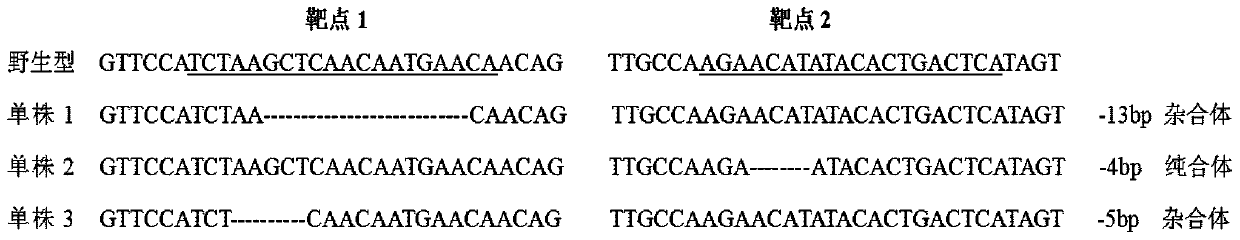Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
120 results about "Genetically modified tomato" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A genetically modified tomato, or transgenic tomato, is a tomato that has had its genes modified, using genetic engineering. The first trial genetically modified food was a tomato engineered to have a longer shelf life (the Flavr Savr), but never made it to market. Currently there are no genetically modified tomatoes available commercially, but scientists are developing tomatoes with new traits like increased resistance to pests or environmental stresses. Other projects aim to enrich tomatoes with substances that may offer health benefits or be more nutritious. As well as aiming to produce novel crops, scientists produce genetically modified tomatoes to understand the function of genes naturally present in tomatoes.
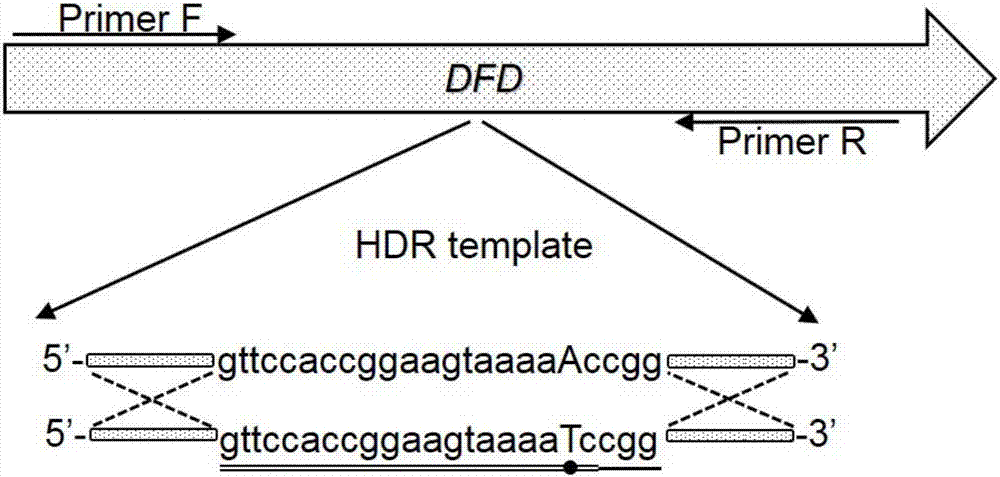
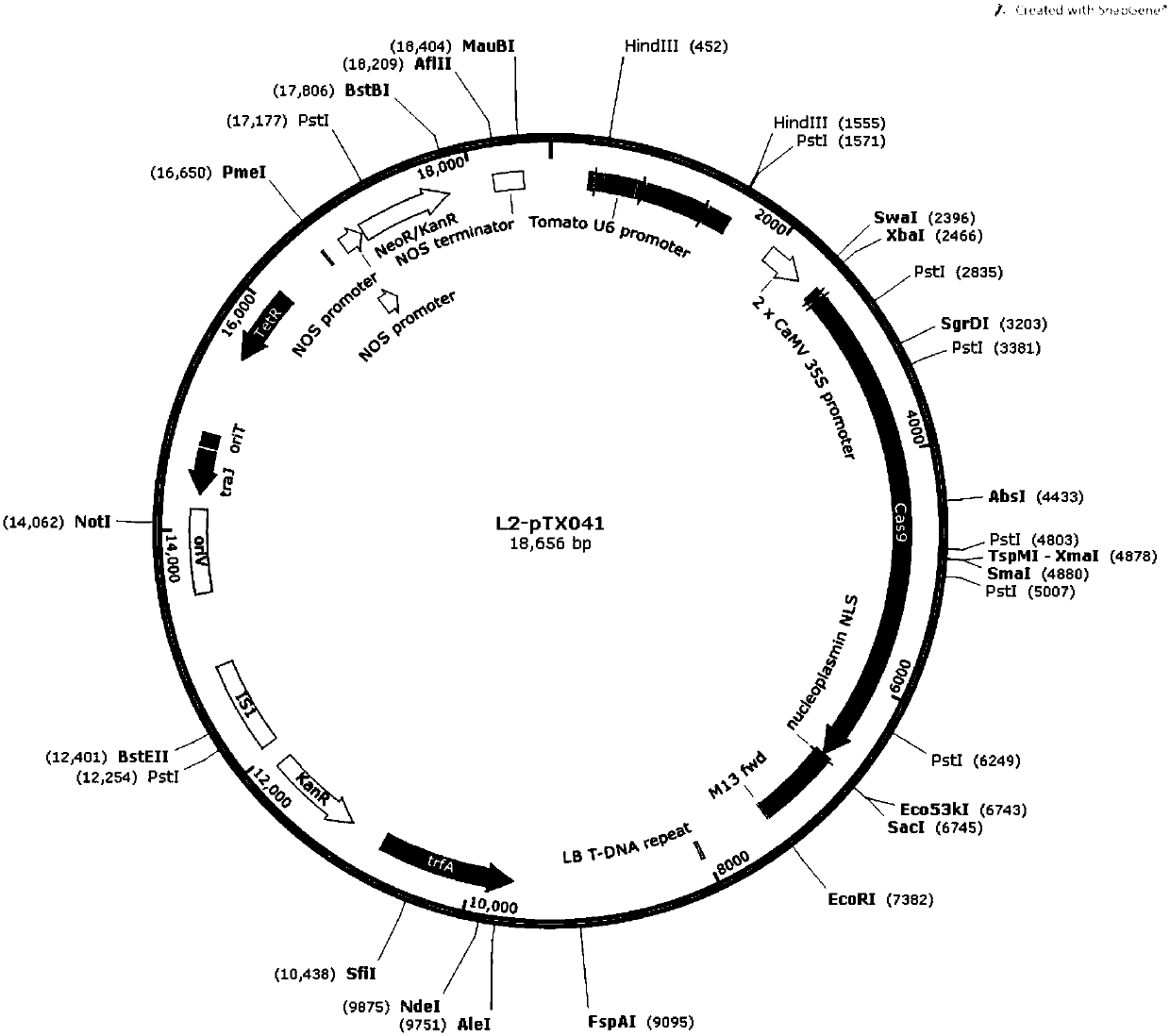
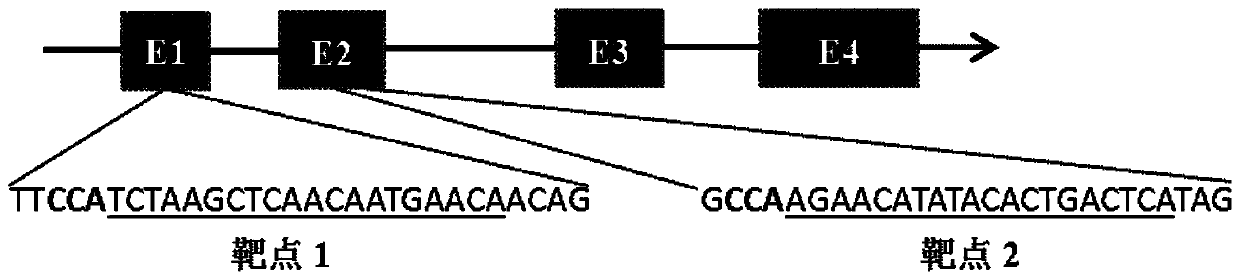
Cas9-mediated tomato gene editing vector and application thereof
InactiveCN107312793AExtended shelf lifeDoes not affect growthHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionGenetic engineeringBiology
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering technology, and specifically discloses a Cas9-mediated tomato gene editing vector and application thereof. A Cas9 gene is introduced into a tomato M82 by constructing a CRISPR / Cas9 tomato plant expression vector, and gene editing is carried out on the DFD gene of the tomato. The invention provides a method for constructing a storage-endurance transgenic tomato, the new storage-endurance tomato product is obtained, so that the storage endurance of the tomato fruit is improved, and besides, the growth and other qualities of plant are not influenced, and the method can compensate for shortcomings of former research programs.
Owner:HORTICULTURE INST OF XINJIANG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
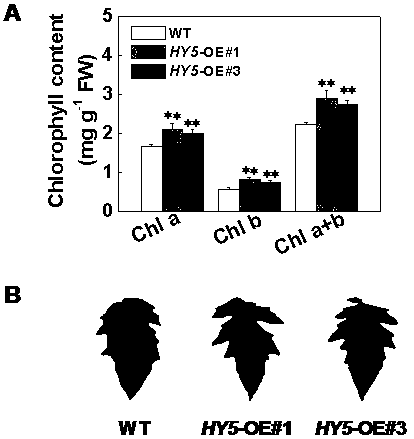
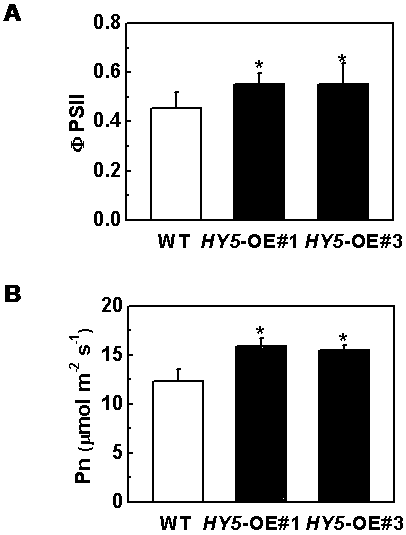
Gene for improving chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis efficiency of tomatoes and application
ActiveCN109628439AImprove photosynthetic efficiencyIncrease chlorophyll contentHybrid cell preparationPlant peptidesGenePhotosynthetic efficiency
The invention relates to a gene for improving chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis efficiency of tomatoes and application. The gene for improving the chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis efficiency of the tomatoes is composed of a tomato S1HY5 gene and protein encoded by the gene. The invention provides the application of the tomato S1HY5 gene or the protein encoded by the tomato SlHY5 gene to the improvement of chlorophyll synthesis of tomato plants and promotion of the photosynthesis of tomato plant leaves and a method for obtaining the transgenic tomato plants with the increased plant chlorophyll and photosynthesis rate. According to the specific method, through a gene overexpression technology, the expression level of the tomato S1HY5 gene is increased, and therefore the chlorophyll of the tomato plants is increased; the functions of increasing the chlorophyll content of the tomatoes and improving the photosynthesis efficiency of the tomatoes are determined, a gene resourceis provided for cultivating the new tomato varieties with the high chlorophyll content, the gene has high application value, and a theoretical basis is laid for a regulation mechanism of optical signals for the chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis of the plants.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
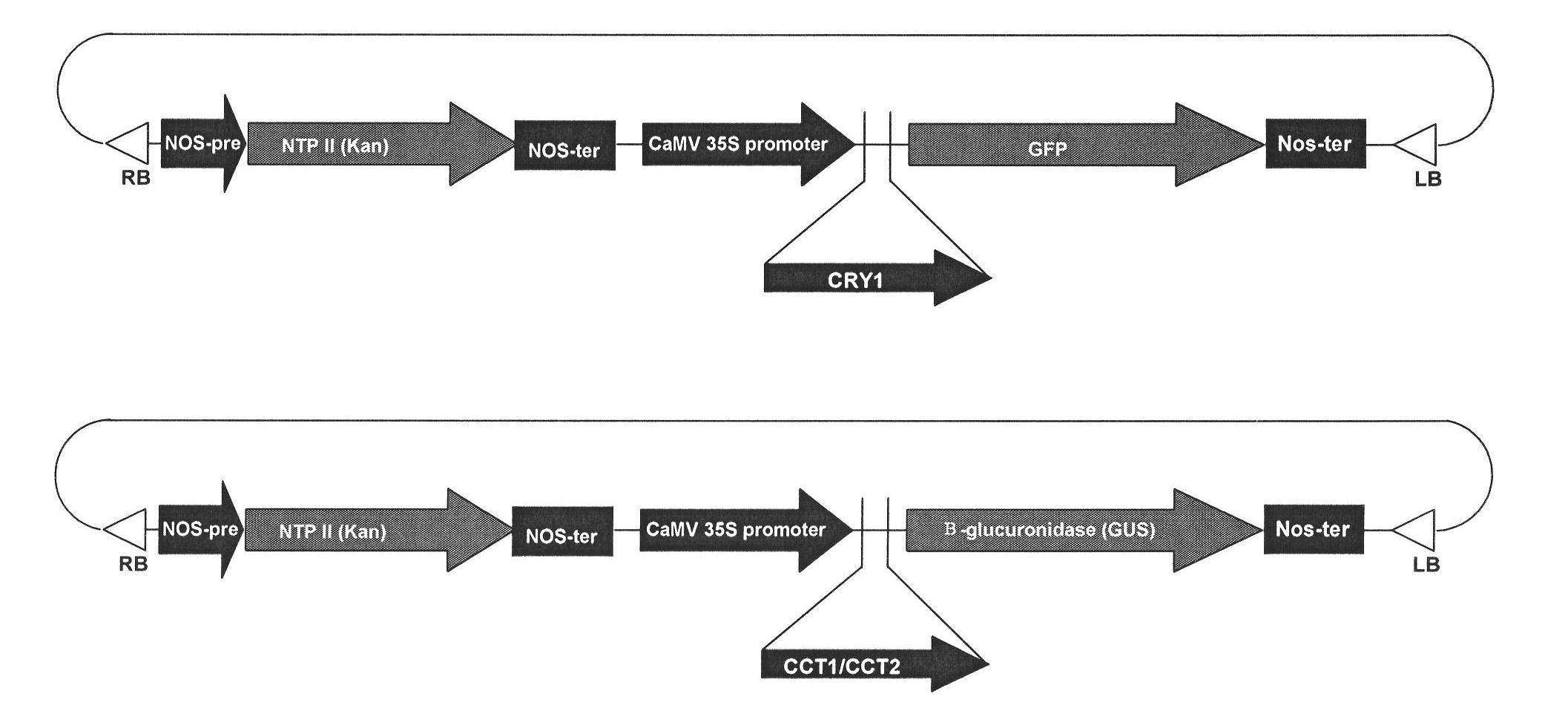
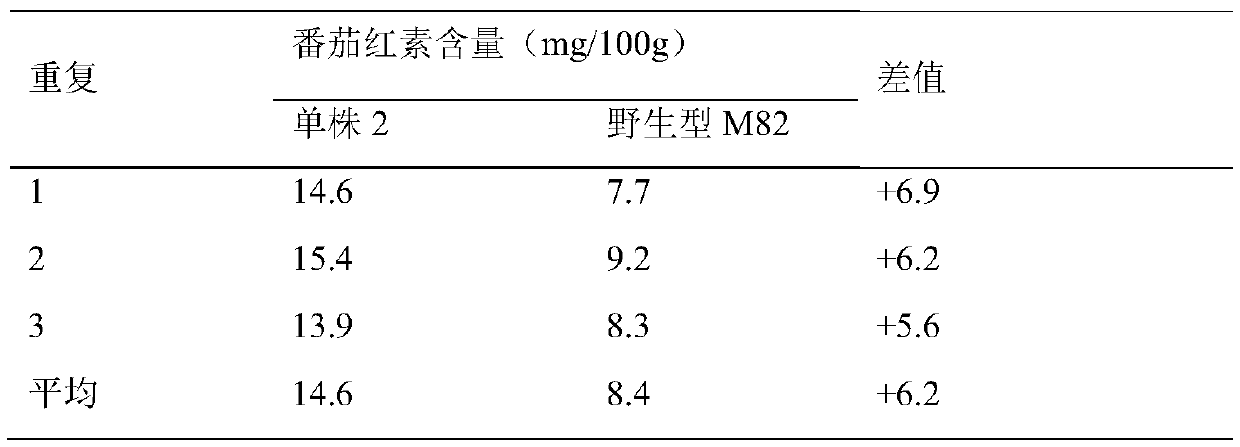
Method for improving carotenoid content of tomato
InactiveCN101979601AIncrease contentEfficient extractionComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceAdditional values
The invention discloses a method for improving carotenoid content of a tomato. Overexpression vectors of cryptochrome gene 1, the c-terminus of the cryptochrome gene 1 and the c-terminus of cryptochrome gene 2 are constructed by a gene engineering means to transform the tomato so as to obtain the transgenic tomato. By the method, the lycopene content and total carotenoid content in the transgenic tomato fruit are greatly improved by 3.6 times and 3.4 times respectively, so that the extraction of the natural lycopene from the tomato is more efficient, and the additional value of the tomato product is greatly improved.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Construction of CRISPR-Cas9 system of tomato PSY 1 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106636182AUnderstanding Molecular MechanismsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGene targetsAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and genetic modification and relates to construction of a CRISPR-Cas9 system of a tomato PSY 1 gene and an application thereof. The construction includes the following steps: (1) according to a cDNA conserved sequence of the tomato PSY 1 gene, designing a DNA sequence of sgRNA, which is represented as the SEQ ID No.1; (2) designing a primer combination used for amplifying a tomato PSY 1 gene target zone in the sgRNA; and (3) performing sgRNA amplification with the primer and purifying an amplified product to obtain a CRISPR-Cas9 Level-1 carrier and a CRISPR-Cas9 Level-2 carrier, which contain the sgRNA of the specific targeted tomato PSY-1 gene. The construction is beneficial to researching on effect that the gene participates in fruit maturity of tomatoes, so that the molecular mechanism of the fruit maturity of tomatoes can be known furthermore. The system can be used for producing PSY 1 gene deleted transgenic tomatoes, and has important effect of culturing a new tomato variety which is tolerant to storage and transportation in future.
Owner:VEGETABELE INST AGRI SCI ACAD SHANXI PROV
Preparation method of pink tomato material
ActiveCN104988160AStrong specificityStrong targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisAgricultural science
The invention provides a preparation method of a pink tomato material, and belongs to the field of plant gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out sequence analysis on the transcription factor S1MYB12 for controlling tomato skins to determine a specific sgRNA sequence; 2, constructing an expression vector containing sgRNA and a Cas9 protein; 3, transforming the obtained recombinant vector to red tomato through an Agrobacterium infection technology to obtain T0 generation transgenic tomato plants; and 4, planting the T0 generation plants with S1MYB12 gene sequence mutation in a greenhouse, selfing to obtain T1 generation plants, and screening plants free from exogenous transgenic components, with S1MYB12 gene sequence homozygous mutation and with pink fruits from the T1 generation plants in order to obtain the pink tomato material. The method has the advantages of low cost, preparation cycle shortening, and obtaining of the pink tomato material within one year; and the pink tomato does not contain exogenous gene, is safe and is free from risk.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Eggplant anthocyanin synthesis-related gene SmMYB1 as well as recombinant expression vector thereof and application of gene SmMYB1 in purple tomato culture
InactiveCN103966235AIncrease anthocyanin contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses an eggplant anthocyanin synthesis-related gene SmMYB1 as well as a recombinant expression vector thereof and an application of the gene SmMYB1 in purple tomato culture. The nucleotide sequence of the eggplant anthocyanin synthesis-related gene SmMYB1 is as shown in SEQ ID No.3; the gene is constructed into a recombinant expression vector which is used for transforming tomato by use of agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation and then a transgenic tomato is obtained; the phenotypes of petals, stigma, anther, fruits, root, stem and leaves of the obtained transgenic tomato are purple, and therefore, the transgenic tomato can be cultured as an ornamental plant; the content of anthocyanin in the fruits of the transgenic tomato is relatively high and the anthocyanin can be used for reducing the risk of suffering from cancers and cardiovascular diseases, and in short, the transgenic tomato has excellent ornamental and edible values.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
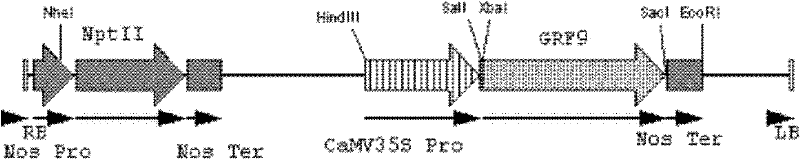
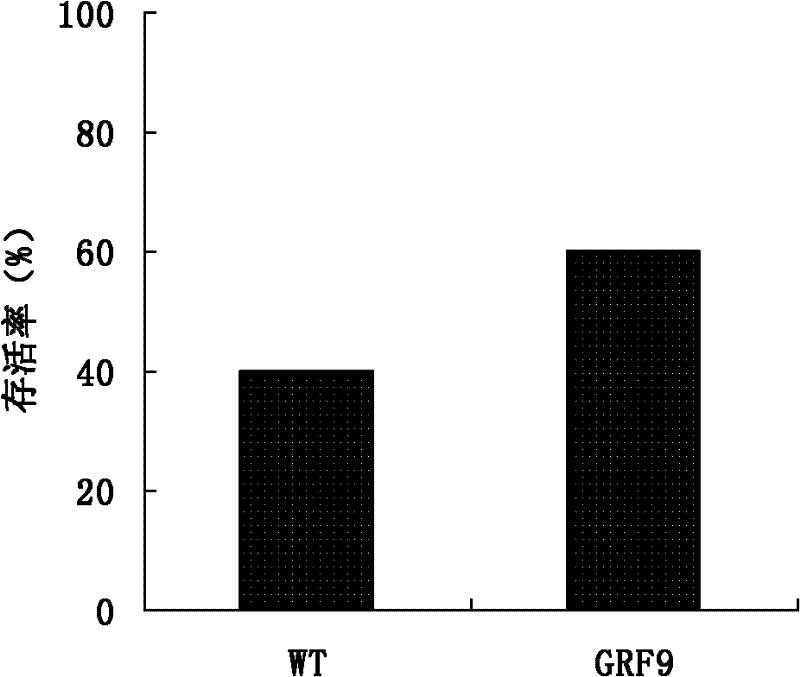
Stress tolerance related 14-3-3 protein GRF9 and application thereof
InactiveCN102391369AImprove tolerance to low phosphorusIncreased/or drought resistancePlant peptidesFermentationPhosphorCrop species
The invention relates to a stress tolerance related 14-3-3 protein GRF9 and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the 14-3-3 protein GRF9 is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. According to a technical scheme in the invention, a genetic technology is adopted and the 14-3-3 protein GRF9 is utilized to screen out transgenetic tomato with substantially improved low phosphor resistance, drought resistance and low temperature resistance. The obtaining of a new transgenetic crop species which can effectively utilize the soil phosphor resource and has the drought resistance and the low temperature resistance has an important meaning to the reduction of the production cost of agricultural plantation and the reduction of water and soil pollution caused by applying a large amount of phosphate fertilizers.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
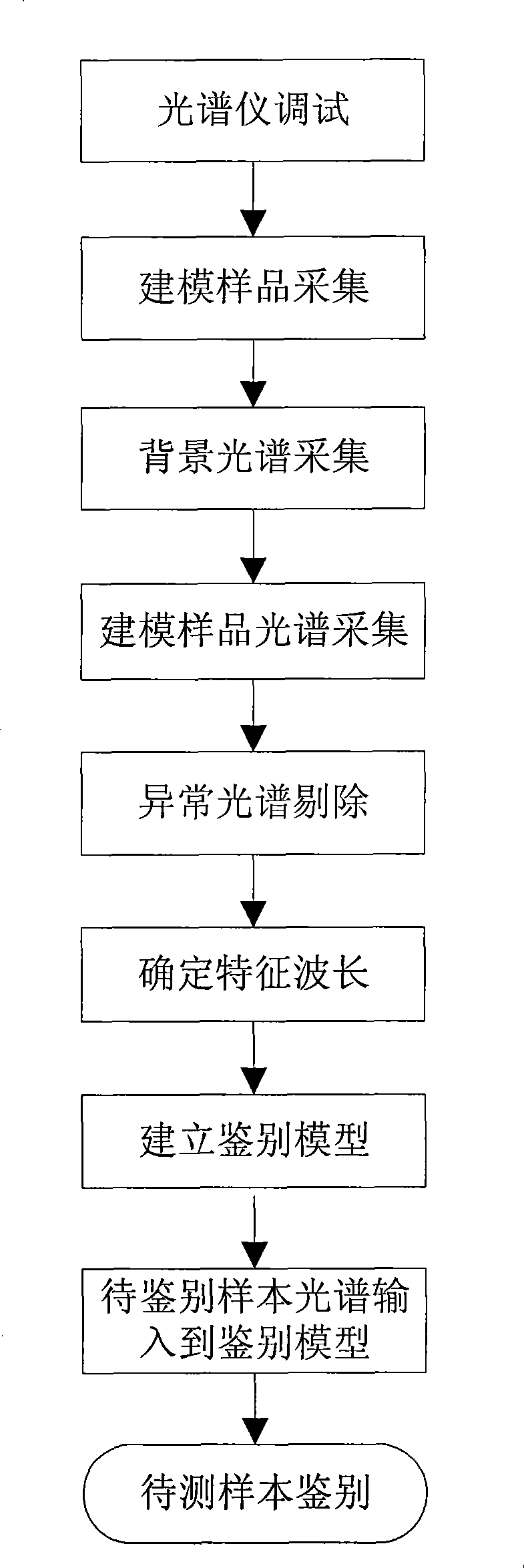
Method and device for identifying transgene tomato based on visible and near-infrared transmission technology
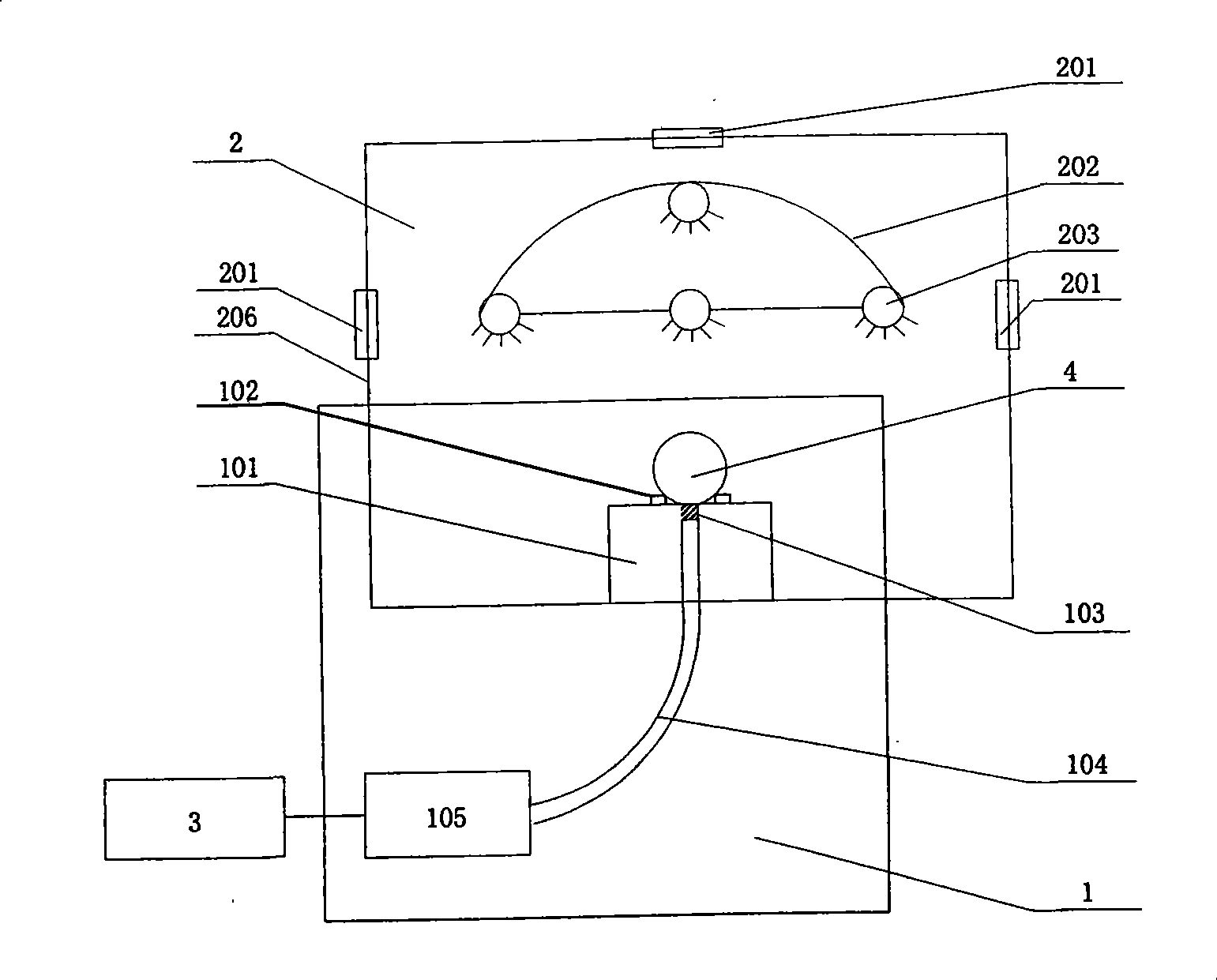
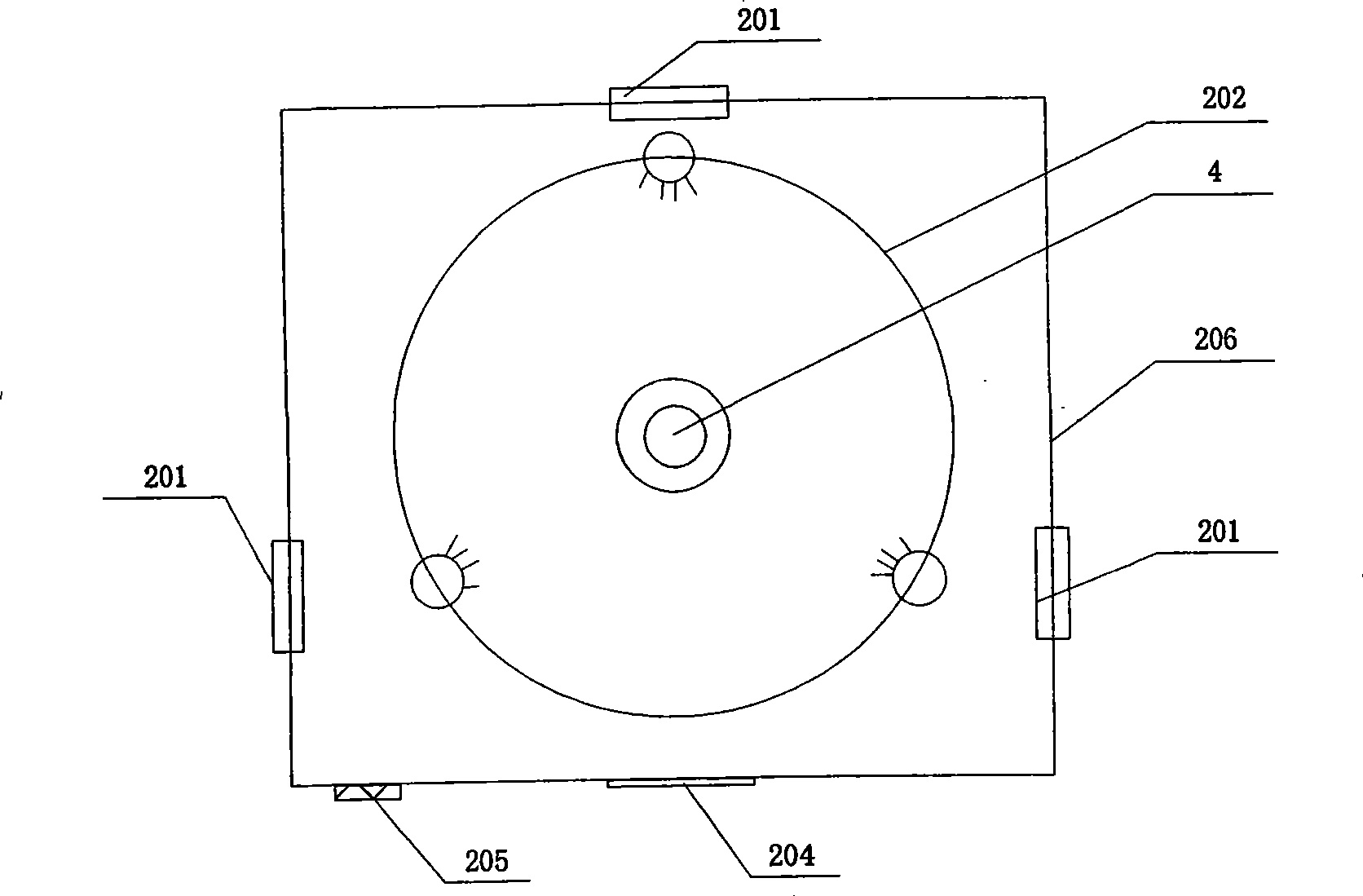
InactiveCN101368904APreprocessing does not need to be cumbersomeHigh precisionColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberLinear regression
The invention discloses a method for identifying the transgenic tomato based on the visible and near infrared transmission technology and a device thereof. A receiving lens in a detection system is fixed in a central hole of an object stage and a test sample is also placed; the receiving optical fiber is connected with the receiving lens and a fiber spectrometer respectively; the fiber spectrometer is connected with a computer through a USB line; a lamp hanger in an illumination system is arranged above the object stage; halogen lamps are respectively arranged on the horizontal circumference of the lamp hanger and at the center of the top part of the lamp hanger; and an adjusting knob is connected with each halogen lamp. The spectra of a modeling sample is collected to find out the characteristic absorption peaks for transgenic tomato identification; the characteristic information of the spectra is extracted through progressive linear regression to determine a plurality of wavelengths used for transgenic tomato identification and establish an identification model: C is equal to A1 minus A2 minus A3; a sample to be identified is collected to find out A1, A2 and A3; and C is calculated in order to determine the type of the sample to be identified and output the results. The invention avoids the tomato size affecting the identification results and has fast modeling speed and high model accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
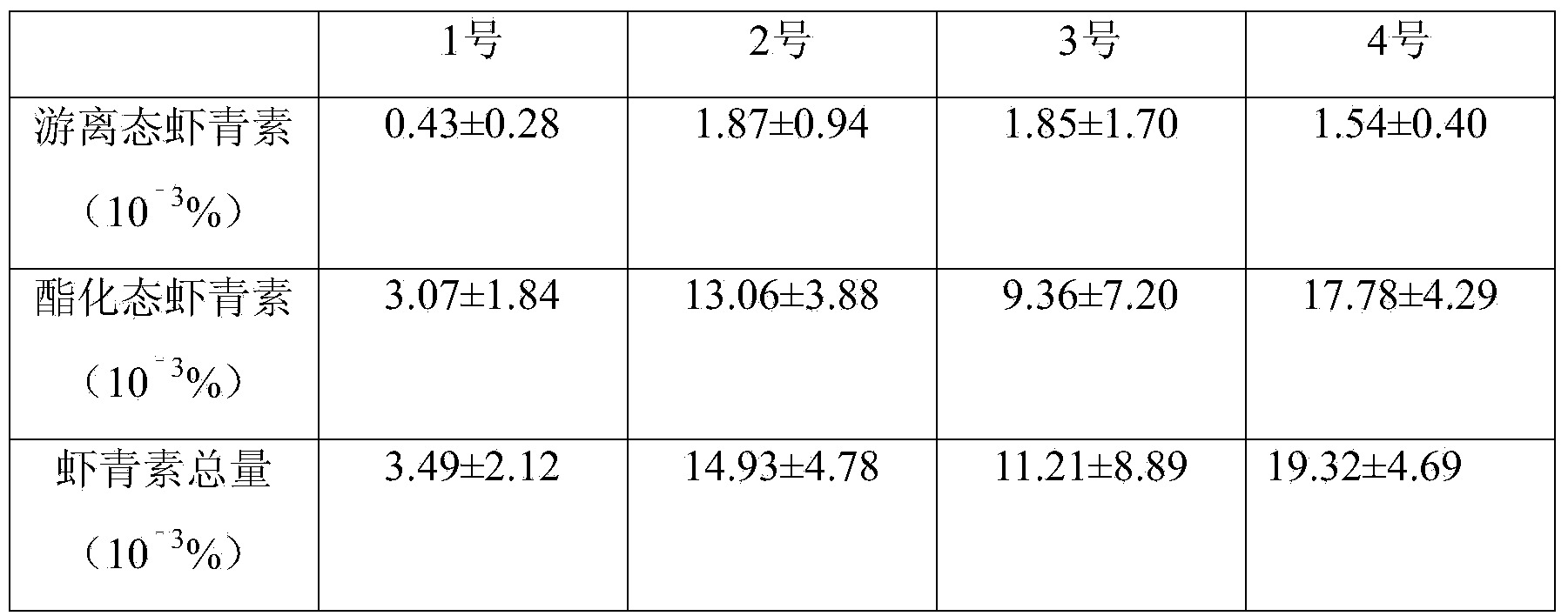
Method for improving yield of transgenic tomato containing astaxanthin and content of astaxanthin in transgenic tomato
InactiveCN104206139AIncrease productionIncreased astaxanthin contentHorticulture methodsFlowering seasonFreeze-drying
The invention provides a method for improving the yield of transgenic tomato containing astaxanthin and the content of the astaxanthin in the transgenic tomato. The method comprises the steps of seeding, fertilizing, shading, marking, treatment after fruit collection, freeze-drying, content detection and the like. The transgenic tomato containing the astaxanthin is taken as a research material, so that the transgenic tomato grows under full lighting, and 0.02% of tomato catalyst solution is sprayed in flowering season. A method for improving the content of astaxanthin in astaxanthin engineering tomato by spraying 0.02% of tomato catalyst solution and a method for improving the yield of the astaxanthin engineering tomato by using full lighting growth are provided. The method has the advantages of simplicity, high operability and the like, and higher economic benefits can be brought for the high-accumulation technology and industrialization of the astaxanthin of the astaxanthin engineering tomato.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
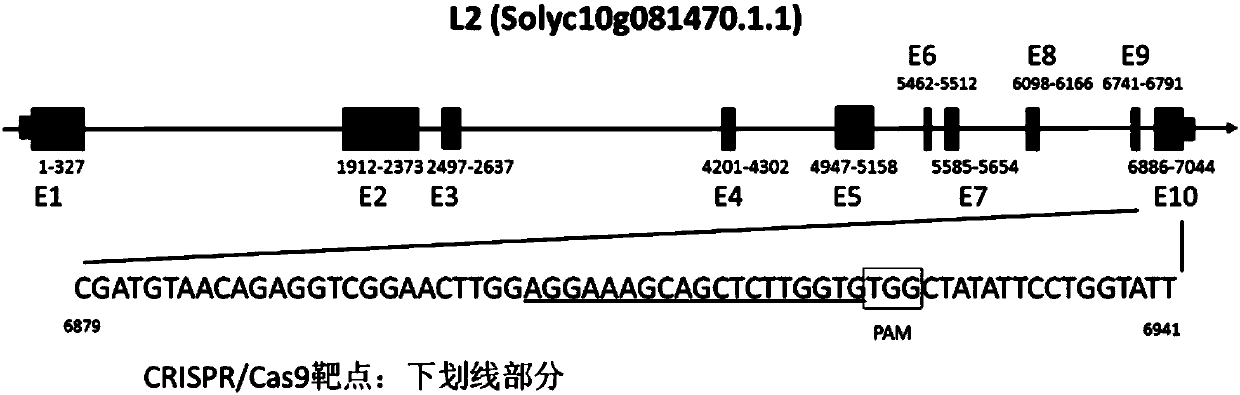
Method for creating tomato ginkgo material by gene editing technology
InactiveCN109929872AQuick changeImprove editing efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationGenome editingPhenotypic trait
The invention discloses a method for creating a tomato ginkgo material by a gene editing technology. The method is characterized in that a sgRNA target sequence for editing the CRIPSR / Cas9 gene for the L2 gene is designed, and then a gene editing vector containing two of the above target sequences is constructed. The experiment proves that the L2 gene can be precisely edited by transforming the gene editing vector into a tomato powder fruit material, the tomato gingko material is obtained, and the non-transgenic tomato ginkgo material with L2 gene homozygous mutation can be screened from the self-bred progeny. The method of the invention is applicable to different varieties of tomato powder fruit or a red fruit material, and has high editing efficiency. Compared with the traditional l2-site backcross transformation, the method can greatly shorten the transformation time and achieve rapid and accurate conversion of parental fruit color traits within 1 year, is not limited by factors such as linkage drag and transgenic safety, and has great breeding application prospects and economic value.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Kiwi fruit gene capable of improving tomato fruit nutrition quality and use thereof
ActiveCN104004768AHigh in sugarIncrease contentFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceBeta-Carotene
The invention discloses a kiwi fruit gene capable of improving tomato fruit nutrition quality and a use thereof. The kiwi fruit gene has a DNA sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence table. The kiwi fruit gene is cloned in a eukaryotic expression vector so that a plasmid containing the kiwi fruit gene sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.1 is obtained. Agrobacterium is transformed by the plasmid and the transformed agrobacterium is used for infecting tomato callus so that a transgenic plant capable of improving tomato fruit sugar content and pigment content is obtained. Compared with the wild tomato fruit, the transgenic tomato fruit has obviously improved sugar content, lycopene content, beta-carotene content and chlorophyll content. The kiwi fruit gene having the DNA sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.1 has an important theory meaning and a practical application value for research, regulation and control of a fruit pigment accumulation process and improvement of fruit nutrition quality.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for cultivating long-storage tomato plants by virtue of silent tomato gene SlNZG
InactiveCN104774869AImprove storabilityImprove economyFermentationGenetic engineeringRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for cultivating long-storage tomato plants by virtue of a silent tomato gene SlNZG. The method comprises the following steps: reversely connecting a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 3 to a pBin19 vector Sac I and Xba I restriction enzyme cutting sites to obtain an RNAi vector pBin19::SlNZG; then transforming agrobacterium by using a pBin19::SlNZG vector to obtain agrobacterium engineering bacteria, then performing transfection on a tomato explant which is cut and pre-cultured by using the agrobacterium engineering bacteria, performing co-culture, induced germination and rooting culture, and finally screening transgenic tomato plants to obtain long-storage tomato plants; and performing SlNZG gene silencing expression on the obtained long-storage tomato plants. Fruit storage tolerance experiments show that the storage tolerance of tomato fruits of which SlNZG genes are silent can be greatly improved; and the method disclosed by the invention can be used for cultivating long-storage tomato varieties.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
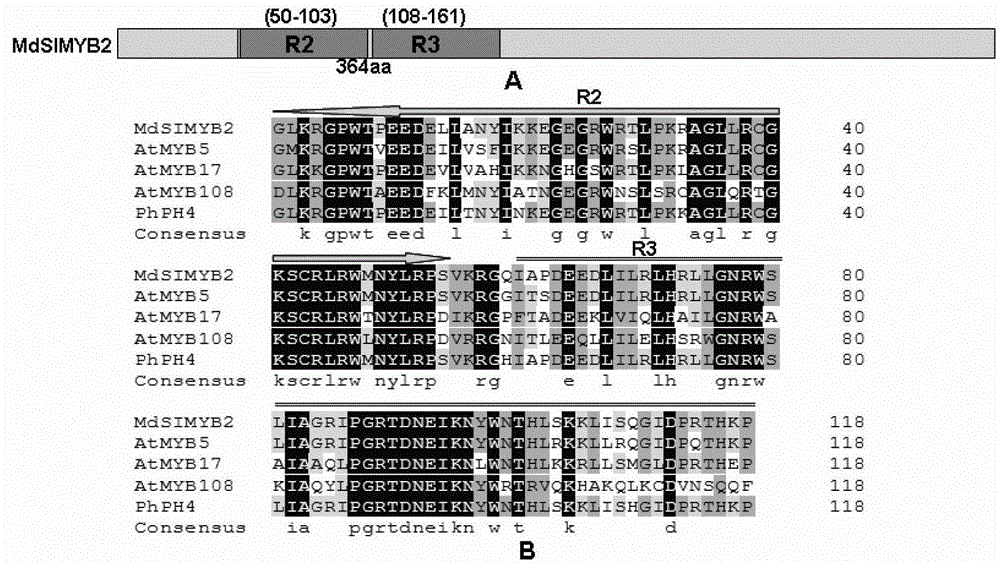
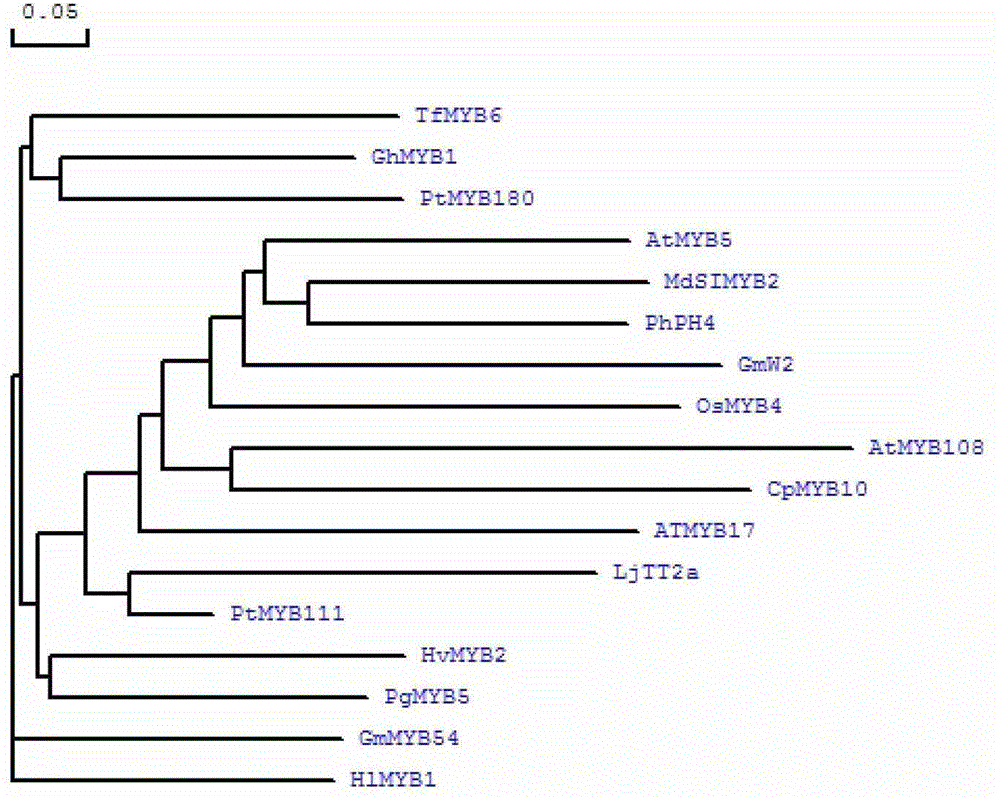
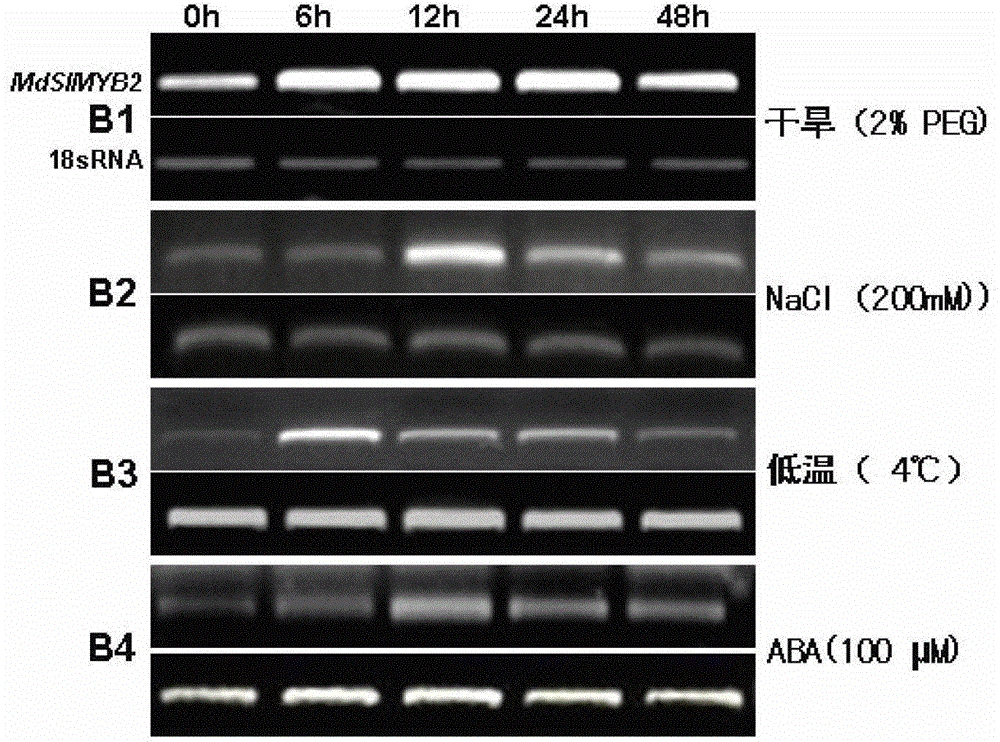
Cloning of apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2 and application of cloning of apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2
ActiveCN102978218ARapid Breeding PathwayEnrich the theoretical system of anti-adversity genetic engineeringPlant peptidesFermentationRapid amplification of cDNA endsSalt resistance
The invention relates to cloning of an apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2 and an application of the cloning of the apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2. A homology-based cloning and rapid-amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) technology is utilized to obtain a novel apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2 from a gala apple, the nucleotide sequence of the MdSIMYB2 is shown in SEQ.ID.NO.1, and the protein amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ.ID.NO.2. The gene is transferred into a tomato, and the stress capabilities of drought resistance, salt resistance, cold resistance and the like of a transgenic tomato strain are improved; and through the overexpressing of the gene MdSIMYB2 in the apple, the expression level of the transgenetic apple can be improved, and moreover, the stress capabilities of drought resistance, salt resistance, cold resistance and the like of a transgenic apple strain are increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Process for producing human insulin using transgenic tomato
InactiveCN1458161AAvoid degradationLow costSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderReticulum cellPlant cell
The present invention utilizes transgenic tomato as bioreactor to produce human insulin. The human insulin is produced through designing plant preference codon, artificially synthesizing several DNAsegment, splicing, and adding endoplasmic reticulum residence sequence of KDEL in the C terminal to avoid the degradation of insulin in plant cell. The gene is transformed into tomato via agrobacterium mediating process under the driving of CaMV35S promoter and fruit specificity promoter 2A12 to express human insulin in tomato fruit. This kind of tomato capable of producing human insulin may become one kind of convenient oral product for preventing and treating some diabetes of depending insulin and autoimmune dysfunction, and may be used to extract human insulin for making injection.
Owner:林忠平
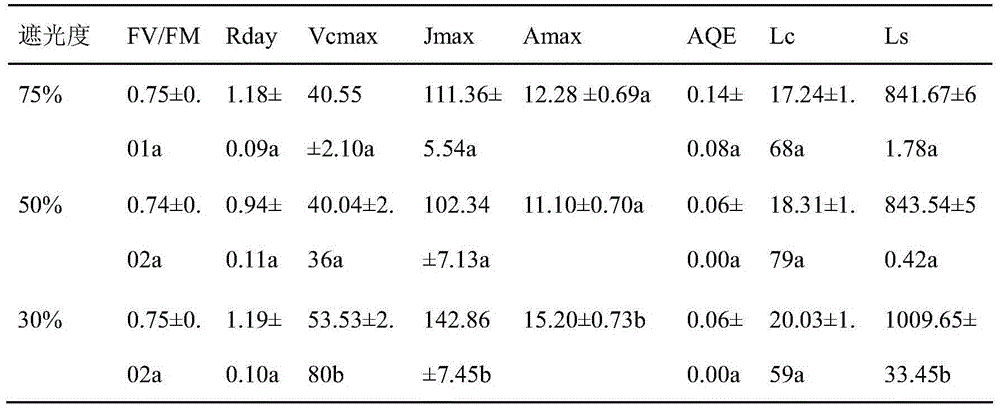
Cultivation method for promoting growth of transgenic tomatoes and accumulation of astaxanthin
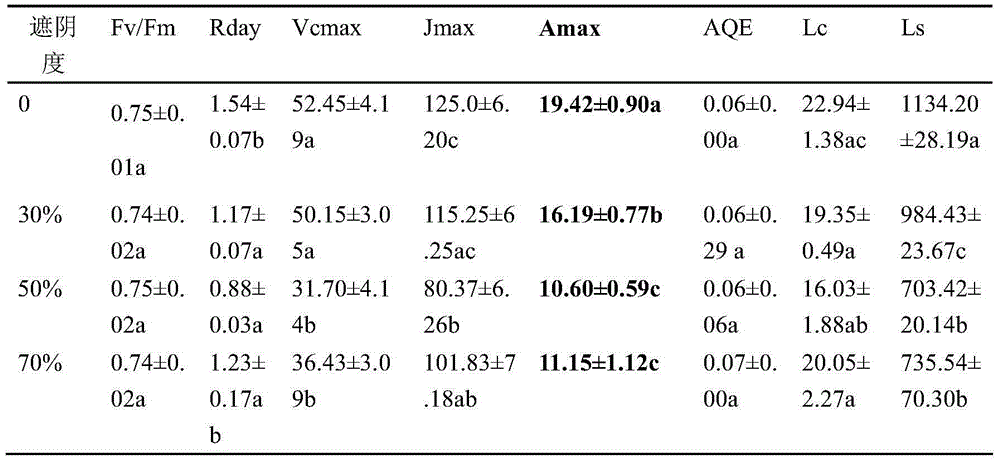
Provided is a cultivation method for promoting growth of transgenic tomatoes and accumulation of astaxanthin. The cultivation method comprises the steps of taking the astaxanthin transgenic tomatoes as materials, sowing seeds of the transgenic tomatoes, transplanting seedlings growing for two months after emergency of seedlings, covering the transgenic tomato seedlings with nylon nets respectively to perform shading processing, measuring light intensity through a quantum illumination meter, performing processing respectively according to four light intensity gradients including shading 75 percent of light, shading 50 percent of light, shading 30 percent of light and performing full illumination, performing photosynthesis measurement respectively at a flowering phase and a fruit phase, harvesting the transgenic tomatoes for three times when the transgenic tomatoes are ripe, and measuring contents of the astaxanthin in the transgenic tomatoes. In the planting process, watering is performed in routine to ensure a good moisture state, cooling processing is performed through fans and wet curtains, and deinsectization and disease prevention are performed at regular intervals. According to the cultivation method, the astaxanthin transgenic tomatoes serve as cell factories to produce the astaxanthin efficiently, photosynthetic capacity of the transgenic tomatoes and astaxanthin contents in fruits are optimal under the conditions that the light intensity is 30 percent of sunlight, and the foundation is laid for establishing an artificial efficient astaxanthin-rich transgenic tomato cultivation technique system.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for making solanum lycopersicum materials having high fruit lycopene content
PendingCN110777163AIncrease contentVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyLycopersene
The invention belongs to the field of a solanum lycopersicum biotechnology and a transgenic technology, and discloses a method for making solanum lycopersicum materials having high fruit lycopene content through gene editing. According to the method disclosed by the invention, through designing an editing target site of an SISGR1 gene, a pCGR1301-CRISPR / Cas9-gRNA expression vector is constructed,through an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediating method, the pCGR1301-CRISPR / Cas9-gRNA expression vector is transformed into a solanum lycopersicum material having low fruit lycopene content, and through antibiotic screening, obtaining positive T0 generation transgenic solanum lycopersicum plants; and performing self cross on the T0 generations to obtain T1 generation plants, screening plants whichdo not contain exogenous transgenic component, but of which SISGR1 genes are subjected to homozygosis mutation and of which fruit lycopene content is high from the T1 generations so that the high lycopene materials are obtained. Through the adoption of the method, the lycopene content in solanum lycopersicum fruits can be markedly increased, and the method has favorable application prospects in solanum lycopersicum high-quality molecular breeding.
Owner:HORTICULTURE INST OF XINJIANG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Transcription factors that enhance traits in plant organs
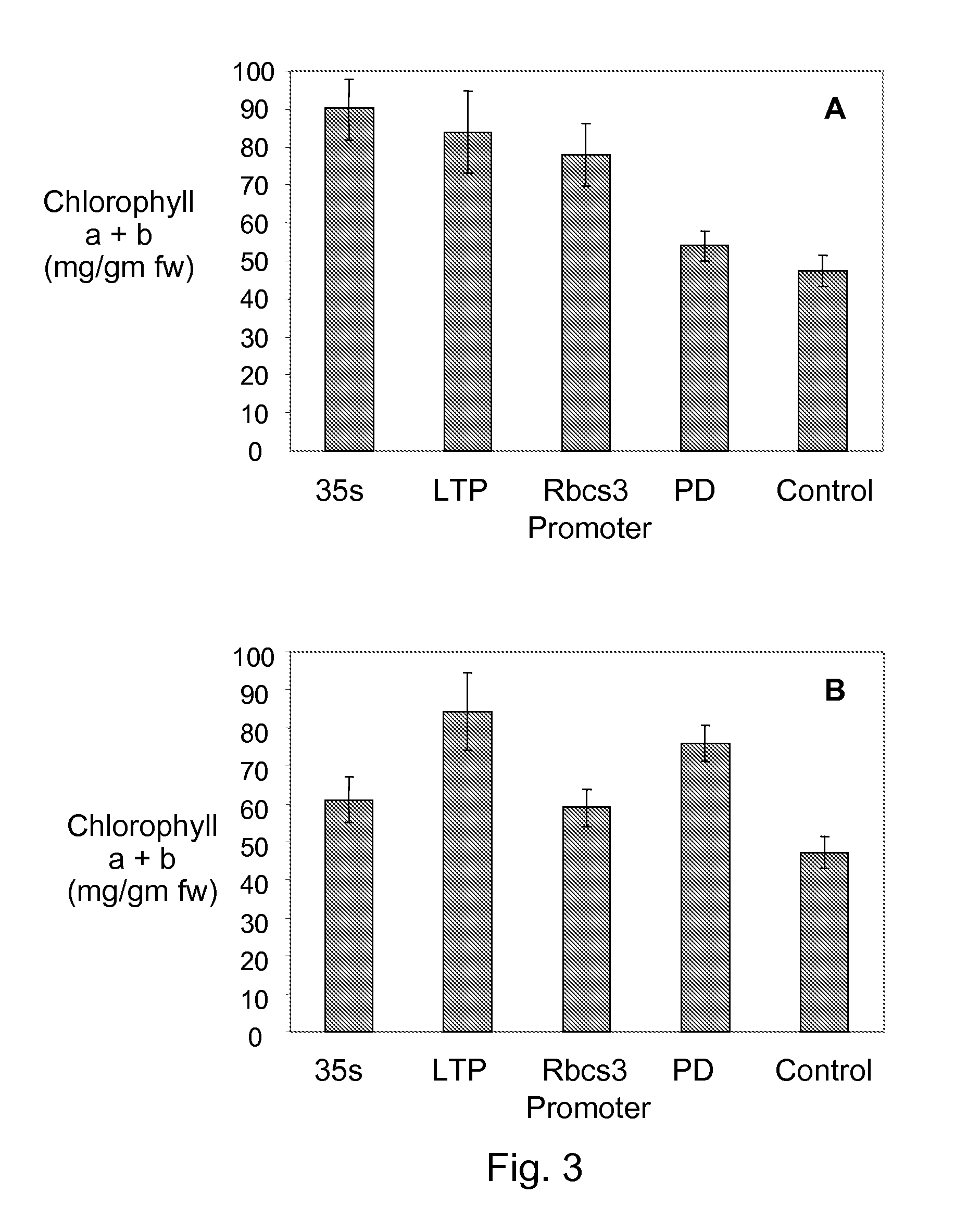
InactiveUS20100154078A1Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesWild typeChloroplast thylakoids
Expression of two Arabidopsis thaliana GARP-family transcription factors, AtGLK1, SEQ ID NO: 2, and AtGLK2, SEQ ID NO: 4, in tomato plants resulted in intensely green fruit that ripen to a normal red color. These Golden2-like (GLK) transcription factors were expressed under the control of several promoters in transgenic tomato lines. When AtGLK1 or AtGLK2 expression was regulated with the constitutive 35S promoter or with three promoters that enhanced expression in fruit tissues, the chlorophyll content of mature green fruit was increased by as much as 100%. The chloroplasts in green fruit expressing AtGLK1 or AtGLK2 developed earlier, were enlarged and had more extensive thylakoid granal development. In addition, expression of AtGLK1 or AtGLK2 resulted in increased starch accumulation in green fruit and higher levels of sugars in ripe fruit. In contrast to wild-type fruit, fruit expressing AtGLK1 developed full green color when they developed in the absence of light. Manipulation of the expression of GLK-like transcription factors in plants may provide a means for improving plant organ nutritional properties, particularly in plants or plant organs grown or maintained under low irradiance.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Tomato fruit maturing gene S10658 and application thereof
ActiveCN108715852ADelayed maturationReduce processPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a tomato fruit maturing gene S10658 and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the tomato gene S10658 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the tomato gene S10658 has a typical NAC family conservative structural domain for encoding NAC proteins. According to the tomato fruit maturing gene S10658, a functional genomics related technology is adopted to verify that the tomato gene S10658 exerts a vital function in tomato fruit maturing. The fruit maturing gene S10658 disclosed by the invention is constructed into a plant expression vector and transferred into a tomatoto interfere the expression; transgenic tomatoes can exert the ability of delaying fruit maturing and can be directly used for controlling the maturing progress of the fruits in production.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
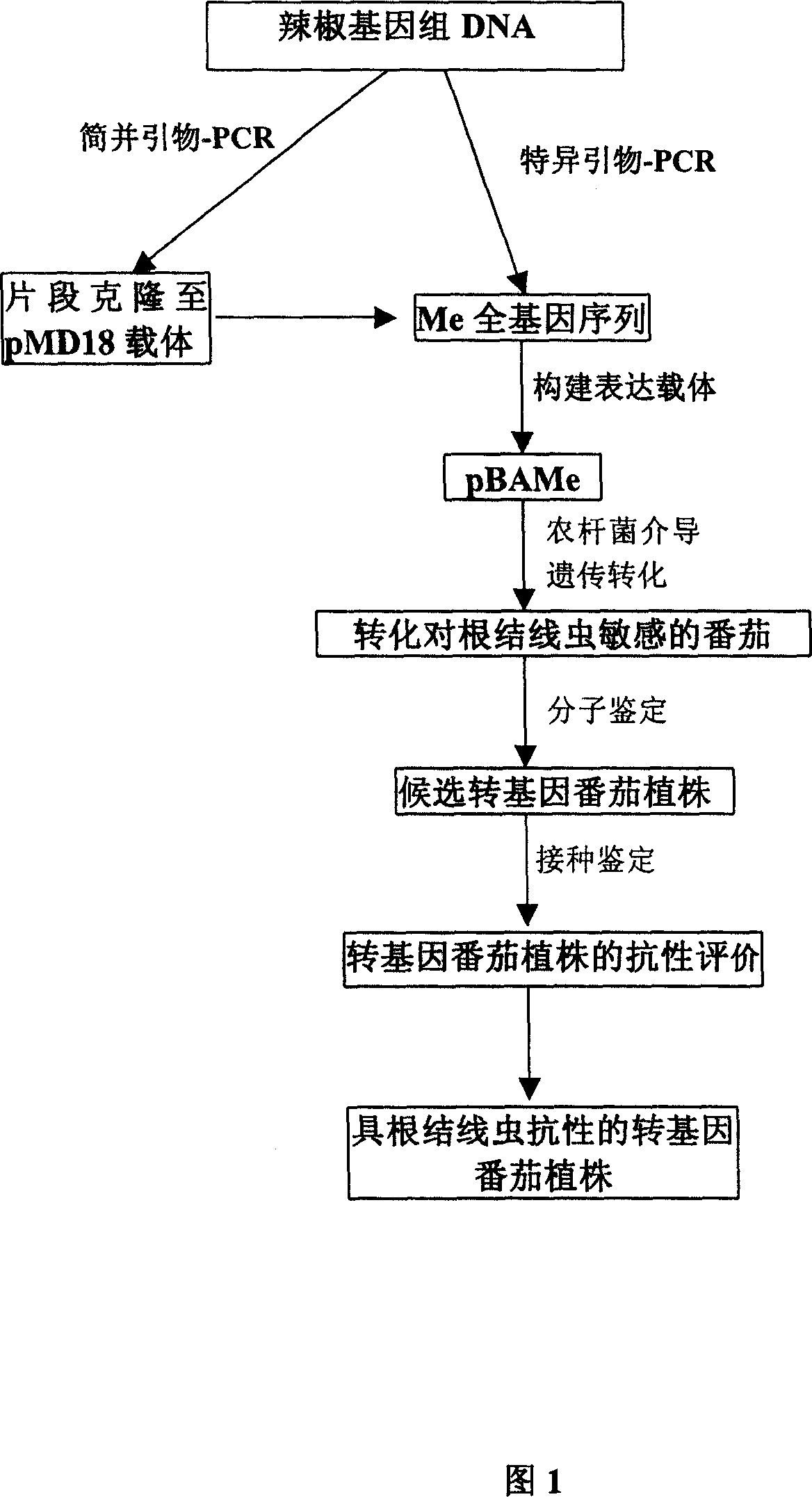
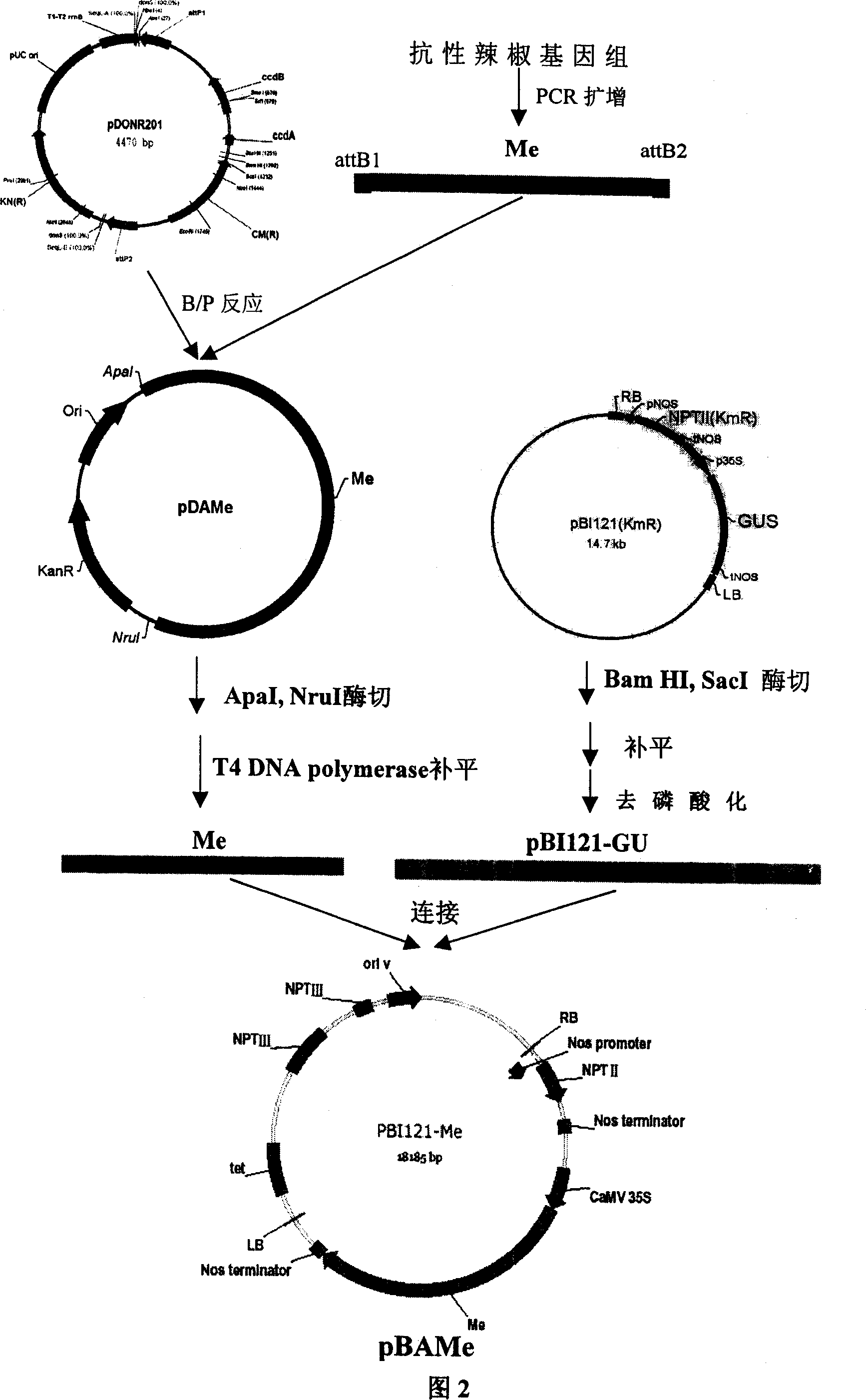
Cloning of gene against meloidogyne of capsicum and application thereof
InactiveCN1952143ASolve the problem of scarcity of germplasm resourcesShorten the breeding periodClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesDNA fragmentationA-DNA
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering technologies. The invention specifically involves the separation and cloning of a DNA fragment. The said DNA fragment gives the plants the tolerant capacity against diseases caused by edlworm. Inserting the DNA fragment into proper vector to obtain plant expressing vector (conservation number: CCTCC-M205110), introducing the plant expressing vector into plant through Agrobacterium-mediated method and the transgenic plants can generate resistance against edlworm. As one of the implementation of cases, nematode resistant transgenic tomatoes have been obtained.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
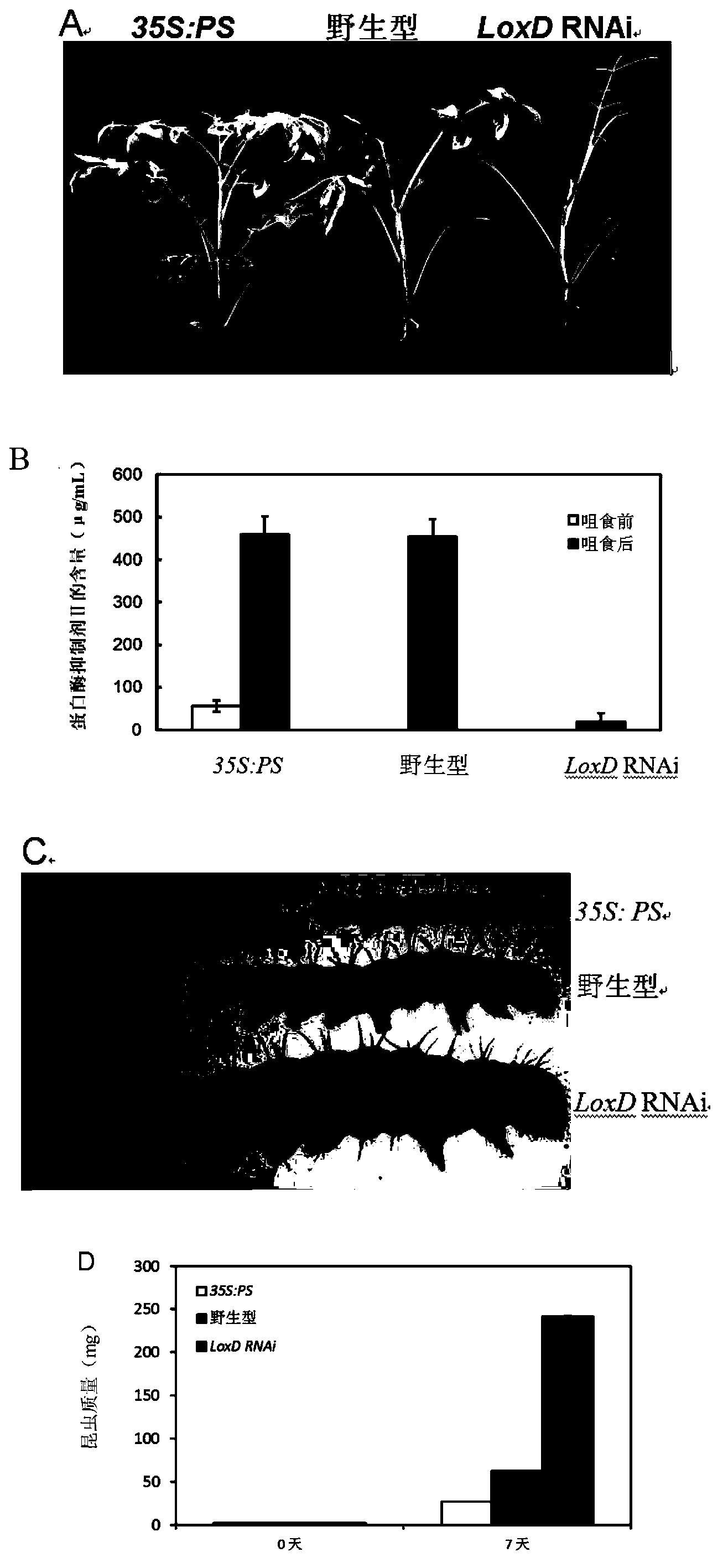
Application of Lox (lipoxygenase) D gene of tomato in regulating and controlling plant resistance
The invention discloses an application of Lox (lipoxygenase) D gene of a tomato in regulating and controlling plant resistance. The nucleotide sequence of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment provided by the invention is 106th-570th nucleotides from the tail end of 5' of sequence 2 in a sequence table. The invention also provides an application of LoxD protein and a coding gene thereof in regulating insect resistance and / or disease resistance of plants, wherein the amino acid sequence of LoxD protein is the sequence 1 in the sequence table, the nucleotide sequence of the LoxD protein coding gene is the sequence 2 in the sequence table. Experiments of the invention prove that a transgenic tomato can be obtained by inhibiting expression of a LoxD gene of a wild tomato, the disease resistance and insect resistance of the transgenic tomato are worse than those of the wild tomato, so that inhibition of expression of LoxD genes of plants lowers the insect resistance and disease resistance of the plants, and the LoxD gene is related to disease resistance of plants.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Parthenocarpic tomatoes and production method thereof
InactiveUS20090089900A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyDNA construct
The invention relates to parthenocarpic tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) which are grown from seeds, which are smaller than wild tomatoes and which, when ripe, display a more intense red colour than wild tomatoes. The tomatoes are obtained by cultivating a transgenic tomato plant which produces said parthenocarpic tomatoes and which is obtained using a method consisting in: (a) introducing a DNA construction into a cell or tissue of a tomato plant, said construction comprising (i) the pea END1 gene promoter or a functional fragment of same and (ii) a cytotoxic gene which is functionally bound to the aforementioned promoter or fragment of same; and (b) regenerating the tomato plant cell or tissue transformed in step (a) in order to produce a transgenic tomato plant that produces parthenocarpic tomatoes. The invention is suitable for use in food and agrifood industries.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
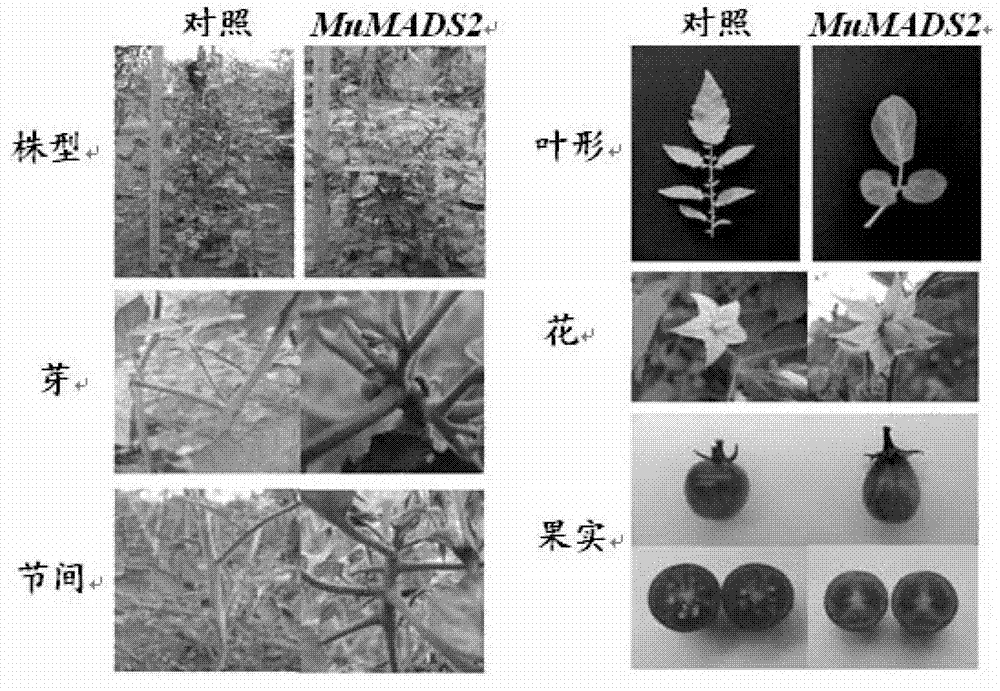
Application of MuMADS2 to culturing of fruit quality-improved transgenic plant
ActiveCN102827263ALower the altitudeReduce in quantityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyExpression gene
The invention provides an application of MuMADS2 to culturing of a fruit quality-improved transgenic plant. The invention provides an application of a MuMADS2 protein or an encoding gene of the MuMADS2 protein to regulation and control of a plant phenotype, improvement on the plant fruit quality and / or increase in a gene expression quantity which is relevant to fruit maturity; and the amino acid sequence of the MuMADS2 protein is a sequence 2 in a sequence table. As proved by the results of reduction in the plant height and reduction in the quantity of fruit seeds in an experiment in which the MuMADS2 is introduced into a tomato for obtaining seven independent strains of a MuMADS2 transgenic tomato driven by a 35S promoter and the MuMADS2 is excessively expressed, the MuMADS2 plays an important role in the processes of fruit development and quality forming.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for improving beauveria bassiana chitinase gene disease resistance and culturing disease resistance plants adopting method
InactiveCN102533819AImprove disease resistanceIncrease resistanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
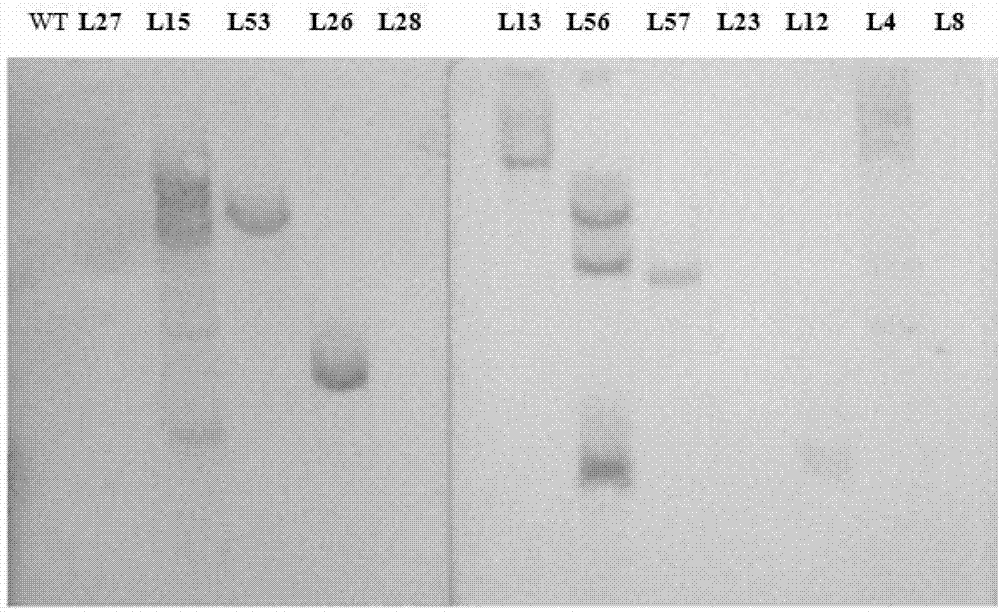
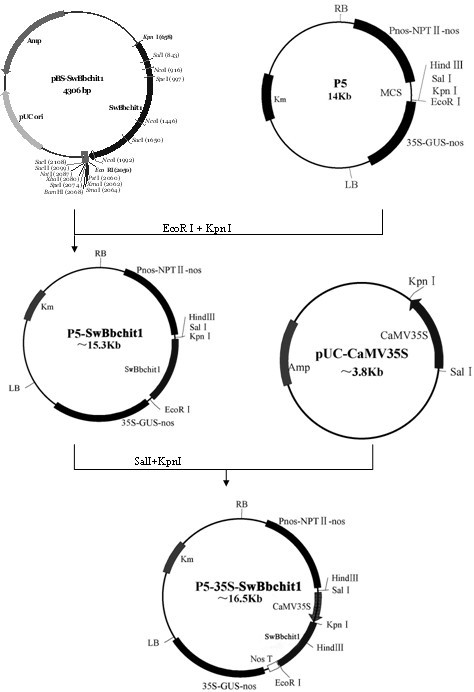
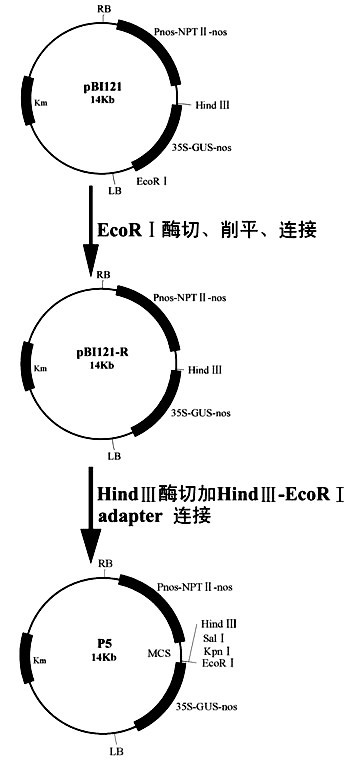
The invention provides a method for improving the beauveria bassiana chitinase gene disease resistance and culturing disease resistance plants adopting the method. The method is characterized in that a chitin binding structure domain of silkworm chitinase genes is fused with beauveria bassiana chitinase genes, and the disease resistance of the beauveria bassiana chitinase genes is improved. A 35S promoter is used for controlling fusion genes SwBbchit1, in addition, plant expression vectors are built and are respectively transferred into cotton and tomatoes, and the disease resistance of the transgenic cotton and tomatoes can be further improved. Compared with the disease resistance of the Bbchit1 transgenic cotton and tomatoes, the disease resistance of the SwBbchit1 cotton and tomatoes obtained by the method provided by the invention is obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Application of grape earliness gene VvWRKY13 in regulation and control of biosynthesis of ethylene in plants
ActiveCN107142275ASolve production problems that are difficult to maintain fruit qualityGenerate noVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsEnzyme GeneEthylene biosynthesis
The invention provides application of a grape earliness gene VvWRKY13 in regulation and control of biosynthesis of ethylene in plants. The application comprises the steps of carrying out leaf dish infestation on an EHA105 agrobacterium tumefaciens strain carrying recombinant plasmids so as to obtain an over-expressed tomato material of VvWRKY13, and carrying out repeated selfing so as to obtain at least three independent pure transgenic lines; and detecting the ethylene generation amounts of transgenic tomato lines in different growth and development periods, the expression amount of key enzyme genes for synthesis of ethylene, relevant phenotypic characters of ethylene, lengths of transgenic fruits in different growth cycles and relevant quality indexes of mature fruits. An experiment result proves that by applying VvWRKY13 to the regulation and control of the key enzyme genes of ethylene and the biosynthesis of ethylene, the expansion period of young fruits of transgenic tomatoes is shortened, the early maturing of the fruits is promoted, the quality functions of the mature fruits are not changed, and the theoretical basis and the experimental foundation are provided for the early-maturing breeding of berry fruits such as the tomatoes.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for acclimatizing tissue culture seedlings of transgenic tomatoes
InactiveCN103535168AImprove survival rateIncrease the steps of seedling hardeningCultivating equipmentsHorticultureMoistureCulture mediums
The invention discloses a method for acclimatizing tissue culture seedlings of transgenic tomatoes. The method comprises the following steps that after the transgenic tissue culture seedlings strongly grow in a rooting culture medium, the height of the seedlings ranges from 4cm to 5cm, and the roots of the seedlings are developed, an opening sealing film of a culture bottle can be opened, 0.5cm to 1cm distilled water is added, the seedlings are acclimated for 2 days in an illumination incubator at the temperature of 25 DEG C, the seedlings are then taken out, residues of the culture medium on the roots are cleaned, the seedlings are transplanted to a nutrient soil flowerpot which is disinfected through high temperature and thoroughly watered, and nutrient soil is composed of flower organic soil, vermiculite and perlite according to the ratio of 2:1:1; the seedlings are covered with a plastic film, so that moisture is preserved and the seedlings are cultured for one week in the illumination incubator at the temperature of 25 DEG C and watered for once through MS culture liquid which is diluted by 10 times during the week; when fresh leaves are grown from the seedlings, the plastic film can be removed; in the transplanting process, the seedlings and the culture soil in the flowerpot are moved to a field together, water and fertilizer management is conducted normally, and the survival rate reaches 100%.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Vegetable leaf vein specific promoter and use thereof
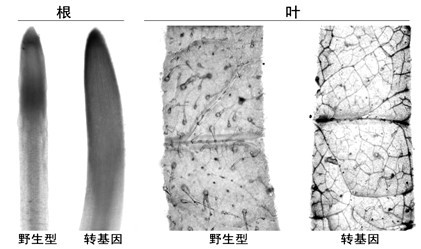
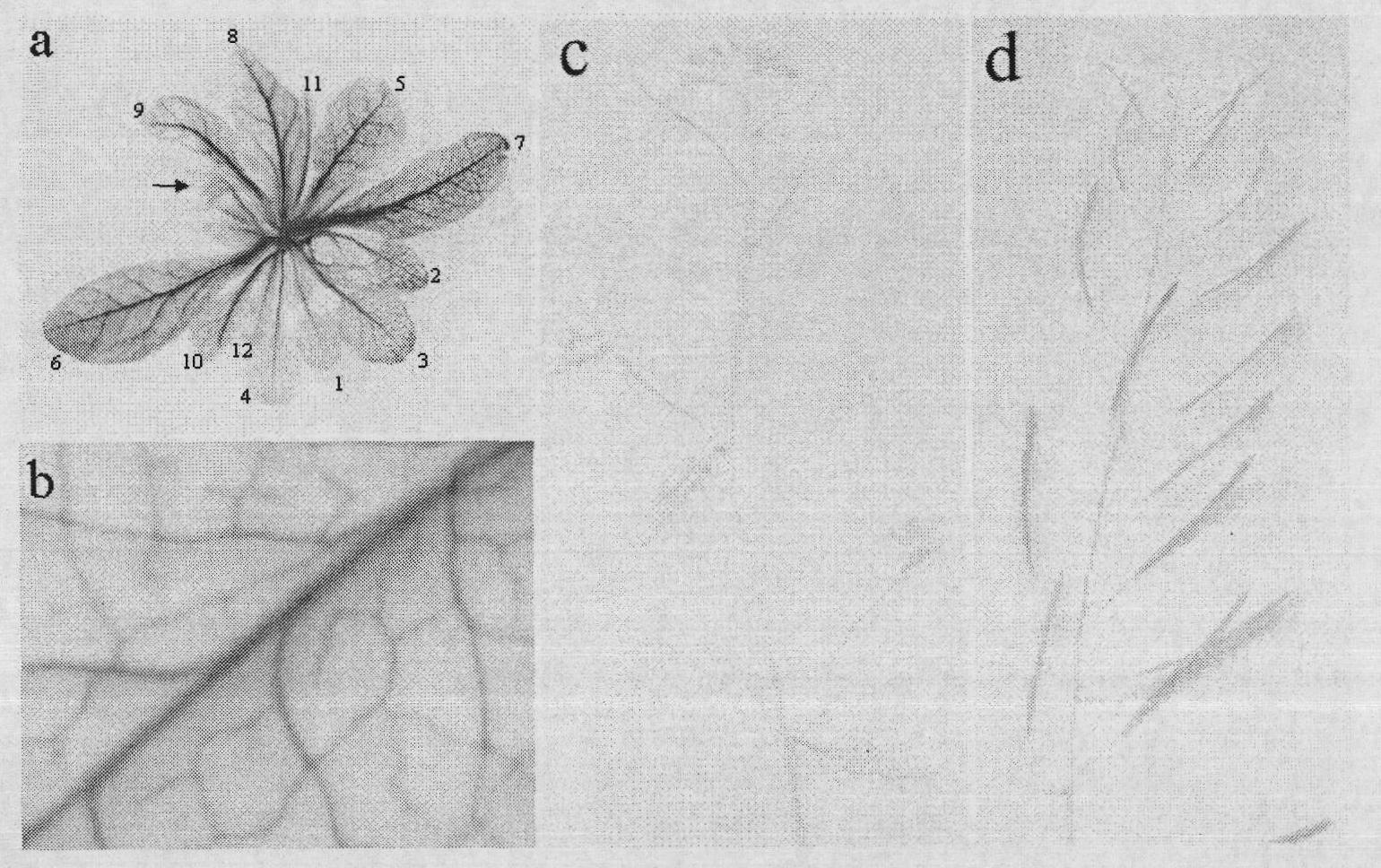
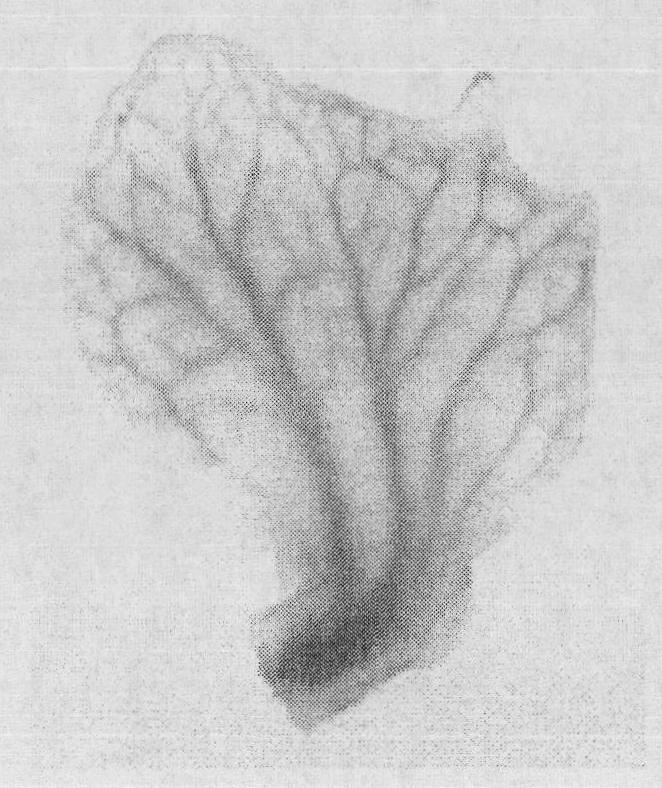
ActiveCN101880666AImplement directional operationsGood characterAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA preparationVeinVascular tissue
The invention discloses a vegetable leaf vein specific promoter and use thereof. With a nucleotide sequence shown by the sequence table 1, the promoter can promote the expression of a target gene in vegetable leaf veins. In the invention, a VS promoter sequence is cloned, and a VS promoter is proved to have unique vein specific activity in arabidopsis thaliana by detecting the expression levels of a 'VS-promoter-GUS' fusion gene in organs of the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana; and meanwhile, the transformation of micro tomato Micro-Tom by the 'VS-promoter-GUS' fusion gene further proves that the 'VS-promoter-GUS' fusion gene is specifically expressed only in the veins of transgenic tomatoes. The promoter of the invention is used to construct a 'promoter-target gene to be expressed' fusion gene, and through phytotransformation transgenic plants in which the target genes are specifically expressed in veins can be obtained. The promoter can be used for studying vegetable vascular tissue differentiation, solute translocation mechanism and the like and has an important value in study and use of plant genetic engineering.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for cultivating high-TYLCV (tomato yellow leaf curl virus)-resistant tomatoes
ActiveCN104313051AShorten the breeding cycleGenetic engineeringFermentationTomato yellow leaf curl virusBiology
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a high-TYLCV (tomato yellow leaf curl virus)-resistant tomatoes. The method comprises the following steps: selecting fragments of AV1 gene, AC1 gene and AC3 gene in a TYLCV genome for gomphosis to obtain polygenes chimera AV1-AC1-AV3, and constructing an interference vector RNAi of a palindromic sequence; carrying out transient expression of dsRNA on tomato cotyledon by virtue of agrobacterium-mediated transformation to obtain a transgenic tomato for transforming the polygenes chimera AV1-AC1-AV3; and if the transgenic tomato shows TYLCV resistance after system infection of the TYLC, is not observed with obvious symptoms and has high-TYLCV resistance, screening out the high-TYLCV-resistant tomato. By utilizing the method, the high-TYLCV-resistant tomato strains can be quickly screened out and cultivated in 2 months, the cultivation period is greatly shortened, and a technical support is provided for preventing and curing TYLCV.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Breeding method of tomato recessive genetic male sterility maintainer line
The invention discloses a breeding method of a tomato recessive genetic male sterility maintainer line. The method comprises the following steps that a first expression cassette for expressing a pollen fertility protein and a second expression cassette for expressing a labeled protein are introduced into a tomato recessive genetic male sterility line to obtain transgenic tomatoes, wherein sterility of the tomato recessive genetic male sterility line is caused by the function loss of the pollen fertility protein or inhibition of the expression of the pollen fertility protein, meanwhile, the transgenic tomatoes meeting the conditions A1), A2) and A3) are the tomato recessive genetic male sterility maintainer line, A1) refers to male fertility, A2) refers to expression of the labeled protein,and A3) refers to insertion of the first expression cassette and the second expression cassette in the same locus of the same chromosome of the tomato recessive genetic male sterility line; the maintainer line serves as a male parent, and the sterility line serves as a female parent for hybridization; a strain capable of expressing the labeled protein in hybrid offspring is a male fertility maintainer line, and a strain incapable of expressing the labeled protein is a sterility line. The method has important application value.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
High efficiency stable expression system of transgene tomato
InactiveCN1821407AReduce expressionGood immunological activityProtozoa antigen ingredientsFermentationTechnological systemRecombinant vaccines
Through cloning to obtain the specific fruit promoters E82.2 and E81.1 gene of excellent pure tomato breed Zhongshu No.5, driving the vaccine molecule with the promoter E82.2 and the compound double promoter E35S-E81.1 and constituting plant expression operon unit with NOS terminator, and introducing to Agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404, engineering bacterium is obtained. By means of optimizing the complete technological system, recombinant vaccine molecule protein with efficient and stable expression and its tomato transforming strain are obtained. The present invention constitutes technological platform of efficient and stable tomato expression for exogenous vaccine molecule and medicinal protein production and provides excellent technological platform for developing oral tomato vaccine and its medicinal protein.
Owner:周晓红 +1
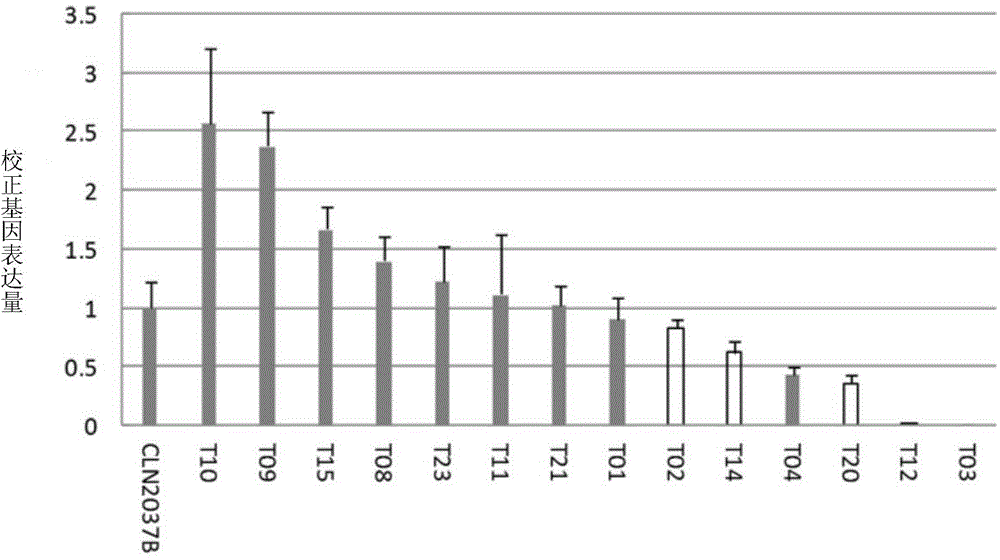
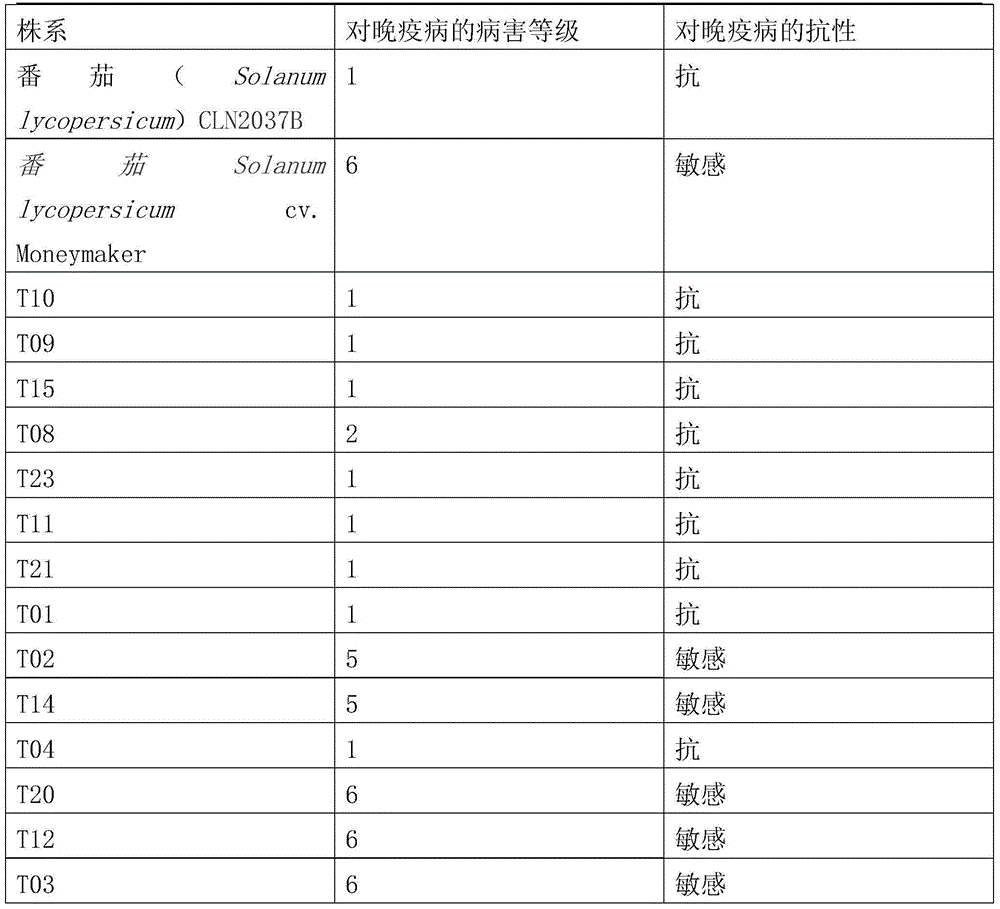
Late blight resistance related protein, and related biomaterial and application thereof
The invention discloses a late blight resistance related protein, and a related biomaterial and application thereof. The late blight resistance related protein is the protein as shown in a) or b): a) the protein comprising amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.2; b) the protein obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues from the amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.2 and related to the late blight resistance. The late blight resistance related protein gene can be transferred into a receptor of a tomato to obtain a transgenic tomato with the improved late blight resistance, so that the late blight resistance related protein gene is the gene related to the late blight resistance, and can be used to encode the protein related to the late blight resistance.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com