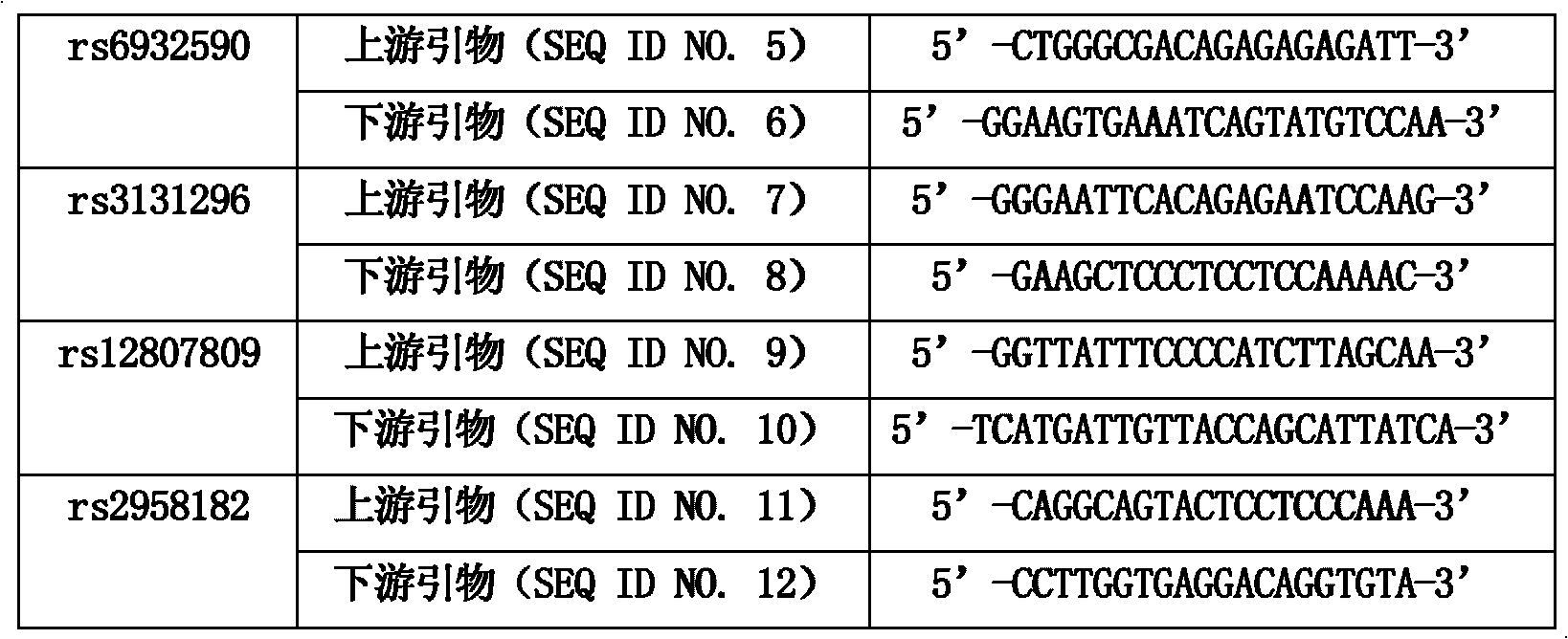
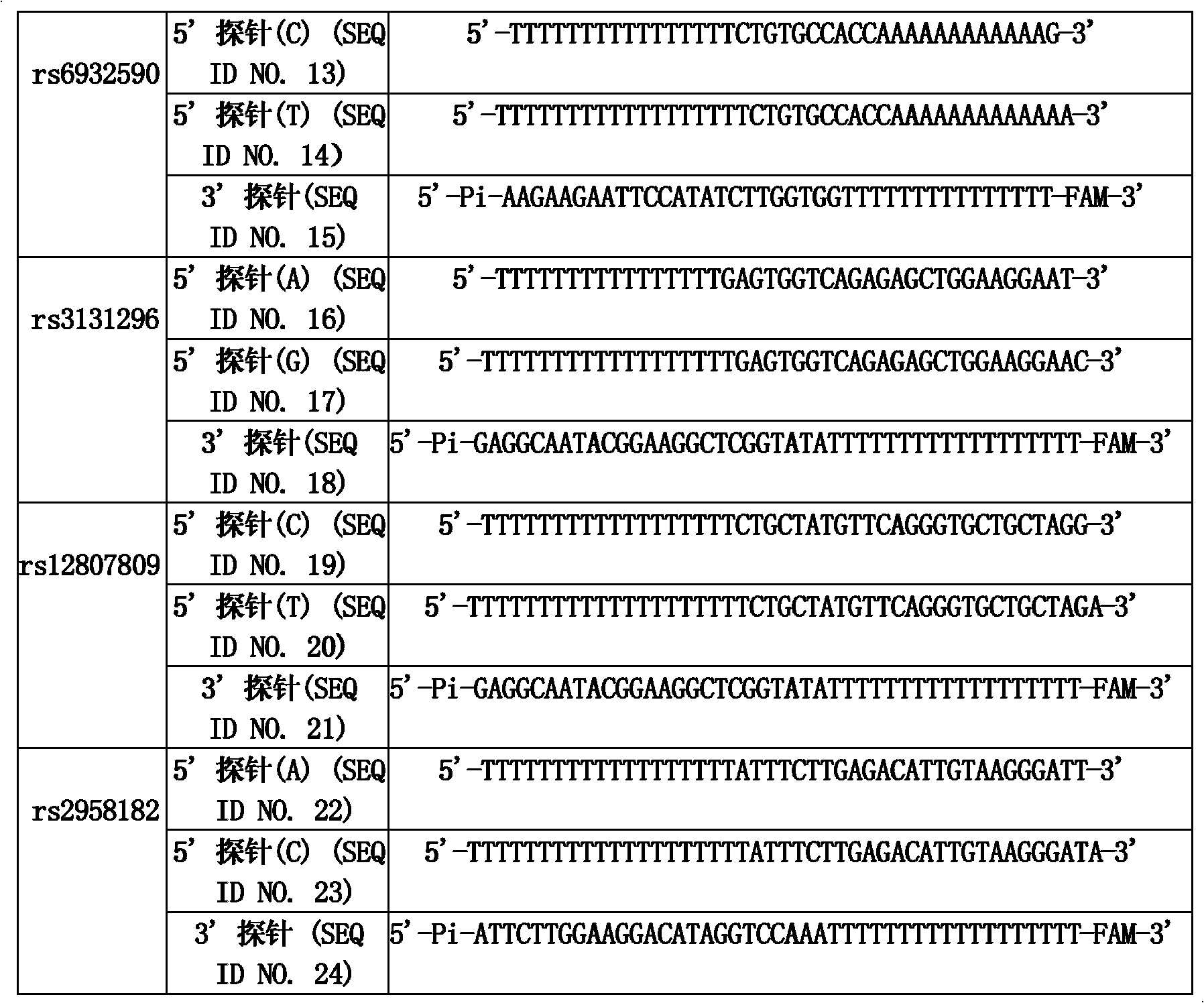
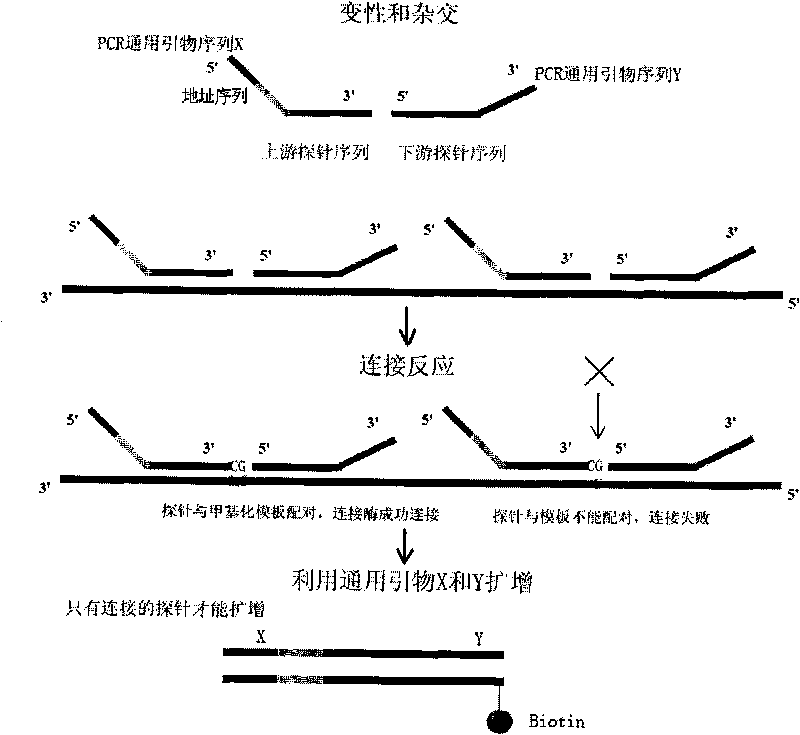
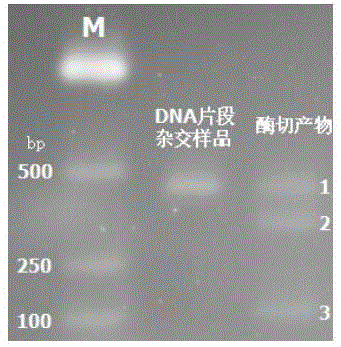
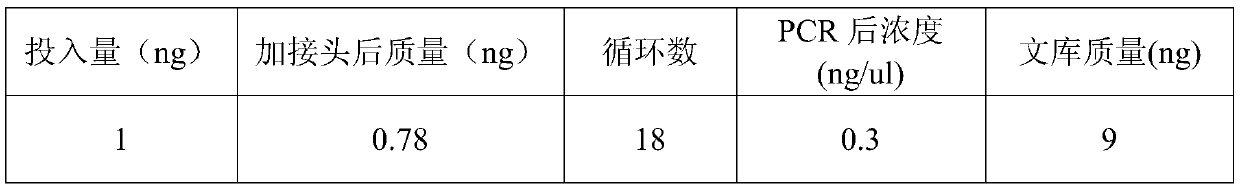
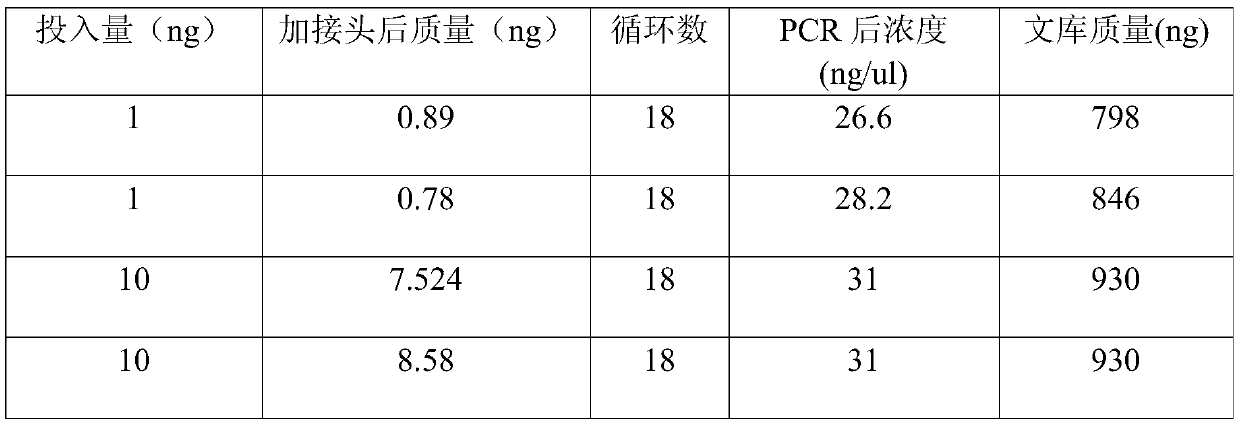
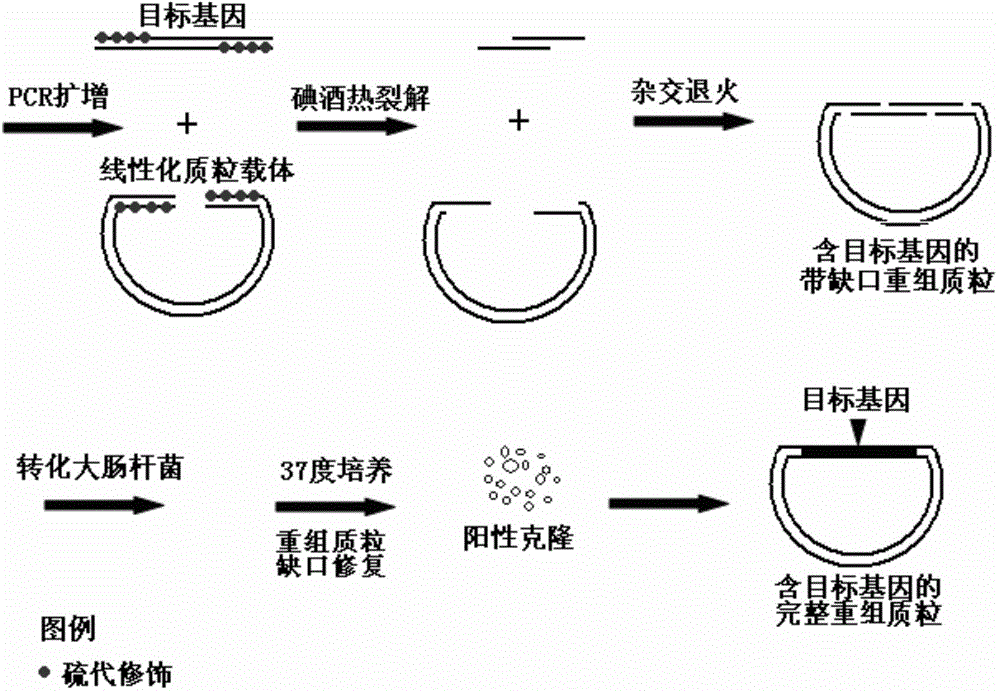
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
140 results about "DNA Ligases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Poly(deoxyribonucleotide):poly(deoxyribonucleotide)ligases. Enzymes that catalyze the joining of preformed deoxyribonucleotides in phosphodiester linkage during genetic processes during repair of a single-stranded break in duplex DNA. The class includes both EC 6.5.1.1 (ATP) and EC 6.5.1.2 (NAD).
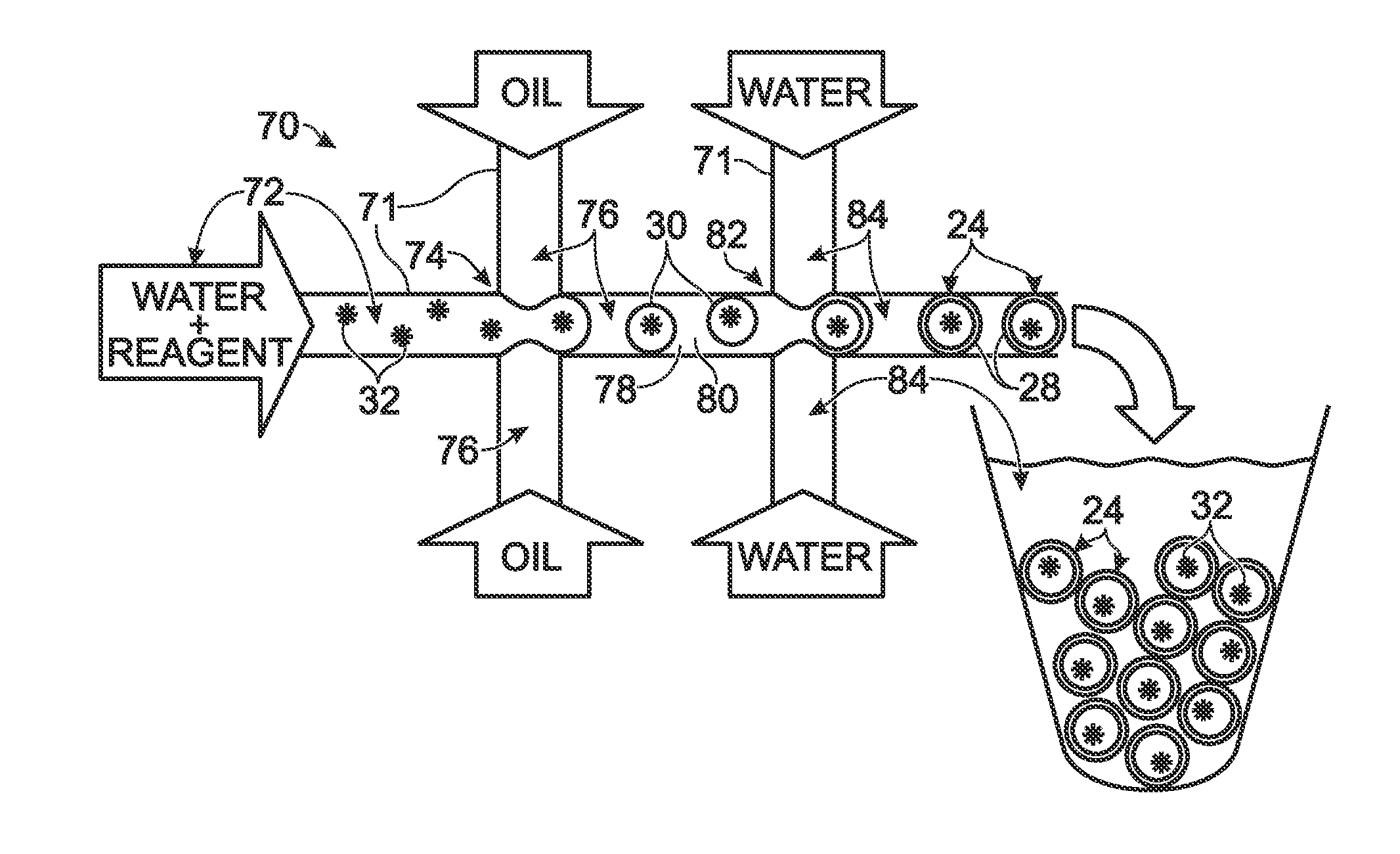
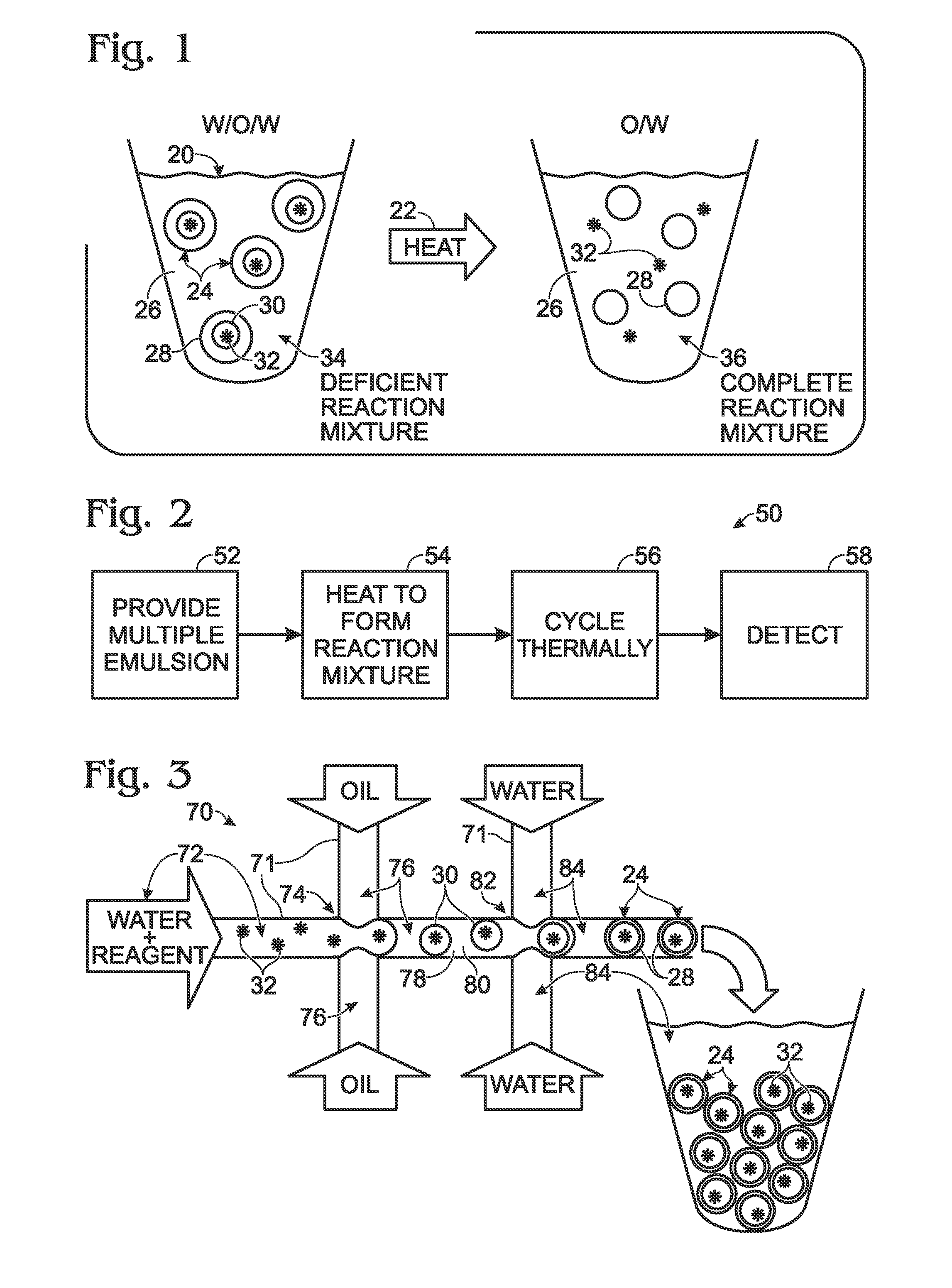
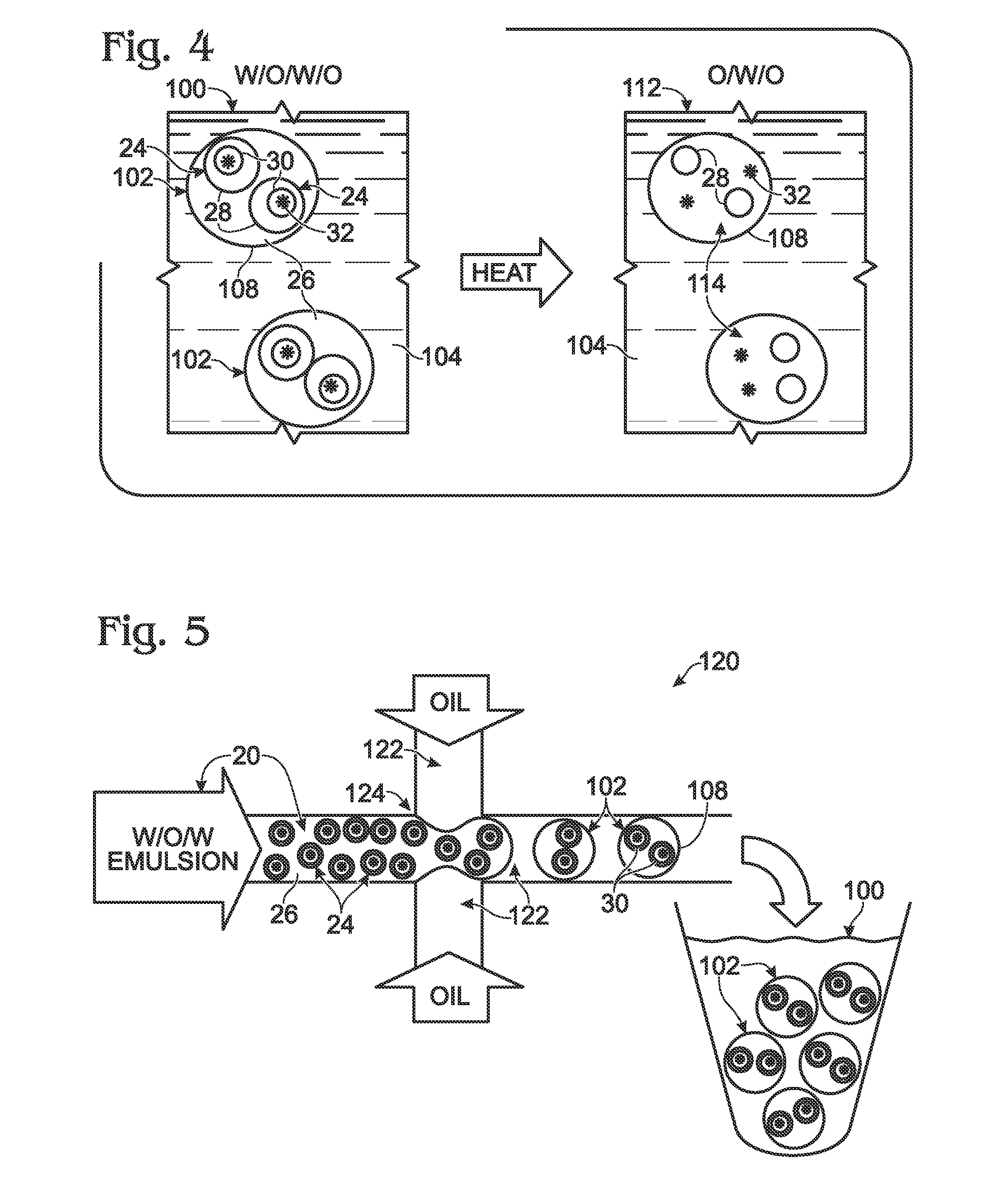
System for hot-start amplification via a multiple emulsion
System, including methods, apparatus, compositions, and kits, for making and using compound droplets of a multiple emulsion to supply an amplification reagent, such as a heat-stable DNA polymerase or DNA ligase, to an aqueous phase in which the compound droplets are disposed. The compound droplets may be induced to supply the amplification reagent by heating the multiple emulsion, to achieve hot-start amplification.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
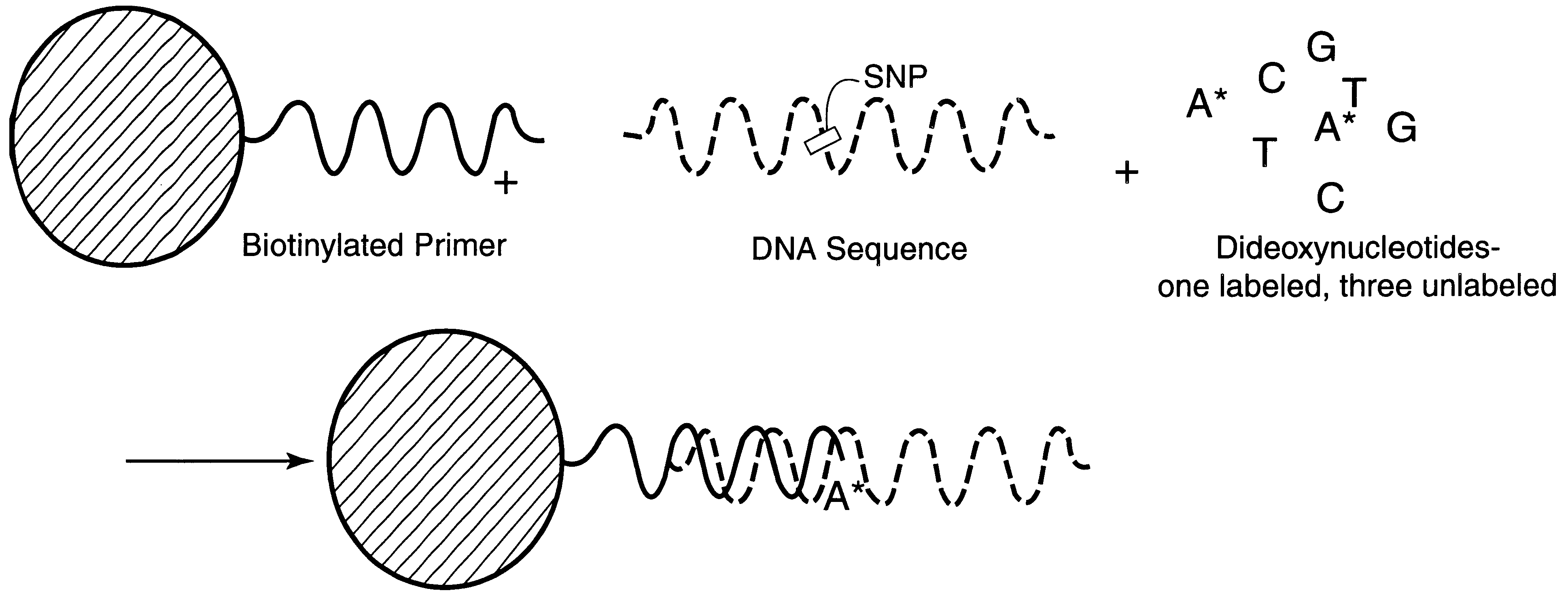
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry
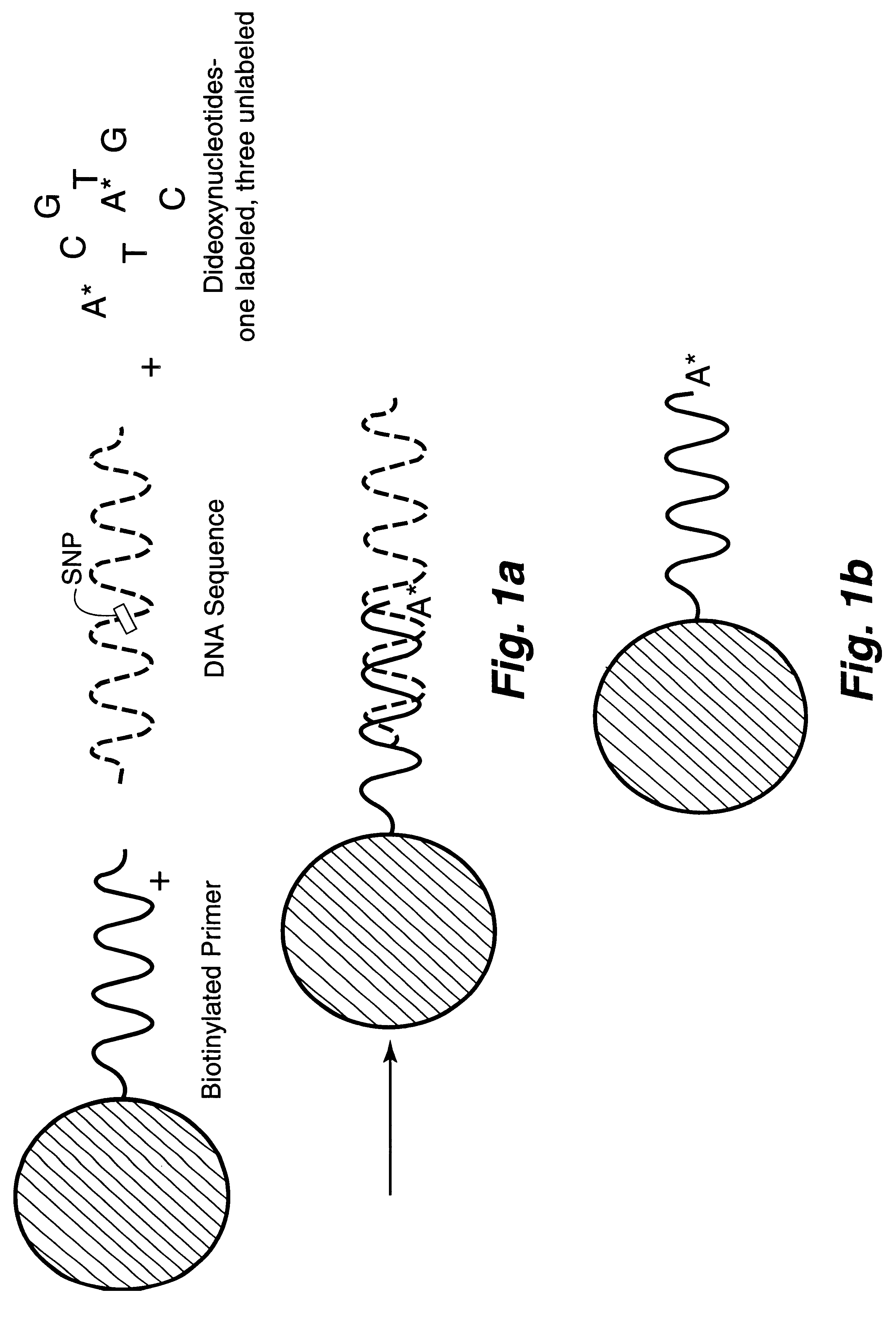
InactiveUS6287766B1Sensitive, homogenous, and flexibleSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereDideoxynucleotide Triphosphates
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry. Primers designed to be immobilized on microspheres are allowed to anneal to the DNA strand under investigation, and are extended by either DNA polymerase using fluorescent dideoxynucleotides or ligated by DNA ligase to fluorescent reporter oligonucleotides. The fluorescence of either the dideoxynucleotide or the reporter oligonucleotide attached to the immobilized primer is measured by flow cytometry, thereby identifying the nucleotide polymorphism on the DNA strand.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
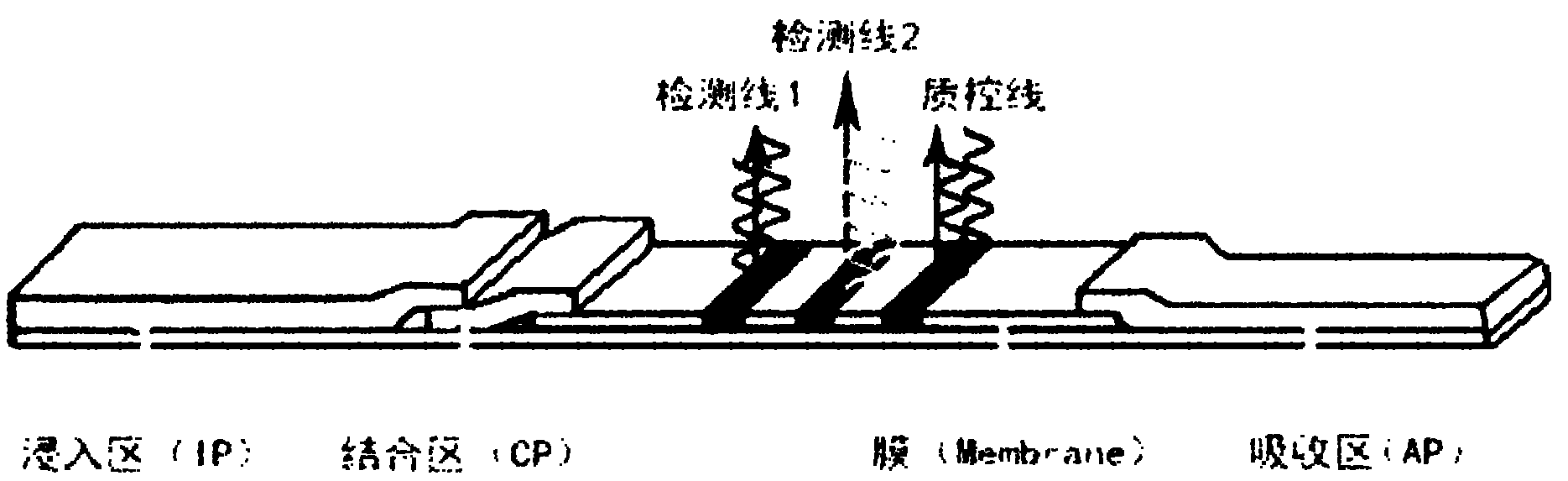
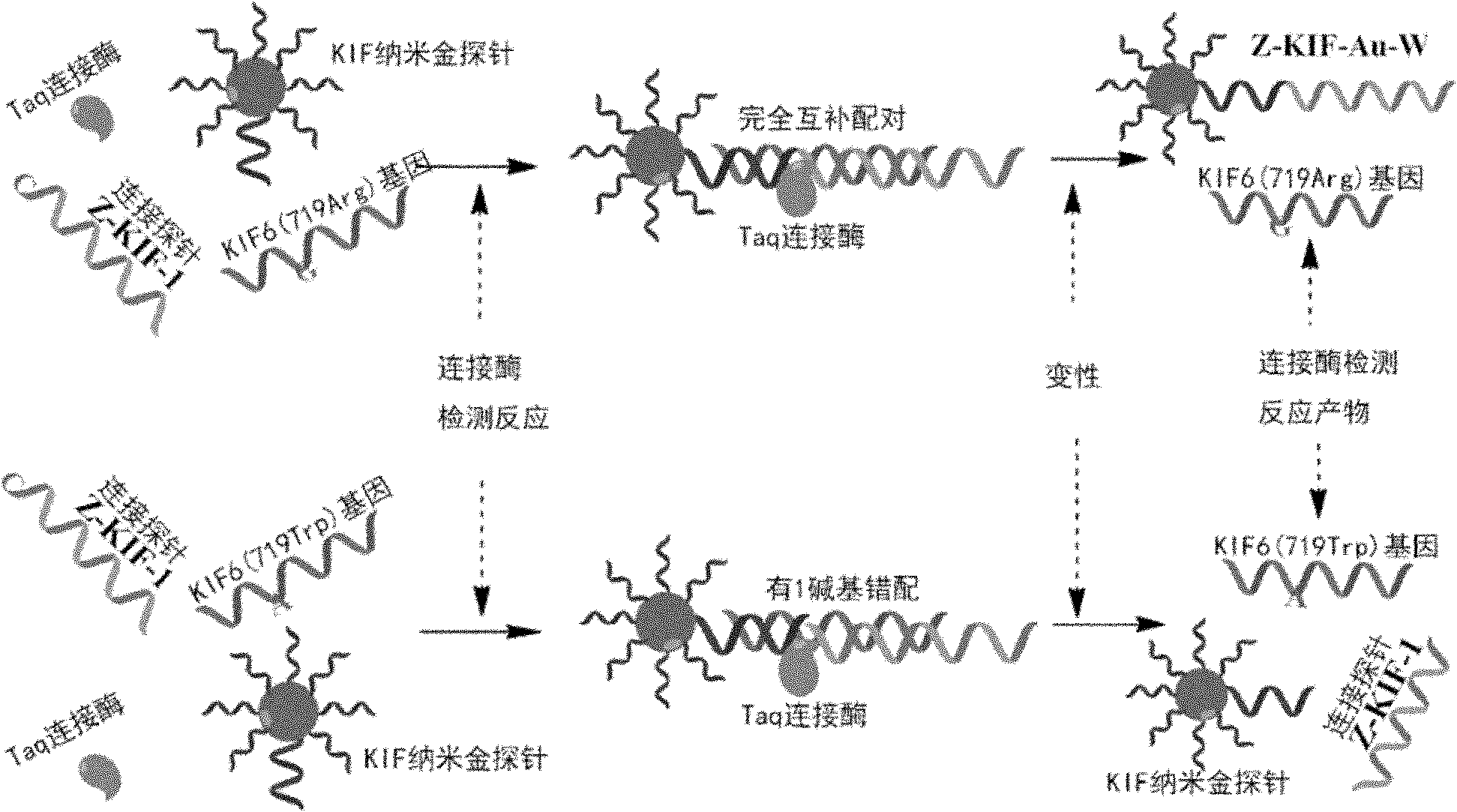
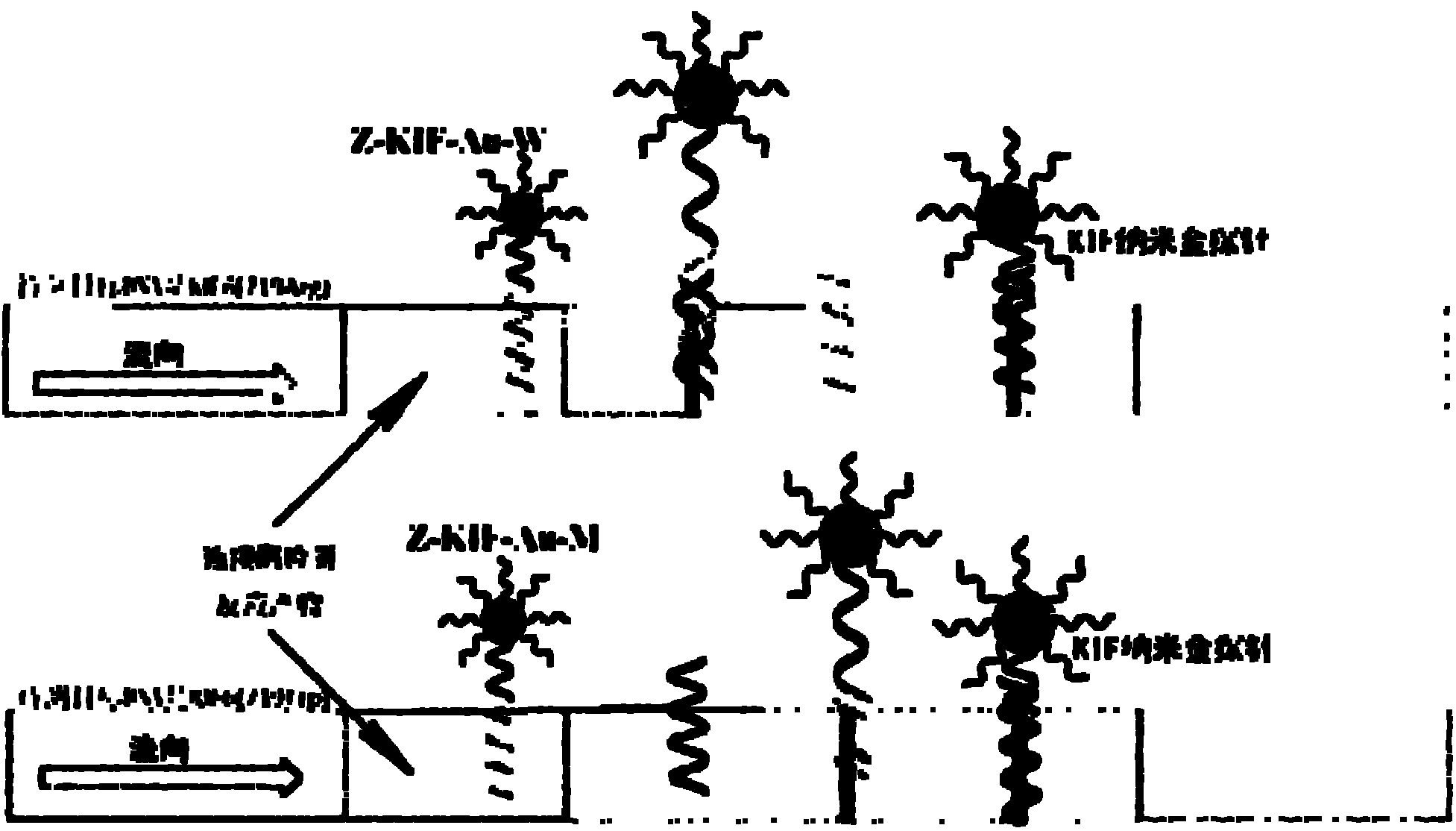
Nucleic acid cross flow test strip-based method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism
ActiveCN102134596AThe result is accurateMeet the requirements of clinical testingMicrobiological testing/measurementGene typeBuffer solution
The invention relates to a nucleic acid cross flow test strip-based method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism, comprising the following steps: firstly, preparing the nucleic acid cross flow test strip; secondly, obtaining a sample to be tested, denaturing and annealing; obtaining water, a nano-gold probe solutions, a connecting probe, Taq DNA ligase buffer solutions and Taq DNA ligase, and blending uniformly to obtain a mixed solution; adding KIF-1 and KIF-2 or the mixed solution of the two to the mixed solution, and blending uniformly; adding the sample to be tested, carrying out hybrid connection, denaturing, and annealing; and finally dropping obtained solutions on the binding area of the nucleic acid cross flow test strip, immersing the immersion area of the test strip into the running buffer solutions, and observing. The method achieves easy operation and low cost, is characterized by specificity, fastness as well as high resolution and sensitivity, and can be applied to the detection on the single nucleotide polymorphism and gene type as well as the identification on different pathogenic microorganisms of genes in hereditary diseases, communicable diseases, tumour and angiocardiopathy in clinical medicines.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and reagent kit for constructing BRCA 1/2 (breast cancer susceptible genes 1/2) detection libraries
InactiveCN106987905AReduce purification operationsReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSingle strandDNA polymerase
The invention discloses a method and a reagent kit for constructing BRCA 1 / 2 (breast cancer susceptible genes 1 / 2) detection libraries. The method includes carrying out fragmentation and tail-end repair on homogenized DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) samples in DNA fragmentation and tail-end repair systems under the effects of interruption enzymes and tail-end repair enzymes; linking products obtained at the previous step with linker sequences under the effects of DNA ligase; utilizing linker linking products obtained at the previous step as templates and carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by the aid of primers of linker sequences under the effects of DNA polymerases; hybridizing probe sequences with BRCA 1 / 2 and products obtained at the previous step to trap DNA fragments with the BRCA 1 / 2 and carrying out elution to obtain hybridization trapped products; carrying out cyclization on single strands of the hybridization trapped products under the effects of ligase to obtain the BRCA 1 / 2 detection libraries. The method and the reagent kit have the advantages that steps for constructing the libraries are simple, convenient and speedy, the cost can be effectively reduced, workload can be relieved, and variation types are comprehensive and accurate and are high in flux.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +3
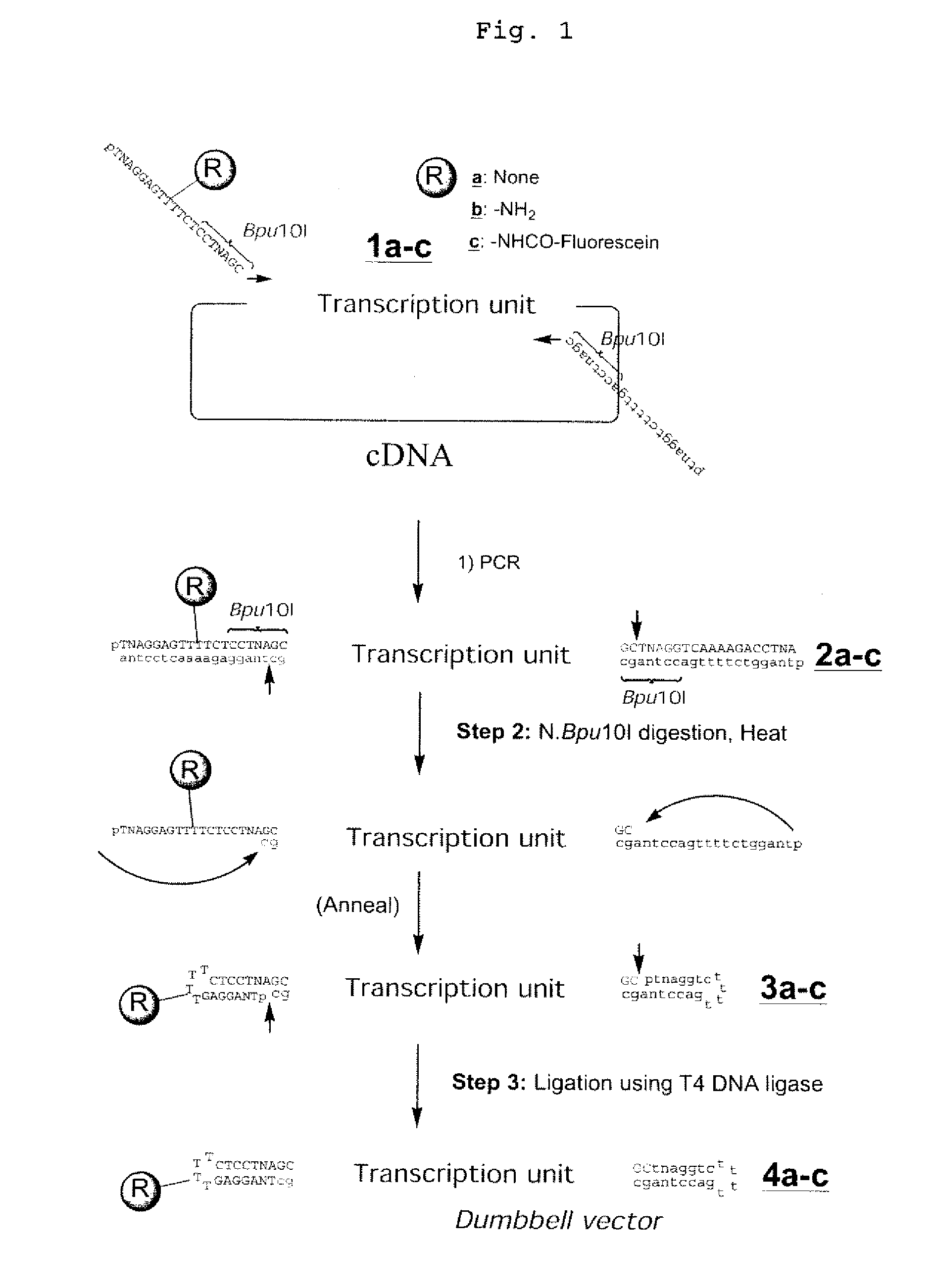
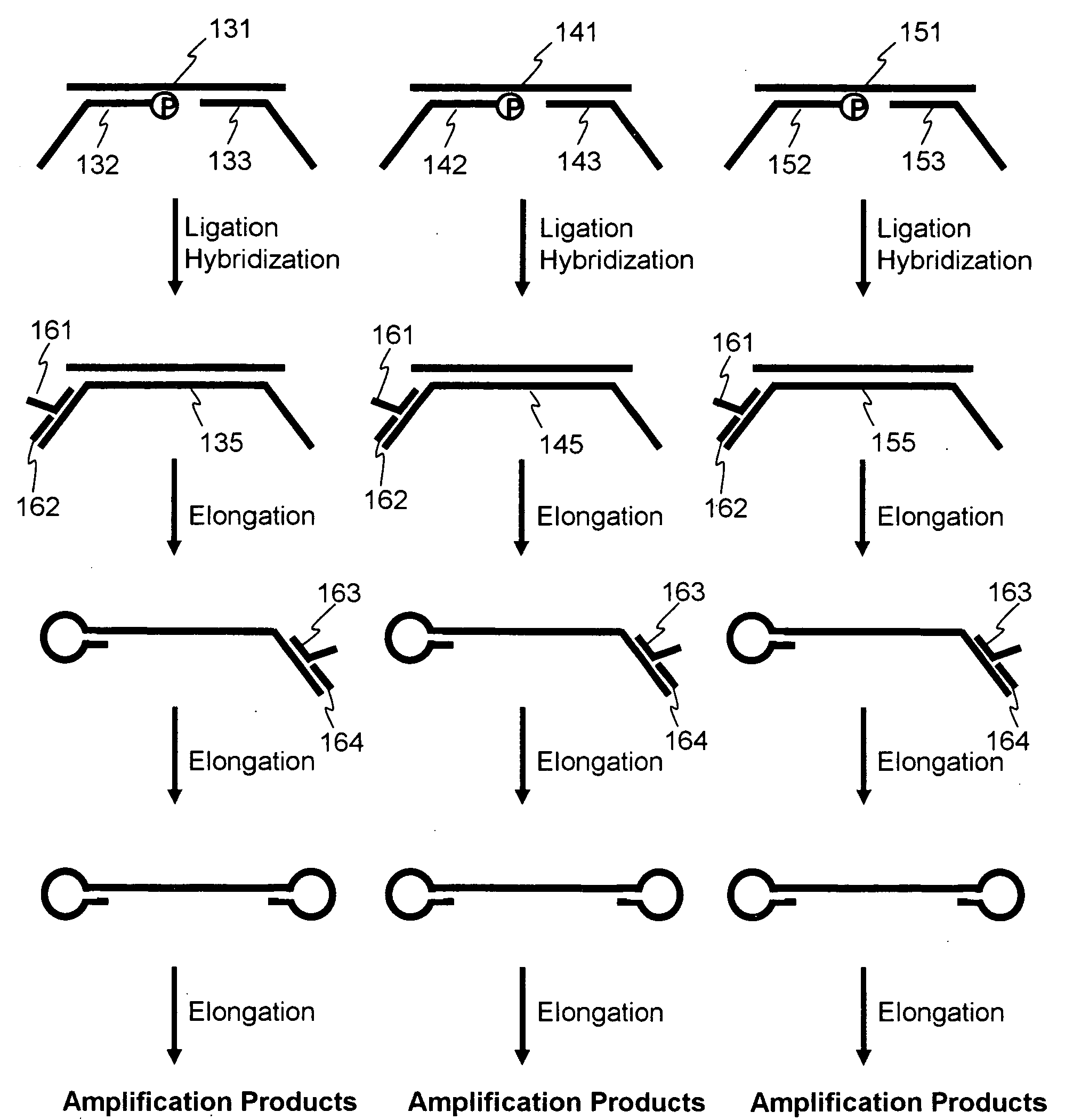
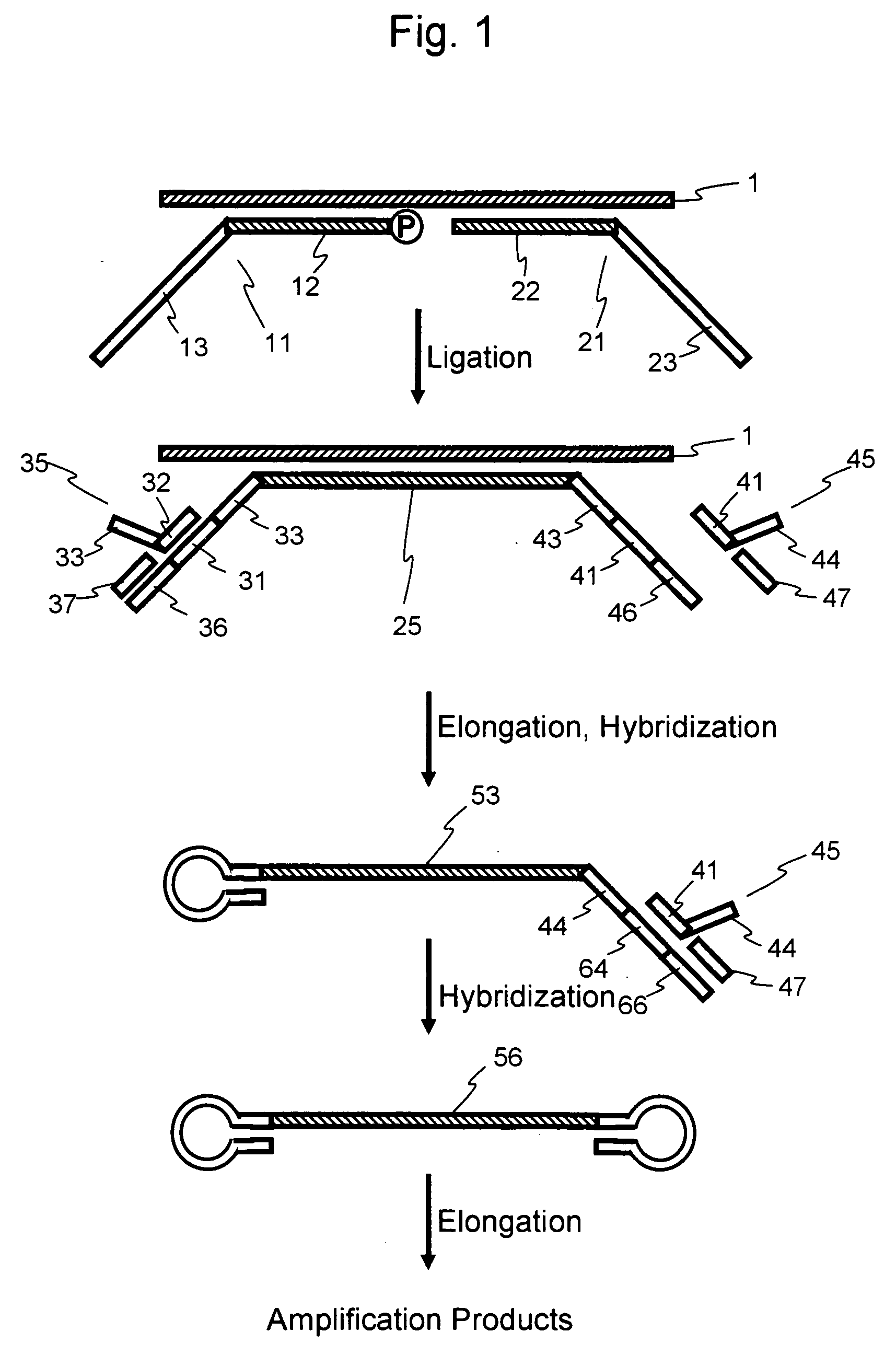
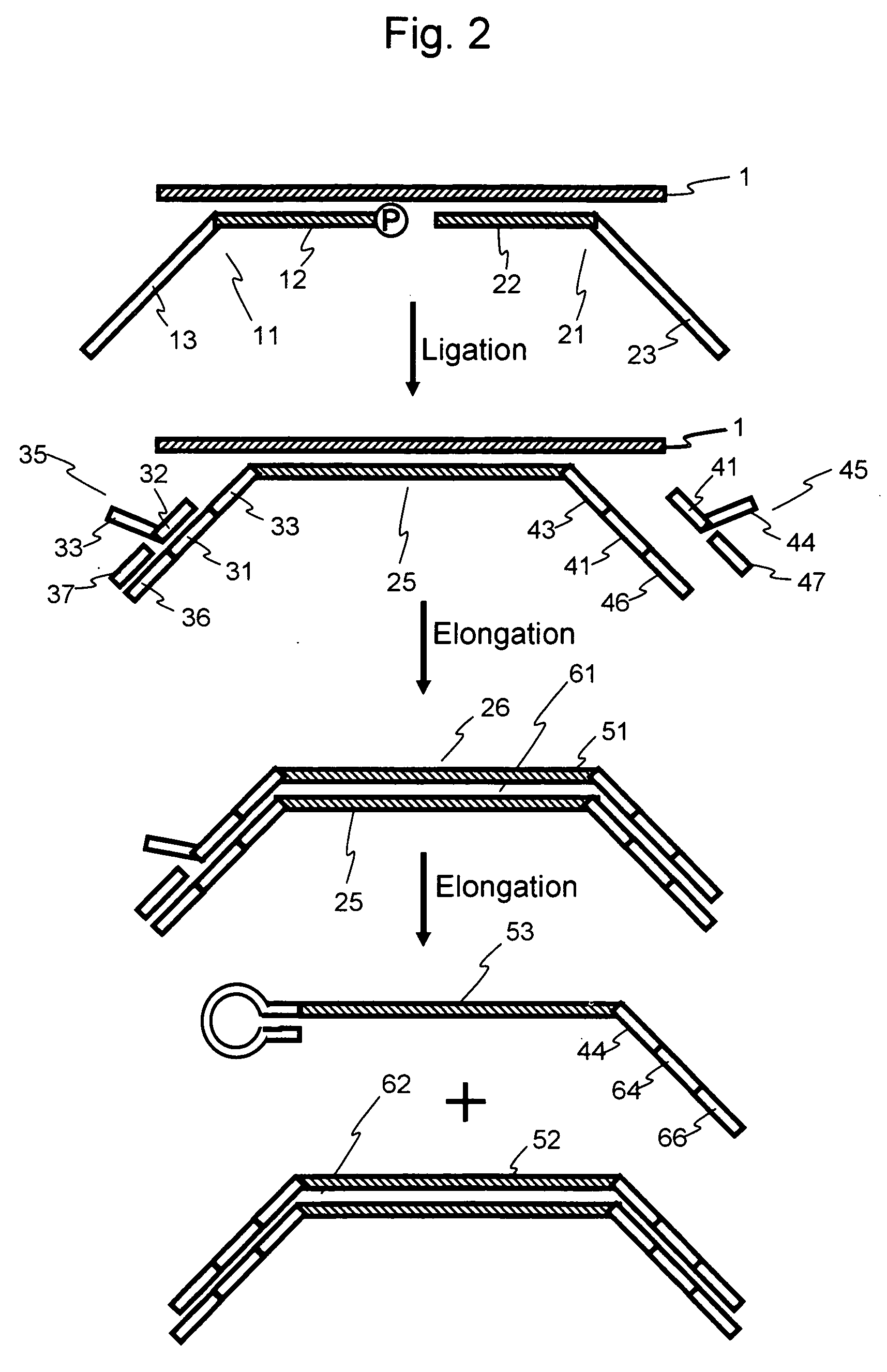
Efficient Process For Producing Dumbbell Dna
InactiveUS20080153763A1Simple methodOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPhosphorylationAmplification dna
The present invention provides a simple method for producing a dumbbell-shaped DNA.A method for producing a dumbbell-shaped DNA, wherein each of sense and antisense strands is connected at both the 5′ and 3′ ends of a linear-shaped double stranded DNA by a single stranded DNA of loop structure, comprising the steps of;1) amplifying a target DNA in a template DNA by PCR using sense and antisense primers, wherein each of the sense and antisense primers contains the following sequence (a) at the 5′ end and also contains the following sequences (b), (c), and (d) in order from the 5′ end to the 3′ end,(a) a part of a sense sequence of a nickase recognition sequence, comprising the sequence of a region between the site where a nick is introduced by the action of a nickase and the 3′ end,(b) a sequence capable of forming a loop structure from a single strand,(c) the entire antisense sequence of the nickase recognition sequence (a),(d) a sequence complementary to all or part of the sequence of the target DNA;2) treating the amplified DNA product of step 1) with a nickase of (a);3) heating and then annealing the nickase treated amplified DNA product of step 2); and4) treating the heated and annealed amplified DNA product of step 3) with DNA ligase, wherein the sense and antisense primers used in step 1) are phosphorylated at the 5′ end, or the amplified DNA product is phosphorylated at the 5′ end after step 1) but before step 4).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Hi-C high-throughput sequencing and database building method for eukaryote DNA
ActiveCN105839196ACyclization efficiency is lowLow effective data rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationAdditive ingredientPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a Hi-C high-throughput sequencing and database building method for eukaryote DNA. According to the DNA-cell-nucleuse intramolecular cyclization step, end-repaired DNA and a cyclizing system are mixed, incubated for 2 h-4 h at the temperature of 4 DEG C to 6 DEG C and then incubated for 4 h-6 h at the temperature of 16 DEG C to 22 DEG C, and materials obtained after intramolecular cyclization are obtained, wherein the ingredients of the cyclizing system comprise T4 ligase damping liquid, BSA, T4 DNA ligase and at least one polyethylene glycol selected from PEG 4000 and PEG 6000. By means of the Hi-C high-throughput sequencing and database building method, the character cyclizing efficiency of DNA can be effectively improved, and the effective data rate obviously higher than that of a traditional method is obtained.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
DNA methylation detection probe, and detection method and detection kit thereof
InactiveCN103589777AImprove acceleration performanceGuaranteed SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA methylationFluorescence
The invention relates to a DNA methylation detection probe, and a detection method and a detection kit thereof. The detection probe comprises a 3' end and a 5' end which are complementary to methylated DNA, and a specific sequence used for initiating an HRCA reaction in the middle. If DNA to be detected is the methylated DNA, the DNA to be detected can be completely complementarily paired with the detection probe, and the 3' end and the 5' end of detection probe are linked under the action of a subsequent DNA ligase to form annular DNA; and if the DNA to be detected is unmethylated DNA, the DNA to be detected cannot be completely complementarily paired with the detection probe, and no annular DNA is formed. The annular DNA can quantitatively analyze the methylation degree of the DNA to be detected through the subsequent HRCA reaction and signal detection, and the HRCA has a signal 10<9>-time amplification capability, so the detection ultrahigh-sensitivity requirement is guaranteed. By using the probe, there is no need to use an expensive fluorescently-labeled probe or carry out PCR amplification in the detection process, so the detection cost is substantially reduced. The detection method has no enzyme site requirements on the methylated DNA, so the method can be widely applied.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
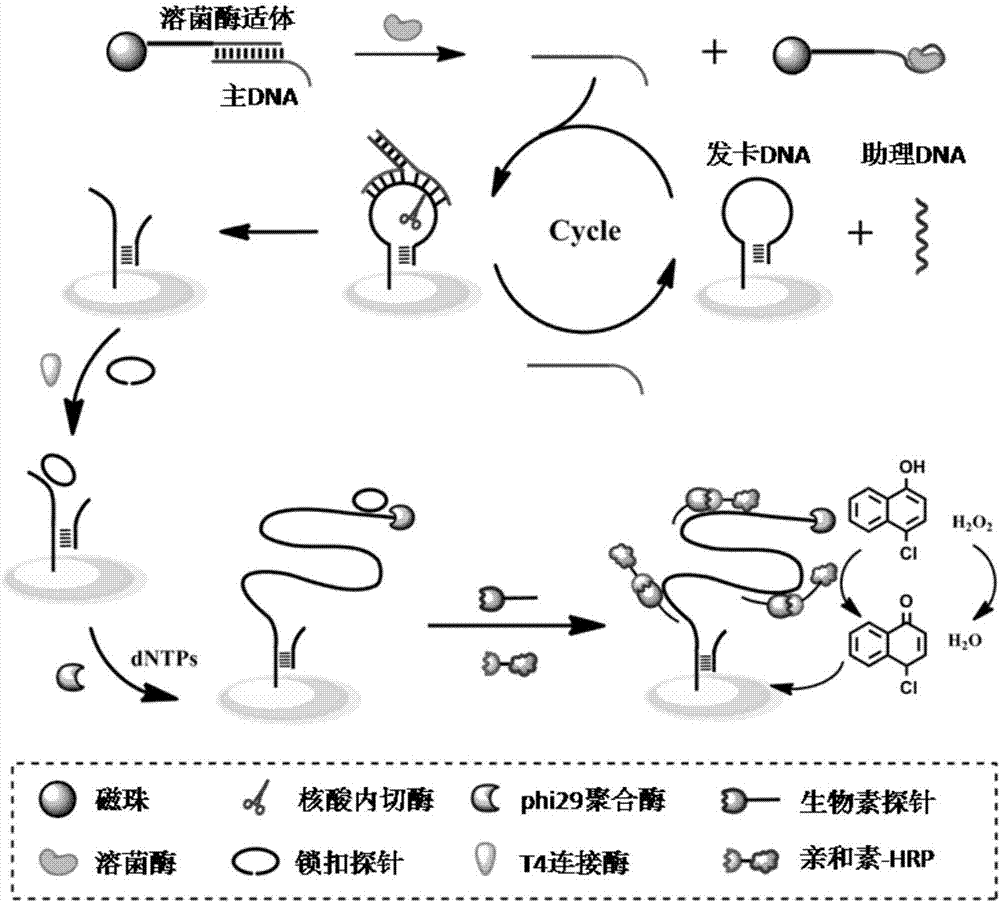
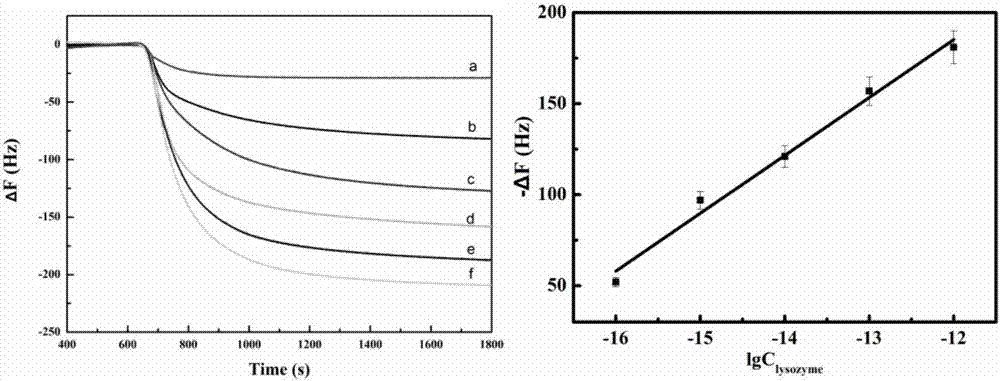
QCM detection method for detecting lysozyme based on multiple signal amplification technologies and application
InactiveCN107419005AEnhanced signalEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAptamerBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention discloses a QCM detection method for detecting lysozyme based on multiple signal amplification technologies and application. The QCM detection method comprises the following steps that DNA hybridizes with lysozyme aptamer partially in a complementary mode, and through the specific binding reaction of the lysozyme and the lysozyme aptamer, the DNA is released; a Y-shaped structure is formed by complementary hybrid of the released DNA with hairpin DNA and assistant DNA modified on a gold leaf, and under the action of restriction enzyme, the hairpin DNA is cut and opened through specific identification sites; under the action of DNA ligase and DNA polymerase, using locking-ring-shaped DNA as a template chain, polymerization growing along the opened hairpin DNA is carried out, and a single chain with a large number of repeated sequences is formed; a signal probe marked with biotin hybridizes with the generated repeated sequences in a complementary mode, and after binding with streptavidin marked by HRP, hydrogen peroxide is catalyzed to oxidize 4-chloro naphthol, and precipitation reaction is generated; and accordingly the chip surface quality is increased, and the high-sensitivity detection of the QCM to the lysozyme is realized.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Recombination and expression for non-antibiotic expression vector of rotavirus Vp6 gene and lactic acid bacteria
InactiveCN1952156AFight reinfectionImprove immunityVirus peptidesFermentationEscherichia coliRotavirus RNA
The invention belongs to the field of biological gene, disclosing the recombination and expression of a rotavirus Vp6 gene and Bacterium acidi lactic nonresistance expression vector and it is characterized in: digesting the cloning vector and vector taking thyA gene as a selection pressure using Sac I and KpnI, purifying and recovering, linking the products with T4 DNA ligase, transforming to thyA gene-deficient E. coli competence E. coli X13, culturing in the medium, and screening to obtain prokaryotic recombinant expression plasmid through growing functional redeem, inducing positive bacteria for expression using threonine to obtain high expression of the recombinant plasmid. Molecular weight of fusion protein is about 44.88 KD. Beneficial effects are: VP6 protein is RV-group-specific antigen, locating at the virus endoconch, occupying 51%of the virus particles. As VP6 mainly stimulates organism to generate mucosal immune antibody sIgA, it plays a very important role in the mucosal immune, thus advanced development of rotavirus Vp6 mediated gene oral mucosal immune genetically engineered vaccine has important significance.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +3
Sequencing library construction kit and using method and application thereof
ActiveCN109797436AImprove utilization efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementT4 polynucleotide kinaseOriginal data
The invention relates to the field of gene detection, in particular to a sequencing library construction kit and a using method and application thereof. The kit comprises restriction endonuclease, a buffer solution for a restriction endonuclease reaction, DNA ligase, a ligase buffer solution, a tail end repair reagent, a sequencing connector, a PCR primer and a PCR amplification system, wherein the tail end repair reagent comprises T4 polynucleotide kinase, T4 DNA polymerase, Klenow DNA polymerase, dNTPs and a repair buffer solution. The sequence of a genome obtained from the kit is largely derived from different positions (intervals of 500 bp or above) on an original genome, so that the utilization efficiency of original data can be improved by 150% or above when the kit is used for analyzing the copy number variation of the genome.
Owner:CARRIER GENE TECH SUZHOU CO LTD
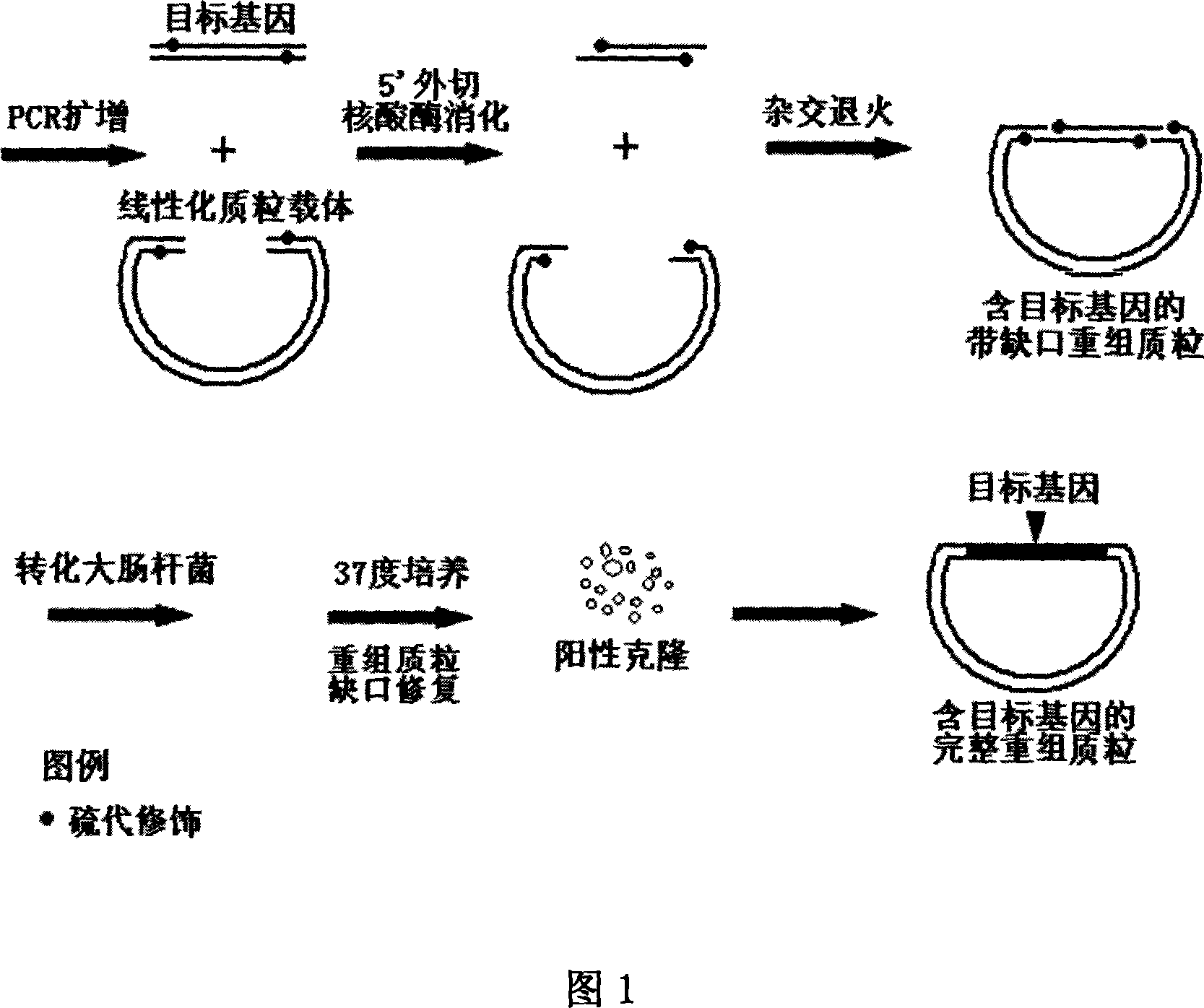
Non-dependent ligase gene cloning process based on thio-modification
The present invention relates to non-dependent ligase gene cloning process based on thio-modification. Each of the amplified target gene and the primer of the plamid vector has The 5' end thio-modified. The cloning process includes: PCR amplification of target gene and plamid vector and purification of PCR products; degrading DNA chain from the 5' end with 5' exonuclease and thio-modification to create 10-20 of 3' single chain raised ends of nucleoside; and direct transformation to colibacillus. The target gene cloning of the present invention has no dependence on restrictive endonuclease and DNA ligase and great operation flux, and may be used in large scale gene cloning.
Owner:苏州博睐恒生物科技有限公司
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid
InactiveUS20040191871A1Increase percentageFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotidePhosphoric acid
In accordance with the invention, there is provided a method for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising the steps: (a) preparing a cleared lysate of the host cells, wherein the cleared lysate comprises unligatable open circular plasmid, wherein the open circular plasmid is not 3'-hydroxyl, 5-phosphate nicked plasmid; (b) incubating the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes in the presence of their appropriate nucleotide cofactors, whereby the unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) incubating the 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid with DNA ligase in the presence of DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, whereby 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) incubating the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with DNA gyrase in the presence of DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, whereby relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. Preferably, the enzymatic steps (b), (c), and (d) are performed in a single step using an enzyme mixture comprising DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, and DNA gyrase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises a 3' terminus deblocking enzyme, such as exonuclease III or 3'-phosphatase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises one or more regenerating enzymes and a high energy phosphate donor, whereby the nucleotide by-products of the nucleotide cofactors generated by DNA ligase and DNA gyrase are converted to back to nucleotide cofactor. Preferably, the enzyme mixture further comprises one or more exonucleases, such as ATP dependent exonuclease, whereby linear chromosomal DNA is selectively degraded.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD DAVID
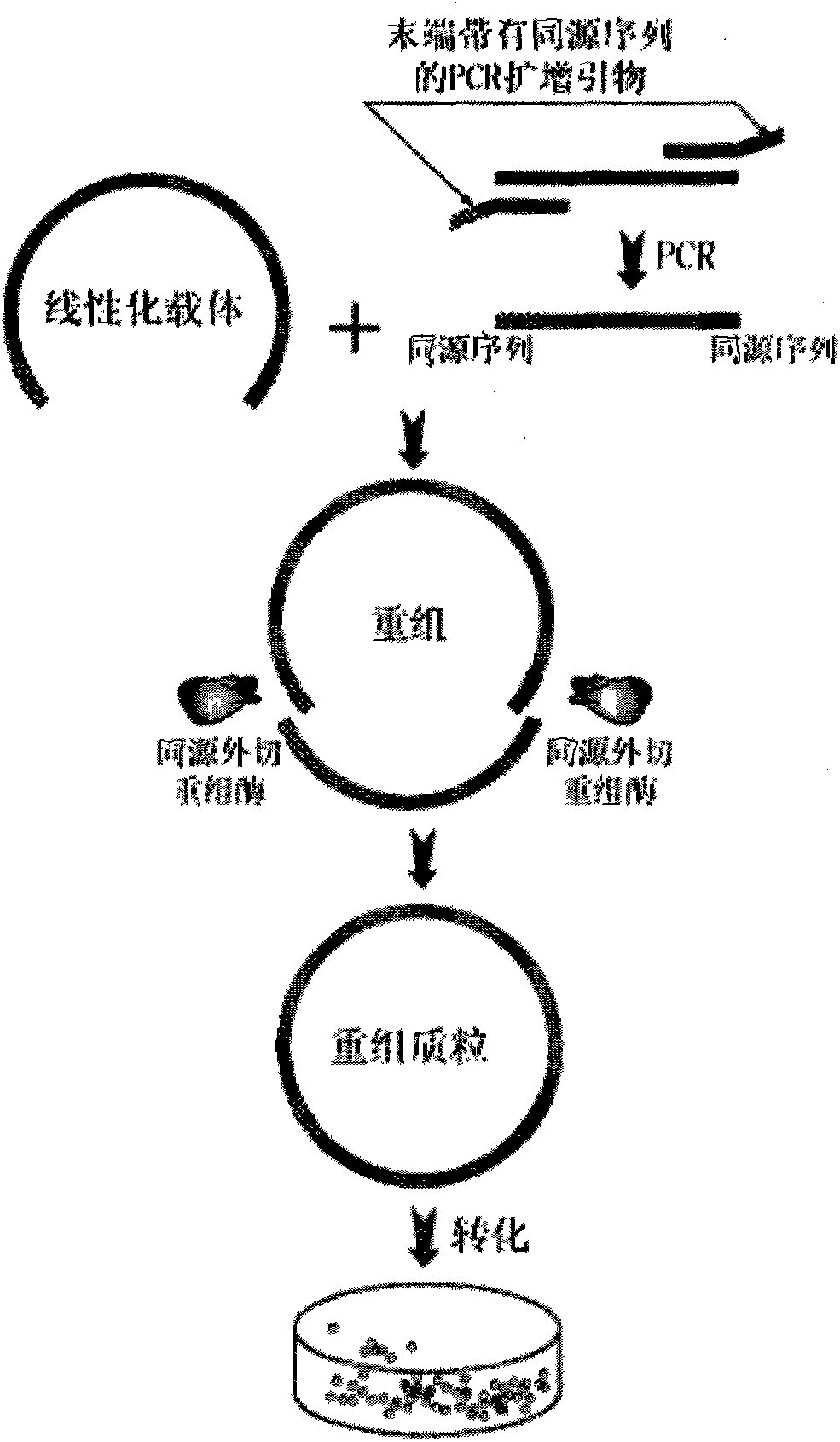
Method for inserting target DNA fragment into vector
InactiveCN101899467AFlexible choiceSolve efficiency problemsVector-based foreign material introductionDual effectDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for inserting a target DNA fragment into a vector. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) designing and synthesizing a primer for amplifying the target DNA fragment and amplifying by using the primer to obtain the target DNA fragment, wherein 3 to 20 bases on the outmost side of the primer are completely complementary with the outmost side of a linear vector; and 2) mixing the target DNA fragment and the linear vector, and adding a recombinant enzyme with the excision enzyme activity and the homologous recombination enzyme activity from ends 3' to 5' for reaction to obtain a recombinant vector into which the target DNA fragment is inserted. The method has the advantages of dual effects of excision and homologous recombination, more flexible selection for the number of bases at the recombinant ends by selecting the number of homologous bases of a PCR product and the linear vector in a wider range (namely 3 to 20 bases), no need of DNA ligase, linearization for the target vector only, no need of enzymatic treatment on the PCR product, direct mixing with a target vector, one-stop solution for all the problems within 20min, realization of perfect seamless connection, simple operation and low cost.
Owner:JIERUI BIOENG SHANGHAI
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid to supercoiled plasmid
InactiveUS20050084938A1Increase productionUniversal procedureHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateGenetics
In one embodiment of the invention, a method is provided for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising: (a) providing a plasmid solution comprised of unligatable open circular plasmid; (b) reacting the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes and appropriate nucleotide cofactors, such that unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) reacting the 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid with a DNA ligase and DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, such that 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) reacting the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with a DNA gyrase and DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, such that relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. In other embodiments, DNA gyrase is replaced by reverse DNA gyrase or reaction (d) is not performed.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD D
Method for constructing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencing library of to-be-detected genome and application thereof
InactiveCN107217309ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexDNA fragmentation
The invention provides a method for constructing a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencing library of a to-be-detected genome. The method comprises the following steps of (1) utilizing restriction enzyme to digest the to-be-detected genome, so as to obtain a digested product; (2) marking the digested product by biotin, so as to obtain a biotin-marked product; (3) linking the biotin-marked product by DNA ligase, so as to obtain a linked product; (4) decrosslinking the linked product; (5) purifying the decrosslinked product; (6) performing ultrasonic and precipitation treatment on the purified product, wherein the precipitation treatment is performed via contact between the ultrasonic product and streptavidin magnesphere so as to obtain a target DNA segment bonded with the streptavidin magnesphere; and (7) constructing the library on the basis of the target DNA segment bonded with the streptavidin magnesphere.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for constructing cDNA library
InactiveCN101377021AReduce usageIncrease success rateVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationCDNA libraryEscherichia coli
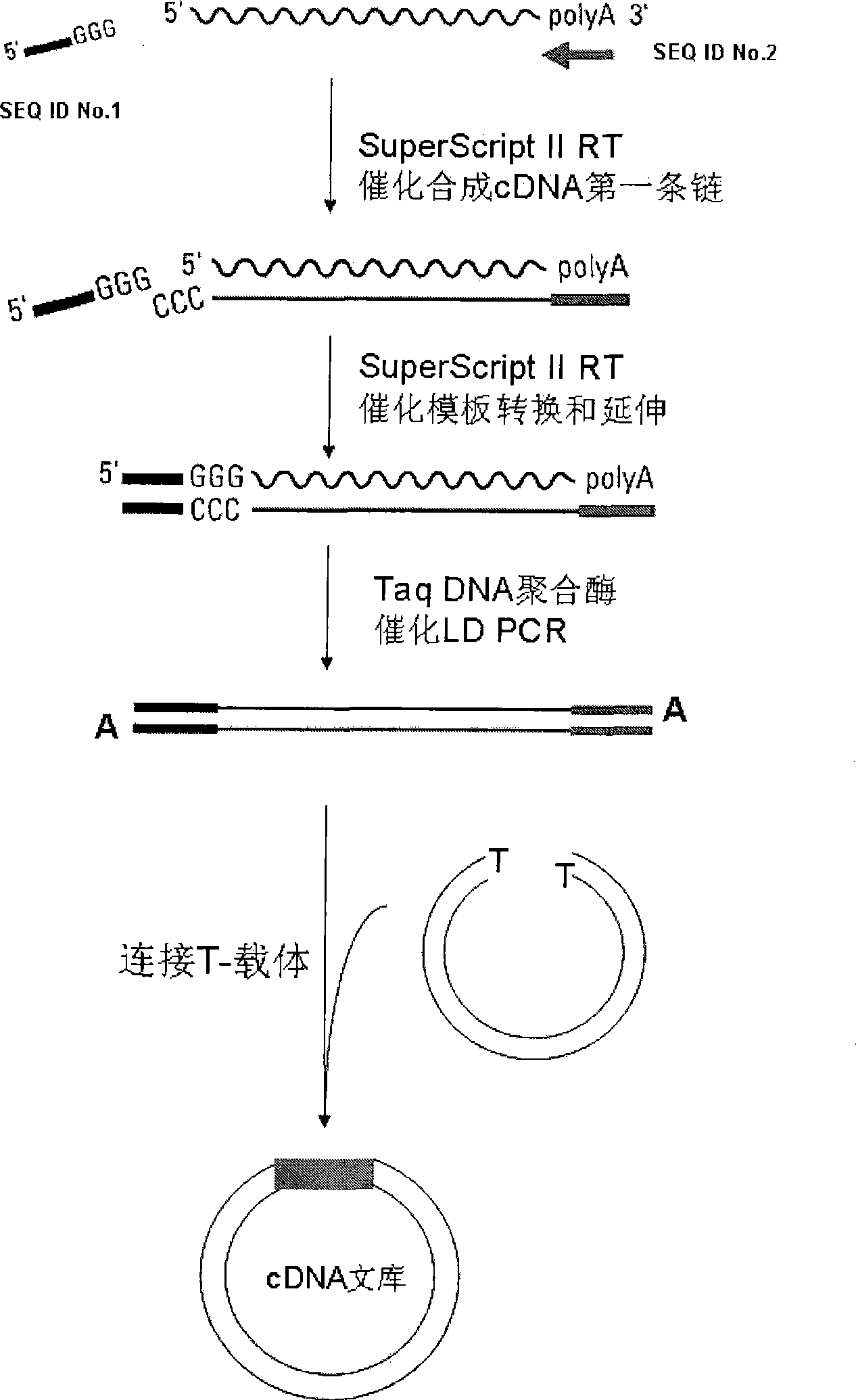
The invention discloses a method for building a cDNA library which is characterized in that the method is simple, quick and does not need endonuclease. The method essentially comprises the following steps: (1) a first cDNA chain is synthesized with general RNA (or mRNA) as the template through reverse transcription with the pair of primers. (2) a second cDNA chain is synthesized with the pair of primers through PCR catalyzed by Tap DAN synthetase. (3) the PCR product obtained in step (2) is directly connected with a T-carrier through DNA ligase, and then colon bacillus competence is converted to obtain the cDNA library. The method has very low cost in building the cDNA library, needs a very small number of RNA templates, and is applicable to biological sample RNA of any source.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Kit for testing schizophrenia related gene and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101985659ASimple and fast operationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDesign softwareNew england
The invention relates to a kit for testing a schizophrenia related gene and a preparation method thereof in the technical field of molecular biology. The kit comprises a PCR reagent group and a LDR reagent group, wherein the PCR reagent group comprises buffer solution, dNTP mixed solution, Taq DNA polymerase, pure water, and four pairs of amplification primers special for PCR, and the LDR reagent group comprises buffer solution, dNTP mixed solution, Taq DNA ligase, pure water, and four pairs of probes special for LDR. The method comprises the steps of: designing and synthesizing PCR primers by using the primer design software PRIMER3, choosing a TM value thereof about 60 degrees, designing and synthesizing the LDR probe which comprises two 5'end probes and a 3'end probe on each locus, and using TAKARA products or New England Biolabs products as the Taq DNA polymerase and the Taq DNA ligase. The invention can realize rapid, efficient and accurate parting for the specific SNP locus in the schizophrenia related gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fluorescent biosensor for detecting triphosadenine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109470673ARealize highly sensitive detectionLow detection limitFluorescence/phosphorescenceExonuclease IExonuclease III
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a fluorescent biosensor for detecting triphosadenine based on rolling circle amplification and incision enzyme feedback amplification. The biosensor comprises two aptamer DNA sequences, a linear padlock probe, a connecting probe, an AP probe, a T4 DNA ligase buffer solution, exonuclease I, exonuclease III, a PBS buffer solution, dNTP, phi29 DNA polymerase and endonuclease IV. A preparation method of the fluorescent biosensor comprises the following steps: (1) constructing an annular template to prepare a compound probe; and (2) combining a compound probe with an incision enzyme and a target object to achieve signal amplification. The probe can be used for achieving detection of high specificity and ultra-sensitivity. The fluorescent biosensor is mild in reaction, fast to detect and good in repeatability.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Immune PCR reagent kit for detecting avian leukemia virus
InactiveCN105779649AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAntigenOrtho position
The invention belongs to the field of biological technical detection and particularly relates to an immune PCR reagent kit for detecting avian leukemia virus. The reagent kit comprises two antibody oligonucleotide probes, a coupled reaction solution, DNA ligase, protease, a Fast Master mixed solution and a Universal q PRC reaction solution. The immune PCR reagent kit uses a biotin-labeled avian leukemia virus preventing special antibody and a commercialized ortho-position connecting reagent, can detect avian leukemia virus antigen through immune PCR and can quickly detect the avian leukemia virus antigen in a high-throughout mode through the immune PCR without carrying out a complex nucleic acid extracting process on a sample. The immune PCR reagent kit for detecting the avian leukemia virus can be applied to clinical detection and purification of avian leukemia virus and will fill domestic and oversea correlated technique blank.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV +1
Method of simultaneously testing multiple gene DNA methylation and application thereof
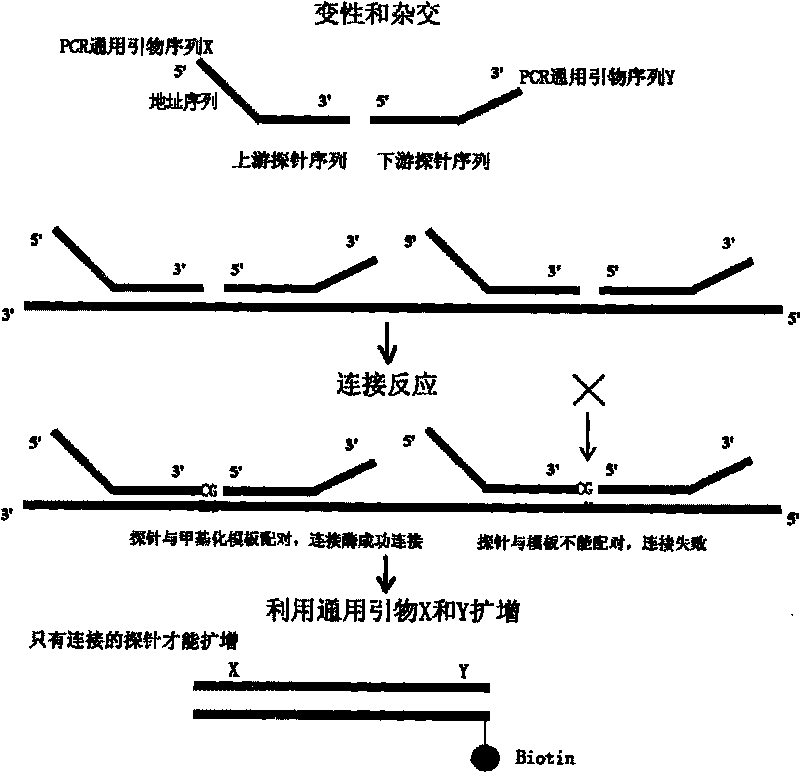
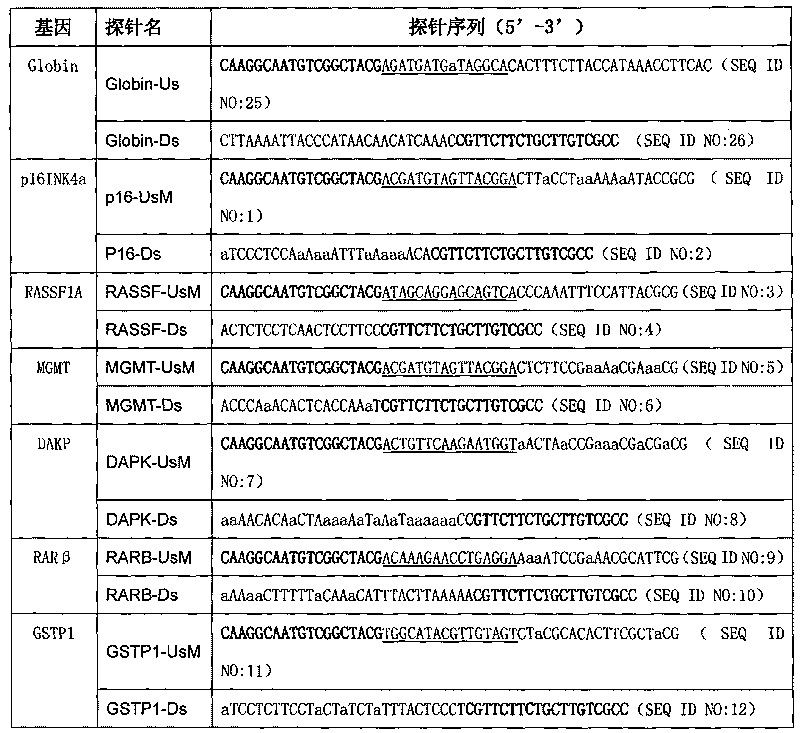
InactiveCN101701251AEasy to readImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationAnalysis data
The invention discloses a method of simultaneously testing multiple gene DNA methylation and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly using the sulfite method to treat a DNA to be tested, then modifying treated DNA to hybridize with a connecting probe, then performing a ligation under the action of DNA ligase, using a general primer to perform PCR amplification, mixing the product with fluorescent coding microspheres crosslinked with various inverse bar codes hybrid probes and reading analysis data with a liquid chip platform. The invention further discloses a kit designed through the method of the invention. The method of simultaneously testing multiple gene DNA methylation can be used for testing DNA methylation in high flux.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEST HOSPITAL
DNA ligase mutants
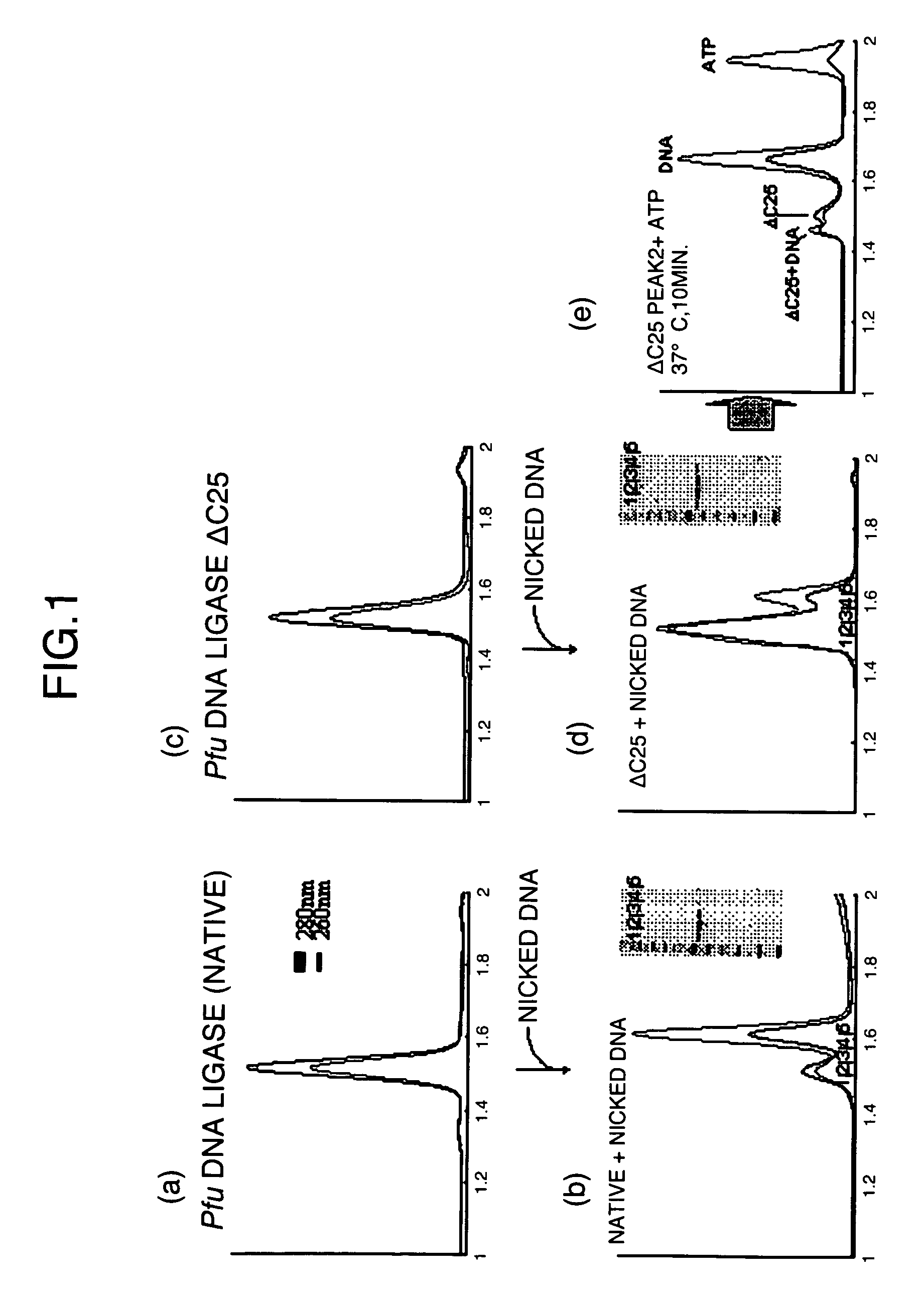
It is intended to obtain DNA ligase improved in binding ability and reactivity with DNA, particularly thermostable DNA ligase improved in binding ability and reactivity with DNA. The present invention provides a DNA ligase mutant improved in binding ability and reactivity with DNA, which is obtained by partially or completely deleting a C-terminal helix portion of DNA ligase. Particularly, the mutant is derived from a thermostable bacterium.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Preparation method of nucleic acid targeted capture sequencing library based on long chain molecule inversion probe
ActiveCN108396057AIncrease the lengthImprove capture efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationConnexonPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nucleic acid targeted capture sequencing library based on a long chain molecule inversion probe. The preparation method comprises the following steps:a, synthesizing a capture probe A, a capture probe B and a connexon C; b, adding phosphorylated probes A and B and the connexon C into a ligase reaction system, simultaneously adding DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) ligase so as to connect the A with the B under the bridging effect of the C; c, combining multiple connection mixtures for different target areas, and separating and purifying the connected product by denaturing electrophoresis or a nucleic acid purification kit to obtain the long chain molecular inversion probe; d, mixing the long chain molecular inversion probe with DNA or cDNA of ato-be-tested sample, hybridizing, adding DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, dNTP and a Mg2<+>-containing buffer solution into a buffer solution, extending the long chain molecular inversion probe and formingclosed molecules under the action of the DNA ligase; e, adding exonuclease to degrade non-cyclic DNA molecules; f) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using primers corresponding to a common sequence region of the long-chain molecular inversion probe to obtain the sequencing library of a targeted region.
Owner:CHONGQING CANCER INST
Preparation method of molecular tag
InactiveCN106119356AReduce wasteIncrease reaction rateMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction rateA-DNA
The invention relates to a preparation method of a molecular tag. The preparation method comprises the following steps: introducing a barcode sequence to a 5' adaptor terminal of a DNA molecular template; extending a 3' adaptor terminal by virtue of DNA polymerase, and complementing the 3' adaptor terminal with the barcode sequence, so that a complementary sequence is obtained; adding DNA polymerase to the complementary sequence, and introducing thymine to a 3' adaptor terminal of the complementary sequence, so that a modified adaptor is obtained; breaking to-be-detected DNA into DNA short segments, and linking the DNA short segments to the modified adaptor by virtue of DNA ligase, so that a DNA ligation product is obtained; amplifying the DNA ligation product by virtue of a polymerase chain reaction, so that an amplification product is obtained; and sequencing the amplification product, then contrasting the amplification product to a human reference genome, and selecting a DNA sequence, which has the minimum base error rate, from a plurality of DNA template copies, so that the molecular tag is obtained. The molecular tag technology, by changing a barcode length, can remove fixed sequences, reduce data waste in sequencing and accelerate a reaction rate, and wrong and actual DNA variations in a DNA amplification process can be effectively distinguished.
Owner:首度生物科技(苏州)有限公司 +2
Method for sensitively detecting human EGFR gene mutation based on enzyme digestion and reagent kit
ActiveCN105420361AGrowth inhibitionEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionMutation detection
In order to overcome defects of existing methods and reagent kits, the invention provides a method for sensitively detecting human EGFR gene mutation based on enzyme digestion and a reagent kit thereof, and belongs to the field of gene mutation detection. The method comprises the steps that heat-resisting DNA ligase and a specific connection primer set for a mutation site are introduced into an EGFR gene segment amplification system, a wild type sample can be directly determined on the basis of an amplified segment strip, or the proportion of a final PCR product of a low-mutation-content sample is made to be higher than 50%; then, a DNA segment hybridization sample containing a mismatched structure at the mutation site is prepared through denaturation and annealing, and therefore a heterozygosis gene segment sample can be effectively detected by means of a mismatched digestion enzyme. The method and the reagent kit can detect EGFR gene mutation with the content as small as 1% in the sample through enzyme digestion, and are high in accuracy rate, short in detection time, low in cost and suitable for clinical detection.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Nucleic acid amplification method
InactiveUS20080318282A1High sensitivitySimple and highly sensitive nucleic acidMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTarget geneHighly sensitive
Provided is a simple and highly sensitive nucleic acid amplification method including hybridizing two types of oligonucleotide probes with a target gene and ligating the oligonucleotide probes with DNA ligase and amplifying the resultant single-stranded oligonucleotide in accordance with LAMP.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
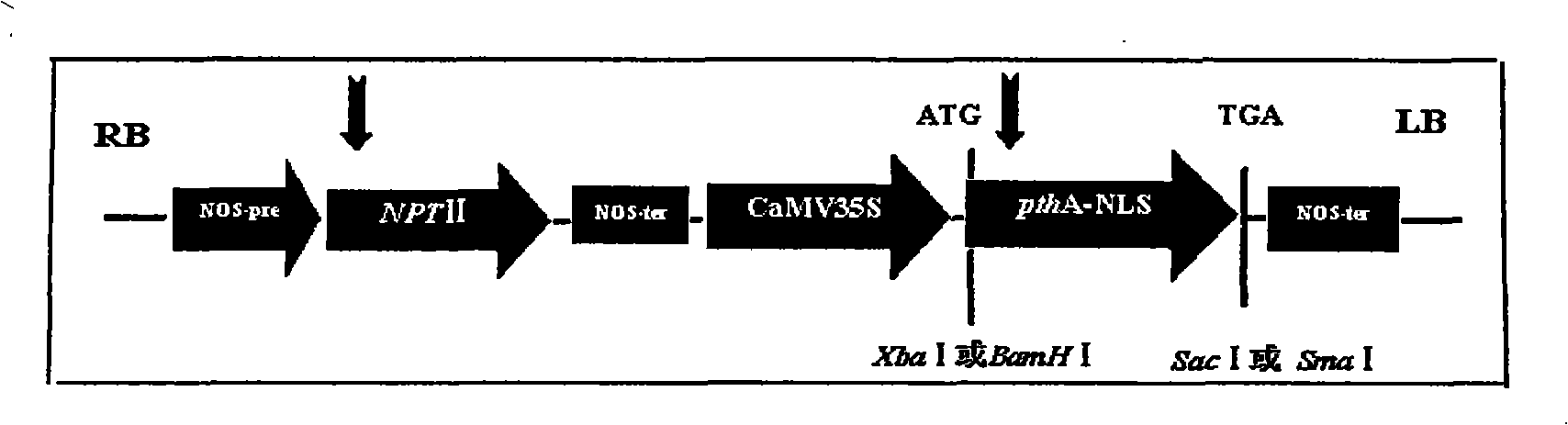
Orange canker resistant pthA-nls gene and its construction method and application
The invention provides an anti-citrus bacterial canker disease pthA-nls gene, a construction method and application thereof. The invention uses the pathogenic gene pthA-mediated broad-spectrum disease resistance theory of the citrus bacterial canker disease to construct a new anti-citrus bacterial canker disease gene (pthA-nls). The construction method comprises the following steps of: (1) primer design; (2) clone of NLS sequence; (3) recovery and enzyme digestion of PCR product; (4) double enzyme digestion of a plant expression vector; (5) connection between product of enzyme digestion of pBI121 and corresponding product of PCR enzyme digestion of the NLS sequence by T4 DNA ligase; (6) acquisition of positive cloned gene pthA-nls by converting ligation product into colon bacillus DH5alpha. The gene pthA-nls can further perform genetic transformation on susceptible varieties of orange so as to acquire new anti-citrus bacterial canker disease germ plasm. The anti-citrus bacterial canker disease pthA-nls gene provides an effective tool for breeding of anti-citrus bacterial canker disease.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
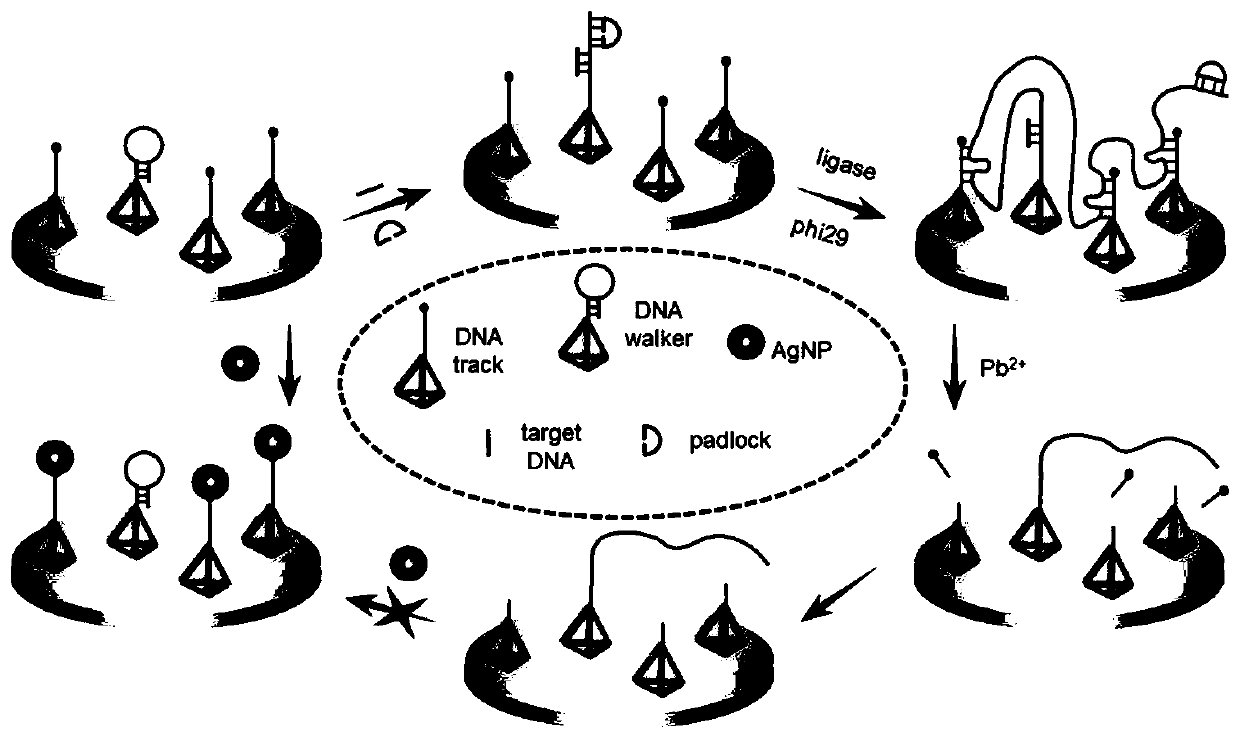
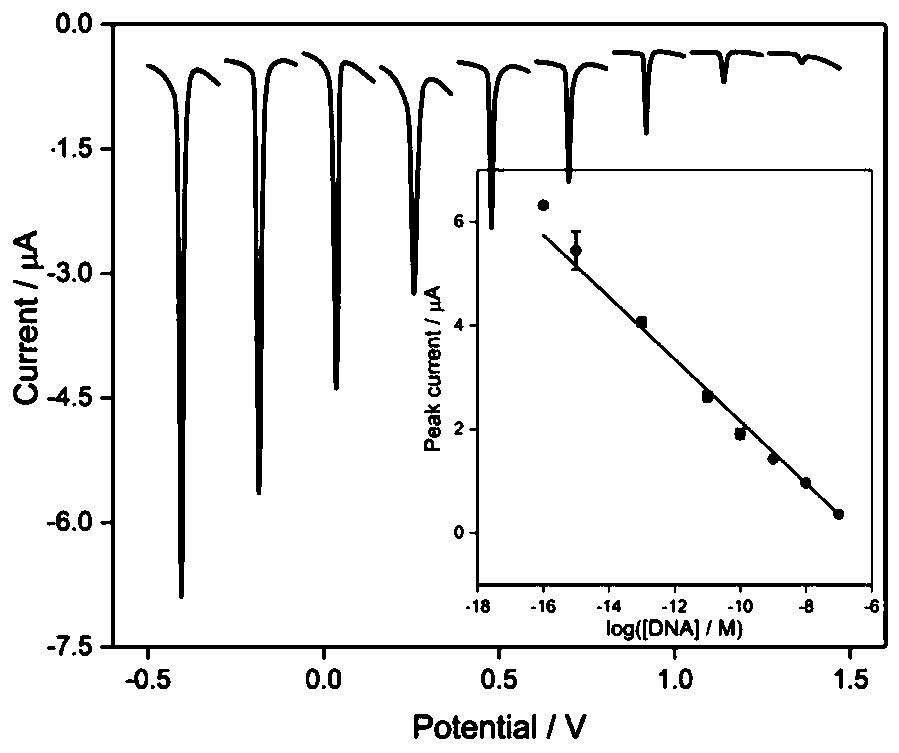
Electrochemical nucleic acid detection method based on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) walking and rolling circle amplification signal magnification
ActiveCN111172246AHigh sensitivityChanging the electrochemical signal strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionPhysical chemistry
The scheme of the invention relates to an electrochemical nucleic acid detection method based on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) walking and rolling circle amplification signal magnification. The method comprises the following steps: designing two DNA tetrahedrons, namely DNA walker and DNA track; immobilizing the DNA tetrahedrons on the surface of an electrode; adding a padlock probe into a sample tobe detected, inserting the electrode into the sample to be detected, and performing incubation; continuously adding DNA ligase and DNA polymerase into the sample to be detected, and performing a reaction; taking out the electrode, soaking the electrode into Pb<2+> at room temperature, performing a reaction, and finally performing incubation with silver nanoparticles; by taking the electrode as aworking electrode, and by using an electrochemical working station, recording a linear volt-ampere scanning curve by using a three-electrode system, detecting variation of volt-ampere current signals,and calculating the concentration of target nucleic acid. The detection method provided by the scheme of the invention is high in sensitivity, high in selectivity, simple and convenient to operate and low in detection cost.
Owner:天津国科医疗科技发展有限公司 +1
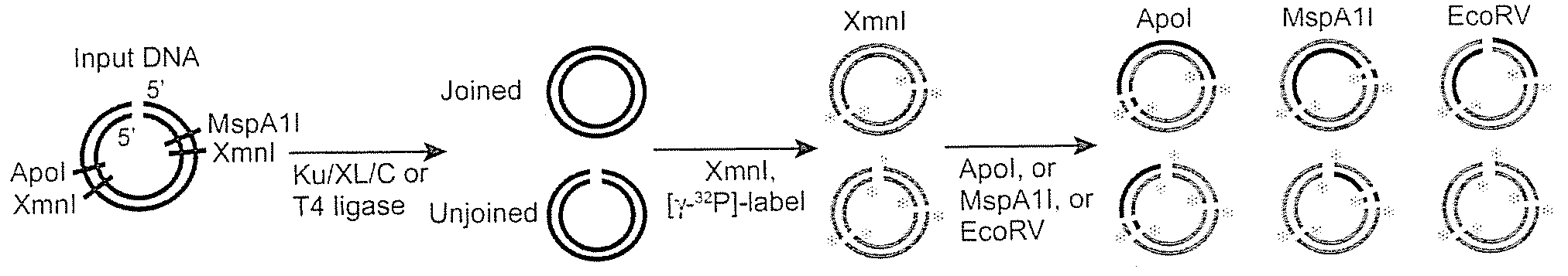
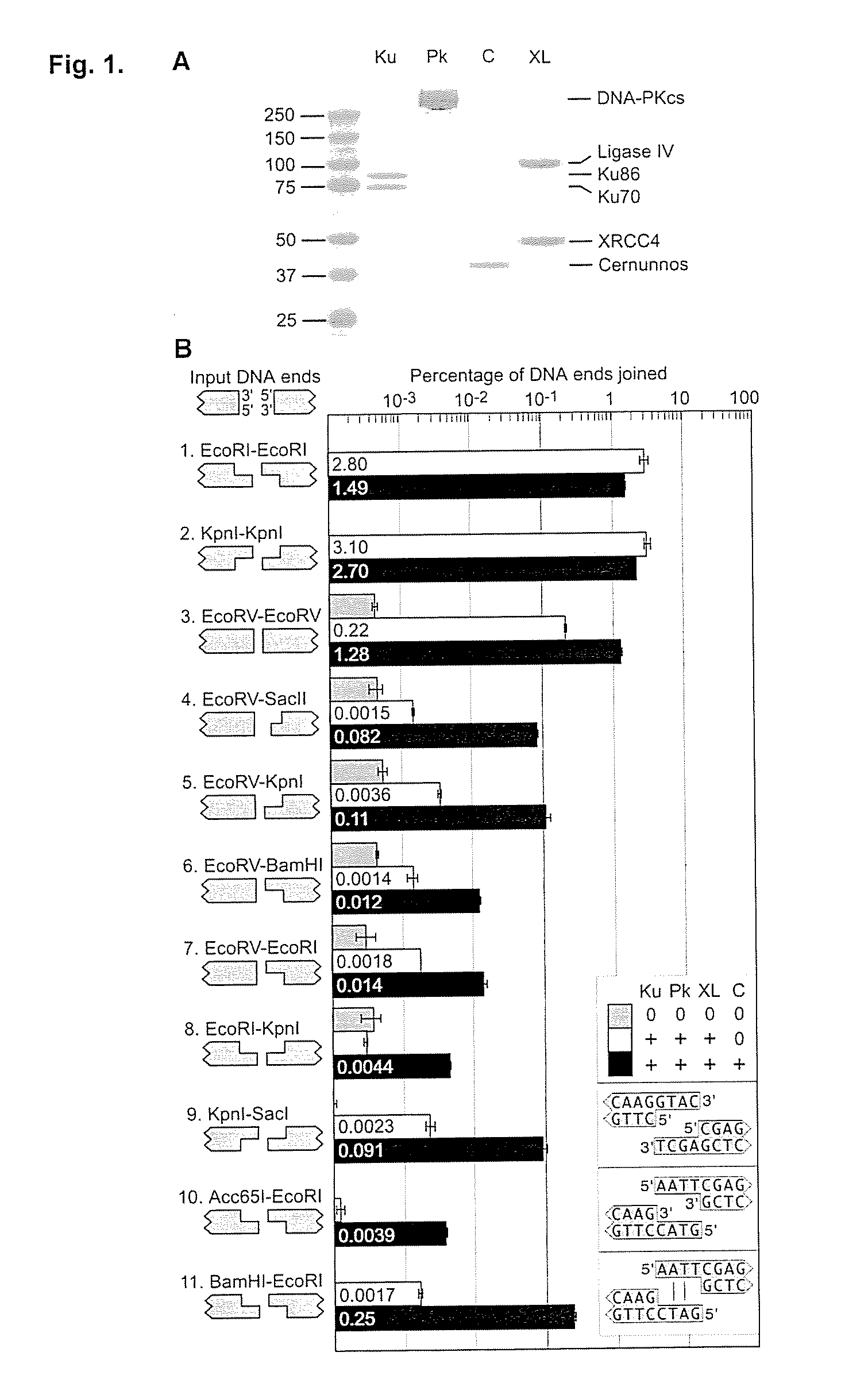
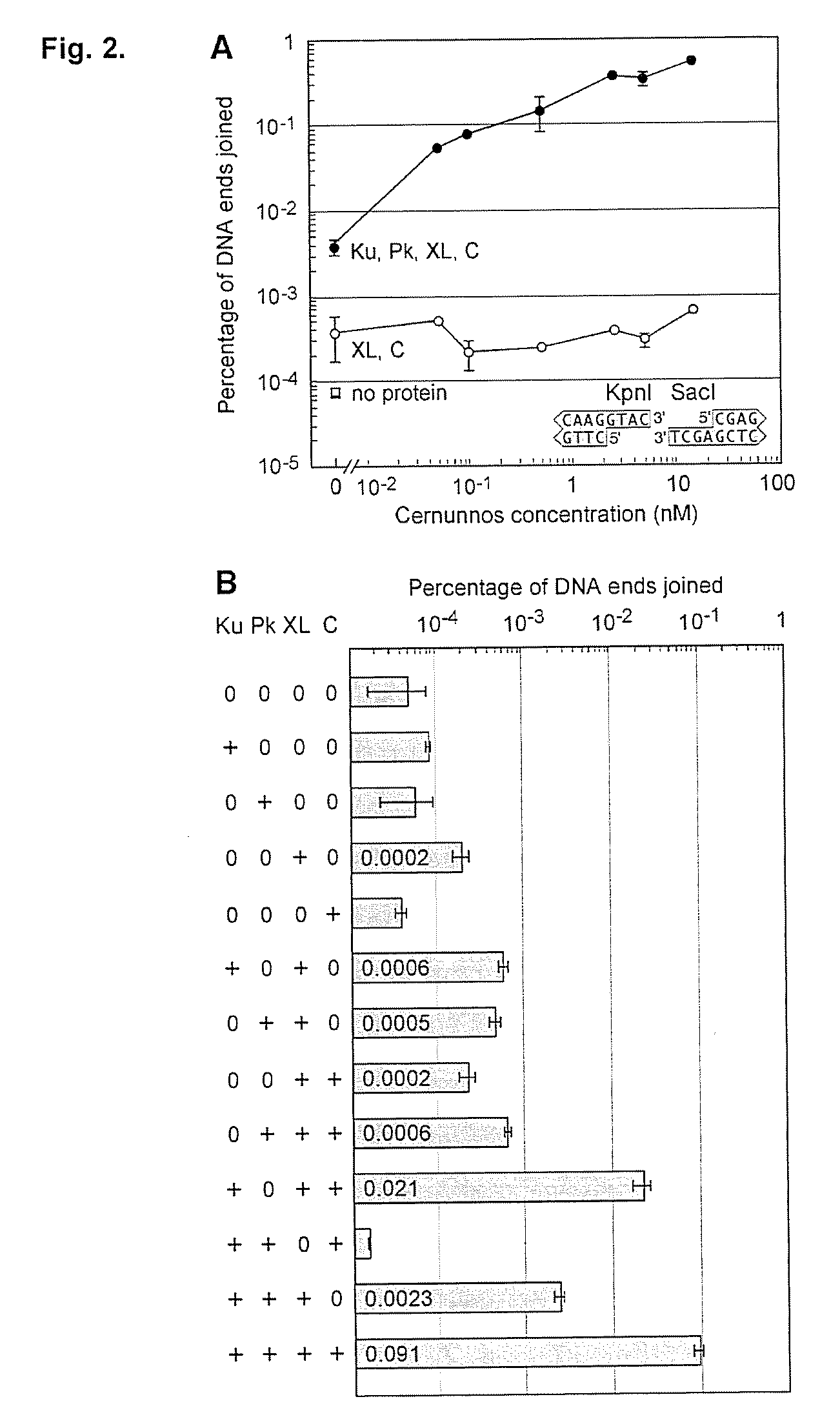
Mismatched end DNA ligase
InactiveUS20080160526A1Easy to keepHigh retention rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLigasesSingle strandBiology
A mismatched end DNA ligase is provided, which ligates two single strands to each other at a high efficiency, even if the other two single strands are not compatible. In one embodiment, the polypeptides of the ligase are Ku, Cernunnos, and XRCC4 / Ligase4 (XL). This association can ligate DNA ends with a 3′ overhang to a recessed 5′ end, to a blunt end, or to a compatible end. In another embodiment, the proteins are Ku, Cernunnos, XRCC4 / Ligase4 (XL) and DNA-PK.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Low-initial-quantity plasma free DNA methylation library-building kit and method
PendingCN110669824AAvoid damageReduce inputMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationEngineeringDNA damage
The invention discloses an enzymatic methylation library-building method. According to the method, through TET enzyme methylation treatment, DNA damage in the methylation library-building process is lowered to a certain extent, and thus the requirement for the input amount of DNA in a nucleic acid sample is lowered; besides, by further cooperating with a one-step reagent for terminal repair and Aaddition reaction, one-tube library building can be realized, and the purification step is reduced; and by further cooperating DNA ligase enhancing liquid, the connection efficiency can be improved, and the library-building quality and the sequencing quality are improved; and the method provided by the invention is low in library-building initial quantity, the DNA input amount can be as low as to1 ng, and the method is suitable for trace library building including cfDNA.
Owner:广州迈格基因科技有限公司
Iodine dissociation type gene cloning method based on sulfo-modifiers
The invention discloses an iodine dissociation type gene cloning method based on sulfo-modifiers. According to the method, phosphodiester bonds between the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of primers of a target gene and a plasmid vector are amplified into the sulfo-modifiers; a base sequence at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of forward primers of the target gene and the plasmid vector and a base sequence at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of reverse primers of the target gene and the plasmid vector are matched in a supplementary mode; after the target gene and the plasmid vector are subjected to PCR amplification, a PCR product is purified; iodine selectively breaks the phosphodiester bonds of the sulfo-modifiers, and under the combined action of existence of the sulfo-modifiers at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends and iodine heat treatment, DNA will generate a 3' single-link protruding end where 20 nucleotides grow. Through the method, cloning of the target gene does not rely on restriction endonuclease, DNA ligase or any other DNA modification enzyme, operation flux is large, and the method can be applied to large-scale gene cloning.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGSHI JUNCHI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com