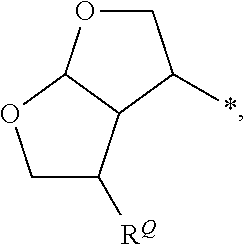
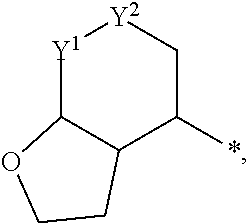
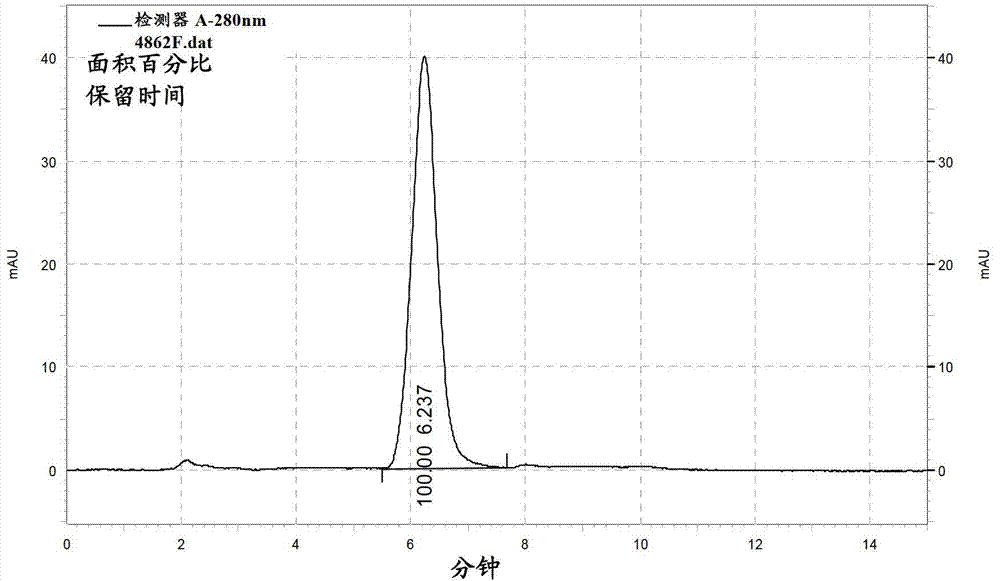
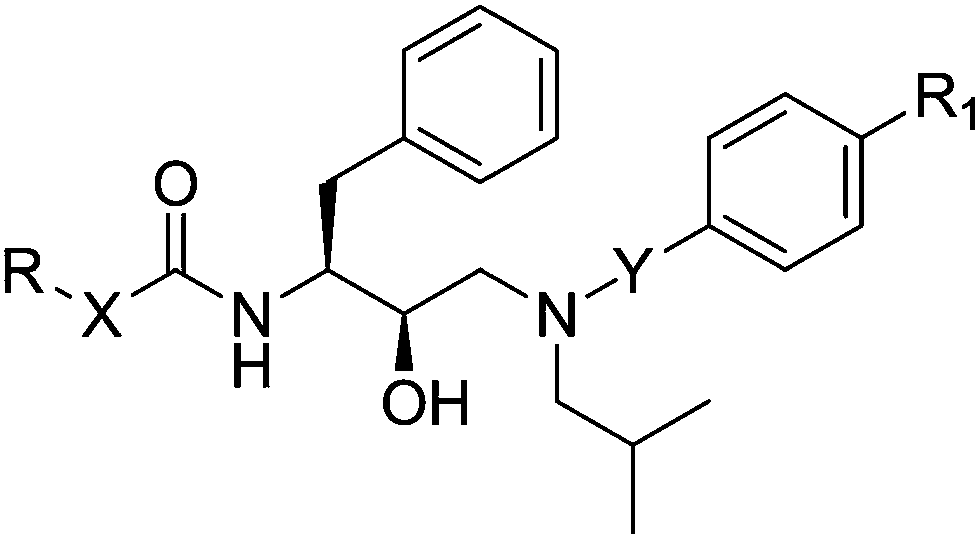
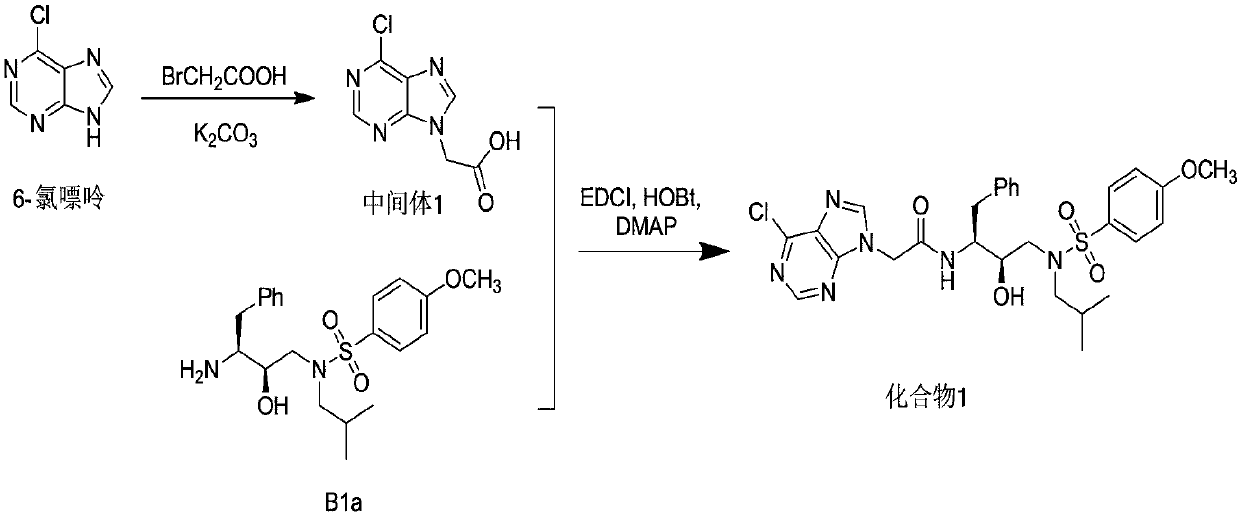
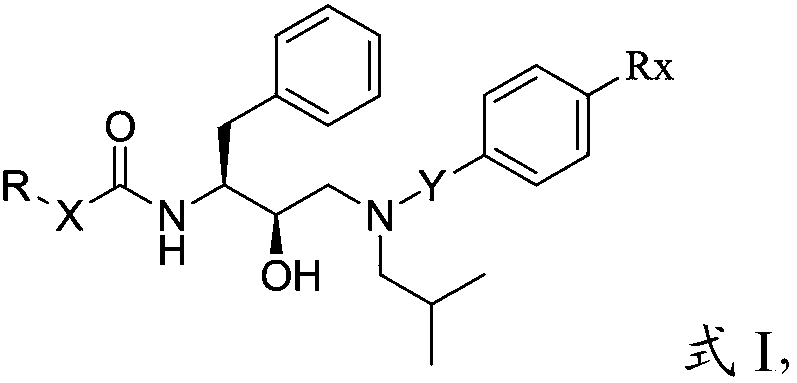
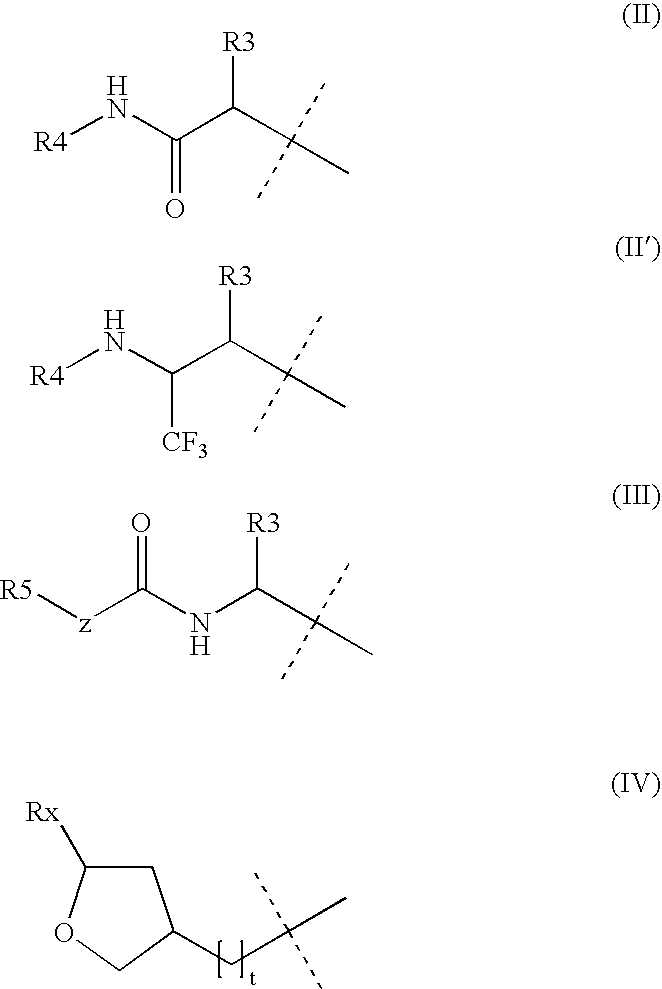
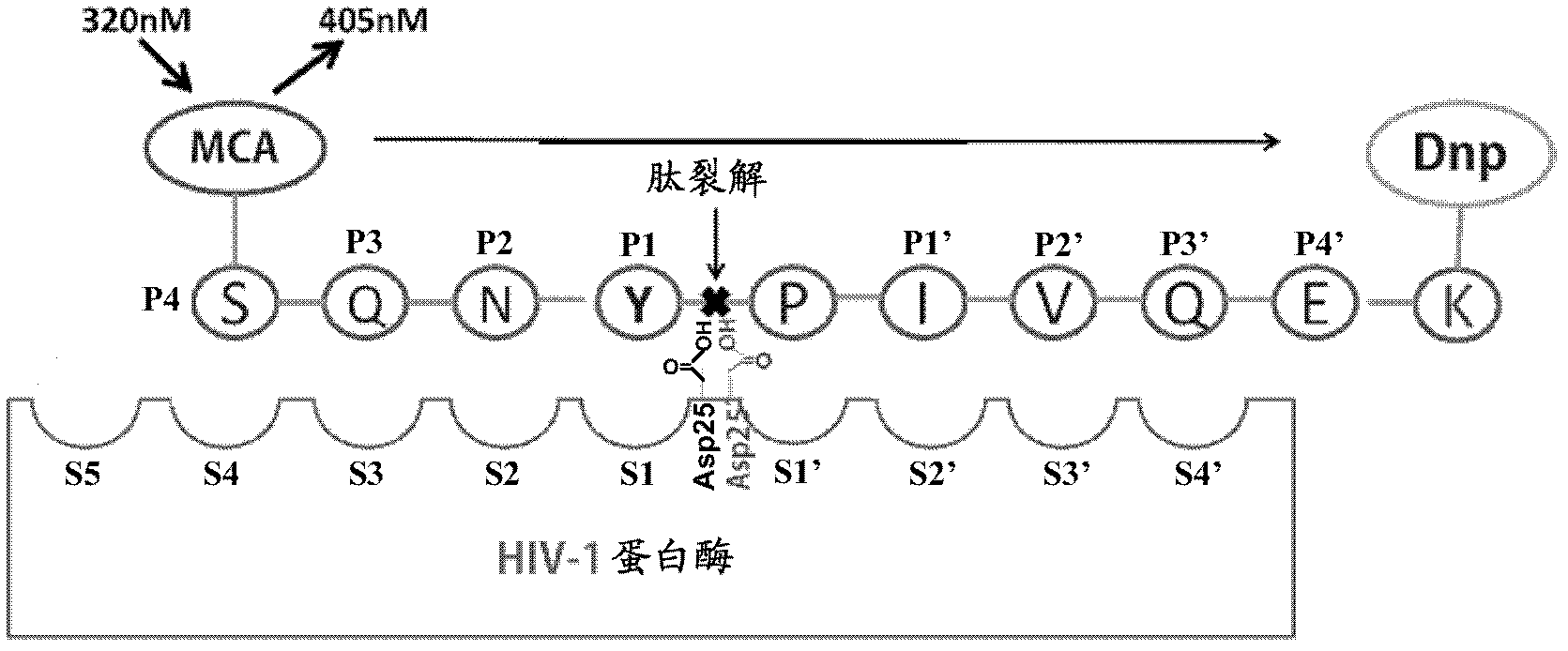
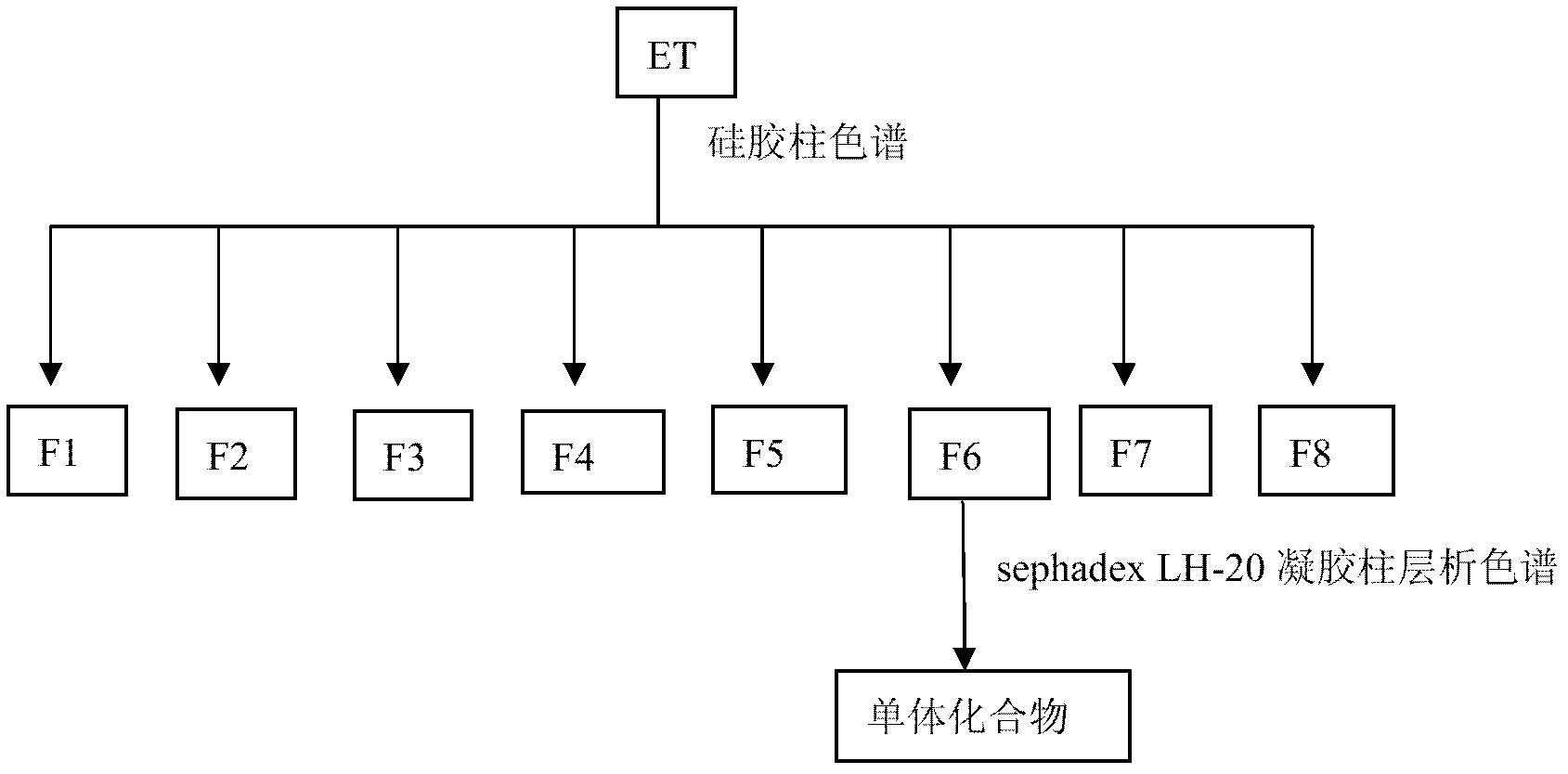
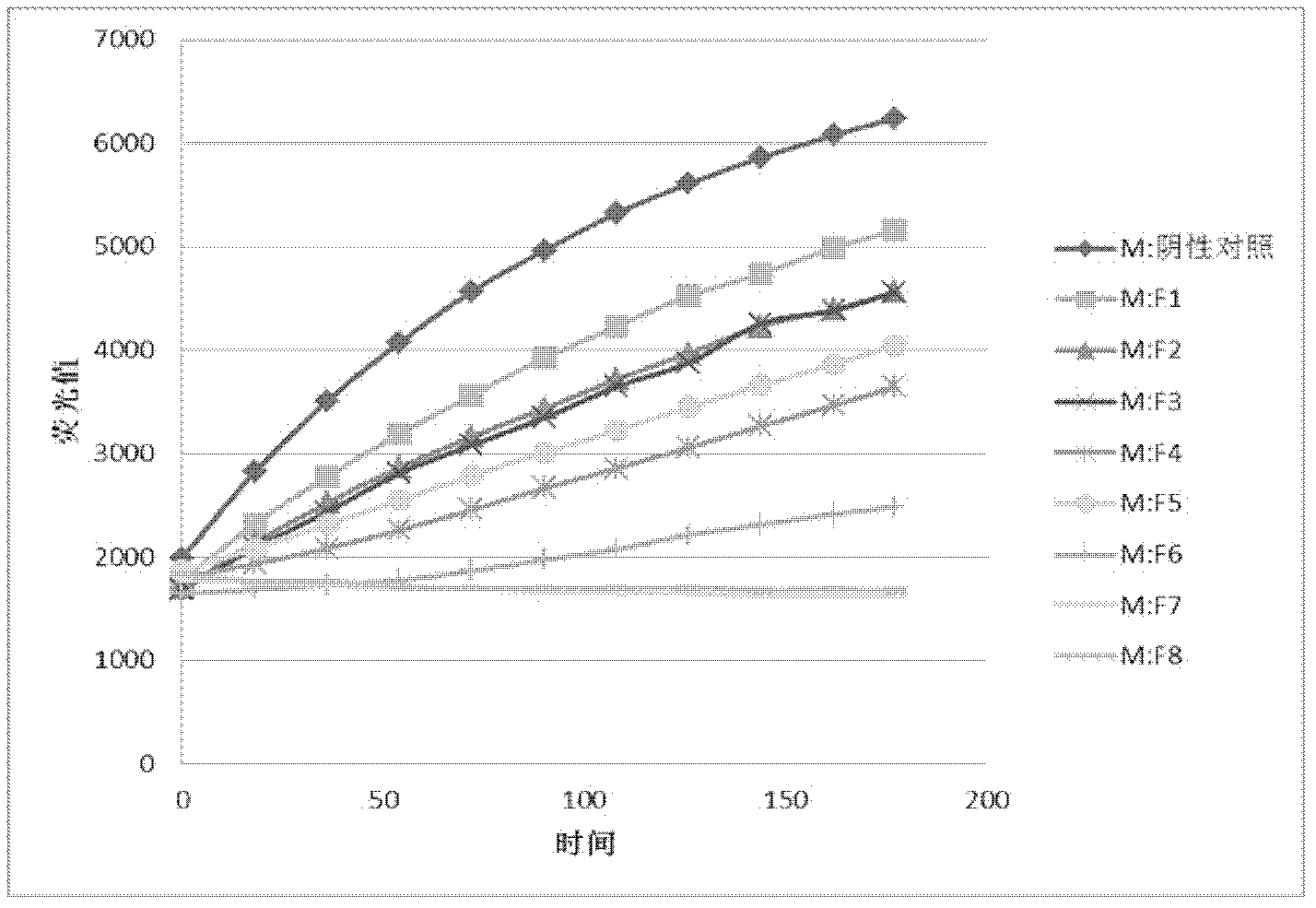
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
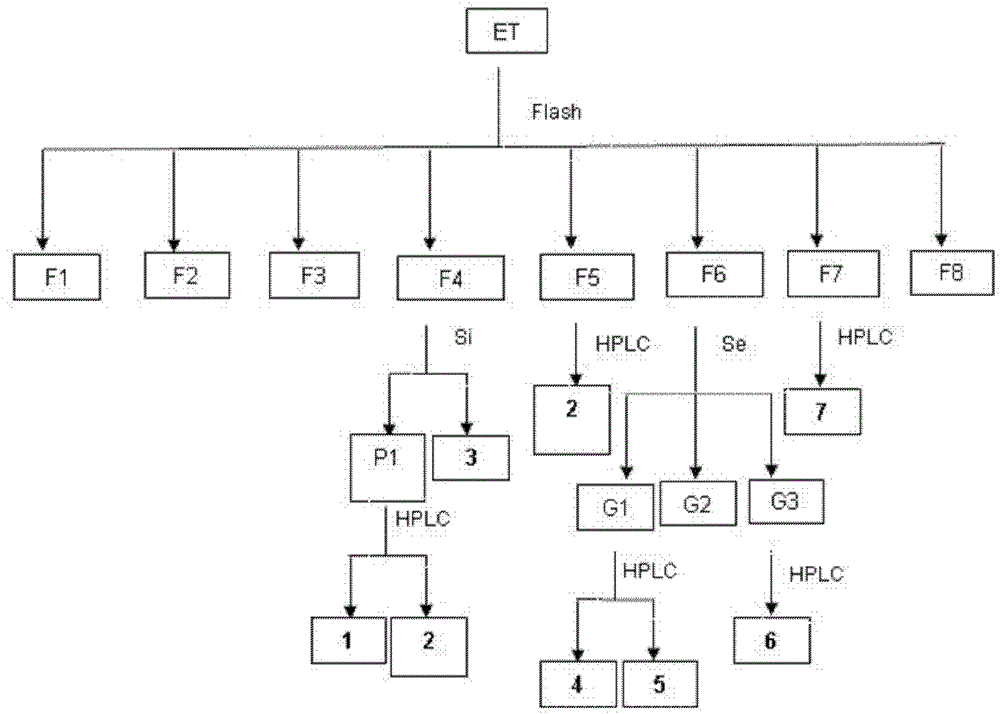
38 results about "HIV-1 protease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
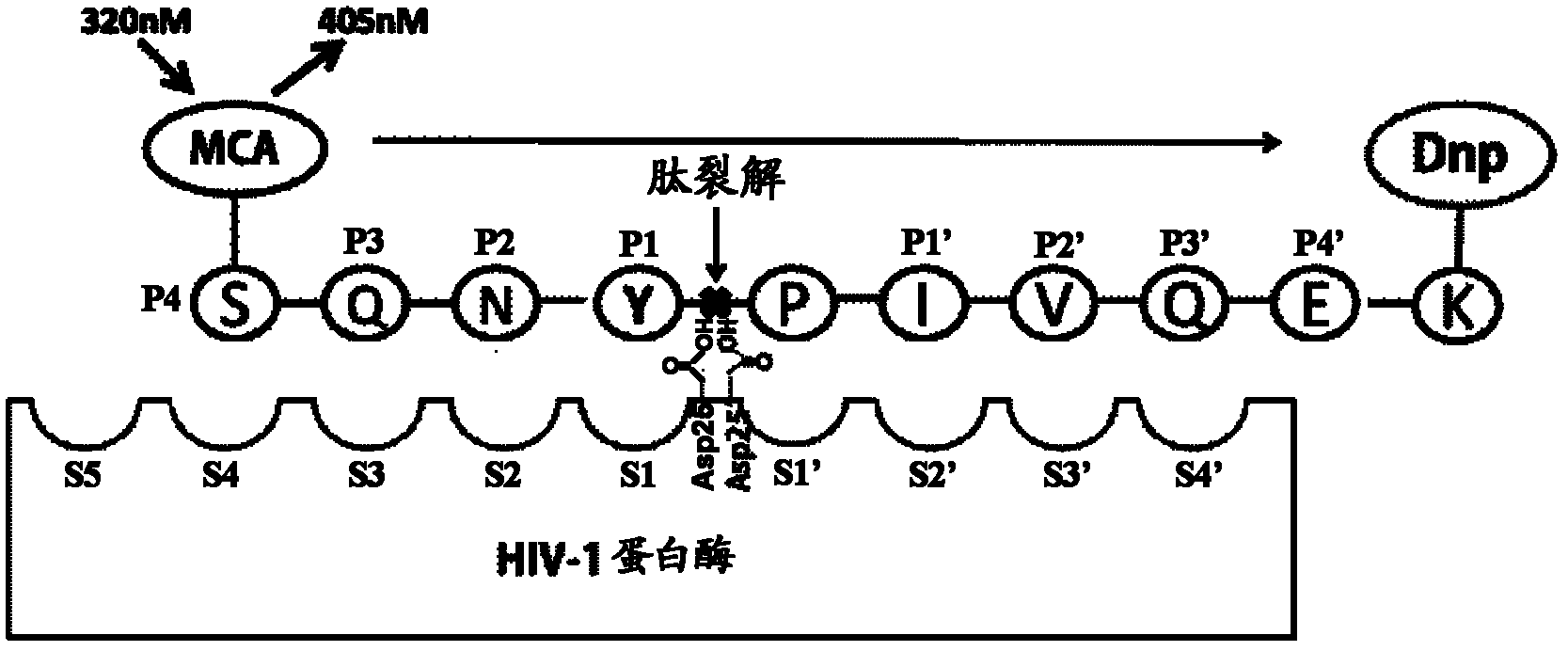
HIV-1 protease (PR) is a retroviral aspartyl protease (retropepsin), an enzyme involved with peptide bond hydrolysis in retroviruses, that is essential for the life-cycle of HIV, the retrovirus that causes AIDS. HIV protease cleaves newly synthesized polyproteins (namely, Gag and Gag-Pol) at nine cleavage sites to create the mature protein components of an HIV virion, the infectious form of a virus outside of the host cell. Without effective HIV protease, HIV virions remain uninfectious.
Combination therapy comprising the use of protein kinase C modulators and Histone Deacetylase inhibitors for treating HIV-1 latency
InactiveUS20100166806A1Adverse propertyPrevent HIV-1-induced cytotoxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryReverse transcriptaseHydroxamic acid
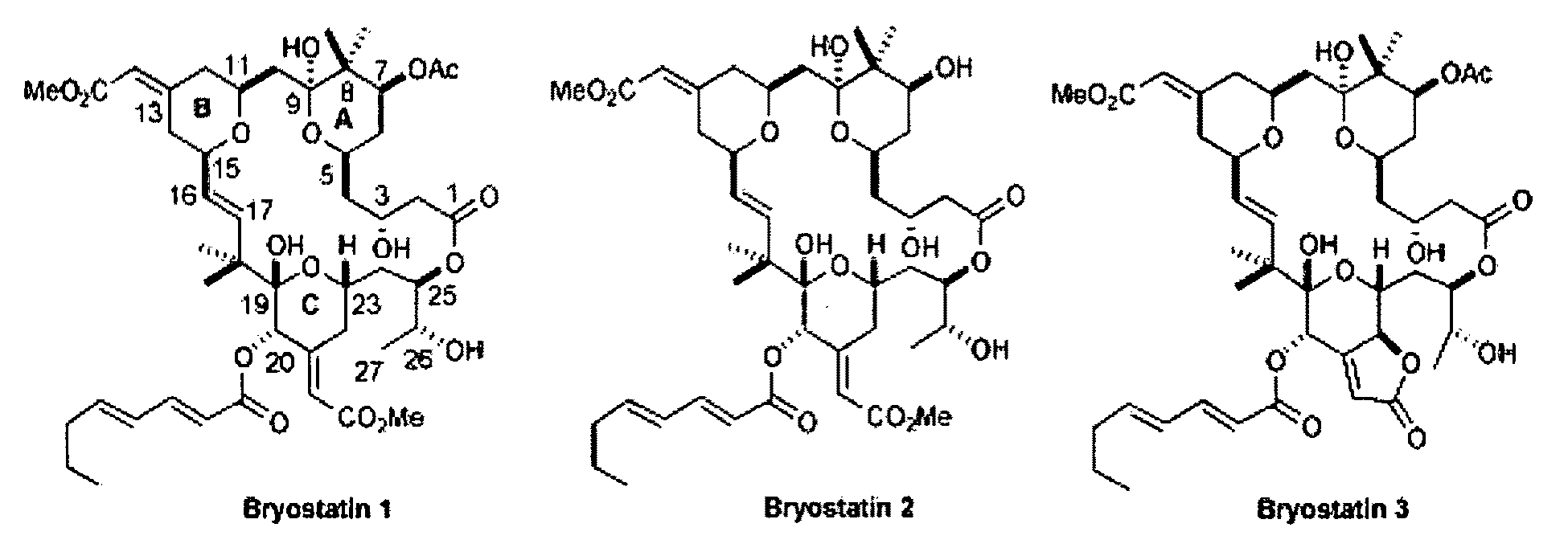
The invention relates to a combination of treatments, more particularly a combination treatment for HIV-1 infection. The present invention is directed to the use of bryostatin-1 and their natural and synthetic derivatives for AIDS therapy, in particular to the use of bryostatins in combination with other active drugs such as Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors and anti-retrovirals, for the treatment of HIV-1 latency. According to the present invention, we provide a combination therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 latency which employs bryostatin-1 (and analogues) and one of the following HDAC inhibitors; valproic acid, butyrate derivatives, hydroxamic acids and benzamides. While HDACi can be used in continuous dosing protocol, bryostatins can be used following a cyclical dosing protocol. Bryostatins can be formulated in pharmaceutical acceptable carriers including nanoparticles, phospholipids nanosomes and / or biodegradable polymer nanospheres. This combination therapy needs to be used in patients treated with antiretroviral therapy (HIV-1 protease inhibitors, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors, HIV-1 integrase inhibitors, CCR5 co-receptor inhibitors and fusion inhibitors).
Owner:APHIOS
Nonpeptide hiv-1 protease inhibitors
InactiveUS20110178123A1Improve the quality of lifeEnhanced HIV managementBiocideOrganic chemistryMedicineHIV Proteinase
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
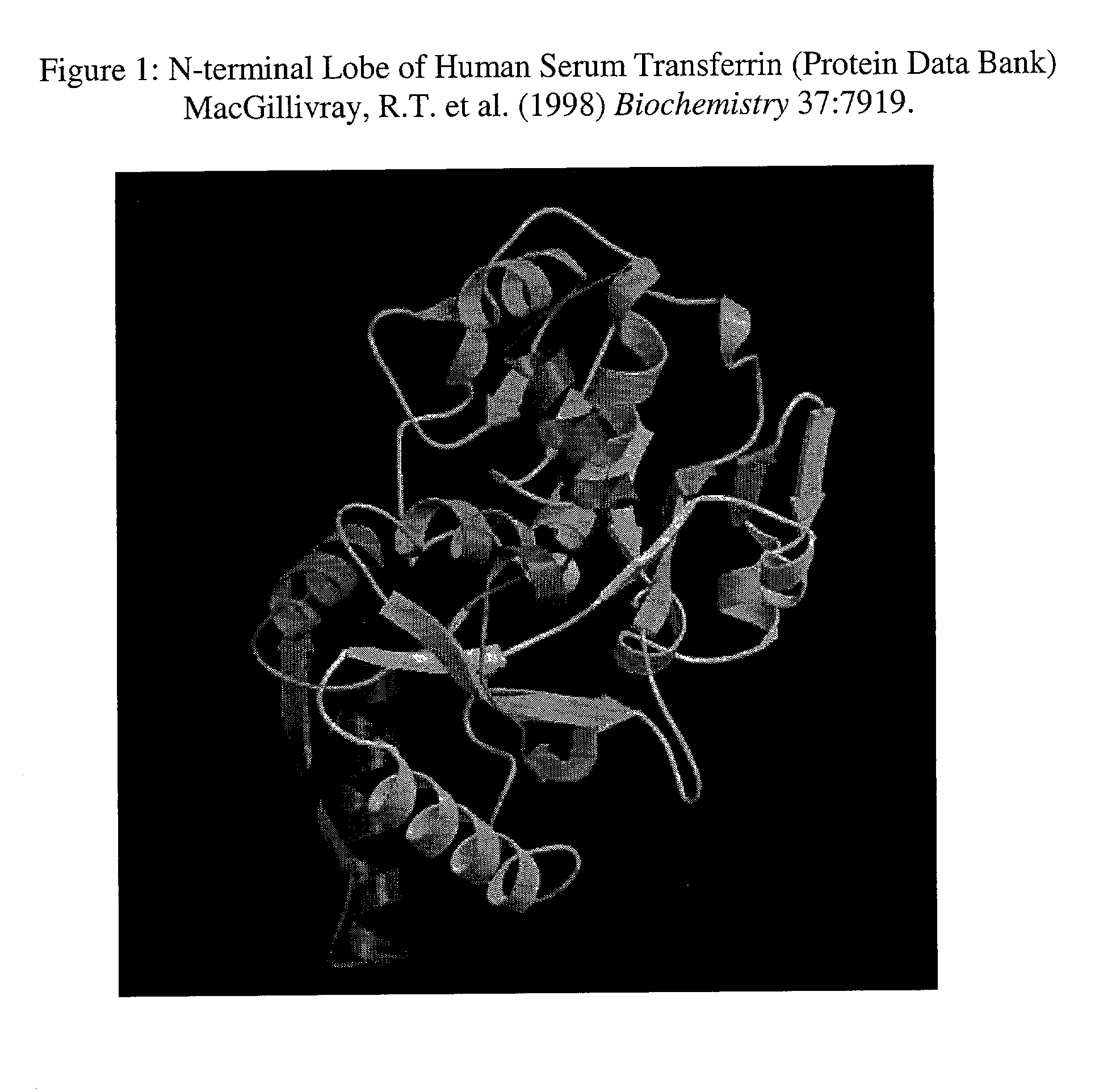
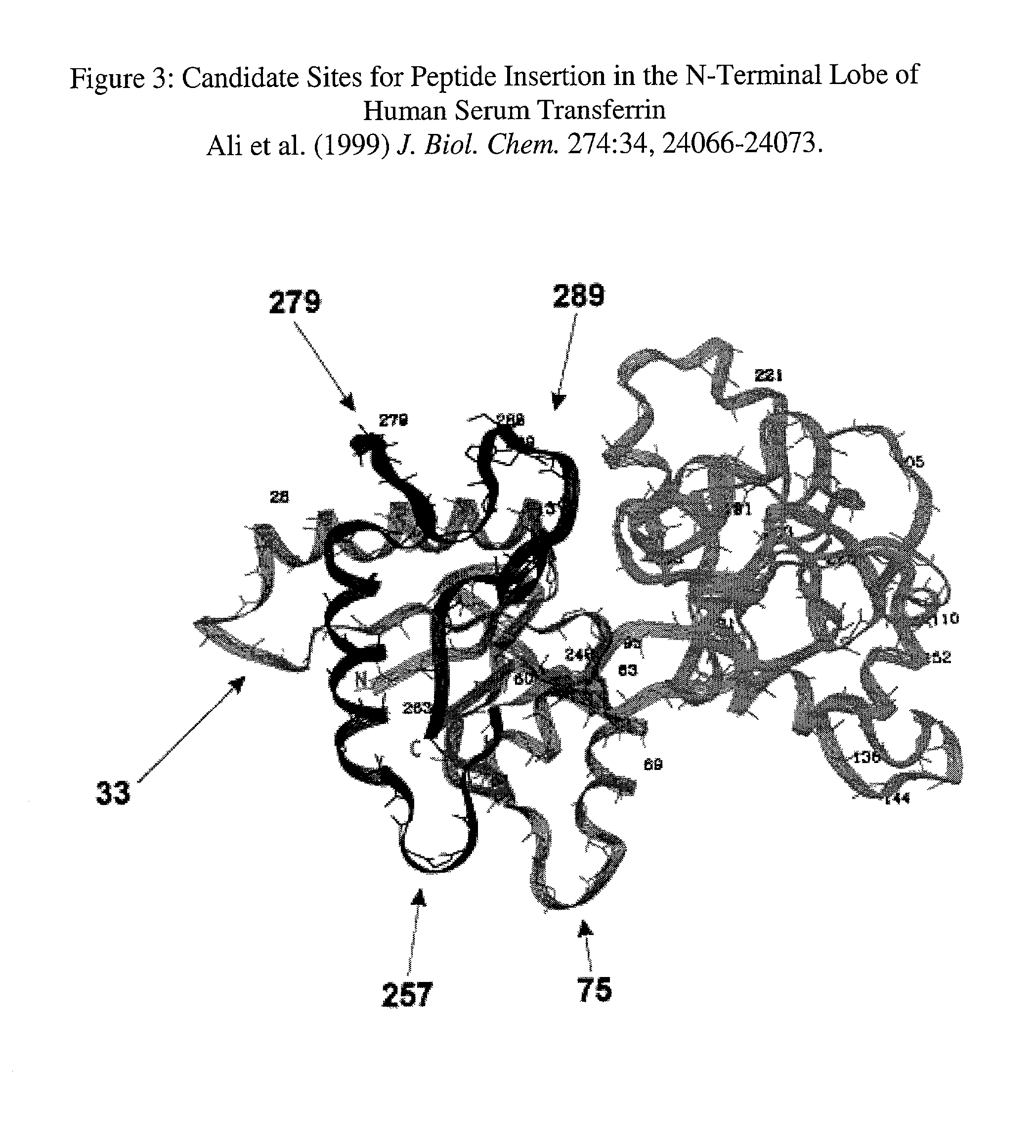
Recombinant human serum transferrins containing peptides for inducing apoptosis in HIV-1 infected cells
InactiveUS20020146794A1Minimal effectFacilitated releaseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesInfected cellMammal
A mammalian protein, like the human serum transferrin (HST), is modified with an inserted peptide sequence flanked at both ends by cleavage sites. The peptide insert contains a motif known to induce apoptosis in cells and the cleavage sites are specific for the viral protease of HIV-1. The delivery of such recombinant transferrin into an HIV-1 infected cell results in the release of the peptide which then induces apoptosis. The peptide is inserted into surface exposed loops of the N-terminal lobe of the HST containing the RGD motif flanked by two modified p17 / p24 HIV-1 protease cleavage sites. When delivered to the infected cell the cleavage of the loop inserted sequences by the HIV-1 protease results in the release of the central RGD-containing peptide sequences. Peptides containing the RGD motif (arginine, glycine, aspartic acid) have been shown to induce cell apoptosis even in small concentrations.
Owner:TOMYCZ NESTOR D
Compounds and methods for treating HIV
ActiveUS20130289067A1High activityExtensive interactionBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseHIV Proteinase
Inhibitors of HIV-1 protease and compositions containing them are described. Use of the inhibitors and compositions containing them to treat HIV, AIDS, and AIDS-related diseases is described.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Combination Therapy Comprising A CCR5 Antagonist, A HIV-1 Protease Inhibtior and a Pharmacokinetic Enhancer
The present invention discloses a novel combination therapy for HIV-1 treatment relying on a combination of at least one CCR5 antagonist, at least one HIV-1 protease inhibitor and at least one pharmacokinetic enhancer of said at least one CCR5 antagonist and / or at least one HIV-1 protease inhibitor. The combination is intended for use in oral treatment of a disorder selected from the group consisting of HIV-1 infection, retroviral infections genetically related to HIV and AIDS, in a treatment-naïve patient infected with CCR5 tropic HIV-1 virus.
Owner:TRESSLER RANDY +1
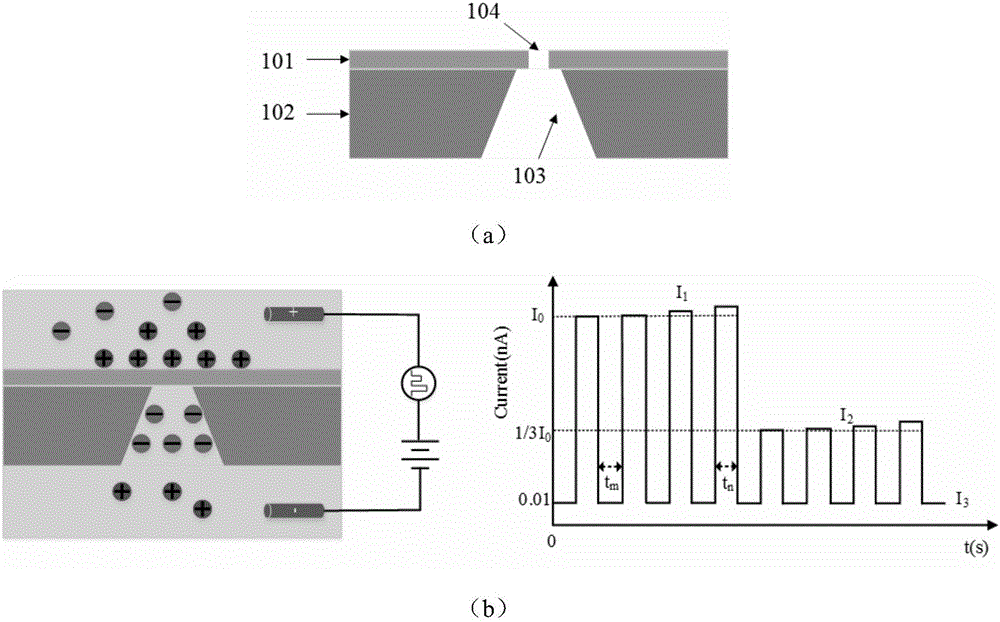
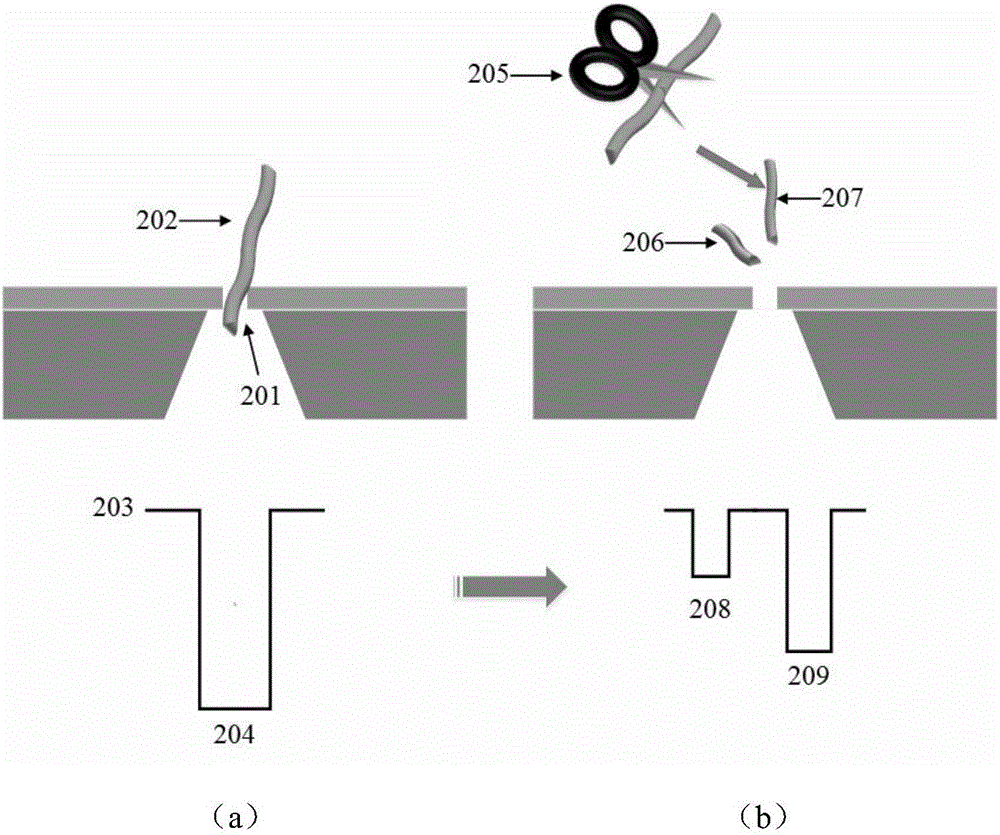
HIV-1 protease detection method based on solid state nanopore
InactiveCN106443008AJudgment activityJudgment concentrationBiological material analysisBiological testingProtein targetProtein precursor
Owner:重庆中科德馨生物科技有限公司
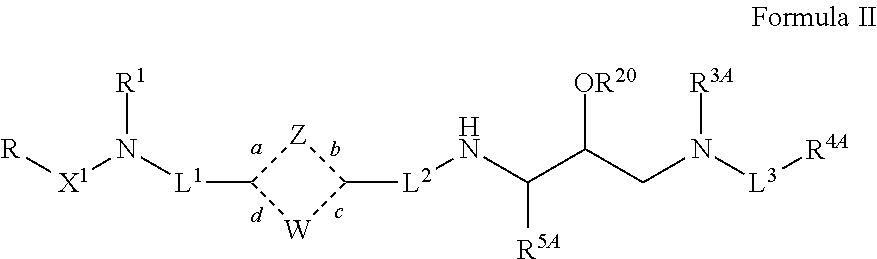
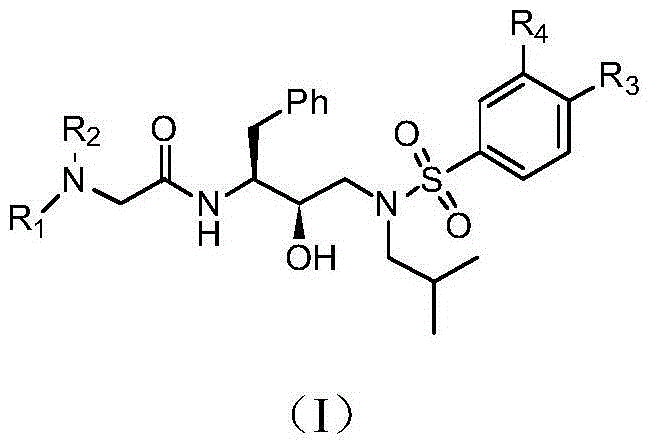
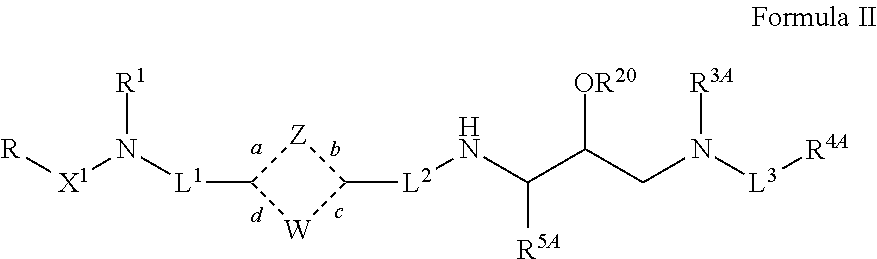
Tertiary amine analogical peptide derivative and application of tertiary amine analogical peptide derivative in inhibiting HIV-1 protease
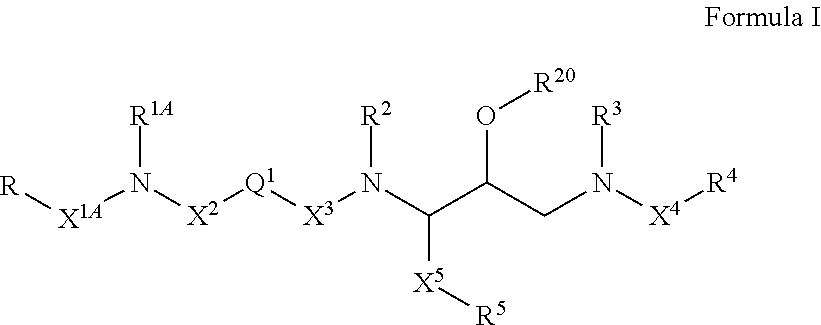
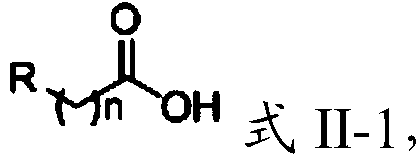
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and relates to a tertiary amine derivative as shown as the general formula I, and pharmaceutically acceptable salt or a prodrug of the tertiary amine derivative. Results of experimental studies show that the tertiary amine derivative has higher capacity of inhibiting the activity of HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus-1) protease and is expected to be developed into an effective drug for resisting Aids.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
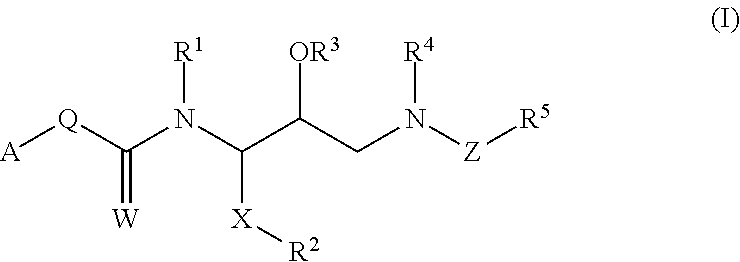
Treatment for lipodystrophy
ActiveUS20170088514A1Reduce productionHigh affinityOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderLipoatrophyReverse transcriptase
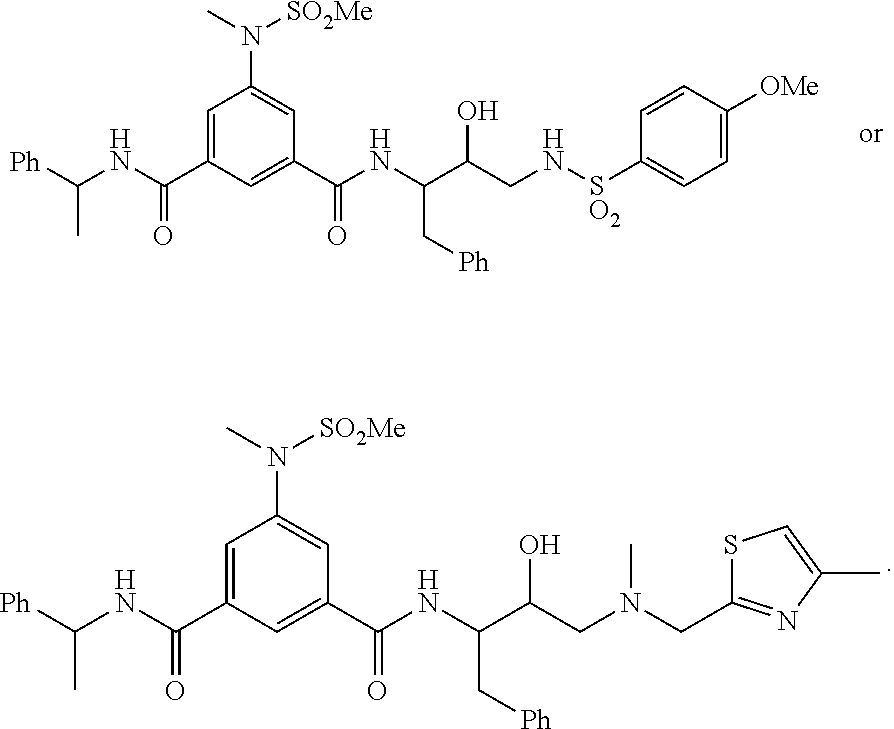
The present invention provides a therapeutic compound of formula (I) and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts for the prevention and treatment of lipodystrophy caused because of HIV infection or combination therapy of HIV-1 protease inhibitors (PIs) and / or reverse transcriptase inhibitors (nRTIs) by neutralizing lipohypertrophy, lipoatrophy and metabolic abnormalities in HIV patient.
Owner:CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD
Application of stilbene glucosides in treating and preventing AIDS
The invention provides an application of stilbene glucosides in preparing drugs for treating and preventing AIDS. Structural formulas of the stilbene glucosides are show as a general formula (I), wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 or R6 independently represent hydrogen, hydroxyl, C1-C4 alkyl, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 acyloxy, halogen, nitryl, trifluoromethyl or a cyano group, and pre-conditions are that at least one of R1, R2 and R3 is the hydroxyl, at least one of R4, R5 and R6 is the hydroxyl, and at least one hydroxyl of R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 is connected with sugar. In the compounds represented by the general formula (I), an inhibitory activity (IC50) for the HIV-1 protease of 2,3,5,4-tetera-hydroxystilbene-2-O-beta-D-glucoside of the stilbene glucosides for reaches 126 [mu]M.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
Oligopeptide compound with HIV-1 protease inhibitory activity, and preparation method and application thereof
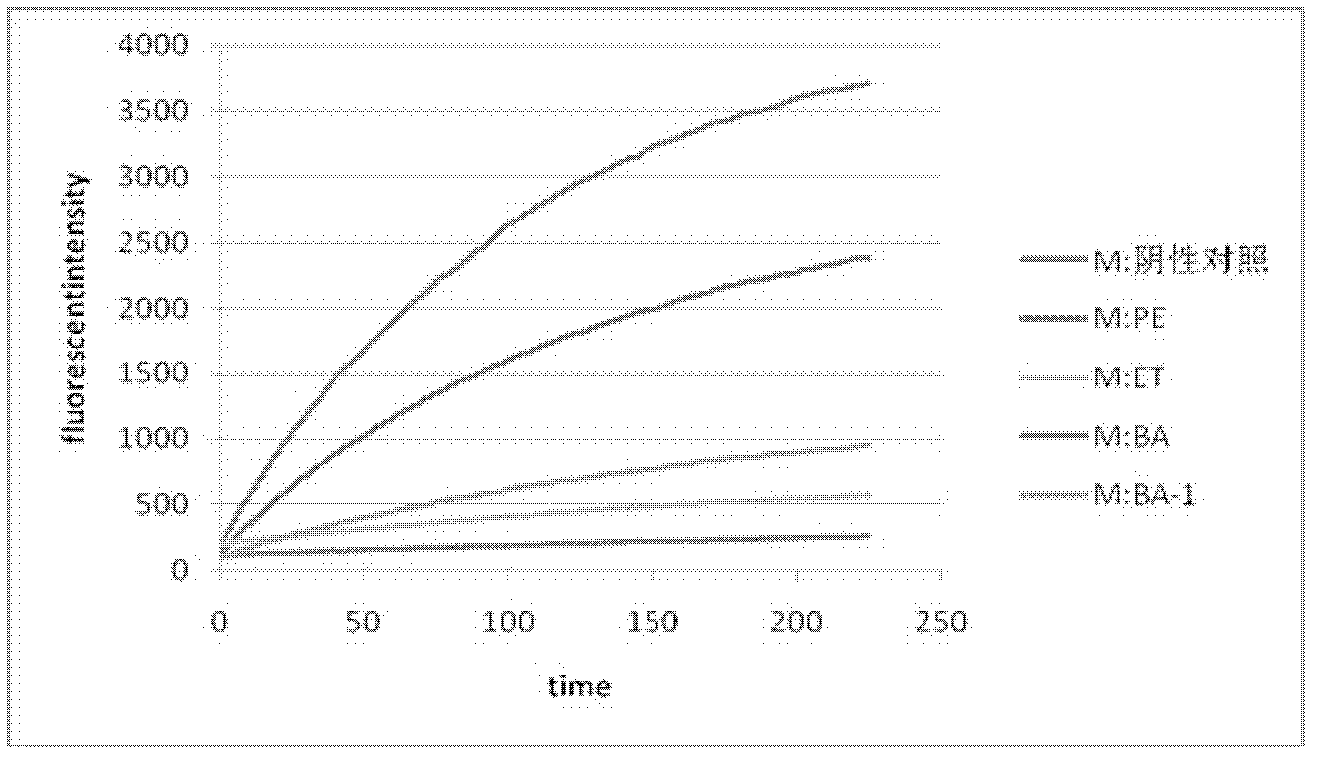
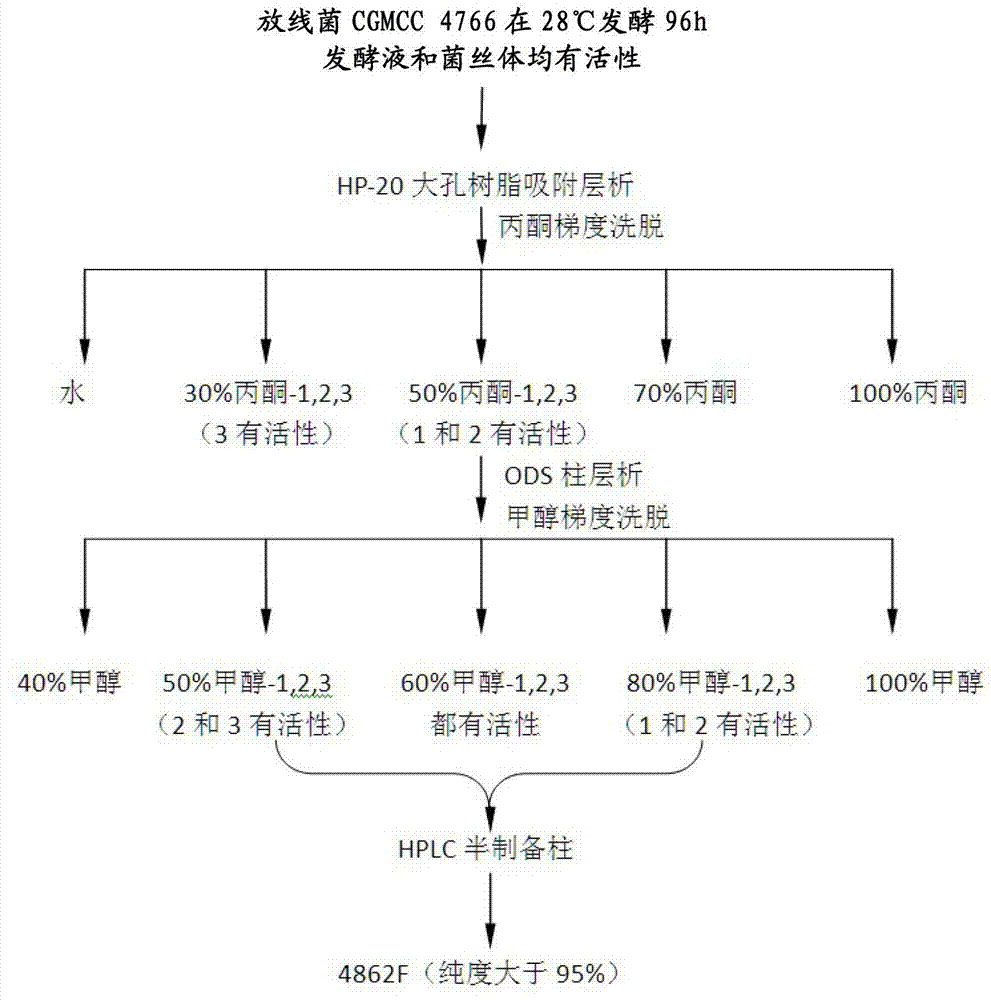
The present invention provides an oligopeptide compound with an amino acid sequence of Tyr-Leu-Val-Leu-His (SEQ ID NO:1) and HIV-1 protease inhibitory activity. The oligopeptide compound provided by the invention can be produced from chemical synthesis, or recombination, or microorganism (particularly actinomycetes) extraction. The invention also provides an extract obtained from microorganism (particularly actinomycetes) and having HIV-1 protease inhibitory activity and a preparation method thereof. The extract contains the oligopeptide compound provided by the invention. The invention also provides microorganisms (particularly actinomycetes, such as Actinomyces CGMCC 4766) for obtaining the oligopeptide compound or extract provided by the invention. The oligopeptide compound or extract provided by the invention can be used for prevention and treatment of HIV infection related diseases, such as AIDS.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Nucleic acid base compound or medically acceptable salt thereof and preparation method and application of compound or salt thereof
ActiveCN108558883AInhibitory activityGood medicineGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAntiviralsReverse transcriptaseHIV Proteinase
The invention provides a nucleic acid base compound or a medically acceptable salt thereof. The compound or the medically acceptable salt thereof has the obvious inhibitory HIV protease and / or reversetranscriptase activity; toxicity studies show that the compound has the good druggability, it is indicated that the compound has a good application prospect by serving as an anti-AIDs drug. Accordingto experimental data, the compound has inhibitory activity on HIV-1 protease and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, and low cytotoxicity exits. The nucleic acid base compound or the medically acceptable salt thereof is expected to become a double-target inhibitor inhibiting the HIV protease and the reverse transcriptase simultaneously.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Amide derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108558808AHigh activityLow cytotoxicityEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesProteinase activityReverse transcriptase
The invention provides an amide derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof with the structure as shown in formula I. A compound or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof has significant activity in inhibiting HIV protease and reverse transcriptase; toxicity study shows that the compound or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof has better druggability, and the compound has better application prospect in using as anti-Aids drugs. According to experimental data, the compound has inhibiting activity both on HIV-1 protease and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and has lower cytotoxicity. The compound or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof is expected to be a double-target inhibitor which can inhibit the HIV protease and the reverse transcriptase.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
HIV type I protease inhibitor screened out from crude extract of Berberis nummularia Bge, and application thereof
The invention provides a method for screening an HIV protease inhibitor based on combination of a fluorogenic substrate and crystal soak. The method comprises the steps of measuring inhibitory activity of a series of compounds that are separated and purified from natural products to the HIV-1 protease; and finally separating and purifying the series of compounds into a single component, wherein the single component is a small molecular inhibitor of the natural products. With the above method, the extract of the Berberis nummularia Bge is found to have effective inhibitory activity for the HIV-1 protease; small molecules with relatively strong combination capacity for the HIV-1 protease are found via the crystal soak method; then the inhibitory activity of the small molecules to the HIV-1 protease is determined via enzyme activity assay; and finally a small molecular inhibitor capable of effectively inhibiting the activity of the HIV-1 protease is provided. Besides, a method for screening anti-HIV materials by the combination of the small molecular substance and an HIV protease compound is provided, novel sites that the HIV protease can interact to the inhibitor are provided, and a method for screening the anti-HIV active materials by using the sites is provided.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
HIV protease inhibitors
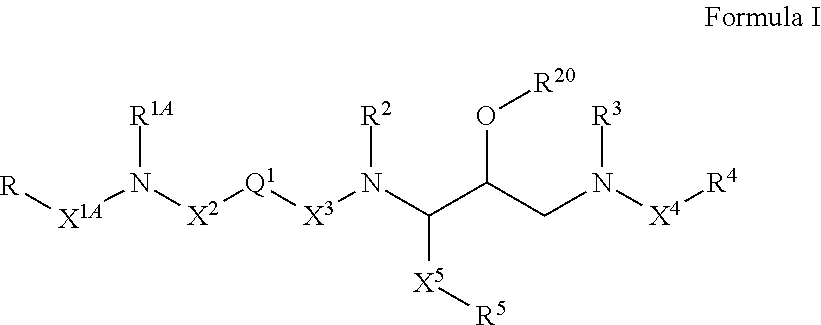
Compounds of the formula I:whereinR1, R2, X and N are as defined in the specification;E is N, CH;A′ and A″ are terminal groups as defined in the specification.The compounds have utility as HIV-1 protease inhibitors.
Owner:MEDIVIR AB
Pharmaceutical applications of traditional Chinese medicine Cassia fistula L. fruit and extract thereof
The invention provides an application of a traditional Chinese medicine Cassia fistula L. fruit in preparing medicines used for treating AIDS, and especially in preparing medicines used for inhibiting HIV-1 protease. A Cassia fistula L. fruit ethyl acetate extract provided by the invention has an HIV-1 protease activity inhibition rate of 83.4%. IC50 of HIV-1 protease inhibition activity of piceatannol separated from Cassia fistula L. fruit is 59mum.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
Chinese medicine lychee seed and pharmaceutical purpose of extractives of Chinese medicine lychee seed
The invention provides a purpose of a Chinese medicine lychee seed in preparing of drugs for treating aids, and particularly provides a purpose in preparing of drugs for restraining HIV-1 protease. The IC 50 value of extractives for inhibitory activity of the Chinese medicine lychee seed to the HIV-1 protease is 10.34 microgram per milliliter.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
Recombinant human serum transferrins containing peptides for inducing apoptosis in HIV-1 infected cells
InactiveUS6528287B2Minimal effectFacilitated releaseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsInfected cellMammal
A mammalian protein, like the human serum transferrin (HST), is modified with an inserted peptide sequence flanked at both ends by cleavage sites. The peptide insert contains a motif known to induce apoptosis in cells and the cleavage sites are specific for the viral protease of HIV-1. The delivery of such recombinant transferrin into an HIV-1 infected cell results in the release of the peptide which then induces apoptosis. The peptide is inserted into surface exposed loops of the N-terminal lobe of the HST containing the RGD motif flanked by two modified p17 / p24 HIV-1 protease cleavage sites. When delivered to the infected cell the cleavage of the loop inserted sequences by the HIV-1 protease results in the release of the central RGD-containing peptide sequences. Peptides containing the RGD motif (arginine, glycine, aspartic acid) have been shown to induce cell apoptosis even in small concentrations.
Owner:TOMYCZ NESTOR D
Nonpeptide HIV-1 protease inhibitors
InactiveUS8791135B2Halting progressionReduce complexityBiocideOrganic chemistryHIV ProteinaseMedicine
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
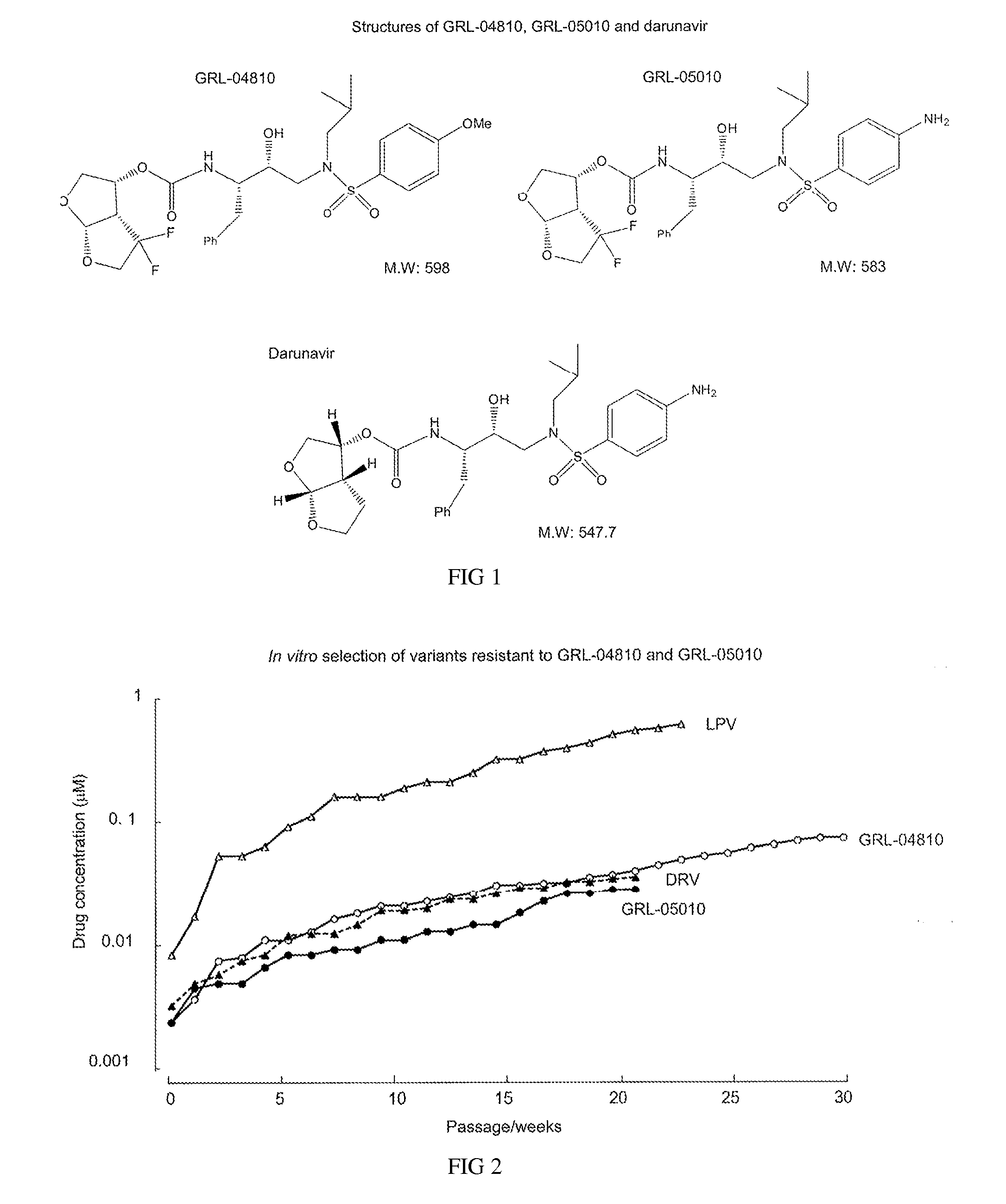
Hiv-1 protease inhibitors
InactiveCN101702908AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityHIV Proteinase
Described are novel protease inhibitors and methods for using said protease inhibitors in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Compunds and methods for treating HIV
Inhibitors of HIV-1 protease and compositions containing them are described. Use of the inhibitors and compositions containing them to treat HIV, AIDS, and AIDS-related diseases is described.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Novel synthetic method of HIV-1 protease inhibitor atazanavir
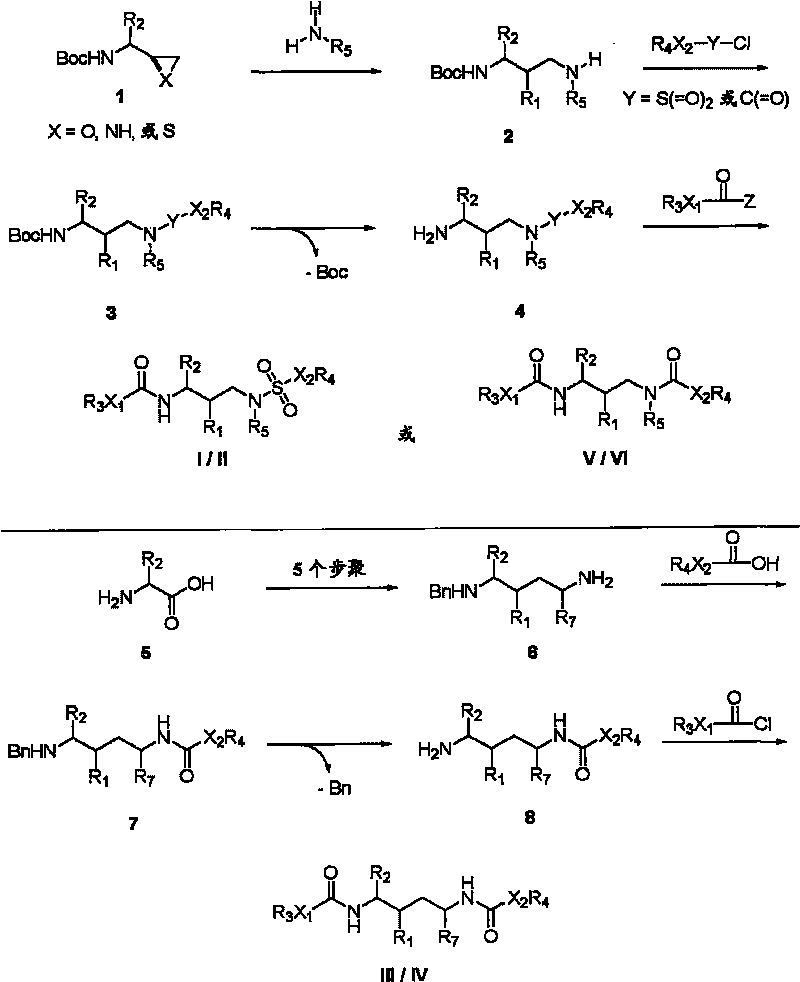
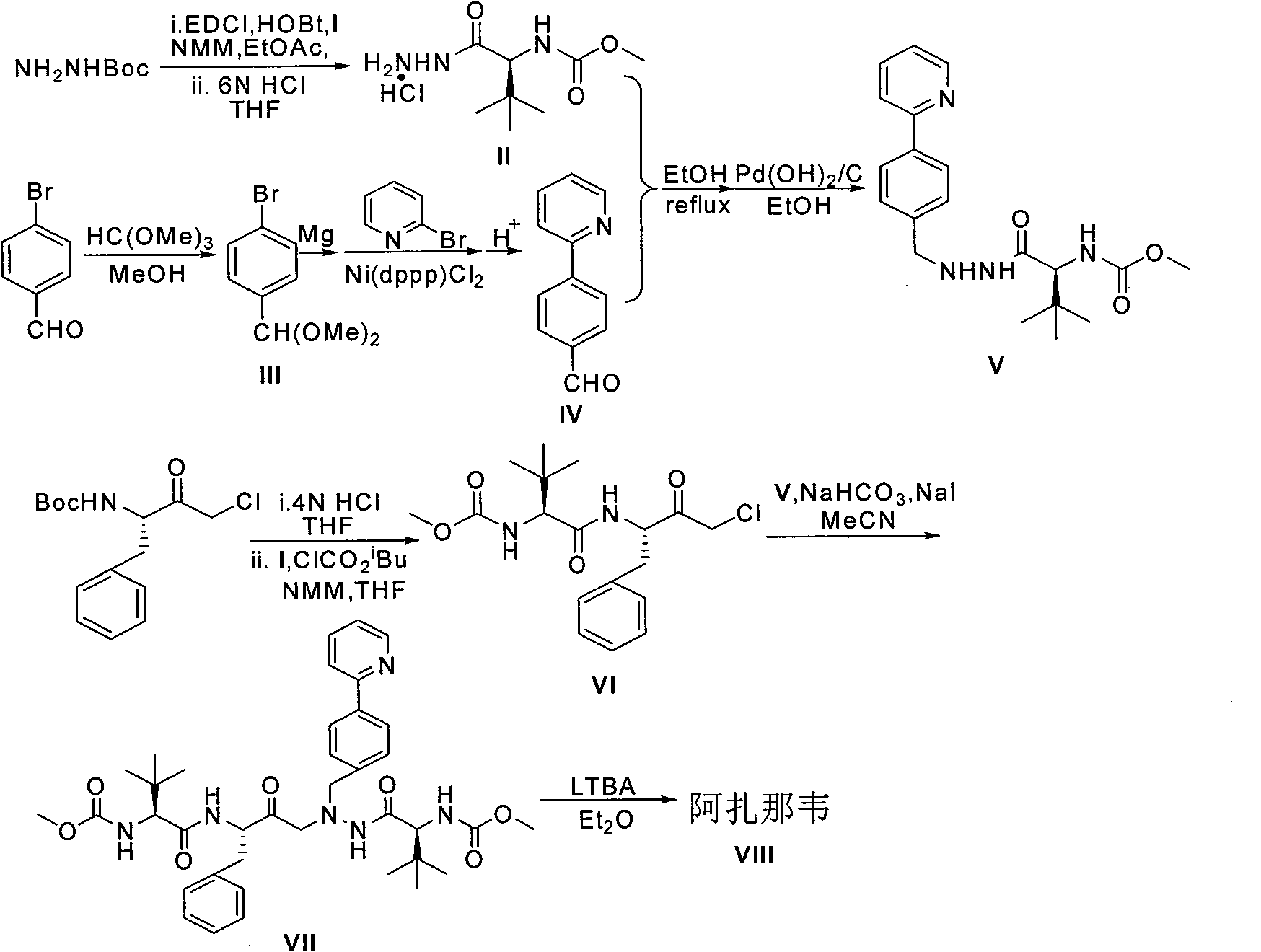
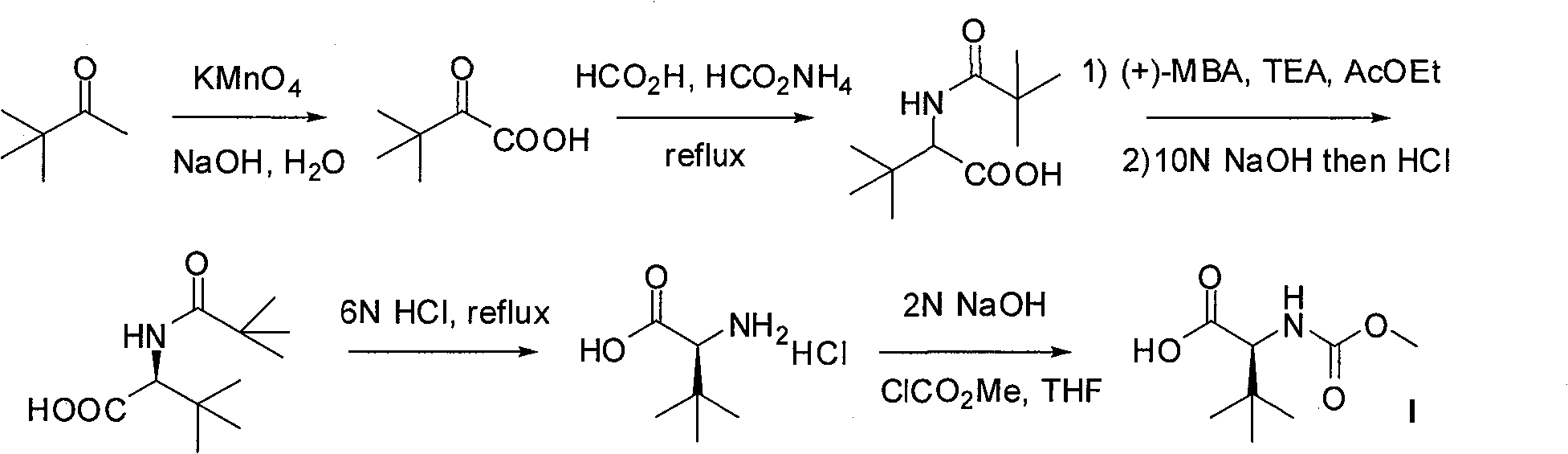
InactiveCN101391978BLow priceEasy recrystallization purificationOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionMethyl carbamateMethyl carbazate
The invention relates to a new synthetic method of an HIV-1 protease inhibitor, Atazanavir, which adopts a convergent-typed synthetic strategy, introduces a construction unit, methoxycarbonyl-tert-lencyl, as an N atom protecting group in the whole early synthetic stage, and takes the diastereomeric selective reduction of aminoketone as the key and final reaction step of the new process. The method comprises the steps that: the compound of formula V, namely, N-1-[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucine]-N-2-[4-(2-pyridyl)-phenmethyl]hydrazine, and the compound of formula VI, namely, (S)-1-((S)-4-chlorine-3-carbonyl-1-phenyl butane-2-yl-2-amino)-3, 3-dimethyl-1-carbonyl butane-2-yl-methyl carbamate, are treated with nucleophilic substitution reaction to generate the compound of formula VII, namely, 1-[4-(2-pyridyl)phenyl]-5(S)-2, 5-bis{[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucineyl] amino}-4-carbonyl-6-phenyl-2-azahexane; and the compound of formula VII is treated with reduction reaction to generate the Atazanavir. The invention has the advantages of less process route steps, easily-controlled reaction conditions, simple and convenient operation, low-price and easily-obtained raw material, high product yield, low cost and being suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
HIV-1 protease inhibitors having gem-di-fluoro bicyclic p2-ligands
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Inhibitor of the folding of the HIV-1-protease as antiviral agent
InactiveUS20070072806A1Toxic reductionEvenly distributedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHIV ProteinaseMonomer
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
Inhibitor of the folding of the HIV-1-protease as antiviral agent
InactiveUS7501398B2Improve solubilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityHIV Proteinase
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
HIV-1 protease inhibitors having gem-di-fluoro bicyclic P2-ligands
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Lignin compounds and their uses
InactiveCN103130620BInhibitory activityHigh inhibition rateHydroxy compound active ingredientsEther separation/purificationHydrogenChemical compound
The invention provides a lignin compound and functions thereof. The structural formula of the lignin compound is as shown in a general formula (I), wherein R1 is from an alkyl group of C1-C4 or an alkyl acyl group of the C1-C4, and R2 is from hydrogen or the alkyl group of the C1-C4 or the alkyl acyl group of the C1-C4. The lignin compound can effectively inhibit activity of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) protease, and inhibitory activity IC 50 of a compound 5-allyl-5'-(1-ethyoxyl-2-hydroxy-propyl group)-biphenyl-2,2'-diphenol on the HIV-1 protease is 200uM.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
A nucleic acid base compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108558883BInhibitory activityGood medicineGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAntiviralsReverse transcriptaseHIV Proteinase
The invention provides a nucleic acid base compound or a medically acceptable salt thereof. The compound or the medically acceptable salt thereof has the obvious inhibitory HIV protease and / or reversetranscriptase activity; toxicity studies show that the compound has the good druggability, it is indicated that the compound has a good application prospect by serving as an anti-AIDs drug. Accordingto experimental data, the compound has inhibitory activity on HIV-1 protease and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, and low cytotoxicity exits. The nucleic acid base compound or the medically acceptable salt thereof is expected to become a double-target inhibitor inhibiting the HIV protease and the reverse transcriptase simultaneously.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
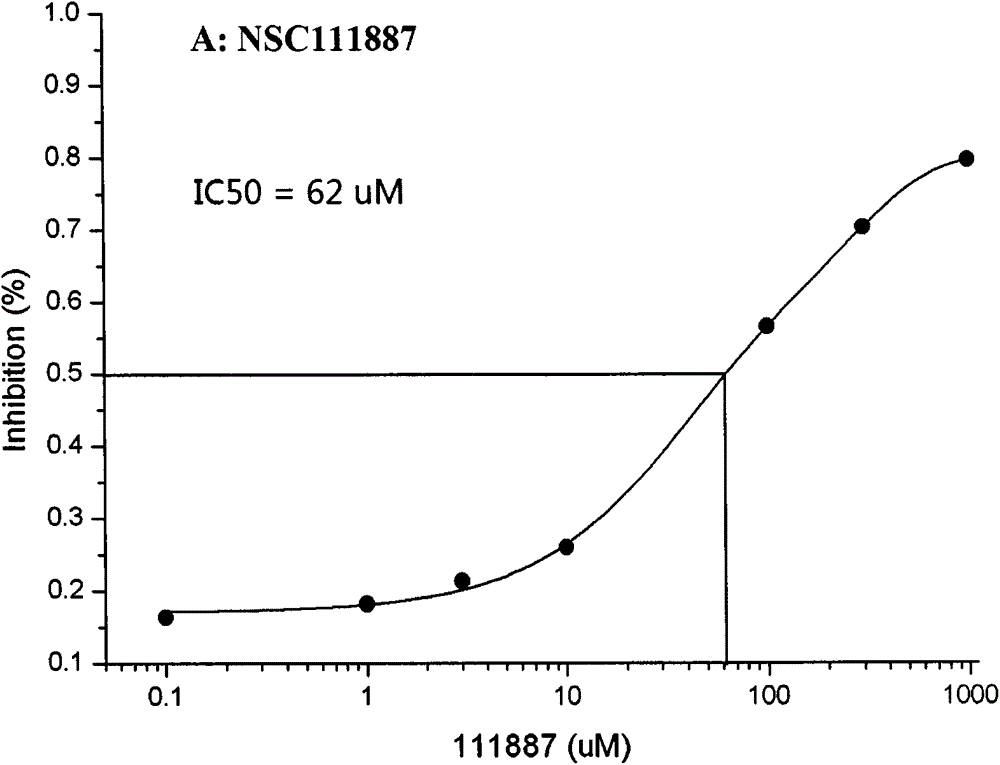
Novel application of National Cancer Institute (NCI) compounds in inhibition of activity of HIV type 1 protease
The invention relates to novel application of NCI compounds, specifically to novel application of the NCI compounds with accession numbers of NSC111887 and NSC121217 in inhibition of the activity of HIV type 1 protease. According to the invention, through integration of conventional anti-HIV-1 protease drug and inhibitor data, computational simulation and an in-vitro compound screening method, molecules of the compounds with the accession numbers of NSC111887 and NSC121217 are found out for the first time, and the compound molecules have the structural characteristics of tripeptide derivatives, certain inhibition capability on the activity of HIV-1 protease and 50% inhibiting concentrations of 62 mu M and 162 mu M, respectively.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
Use of mutant hiv-1 protease or siv protease as an adjuvant
InactiveUS20110059127A1Enhance cell-mediated immune responseEfficient use ofAntiviralsWhole-cell/virus/DNA/RNA ingredientsHPV AntigenImmunodeficiency virus
The present invention relates to a mutant HIV-1 (Human immunodeficiency virus-1) protease capable of effectively enhancing cell-mediated immune responses to DNA vaccination, and use of a nucleic acid encoding the same as a vaccine adjuvant. The mutant HIV-1 protease according to the present invention has inactivated or attenuated proteolytic activity, while retaining chaperone-like activity. When the mutant HIV-1 protease is used together with a DNA vaccine against the HIV-1 envelope protein or the HPV antigen (E6 or E7), cell-mediated immune responses can be effectively enhanced for the prevention or treatment of AIDS or cervical cancer.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
System and compositions for isolating suppressors of HIV-1 protease
InactiveCN101501210AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisYeastProteinase activity
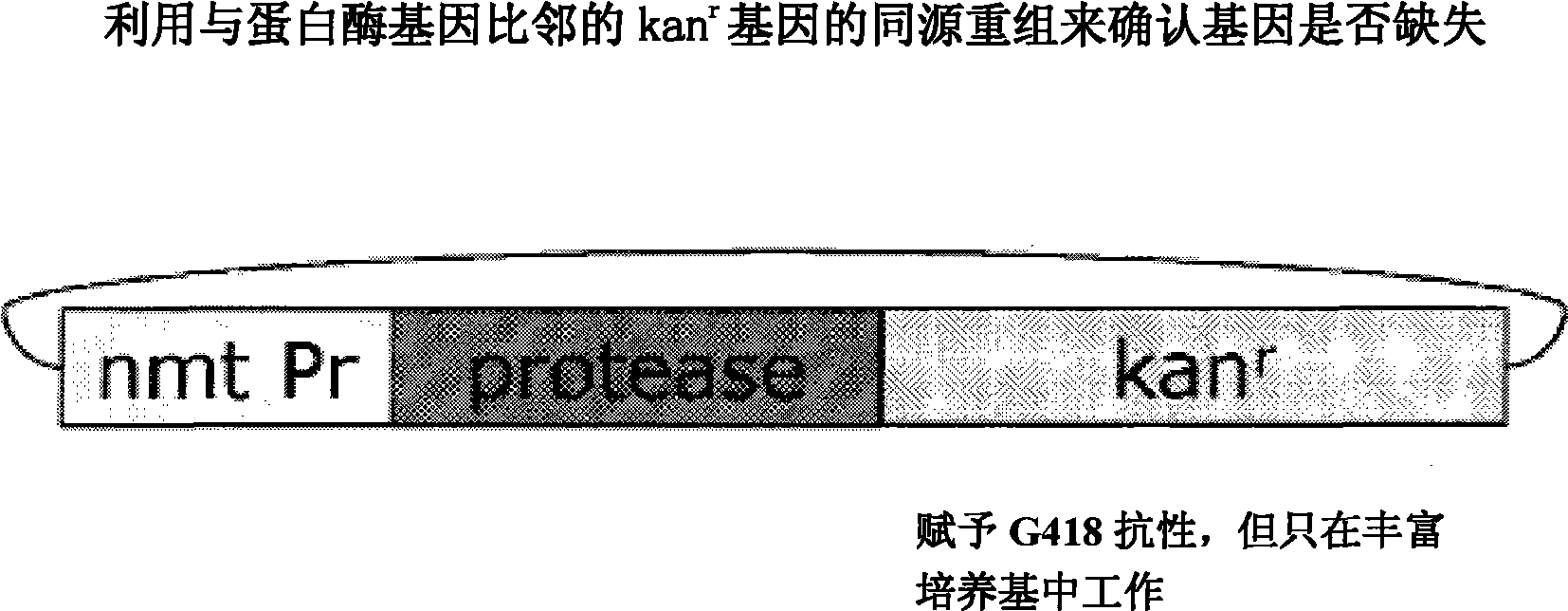
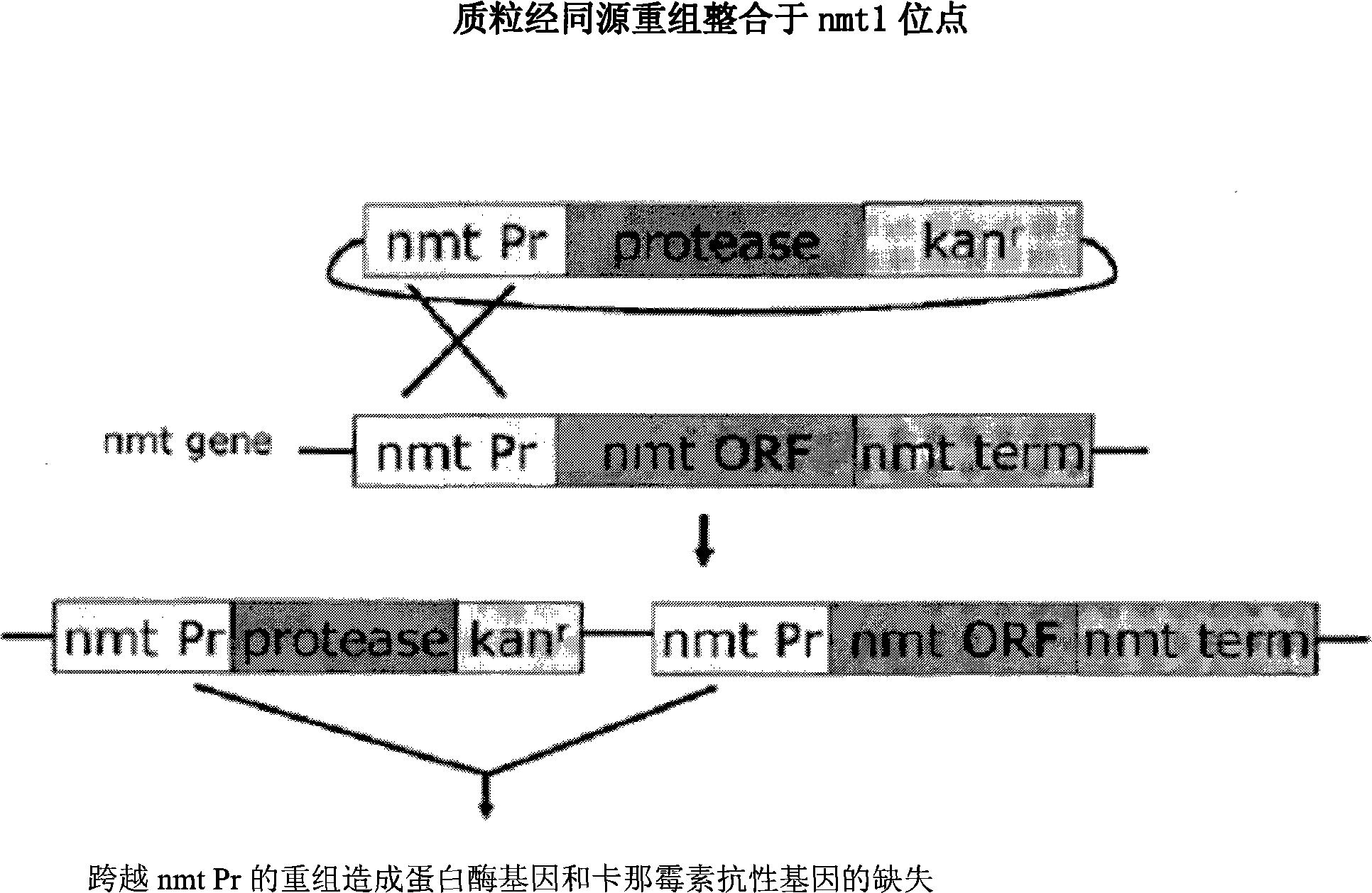
The present invention relates to a yeast screening assay for the identification of suppressors of a protease, such as the HIV-I protease and / or HIV-2 protease, for example. Upon overexpression of HIV-I protease in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, for example, the cell dies, but in the presence of a candidate inhibitor with protease suppressor activity, the cell lives, thereby providing an assay for the identification of one or more suppressors. In additional aspects, there is an in vivo protease activity screen, used alternatively or additionally to a viability screen, such as for cleavage of a HIV-I protease-specific site. In further aspects, the suppressor is employed for the treatment of an individual infected with HIV virus or with AIDS.
Owner:SUZHOU SIRNAOMICS BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com