T5 exonuclease-based method to identify DNA topoisomerase inhibitors
a topoisomerase inhibitor and exonuclease technology, applied in the field of t5 exonuclease-based method to identify dna topoisomerase inhibitors, can solve the problems of inability to use high throughput screening (hts) assays, labor-intensive and time-consuming agarose gel electrophoresis, and inability to synthesis this type of fluorescently labeled dna molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Property of T5 Exonuclease
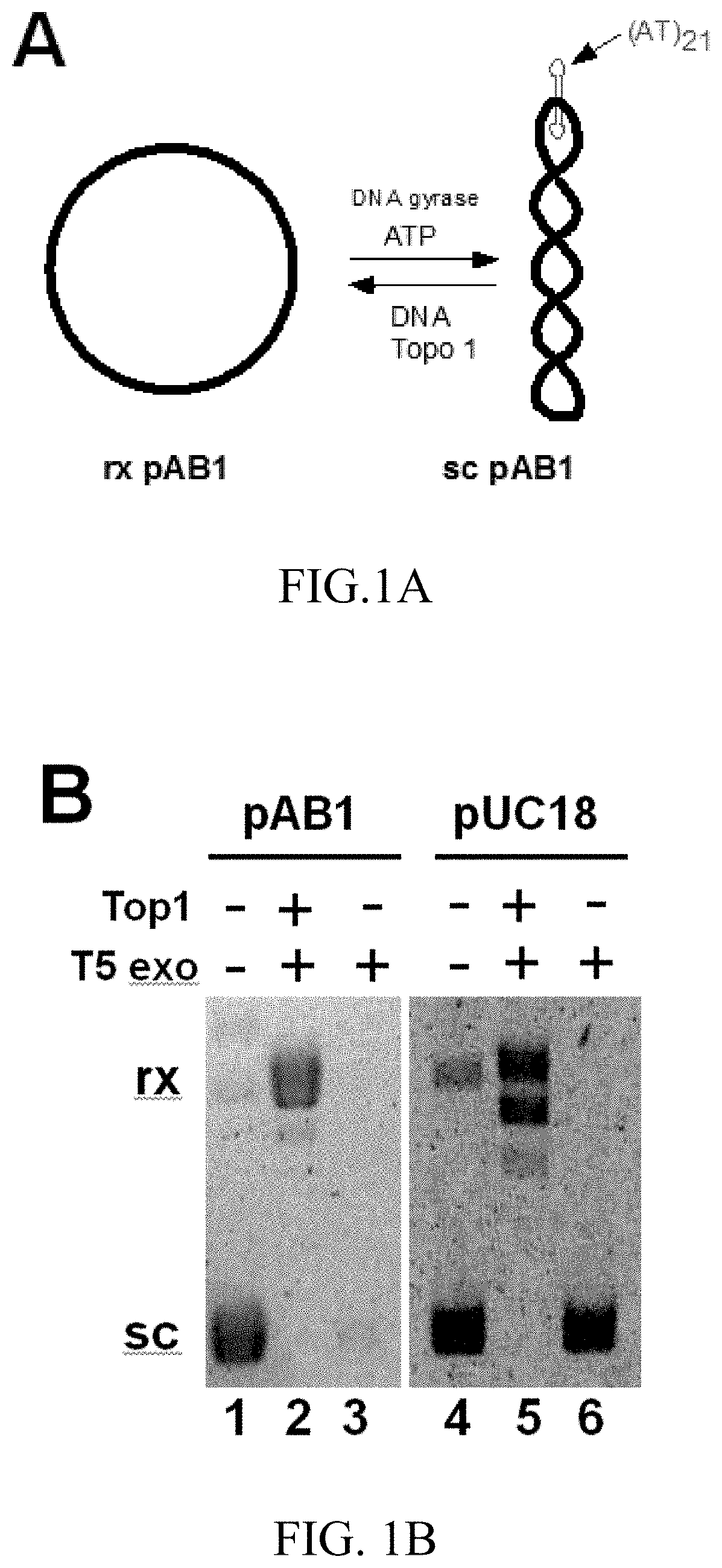
[0093]FIG. 1 shows a unique property of T5 exonuclease that completely digested the sc pAB1 carrying a AT hairpin structure (FIG. 1A and lane 3 of FIG. 1B). T5 exonuclease was not able to digest rx pAB1 (lane 2 of FIG. 1B) and rx & sc pUC18. This unique property of T5 exonuclease can be used to configure HTS assays to identify Topo inhibitors.
example 2
ease-Based HTS Assay for Bacterial DNA Gyrase
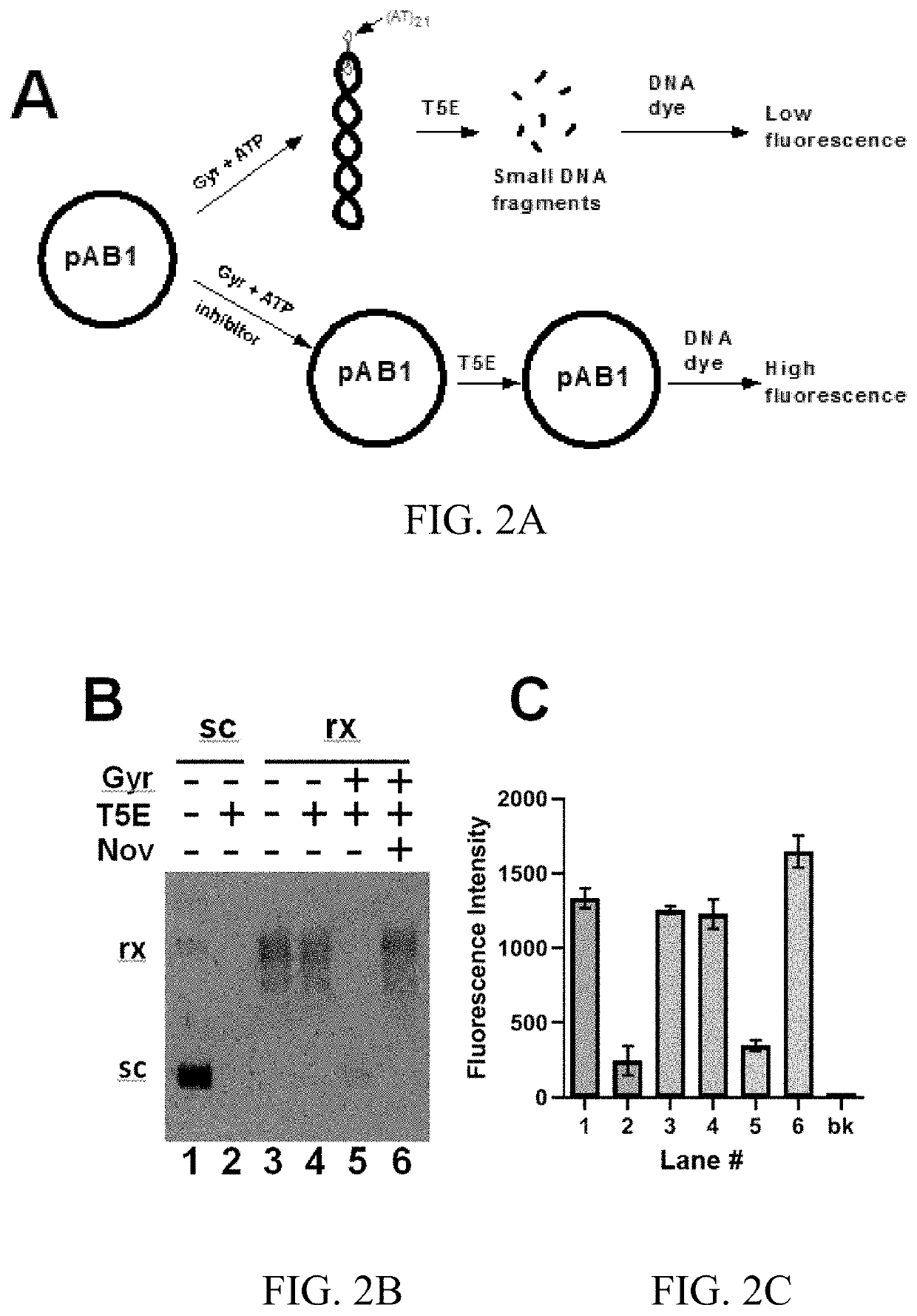
[0094]FIG. 2A shows a method to screen / identify inhibitors or other molecules targeting bacterial DNA gyrase. This method can be easily configured into a high throughput format. In the absence of gyrase inhibitors, prokaryotic DNA gyrase can convert the rx DNA templates into the sc form. This conversion results in the formation of a hairpin structure in the plasmid. As a result, the sc pAB1 can be completely digested by T5 exonuclease (lane 5 of FIG. 2B). In contrast, gyrase inhibitor novobiocin completely inhibited the bacterial gyrase activities and prevented the conversion of the rx plasmid pAB1 into sc form. T5 exonuclease could not digest rx pAB1 (lane 6 of FIG. 2B).
[0095]A DNA-staining dye, such as ethidium homodimer 1 (EthD1), can differentiate these two T5 exonuclease-based reactions (FIG. 2C). In the presence of a gyrase inhibitor, the fluorescence intensity of EthD1 is significantly higher comparing with the DNA sample in the ab...
example 4
of DNA Intercalators by T5 Exonuclease-Based HTS Assay
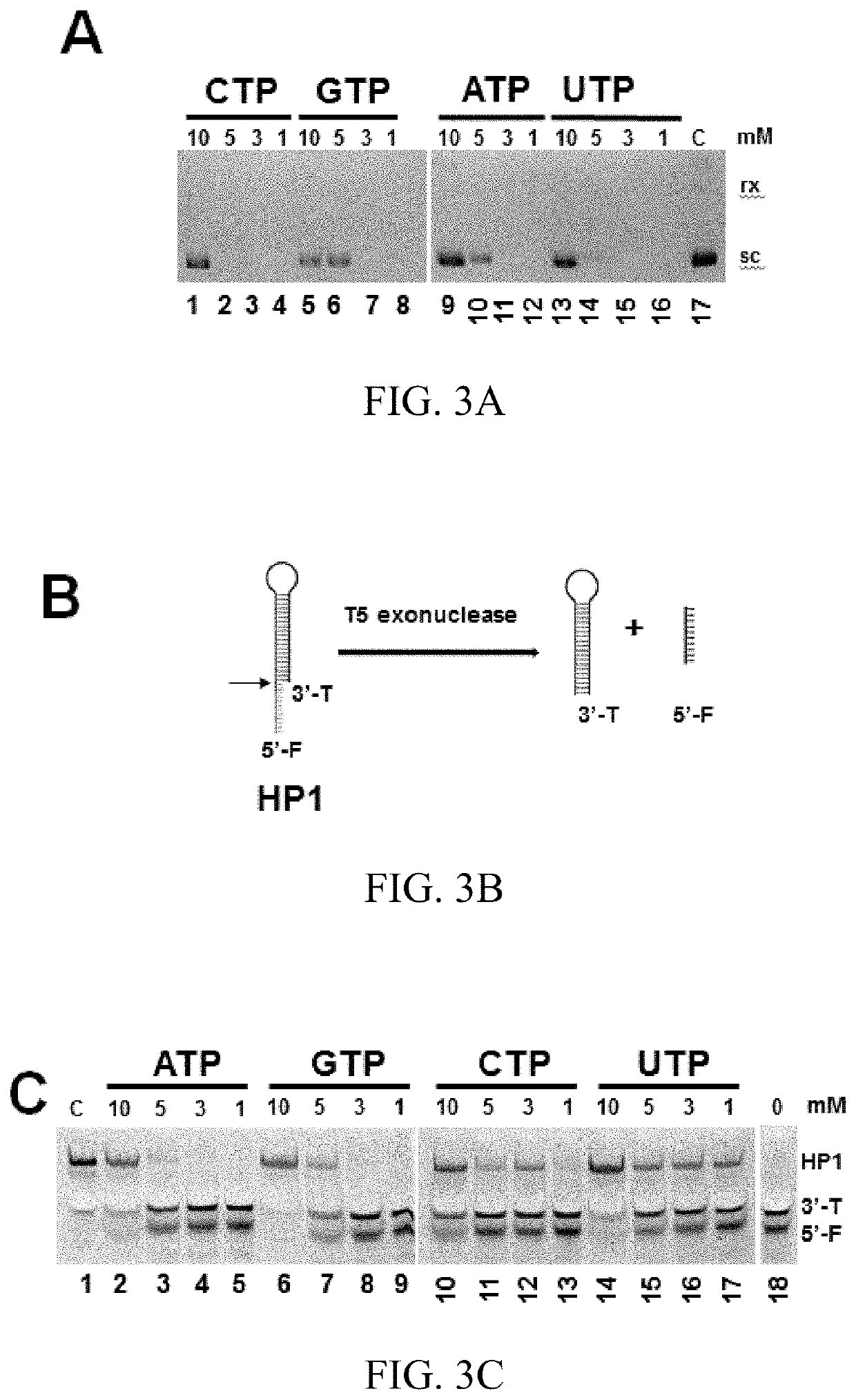
[0104]The T5E-based HTS assay can be used to identify DNA intercalators. In the absence of the DNA intercalator, the sc pAB1 is digested by T5E, which cannot bind to the DNA dye, leading to no or litter fluorescence (FIG. 8). In the presence of the DNA intercalator, the sc pAB1 is converted into the relaxed form, which cannot be digested by T5E. As a result, the rx pAB1 can bind to the DNA dye, leading to a high fluorescence (FIG. 8).
[0105]The compounds were added in the screening plate as indicated in Table 1. The screening results are shown in Table 3. The fluorescence was measured at λem of 617 nm with λex=528 nm using a plate reader. The results indicate that the compounds in 5A (ethacridine), and 2G (echinomycin) are DNA intercalators.
TABLE 3HTS screening of 50-compound library for DNA intercalators1234567A2235752302041367207252B178286191183246249175C202153198207214207D170259218206220314E196185220213207226F173159200217222181...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com