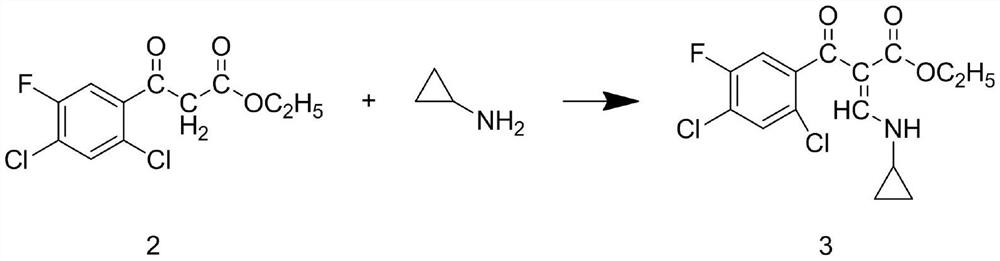
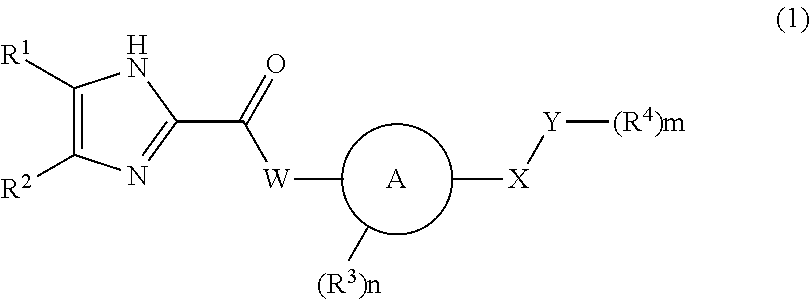
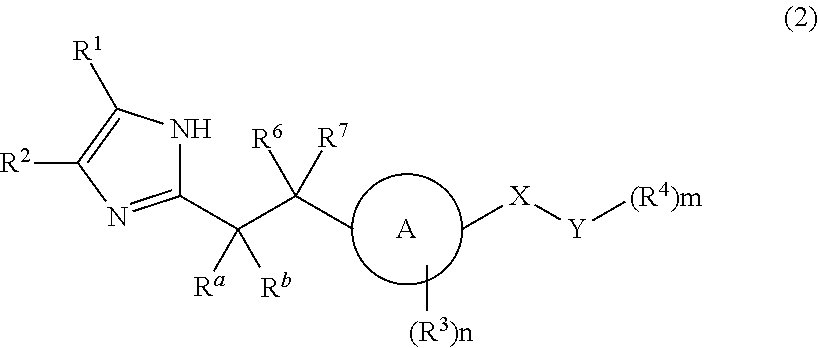
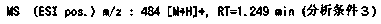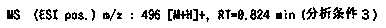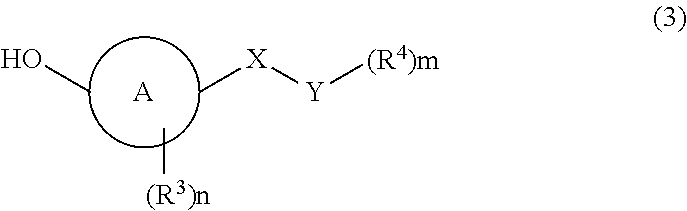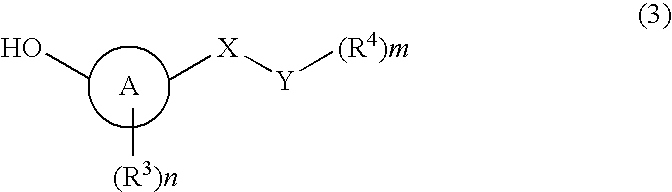Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "DNA Gyrase Inhibitors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Two classes of antibiotics that inhibit gyrase are: The aminocoumarins (including novobiocin). Aminocoumarins work by competitive inhibition of energy transduction of DNA gyrase by binding to the ATPase active site located on the GyrB subunit. The quinolones (including nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin).
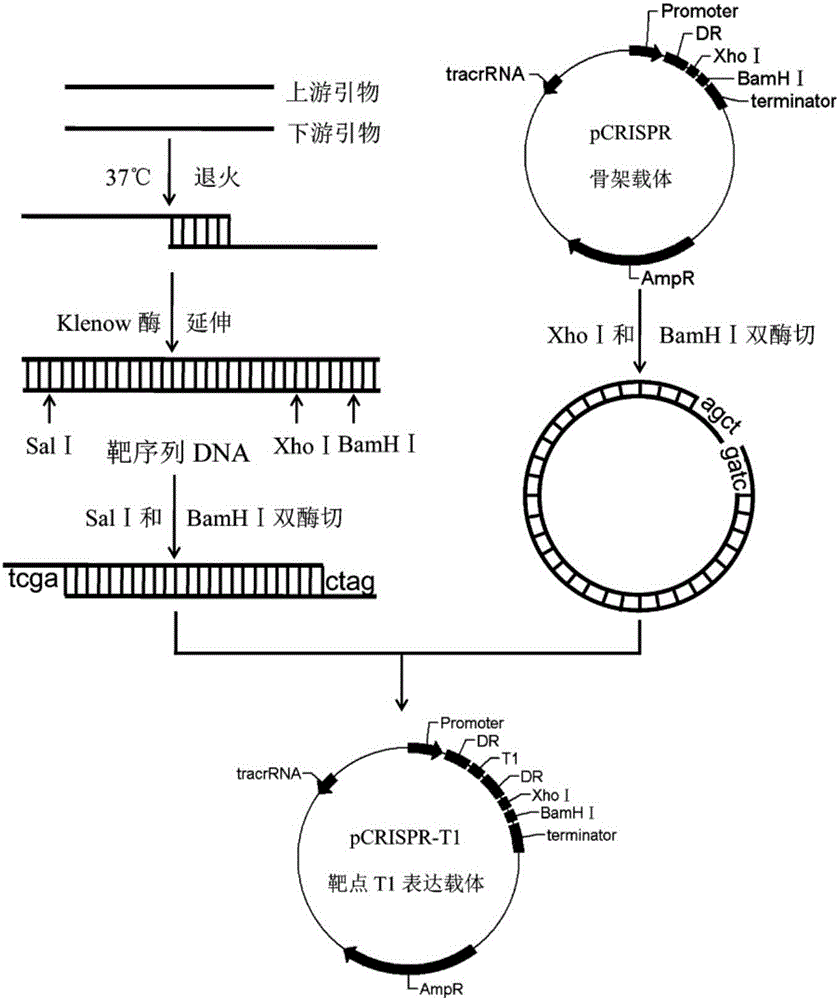
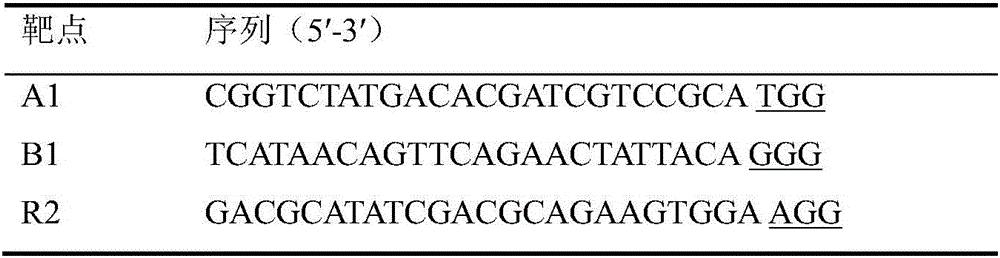
Multi-target-point CRISPR/Cas9 expression vector based on bacteriostasis and sterilization
InactiveCN106554969ATo achieve the effect of antibacterial and bactericidalVectorsOxidoreductasesA-DNADihydrofolate reductase
The invention discloses a multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector based on bacteriostasis and sterilization. The gene sequence of the multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector is SEQ ID NO1 and the gene sequence of a Cas9 expression vector is SEQ ID NO2. A construction method of the expression vector comprises: using a DNA segment of an oriented RNA specific recognition gene, mediating Cas9 protein to cut a DNA double strand to produce a double strand incision and break a DNA sequence, and therefore breaking the principle of DNA coding of functional protein to construct the multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector. Through comparison with a negative contrast, after CRISPR / Cas9 acts on DNA gyrase and dihydrofolate reductase, the survival rate of bacteria is only 10%, and the sterilization effect can reach no less than 90%.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF TECH
Oligonucleotides for detection of Bacillus cereus group bacteria harmful to mammals, and method of detection with the oligonucleotides
A method of detection is provided that permits differentiation of each of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Bacillus anthracis from other microorganisms, using oligonucleotide primers for amplification of the target nucleotide sequences characteristic to Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Bacillus anthracis, consisting of the oligonucleotide (A) having a nucleotide sequence obtained from SEQ ID NO:1 and containing at least one site that can amplify a nucleotide sequence characteristic to Bacillus cereus, the oligonucleotide (B) having a nucleotide sequence obtained from SEQ ID NO:3 and containing at least one site that can amplify a nucleotide sequence characteristic to Bacillus thuringiensis, and the oligonucleotide (C) having a nucleotide sequence obtained from SEQ ID NO:5 and containing at least one site that can amplify a nucleotide sequence characteristic to Bacillus anthracis. Also provided are a method of detection of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Bacillus anthracis by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a primer specific to the DNA gyrase sub-unit B (gyrB) gene and a method of detection of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, and Bacillus anthracis in a sample by differentiation on the genetic level.
Owner:NIPPON SUISAN KAISHA LTD
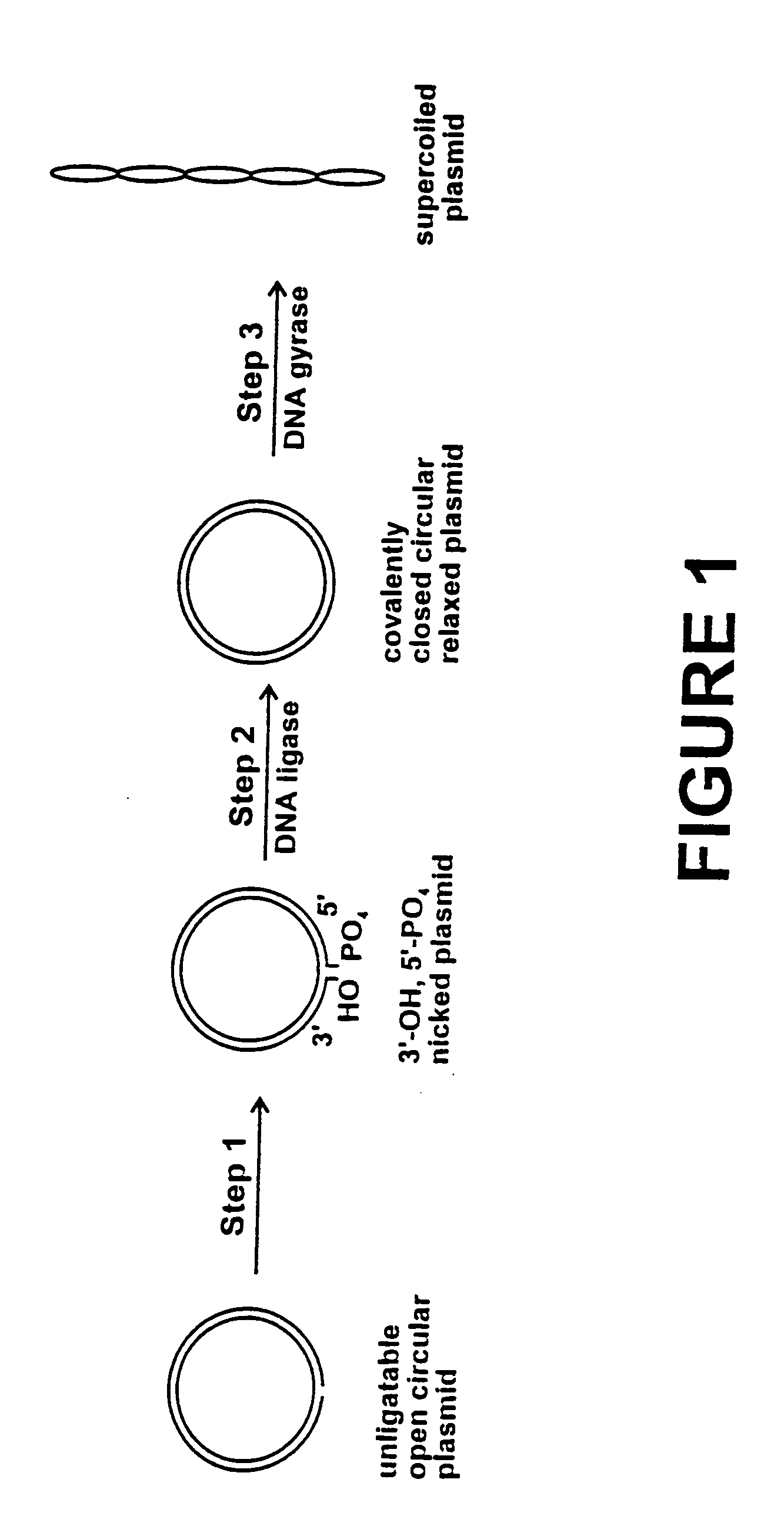
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid to supercoiled plasmid
InactiveUS20050069991A1Increase productionUniversal procedureHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphoric acidDNA Gyrase Inhibitors
In one embodiment of the invention, a method is provided for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising: (a) providing a plasmid solution comprised of unligatable open circular plasmid; (b) reacting the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes and appropriate nucleotide cofactors, such that unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) reacting the 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid with a DNA ligase and DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, such that 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) reacting the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with a DNA gyrase and DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, such that relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. In other embodiments, DNA gyrase is replaced by reverse DNA gyrase or reaction (d) is not performed.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD D
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid
InactiveUS20040191871A1Increase percentageFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotidePhosphoric acid
In accordance with the invention, there is provided a method for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising the steps: (a) preparing a cleared lysate of the host cells, wherein the cleared lysate comprises unligatable open circular plasmid, wherein the open circular plasmid is not 3'-hydroxyl, 5-phosphate nicked plasmid; (b) incubating the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes in the presence of their appropriate nucleotide cofactors, whereby the unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) incubating the 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid with DNA ligase in the presence of DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, whereby 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) incubating the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with DNA gyrase in the presence of DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, whereby relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. Preferably, the enzymatic steps (b), (c), and (d) are performed in a single step using an enzyme mixture comprising DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, and DNA gyrase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises a 3' terminus deblocking enzyme, such as exonuclease III or 3'-phosphatase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises one or more regenerating enzymes and a high energy phosphate donor, whereby the nucleotide by-products of the nucleotide cofactors generated by DNA ligase and DNA gyrase are converted to back to nucleotide cofactor. Preferably, the enzyme mixture further comprises one or more exonucleases, such as ATP dependent exonuclease, whereby linear chromosomal DNA is selectively degraded.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD DAVID
Oligonucleotides used for detecting vibrio parahaemolyticus and method of detection therewith
InactiveUS6048697AHigh sensitivityOptimization orderSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNAVibrio parahaemolyticus
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 00991 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 6, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 6, 1999 PCT Filed Mar. 25, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 35970 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 2, 1997An oligonucleotide is provided which has a nucleotide sequence derived from SEQ ID NO:1, characterized in that it contains at least one site capable of amplifying a nucleotide sequence characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The oligonucleotide may have a nucleotide sequence not derived from SEQ ID NO:3, or incapable of amplifying nucleotide sequences originating in Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio harveyi, and may be represented by SEQ ID NO:5 or SEQ ID NO:6. A method of detecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus in a specimen is also provided which comprises preparing a primer set comprising two of the above oligonucleotides, selectively amplifying therewith a DNA gyrase subunit B gene sequence contained in the specimen as a target, and determining whether or not there is a gyrB unit specific for Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the specimen. Also provided is a primer which reacts specifically with a gyrB gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus to thereby differentiate and identify the same among other Vibrios and strains other than the genus Vibrio. The Vibrio parahaemolyticus-specific primer serves to detect 285-bp gyrB gene fragments specific for this Vibrio by the PCR method without the necessity for DNA extraction or like operations from bacterial cells.
Owner:NIPPON SUISAN KAISHA LTD
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid to supercoiled plasmid
InactiveUS20050084938A1Increase productionUniversal procedureHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateGenetics
In one embodiment of the invention, a method is provided for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising: (a) providing a plasmid solution comprised of unligatable open circular plasmid; (b) reacting the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes and appropriate nucleotide cofactors, such that unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) reacting the 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid with a DNA ligase and DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, such that 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) reacting the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with a DNA gyrase and DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, such that relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. In other embodiments, DNA gyrase is replaced by reverse DNA gyrase or reaction (d) is not performed.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD D
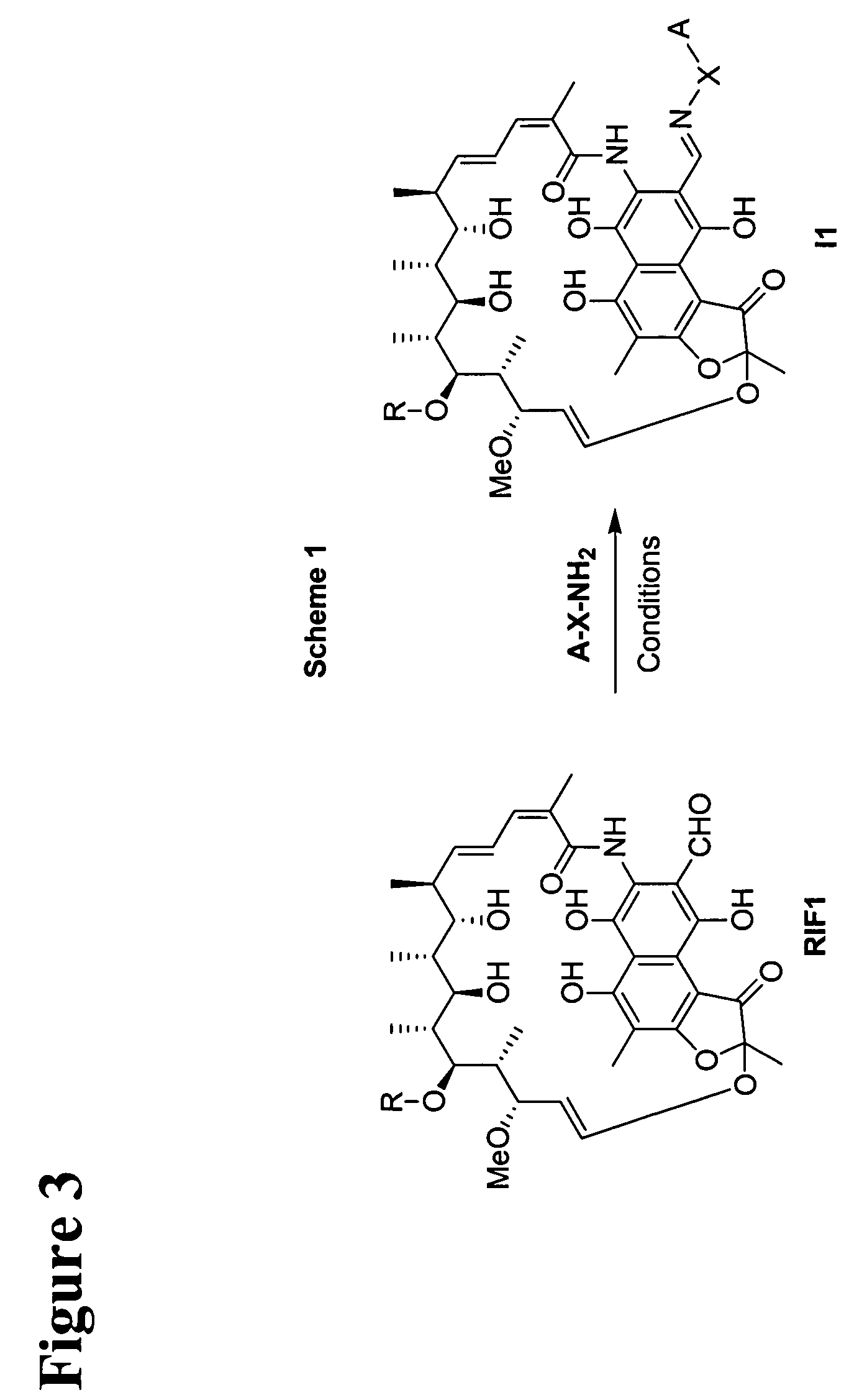
Rifamycin imino derivatives effective against drug-resistant microbes
The present invention relates to rifamycin 3-iminomethylenyl (—CH═N—) derivatives having antimicrobial activities, including activities against drug-resistant microorganisms. The claimed rifamycin derivative has a rifamycin moiety covalently linked to a linker through an iminomethylenyl (—CH═N—) group at the C-3 carbon of the rifamycin moiety and the linker is, in turn, covalently linked to a quinolone structure or its pharmacophore within the DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV inhibitor family. The inventive rifamycins are novel and exhibit activity against both rifampin and ciprofloxacin-resistant microorganisms.
Owner:TENNOR THERAPEUTICS (SUZHOU) LTD
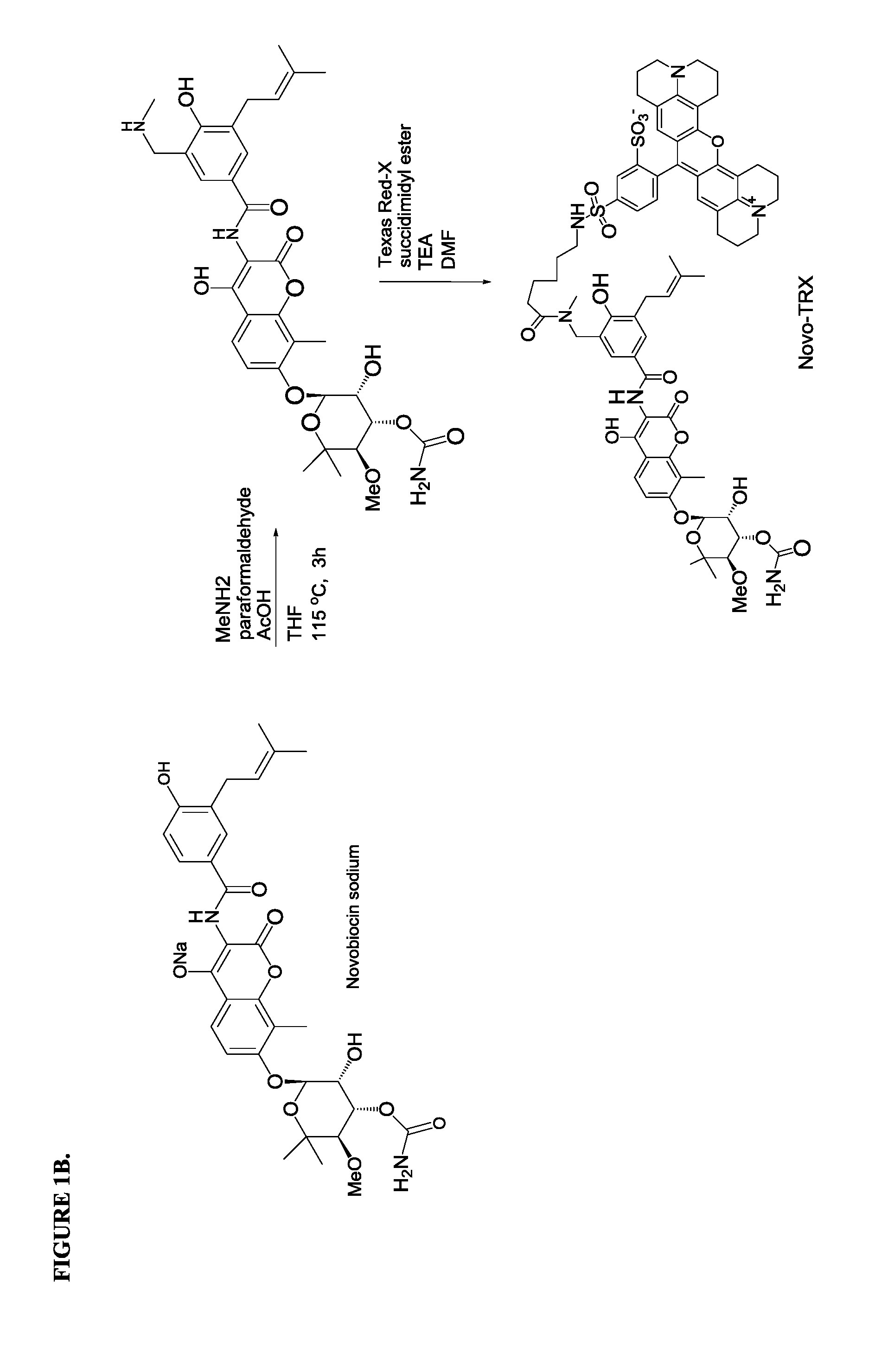
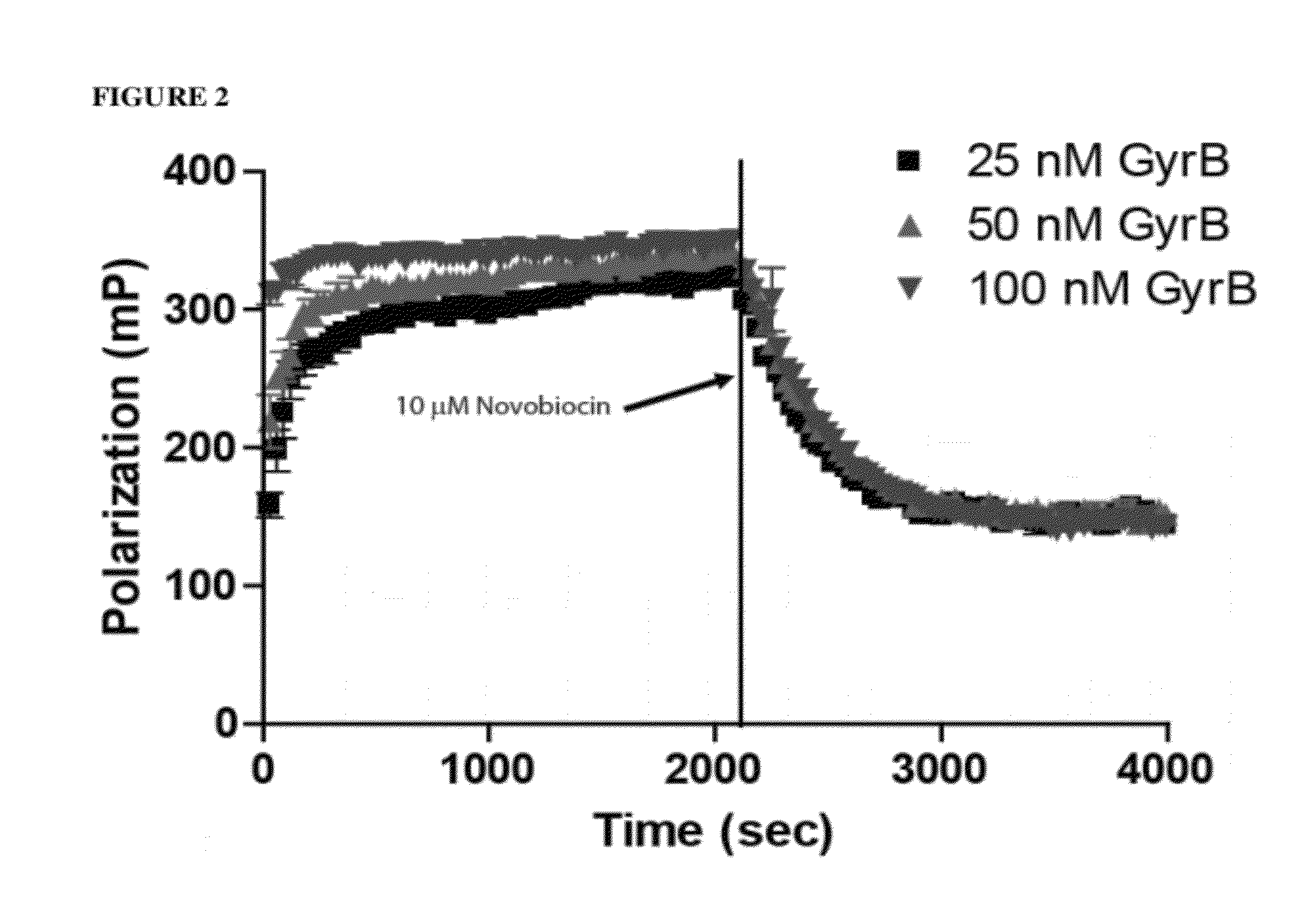
Topoisomerase Binding Probe and Method of Use
ActiveUS20120225788A1Inhibit bindingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAminocoumarinsDNA underwinding
An aminocoumarin conjugated to a fluorescent label through a secondary amine, is operative as a fluorescent polarization probe of the DNA gyrase B or topoisomerase IV E subunit. The probe is used for detecting topoisomerase inhibitor binding by fluorescence polarization, particularly in a high-through put topoisomerase inhibitor assay.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid to supercoiled plasmid
InactiveUS20060057683A1Increase productionUniversal procedureFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphateGenetics
In one embodiment of the invention, a method is provided for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising: (a) providing a plasmid solution comprised of unligatable open circular plasmid; (b) reacting the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes and appropriate nucleotide cofactor(s), such that unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) reacting the 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid with a DNA ligase and DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, such that 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) reacting the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with a DNA gyrase and DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, such that relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. In other embodiments, DNA gyrase is replaced with reverse DNA gyrase or reaction (d) is not performed.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD D
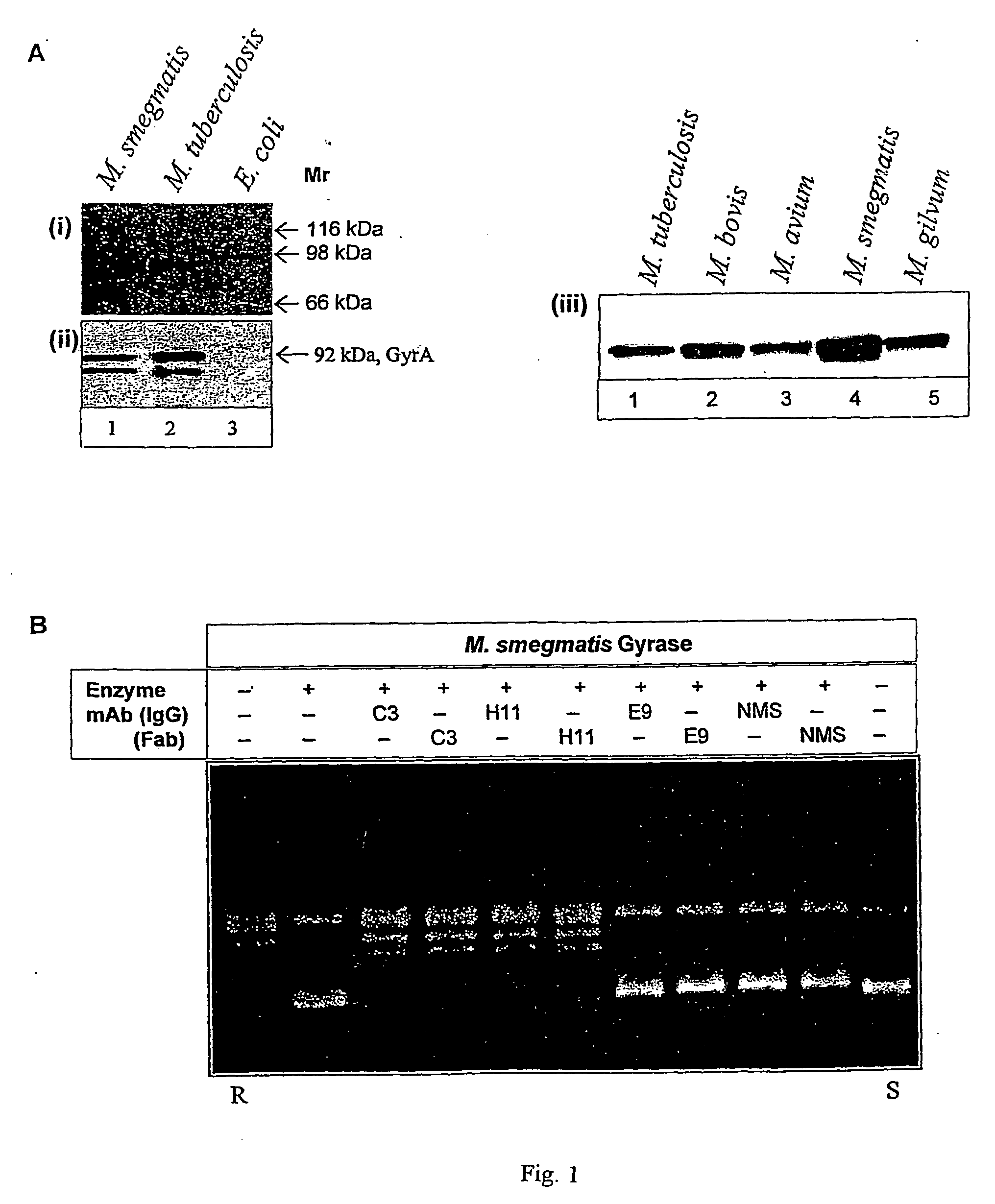
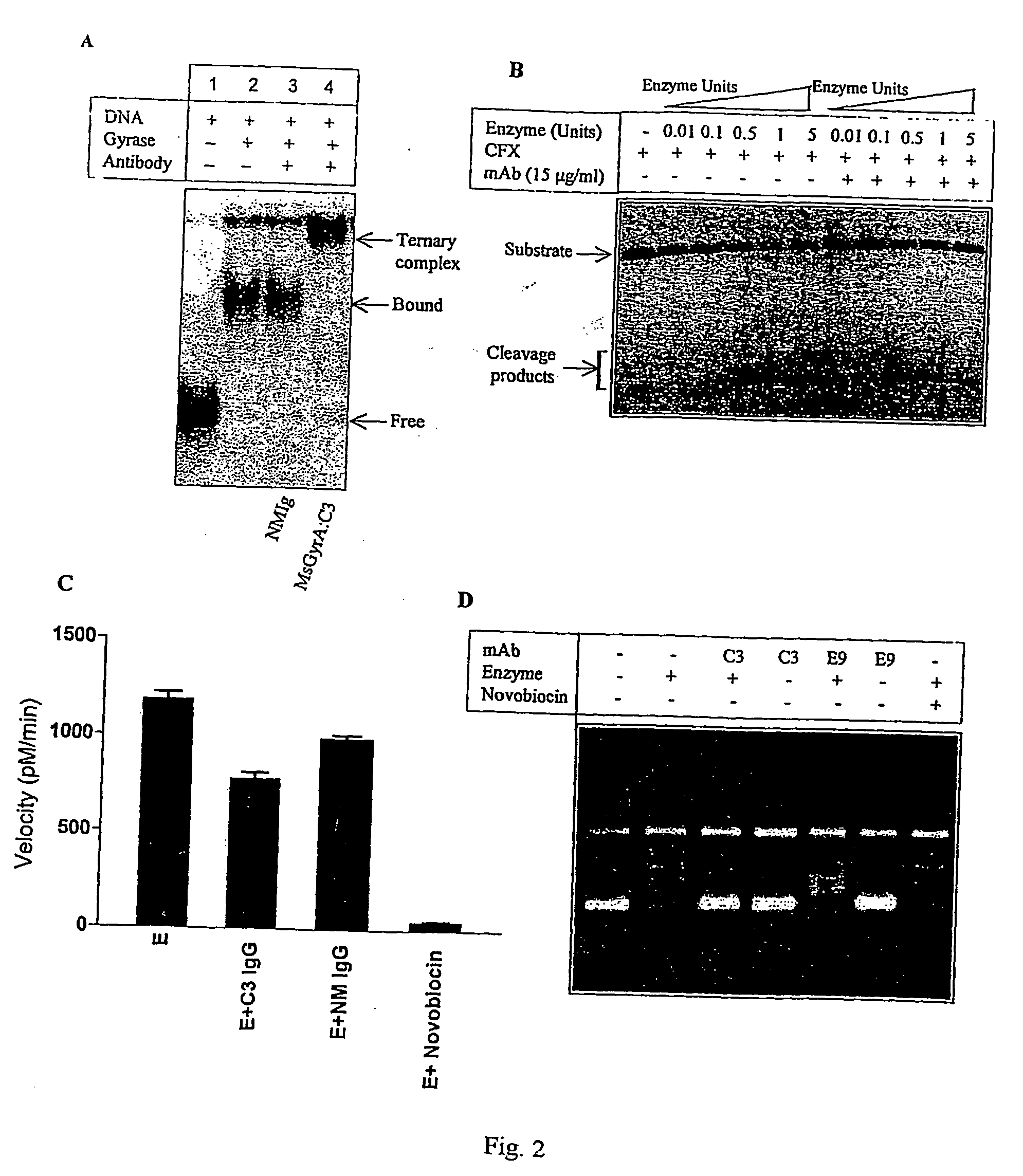
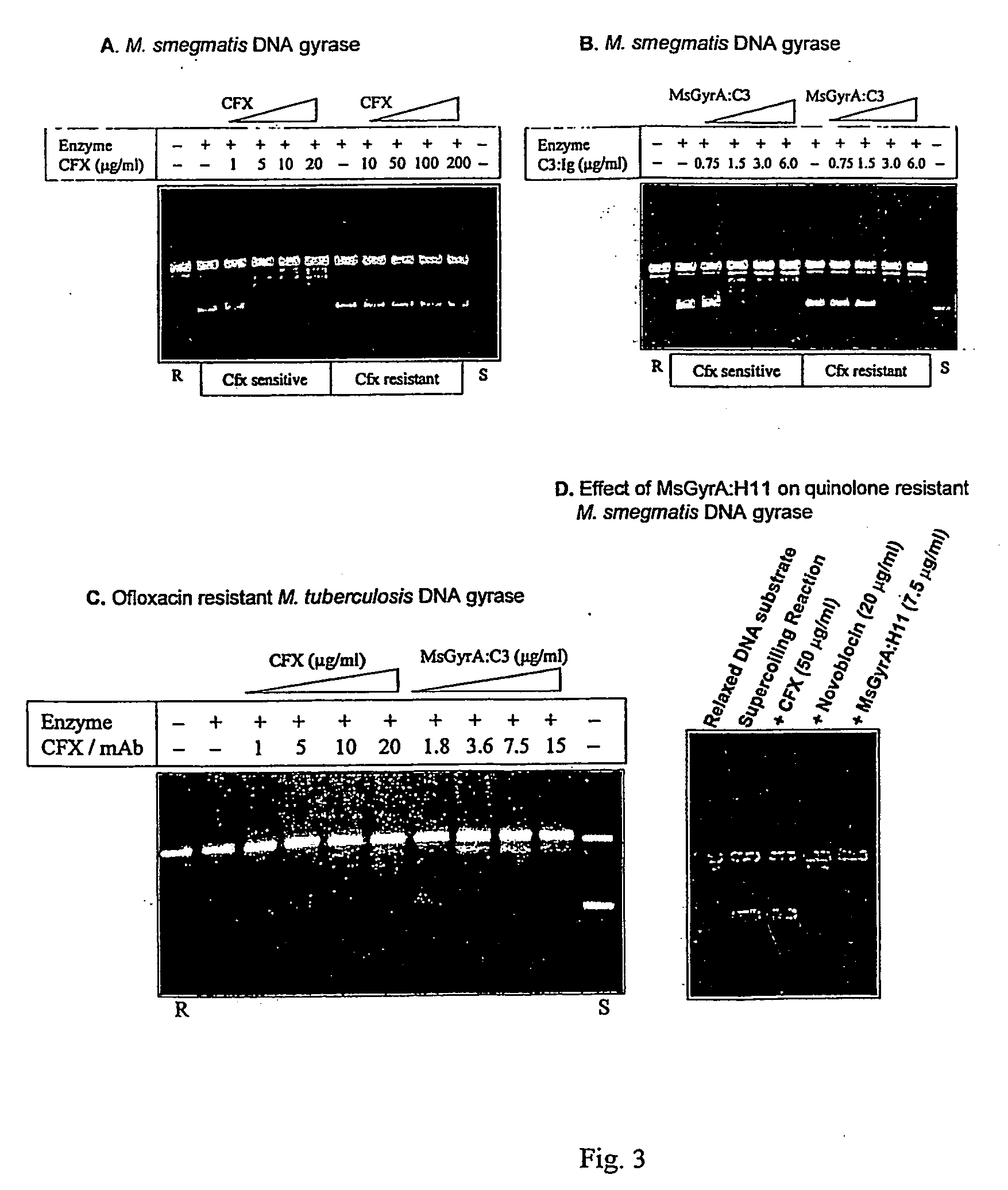
Monoclonal antibody derived peptide inhibitors for mycobacterial dna gyrase
InactiveUS20060229438A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMicroorganismSingle-Chain Antibodies
The present invention relates to the development of monoclonal antibodies that specifically inhibit DNA gyrase from M. tuberculosis. M. smegmaris and possibly from other related bacterial species. More particularly, it has been shown that the inhibition of the enzyme is by a hitherto unknown and novel mechanism. The present invention also relates to a DNA sequence of single chain antibody consisting of complementarity determining regions of mAb. The monoclonal antibody, single chain antibody and peptides derived thereof could be useful for developing lead molecules for tuberculosis therapy. The antibodies and derived materials could be useful for a variety of purposes, including diagnosis of mycobacterial infections. The present invention also relates to the modification of antibodies and derived materials for use against diverse microbial infections and other potential applications derived thereof.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
2(1H)-quinolinone derivative
InactiveCN110446699AStrong GyrB/ParE inhibitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsQuinolizineIsomerase
Owner:TAISHO PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Elizabethkingia meningoseptica loop-mediated isothermal DNA amplification rapid detection kit and detection method
InactiveCN106119383AGuaranteed reliabilityFast, sensitive and accurate detection methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesElectrophoresisElizabethkingia meningoseptica
The invention discloses an elizabethkingia meningoseptica loop-mediated isothermal DNA amplification detection kit and a detection method, wherein the kit, on the basis of a bio-information platform, is subjected to large-scale genome analysis; four specific primers are designed in accordance with a DNA gyrase gene of the elizabethkingia meningoseptica; and in combination with the LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA) technology, the rapid, sensitive and accurate detection method is established in accordance with the elizabethkingia meningoseptica, and the rapid detection kit applicable to the method is constructed. With the implementation of the rapid detection kit and the detection method disclosed by the invention, observation and identification with naked eyes can be conducted after a reaction, and any other analysis steps such as electrophoresis and the like can be avoided; the detection kit and the detection method have the advantages of being short in detection time, strong in specificity, low in requirement on instrument and equipment, simple and convenient to operate and the like; and the detection kit and the detection method are applicable to the rapid detection of clinical samples, environment samples, food samples and the like.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
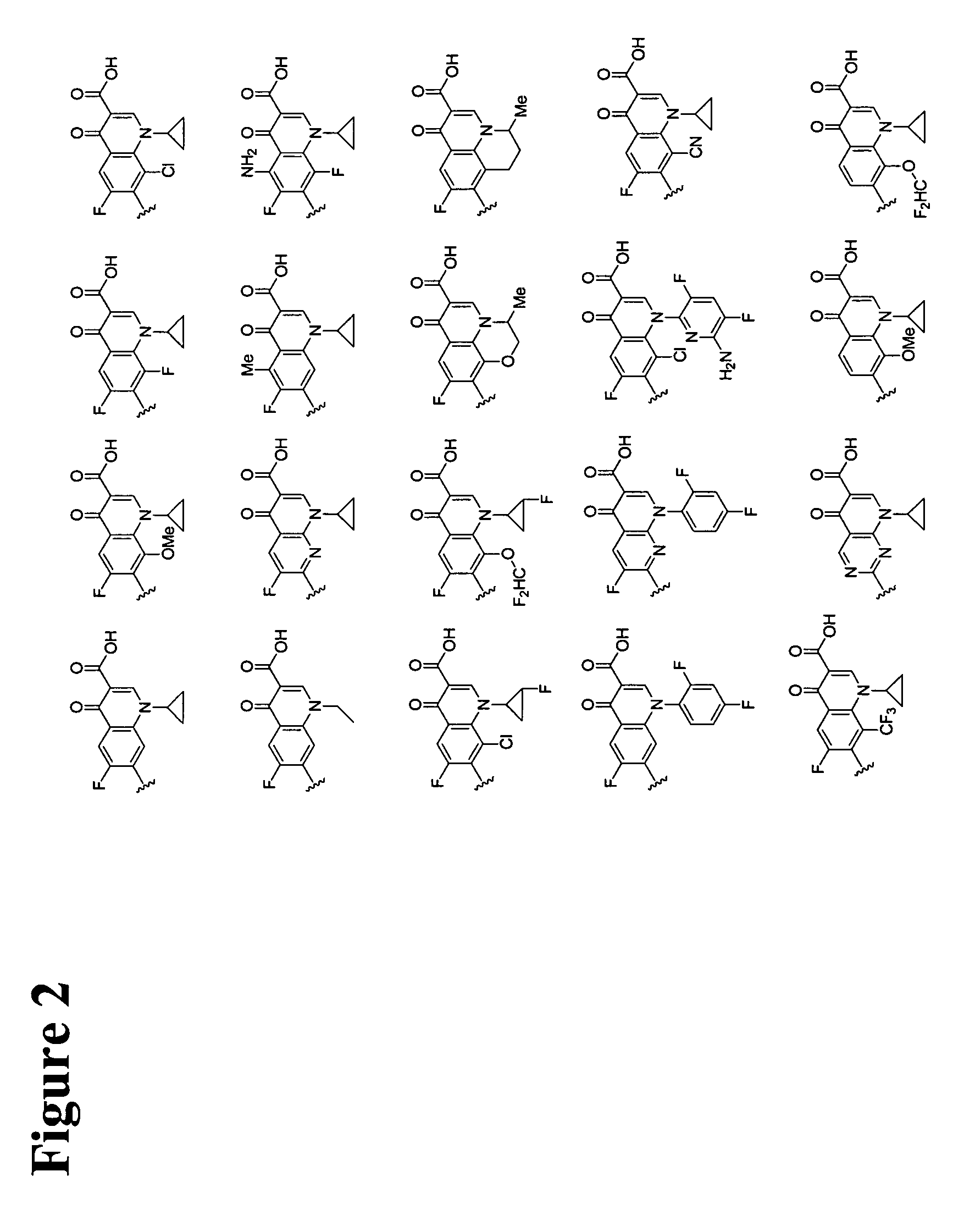
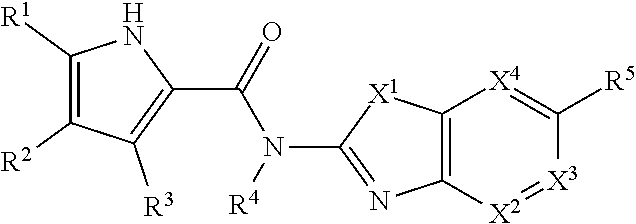
Pyrrole derivatives as DNA gyrase and topoisomerase inhibitors
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
High-flexibility stitch closure line and production technology thereof
The invention discloses a high-flexibility stitch closure line and a production technology thereof. In a stitch closure line production process, an antibacterial agent is prepared and is prepared in away that chitosan is taken as a carrier to carry an intermediate 5; when the stitch closure line is used for suturing a wound, cells on the wound can absorb carboxymethyl cellulose on a micro-capsule, and the micro-capsule disintegrates to release collagen and the antibacterial agent; the antibacterial agent is of a gel form and can be attached to the surface of the wound, so that the intermediate 5 can be released and acts on bacteria DNA gyrase, and DNA duplication is disturbed to cause bacteria to die; and meanwhile, the intermediate 5 can break a cell serous membrane, bacteria content runs off to cause the bacteria to die, so that a wound suturing part is free from bacteria infection, wound healing speed is improved, in addition, the stitch closure line has good flexibility, and the wound can be easily recovered.
Owner:安徽正美线业科技股份有限公司
Compound ofloxacin injection and its preparation method
InactiveCN101007164AImprove survival rateReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide effectTrimethoprim
The invention disclosed a kind of complex ofloxacin injection as well as preparing method. The injection contains 5-20 shares of ofloxacin, 5-25 shares of sulphuric acid colistin, 1-20 shares of trimethoprim and 50-300 shares of propylene glycol. The preparing procedure includes the following steps: (1) weighing materials; (2) putting the sulphuric acid colistin into injection water, stirring until it's all soluble; (3) heating propylene glycol to 75-85DEG C, adding trimethoprim, stirring to make it soluble; (4) putting together the solution of step (2) and (3), clarifying the solution, regulating the ph value of the solution, adding water to 1000 shares to get the preparation. Ofloxacin has the antibacterial activity of the third generation quinolones which can inhibit the bacteria prokaryotic cell DNA gyrase and DNA replication. Sulphuric acid colistin has no residue and side effects in animal bodies. The combination of the two medicines can widen the antibacterial spectrum and increase the curative effect.
Owner:TIANJIN SHENGJI GRP CO LTD
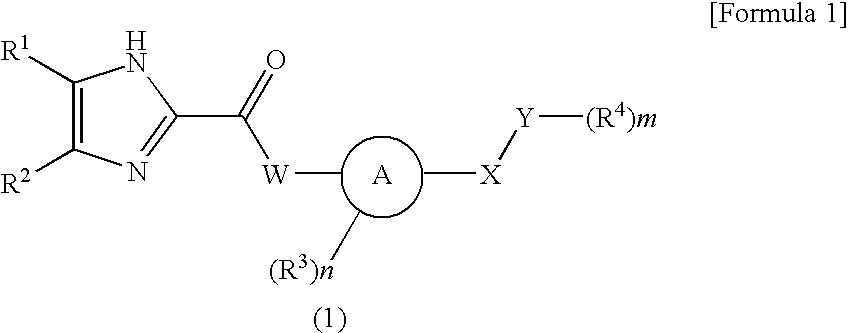
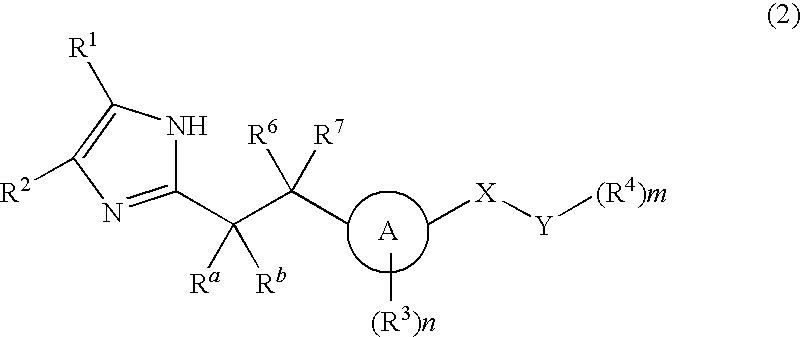
Imidazole carbonyl compound
To develop an antibiotic having a novel mechanism of action, the present inventors have searched for a compound that has weak cytotoxicity, the physical property of high solubility in water, the effect of inhibiting both DNA gyrase GyrB and topoisomerase IV ParE subunits, and sufficient antibacterial activity. As a result, the present inventors have completed the present invention by finding that a compound of the present invention represented by the general formula (1), a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, and a prodrug thereof have desirable properties. The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition (particularly, a preventive or therapeutic composition for infectious disease) comprising a compound represented by the formula (1), a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, or a prodrug thereof as an active ingredient.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
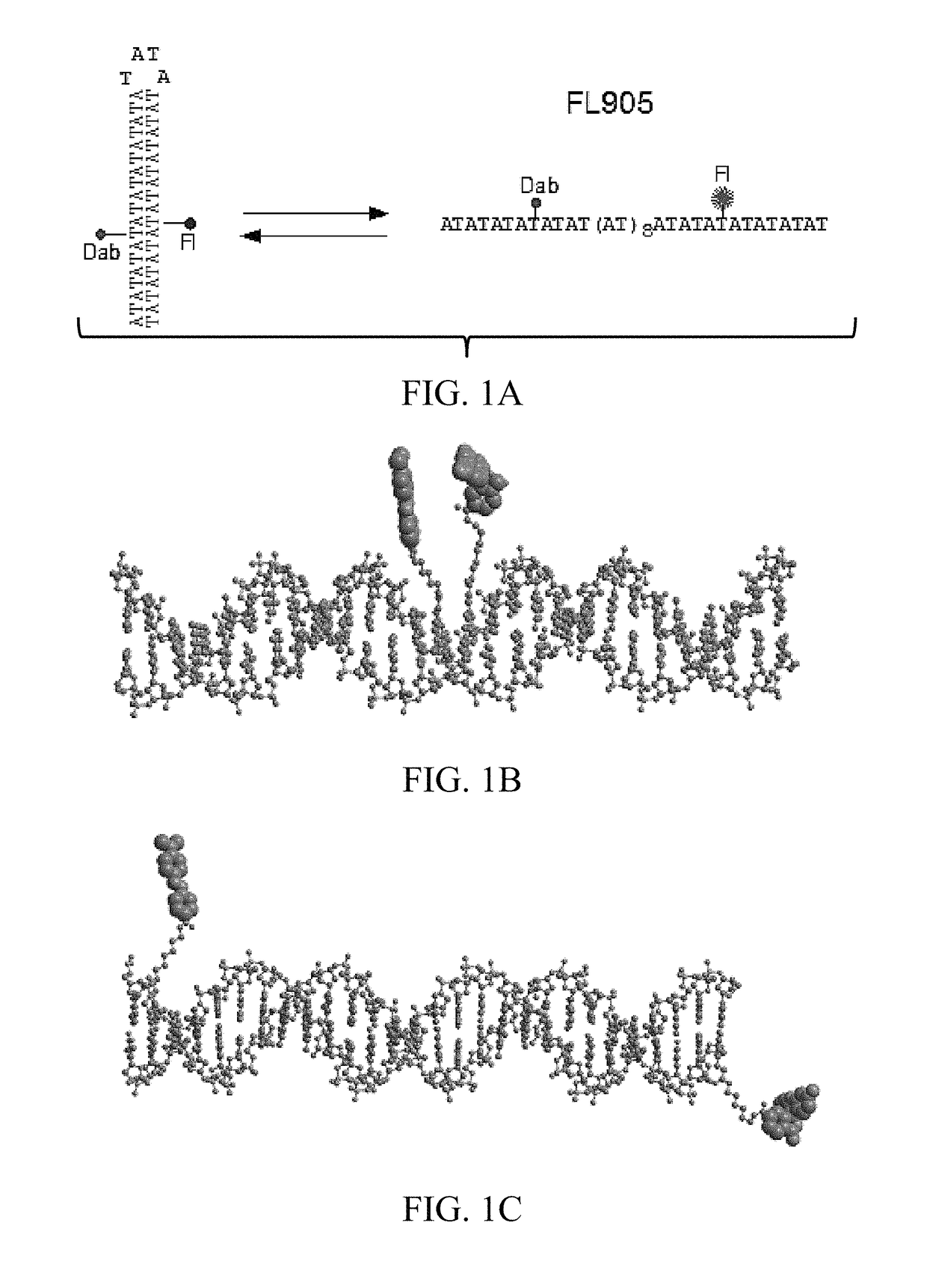
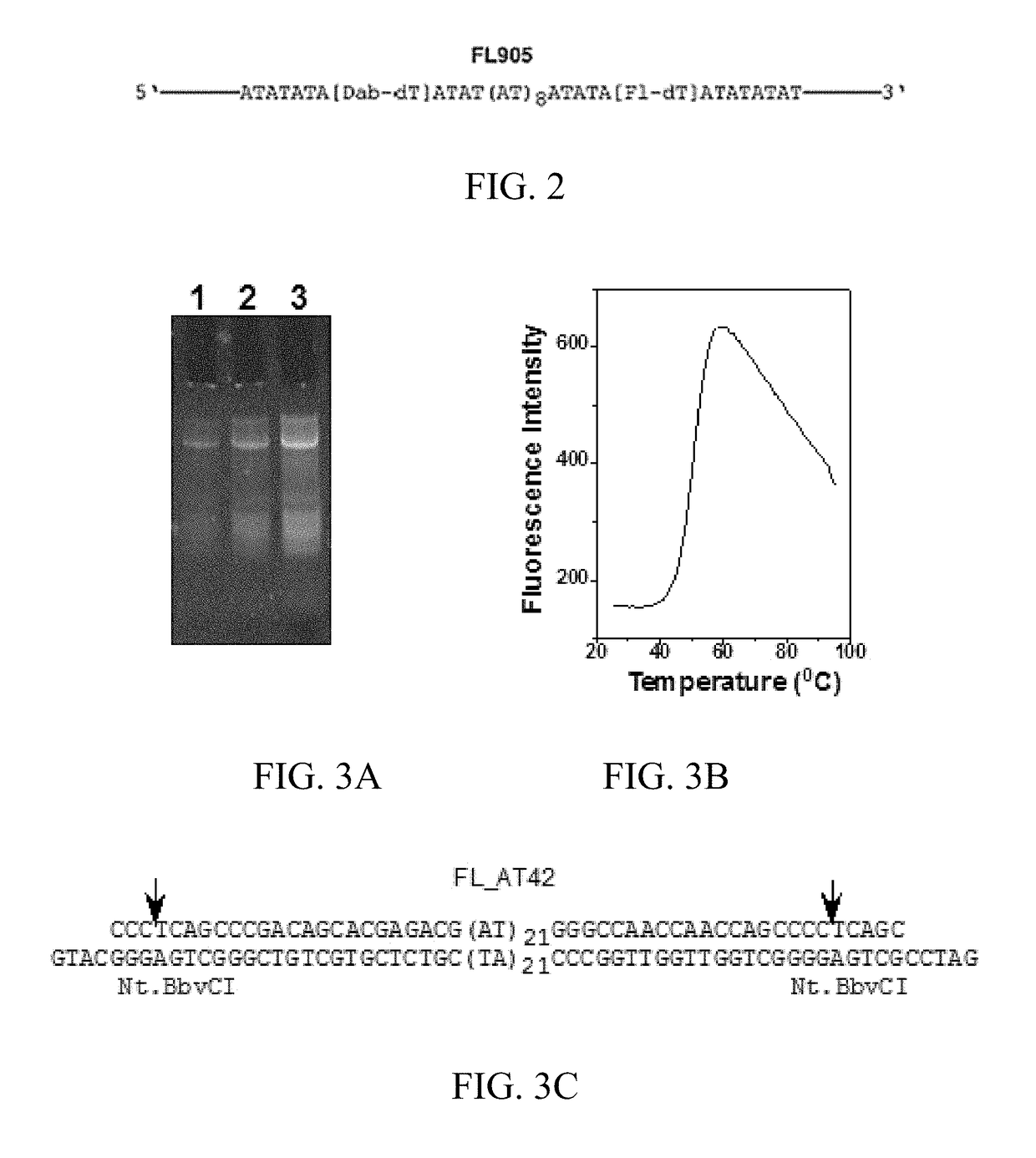
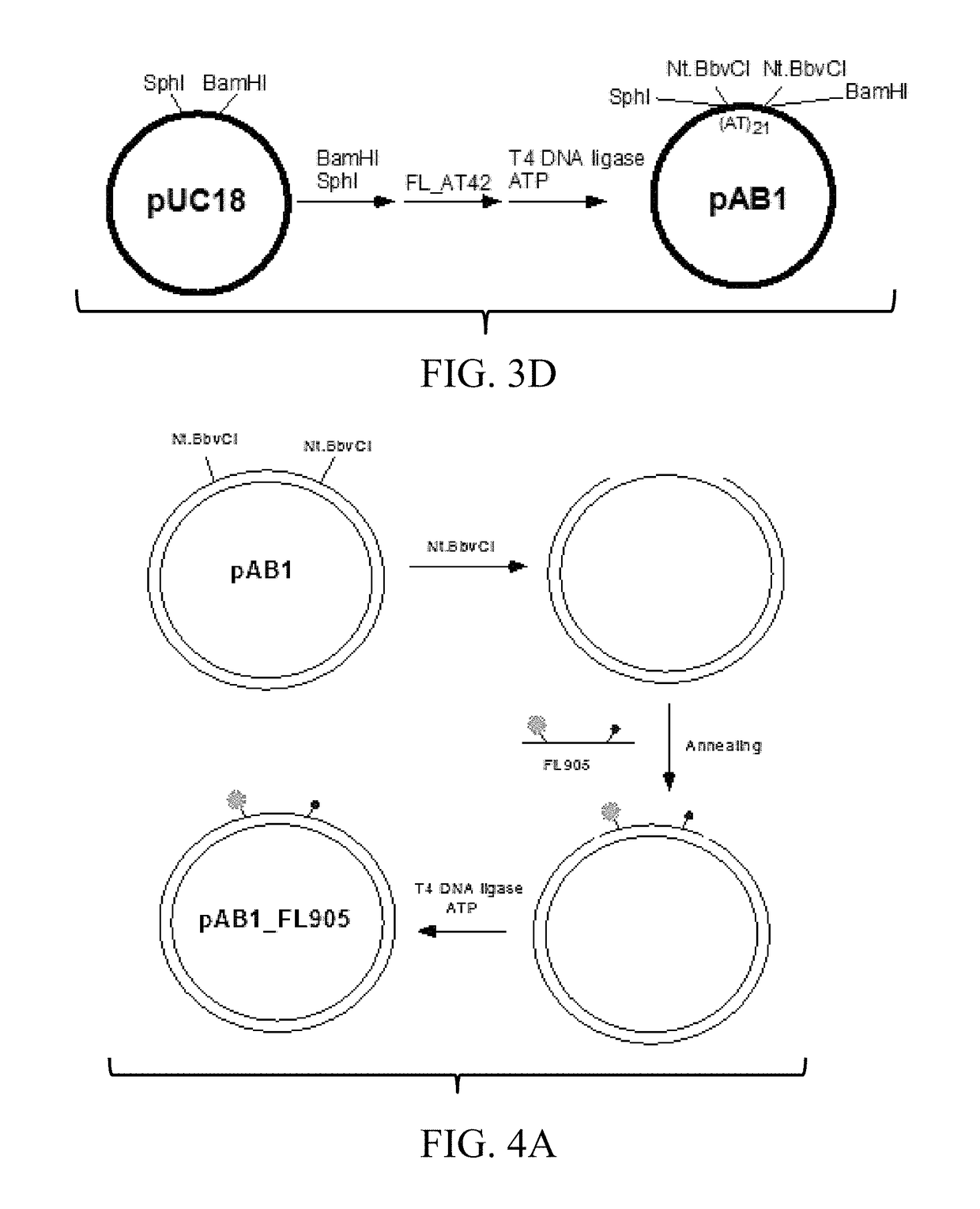
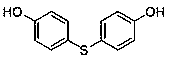
Labeled circular DNA molecules for analysis of DNA topology, and topoisomerases and for drug screening
ActiveUS9890416B2Easy to useImprove detection efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis dnaDNA underwinding
The present invention provides labeled circular plasmid DNA molecules for studying DNA topology and topoisomerases. The molecules of the present invention also provide tools for high throughput drug screening for inhibitors of DNA gyrases and DNA topoisomerases for anticancer drug discovery and antibiotics discovery.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Medicine binding pocket of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) gyrase and application thereof
The invention discloses a medicine binding pocket of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) gyrase. The medicine binding pocket is characterized in that an ATP (adenosine triphosphate) enzyme structure domain ofa B subunit of the DNA gyrase is used as a study object, a compound segment is used as a probe, and the protein heat stability transfer experiment, an ATP enzyme hydrolysis activity experiment and anX-ray crystallography diffraction method are performed, so as to find that a novel medical ligand binding pocket exists on the B subunit of the DNA gyrase of the bacteria; the medicine binding pocketis induced by the screened segment probe 4-phenoxyphenol or 4,4'-dyhydroxy diphenyl sulfide. The novel ligand binding pocket has the advantages that an inhibitor for the DNA gyrase with a novel binding mode is designed and screened; the screened compound segment provides basis elements for the segment growth, integration and connection for the design of novel antibacterial medicines; by using thenovel medical pocket as a starting point, the screened segment is spliced with the existing inhibitor to obtain the inhibitor for the DNA gyrase with high affinity and high selectivity, and the problem of medicine resistance property of the existing inhibitor is expected to be solved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Imidazole carbonyl compound
ActiveUS8536197B2Excellent in sufficient antibacterial activityWeak cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSolubilityMechanism of action
An antibiotic compound having a novel mechanism of action, weak cytotoxicity, high solubility in water, effective in inhibiting both DNA gyrase GyrB and topoisomerase IV ParE subunits, and having antibacterial activity.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Medicinal composition for preventing and controlling poultry intestinal canal disease and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101239060AInfection effect is goodGood control effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a medicine compound for curing and preventing the inflammatory bowel diseases suffered by the poultry, and the method for preparing such medicine compound. The ingredients and the weight percentages of the ingredients are respectively 1 to 10 percent enrofloxacin, 1 to 10 percent lincomycin hydrochloride, 1 to 10 percent latent solvent, and 100 percent other additive accessories. The preparation method is mixing and fully agitating the 1 to 10 percent enrofloxacin, the 1 to 10 percent lincomycin hydrochloride, the 1 to 10 percent latent solvent, and the other additive accessories, which are crushed and screened, according to the weight percentages, so a medicine compound for curing and preventing the inflammatory bowel diseases suffered by the poultry comes into being. The formulation of the invention is reasonable and scientific, the use is convenient, and the function of double sterilization is achieved. The enrofloxacin can effectively restrict the compounding and duplication of DNA so as to kill the bacteria, through the action onto the A subunit of the DNA gyrase. The lincomycin hydrochloride can kill the bacteria through restricting the compounding to the protein of the cells of the bacteria. Both functions together make the sterilization quick and highly efficient, and the medicine compound applicable for large-scale production and popularization.
Owner:吴忠尚
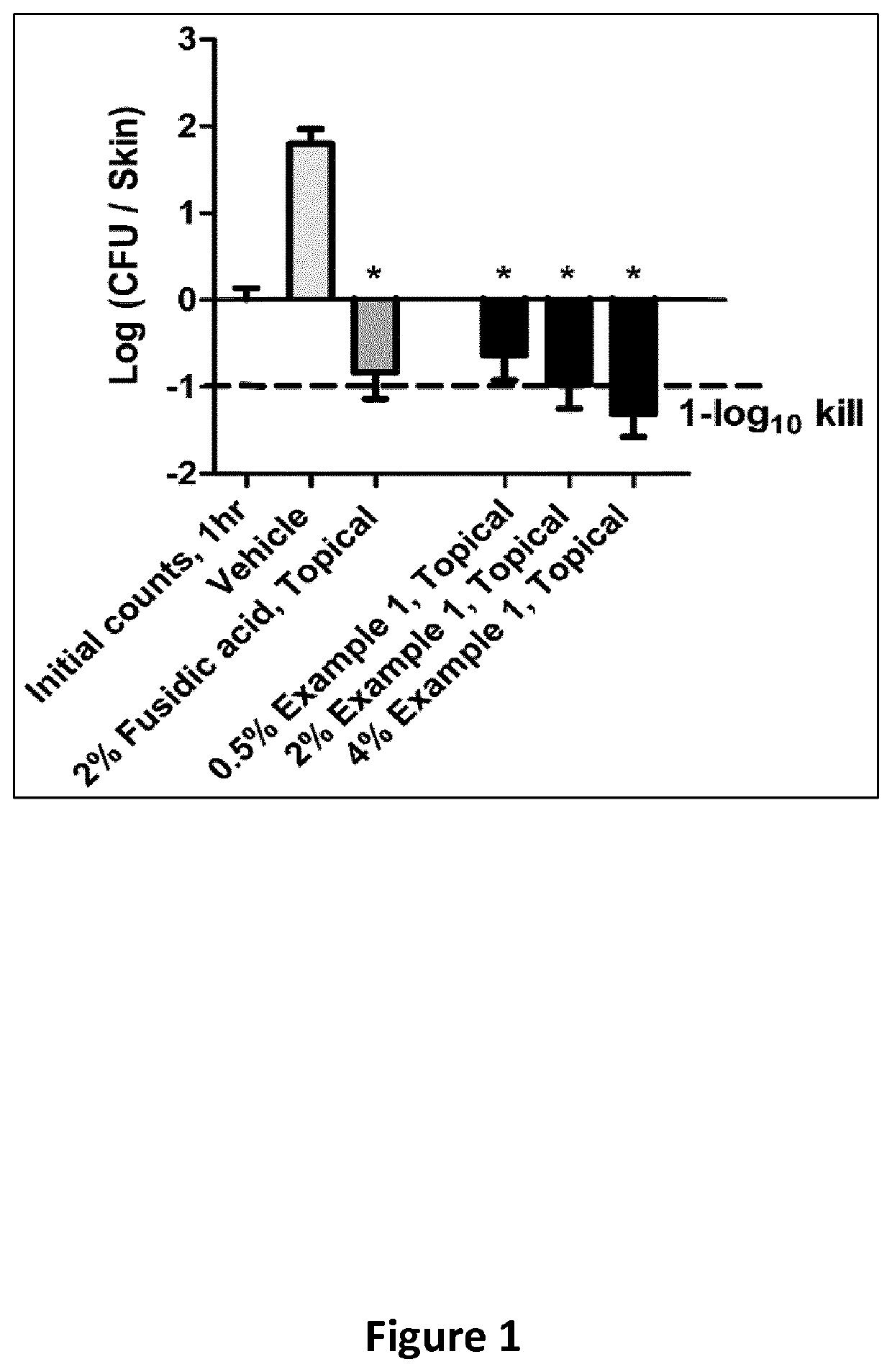
Methods of treatment for bacterial infections
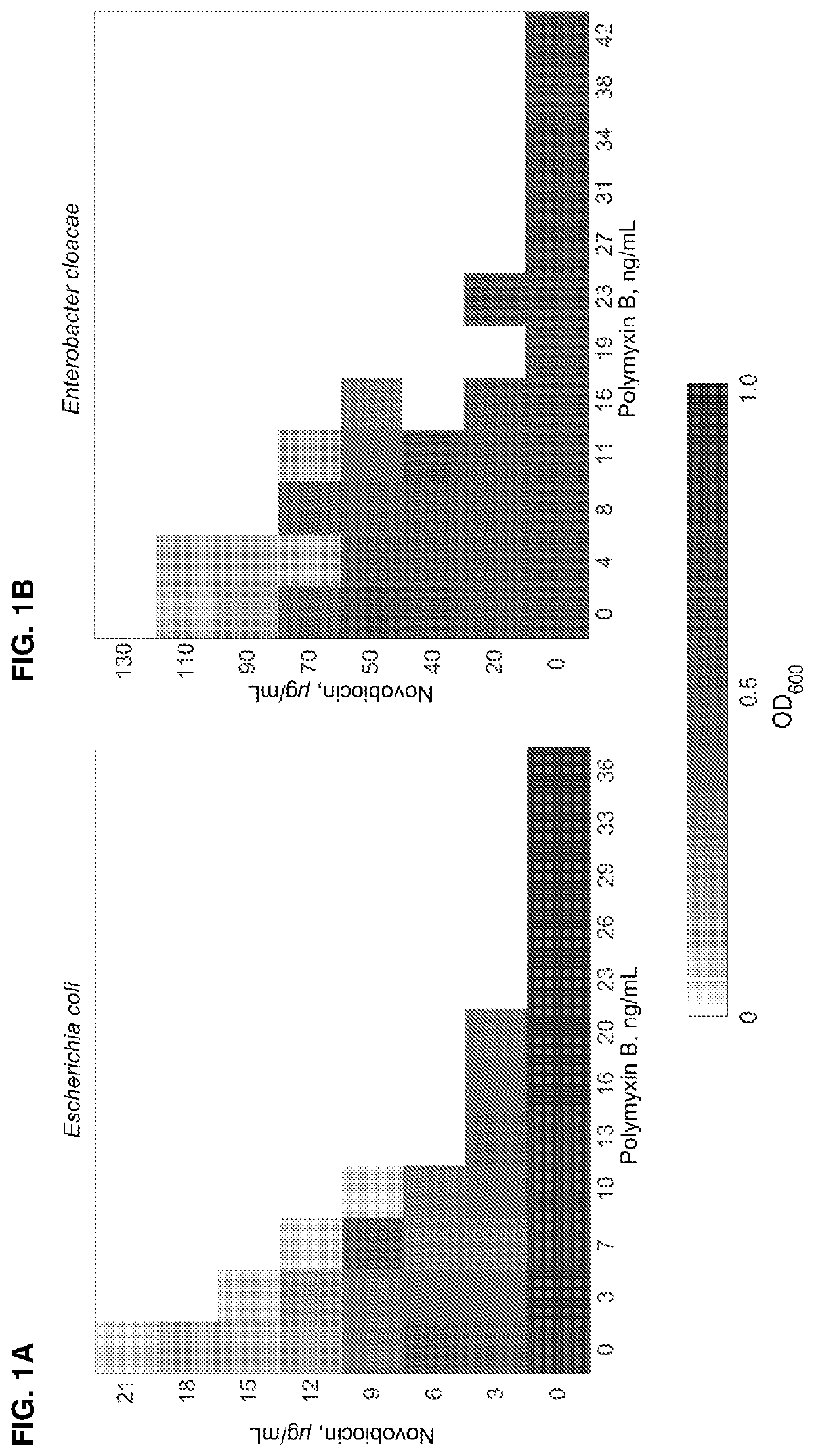
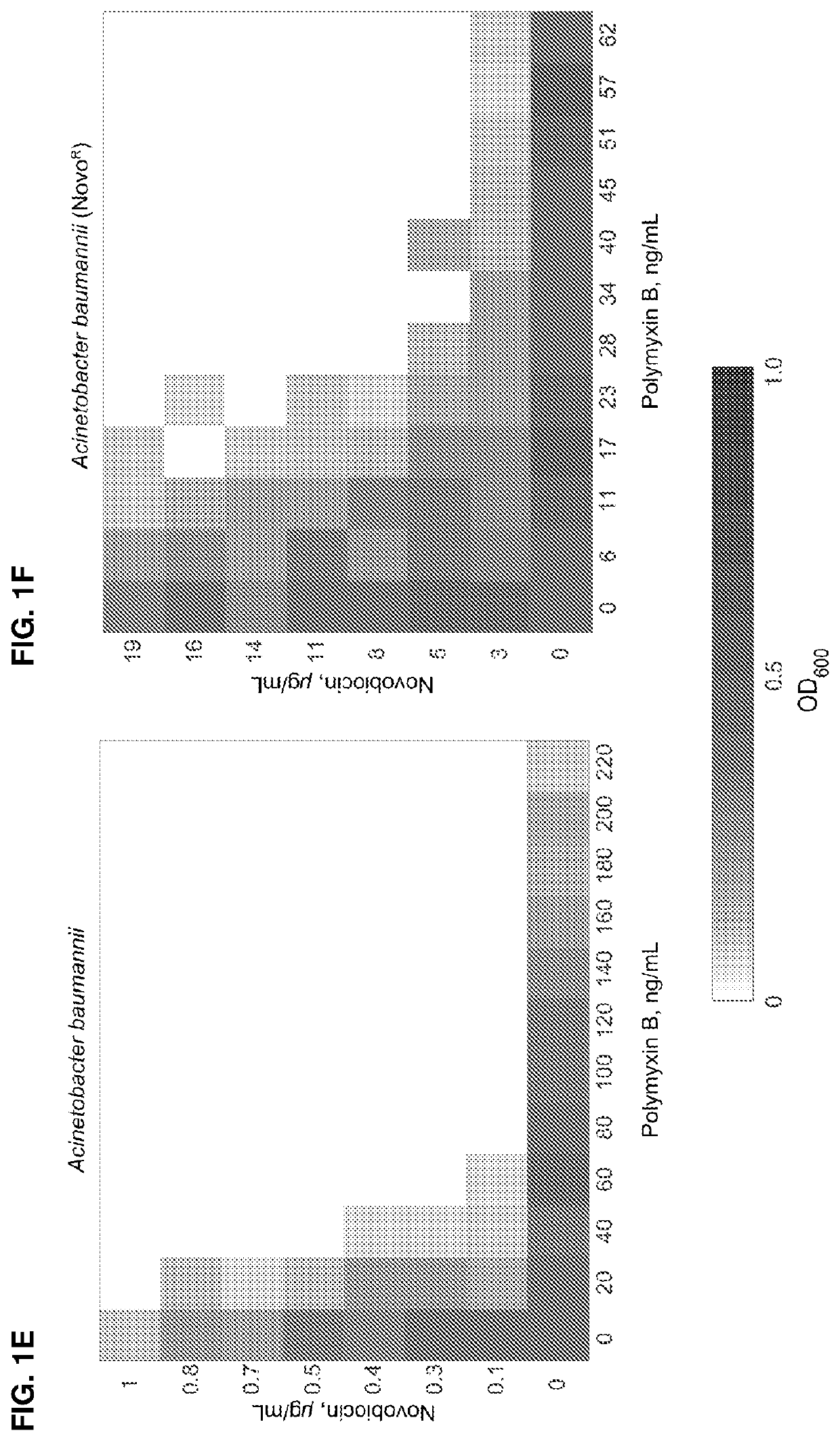
ActiveUS11191773B2Decrease in levelReduce and eliminate bacterial infectionAntibacterial agentsBiocideAminocoumarinsGram-negative bacterial infections
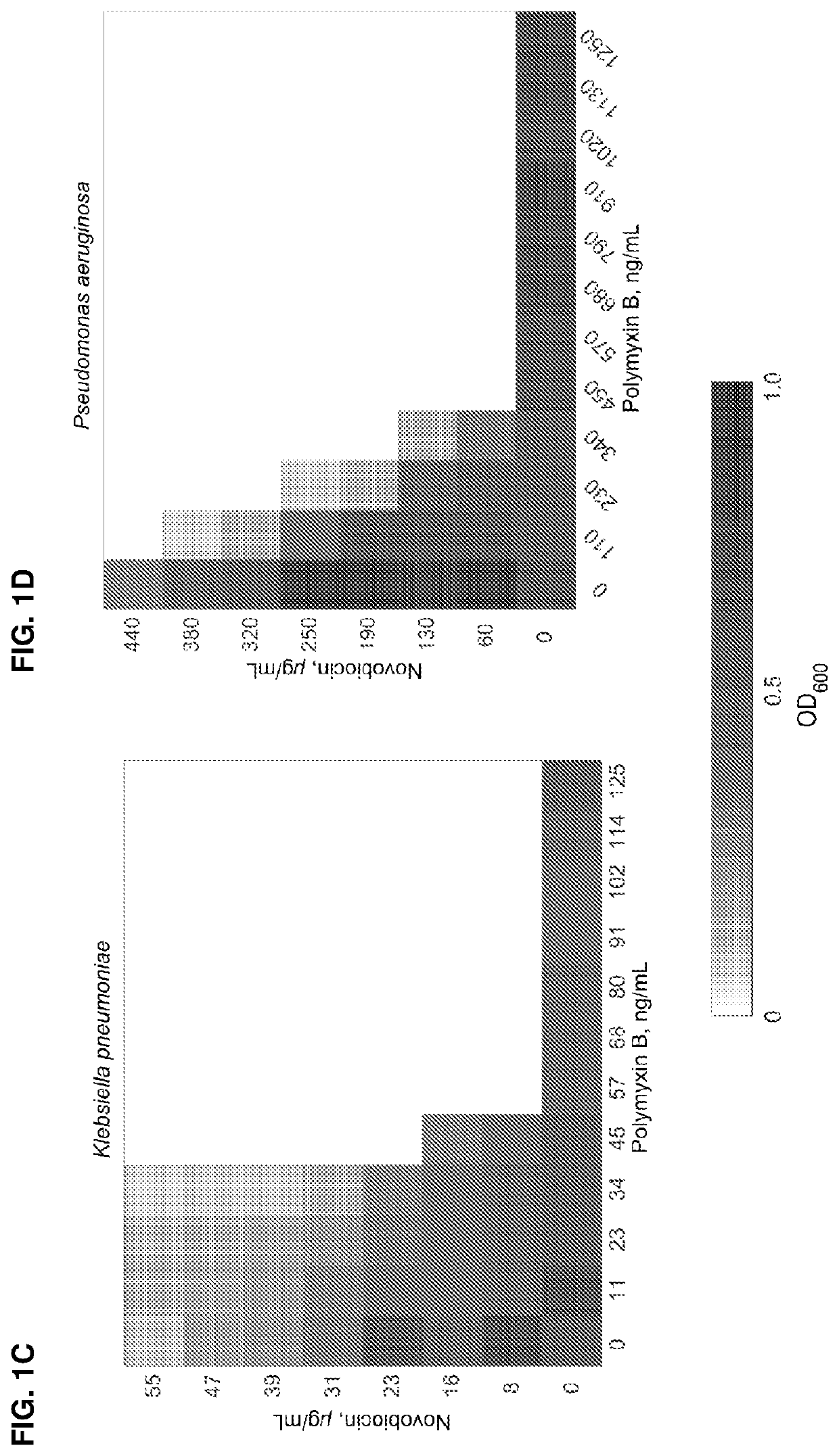
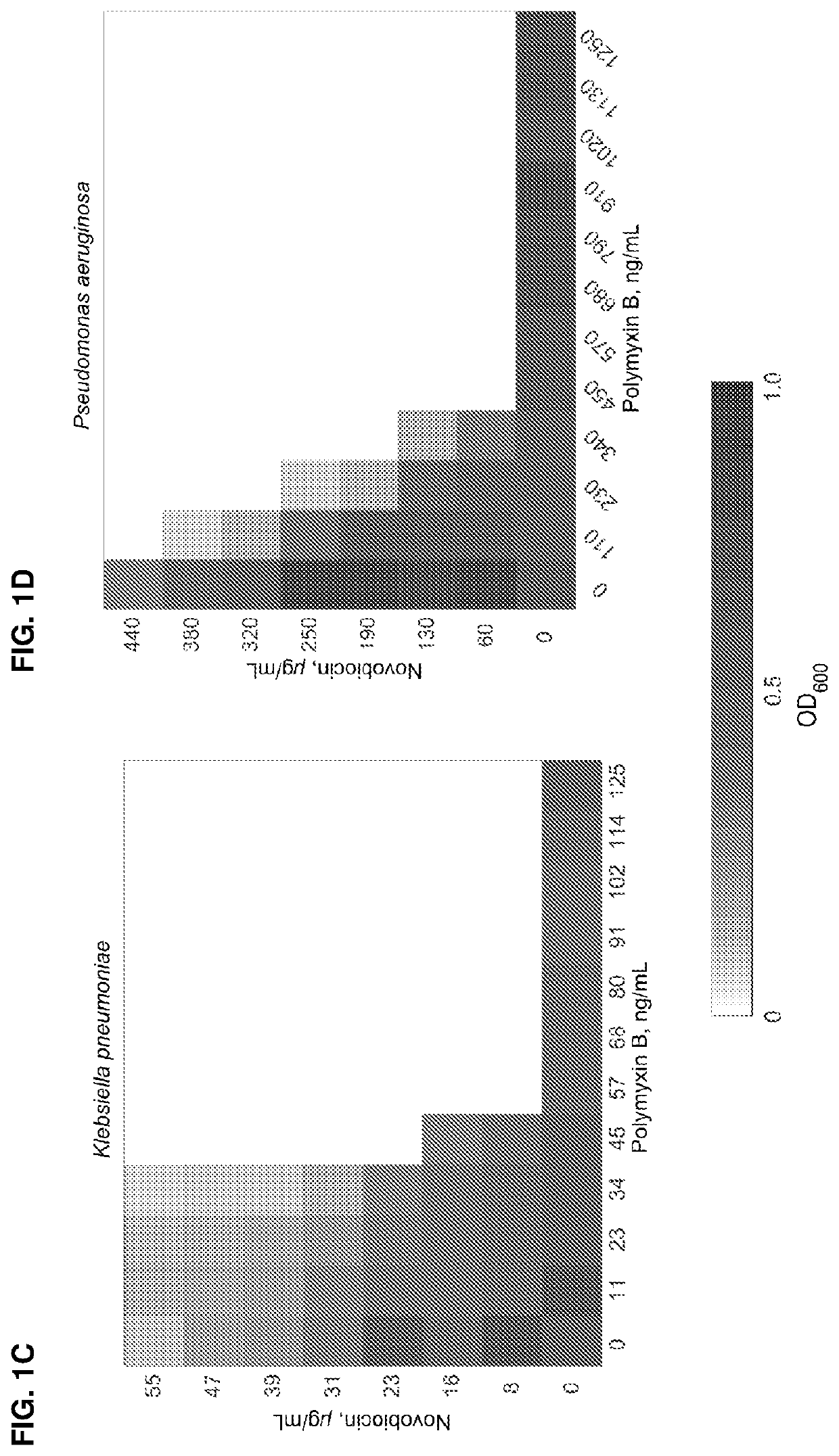
This invention features new compositions and methods that are useful in treating a host with a Gram-negative bacterial infection. Combination therapies comprising an aminocoumarin compound and a polymyxin compound are disclosed, including certain combinations that exhibit synergistic effects. Furthermore, aminocoumarin compounds are described having altered inhibition of DNA gyrase in Gram-negative bacteria and / or the ability to target the transport proteins responsible for assembling lipopolysaccharide in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
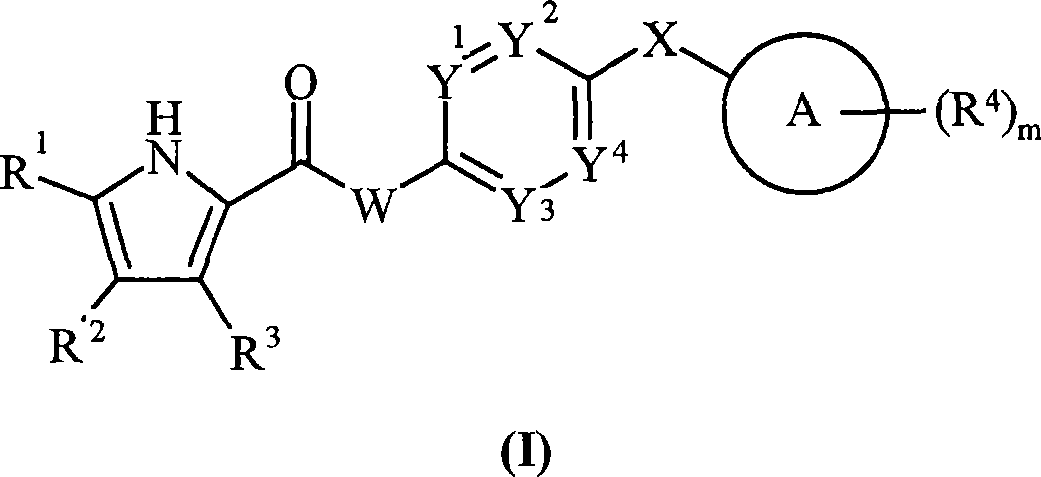
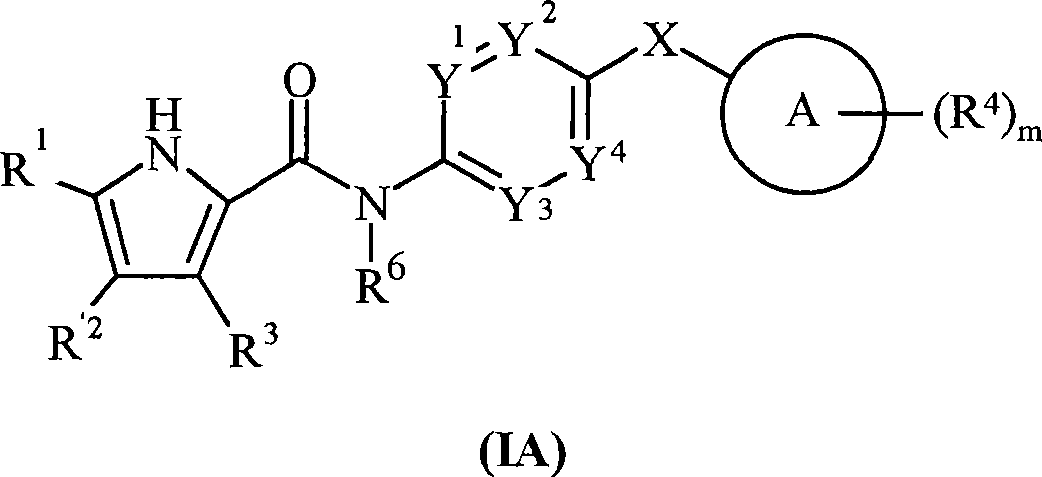
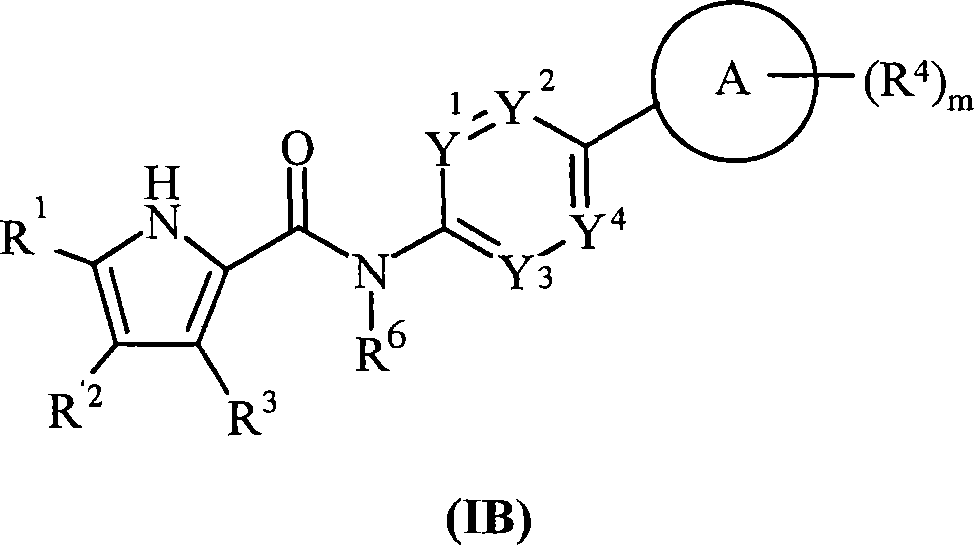
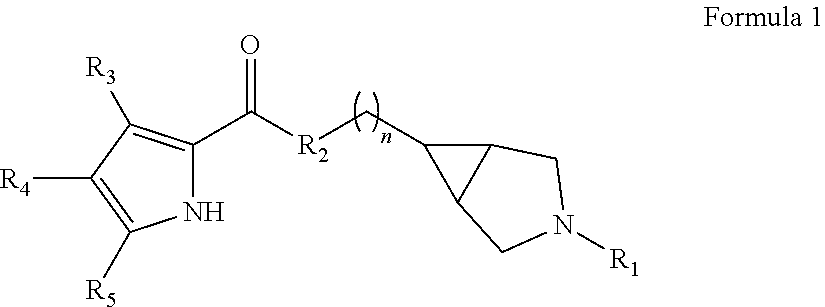
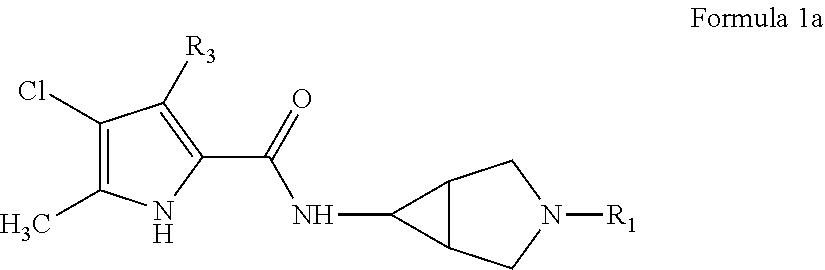
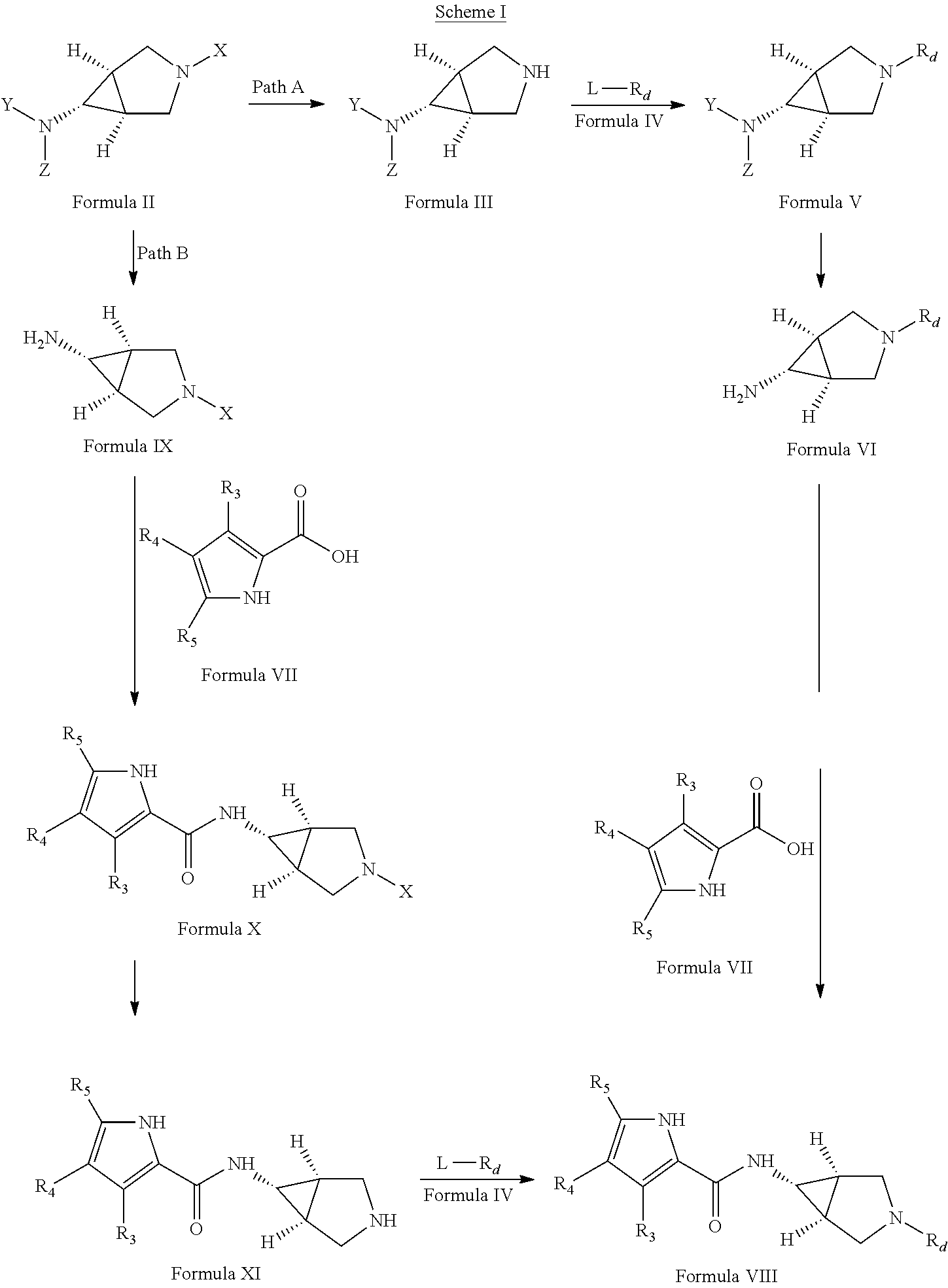
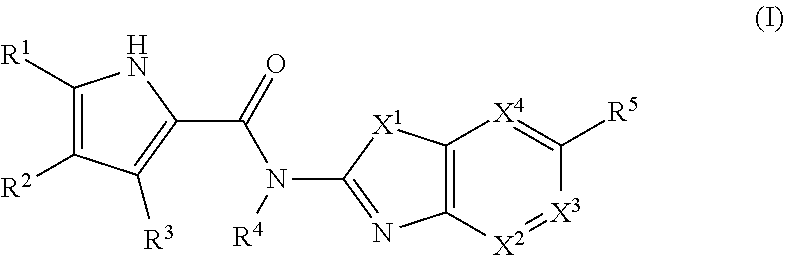
Pyrrole carboxylic acid derivatives as antibacterial agents
The present invention provides DNA Gyrase and / or Topo IV inhibitors of Formula (I), which can be used as antibacterial agents. Compounds disclosed herein can be used for treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed by gram positive, gram negative and anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Pseudomonus spp., Acenetobacter spp., Mvraxalla spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasma spp., Legionella spp., Mycobacterium spp., Helicobacter, Clostridium spp., Bacteroides spp., Cotynebacterium, Bacillus spp., Enterobactericeae (E. coli, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., etc.) or any combination thereof. Also provided, are processes for preparing compounds disclosed herein, pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds disclosed herein, and methods of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Method for detection of microorganism and kit for detection of microorganism
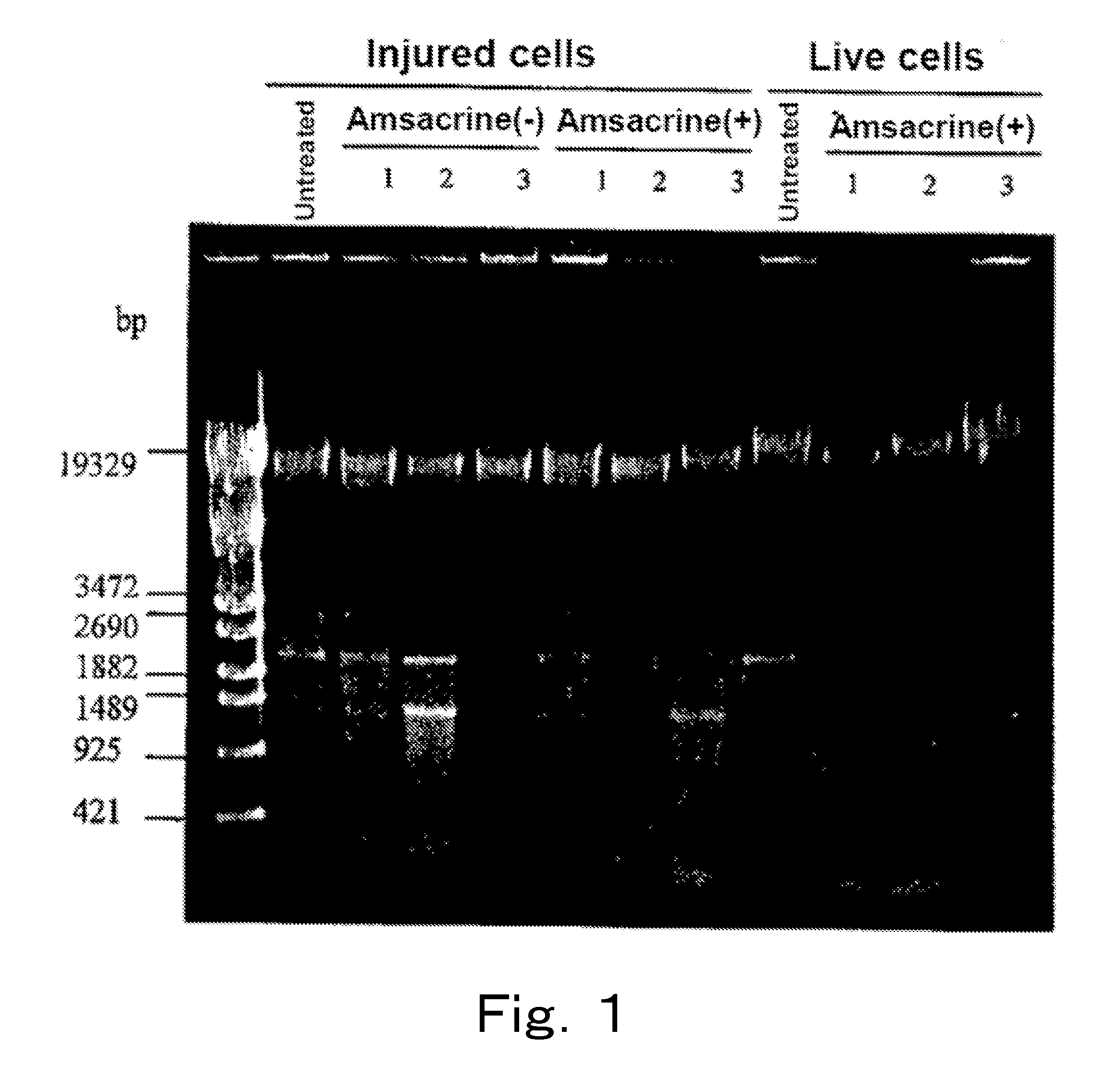
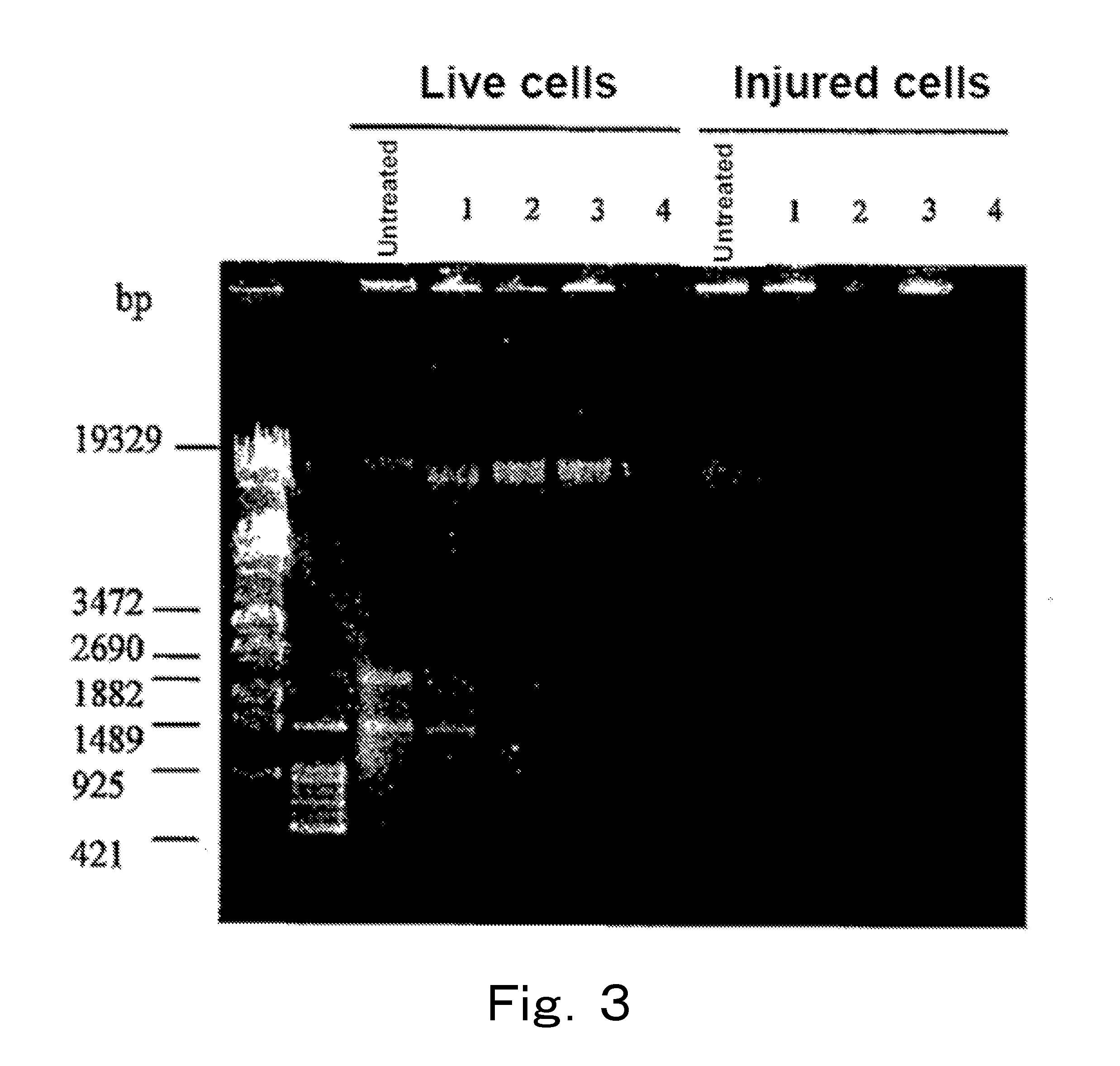
InactiveUS20150086995A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicroorganismDNA underwinding
Live cells of a microorganism in a test sample are detected by the following steps:a) the step of treating the test sample with a topoisomerase poison and / or a DNA gyrase poison,b) the step of extracting DNA from the test sample, and amplifying a target region of the extracted DNA by PCR, andc) the step of analyzing an amplification product.
Owner:MORINAGA MILK IND CO LTD
Methods of treatment for bacterial infections
ActiveUS20200163985A1Reduce riskAvoid developmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideAminocoumarinsGram-negative bacterial infections
This invention features new compositions and methods that are useful in treating a host with a Gram-negative bacterial infection. Combination therapies comprising an aminocoumarin compound and a polymyxin compound are disclosed, including certain combinations that exhibit synergistic effects. Furthermore, aminocoumarin compounds are described having altered inhibition of DNA gyrase in Gram-negative bacteria and / or the ability to target the transport proteins responsible for assembling lipopolysaccharide in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Hydroxyalkyl thiadiazole derivatives
ActiveUS10399968B2Improved profileImprove solubilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHuman useResistant bacteria
Problem to be Solved There is a need for a new antibiotic having a novel mechanism of action which exhibit strong antibacterial activity not only against sensitive bacteria but also against resistant bacteria thereof, and at the same time possesses excellent solubility an a safety profile amenable to human use. Solution to the Problem As a result of intensive research, the present inventors have found that a compound represented by general formula (I), ##STR00001## a stereoisomer, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof inhibits DNA gyrase GyrB subunit and / or topoisomerase IV ParE subunit possesses excellent solubility and a safety profile for use in humans for the treatment of bacterial infectious diseases.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Topoisomerase inhibitors with antibacterial and anticancer activity
ActiveUS11274106B2Impressive activityHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDeoxynybomycinEnzyme Inhibitor Agent
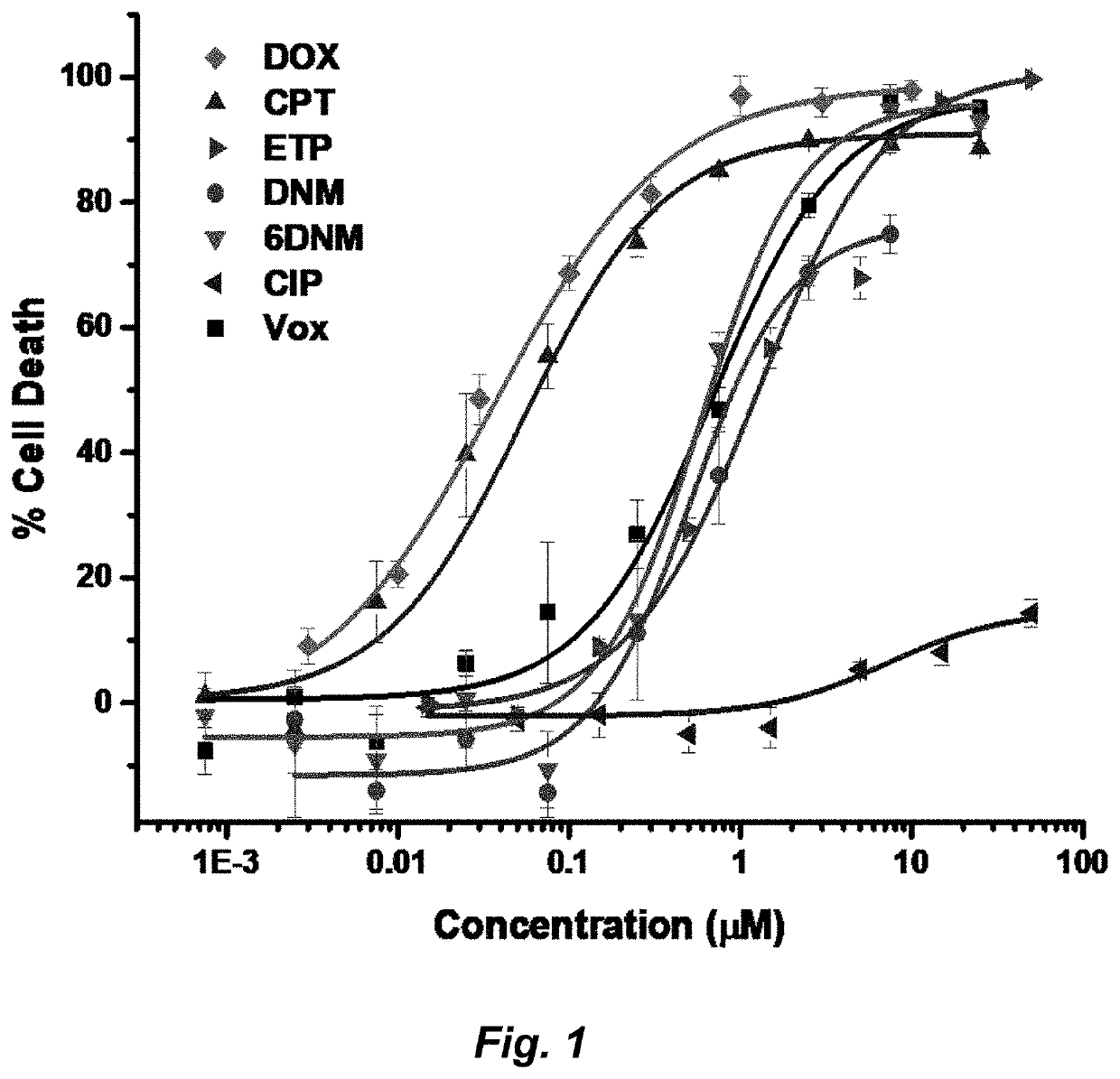
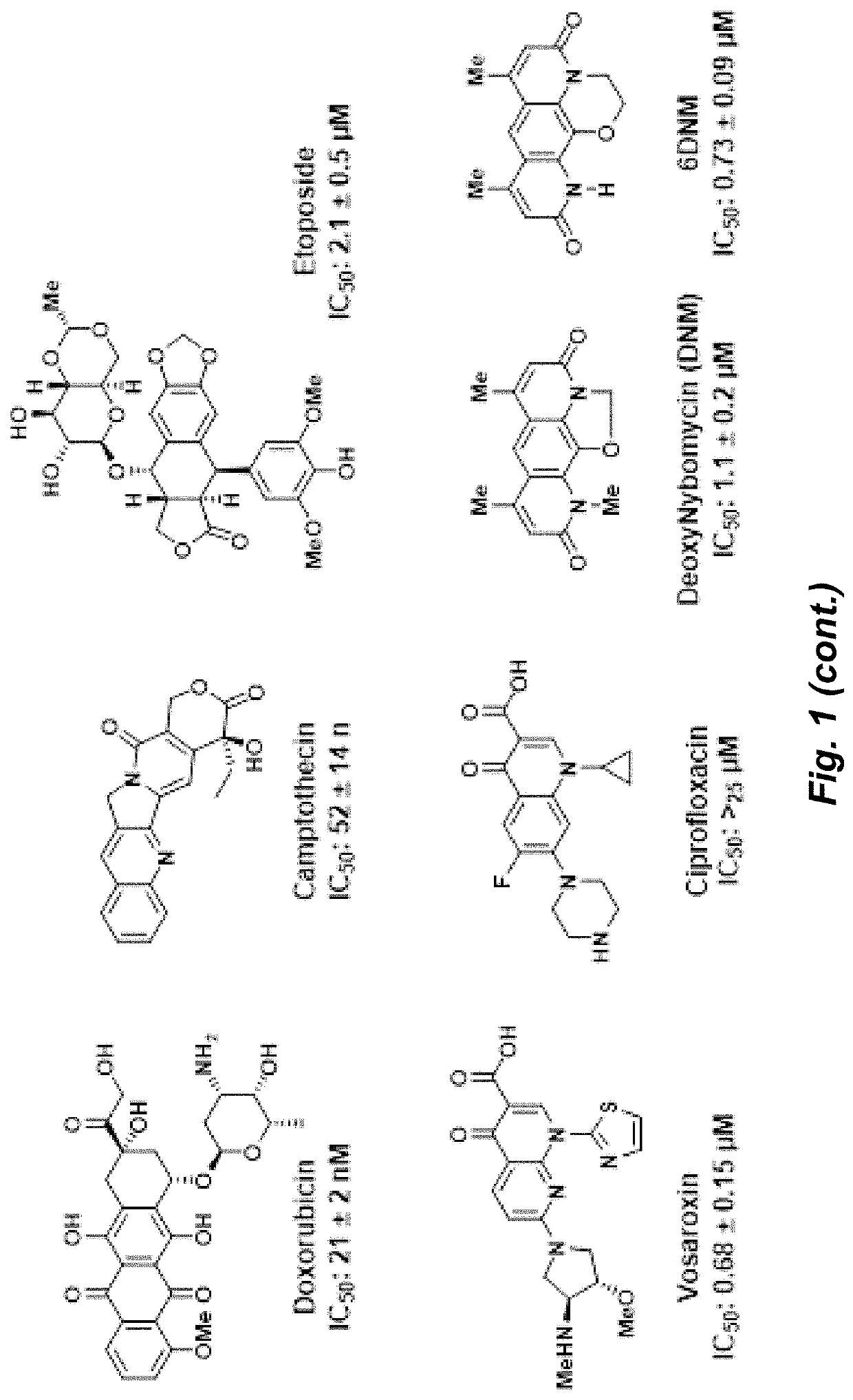
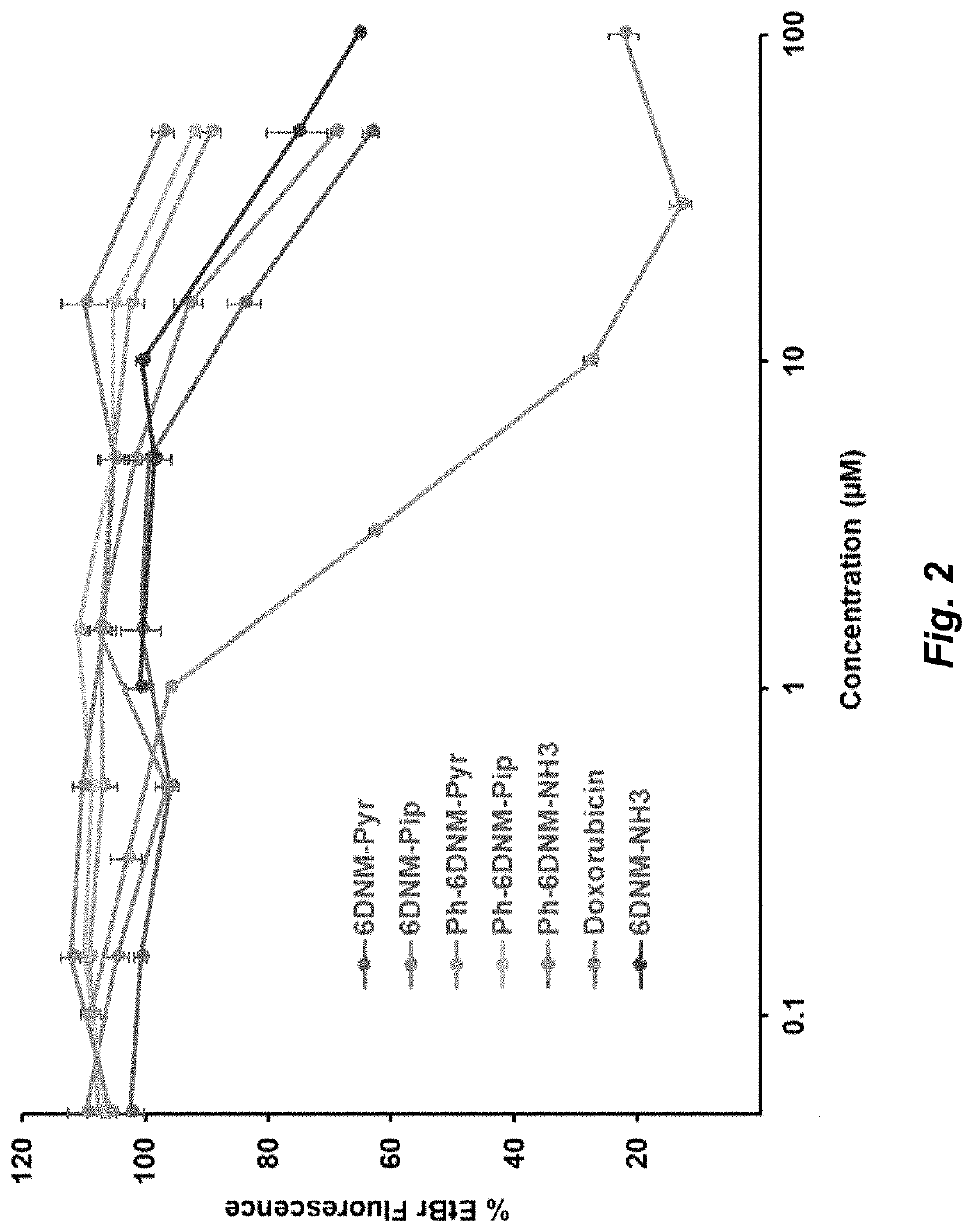
Herein is described the conversion of deoxynybomycin (DNM), a natural product and DNA gyrase inhibitor with minimal cytotoxicity, into a compound (Formula I) that has anticancer activity. Detailed in vitro and cell culture experiments demonstrate that these compounds inhibit Top2 and also act upon topoisomerase I. Similar approaches are applicable to other classes of gyrase inhibitors and other antibacterial targets for discovery of new anticancer drugs.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid to supercoiled plasmid
InactiveUS20050255563A1Increase productionUniversal procedureMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGeneticsPhosphoric acid
In one embodiment of the invention, a method is provided for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising: (a) providing a plasmid solution comprised of unligatable open circular plasmid; (b) reacting the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes and appropriate nucleotide cofactors, such that unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) reacting the 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid with a DNA ligase and DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, such that 3′-hydroxyl, 5′-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) reacting the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with a DNA gyrase and DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, such that relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. In other embodiments, DNA gyrase is replaced with reverse DNA gyrase or reaction (d) is not performed.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD D
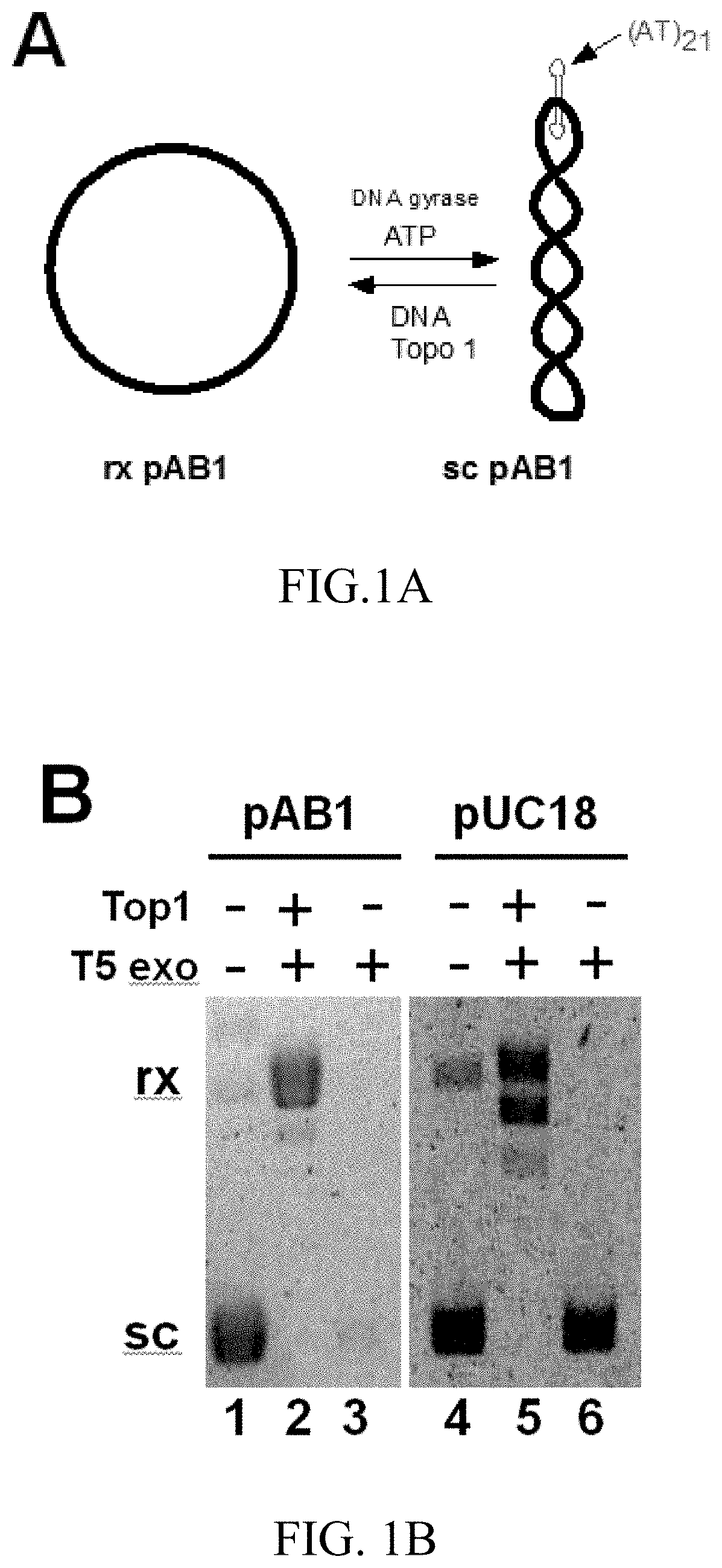
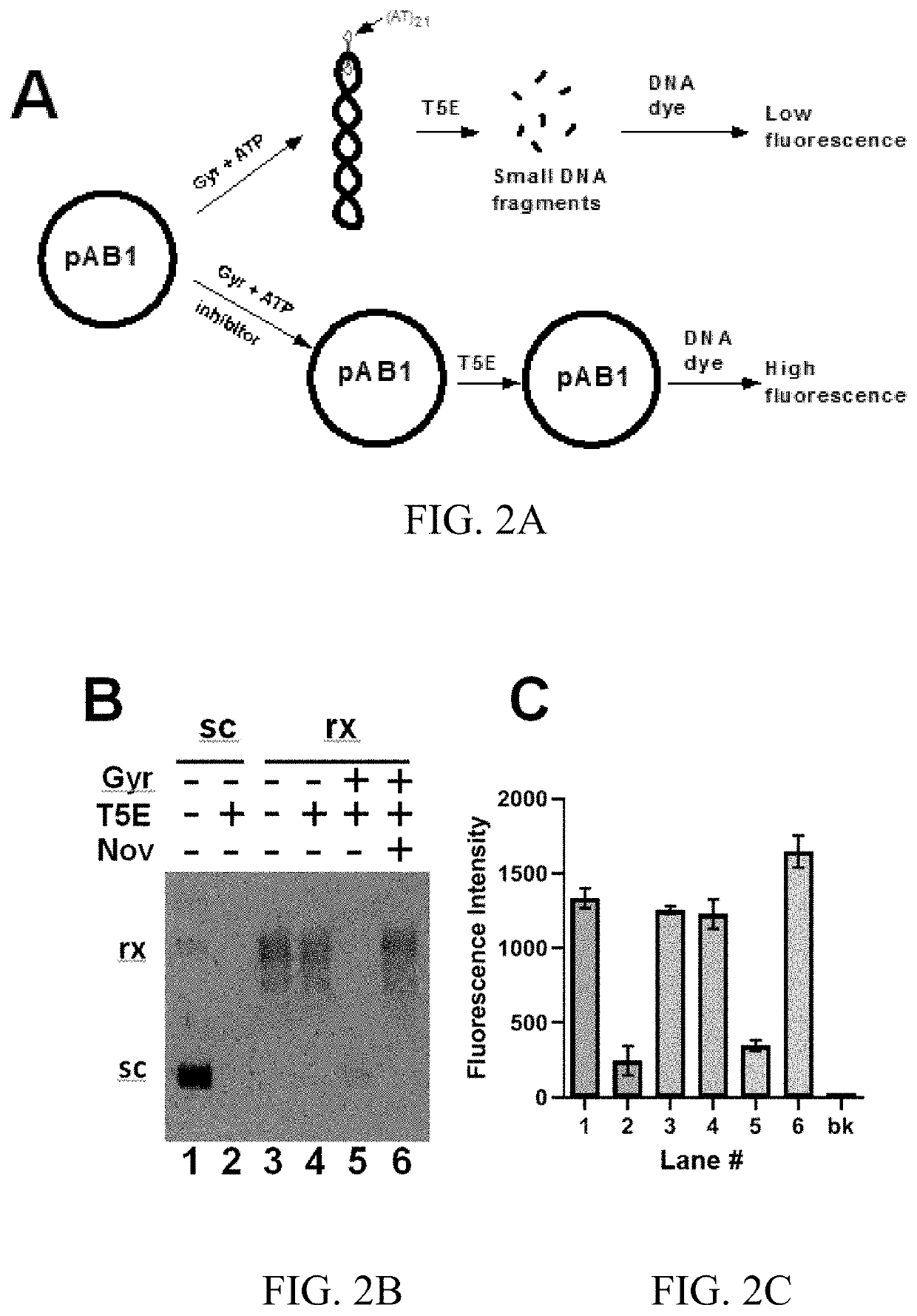
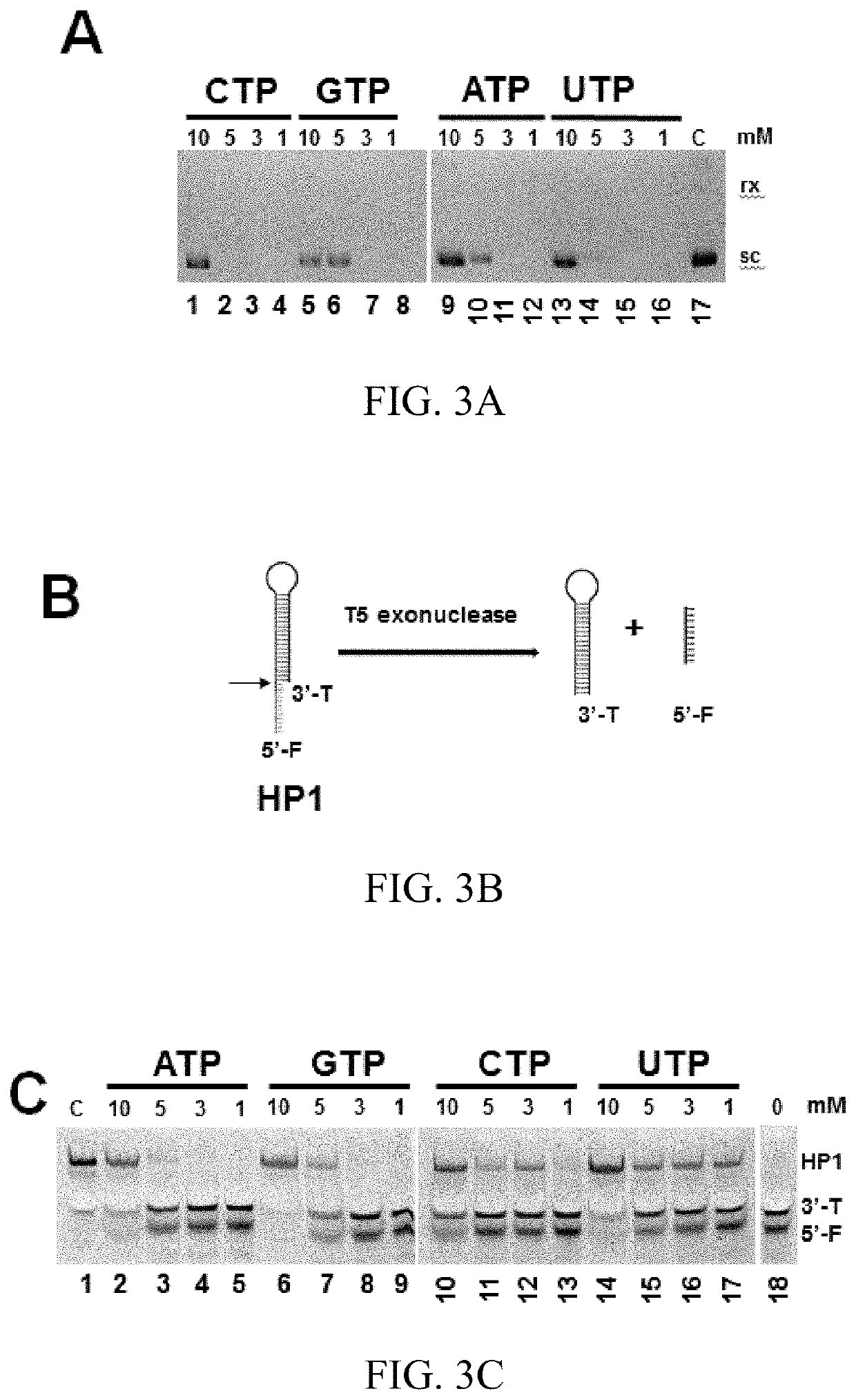
T5 exonuclease-based method to identify DNA topoisomerase inhibitors
ActiveUS20220119858A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPlasmid dna
The present invention provides assays and methods for studying DNA topology and topoisomerases. The assays and methods utilize a circular plasmid DNA comprising one or more hairpin structures and the ability of T5 exonuclease (T5E) to digest the circular plasmid DNA in a specific configuration. The assays and methods can be used as a high throughput screening for inhibitors of, for example, DNA gyrases and DNA topoisomerases I for anticancer drug and antibiotics discovery.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
New class of DNA gyrase and/or topoisomerase iv inhibitors with activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
The present invention relates to compounds having a structure of general formula (I), processes for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions containing them as the active ingredient, to their use as medicaments and to their use in the manufacture of medicaments for use in the treatment of bacterial infections in humans and warm-blooded animals.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LJUBLJANA +1
Topoisomerase binding probe and method of use
An aminocoumarin conjugated to a fluorescent label through a secondary amine, is operative as a fluorescent polarization probe of the DNA gyrase B or topoisomerase IV E subunit. The probe is used for detecting topoisomerase inhibitor binding by fluorescence polarization, particularly in a high-through put topoisomerase inhibitor assay.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com