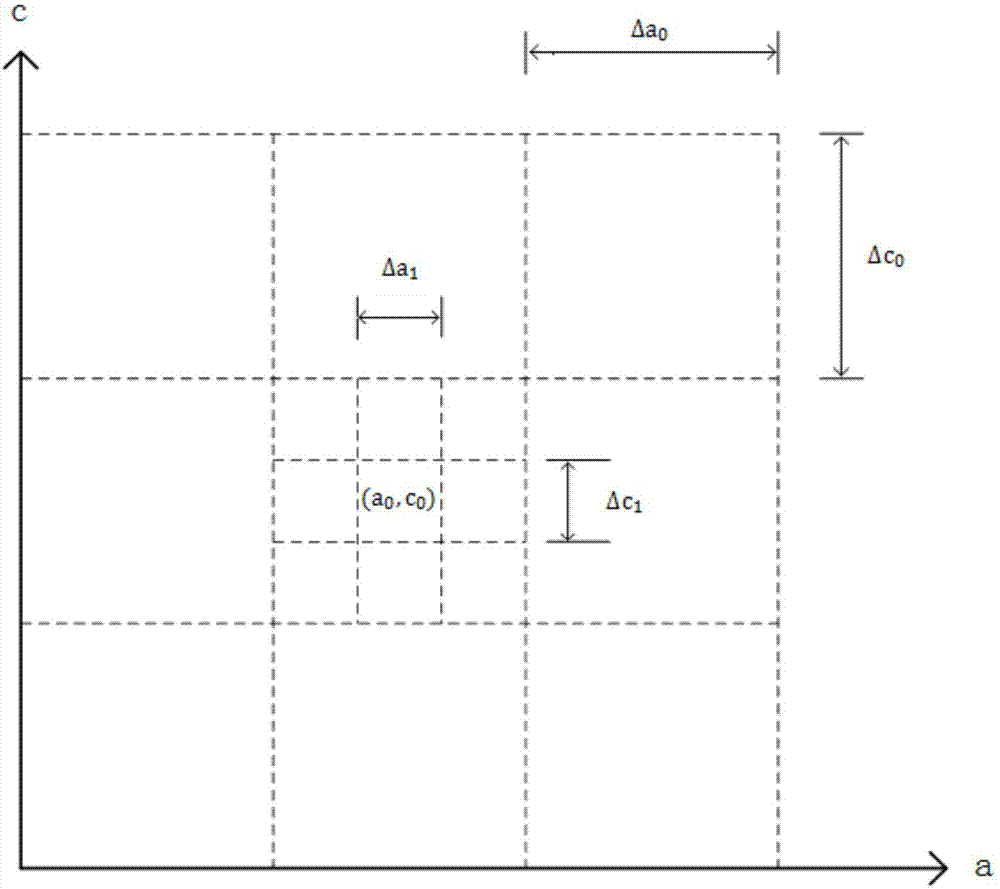
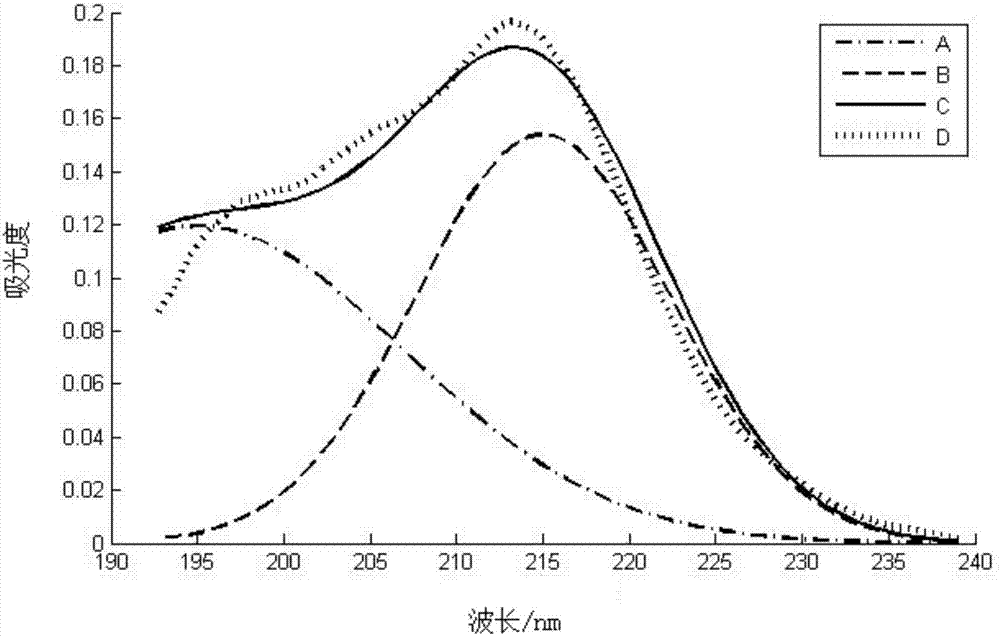
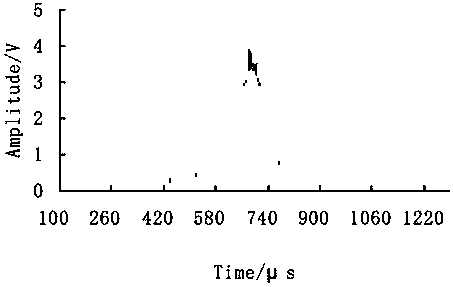
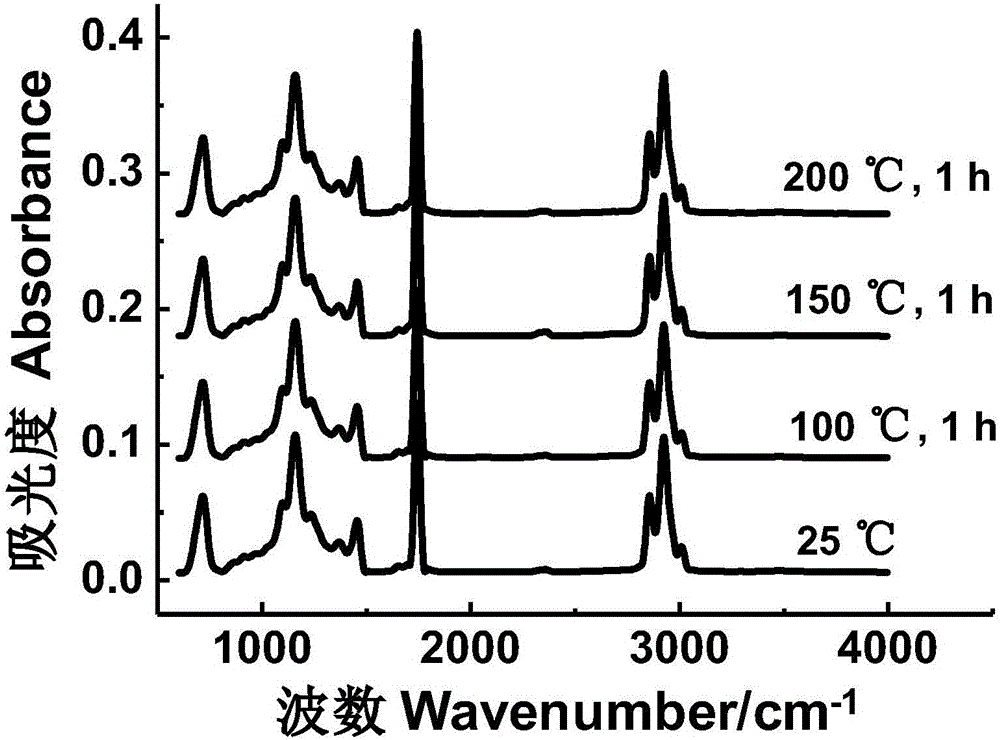
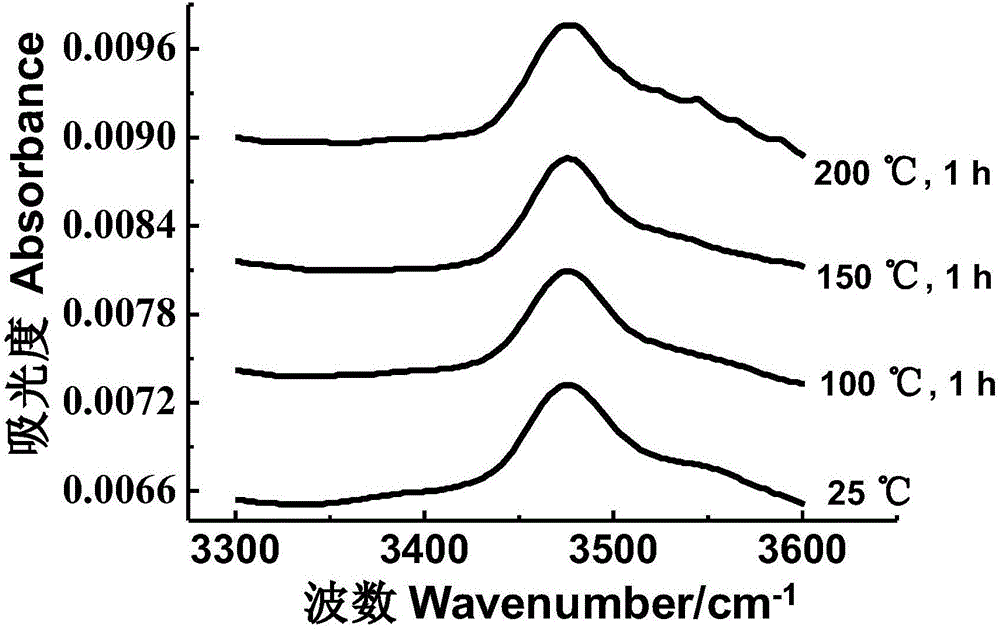
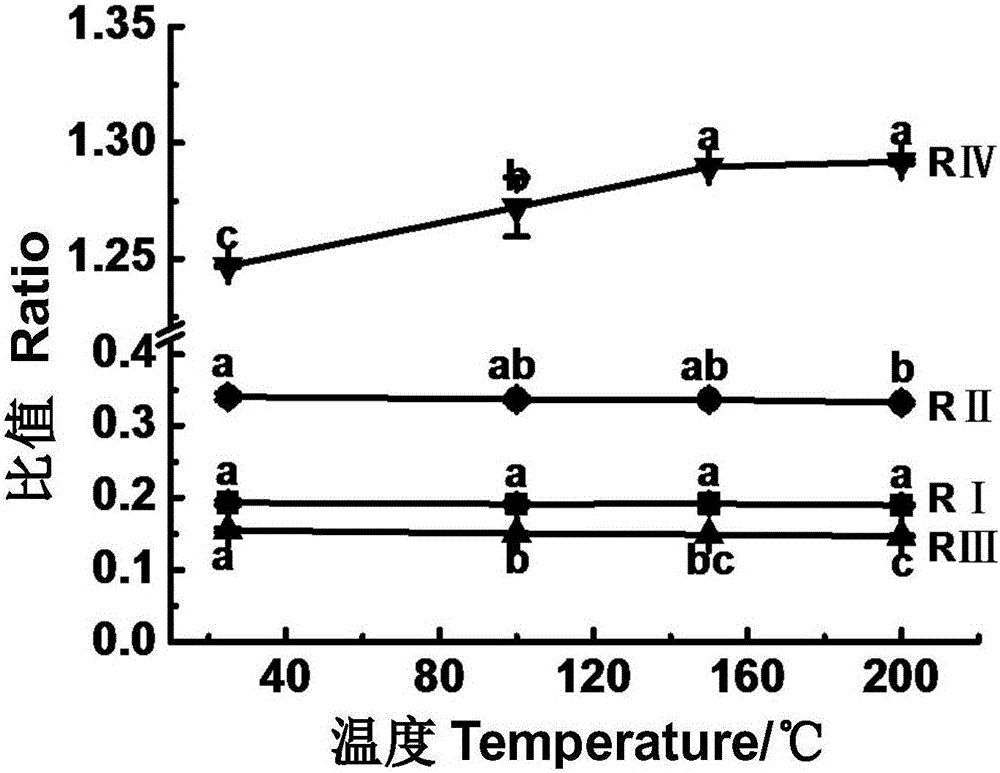
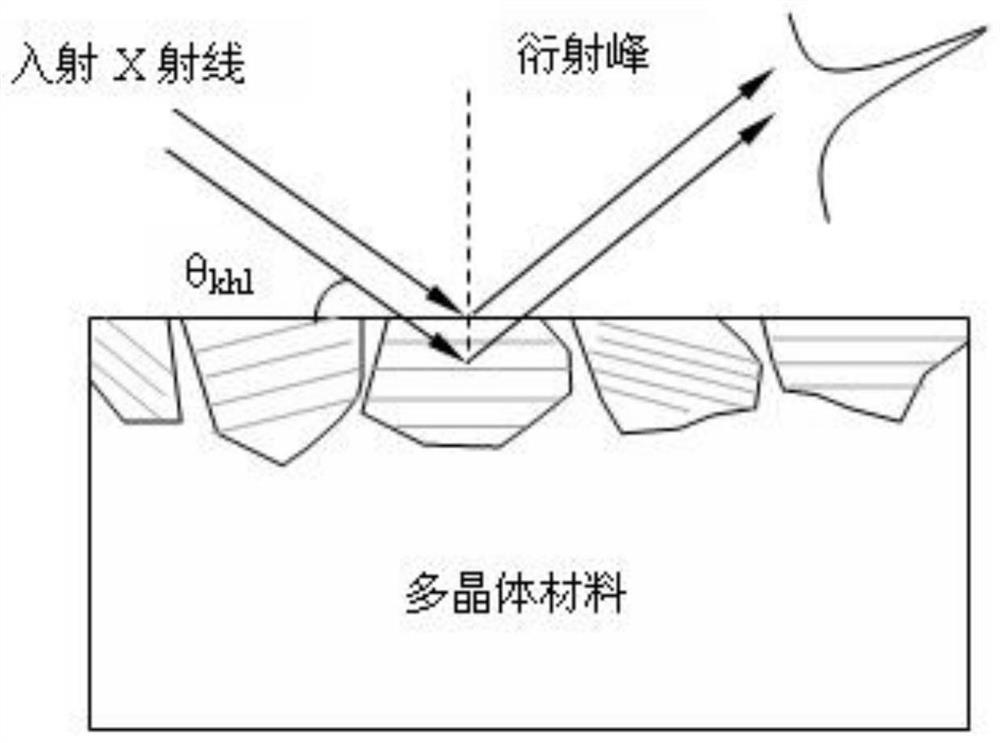
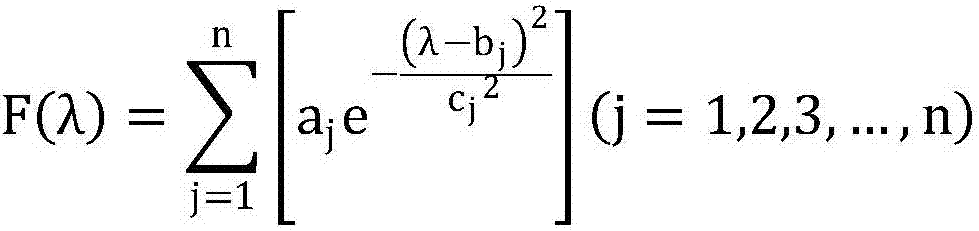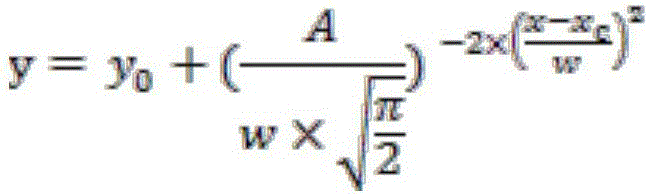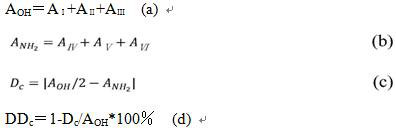Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Peak fitting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Peak fitting involves fitting a number of analytical line shapes to XANES data. The typical approach is to simulate the XANES data using one or two step-like functions and several peak functions for the peaks in the data. The centroids, amplitudes, and widths of the various line shapes are either fixed or varied to best fit the data.
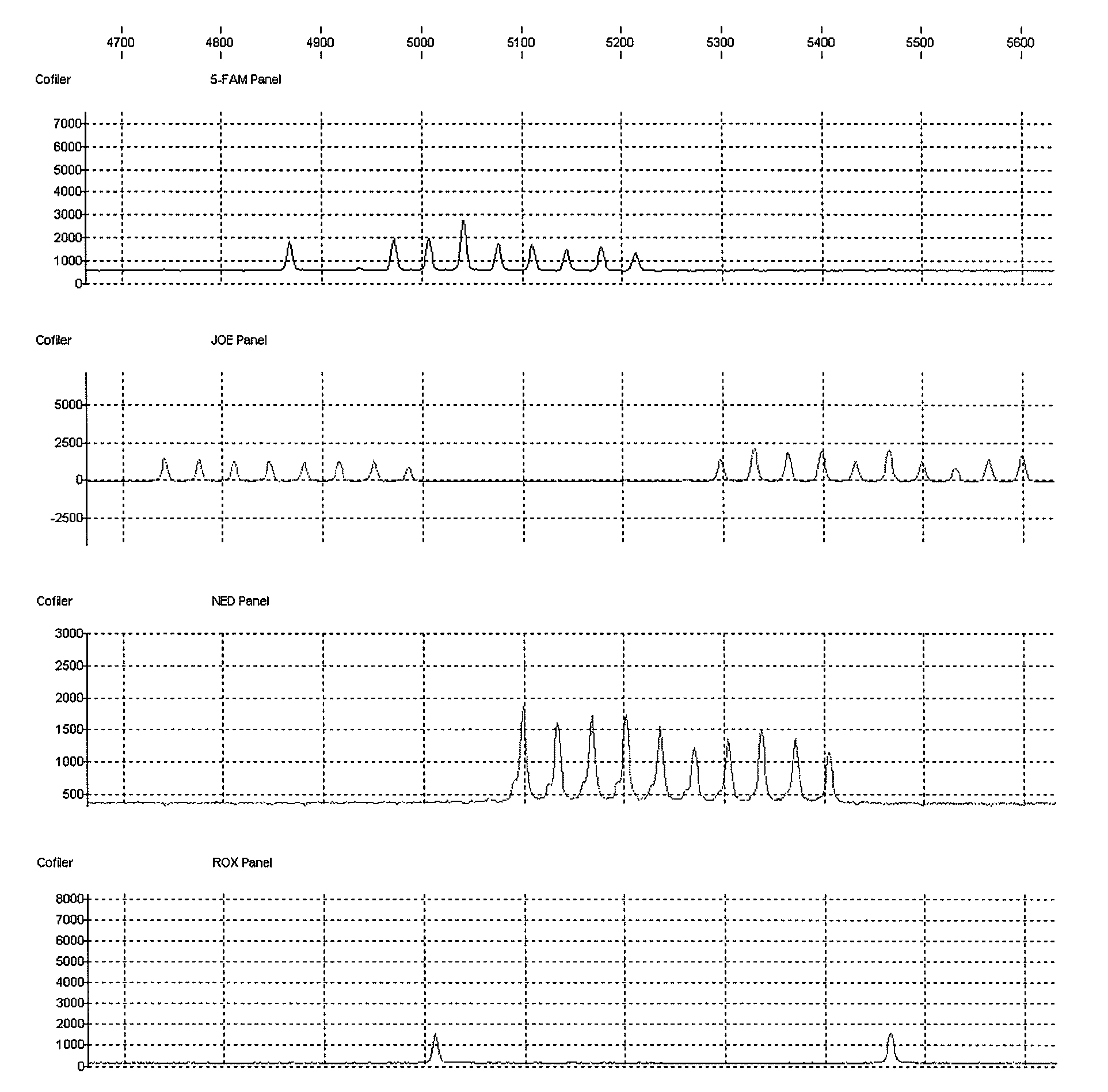
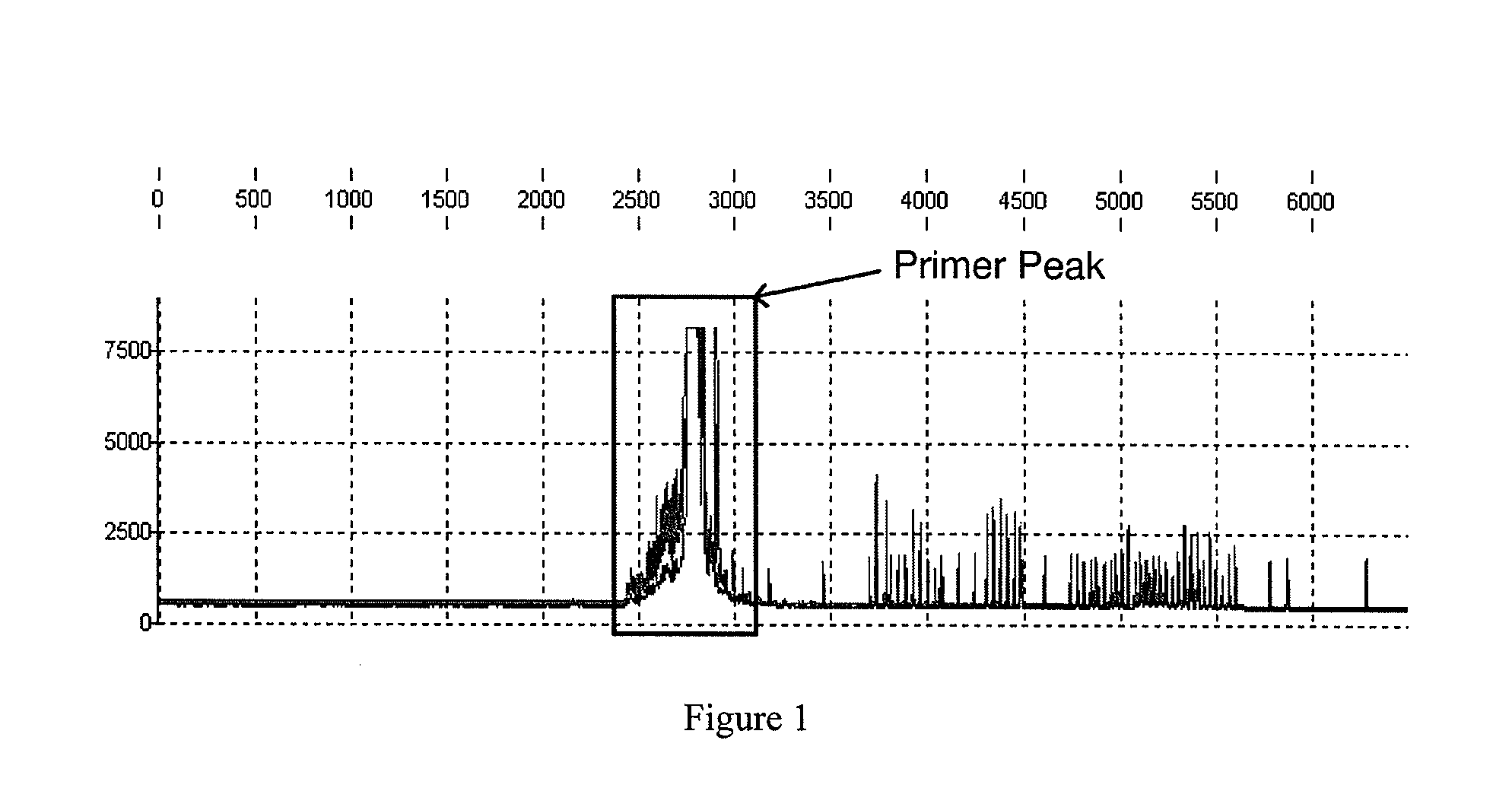
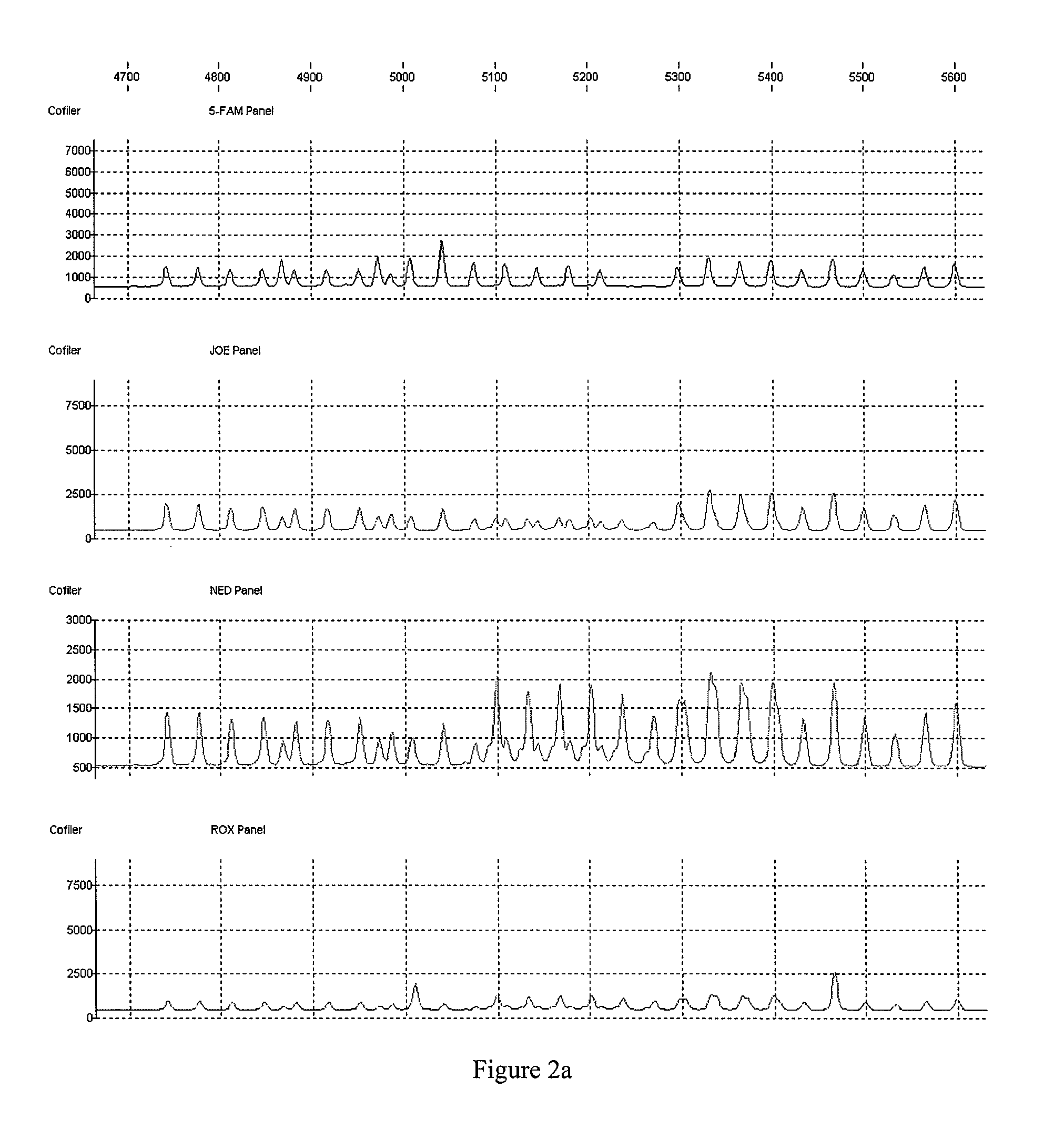
Method and apparatus for allele peak fitting and attribute extraction from DNA sample data
InactiveUS20090228245A1Low costComponent separationComputation using non-denominational number representationAnalysis dnaAllele
Analysis of DNA is critical to many applications including identifying perpetrators of crimes based on genetic evidence left at crime scenes. An initial step to analyzing DNA data is detection, identification, and quantization of allele peaks in the DNA data. The invention provides a method and apparatus for accurately and expeditiously performing this initial step by sequentially checking unfitted peaks against various models including a default model, a hybrid peak model, a dual fit model and, in special situations, a narrow fit function and a saturated fit function.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
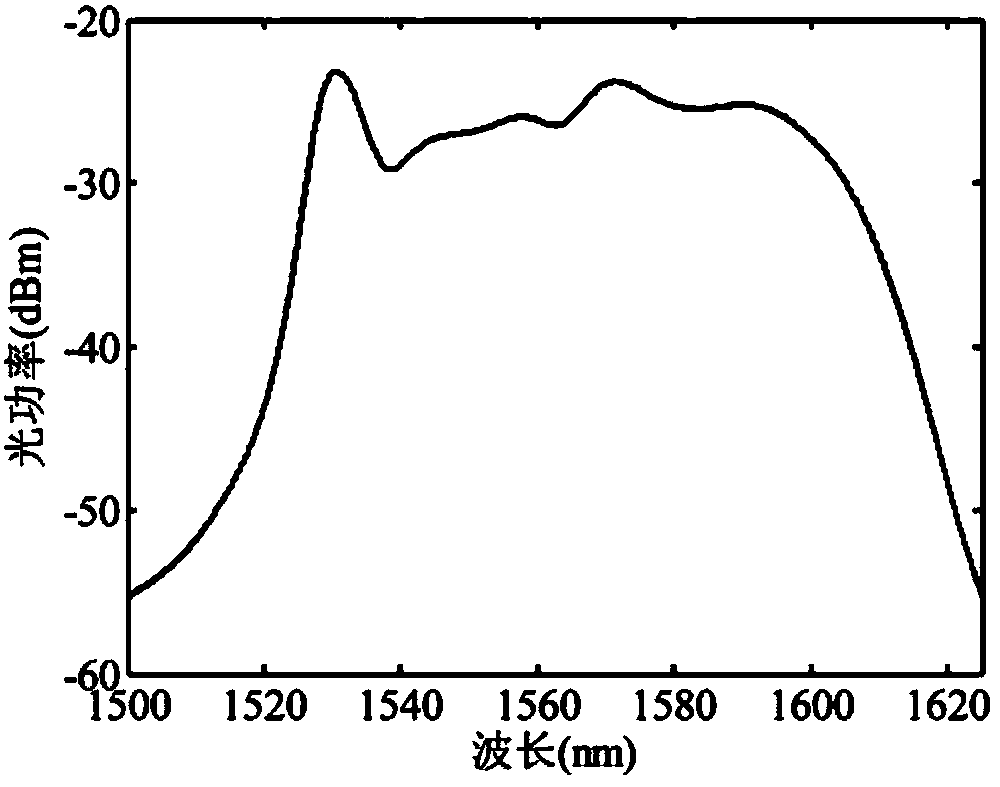
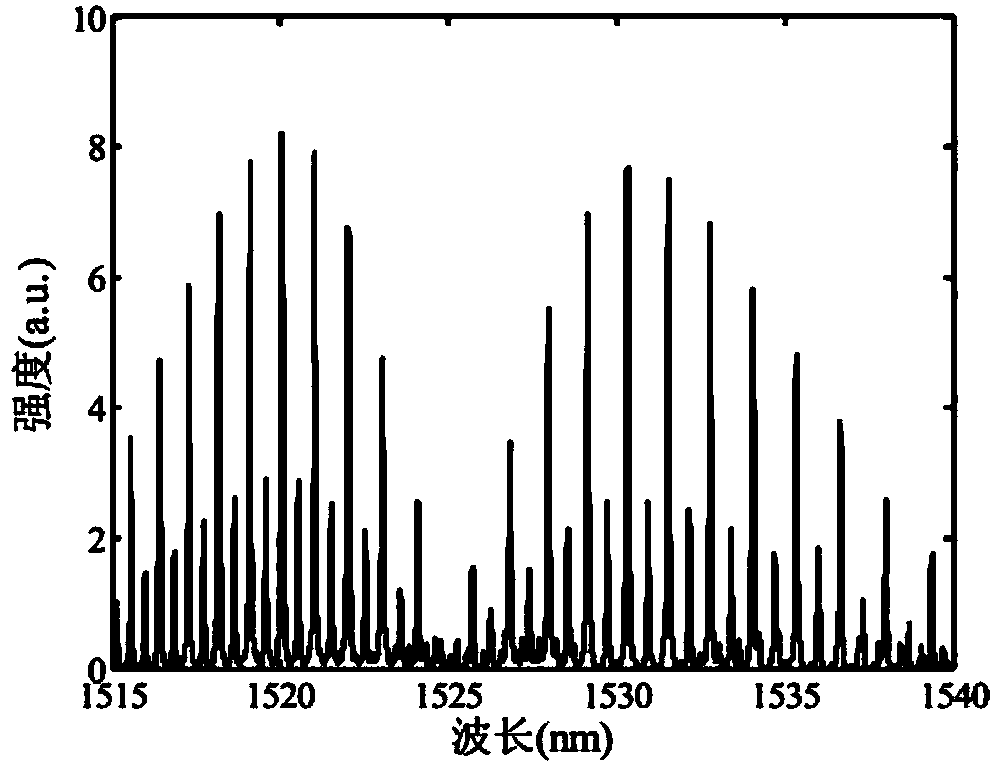
Device and method for calibrating optical fiber scanning light source wavelength based on gas absorption spectral lines
ActiveCN103411686AImprove stabilityHigh precisionOptical measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsForming gasLine width
The invention discloses a device and method for calibrating an optical fiber scanning light source wavelength based on gas absorption spectral lines. The device and method are suitable for the precise locating of a scanning light source output wavelength based on an F-P filter in the field of optical fiber communication and sensing. The device and method provide multiple reference wavelengths for the wavelength calibration of an optical fiber scanning light source by utilizing the multiple absorption spectral lines of gas molecules in a near-infrared wave band, and are high in stability. In the calibration process, broadband light passes through the F-P filter driven by continuous voltages, outputs narrow-linewidth scanning light, and interacts with the gas molecules in a gas chamber to form gas absorption spectrums. Through base line extraction, absorption peak fitting and absorption wavelength query, the driving voltage and the absorption wavelength corresponding to each absorption spectral line of the gas are obtained. According to the voltage-wavelength corresponding relation of each spectral line, calibration is carried out on the output wavelength of the optical fiber scanning light source, and system wavelength locating is carried out through spline interpolation. The device and method have the advantages of being simple in device, easy to integrate, high in precision and the like, and have wide application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fire extinguishing system and fittings
InactiveUS7487841B1Facilitate and reduce number of componentIncrease water flowMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesRoof pitchLine tubing
A building inside fire extinguishing system, the building having a standard roof pitch and corresponding peak angle. The system including a main water supply line extending along the base or lower margin of the roof and having spaced parallel upright pipe nipples attached to the main water supply line, a plurality of feed lines extending upwardly from the main water supply line parallel to the roof and a plurality of spaced water sprinkler heads operably attached to each of the feed lines. To interconnect the upper end of each upright nipple, an array of roof slope sprinkler fittings is provided, one of which is selected angularly matching the roof pitch. These sprinkler fittings each include an angled hollow body having a female threaded inlet and a female threaded outlet angularly oriented at different standard roof pitch angles one of which will equal the standard pitch of the roof. Each fitting is threadable directly to and between the pipe nipple and a lower end of the feed line. A separate array of roof peak fittings connecting the upper ends of each pair of aligned feed lines may also be provided.
Owner:GONCI KENNETH A
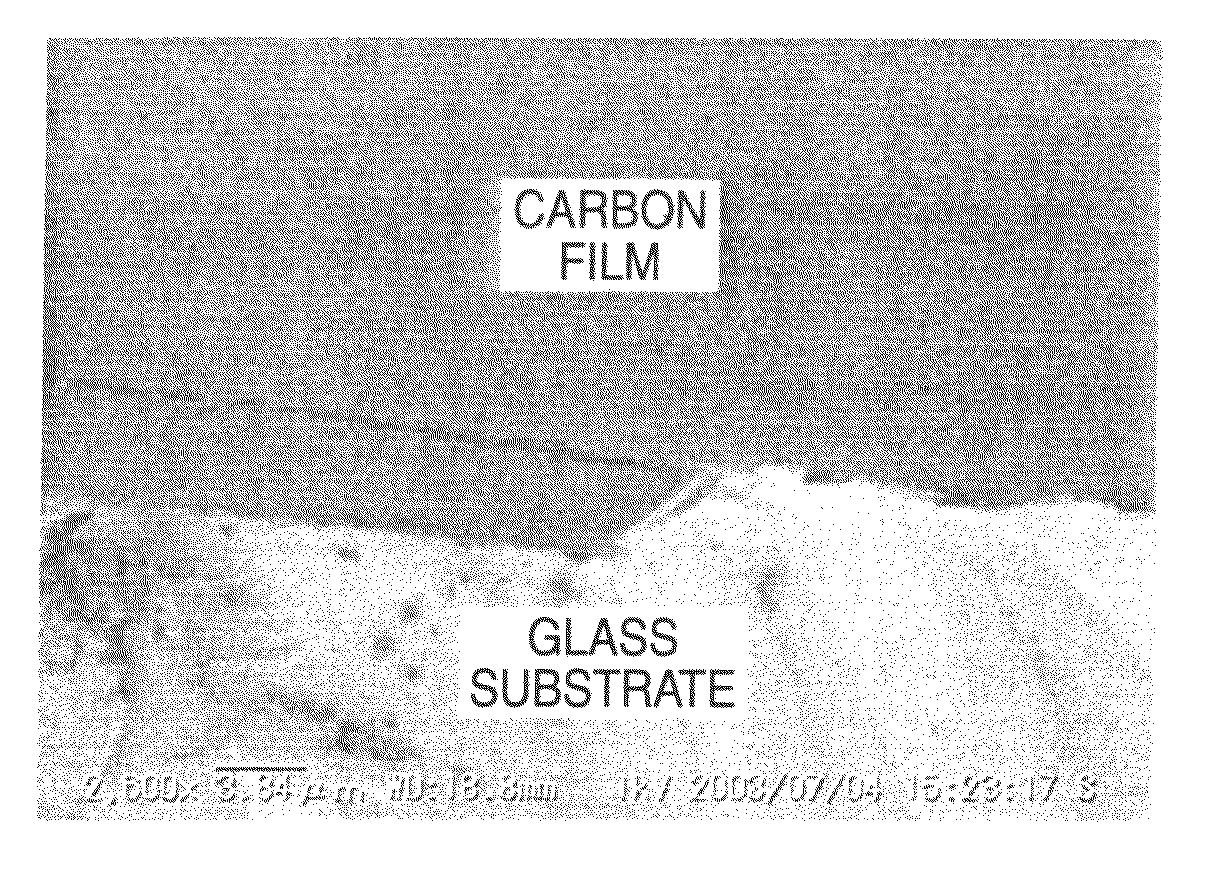
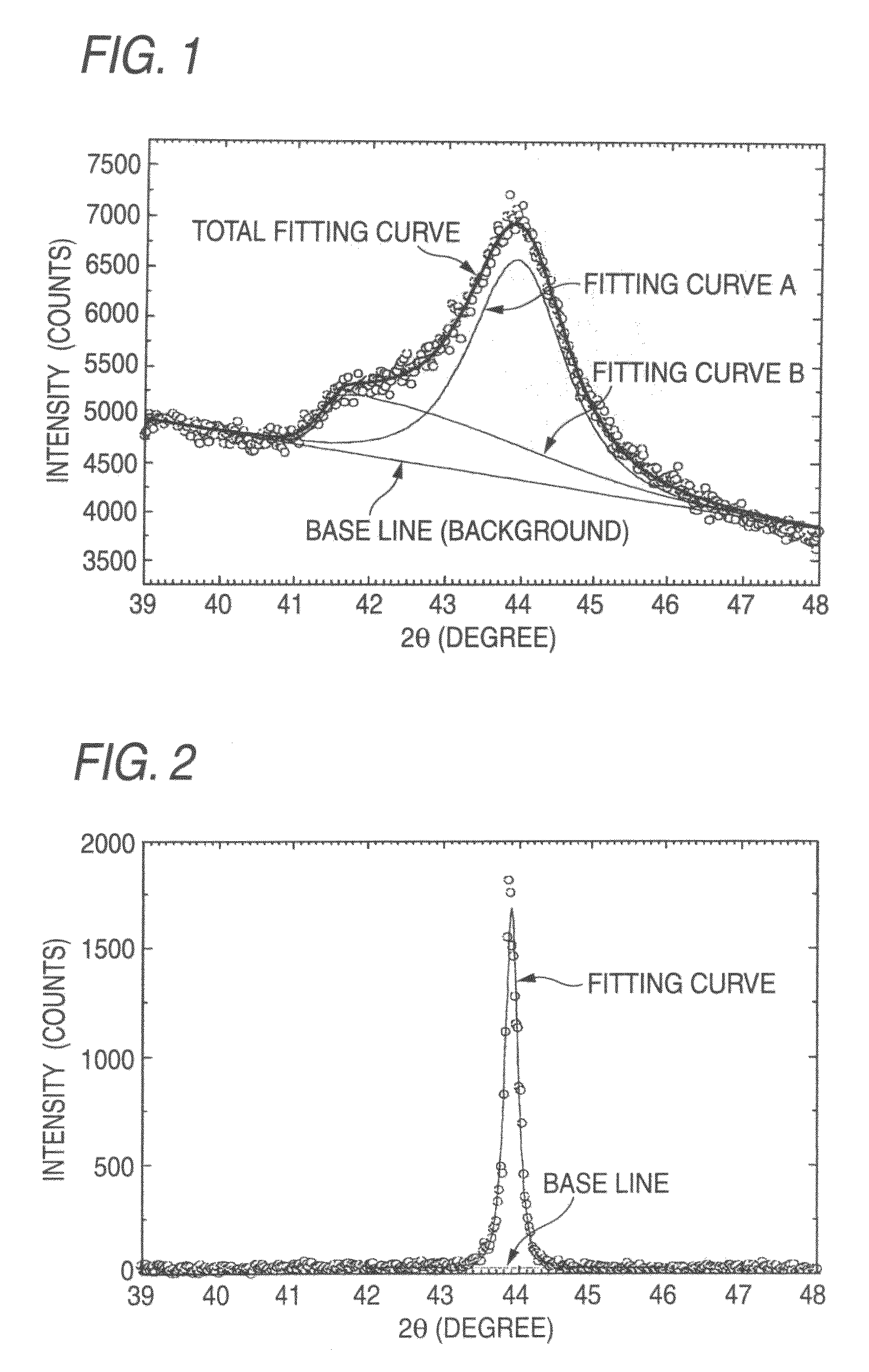
Carbon film
InactiveUS20070172660A1High transparencySmall double refractivityUltra-high pressure processesLayered productsCarbon filmRefractive index
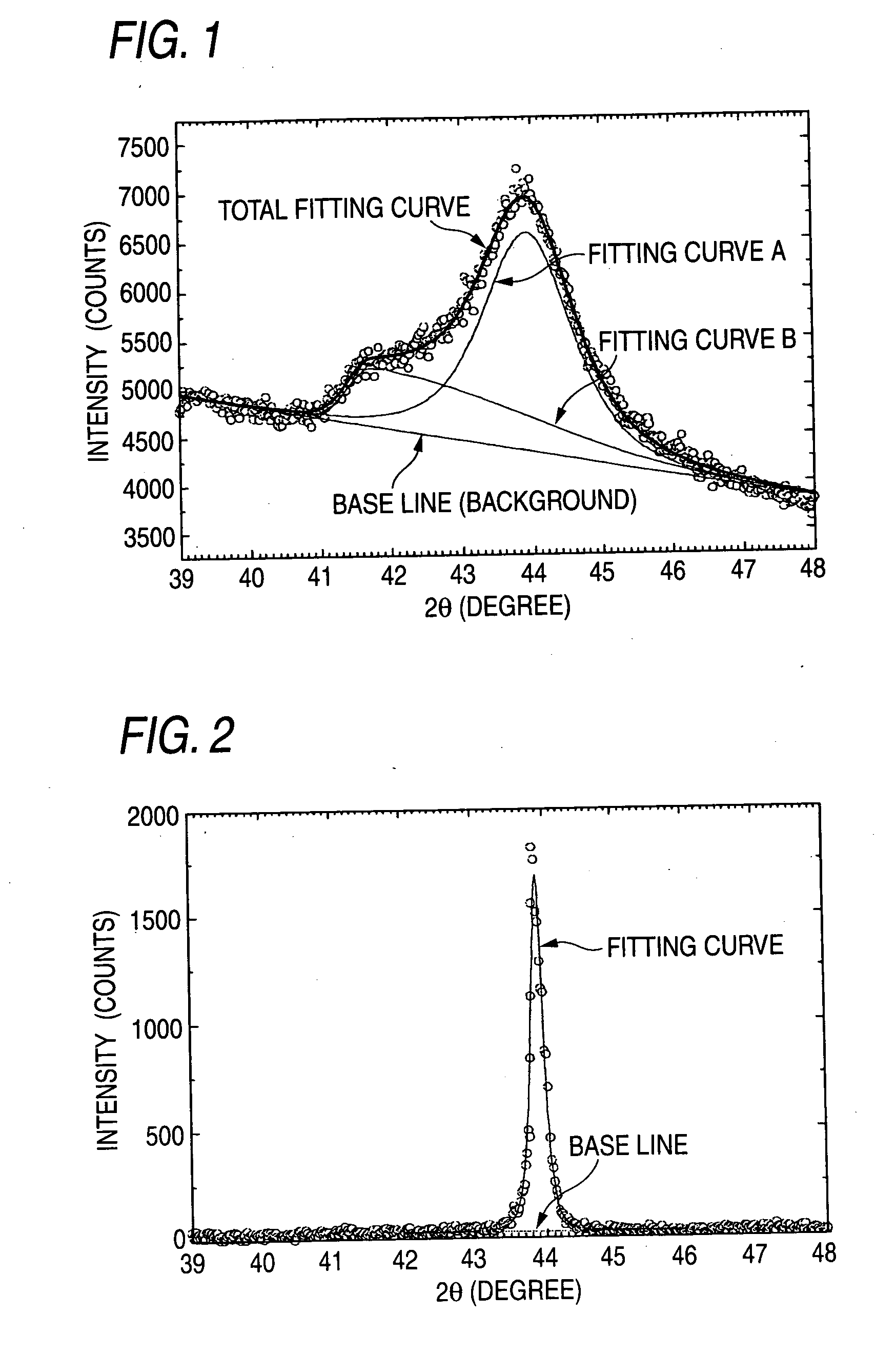
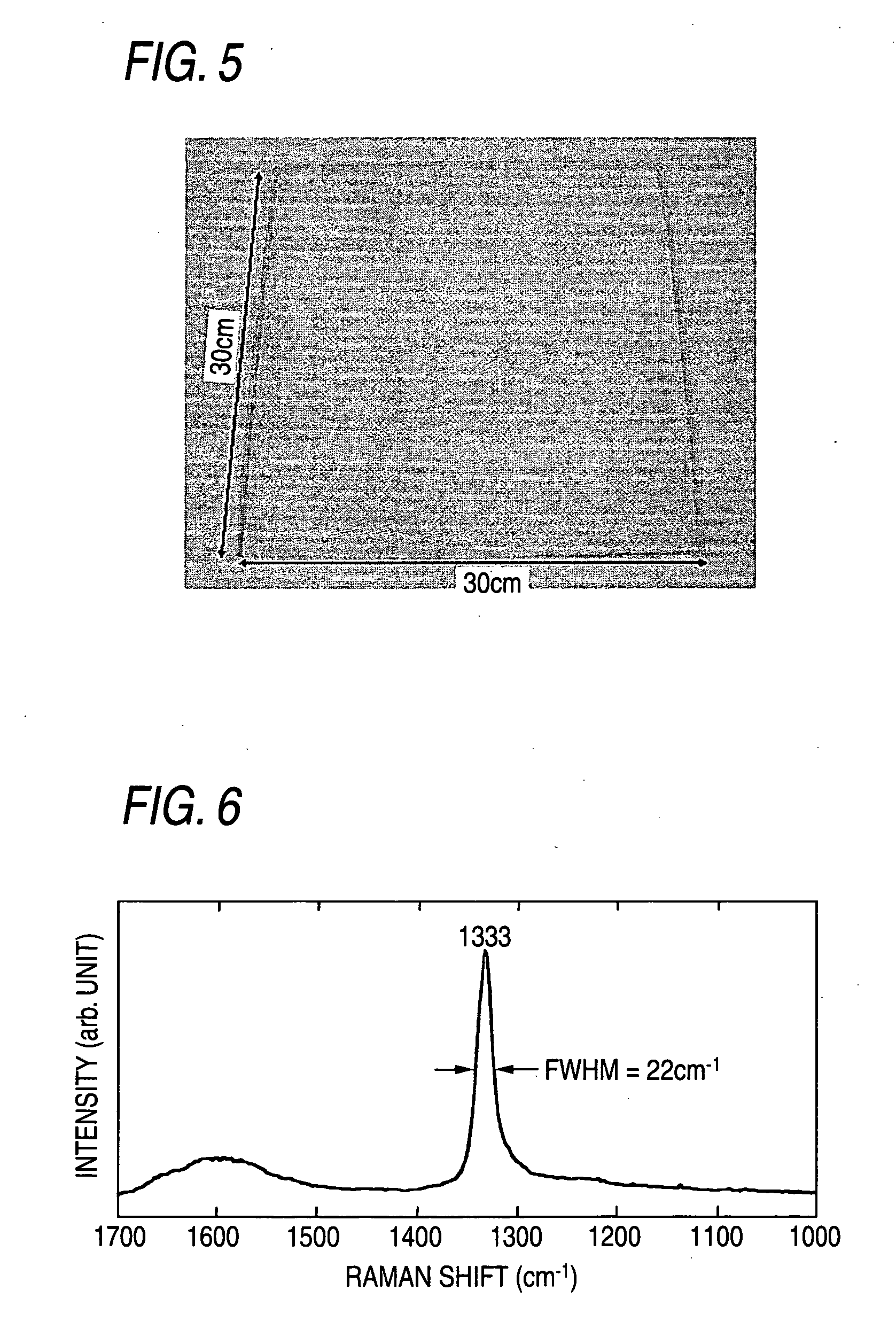
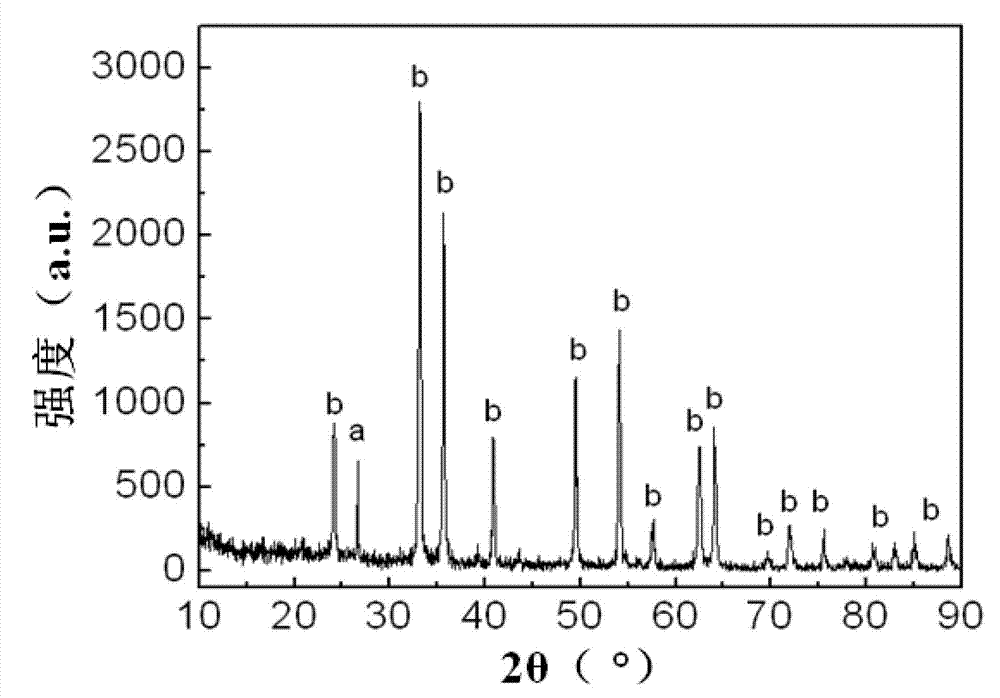
Problem To provide a carbon film and a laminate having optical characteristics of retaining high transparency, having high refraction index and less double refractivity, being excellent in electric insulating property, being capable of being coated at good adhesion to various substrates, and being capable of being formed at a low temperature, and applications thereof. Means for Solving the Problem The invention relates to a carbon film which has an approximate spectrum curve obtainable by superimposing, on a peak fitting curve A at a Bragg's angle (2θ±0.3°) of 43.9°, a peak fitting curve B at 41.7° and a base line in an X-ray diffraction spectrum by a CuKa1 ray, and has a film thickness of from 2 mm to 100 μm. The intensity of the fitting curve B relative to the intensity of the fitting curve A is preferably from 5 to 90% in the approximated spectrum described above. In the carbon film, the Raman shift has a peak at a 1333±10 cm−1 in the Raman scattering spectrum, and the half-value width of the peak is from 10 to 40 cm−1. Further, the invention relates to a laminate characterized by disposing, on the substrate, a carbon aggregate film of 2 nm to 100 μm thickness comprising an aggregate of carbon particles having an approximate spectrum curve described above. Moreover, the invention relates to an optical device, optical glass, wrist watch, electronic circuit substrate, or grinding tool having the laminate described above.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Gaussian multi-peak fitting-based spectrum analysis algorithm
ActiveCN107462535AHigh affinityKeep valid informationColor/spectral properties measurementsComplex mathematical operationsSpectral curveMixed spectrum
The invention discloses a Gaussian multi-peak fitting-based spectrum analysis algorithm. The Gaussian multi-peak fitting-based spectrum analysis algorithm comprises the following steps: determining an absorption fitting function containing an undetermined Gaussian feature parameter, performing mathematical modeling on fitting error, determining center coordinate and iteration step of an iteration initial value, continuously performing iteration, performing comparison and changing the iteration step length until the optimal fitting error is obtained, and reversely deducing the center coordinate value, namely the to-be-determined feature parameter, of the corresponding division unit by the optimal fitting error, and determining the absorption fitting function so as to decompose the mixed spectrum into a plurality of sub-peaks. The Gaussian multi-peak fitting-based spectrum analysis algorithm has the following advantages: a Gaussian function curve and a spectroscopic data curve have high affinity and can express parameters, such as peak shape, peak height and peak position in the spectrogram, with clear physical significance; and the mixed absorption spectrum curve is decomposed into a plurality of Gaussian function curves, the effective information of the original spectrum data can be remained, the original spectrum data is unified into a small amount of uniquely determined Gaussian feature parameters, and the aims of simplifying the spectrum data and researching the refined structure are fulfilled.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
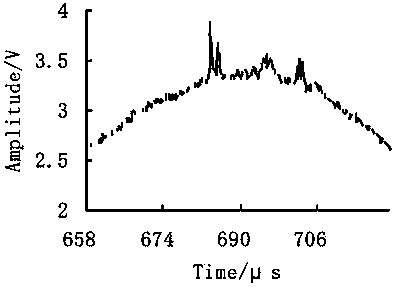
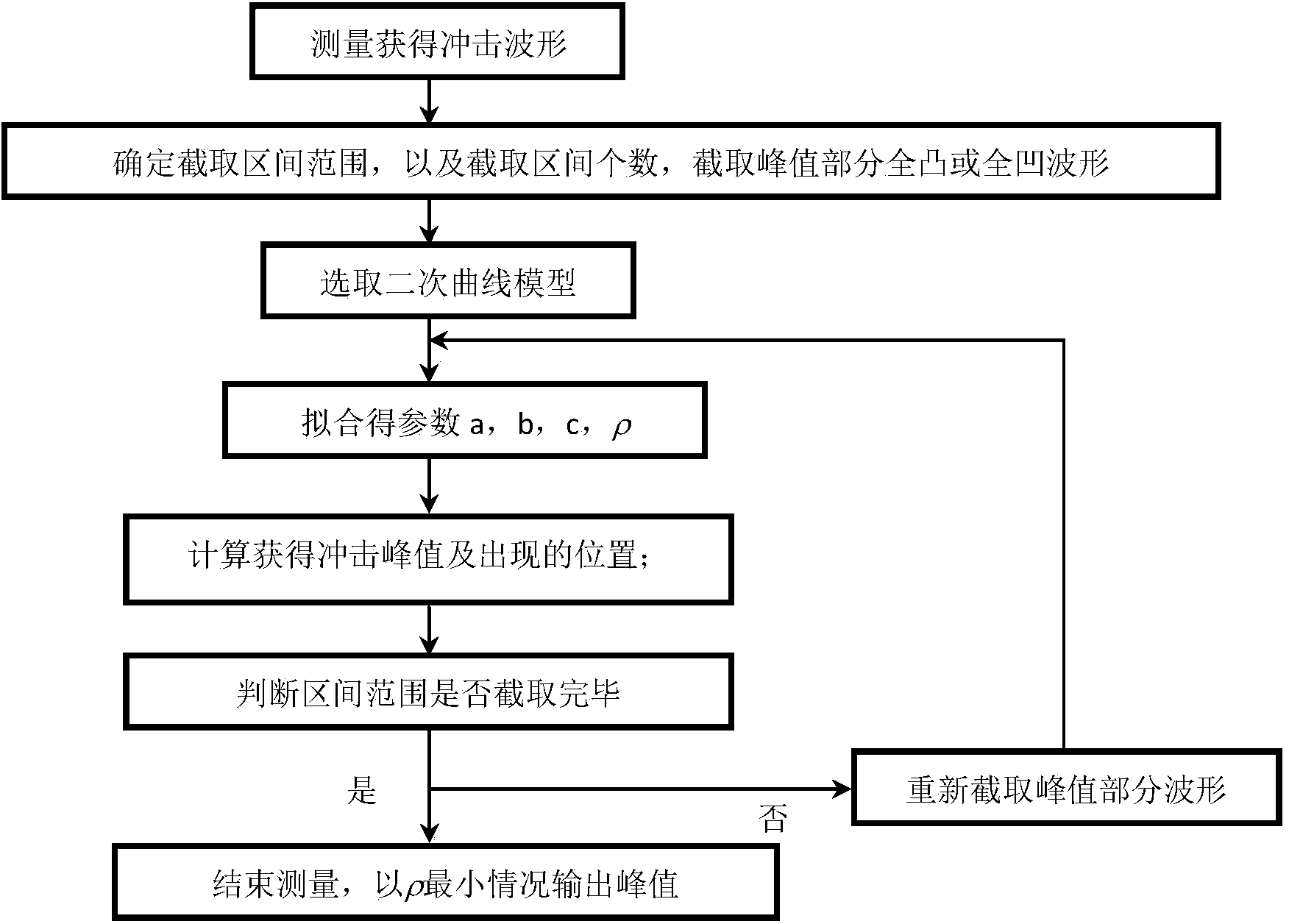
Shock waveform peak measurement method based on quadratic curve fitting
InactiveCN104166793AUnlimited Amplitude ResolutionAccurate and objective pulse peakSpecial data processing applicationsCurve fittingSample sequence
The invention relates to a shock waveform peak measurement method based on quadratic curve fitting and belongs to the field of vibration shock and mechanical engineering and the technical field of metering testing. The shock waveform peak measurement method based on quadratic curve fitting comprises the particular steps that a shock excitation source is used for generating shock excitation, a sensor and a matched waveform data collection system are used for carrying out waveform measurement, and a complete shock measurement waveform uniformly-spaced sampling sequence is obtained; the maximum value and the minimum value of the shock waveform are obtained through a comparison method; a full-convex or full-concave waveform, close to the peak, between the maximum value and the minimum value is cut out in the shock measurement waveform uniformly-spaced sampling sequence and used for peak calculation; the three-parameter fitting process of the shock waveform peak is carried out through a parabola fitting method; the shock measurement waveform peak and the position where the shock measurement waveform peak occurs are calculated through the fitting peak; a fitting residual valid value is given out as an auxiliary criterion of the advantage and disadvantage of peak fitting. The shock waveform peak measurement method based on quadratic curve fitting has the calculation advantages that a peak filter is not needed, the peak and the position where the peak occurs are given out, and the accuracy and the resolving ability are higher.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGCHENG INST OF METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
Preparation method of graphene-based nanocomposite
The invention relates to a preparation method of a composite, in particular to a preparation method of a graphene-based nanocomposite. The preparation method of the graphene-based nanocomposite aims to solve the problem that a preparation method of a graphene-based nanocomposite is difficult to quantitatively control load capacity of metallic oxides on the graphene surface in the prior art. The preparation method includes the steps of 1, preparation of oxidized graphene; 2, XPS (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy) test analysis; 3, preparation of oxidized graphene dispersion liquid; 4, preparation of precursor solution; 5, reaction; and 6, washing and drying. The types and the quantity of oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the oxidized graphene are determined by means of XPS testing and C1s diffraction peak fitting analysis, and the load capacity of the metallic oxides on the graphene surface can be quantitatively controlled. The graphene-based nanocomposite prepared by the preparation method can be applied to the fields of energy storage, photocatalysis and sensors.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
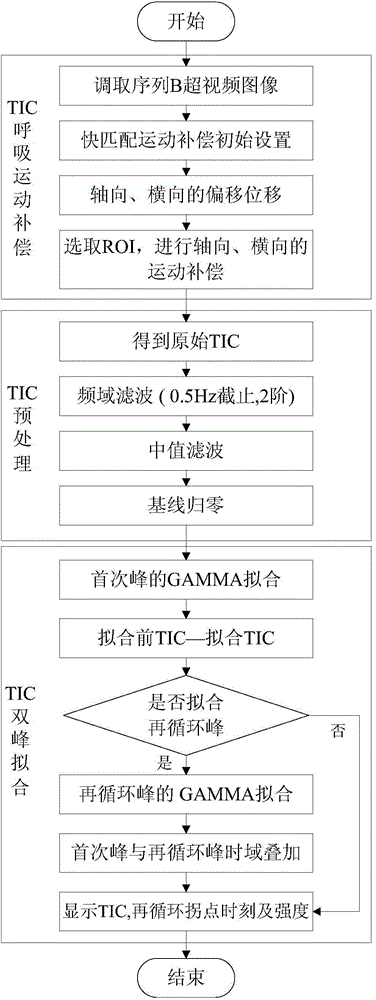
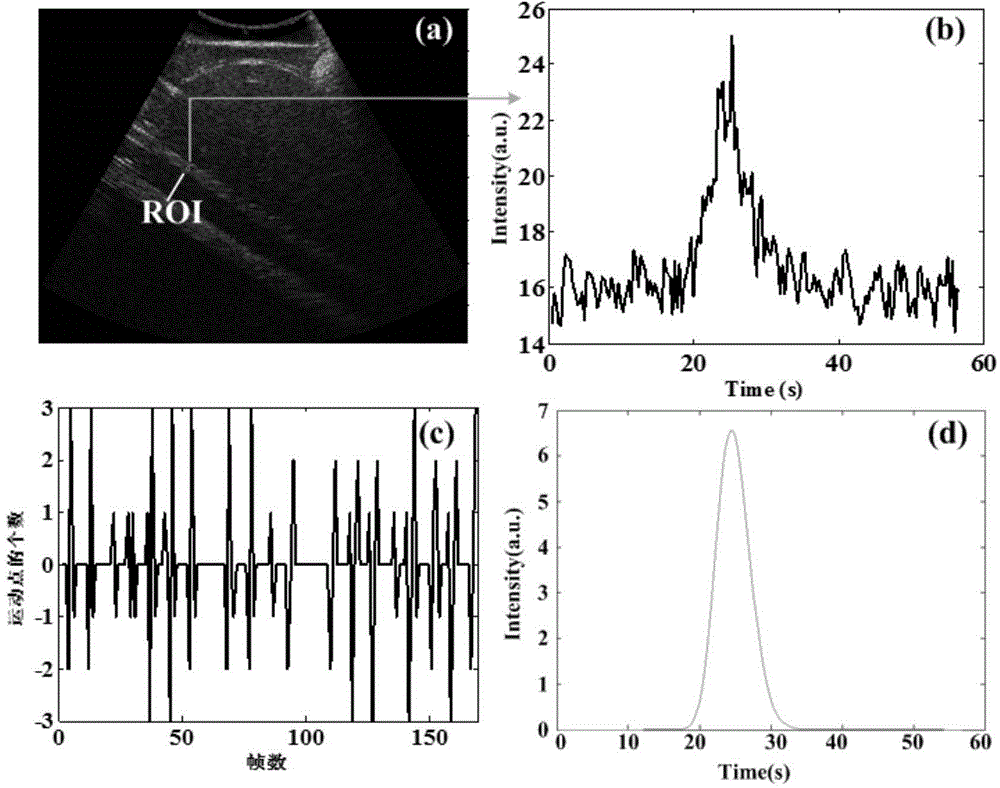
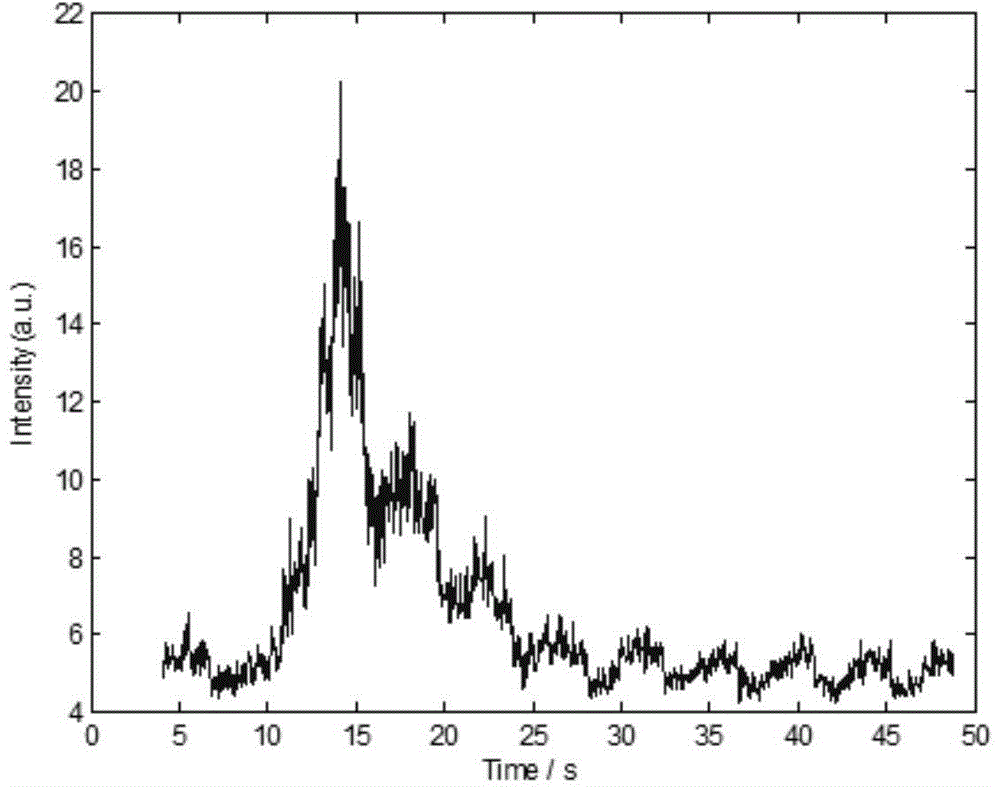
Respiratory motion compensation and bimodal fitting method for time intensity curve
ActiveCN104688269AImprove accuracyEliminate distractionsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsTime domainErrors and residuals
The invention provides a respiratory motion compensation and bimodal fitting method for a time intensity curve. The method comprises the following steps: based on a block matching method taking a accumulative absolute error as a standard, carrying out respiratory motion compensation for the time intensity curve extracted from a serial B ultrasound contrastographic picture, and then carrying out pretreatment by utilizing frequency domain filtering, time domain filtering and baseline zeroing; carrying out recycling peak fitting determination for the pretreated time intensity curve; if a recycling peak exists, carrying out recycling peak fitting, outputting a result after motion compensation and bimodal fitting, and outputting the moment and the intensity of a recycling inflection point. The invention provides the respiratory motion compensation and bimodal fitting method for the time intensity curve and a microvesicle recycling inflection point identification method, so that the accuracy of TIC fitting is improved, and more accurate blood perfusion information can be obtained. A new method is possibly provided for detection of microcirculation clinically, and the method has an important significance on the evaluation of blood perfusion.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
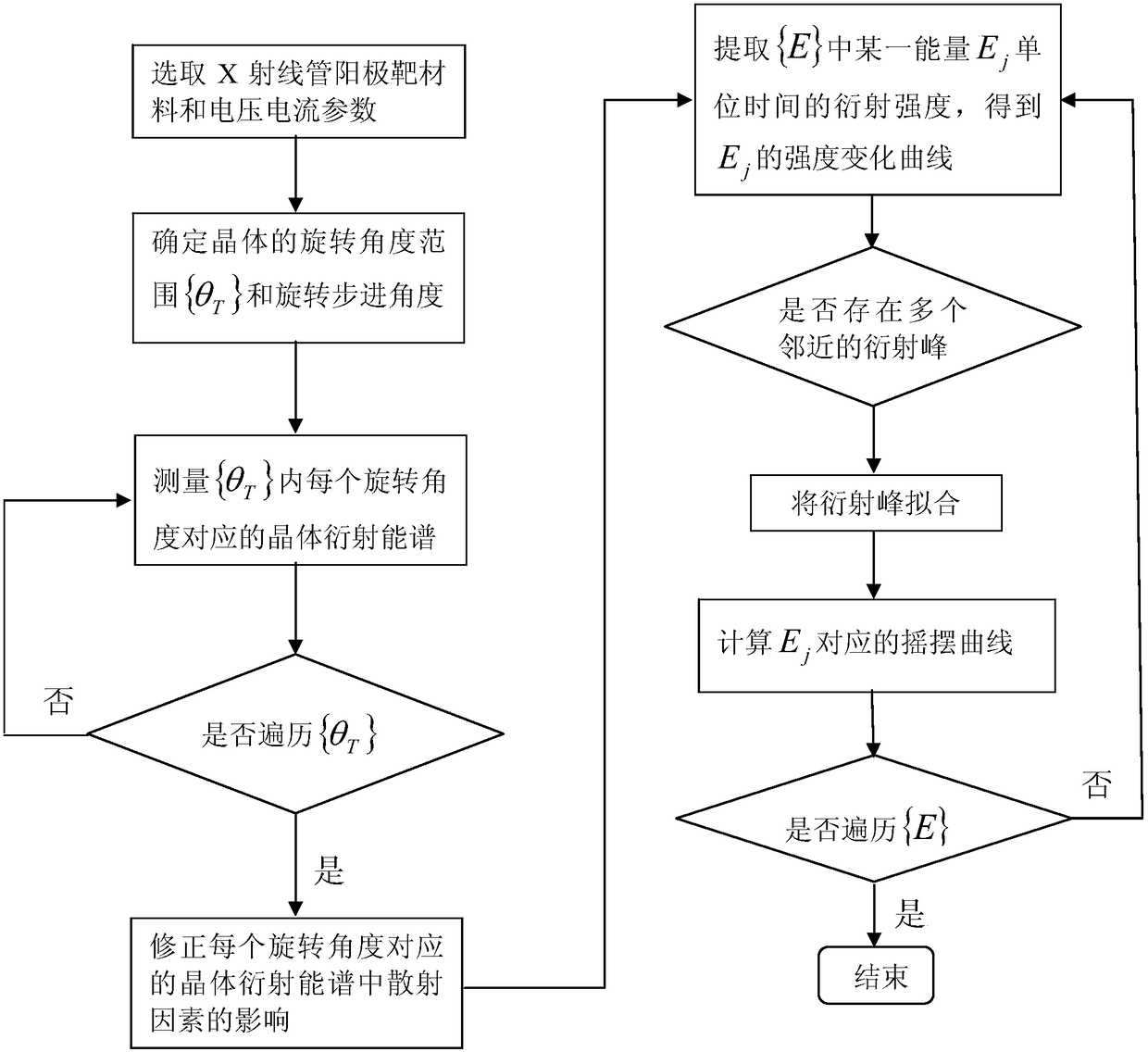
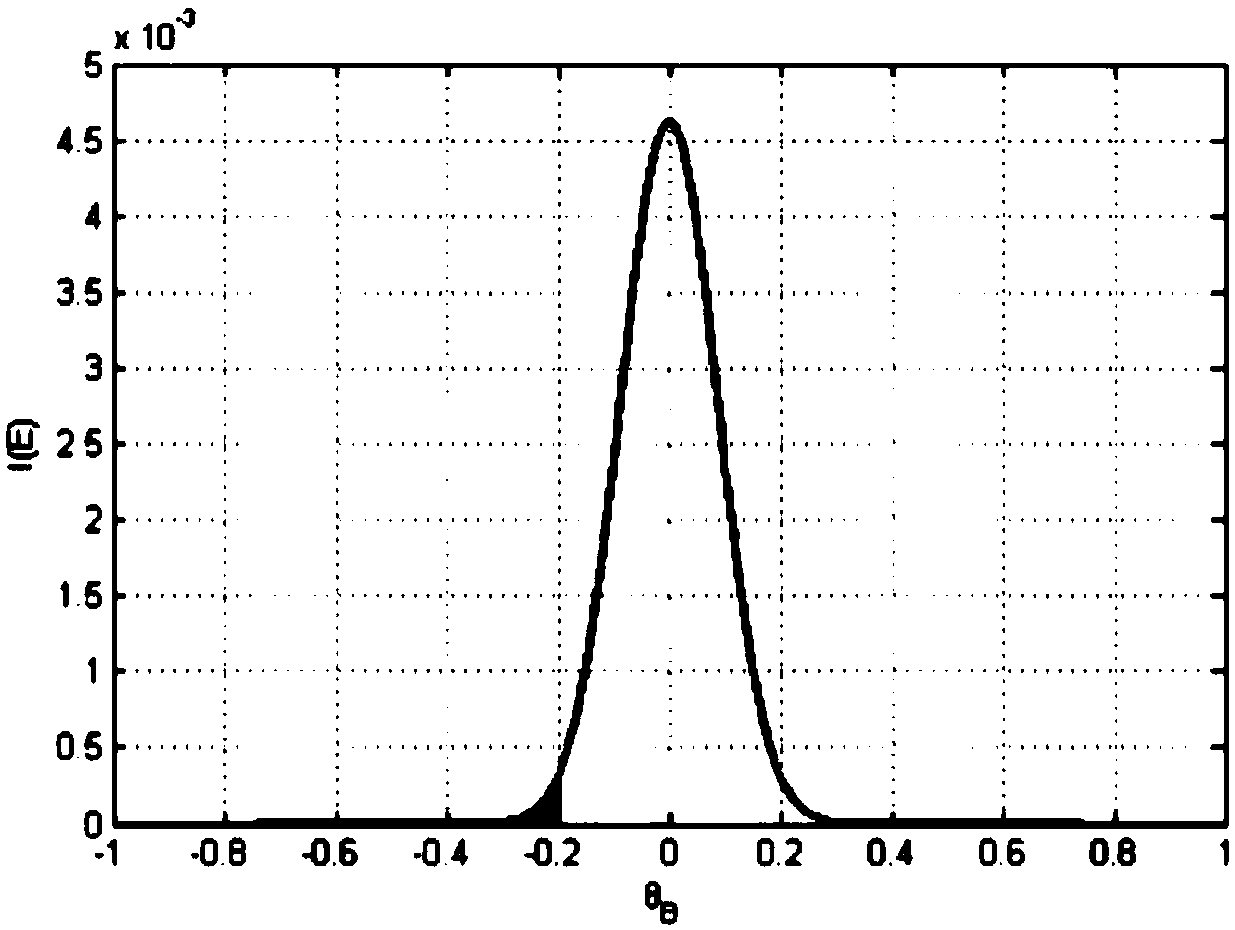
Crystal rocking curve measurement method based on energy resolution detector
InactiveCN105866151AExtended energy rangeRealize measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRocking curveLattice plane
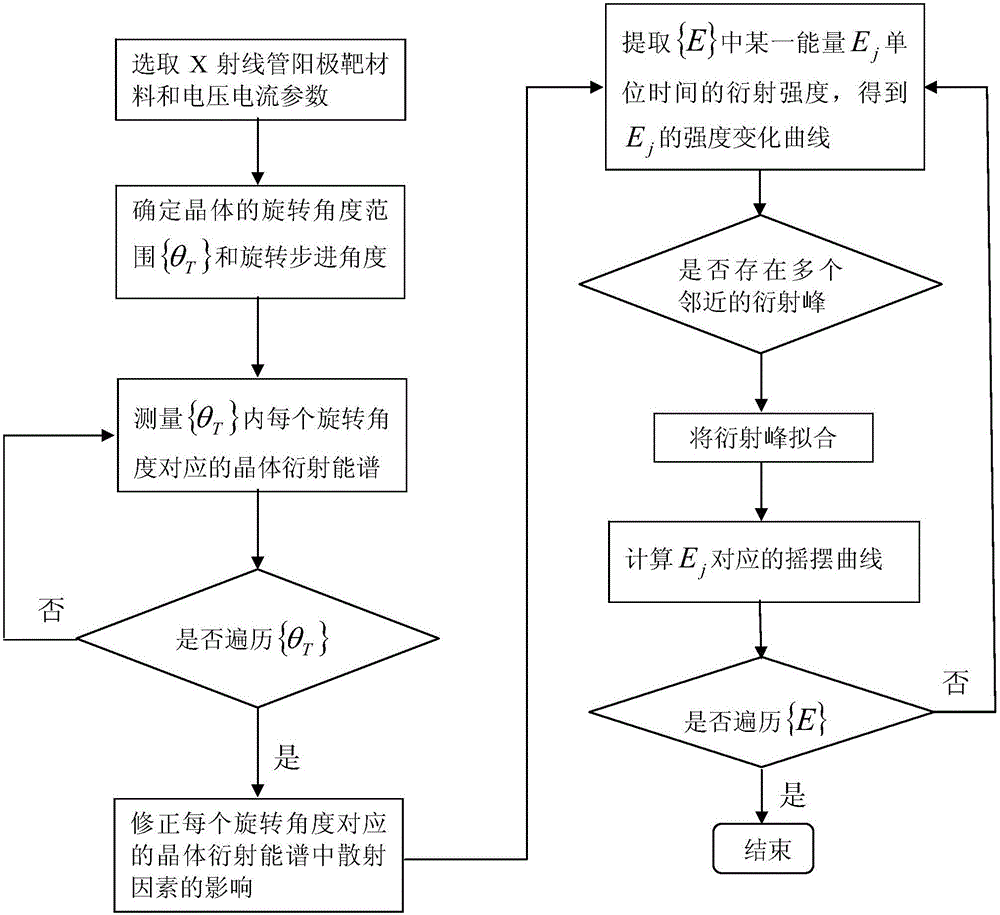
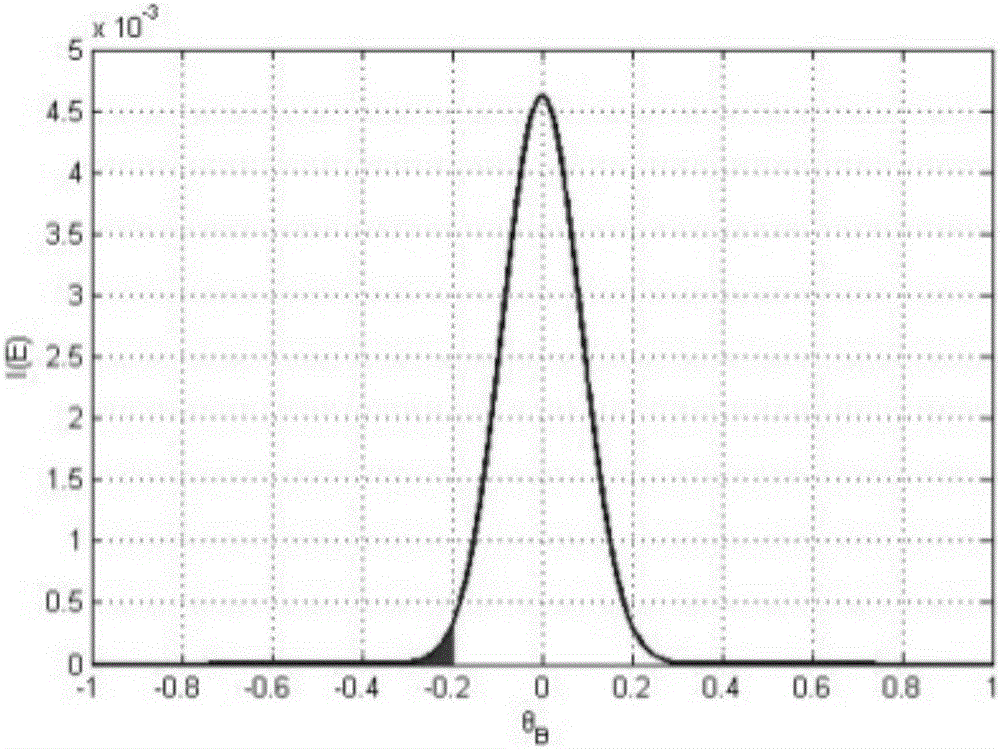
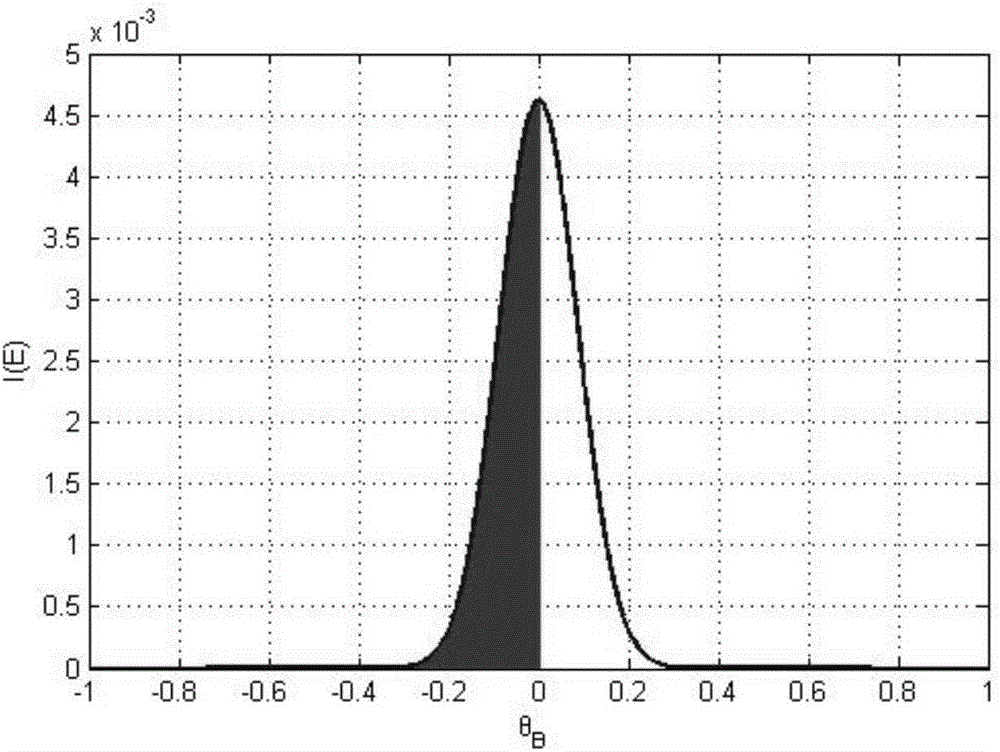
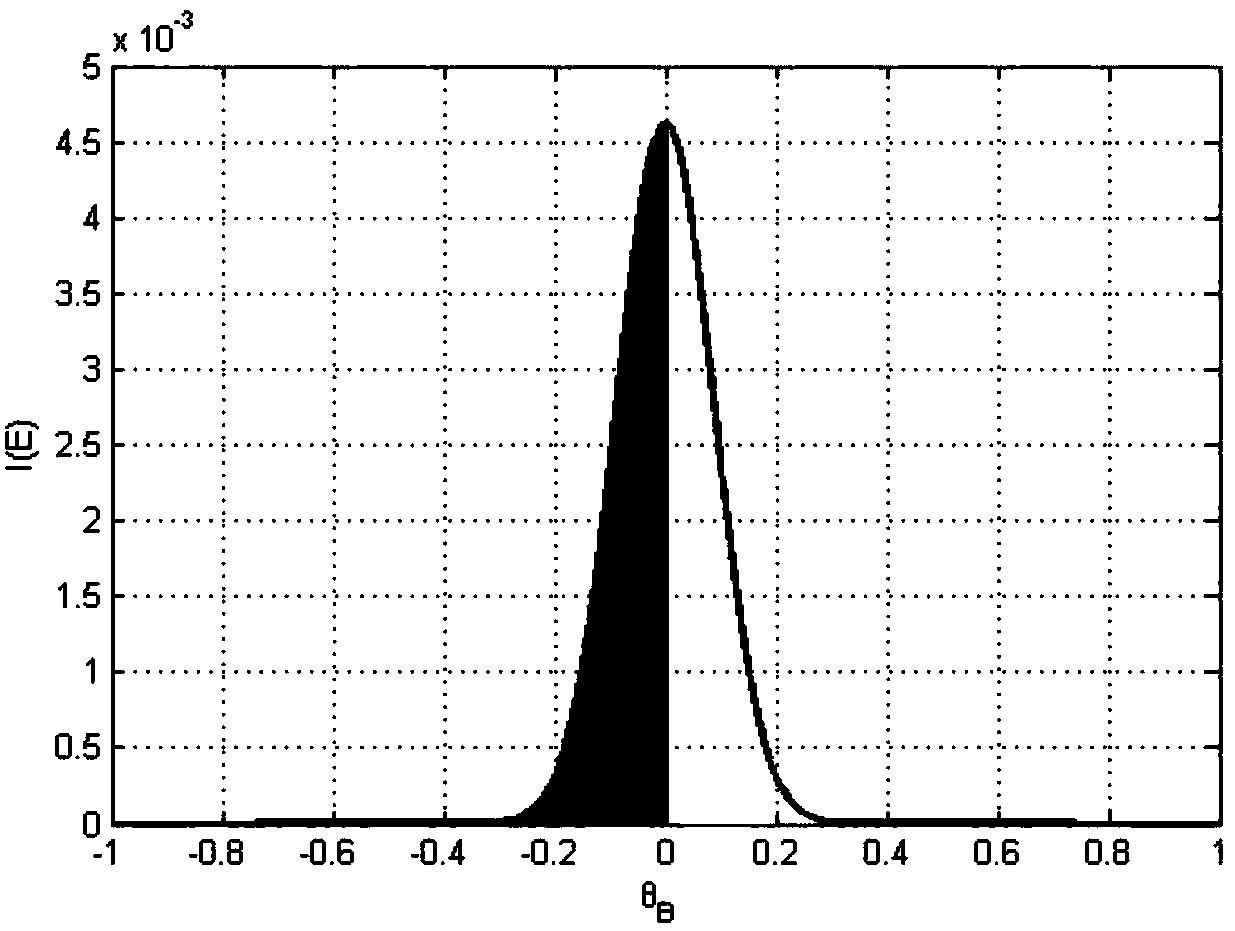
The invention relates to a crystal rocking curve measurement method based on an energy resolution detector, comprising the steps of 1, selecting an X-ray tube anode target material and voltage / current parameters based on an X-ray energy range {E} for measurement; 2, determining a Bragg diffraction angle range {theta B}, a crystal rotation angle range {theta T} and a rotation stepping angle; 3, measuring a crystal diffraction energy spectrum of each rotation angle within the {theta T}; 4, correcting the effect of scattering factors in the crystal diffraction energy spectrums; 5, extracting the diffraction strength of X-ray of energy Ej in {E} within a unit interval when theta Ti = theta Bi, so as to obtain a strength variation curve of Ej; 6, performing diffraction peak fitting on the strength variation curve; 7, figuring out a first-order derivative of a fitted diffraction peak, selecting absolute values of a part of the diffraction peak where the slope of the first-order derivative is not less than 0, i.e., the left and right branches of a rocking curve, and splicing to obtain the rocking curve of Ej; 8, repeating steps 5-7 until {E} is traversed, thereby obtaining the rocking curve of the X ray of all energies in {E} to a certain lattice plane of a crystal.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Spectrum segmentation and spectrum comparison method based on spectrum peak-splitting fitting
PendingCN112557332AImprove the rate of correct judgmentEliminate Spectral Similarity Calculation IssuesRaman scatteringCharacter and pattern recognitionFt ir spectraComputational physics
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Carbon film
InactiveUS20120199553A1High transparencySmall double refractivityUltra-high pressure processesDecorative surface effectsCarbon filmRefractive index
ProblemTo provide a carbon film and a laminate having optical characteristics of retaining high transparency, having high refraction index and less double refractivity, being excellent in electric insulating property, being capable of being coated at good adhesion to various substrates, and being capable of being formed at a low temperature, and applications thereof.Means for Solving the ProblemThe invention relates to a carbon film which has an approximate spectrum curve obtainable by superimposing, on a peak fitting curve A at a Bragg's angle (2θ±0.3°) of 43.9°, a peak fitting curve B at 41.7° and a base line in an X-ray diffraction spectrum by a CuKa1 ray, and has a film thickness of from 2 mm to 100 μm. The intensity of the fitting curve B relative to the intensity of the fitting curve A is preferably from 5 to 90% in the approximated spectrum described above. In the carbon film, the Raman shift has a peak at a 1333±10 cm−1 in the Raman scattering spectrum, and the half-value width of the peak is from 10 to 40 cm−1. Further, the invention relates to a laminate characterized by disposing, on the substrate, a carbon aggregate film of 2 nm to 100 μm thickness comprising an aggregate of carbon particles having an approximate spectrum curve described above. Moreover, the invention relates to an optical device, optical glass, wrist watch, electronic circuit substrate, or grinding tool having the laminate described above.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
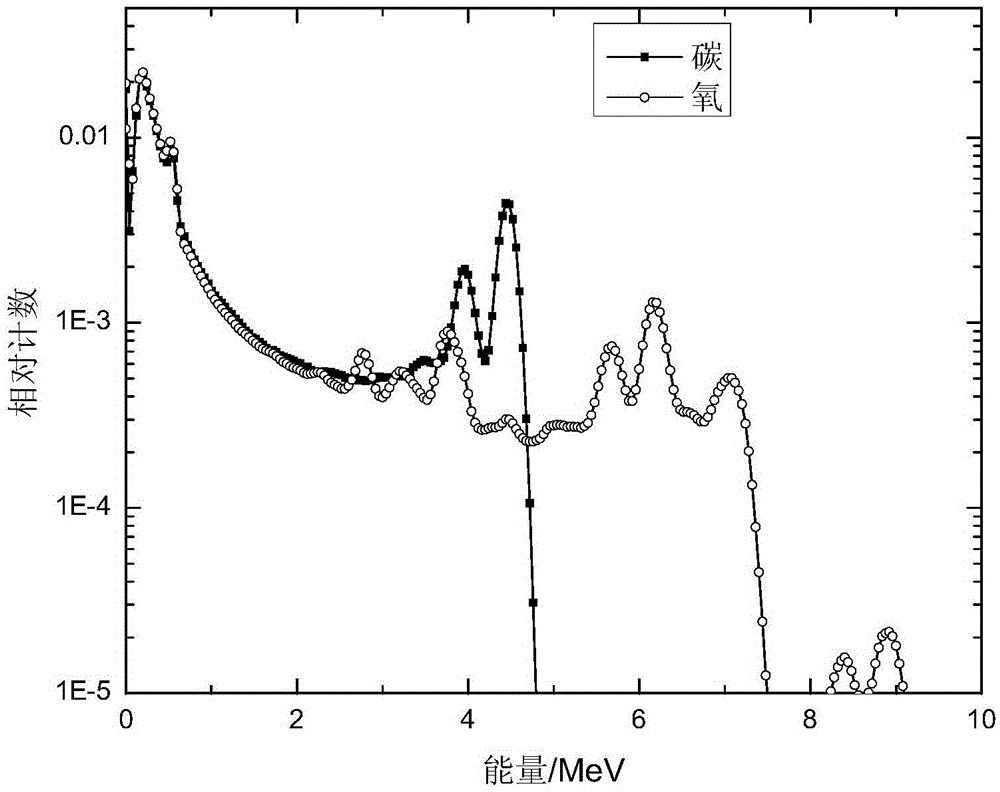
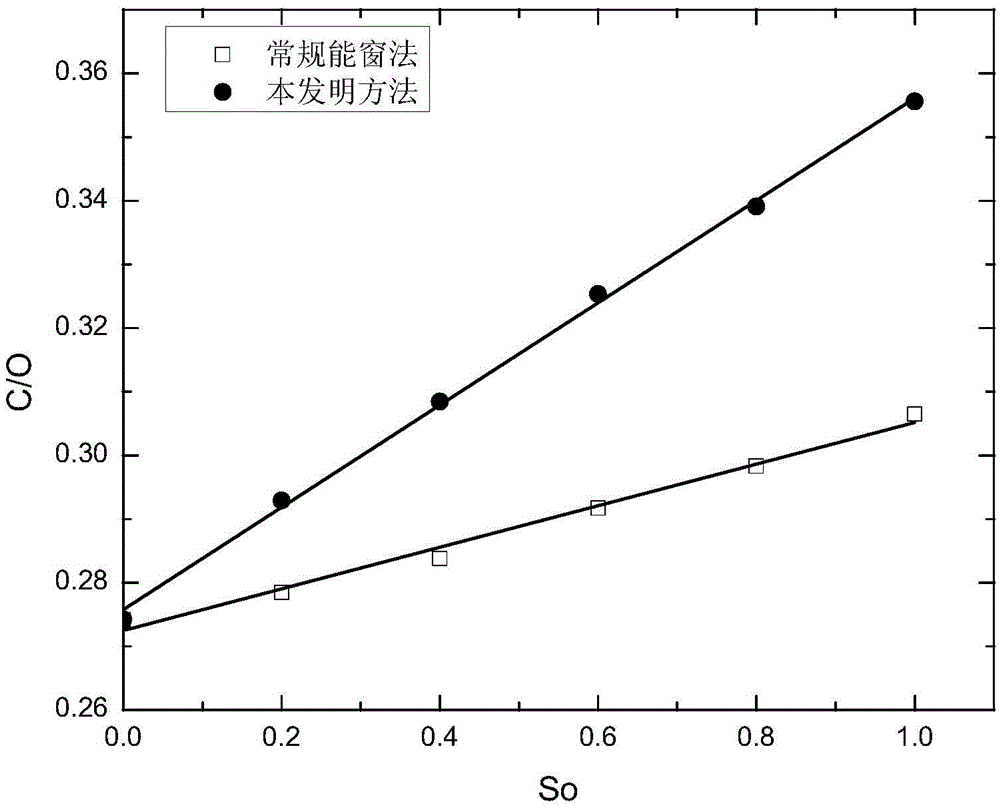
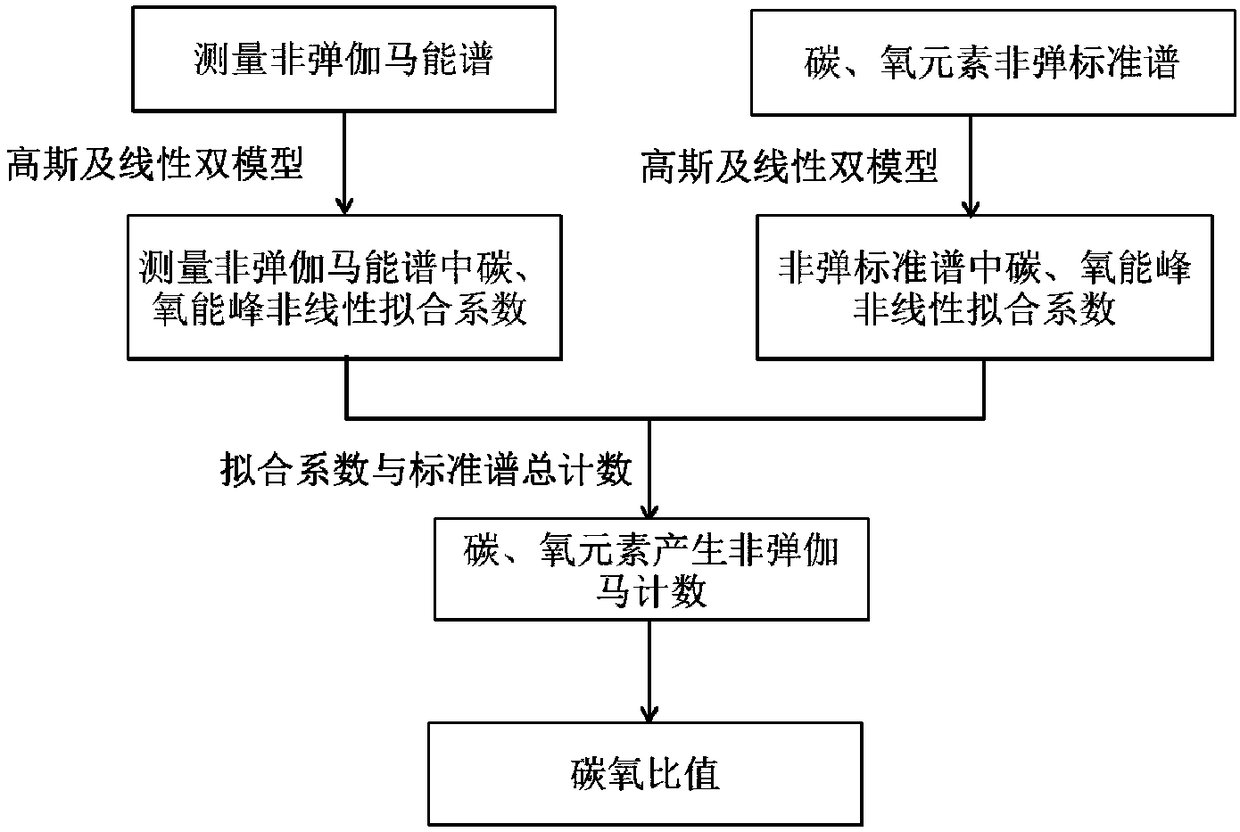
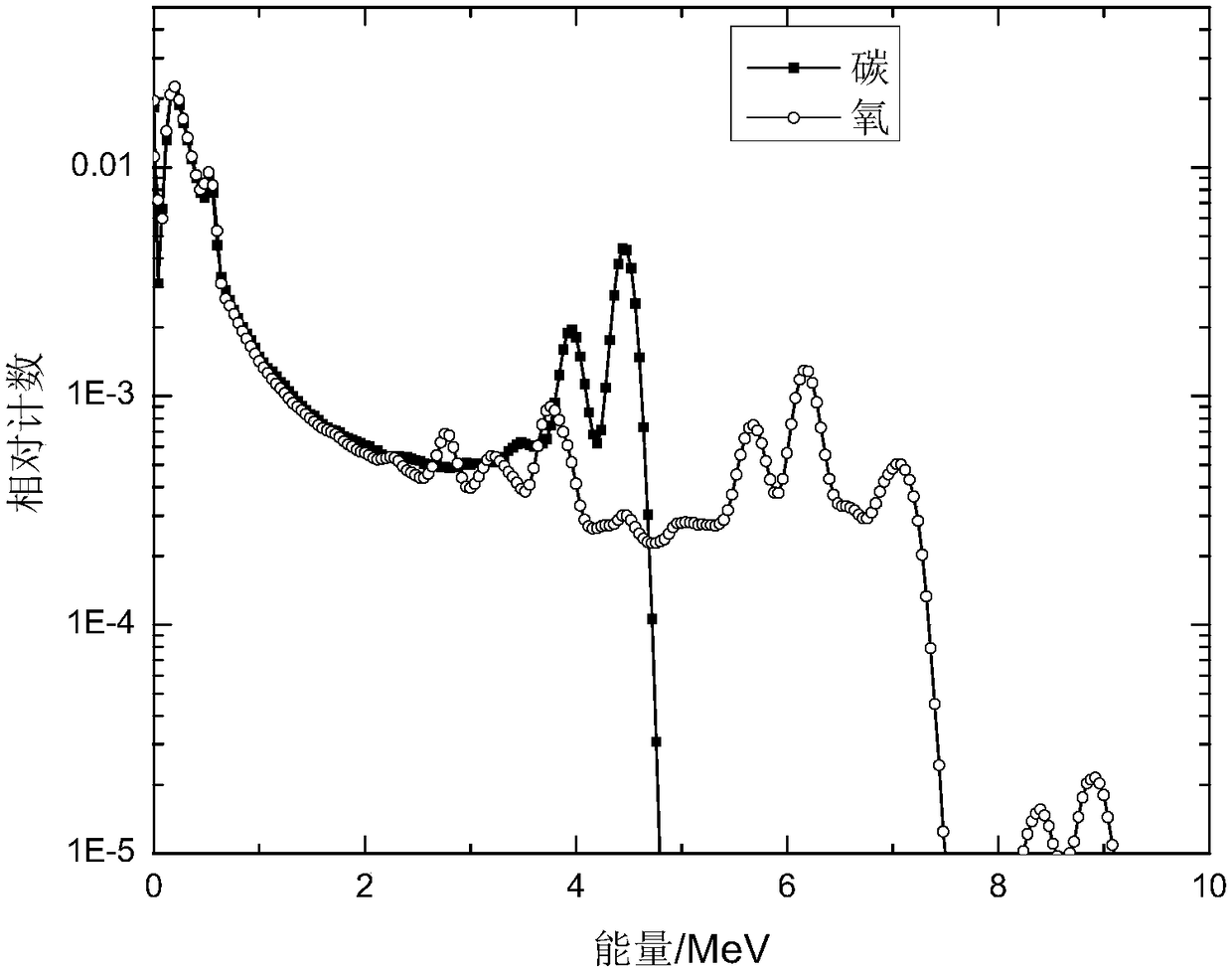
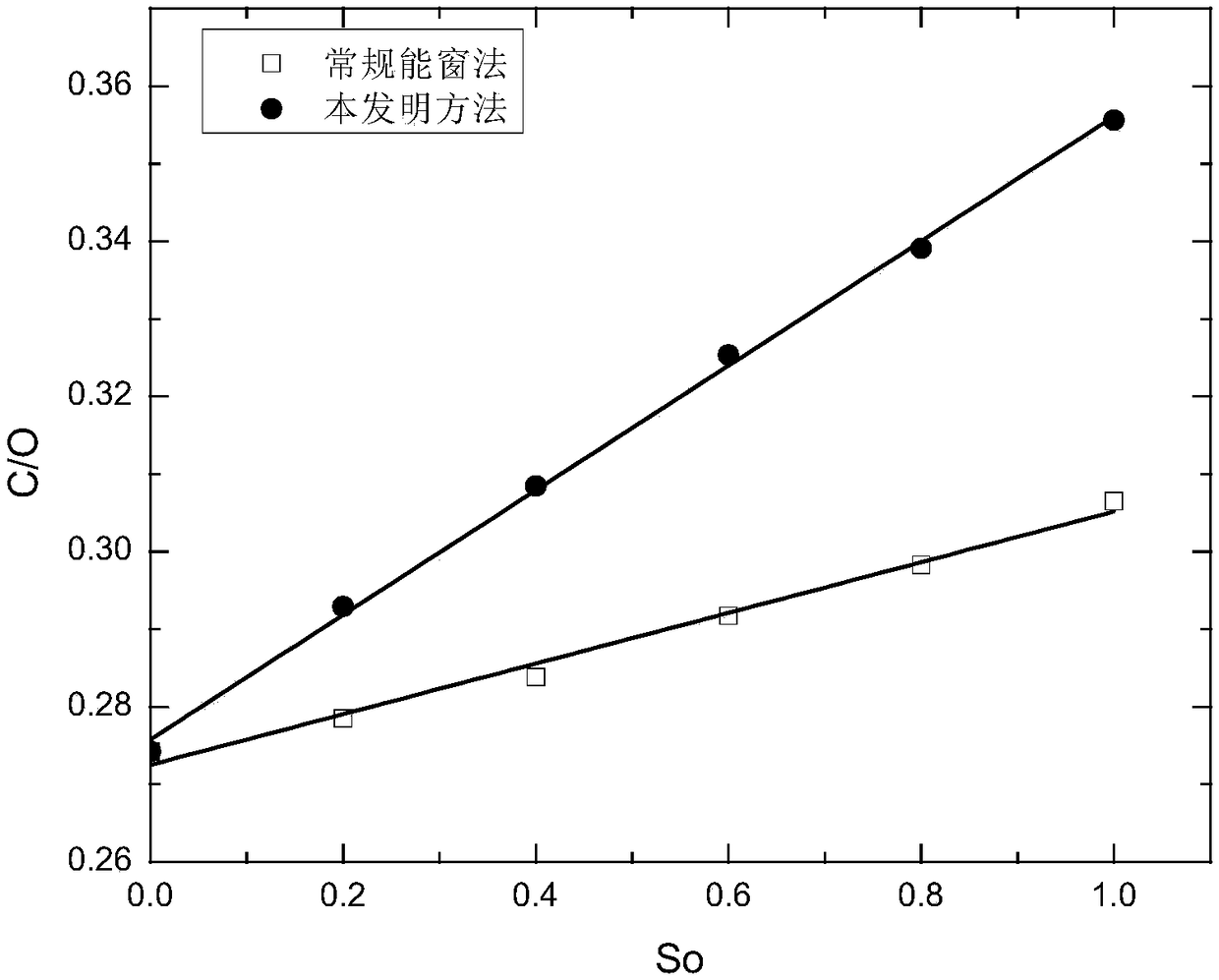
Carbon-oxygen ratio calculation method used for determining remaining oil saturation
InactiveCN105673006AImprove responsivenessReduce the impact of calculating the carbon-to-oxygen ratioBorehole/well accessoriesResponse sensitivityOxygen
The invention discloses a carbon-oxygen ratio calculation method used for determining remaining oil saturation. Firstly, a Gaussian and linear dual model is used for fitting and actually measuring carbon and oxygen energy peaks of inelastic gamma-ray spectrum data, and characteristic peak fitting coefficients are obtained; then, the same fitting model is used for fitting energy peaks corresponding to carbon and oxygen standard gamma-ray spectra; the ratio of height of measurement spectrum carbon peak Gaussian components and height of standard spectrum carbon peak Gaussian components is multiplied by the total number of carbon element standard spectra, so that inelastic gamma-ray generated by a carbon element is counted; the ratio of height of measurement spectrum oxygen peak Gaussian components and height of standard spectrum oxygen peak Gaussian components is multiplied by the total number of oxygen element standard spectra, so that inelastic gamma-ray generated by an oxygen element is counted; the two numbers are divided to generate the carbon-oxygen ratio. The method reduces influences of gamma-ray generated by other elements on the carbon-oxygen ratio, and improves response sensitivity of the carbon-oxygen ratio to oil saturation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
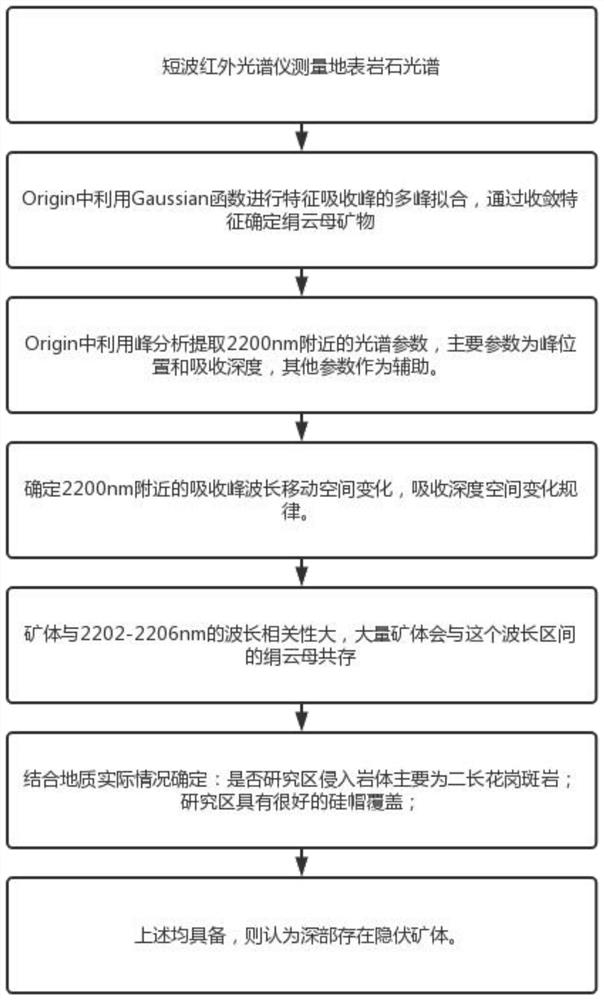
Hydrothermal deposit prospecting method and system based on white mica wavelength change
ActiveCN114280684ASimplify workSimple methodScattering properties measurementsOptical detectionComputational physicsWavelength
The invention discloses a hydrothermal deposit prospecting method and system based on white mica wavelength change. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring spectral reflection data, drawing a characteristic curve based on the spectral reflection data, performing multi-peak analysis on the characteristic curve to obtain a characteristic absorption peak, and performing multi-peak fitting on the characteristic absorption peak to obtain a characteristic wave peak; and performing parameter calculation on the characteristic wave crest to obtain characteristic wave crest parameter data, and analyzing the characteristic wave crest parameter data to obtain a prospecting result. The method is simple and easy to implement, short in analysis time and capable of rapidly completing data measurement, analysis and application, and cost is reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
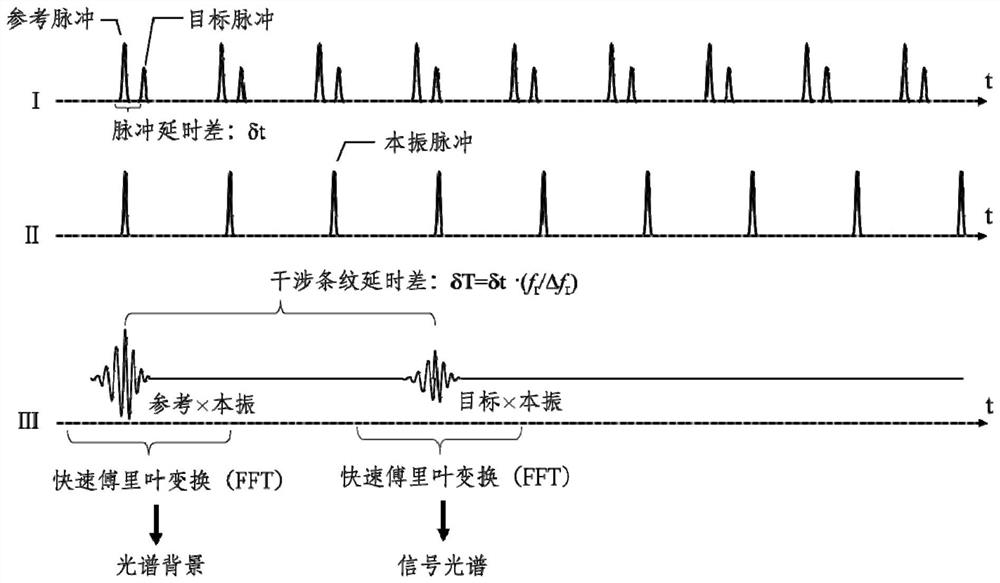
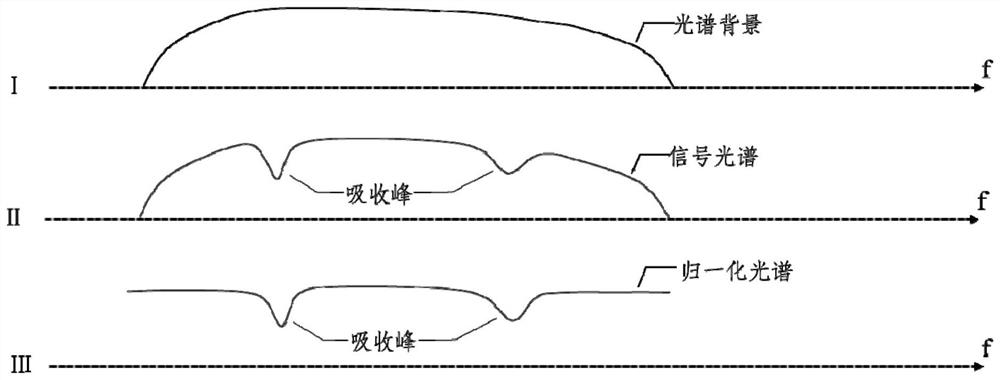
High-precision laser spectrum ranging method based on optical comb
PendingCN114019525ARanging Accuracy LimitsRealize high-precision laser rangingElectromagnetic wave reradiationRefractive indexAbsorbance spectra
The invention provides a high-precision laser spectrum ranging method based on optical combs. The high-precision laser spectrum ranging method comprises the following steps: s1, measuring target pulse flight time by using a double-optical-comb method; s2, carrying out Fourier transform on the double-optical-comb interference signal data to obtain spectral information; s3, performing normalization processing and absorption peak fitting on the signal spectrum; s4, calculating the atmospheric temperature and the gas pressure in the light path through the absorption spectrum; s5, correcting the air refractive index in the light path by using the obtained atmospheric temperature and gas pressure to obtain the corrected air refractive index; s6, calculating the target distance according to the corrected air refractive index. By utilizing the characteristic of wide spectrum range of the optical comb, on the basis of optical comb pulse flight time distance measurement, measurement of absorption spectral lines of water molecules in the atmosphere is simultaneously realized, atmospheric temperature and gas pressure information is obtained by utilizing spectral line fitting, the air refractive index is corrected in real time, and the distance measurement precision is improved; therefore, the problem of poor distance measurement precision caused by atmosphere uncertainty in the prior art is solved.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +6
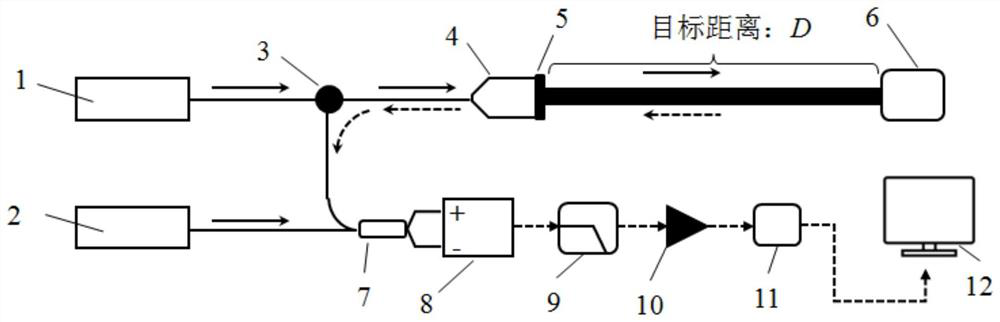
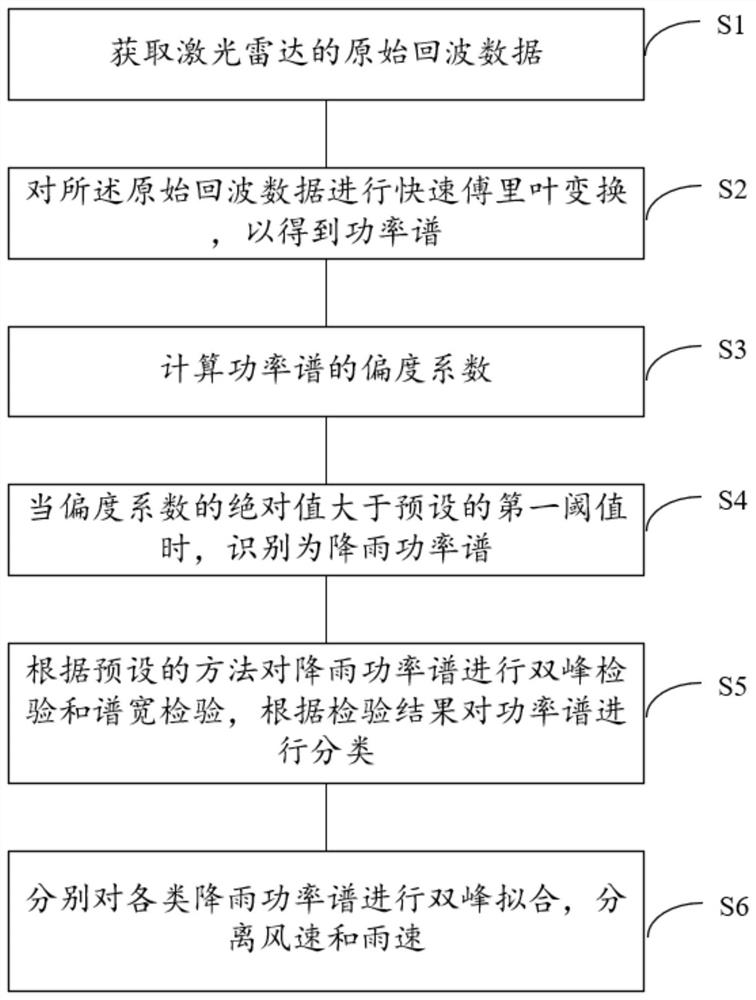
Rainfall identification method and device based on wind measurement laser radar
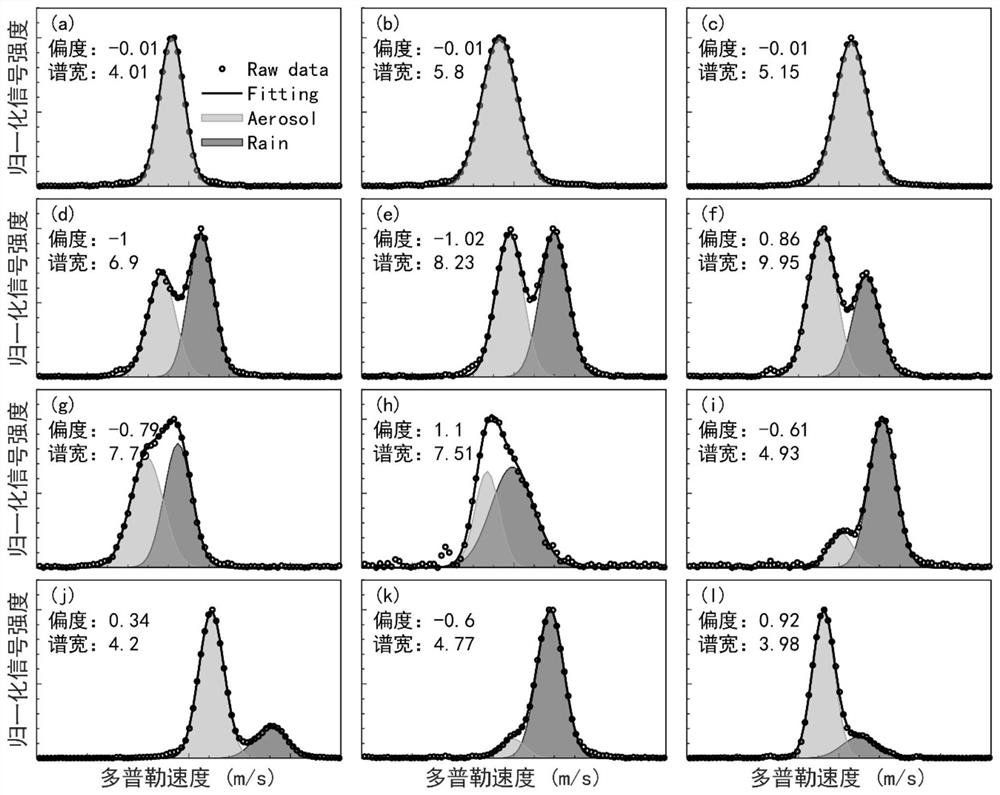
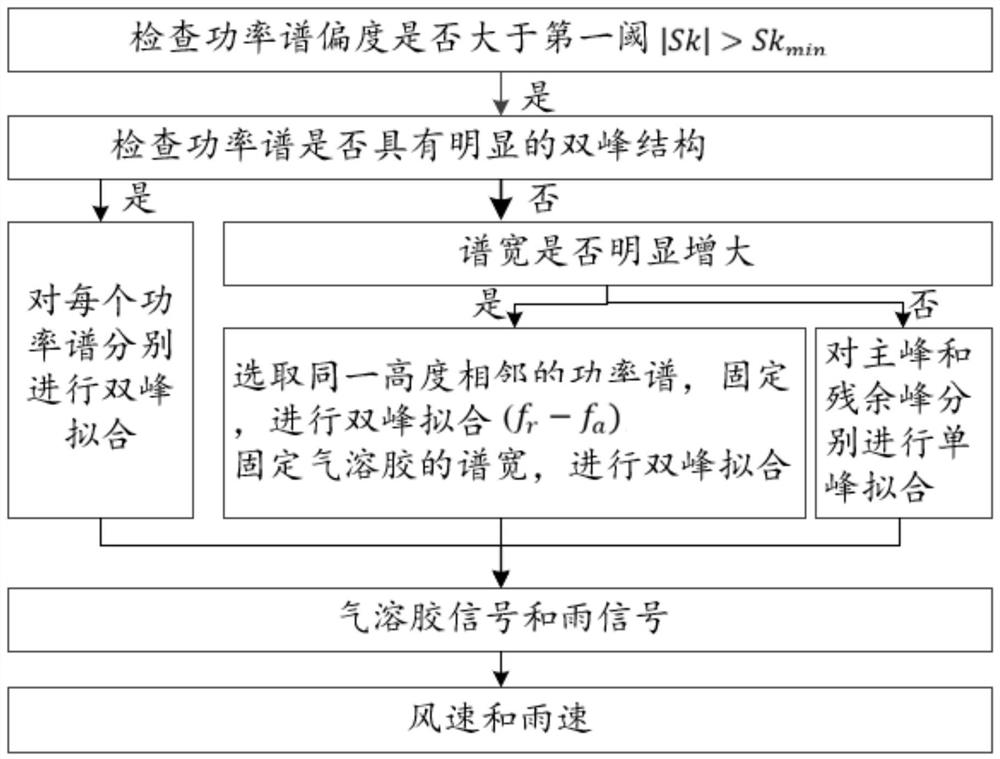
PendingCN112526548AAccurate identificationPrecise separabilityWeather condition predictionElectromagnetic wave reradiationTemporal resolutionWind lidar
The invention discloses a rainfall identification method and device based on a wind measurement laser radar. According to the method and device of the invention, the skewness coefficient of the powerspectrum of the wind measurement laser radar can be utilized to identify rainfall and perform wind speed and rain speed separation. The basic principles of the method are as follows: aerosol and raindrop signals exist at the same time under a rainfall condition, the power spectrum has obvious skewness, and a rainfall power spectrum is identified according to the skewness; double-peak inspection iscarried out on the identified rainfall power spectrum; double-peak fitting is directly carried out on a power spectrum with an obvious double-peak structure, and double-peak fitting is carried out ona power spectrum without the obvious double-peak structure through few fitting parameters. And finally, separation of wind speed and rain speed is realized. The method is applied to guaranteeing aviation safety, contributes to improving a climate model, a weather forecast model and an atmospheric pollution diffusion model, and has the advantages of high flexibility, high spatial-temporal resolution and high accuracy.
Owner:南京泰爱信科技有限公司
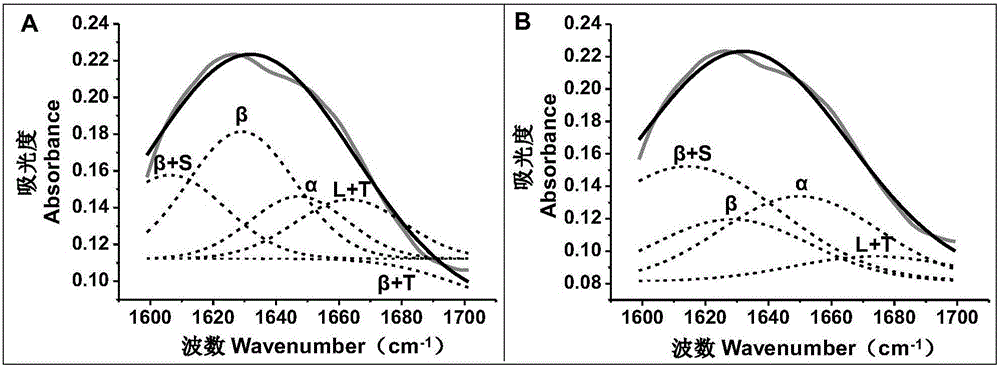
Method of analyzing protein secondary structure in peony on the basis of infrared spectroscopy and Gauss multi-peak fitting
InactiveCN106198438AReduce experiment costShort experiment cycleMaterial analysis by optical meansCrystallographyProtein secondary structure
The invention discloses a method of analyzing a protein secondary structure in peony on the basis of infrared spectroscopy and Gauss multi-peak fitting. The method includes the steps of: grinding a dry peony sample into powder and performing FTIR scanning through a potassium bromide tabletting method; performing Gauss single-peak fitting and performing Gauss multi-peak fitting to the fit single peaks according to characteristic peak positions of different protein secondary structures; and calculating the percentage ratios of various protein secondary structures in the sample according the peak area. The method has the following advantages: 1) the method allows the analysis on the protein secondary structure directly on the level of the plant without extraction and purification of proteins, so that experimental cost is greatly reduced and experimental period and labor and material resources are reduced; and 2) data collection and analysis in the method are based on the FTIR spectroscopic method and the Gauss multi-peak fitting, so that the method is simple and effective, has high accuracy and strong data persuasion.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY & FRUIT TREE WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI & TECH
Affinity chromatography-based method for measuring supramolecular interaction dissociation rate constant
The invention relates to an affinity chromatography-based method for measuring a dissociation rate constant, and especially aims at relatively extensive and relatively weak supramolecular interaction. The affinity chromatography-based method is a method for firstly fixing a host molecule and then measuring the host molecule, and comprises the following steps: under a certain temperature condition and at various flow rates, respectively acquiring chromatography flow curves of a first to-be-analyzed guest molecule and a second to-be-analyzed guest molecule on an affinity chromatography column which is bonded with a target host molecule, calculating retention time, half peak width and tower plate height by peak fitting, and calculating the dissociation rate constant. According to the method disclosed by the invention, special apparatus and equipment are not needed, and a normal chromatographic analysis method is adopted, so that the dynamic speed constant of the supramolecular weak interaction can be measured; meanwhile, the method can be combined with various detectors of ultraviolet rays, fluorescence, mass spectrum and the like to achieve unique advantages in detection of low-concentration drugs with poor water solubility as well as low-cost and quick measurement of supramolecular interaction dynamic parameters.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
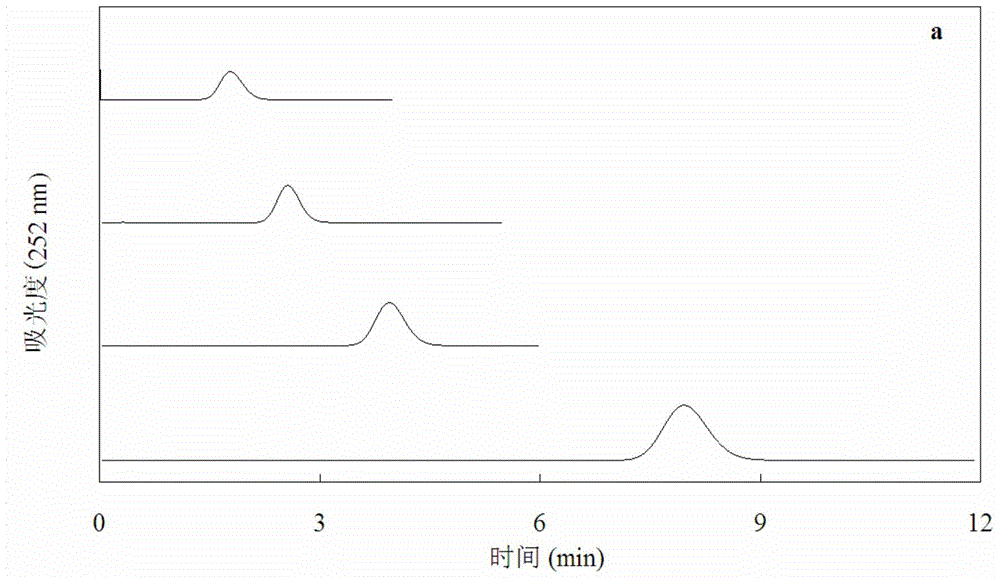
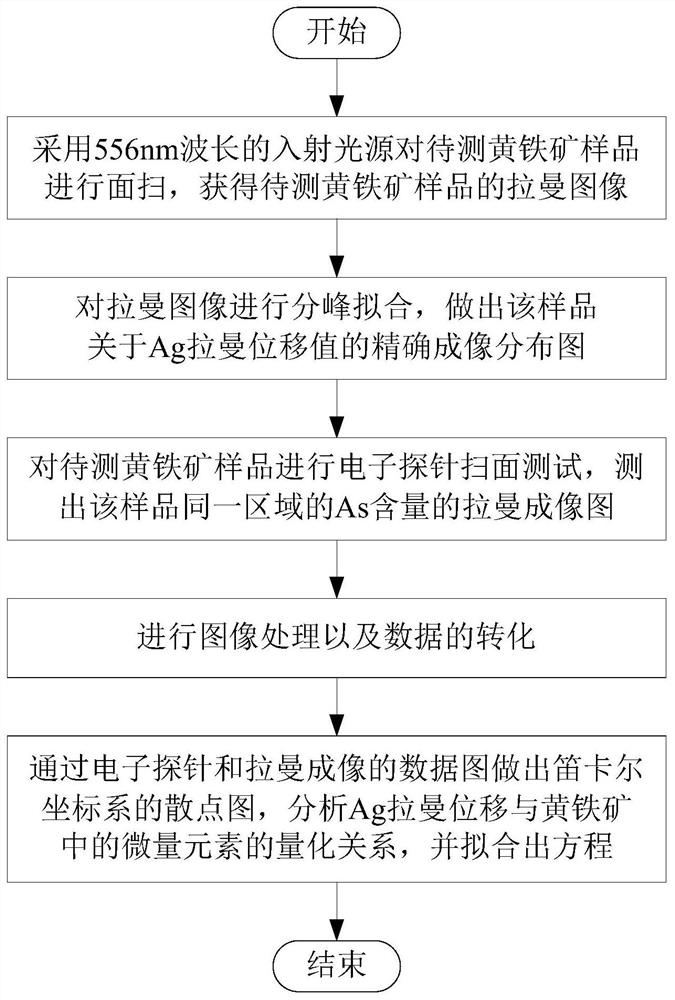
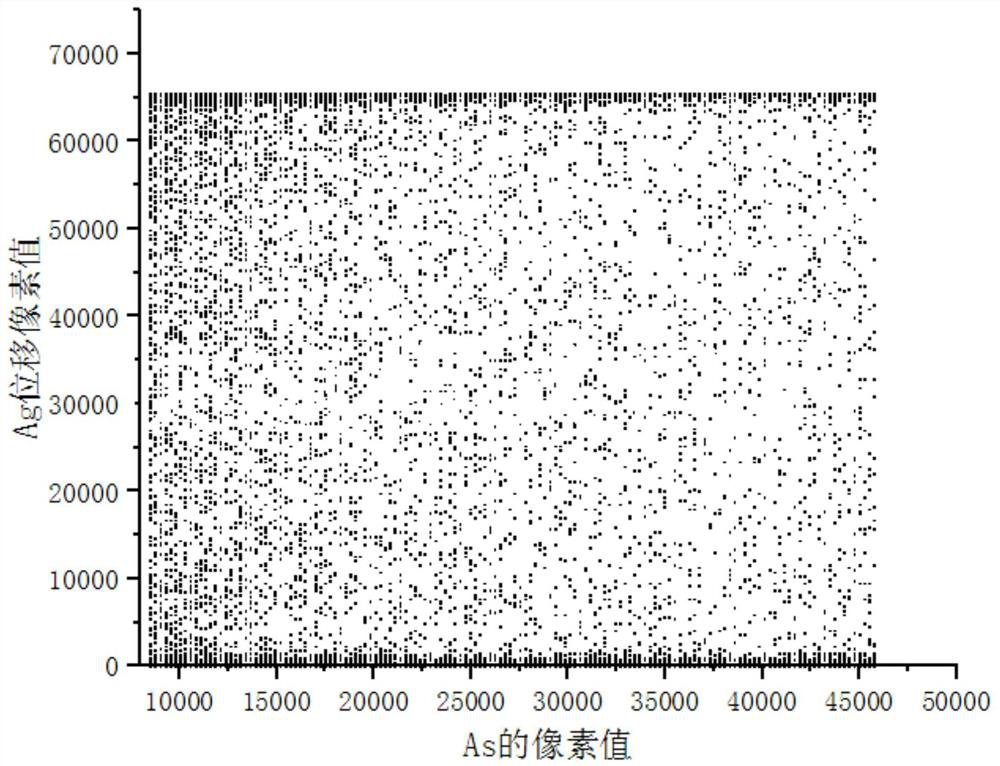
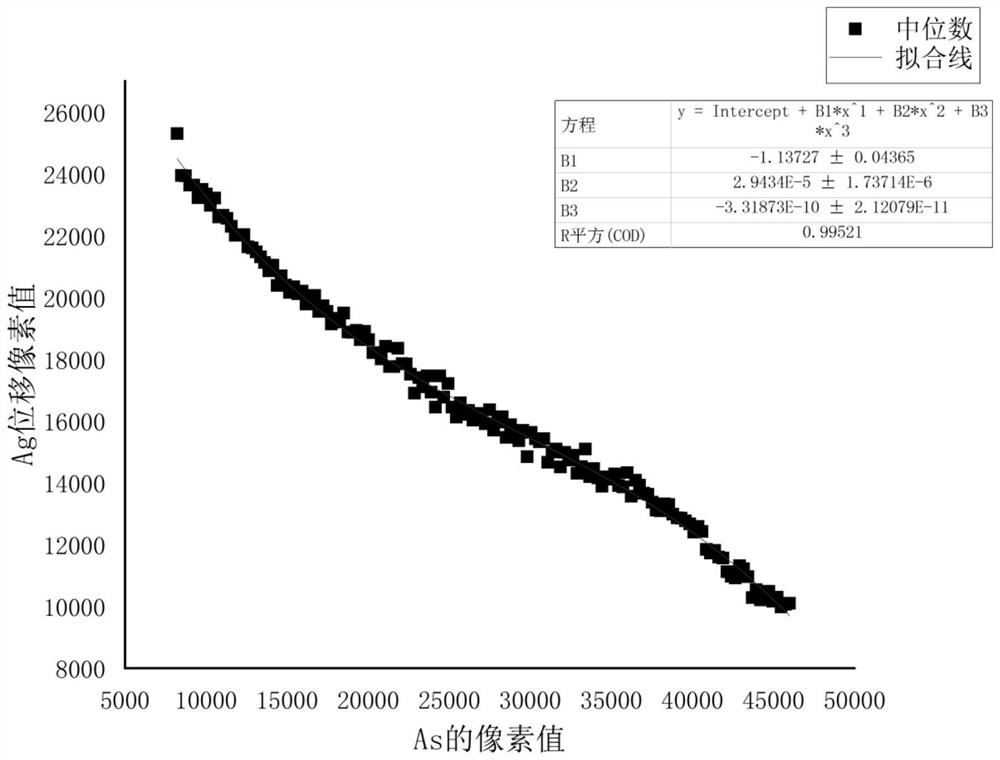
Quantitative analysis method for As element in pyrite by using mineral Raman parameters
ActiveCN113295666AReduce preparation timeFast SNRMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRaman scatteringRaman imagingData graph
The invention discloses a quantitative analysis method for As content in pyrite by using mineral Raman parameters. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out pyrite Raman spectrum imaging scanning; S2, carrying out peak-splitting fitting on the Raman image, and making a precise imaging distribution diagram of the sample about the Ag Raman displacement value; S3, measuring a Raman imaging graph of the As content in the same area of the sample; S4, performing Photoshop proofreading and matching on the precise imaging distribution diagram related to the Ag Raman displacement value and the As content Raman imaging diagram, and converting the precise imaging distribution diagram and the As content Raman imaging diagram into a data diagram; and S5, making a scatter diagram of a Cartesian coordinate system through the electronic probe and the Raman imaging data diagram, analyzing the quantitative relation between the Ag Raman shift and the As content in the pyrite, and fitting an equation. According to the method, the As content in the pyrite is quantitatively analyzed by utilizing the mineral Raman parameters, the operation is simple, and the test speed is high. Raman spectrum characteristic signals are strong, the signal-to-noise ratio is high, the specificity is high, the recognition accuracy can be improved, and misrecognition is reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
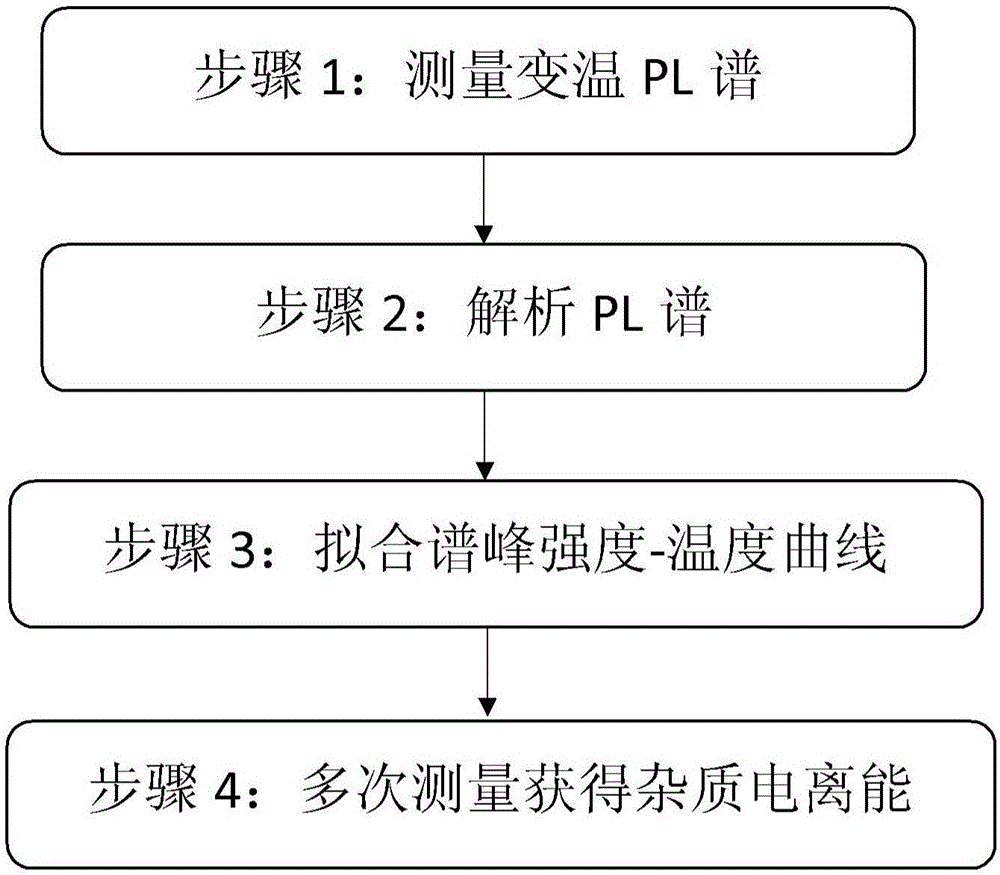
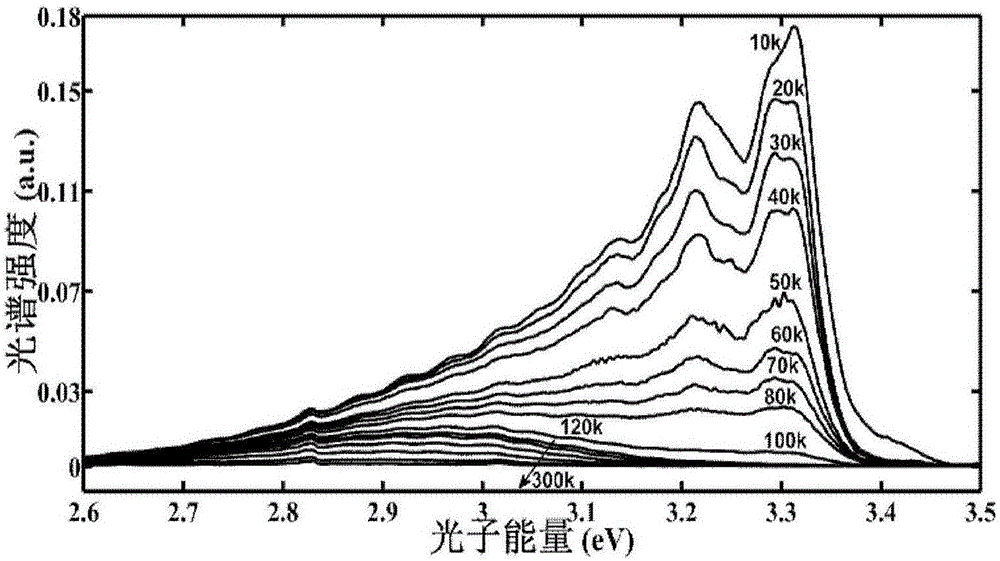
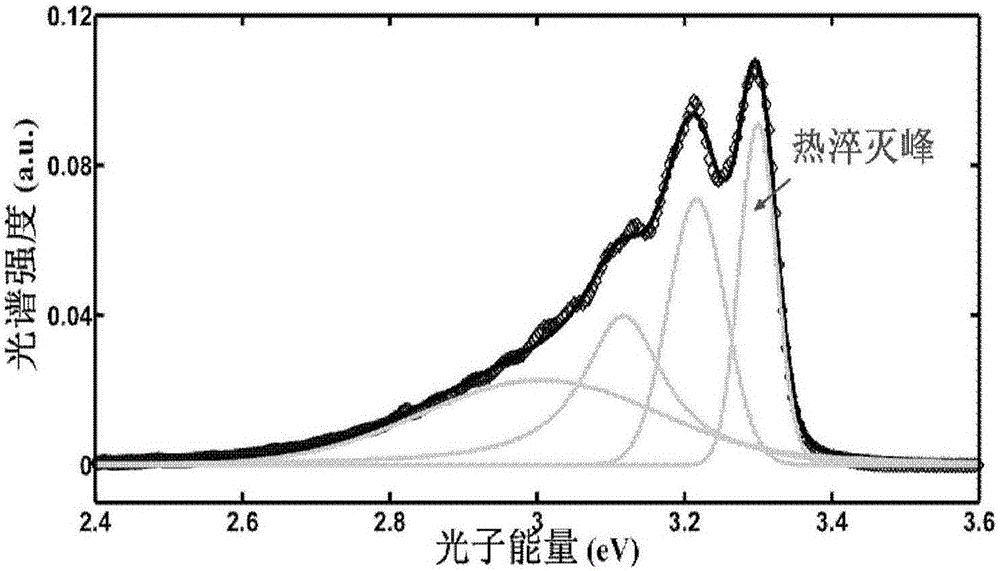
Nondestructive measurement method adopting heterotherm PL spectrum for obtaining semiconductor material impurity ionization energy
InactiveCN106841146AOvercoming complex and lossy technical shortcomingsHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescenceSemiconductor materialsPeak fitting
The invention discloses a nondestructive measurement method adopting a heterotherm PL spectrum for obtaining semiconductor material impurity ionization energy. By analyzing the thermal quenching behavior of a semiconductor material that the heterotherm PL spectrum peak intensity is lowered along with increase of temperature, the impurity ionization energy of the semiconductor material is obtained. The method comprises the specific steps that 1, the heterotherm PL spectrum of the semiconductor material to be measured is measured; 2, the thermal quenching peak intensity of the semiconductor material to be measured under different temperatures is obtained through spectrum peak fitting; 3, fitting is performed on thermal quenching peak spectrum strength-temperature relation experiment data, and the impurity ionization energy, including donor impurity ionization energy and acceptor impurity ionization energy, of the semiconductor material is obtained; 4, the steps 1-3 are executed repeatedly, the impurity ionization energy of the semiconductor material to be measured is measured repeatedly, and by adopting the least square method, the impurity ionization energy obtained after repeated measurement is calculated. The nondestructive spectrum analysis technology is utilized, the technical defect that an existing testing method is complex and destructive is overcome, and the method is rapid, easy and convenient to implement, high in precision and nondestructive to tested materials.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flight time mass spectrum peak fitting method
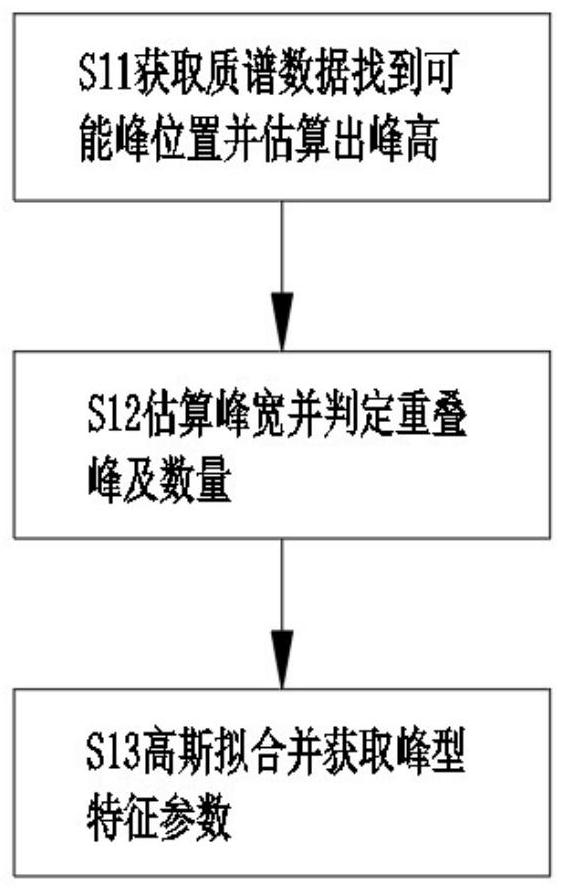
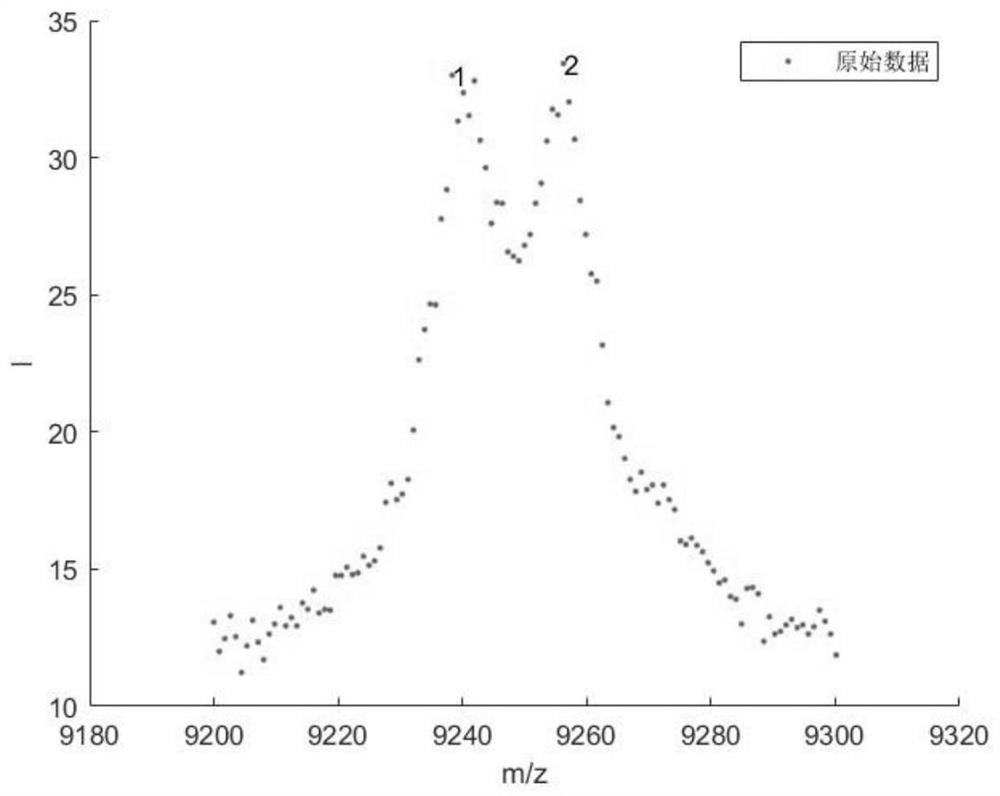
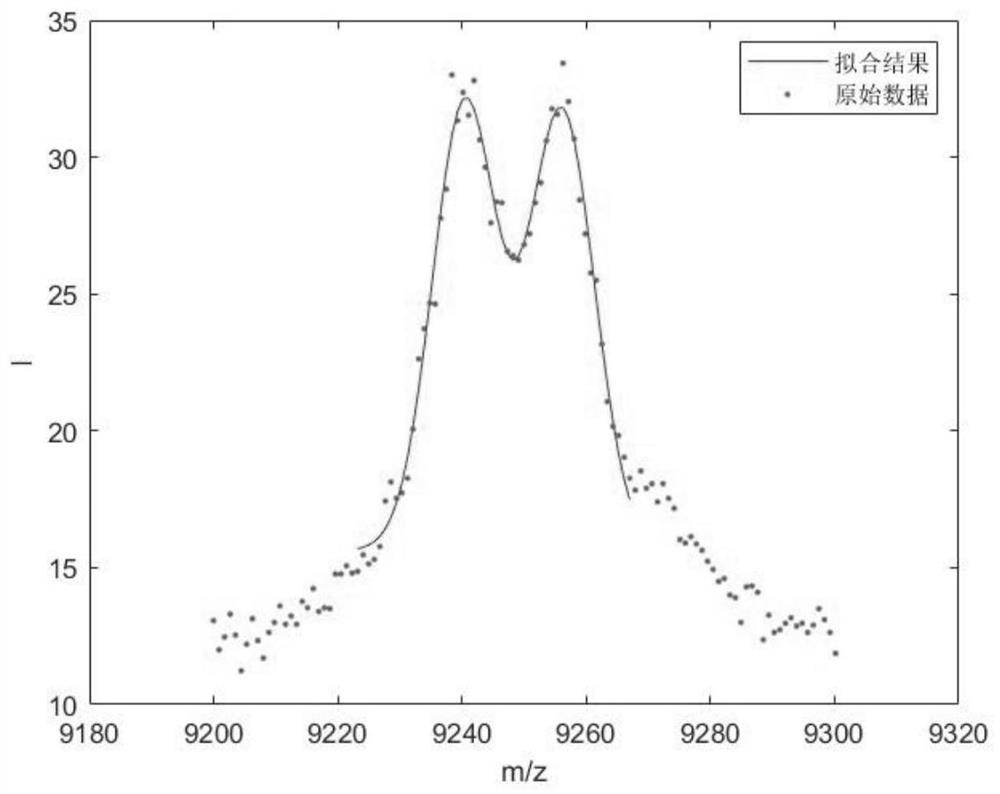
PendingCN114487072AGuaranteed accuracyOvercome the problem of increasing noise and affecting the signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansComplex mathematical operationsComputational physicsMass-to-charge ratio
The invention discloses a time-of-flight mass spectrum peak fitting method, which comprises the following steps of: segmenting a whole time-of-flight nucleic acid mass spectrum according to a certain interval length, and calculating an intensity threshold value and a second derivative threshold value of each segment: finding a first derivative of an ion intensity zero crossing point in each segment, and determining a possible Gaussian peak position; selecting ion strength meeting conditions from possible Gaussian peak positions to obtain determined Gaussian peak positions, and determining the number l of all Gaussian peaks and the mass-to-charge ratio m / zi and peak height Hi of the Gaussian peaks; according to a semi-empirical formula, calculating to obtain the peak width Wi of a Gaussian peak; taking the mass-to-charge ratio m / zi and the peak width Wi of the Gaussian peak, and taking 4Wi as a Gaussian fitting region, and taking the Gaussian fitting region as an iterative initial value of a Gaussian peak least square method; and substituting the nucleic acid mass spectrum data of all sampling points in the Gaussian fitting area 4Wi into the Gaussian fitting function f (xi) for iterative solution to obtain the mass-to-charge ratio m / zfit, the peak width Wfit and the peak height Hfit of an accurate fitting Gaussian peak.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DIGENA DIAGNOSTIC TECH CO LTD
Differential scanning calorimetry DSC curve peak-splitting fitting method
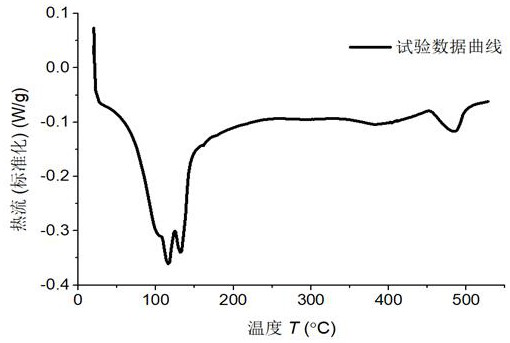
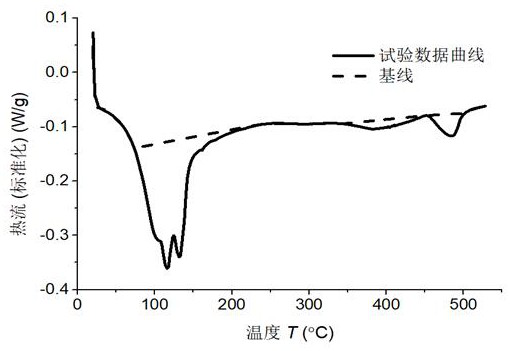
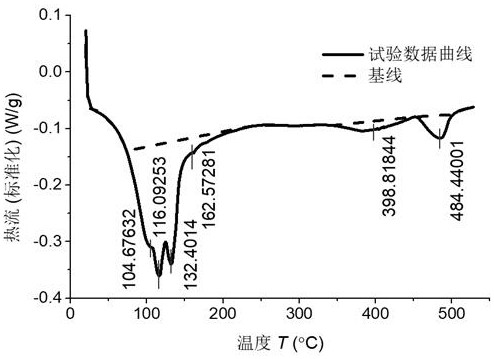
PendingCN111781240AImprove calculation accuracyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial heat developmentHeat flowTemperature curve
The invention discloses a differential scanning calorimetry DSC curve peak-splitting fitting method. According to the method, a heat flow rate-temperature curve is drawn by utilizing DSC test data; determining a baseline required for calculating the peak area; determining the position of a possible endothermic (exothermic) peak tip; according to the base line and the peak tip position, a Bigaussian function is adopted to perform peak division on the coincident peaks; dividing substance types to which different peaks belong according to peak temperature positions of measured substances, superposing the different peaks of the same type of substances to obtain peak areas of the substances, calculating enthalpy change values according to the peak areas, and obtaining concentrations of the substances according to the enthalpy change values. According to the method, the overlapping peaks of the DSC curve can be well distinguished so that the concentration of each substance is accurately calculated, and the calculation precision of the concentration of an erosion product is greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
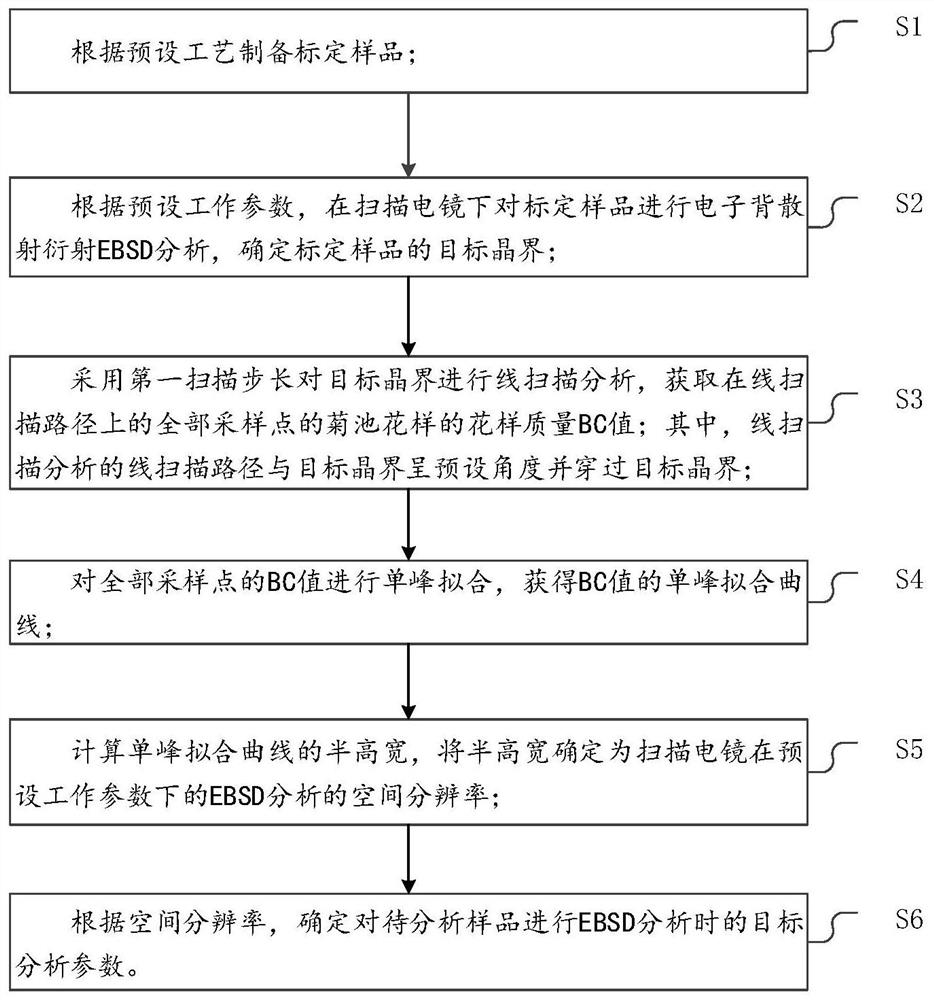
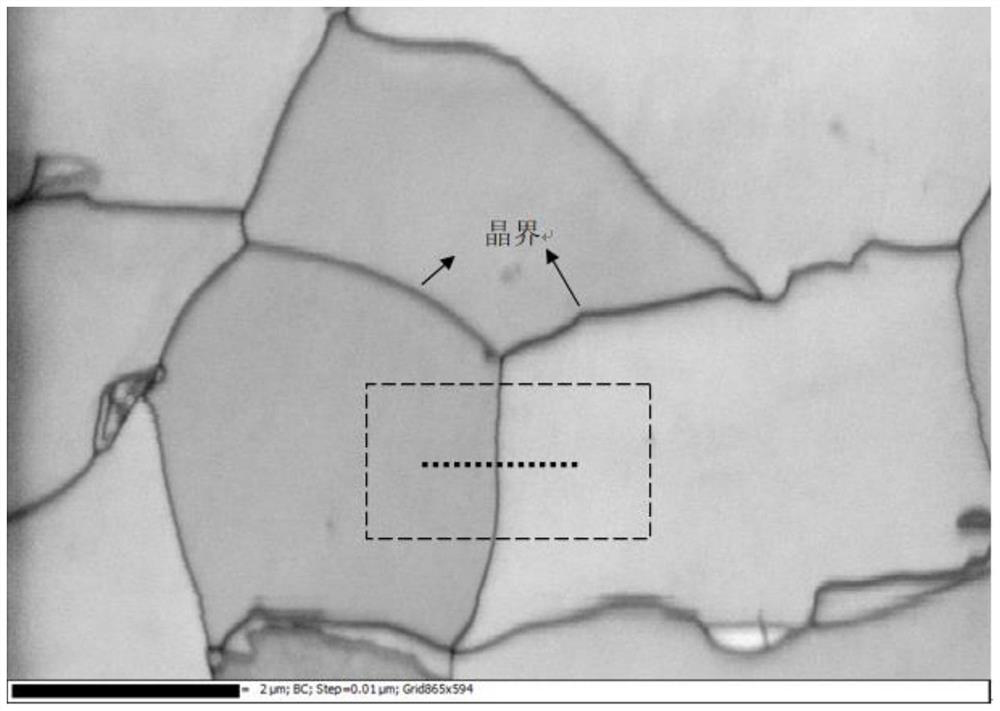
Analysis method of electron backscatter diffraction
PendingCN111678932AImprove accuracyEasy for quantitative analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTesting metal structuresImage resolutionPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses an analysis method of electron backscatter diffraction. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a calibration sample according to a preset process,according to preset working parameters, performing electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) analysis on the calibration sample under a scanning electron microscope, and determining a target grain boundary of the calibration sample, carrying out line scanning analysis on the target grain boundary by adopting afirst scanning step length to obtain pattern quality BC values of the chrysanthemum pool patterns of all sampling points on an online scanning path,carrying out single-peak fitting on all the BC values to obtain a single-peak fitting curve of the BC values,determining the full width at half maximum of thesingle-peak fitting curve, and determining the full width at half maximum as the spatial resolution of EBSD analysis of the scanning electron microscope under preset working parameters,and accordingto the spatial resolution, determining a target analysis parameter when the to-be-analyzed sample is subjected to EBSD analysis. According to the method, the spatial resolution of the EBSD under the current working parameters can be analyzed more conveniently and quickly, and the EBSD analysis accuracy of the to-be-analyzed sample is improved on the basis.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Rare metal prospecting method based on ground object hyperspectral remote sensing mineral combination zoning
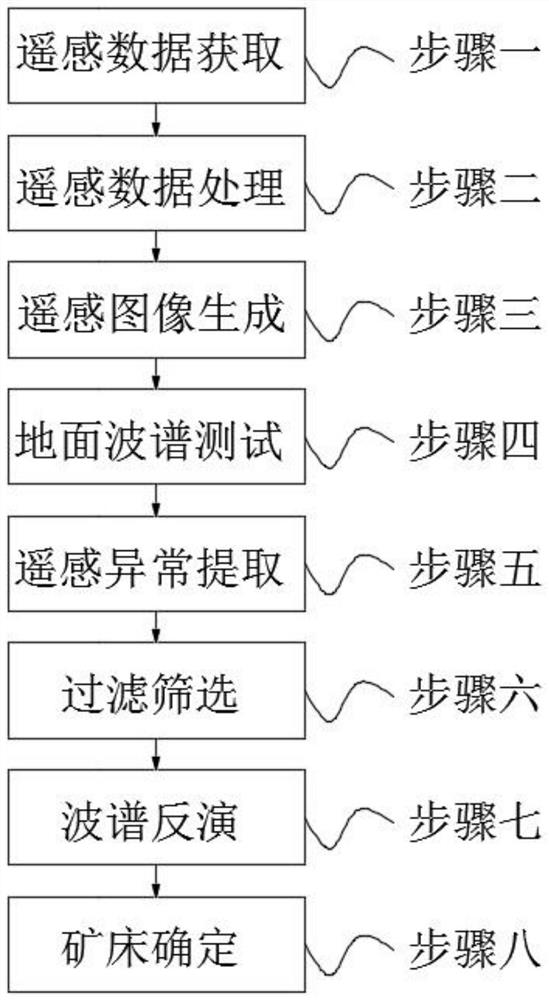
InactiveCN113189020AImprove inversion accuracyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisGeophysicsPeak fitting
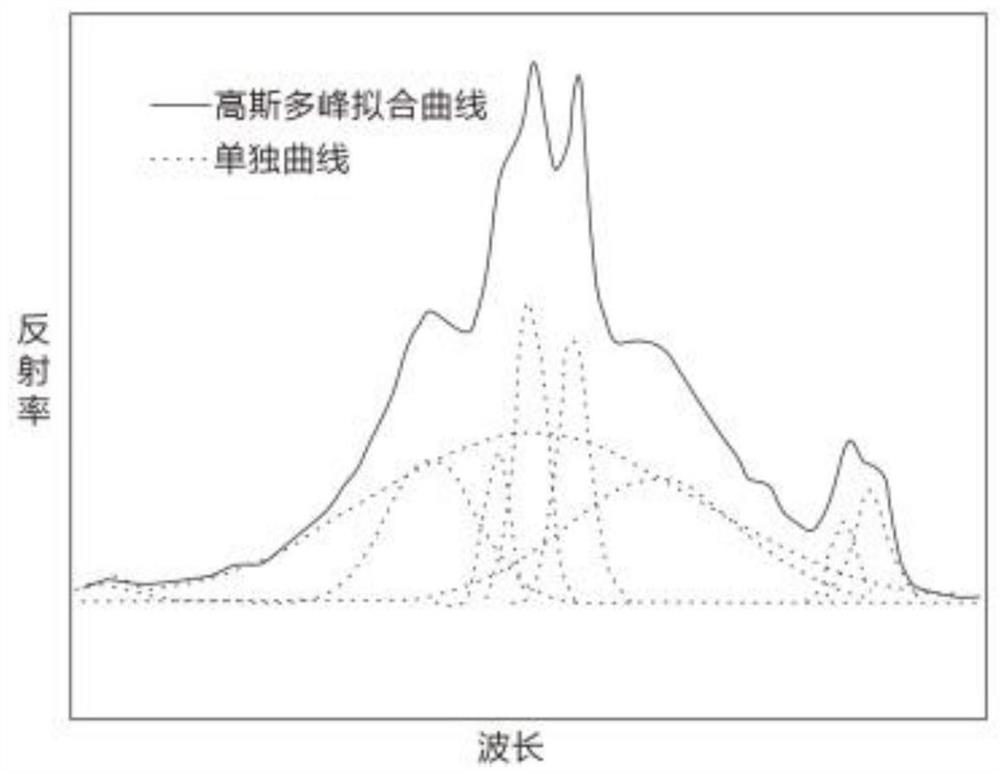
The invention discloses a rare metal prospecting method based on ground object hyperspectral remote sensing mineral combination zoning. The rare metal prospecting method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring remote sensing data; step 2, remote sensing data processing; step 3, remote sensing image generation; step 4, testing a ground spectrum; step 5, remote sensing anomaly extraction; step 6, filtering and screening; step 7, carrying out wave spectrum inversion; step 8, determining an ore deposit; according to the method, multiple absorption peaks of a ground feature spectral curve are determined through Gaussian multi-peak fitting, mineral combination information extraction is carried out, the inversion precision of ground feature spectral absorption characteristics on a remote sensing image can be improved, meanwhile, the ASD spectral curve of a real sample in a working area is compared with ASD spectral curves of different minerals in a USGS standard mineral library, the zoning features of different types of ore deposits can be obtained, interference factors and abnormal information are removed by performing abnormal screening and filtering on the remote sensing image, and the accuracy of the remote sensing image can be improved.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
A spectral analysis method based on Gaussian multi-peak fitting
ActiveCN107462535BHigh affinityKeep valid informationColor/spectral properties measurementsComplex mathematical operationsMixed spectrumGaussian function
The invention discloses a Gaussian multi-peak fitting-based spectrum analysis algorithm. The Gaussian multi-peak fitting-based spectrum analysis algorithm comprises the following steps: determining an absorption fitting function containing an undetermined Gaussian feature parameter, performing mathematical modeling on fitting error, determining center coordinate and iteration step of an iteration initial value, continuously performing iteration, performing comparison and changing the iteration step length until the optimal fitting error is obtained, and reversely deducing the center coordinate value, namely the to-be-determined feature parameter, of the corresponding division unit by the optimal fitting error, and determining the absorption fitting function so as to decompose the mixed spectrum into a plurality of sub-peaks. The Gaussian multi-peak fitting-based spectrum analysis algorithm has the following advantages: a Gaussian function curve and a spectroscopic data curve have high affinity and can express parameters, such as peak shape, peak height and peak position in the spectrogram, with clear physical significance; and the mixed absorption spectrum curve is decomposed into a plurality of Gaussian function curves, the effective information of the original spectrum data can be remained, the original spectrum data is unified into a small amount of uniquely determined Gaussian feature parameters, and the aims of simplifying the spectrum data and researching the refined structure are fulfilled.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for rapidly identifying oxidation degree of peony seeds and secondary protein structures
InactiveCN106338489AReduce dosageReduce experiment costMaterial analysis by optical meansStructure analysisOriginal data
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying oxidation degree of peony seeds and secondary protein structures. The method comprises the steps that FTIR scanning is conducted on peony seed oil by adopting an in-situ method, drawing is performed according to obtained FTIR original data, characteristic peak position, absorbance specific value and Gaussian multi-peak fitting analysis is conducted on an original graph to obtain the percentage of the oxidation degree of peony seeds and the secondary protein structures. The method has the advantages that 1, oxidation degree analysis can be directly conducted on an oil sample, the sample usage amount is small, other chemical reagents are not needed, and the experiment costs are remarkably saved; 2, secondary structure analysis can be directly conducted on the protein in the oil sample without extraction and purification, the work amount can be remarkably reduced, an experimental period can be shortened, and the research efficiency can be improved; 3, data acquisition and analysis are performed based on an FTIRpower-spectral method, characteristic peak-to-peak type, an absorbance specific value and Gaussian multi-peak fitting according to the method, and the method is simple, effective, high in accuracy and strong in data persuasion.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY & FRUIT TREE WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI & TECH
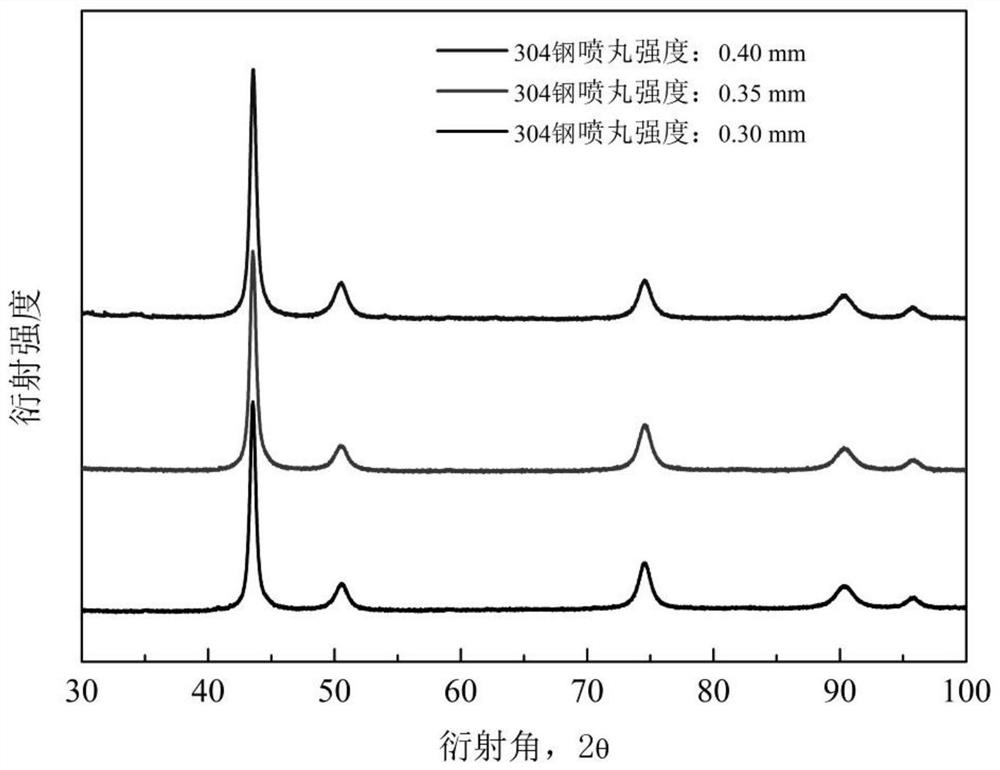
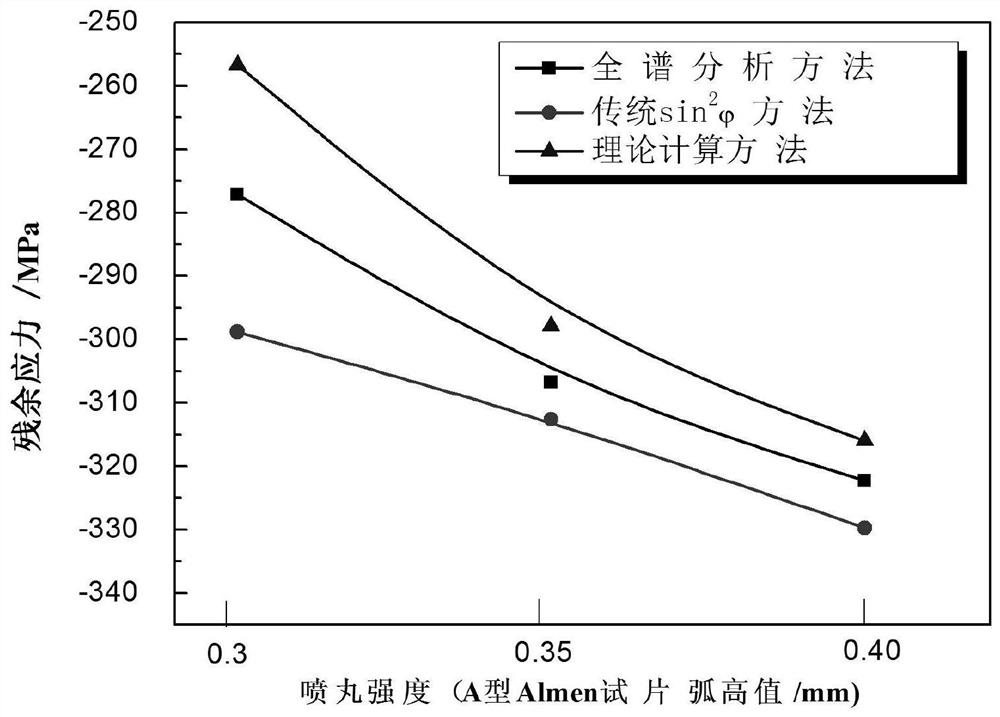
Method for measuring residual stress of polycrystalline material in X-ray diffraction full-spectrum multi-peak fitting mode
PendingCN112729647AAvoid influenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationApparatus for force/torque/work measurementPolycrystalline materialRay
The invention provides a method for measuring residual stress of a polycrystalline material in an X-ray diffraction full-spectrum multi-peak fitting mode. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining plane strain of a polycrystalline material by utilizing an X-ray diffraction full-spectrum spectral line of the material and adopting a multi-peak fitting mode on the basis of considering polycrystalline grain orientation, and combining the stress-strain relationship of the polycrystalline material on the basis, and finally calculating the residual stress value of the polycrystalline material. According to the method, multiple pieces of diffraction peak information are adopted in the material strain calculation process, the grain orientation of the polycrystalline material is considered, the influence of preferred orientation of the polycrystalline material on a traditional X-ray diffraction stress analysis method is avoided, and the convenient and rapid method is provided for measuring the residual stress of the polycrystalline material.
Owner:宁波经略海洋科技有限公司
A Measuring Method of Crystal Rocking Curve Based on Energy Resolution Detector
InactiveCN105866151BExtended energy rangeRealize measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRocking curvePower flow
The invention relates to a crystal rocking curve measurement method based on an energy resolution detector, comprising the steps of 1, selecting an X-ray tube anode target material and voltage / current parameters based on an X-ray energy range {E} for measurement; 2, determining a Bragg diffraction angle range {theta B}, a crystal rotation angle range {theta T} and a rotation stepping angle; 3, measuring a crystal diffraction energy spectrum of each rotation angle within the {theta T}; 4, correcting the effect of scattering factors in the crystal diffraction energy spectrums; 5, extracting the diffraction strength of X-ray of energy Ej in {E} within a unit interval when theta Ti = theta Bi, so as to obtain a strength variation curve of Ej; 6, performing diffraction peak fitting on the strength variation curve; 7, figuring out a first-order derivative of a fitted diffraction peak, selecting absolute values of a part of the diffraction peak where the slope of the first-order derivative is not less than 0, i.e., the left and right branches of a rocking curve, and splicing to obtain the rocking curve of Ej; 8, repeating steps 5-7 until {E} is traversed, thereby obtaining the rocking curve of the X ray of all energies in {E} to a certain lattice plane of a crystal.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
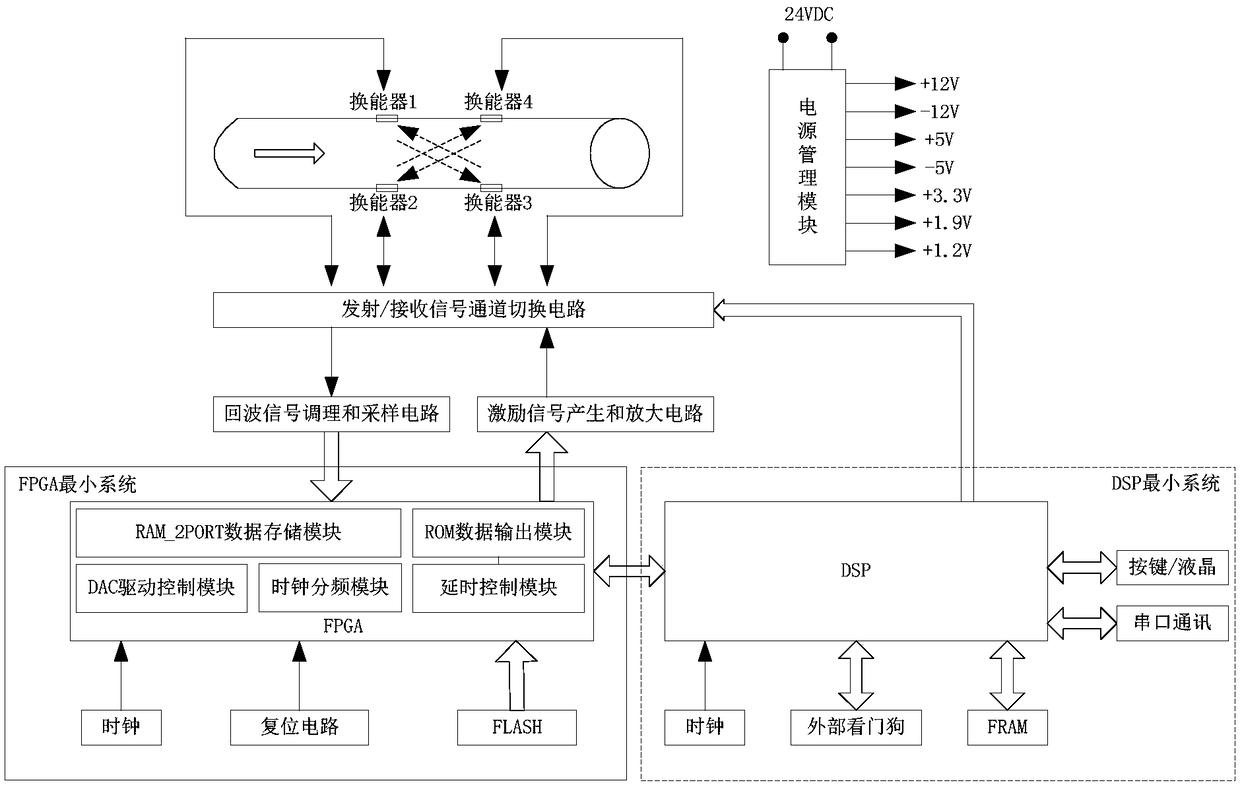
Signal processing method of gas ultrasonic flowmeter based on echo rising segment peak fitting and echo energy point positioning
The invention provides a gas ultrasonic flowmeter signal processing method based on echo ascent stage peak value fitting. The method includes the steps that firstly, multiple peak value points are selected at the ascent stage of echo signals according to the fitting peak value range; all the peak value points are subjected to least square fitting, and a feature straight line is obtained; intersections of the straight line and transverse axis sampling points serve as feature points, the downcurrent and countercurrent propagation time of ultrasonic signals is determined, and the gas flow is calculated. A gas ultrasonic flowmeter signal processing method based on echo energy point positioning includes the steps that firstly, energy values for positioning energy points serve as reference, and four most-adjacent peak value energy points are found for linear fitting; the energy points, corresponding to the energy values, on a fitting straight line are found as feature points, the downcurrent and countercurrent propagation time of the ultrasonic signals is determined, and the gas flow is calculated.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
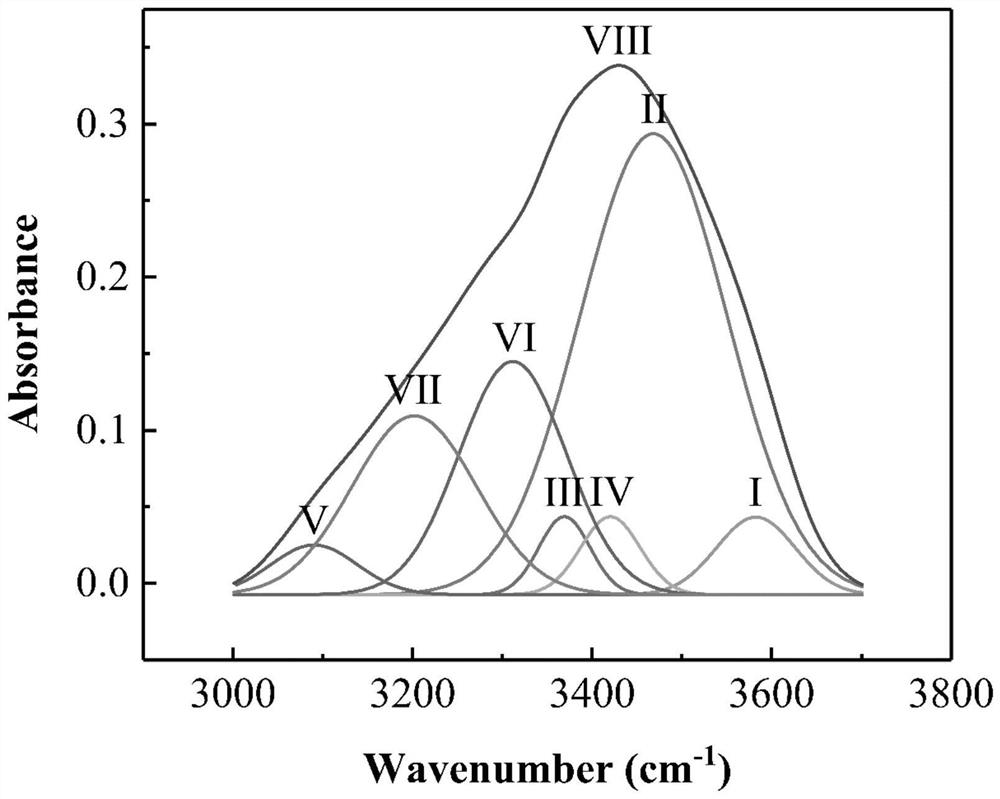
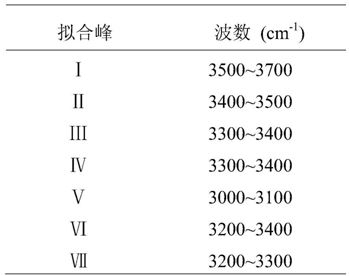
A Calculation Method of Infrared Fitting Calculation of Chitosan Deacetylation Degree
ActiveCN110514615BGuaranteed accuracyThe calculation formula is simpleMaterial analysis by optical meansFt ir spectraCalculation methods
The invention discloses a calculation method for calculating the deacetylation degree of chitosan by infrared fitting. After correcting the infrared spectrogram curve of the chitosan to be measured, carry out peak fitting according to the wave number of different functional group positions, and account for 3700-3000cm by the area of each fitting peak ‑1 The deacetylation degree of chitosan can be obtained by simple addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of the percentage of chitosan infrared spectrum peak area to be measured within the range. Adopt the method of the present invention to divide the peak to fit the infrared spectrum of chitosan, can correctly reduce each functional group of chitosan at 3700-3000cm ‑1 The independent vibration of the chitosan to be tested can be obtained to obtain the number of hydroxyl groups and amino groups contained in the chitosan to be tested, and finally the degree of deacetylation of the chitosan to be tested can be calculated. The calculation formula of the invention is simple, the result is accurate, the deacetylation degree of the chitosan can be calculated and checked, and the invention can be applied to the quality inspection department to quickly test samples.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
A Calculation Method of Carbon-Oxygen Ratio for Determining Remaining Oil Saturation
InactiveCN105673006BImprove responsivenessReduce the impact of calculating the carbon-to-oxygen ratioBorehole/well accessoriesResponse sensitivityOxygen
The invention discloses a carbon-oxygen ratio calculation method used for determining remaining oil saturation. Firstly, a Gaussian and linear dual model is used for fitting and actually measuring carbon and oxygen energy peaks of inelastic gamma-ray spectrum data, and characteristic peak fitting coefficients are obtained; then, the same fitting model is used for fitting energy peaks corresponding to carbon and oxygen standard gamma-ray spectra; the ratio of height of measurement spectrum carbon peak Gaussian components and height of standard spectrum carbon peak Gaussian components is multiplied by the total number of carbon element standard spectra, so that inelastic gamma-ray generated by a carbon element is counted; the ratio of height of measurement spectrum oxygen peak Gaussian components and height of standard spectrum oxygen peak Gaussian components is multiplied by the total number of oxygen element standard spectra, so that inelastic gamma-ray generated by an oxygen element is counted; the two numbers are divided to generate the carbon-oxygen ratio. The method reduces influences of gamma-ray generated by other elements on the carbon-oxygen ratio, and improves response sensitivity of the carbon-oxygen ratio to oil saturation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com