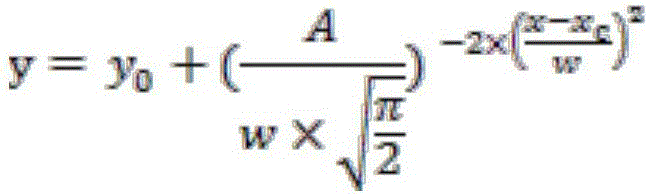Method of analyzing protein secondary structure in peony on the basis of infrared spectroscopy and Gauss multi-peak fitting
A technology of secondary structure and analysis method, applied in the field of spectral analysis, can solve the problems of long period, narrow data coverage, high cost, and achieve the effects of high accuracy, shortened experimental period, and strong data convincing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Identification and analysis of protein secondary structure in peony
[0023] The dried peony root sample was ground into powder, and the potassium bromide tablet method was used for FTIR scanning. Perform Gaussian single-peak fitting on the original spectrum, and then perform Gaussian multi-peak fitting on the fitted single peak according to the peak positions of the characteristic peaks of different protein secondary structures, and calculate the percentage of various protein secondary structures in the sample according to the peak area.
[0024] The specific operation method is as follows:
[0025] (1) Take 1-2 mg of dried peony root and 200 mg of dried KBr and grind it into a uniform fine powder (about 2 μm in diameter) to avoid the influence of scattered light. Put the bottom mold into the mold cavity (note that the polished side is upward), add a small amount of sample to the mold core, scrape the sample in the mold with a medicine spoon, and make the c...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Protein secondary structure analysis in peony root
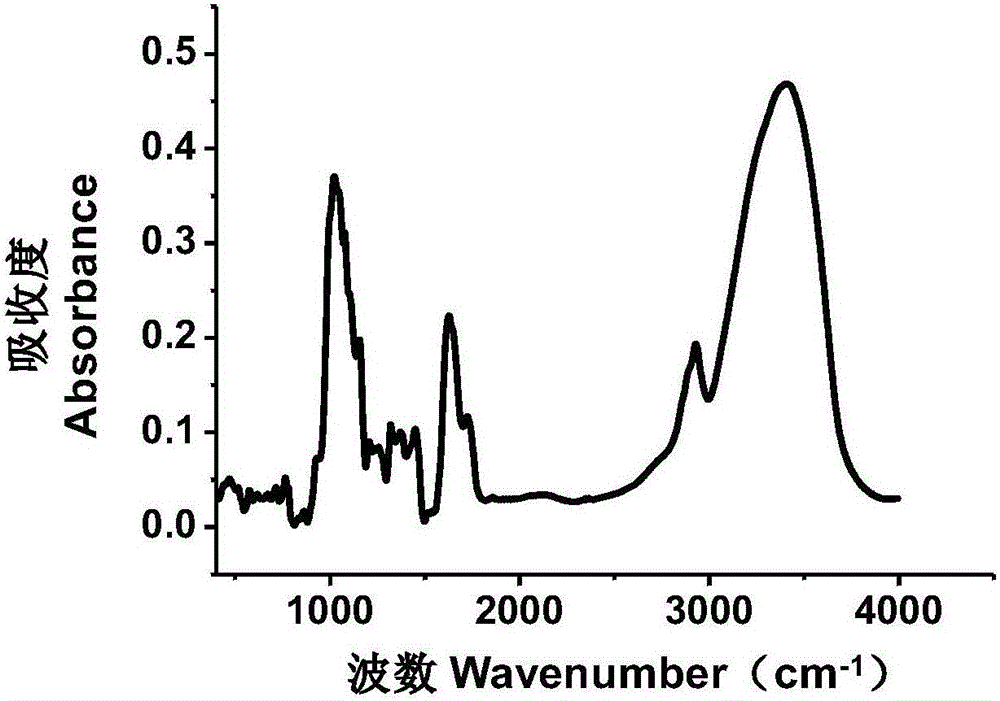
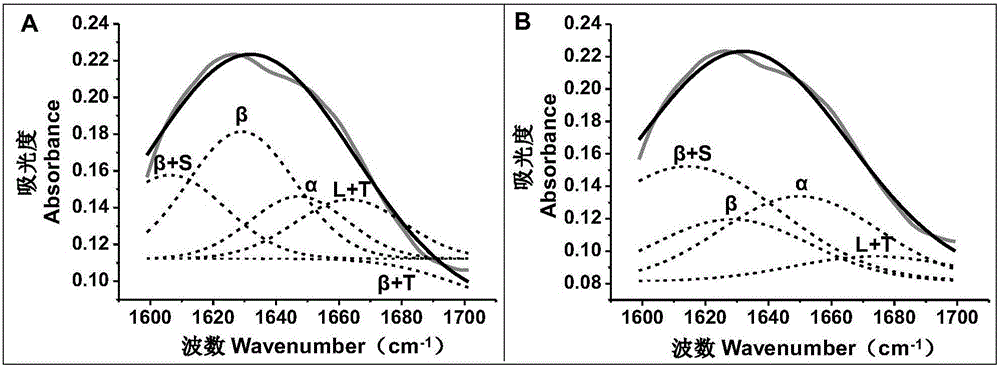
[0030] The operation steps described in Example 1 were selected to analyze the secondary structure of the protein in the peony root. The FTIR curve of peony root is as follows figure 1 As shown, it shows that there is a peak of amino I in peony root, that is, at 1600-1700cm -1 There is an infrared absorption peak. For 1600-1700cm -1 spectrogram ( figure 2 The gray solid line in Figure A and Figure B) is used for Gaussian unimodal fitting, and the results are as follows figure 2 As shown by the solid black lines in Figures A and B, the fitting equation is:
[0031] y = y 0 + ( A w × π 2 ) - ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3: Analysis of protein secondary structure in peony branches
[0037] Dry peony branch is ground into powder, and specific operation method is according to the operation method of embodiment 1. FTIR results of peony branches show at 1600-1700cm -1 There is an infrared absorption peak at , and its Gaussian single-peak fitting equation is:
[0038] y = y 0 + ( A w × π 2 ) - 2 × ( x - x c w ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com