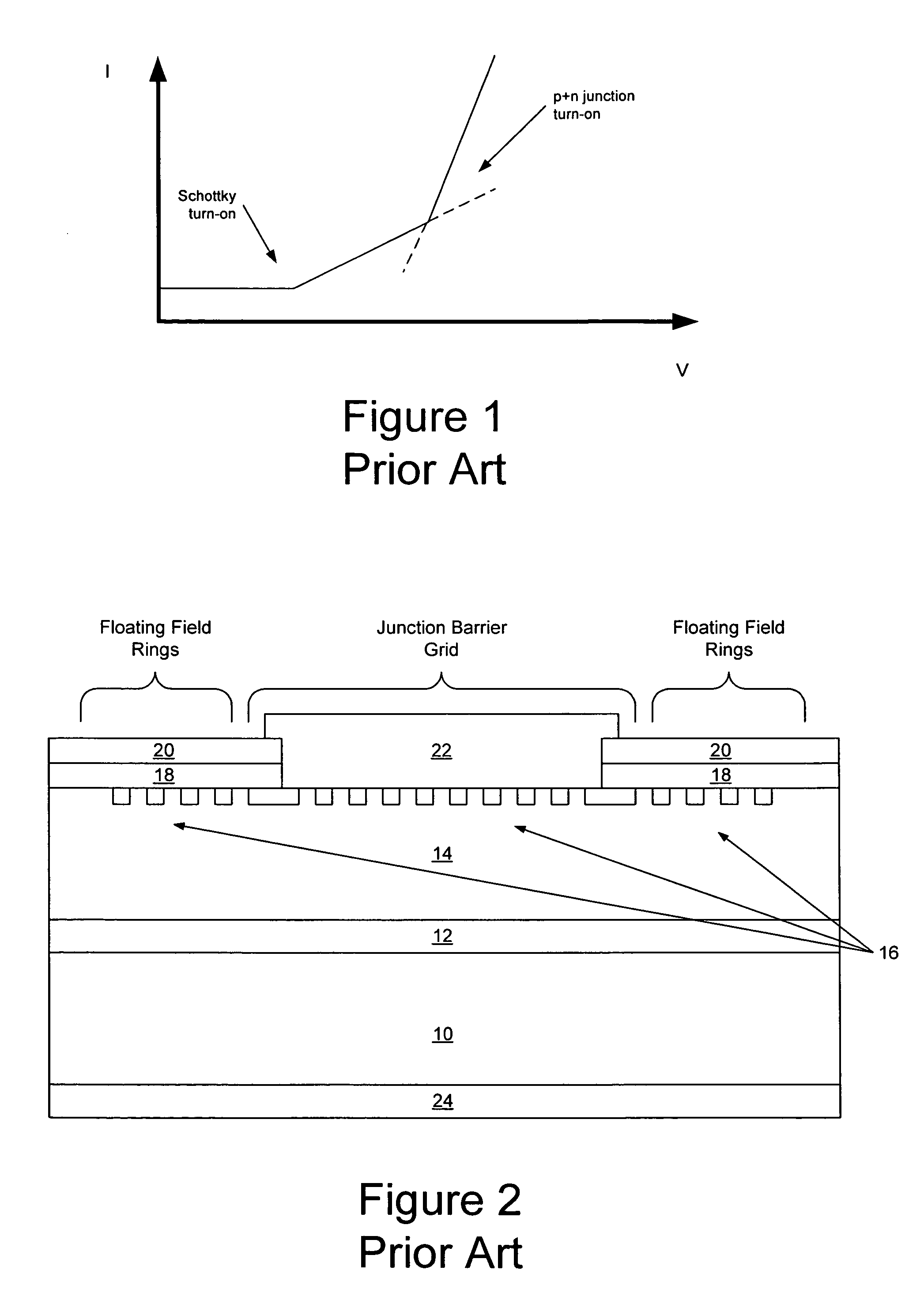
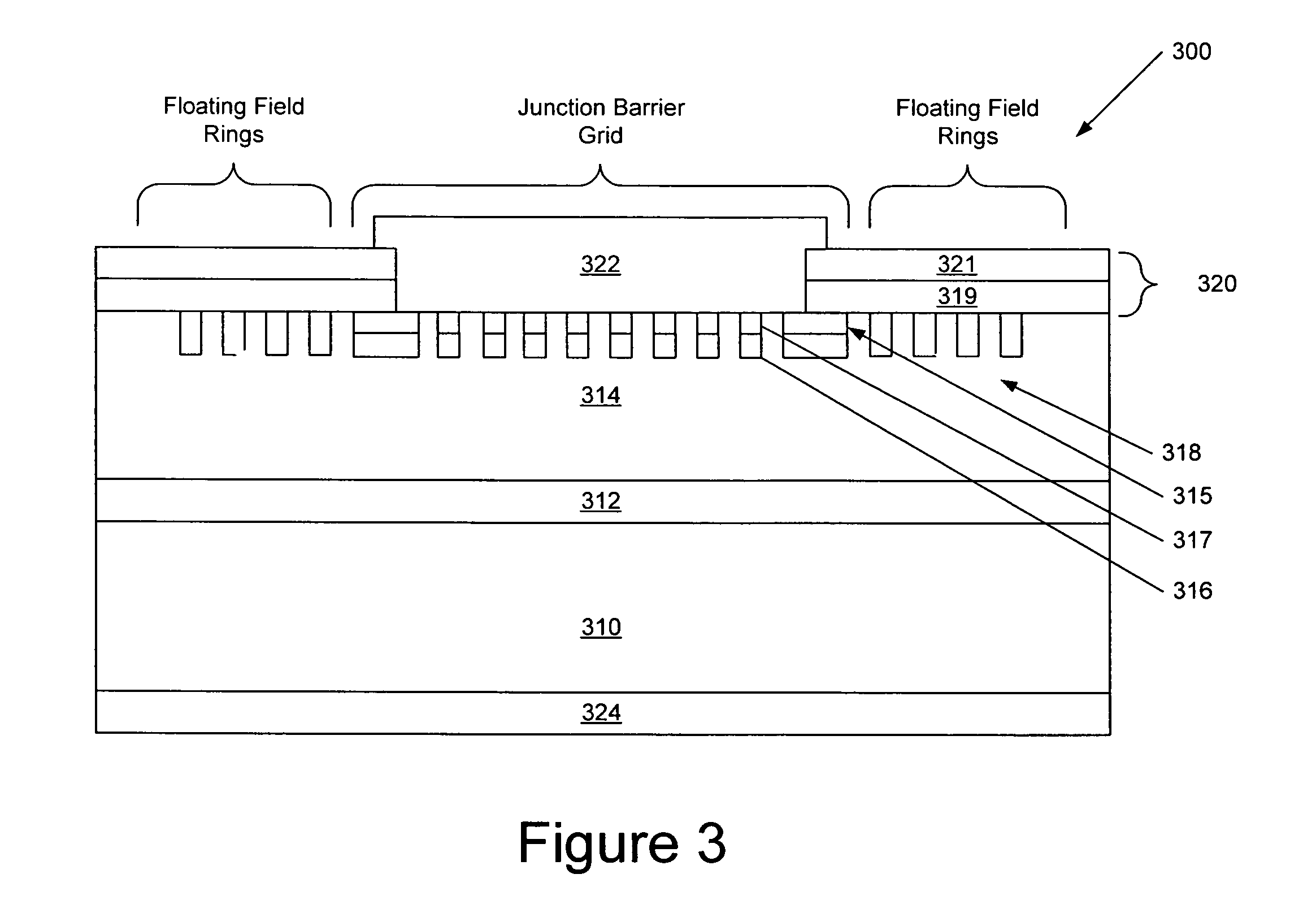
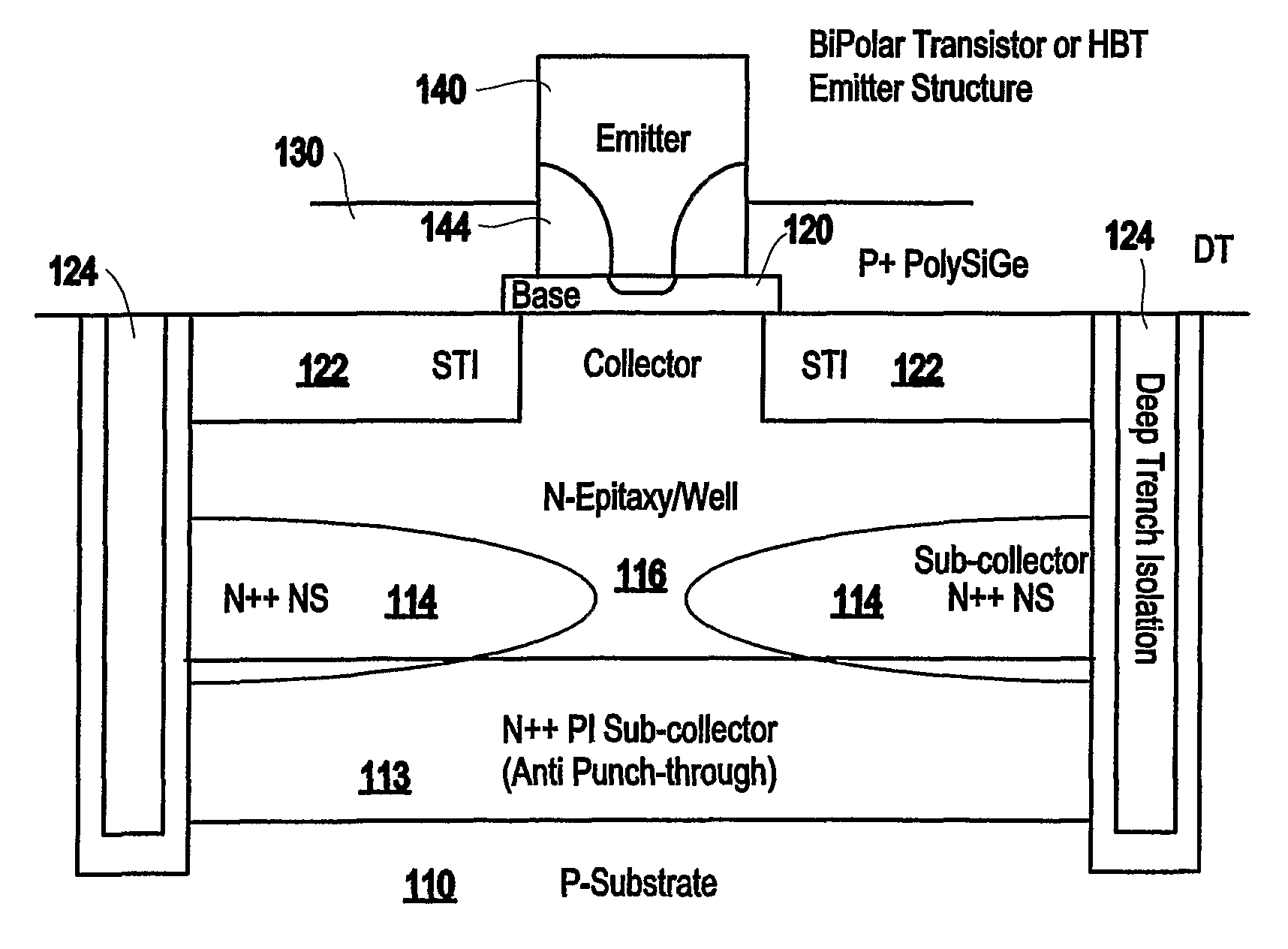
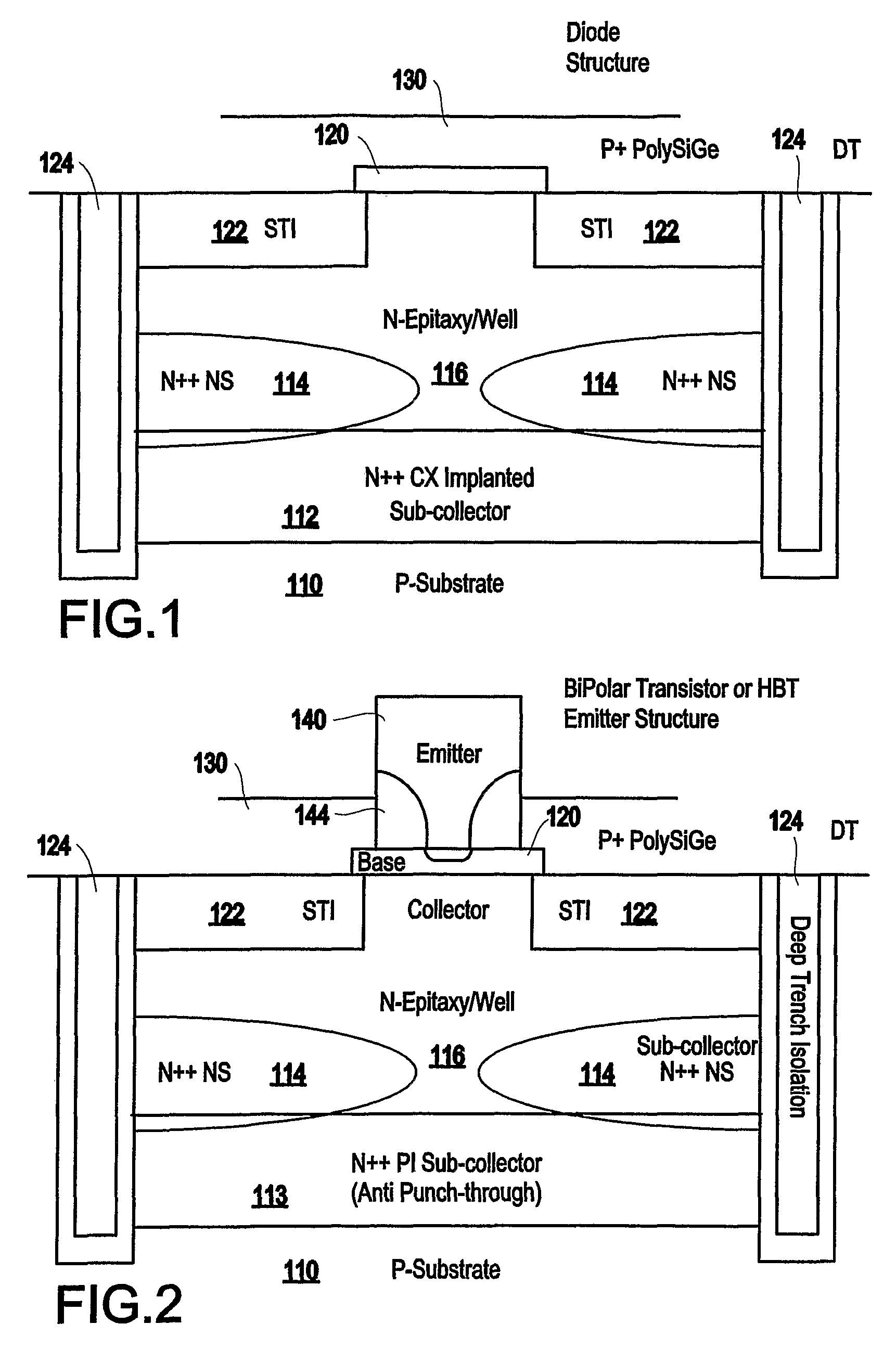
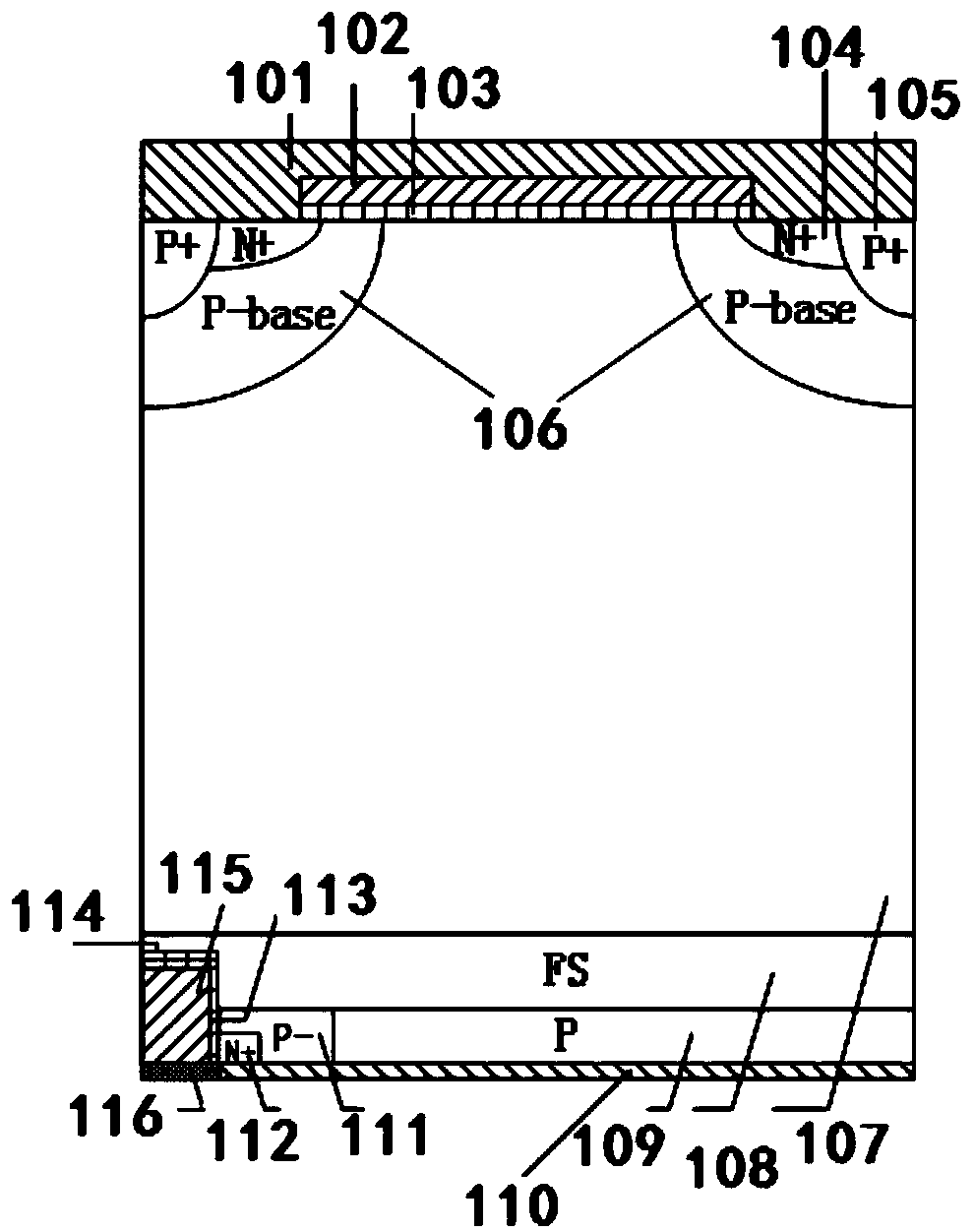
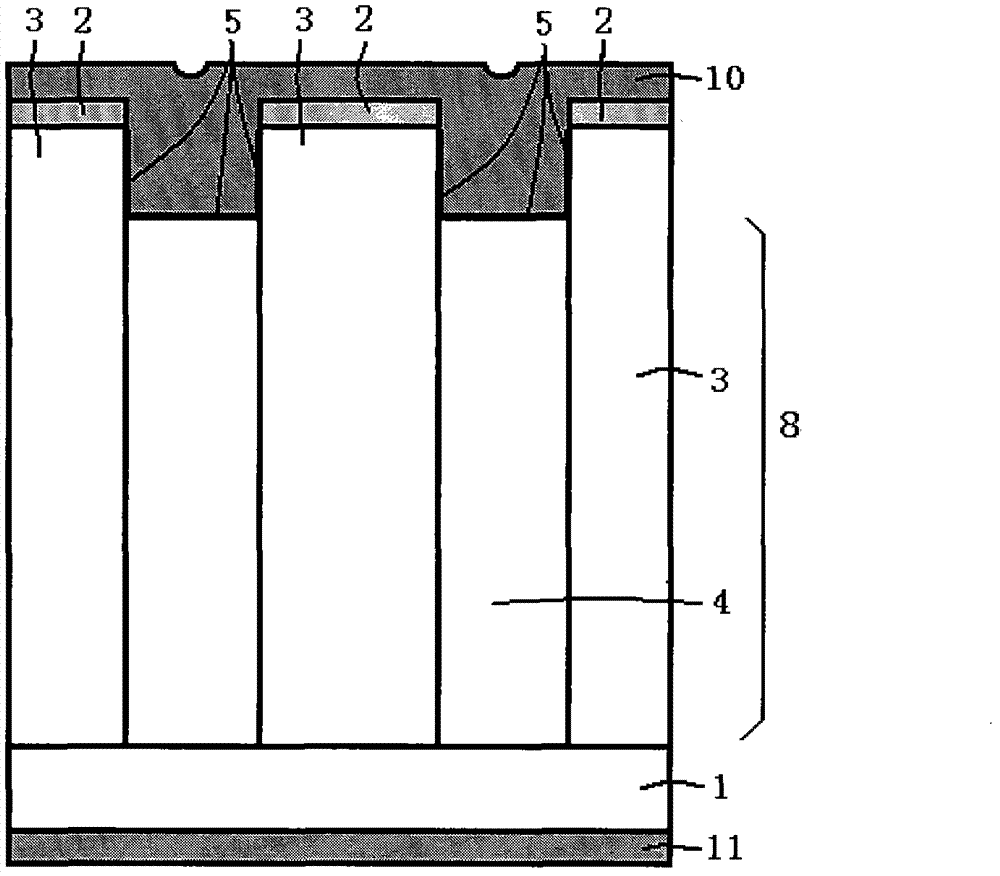
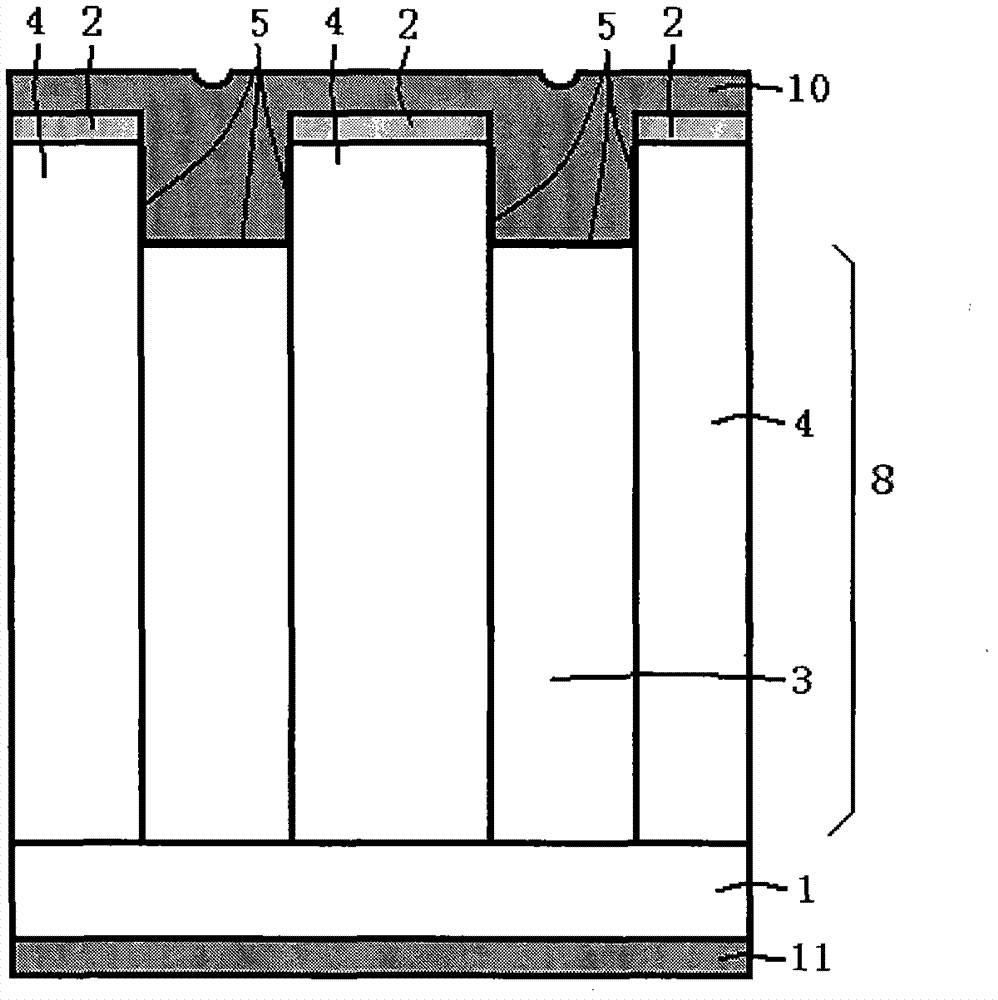
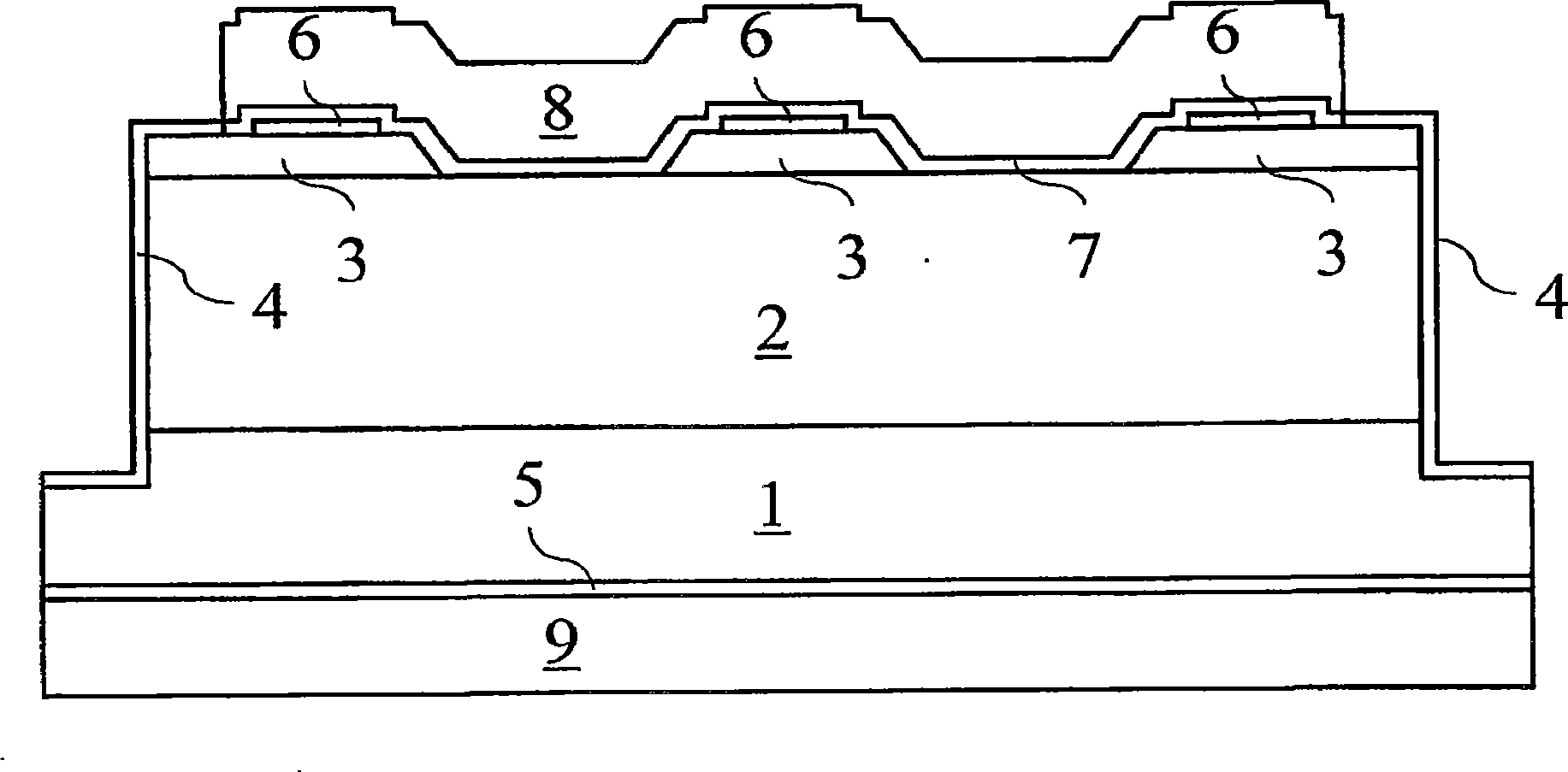
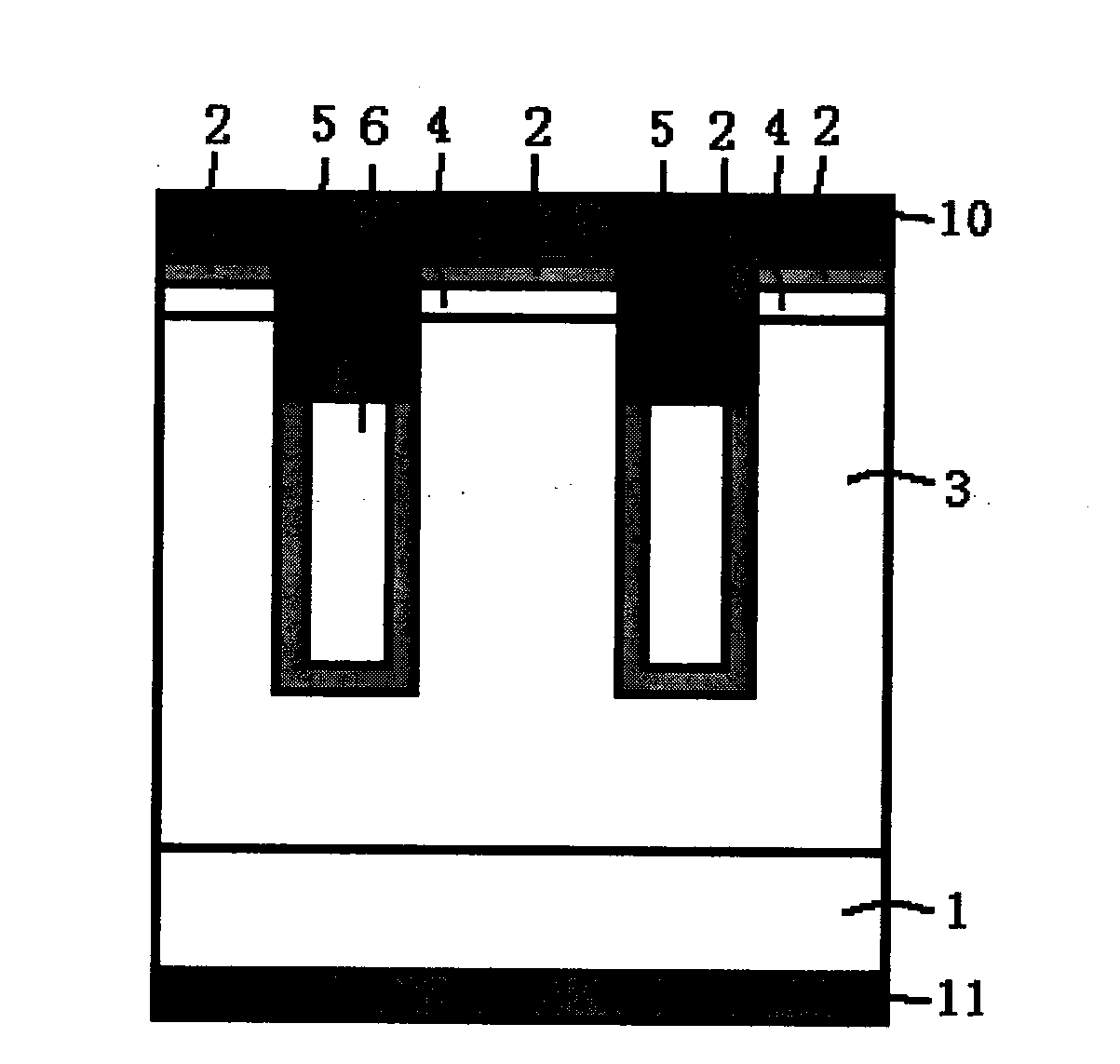
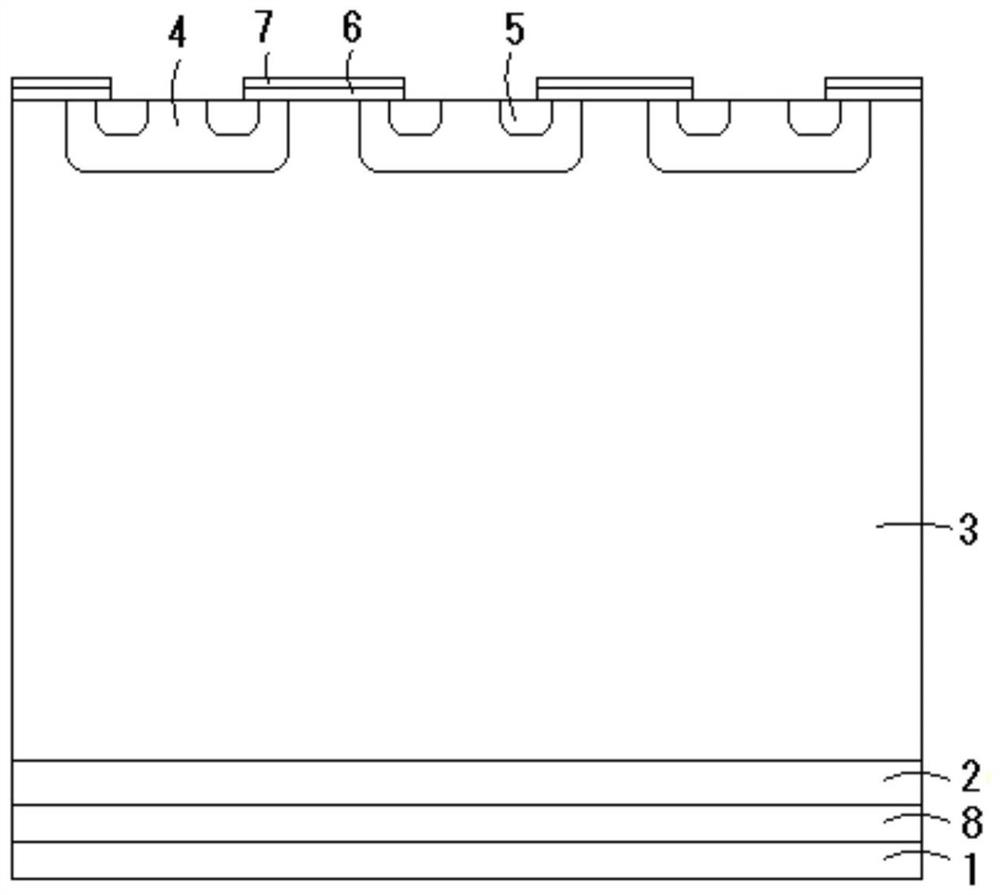
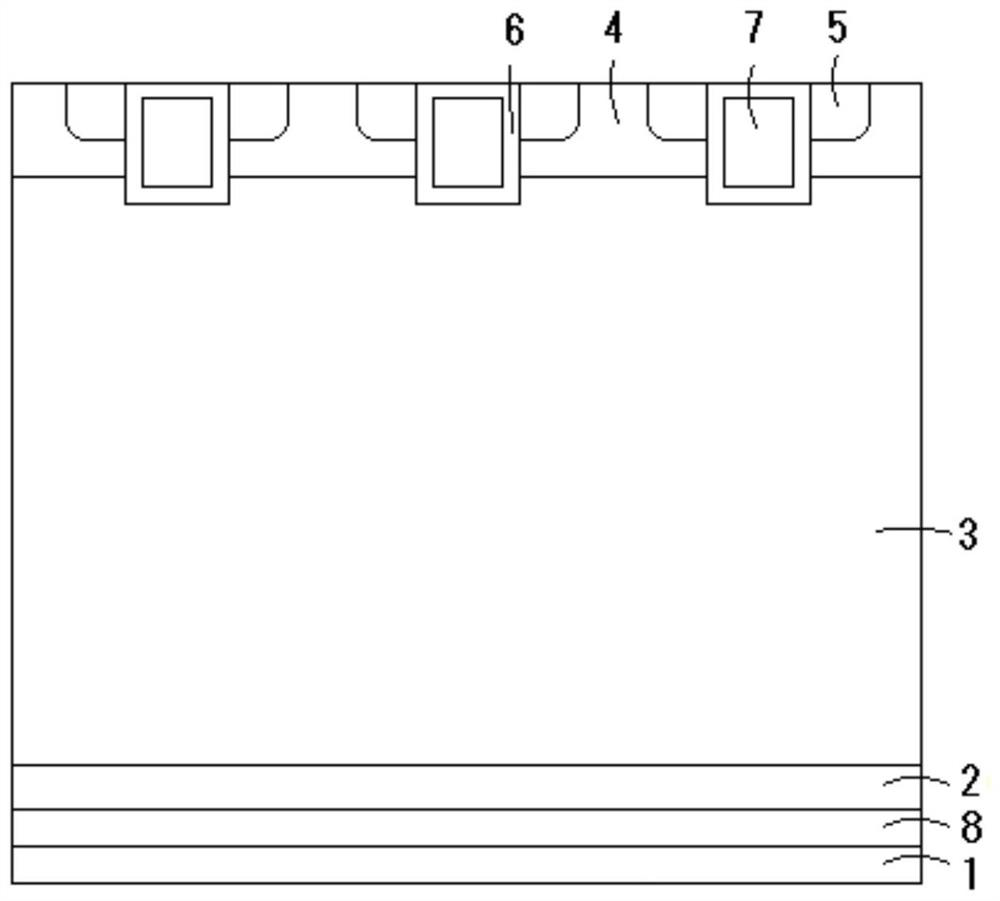
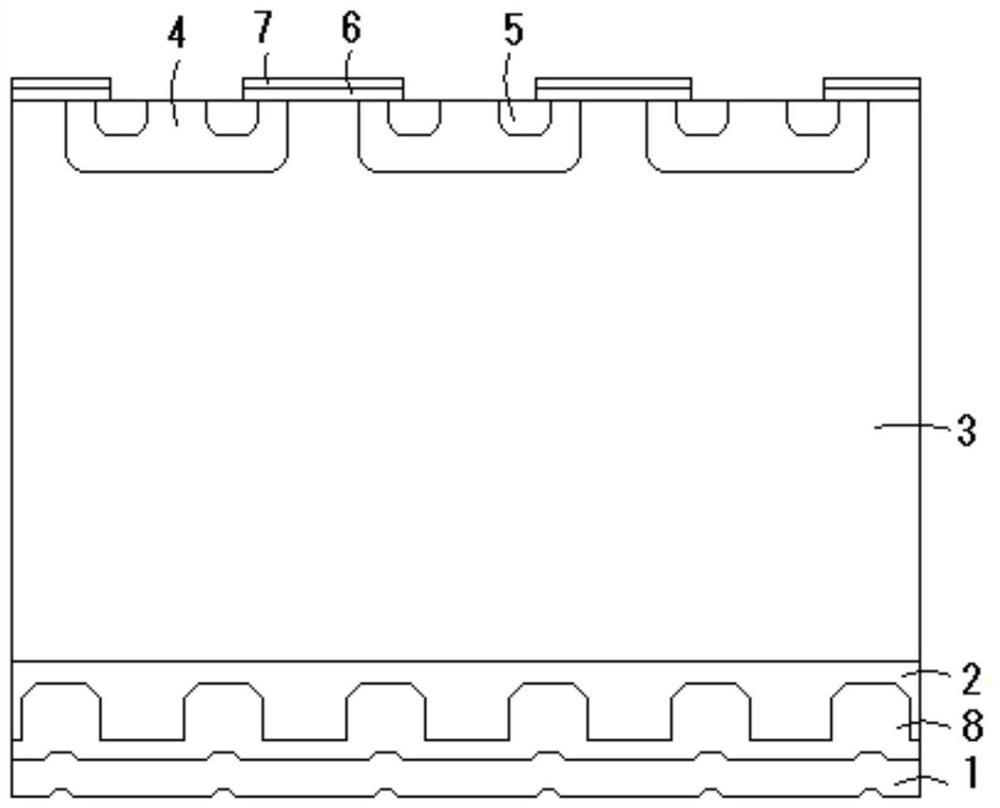
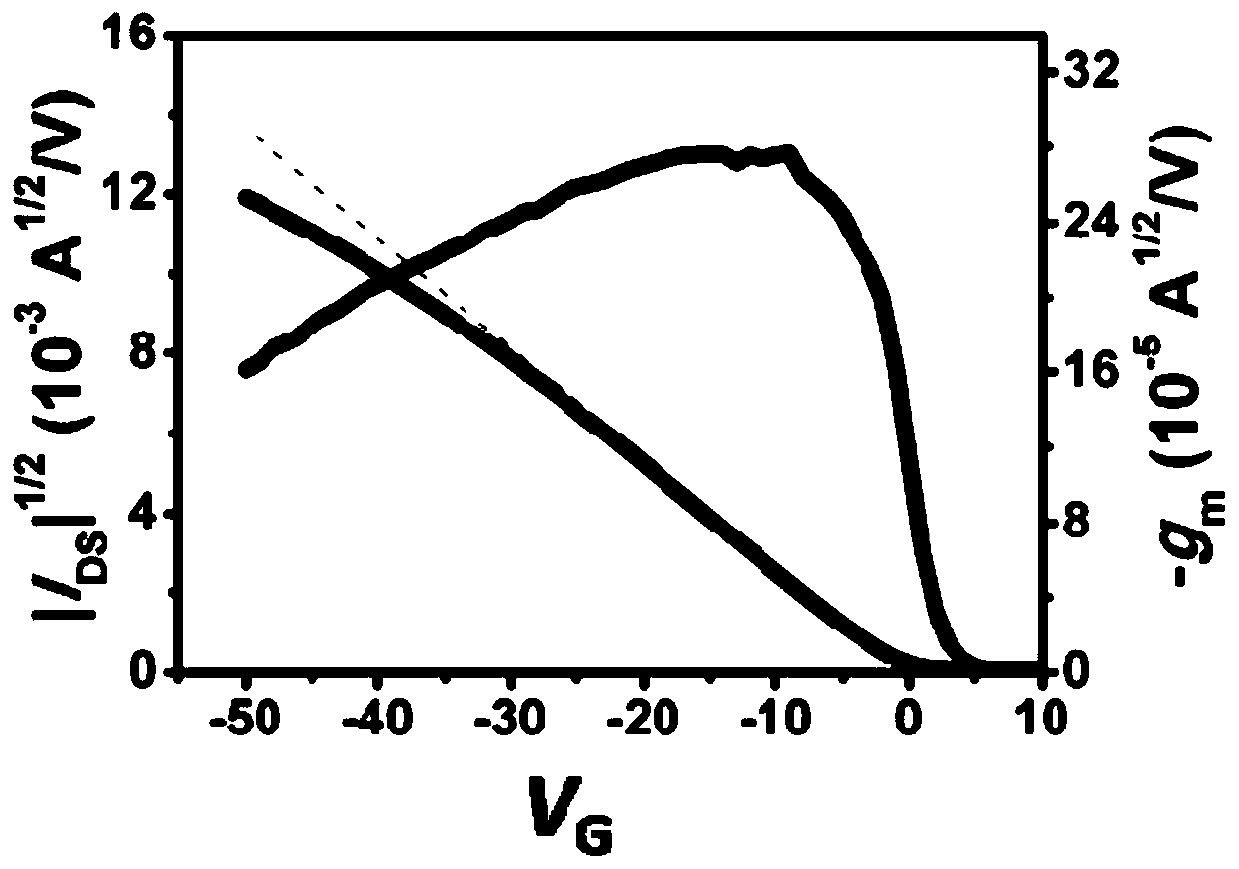
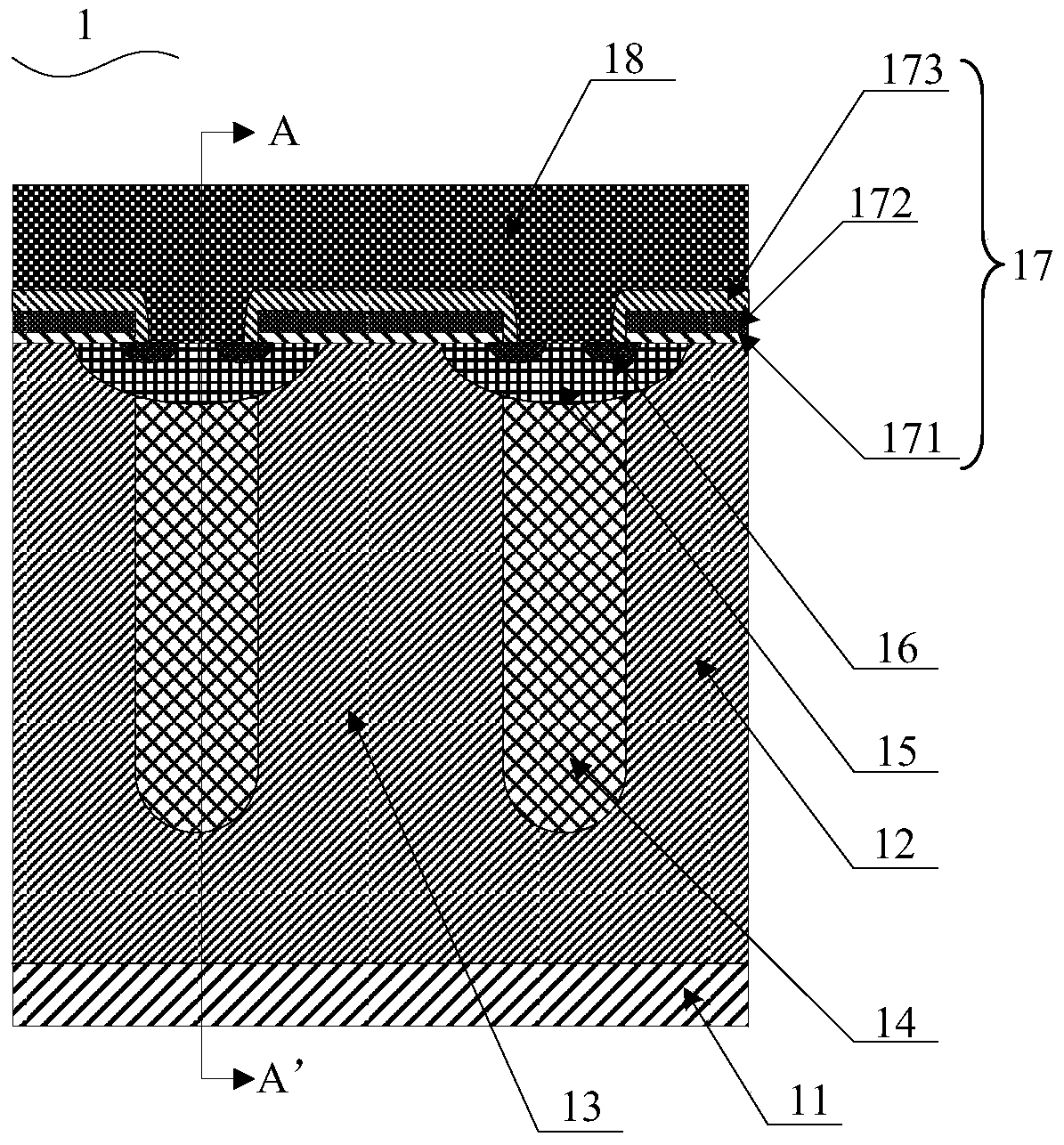
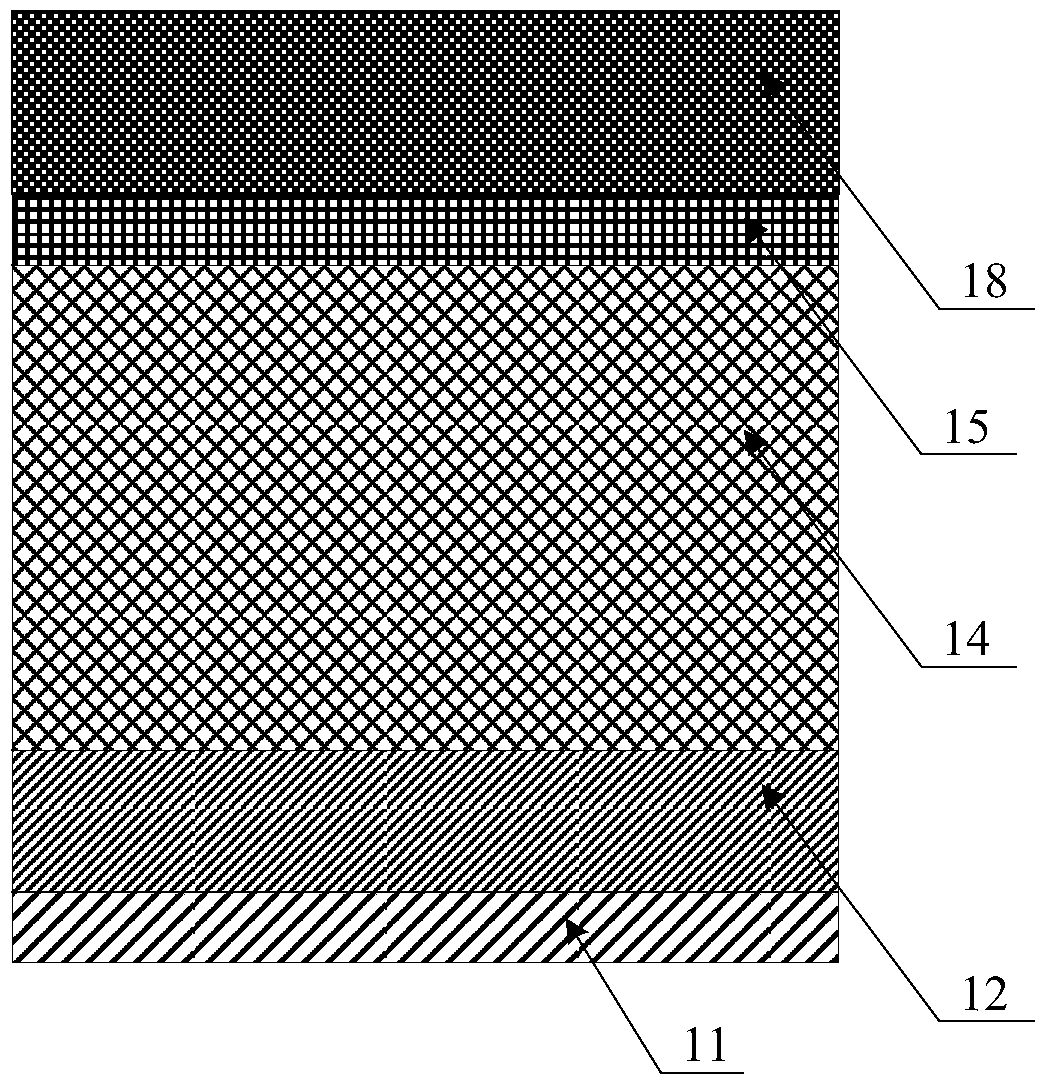
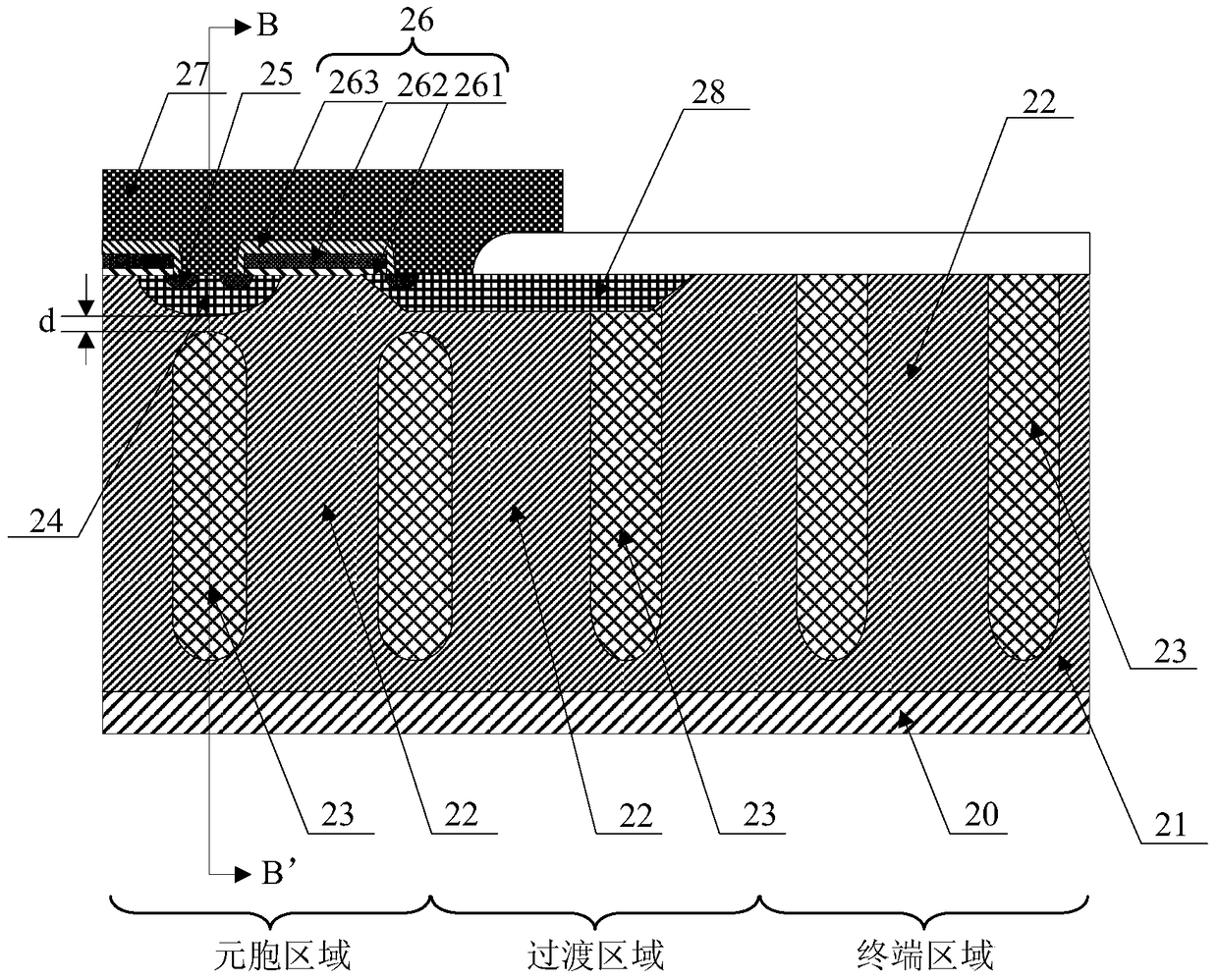
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Minority carrier injection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
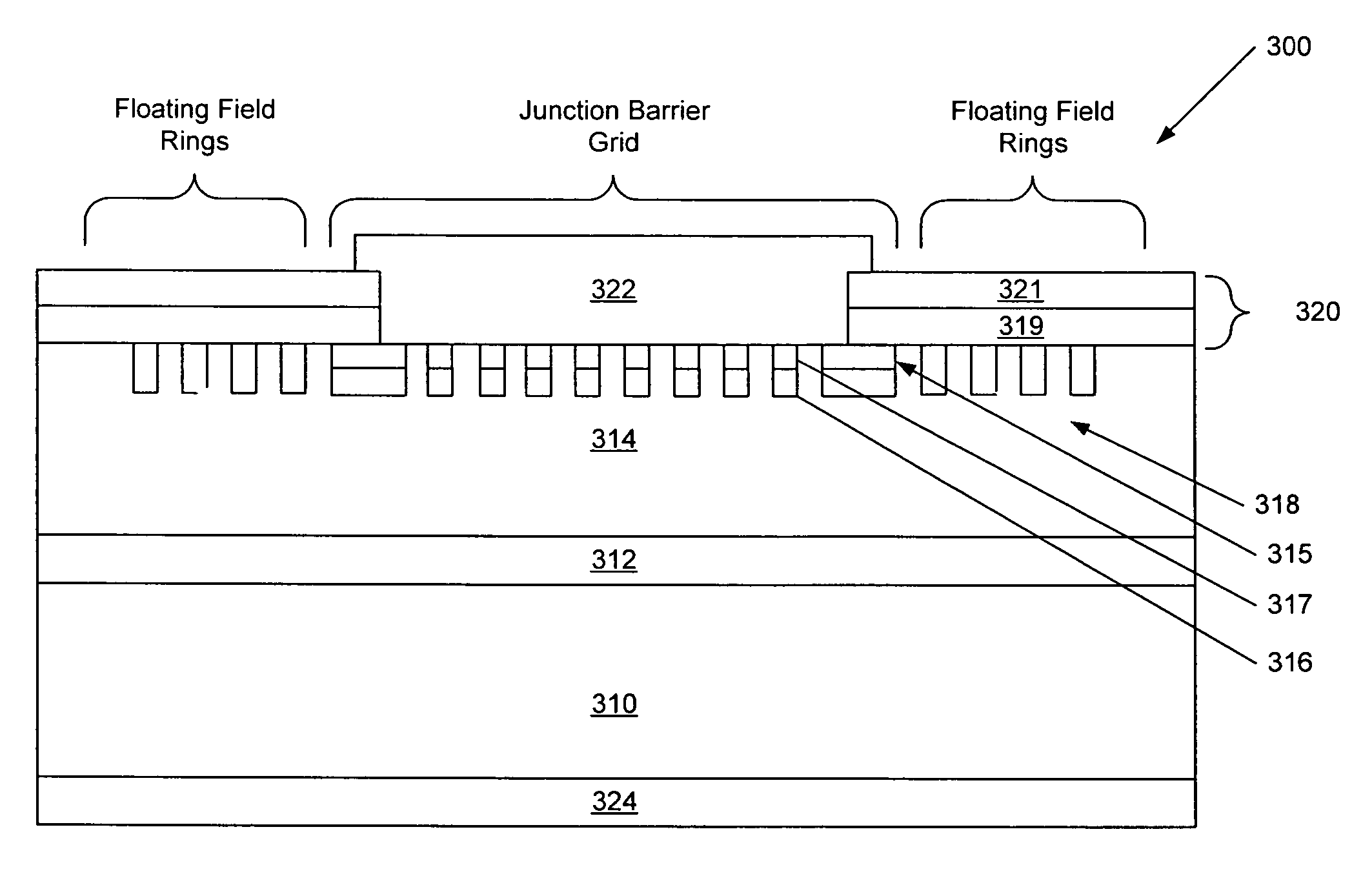
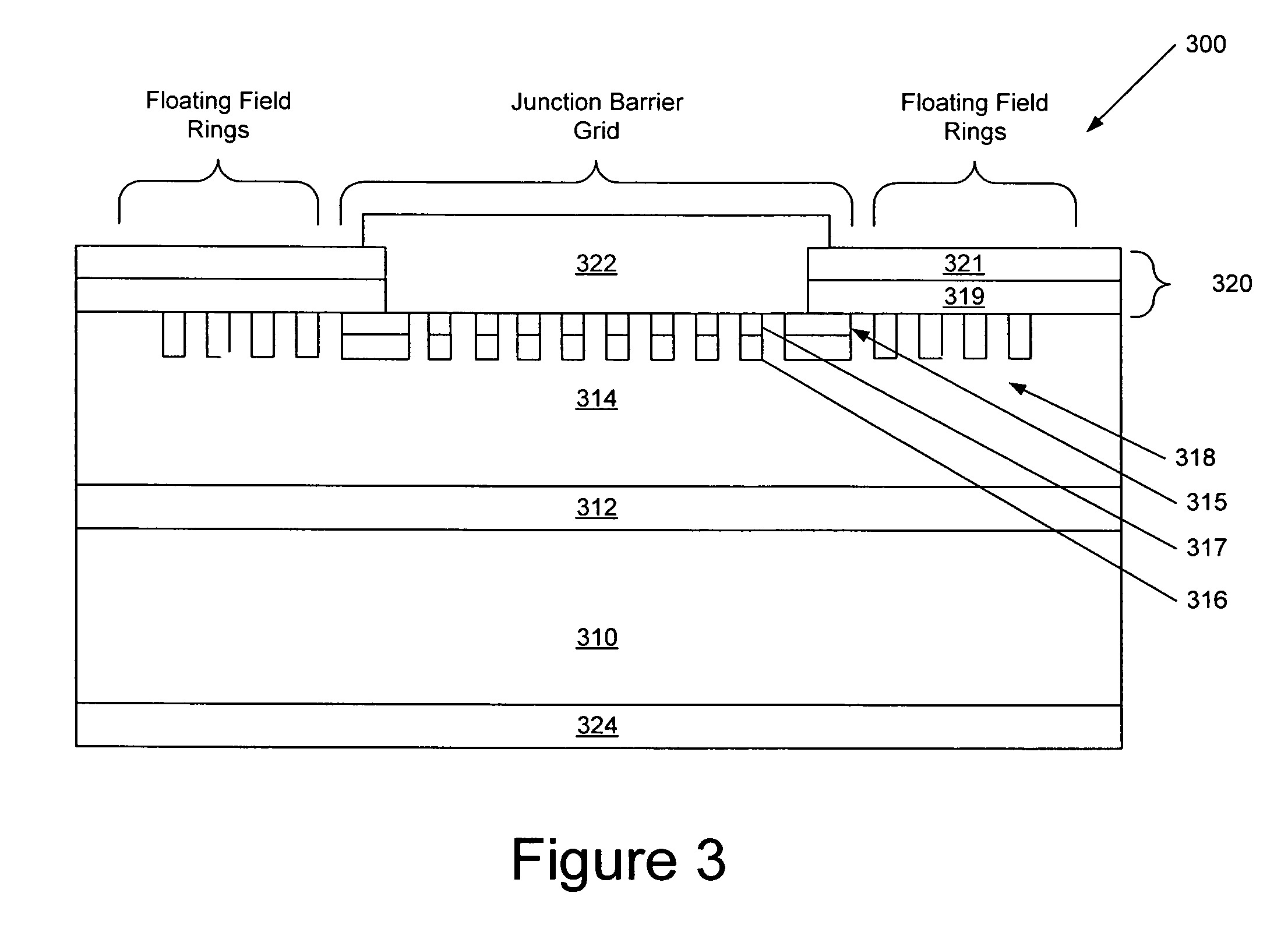
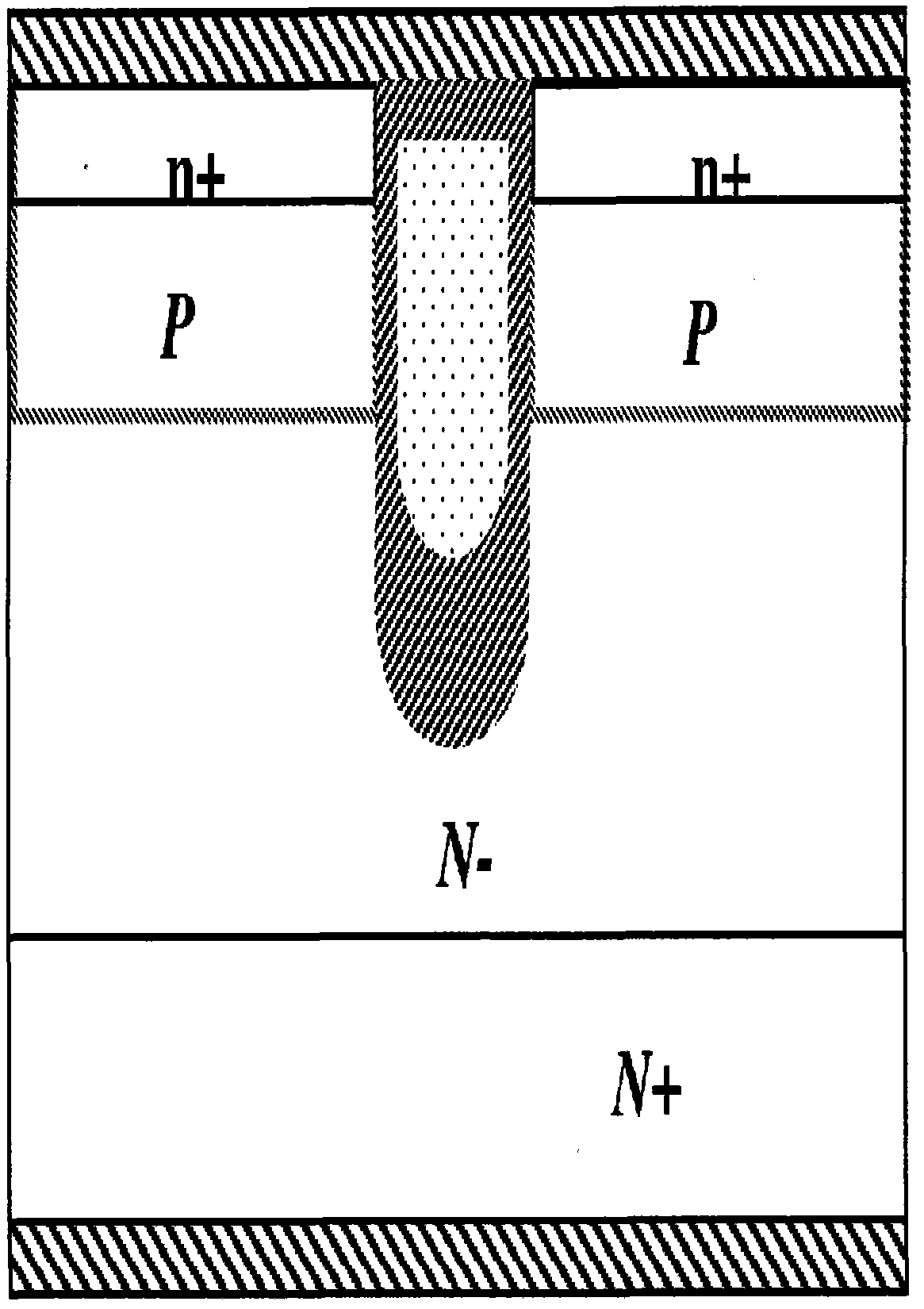
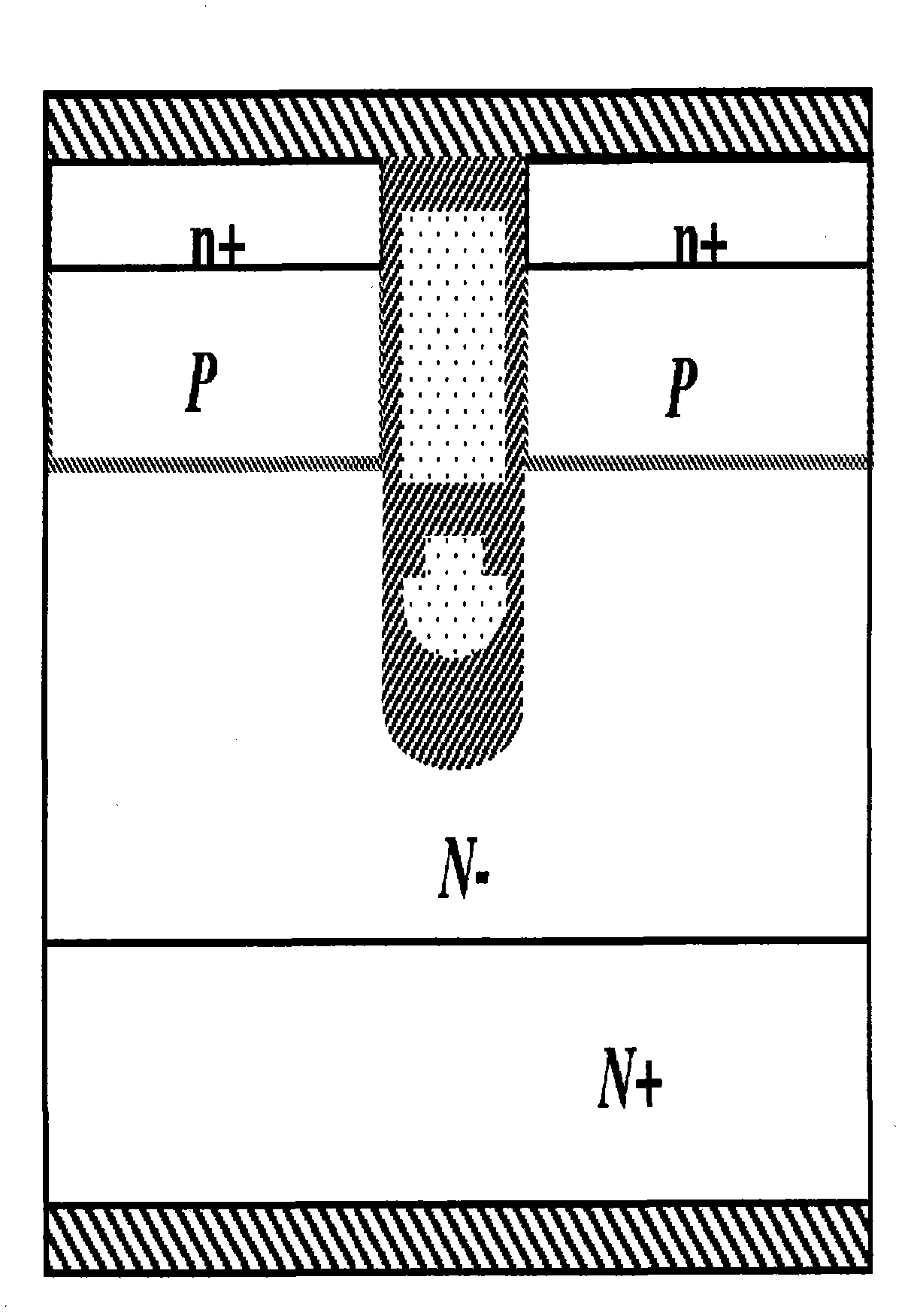
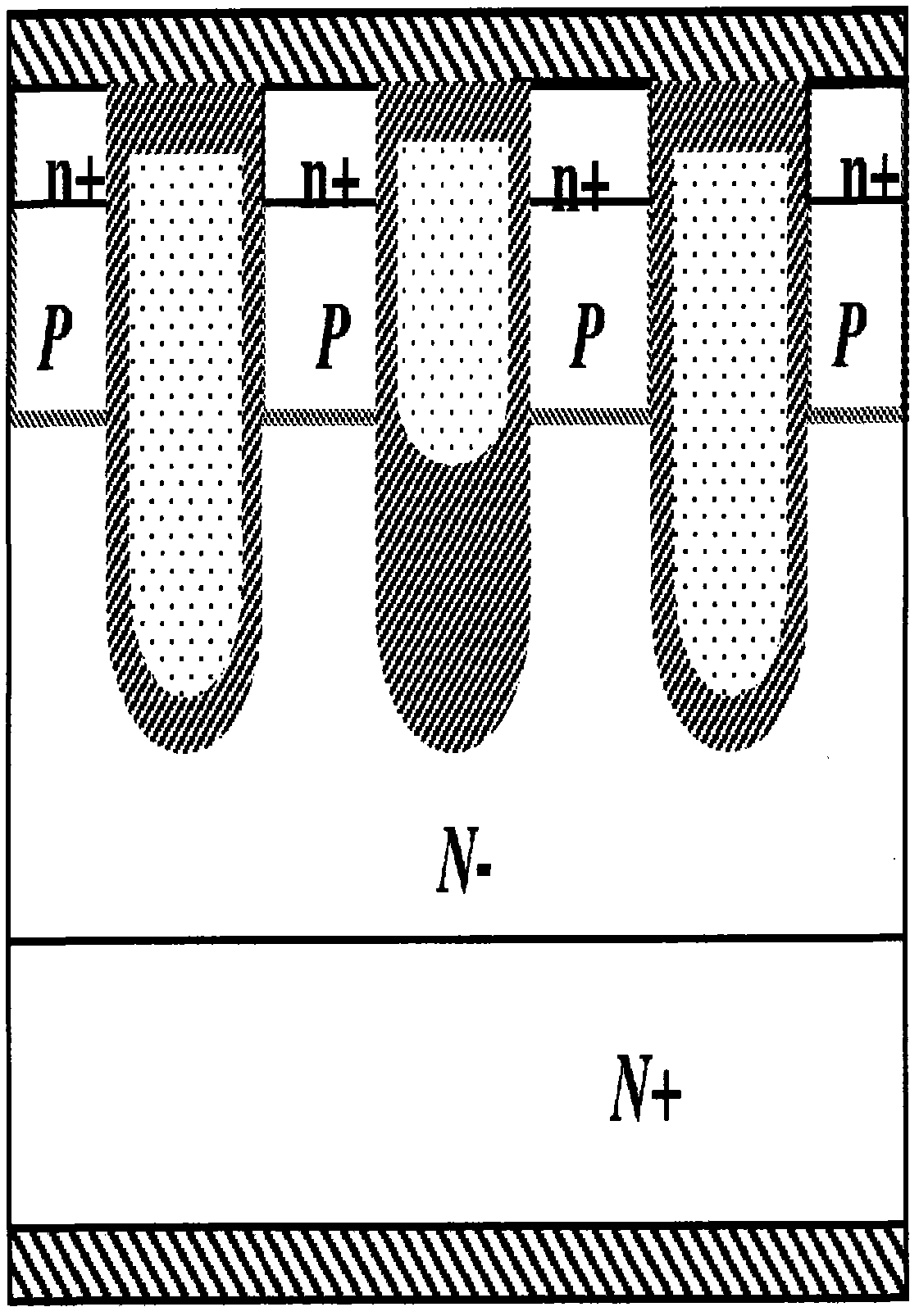
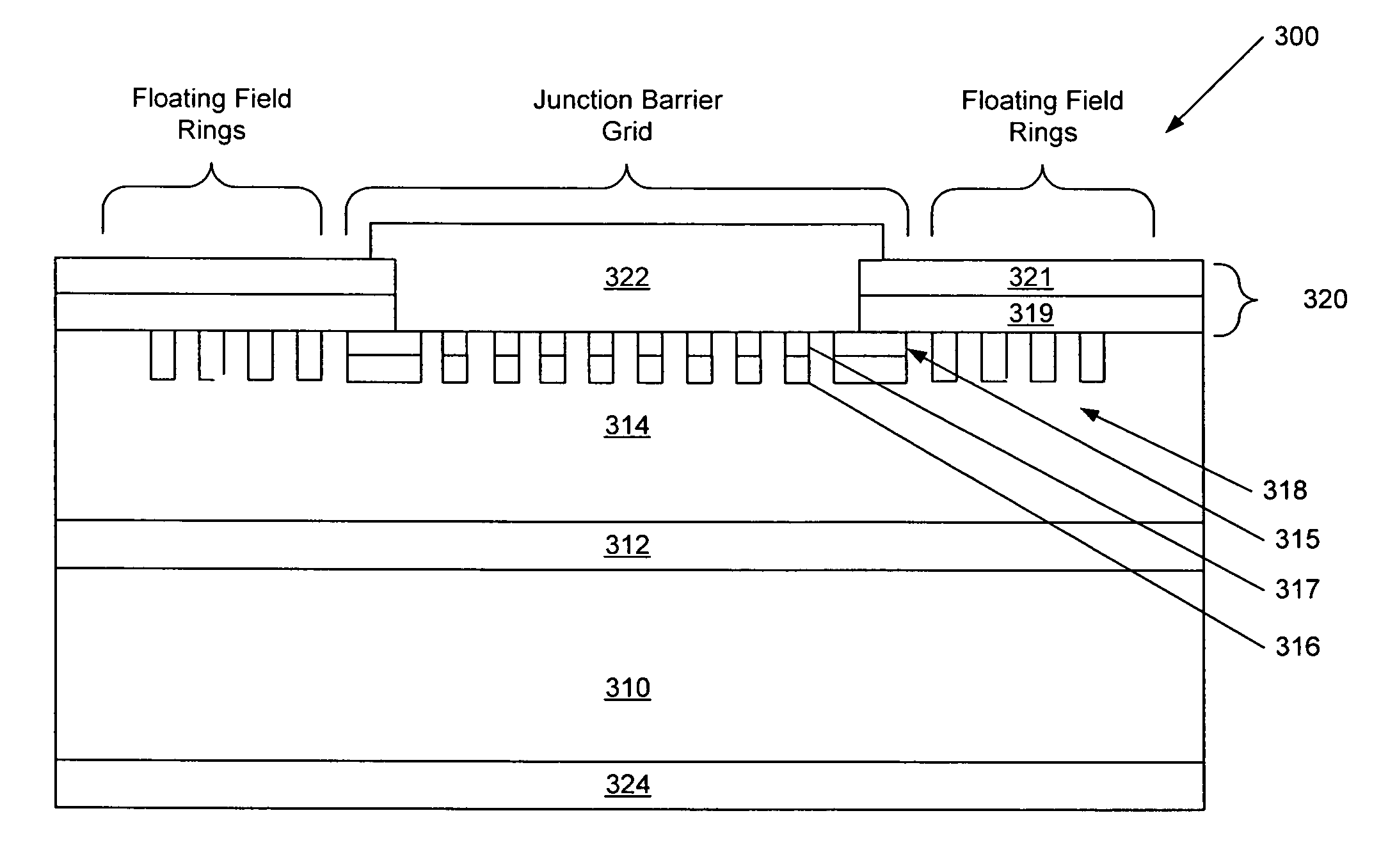
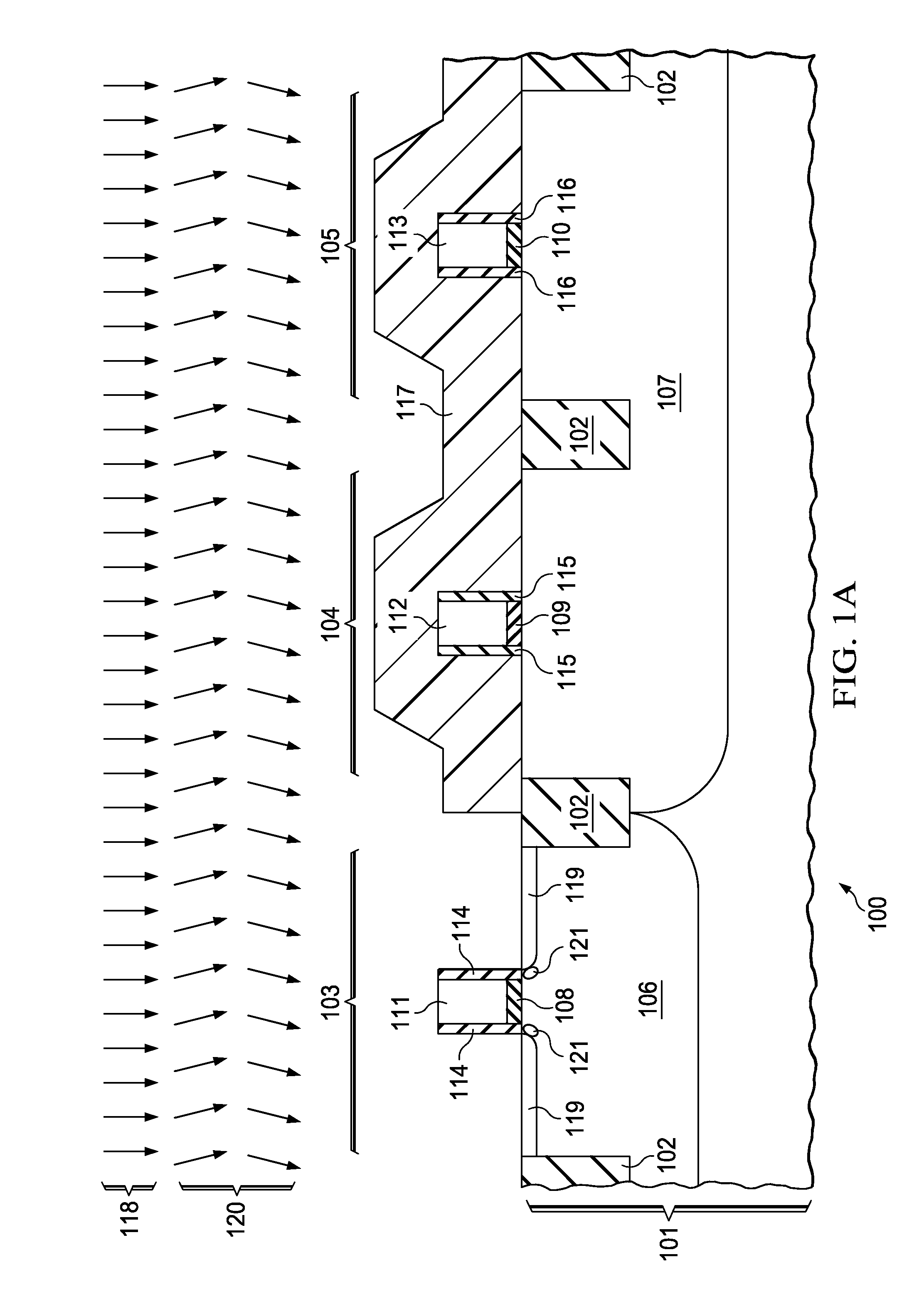
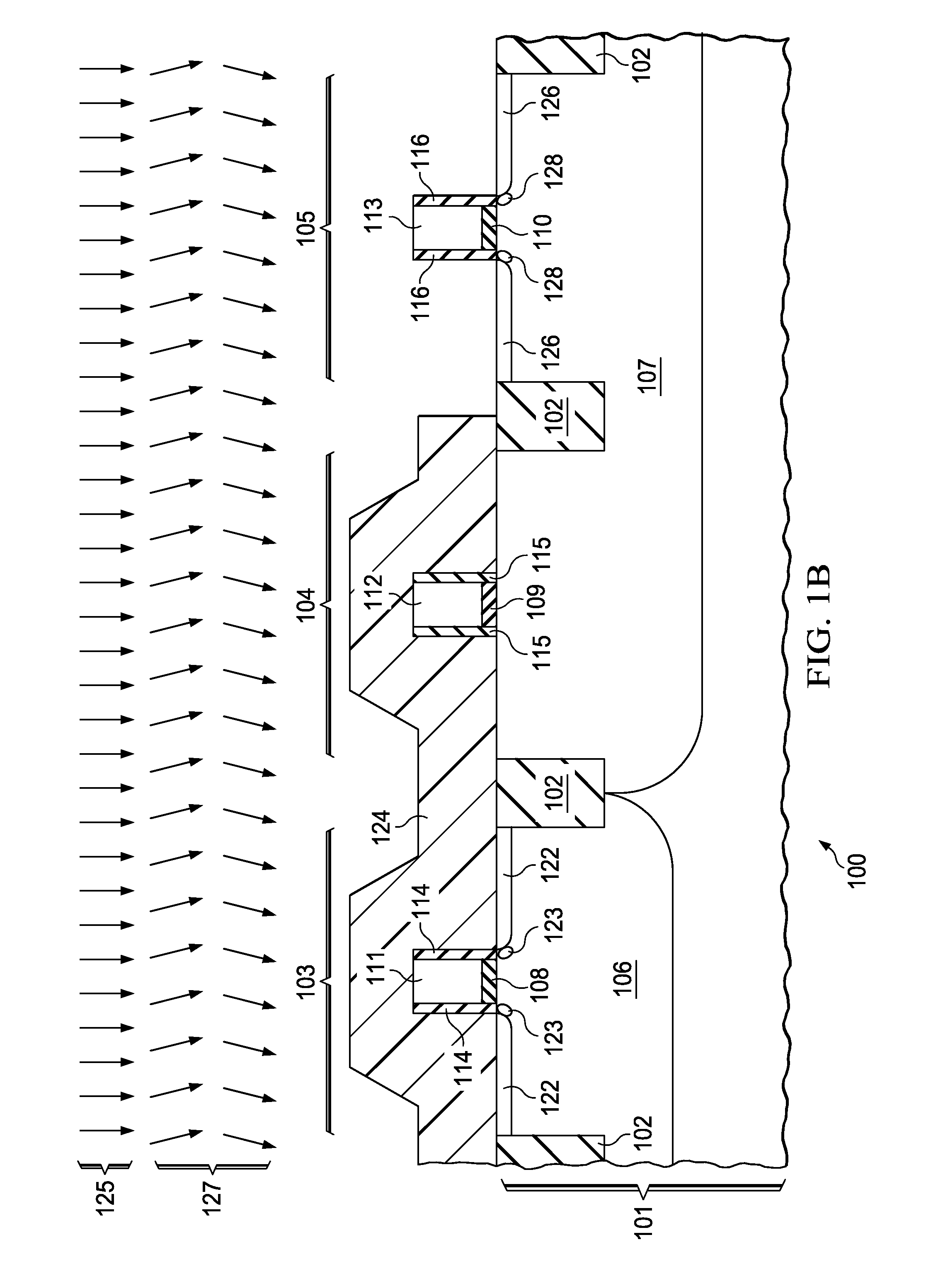
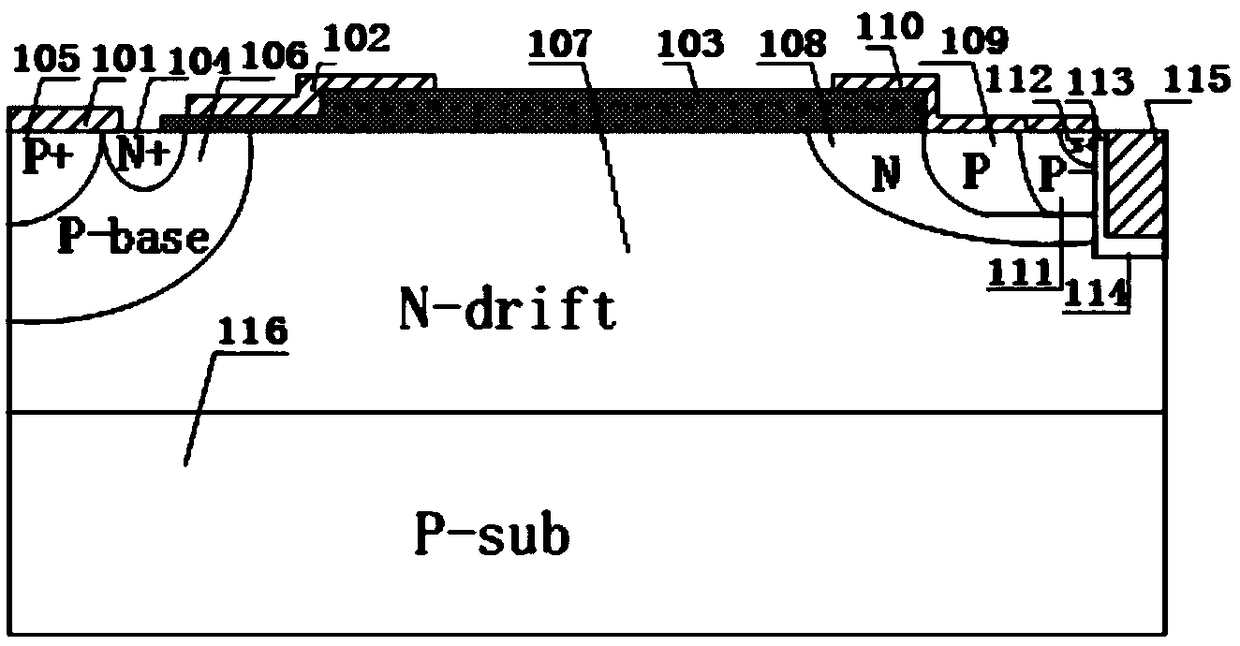
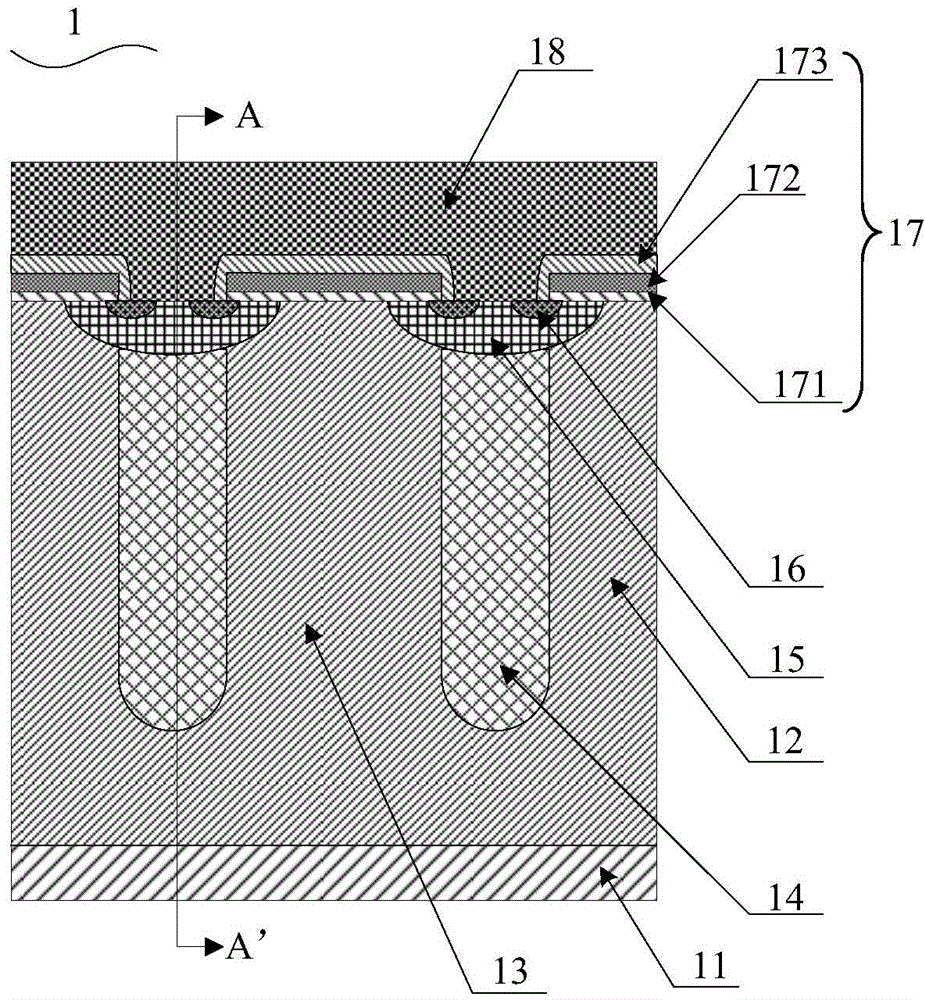
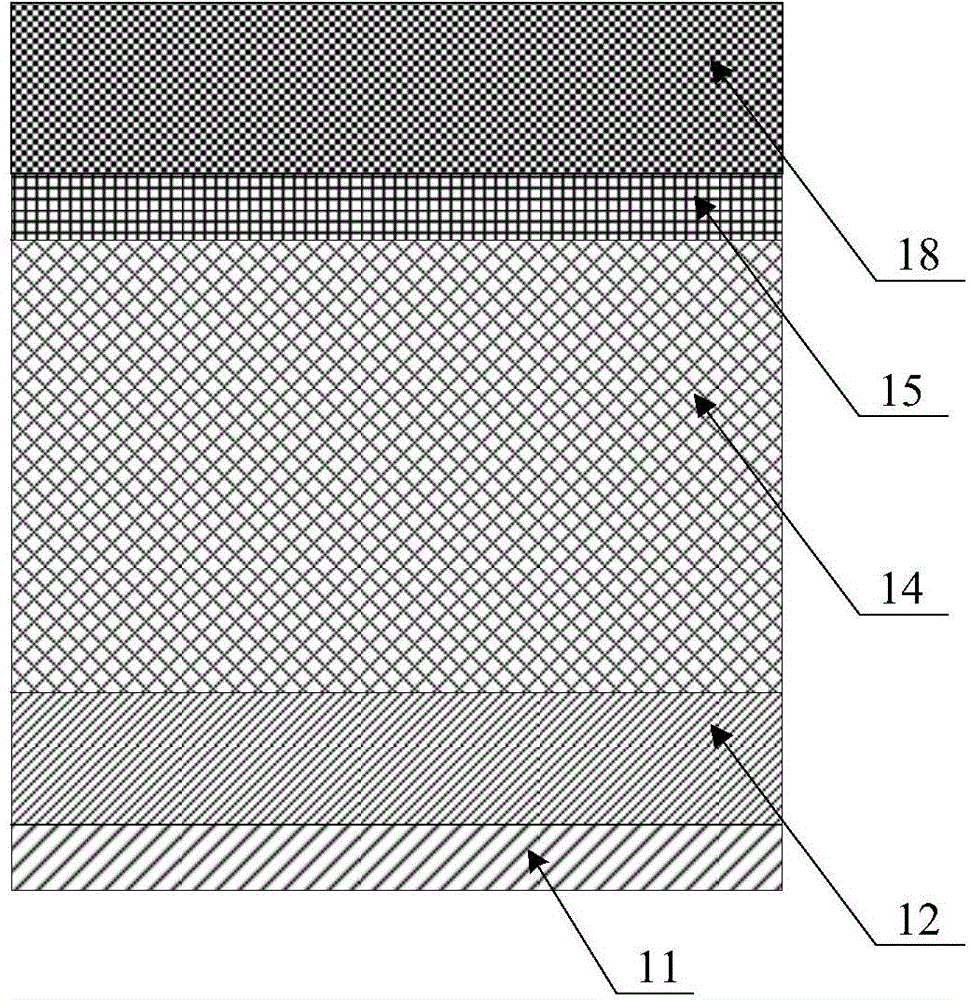
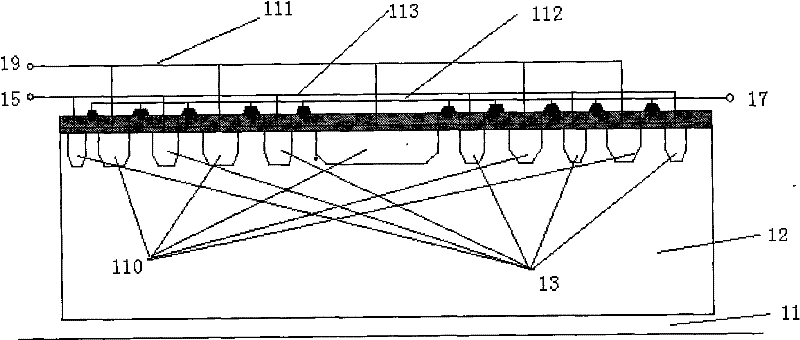
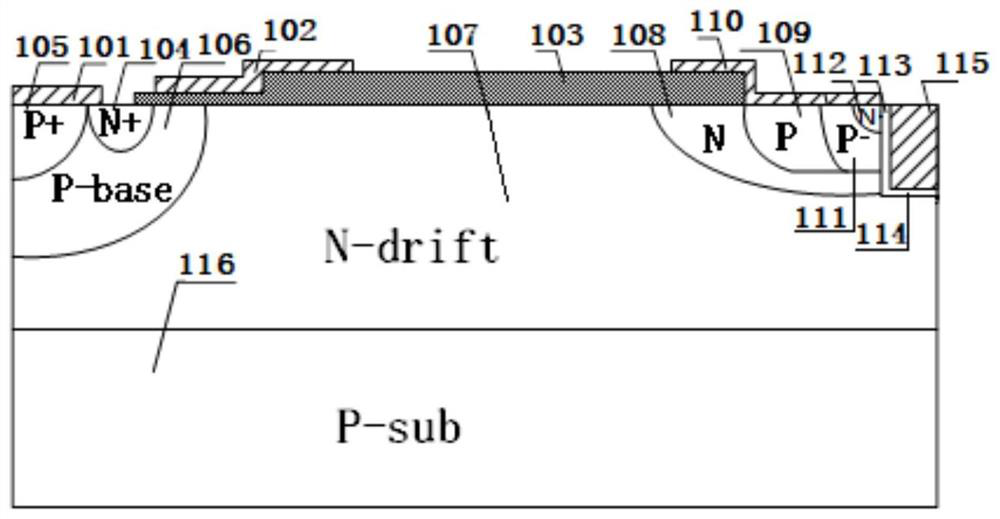
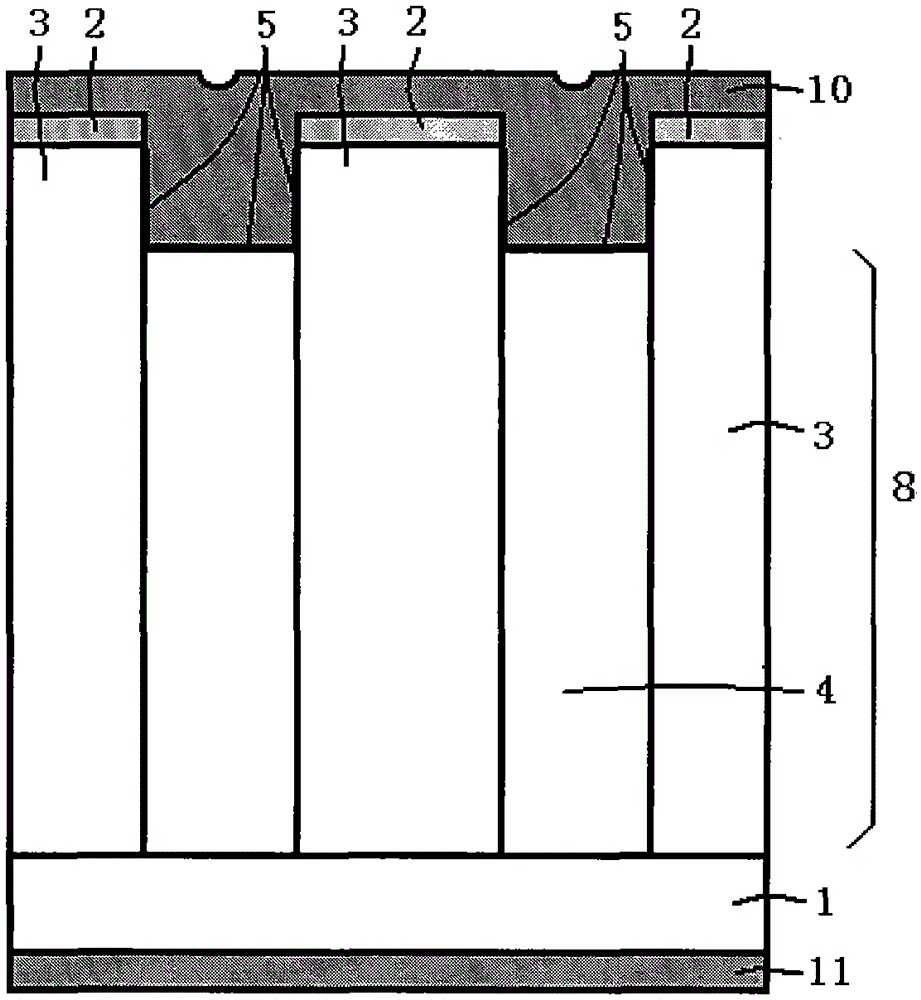
Silicon carbide junction barrier schottky diodes with supressed minority carrier injection
ActiveUS20060255423A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky diodeSilicon
Integral structures that block the current conduction of the built-in PiN diode in a junction barrier Schottky (JBS) structure are provided. A Schottky diode may be incorporated in series with the PiN diode, where the Schottky diode is of opposite direction to that of the PiN diode. A series resistance or and insulating layer may be provided between the PiN diode and a Schottky contact. Silicon carbide Schottky diodes and methods of fabricating silicon carbide Schottky diodes that include a silicon carbide junction barrier region disposed within a drift region of the diode are also provided. The junction barrier region includes a first region of silicon carbide having a first doping concentration in the drift region of the diode and a second region of silicon carbide in the drift region and disposed between the first region of silicon carbide and a Schottky contact of the Schottky diode. The second region is in contact with the first region of silicon carbide and the Schottky contact. The second region of silicon carbide has a second doping concentration that is less than the first doping concentration.
Owner:CREE INC
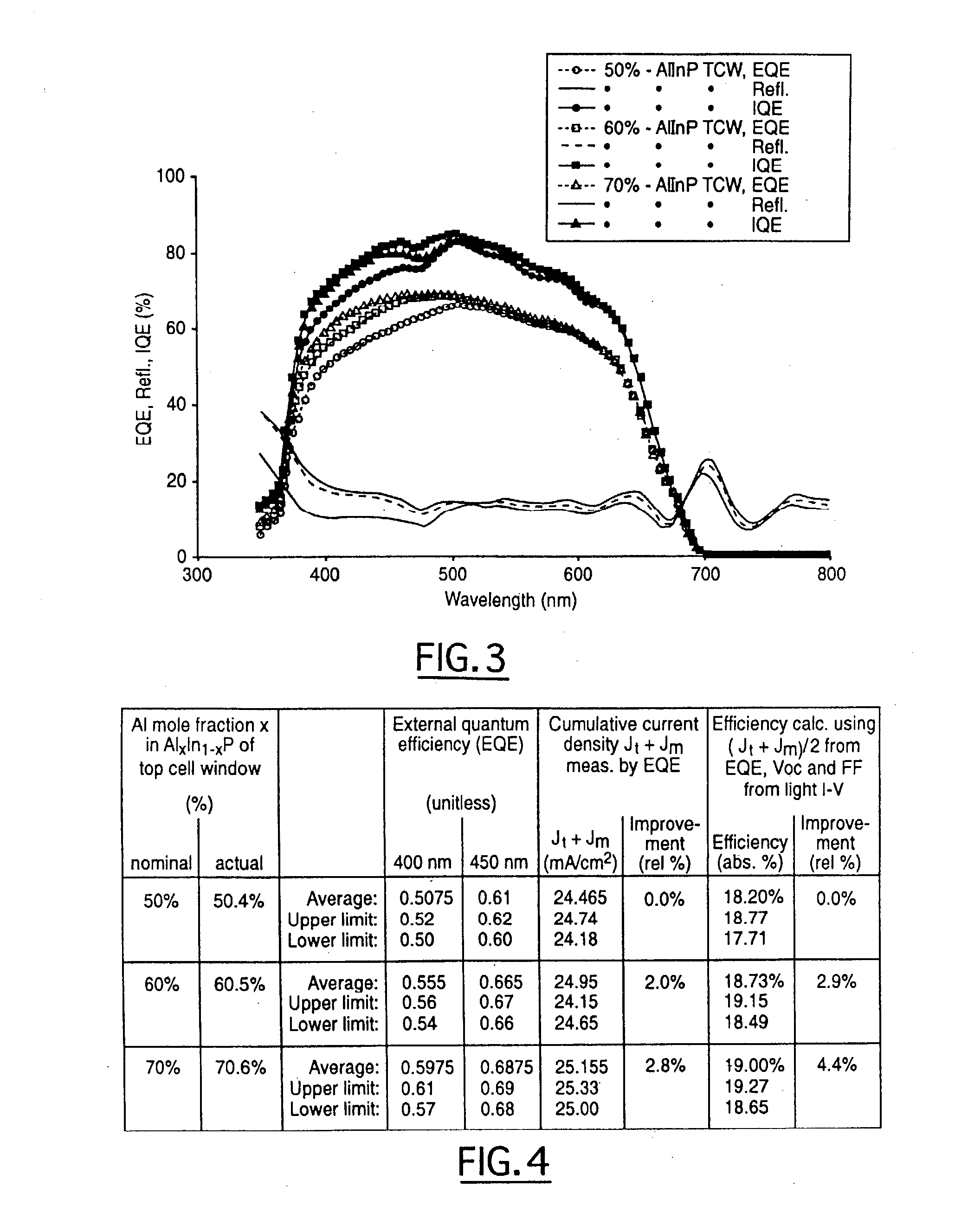
Wide-bandgap, lattice-mismatched window layer for a solar conversion device
ActiveUS7119271B2Improved surface passivationEnhanced light trapping effectPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLattice mismatchCell layer
A photovoltaic cell or other optoelectronic device having a wide-bandgap semiconductor used in the window layer. This wider bandgap is achieved by using a semiconductor composition that is not lattice-matched to the cell layer directly beneath it and / or to the growth substrate. The wider bandgap of the window layer increases the transmission of short wavelength light into the emitter and base layers of the photovoltaic cell. This in turn increases the current generation in the photovoltaic cell. Additionally, the wider bandgap of the lattice mismatched window layer inhibits minority carrier injection and recombination in the window layer.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Semiconductor device structures and related processes
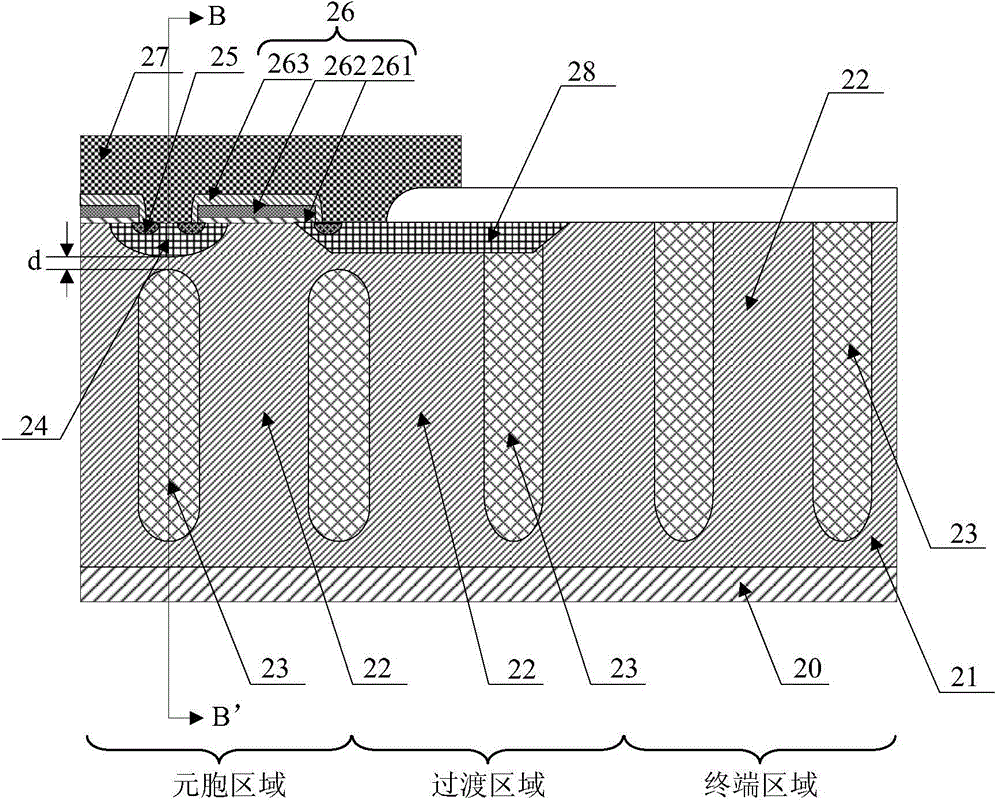
ActiveCN102007584AIncrease the on-resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETDopant
Improved highly reliable power RFP structures and fabrication and operation processes. The structure includes plurality of localized dopant concentrated zones beneath the trenches of RFPs, either floating or extending and merging with the body layer of the MOSFET or connecting with the source layer through a region of vertical doped region. This local dopant zone decreases the minority carrier injection efficiency of the body diode of the device and alters the electric field distribution during the body diode reverse recovery.
Owner:MAXPOWER SEMICON INC
Tuneable semiconductor device
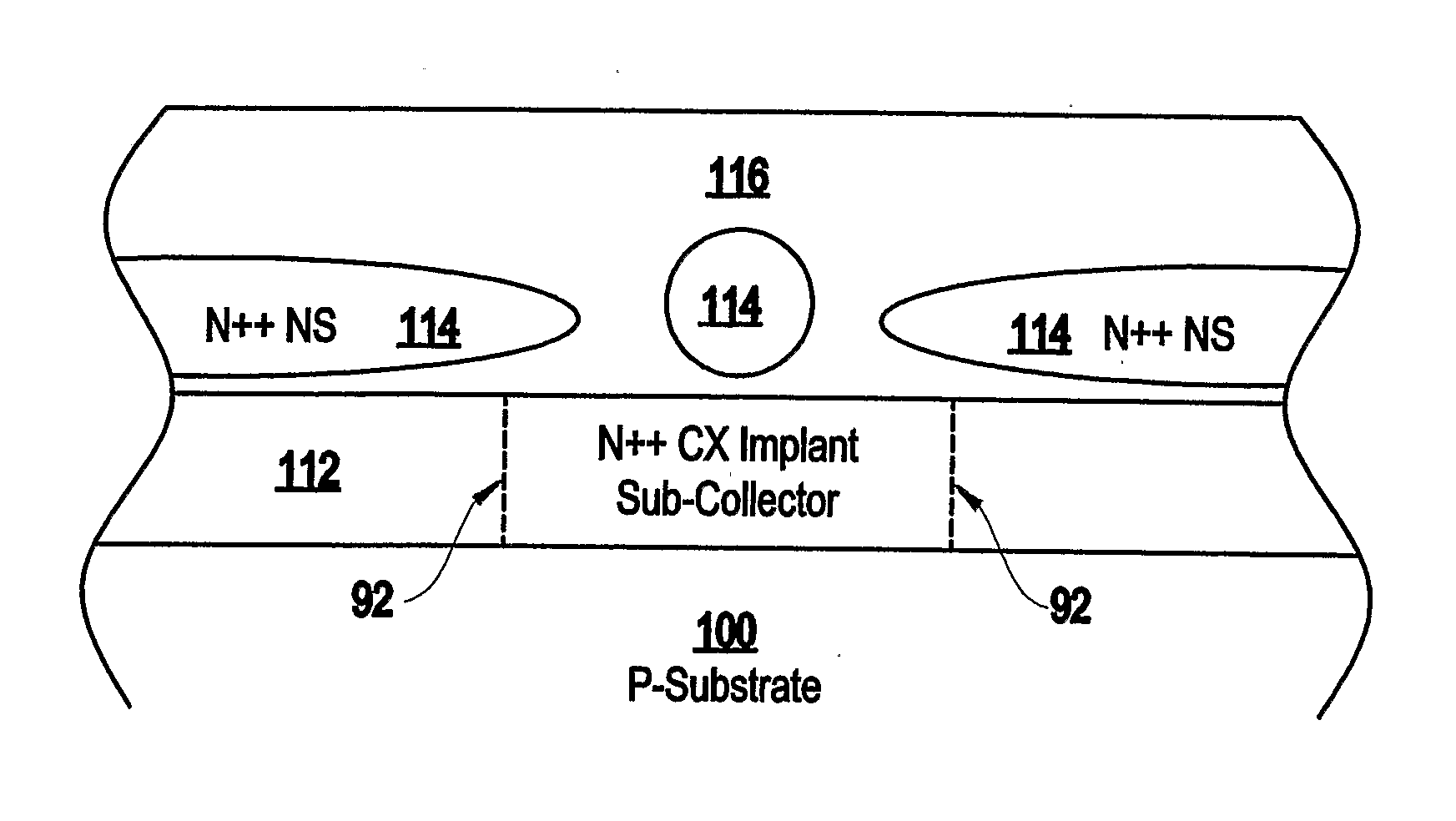
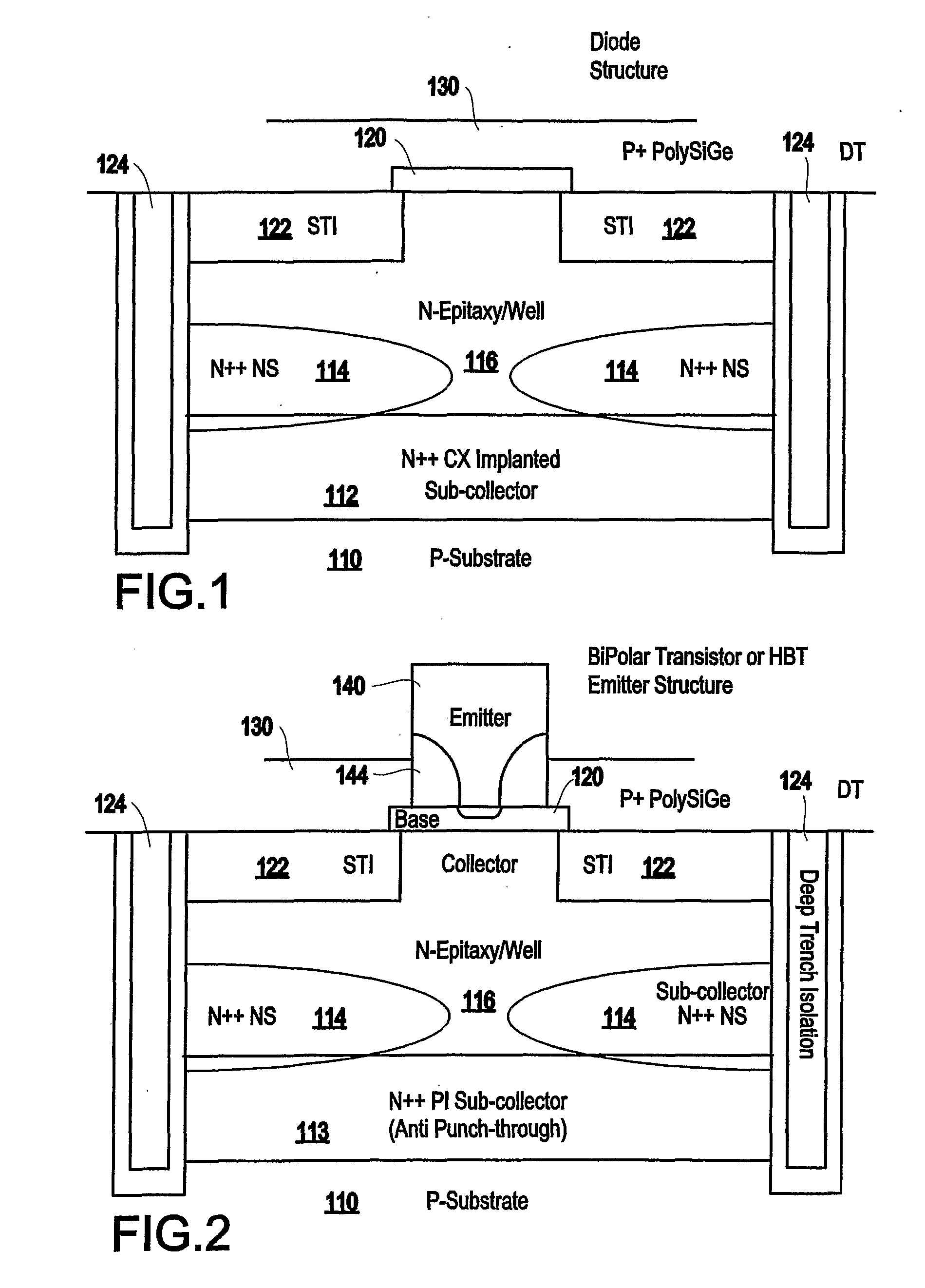
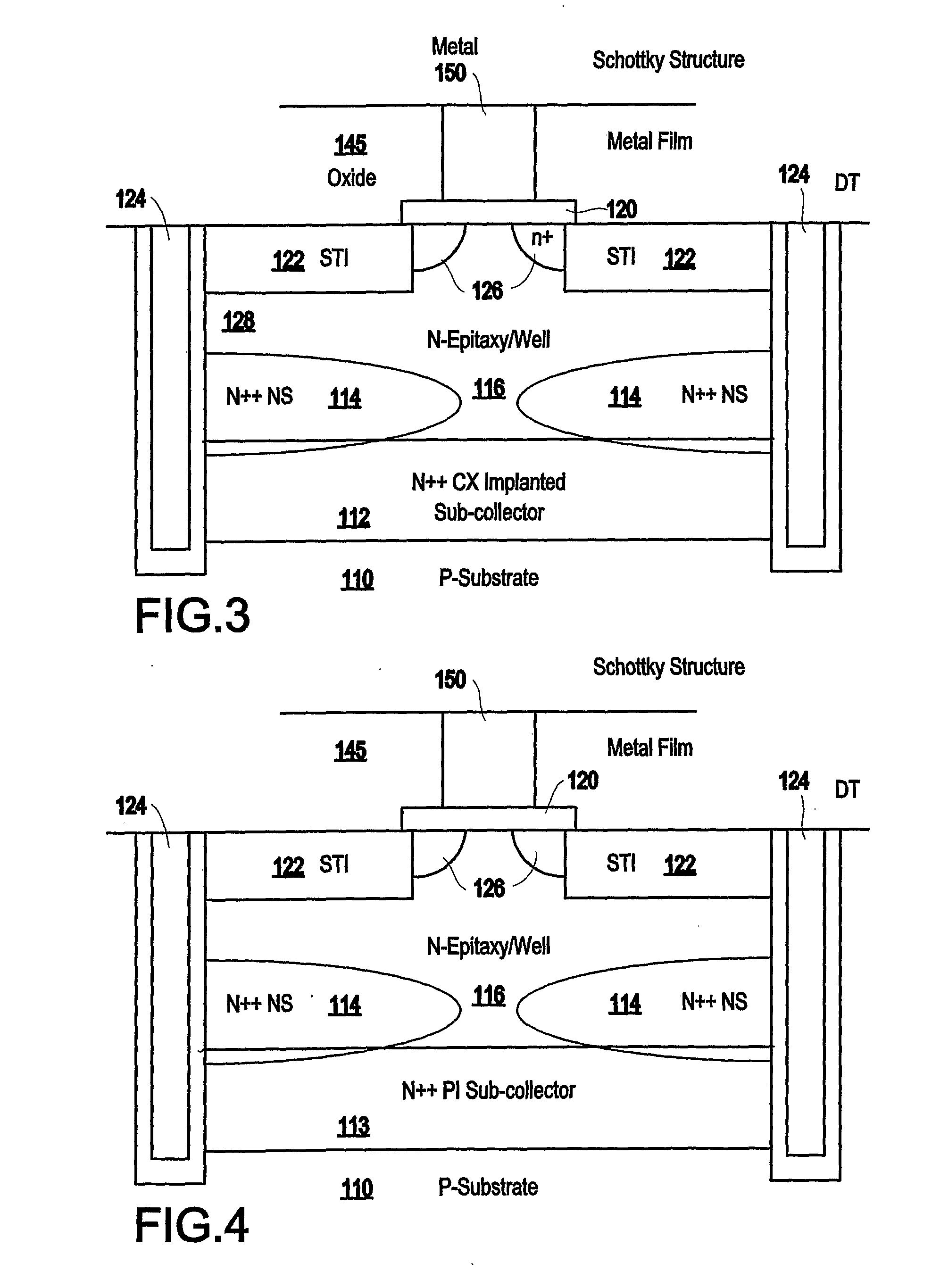
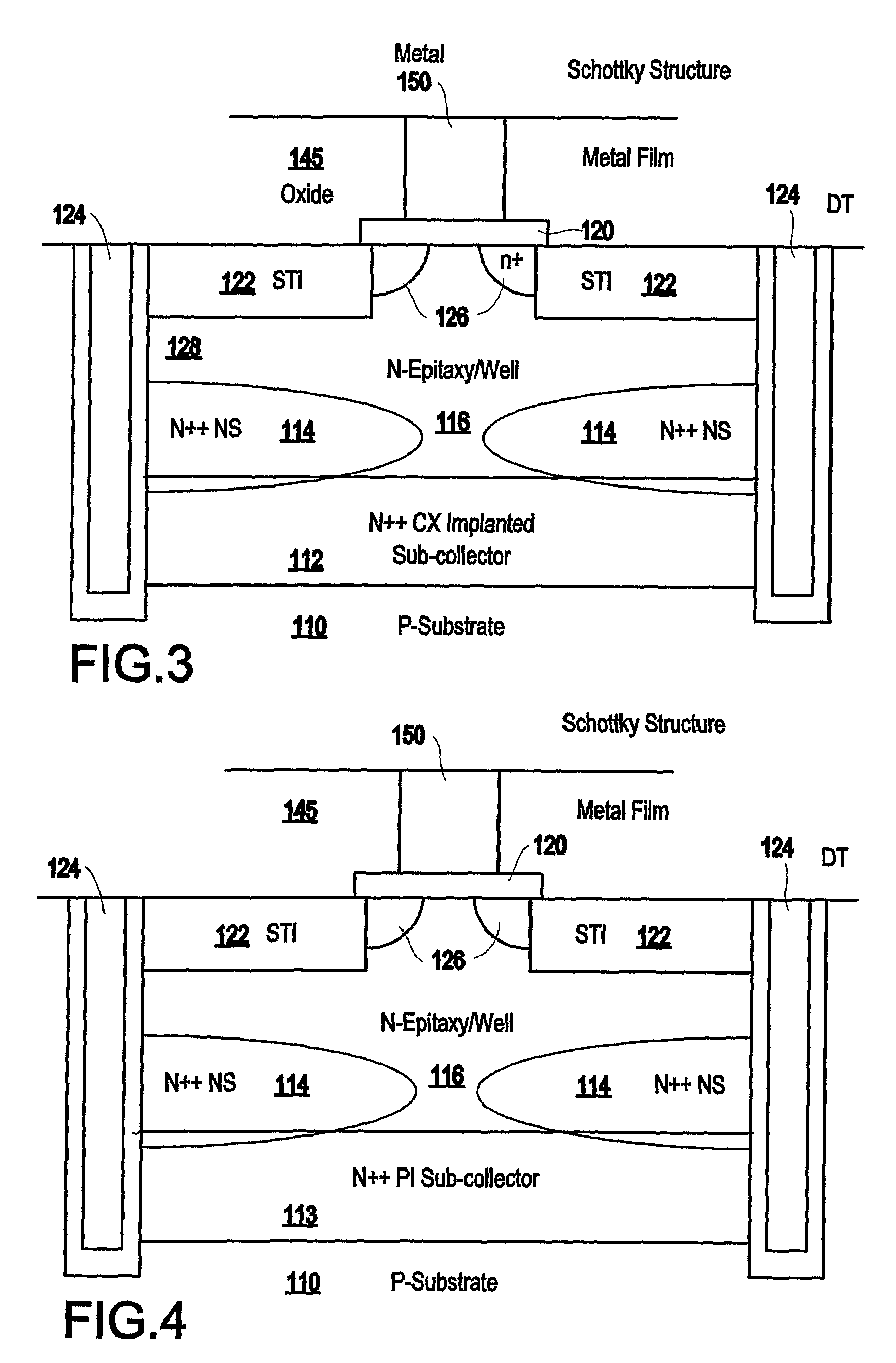
Disclosed is a method of forming a semiconductor structure that includes a discontinuous non-planar sub-collector having a different polarity than the underlying substrate. In addition, this structure includes an active area (collector) above the sub-collector, a base above the active area, and an emitter above the base. The distance between the discontinuous portions of the discontinuous sub-collector tunes the performance characteristics of the semiconductor structure. The performance characteristics that are tunable include breakdown voltage, unity current gain cutoff frequency, unity power gain cutoff frequency, transit frequency, current density, capacitance range, noise injection, minority carrier injection and trigger and holding voltage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
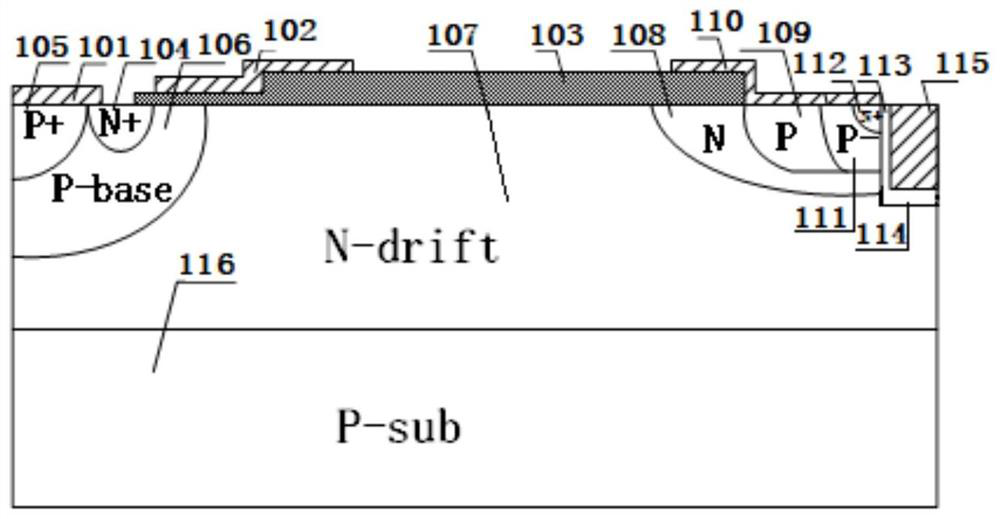
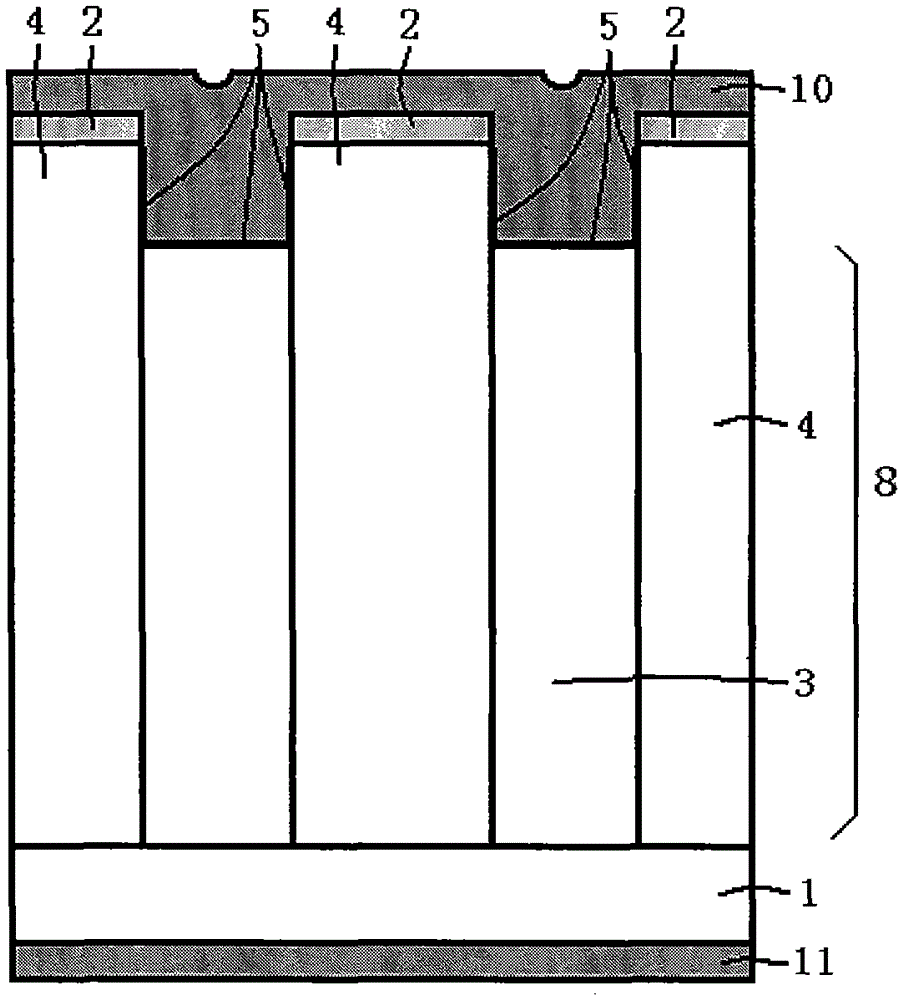
Silicon carbide junction barrier Schottky diodes with suppressed minority carrier injection
ActiveUS8901699B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky diodeMaterials science
Integral structures that block the current conduction of the built-in PiN diode in a junction barrier Schottky (JBS) structure are provided. A Schottky diode may be incorporated in series with the PiN diode, where the Schottky diode is of opposite direction to that of the PiN diode. A series resistance or and insulating layer may be provided between the PiN diode and a Schottky contact. Silicon carbide Schottky diodes and methods of fabricating silicon carbide Schottky diodes that include a silicon carbide junction barrier region disposed within a drift region of the diode are also provided. The junction barrier region includes a first region of silicon carbide having a first doping concentration in the drift region of the diode and a second region of silicon carbide in the drift region and disposed between the first region of silicon carbide and a Schottky contact of the Schottky diode. The second region is in contact with the first region of silicon carbide and the Schottky contact. The second region of silicon carbide has a second doping concentration that is less than the first doping concentration.
Owner:CREE INC
Tuneable semiconductor device with discontinuous portions in the sub-collector
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
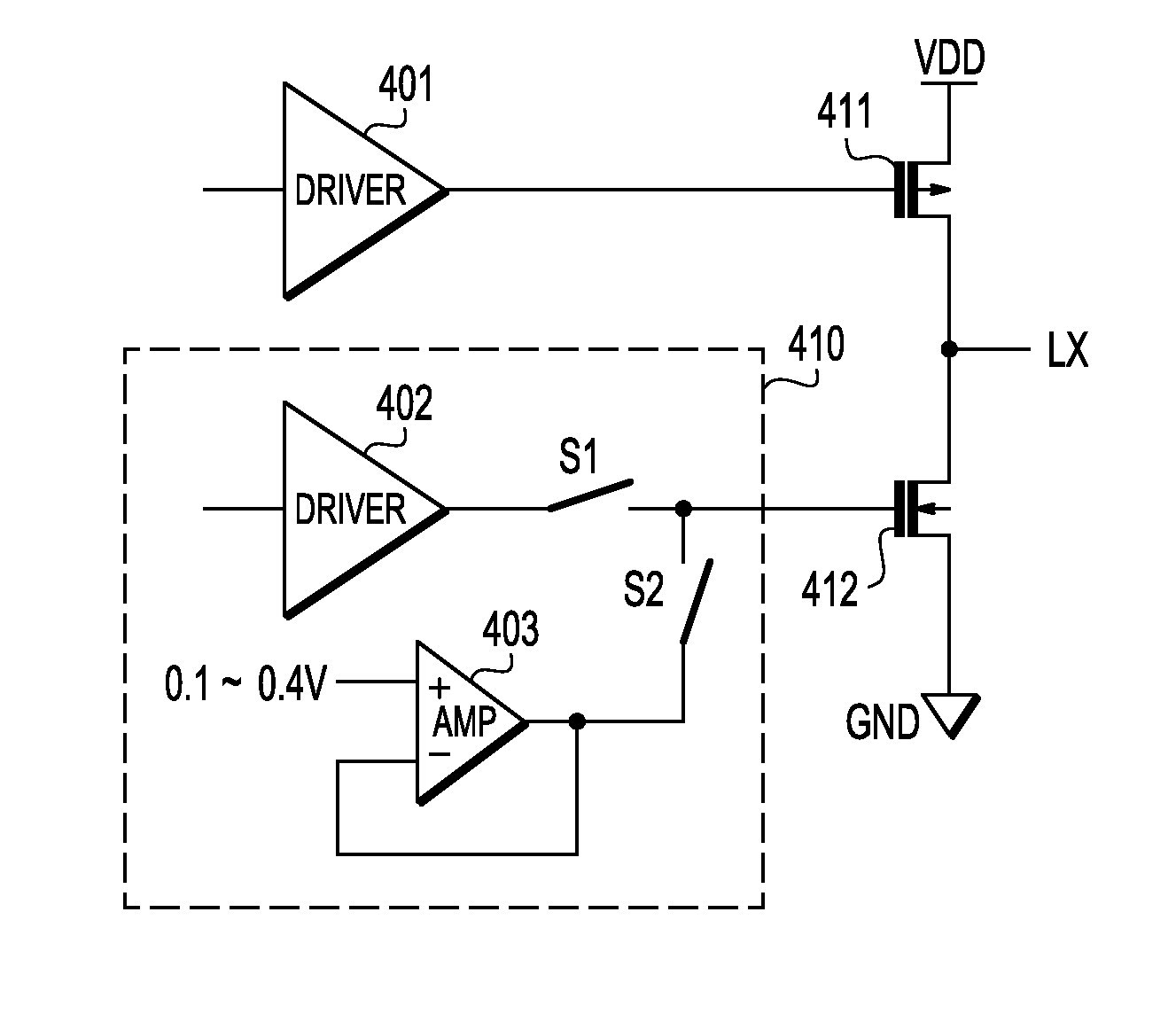
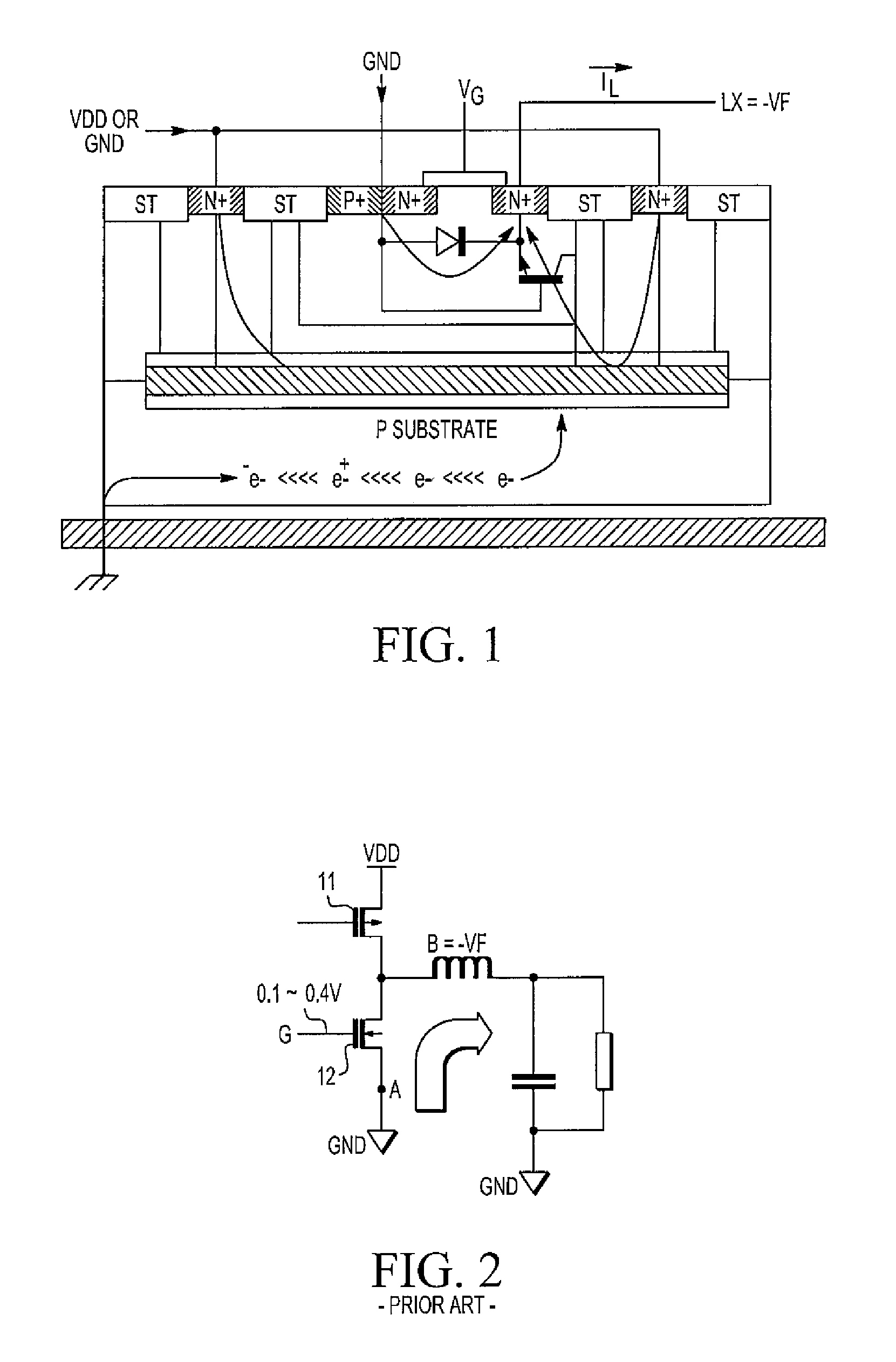
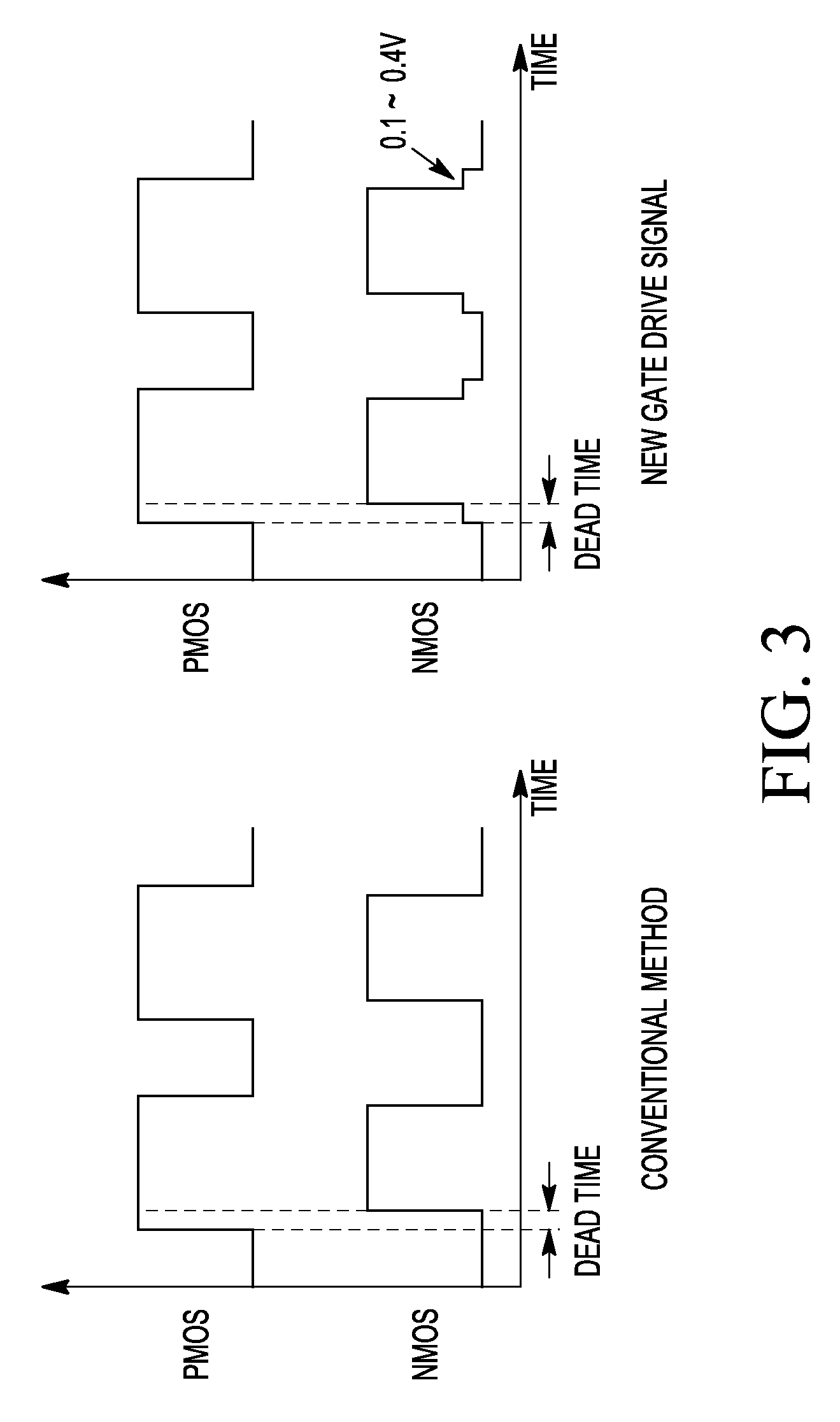
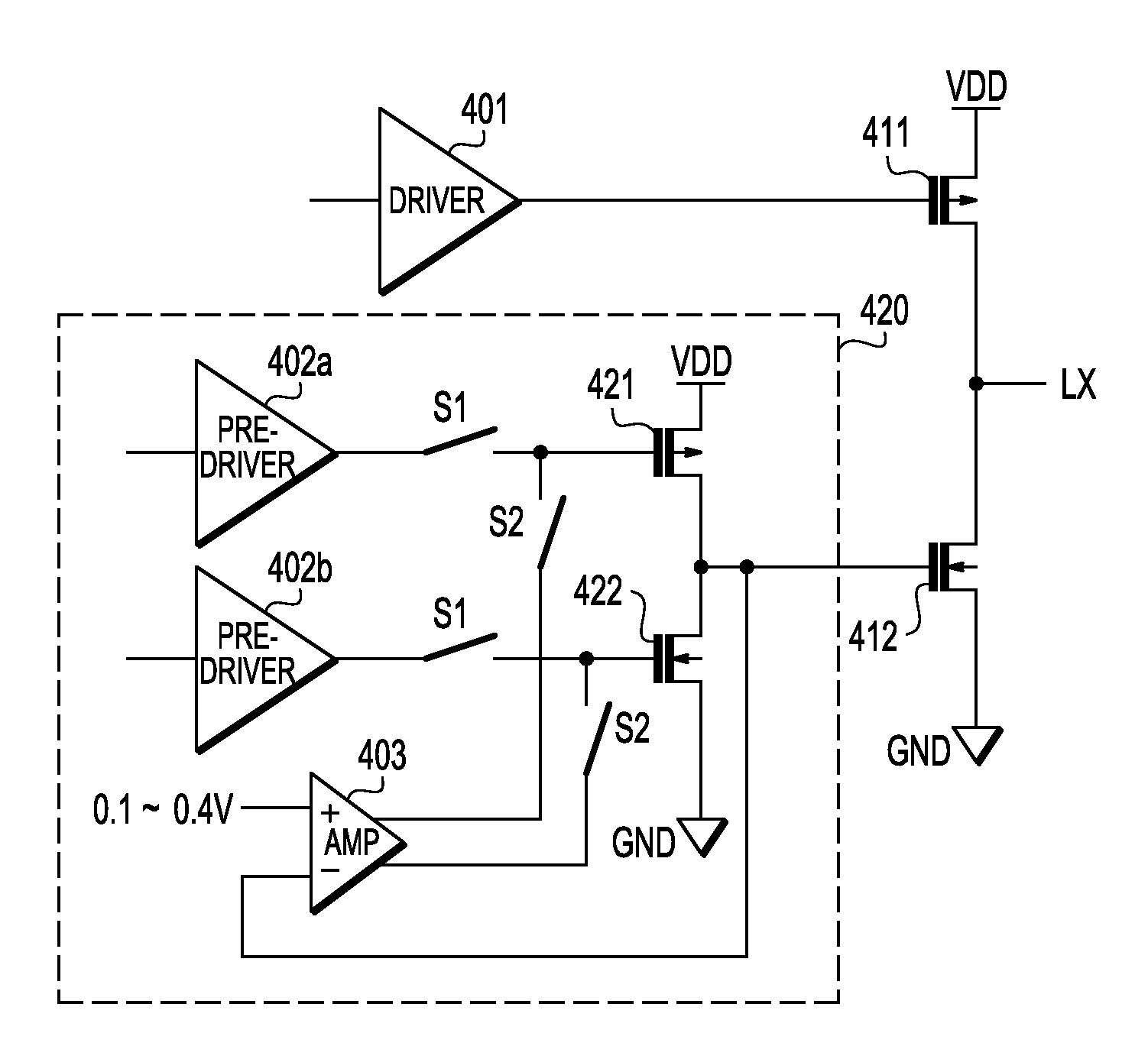
Gate driver circuit for H bridge circuit
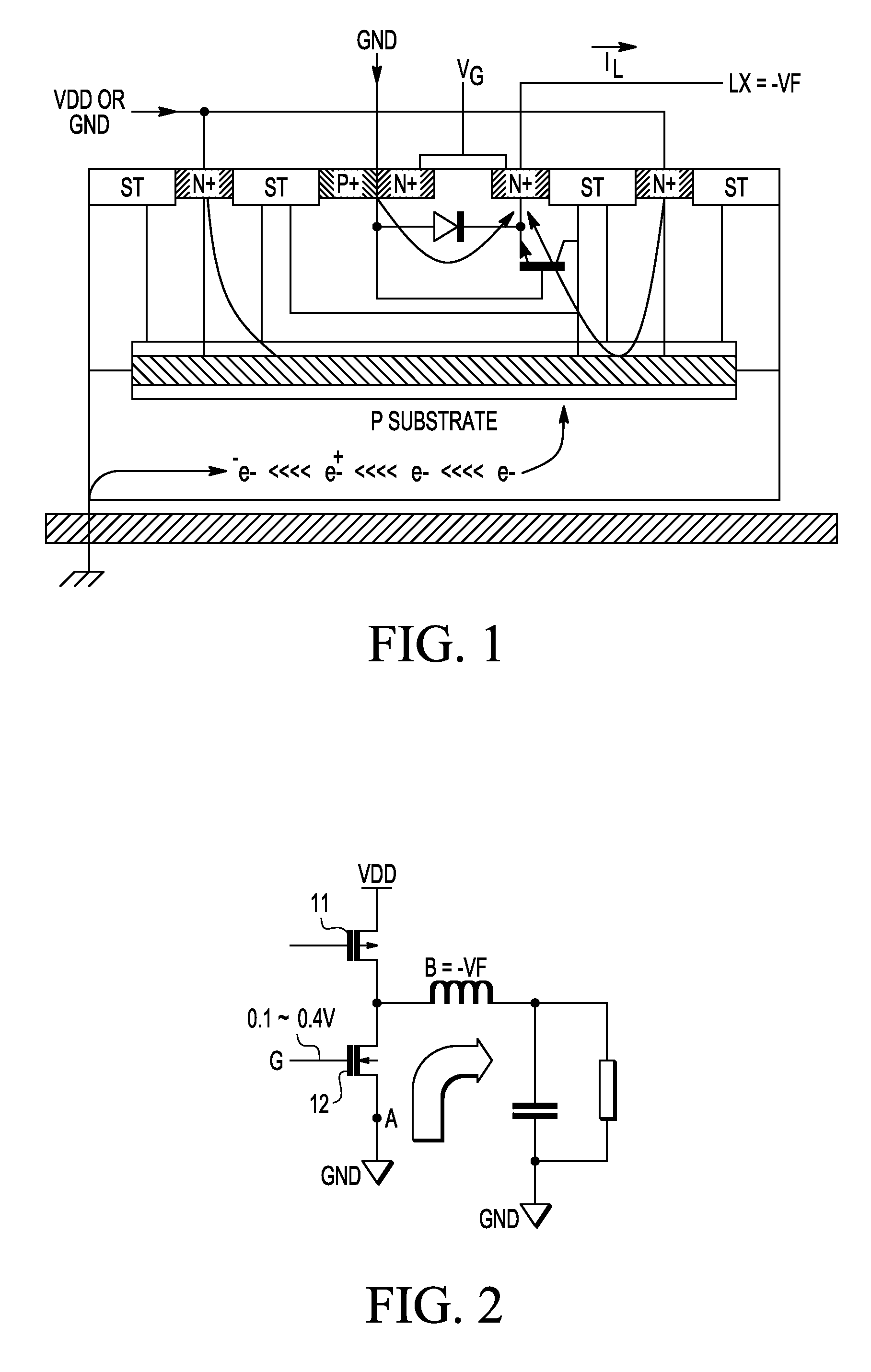
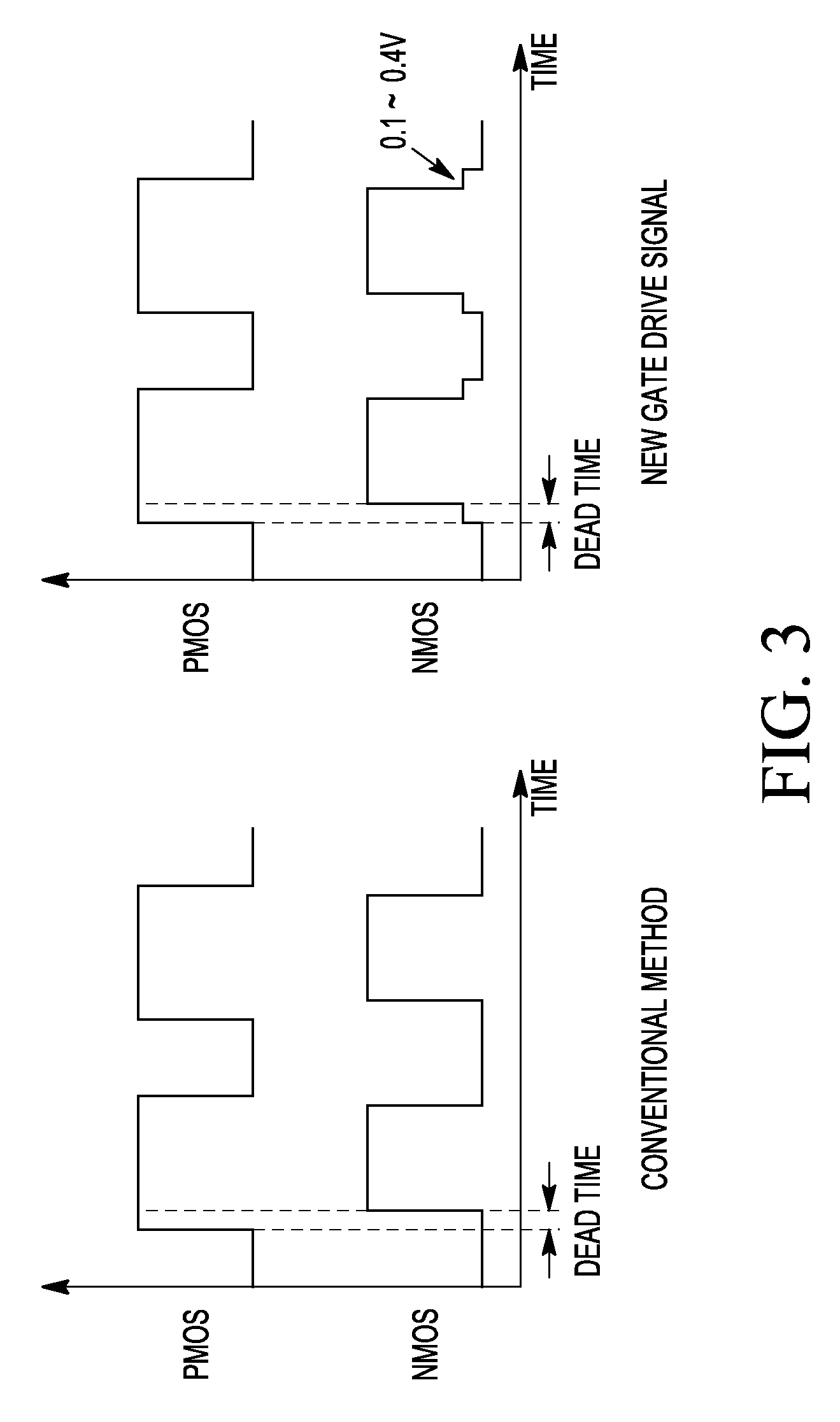
ActiveUS7940092B2Total current dropIncrease currentTransistorAc-dc conversionEngineeringMinority carrier injection
An H bridge circuit includes a gate driver circuit coupled to a gate of an NMOS device. The output of the gate driver circuit is at a voltage from 0.1V to 0.4V during a dead time of the H bridge circuit. The gate voltage of the NMOS device is biased at 0.1˜0.4V to overcome the problems of minority carrier injection and power dissipation as compared with VG=0 in a conventional H bridge circuit.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Gate drive method for h bridge circuit
ActiveUS20100079194A1Total current dropIncrease currentTransistorAc-dc conversionGate voltageGate driver
An H bridge circuit includes a gate driver circuit coupled to a gate of an NMOS device. The output of the gate driver circuit is at a voltage from 0.1V to 0.4V during a dead time of the H bridge circuit. The gate voltage of the NMOS device is biased at 0.1˜0.4V to overcome the problems of minority carrier injection and power dissipation as compared with VG=0 in a conventional H bridge circuit.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Two terminal quantum device using mos capacitor structure
ActiveUS20100045365A1Easy to fillAdding complexitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectric variable regulationCMOSDevice form
A gated quantum well device formed as an MOS capacitor is disclosed. The quantum well is an inversion region less than 20 nanometers wide under the MOS gate. The device may be fabricated in either polarity, and integrated into a CMOS IC, configured as a quantum dot device or a quantum wire device. The device may be operated as a precision charge pump, with a minority carrier injection region added to speed well filling.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
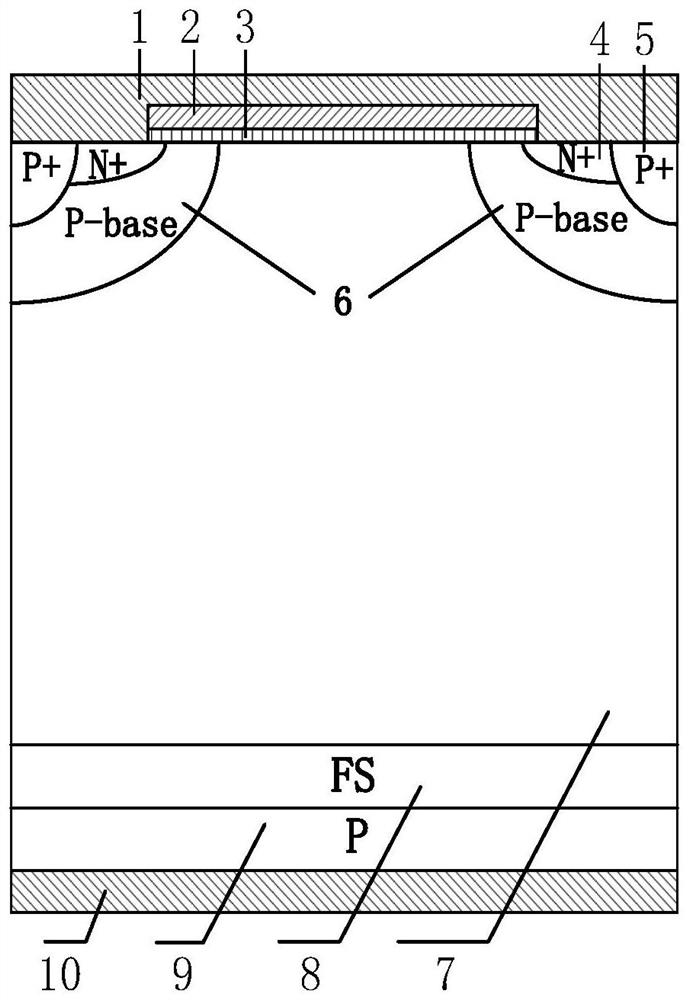
A bipolar power semiconductor device and a preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109065607AReduce forward voltage dropLow Average Forward Voltage DropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceReverse recovery
The invention relates to a bipolar power semiconductor device and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of semiconductor power devices. When the cathode structure of the conventional bipolar power semiconductor device is kept unchanged, by introducing an anode trench gate structure and a source region and / or a base region into the anode region of the device, the forward conduction voltage drop of the anode diode is bypassed by controlling the anode trench gate structure without affecting the normal operation and opening of the device, so that the effect of reducing theforward conduction voltage drop of the power semiconductor device is achieved. After the anode diode is bypassed, the minority carrier injection from the anode region to the drift region decreases, and the reverse recovery time of the device is shortened when the device is turned off, which improves the turn-off speed of the device and reduces the switching loss. The invention improves the carrier concentration distribution of the whole N-type drift region and the compromise between the positive conduction voltage drop and the switching loss. Moreover, the fabrication method of the device does not require additional process steps, and is compatible with the traditional device fabrication method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Super junction Schottky semiconductor device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103367396AImprove reverse breakdown voltageIncrease the doping concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceSchottky barrier
The invention discloses a super junction Schottky semiconductor device. When the semiconductor device is accessed to a certain reverse bias voltage, charge compensation is formed by a second conductive semiconductor material and a first conductive semiconductor material, a super junction structure is formed, the reverse breakdown voltage of the device is enhanced, and characteristics of conduction or blocking of the device are improved. Meanwhile, when the semiconductor device is accessed to a certain forward bias voltage, a first type Schottky barrier junction (assuming that the first conductive semiconductor layer adopts an N type semiconductor material) is in the forward bias conduction state, and a second type Schottky barrier junction (assuming that the second conductive semiconductor layer adopts a P type semiconductor material) is in the reverse bias cut-off state, therefore when in the forward conduction state, the device is still a conductive device with a single carrier, and minority carrier injection does not exist in the conductive device with the single carrier. The device has good switching characteristics. The invention also provides a preparation method of the super junction Schottky semiconductor device.
Owner:北海惠科半导体科技有限公司
Semiconductor device with surge current protection and method of making the same
InactiveCN101449385APhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHigh current densityOhmic contact
The present invention provides a wide bandgap semiconductor device with surge current protection and a method of making the device. The device comprises a low doped n-type region formed by plasma etching through the first epitaxial layer grown on a heavily doped n-type substrate and a plurality of heavily doped p-type regions formed by plasma etching through the second epitaxial layer grown on the first epitaxial layer. Ohmic contacts are formed on p-type regions and on the backside of the n-type substrate. Schottky contacts are formed on the top surface of the n-type region. At normal operating conditions, the current in the device flows through the Schottky contacts. The device, however, is capable of withstanding extremely high current densities due to conductivity modulation caused by minority carrier injection from p-type regions.
Owner:PI
Preparation method for semiconductor device with improved surge current resistance
InactiveCN103887169AImprove reliabilityAvoid premature breakdownSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEtchingLine width
The invention discloses a preparation method for a semiconductor device with improved surge current resistance. The semiconductor device is an improved TMBS diode. According to the semiconductor device, metal Cr is utilized to act as an etching mask film to form a deep groove structure on the surface of a SiC drift layer. Wet etching is performed so that line width of the Cr mask film is narrowed, two sides of a mesa which is not etched are exposed to act as an injection mask film to perform Al-ion injection on the surface of the SiC drift layer, and P-type injection regions are formed on the two sides of the mesa. A PN-junction is formed by the injection regions and an N-type drift region. The PN-junction participates in conduction under the condition of high current. The conductance modulation effect is formed by utilizing minority-carrier injection so that the semiconductor device is enabled to have surge current resistance. Besides, a P-injection region can be formed on the bottom part of a groove simultaneously. The bottom part of the groove can be protected by the P-region under the reverse blocking state of the device, the situation that electric field concentration is formed on a non-ideal etching surface can be avoided, early breakdown can be prevented and thus reliability of the device can be enhanced.
Owner:HANGZHOU ENNENG TECH
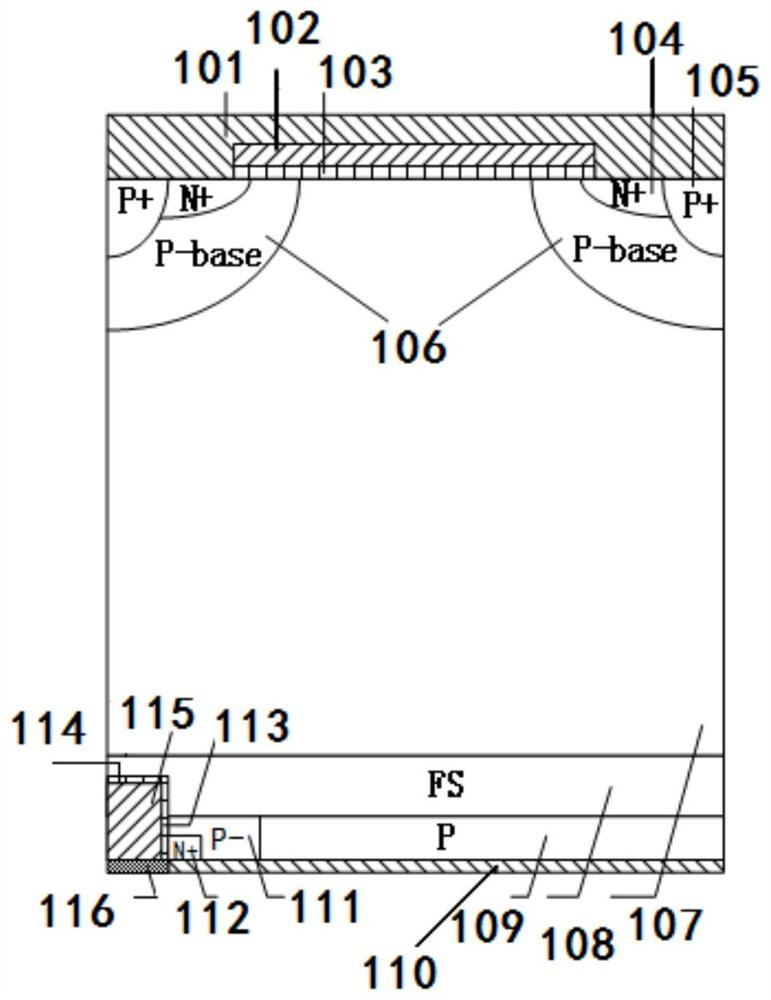
A lateral bipolar power semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109065608AReduce forward voltage dropLow Average Forward Voltage DropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceReverse recovery
A lateral bipolar semiconductor power device and a preparation method thereof belong to the technical field of semiconductor power device. When the cathode structure of the conventional bipolar powersemiconductor device is kept unchanged, by introducing an anode trench gate structure and a source region and / or a base region into the anode region of the device, the forward conduction voltage dropof the anode diode is bypassed by controlling the anode trench gate structure without affecting the normal operation and opening of the device, so that the effect of reducing the forward conduction voltage drop of the power semiconductor device is achieved. After the anode diode is bypassed, the minority carrier injection from the anode region to the drift region decreases, and the reverse recovery time of the device is shortened when the device is turned off, which improves the turn-off speed of the device and reduces the switching loss. The invention improves the carrier concentration distribution of the whole N-type drift region and the compromise between the positive conduction voltage drop and the switching loss. Moreover, the fabrication method of the device does not require additional process steps, and is compatible with the traditional device fabrication method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Two terminal quantum device using MOS capacitor structure
ActiveUS8026507B2Adding complexityAdding costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectric variable regulationCMOSDevice form
A gated quantum well device formed as an MOS capacitor is disclosed. The quantum well is an inversion region less than 20 nanometers wide under the MOS gate. The device may be fabricated in either polarity, and integrated into a CMOS IC, configured as a quantum dot device or a quantum wire device. The device may be operated as a precision charge pump, with a minority carrier injection region added to speed well filling.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
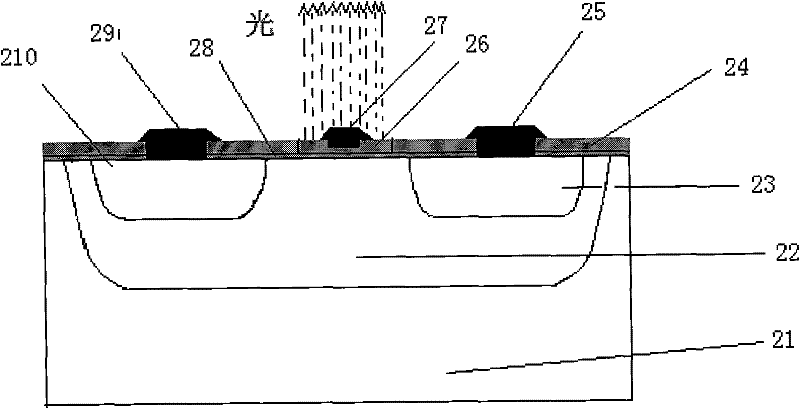
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor)-process compatible grid-control p-n junction forward-direction injection type silicon light-emitting device and production method thereof
InactiveCN101777568ALow working voltageHigh luminous intensitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi cmos technologyP–n junction
The invention belongs to the field of silicon-substrate photoelectronic technology based on micro electronic technique and relates to a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor)-process compatible grid-control p-n junction forward-direction injection type silicon light-emitting device and a production method thereof. The device comprises a p silicon substrate and an n well; an emitting electrode p+ doped area and an N well electrical contact N + doped area are made in the n well; an ultrathin gate oxide layer is grown on the surface of the N well; a field oxide layer and a polysilicon gate are arranged on the ultrathin gate oxide layer; an anode and a cathode are respectively made on the emitting electrode p+ doped area and the N well electrical contact N+ doped area; and a gate electrode is made on the polysilicon gate. The invention belongs to p-n junction forward-direction minority carrier injection type light-emitting devices, has low working voltage and can share one power supply with CMOS technology.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Schottky semiconductor device with grooves and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103378177AImprove forward conduction characteristicsImprove affordabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierEngineering
The invention discloses a Schottky semiconductor device with grooves. The Schottky semiconductor device with the grooves comprises an MOS structure, a PN junction and a Schottky barrier junction. The electric field distribution of reverse bias voltage is changed through the MOS structure, and therefore the forward-direction conductive character of a component is improved. The bearing capacity of transient high voltage of the component is improved through the PN junction. When the semiconductor device is under the forward-direction small electric current density state, the PN junction is not opened, and therefore minority carrier injection of the component is reduced, and the reverse recovery character of the component is improved. The invention provides a preparation method of the Schottky semiconductor device with the grooves.
Owner:北海惠科半导体科技有限公司
Insulated gate bipolar transistor
InactiveCN114256340AReduce in quantityInhibit injectionSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsMaterials science
The invention provides an insulated gate bipolar transistor, which is characterized in that an N-type adjusting region is arranged between a substrate P + emitter region and an N-type base region, N-type conductive impurities are doped with polycrystalline or amorphous semiconductor materials, the N-type adjusting region inhibits minority carrier injection, and the number of minority carriers in the N-type base region is controlled and reduced; according to the invention, a device can be manufactured on a thick substrate slice, and minority carrier injection of a P-type emitter region at the back of the insulated gate bipolar transistor is inhibited; high-frequency characteristics of the device are improved and power consumption of the device is reduced.
Owner:朱江
Semiconductor device with super-junction structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105576022AReduce capacitanceReduce switching lossesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceReverse recovery
The invention provides a semiconductor device with a super-junction structure. The semiconductor device comprises a cellular area. The cellular area comprises a second-conductive-type first body area, first-conductive-type guide pillars and second-conductive-type guide pillars. A preset distance is kept between each second-conductive-type guide pillar and the first body area above the second-conductive-type guide pillars. The second-conductive-type guide pillars are partially or totally separated from the first body area above the second-conductive-type guide pillars. Capacitance between a source electrode and a drain electrode can be effectively reduced, and furthermore switching loss of the semiconductor device is reduced. The semiconductor device further has functions of restraining minority-carrier injection, restraining minority-carrier extraction in a reverse recovery period, improving a reverse recovery characteristic and reducing loss and voltage oscillation in a reverse recovery period. Through controlling the connecting area between the second-conductive-type guide pillars in the cellular area and the first body area above the second-conductive-type guide pillars, semiconductor device breakdown in the cellular area can be ensured, and furthermore durability of the semiconductor device can be improved.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES MICROELECTRONICS (CHONGQING) CO LTD
Semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
PendingUS20220223583A1Improve electrification abilityIncreasing minority carrier injection efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
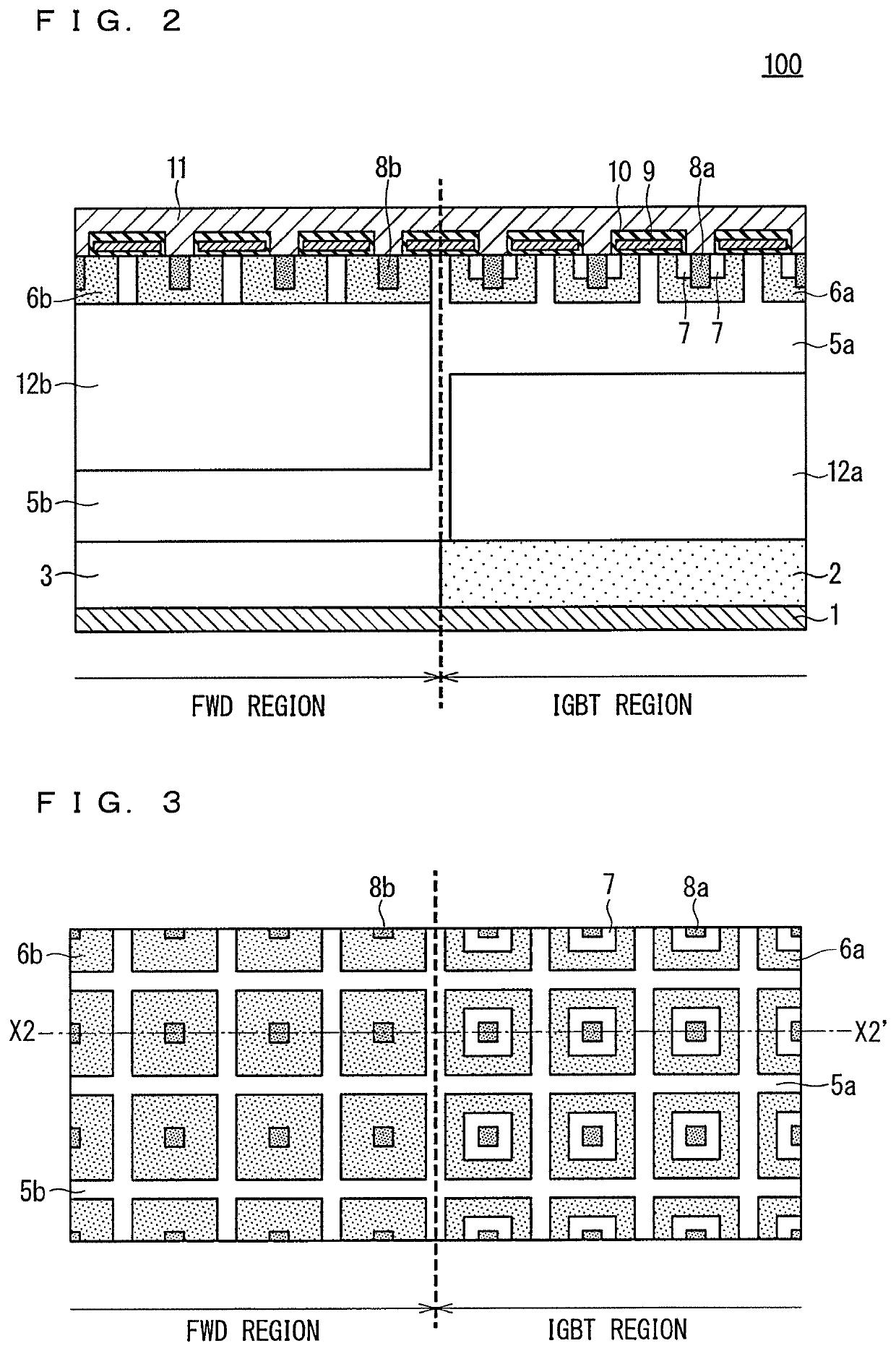
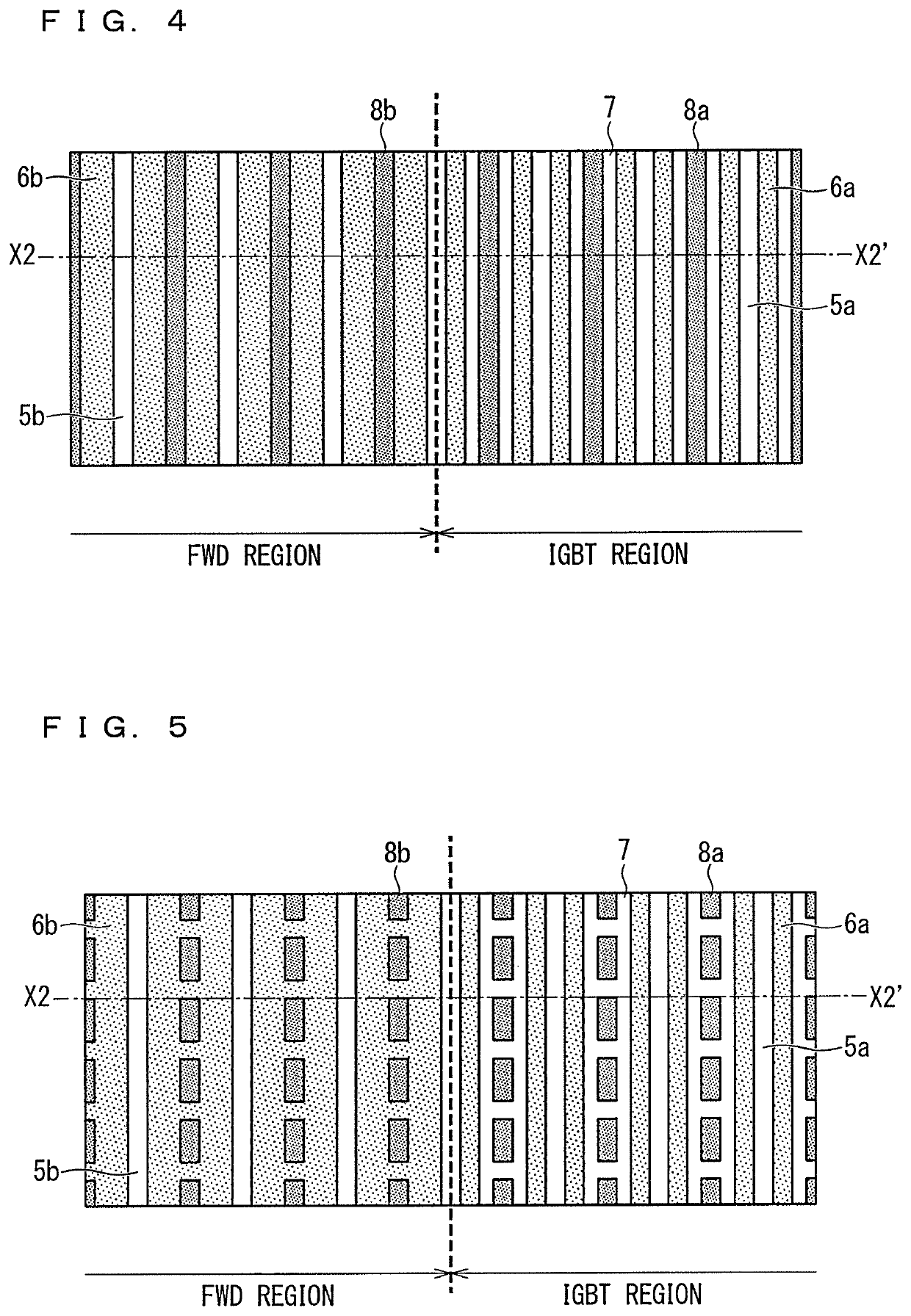
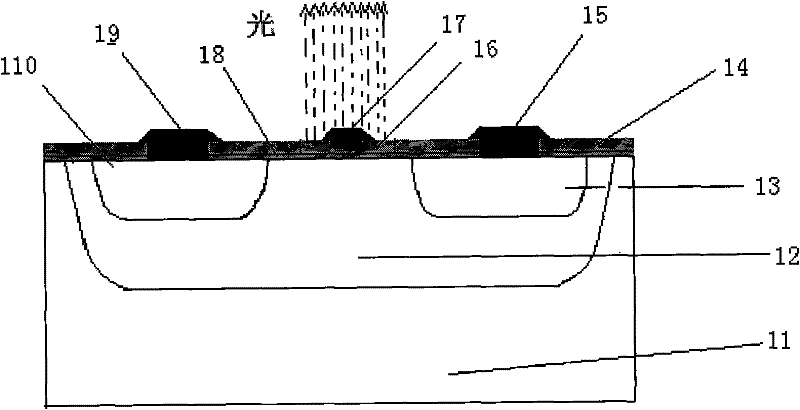
In order to improve energization capacity, minority carrier injection efficiency is increased. In a semiconductor device, an IGBT includes a first drift layer, a collector region, a base region, an emitter region, an insulating film, a gate electrode, and a first high carrier lifetime region formed at a position closer to the collector region than the base region and having a longer carrier lifetime than the first drift layer. An FWD includes a second drift layer, an anode region, and a second high carrier lifetime region formed at a position closer to the anode region than a lower surface of the second drift layer and having a longer carrier lifetime than the second drift layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor)-process compatible grid-control p-n junction forward-direction injection type silicon light-emitting device and production method thereof
InactiveCN101777568BHigh luminous intensityLuminous intensity is not adjustableSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi cmos technologyP–n junction
The invention belongs to the field of silicon-substrate photoelectronic technology based on micro electronic technique and relates to a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor)-process compatible grid-control p-n junction forward-direction injection type silicon light-emitting device and a production method thereof. The device comprises a p silicon substrate and an n well; an emitting electrode p+ doped area and an N well electrical contact N + doped area are made in the n well; an ultrathin gate oxide layer is grown on the surface of the N well; a field oxide layer and a polysilicon gate are arranged on the ultrathin gate oxide layer; an anode and a cathode are respectively made on the emitting electrode p+ doped area and the N well electrical contact N+ doped area; and a gate electrode is made on the polysilicon gate. The invention belongs to p-n junction forward-direction minority carrier injection type light-emitting devices, has low working voltage and can share one power supply with CMOS technology.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
A bipolar power semiconductor device and its preparation method
ActiveCN109065607BReduce forward voltage dropLow Average Forward Voltage DropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceReverse recovery
A bipolar power semiconductor device and a preparation method thereof belong to the technical field of semiconductor power devices. On the premise of keeping the cathode structure of the traditional bipolar power semiconductor device unchanged, the present invention introduces an anode trench gate structure, source region and / or base region into the anode region of the device, without affecting the normal operation and opening of the device. In this case, by controlling the anode trench gate structure, the forward conduction voltage drop of the anode diode is bypassed, thereby achieving the effect of reducing the forward conduction voltage drop of the power semiconductor device. After the anode diode is bypassed, the minority carrier injection from the anode region to the drift region is reduced, the reverse recovery process time of the device is shortened when the device is turned off, the turn-off speed of the device is improved, and the switching loss is reduced. The invention improves the carrier concentration distribution of the entire N-type drift region and the compromise between the forward conduction voltage drop and switching loss; and the manufacturing method of the device does not need to add additional process steps, and is compatible with the traditional device manufacturing method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Controlled doping from low to high levels in wide bandgap semiconductors
InactiveUS20170154963A1Improve abilitiesImprove efficiencyLaser active region structureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrierBroadband
The energy of formation of a point defect in a compound semiconductor is a function of the process conditions and the Fermi energy (the energy of the charge carriers). In wide bandgap semiconductors or insulators, the contribution of this energy to the formation energy of charged point defects is significant. For doping for n- or p-type conductivity, the larger the energy gap, the higher the concentration of compensating point defects that is at equilibrium with the system. This is a fundamental problem with wide bandgap materials that will be directly addressed with these capabilities. In this approach, minority carrier injection is used to modify the quasi-Fermi level to control the formation energy of the point defects. Increasing the formation energy of unwanted point defect through an external excitation that leads to excess minority carriers during the growth of the semiconductor device structure leads to a reduction in compensating point defects.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Light-emitting device, display panel and manufacturing method of light-emitting device
PendingCN114792763AImprove the problem of injection imbalanceImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron holeEngineering
The invention discloses a light-emitting device, a display panel and a manufacturing method of the light-emitting device, and aims to solve the problems that materials which are high in mobility and matched in energy level are difficult to find at present, and injection of holes and electrons is unbalanced. The light-emitting device comprises a light-emitting area and a regulation and control area which are located between the first electrode layer and the second electrode layer. The light-emitting region includes: a light-emitting layer; for the light-emitting region, one of the first electrode layer and the second electrode layer, which has a small number of carriers injected into the light-emitting layer in unit time, is used as a minority carrier injection electrode layer, and the other one is used as a multi-carrier injection electrode layer; the regulation and control region comprises an insulating layer and a carrier transport layer which are arranged in a laminated manner; the carrier transport layer is in contact with the minority carrier injection electrode layer, the insulating layer is in contact with the multi-carrier injection electrode layer, and the side wall of the carrier transport layer is in contact with the side wall of the light-emitting layer.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
p‑i‑n—‑n-type gan single-photon avalanche detector
ActiveCN106409967BIncrease the diffusion lengthReduce scatterSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionQuantum efficiency
Owner:THE 44TH INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
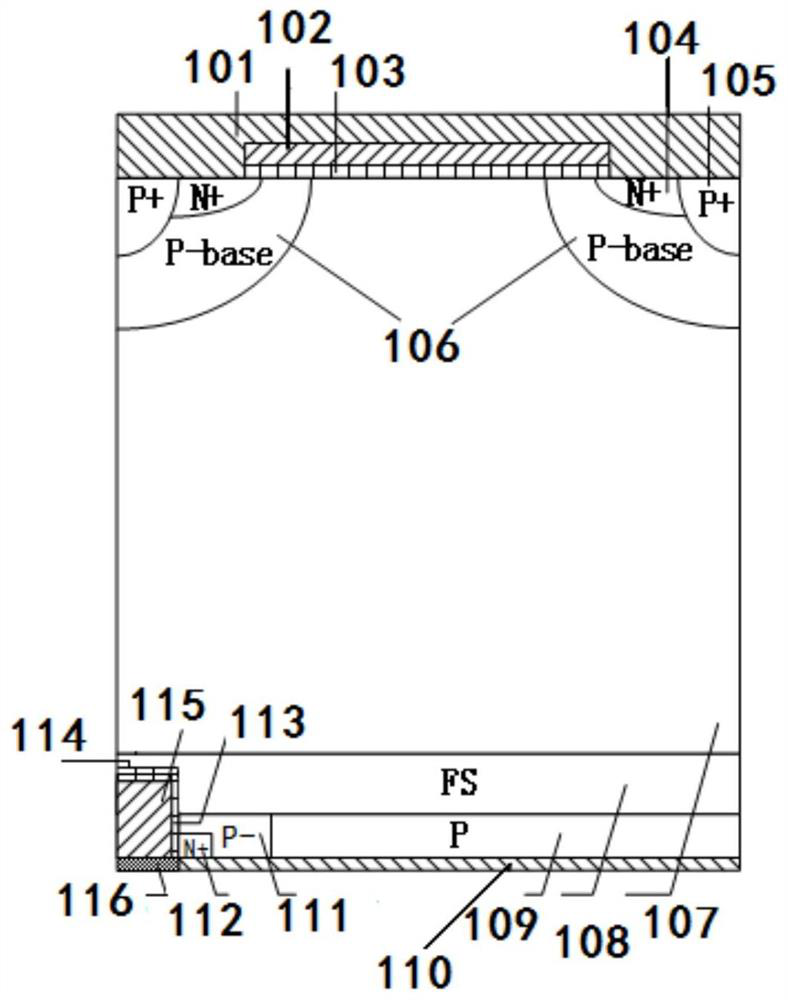
A kind of lateral bipolar power semiconductor device and its preparation method
ActiveCN109065608BReduce forward voltage dropLow Average Forward Voltage DropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceReverse recovery
A lateral bipolar semiconductor power device and a preparation method thereof belong to the technical field of semiconductor power devices. On the premise of keeping the cathode structure of the traditional bipolar power semiconductor device unchanged, the present invention introduces an anode trench gate structure and source region and / or base region in the anode region of the device, without affecting the normal operation and turn-on of the device. Under the circumstance, by controlling the anode trench gate structure, the forward conduction voltage drop of the anode diode is bypassed, so as to achieve the effect of reducing the forward conduction voltage drop of the power semiconductor device. After the anode diode is bypassed, the minority carrier injection from the anode region to the drift region is reduced, the reverse recovery process time of the device during turn-off is shortened, the turn-off speed of the device is improved, and the switching loss is reduced. The invention improves the carrier concentration distribution of the entire N-type drift region and the compromise between the forward conduction voltage drop and switching loss; and the device fabrication method does not require additional process steps, and is compatible with the traditional device fabrication method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A sic power device
The invention belongs to the field of power semiconductors, and specifically provides a SiC power device, including a SiC MOSFET and a SiC IGBT; wherein: for a SiC MOSFET device integrated with a PN junction body diode, the reverse recovery charge of the body diode and related losses can be greatly reduced , Reduce the reverse recovery peak current, reduce EMI noise; for SiC MOSFET devices with integrated N-type Schottky diodes or integrated heterojunction diodes, it can reduce the voltage drop when the MOSFET is reversed, eliminate the minority carrier injection effect, thereby reducing the diode Conduction loss and reverse recovery loss; for reverse-conducting SiC IGBT devices with integrated PN junction body diodes, it can greatly reduce the reverse recovery charge of the body diode and related losses, reduce the reverse recovery peak current, and reduce EMI noise; For the reverse conduction SiC IGBT device integrated with N-type Schottky diode or heterojunction diode, it can reduce the voltage drop when the reverse conduction IGBT conducts in reverse, eliminate the minority carrier injection effect, and reduce the diode conduction loss and reverse recovery loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
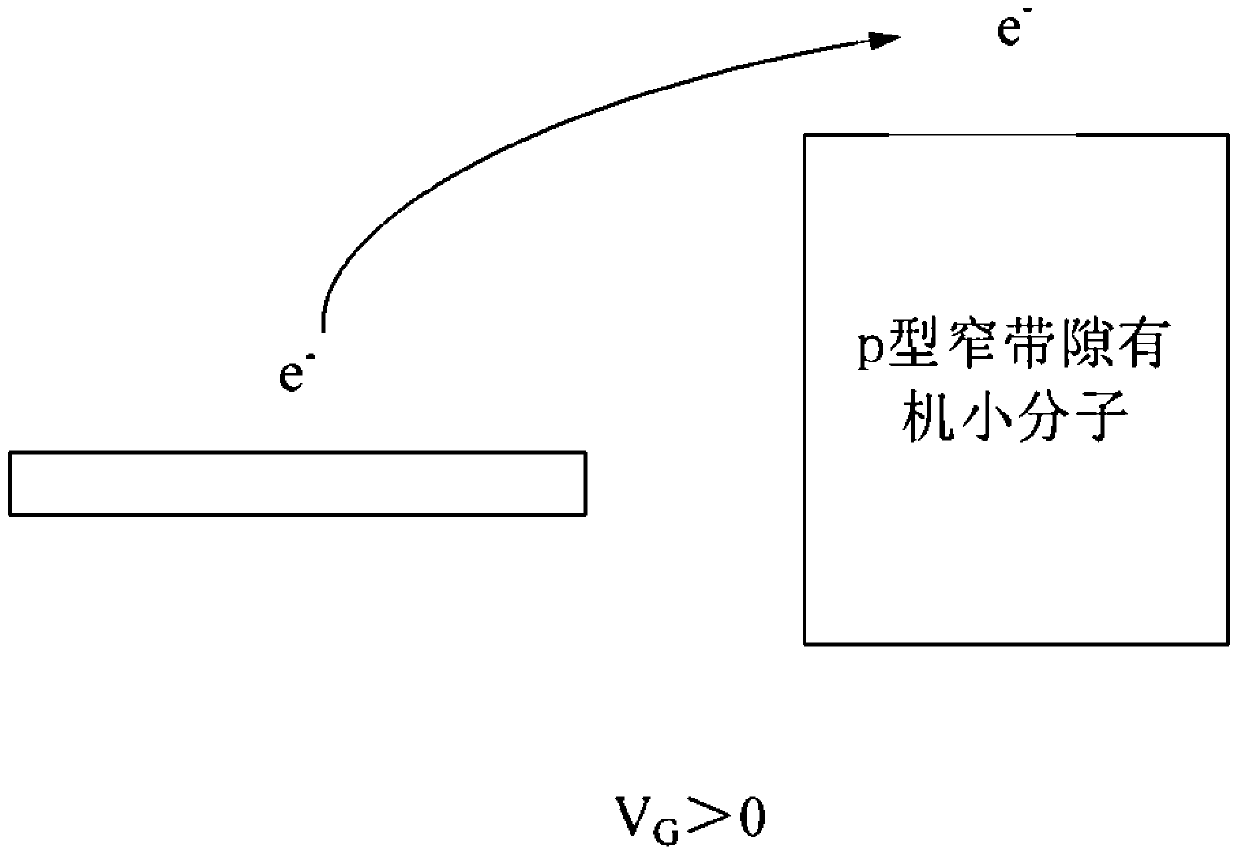
Method for avoiding minority carrier injection of field effect transistor and field effect transistor
ActiveCN111192959AInhibit injectionImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField effectOrganic semiconductor
The invention provides a method for avoiding minority carrier injection of a field effect transistor based on p-type narrow band gap organic small molecules and the field effect transistor. The methodcomprises the following step: loading p-type wide-band gap organic semiconductors between a source electrode and a p-type narrow-band gap organic small molecular layer and between a drain electrode and the p-type narrow-band gap organic small molecular layer. According to the embodiment of the invention, p-type wide-band gap organic semiconductors are loaded between the source electrode and the p-type narrow-band gap organic small molecular layer and between the drain electrode and the p-type narrow-band gap organic small molecular layer, so that injection of minority carriers (electrons) isavoided from the source.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Semiconductor device with superjunction structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105576022BReduce capacitanceReduce switching lossesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceReverse recovery
The invention provides a semiconductor device with a super-junction structure. The semiconductor device comprises a cellular area. The cellular area comprises a second-conductive-type first body area, first-conductive-type guide pillars and second-conductive-type guide pillars. A preset distance is kept between each second-conductive-type guide pillar and the first body area above the second-conductive-type guide pillars. The second-conductive-type guide pillars are partially or totally separated from the first body area above the second-conductive-type guide pillars. Capacitance between a source electrode and a drain electrode can be effectively reduced, and furthermore switching loss of the semiconductor device is reduced. The semiconductor device further has functions of restraining minority-carrier injection, restraining minority-carrier extraction in a reverse recovery period, improving a reverse recovery characteristic and reducing loss and voltage oscillation in a reverse recovery period. Through controlling the connecting area between the second-conductive-type guide pillars in the cellular area and the first body area above the second-conductive-type guide pillars, semiconductor device breakdown in the cellular area can be ensured, and furthermore durability of the semiconductor device can be improved.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES MICROELECTRONICS (CHONGQING) CO LTD
A kind of super junction Schottky semiconductor device and its preparation method
ActiveCN103367396BImprove reverse breakdown voltageIncrease the doping concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a super junction Schottky semiconductor device. When the semiconductor device is accessed to a certain reverse bias voltage, charge compensation is formed by a second conductive semiconductor material and a first conductive semiconductor material, a super junction structure is formed, the reverse breakdown voltage of the device is enhanced, and characteristics of conduction or blocking of the device are improved. Meanwhile, when the semiconductor device is accessed to a certain forward bias voltage, a first type Schottky barrier junction (assuming that the first conductive semiconductor layer adopts an N type semiconductor material) is in the forward bias conduction state, and a second type Schottky barrier junction (assuming that the second conductive semiconductor layer adopts a P type semiconductor material) is in the reverse bias cut-off state, therefore when in the forward conduction state, the device is still a conductive device with a single carrier, and minority carrier injection does not exist in the conductive device with the single carrier. The device has good switching characteristics. The invention also provides a preparation method of the super junction Schottky semiconductor device.
Owner:北海惠科半导体科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com