Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "N-linked glycosylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
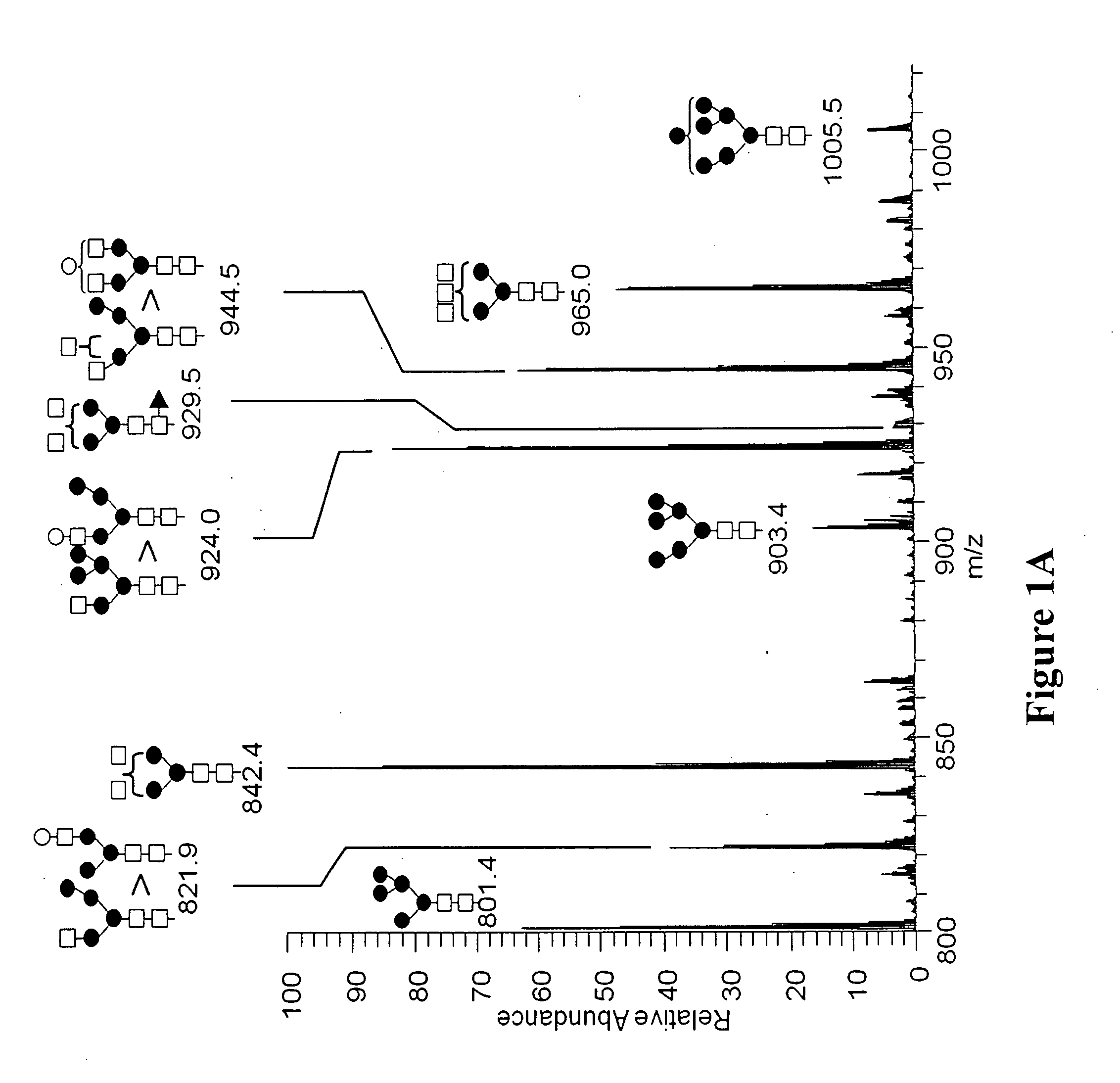
N-linked glycosylation, is the attachment of an oligosaccharide, a carbohydrate consisting of several sugar molecules, sometimes also referred to as glycan, to a nitrogen atom (the amide nitrogen of an asparagine (Asn) residue of a protein), in a process called N-glycosylation, studied in biochemistry. This type of linkage is important for both the structure and function of some eukaryotic proteins. The N-linked glycosylation process occurs in eukaryotes and widely in archaea, but very rarely in bacteria. The nature of N-linked glycans attached to a glycoprotein is determined by the protein and the cell in which it is expressed. It also varies across species. Different species synthesize different types of N-linked glycan.
Erythropoietin compositions
Methods and materials are provided for the production of compositions of erythropoietin protein, wherein said compositions comprise a pre-selected N-linked glycosylation pattern as the predominant N-glycoform.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against Bacillus anthracis infection
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based anthrax vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding Bacillus anthracis antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the B. anthracis antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. In certain embodiments, the coding regions are also modified so as to remove potential N-linked glycosylation sites. B. anthracis antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to protective antigen (PA), lethal factor (LF), and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to B. anthracis in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized B. anthracis antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized B. anthracis antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
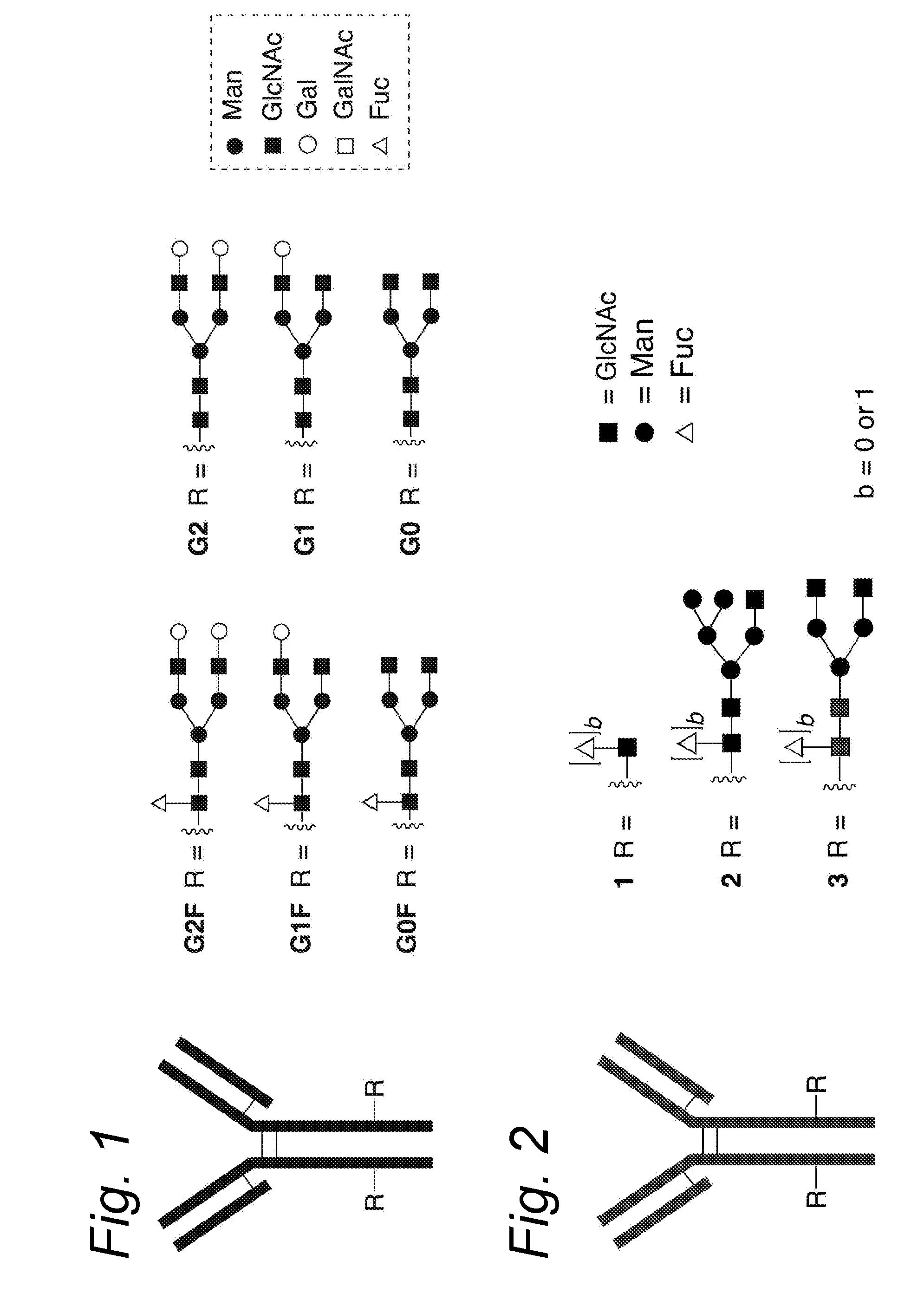
Glycoengineered antibody, antibody-conjugate and methods for their preparation
PendingUS20160235861A1Enhanced lipophilic interactionImprove stabilityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHeavy chainAntibody conjugate
The invention relates to glycoengineered antibodies and antibody-conjugates. In particular, the invention relates to an antibody conjugate, prepared from IgG antibody comprising at least two N-linked glycosylation sites on the combination of a single heavy chain and single light chain. The invention further relates to methods for the preparation of the antibody-conjugates according to the invention. In particular, the invention relates to an antibody-drug conjugate that is conjugated to different toxins, and the a process for the preparation thereof.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
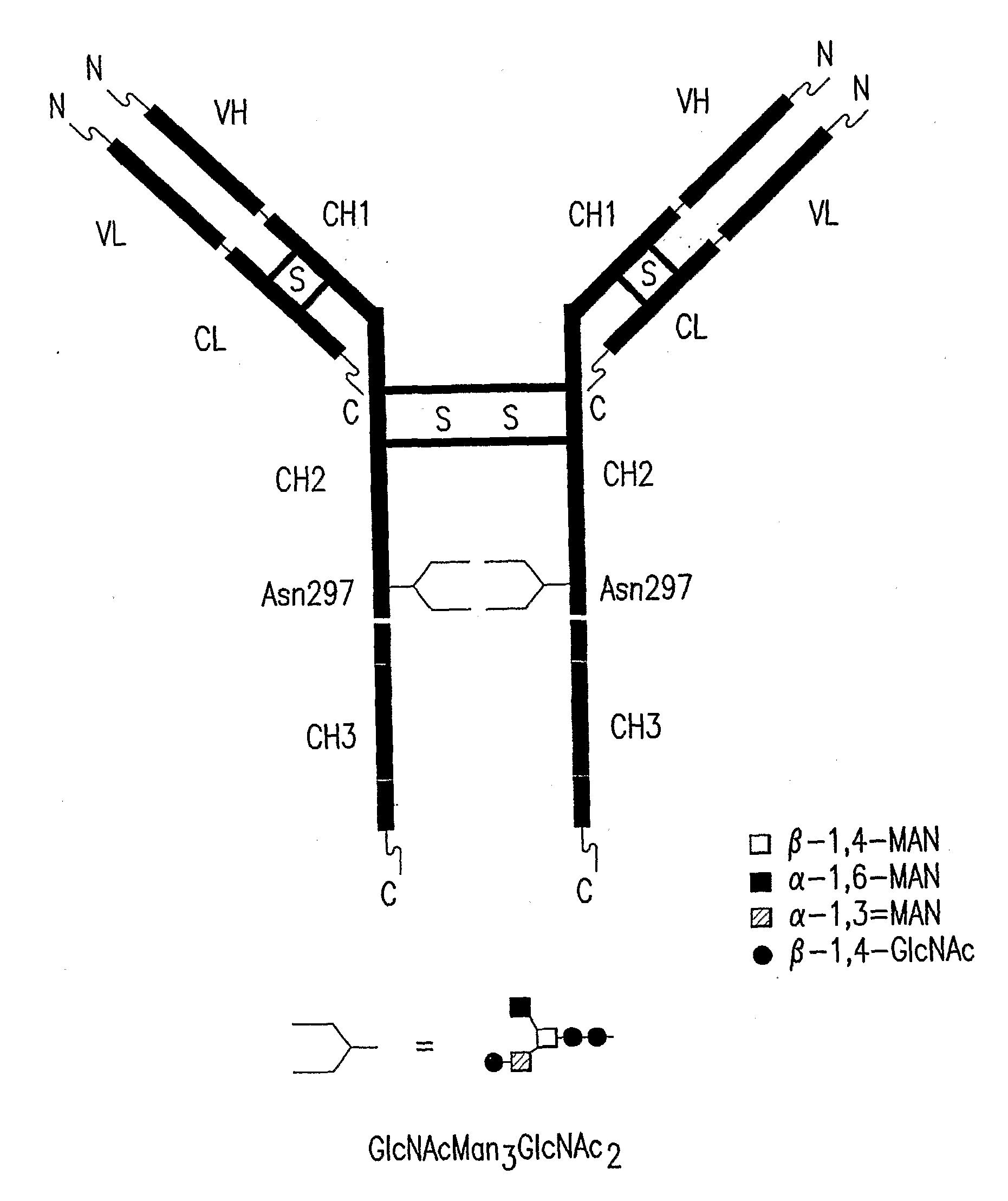
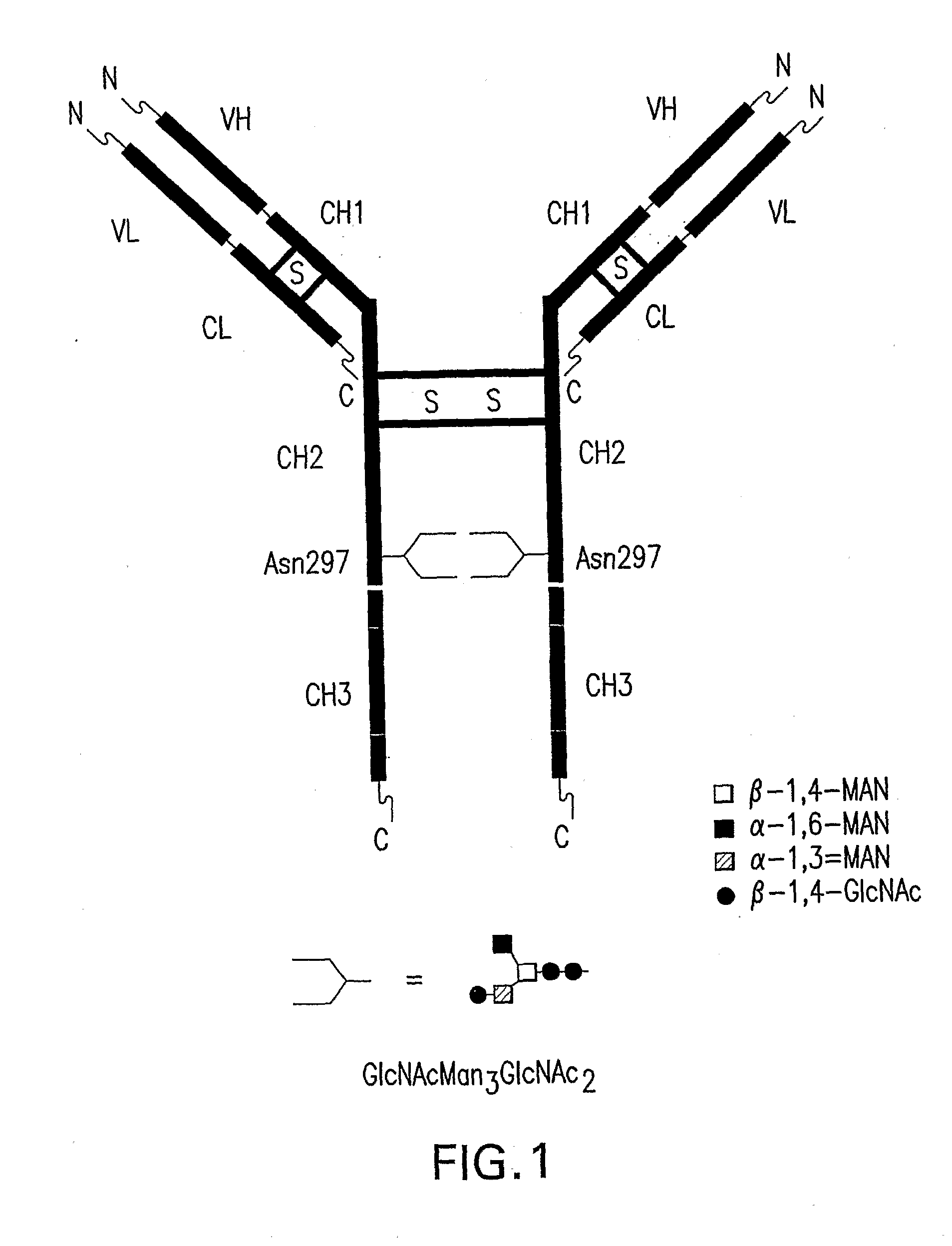
Immunoglobulins Comprising Predominantly a Glcnacman3Glcnac2 Glycoform
InactiveUS20090136525A1Improve bindingReduce the binding forceAnimal cellsAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulin FragmentsGlycan biosynthesis
Compositions and methods for producing compositions comprising immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin fragments having an N-linked glycosylation pattern consisting predominantly of the GlCNAcMan3GlcNAc2 N-glycan structure are disclosed. The GlCNAcMan3GlcNAc2 N-glycan structure effects an increase in binding to the FcγRiπ receptors and a decrease in binding to the FcγRH receptors.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Erythropoietin compositions
Methods and materials are provided for the production of compositions of erythropoietin protein, wherein said compositions comprise a pre-selected N-linked glycosylation pattern as the predominant N-glycoform.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Recombinant Method for Production of an Erythropoiesis Stimulating Protein
InactiveUS20090029907A1Increase the number ofHigh sialic acid contentPeptide/protein ingredientsRecombinant DNA-technologyErythroid cellBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to the recombinant method used for the production of a highly glycosylated form (in total five N linked glycosylations as opposed to three N linked glyosylations in the natural EPO) of erythropoietin. The added sites for glycosylation will result in greater number of carbohydrate chains, and higher sialic acid content than human EPO, which in turn would impart to the recombinant molecule a longer half-life. The invention further relates to the construction of expression cassettes comprising nucleic acid sequences encoding for the highly glycosylated form of Erythropoietin and stable expression in the host cells. The invention further relates to the optimized method for purification of the erythropoiesis stimulating protein. The recombinant EPO according to the invention, and the salts and functional derivatives thereof, may comprise the active ingredient of pharmaceutical compositions for an increase in the hematocrit for treatment of anemia and for restoration of patient well being and quality of life.
Owner:AVESTHAGEN
Composition comprising isolated human CTLA4-Fc fusion protein produced in a transgenic chicken
The invention encompasses among other things fusion proteins including Fc fusion proteins such as CTLA4-Fc having avian N-linked glycosylation patterns obtained from egg white of eggs laid by transgenic avians.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Recombinant ectodomain expression of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in yeast
The present invention provides Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) gD, gC, gB and / or gE recombinant glycoproteins having a particular pre-selected N-linked glycosylation pattern as the predominant N-glycoform. The present invention also provides methods of producing these recombinant glycoproteins in yeast, preferably Pichia pastoris, which may be glycoengineered to provide particular glycosylation patterns. The present invention further provides vaccines comprising gD and gC, and optionally gB and / or gE, at least one of which has a particular pre-selected N-linked glycosylation pattern as the predominant N-glycoform. The recombinant glycoproteins are produced by a method which, in one embodiment, comprises transforming a yeast of the genus Pichia with an expression vector containing a DNA encoding an HSV glycoprotein, which is under regulation of a promoter functional in a yeast of the genus Pichia, culturing the yeast in a medium, and recovering the recombinant glycoprotein from the obtained culture. DNA encoding the recombinant glycoproteins is preferably codon-optimized to achieve optimal expression in Pichia.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
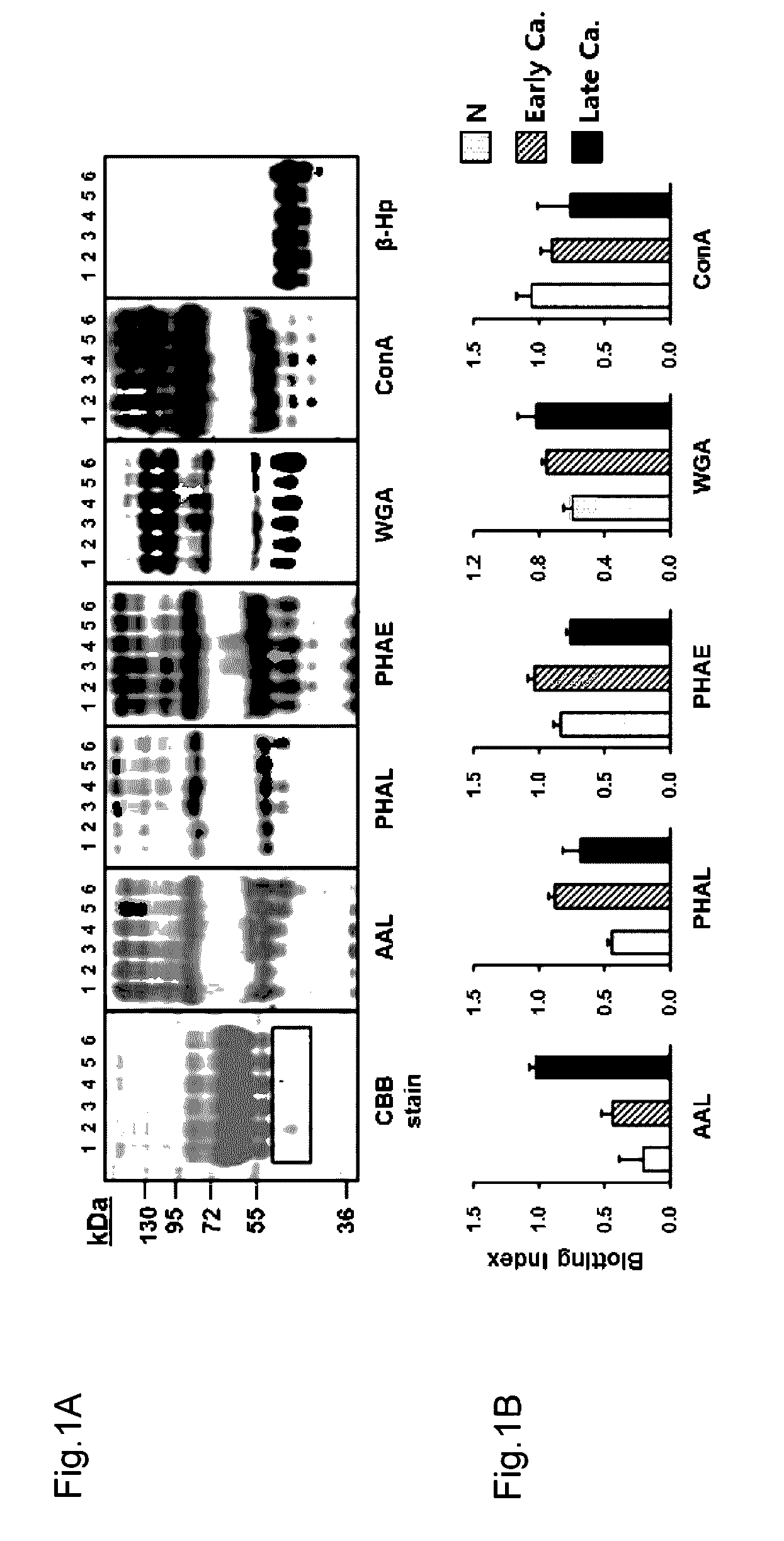
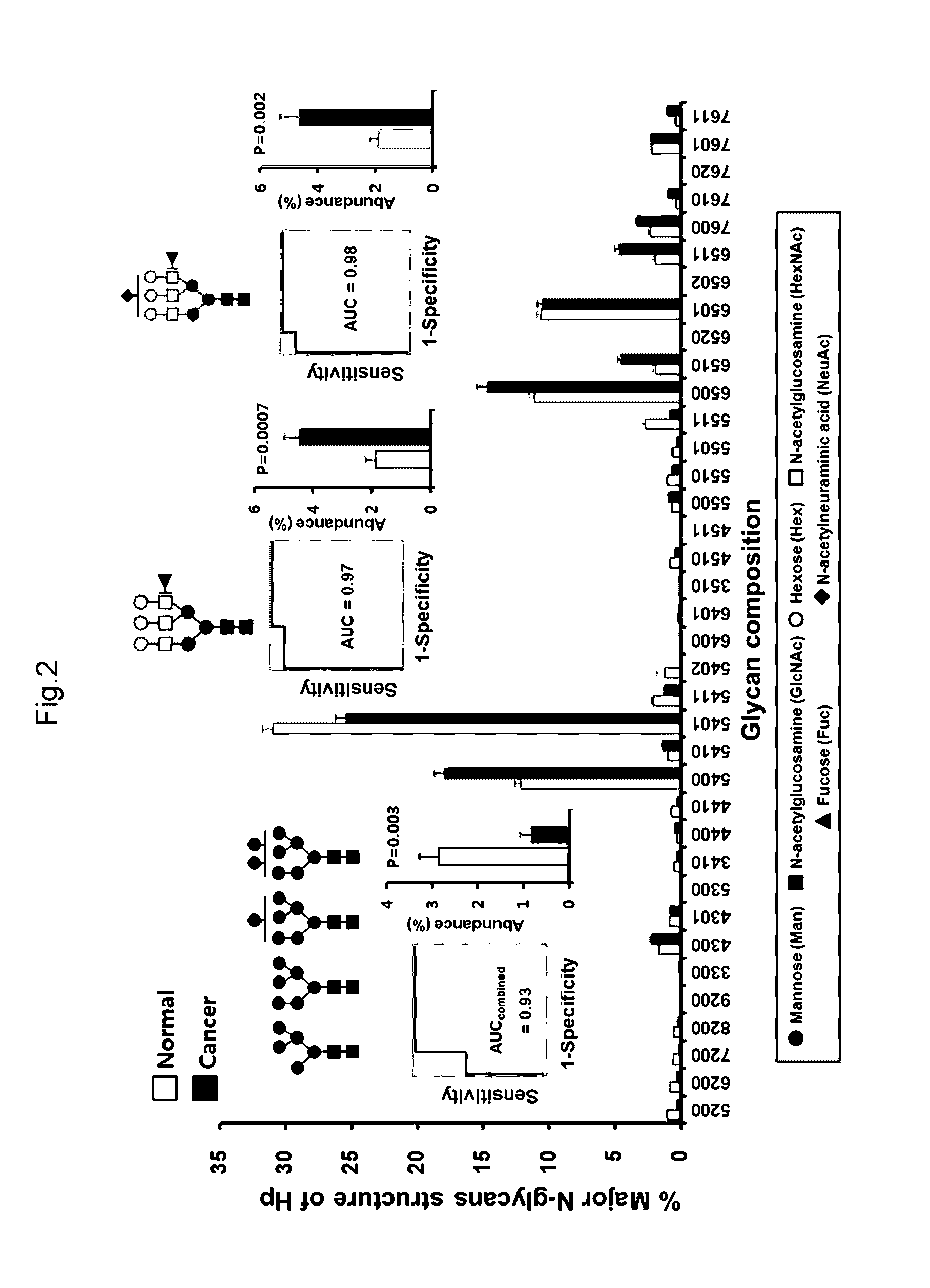
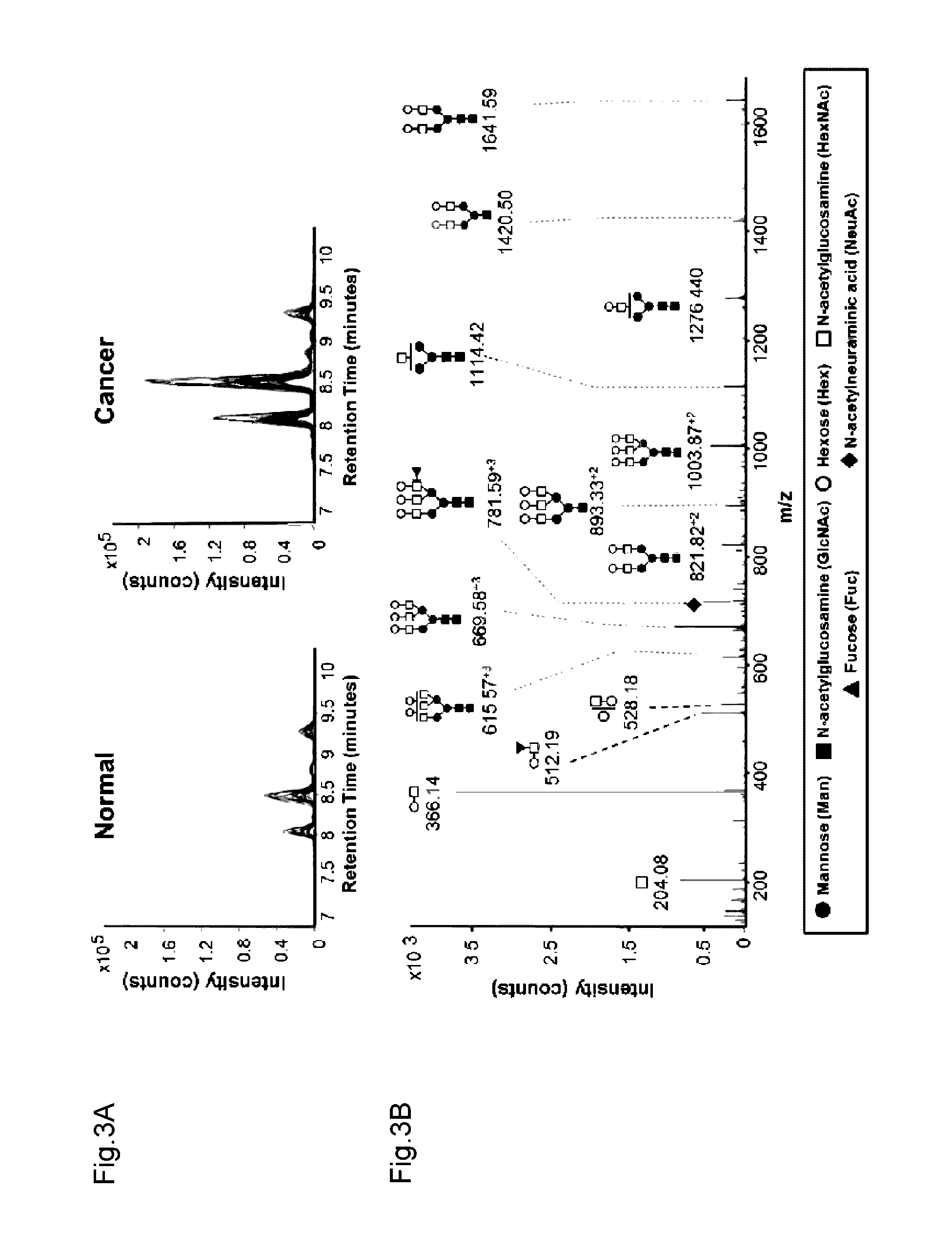
Novel method for gastric cancer diagnosis
InactiveCN106029906AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFucosylationHigh mannose
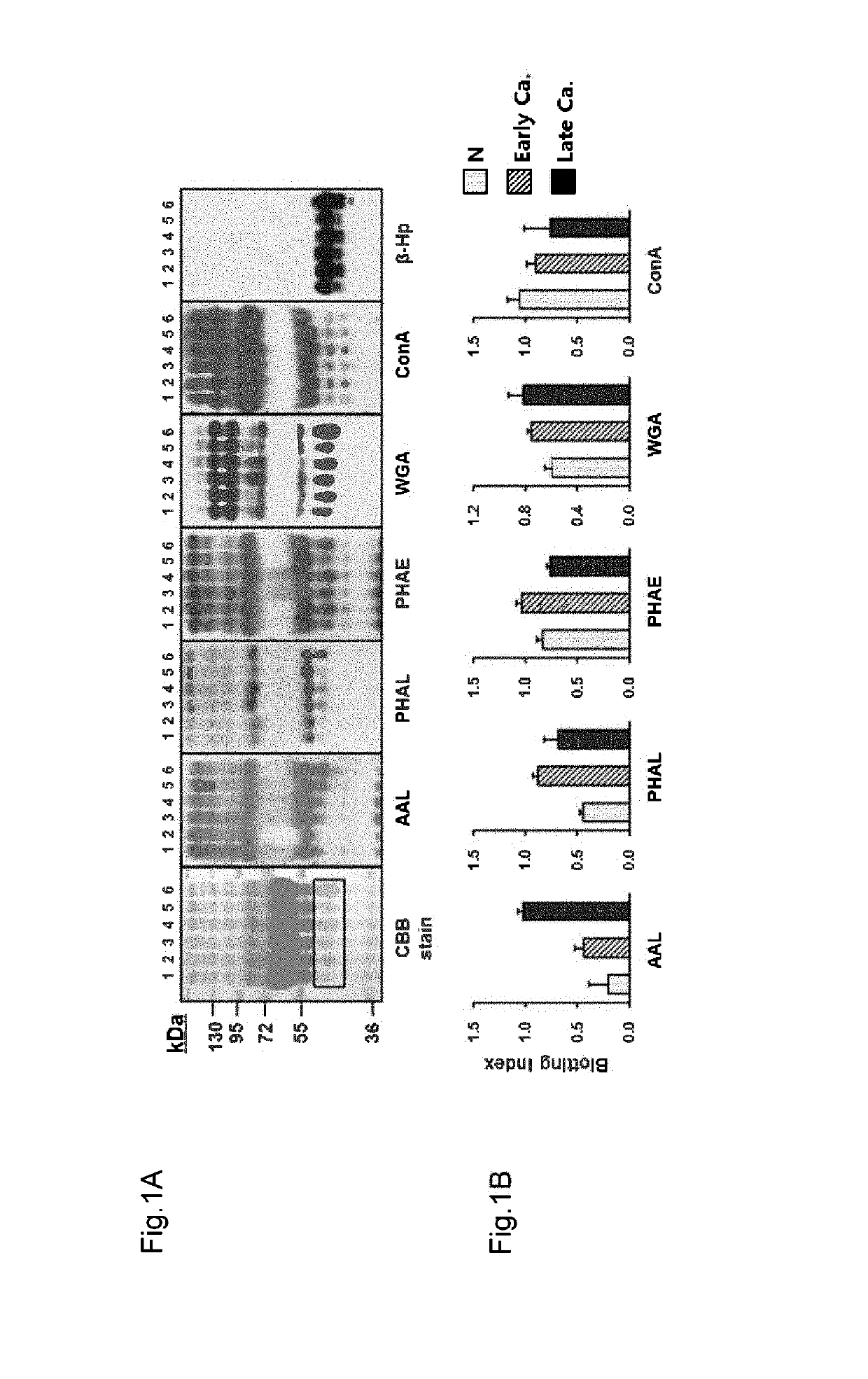
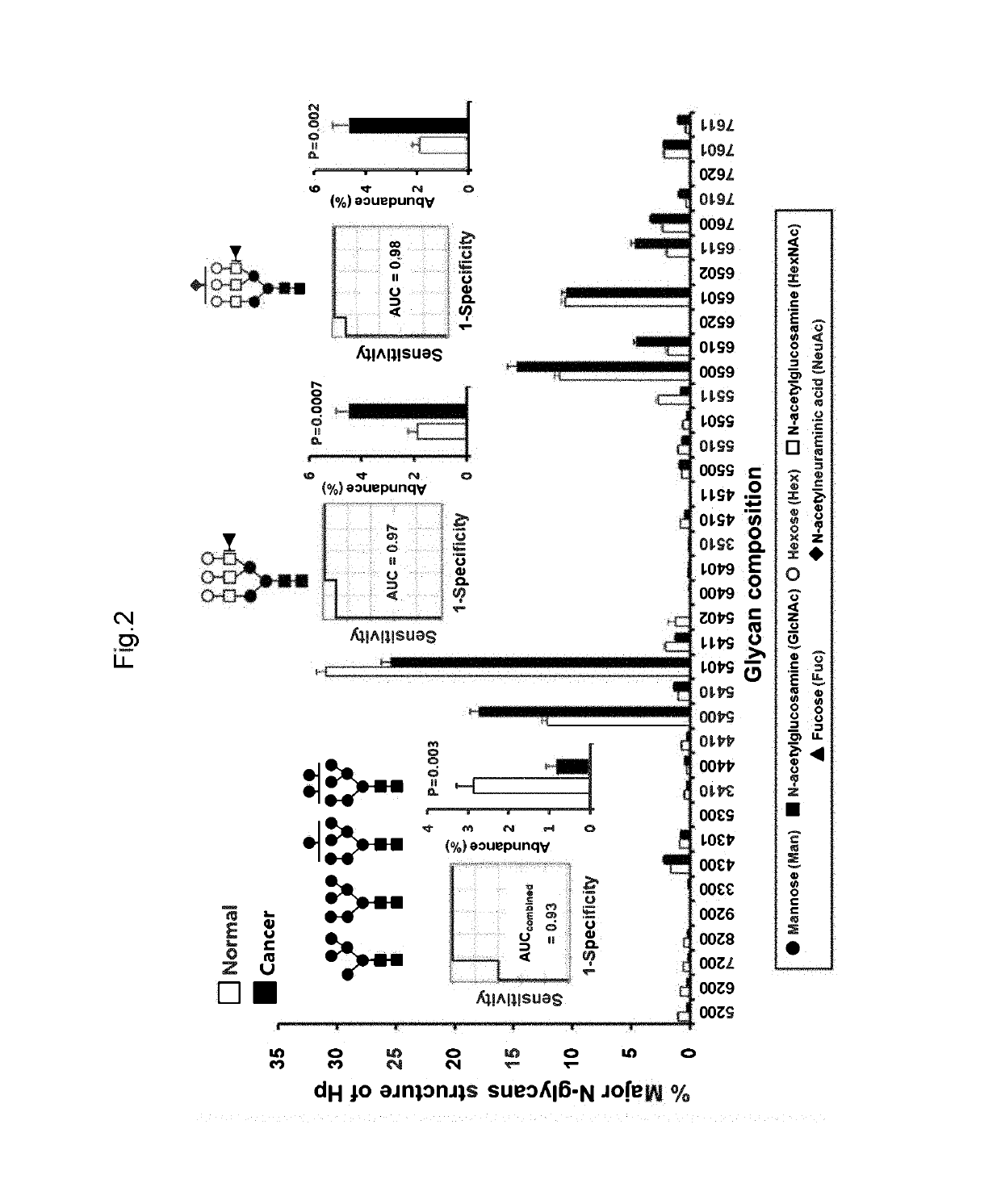
The present invention relates to a method for gastric cancer diagnosis through the detection of glycan changes, and to a kit for gastric cancer diagnosis. More specifically, based on, among the changes in N-linked glycosylation of the gastric cancer patient-derived haptoglobin, which are detected through lectin and mass spectrometry, the increase in fucosylation, the increases or significant changes in particular glycan structures according to the classification of antennary, or the reduction in high-mannose structure of the N-linked glycan compared with normal persons, the discovered N-glycosylation structures can be favorably used for a method for gastric cancer diagnosis using lectin, as a diagnostic marker, or mass spectrometry, and a kit for diagnosing gastric cancer.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Glycoengineered antibody, antibody-conjugate and methods for their preparation
PendingUS20160257764A1Low standard deviationAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsHeavy chainAntibody conjugate
The invention relates to glycoengineered antibodies and antibody-conjugates. In particular, the invention relates to an antibody conjugate, prepared from an IgG antibody comprising one N-linked glycosylation site on the combination of a single heavy chain and single light chain, wherein the N-linked glycosylation site is a mutant N-linked glycosylation site as compared to its wild type counterpart. The invention further relates to methods for the preparation of the antibody-conjugates according to the invention.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
N-linked glycosylation alteration in E0 and E2 glycoprotein of classical swine fever virus and novel classical swine fever virus vaccine
InactiveUS20100104597A1Slow onsetDelaying severitySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesVirulent characteristicsWild type
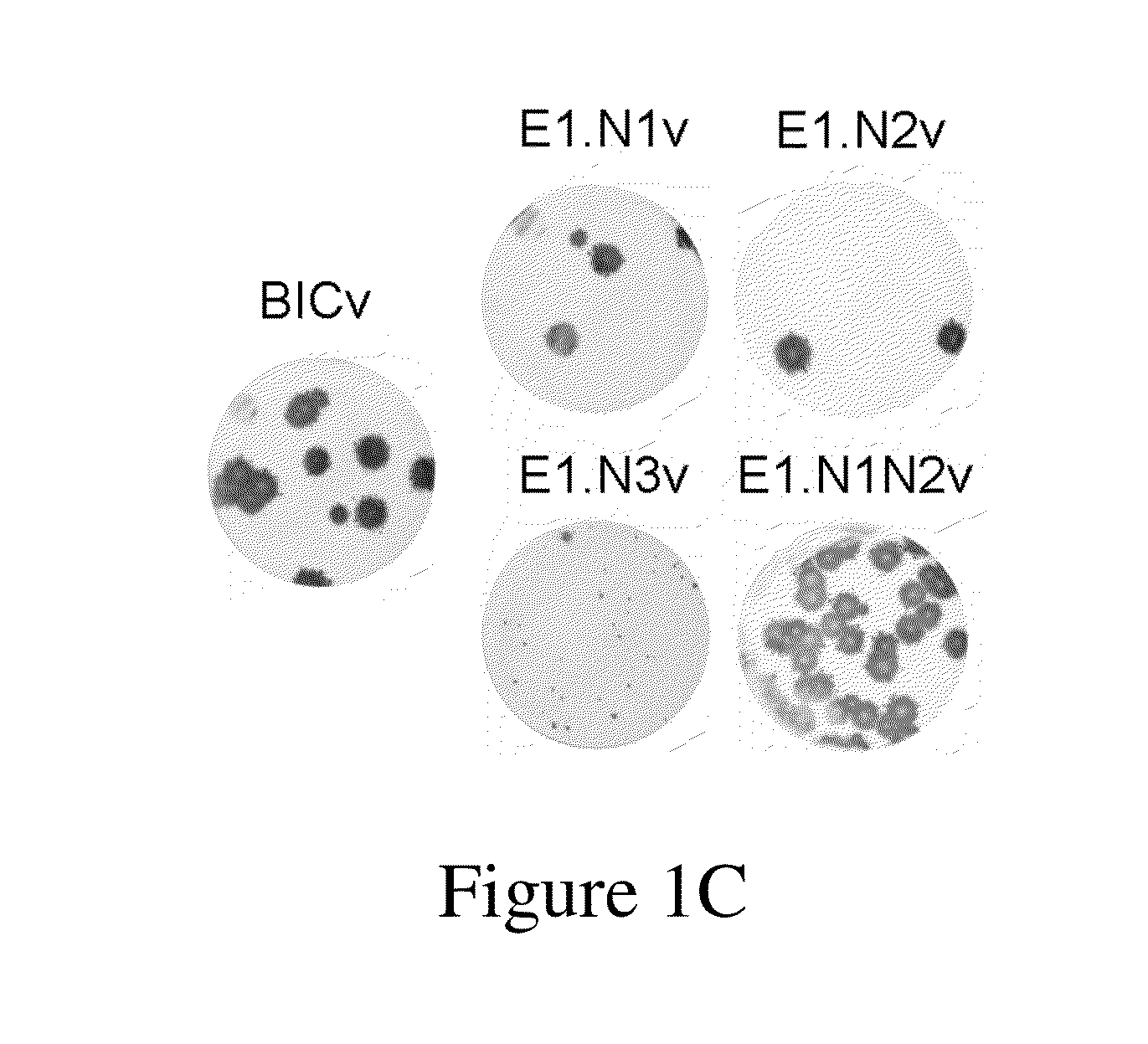
E2 is one of the three envelope glycoproteins of Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV). E2 is involved in several functions including virus attachment and entry to target cells, production of antibodies, induction of protective immune response in swine, and virulence. Seven putative glycosylation sites in E2 were modified by site directed mutagenesis of a CSFV Brescia infectious clone (BICv). A panel of virus mutants was obtained and used to investigate whether the removal of putative glycosylation sites in the E2 glycoprotein would affect viral virulence / pathogenesis in swine. We observed that rescue of viable virus was completely impaired by removal of all putative glycosylation sites in E2, but restored when mutation N185A reverted to wild-type asparagine produced viable virus that was attenuated in swine. Single mutations of each of the E2 glycosylation sites showed that amino acid N116 (N1v virus) was responsible for BICv attenuation. N1v efficiently protected swine from challenge with virulent BICv at 3 and 28 days post-infection suggesting that glycosylation of E2 could be modified for development of CSF live-attenuated vaccines. Additionally, a new developed virus, contained deletions of putative glycosylation sites N1 in E2 and N1 in E0 (6b), called N1E0 / 2v, induce a solid protection against the challenge at 3 and 28 days post-inoculation.
Owner:BORCA MANUEL +1
Trans-N-glycosidase BtNGT and application thereof
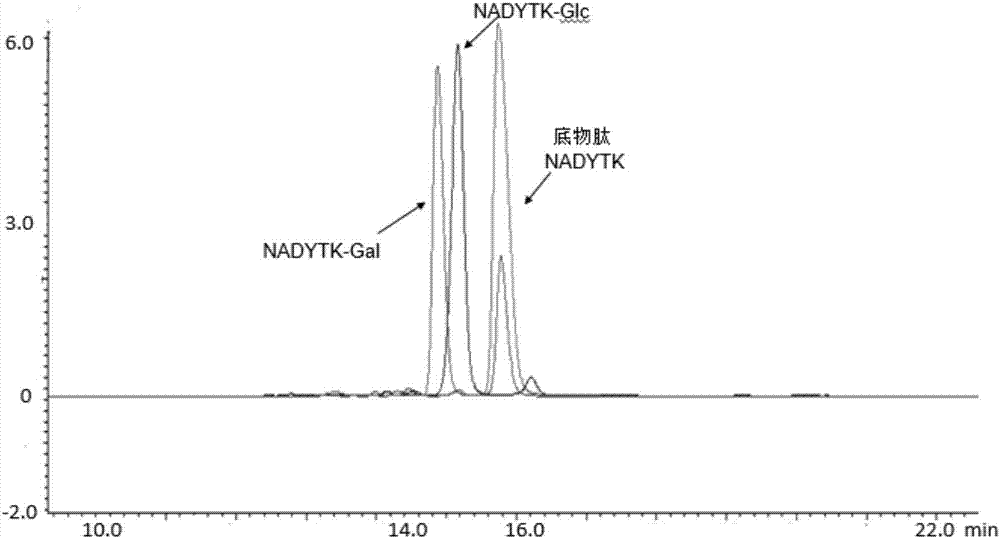
The invention discloses a trans-N-glycosidase BtNGT, which is derived from bibersteinia trehalosi, and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses an application of the trans-N-glycosidase BtNGT in carrying out N-linked glycosylation modification on polypeptide, the trans-N-glycosidase BtNGT can serve as a tool enzyme for polypeptide glycosylation modification to simply and rapidly utilize UDP-Glc or UDP-Gal to glycosylate polypeptide containing N-X-S / T sequence, other glycosyltransferases can then be utilized to modify the carbohydrate chain of glycopeptide, and thereby a target glycopeptide is obtained. A new approach to the glycosylation modification of polypeptide and protein is provided, and a simple method is provided for the synthesis of glycoprotein vaccines.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
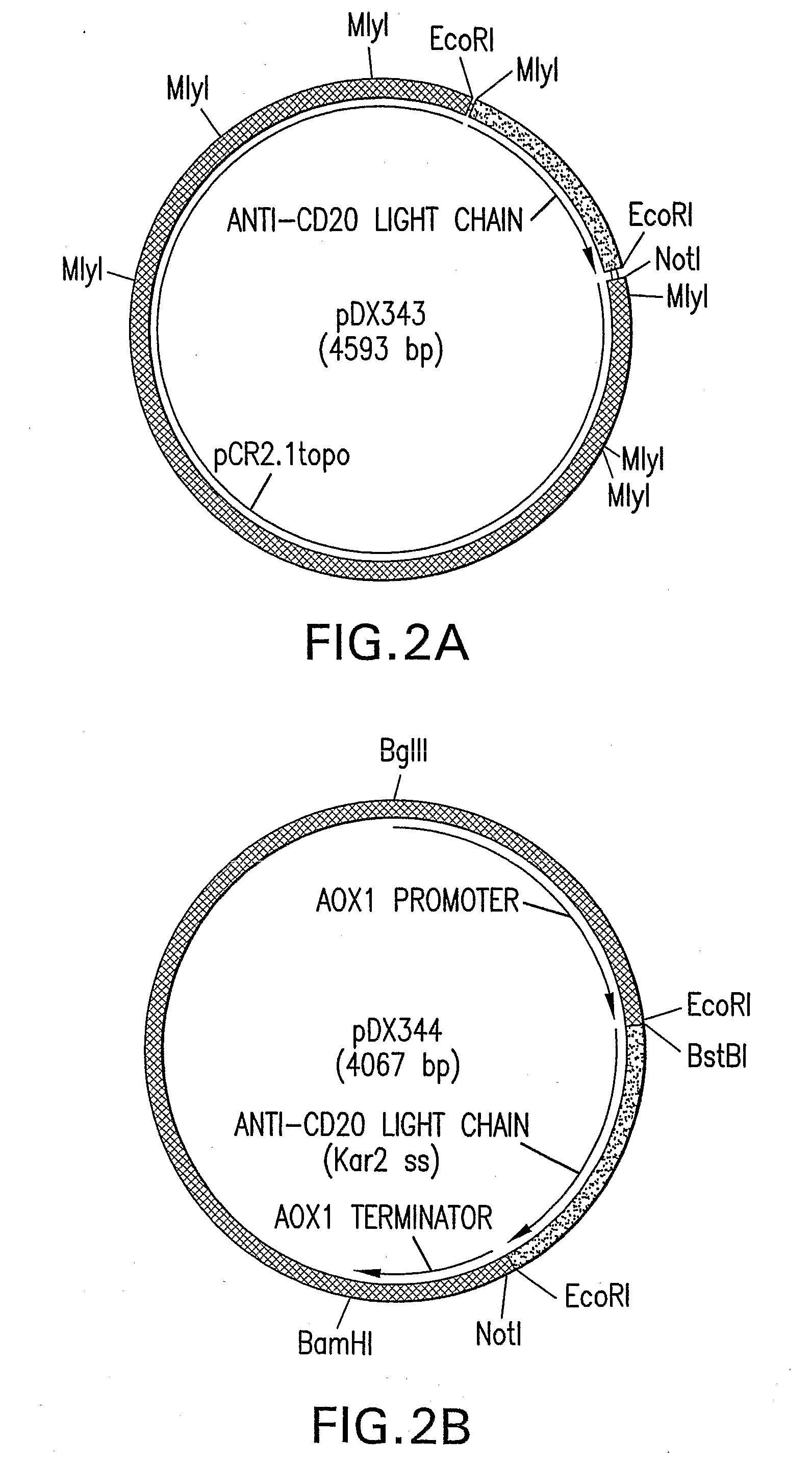
Avian derivedantibodies
InactiveUS20100303806A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsFowlCytotoxic antibody
The invention encompasses among other things antibodies including cytotoxic antibodies such as anti-CD20 having avian N-linked glycosylation patterns obtained from egg white of eggs laid by transgenic avians.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
N-Linked Glycosylation Alteration in E1 Glycoprotein of Classical Swine Fever Virus And Novel Classical Swine Fever Virus Vaccine
ActiveUS20120014992A1Reduce severityAltered glycosylation patternSsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesPost infectionEnv Glycoproteins
E1, along with Erns and E2 is one of the three envelope glycoproteins of Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV). Our previous studies indicated that glycosylation status of either E2 or Erns strongly influence viral virulence in swine. Here, we have investigated the role of E1 glycosylation of highly virulent CSFV strain Brescia during infection in the natural host. The three putative glycosylation sites in E1 were modified by site directed mutagenesis of a CSFV Brescia infectious clone (BICv). A panel of virus mutants was obtained and used to investigate whether the removal of putative glycosylation sites in the E1 glycoprotein would affect viral virulence / pathogenesis in swine. We observed that rescue of viable virus was completely impaired by removal of all three putative glycosylation sites in E1. Single mutations of each of the E1 glycosylation sites showed that CSFV amino acid N594 (E1.N3 virus), as well the combined mutation of N500 and N513 (E1.N1N2 virus) resulted in BICv attenuation. Infection of either E1.N1N2 or E1.N3 viruses were able to efficiently protected swine from challenge with virulent BICv at 3 and 28 days post-infection. These results, along with those demonstrating the role of glycosylation of Erns and E2, suggest that manipulation of the pattern of glycosylation could be a useful tool for development of CSF live-attenuated vaccines.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Engineered monomeric antibody fragments
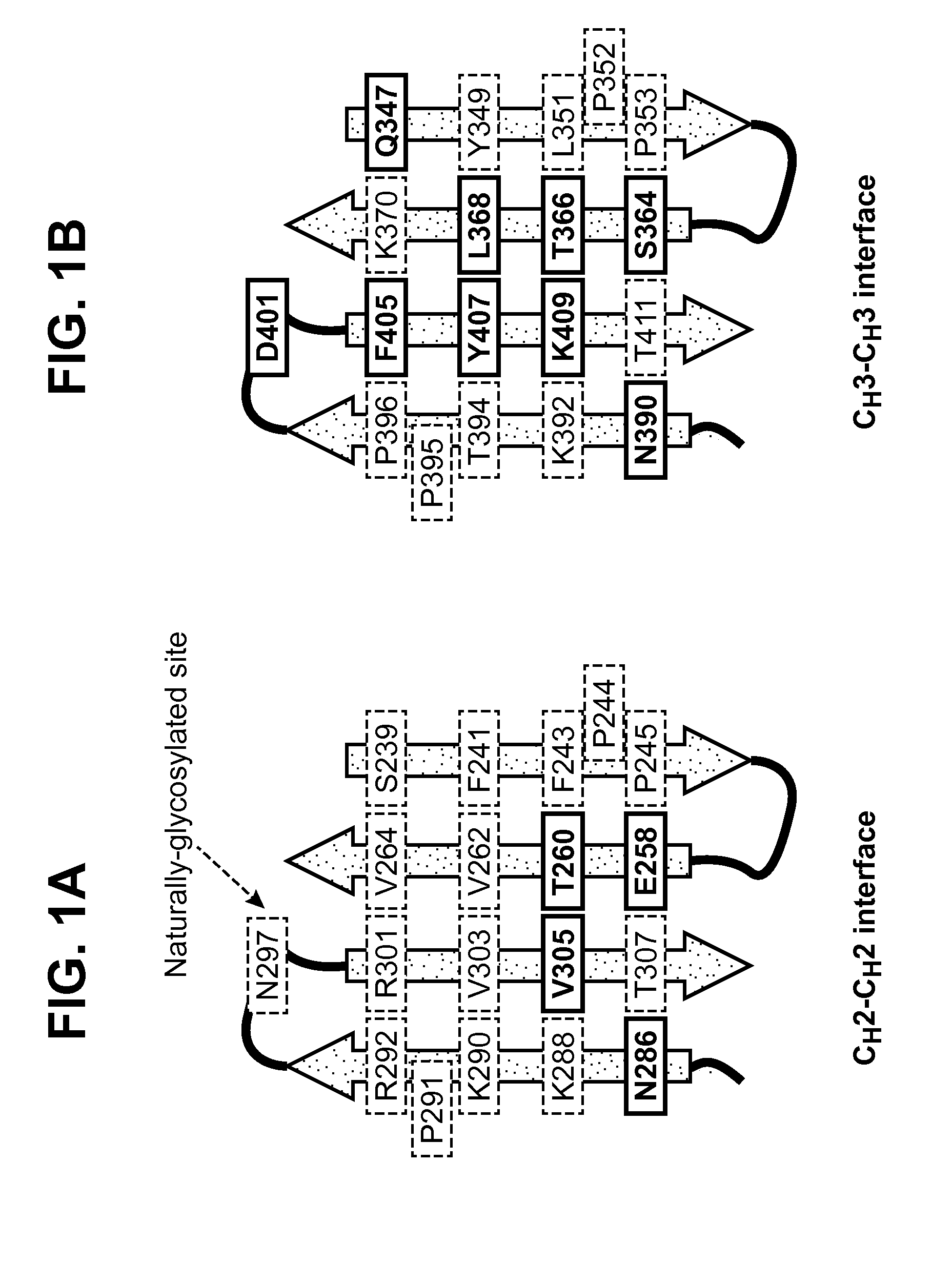
The present invention relates to monomeric polypeptides comprising an engineered monomeric antibody fragment (e.g., monomeric Fc-containing polypeptides) wherein the monomeric Fc comprises one or more engineered N-linked glycosylation sites in the CH3-CH3 dimerization interface. Methods for producing such engineered monomeric antibody fragments and their use in diagnostics and therapeutics are also provided.
Owner:PFIZER INC
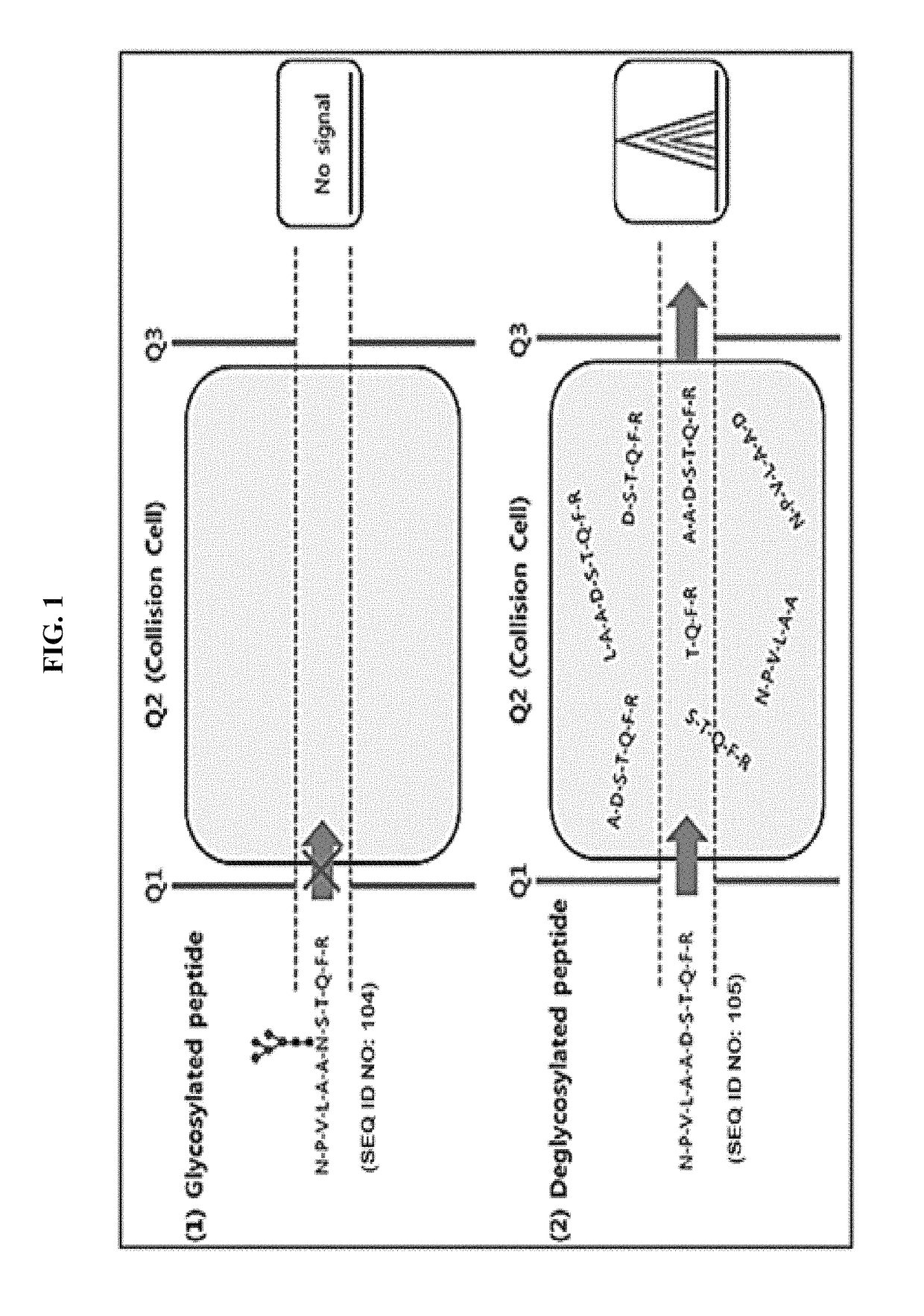
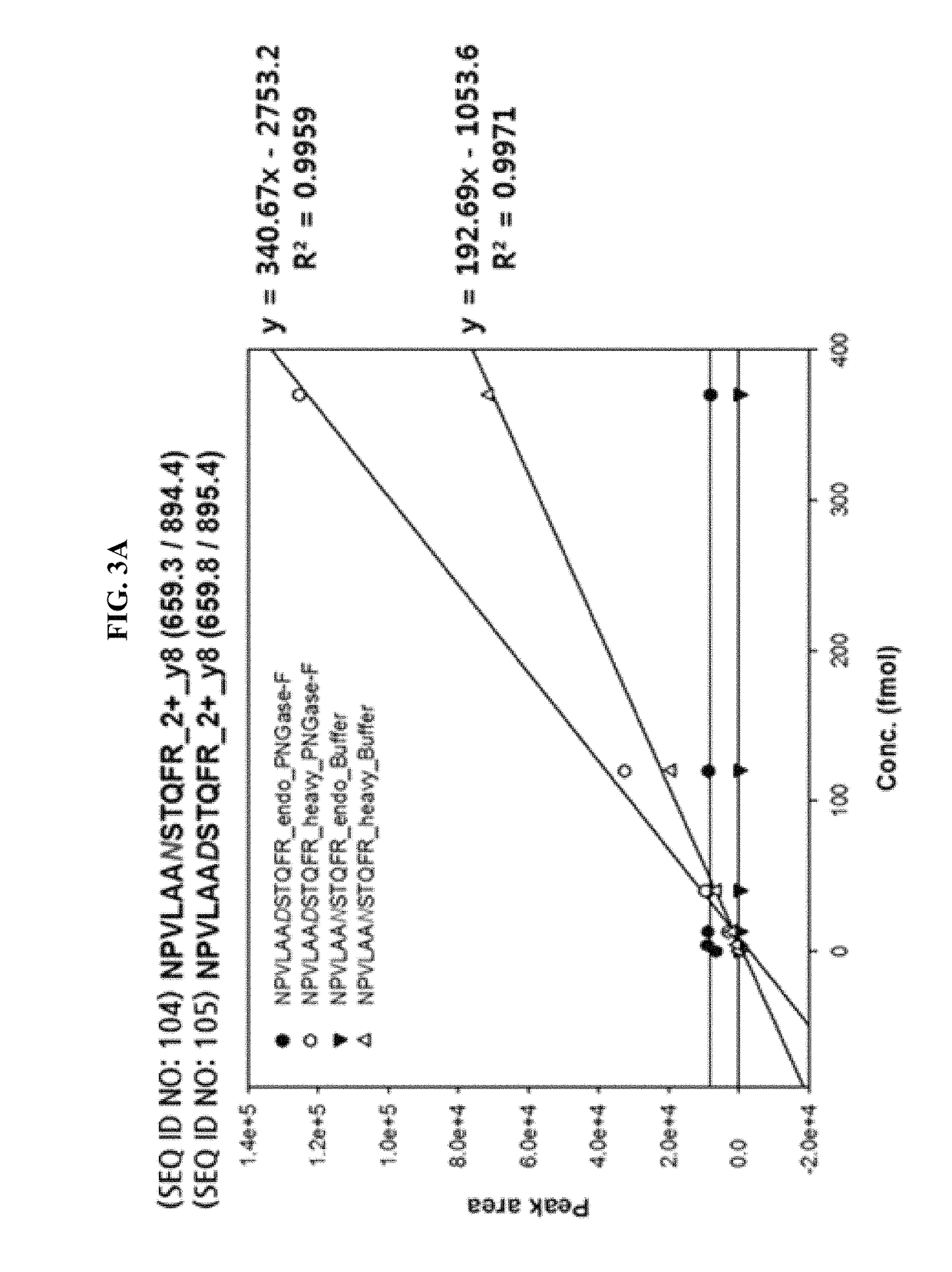
Method for diagnosing cancer through detection of deglycosylation of glycoprotein
ActiveUS9938561B2Efficiently employedHigh sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineSubject matter
Provided is a method for diagnosing cancer through a difference with a control group in view of the ratio of a deglycosylated peptide fragment and a non-glycosylated peptide fragment in a protein including an N-linked glycosylation motif. Further provided is a method for diagnosing cancer through the detection of the glycosylation ratio in the protein according to the subject matter enables the diagnosis of cancer with high specificity and sensitivity using at least one existing marker, and can be useful in discovering new markers for diagnosing cancer.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Method for diagnosis of colorectal cancer using mass spectrometry of n-glycans
InactiveUS20180164320A1High sensitivityStrong specificitySugar derivativesComponent separationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass spectrometry imaging
The present invention relates to a method of diagnosing colorectal cancer by detection of glycan changes, and more particularly to a method of diagnosing colorectal cancer using mass spectrometry, in which, when specific glycan structures increase, decrease or significantly change due to a change in N-linked glycosylation of a colorectal cancer patient-derived glycoprotein, as detected by mass spectrometry, the glycan structures are selected as diagnostic markers.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
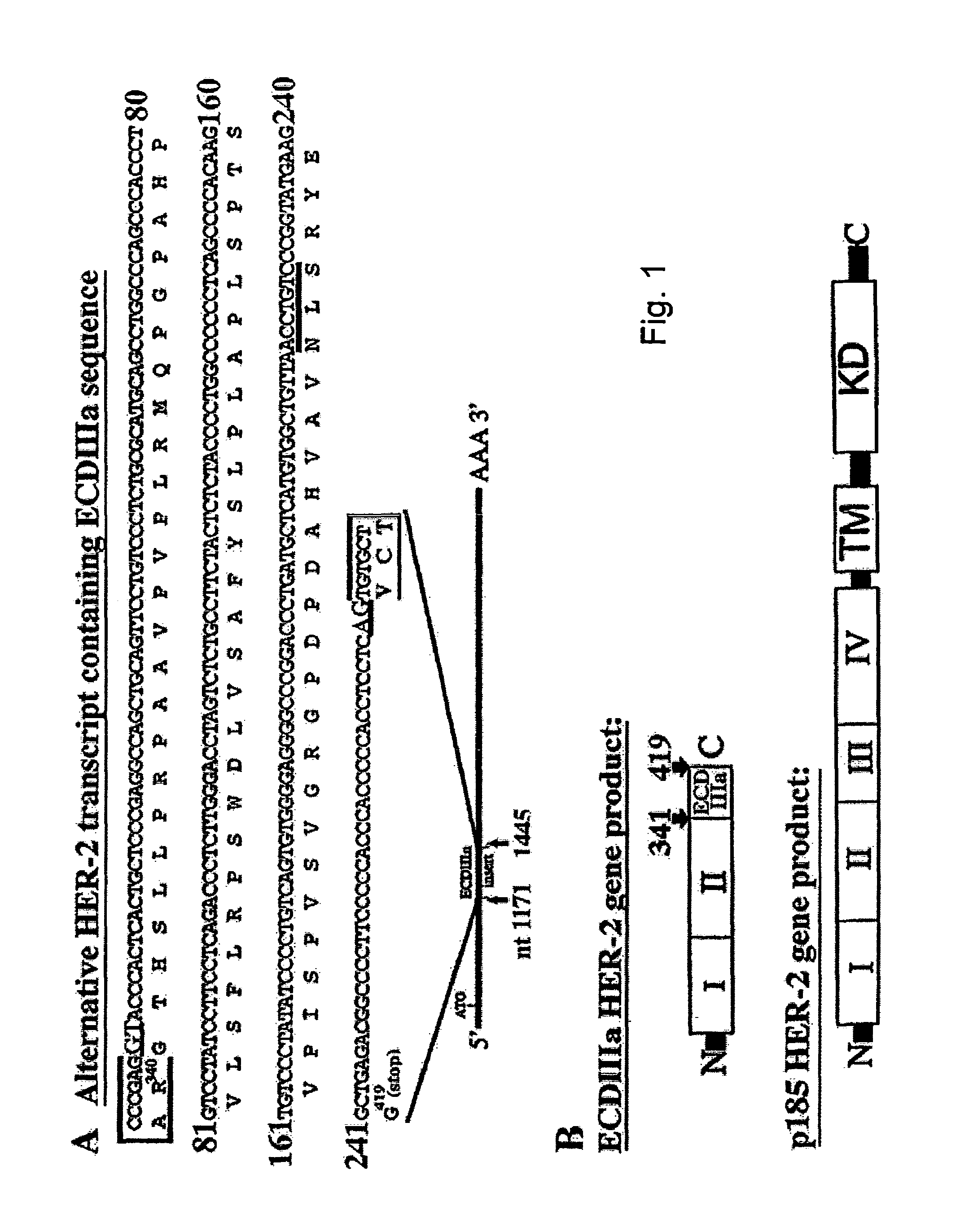
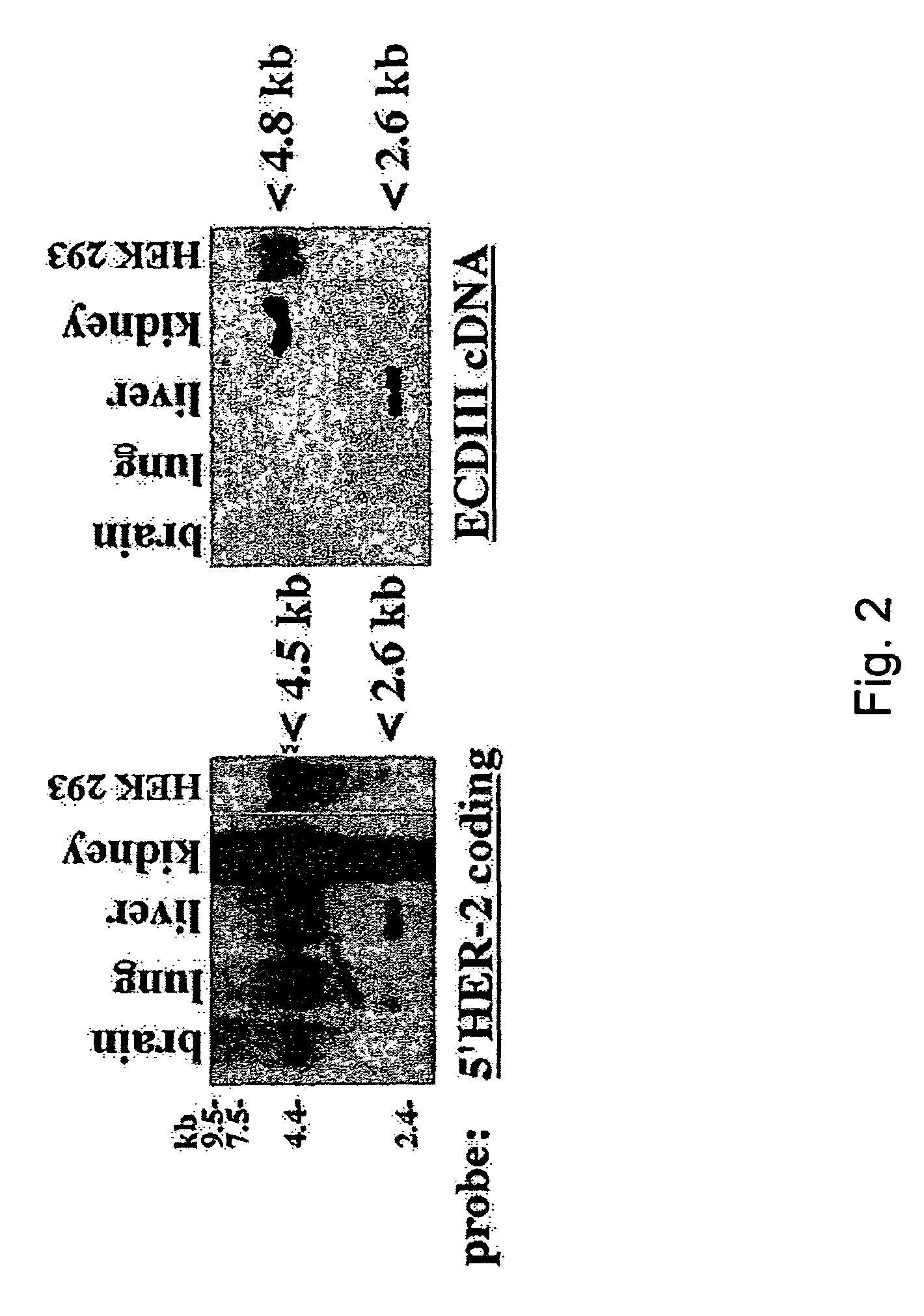
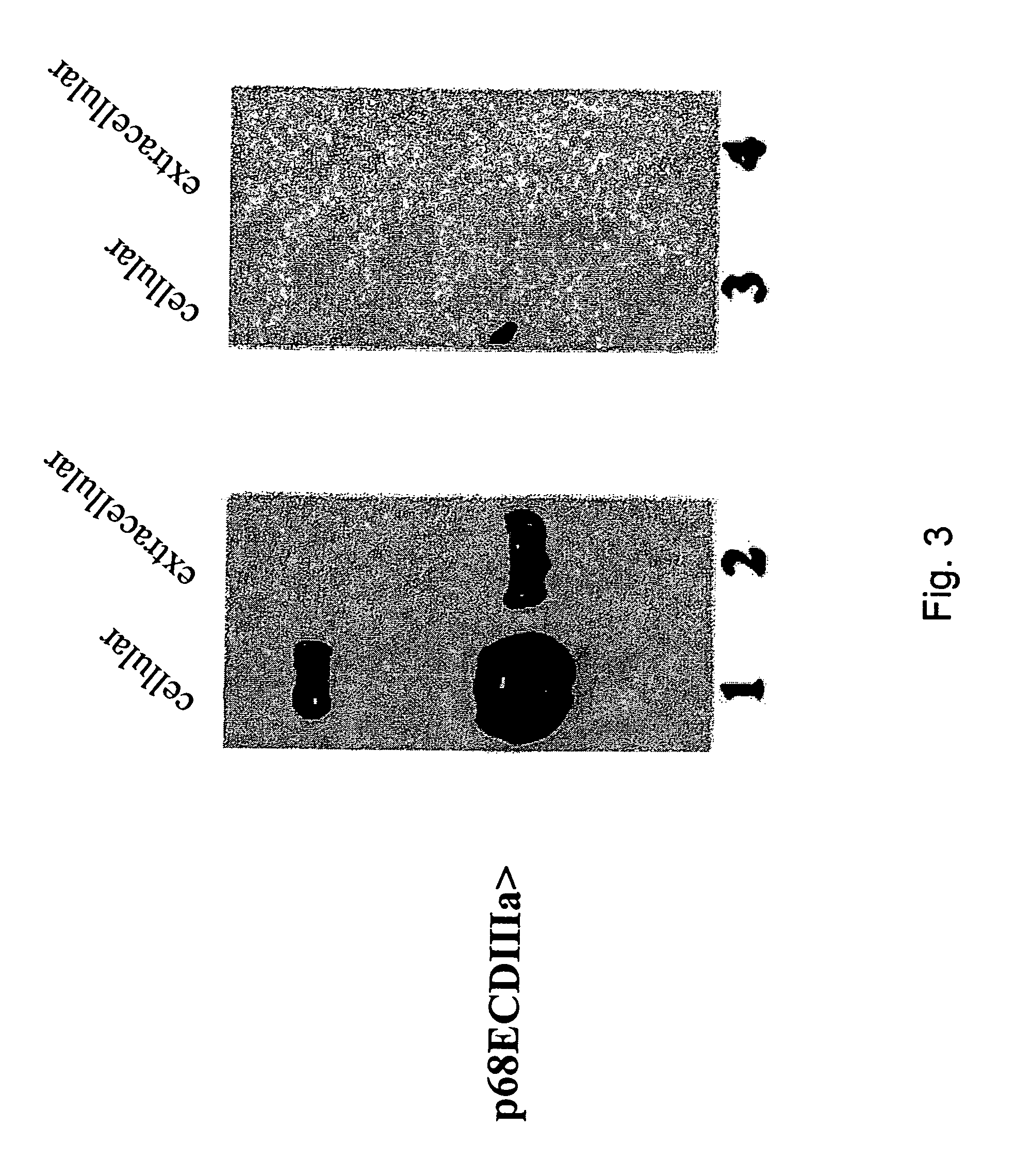
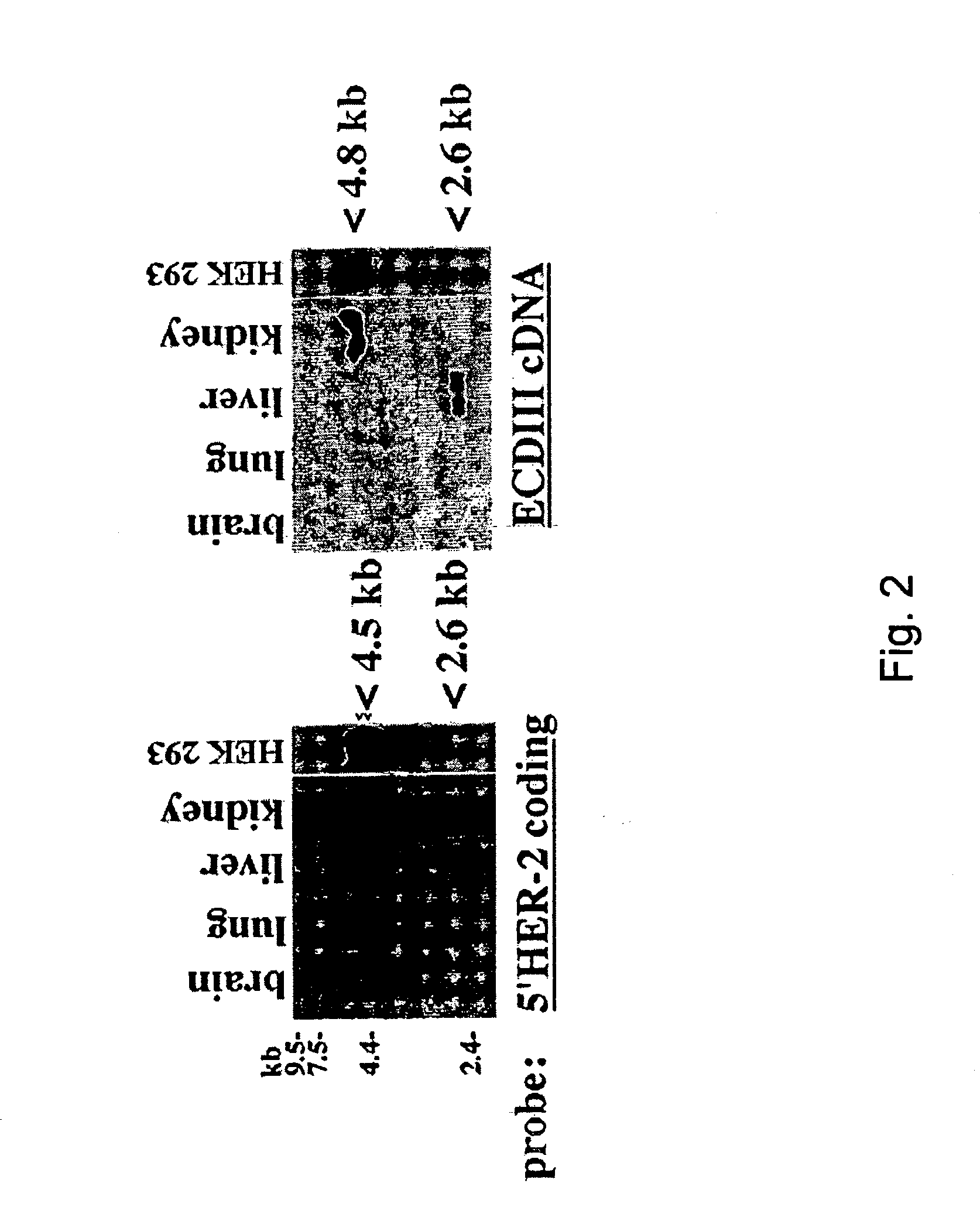
HER-2 binding antagonists
There is disclosed a pharmaceutical composition for treating solid tumors that overexpress HER-2, comprising an agent selected from the group consisting of (a) an isolated polypeptide having from about 50 to 79 amino acids taken from the sequence of SEQ ID NO. 1, wherein the polypeptide binds to the extracellular domain ECD of HER-2 with an affinity binding constant of at least 108 M−1, (b) an isolated and glycosylated polypeptide having from about 300 to 419 amino acids taken from the sequence of SEQ ID NO. 2, wherein the C terminal 79 amino acids are present, and wherein at least three N-linked glycosylation sites are present, (c) a monoclonal antibody that binds to the ECD of HER-2, and (d) combinations thereof, with the proviso that the agent cannot be the monoclonal antibody alone, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
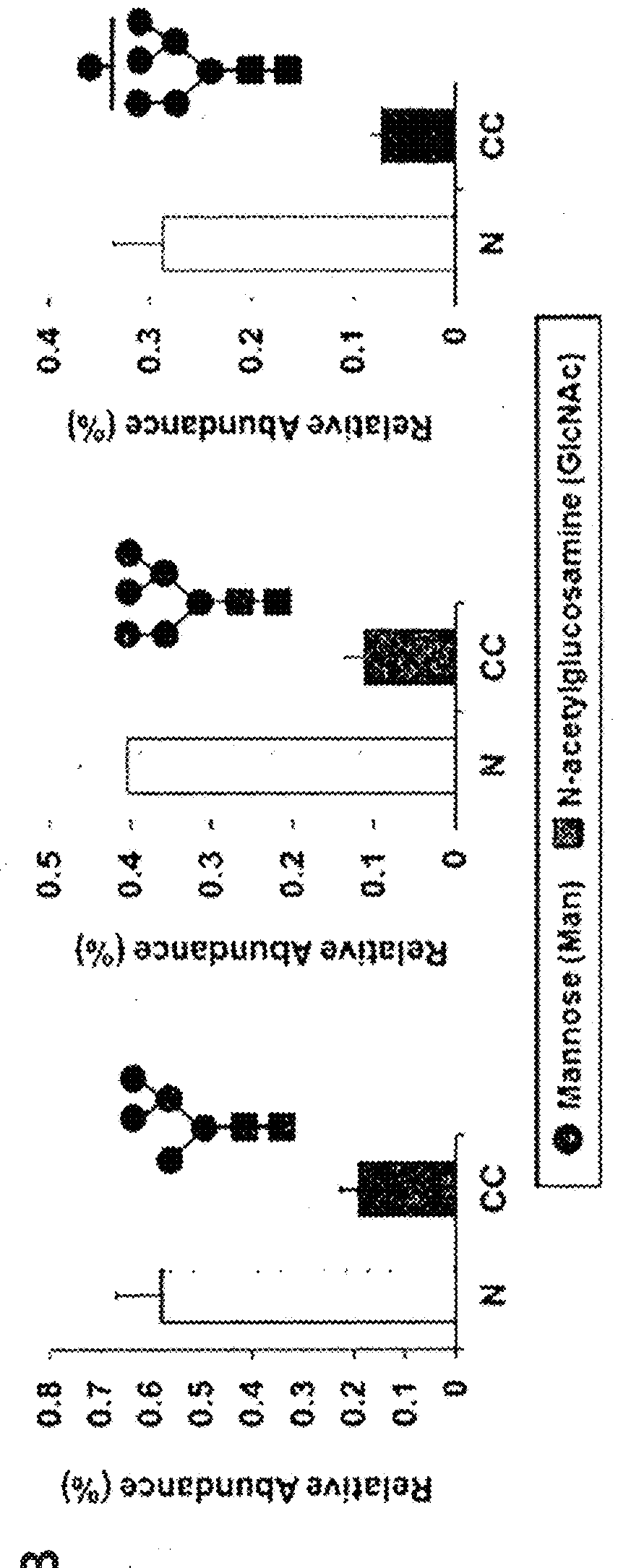
Novel diagnostic method for gastric cancer
This invention relates to a method for gastric cancer diagnosis through the detection of glycan changes, and to a kit for gastric cancer diagnosis. More specifically, based on the fact that in gastric cancer patient-derived haptoglobin, there are changes in N-linked glycosylation of haptoglobin, which are detected through lectin and mass spectrometery, that is, an increase in fucosylation, increases or significant changes in specific glycan structures depending on the classification of antennary structures, or a remarkable decrease in a high mannose structure of the N-glycan as compared to normal persons, N-glycan structures identified using the changes in N-linked glycosylation of haptoglobin may be usefully used as a diagnosis marker in a method for gastric cancer diagnosis using lectin or mass spectrometry, and a kit for gastric cancer diagnosis.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
A recombinant method for production of an erythropoiesis stimulating protein
InactiveCN101228185AProlonged Circulatory Half-LifeLong retention timePeptide/protein ingredientsErythropoietinHalf-lifeBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to a recombinant method for the production of erythropoietin in a highly glycosylated form (5 N-linked glycosylation in total relative to the 3 N-linked glycosylation in native EPO). The increased glycosylation sites will result in a higher number of sugar chains, and a higher sialic acid content than human EPO, which will result in a longer half-life for the recombinant molecule. The present invention also relates to the construction of an expression cassette comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a highly glycosylated form of erythropoietin, and stable expression in host cells. The present invention also relates to optimized methods for purifying erythropoietic proteins. The recombinant EPO and its salts and functional derivatives of the present invention can contain active ingredients for increasing hematocrit in pharmaceutical compositions, and thus can be used to treat anemia and restore the health status and quality of life of patients.
Owner:阿维斯塔金格兰技术有限公司
Compositions and methods for production of aglycosylated plasminogen
InactiveUS20120220015A1Increase productionHigh yieldSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseDrug biological activity
Compositions and methods for producing aglycosylated plasminogen (PLG) polypeptides and fragments and variants thereof are provided. Compositions of the invention include isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding aglycosylated PLG polypeptides in which the asparagine (Asn) residue corresponding to residue Asn-289 of the mature human PLG polypeptide has been substituted with an amino acid residue that does not support N-linked glycosylation at that position of the PLG polypeptide, as well as the aglycosylated PLG polypeptides encoded thereby. Expression constructs comprising these PLG-encoding nucleic acid molecules and transgenic plants comprising these expression constructs are also provided. Methods of the invention comprise introducing a PLG-encoding nucleic acid molecule of the invention into a plant of interest and culturing the plant under conditions to produce the aglycosylated PLG polypeptide. The aglycosylated PLG polypeptide allows for significant increases in production and yield of PLG from a plant-based expression system without comprising the ability of the PLG product to be activated to a polypeptide capable of binding fibrin and having serine protease activity, including biologically active plasmin that is also glycosylated. The activated aglycosylated plasmin is useful to treat diseases or conditions associated with a thrombus.
Owner:SYNTHON BIOPHARMACEUTICALS BV
Erythropoietin compositions
Owner:GLYCOFI
Recombinant human kininogenase and application thereof
ActiveCN104861057AExtended half-lifeHigh glycoform complexityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsSide effectHalf-life
The invention relates to high-molecular-weight recombinant human kininogenase, and a preparation method and application thereof. Specifically, the invention relates to the high-molecular-weight recombinant human kininogenase prepared by using a mammal cell culture production method and specific purifying technology for the first time. According to results of SDS-PAGE electrophoresis determination, the molecular weight of the high-molecular-weight recombinant human kininogenase is 43 to 49 KDa; the high-molecular-weight recombinant human kininogenase is glycoprotein and contains three N-Link glycosylation binding sites which are respectively located at Asn78, Asn84 and Asn141; and compared with kininogenase originated from human urine, the high-molecular-weight recombinant human kininogenase has a more complicated and more complete glycosylation level and obviously reduces a deamidation level. The high-molecular-weight recombinant human kininogenase obtained in the invention can substantially prolong in-vivo half-life and reduce side effects. The invention also relates to application of the high-molecular-weight recombinant human kininogenase in treatment of kidney failure.
Owner:UNICOHEALTH CO LTD
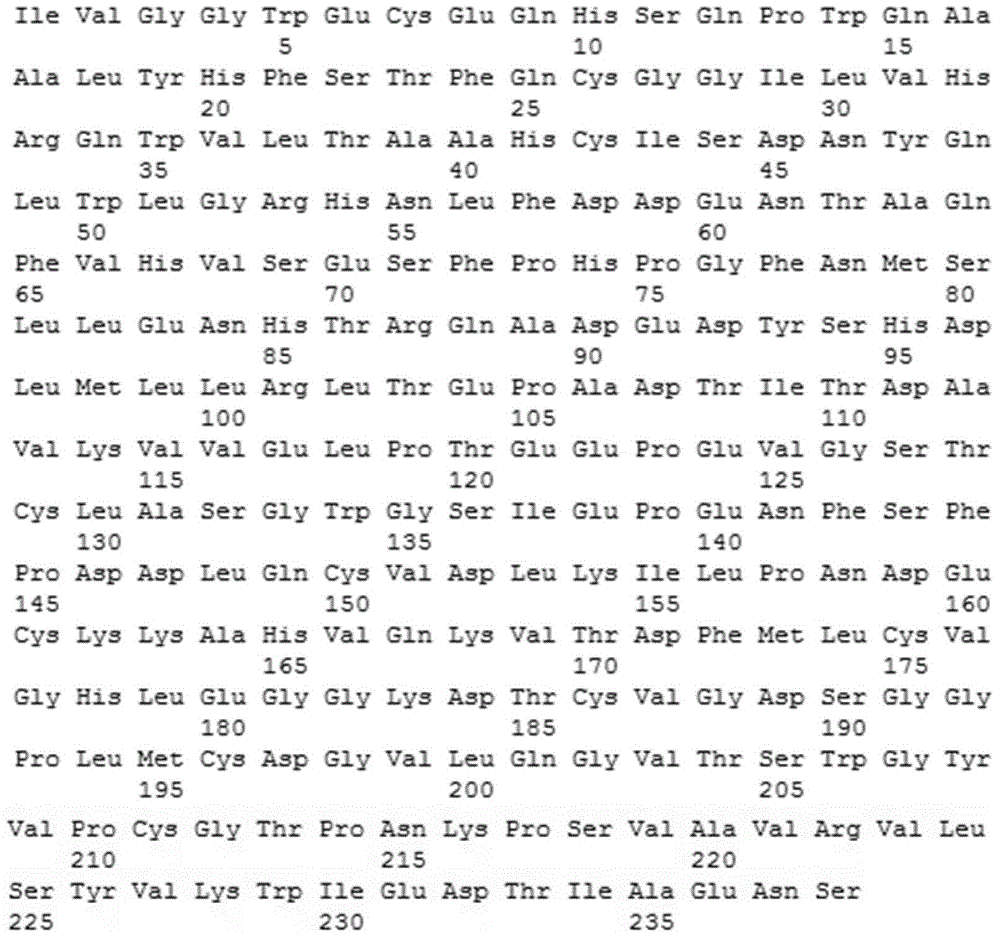
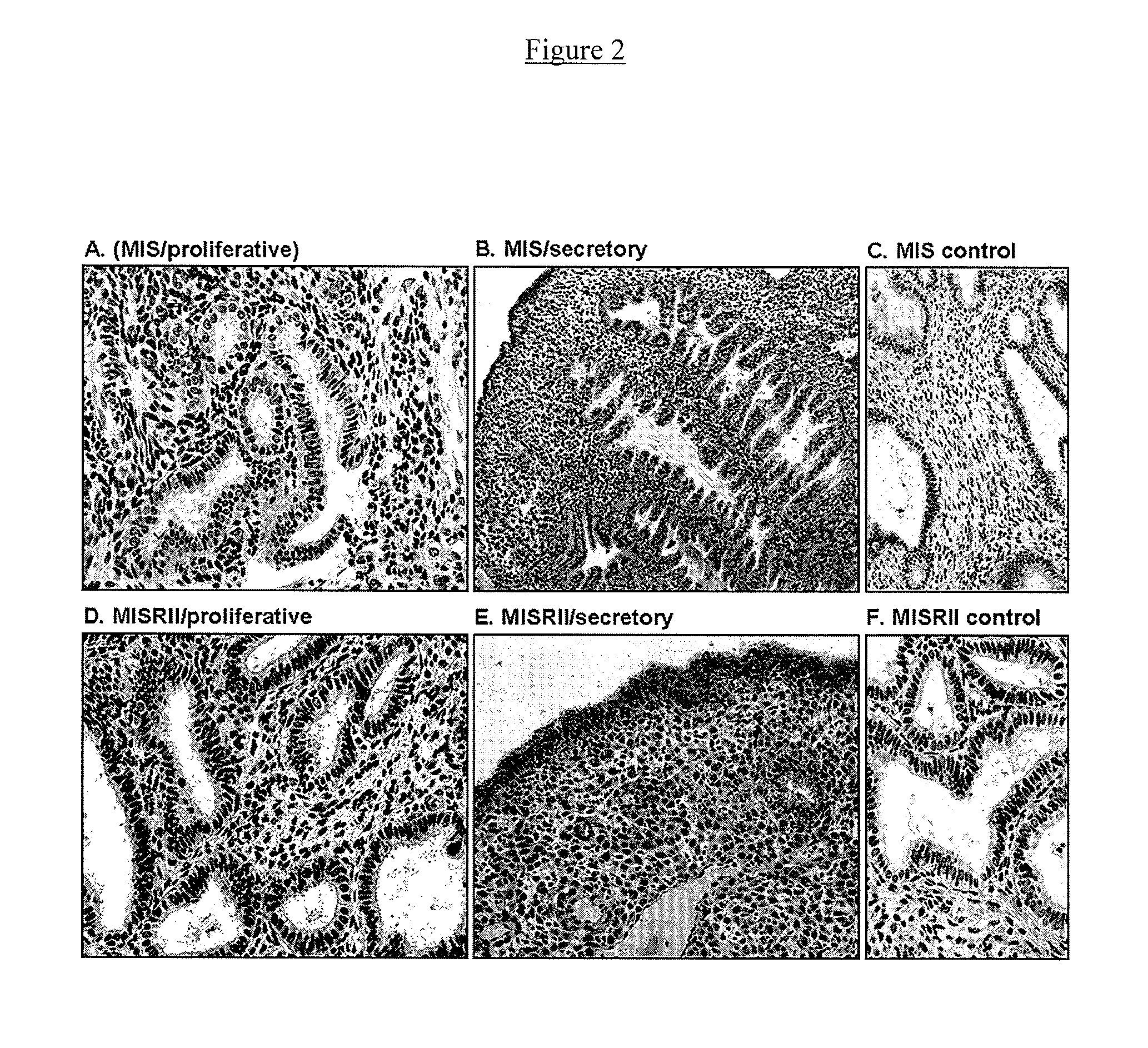
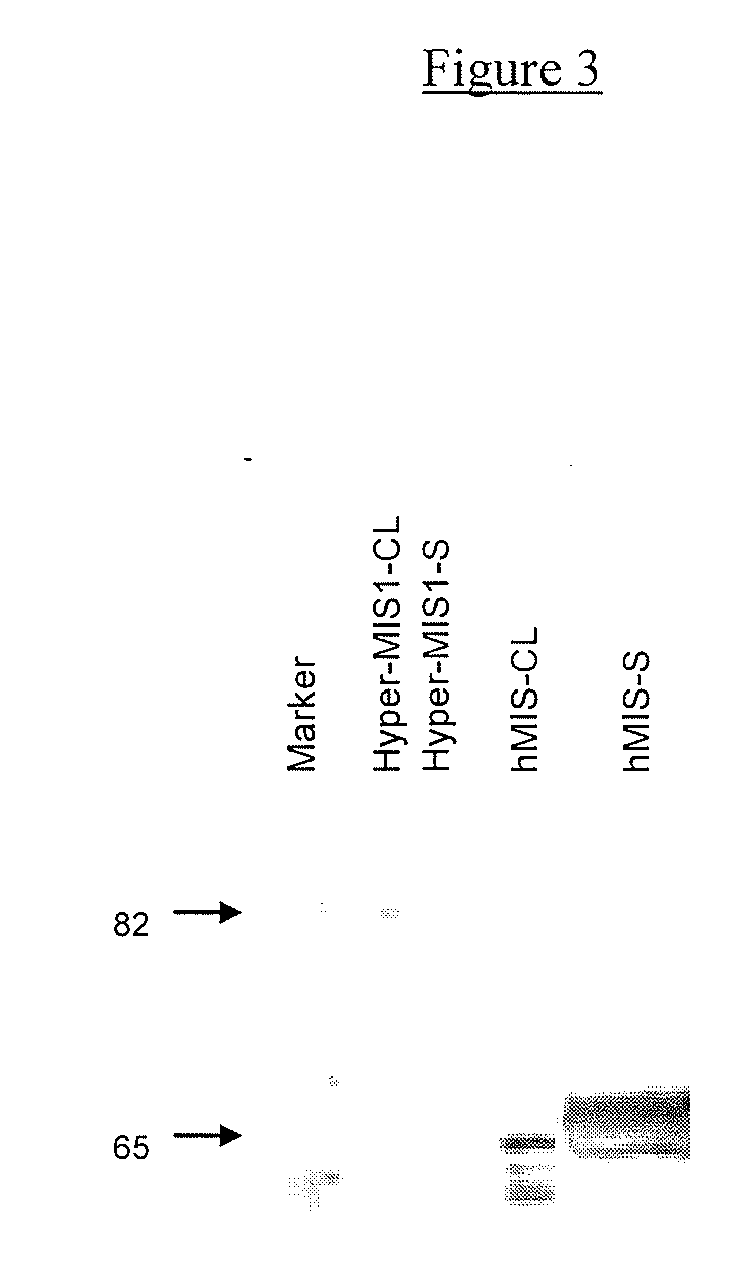
Mullerian inhibiting substance (MIS) analogues
Mullerian Inhibiting Substance analogues are disclosed which comprise one or more non-naturally occurring N-linked glycosylation sites, protease cleavage sites, and / or tags such as an epitope tag. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compositions and methods of using such compositions, for example in the treatment of conditions associated with uncontrolled growth of a tissue derived from a Mullerian duct, such as the condition endometriosis.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Factor VIII Muteins with Reduced Immonugenicity
The invention relates to modified Factor VIII molecules with reduced N-linked glycosylation and reduced immunogenicity. The invention also relates to methods of using modified Factor VIII molecules, for example, to treat patients afflicted with hemophilia.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
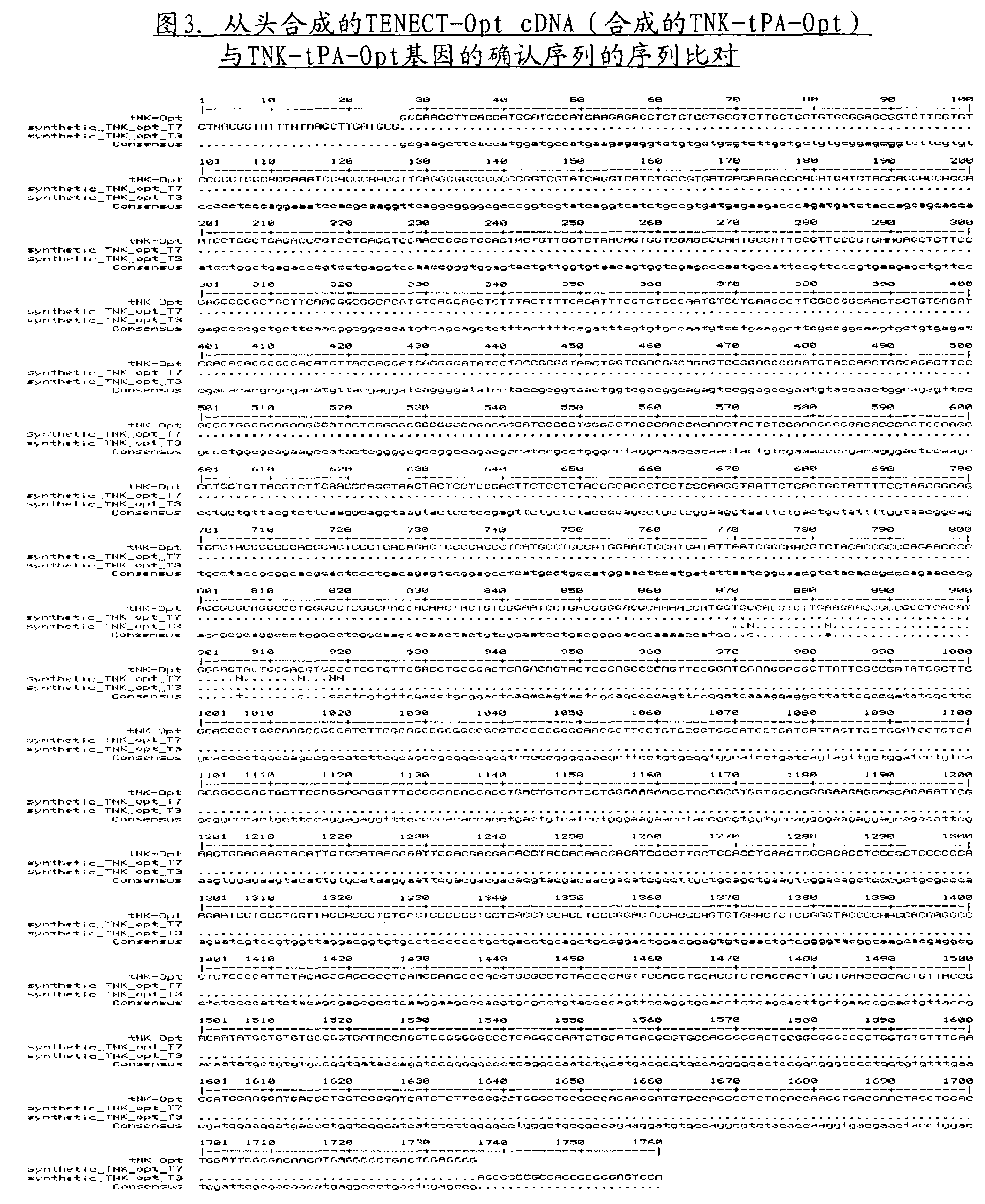
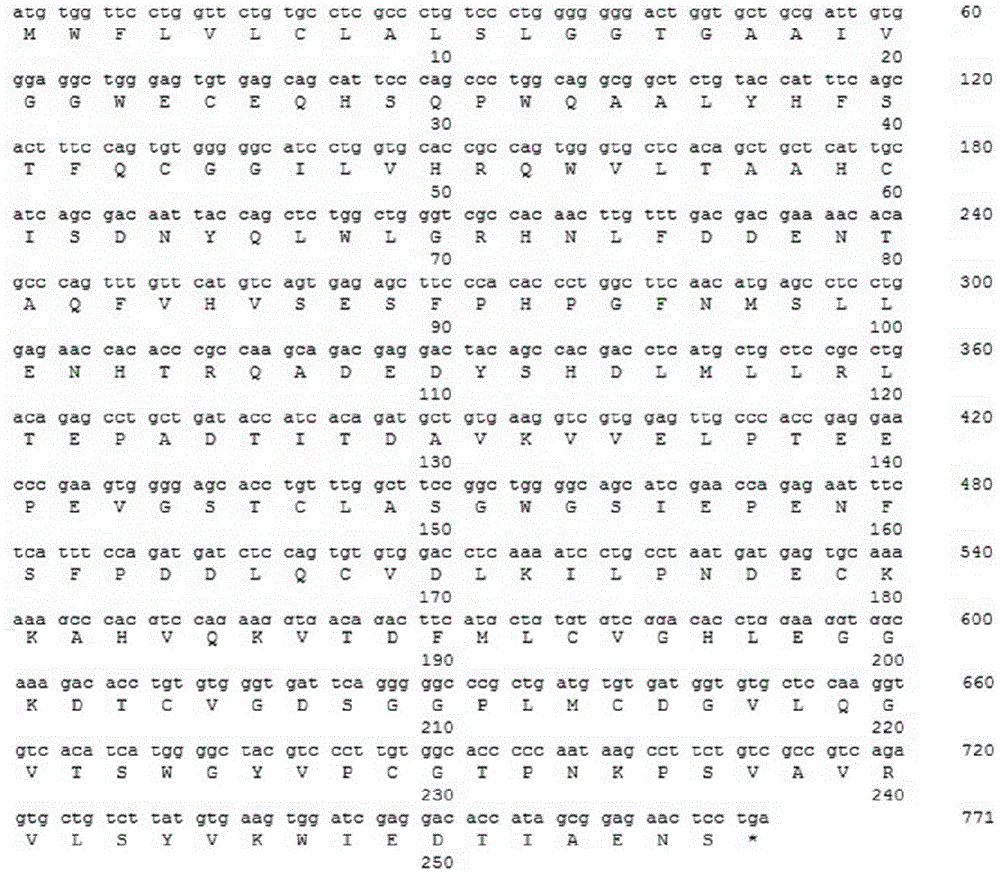
Method for production of a bioengineered form of tissue plasminogen activator
The present invention relates to the recombinant method used for the production of soluble form of human tissue plasminogen activator variant. In this variant the threonine at position 103 of the endogenous tissue plasminogen activator is replaced by an asparagine leading to a new glycosylation site. At position 117 of the endogenous tissue plasminogen activator asparagine has been replaced by glutamine, leading to the removal of an N linked glycosylation site. At position 296-299 the amino acids lysine, histidine, arginine, and arginine have been replaced by four alanine amino acids. The invention further relates to the de novo synthesis of the nucleic acid sequence encoding tissue plasminogen activator, transformation of the constructed nucleic acid sequences into competent bacteria and sub-cloning of the same into mammalian expression vectors for the expression of the desired protein. DNA constructs comprising the control elements associated with the gene of interest have been disclosed. The recombinant human tissue plasminogen activator, according to the invention, and the salts and functional derivatives thereof, may comprise the active ingredient of pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of treatment of heart attack and stroke patients. These compositions are yet another aspect of the present invention.
Owner:阿维斯塔金格兰技术有限公司
A recombinant human kallikrein
ActiveCN104830822BExtended half-lifeHigh glycoform complexityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesSide effectPurification methods
The invention relates to a high molecular weight recombinant human kallikrein and its preparation method and use. The high molecular weight recombinant human kallikrein is obtained by a mammalian cell culture production method and a specific purification method. A SDS-PAGE electrophoresis determination result shows that the high molecular weight recombinant human kallikrein is glycoprotein with molecular weight of 43-49KDa and contains 3 N-Link glycosylation binding sites respectively located at Asn78, Asn84 and Asn141. Compared with the existing human urine-derived human kallikrein, the high molecular weight recombinant human kallikrein has a complex and complete glycosylation level and obviously reduces a decarboxyamidation level. The high molecular weight recombinant human kallikrein can substantially prolong a half life in vivo and reduce side effects. The invention also relates to a research on application of the high molecular weight recombinant human kallikrein in cerebral infarction treatment.
Owner:UNICOHEALTH CO LTD
Diagnostic method for gastric cancer
This invention relates to a method for gastric cancer diagnosis through the detection of glycan changes, and to a kit for gastric cancer diagnosis. More specifically, based on the fact that in gastric cancer patient-derived haptoglobin, there are changes in N-linked glycosylation of haptoglobin, which are detected through lectin and mass spectrometery, that is, an increase in fucosylation, increases or significant changes in specific glycan structures depending on the classification of antennary structures, or a remarkable decrease in a high mannose structure of the N-glycan as compared to normal persons, N-glycan structures identified using the changes in N-linked glycosylation of haptoglobin may be usefully used as a diagnosis marker in a method for gastric cancer diagnosis using lectin or mass spectrometry, and a kit for gastric cancer diagnosis.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Her-2 binding antagonists
There is disclosed a pharmaceutical composition for treating solid tumors that overexpress HER-2, comprising an agent selected from the group consisting of (a) an isolated polypeptide having from about 50 to 79 amino acids taken from the sequence of SEQ ID NO. 1 or SEQ ID NO:12, wherein the polypeptide binds to the extracellular domain ECD of HER-2 at an affinity of at least 108, (b) an isolated and glycosylated polypeptide having from about 300 to 419 amino acids taken from the sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 or SEQ ID NO:13, wherein the C terminal 79 amino acids are present, and wherein at least three N-linked glycosylation sites are present, (c) a monoclonal antibody that binds to the ECD of HER-2, and (d) combinations thereof, with the proviso that the agent cannot be the monoclonal antibody alone, and pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Also disclosed are prognostic and diagnostic assays.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Method for Production of a Bioengineered Form of Tissue Plasminogen Activator
The present invention relates to the recombinant method used for the production of soluble form of human tissue plasminogen activator variant. In this variant the threonine at position 103 of the endogenous tissue plasminogen activator is replaced by an asparagine leading to a new glycosylation site. At position 117 of the endogenous tissue plasminogen activator asparagine has been replaced by glutamine, leading to the removal of an N linked glycosylation site. At position 296-299 the amino acids lysine, histidine, arginine, and arginine have been replaced by four alanine amino acids. The invention further relates to the de novo synthesis of the nucleic acid sequence encoding tissue plasminogen activator, transformation of the constructed nucleic acid sequences into competent bacteria and sub-cloning of the same into mammalian expression vectors for the expression of the desired protein. DNA constructs comprising the control elements associated with the gene of interest have been disclosed. The recombinant human tissue plasminogen activator, according to the invention, and the salts and functional derivatives thereof, may comprise the active ingredient of pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of treatment of heart attack and stroke patients. These compositions are yet another aspect of the present invention.
Owner:AVESTHAGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com