Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
260 results about "Plasma nitridation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
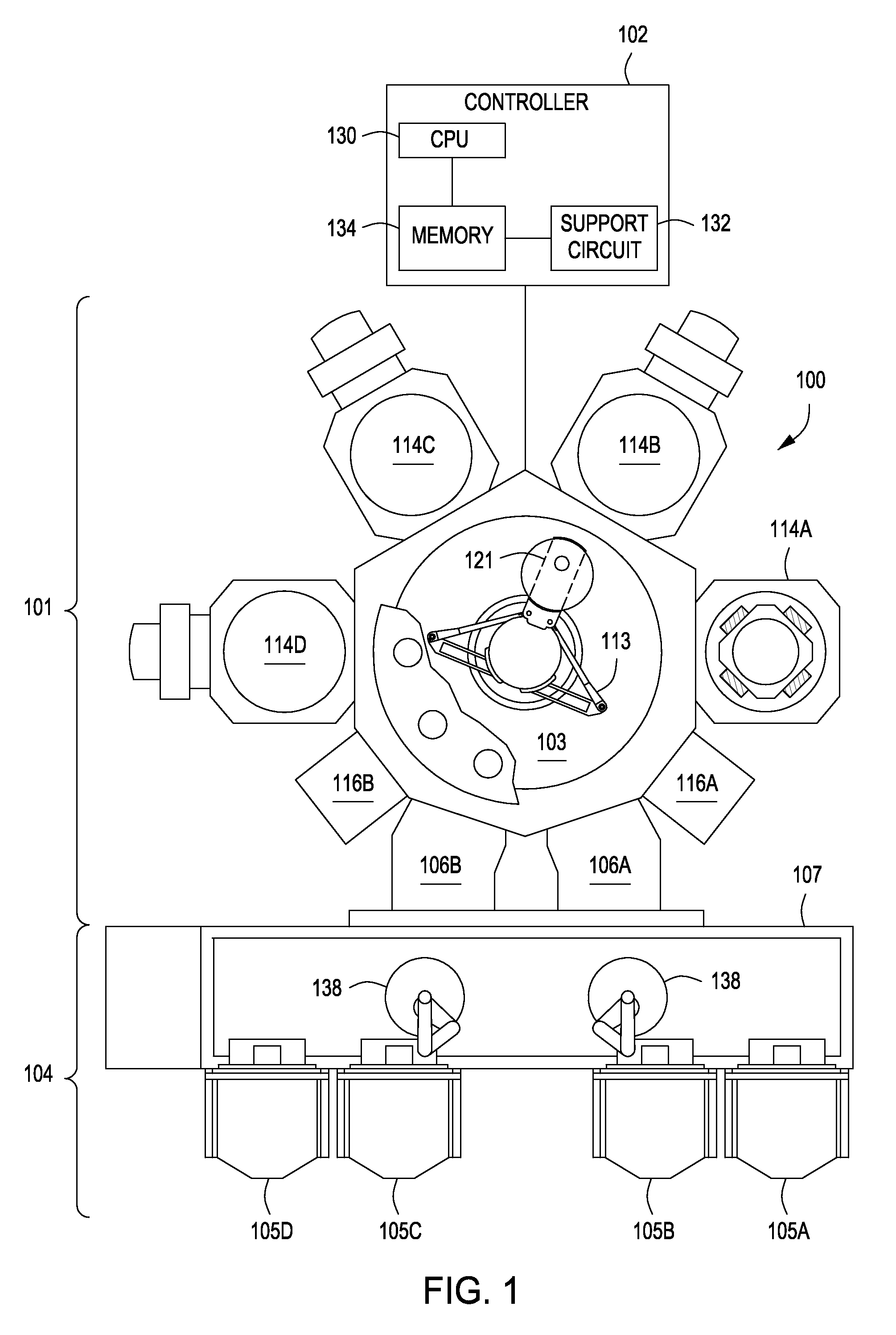
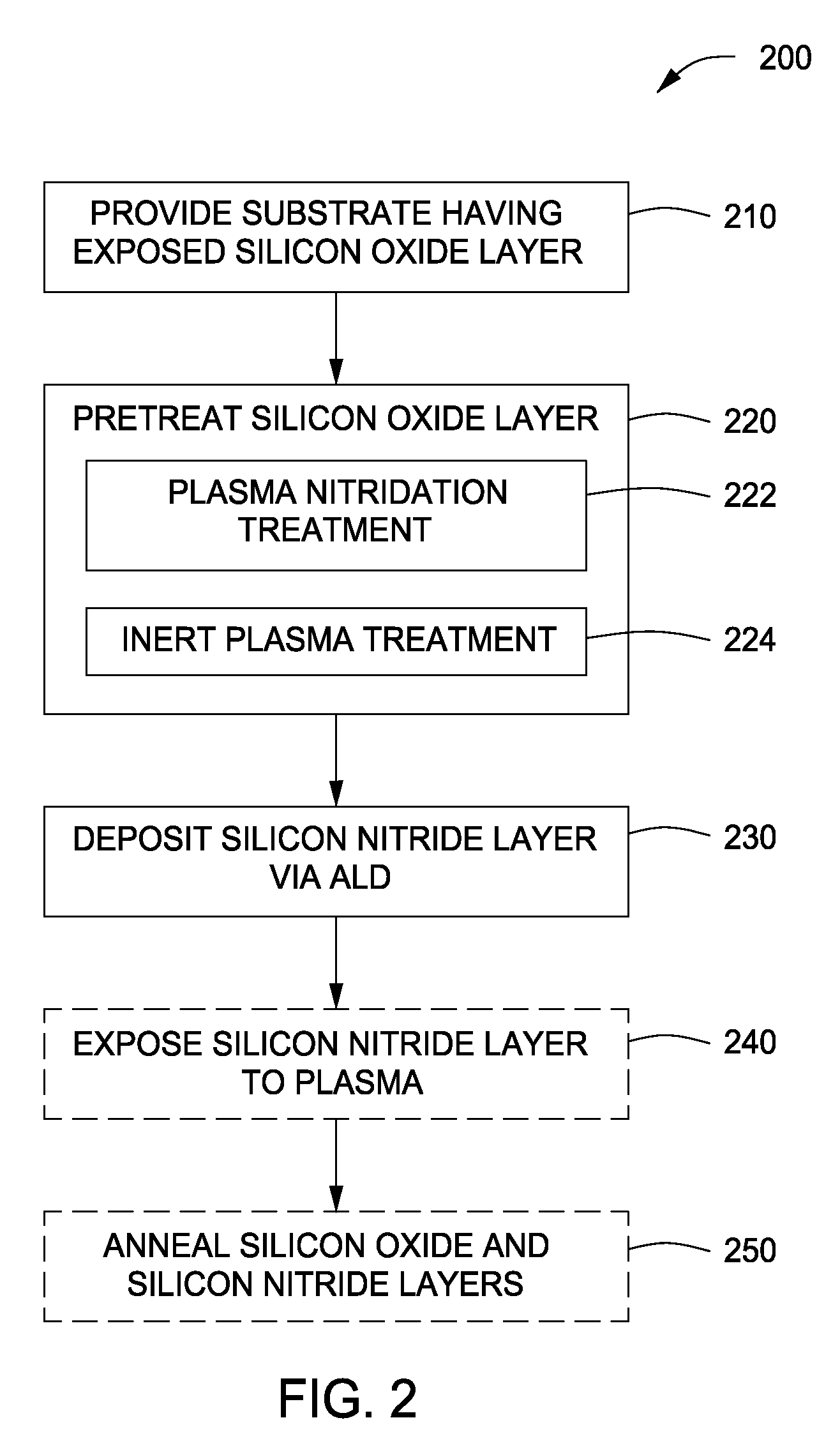
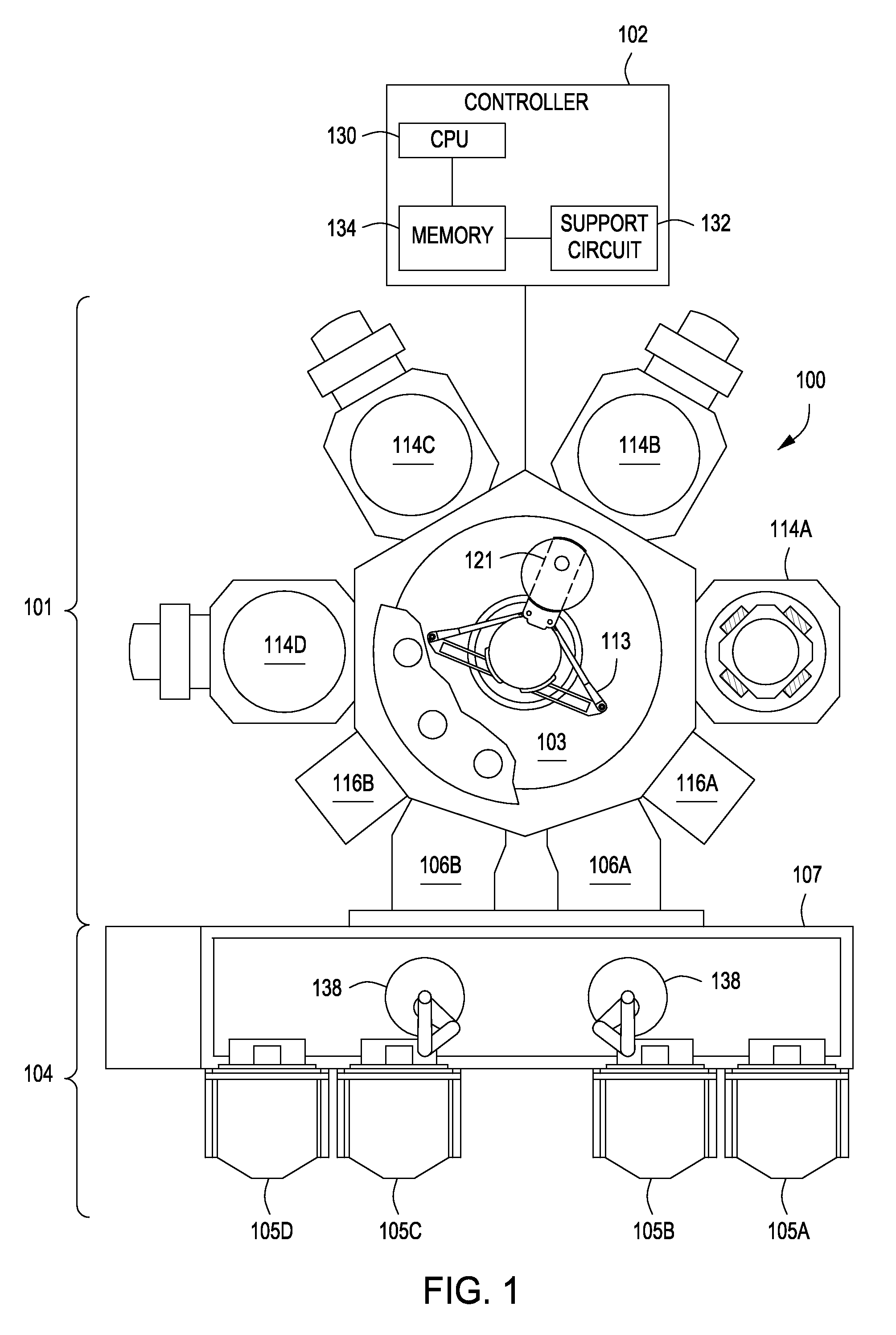
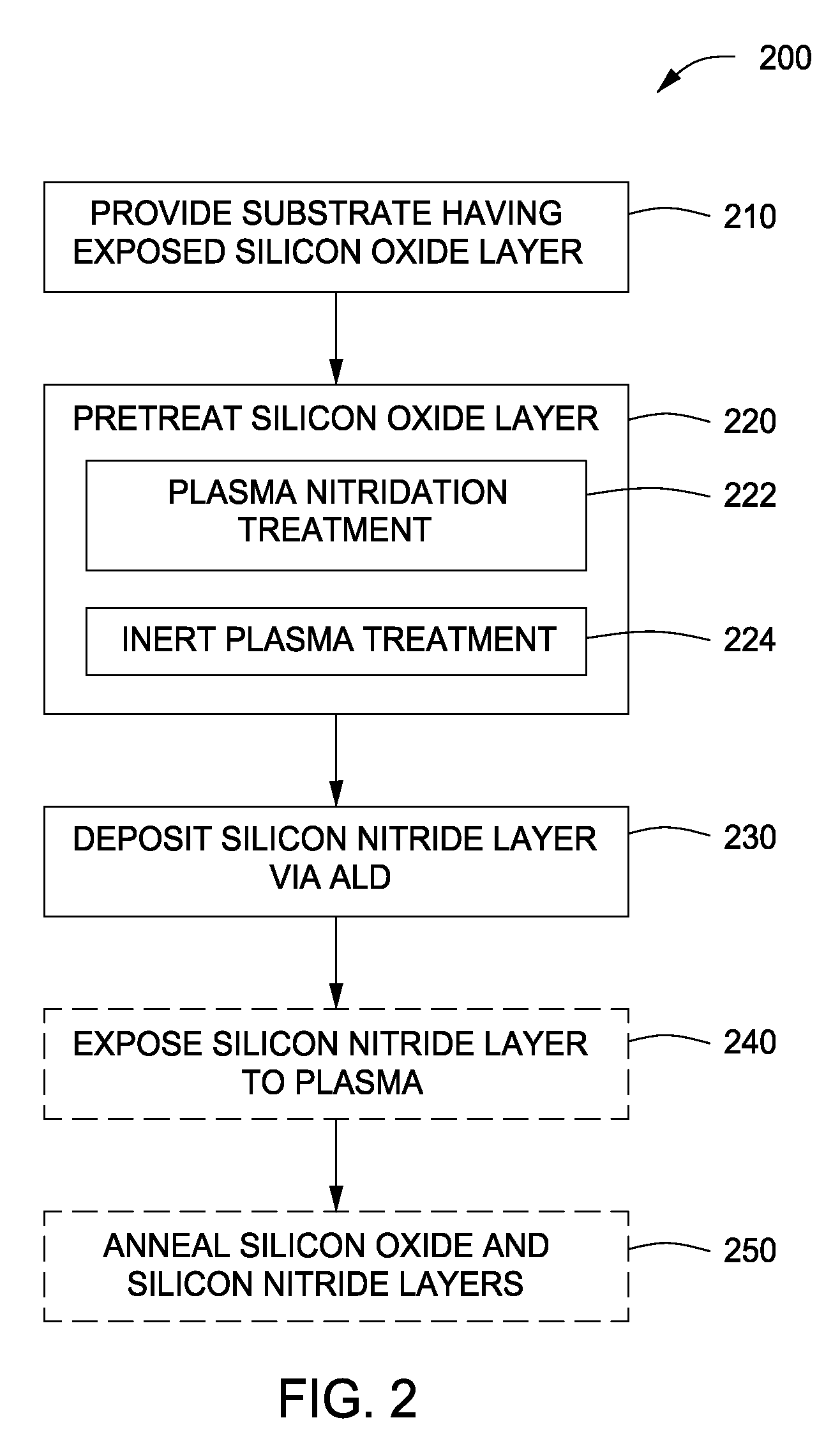
Method of forming dielectric layers on a substrate and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20090035927A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma nitridationSilicon oxide
Methods of forming dielectric layers on a substrate comprising silicon and oxygen are disclosed herein. In some embodiments, a method of forming a dielectric layer on a substrate includes provide a substrate having an exposed silicon oxide layer; treating an upper surface of the silicon oxide layer with a plasma; and depositing a silicon nitride layer on the treated silicon oxide layer via atomic layer deposition. The silicon nitride layer may be exposed to a plasma nitridation process. The silicon oxide and silicon nitride layers may be subsequently thermally annealed. The dielectric layers may be used as part of a gate structure.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
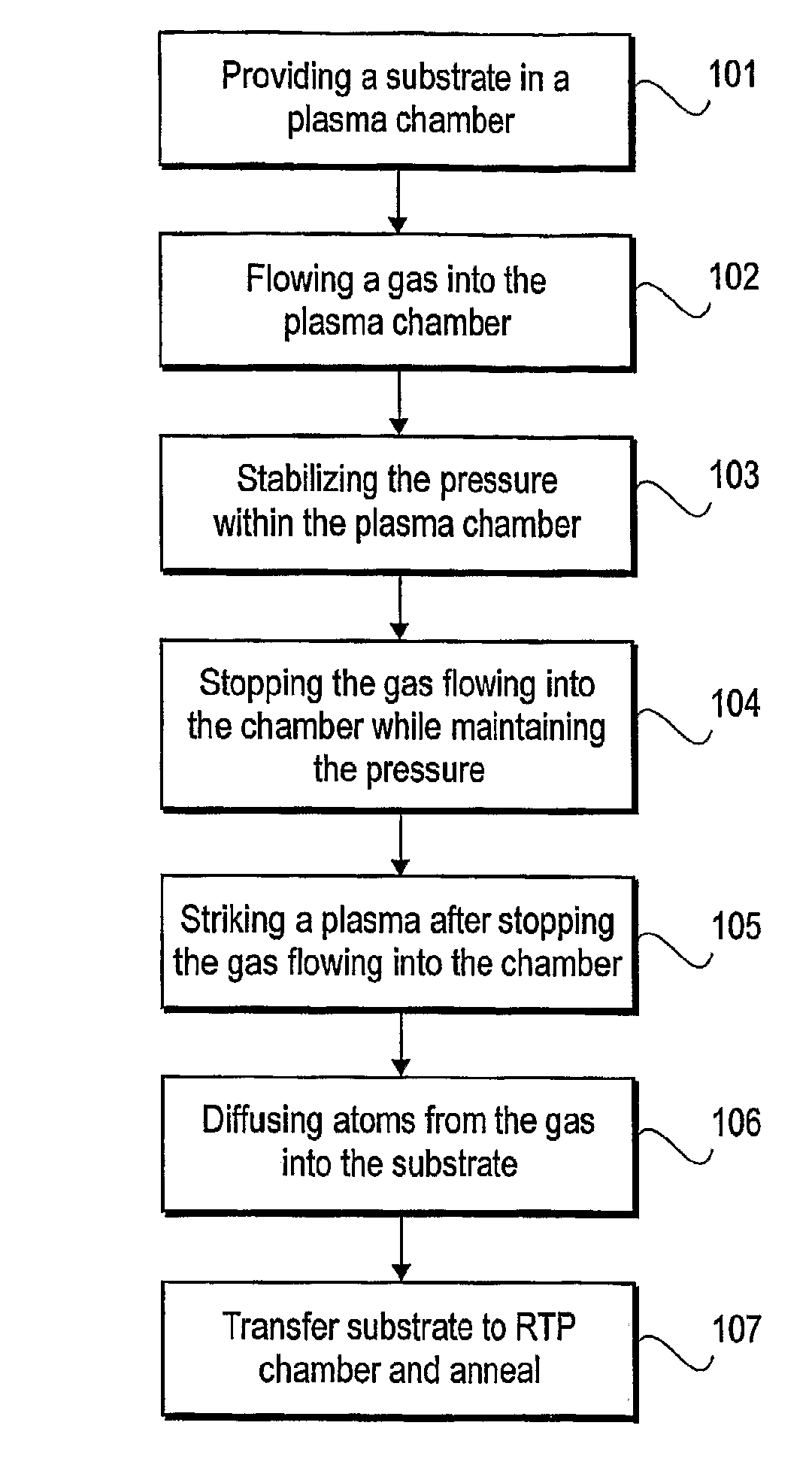
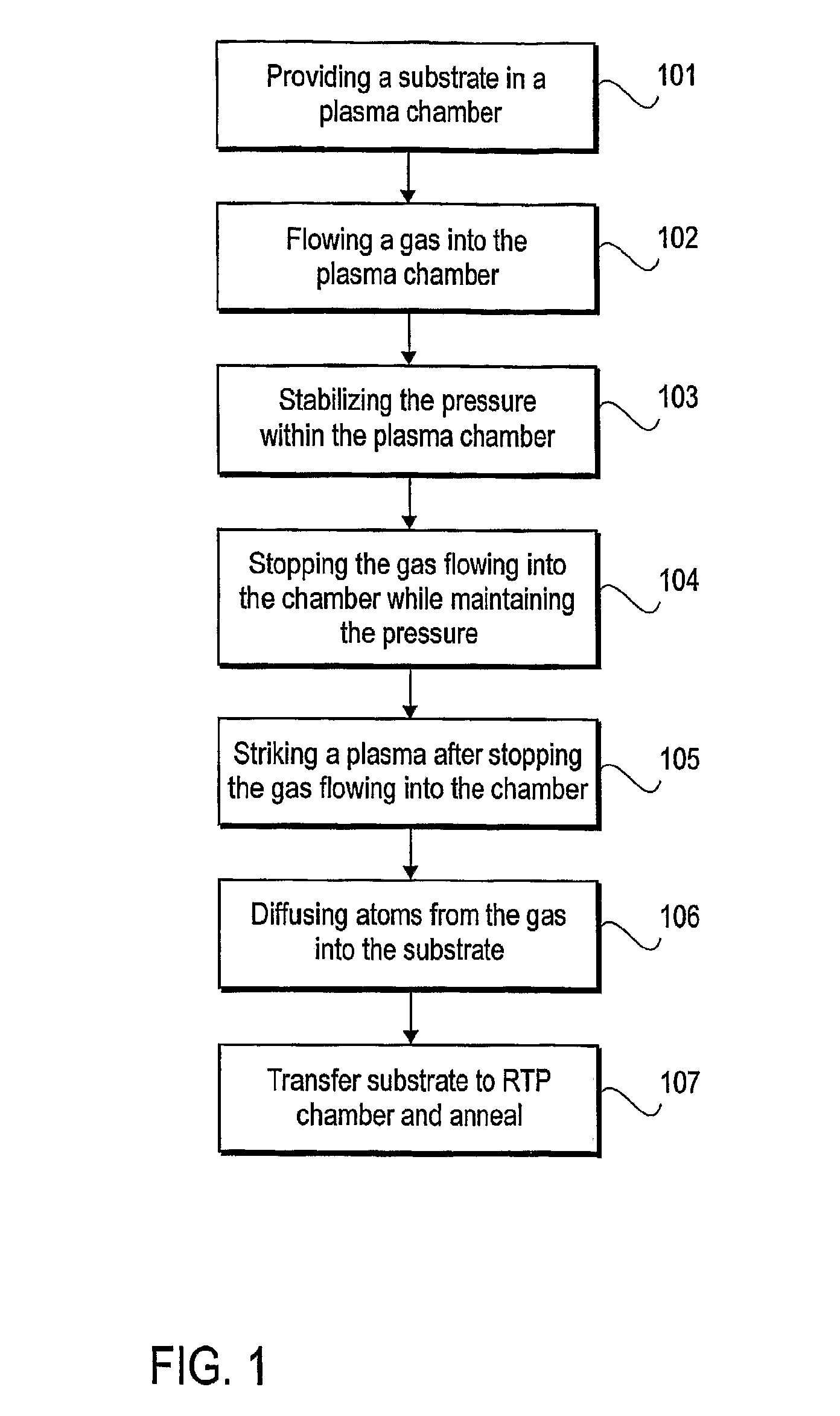
Elimination of flow and pressure gradients in low utilization processes
InactiveUS7955646B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricChemical vapor deposition
The amount of atoms diffused into a substrate may be made uniform or the thickness of a thin film may be made uniform in a low species utilization process by stopping the flow of gas into a reaction chamber during the low species utilization process. Stopping the flow of gas into a reaction chamber may entail closing the gate valve (the valve to the vacuum pump), stabilizing the pressure within the reaction chamber, and maintaining the stabilized pressure while stopping the gas flowing into the chamber. Low species utilization processes include the diffusion of nitrogen into silicon dioxide gate dielectric layers by decoupled plasma nitridation (DPN), the deposition of a silicon dioxide film by rapid thermal processing (RTP) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and the deposition of silicon epitaxial layers by CVD.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor on insulator structure comprising a plasma nitride layer and method of manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20190067085A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structurePlasma deposition
A method is provided for preparing a semiconductor-on-insulator structure comprising a silicon nitride layer deposited by plasma deposition.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
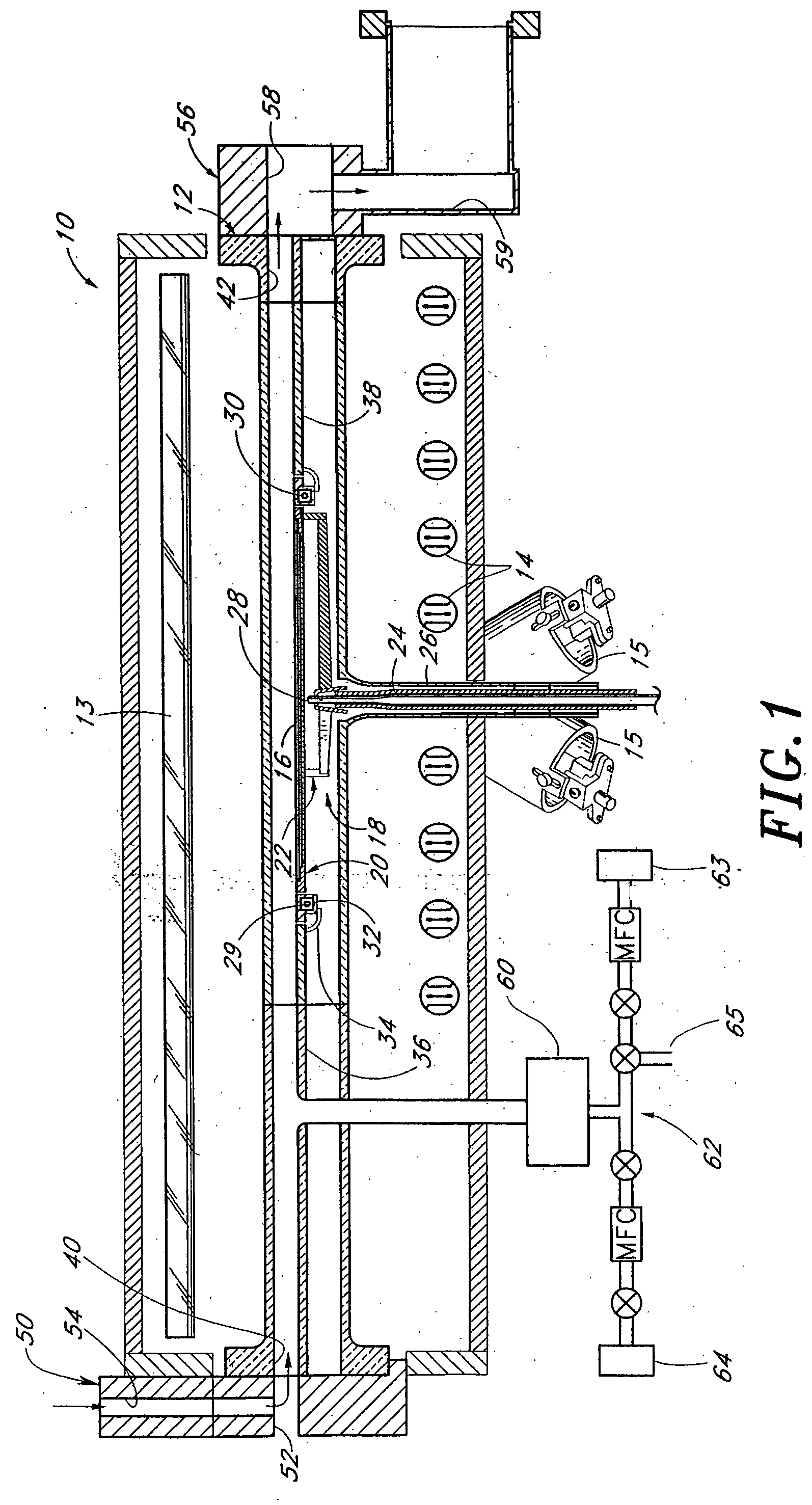
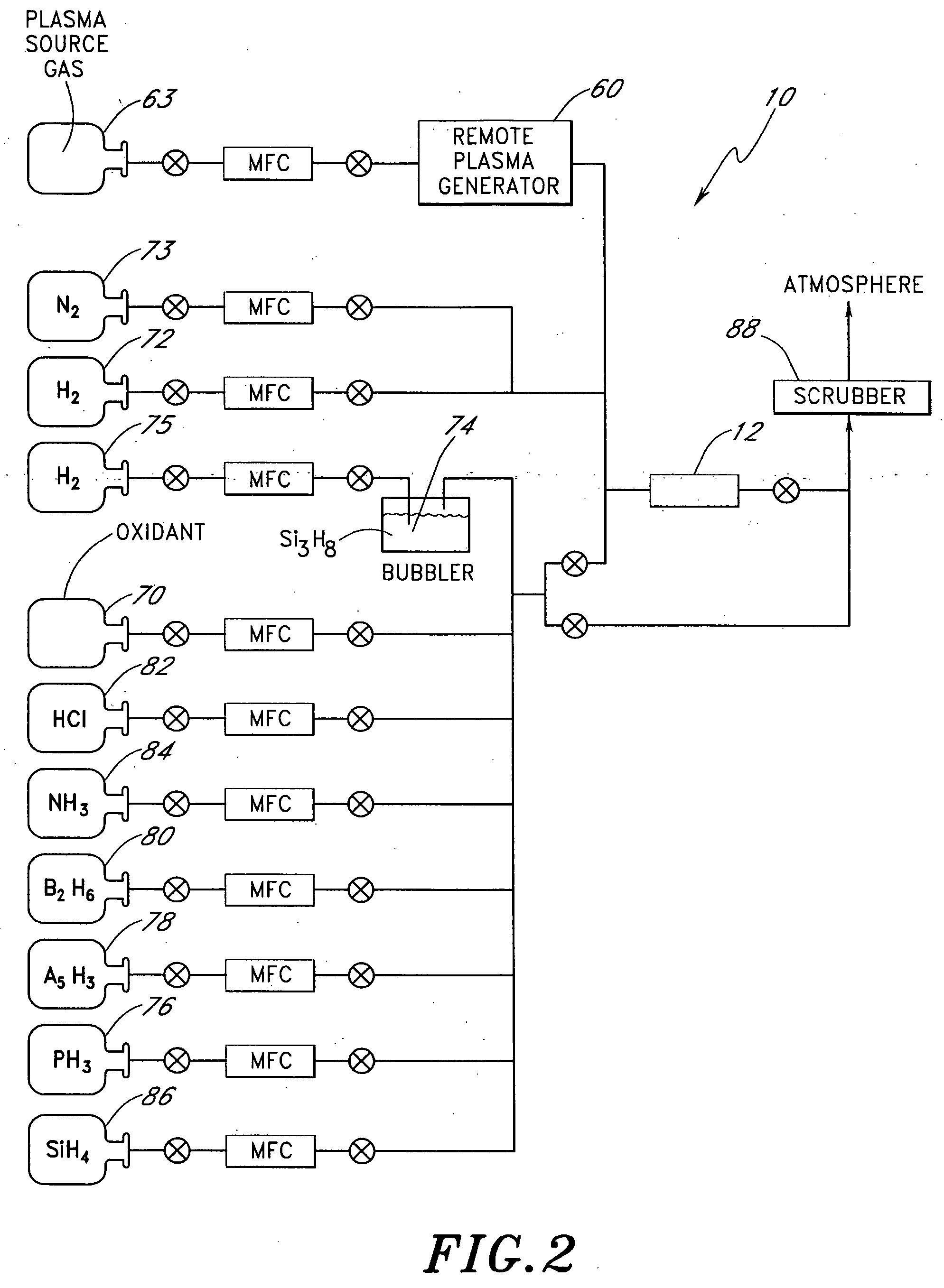
Advanced platform for processing crystalline silicon solar cells
InactiveUS20100087028A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseEngineering
The present invention generally provides a batch substrate processing system, or cluster tool, for in-situ processing of a film stack used to form regions of a solar cell device. In one configuration, the film stack formed on each of the substrates in the batch contains one or more silicon-containing layers and one or more metal layers that are deposited and further processed within the various chambers contained in the substrate processing system. The processing chambers may be, for example, physical vapor deposition (PVD) or sputtering chambers, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) chambers, low pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) chambers, hot wire chemical vapor deposition (HWCVD) chambers, plasma nitridation (DPN) chambers, ion implant / doping chambers, atomic layer deposition (ALD) chambers, plasma etching chambers, annealing chambers, rapid thermal oxidation (RTO) chambers, rapid thermal annealing (RTA) chambers, substrate reorientation chambers, laser annealing chambers, and / or plasma cleaning stations. In one embodiment, a batch of solar cell substrates is simultaneously transferred in a vacuum or inert environment to prevent contamination from affecting the solar cell formation process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
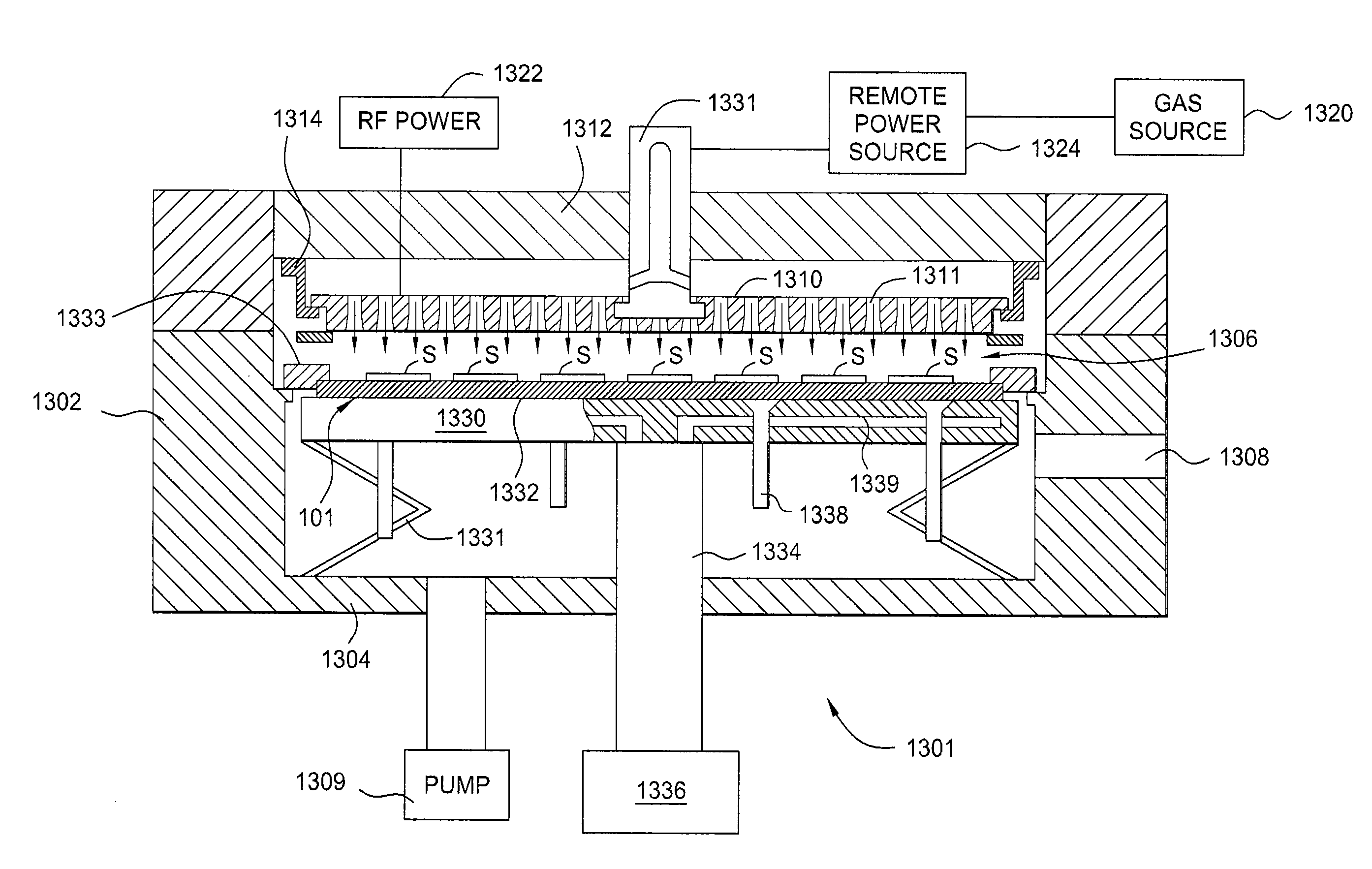
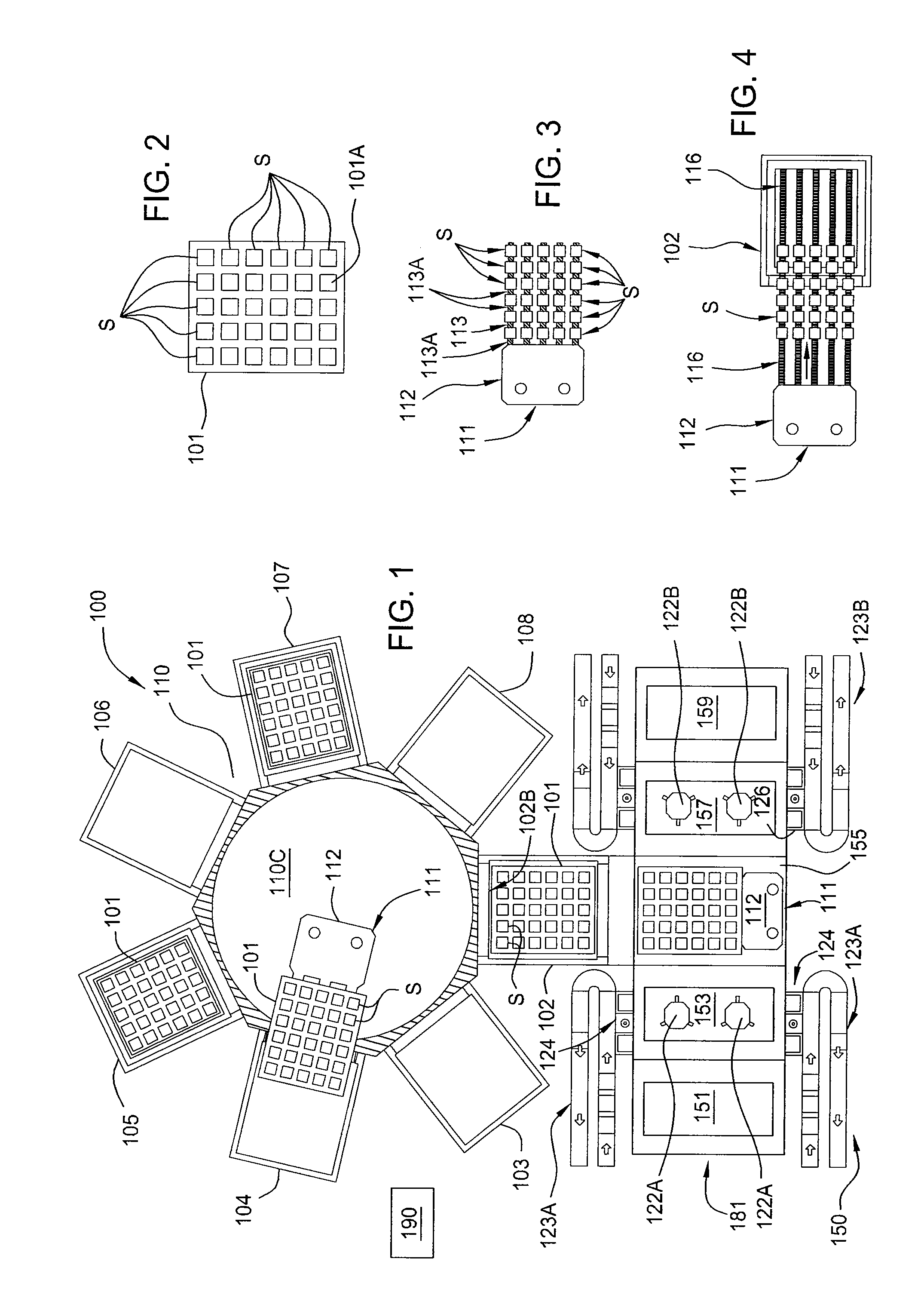
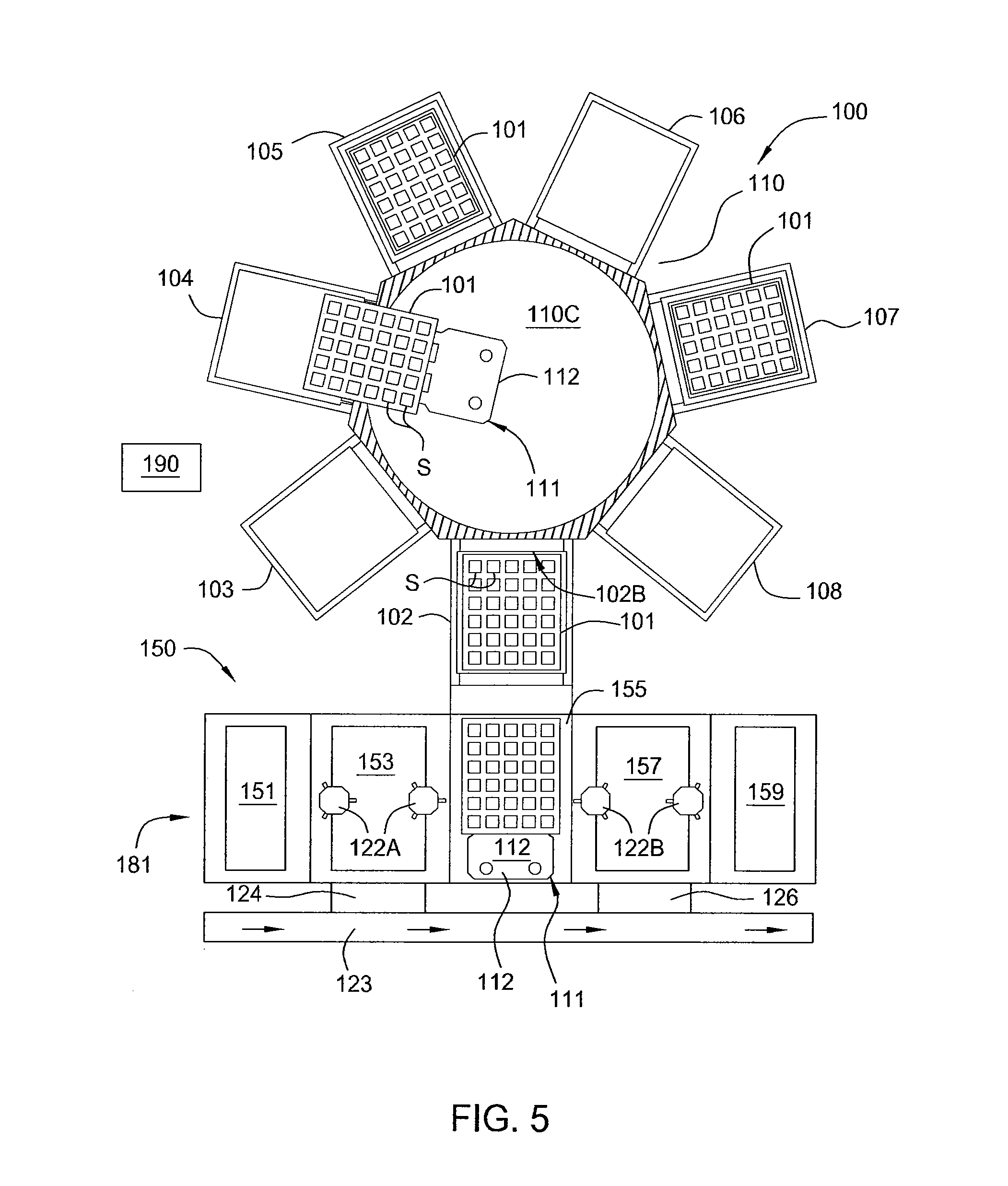
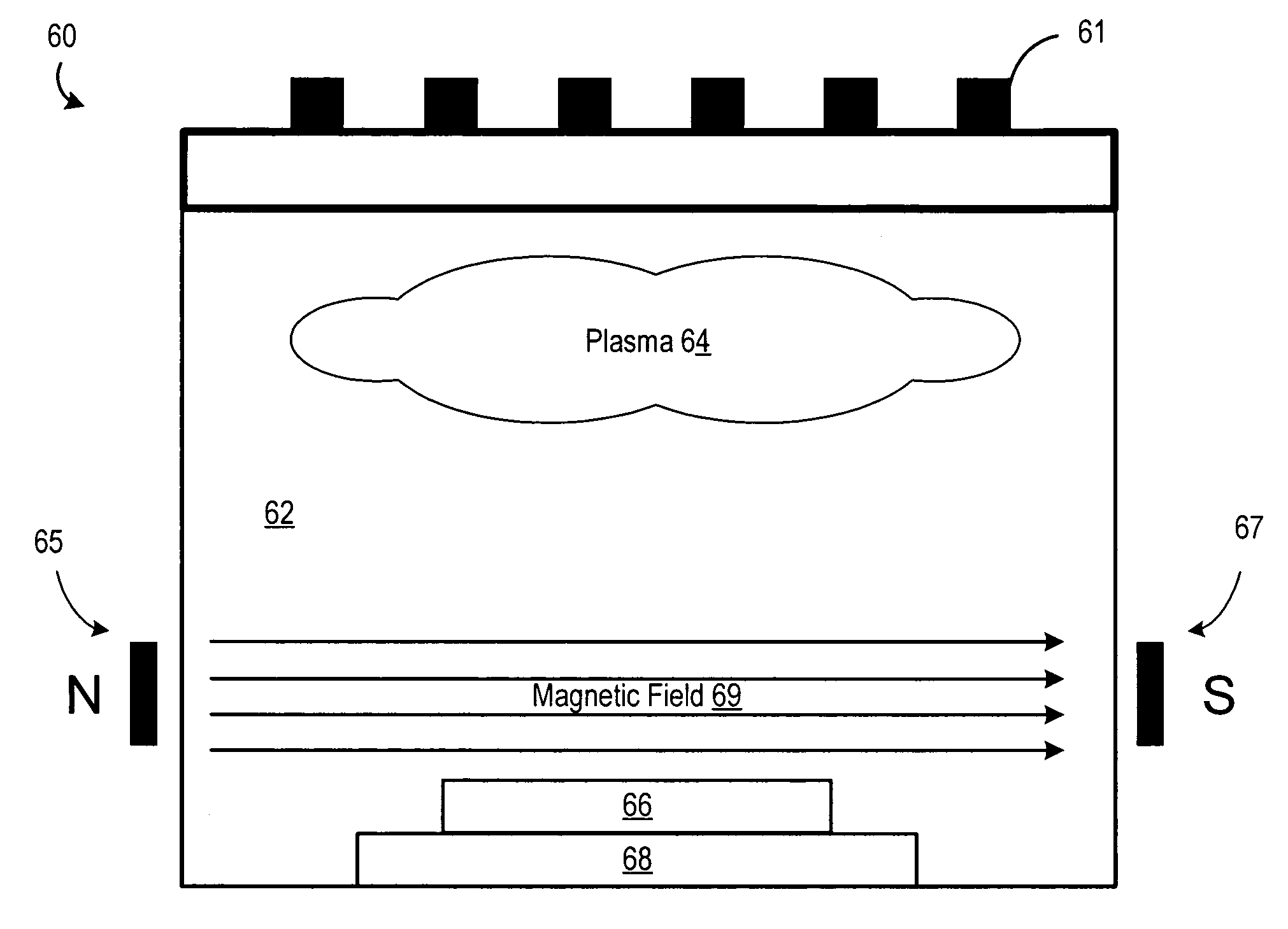
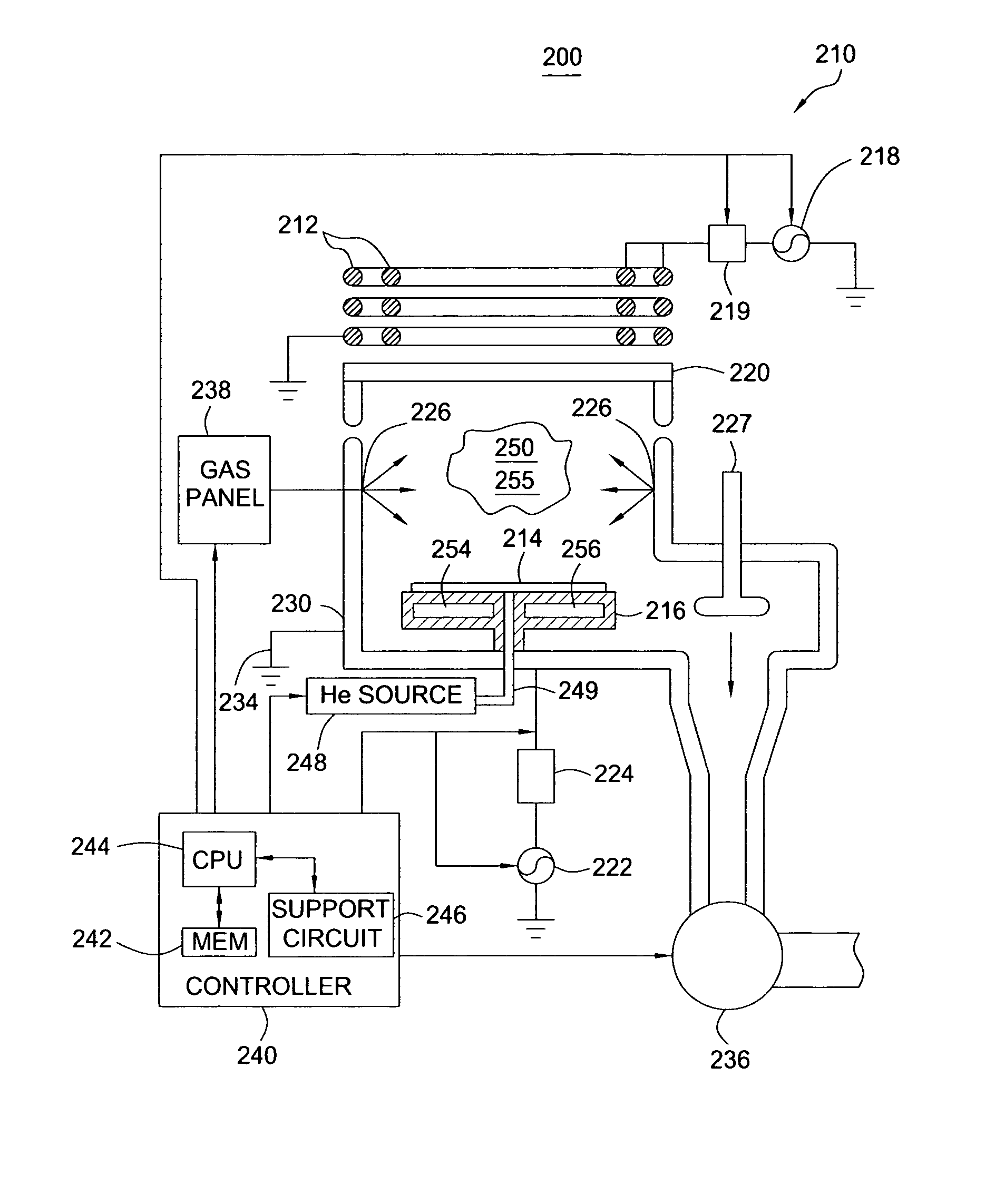
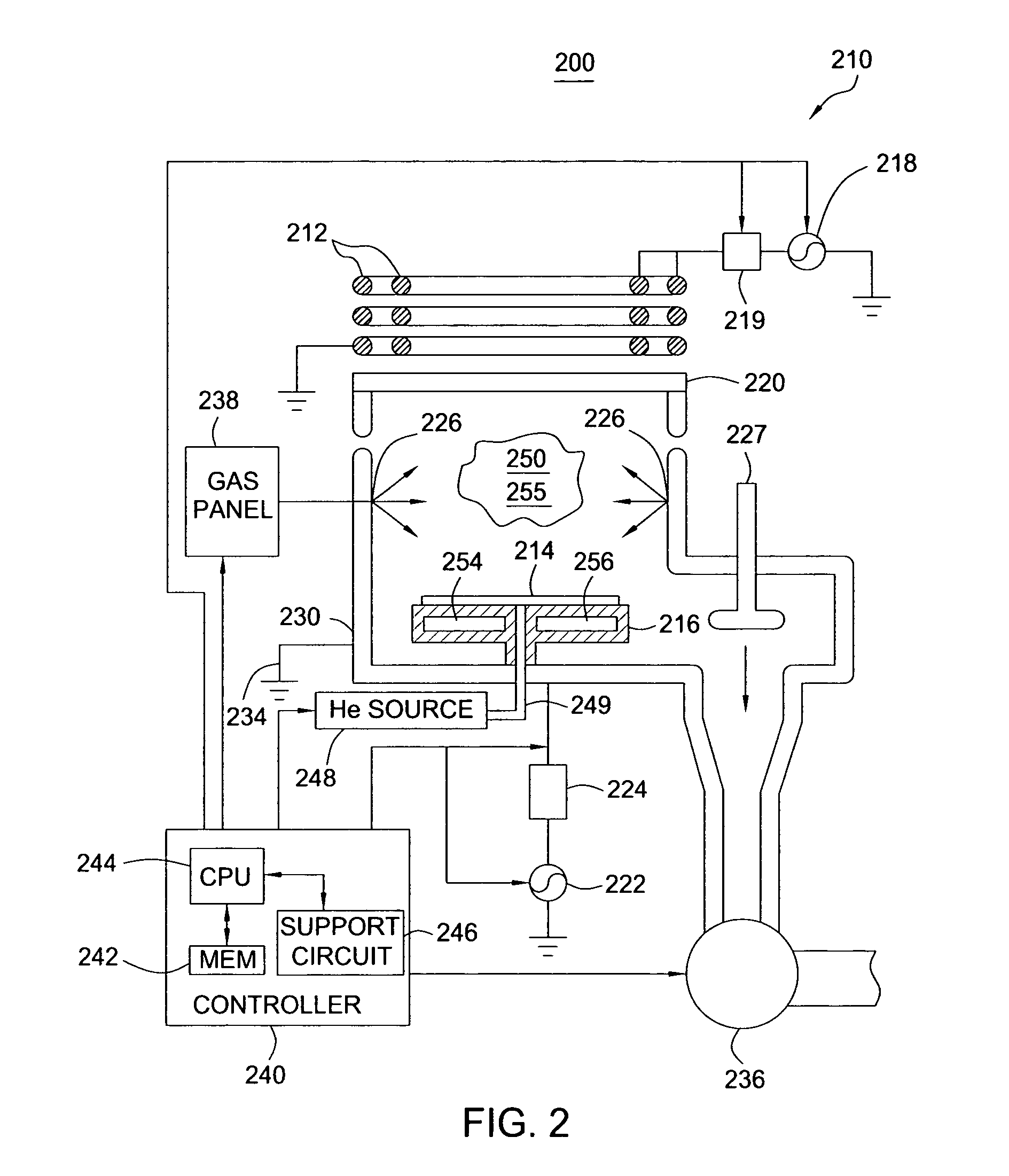
Method and apparatus for improving nitrogen profile during plasma nitridation
InactiveUS20070049048A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenManufactured apparatus
A semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and process for forming a nitrided dielectric film includes generating a plasma source (44) over a wafer structure (46), where the plasma source (44) includes neutral species (such as nitrogen atoms) and charged species (such as nitrogen ions) that are formed in an inductively coupled plasma reactor. Before the charged species in the plasma (44) can penetrate the wafer structure (46), an electrically connected mesh structure (45, 47) between the plasma source (44) and wafer structure (46) blocks the charged species. In addition or in the alternative, a magnetic field (69) aligned in parallel with the surface of the wafer structure (66) is established in close proximity to the wafer structure (66) in order to trap the charged species. By removing charged species, an improved, narrower nitrogen concentration profile is obtained.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
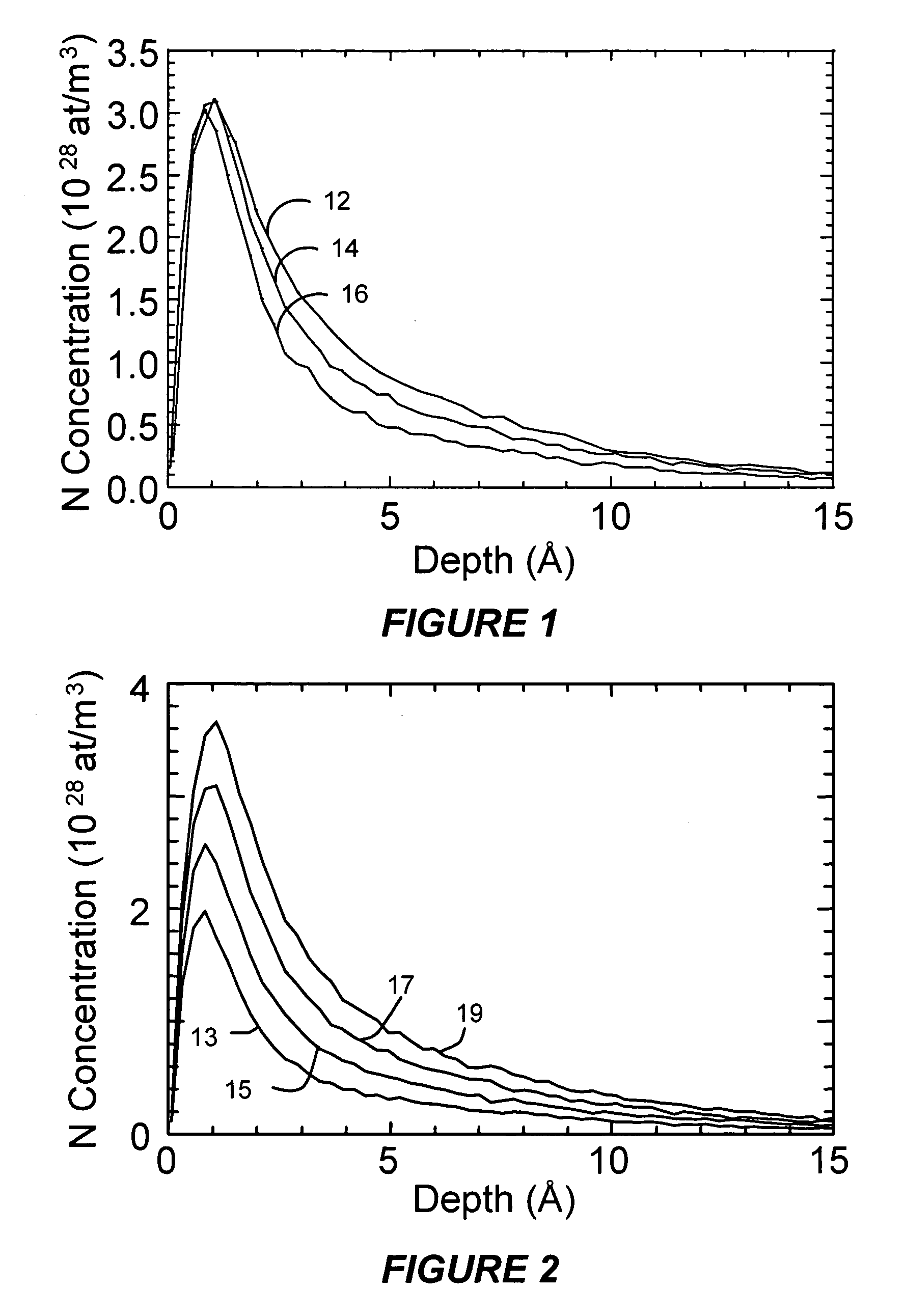
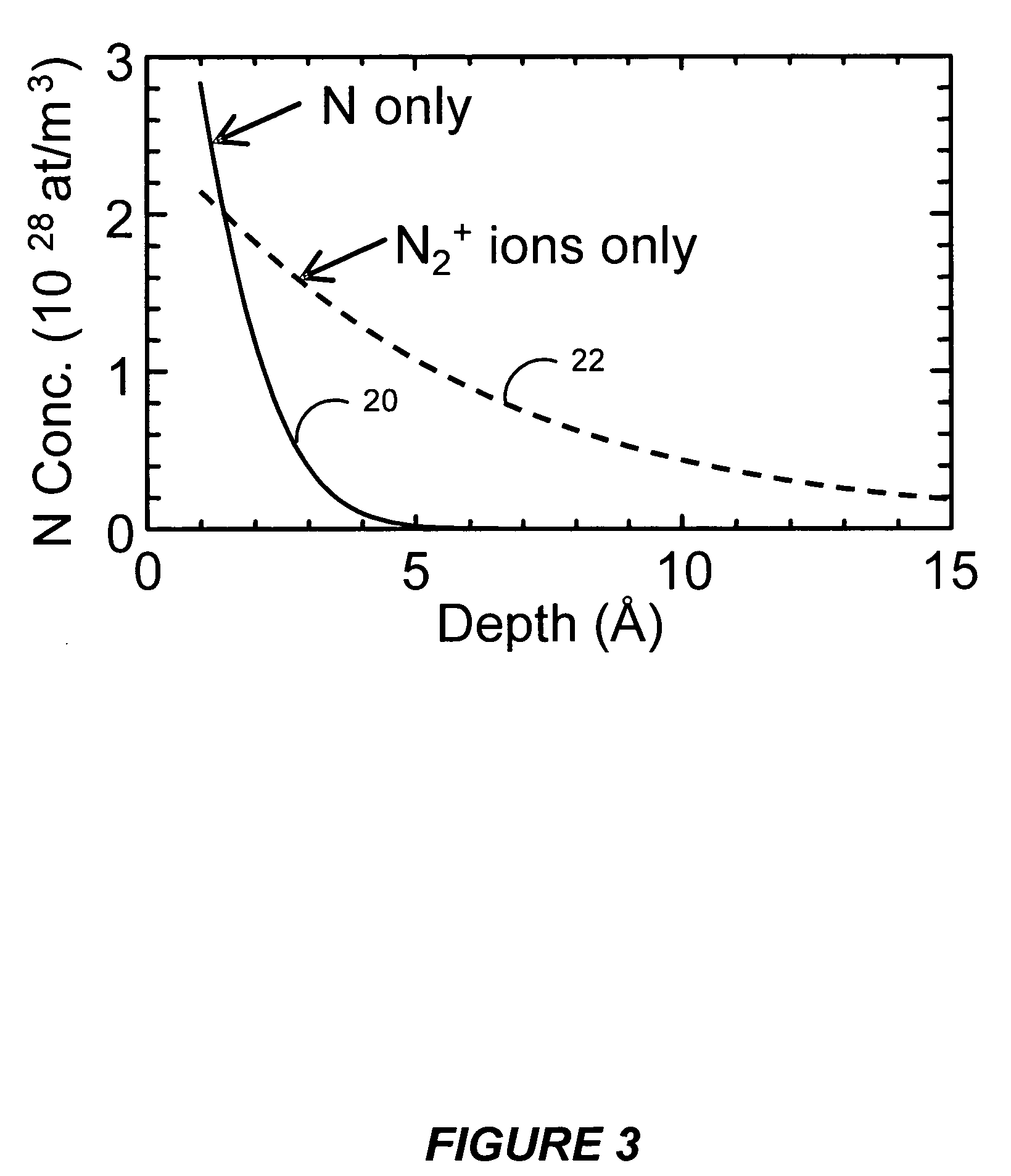
Nitrogen profile engineering in HI-K nitridation for device performance enhancement and reliability improvement
InactiveUS20070049043A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricPerformance enhancement
A method and apparatus for forming a nitrided gate dielectric. The method comprises incorporating nitrogen into a dielectric film using a plasma nitridation process to form a nitrided gate dielectric. The first step involves providing a substrate comprising a gate dielectric film. The second step involves inducing a voltage on the substrate. Finally, the substrate is exposed to a plasma comprising a nitrogen source while maintaining the voltage to form a nitrided gate dielectric on the substrate. In one embodiment, the voltage is induced on the substrate by applying a voltage to an electrostatic chuck supporting the substrate. In another embodiment, the voltage is induced on the substrate by applying a DC bias voltage to an electrode positioned adjacent the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Remote plasma activated nitridation
ActiveUS20060110943A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaMicrowave
A nitrogen precursor that has been activated by exposure to a remotely excited species is used as a reactant to form nitrogen-containing layers. The remotely excited species can be, e.g., N2, Ar, and / or He, which has been excited in a microwave radical generator. Downstream of the microwave radical generator and upstream of the substrate, the flow of excited species is mixed with a flow of NH3. The excited species activates the NH3. The substrate is exposed to both the activated NH3 and the excited species. The substrate can also be exposed to a precursor of another species to form a compound layer in a chemical vapor deposition. In addition, already-deposited layers can be nitrided by exposure to the activated NH3 and to the excited species, which results in higher levels of nitrogen incorporation than plasma nitridation using excited N2 alone, or thermal nitridation using NH3 alone, with the same process temperatures and nitridation durations.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Duplex coated steel composite products and method of manufacturing them
InactiveUS6110571AEasy to useElevation is easyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCarbidePlasma nitridation
Duplex coated steel composite products comprising a first layer of a nitrided layer formed by applying glow discharge at a current density from 0.001 to 2.0 mA / cm2 to the surface of metal parts by using gaseous ammonia and gaseous hydrogen while maintaining the temperature of the metal parts at 300 to 650 DEG C., thereby applying plasma nitriding and a second layer comprising a hard film comprising a nitride, carbide and / or carbonitride of one or more of elements selected from Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta and Cr coated on the first layer by the PVD method of a laminate film or a gradient laminate film of such hard film. The treated products are excellent in adhesion with the substrate and durability and have both oxidation resistance and wear resistance.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
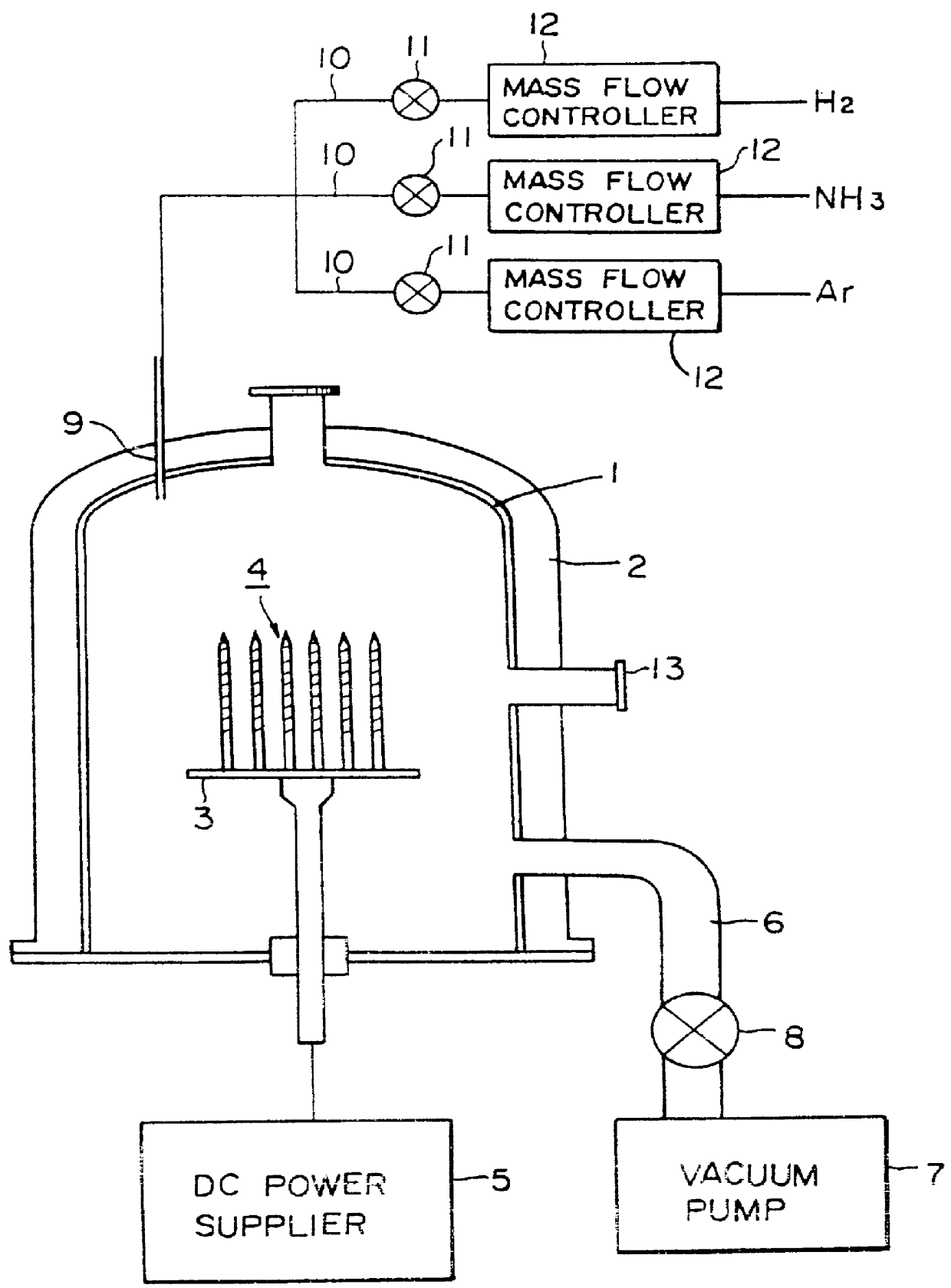
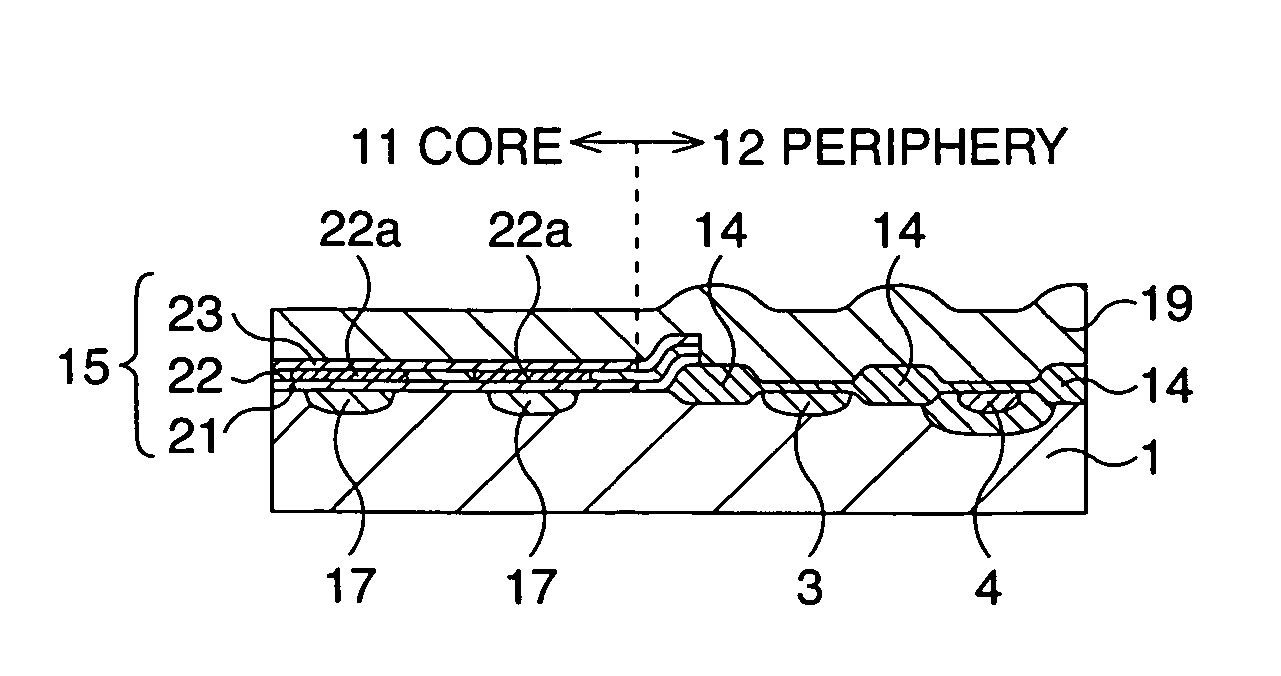
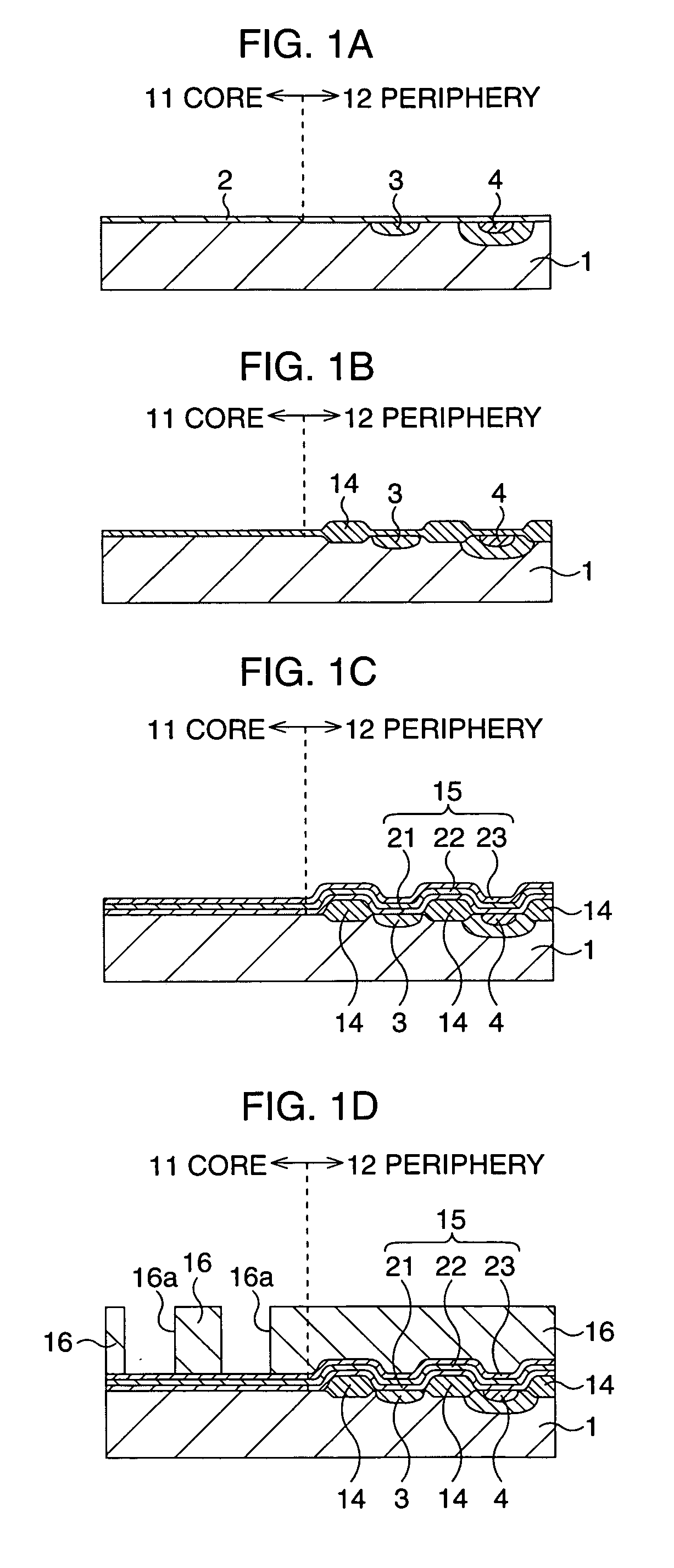
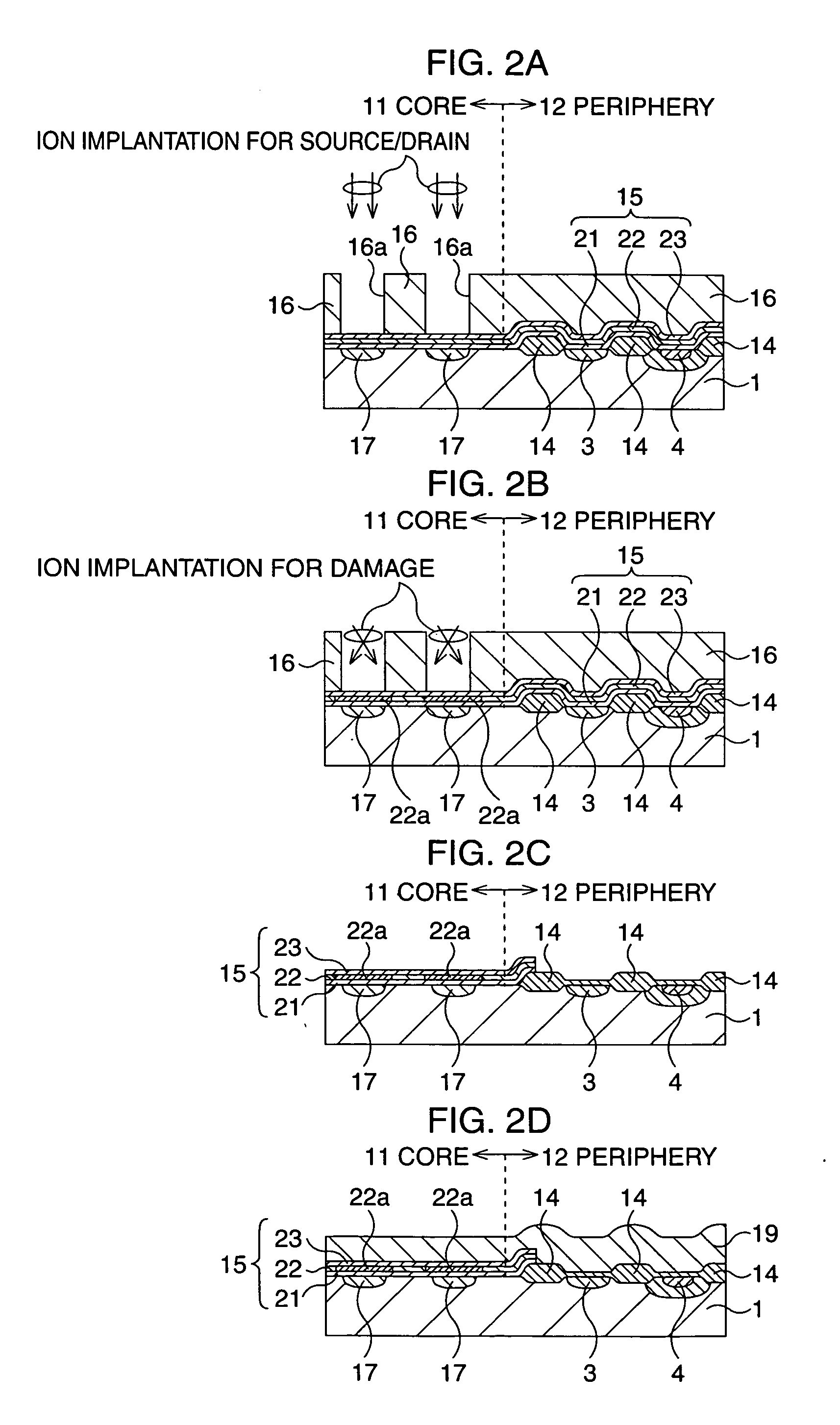
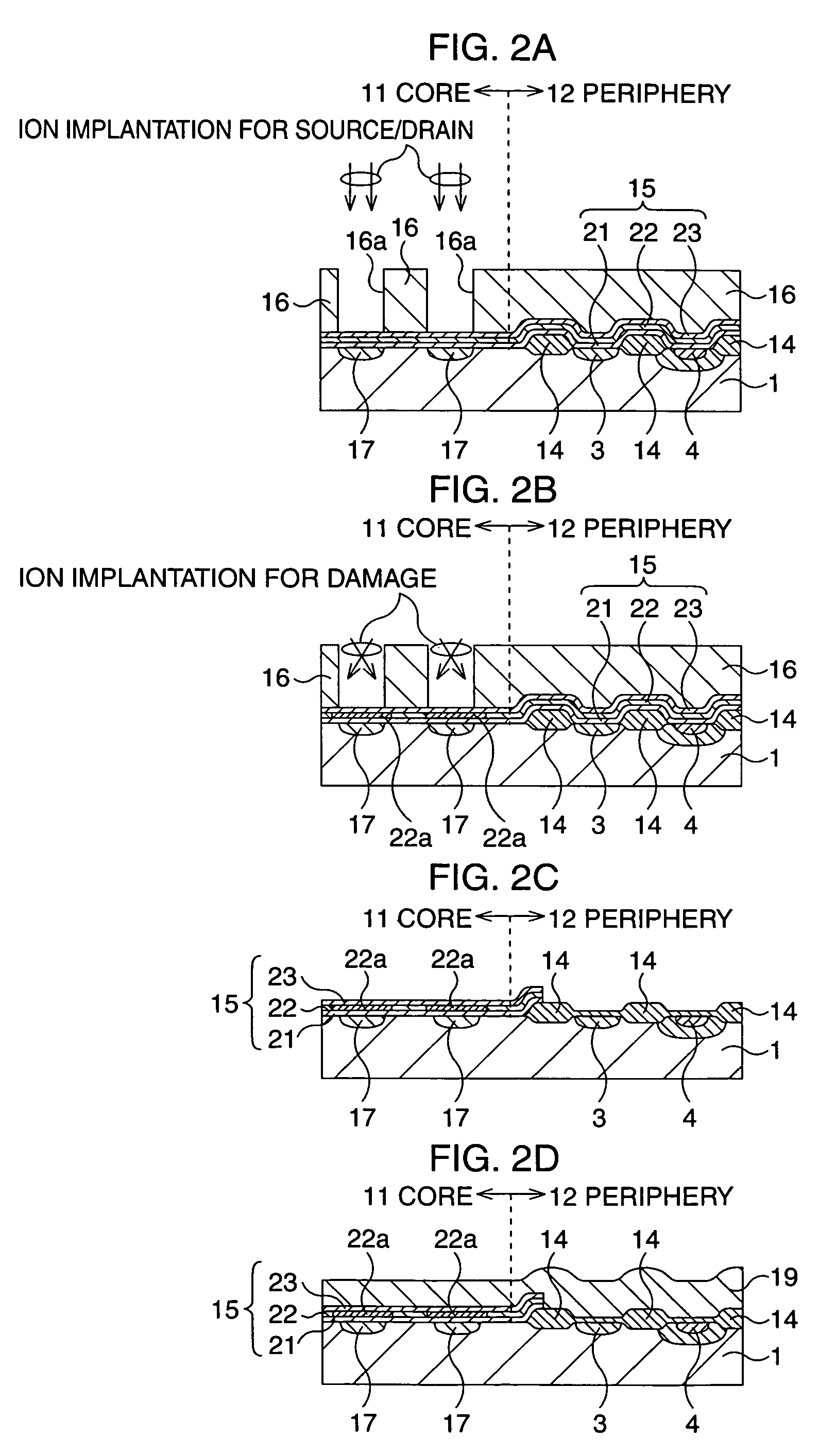
Semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
After an ONO film in which a silicon nitride film (22) formed by a plasma nitriding method using a plasma processor having a radial line slot antenna is sandwiched by silicon oxide films (21), (23), a bit line diffusion layer (17) is formed in a memory cell array region (11) by an ion implantation as a resist pattern (16) taken as a mask, then lattice defects are given to the silicon nitride film (22) by a further ion implantation. Accordingly, a highly reliable semiconductor memory device can be realized, in which a high quality nitride film is formed in a low temperature condition, in addition, the nitride film can be used as a charge trap film having a charge capture function sufficiently adaptable for a miniaturization and a high integration which are recent demands.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Method and apparatus for plasma nitridation of gate dielectrics using amplitude modulated radio-frequency energy
ActiveUS7179754B2Reduce the temperatureTransistorSolid-state devicesElectron temperatureGate dielectric
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
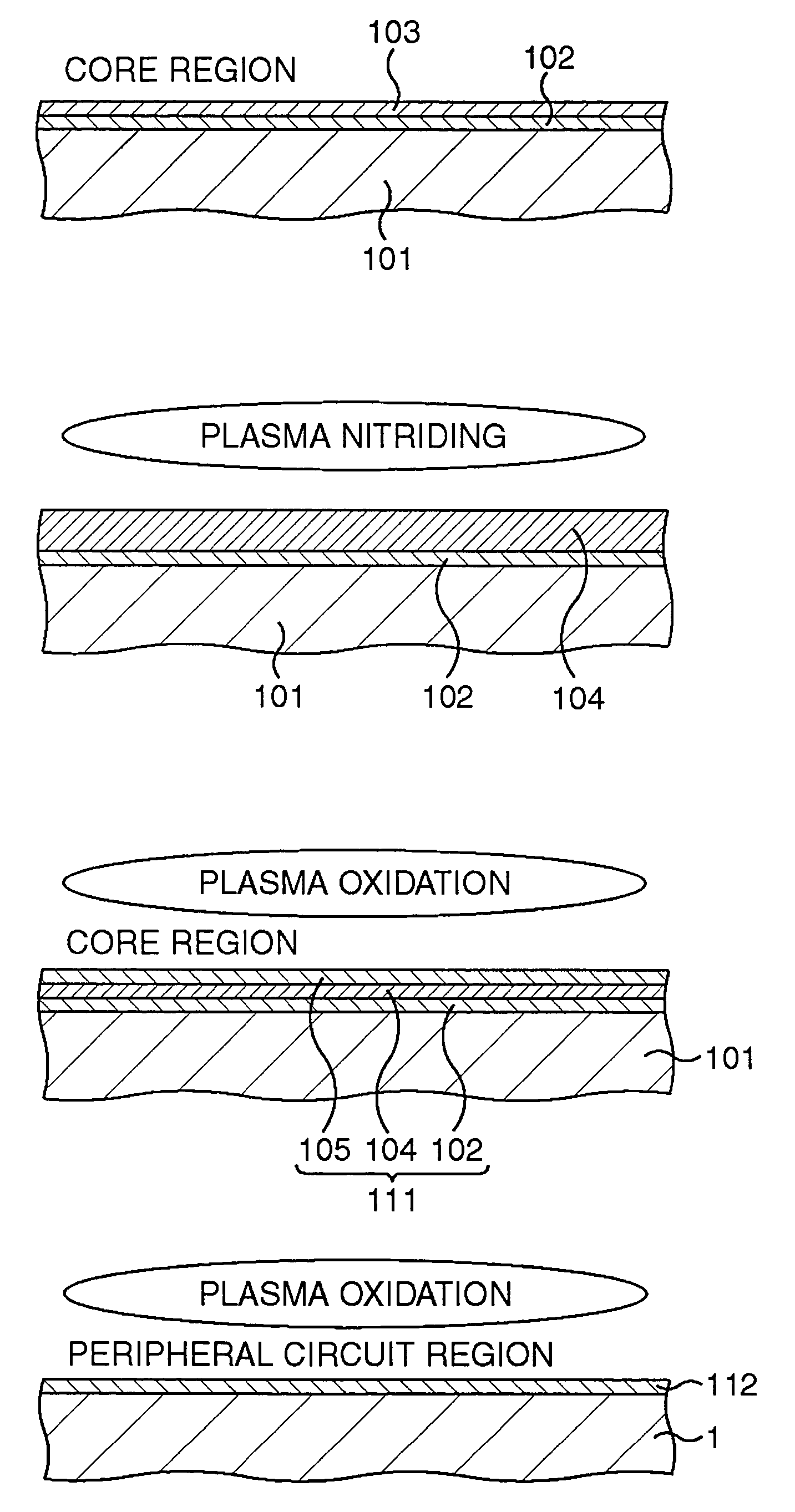
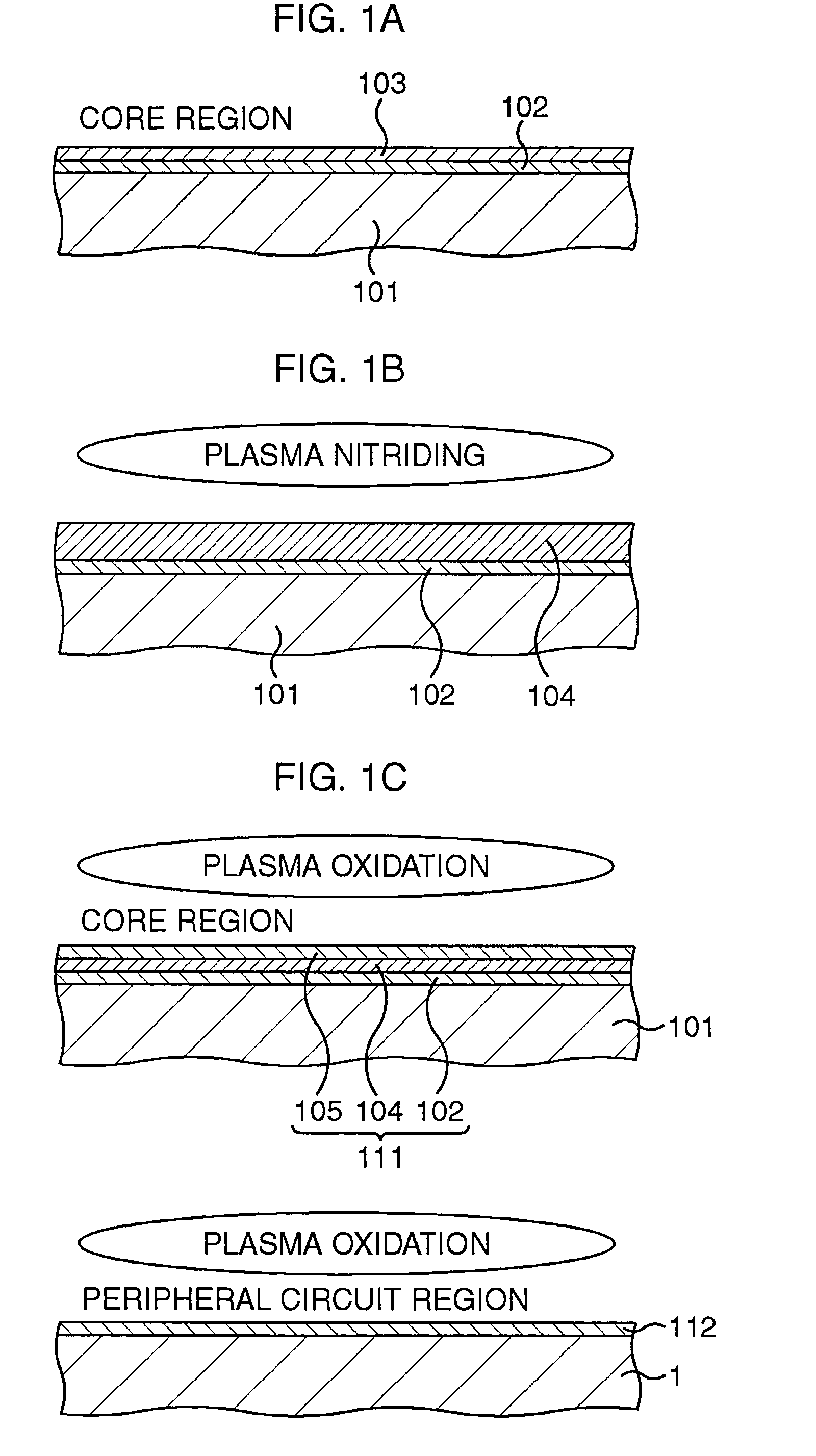
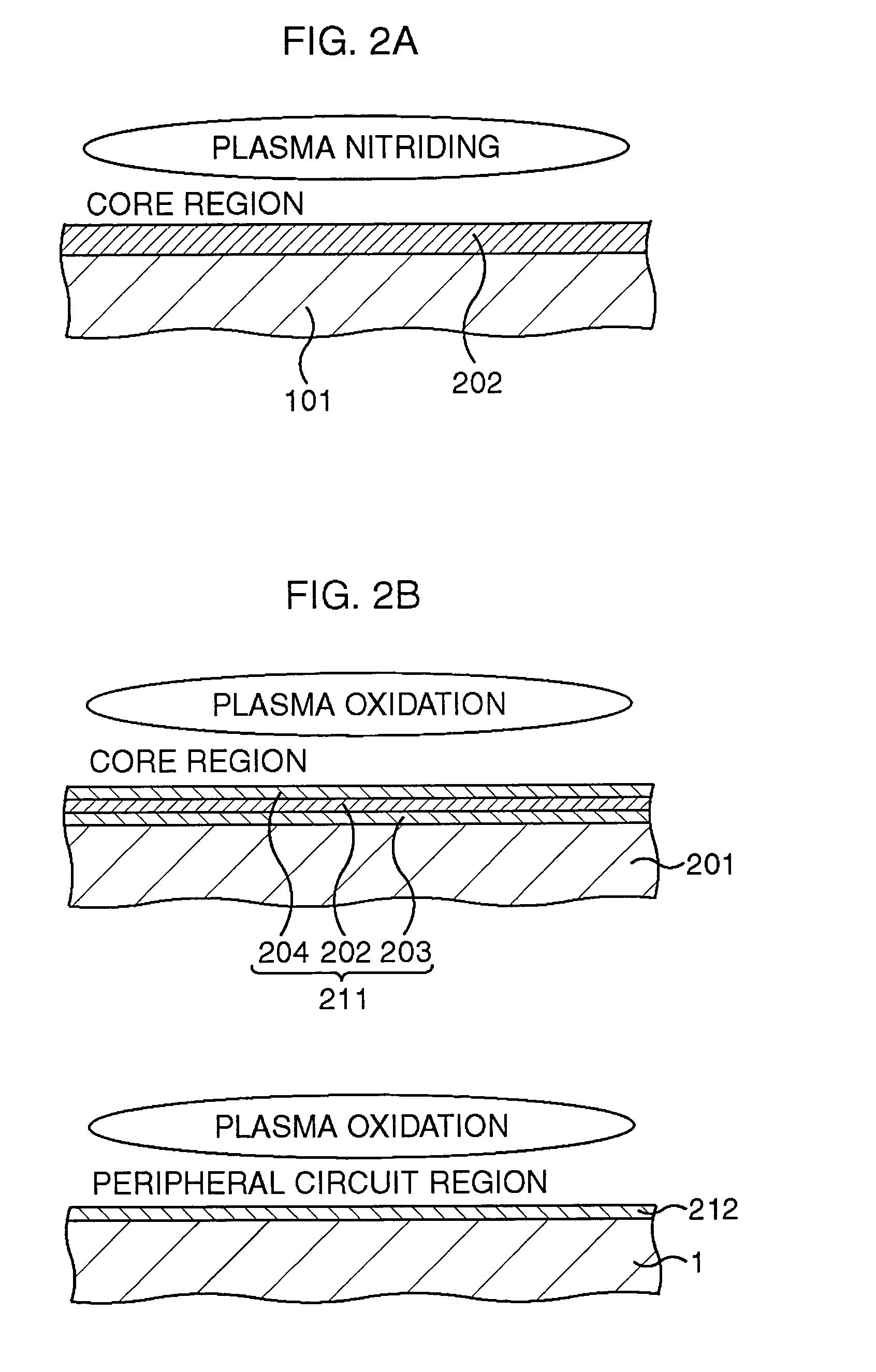
Semiconductor memory device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060228899A1Improve reliabilityQuality improvementTransistorSolid-state devicesSurface layerDevice material
After a lower silicon oxide film is formed on a silicon region, a silicon film is formed on the lower silicon oxide film by, for example, a thermal CVD method. Subsequently, the silicon film is completely nitrided by a plasma nitriding method to be replaced by a silicon nitride film. Subsequently, a surface layer of the silicon nitride film is oxidized by a plasma oxidizing method to be replaced by an upper silicon oxide film. An ONO film as a multilayered insulating film composed of the lower silicon oxide film, the silicon nitride film, and the upper silicon oxide film is formed.
Owner:SPANSION LLC
Semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Semiconductor memory device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7098147B2Improve reliabilityQuality improvementTransistorSolid-state devicesSurface layerPlasma nitridation
After a lower silicon oxide film is formed on a silicon region, a silicon film is formed on the lower silicon oxide film by, for example, a thermal CVD method. Subsequently, the silicon film is completely nitrided by a plasma nitriding method to be replaced by a silicon nitride film. Subsequently, a surface layer of the silicon nitride film is oxidized by a plasma oxidizing method to be replaced by an upper silicon oxide film. An ONO film as a multilayered insulating film composed of the lower silicon oxide film, the silicon nitride film, and the upper silicon oxide film is formed.
Owner:SPANSION LLC
Method and apparatus of fabricating semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070166892A1Increase amount of introductionFacilitated DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPlasma nitridationEngineering
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for improved plasma nitridation of ultra thin gate dielectrics
InactiveUS20020130377A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricComputational physics
A method for forming a gate dielectric for an integrated circuit device. In an exemplary embodiment of the invention, the method includes forming an initial oxynitride layer upon a substrate material, the oxynitride layer having an initial physical thickness. The initial oxynitride layer is then subjected to a plasma nitridation, the plasma nitridation resulting in final oxynitride layer having a final physical thickness.
Owner:IBM CORP
Selective nitridation of gate oxides
ActiveUS7138691B2Reduce diffuseInvention improvedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantRemote plasma
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC +1
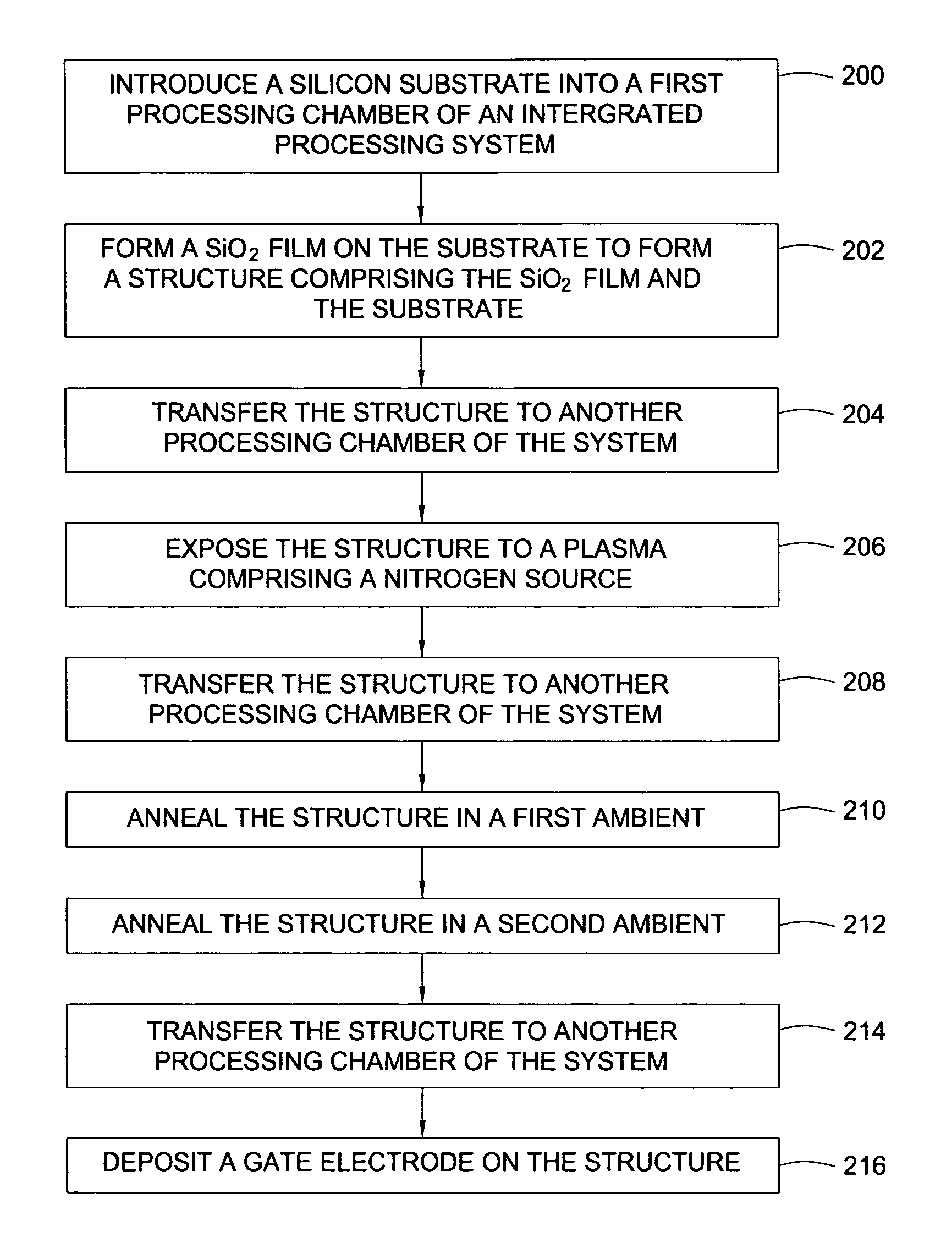
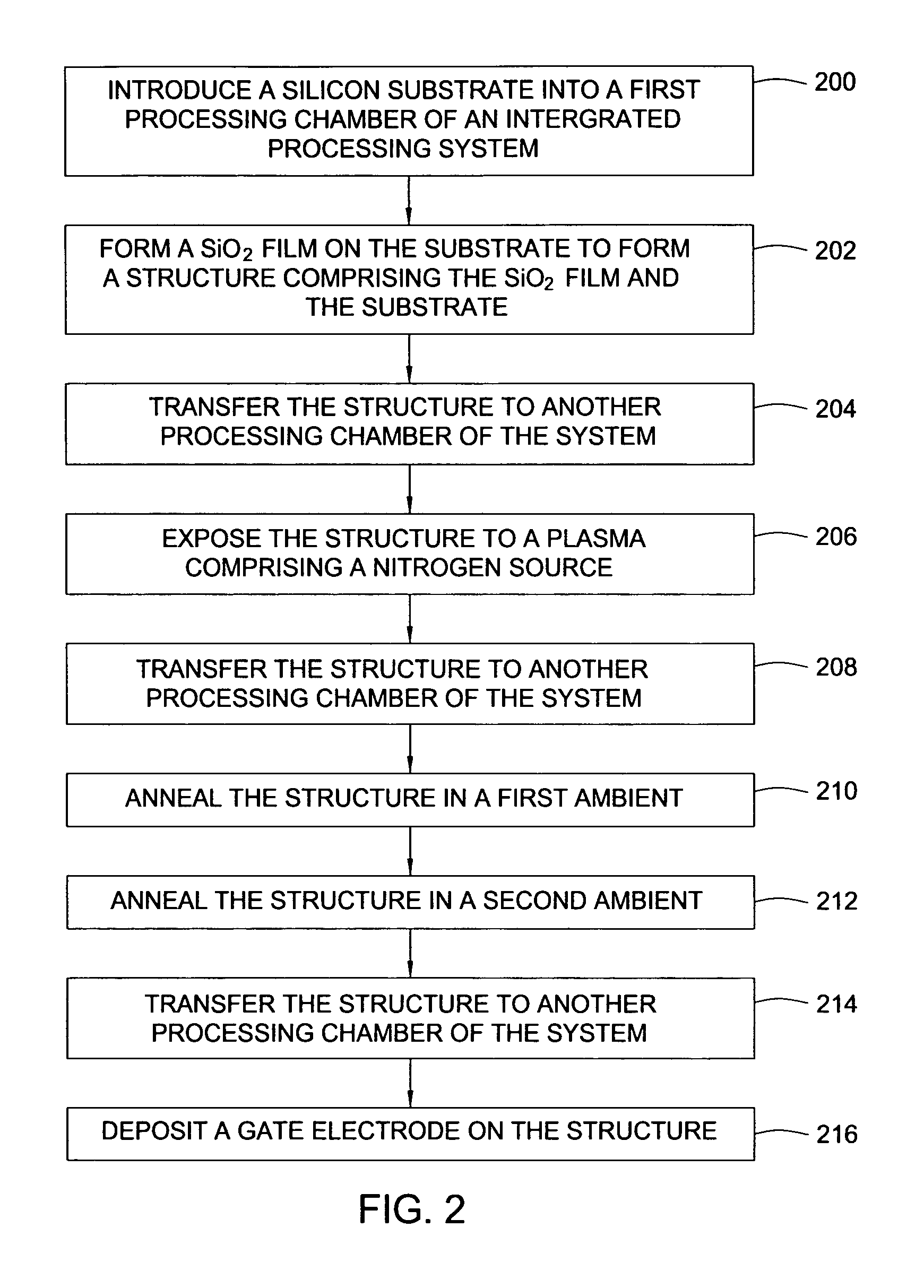
Two-step post nitridation annealing for lower EOT plasma nitrided gate dielectrics
InactiveUS20080090425A9Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricMetallurgy
A method of forming a dielectric film that includes nitrogen. The method includes incorporating nitrogen into a dielectric film using a plasma nitridation process to form a silicon oxynitride film. The silicon oxynitride film is annealed first in an inert or reducing ambient at a temperature ranging between about 700° C. and 1100° C. The silicon oxynitride film is annealed for the second time in an oxidizing ambient at a temperature ranging between about 900° C. and 1100° C.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
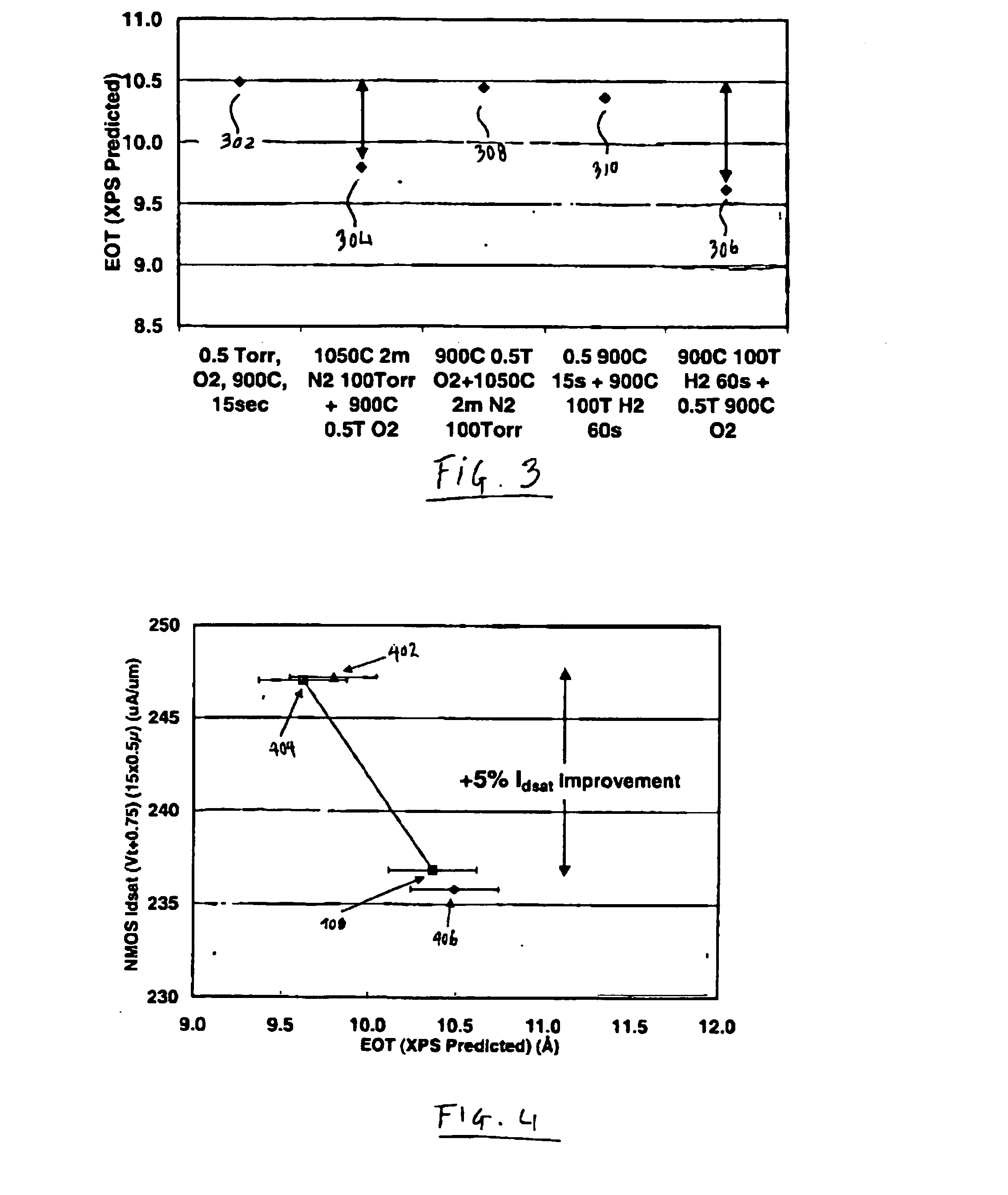
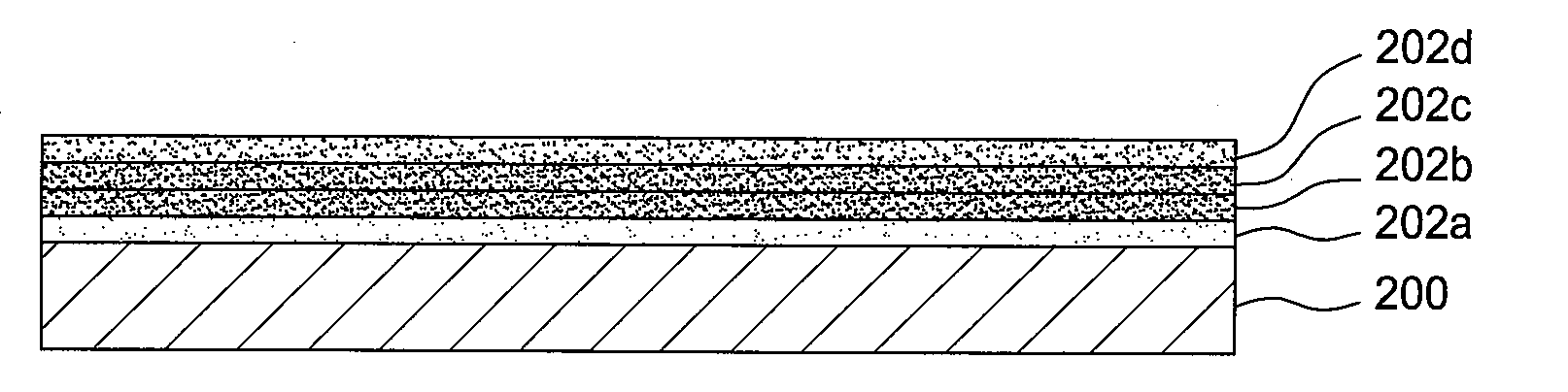
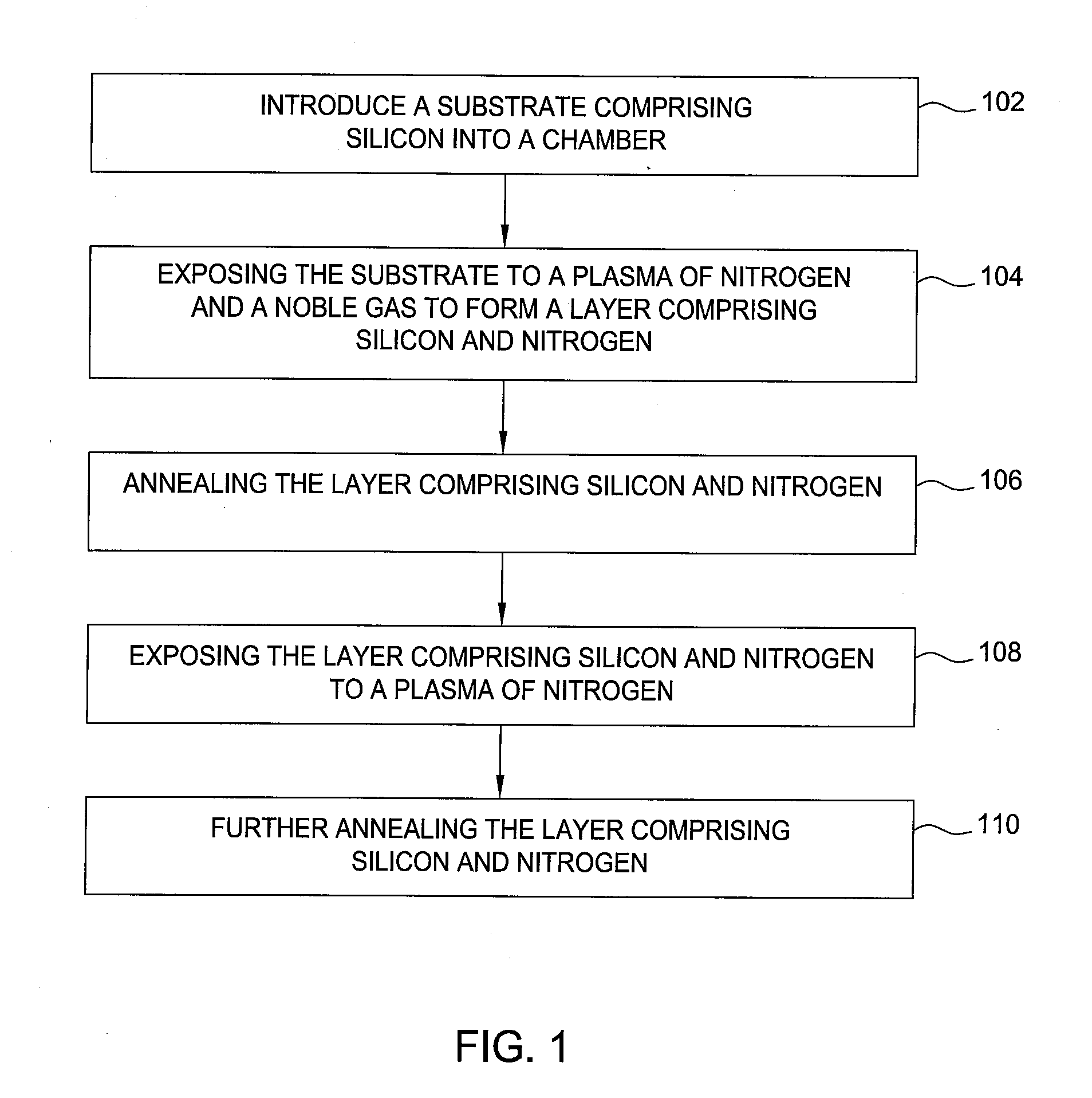
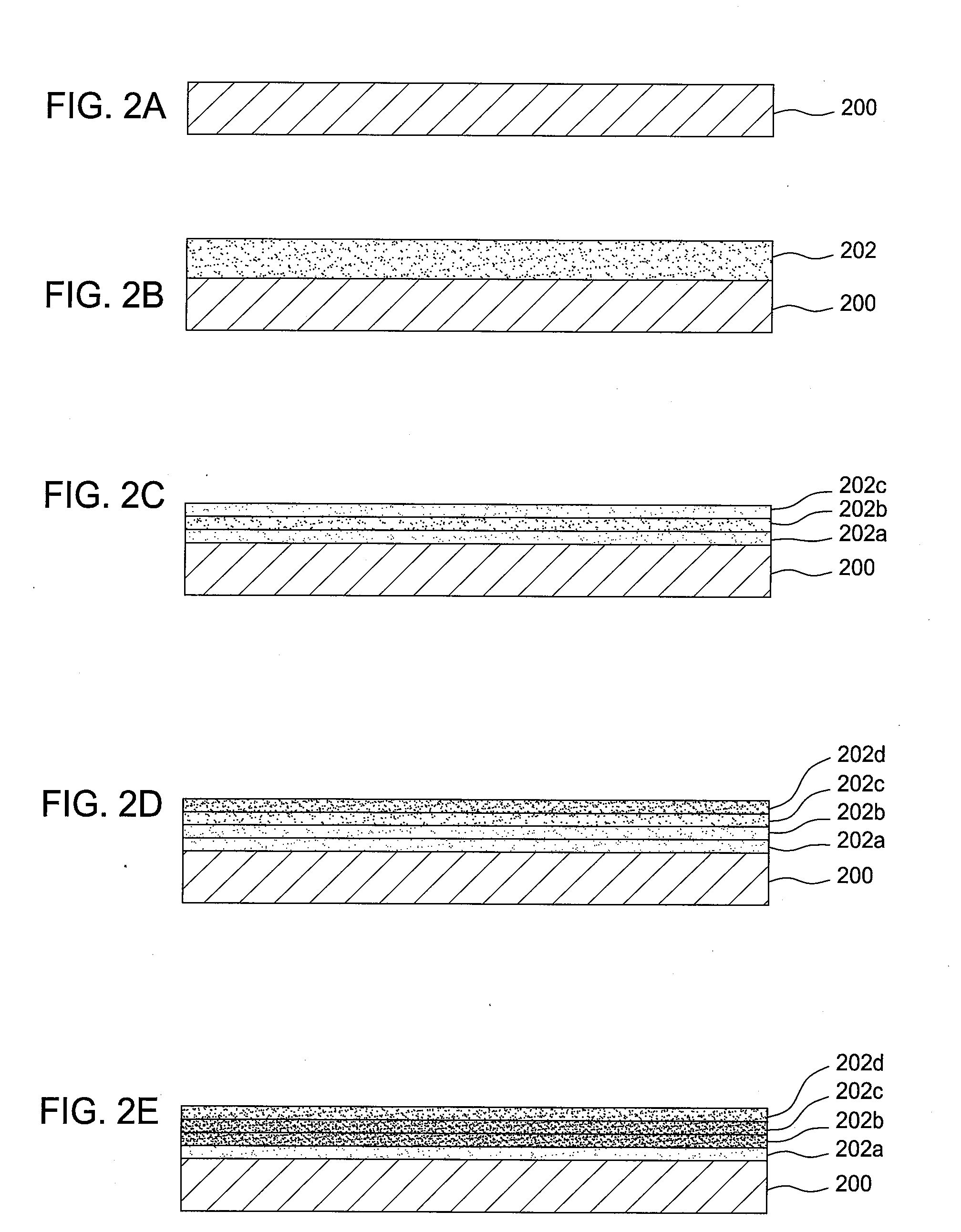
CMOS sion gate dielectric performance with double plasma nitridation containing noble gas
A method of forming a layer comprising silicon and nitrogen on a substrate is provided. The layer may also include oxygen and be used as a silicon oxynitride gate dielectric layer. In one aspect, forming the layer includes exposing a silicon substrate to a plasma of nitrogen and a noble gas to incorporate nitrogen into an upper surface of the substrate, wherein the noble gas is argon, neon, krypton, or xenon. The layer is annealed and then exposed to a plasma of nitrogen to incorporate more nitrogen into the layer. The layer is then further annealed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods of forming NAND memory with virtual channel
ActiveUS7494870B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma nitridationFixed charge
A string of nonvolatile memory cells are connected together by source / drain regions that include an inversion layer created by fixed charge in an overlying layer. Control gates extend between floating gates so that two control gates couple to a floating gate. A fixed charge layer may be formed by plasma nitridation.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Duplex coated steel composite products and method of manufacturing them
InactiveUS6117280AHigh adhesion and durabilityIncreased durabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCarbidePlasma nitridation
Duplex coated steel composite products comprising a first layer of a nitrided layer formed by applying glow discharge at a current density from 0.001 to 2.0 mA / cm2 to the surface of metal parts by using gaseous ammonia and gaseous hydrogen while maintaining the temperature of the metal parts at 300 to 650 DEG C., thereby applying plasma nitriding and a second layer comprising a hard film comprising a nitride, carbide and / or carbonitride of one or more of elements selected from Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta and Cr coated on the first layer by the PVD method of a laminate film or a gradient laminate film of such hard film. The treated products are excellent in adhesion with the substrate and durability and have both oxidation resistance and wear resistance.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for incorporating nitrogen in oxide films
ActiveUS20070111458A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenPlasma nitridation
In a first aspect, a first method is provided. The first method includes the steps of (1) preconditioning a process chamber with an aggressive plasma; (2) loading a substrate into the process chamber; and (3) performing plasma nitridation on the substrate within the process chamber. The process chamber is preconditioned using a plasma power that is at least 150% higher than a plasma power used during plasma nitridation of the substrate. Numerous other aspects are provided.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of hardening a nano-imprinting stamp
InactiveUS6916511B2Stronger and tougherExtended service lifeNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsChemical reactionNitrogen
A method of forming a hardened nano-imprinting stamp is disclosed. The hardened nano-imprinting stamp includes a plurality of silicon-based nano-sized features that have an hardened shell of silicon carbide, silicon nitride, or silicon carbide nitride. The hardened shell is made harder than the underlying silicon by a plasma carburization and / or a plasma nitridation process. During the plasma process atoms of carbon and / or nitrogen bombard and penetrate a plurality of exposed surfaces of the nano-sized features and chemically react with the silicon to form the hardened shell of silicon carbide, silicon nitride, or silicon carbide nitride.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Plasma-nitriding method
InactiveUS20120251737A1Improve the immunityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogen plasmaMicrowave
A plasma-nitriding method for plasma-nitriding a silicon nitride film includes loading a target object into a processing chamber and mounting the target object on a mounting table; heating the target object; supplying a processing gas containing a nitrogen-containing gas and a rare gas into the processing chamber while introducing a microwave into the processing chamber, generating an electric field in the processing chamber, and generating a plasma by exciting the processing gas; and plasma-nitriding and modifying a silicon nitride film formed on the target object by the generated plasma. The silicon nitride film is a silicon nitride film formed at a film forming temperature ranging from 200° C. to 400° C. by an ALD method, and the silicon nitride film is plasma-nitrided at a processing temperature whose maximum is equal to the film forming temperature in the ALD method to form a silicon nitride film modified by a low-temperature nitrogen-containing plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Manufacturing method for two-step post nitridation annealing of plasma nitrided gate dielectric
ActiveUS20060292844A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricNitrogen
A method of forming a silicon oxynitride gate dielectric. The method includes incorporating nitrogen into a dielectric film using a plasma nitridation process to form a silicon oxynitride film. The silicon oxynitride film is annealed in a first ambient. The first ambient comprises an inert ambient with a first partial pressure of oxygen at a first temperature. The silicon oxynitride film is then annealed in a second ambient comprising a second partial pressure of oxygen at a second temperature. The second partial pressure of oxygen is greater than the first partial pressure of oxygen.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of generating multiple oxides by plasma nitridation on oxide
InactiveUS7118974B2Little and no effect integrityAvoid degradation in device performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantPlasma nitridation
A method of forming multiple gate oxide thicknesses on active areas that are separated by STI isolation regions on a substrate. A first layer of oxide is grown to a thickness of about 50 Angstroms and selected regions are then removed. A second layer of oxide is grown that is thinner than first growth oxide. For three different gate oxide thicknesses, selected second oxide growth regions are nitridated with a N2 plasma which increases the dielectric constant of a gate oxide and reduces the effective oxide thickness. To achieve four different gate oxide thicknesses, nitridation is performed on selected first growth oxides and on selected second growth oxide regions. Nitridation of gate oxides also prevents impurity dopants from migrating across the gate oxide layer and reduces leakage of standby current. The method also reduces corner loss of STI regions caused by HF etchant.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method of forming dielectric layers on a substrate and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7910497B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma nitridationSilicon oxide
Methods of forming dielectric layers on a substrate comprising silicon and oxygen are disclosed herein. In some embodiments, a method of forming a dielectric layer on a substrate includes provide a substrate having an exposed silicon oxide layer; treating an upper surface of the silicon oxide layer with a plasma; and depositing a silicon nitride layer on the treated silicon oxide layer via atomic layer deposition. The silicon nitride layer may be exposed to a plasma nitridation process. The silicon oxide and silicon nitride layers may be subsequently thermally annealed. The dielectric layers may be used as part of a gate structure.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
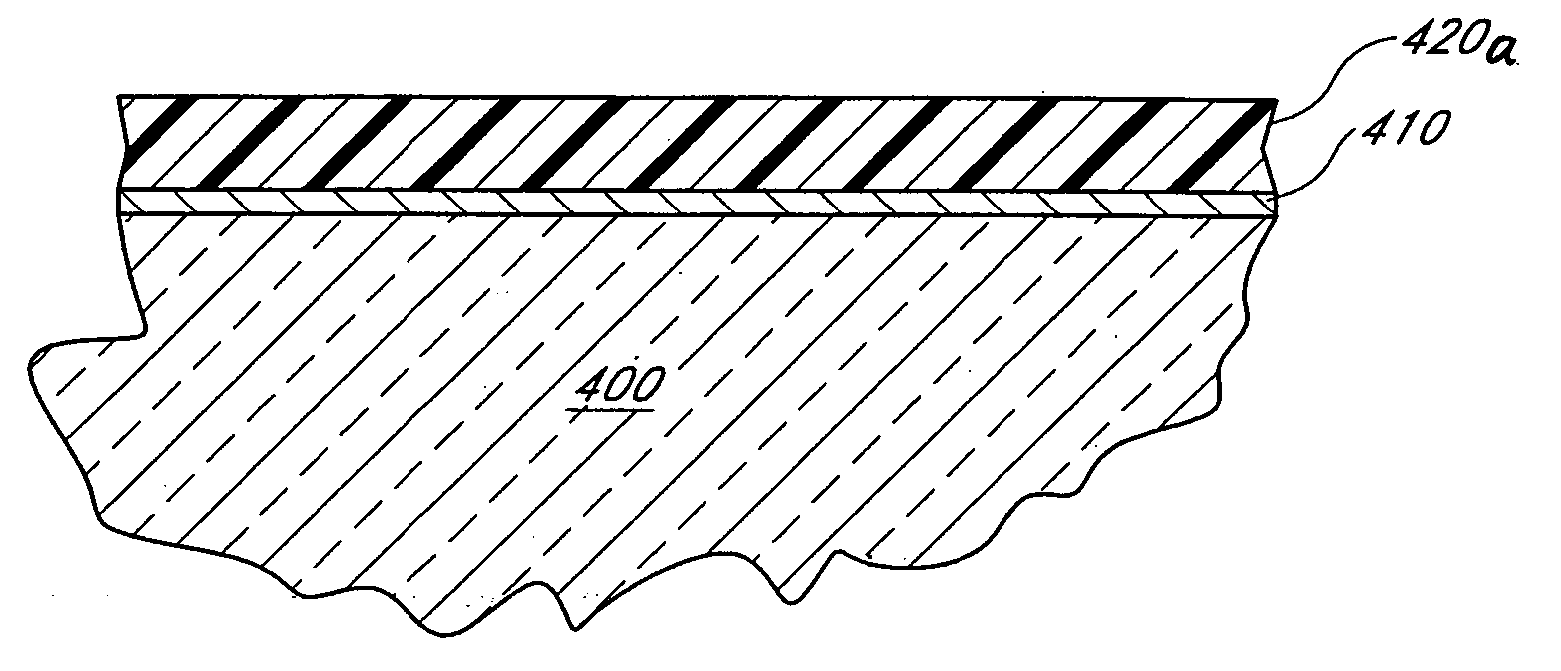
Semiconductor nonvolatile memory device, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060166440A1Reduce harmHard defectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma nitridationSilicon oxide
The present invention realizes a semiconductor nonvolatile memory device where a leak current does not easily flow through a tunnel insulating film, and a manufacturing method thereof A silicon nitride oxide film constituting a tunnel insulating film is formed by radically nitriding a surface of a silicon oxide film. The film formed by a radical nitriding process makes it difficult for defects to occur in the film, in comparison with a nitride film formed by a CVD method. In addition, the radical nitriding process causes less plasma damage, in comparison with a conventional simple plasma nitriding process. It is therefore possible to obtain a semiconductor nonvolatile memory device where a leak current does not easily flow through a tunnel insulating film.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Method of making nitrided active elements
InactiveUS6473960B1High resistivityImprove wear resistanceConstruction of head windingsElectrical transducersCelsius DegreeEngineering
A method of manufacturing an active element for use with a magnetic head includes depositing a magnetic material to form a magnetic member, and nitriding the magnetic member after the depositing step. Preferably, the depositing step comprises depositing nickel-iron alloy, and the nitriding step comprises plasma nitriding the magnetic member. Advantageously, plasma nitriding may be performed at a temperature below 300 degrees Celsius to avoid adverse effects to components of the active element, such as organic planars. Active elements manufactured according to the method of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
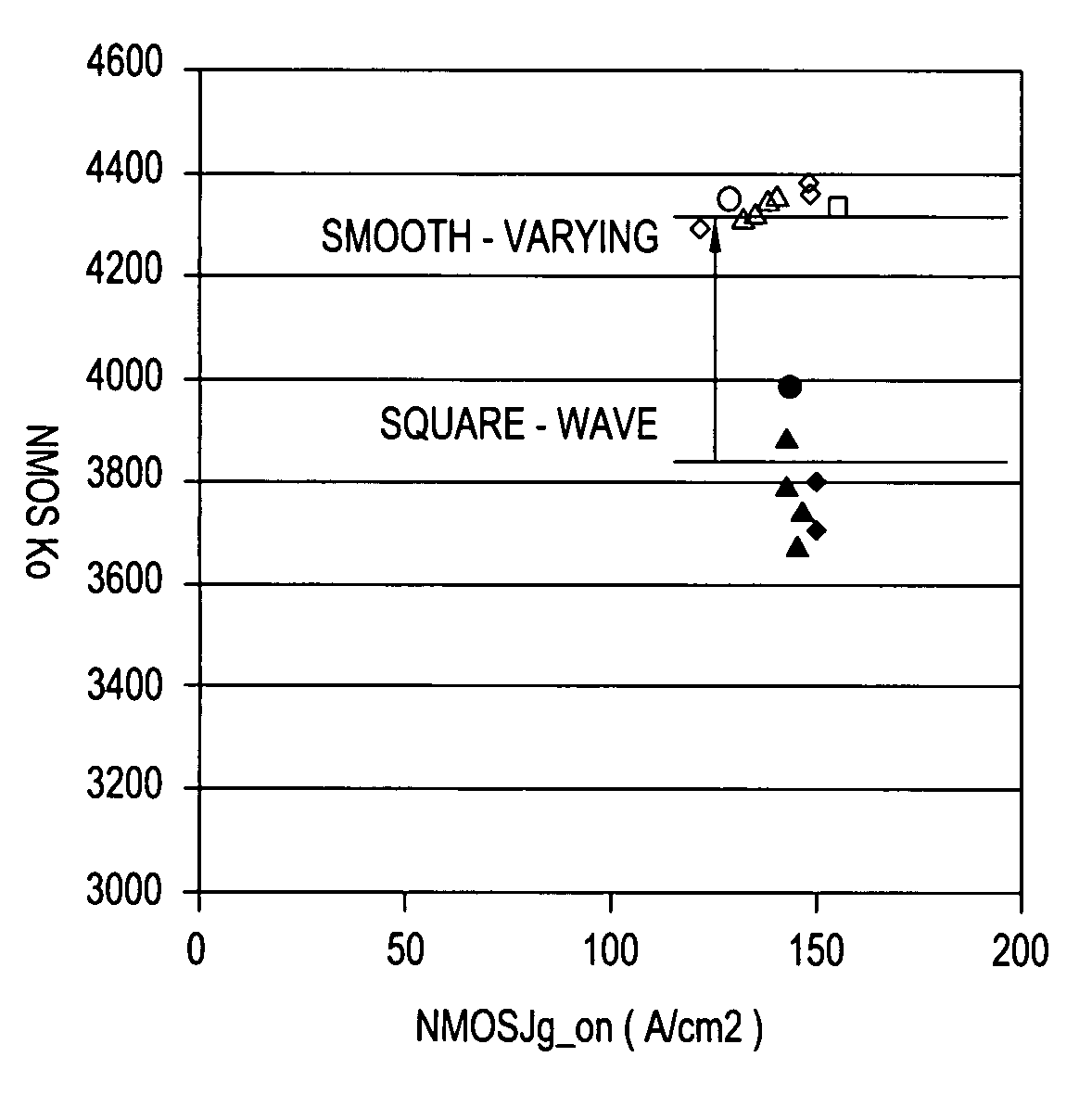
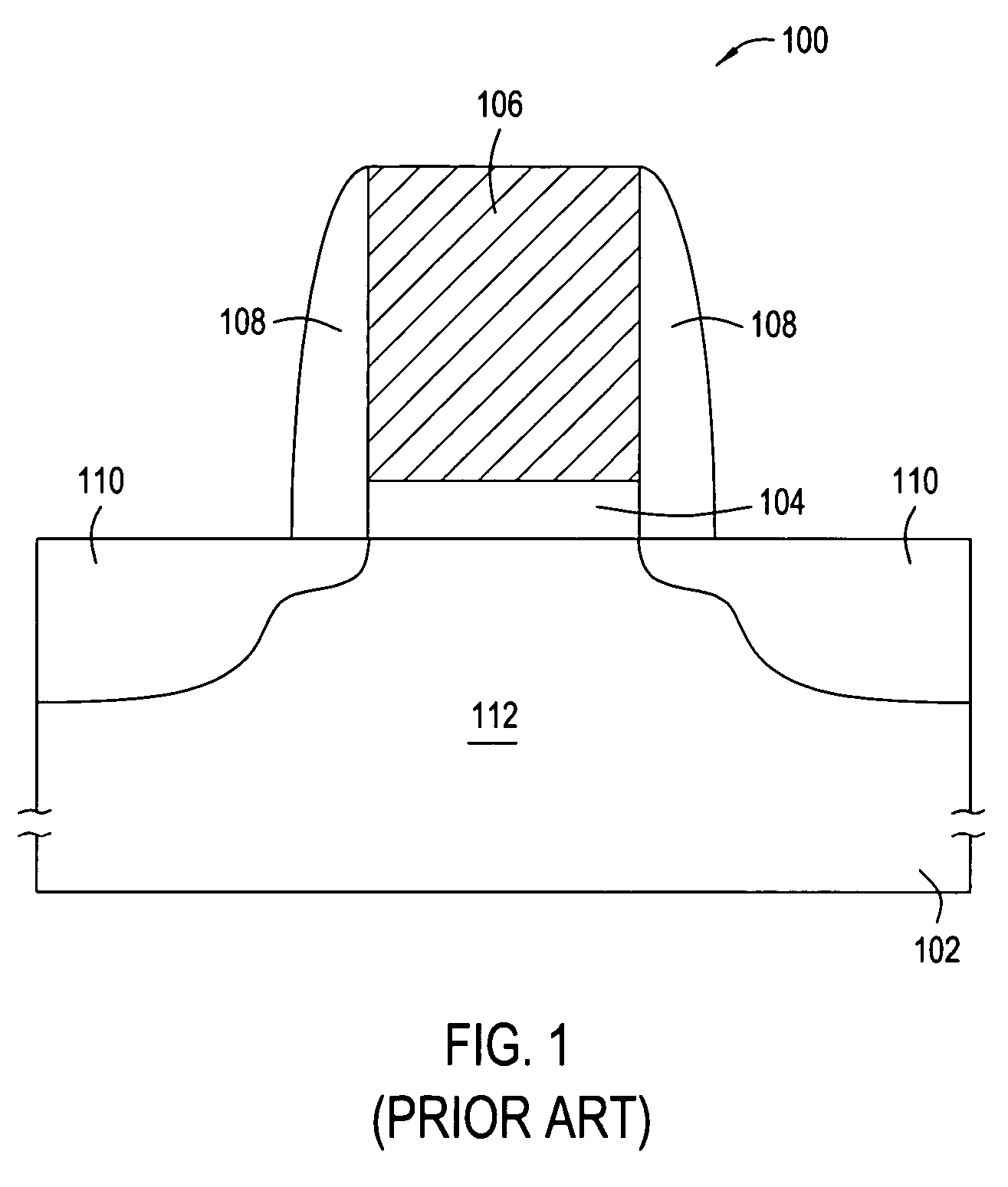
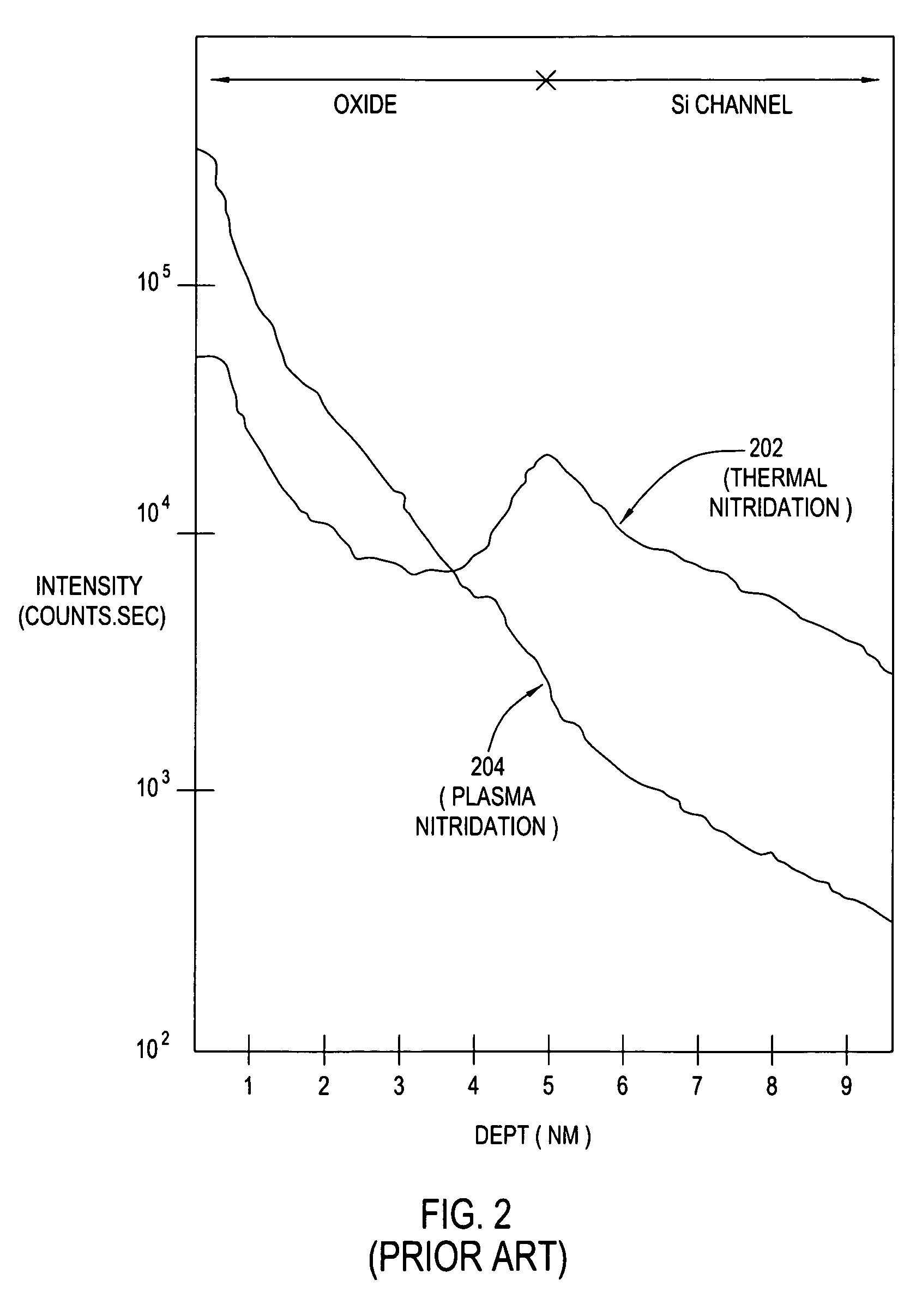
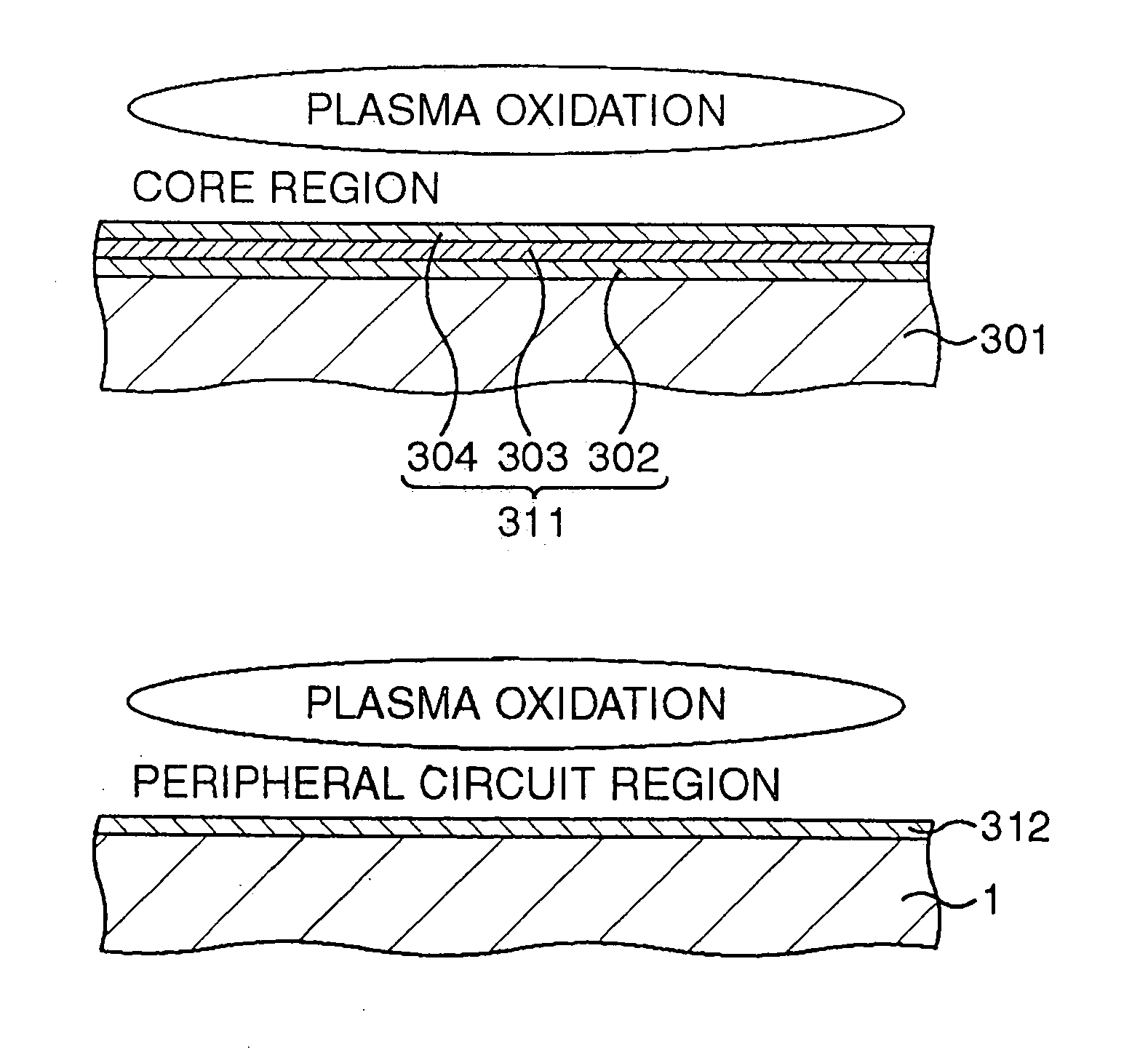
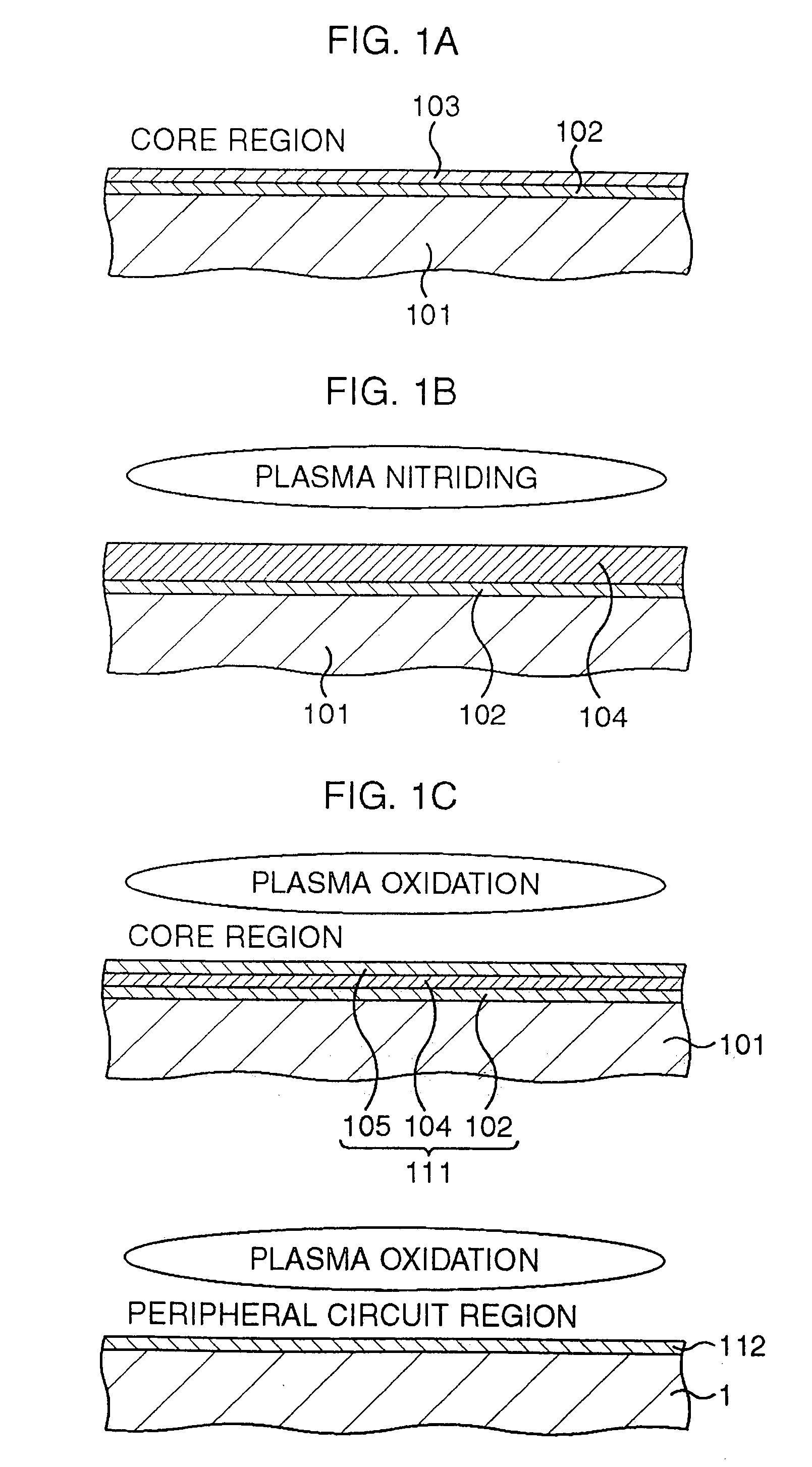
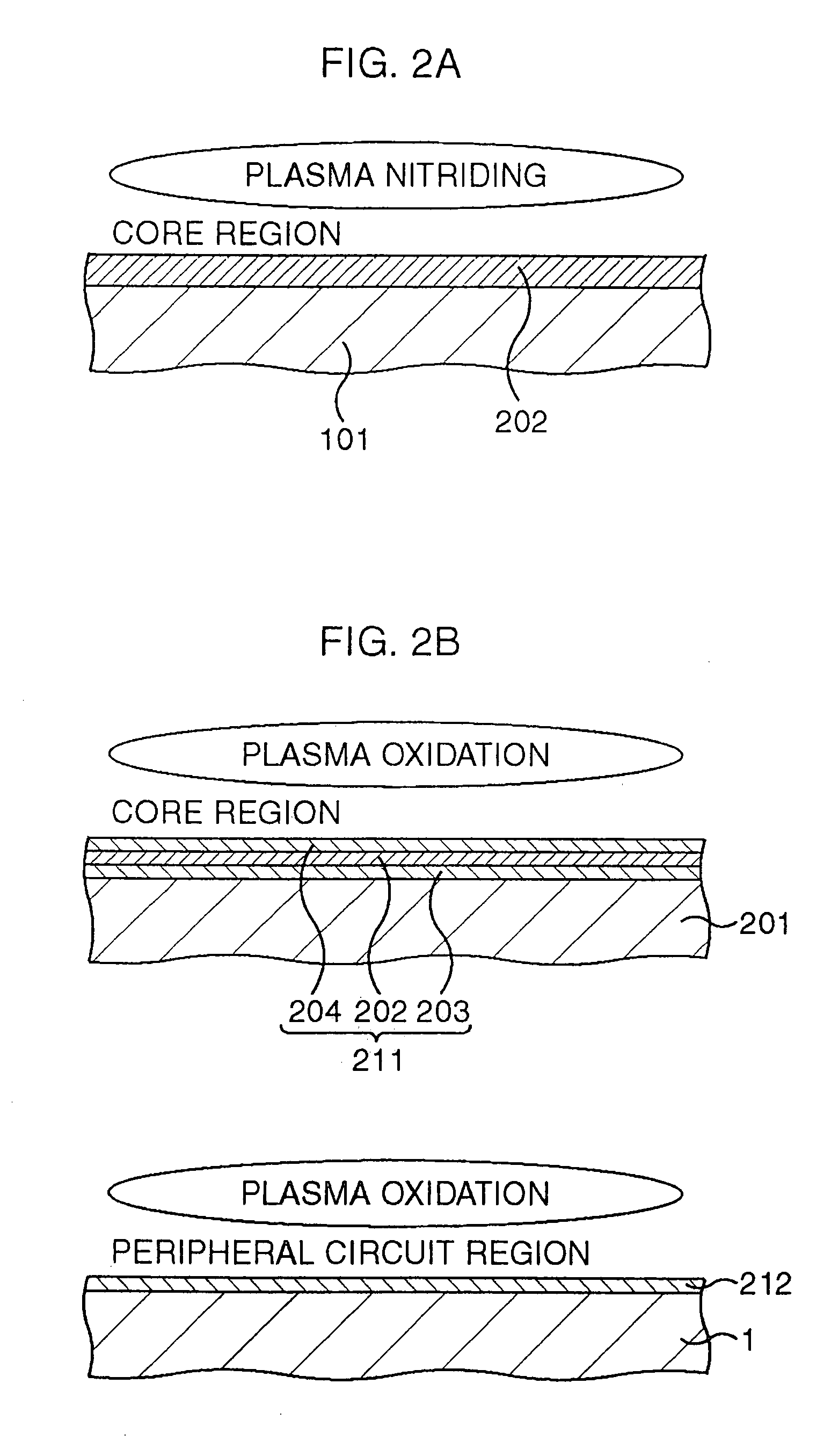
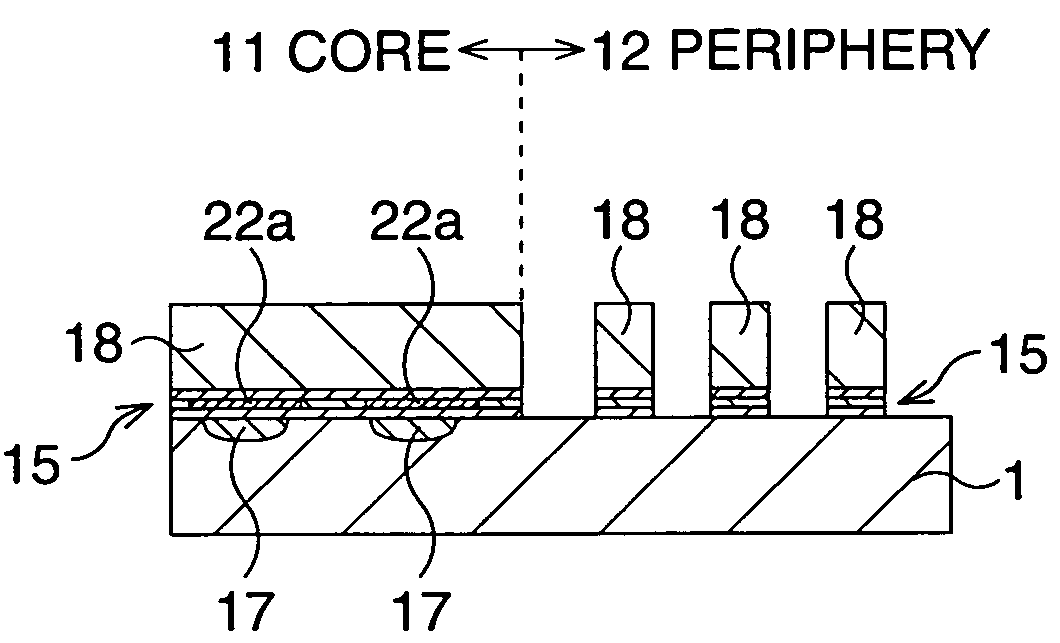
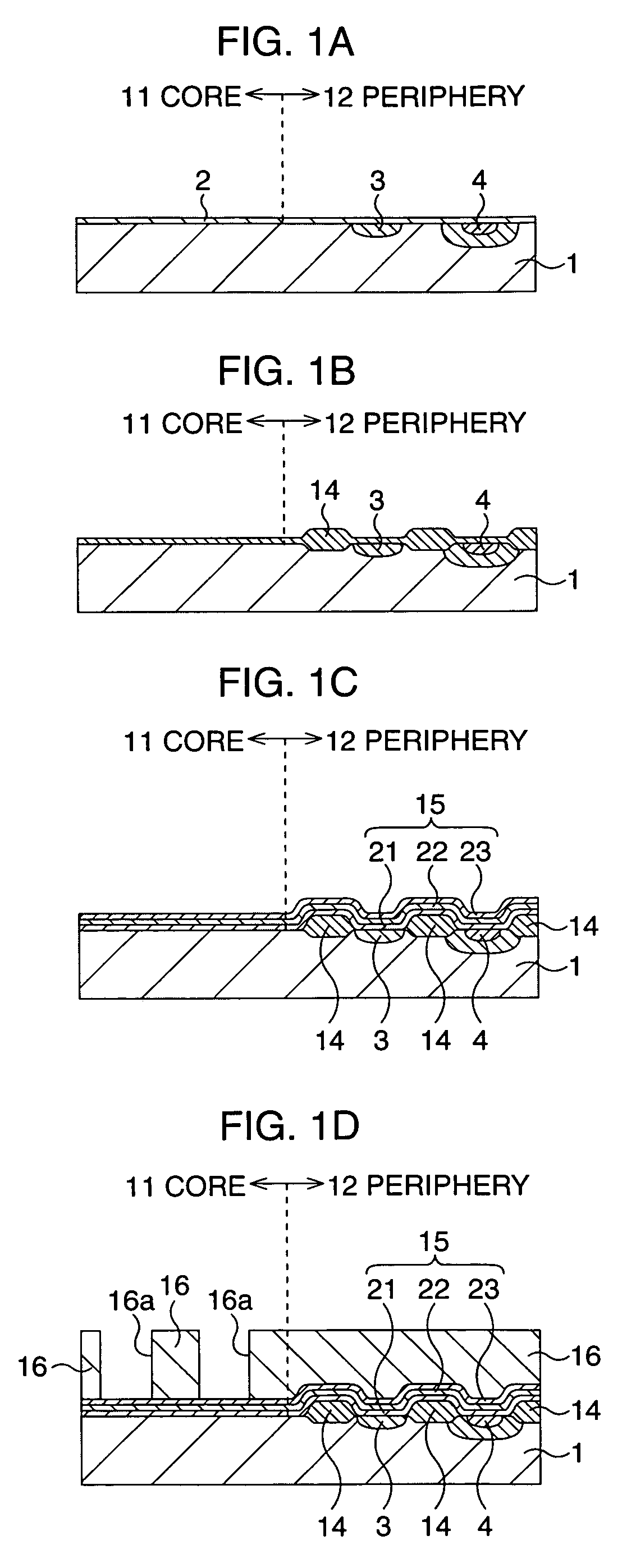
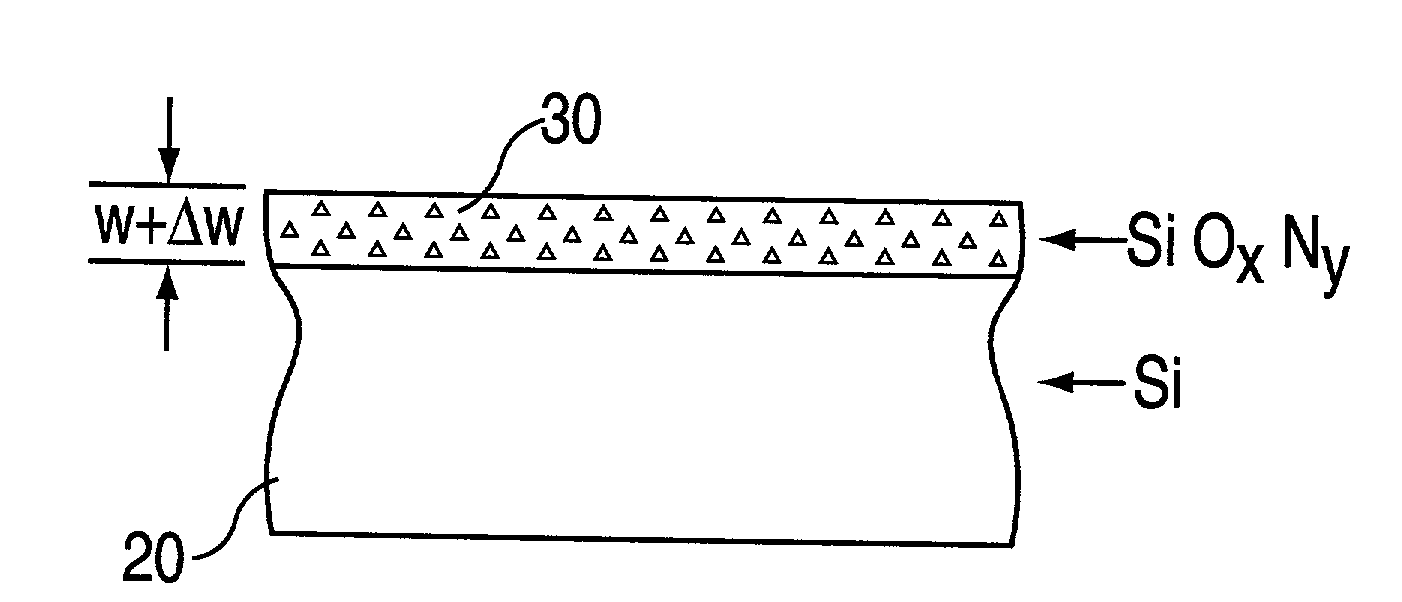
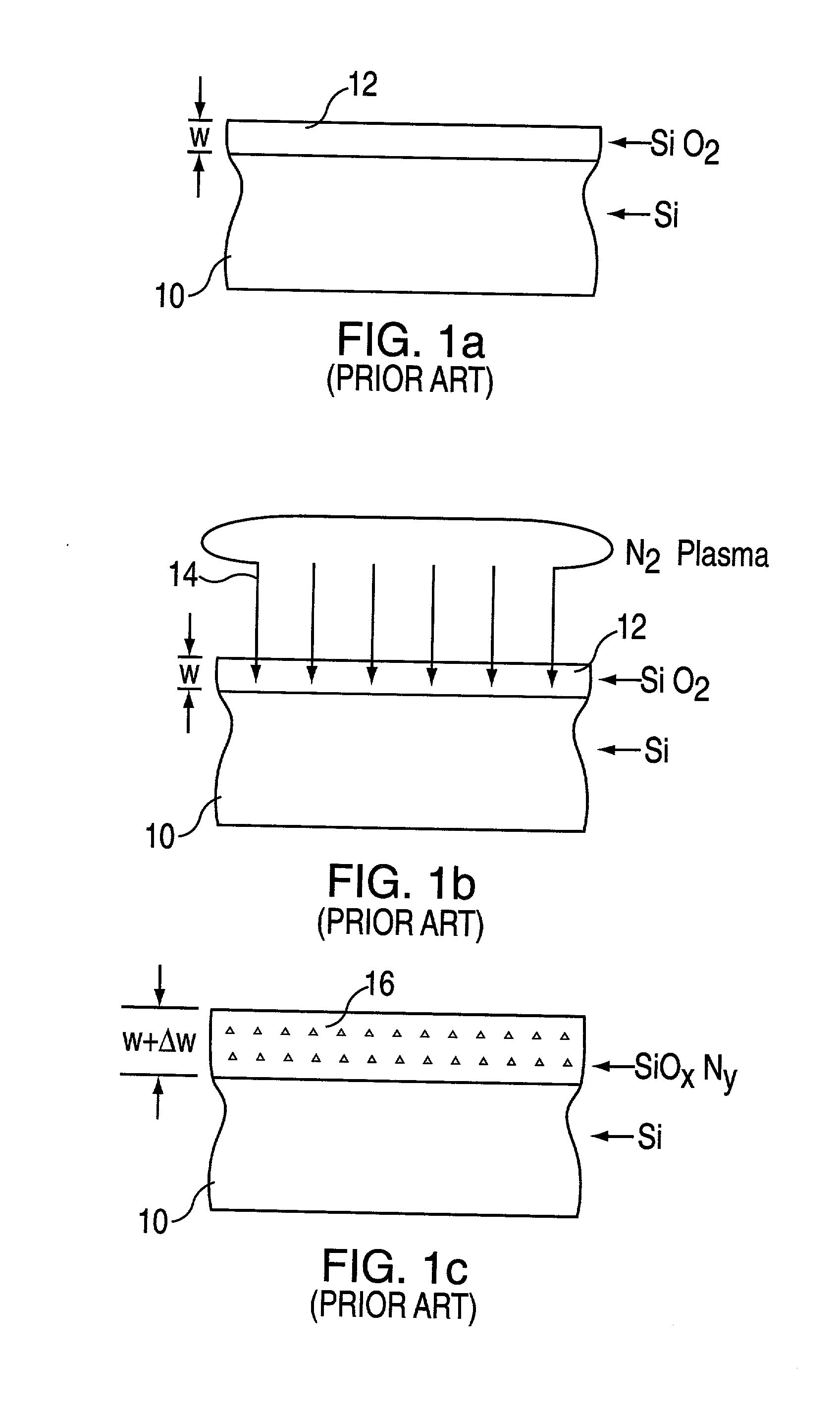
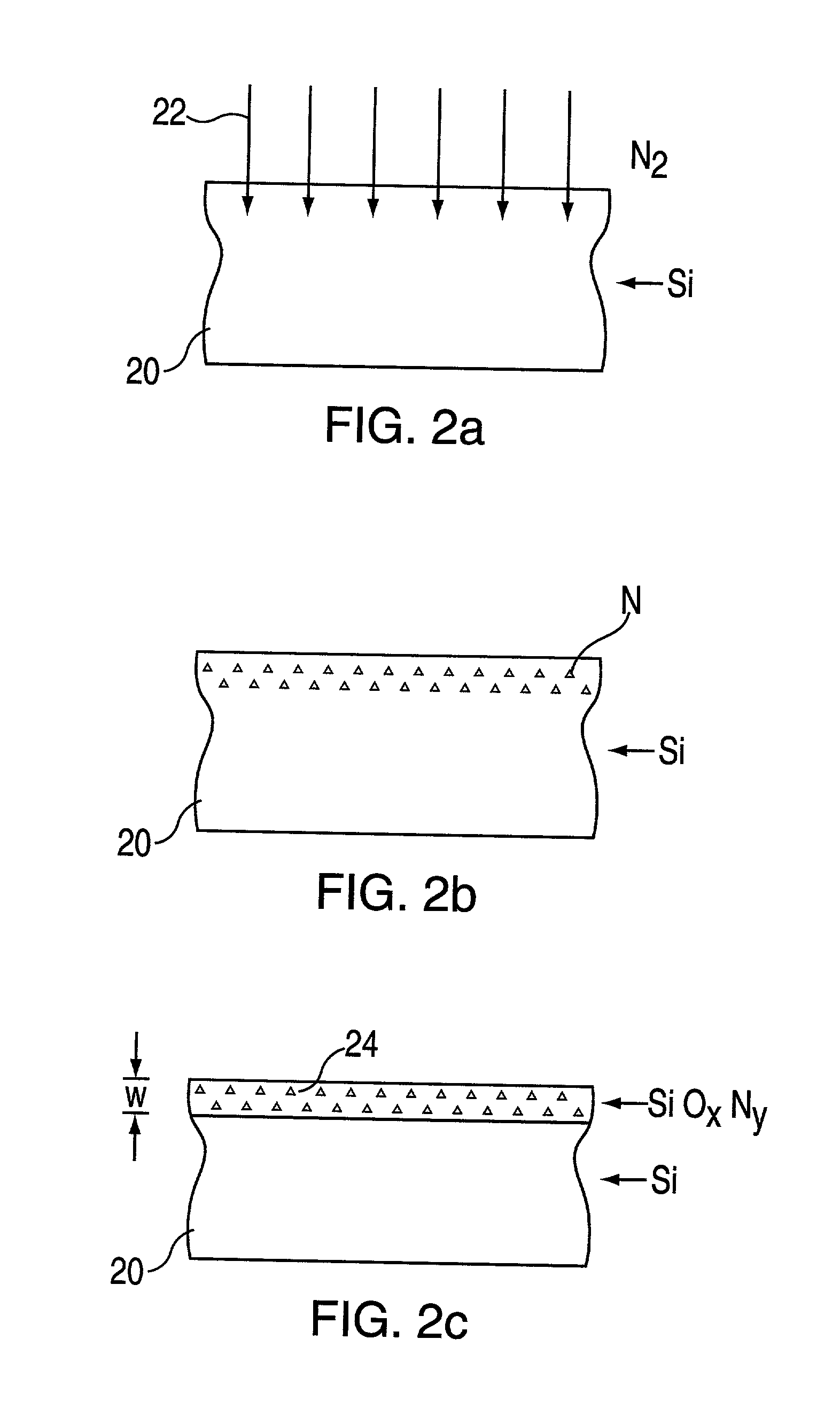
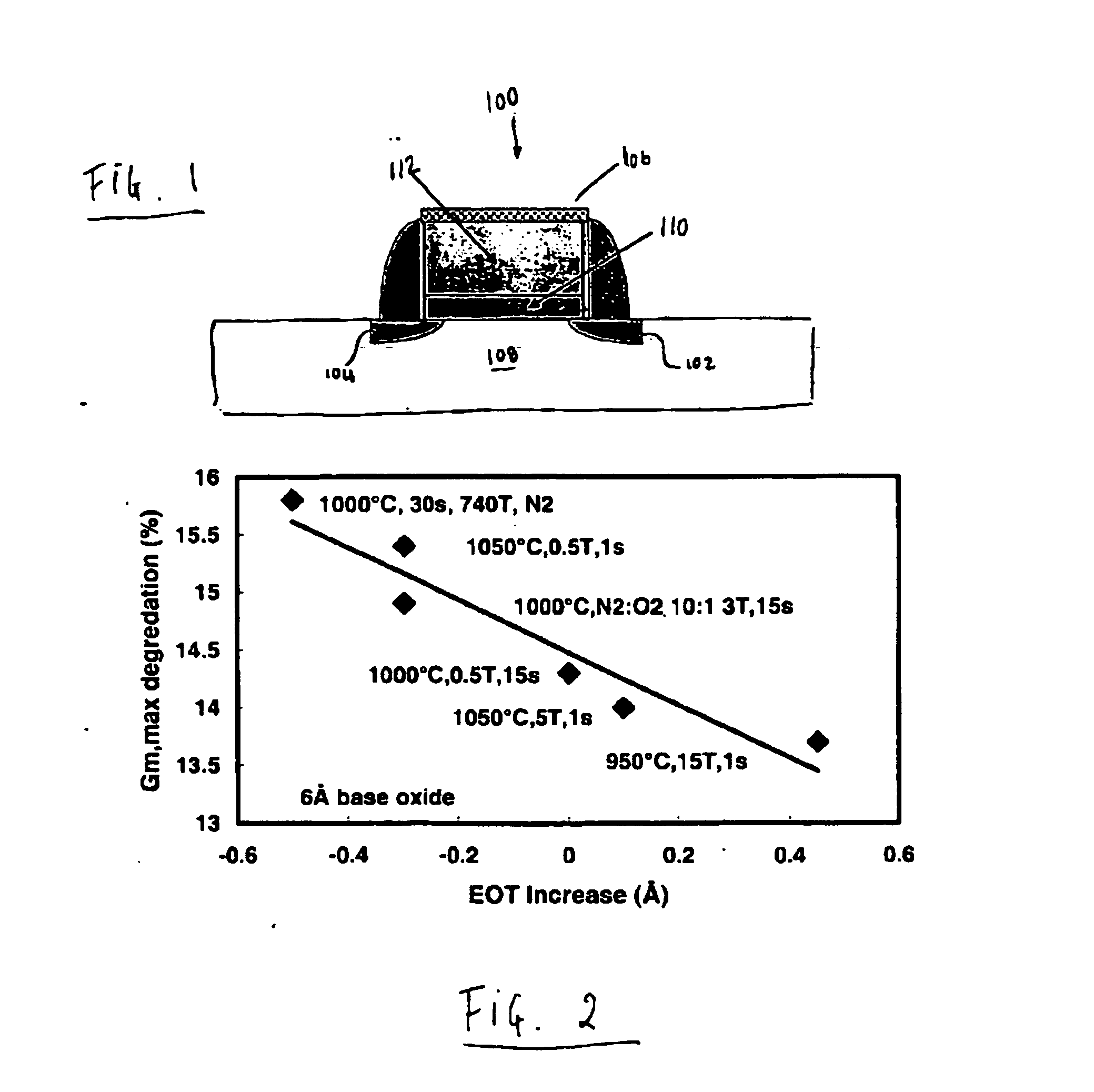
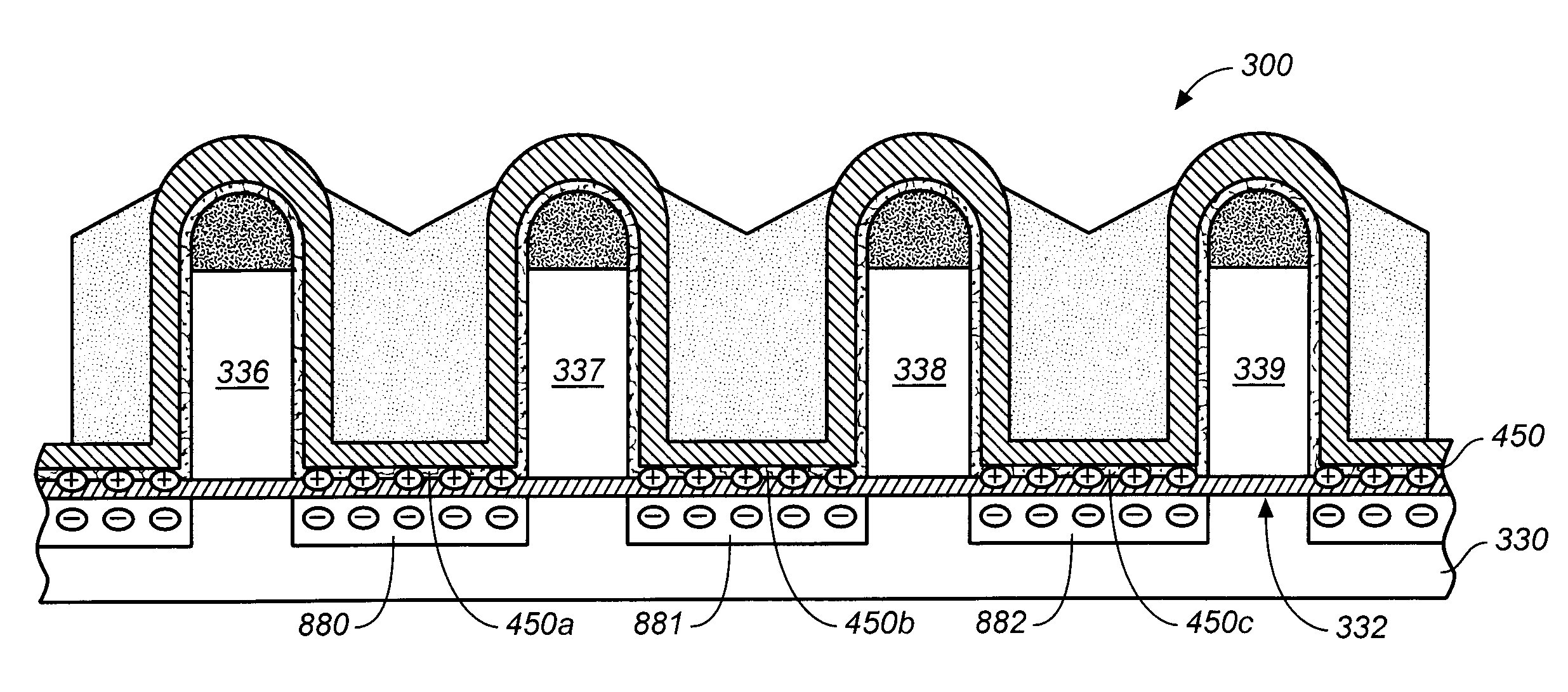
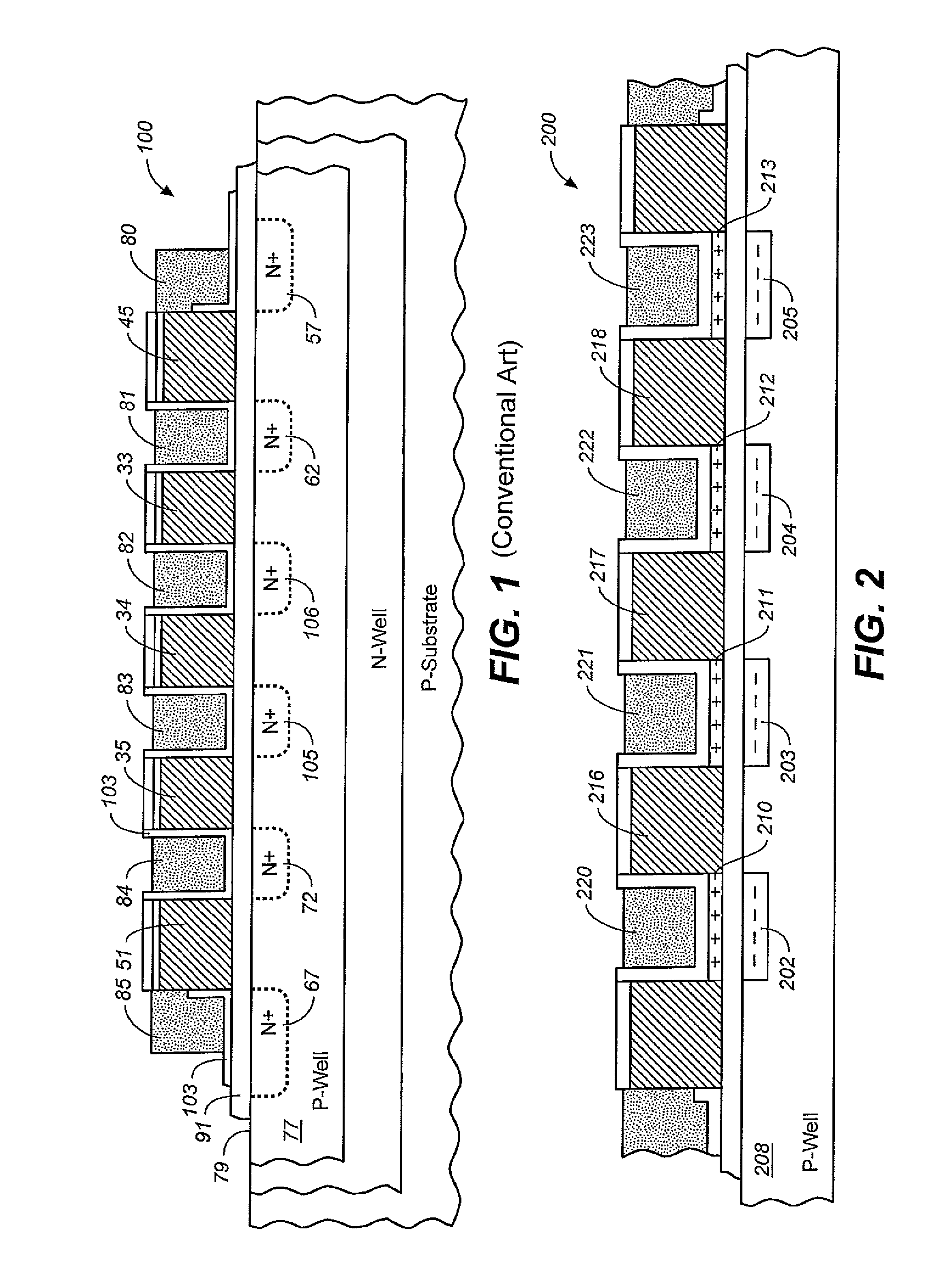
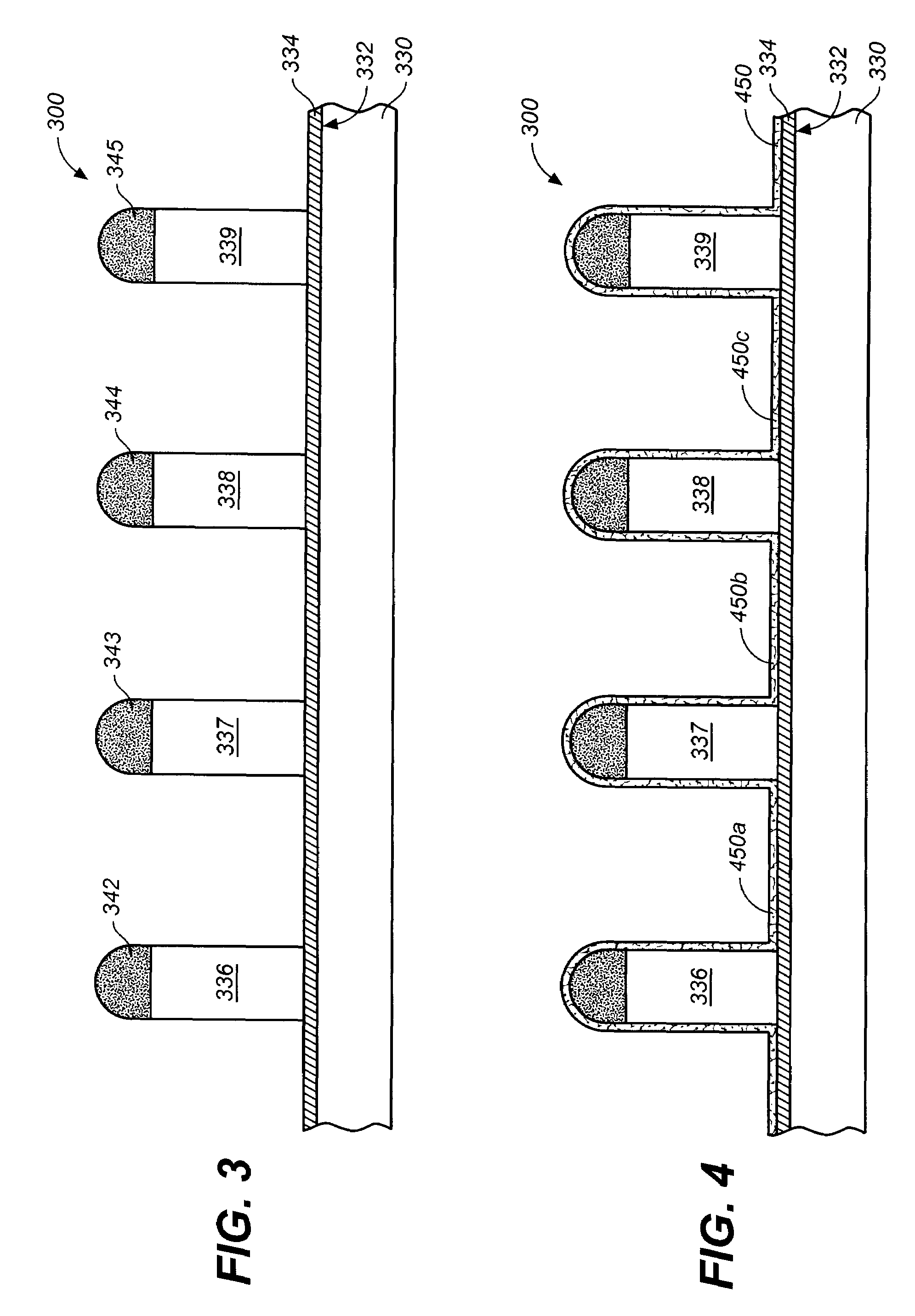
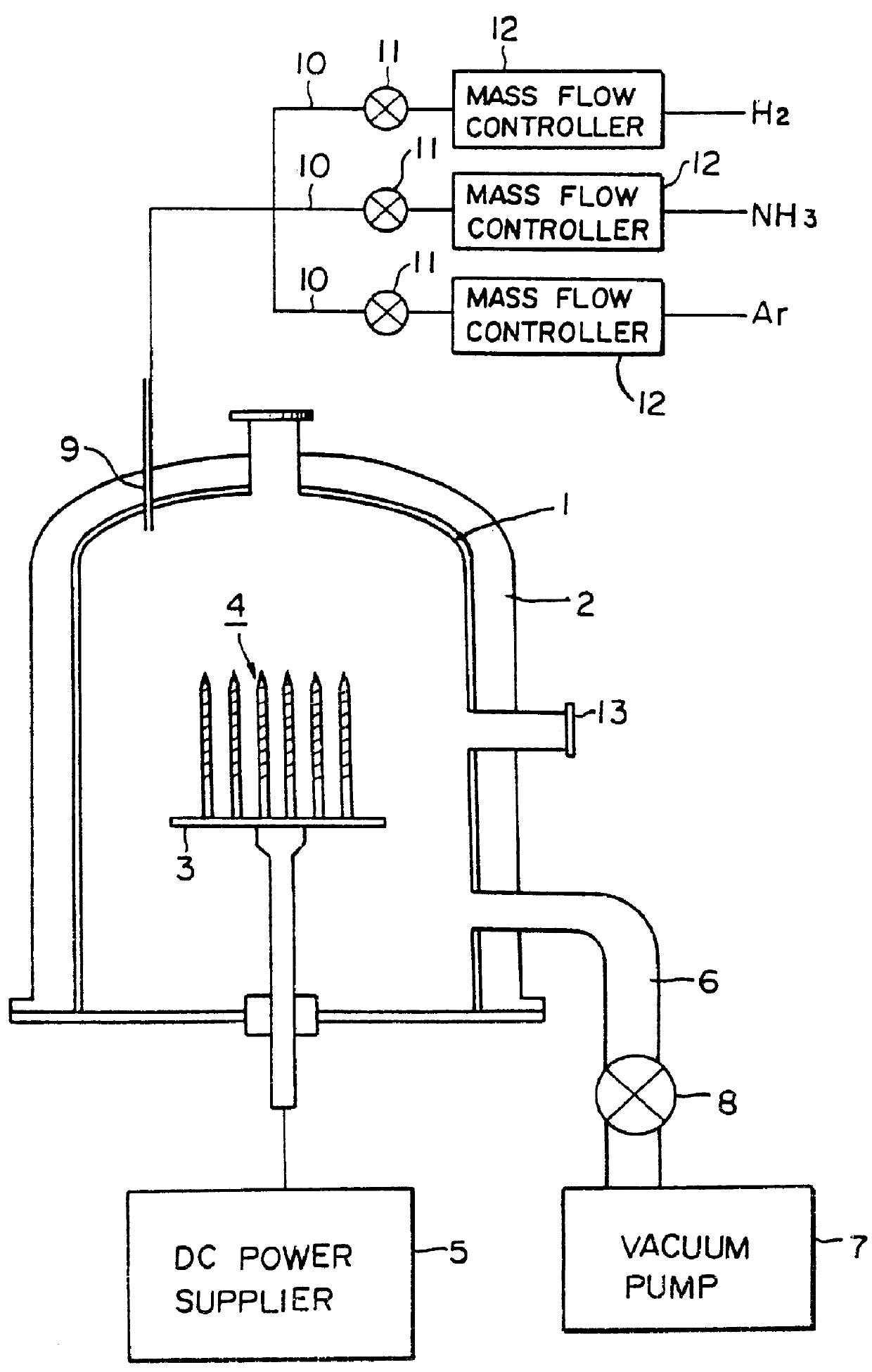
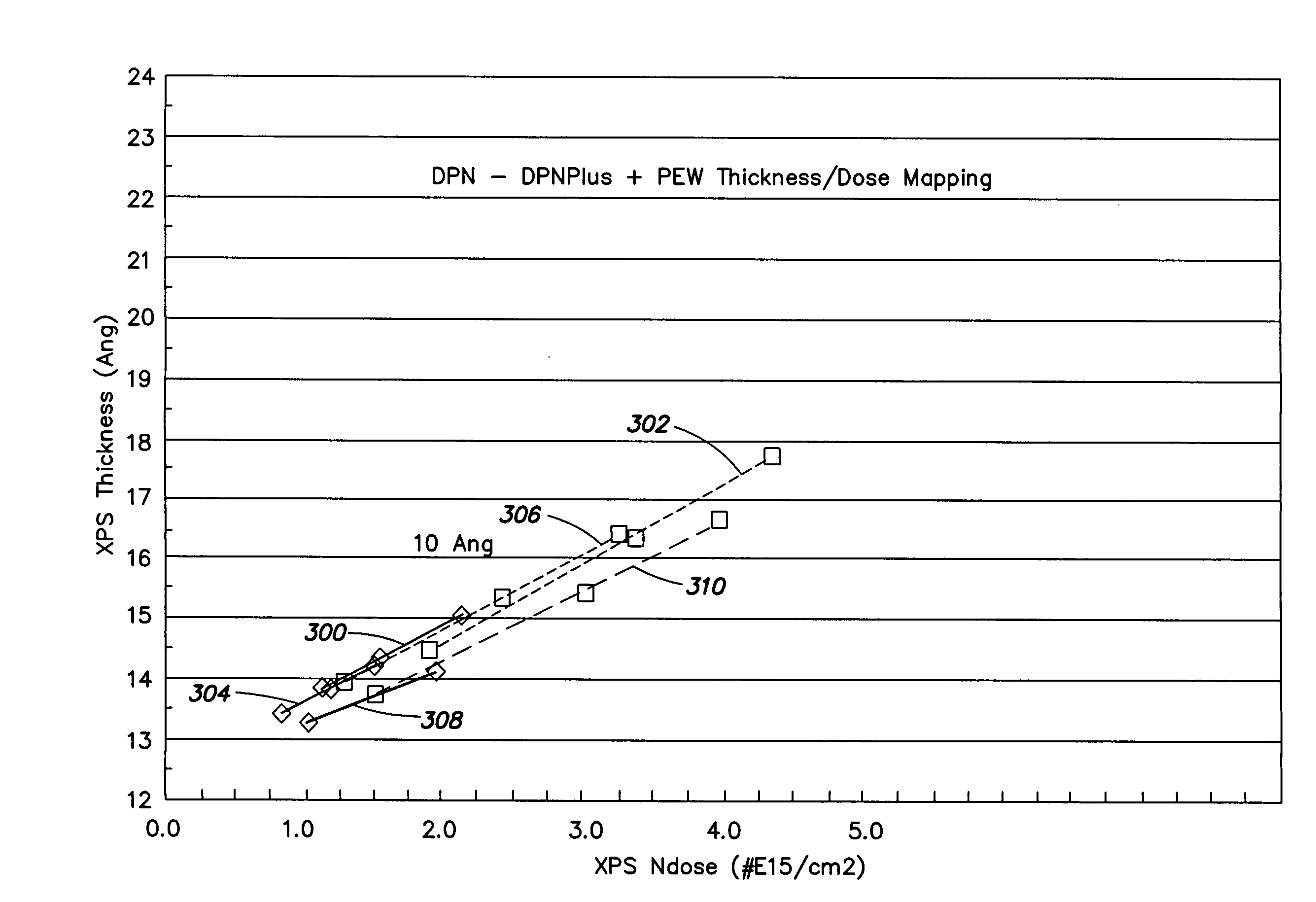
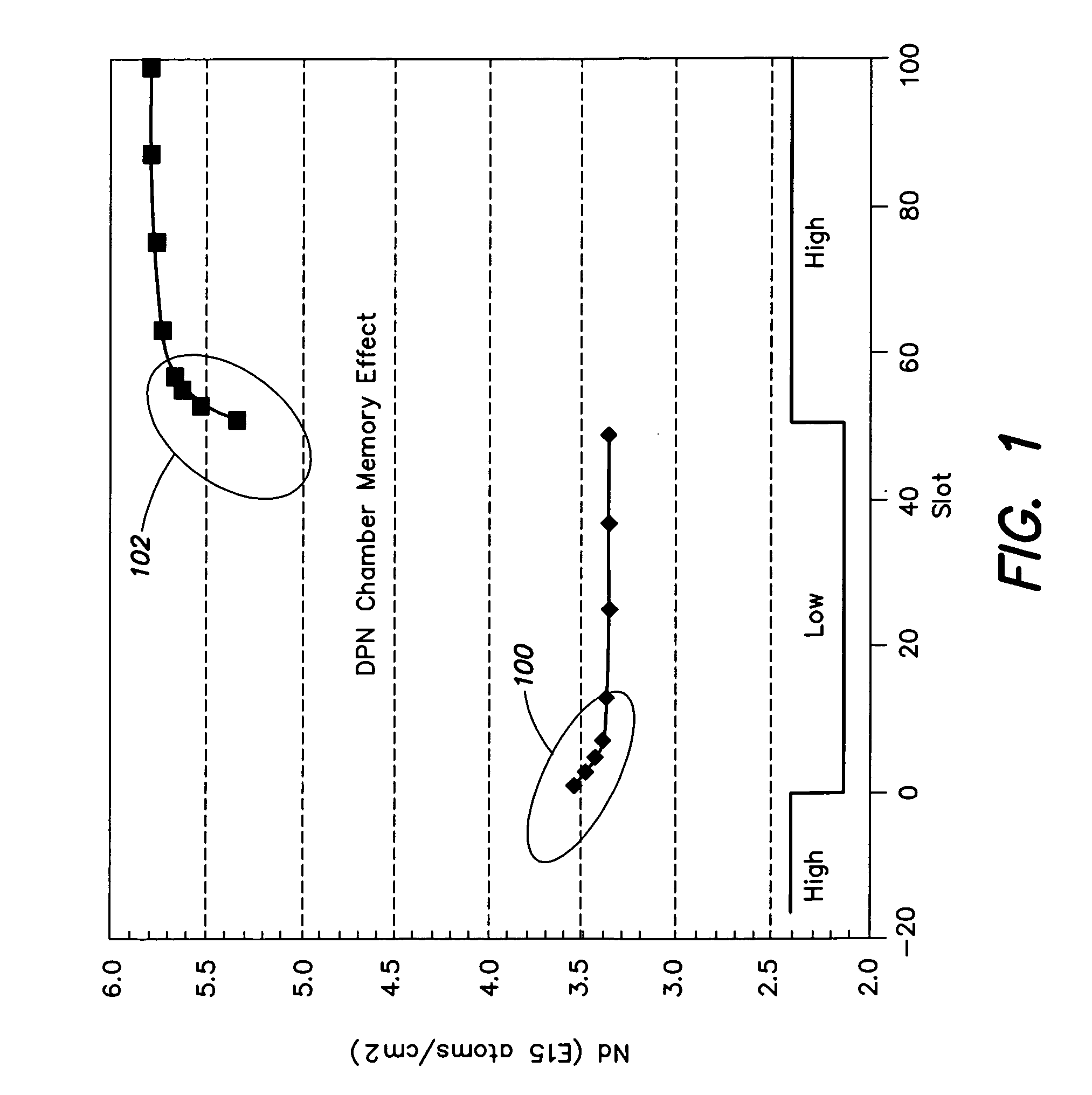
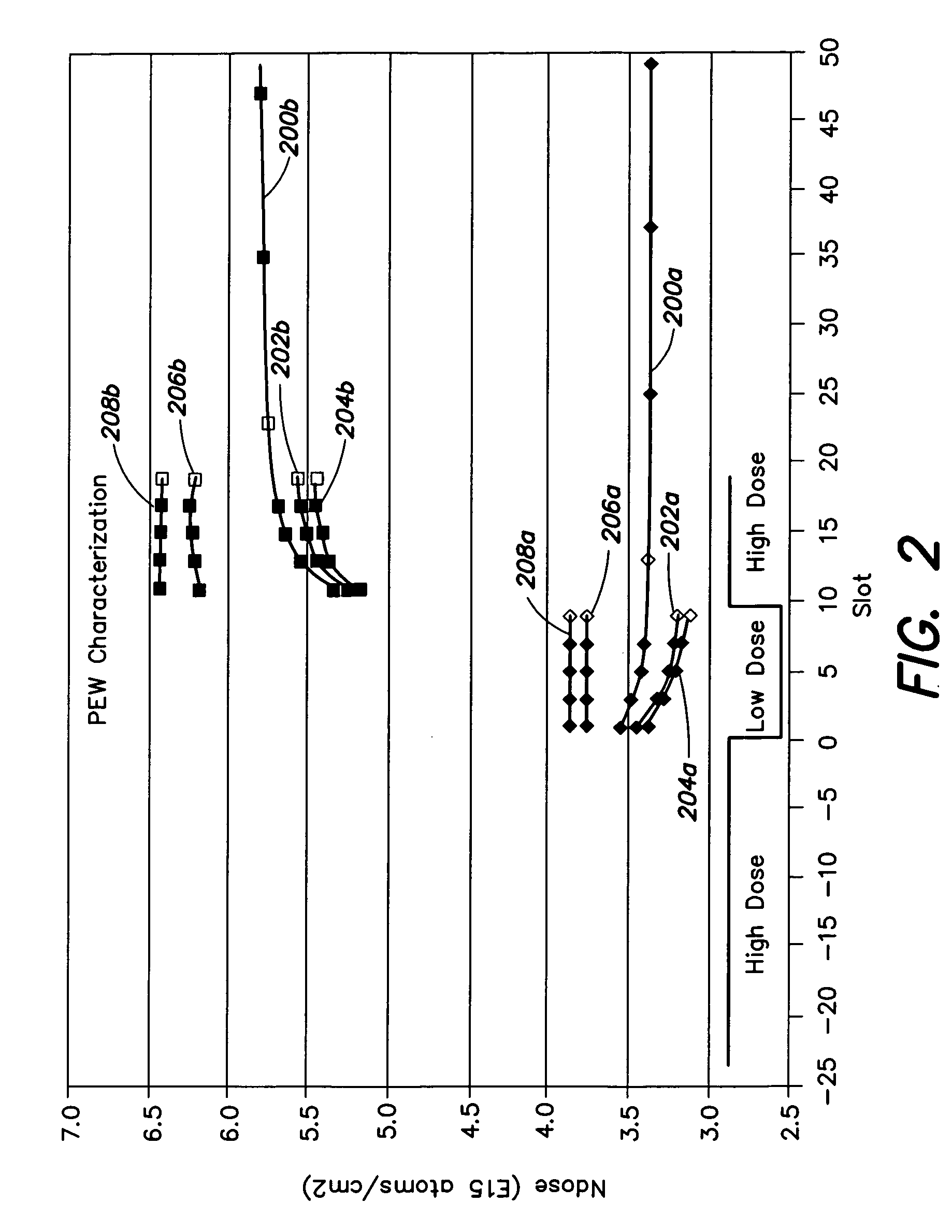
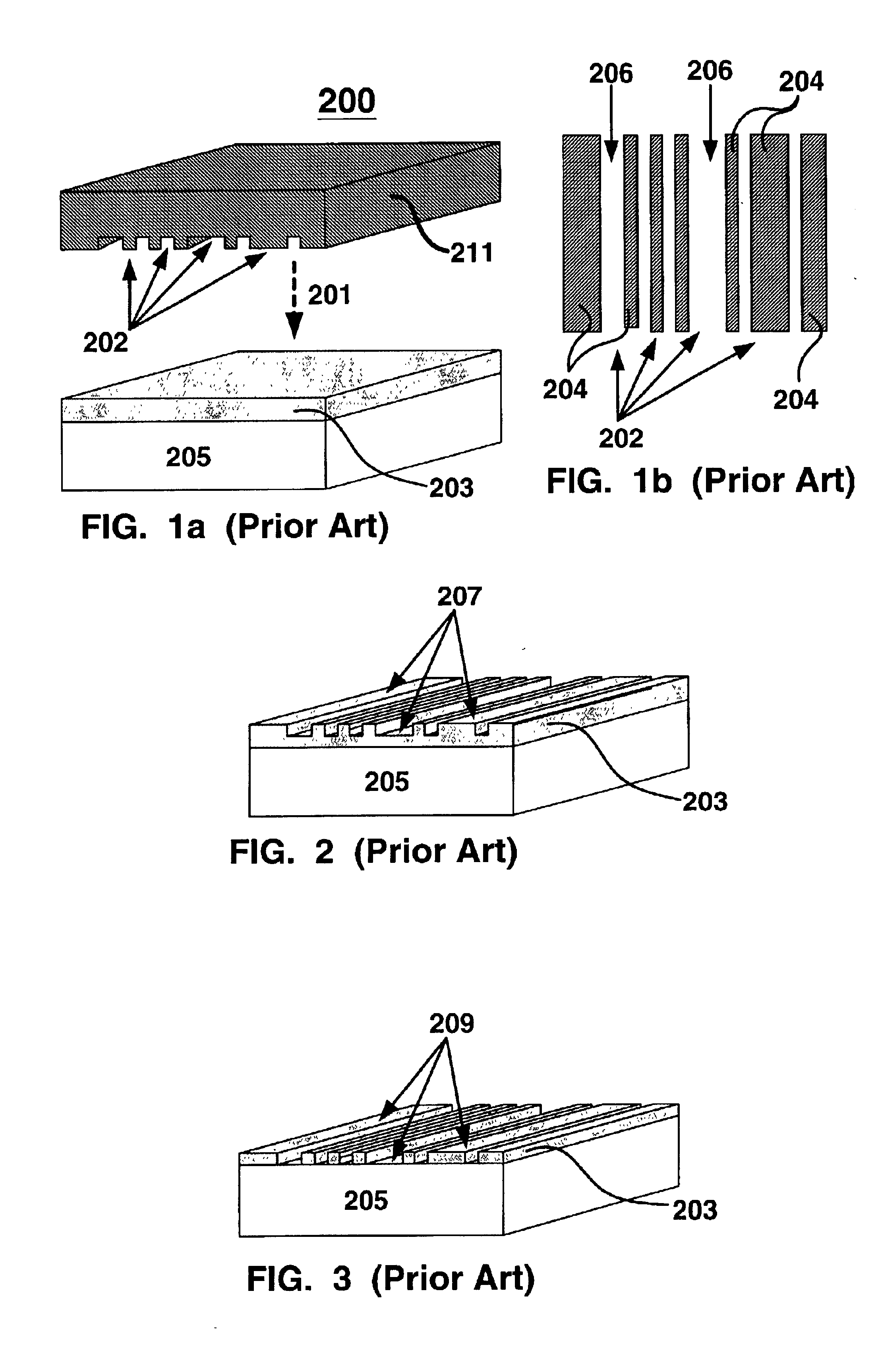
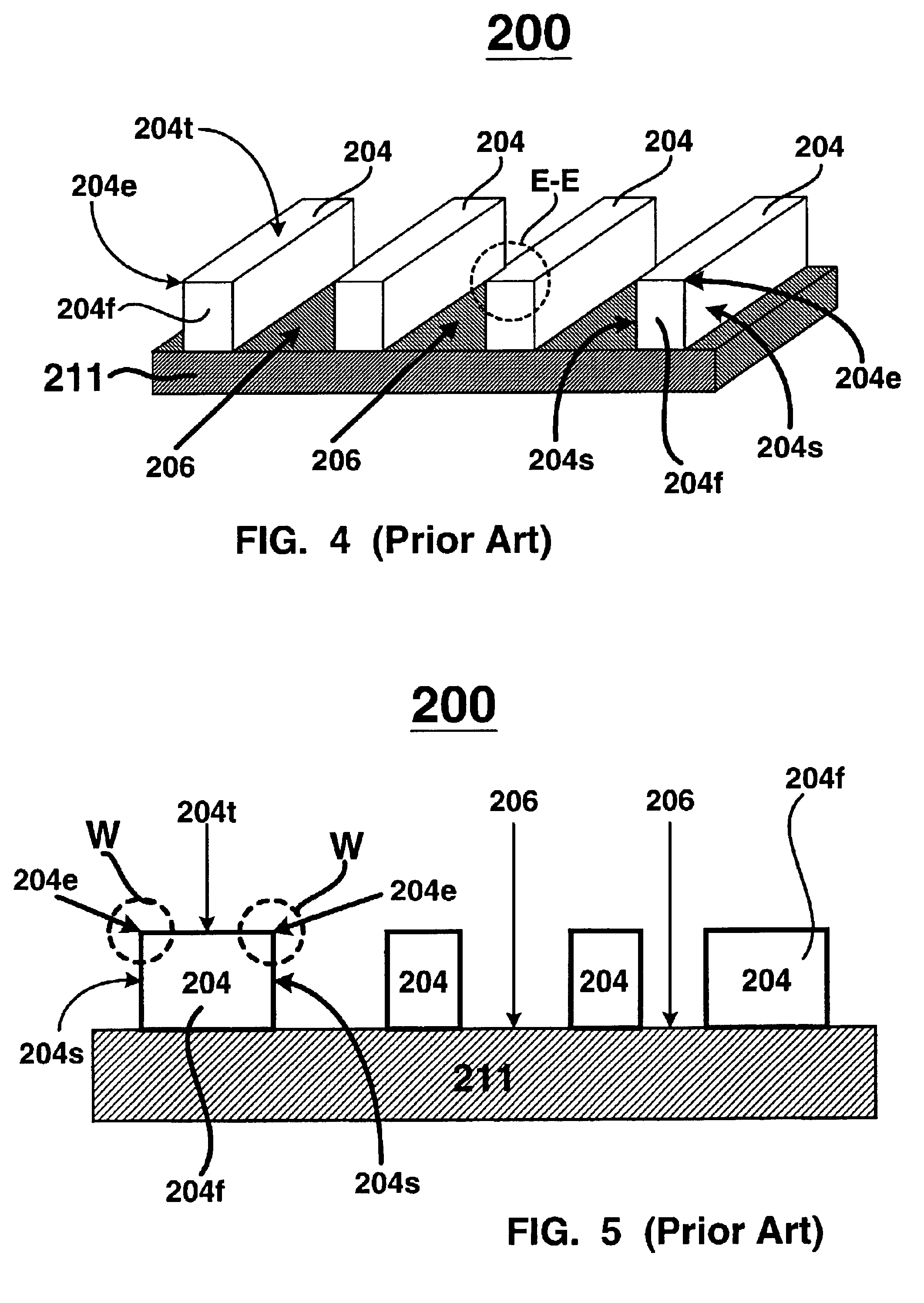
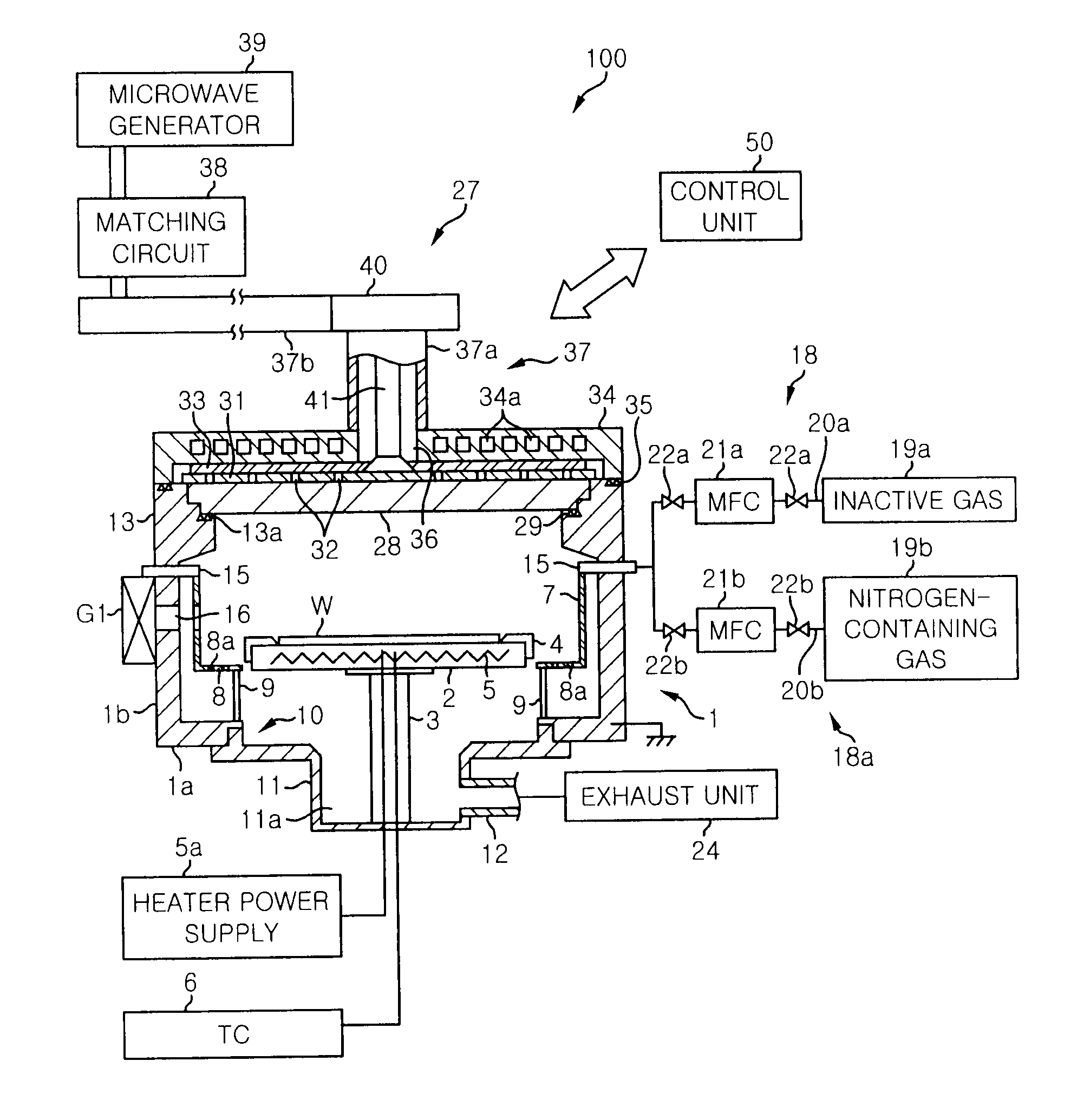
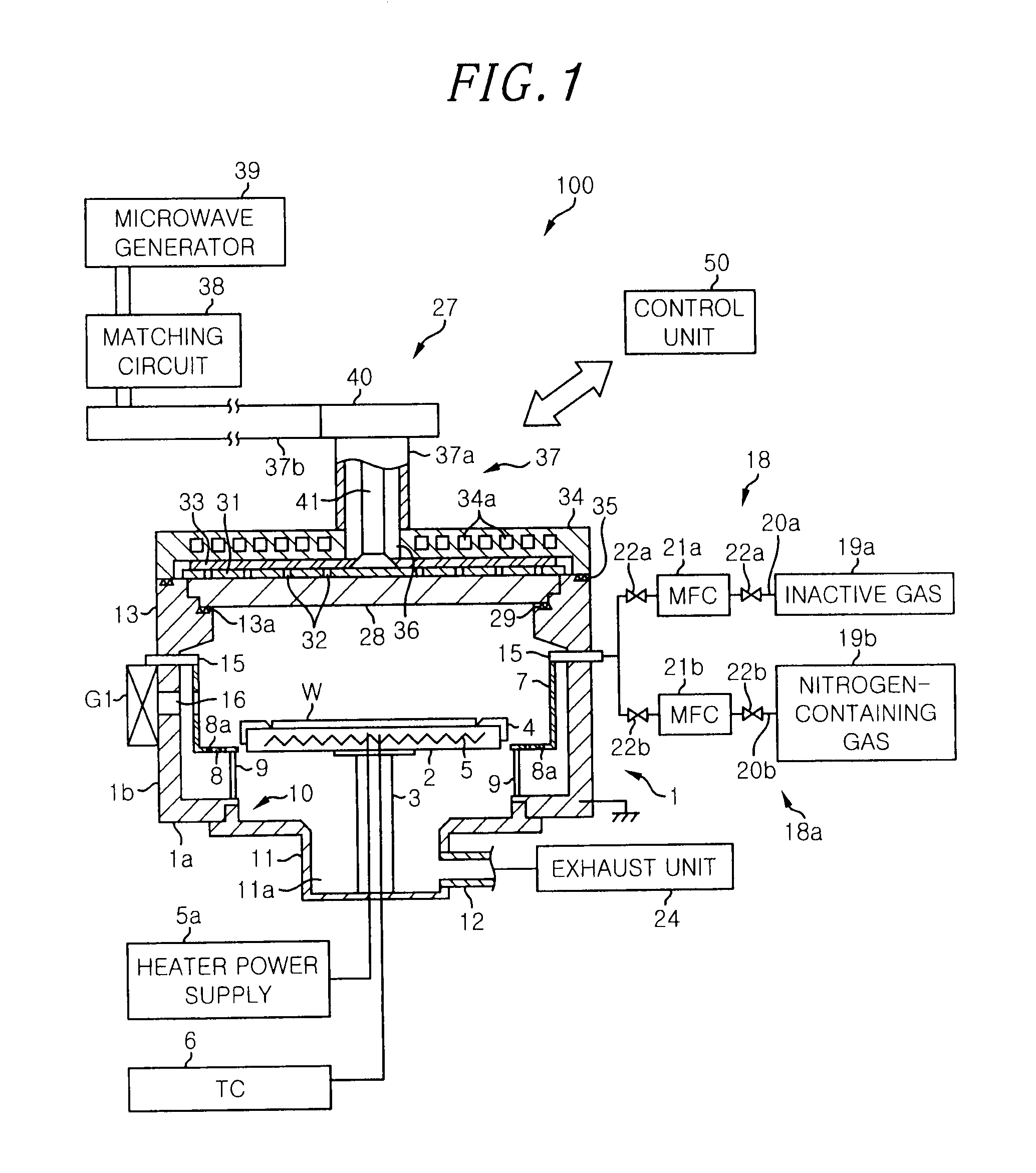
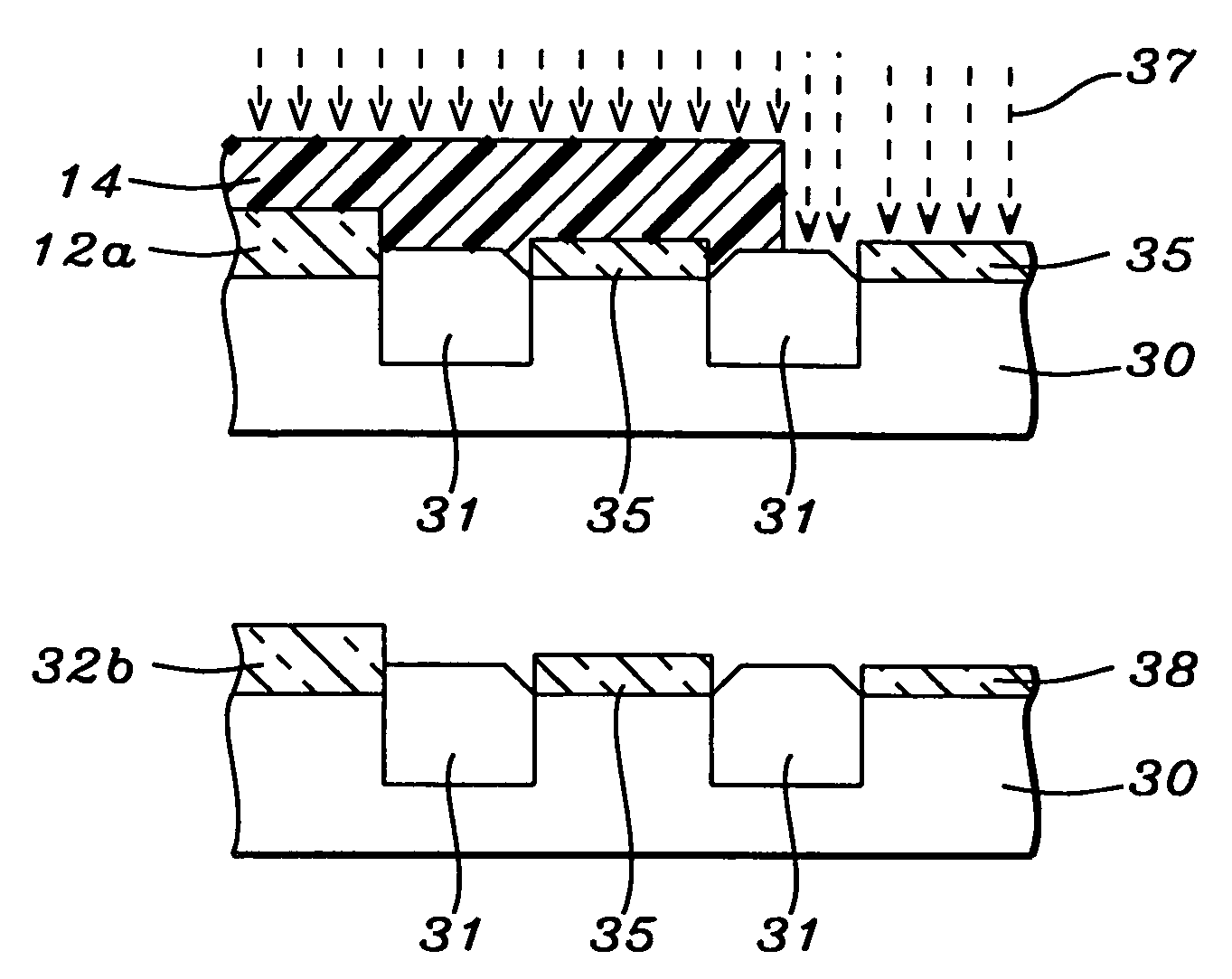
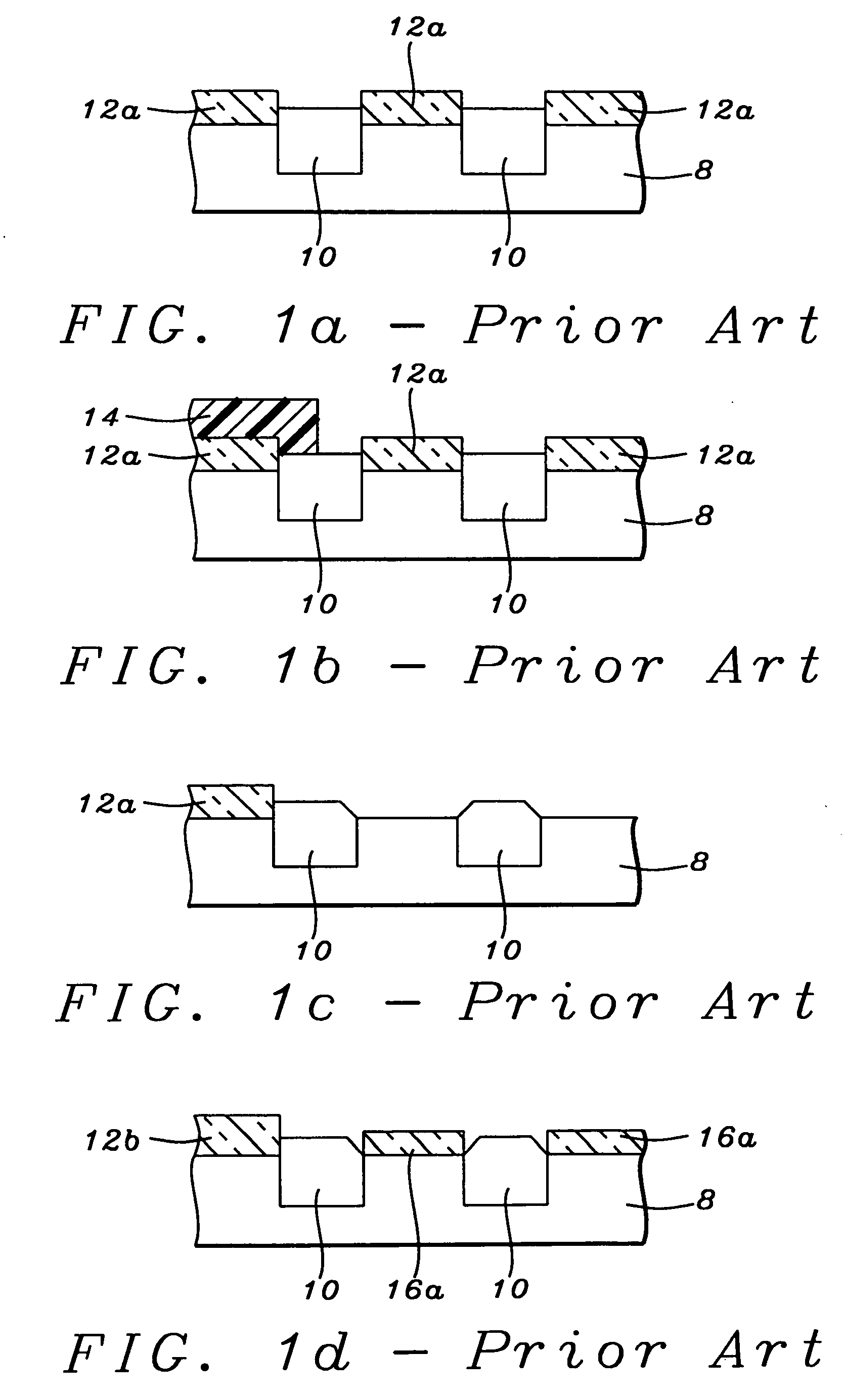
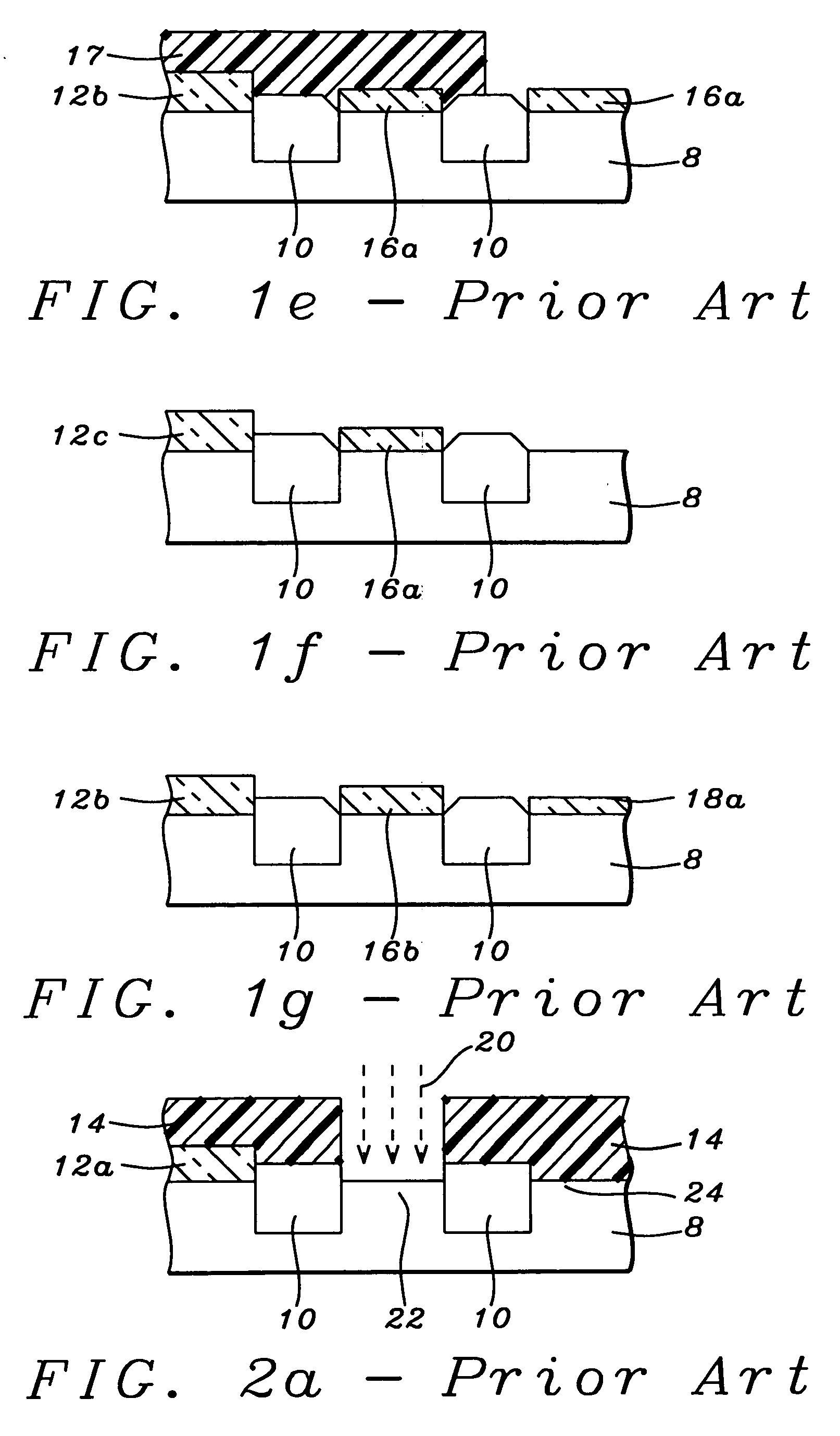
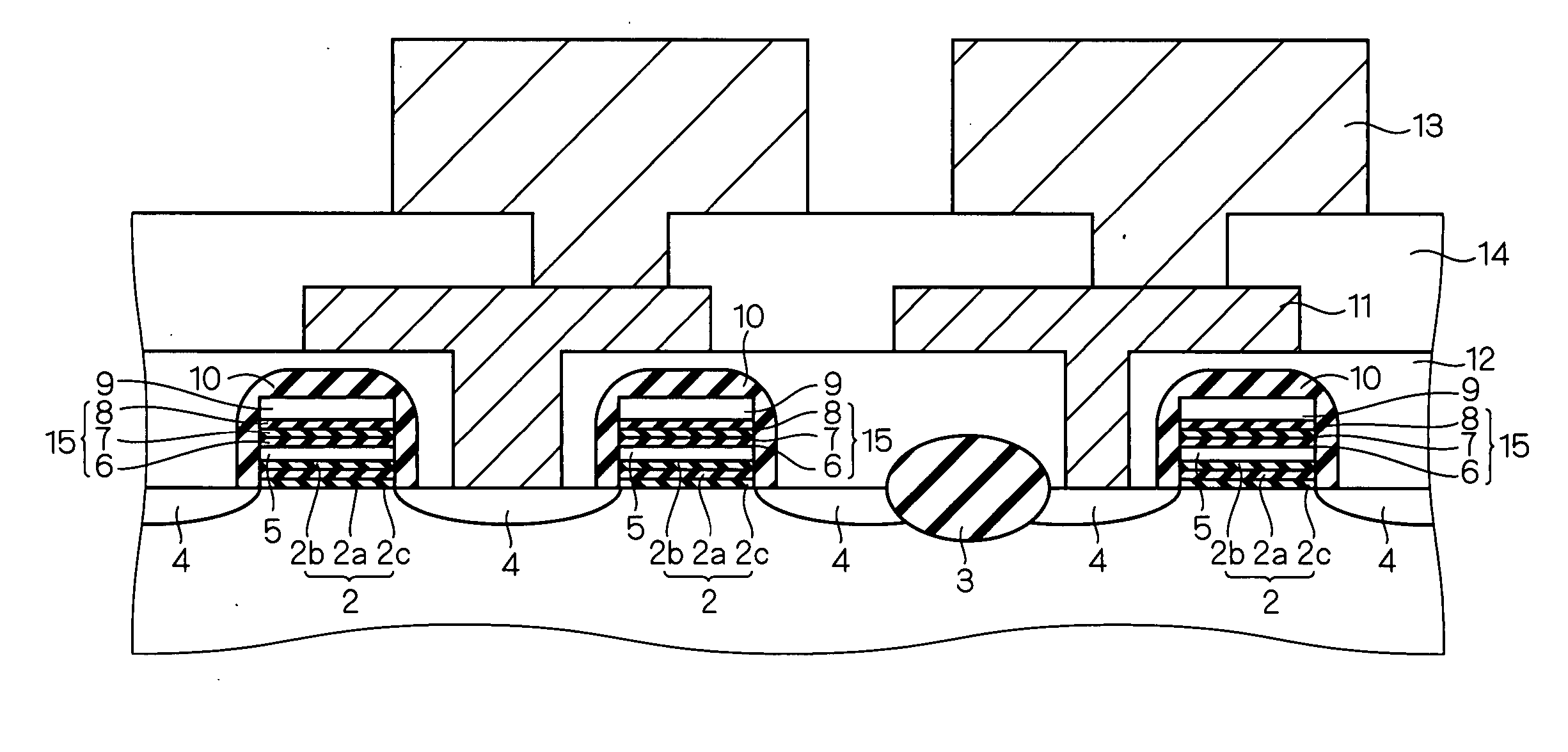
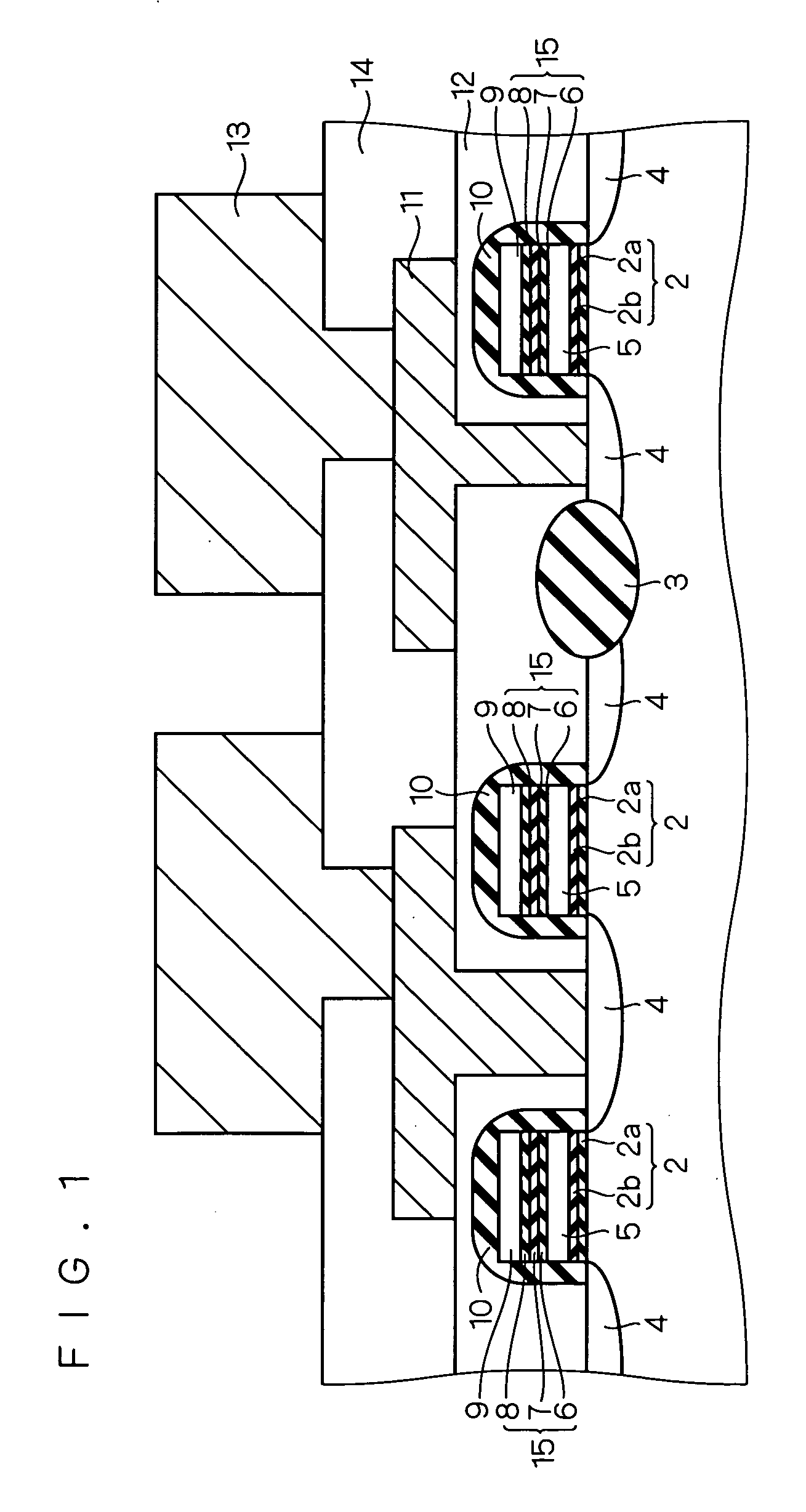
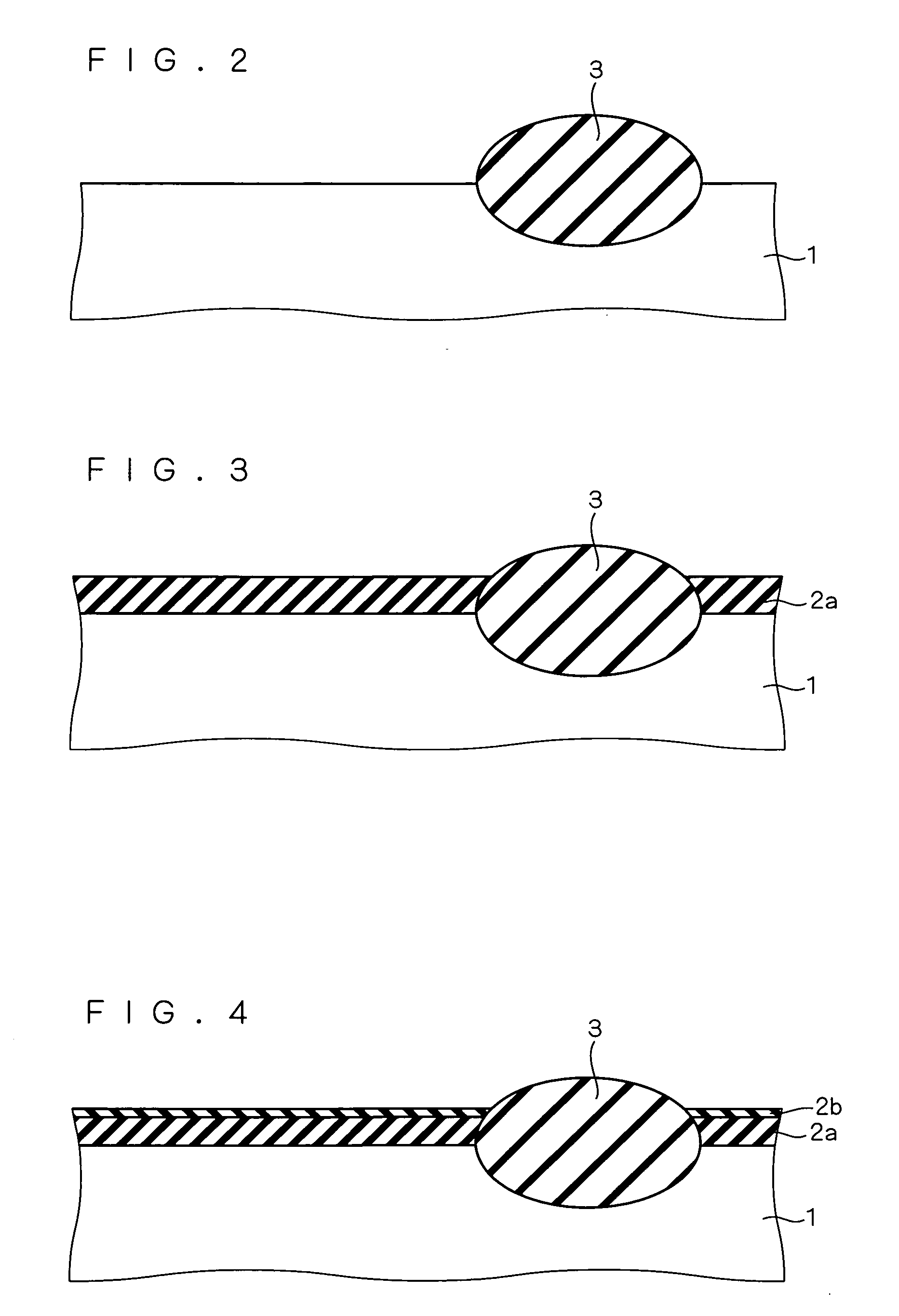
[method for forming nitrided tunnel oxide laye]
ActiveUS20050090062A1Reducing positiveReduced carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitrogenSilicon oxide
A method for forming a nitrided tunnel oxide layer is described. A silicon oxide layer as a tunnel oxide layer is formed on a semiconductor substrate, and a plasma nitridation process is performed to implant nitrogen atoms into the silicon oxide layer. A thermal drive-in process is then performed to diffuse the implanted nitrogen atoms across the silicon oxide layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
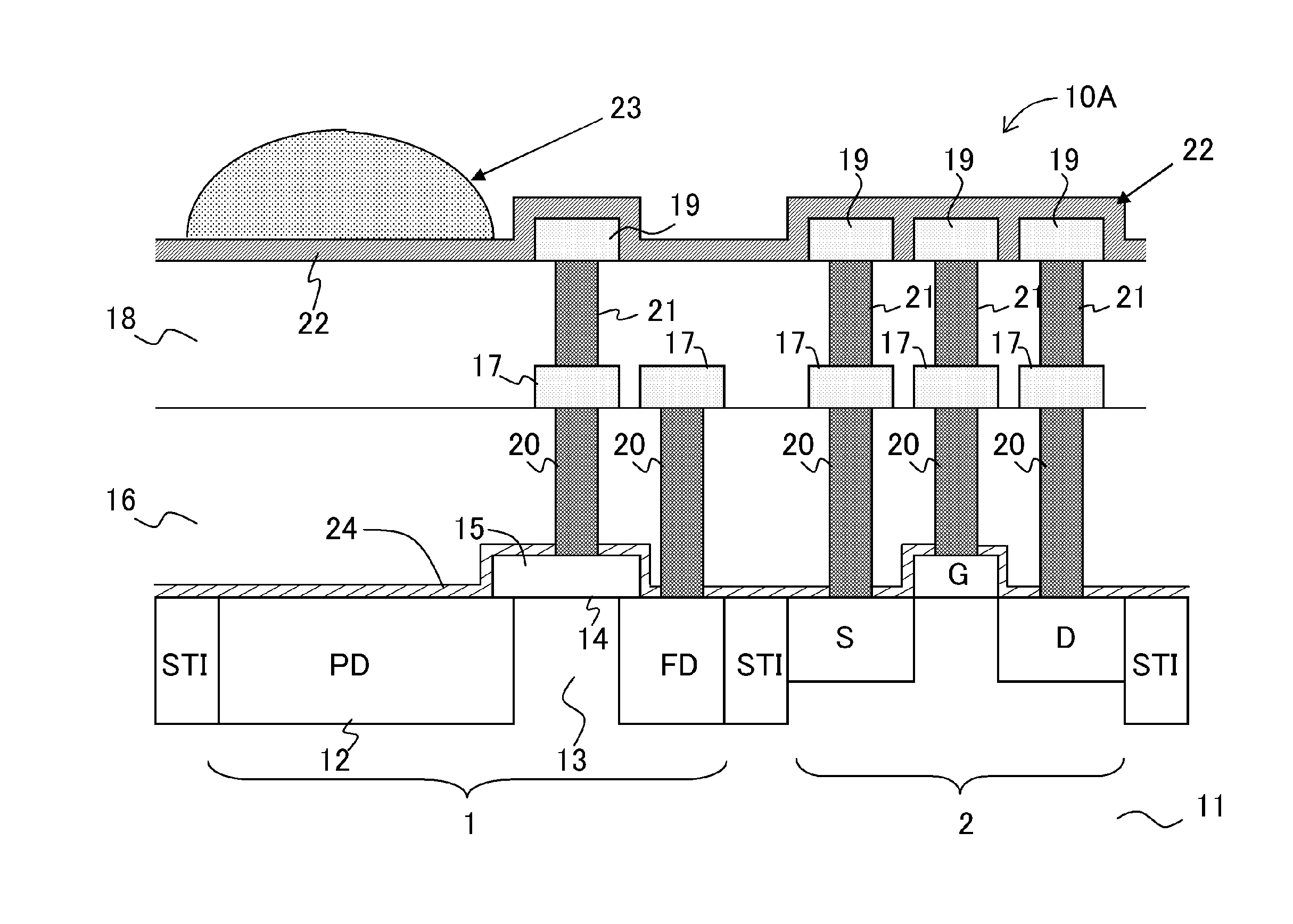
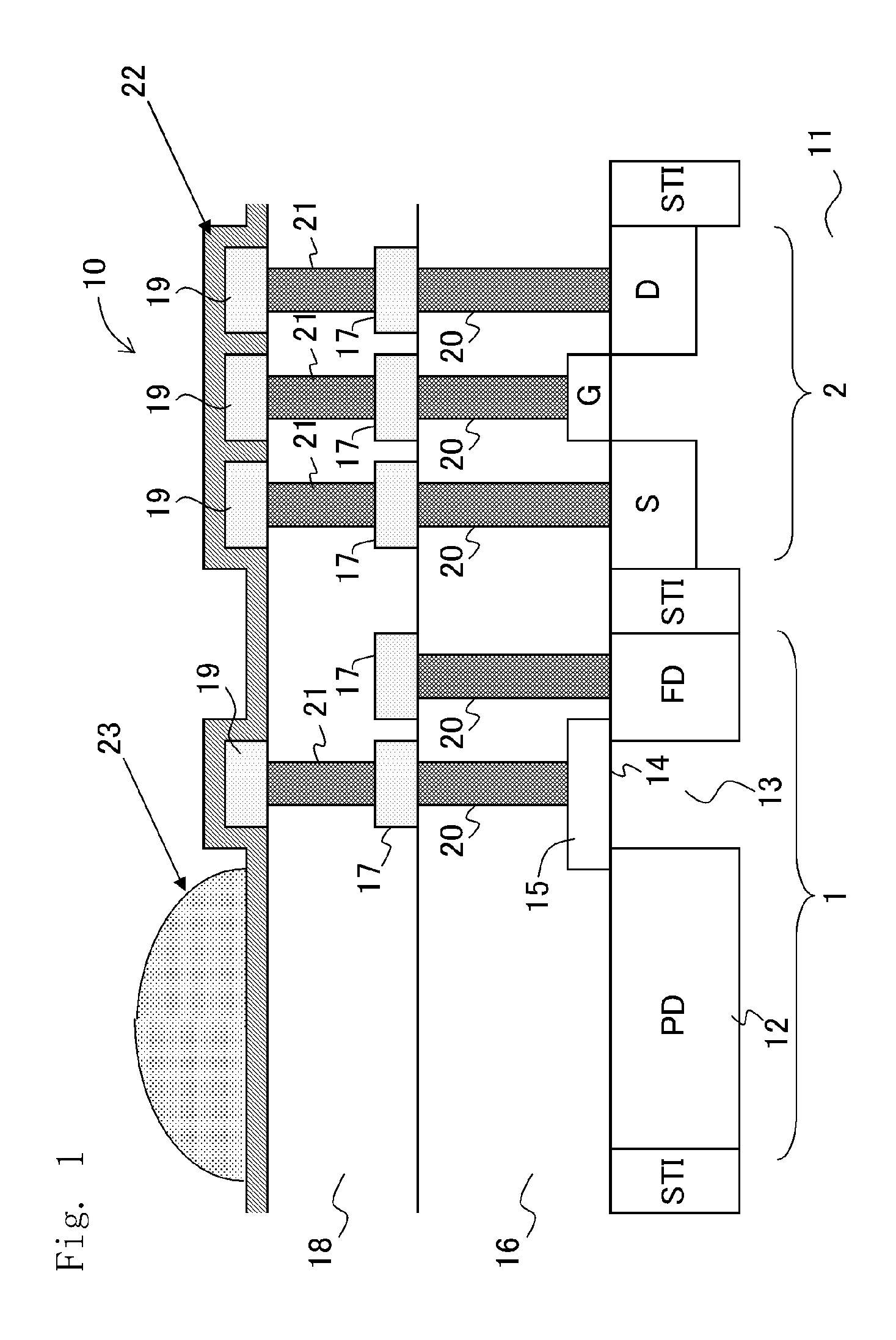
Method for manufacturing a solid-state image capturing element
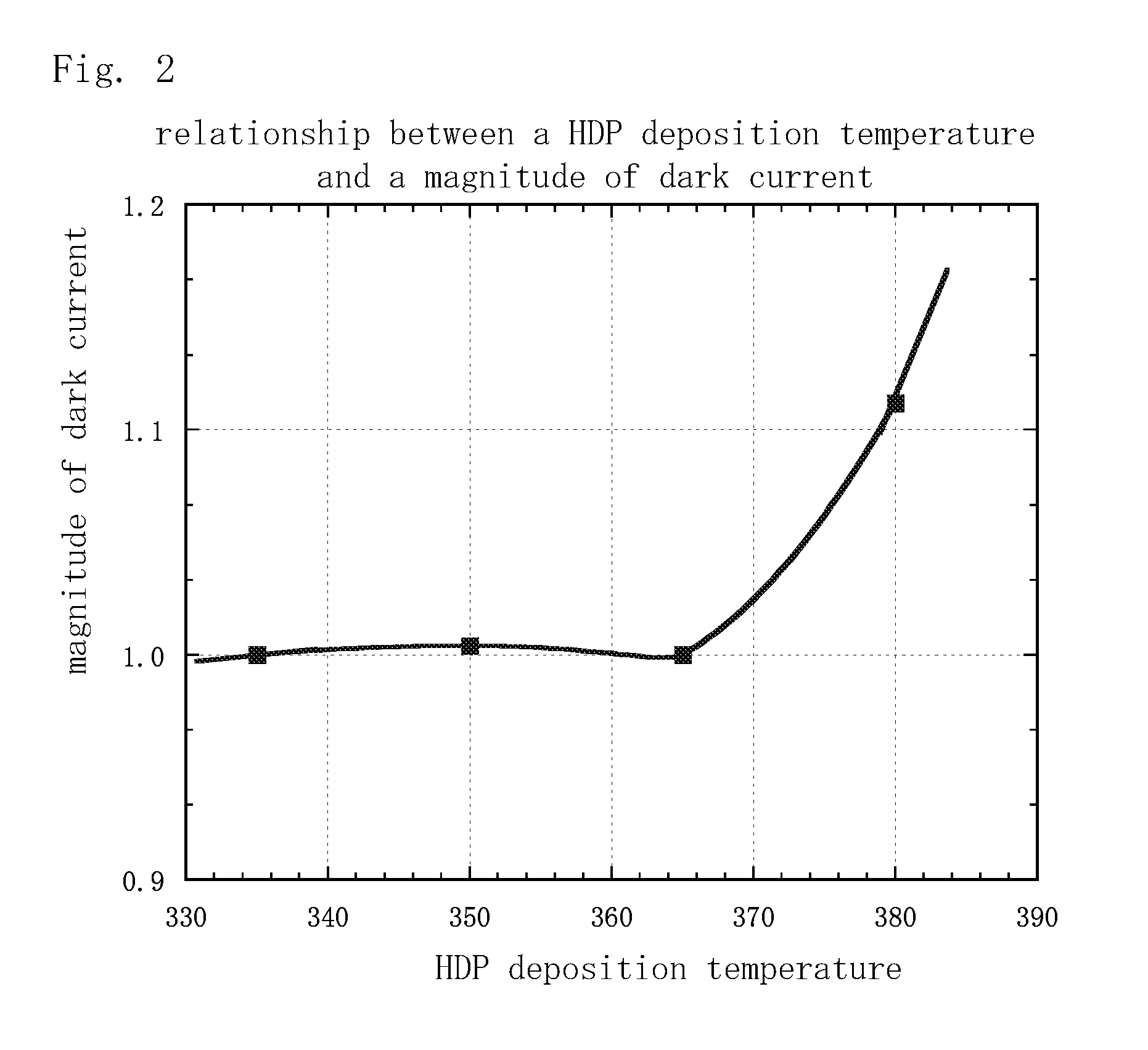
InactiveUS20110159632A1Suppress signal deteriorationIncrease in fine white defectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition temperatureRefractive index
The deposition temperature of the HDP film can be controlled to 365° C. or below, preferably within a temperature range of 335° C. to 365° C., and more preferably 335° C. to 350° C., or at 350° C. Thus, it becomes possible to suppress signal deterioration due to dark current and an increase in fine white defects, and to prevent deterioration of picture quality, even when the HDP film with a favorable embedding capability between fine wiring is used as an interlayer insulation film. An RF power is set to 850 W to 1500 W, so that dark current can be suppressed even more. Further, a plasma silicon nitride film with a refractive index of 1.9 or more and 2.15 or less for a blue wavelength is formed, so that it becomes possible to suppress the lowering of a blue sensitivity in the light receiving elements to further improve picture quality.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![[method for forming nitrided tunnel oxide laye] [method for forming nitrided tunnel oxide laye]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/70e5d8ad-56a7-4481-a467-159709ee24dc/US20050090062A1-20050428-D00000.png)
![[method for forming nitrided tunnel oxide laye] [method for forming nitrided tunnel oxide laye]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/70e5d8ad-56a7-4481-a467-159709ee24dc/US20050090062A1-20050428-D00001.png)
![[method for forming nitrided tunnel oxide laye] [method for forming nitrided tunnel oxide laye]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/70e5d8ad-56a7-4481-a467-159709ee24dc/US20050090062A1-20050428-D00002.png)