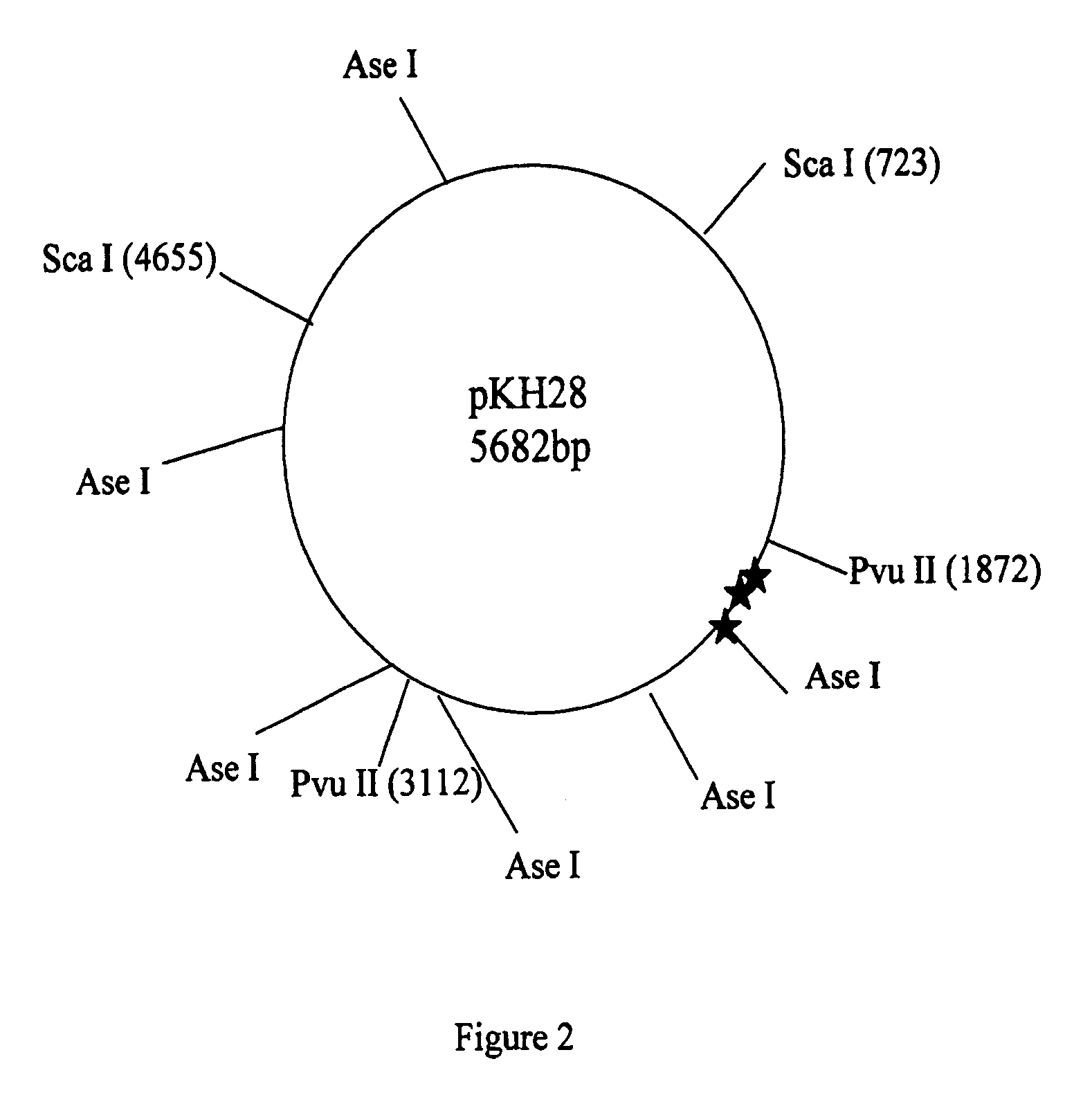
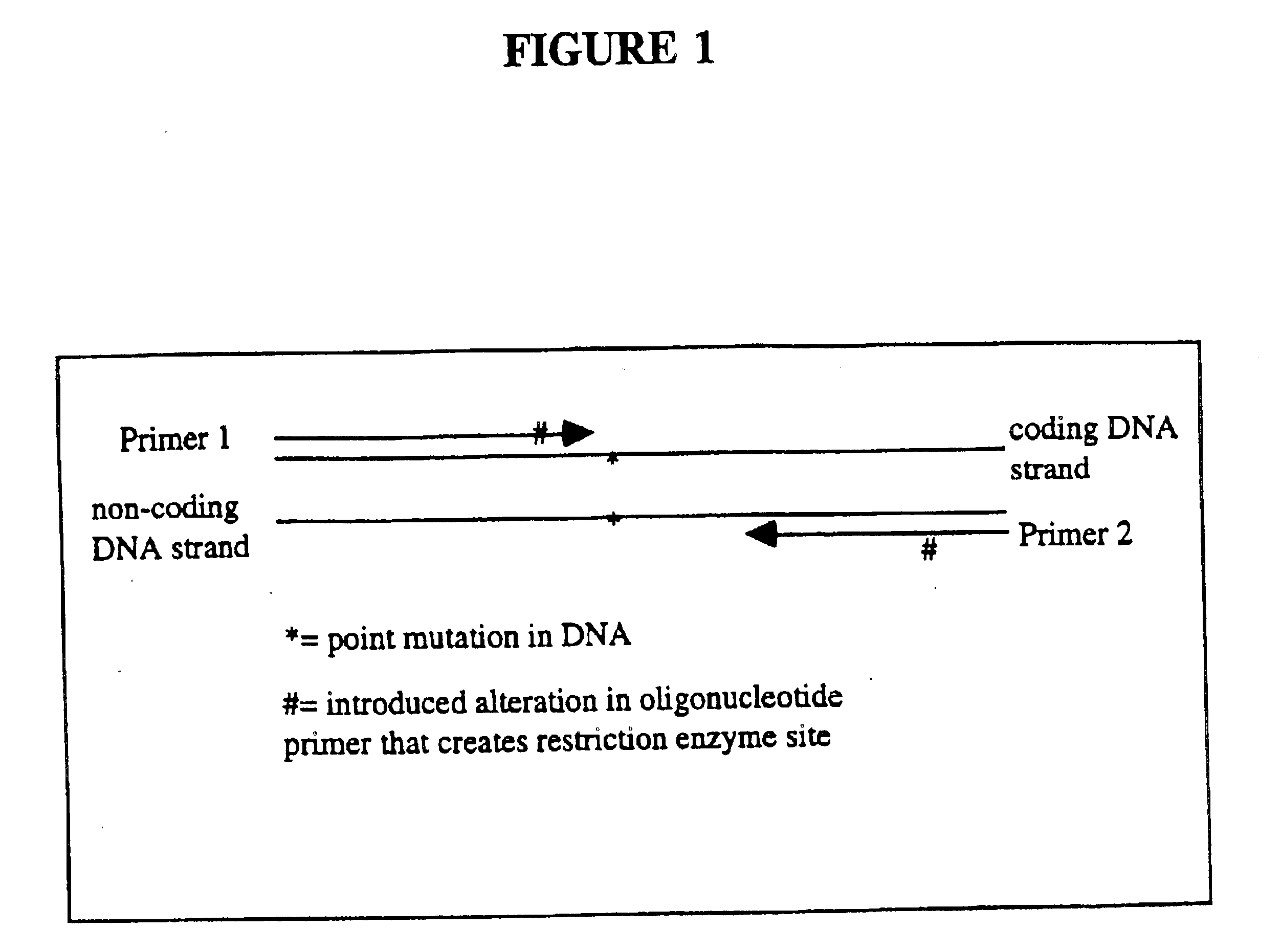
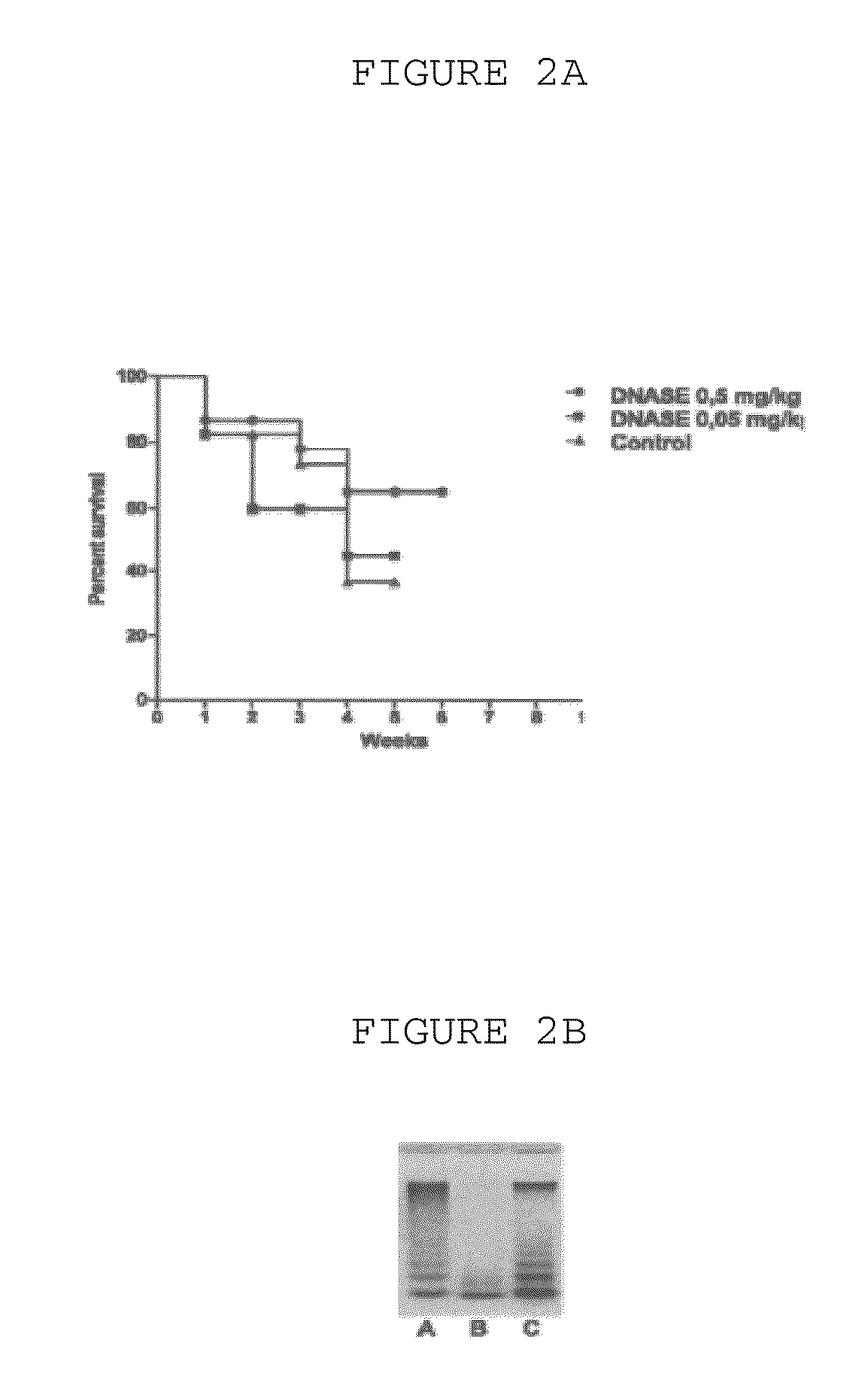
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114 results about "Dna mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
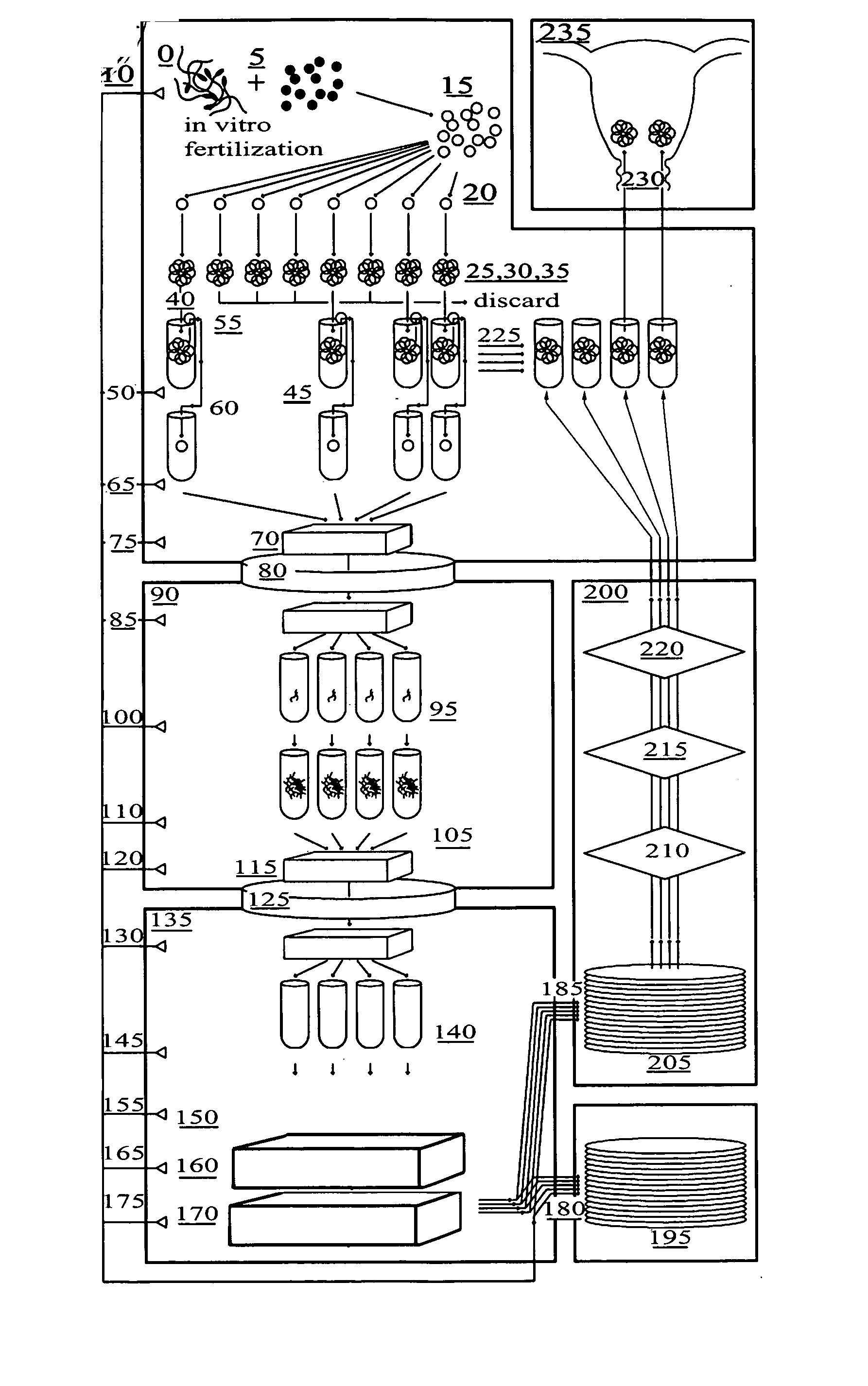
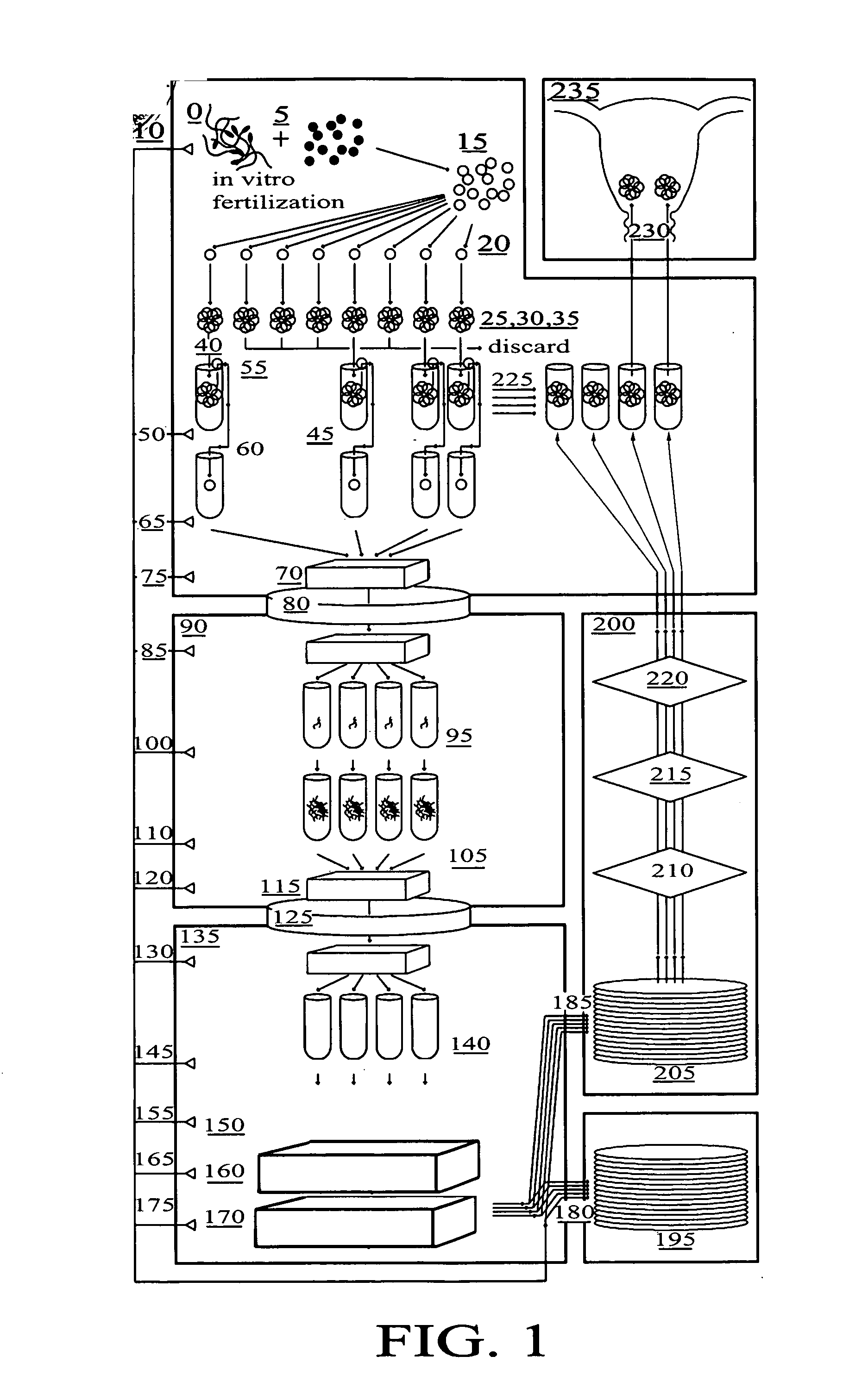
Method for genetic testing of human embryos for chromosome abnormalities, segregating genetic disorders with or without a known mutation and mitochondrial disorders following in vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo culture and embryo biopsy
InactiveUS20080085836A1Reduce significant riskImprove the level ofLibrary screeningLibrary member identificationLess invasiveContamination
We describe a method for interrogating the content and primary structure of DNA by microarray analyses and to provide comprehensive genetic screening and diagnostics prior to embryo transfer within an IVF setting. We will accomplish this by the following claims: 1) an optimized embryo grading system, 2) a less invasive embryo biopsy with reduced cellular contamination, 3) an optimized DNA amplification protocol for single cells, 4) identify aneuploidy and structural chromosome abnormalities using microarrays, 5) identifying sub-telomeric chromosome rearrangements, 6) a modified DNA fingerprinting protocol, 7) determine imprinting and epigenetic changes in developing embryos, 8) performing genome-wide scans to clarify / diagnose multi-factorial genetic disease and to determine genotype / haplotype patterns that may predict future disease, 9) determining single gene disorders with or without a known DNA mutation, 10) determining mtDNA mutations and / or the combination of mtDNA and genomic (nuclear) DNA aberrations that cause genetic disease.
Owner:KEARNS WILLIAM G +1
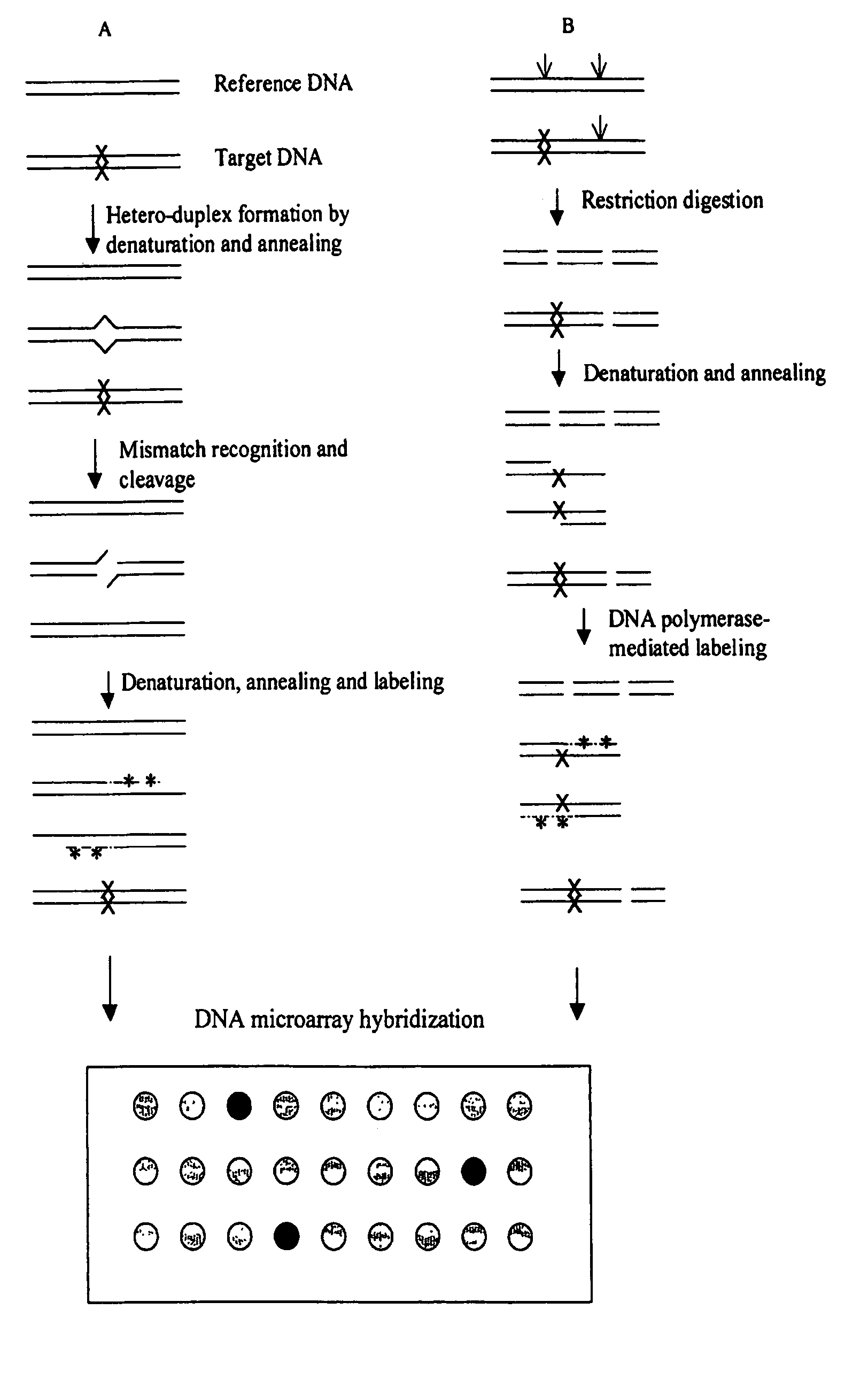
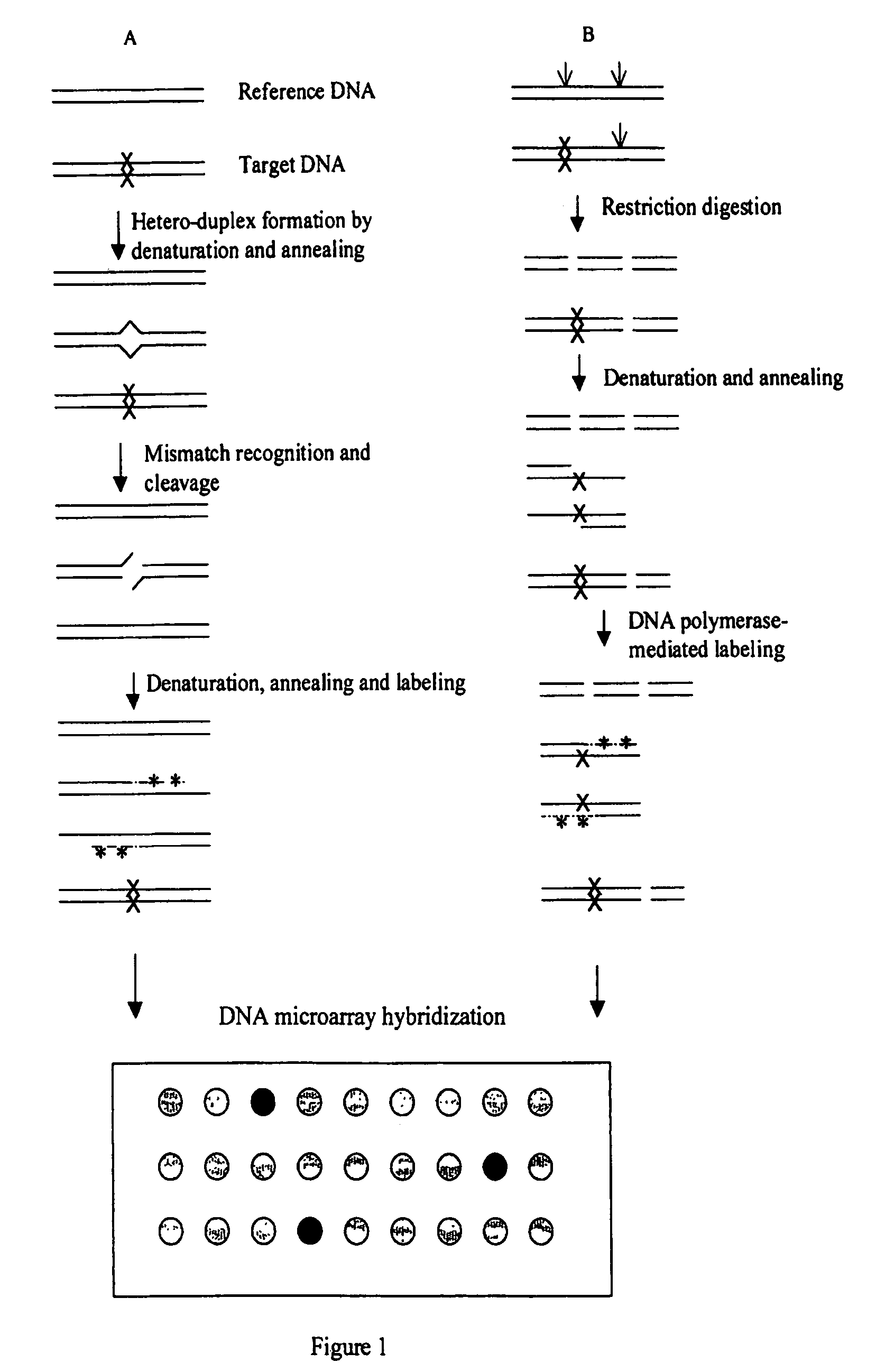
Methods for detecting and localizing DNA mutations by microarray
InactiveUS7378245B2Reduce impactMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNA microarrayHeteroduplex
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OREGON
Detection of extracellular tumor-associated nucleic acid in blood plasma or serum using nucleic acid amplification assays
InactiveUS6939675B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementNeoplasmBlood plasma
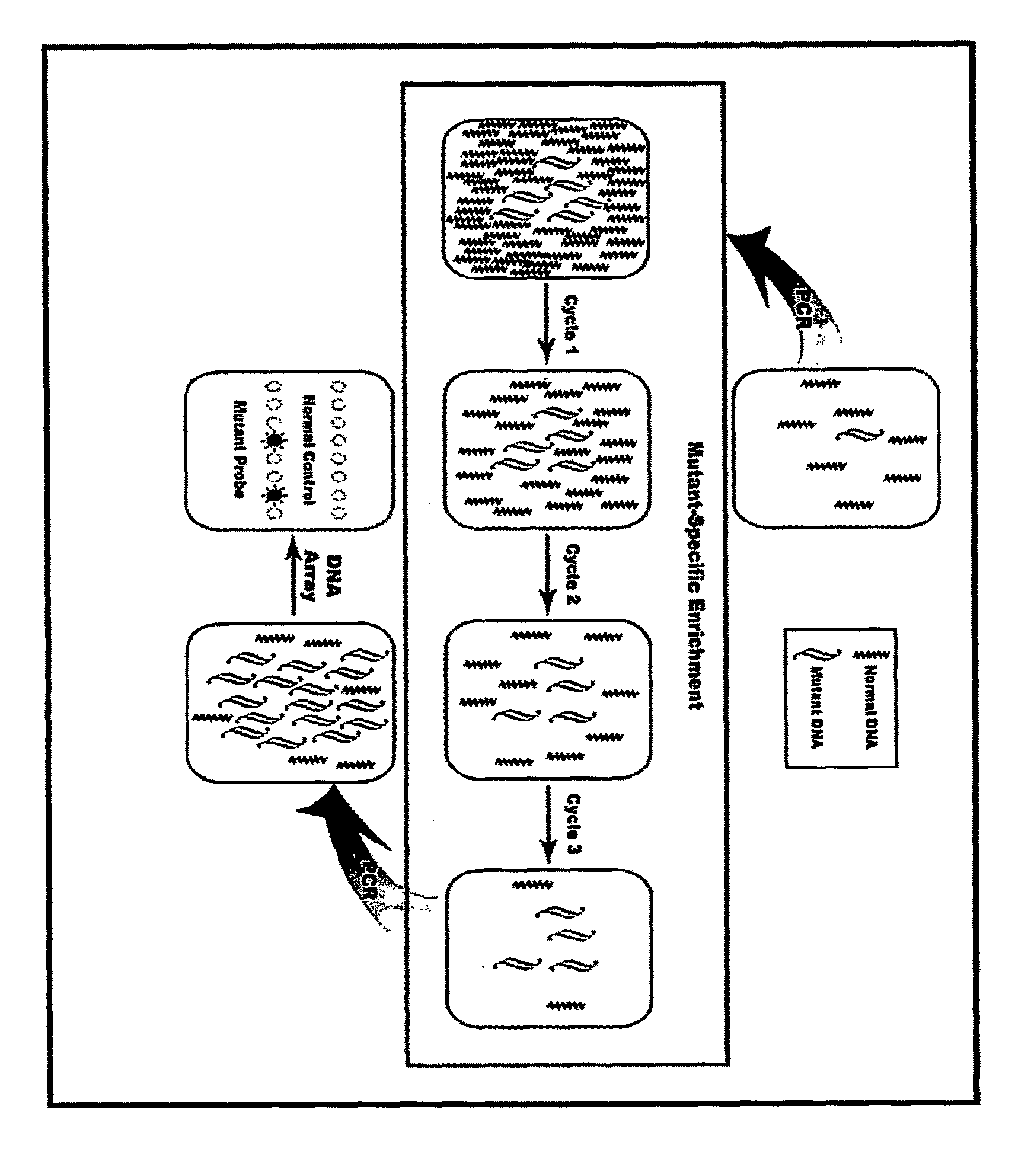
This invention relates to detection of specific extracellular nucleic acid in plasma or serum fractions of human or animal blood associated with neoplastic or proliferative disease. Specifically, the invention relates to detection of nucleic acid derived from mutant oncogenes or other tumor-associated DNA, and to those methods of detecting and monitoring extracellular mutant oncogenes or tumor-associated DNA found in the plasma or serum fraction of blood by using rapid DNA extraction followed by nucleic acid amplification with or without enrichment for mutant DNA. In particular, the invention relates to the detection, identification, or monitoring of the existence, progression or clinical status of benign, premalignant, or malignant neoplasms in humans or other animals that contain a mutation that is associated with the neoplasm through detection of the mutated nucleic acid of the neoplasm in plasma or serum fractions. The invention permits the detection of extracellular, tumor-associated nucleic acid in the serum or plasma of humans or other animals recognized as having a neoplastic or proliferative disease or in individuals without any prior history or diagnosis of neoplastic or proliferative disease. The invention provides the ability to detect extracellular nucleic acid derived from genetic sequences known to be associated with neoplasia, such as oncogenes, as well as genetic sequences previously unrecognized as being associated with neoplastic or proliferative disease. The invention thereby provides methods for early identification of colorectal, pancreatic, lung, breast, bladder, ovarian, lymphoma and all other malignancies carrying tumor-related mutations of DNA and methods for monitoring cancer and other neoplastic disorders in humans and other animals.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method for treating systemic DNA mutation disease
ActiveUS8388951B2Lower Level RequirementsGood treatment effectPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseA-DNA
A treatment for systemic DNA mutation diseases accompanied with development of somatic mosaicism and elevation of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. The inventive method consist from introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic DNA mutation diseases when said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNASE enzyme: said agent might be administered in doses and regimens which sufficient to decrease number average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease of number average molecular weight might be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNASE enzyme may be further applied in a dose and regime that provide a DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma exceeding 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Method of genetic testing in heritable arrhythmia syndrome patients
InactiveUS20050142591A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSyndrome patientGenetic Screening (procedure)
A method of diagnosing heritable arrhythmia syndrome in a patient is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of (a) isolating a nucleic acid sample from the patient and (b) comparing the nucleic acid sample to the compendium of novel DNA mutations disclosed in Table 1, wherein the comparison is to the mutations described from at least one of the genes selected from the group consisting of KCNQ1, KCNH2, SCN5A, and KCNE2.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
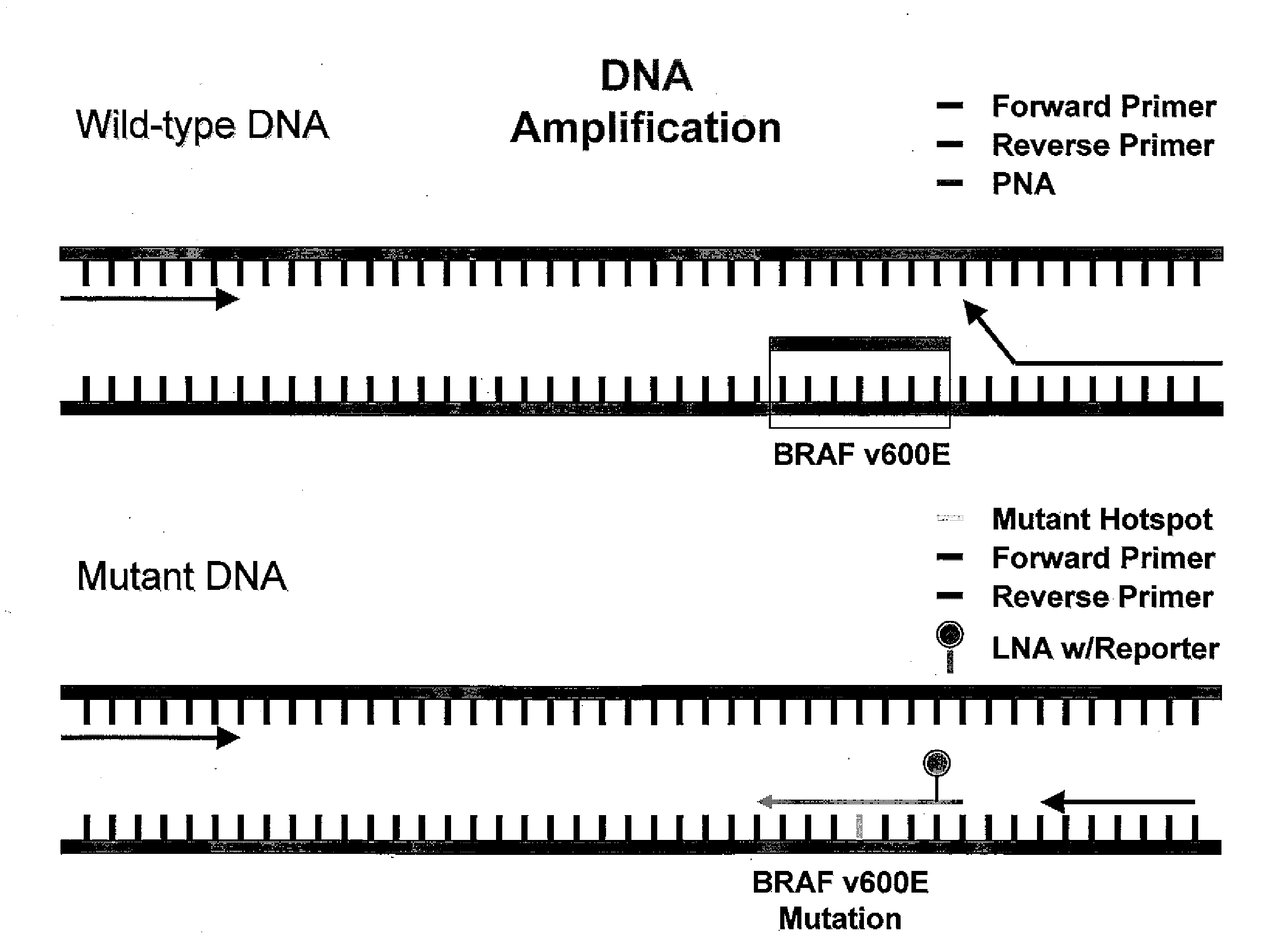
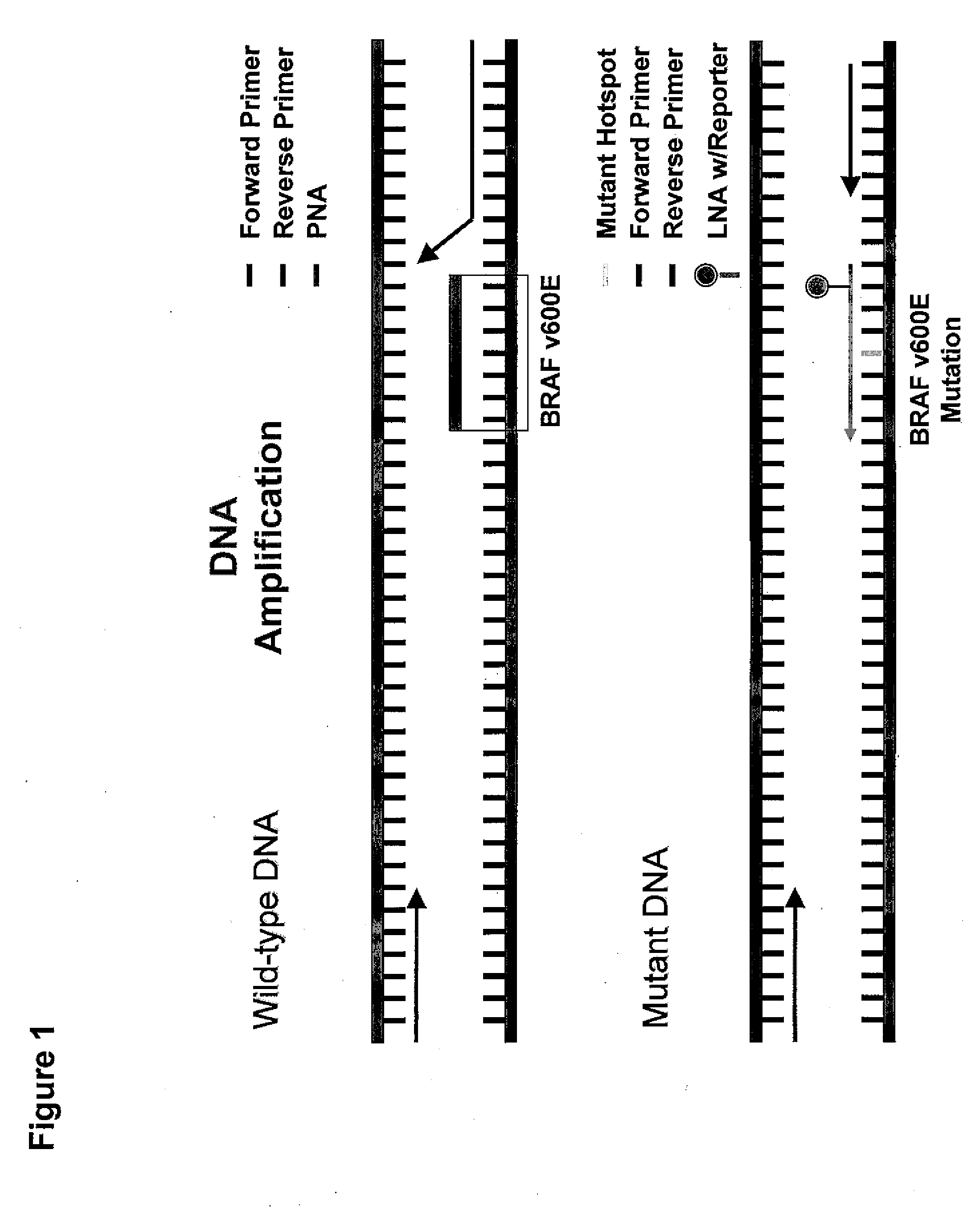
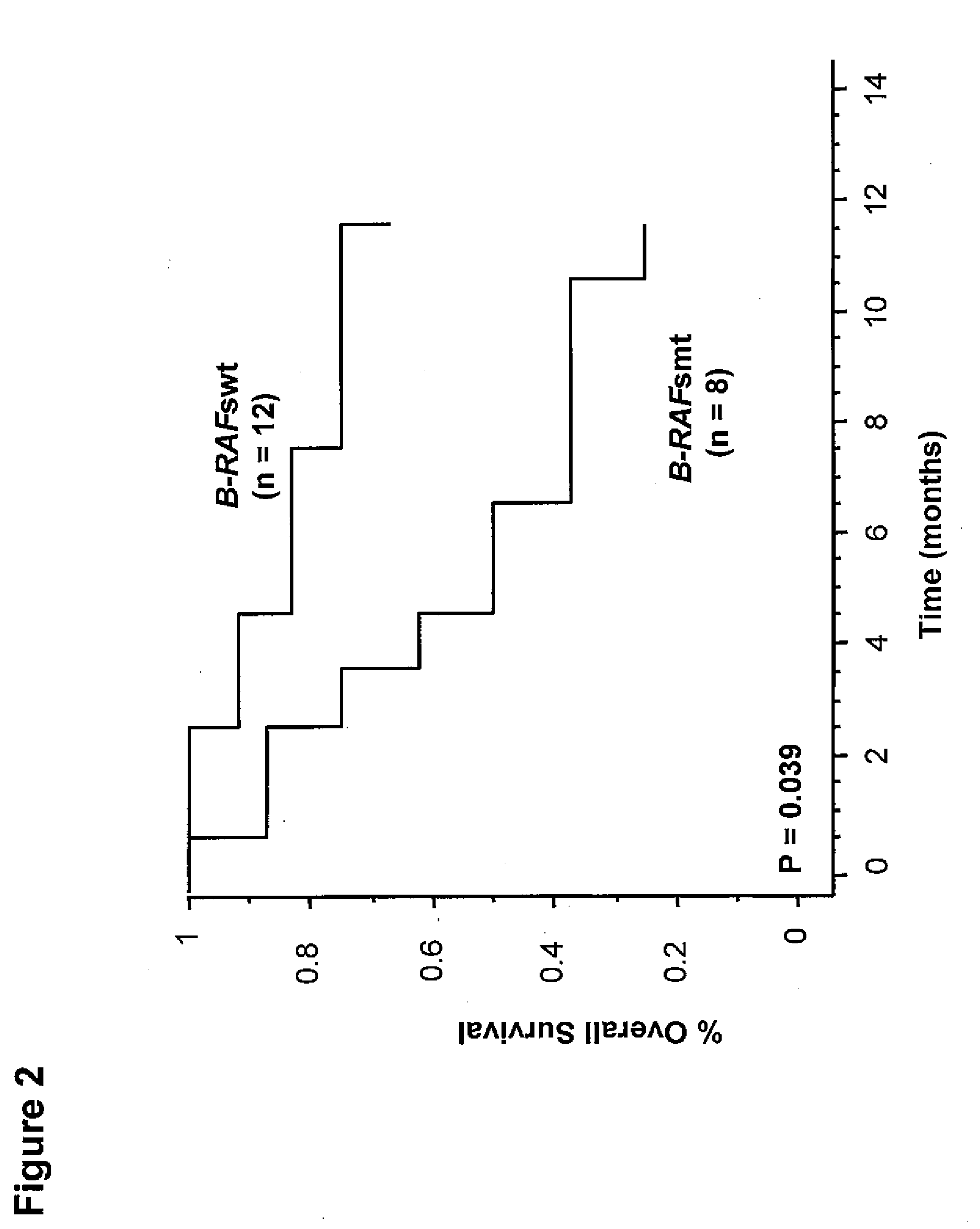
Utility of b-raf DNA mutation in diagnosis and treatment of cancer
The present invention discloses a method of detecting a wild-type or mutant B-RAF gene in a body fluid sample from a subject. Also disclosed are methods of using B-RAF as a biomarker for detecting cancer, predicting the outcome of cancer, and monitoring the treatment of cancer or the status of cancer. Furthermore, the invention discloses methods and compositions for detecting a mutant gene with a peptide nucleic acid clamp capable of hybridizing to a wild-type gene and a locked nucleic acid probe capable of hybridizing to a mutant of the gene.
Owner:JOHN WAYNE CANCER INST
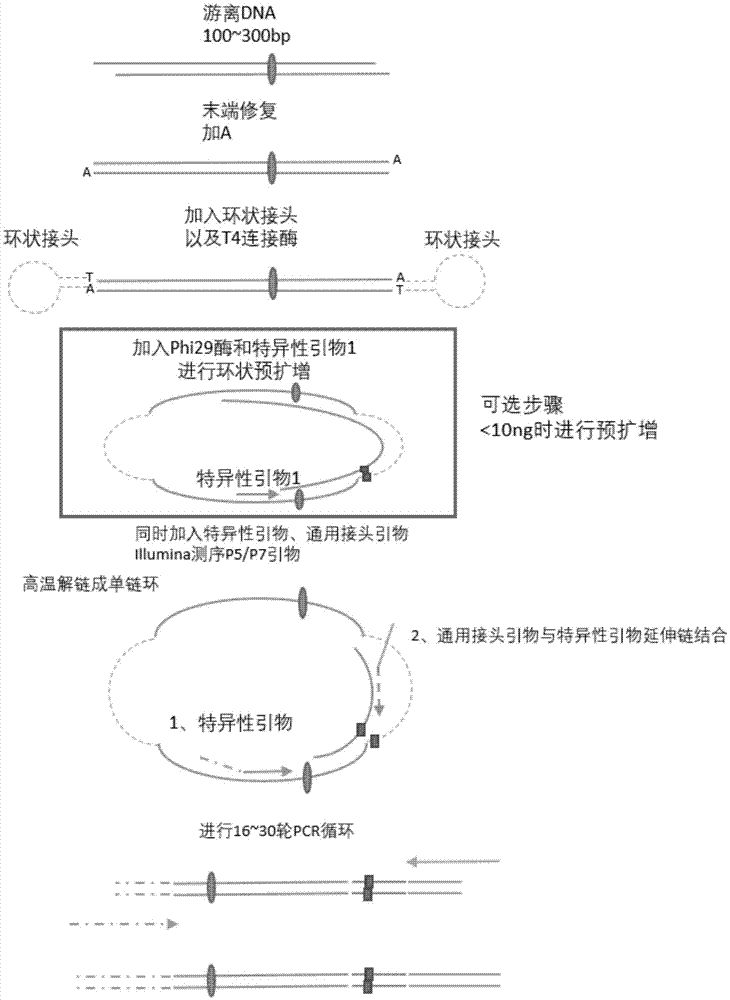
Method for performing multi-target-site amplification library construction on plasma free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
The invention discloses a method for performing multi-target-site amplification library construction on plasma free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The method sequentially comprises steps as follows: 1), tail end repairing and A addition are performed; 2), linker connection is performed: a linker DNA with an annular hairpin structure formed through annealing is added to a DNA fragment with A addition at the tail end in the step 1), so that double-stranded DNA after being combined with annular hairpin linkers on two sides is obtained; when the amount of plasma free DNA extracted and purified in the step 1) is smaller than or equal to 10 ng, a step 3) is performed; otherwise, when the amount of plasma free DNA extracted and purified in the step 1) is larger than 10 ng, a step 4) is performed; step 3), a specific primer I, Phi29 enzyme and a buffer solution are added to DNA with linker addition in the step 2), and linear amplification is performed; step 4), PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed: amplification products constitute a free DNA mutation site enrichment sequencing library.
Owner:HANGZHOU GUKUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Droplet capture chip and microfluidic chip
InactiveCN105802843ASensitive multiplex detectionRapid multiplexingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTotally integrated automationDna mutation
The invention provides a droplet capture chip. The droplet capture chip has the beneficial effects that a plurality of droplet capture chambers are arranged in the droplet capture chip, so that droplets can directly undergo in situ amplification and in situ detection after being captured; droplet generation and droplet capture are integrated on one microfluidic chip, so that convenient and rapid totally integrated automation detection is achieved, the intermediate links can be reduced and the analysis speed can be increased; the imaging information of the droplet capture chip is directly captured with a CCD (charge-coupled device), the CCD is simple and is easy to operate, and the accuracy rate of the obtained result is high; high-sensitivity detection can be achieved by scanning each fixed droplet by laser-induced fluorescence; the droplet capture chip and the microfluidic chip can make up for the deficiency of the detection technology of existing blood circulation DNA mutation, can achieve more sensitive simultaneous detection of multiple mutations and have great significance in increasing the clinical application value of blood circulation DNA in tumor diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
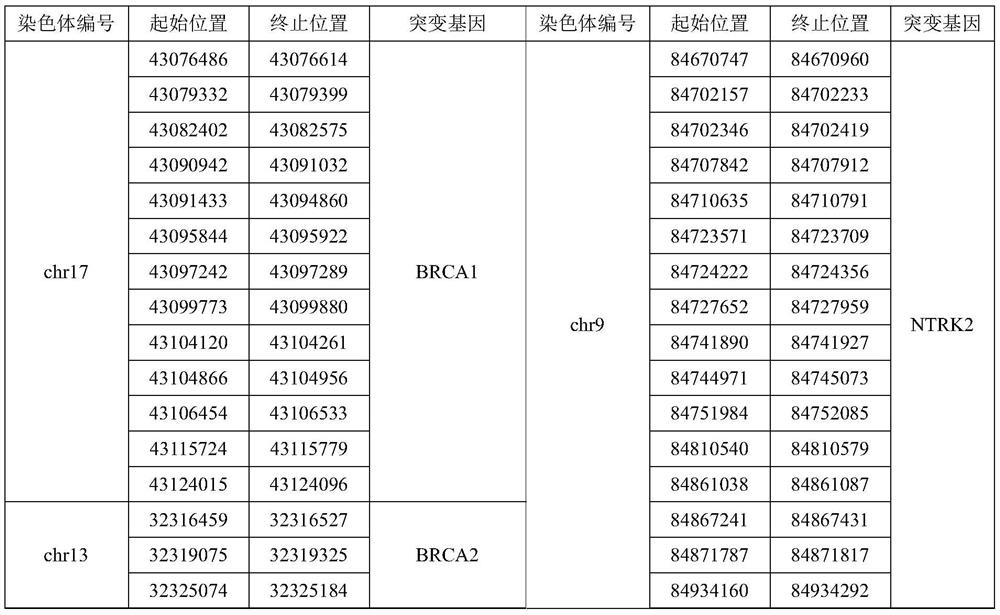
Gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, detection method used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation and application of gene panel
InactiveCN111647648AComprehensive immunotherapyComprehensive treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHuman DNA sequencingGenome human
The invention relates to a gene panel used for detecting breast cancer gene mutation, and a detection method and application of the gene panel. The panel disclosed by the invention comprises 54419 pieces of targeted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) probes. The targeted DNA comprises the exon regions of 445 pieces of genes on the human genomes, 2573 pieces of MSI (microsatellite instability) sites and 566 position intervals used for detecting gene fusion. The detection method in the invention can be used for detecting SNV (single nucleotide variation), Indel (Insertion and Deletion), CNV (Copy Number Variation), Fusion, MSI, TMB (Tumor Mutational Burden), HLA (human leucocyte antigen) parting and the like of a tumor somatic cell multi-site DNA mutation. An optimal individual treatment medicine and scheme can be conveniently selected according to the genome features of patients in a breast cancer immunotherapy process.
Owner:北斗生命科学(广州)有限公司 +1
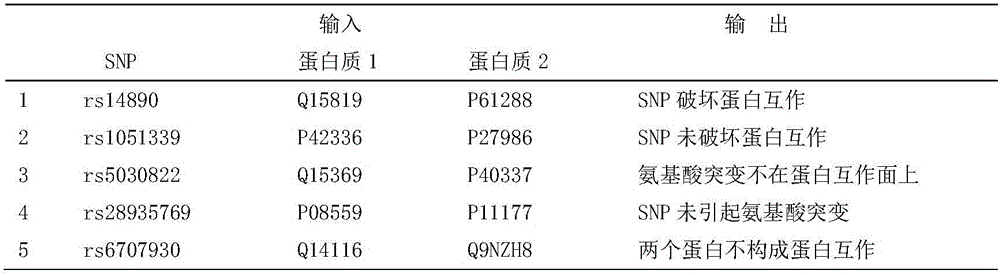
Forecasting method for forecasting DNA-mutation-influenced protein-protein interaction based on multivariate data
The invention discloses a forecasting method for forecasting DNA-mutation-influenced protein-protein interaction (PPI) based on multivariate data. The forecasting method includes the steps that whether the influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) on DNA on PPI is generated or not serves as a researching object, seven characteristics related to the structures and functions of protein and amino acid sequences are adopted, a support vector machine (SVM) and the ensemble learning algorithm are used as a classifying device, and whether PPI is damaged by the SNP or not is forecasted; meanwhile, whether the interaction effect exists between protein or not and whether amino acid variation caused by the SNP occurs on the PPI interface or not are judged.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
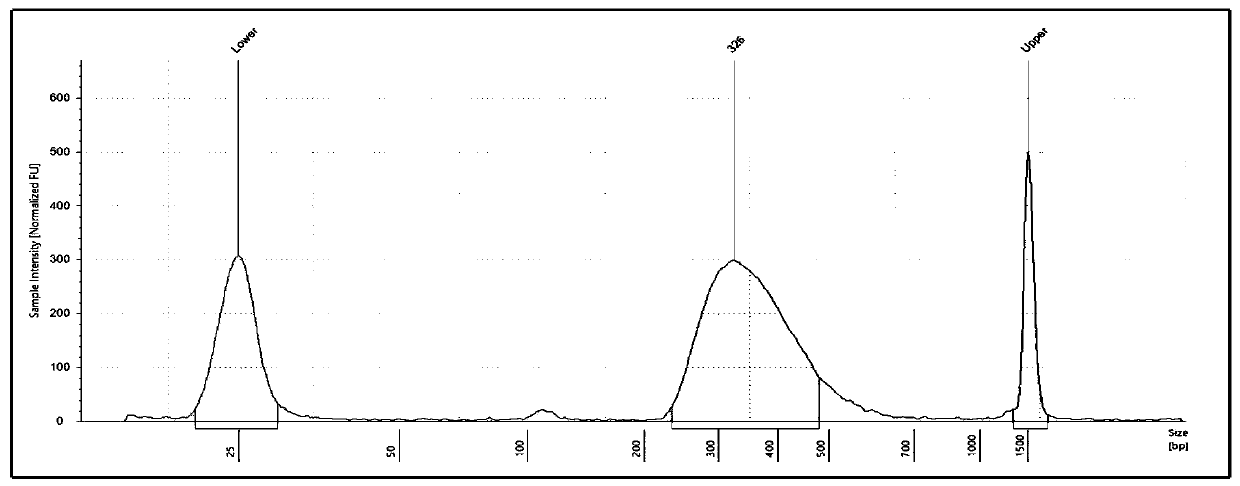
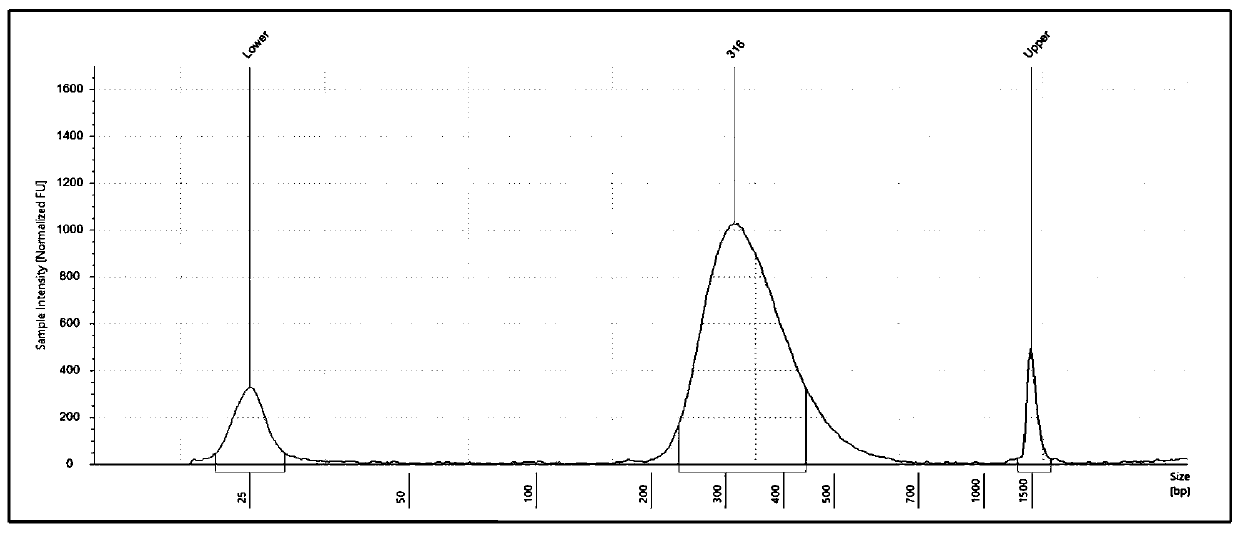
Gene panel for predicting new antigen load and detecting genome mutation
PendingCN110592213AQuick forecastEfficient forecastingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAntigenIndividualized treatment
The invention relates to the fields of biotechnology, DNA mutation detection technology and bioinformatics, in particular to a gene panel for predicting a new antigen load and detecting genome mutation. Specifically, the invention relates to the gene panel which combines 839 genes and integrates 511 gene fusion events. The gene panel provided by the invention can rapidly, efficiently and accurately predict a new antigen load, and can also detect DNA mutation of multiple sites at one time, so that an optimal individualized treatment drug and scheme can be selected according to genomic characteristics of a patient in a cancer immunotherapy process. In addition, the gene panel provided by the invention can also be used for measuring various types of biomarkers such as SNV, Indel, CNV, gene fusion, MSI, TMB and HLA.
Owner:深圳市新合生物医疗科技有限公司
Circulating tumor dissociating DNA mutation detection quality control products and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108517360AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationEnzyme digestionMutation detection
The invention discloses circulating tumor dissociating DNA mutation detection quality control products and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medical science, clinicallaboratory science and biology. The ctDNA mutation detection quality control product consists of genomic DNA after enzyme digestion and ultrasound-interrupted DNA fragments containing tumor-associated gene mutation. A method used for preparing EQA quality control products is provided by the ctDNA mutation detection quality control product obtained by mixed production of the ultrasound-interruptedDNA fragments containing different gene mutation and the genomic DNA after the enzyme digestion. The preparation method is still the first case.
Owner:ANNOROAD GENE TECH BEIJING
Method for Treating Systemic DNA Mutation Disease
ActiveUS20100303796A1Lower Level RequirementsGood treatment effectHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsA-DNABlood plasma
A treatment for systemic DNA mutation diseases accompanied with development of somatic mosaicism and elevation of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. The inventive method consist from introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic DNA mutation diseases when said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNASE enzyme: said agent might be administered in doses and regimens which sufficient to decrease number average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient;such decrease of number average molecular weight might be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNASE enzyme may be further applied in a dose and regime that provide a DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma exceeding 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
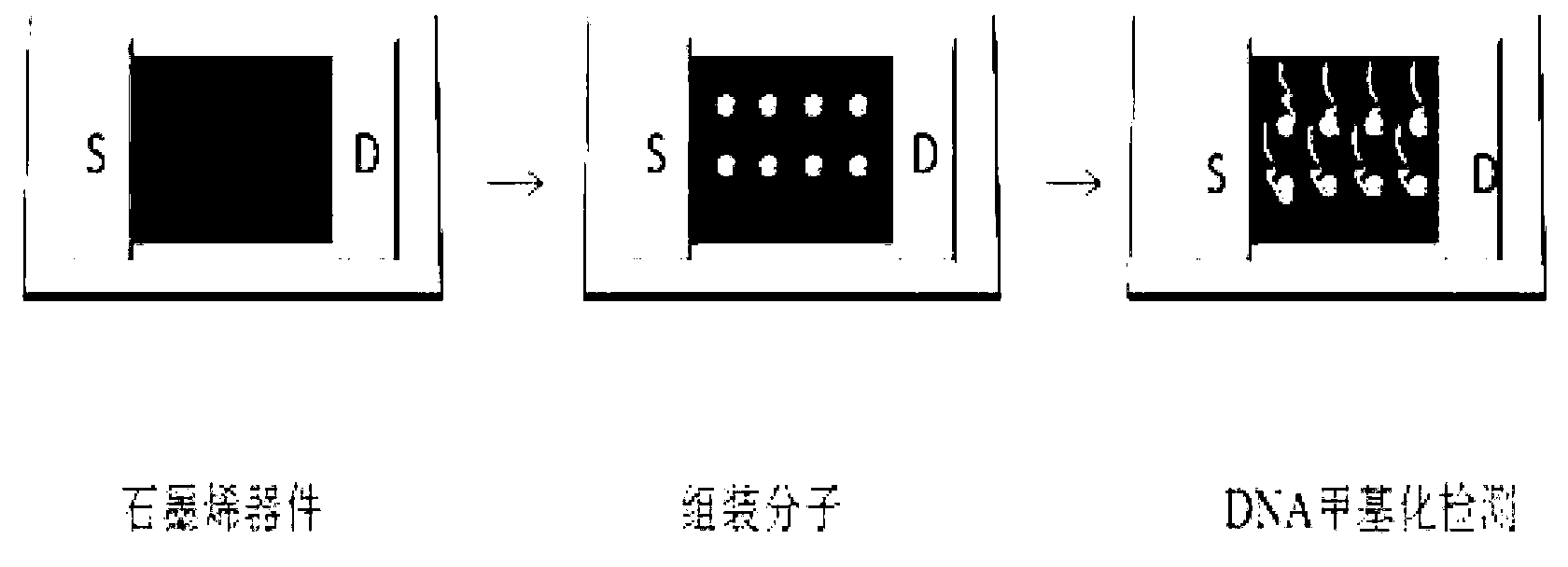
Method for detecting DNA mutation based on graphene sensor
InactiveCN103323494AImprove stabilityQuick responseMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDNA methylationDna mutation
The invention discloses a method for detecting DNA mutation (SNP and DNA methylation) based on graphene sensor. The method comprises the steps that: (1) a graphene molecular device is constructed; (2) a connection molecule is assembled on the surface of the graphene molecular device obtained in the step (1); (3) the designed detection probe is connected on the assembled molecule; and (4) a DNA mutation sample is subjected to electrical signal detection based on the graphene device. According to the invention, DNA mutation detection is realized through electrical signals by using the functionalized graphene molecular device.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
DNA mutation detection employing enrichment of mutant polynucleotide sequences and minimally invasive sampling
ActiveUS20160194691A1Improved and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationOligomerNucleotide
The invention relates to a method for enriching a target polynucleotide sequence containing a genetic variation said method comprising: (a) providing two primers targeted to said target polynucleotide sequence; (b) providing a target specific xenonucleic acid clamp oligomer specific for a wildtype polynucleotide sequence; (c) generating multiple amplicons using PCR under specific temperature cycling conditions; and (d) detecting said amplicons.
Owner:DIACARTA LTD
Detection technical system for enriching low-abundance DNA mutation based on nuclease-coupled PCR principle and application thereof
The invention provides a detection system for enriching low-abundance mononucleotide mutant genes based on a nuclease-coupled PCR principle. The invention particularly provides a method for increasingthe relative abundance of a target nucleic acid, which comprises the following steps: (a) providing a nucleic acid sample containing a target nucleic acid and a non-target nucleic acid, wherein the abundance of the target nucleic acid in the nucleic acid sample is F1a; (b) using the nucleic acid in the nucleic acid sample as a template, performing PCR and nucleic acid cleavage reaction in the amplification-cleavage reaction system to obtain amplification-cleavage reaction product; the target nucleic acid is amplified the abundance of the amplification-cleavage reaction product is F1b, and theratio of F1b / F1a is more than or equal to 10. The detection system has the advantages of non-invasion, easy operation, high speed and the like, the sensitivity can reach 0.01%, and the DNA quantity of the sample can be reduced to aM grade.
Owner:JIAOHONG BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
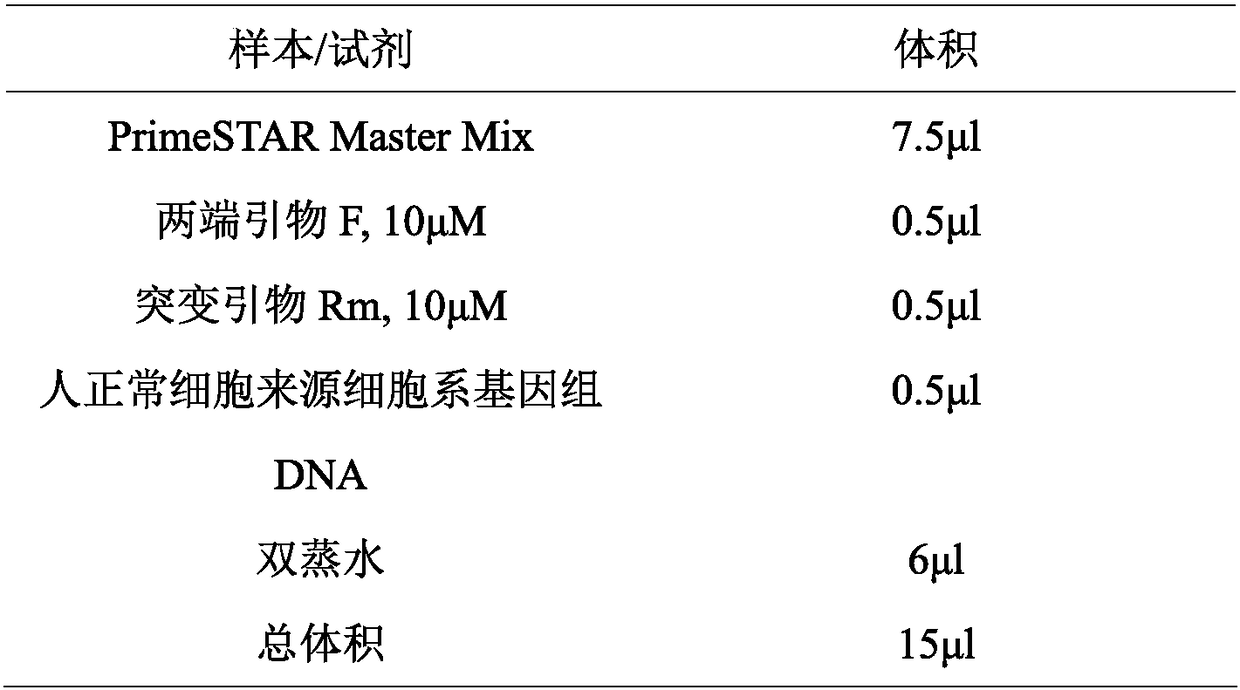
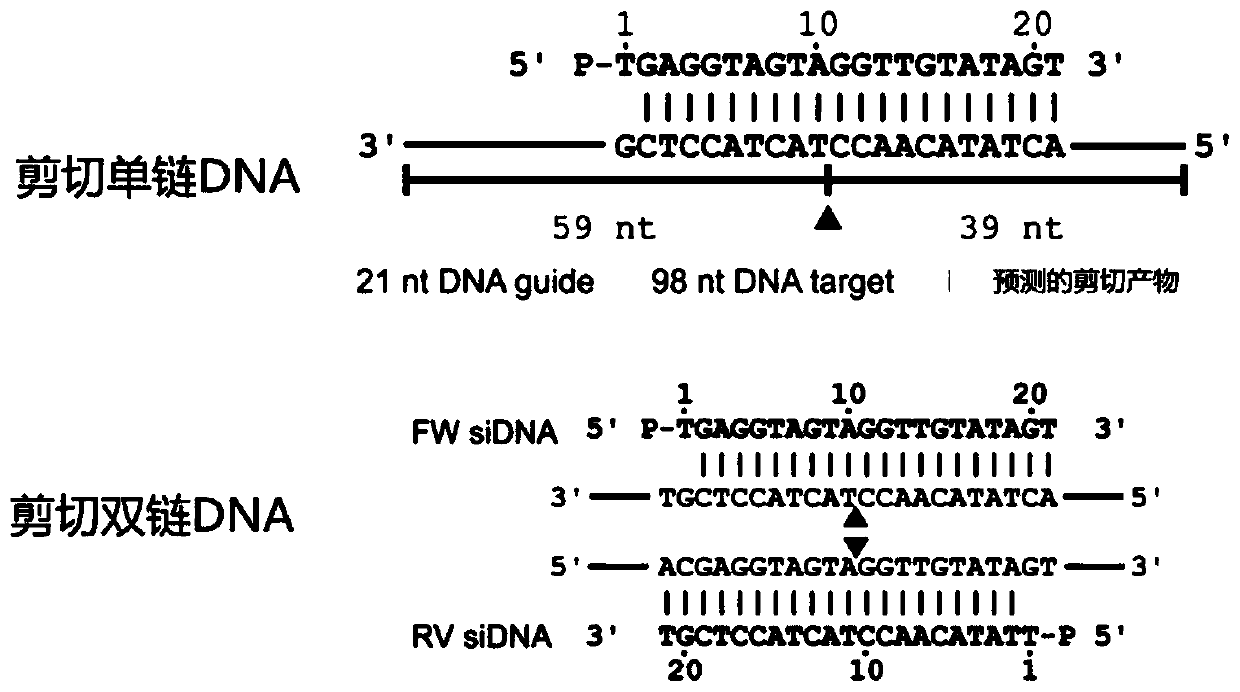
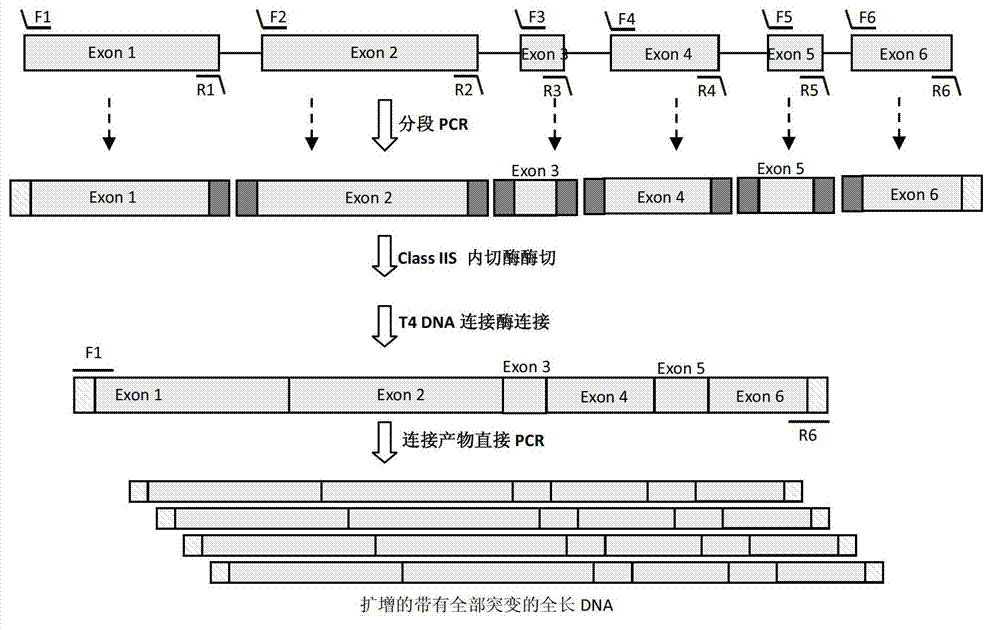
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) multi-site directed mutation method
The invention provides a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) multi-site directed mutation method which comprises the following steps: designing Class IIS-containing restriction enzyme recognition site and cleavage site according to DNA mutation sites, performing segmented polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, digestion and connecting reaction to obtain a connecting product, directly performing PCR amplification by using the connecting product, and realizing DNA multi-site mutation. The DNA multi-site directed mutation can be rapidly and efficiently realized simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
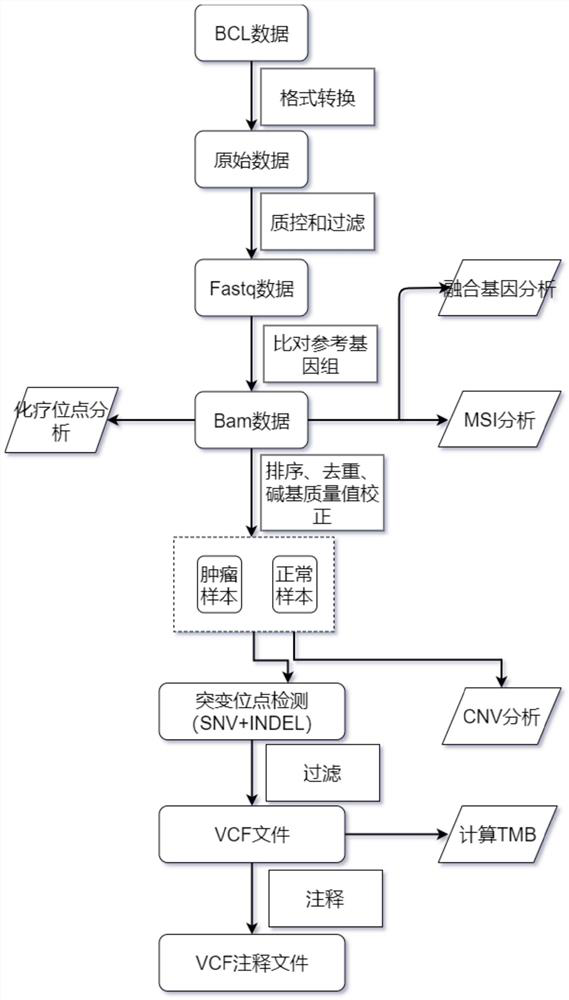
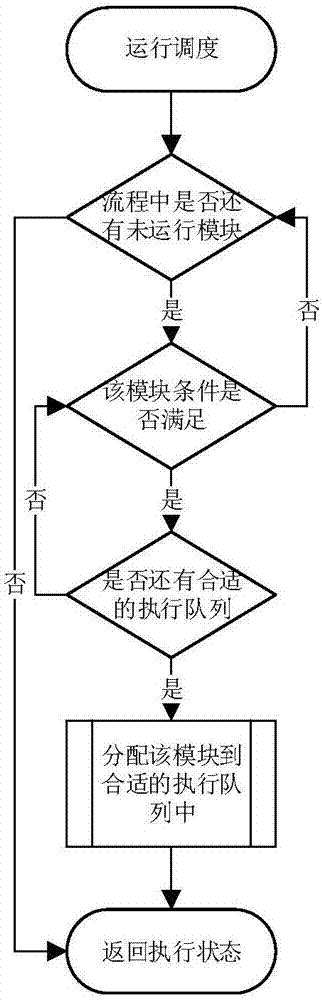
Bioinformatics analysis method and system for next-generation sequencing DNA mutation detection
InactiveCN107122626AImprove maintainabilityImprove stabilitySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsInformation analysisAnalysis data
The invention provides a bioinformatics analysis method and system for next-generation sequencing DNA mutation detection. The system comprises a bio-information analysis module used for providing basic component units of a biological analysis process and finishing basic functions of bio-information analysis, an intermediate data conversion module used for performing format conversion on data generated by the bio-information analysis module and providing biological analysis data sources and results meeting the requirements, and a running environment configuration module used for configuring relative paths or absolute paths of all input files, output files, configuration files, data files, temporary files, log records, scripts and applications during running of different biological analysis processes and running related environment variables. According to the method and the system, the design is performed only for the DNA mutation detection, namely, a specific bio-information analysis process, so that unnecessary functions are prevented from being introduced, the maintainability and stability of the system are improved, and the flexibility maximization of process establishment is ensured.
Owner:上海海云生物科技有限公司
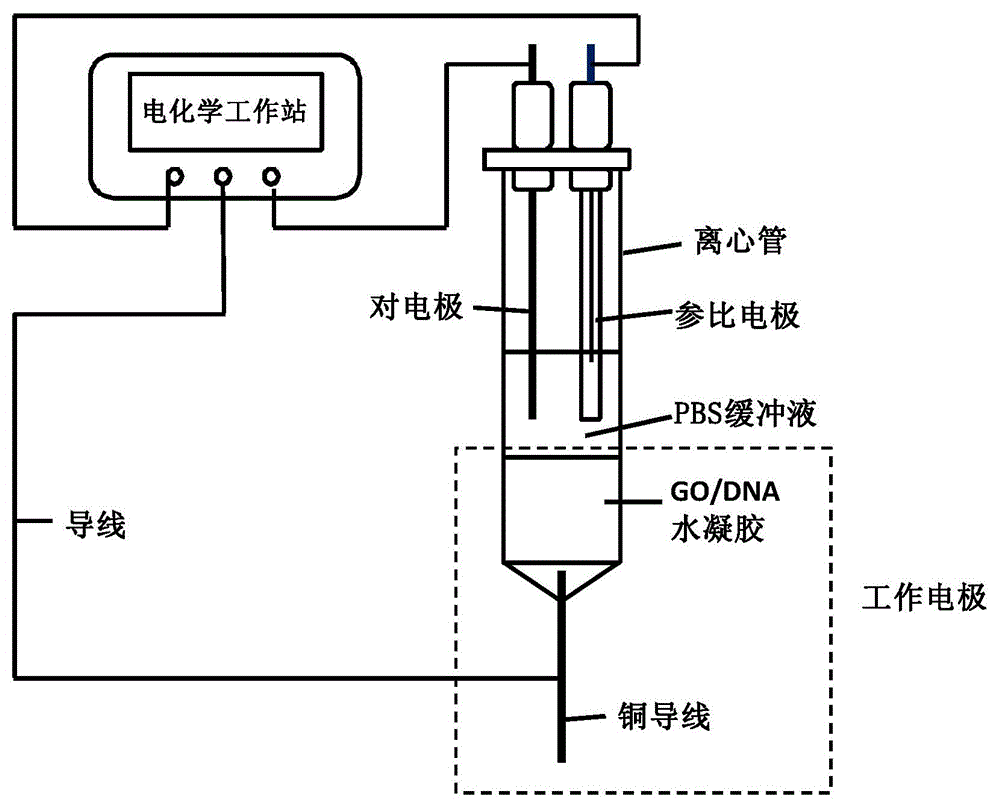
Preparation method and application of hydrogel electrode
ActiveCN104086786AEasy to prepareLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCopper wirePotassium
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a hydrogel electrode and relates to hydrogel electrodes. The preparation method of the hydrogel electrode comprises the following steps: with graphite powder as a raw material, adding sodium nitrate, sulphuric acid and potassium hypermanganate, mixing and then carrying out reaction until a thick mixture is formed; then adding pure water for the first time, further carrying out reaction, then adding pure water for the second time and stopping reaction, then adding a hydrogen peroxide solution for removing unreacted potassium hypermanganate, washing, centrifuging, and drying, so that graphite oxide solids are obtained, and carrying out ultrasonic treatment on the graphite oxide solids, so that a uniformly dispersed graphene oxide aqueous solution is obtained; mixing the graphene oxide aqueous solution with DNA of milt, then adding the mixture into a centrifugal tube to be heated, and after gel is stably formed, inserting a copper wire into a small hole in the bottom of the centrifugal tube to be fixed, so that a graphene oxide and milt-DNA compounded hydrogel electrode is obtained. The graphene oxide and milt-DNA compounded hydrogel electrode can be used for preparing a graphene oxide and milt-DNA composite hydrogel biosensor and can be applied to detection of mutation of mitochondrial DNA of ovarian cancer.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Detection primer, detection kit and detection method of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) mitochondrial DNA gene mutations
ActiveCN106755335AResolve SensitivitySolve the characteristicsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic dnaGene mutation
The invention relates to a detection primer, a detection kit and a detection method of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) mitochondrial DNA gene mutations. The invention, on the basis of Sanger sequencing principle, has the characteristics of being highly sensitive, stable and accurate; four most common pathogenic mutations of LHON mtDNA can be simultaneously detected, so that the problems of an existing LHON mitochondrial DNA mutation detection method, which is low in sensitivity, not strong enough in specificity, capable of causing pollution easily, high in expense and the like, can be solved; therefore, an accurate gene diagnosis method is provided for LHON; and the invention has important implications for genetic counseling and gene therapy of the disease (the LHON).
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
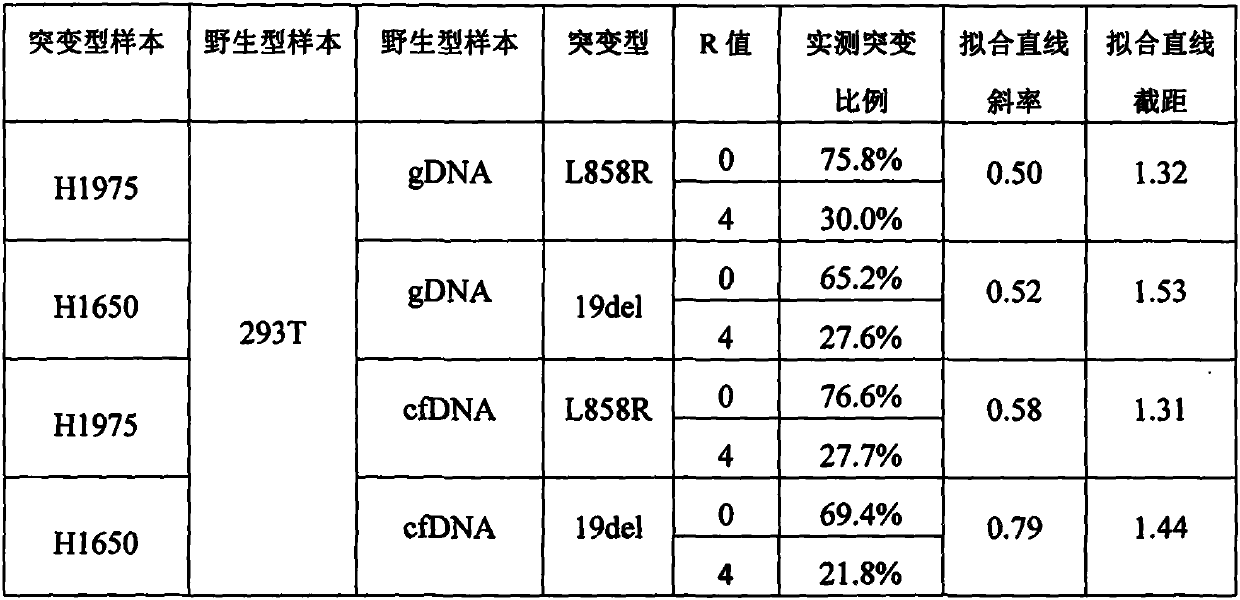
Method for preparing gene mutation reference substance
PendingCN110878333AAvoid differences in properties such as sequence compositionAccurately determineMicrobiological testing/measurementGenes mutationWild type
The invention discloses a method for preparing a gene mutation reference substance. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing mutant genome DNA and wild genome DNA according to at least two proportions, measuring the mutation proportion of the prepared reference substance, and calculating a slope and intercept of a fitting straight line; and then preparing the mutation reference substance with any mutation proportion which does not exceed the initial mutation type genome DNA mutation proportion according to the target requirement without verifying themutation proportion of the reference substance obtained by dilution.
Owner:JIAXING ACCB DIAGNOSTICS
Methods for identifying multiple DNA alteration markers in a large background of wild-type DNA
Methods for simultaneously surveying the status of a large number of DNA mutation markers are described. In addition, methods for simultaneously determining the methylation status at multiple sites of a collection of genes, in a single assay, are described.
Owner:CLEVELAND STATE UNIVERSITY
Human multi-gene mutation detection kit based on high-throughput sequencing method
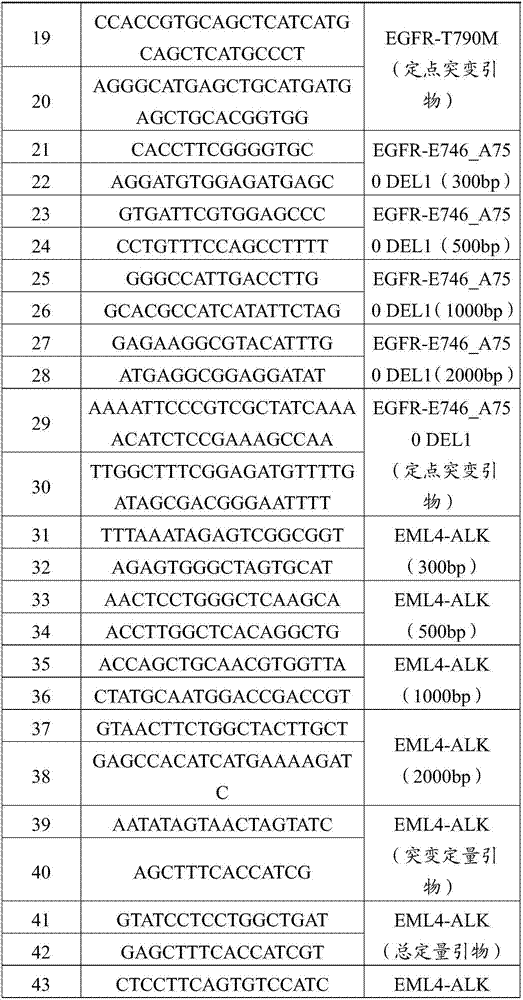
InactiveCN107164513AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMutation detectionEGFR Gene Mutation
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a human multi-gene mutation detection kit based on a high-throughput sequencing method and an application thereof. The kit includes a KRAS gene mutation detection primer pair, an EGFR gene mutation detection primer pair and an ALK gene fusion detection primer pair. The kit can simultaneously detect DNA mutation and RNA fusion, is high in sensitivity and low in detection limit, is high in specificity, has good repeatability, and can reach 100% in both accuracy and positive coincident rate.
Owner:SINGLERA GENOMICS (SHANGHAI) LTD
JAK2 V617F mutation detection application
ActiveCN103243153ADetection time savingLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementJanus kinase 2Nucleic acid detection
The invention belongs to the field of nucleic acid detection, and particularly relates to the detection of JAK2 (Janus Kinase 2) gene V617F locus DNA mutation (G1849T) and a test kit and a primer pair used for the detection. The present invention discloses a method for detecting V617F mutation in the JAK2 gene, which comprises (1) performing PCR amplification for the samples to be tested, and (2) performing melting analysis by using a melting analyzer. Further, the present invention also discloses the test kit and the primer pair for the detection method.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Method for detecting DNA mutation by nanometer gold
InactiveCN101344481AGood dispersionReduce aggregationMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsWild typeUv vis absorbance
The invention discloses a DNA mutation test method in use of nano-Au, relates to a DNA mutation test method, and provides a DNA mutation test method that uses a nano-Au probe. The DNA mutation test method leads wild single-stranded DNA, a probe that is completely complementary with a wild single-stranded DNA sequence and the nano-Au to be mixed, statically placed, added with a sodium chloride solution, and then statically placed, thus obtaining an architecture 1; the DNA mutation test method further leads mutant single-stranded DNA, the probe that is completely complementary with the wild single-stranded DNA sequence and the nano-Au to be mixed, statically placed, added with the sodium chloride solution, and then statically placed, thus obtaining an architecture 2; the sodium chloride solution is added into and evenly mixed with the architecture 1, the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum detection is implemented, and an absorbance value that is obtained at a 520nm position is taken as an absorbance value 1; the sodium chloride solution is added into and evenly mixed with the architecture 2, the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum detection is implemented, and an absorbance value that is obtained at a 520nm position is taken as an absorbance value 2; when the absorbance values 2 and 1 have marked difference, mutation is determined to exist. The DNA mutation test method does not need any modification of the DNA and the nano-Au, thus simplifying sample processing.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
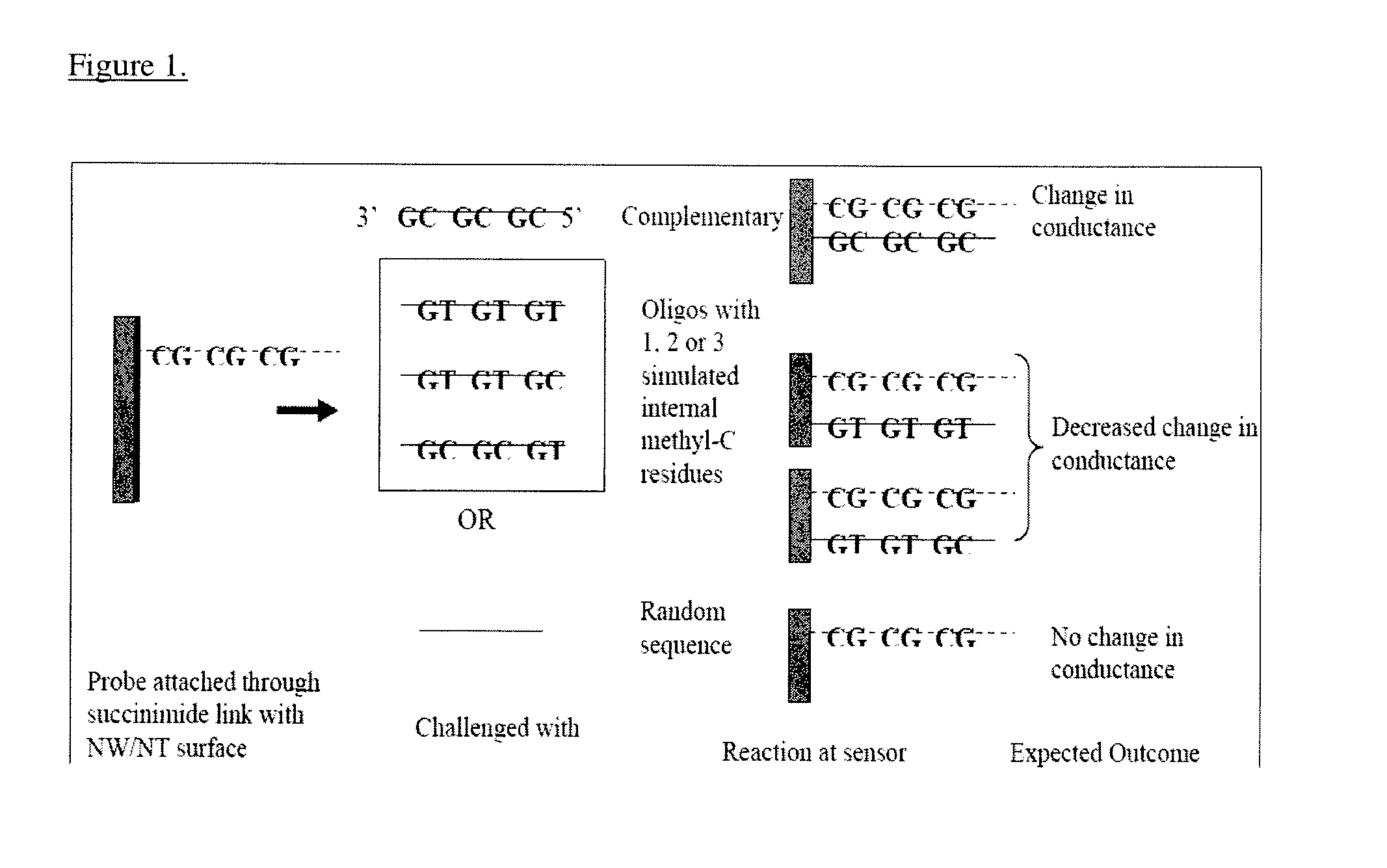
Detection of methylated DNA and DNA mutations
The present invention relates to various methods of detecting DNA methylation and defected DNA. In one embodiment, the invention provides a nanosensor bound to a probe that is complementary to a DNA methylation sequence.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Quality control product for detecting fragmented DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) mutation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107475387ASimulate the realMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a quality control product for detecting fragmented DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) mutation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking mutant genome DNA or a constructed mutant plasmid as a template and carrying out primer amplification to obtain a mutant DNA fragment; randomly breaking the mutant DNA fragment to obtain a fragmented mutant DNA sample; mixing the fragmented mutant DNA sample with a fragmented wild genome DNA sample to prepare the quality control product. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the mutant DNA fragment is randomly broken and fragment lengths, which are adaptive to the samples, can be obtained through breaking according to different detection samples. Furthermore, the method is simple to operate; compared with a synthesis method, enzyme digestion sites and protective basic groups do not need to be added at two ends of a sequence. Furthermore, according to the quality control product prepared by the method, the mutant DNA fragment is randomly broken and broken points are random; the prepared quality control product can be used for more really simulating a clinical sample.
Owner:GENOSABER BIOTECH SHANGHAI +1
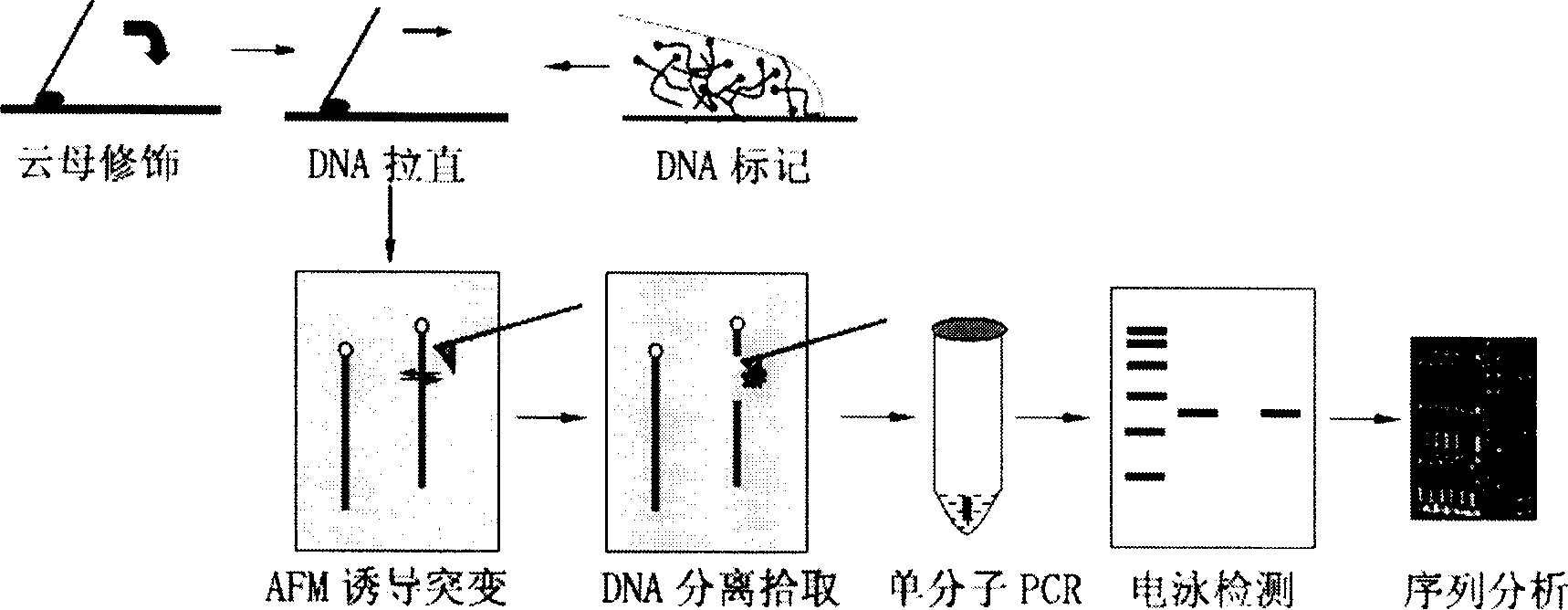
Method for atom force microscope inducing single molecule DNA positoning mutation
InactiveCN1766104AGood effectEasy to operate and controlDNA preparationDNA fragmentationDna targeting
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Gene relevant mutational site of mitochondrial deaf and application
InactiveCN101875938AHelps to rule outAids in diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomicsNew mutation
The invention belongs to the field of genomics, particularly relating to the deaf relevant mutation 12201 T>C of mitochondrial gene and application. The sequence in which the deaf relevant mutation 12201 T>C of mitochondrial gene of the invention is positioned has the structure of sequence 1. The invention can adopt the deaf relevant mutation of mitochondrial gene to preferentially detect the mitochondria mutational site of deaf patients, which is favourable for eliminating or diagnosing deaf caused by mitochondrial gene mutation; a diagnostic probe prepared by deaf relevant new mutation of the mitochondrial gene, a primer for introducing mutation to cause enzyme cutting site and a kit are adopted to conveniently and quickly screen deaf relevant to mitochondria. The invention provides the reference base for function change caused by gene mutation and provides a favorable chance for disclosing the molecular mechanism of deaf caused by the mitochondria DNA mutation.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
Methods for identifying multiple DNA alteration markers in a large background of wild-type DNA
Methods for simultaneously surveying the status of a large number of DNA mutation markers are described. In addition, methods for simultaneously determining the methylation status at multiple sites of a collection of genes, in a single assay, are described.
Owner:CLEVELAND STATE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com