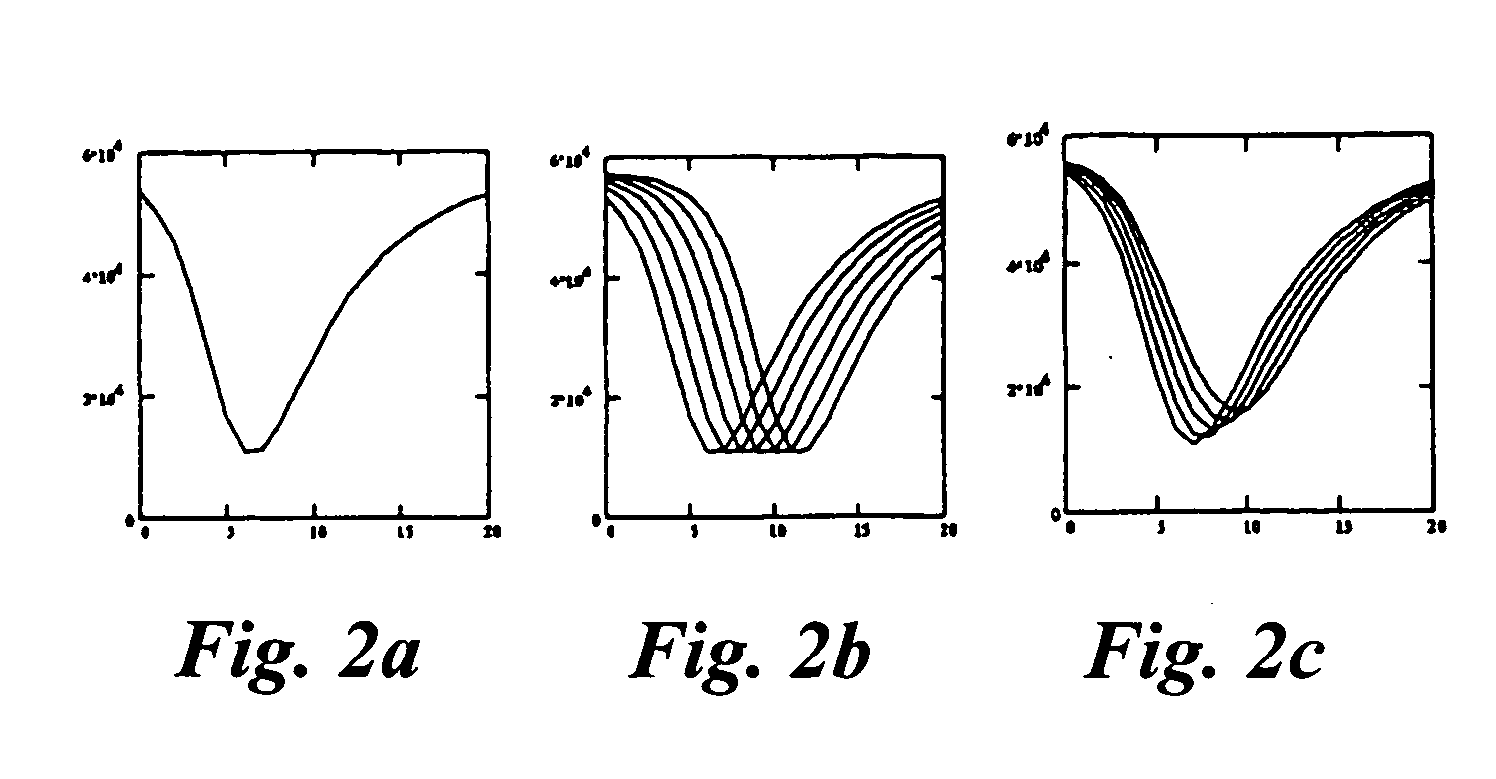Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Scatchard plot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Scatchard equation is an equation used in molecular biology to calculate the affinity and number of binding sites of a receptor for a ligand. It is named after the American chemist George Scatchard.
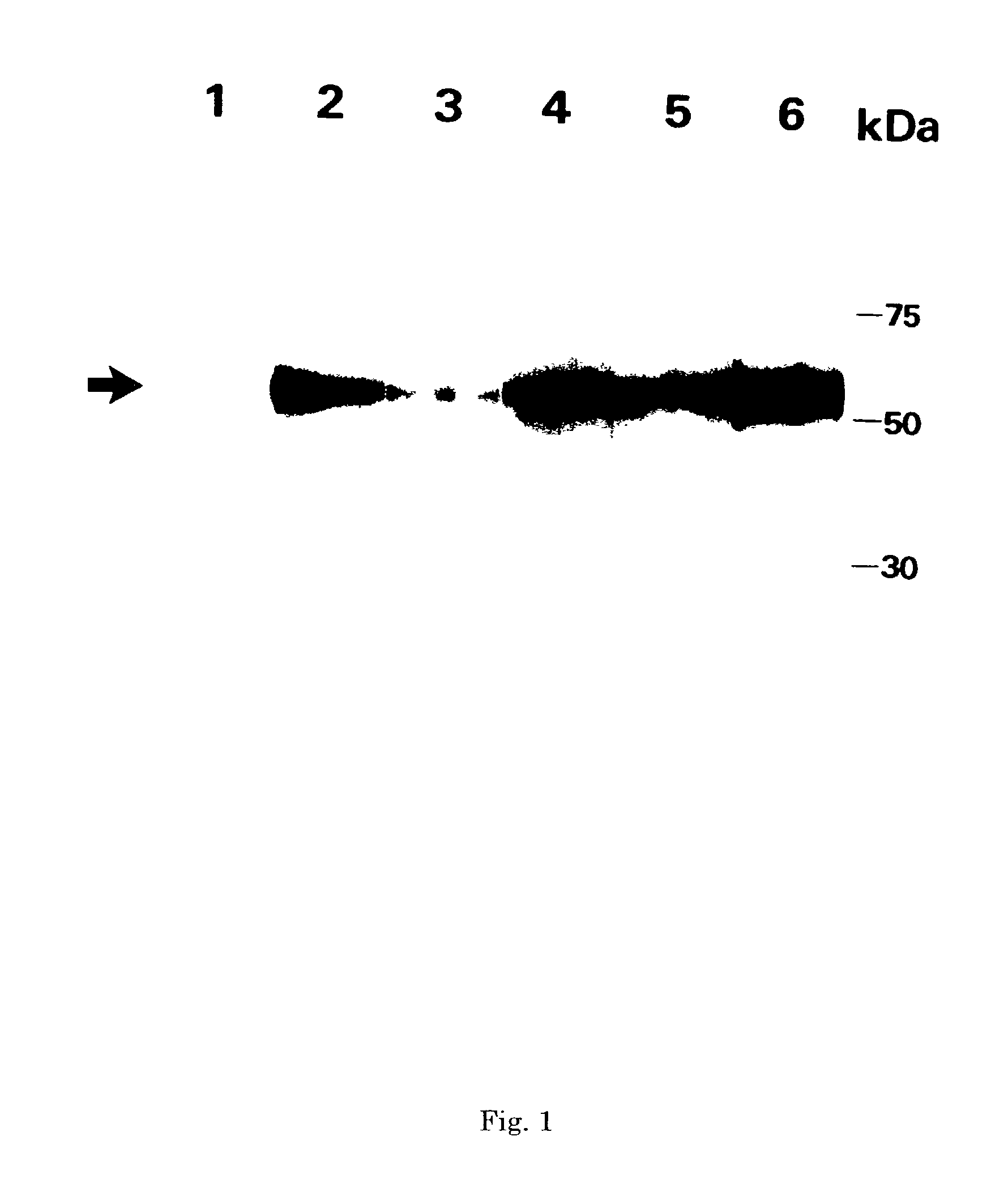
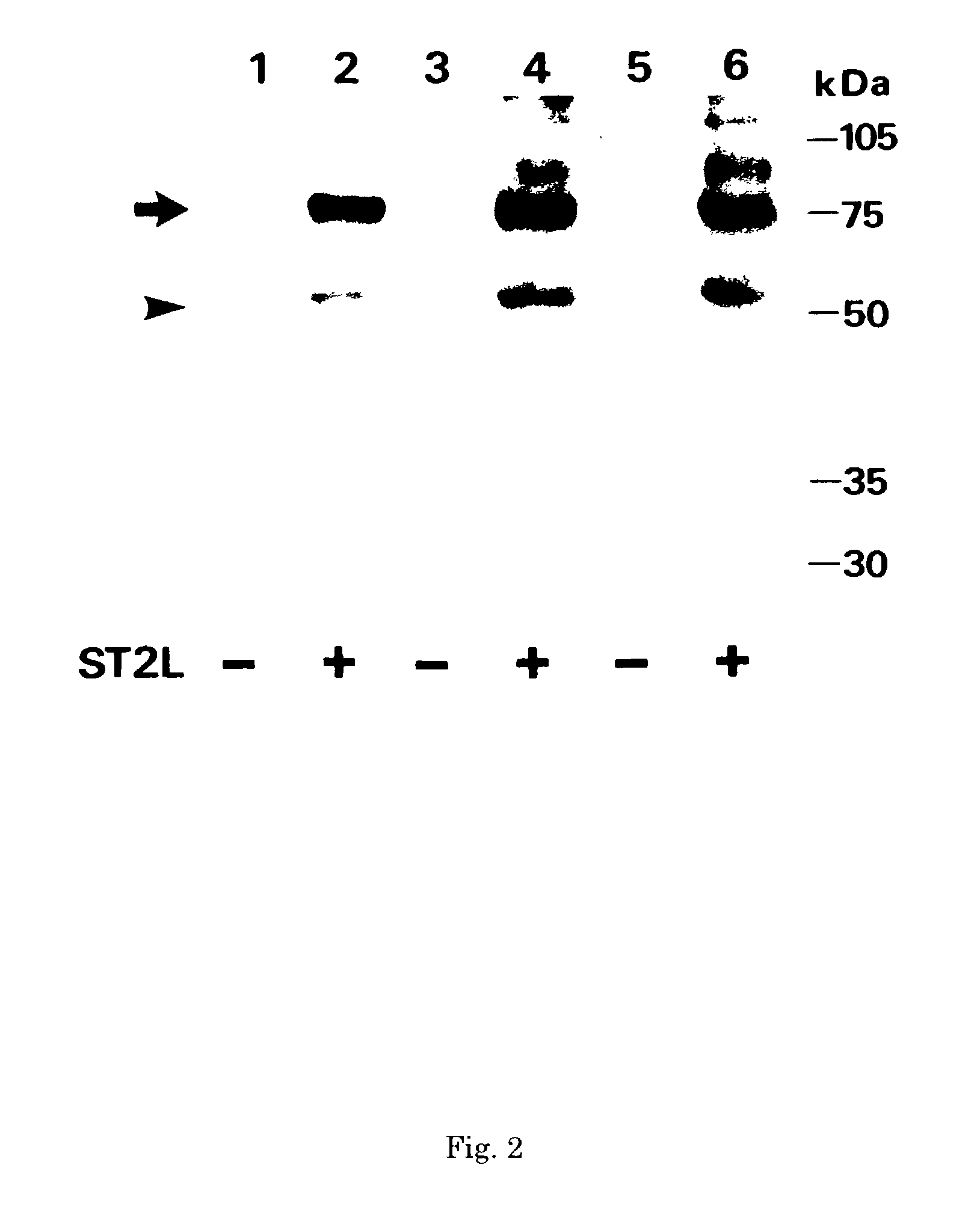
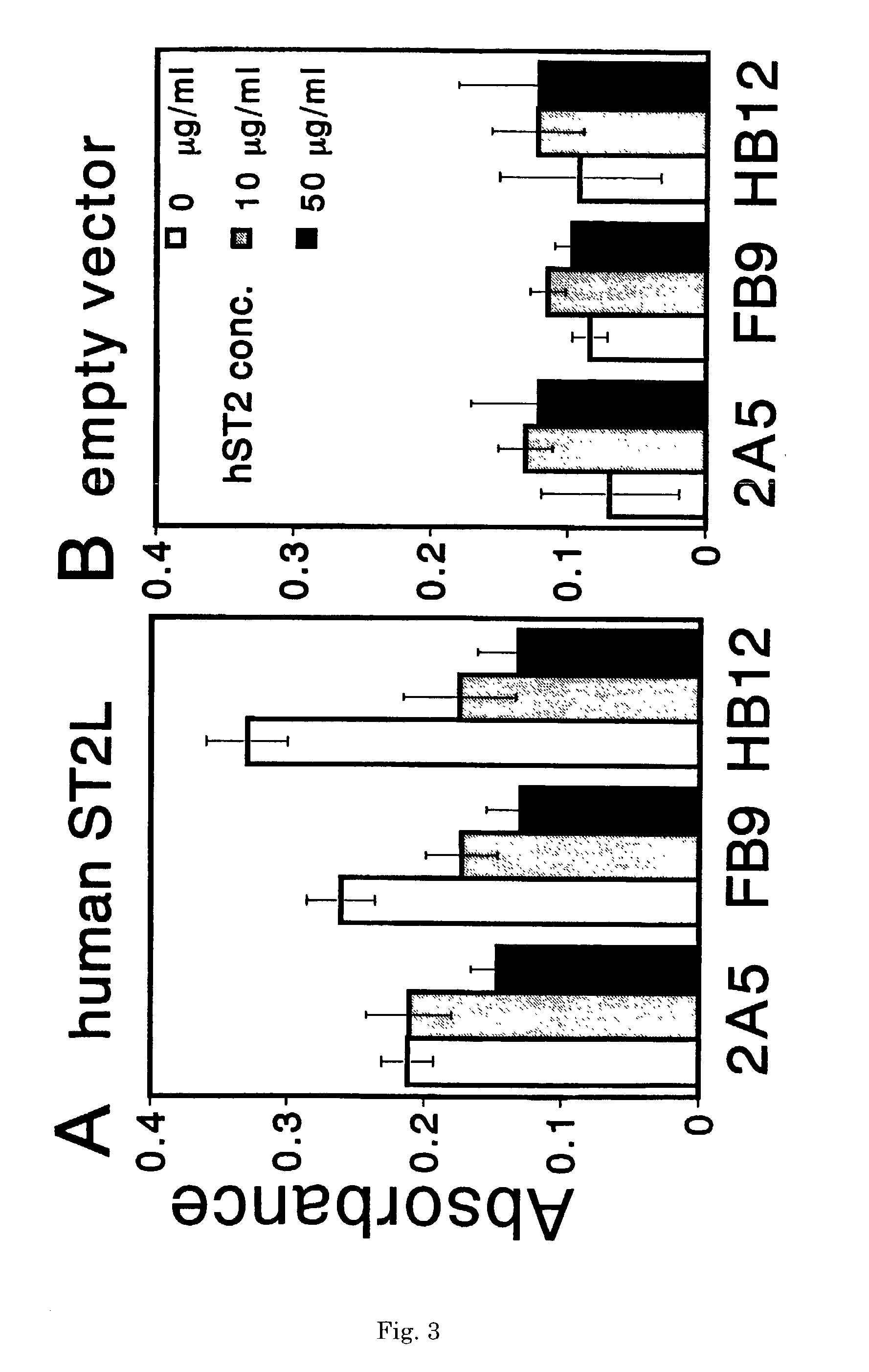
Monoclonal antibody and method and kit for immunoassay of soluble human ST2
InactiveUS7087396B2The process is convenient and fastAnimal cellsEnzymologyImmobilized AntibodiesMonoclonal antibody
A method for determining a soluble human ST2 in a sample conveniently at a high sensitivity and an assay kit are provided. By an immunological method comprising a step for bringing a sample into contact with an immobilized antibody formed by binding to an insoluble support a first anti-human ST2 antibody which binds specifically to a non-denatured human ST2, a step for labelling a first reaction product generated in the previous step by reacting said first reaction product with a second anti-human ST2 antibody which binds specifically to a non-denatured human ST2 by recognizing a site different from the site on ST2 where said first anti-human ST2 antibody binds and which is labelled with a label, and a step for determining the amount of the label on said first reaction product which has been labelled, a soluble human ST2 in a sample is determined. In addition, a recombinant ST2 is employed as a standard to prepare a calibration curve, based on which the ST2 in a sample is quantified.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
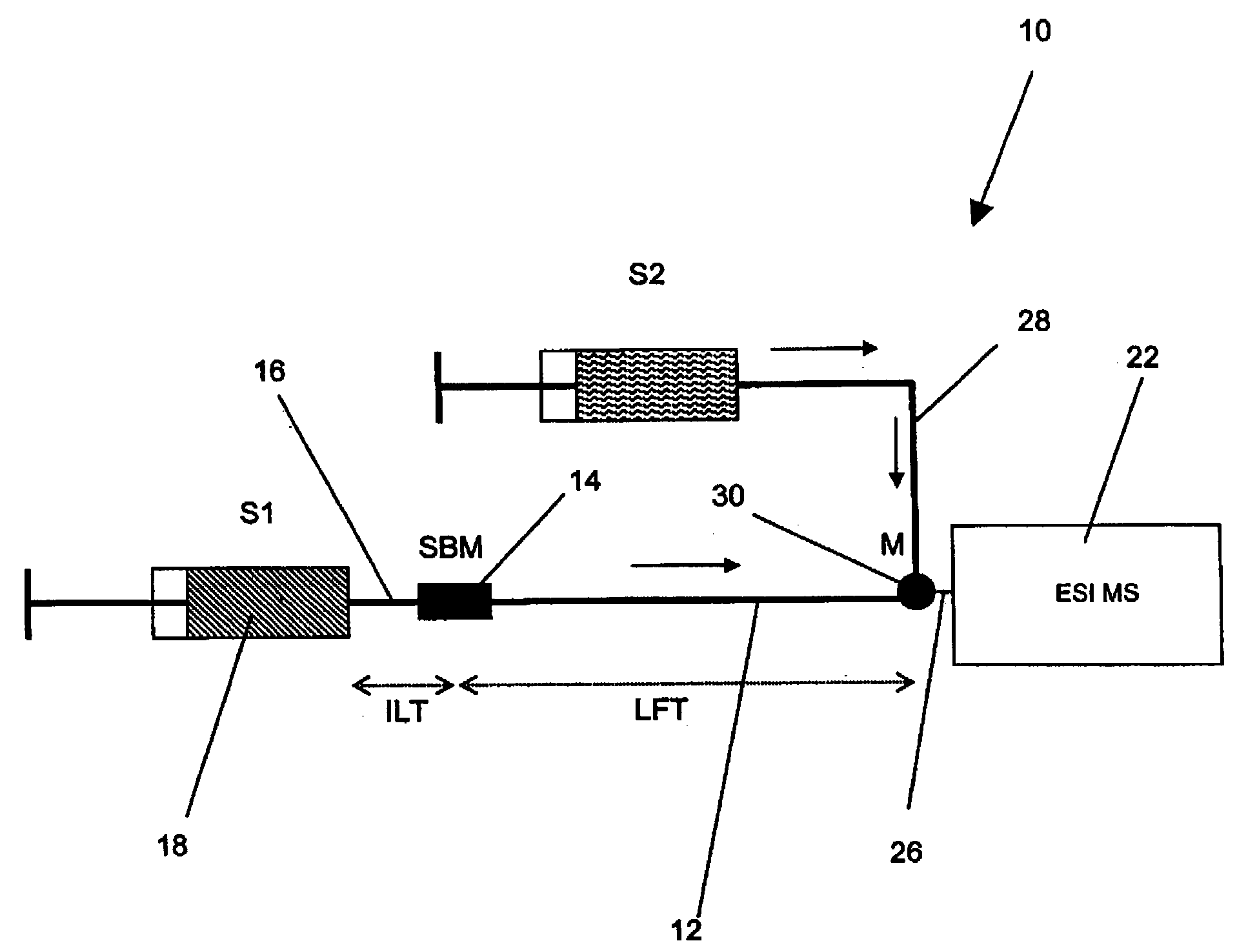
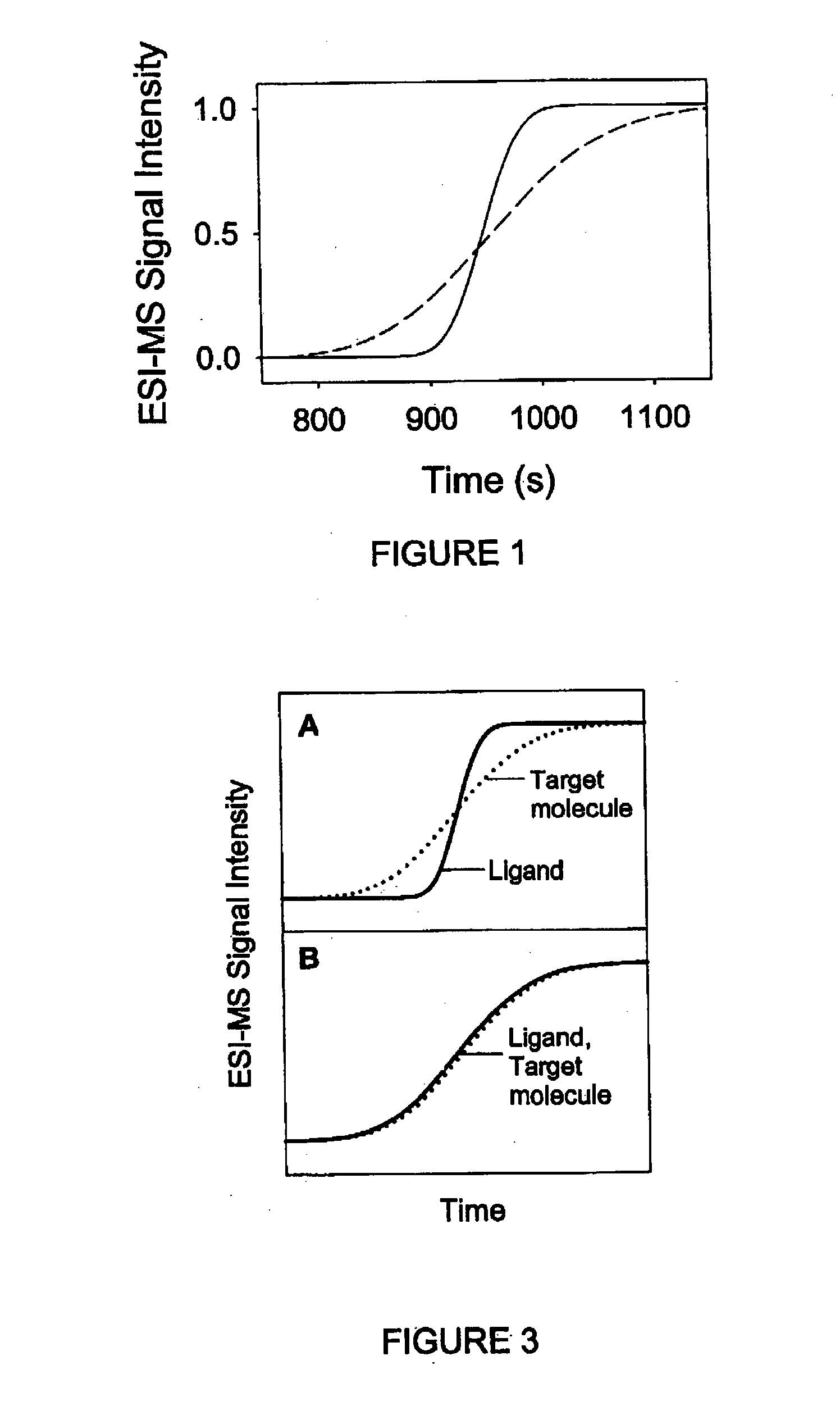
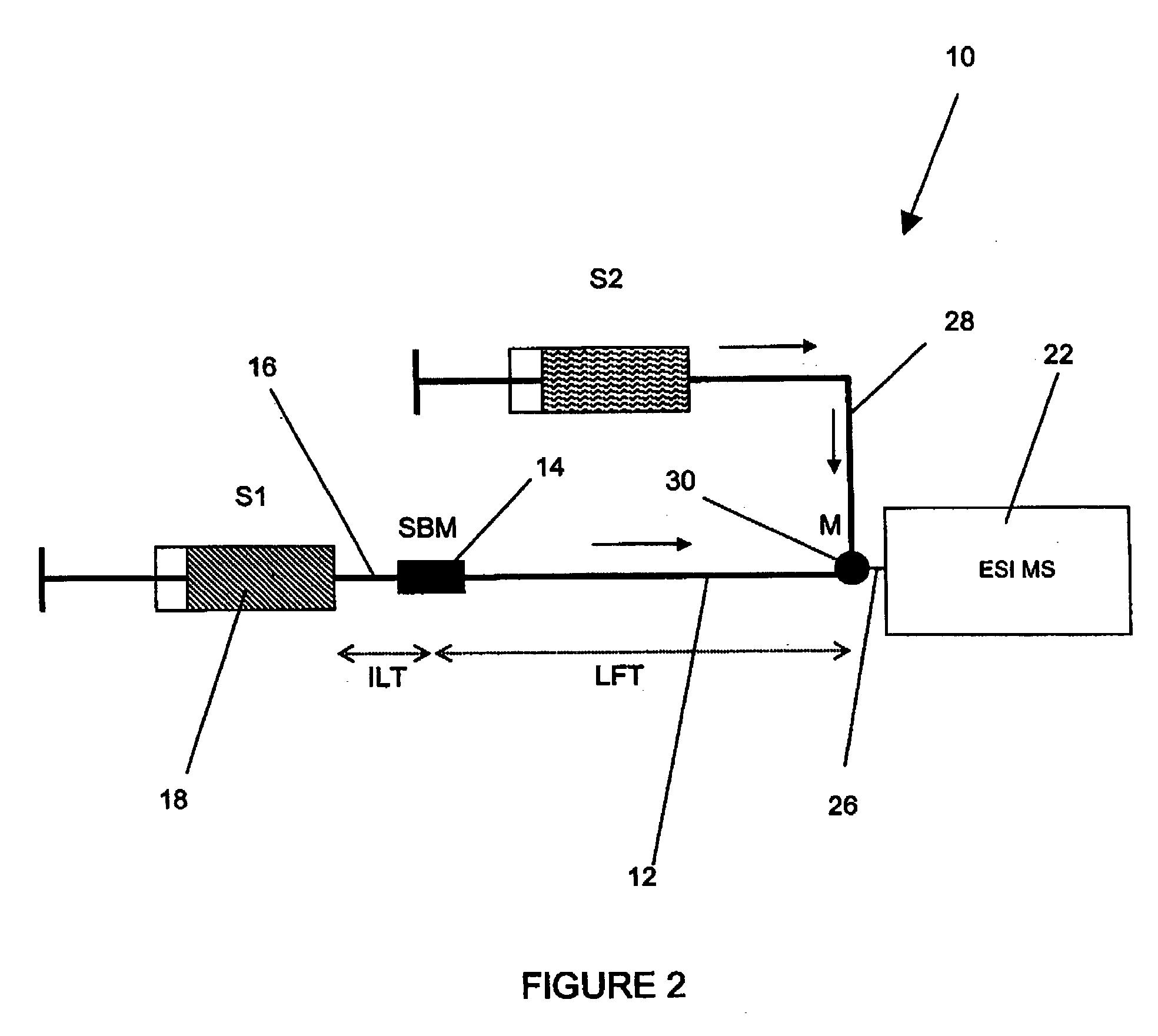
Method and apparatus for the detection of noncovalent interactions by mass spectrometry-based diffusion measurements
InactiveUS20030234356A1Accurate measurementShorten the timeSamples introduction/extractionSurface/boundary effectHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGas phase
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting the noncovalent binding of a potential ligand (such as a drug candidate) to a target, e.g. a biochemical macromolecule such as a protein. The method is based on the Taylor dispersion of an initially sharp boundary between a carrier solution, and an analyte solution that contains the potential ligand(s) and the target. Dispersion profiles of one or more potential ligands are monitored by mass spectrometry at the exit of the laminar flow tube. Potential ligands will usually be relatively small molecules that have large diffusion coefficients. In the absence of any noncovalent interactions in solution, very steep dispersion profiles are expected for these potential ligands. However, a ligand that binds to a large target in solution, will show an apparent diffusion coefficient that is significantly reduced, thus resulting in a more extended dispersion profile. Noncovalent binding can therefore be detected by monitoring dispersion profiles of potential ligands in the presence and in the absence of the target. In contrast to other mass spectrometry-based methods for detecting noncovalent interactions, this method does not rely on the preservation of specific noncovalent interactions in the gas phase. This method has an excellent sensitivity and selectivity, therefore it can be used for testing multiple potential ligands simultaneously. The method is therefore useful for the high throughput screening of compound libraries.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
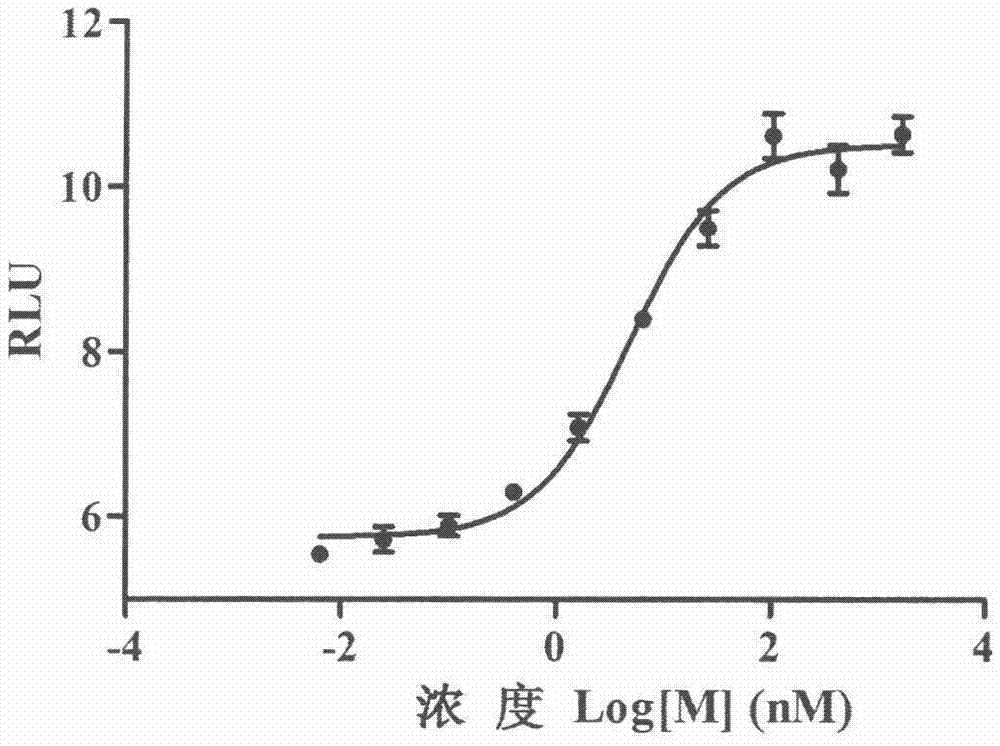
Method for determining receptor affinity of GLP-1 receptor agonist
InactiveCN104846061AQuick evaluationQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosolResponse element
The invention provides a method for determining the receptor affinity of a GLP-1 receptor agonist. The method is based on a tool cell line, namely CHO-GLP-1R-CRE-Luc<+>, when a sample to be determined is combined with GLP-1 receptor on the surface of a cell, the receptor-mediated signal cascade reaction can be activated, cAMP-response element (CRE) is activated specifically, the expression of the luciferase reporter gene is promoted, the quantity of luciferase in cytosol is detected for drawing and fitting to obtain a dose-effect curve of acting of the sample and the GLP-1 receptor; and the half effective concentration (EC50) is calculated. By inspecting and optimizing all influence factors in the determining process, the method for determining the receptor affinity of the GLP-1 receptor agonist is finally established. The method has the advantages of being high in specificity, precision and accuracy, good in durability and convenient to operate, and the like. The method can be used for determining the receptor affinity of the GLP-1 receptor agonist, and thus such type of drug can be fast evaluated and screened.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
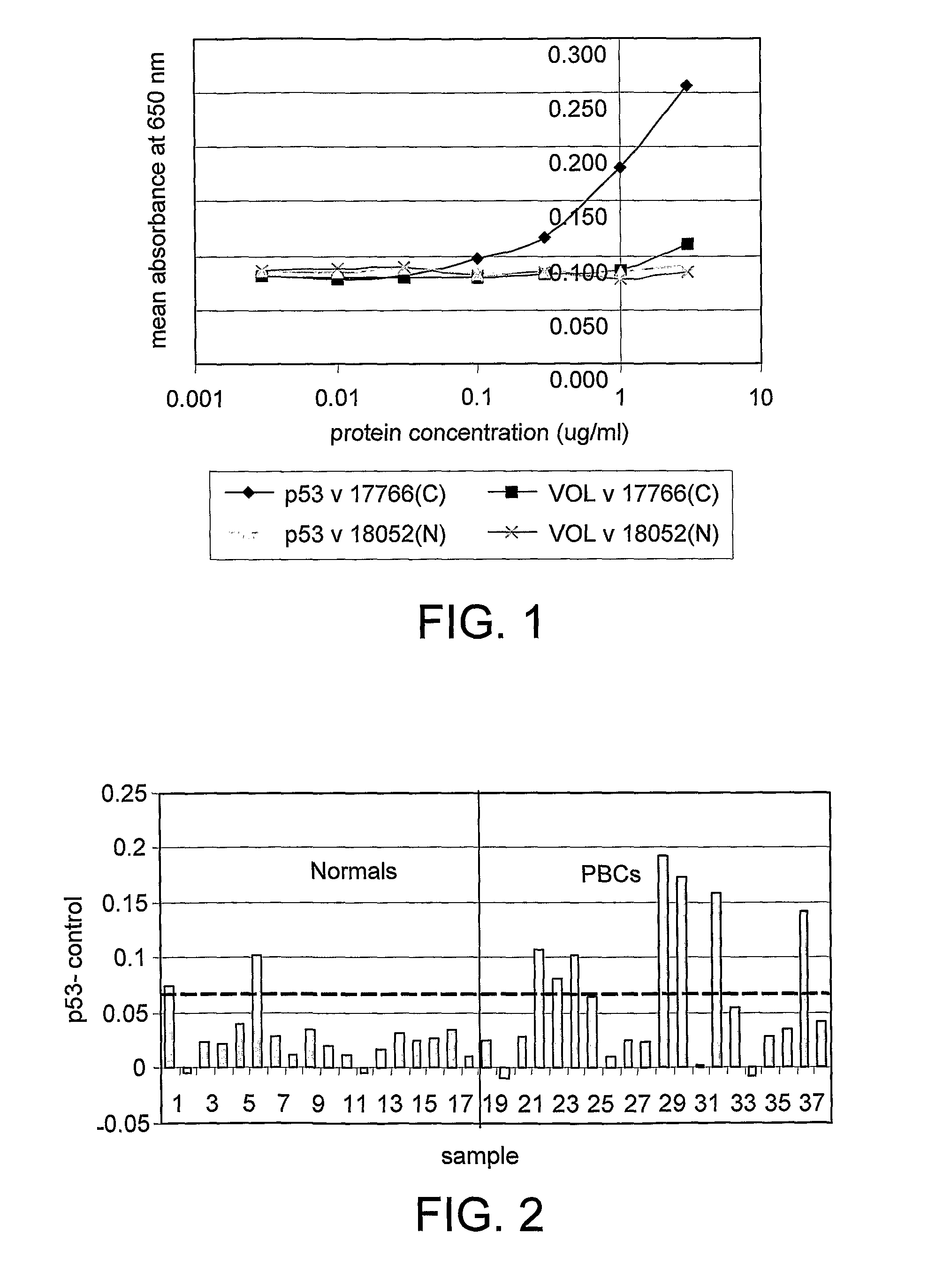
Immunoassay methods
ActiveUS8722339B2Reduce morbidityHigh sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingTest sampleImmunoassay method
The invention relates to a method of detecting a disease state or disease susceptibility in a mammalian subject which comprises detecting an antibody in a test sample comprising a bodily fluid from said mammalian subject wherein said antibody is a biological marker of a disease state or disease susceptibility, the method comprising: (a) contacting said test sample with a plurality of different amounts of an antigen specific for said antibody, (b) detecting the amount of specific binding between said antibody and said antigen, (c) plotting or calculating a curve of the amount of said specific binding versus the amount of antigen for each amount of antigen used in step (a) and (d) determining the presence or absence of said disease state or disease susceptibility based upon the amount of specific binding between said antibody and said antigen at each different antigen concentration used.
Owner:ONCIMMUNE
Bispecific antibody biological activity and titer detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN107064092AEfficient screeningHigh bispecific binding activityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntigen bindingSpecific antibody
The invention discloses a bispecific antibody biological activity and titer detection method. The method includes: detecting two antigen binding sites of a bispecific antibody at the same time; performing four-parameter fitting according to a fluorescence ratio and the concentration of a standard sample to obtain a standard curve; calculating the concentration of a to-be-tested sample according to the standard curve. By adoption of the method, intact antibody modules and cell strains high in bispecific binding activity and expression can be screened out more effectively; the method has the advantage of low reaction volume, and experiment reagent cost can be saved maximally; the method can be widely popularized and applied to CLD clone high-throughput screening.
Owner:SHANGHAI WUXI BIOLOGIC TECH CO LTD
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) type I receptor gene of chlamys farreri and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) locus of TGF-beta type I receptor gene
InactiveCN102899330AImprove seed selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidMolecular genetics
The invention relates to the cloning of a transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily type I receptor gene Tgfbrl1 of chlamys farreri in a molecular genetic marker technology, a screening and typing technology of a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) locus which is relevant with the weight of adductor muscles in the gene and a method for the application of the gene to the breeding of the high-yield chlamys farreri. A total-length complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) sequence of the Tgfbr1 gene of the chlamys farreri is obtained by utilizing a homology-based cloning strategy; an SNP lotus is discovered by blastn comparison, and primers and a probe are designed for the locus; and SNP typing is performed in a natural population of the chlamys farreri by using a high-resolution melting curve technology, and the weight of the adductor muscle of an individual is measured. Statistic analysis displays that the loci c.1815C>T are obviously relevant with the weight of the adductor muscles of the chlamys farreri, and the weight of the adductor muscles of individuals with TT genetypes is obviously higher than that of the adductor muscles of individuals with CC and CT genetypes. In the selective breeding process of the high-yield chlamys farreri, the breeding candidate colonies of the chlamys farreri can be subjected to c.1815C>T typing, and the individuals of which the loci c.1815C>T are TT genetypes are used as a breeding parent preferably by combining typing information of other loci which are relevant with growth properties.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for assaying a drug candidate to estimate a pharmacokinetic parameter associated therewith
InactiveUS20050037418A1Microbiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSolubilityDrug compound
A method and apparatus for assaying a drug candidate with a biosensor having one or more sensing surface-bound biomolecules associated therewith are disclosed. The method comprises the steps of measuring the binding interaction between the drug candidate and the one or more sensing surface-bound biomolecules of the biosensor to obtain an estimate of at least one binding interaction parameter of the drug candidate, and then comparing the estimated binding interaction parameter against a mathematical expression correlated from binding interaction data associated with known drug compounds to determine an estimate of at least pharmacokinetic parameter of absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion (ADME) that is related to the drug candidate. The present invention allows for the simultaneous measurement of different pharmacokinetic parameters of the drug candidate, as well as an indication of the drug candidate's solubility, by use of a single analytical instrument. The pharmacokinetic data may be represented as a ADME characterization profile; such ADME profiles are of great utility for purposes of drug screening and lead optimization.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Methods and systems for identifying ligand-protein binding sites
PendingUS20170316147A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingDrug protein interactionsPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a novel integrated structure and system-based approach for drug target prediction that enables the large-scale discovery of new targets for existing drugs Novel computer-readable storage media and computer systems are also provided. Methods and systems of the invention use novel sequence order-independent structure alignment, hierarchical clustering, and probabilistic sequence similarity techniques to construct a probabilistic pocket ensemble (PPE) that captures even promiscuous structural features of different binding sites for a drug on known targets. The drug's PPE is combined with an approximation of the drug delivery profile to facilitate large-scale prediction of novel drug-protein interactions with several applications to biological research and drug development.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
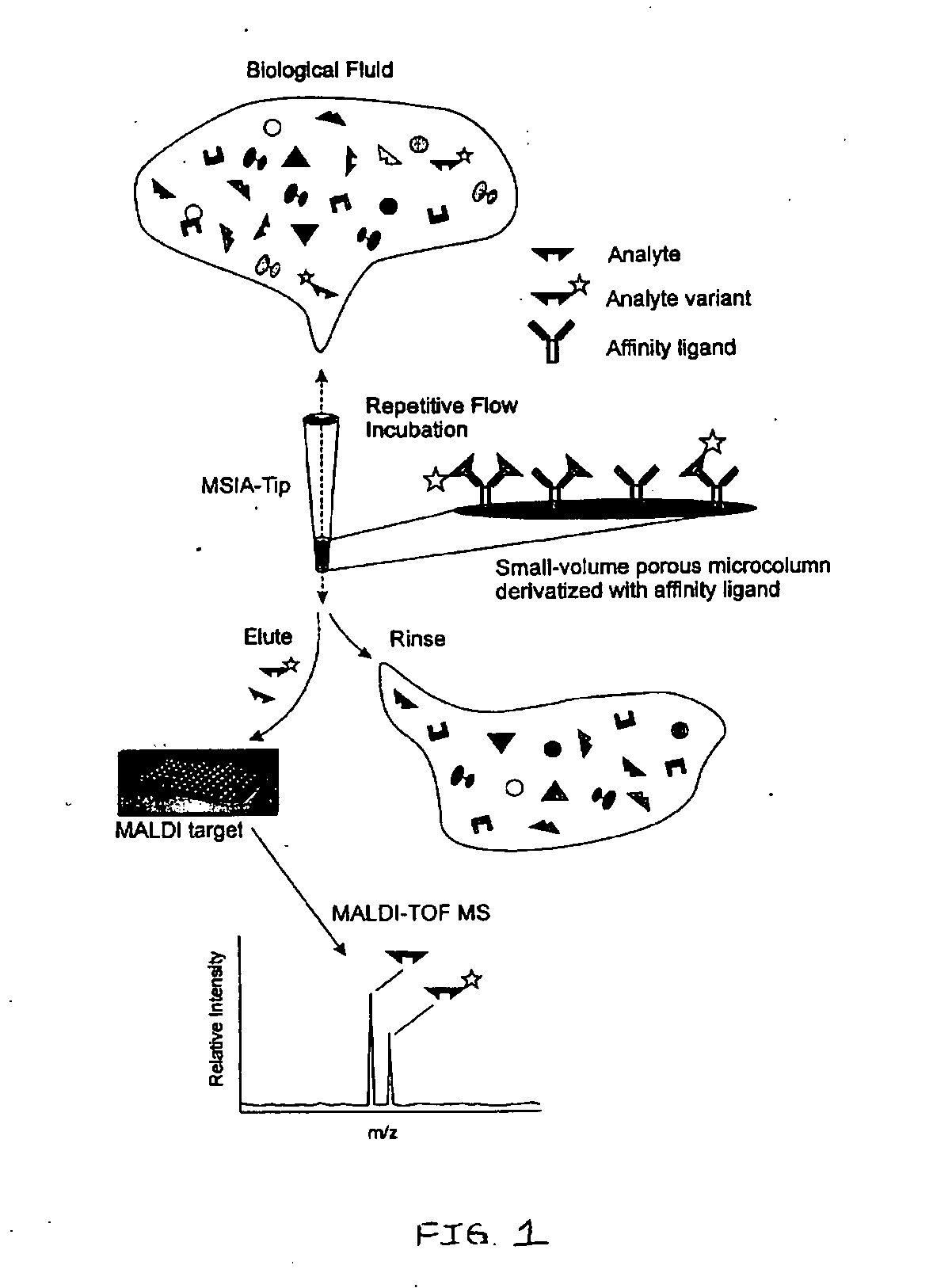
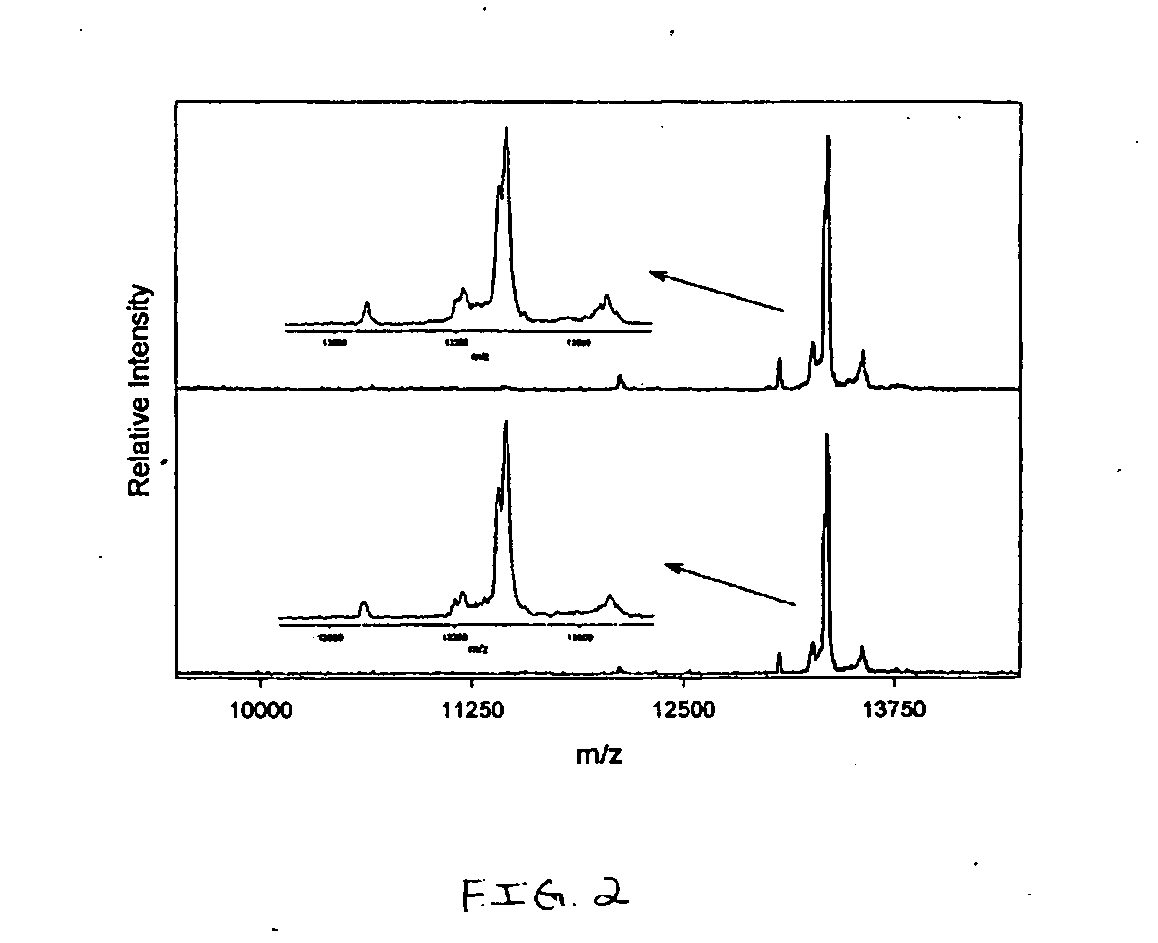
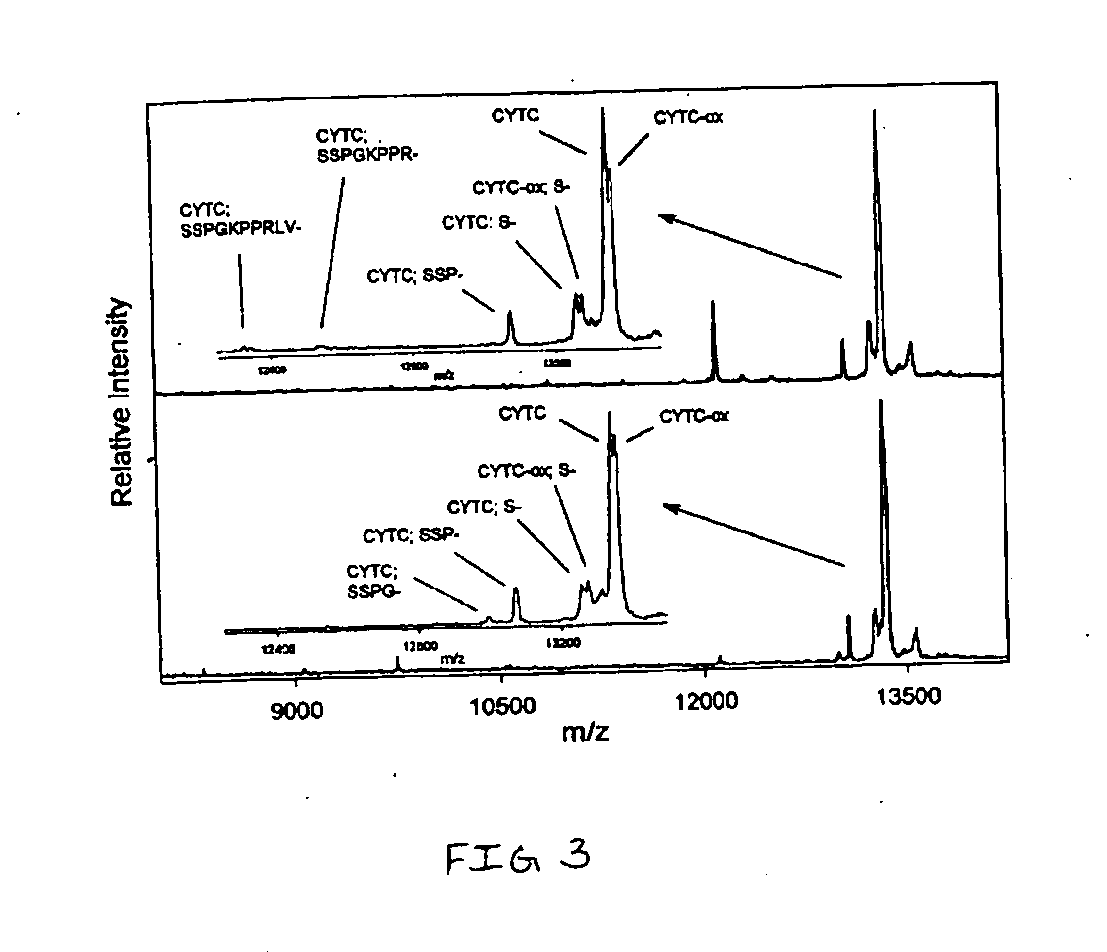
Analysis of proteins from biological fluids using mass spectrometric immunoassay
InactiveUS20060127948A1Sufficient dynamic rangeBiological testingImmunoassaysDrug targetMass spectrometric immunoassay
Presented herein are methods, devices and kits for the mass spectrometric immunoassay (MSIA) of proteins present in complex biological fluids or extracts. Pipettor tips containing porous solid supports that are covalently derivatized with affinity ligand and used to extract specific proteins and their variants from various biological fluids. Nonspecifically bound compounds are rinsed from the extraction devices using a series of buffer and water rinses, after which the wild type protein (and / or its variants) are eluted directly onto a target in preparation for analysis such as matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Mass spectrometry of the eluted sample then follows with the retained proteins identified via accurate molecular mass determination. Protein and variant levels can be determined using quantitative methods in which the protein / variant signals are normalized to signals of internal reference standard species (either doped into the samples prior to the MSIA analysis, or other endogenous protein co-extracted with the target proteins) and the values compared to a working curves constructed from samples containing known concentrations of the protein or variants. Such MSIA devices, kits and methods have significant application in the fields of; basic research and development, proteomics, protein structural characterization, drug discovery, drug-target discovery, therapeutic monitoring, clinical monitoring and diagnostics, as well as in the high throughput screening of large populations to establish and recognize protein / variant patterns that are able to differentiate healthy from diseased states.
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
Fluorescent probe for detecting ochratoxin A and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113372414AQualitative identificationLibrary screeningPeptide preparation methodsFluoProbesSingle strand
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting ochratoxin A and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biochemistry. The fluorescent probe is characterized in that OTA is taken as a target, and a phage surface random display 12-mer peptide library is used to screen out a recombinant phage specifically bound to the OTA. By extracting single-stranded DNA of the recombinant phage for sequencing and sequence comparison, an OTA specific affinity ligand sequence, Met-Pro-Met-Phe-Lys-His-Arg-Met-Phe-His-Thr-His is obtained. Afterwards the fluorescent probe specifically bound to OTA, FITC-Acp-Met-Pro-Met-Phe-Lys-His-Arg-Met-Phe-His-Thr-His is obtained by solid-phase polypeptide synthesis and fluorescence labeling. The construction method comprises the following steps: 1, screening a specific affinity ligand; 2, extracting recombinant phage DNA and determining a target sequence; 3, preparing a fluorescent probe; and 4, establishing a standard detection curve. The fluorescent probe of the present invention has the beneficial effects of 1, replacing an OTA monoclonal antibody; and 2, qualitatively identifying OTA and detecting content of the OTA in a sample.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for determining binding amount of biotinylated antibody of streptavidin labeled microspheres
PendingCN113624957AHigh sensitivityImprove anti-interference abilityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceStreptavidinAntibody
The invention provides a method for determining the binding amount of a biotinylated antibody of streptavidin labeled microspheres. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparation of the biotinylated antibody: diluting 2mg of the antibody to 5mg / ml by using a PBS buffer solution, adding a certain amount of sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin, uniformly shaking, reacting for 1 hour at room temperature, and dialyzing and purifying; 2) preparation of an acridinium ester-biotinylated antibody: diluting the biotinylated antibody in the step 1) to 2mg / ml, adding a certain amount of DMSO solution of acridinium ester, uniformly shaking, reacting for 2 hours in a dark place at room temperature, dialyzing and purifying in a dark place, and quantifying by using a BCA method; 3) drawing a standard curve, and reading a luminescence value RLU; and drawing an acridinium ester-biotinylated antibody addition mass-RLU relation curve. The method has the advantages that compared with a fluorescence method, the chemiluminescence method is higher in sensitivity and higher in anti-interference capability; and compared with a microsphere compound test method, the chemiluminescence method is simpler in operation and more accurate in result.
Owner:杭州博岳生物技术有限公司
Method for detecting concentration of target molecule in mixed systemand kit
ActiveCN112986551AEasy to operateShort timeBiological testingAgainst vector-borne diseasesMolecular bindingMixed systems
The invention discloses a method for detecting the concentration of a target molecule in a mixed system and a kit. The invention relates to a method for quantitatively detecting the concentration of a target molecule X. The method comprises the steps of adding a reporter molecule A into a reaction system containing the target molecule X for at least first given time, wherein specific binding activity exists between the reporter molecule A and the target molecule X; adding a competitive molecule B into the reaction system, wherein specific binding activity exists between the competitive molecule B and the reporter molecule A, the competitive molecule B and the target molecule X do not have any binding activity, and when the target molecule X does not exist, fluorescence intensity L0 with given intensity is emitted when the competitive molecule B is combined with the reporter molecule A; and uniformly mixing the system, and detecting the fluorescence intensity L of the system after waiting for at least a second given time, wherein in the ideal concentration range, a linear relation between the concentration of the target molecule X and the L0-L value can be established, and the established linear relation is used as a standard curve, and the concentration of the target molecule X can be calculated according to the actually measured fluorescence intensity change value L0-L. The invention also relates to a kit matched with the method.
Owner:北京聚树生物科技有限公司
Kit for detecting homocysteine
InactiveCN111593091AMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionInformation CardBlood specimen
The invention relates to the technical field of medical detection, in particular to a kit for detecting homocysteine. The kit for detecting homocysteine comprises a shell, a reagent and an informationcard, wherein a standard curve of absorbance values to concentration values is stored in the information card, a correction factor is stored in the information card, and the correction factor is usedfor correcting the concentration of homocysteine in a blood sample when the to-be-detected blood sample is whole blood; and the reagent comprises a treatment solution, a first reaction solution and asecond reaction solution, the treatment solution is used for converting protein-binding homocysteine in the blood sample into free homocysteine, and the first reaction solution and the second reaction solution are used for reacting with the free homocysteine. When the kit for detecting the homocysteine is in use, an analyzer can be used for directly obtaining the concentration of the homocysteineaccording to the absorbance value-to-concentration value standard curve which is stored in the information card, so that the kit is very convenient. In addition, the concentration of the homocysteinein the whole blood sample can be corrected through the correction factor.
Owner:深圳市希莱恒医用电子有限公司
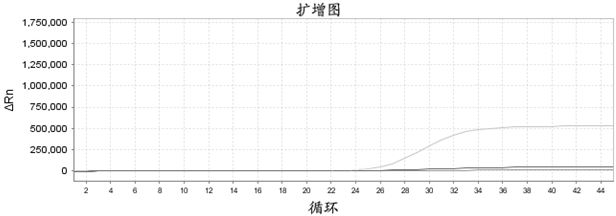
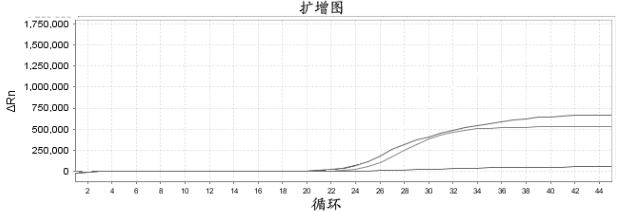
Composition, kit and method for detecting SARS-CoV-2 and application of composition, kit and method
ActiveCN114410848AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biological detection. In particular, the invention relates to the detection of SARS-CoV-2; more specifically, the invention relates to a composition, a kit and a method for detecting SARS-CoV-2 and application thereof. The invention provides a kit containing the composition, application of the composition and a method for detecting and typing the SARS-CoV-2 variant. By detecting variation sites with different characteristic functions, the Armike and Delta variants are subjected to typing, so that the typing detection of the SARS-CoV-2 variants is realized in a single-tube reaction system at the same time. Different strains can be treated differently, so that treatment and prevention are more efficient. The composition disclosed by the invention is low in cost, high in flux and simple and convenient to operate, and a result reading process can be judged through an amplification curve Ct value. The whole detection process is carried out under a single-tube closed condition, so that false positive and environmental pollution are avoided.
Owner:深圳联合医学检验实验室
Determination method for dynamic loading capacity of affinity chromatography filler
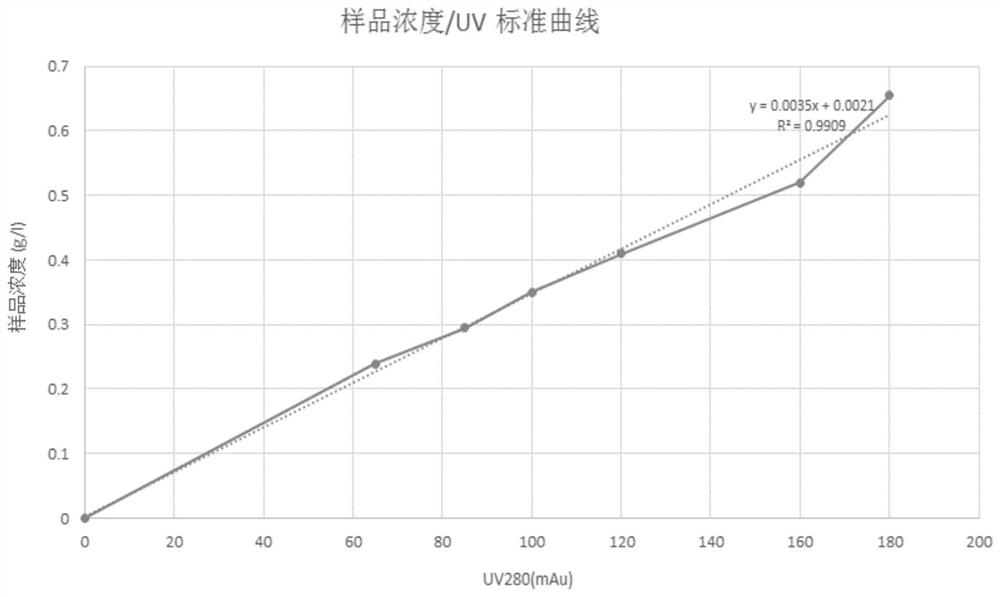
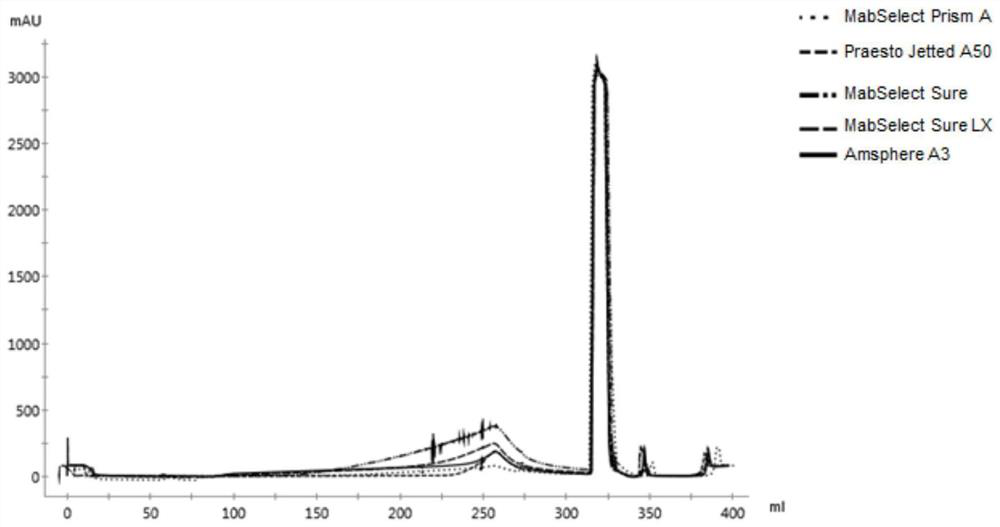
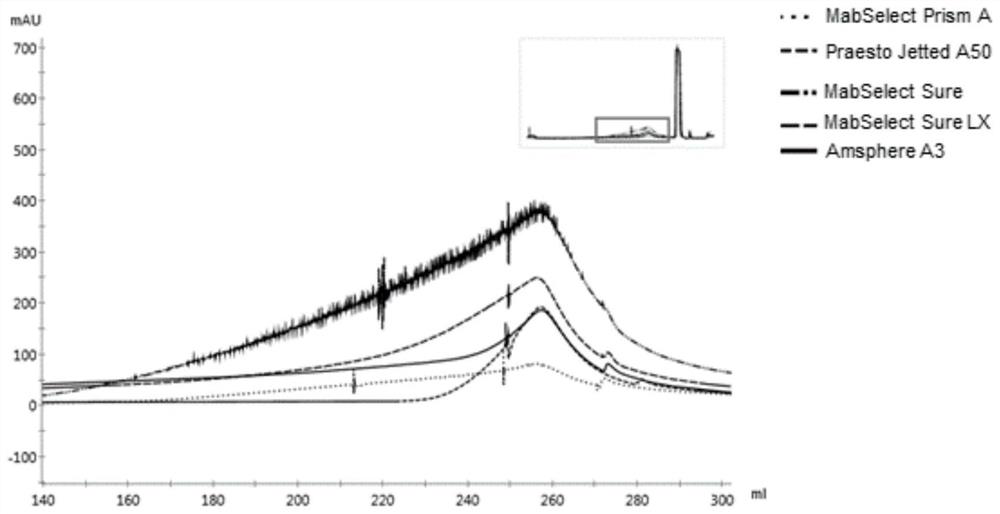
PendingCN114280208AQuick judgmentSimple calculationComponent separationOther chemical processesProtein solutionUv absorbance
The invention discloses a method for measuring the dynamic loading capacity of an affinity chromatography filler, which comprises the following steps: 1) loading a sample onto a chromatographic column filled with the affinity chromatography filler to be screened, collecting flow-through liquid, and recording the loading volume; the sample loading volume is the total sample loading volume when the concentration of the penetrating protein sample corresponding to the ultraviolet absorption value reaches 5%-10% of the concentration of the target protein in the sample; the sample is a protein solution; and 2) calculating the dynamic loading capacity of the affinity chromatography filler according to the sample concentration-ultraviolet absorption value standard curve and the sample loading volume in the step 1). According to the property characteristics of affinity adsorption of the affinity filler and the antibody, an affinity adsorption kinetic model is constructed, the advantages of a traditional static binding capacity determination method and a current standard dynamic binding capacity determination method can be considered, and the method is short in time consumption, low in cost and high in accuracy.
Owner:鼎康(武汉)生物医药有限公司
Ratio fluorescence immunochromatography detection test strip and detection method thereof
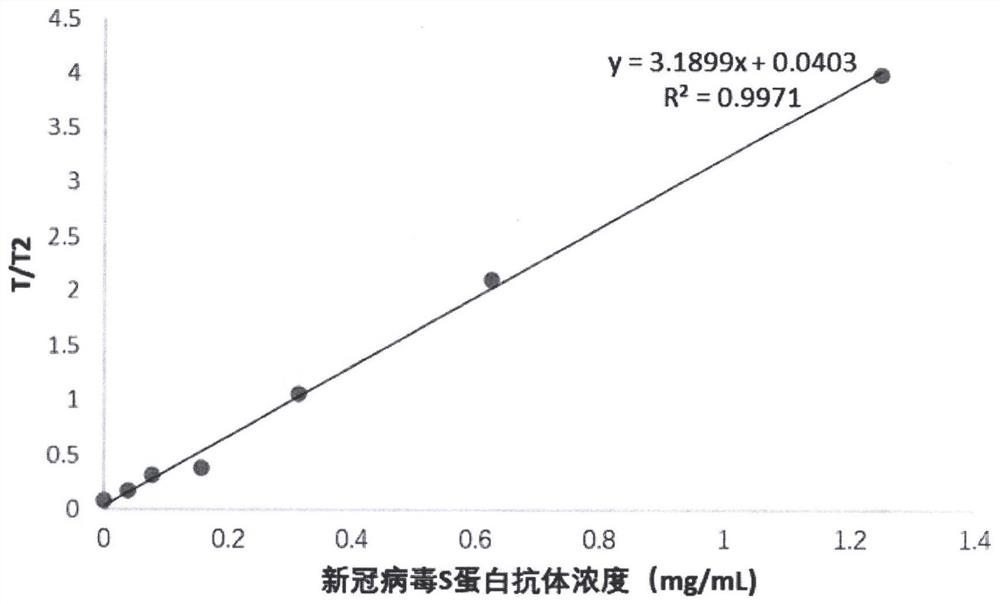
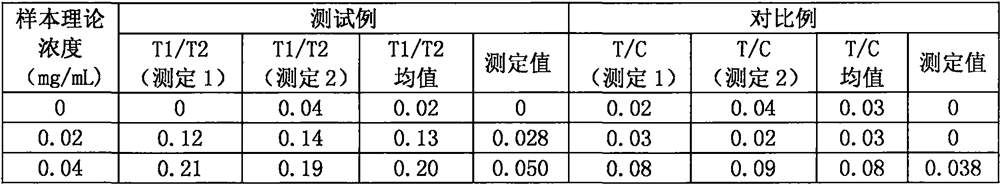
The invention provides a ratio fluorescence immunochromatography detection test strip. The test strip comprises a sample pad, a marking pad, a coating film and a water absorption pad which are connected in sequence; a calibration line C, a test line T1 and a test line T2 are sequentially arranged on the coating film, and the line C is coated with an independent quality control antibody; the marking pad contains a fluorescently-labeled recombinant antigen and a fluorescently-labeled independent quality control antigen; the T1 line is coated with a recombinant antigen; and the T2 line is coated with a recombinant antigen ligand. According to the invention, the ratio (T1 / T2) of the fluorescence detection signals on the T1 line and the T2 line is determined, the ratio (T1 / T2) is positively correlated with the antibody concentration in the sample, and a correlation calibration curve equation is established so as to establish a qualitative or quantitative detection fluorescence immunochromatography detection method; according to the test strip and the method provided by the invention, the interference of a fluorescence detection background signal is overcome, and the sensitivity, the accuracy and the credibility of fluorescence immunochromatography are improved.
Owner:BEIJING NORTH INST OF BIOLOGICAL TECH
Composition, kit, method for detecting sars-cov-2 and use thereof
ActiveCN114410848BMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyBiochemistry
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology detection; in particular, it relates to the detection of SARS-CoV-2; more specifically, it relates to a composition, kit, method and use for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. The present invention provides a kit comprising the composition, use of the composition, and a method for detecting and typing SARS-CoV-2 variant strains. By detecting different characteristic functional variation sites, Omicron and Delta mutants were typed, so as to simultaneously realize the detection of SARS-CoV-2 mutant typing in a single-tube reaction system. This enables different strains to be treated differently, making treatment and prevention more efficient. The composition of the invention has low cost, high throughput and simple operation, and the result reading process can be determined by the Ct value of the amplification curve. The whole process of detection is carried out under single-tube closed conditions to avoid false positives and environmental pollution.
Owner:深圳联合医学检验实验室
Quantitative determination method for specific IgG antibody in plasma
PendingCN113075398AGood test resultLow detection limitDisease diagnosisSignalling moleculesQuantitative determination
The invention discloses a quantitative determination method for a specific IgG antibody in plasma, which belongs to the field of antibody detection. The method comprises the following steps of 1) dividing one plasma sample into two groups as to-be-detected plasma and to-be-treated contrast plasma, (2) incubating excessive antigens and to-be-treated contrast plasma, and neutralizing to-be-detected antibodies in the to-be-treated contrast plasma to obtain contrast plasma, 3) taking to-be-detected plasma and contrast plasma as samples, combining the to-be-detected plasma and the contrast plasma with corresponding antigens connected to the solid-phase carrier, successively combining the antigen-antibody compound with IgG antibodies and signal molecules to generate quantifiable data, and subtracting two groups of quantifiable data to obtain detection data, 4) diluting thousands of mixed plasma serving as a standard substance into different concentrations according to the steps 1)-3) to make a standard curve, and 5) substituting detection data of a to-be-detected sample into the standard curve to obtain the content of the specific IgG antibody in the plasma. According to the determination method, the influence of non-specific binding can be eliminated, and the detection result is reliable.
Owner:BLOOD TRASFUSION INST CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Quantitative detection device and detection method of biological fluid samples
The invention discloses a biological fluid sample quantitative detection device, which comprises a test strip arranged in a box, a memory for color intensity data and a reader for the color intensity data; the bottom layer of the test strip is a substrate, and the substrate is provided with It has a porous test main membrane; a second membrane is arranged upstream of the main test membrane, and a sample application site and a label ligand site are arranged on the second membrane, and the biological fluid sample and its complex to be tested are promoted by capillary action , the labeled ligand can flow; the downstream of the main test membrane is provided with a third membrane, and the third membrane is used to absorb the biological fluid sample to be tested that has passed the test main membrane at the end of the downstream of the main test membrane; the box cover is provided with There are two sample injection holes and a viewing window, and the detection device of the present invention can use the light reflection intensity of the known concentration standard strip to draw a standard curve, so as to perform rapid, effective and accurate quantitative analysis on biological fluid samples.
Owner:李金波
Method for measuring kinetic and thermodynamic parameters on solid-liquid interface
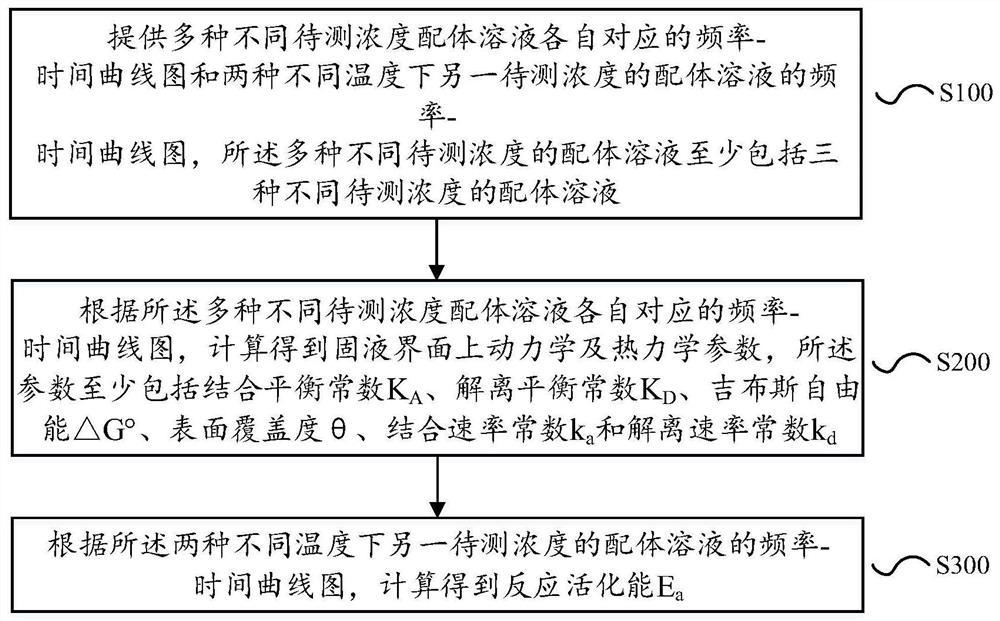
PendingCN113125552AThe determination method is simple and fastAvoid systematic errorsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial weighingAptamerDissociation rate constant
The invention discloses a method for measuring kinetic and thermodynamic parameters on a solid-liquid interface, which comprises the steps of according to frequency-time curve graphs corresponding to various ligand solutions with different concentrations to be measured and frequency-time curve graphs of another ligand solution with the concentration to be measured at two different temperatures, analyzing and calculating an output frequency-time curve of a micro-cantilever sensor to obtain dynamic and thermodynamic parameters (the binding / dissociation equilibrium constant KA / KD, the Gibbs free energy [delta]G degree, the surface coverage [theta], the binding / dissociation rate constant ka / kd and the reaction activation energy Ea) of a nucleic acid aptamer and a ligand thereof on the solid-liquid interface. The method overcomes the defects that a traditional method is expensive in instrument, tedious in operation, single in parameter determination and the like, has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, low in cost, simple and rapid in operation, free of marking and correction, capable of effectively avoiding system errors, capable of determining related parameters at a time and the like, and is suitable for determination of dynamic and thermodynamic parameters of multiple nucleic acid aptamers and ligands thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rapid modification and screening method for antibody pH-dependent binding activity
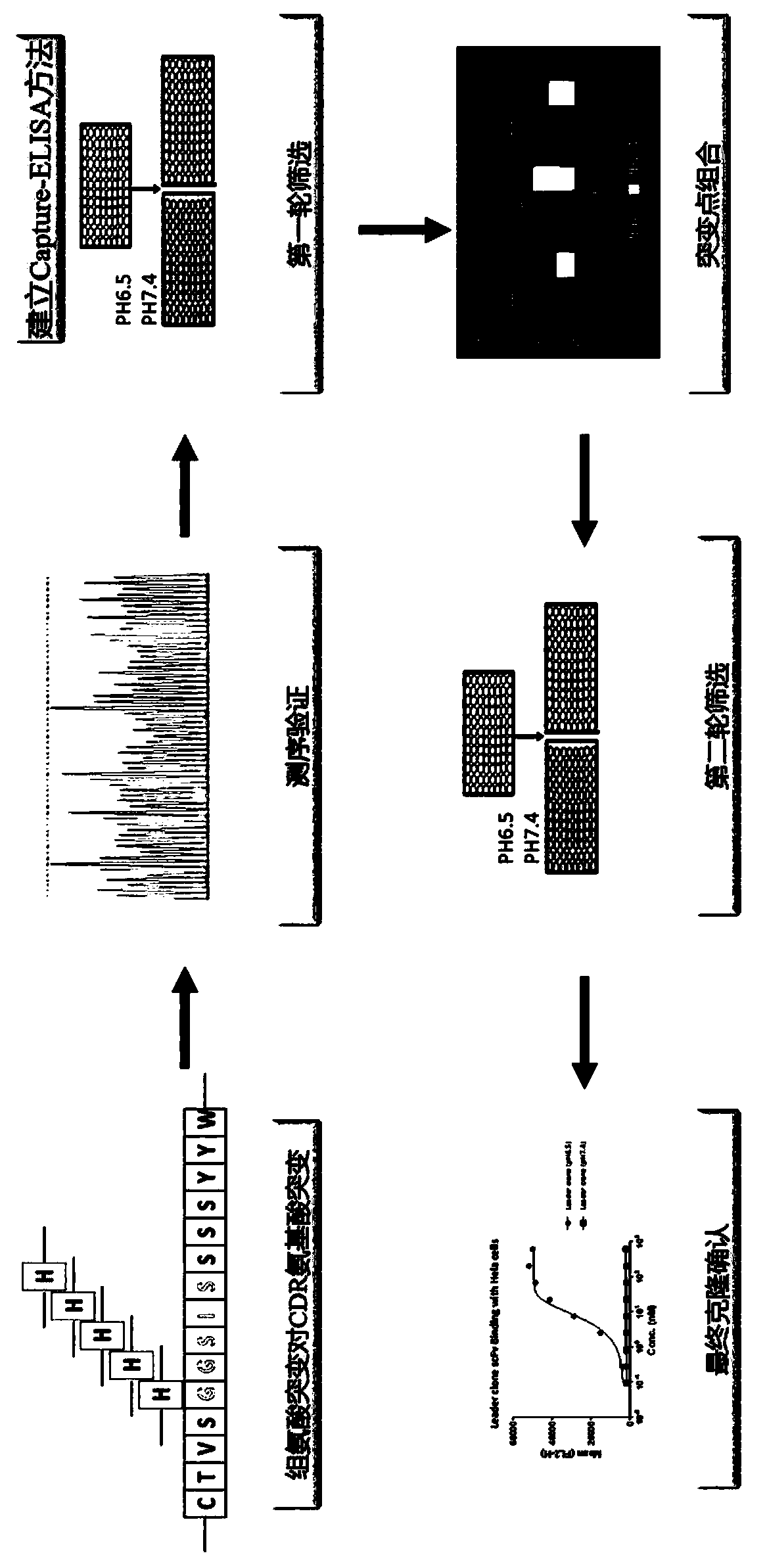
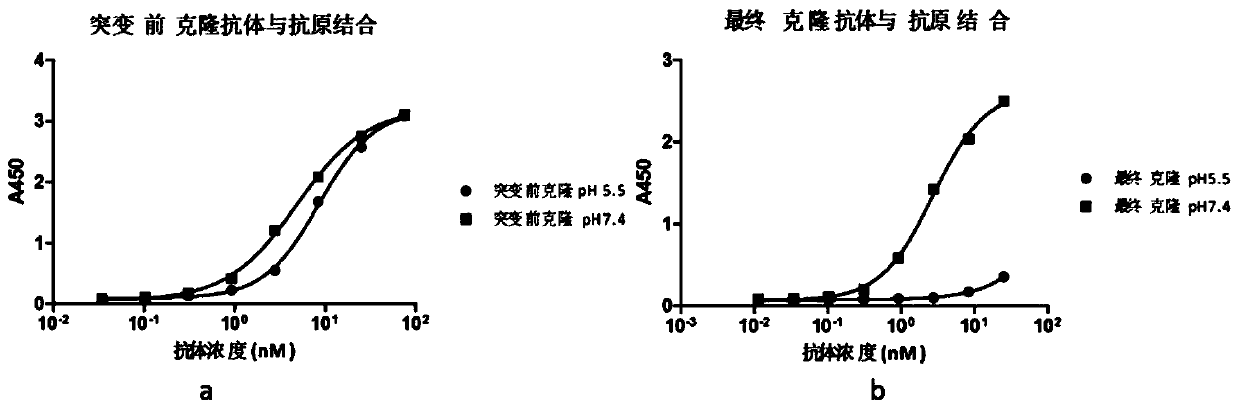
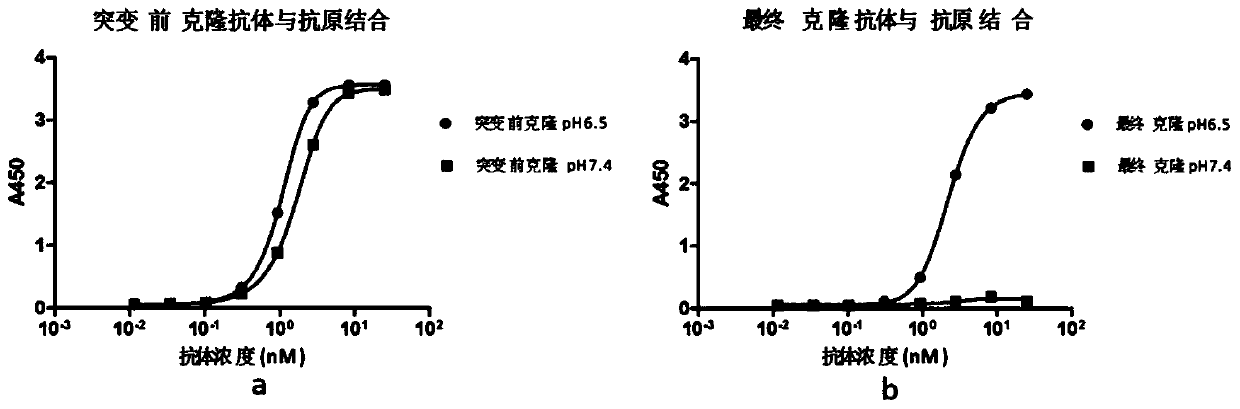
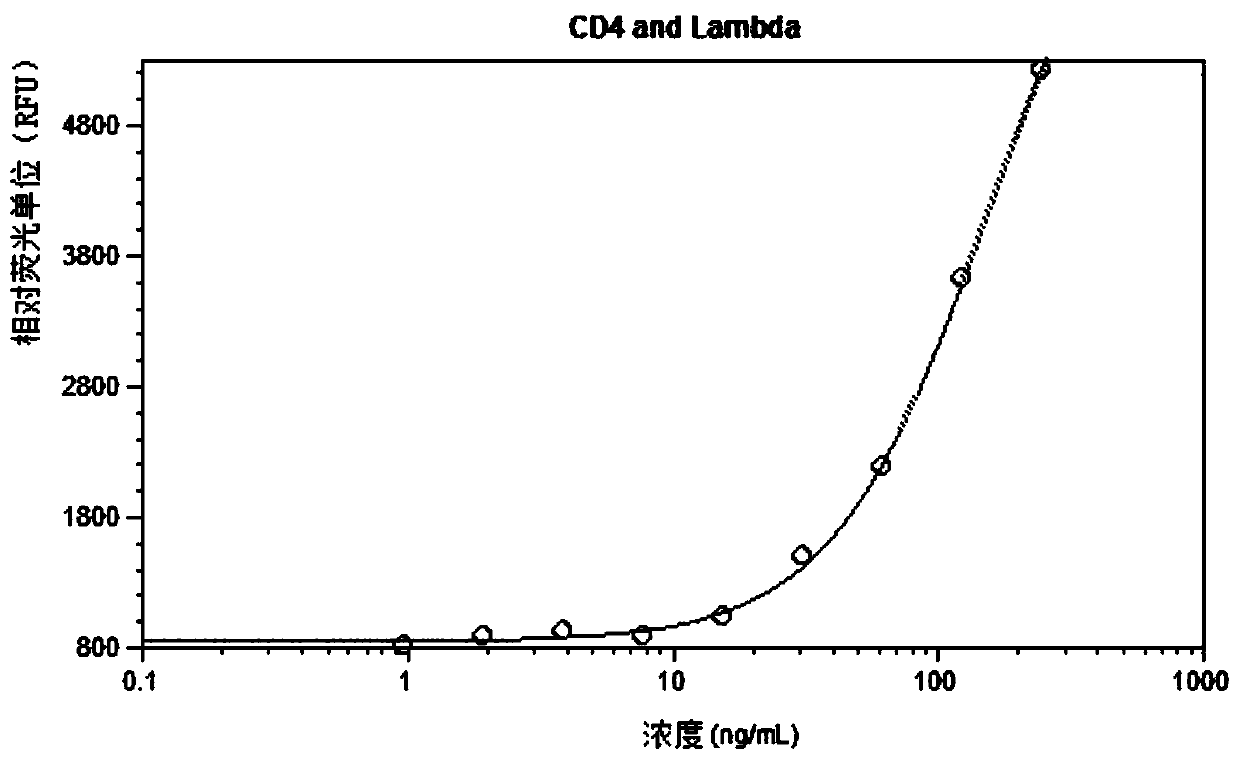
InactiveCN110669778AEasy to transformGuaranteed stabilityImmunoglobulinsBiological testingAntigenHigh flux
The invention discloses a method for transforming and screening antibody pH-dependent binding activity. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a wild antibody scFv plasmid template; (2) performing site-specific mutagenesis on six CDR regions of an antibody, and replacing each amino acid in the CDR regions with histidine; (3) establishing a Capture-ELISA condition and carrying out high-throughput screening; and (4) performing KD-ELISA and FACS detection: carrying out gradient dilution on a sample, carrying out KD-ELISA detection by using buffers with different pH values, anddetermining the pH-dependent binding activity of targets cloned on the antigen surface and cell surface according to a curve drawn by detection data. The method provided by the invention can be usedfor obtaining the antibody with pH-dependent binding activity in a high-flux, high-efficiency and low-cost manner.
Owner:SHANGHAI WUXI BIOLOGIC TECH CO LTD +2
A method for detecting biological activity and titer of bispecific antibody and its application
ActiveCN107064092BEfficient screeningHigh bispecific binding activityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntigen bindingSpecific antibody
Owner:SHANGHAI WUXI BIOLOGIC TECH CO LTD
Calibration Reagent and Method
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a multiplex assay, comprising: adding a calibration reagent to a solid phase on which a plurality of capturing agents are immobilised, adding a detection molecule which has a capacity to bind to the calibration reagent, detecting bound detection molecule, thereby creating a calibration curve, wherein the calibration reagent comprises at least two different binding molecules, wherein each binding molecule has a capacity to bind specifically to a capturing agent immobilised on the solid phase and a capacity to bind to a detection molecule. Further provided is a multiplex assay system comprising such a calibration reagent.
Owner:PHADIA AB
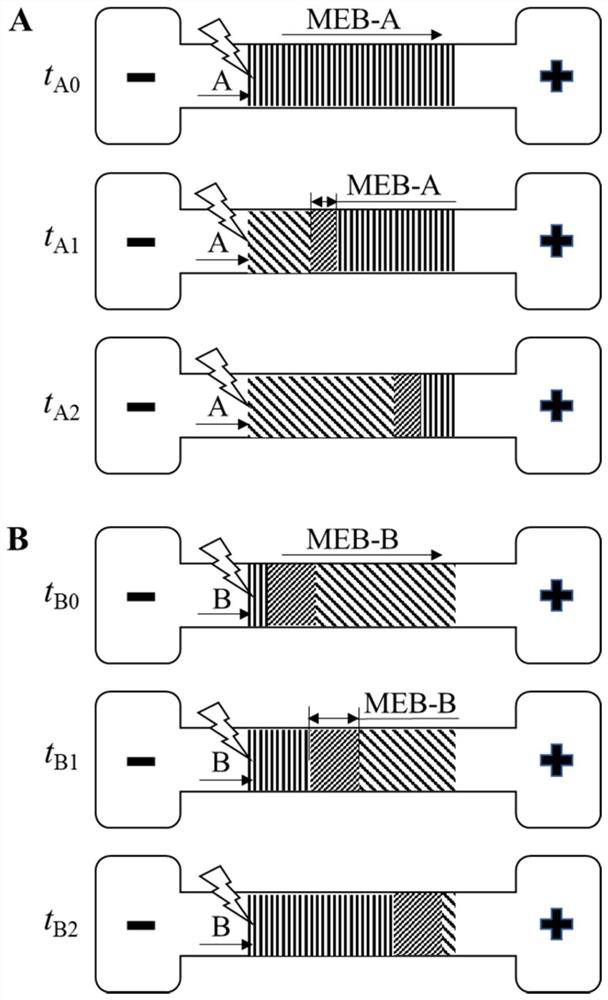
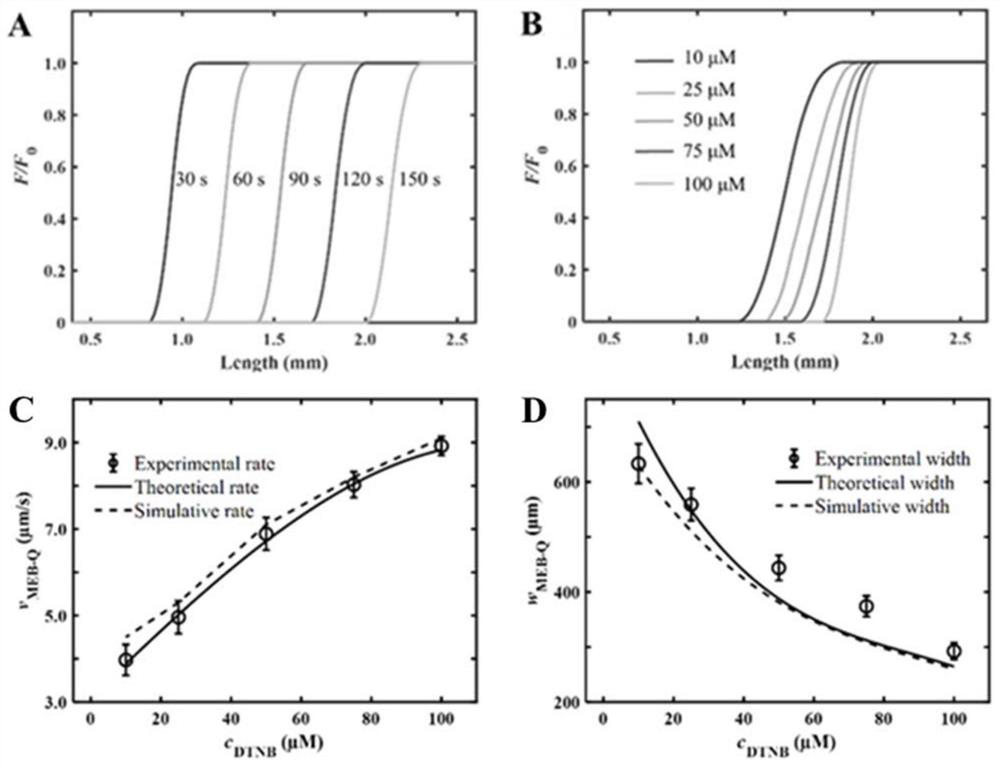
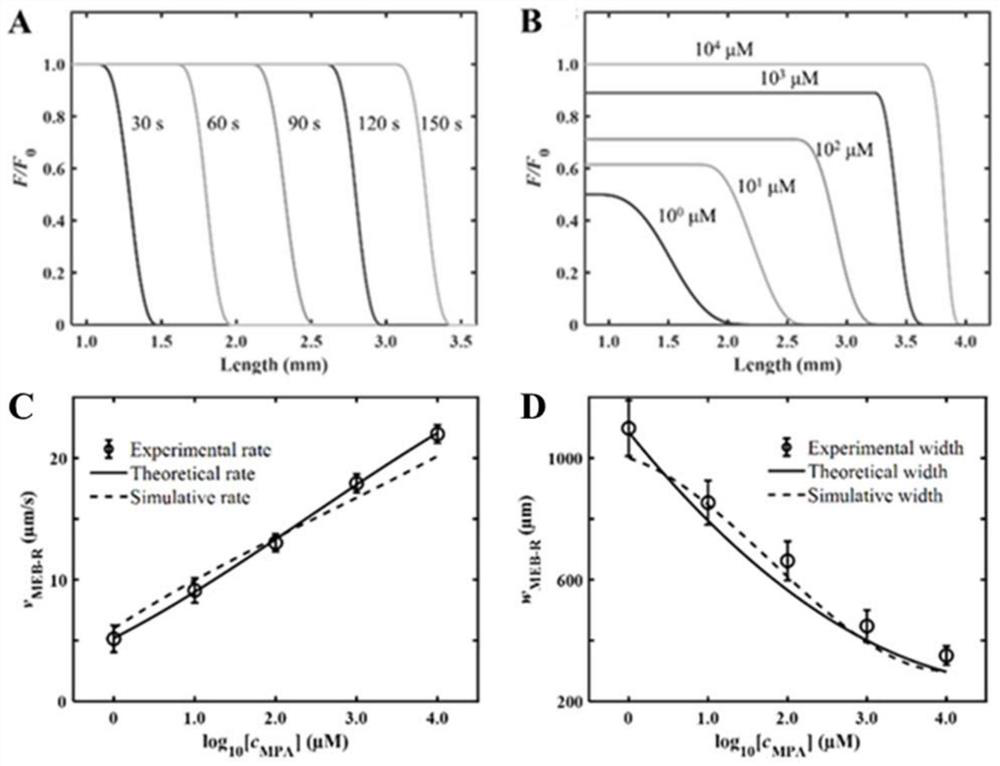
A Method for Visual Detection of Substance Concentration Based on Mobile Exchange Interface
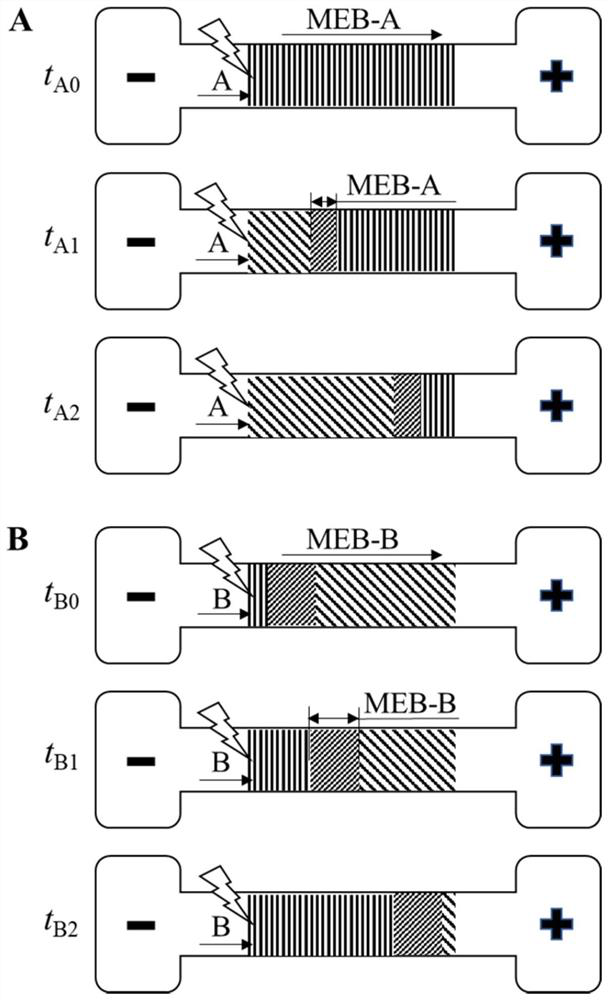
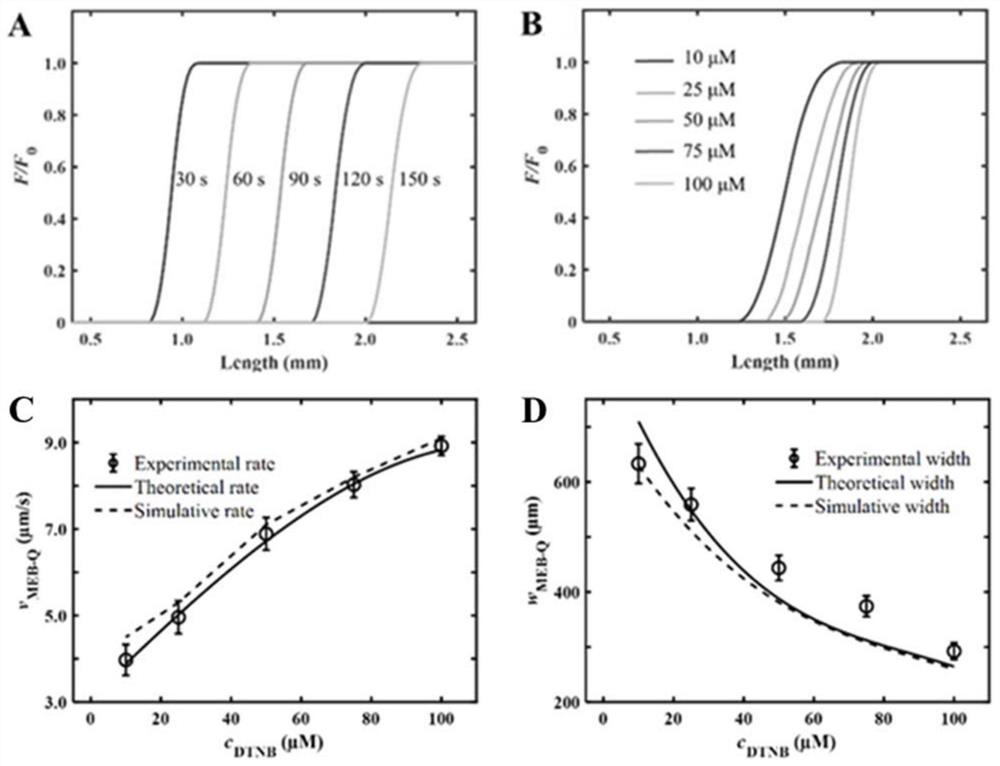
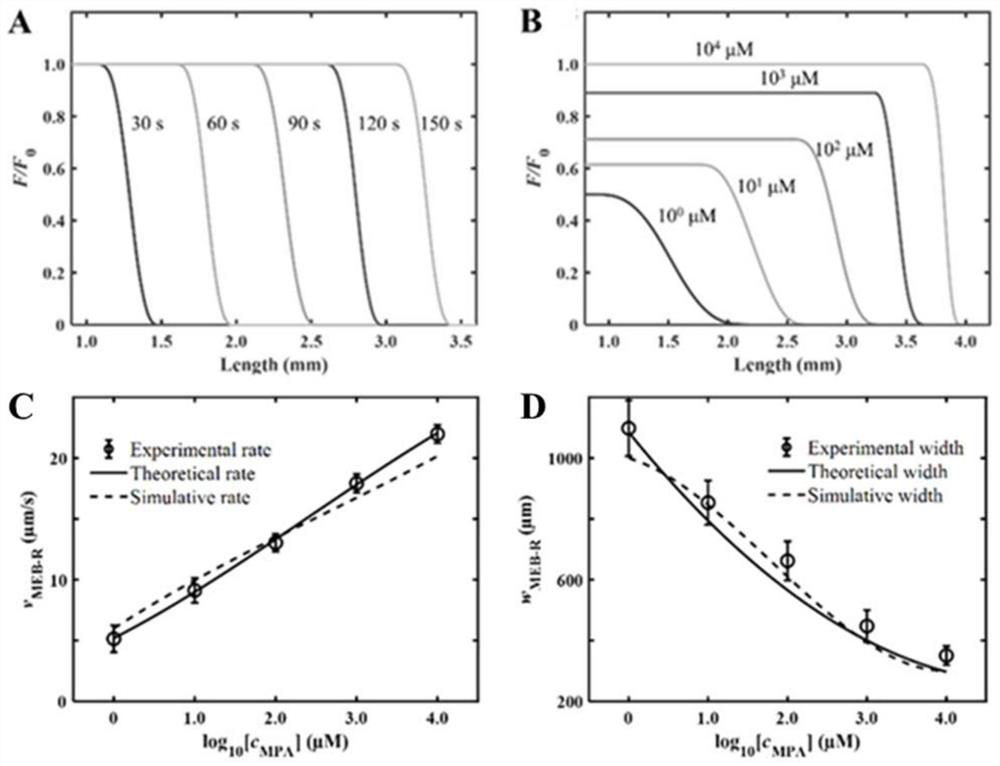
ActiveCN113063834BEasy to handleLow detection consumptionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresesAnalyte
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for visually detecting substance concentration based on mobile switching interface
ActiveCN113063834AEasy to handleLow detection consumptionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresesNanoparticle
The invention discloses a method for visually detecting substance concentration based on a mobile exchange interface. The method mainly comprises the steps of 1) enabling different ligands to be subjected to a replacement reaction on the surface of a solid-phase substance (such as nano-particles and cells) to form an optical signal; (2) fixing the solid-phase substance in an electrophoresis channel in advance by using gel (or a self-filling mode and the like), driving a to-be-detected substance to move in the channel in an electrophoresis mode, and replacing a ligand on the surface of the solid-phase substance to form a mobile exchange interface; and 3) recording the interface movement condition, establishing a standard curve of the interface migration rate, the interface width and the substance concentration, and calculating the substance concentration (or the ligand replacement reaction rate) of the reaction on the surface of the solid-phase substance. The method has the advantages of simple operation flow, low cost, visualization and no need of dependence on expensive instruments.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
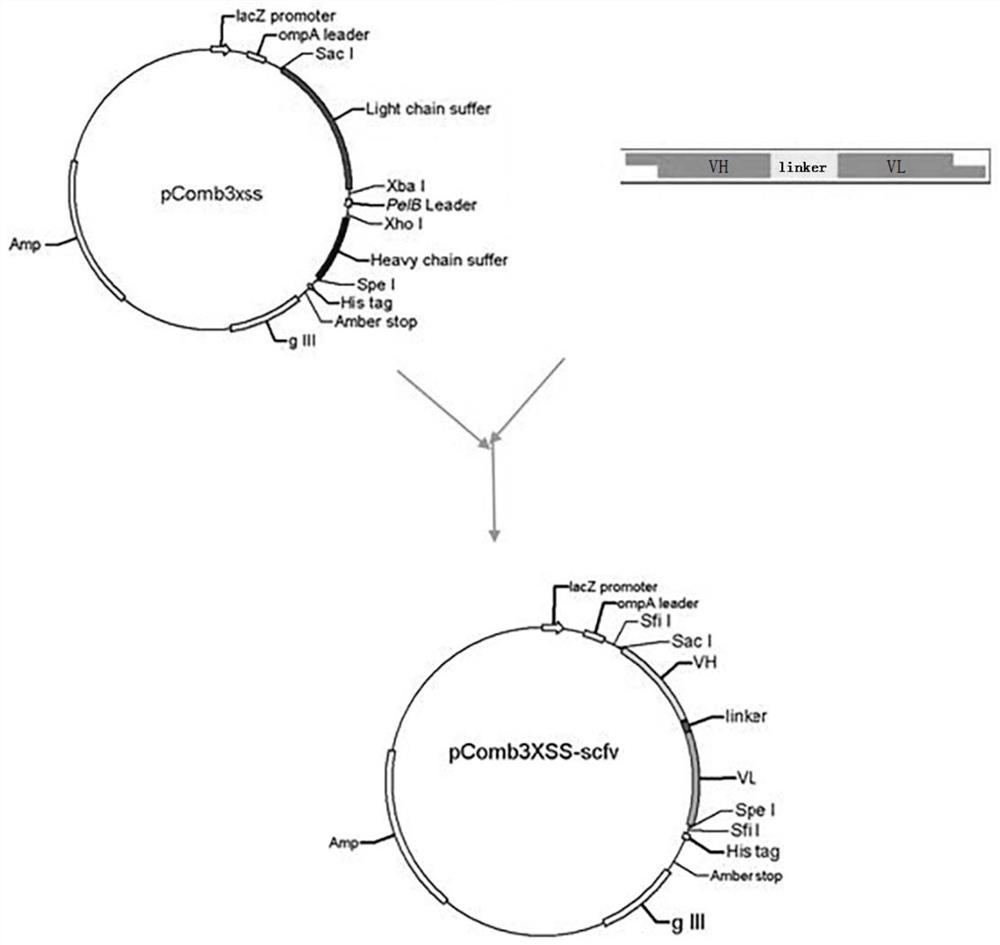
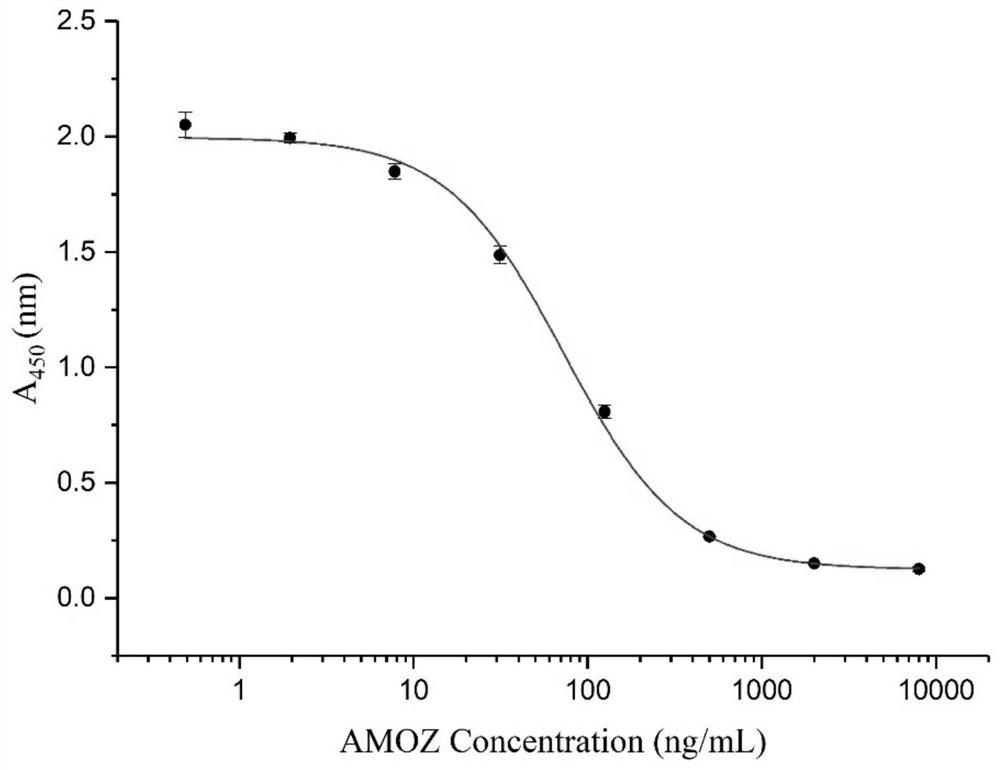
A single-chain antibody that directly recognizes 3-amino-5-morpholinomethyl-2-oxazolidinone and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108218992BRapid Test ScreeningLow costBiological material analysisImmunoglobulinsSingle-Chain AntibodiesOxazolidone
The invention discloses a single-chain antibody (scFv) directly recognizing 3-amino-5-morpholinomethyl-2-oxazolidinone (AMOZ), its preparation method and application. The single-chain antibody includes a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region, the sequences of which are shown in SEQ ID NO. The sequences shown have the same functional amino acid sequence. The binding of the single-chain antibody scFv provided by the invention to the antigen can be competitively inhibited by the free hapten, IC 50 The detection limit is 72.93ng / mL, and the detection limit is 13.35ng / mL, which has good antigen binding activity; the linear detection range is between 24.98~212.92ng / mL through the standard curve. The genetically engineered antibody has good application prospects in the immunodetection of AMOZ and the rapid detection and screening of a large number of samples.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
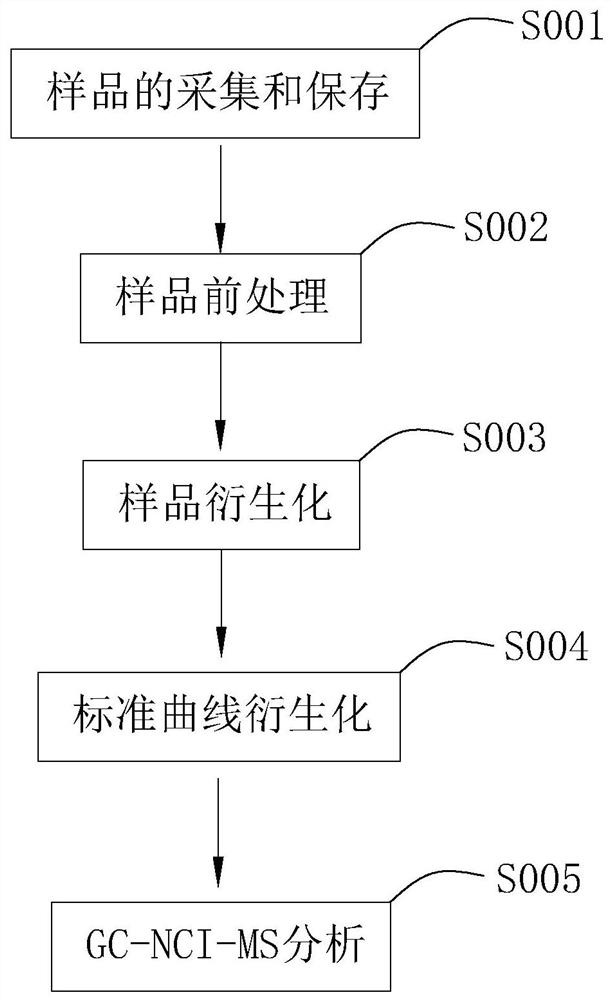
A detection method for phenolic endocrine disrupting substances
ActiveCN109142557BAchieve separationHigh selectivityComponent separationPerturbateurs endocriniensChemical ionization
The present invention relates to the field of analysis of environmental pollutants. Aiming at the problem of relatively large detection errors of phenolic substances, a detection method for phenolic endocrine disrupting substances is provided. The technical scheme is as follows, including the following steps: (1) Sample collection and storage; (2) sample pretreatment; (3) sample derivatization; (4) standard curve derivatization; (5) GC‑NCI‑MS analysis. Use the detection method of GC-NCI-MS to detect and analyze the samples to improve the accuracy of the analysis and detection data, and then derivatize the samples to facilitate the analysis and detection of the samples, and at the same time use the internal standard method of the standard curve to reduce the detection cost by comparison In addition, it is detected by negative chemical ionization (NCI), which has high selectivity and sensitivity to the target compound in the sample, and improves the accuracy of detection.
Owner:广州国邦检测认证有限公司
A kind of ELISA method and application of measuring bispecific antibody BSAB in serum
ActiveCN112285366BHigh measurement sensitivityQuantitatively accurateBiological material analysisBiological testingAntigenElisa method
Owner:南京广祺医药科技有限公司
A method for detecting PD-L1 protein on the surface of extracellular vesicles by nucleic acid aptamer of programmed death receptor-ligand 1
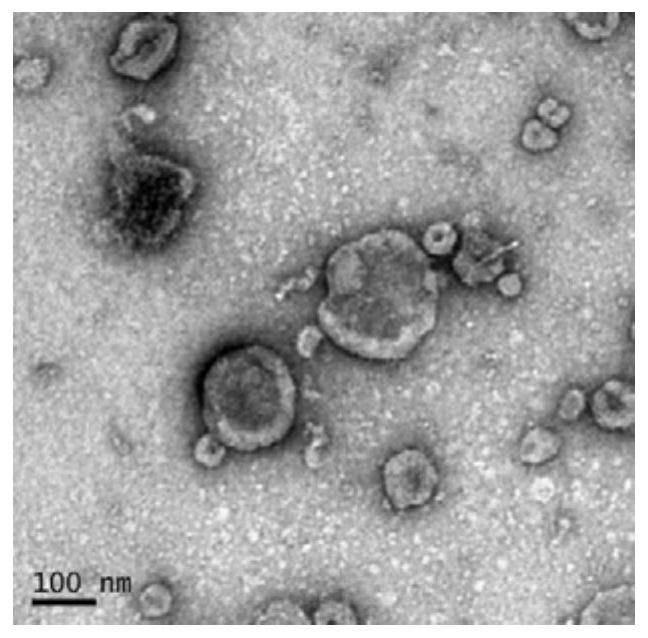
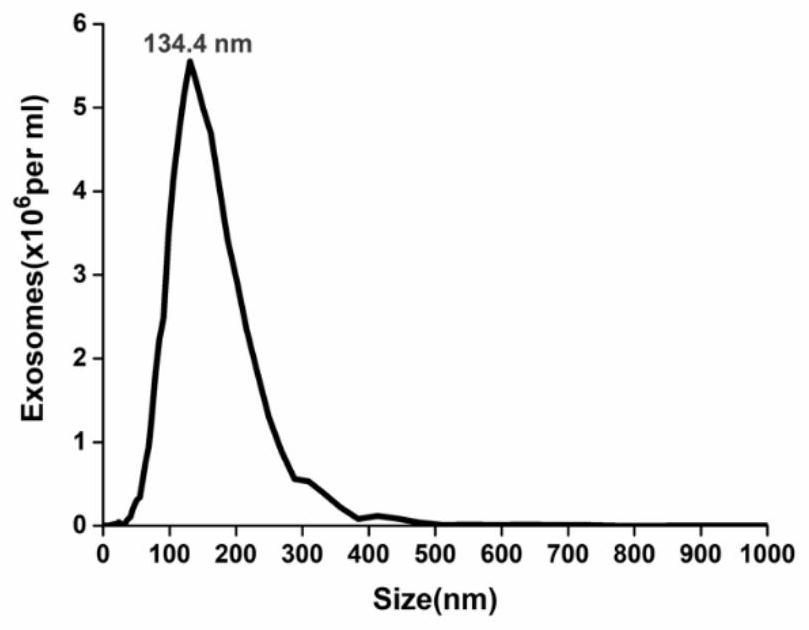
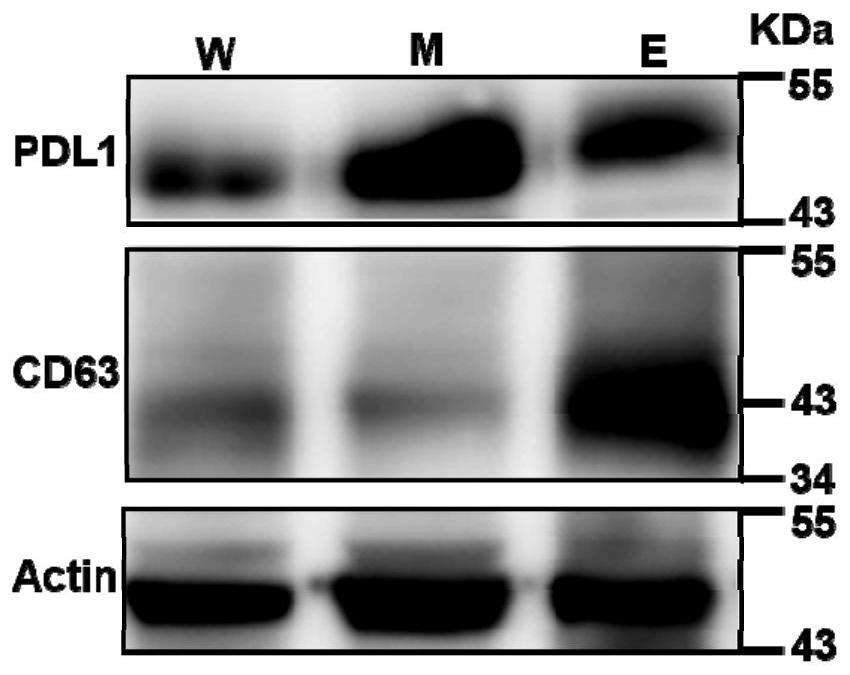
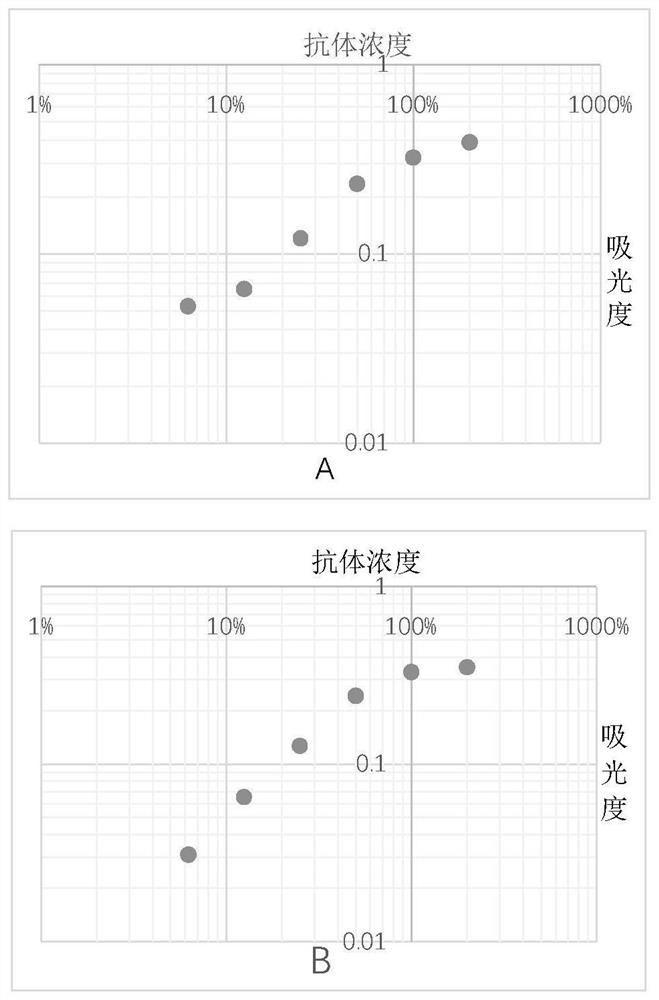
ActiveCN110108885BConsume a small amountHigh sensitivityMaterial analysisDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerExtracellular vesicle
The invention discloses a method of detecting an extracellular vesicle surface PD-L1 protein by aptamer of a programmed death receptor-ligand 1 (PD-L1). The method comprises the following steps: 1) asample mixture of a PD-L1 aptamer with a constant concentration and extracellular vesicles with different concentrations is prepared; 2) the sample mixture is placed in a microscale thermophoresis (MST) device for measurement; and 3) the fluorescence of each sample mixture with a different extracellular vesicle concentration is measured, drawing is carried out on the obtained normalized fluorescence in relative to time, an MST trajectory is fit, drawing is then carried out on the normalized fluorescence of the MST trajectory in relative to the extracellular vesicles, a binding curve associatedwith the extracellular vesicle concentration and the normalized fluorescence is fit, and thus, extracellular vesicle surface PD-L1 protein detection is realized. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed in the invention has the advantages that the sensitivity is high, the operation is simple and convenient, the detection is quick and efficient, few samples are consumed, an economic and affordable price is realized, and the potential for wide promotion is realized.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Quantitative determination method for specific IgM antibody in plasma
PendingCN113063949AEliminate the effects ofEasy to detectDisease diagnosisColor/spectral properties measurementsSignalling moleculesSpecific igm
The invention discloses a quantitative determination method for a specific IgM antibody in plasma, and belongs to the field of antibody detection. The method comprises the following steps: 1) dividing one plasma sample into two groups as to-be-detected plasma and to-be-treated contrast plasma; (2) incubating excessive antigens and to-be-treated control plasma, and neutralizing to-be-detected antibodies in the to-be-treated control plasma to obtain control plasma; 3) taking to-be-detected plasma and the control plasma as samples, combining the to-be-detected plasma and the contrast plasma with corresponding antigens connected to the solid-phase carrier, successively combining the antigen-antibody complex with the IgM antibody and the signal molecule to generate quantifiable data, and subtracting two groups of quantifiable data to obtain detection data; (4) diluting the mixed plasma of thousands of persons as a standard substance into different concentrations according to the steps (1)-(3) to make a standard curve; and 5) substituting detection data of a sample to be detected into the standard curve to obtain the content of the specific IgM antibody in the plasma. According to the determination method, the influence of non-specific binding can be eliminated, and the detection result is reliable.
Owner:BLOOD TRASFUSION INST CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com