Detection technical system for enriching low-abundance DNA mutation based on nuclease-coupled PCR principle and application thereof
A nucleic acid and nucleic acid sample technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as high equipment and reagent prices, high experimental operation requirements, and difficult synthesis of MGB probes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0106] Primer and detection probe design
[0107] Primer design follows the principles: primer requirements: ① avoid a series of bases in the primer sequence, especially a series of G; The last 5 bases at the 3′ end of the primer should not have more than 2 bases (G+C); ⑤The closer the downstream primer is to the probe, the better, and the fragments can overlap. The amplified fragment is preferably 75-150 bp.
[0108] The principle to be followed in the design of the detection probe: the detection probe specifically binds to the target gene, and its binding site is in any region of the target gene. The 5' end of the probe is labeled with a fluorescent reporter group (Reporter, R), such as FAM, VIC, etc., and the 3' end is labeled with a quencher group (Quencher, Q). Probe design requirements: ①The 5′ end of the probe cannot be G; ②The length of the probe should not be less than 13bp; ③Avoid a series of repeated base sequences; ④The Tm is 65-70°C, and the theoretical annealing...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Oligonucleotide gDNAs design and optimization
[0113] The core principle of this method for enriching low-abundance mutant target genes is that: on the one hand, the affinity of the PfAgo-gDNA complex to nucleic acid substrates is significantly improved by phosphorylation modification of the 5' end of gDNAs. At the same time, at the beginning of the establishment of this method, it was found that there is a seed region on the gDNA, and the specificity of the interaction between the PfAgo-gDNA complex and the substrate is determined by the seed sequence in gDNAs. This method explores the effect of different nucleotides (bases) on improving the specific targeting of the PfAgo-gDNA complex in conjunction with the target DNA substrate by exploring different positions (the second to the fifteenth nucleotides) in the gDNAs seed region and Its rules, analysis and induction of the design rules of the gDNAs seed region used to identify single nucleotide variation, are as follow...
Embodiment 3
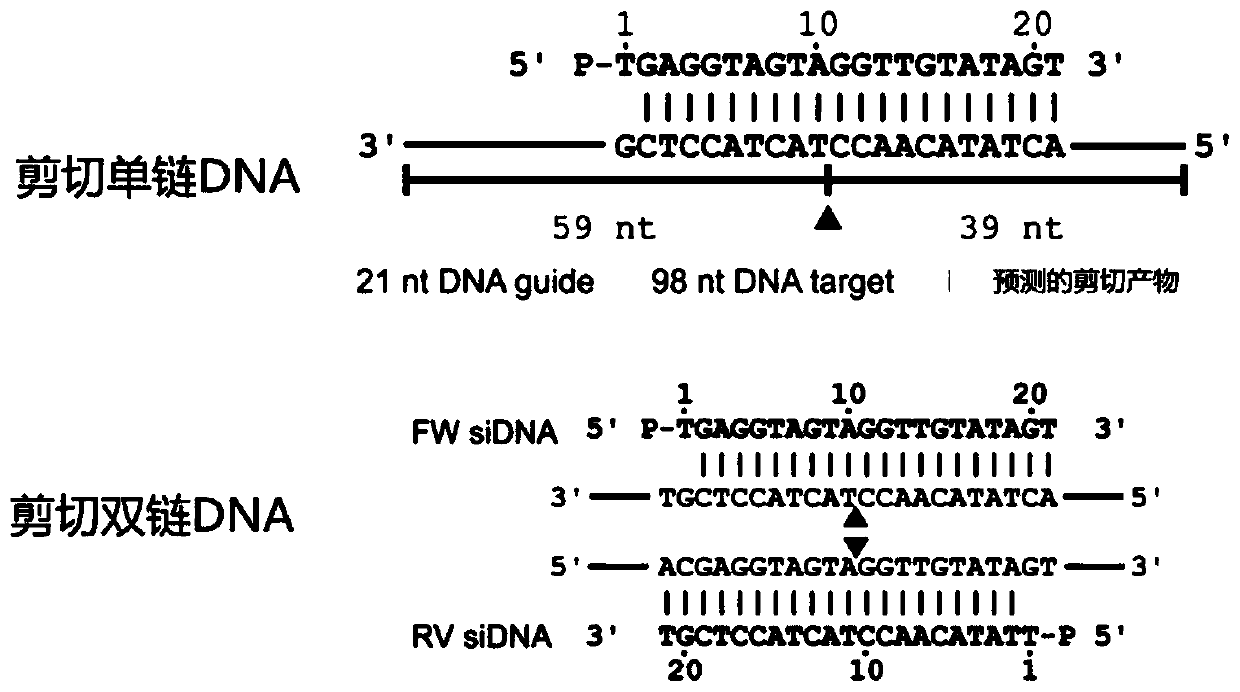
[0120] Differential cleavage of ssDNA and dsDNA by PfAgo-gDNA complex
[0121] In this embodiment, it is mainly tested whether the PfAgo-gDNA complex still has a good ability to distinguish and cut ssDNA, dsDNA and dsDNA under the PCR working system under the common PCR reaction buffer and other components.
[0122] 3.1 Method
[0123]The components and working conditions involved in this example mainly include: 2×PCR Taq Master Mix, forward and reverse primers, forward and reverse gDNAs, PfAgo, MnCl 2 , templates (pure wild, pure mutant, and half of wild and mutant), etc., as shown in Table 8.
[0124] Table 8 takes the 25 μL system as an example, the components and preparation sequence of the PfAgo enrichment reaction system.
[0125] The description of each component in Table 8 is as follows:
[0126] 2×PCR Taq Master Mix reaction solution is prepared from 2×PCR buffer, dNTPs and hot start enzyme. 2×PCR buffer: KCl, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 3mM MgCl 2 , Tris-HCl, pH 8.3 (25...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com