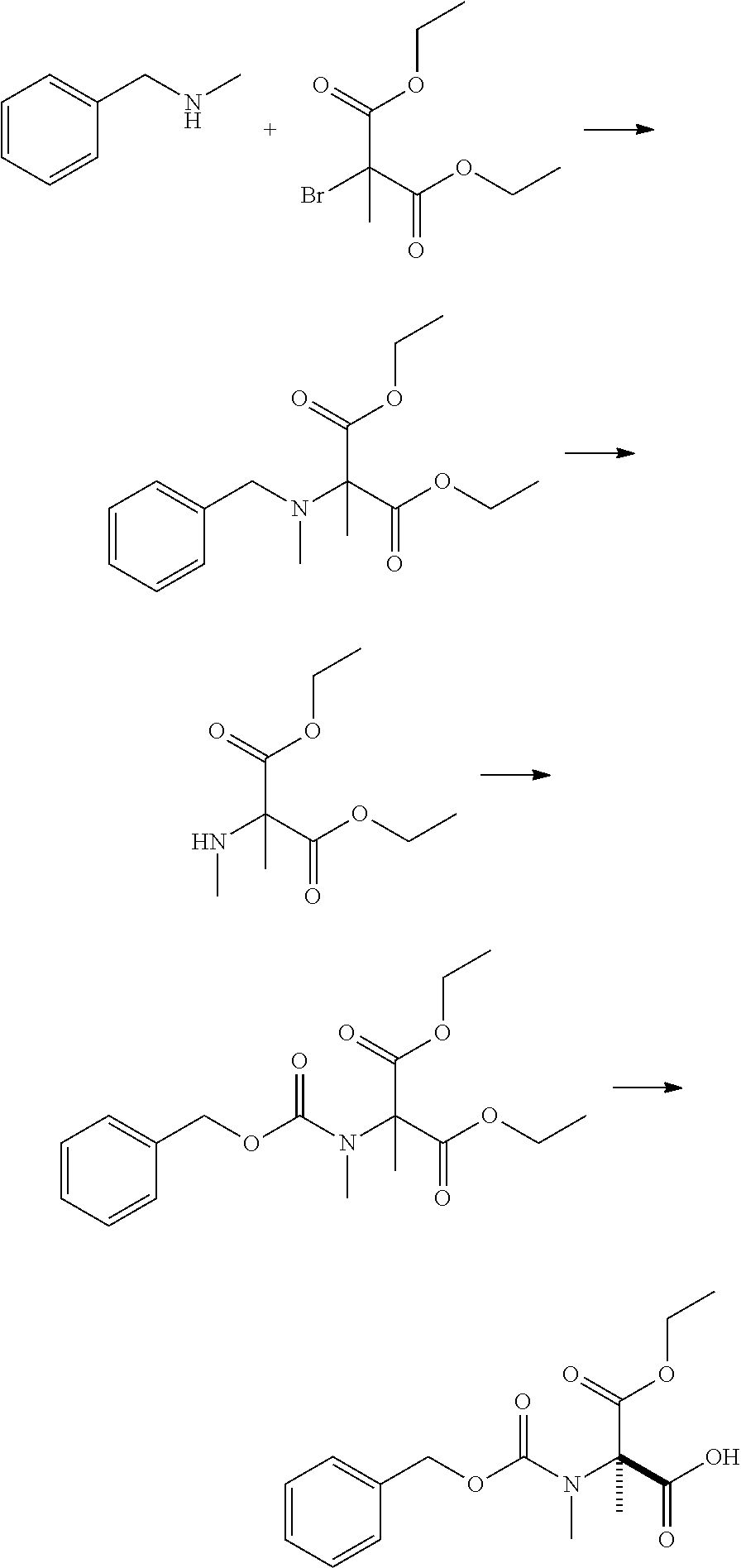
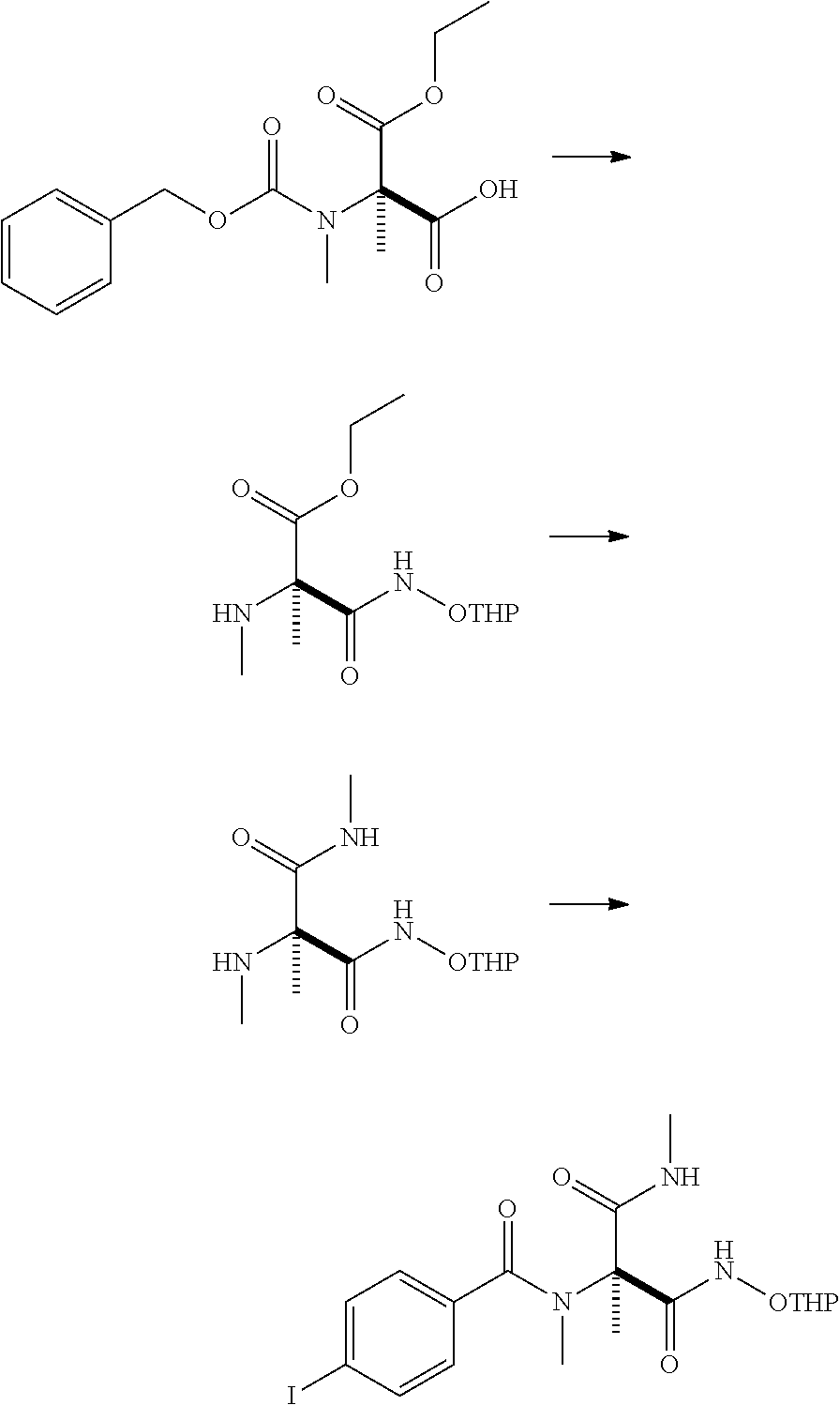
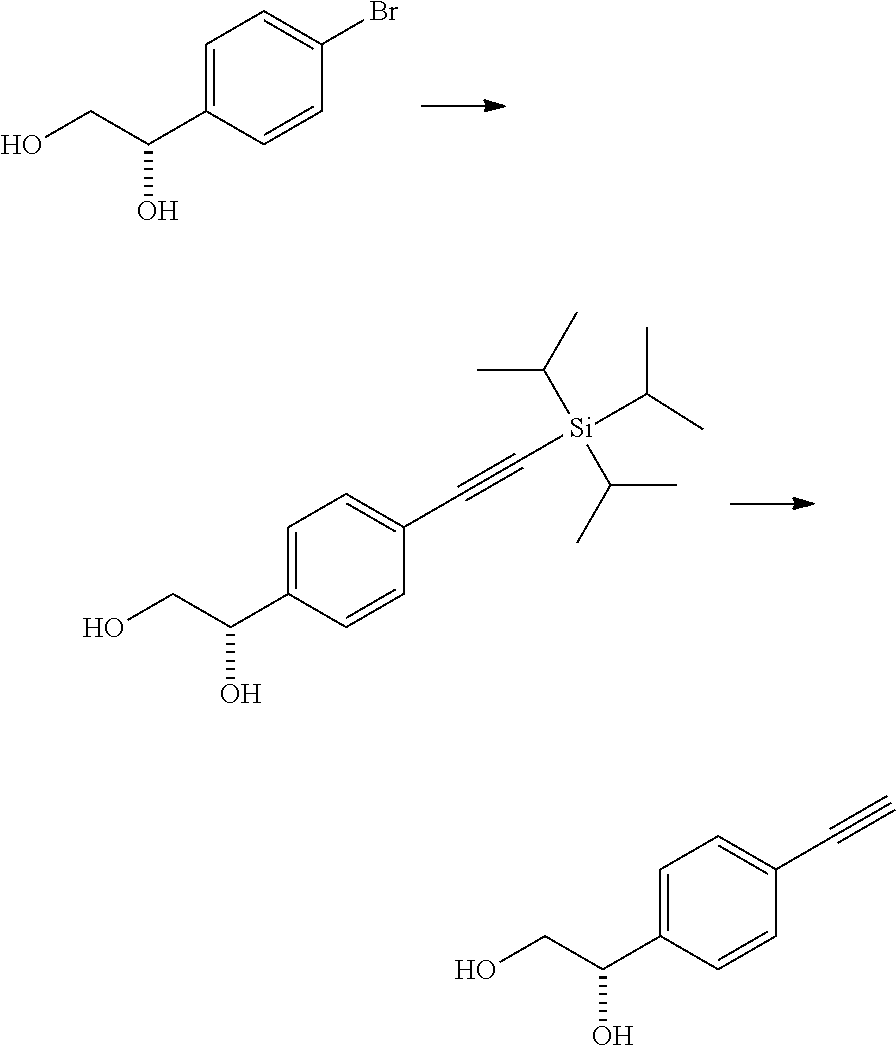
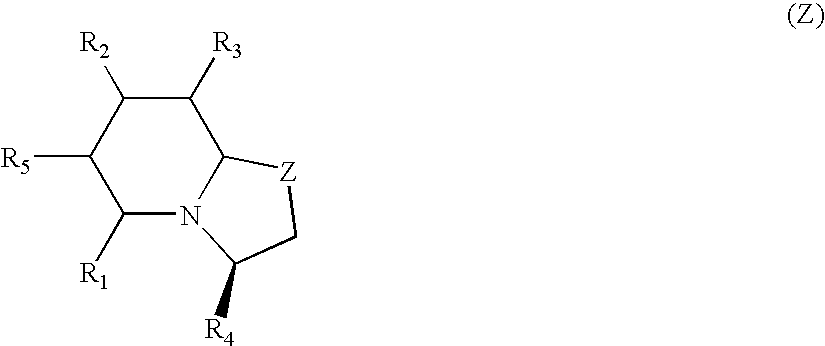
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Gram-negative bacterial infections" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
About Gram Negative Infection: A Gram Negative Infection is a bacterial infection caused by a gram-negative bacteria. Gram-negative infections include those caused by Klebsiella, Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and E. coli., as well as many other less common bacteria.
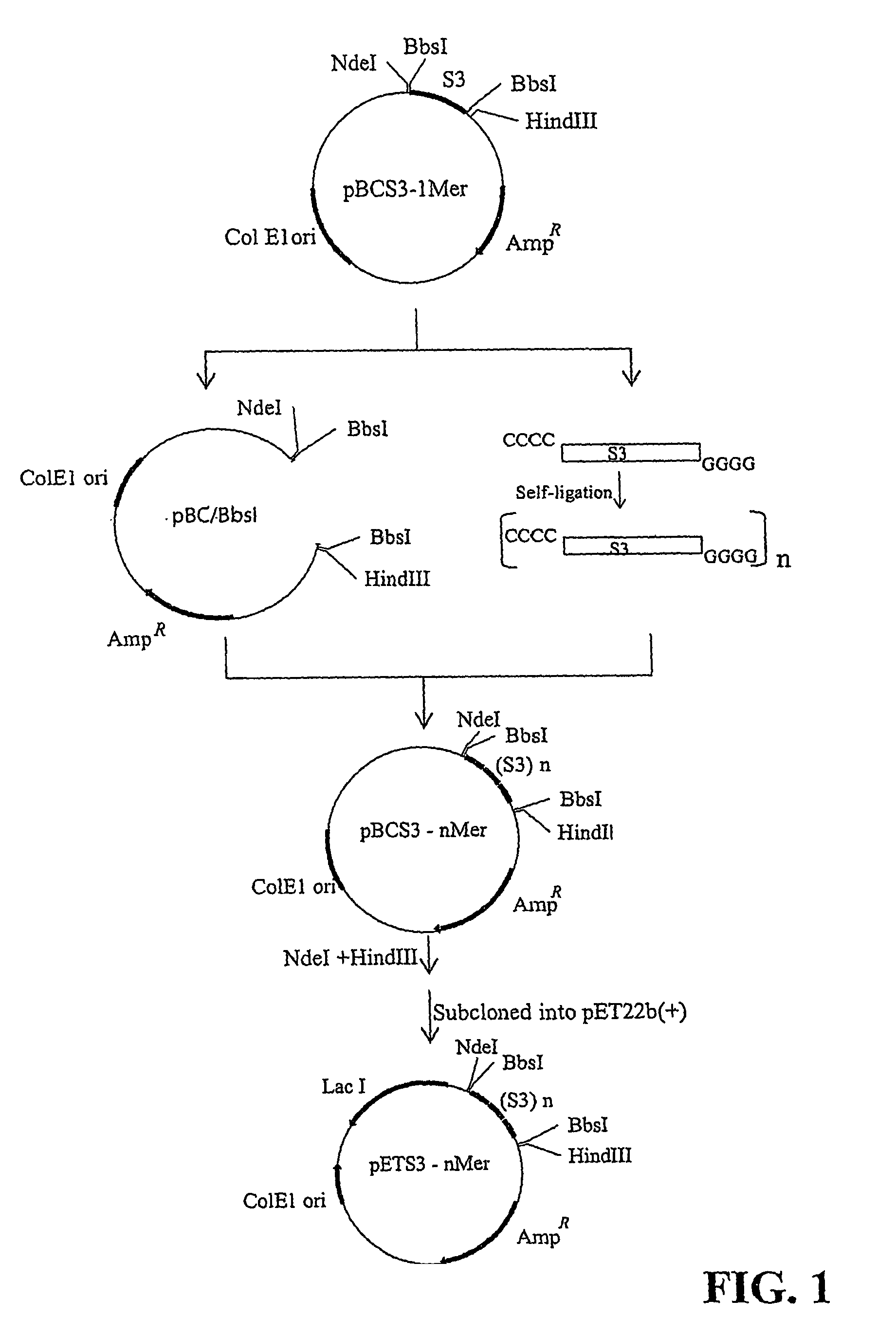
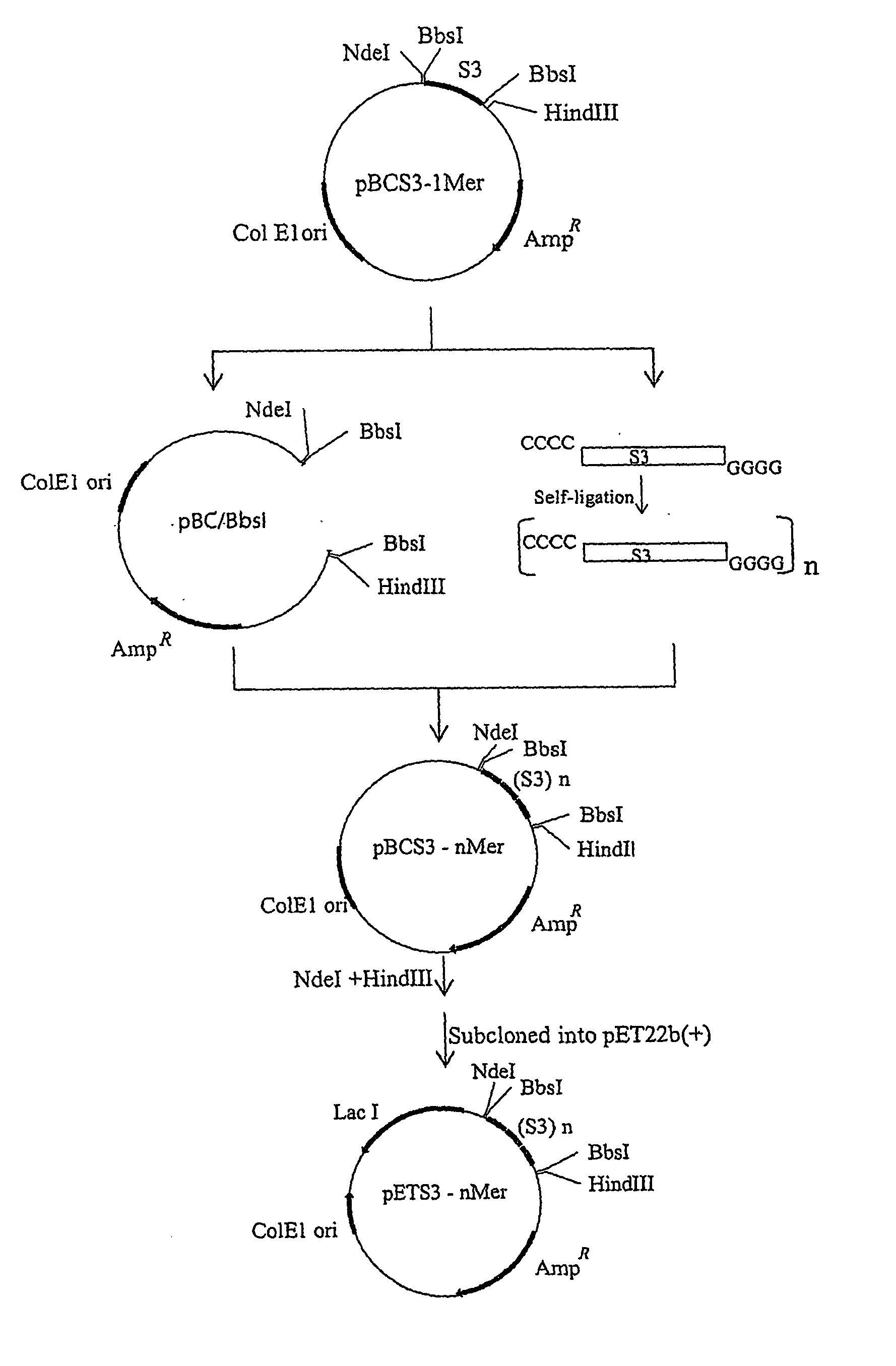
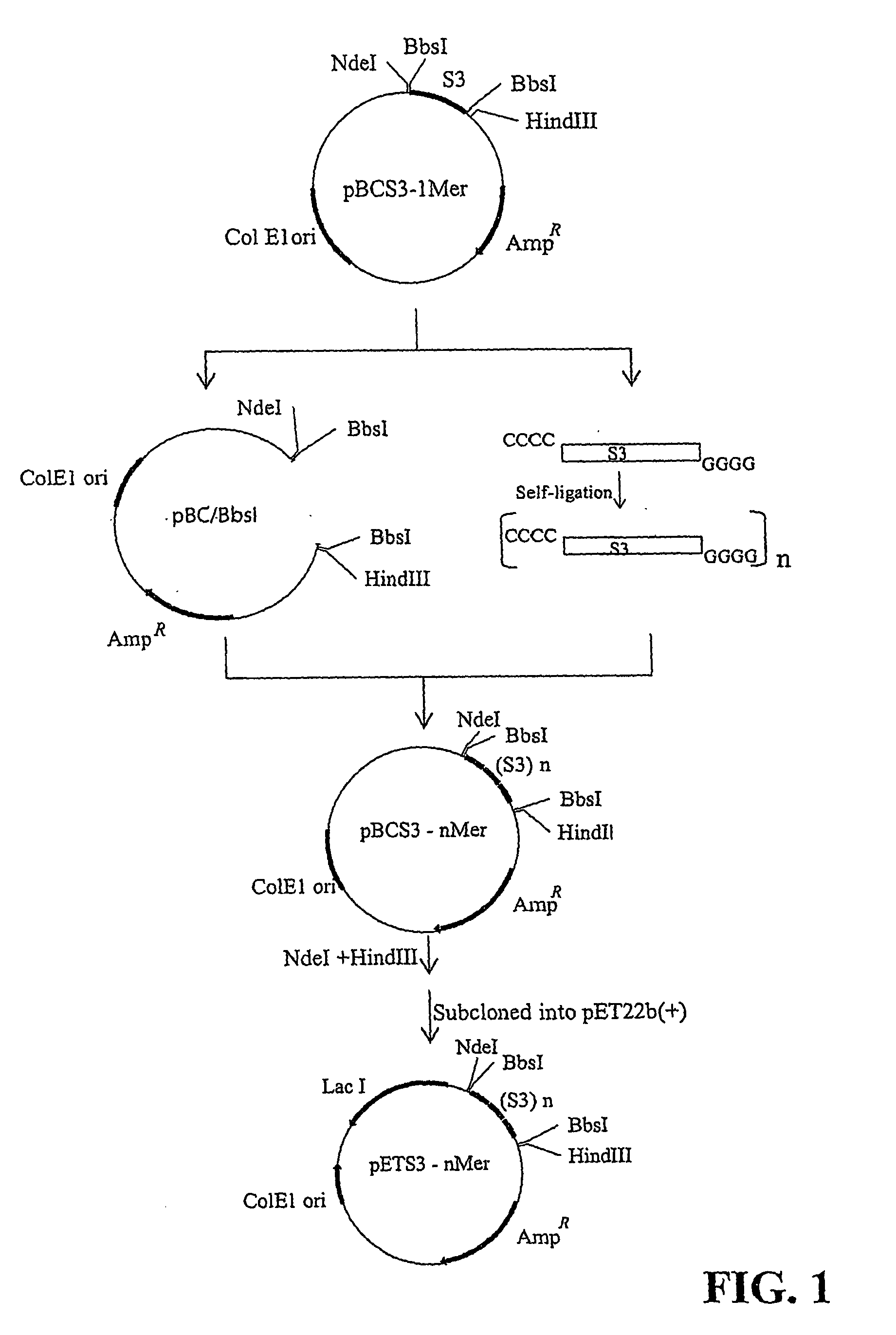
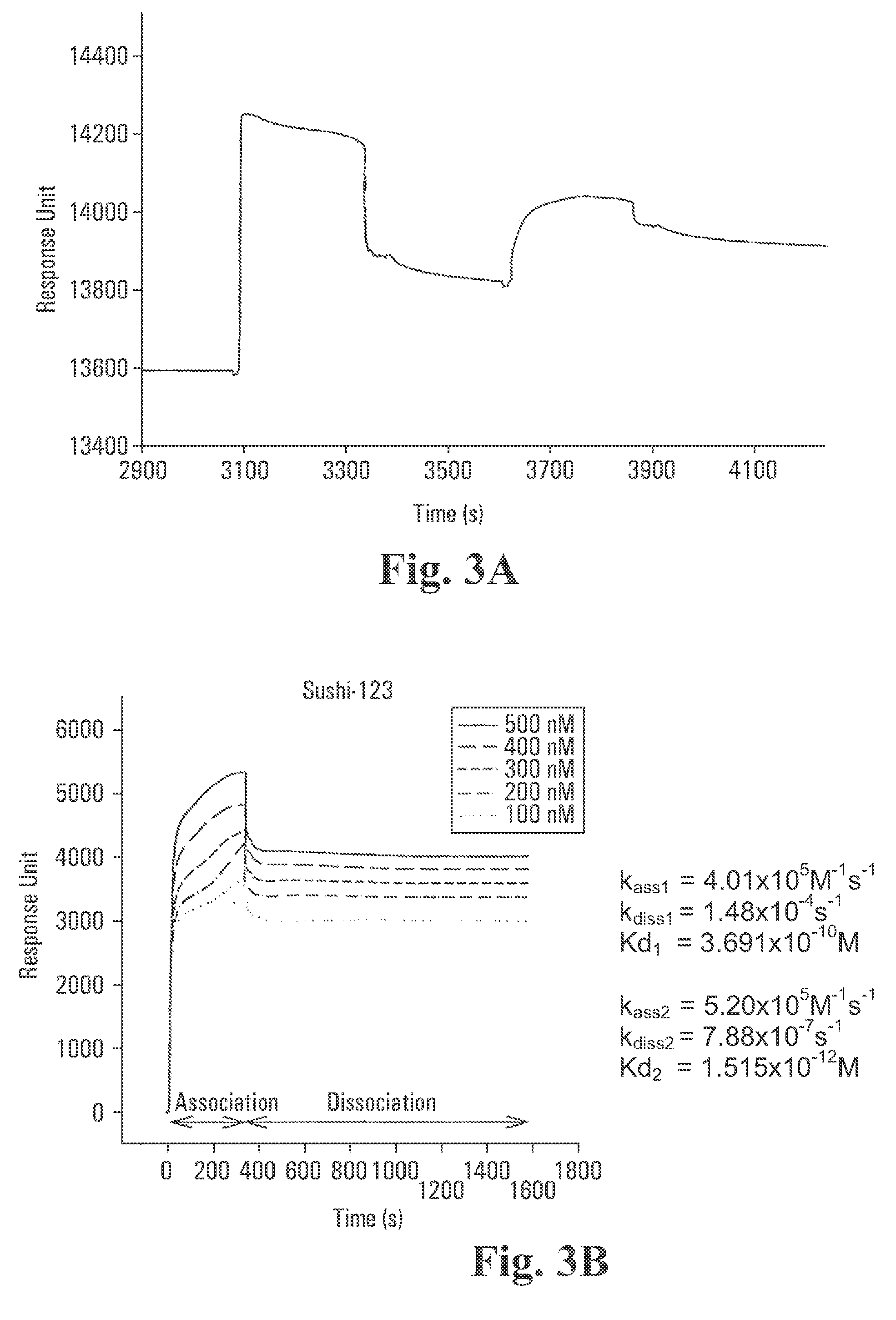
Sushi peptide multimer
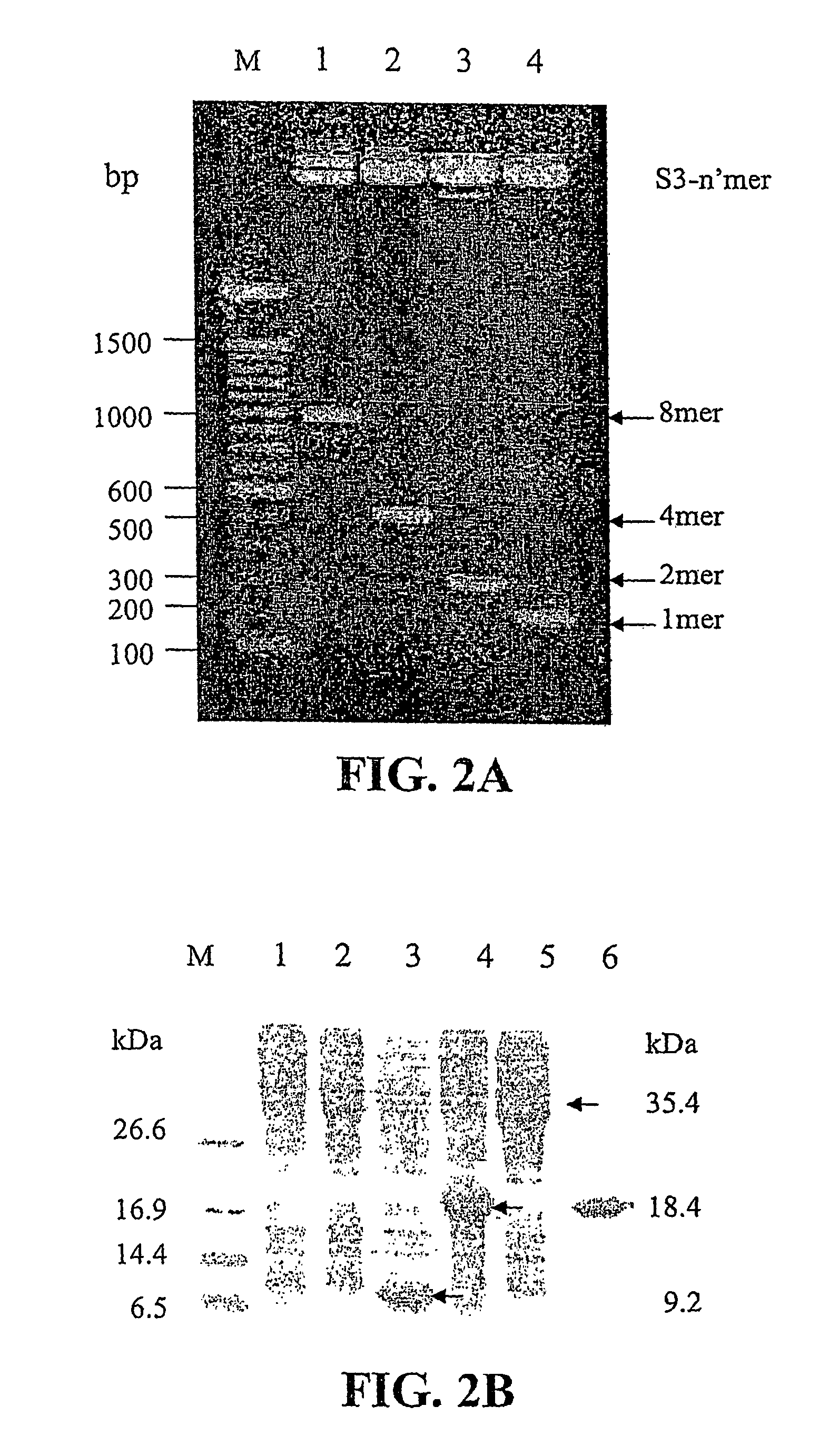
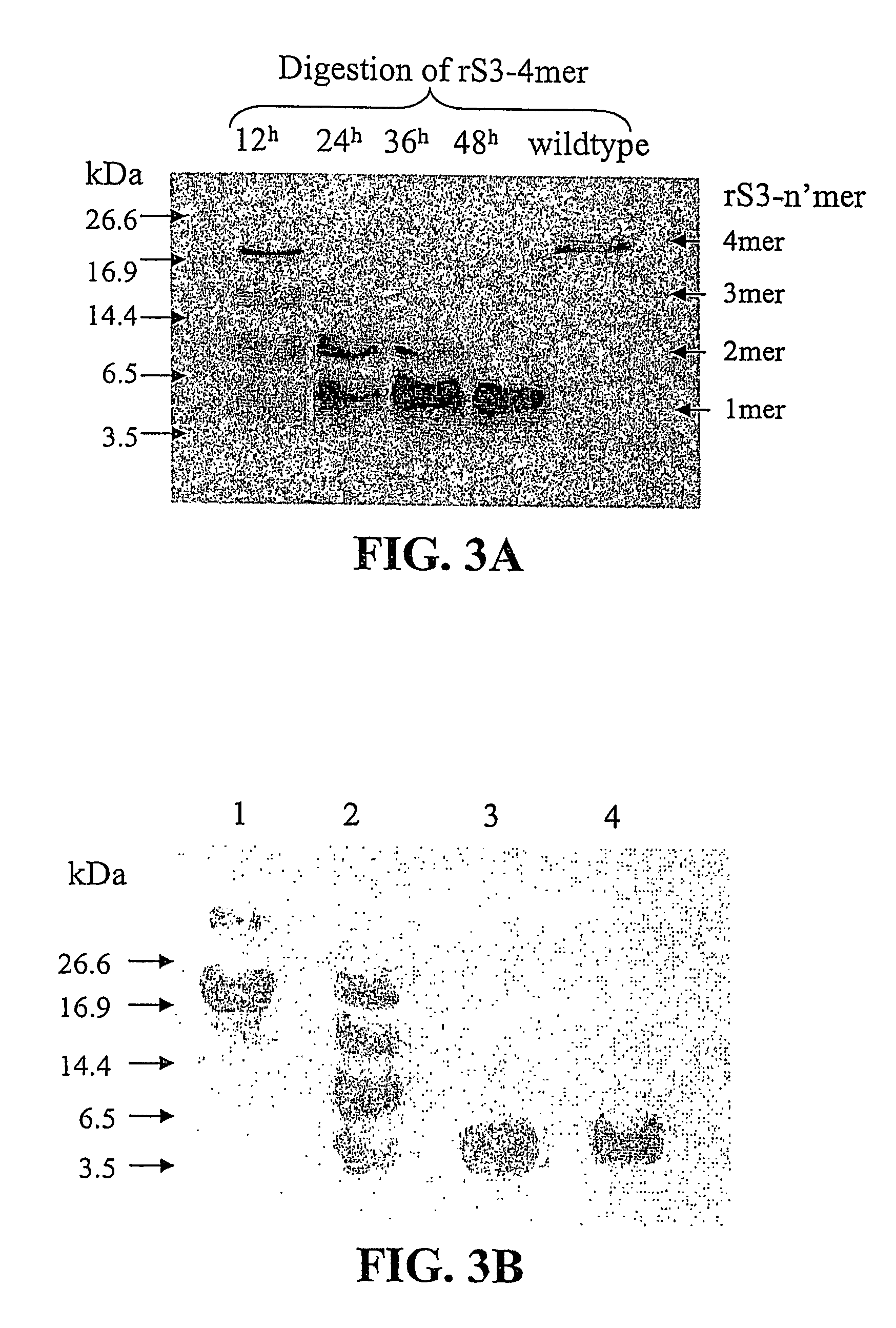
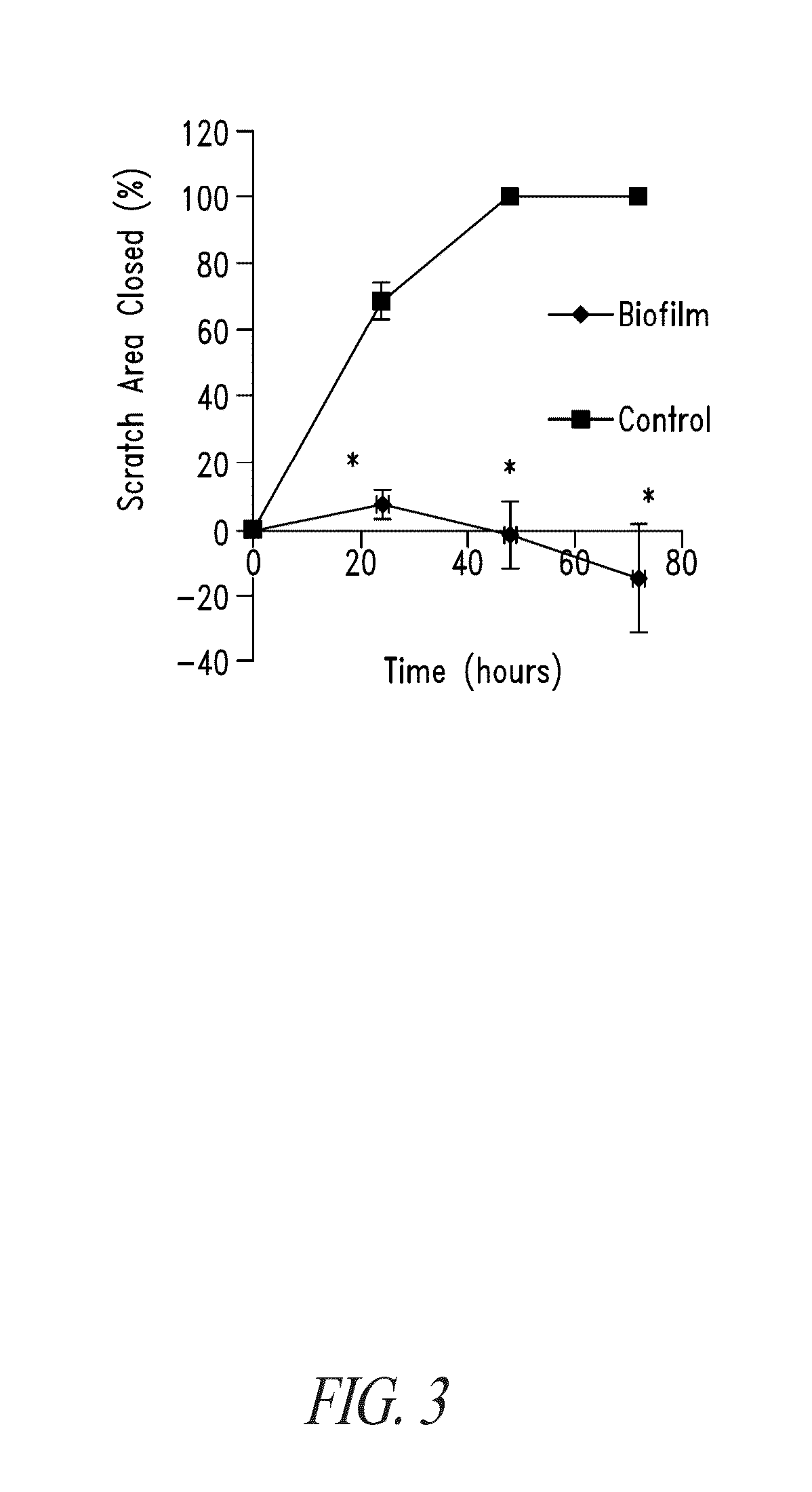
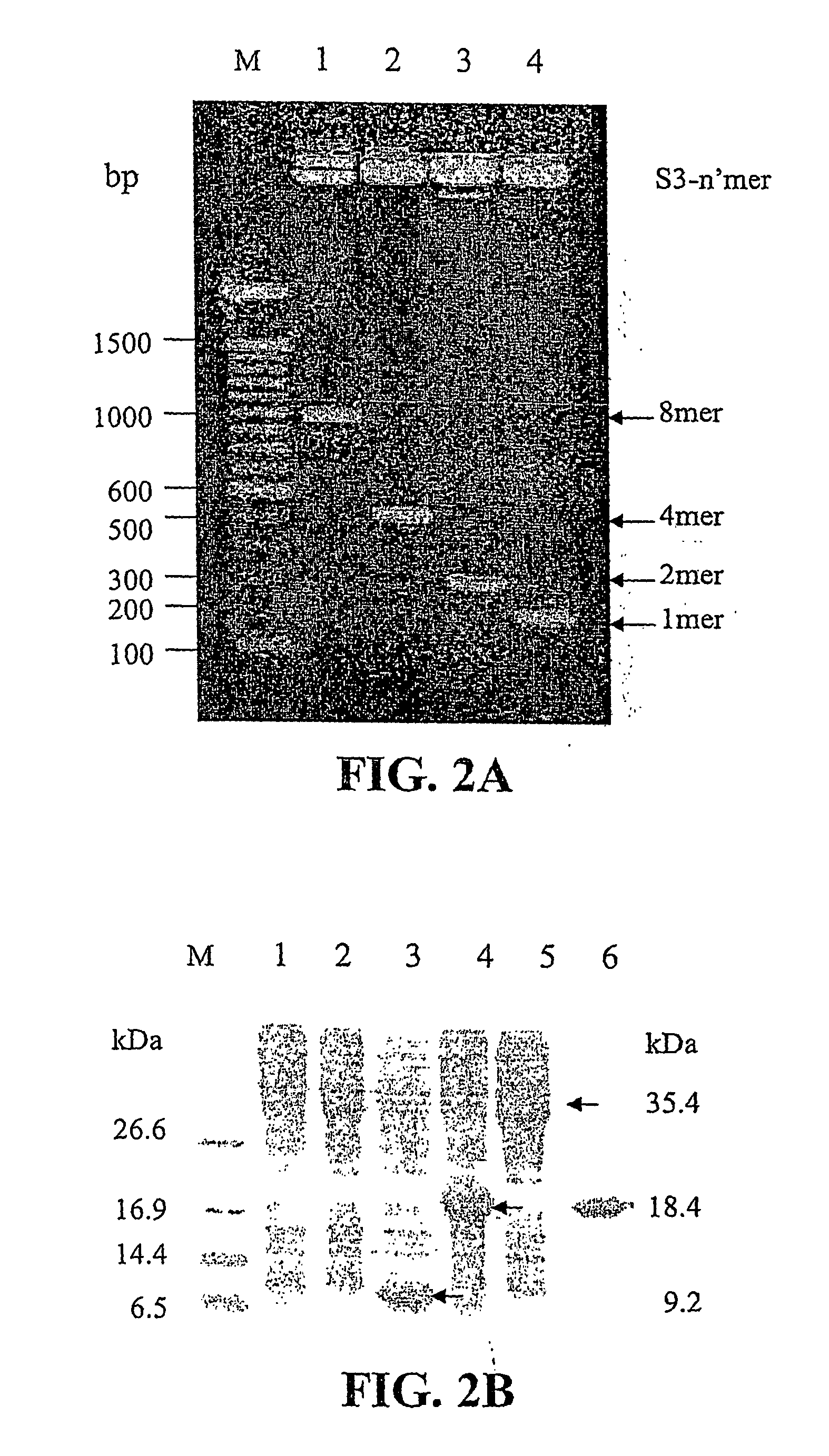
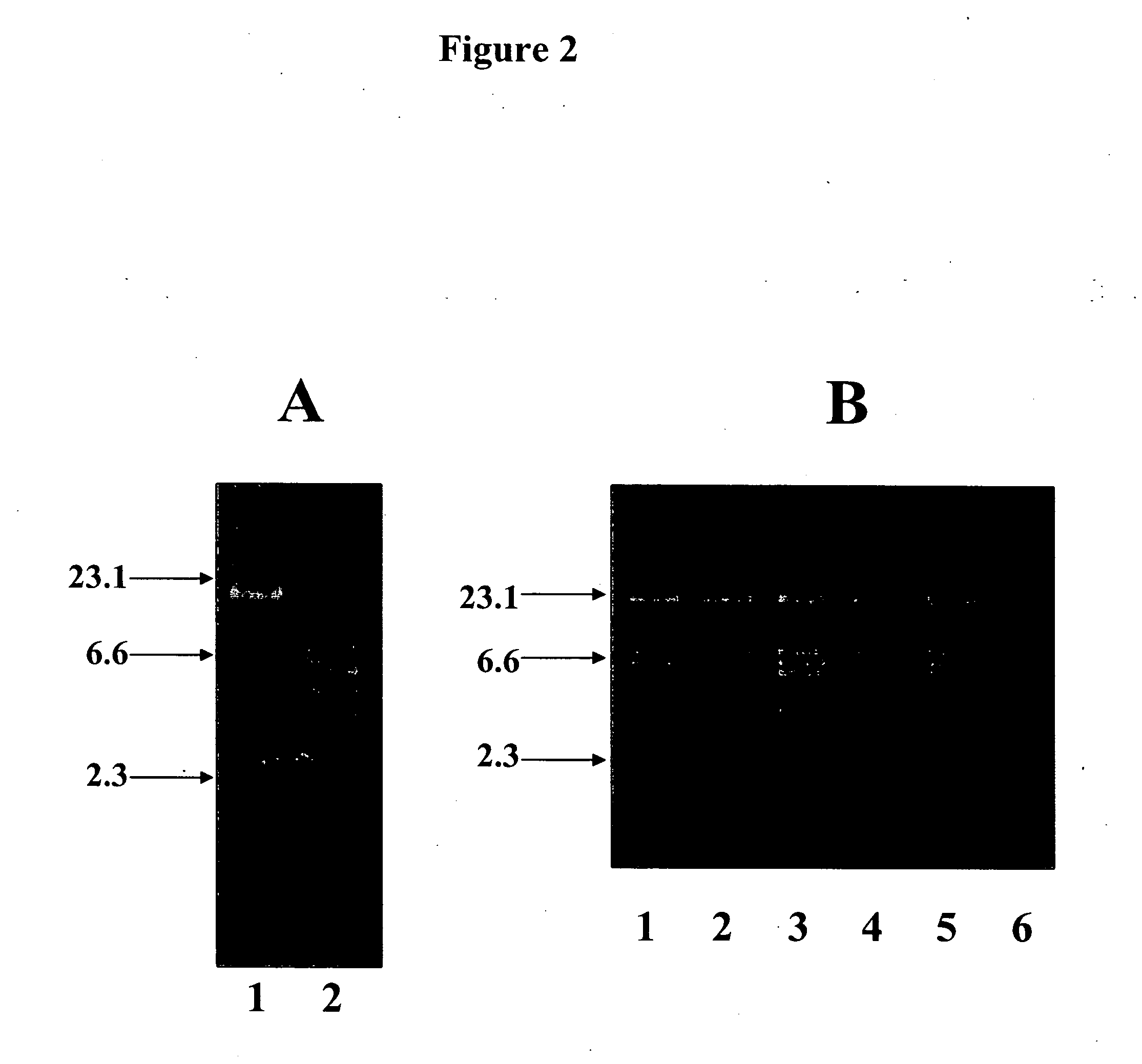
Endotoxin, also known as lipopolysaccharides (LPS), is the major mediator of septic shock due to Gram-negative bacterial infection. Chemically synthesized S3 peptide, derived from Sushi3 domain of Factor C, which is the endotoxin-sensitive serine protease of the limulus coagulation cascade, binds and neutralizes LPS activity. Fluorescent tagged-S3 is shown to detect LPS-containing bacteria. For large-scale production of S3 and to mimic other pathogen-recognizing molecules, tandem multimers of the S3 gene were constructed and expressed in E. coli. Tetramer of S3 for example is shown to display an enhanced inhibitory effect on LPS-induced activities. An affinity matrix based on tetramer of S3 is also shown to be particularly efficient at removing LPS.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
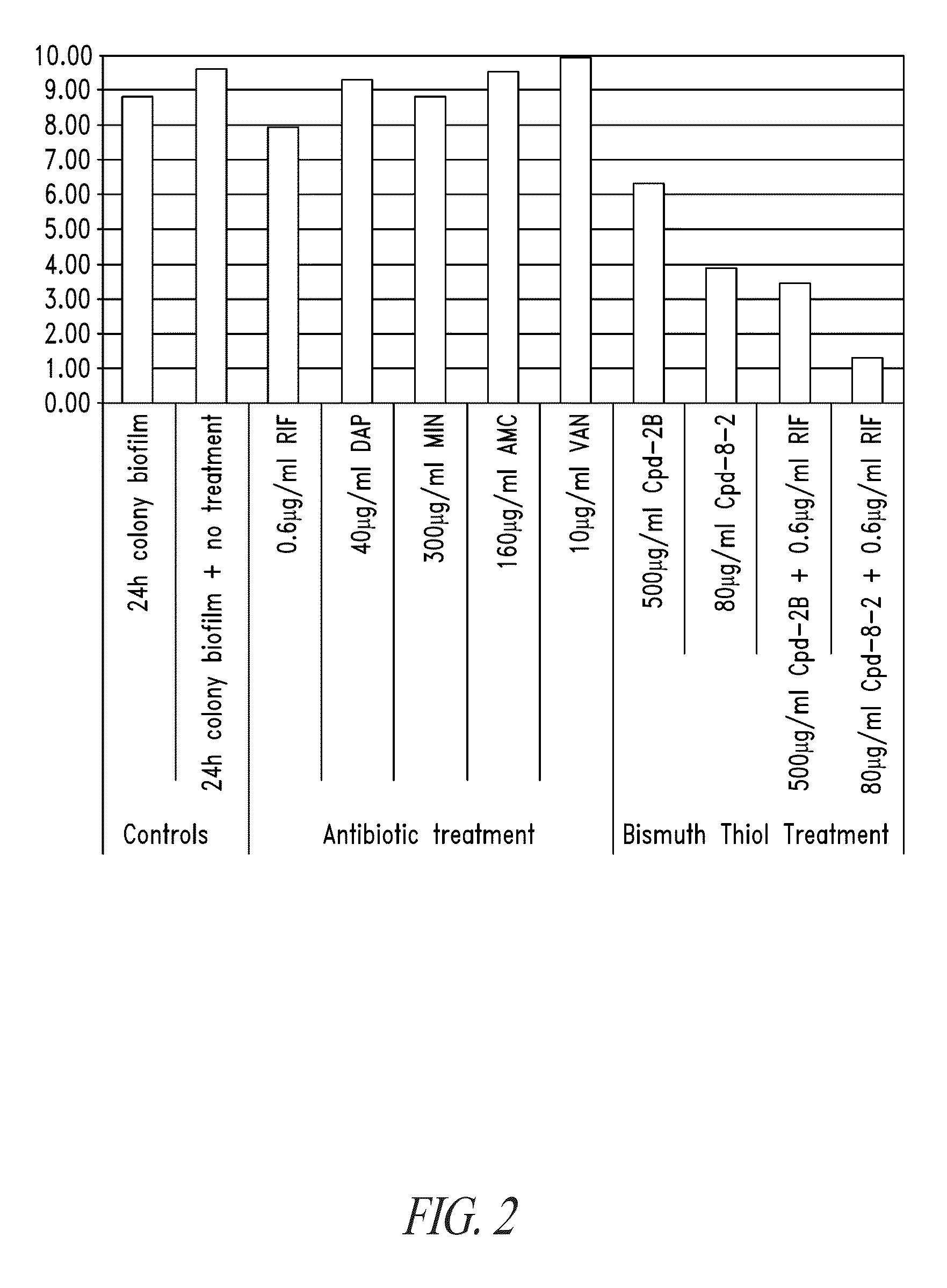
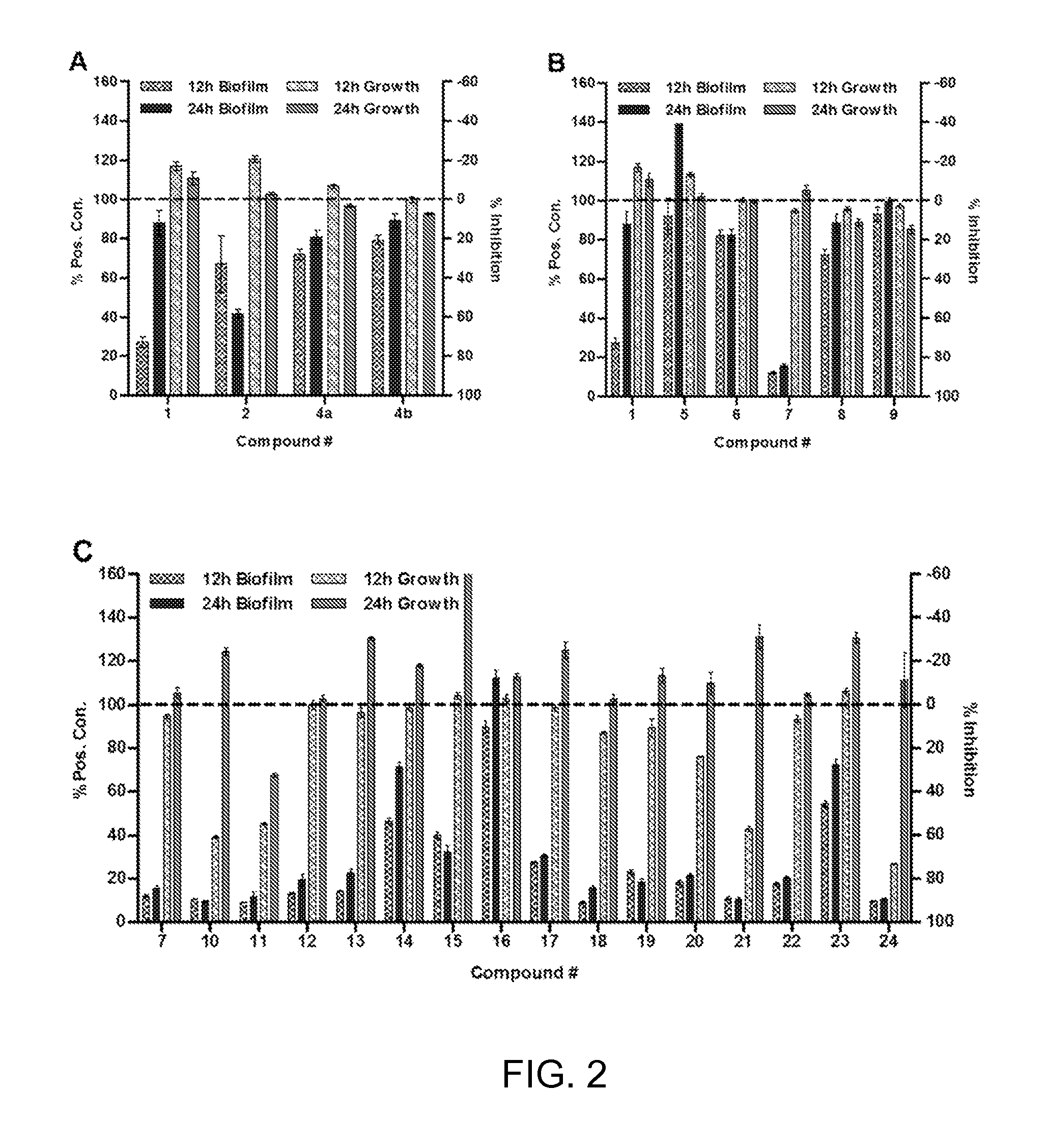
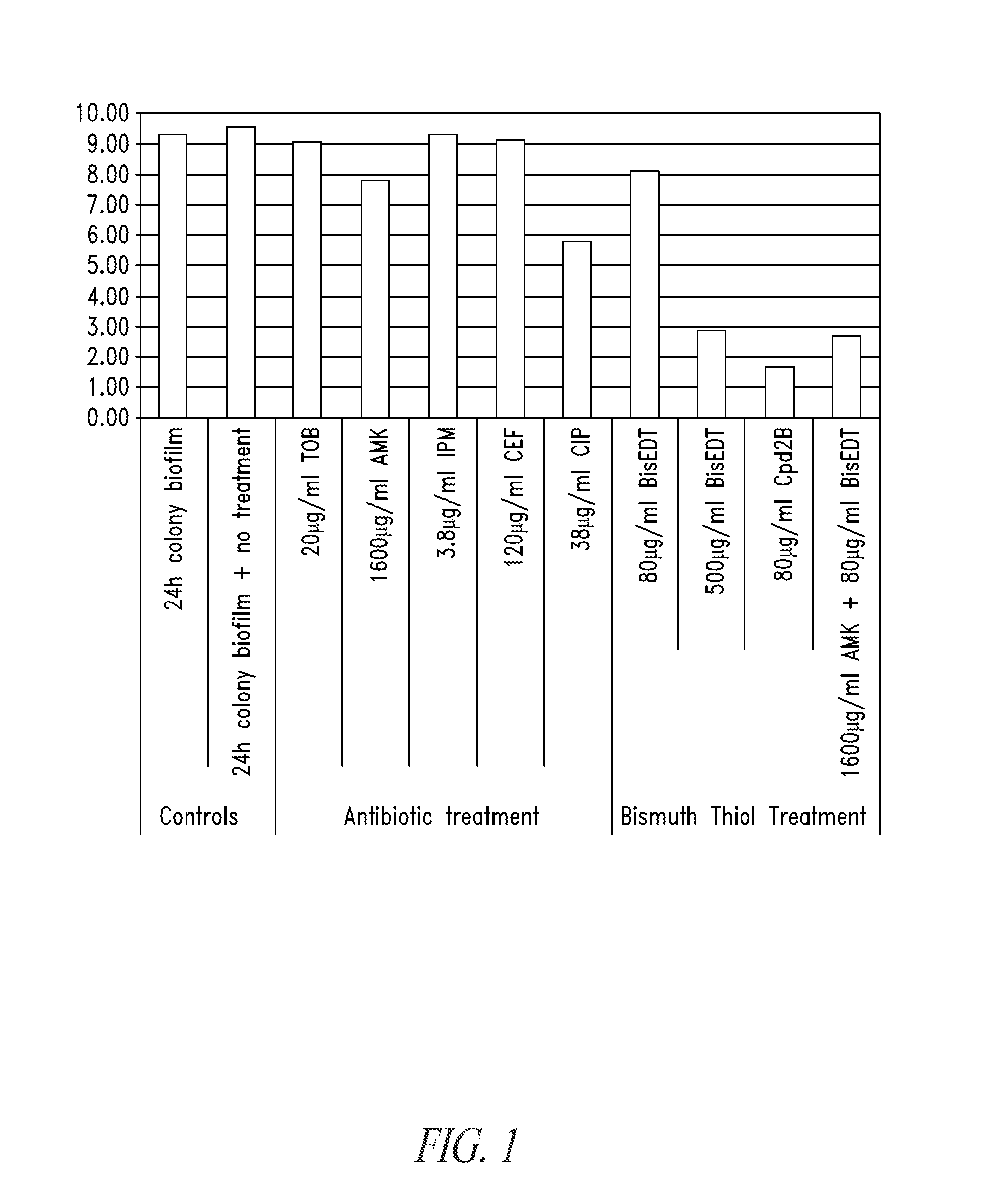
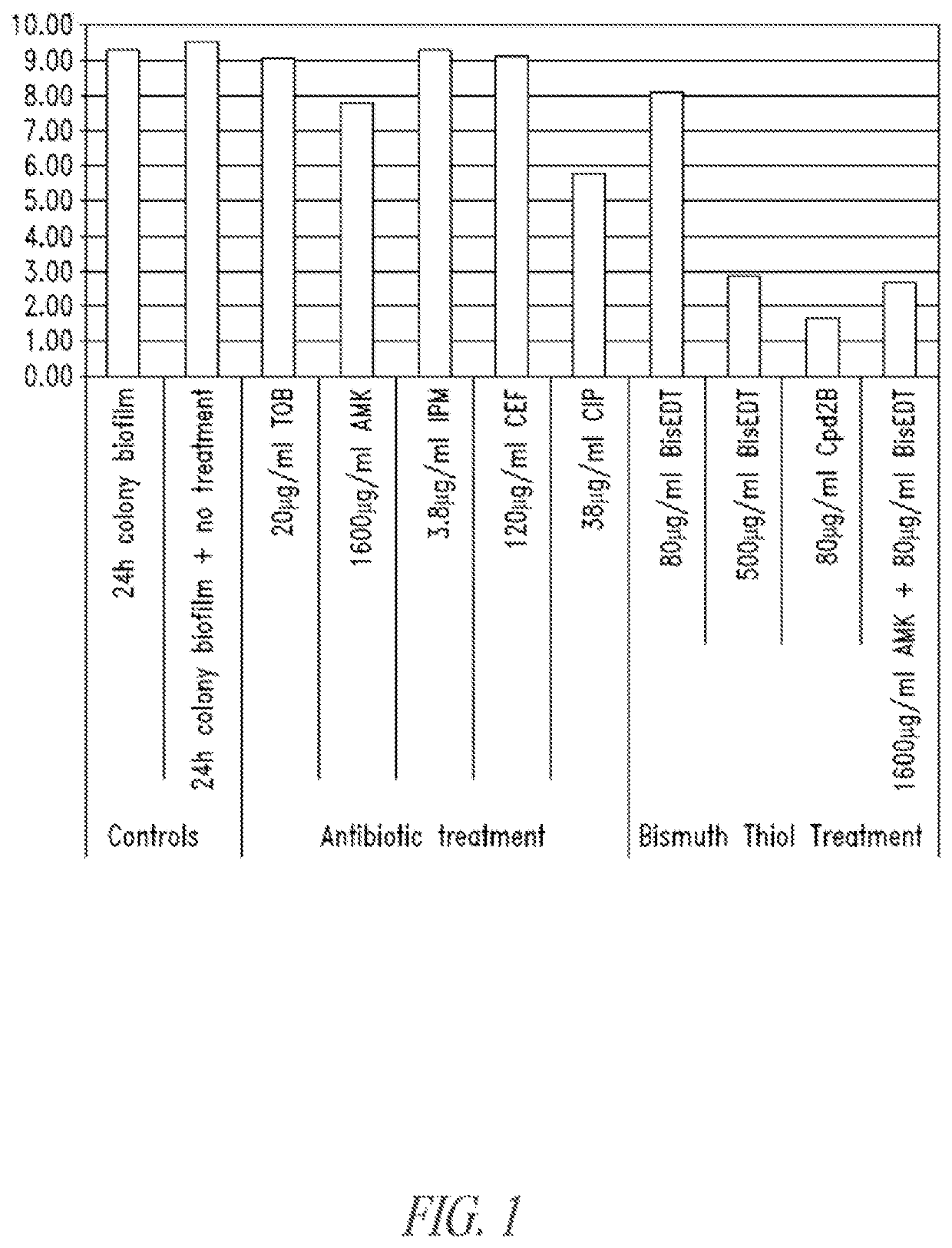
Bismuth-thiols as antiseptics for agricultural, industrial and other uses
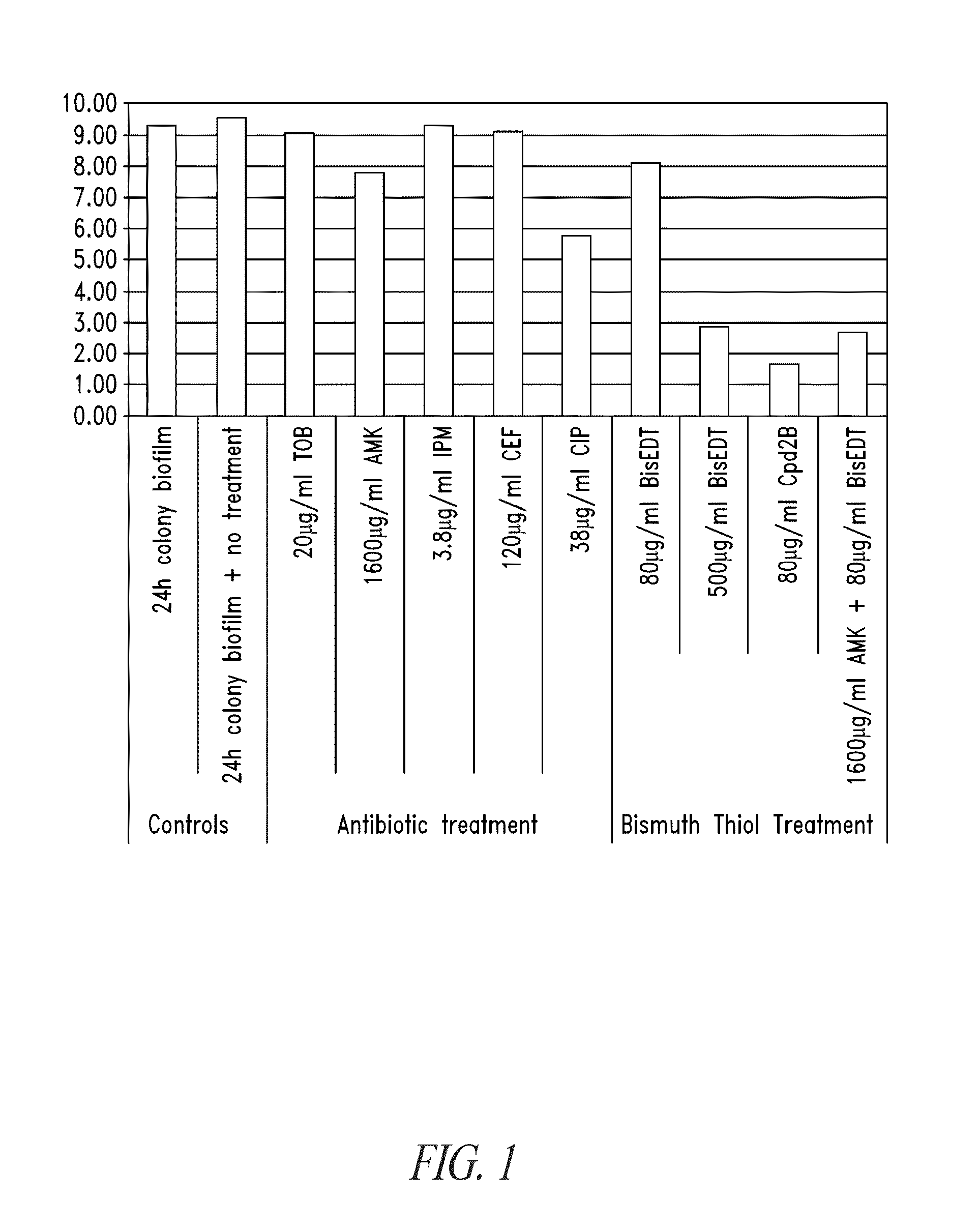
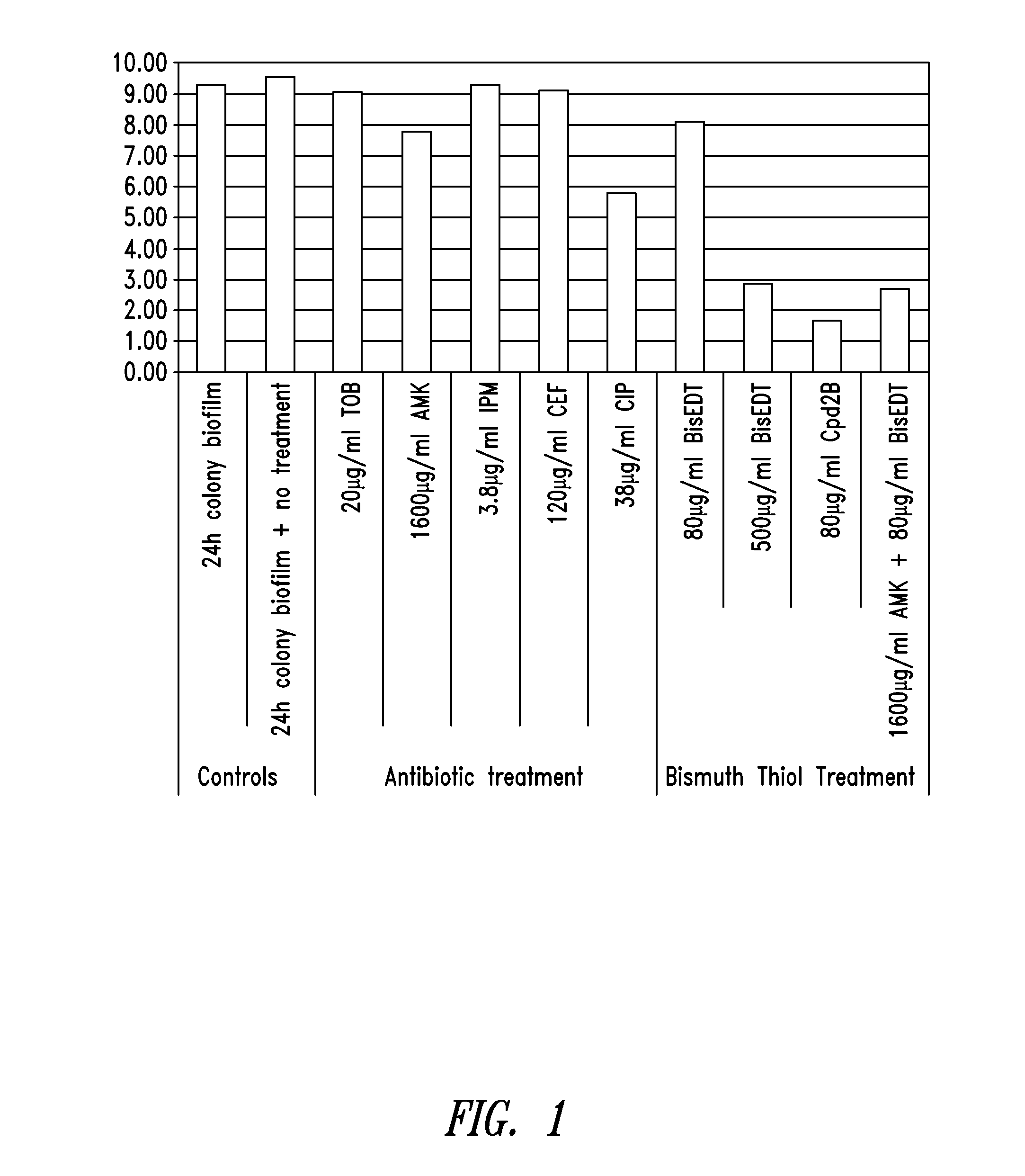
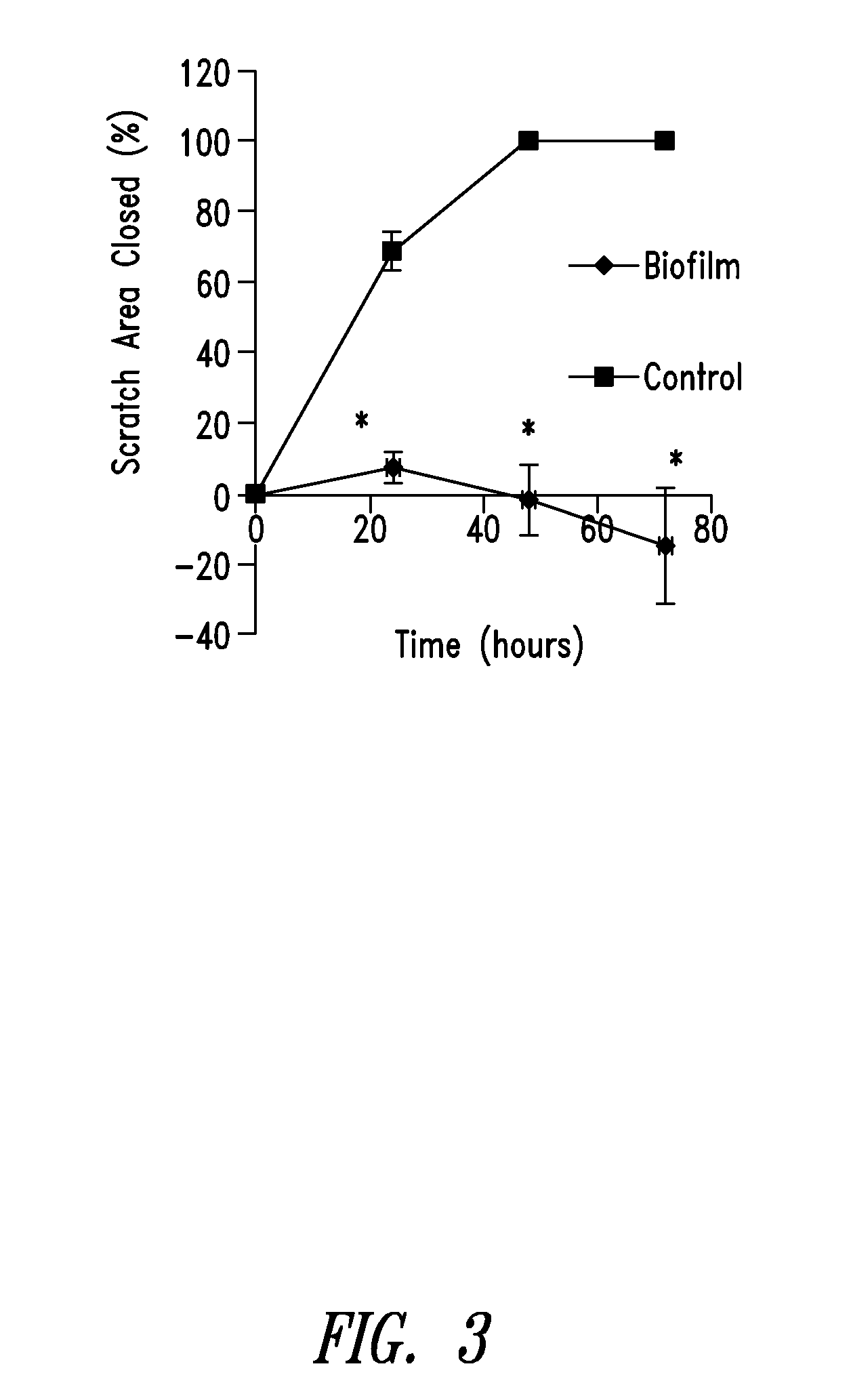
Compositions and methods, including novel homogeneous microparticulate suspensions, are described for treating natural and artificial surfaces that contain bacterial biofilm, including unexpected synergy or enhancing effects between bismuth-thiol (BT) compounds and certain antibiotics, to provide formulations including antiseptic formulations. Previously unpredicted antibacterial properties and anti-biofilm properties of disclosed BT compounds and BT compound-plus-antibiotic combinations are also described, including preferential efficacies of certain such compositions for treating certain gram-positive bacterial infections, and distinct preferential efficacies of certain such compositions for treating certain gram-negative bacterial infections.
Owner:MICROBION
Sushi Peptide Multimer
Endotoxin, also known as lipopolysaccharides (LPS), is the major mediator of septic shock due to Gram-negative bacterial infection. Chemically synthesized S3 peptide, derived from Sushi3 domain of Factor C, which is the endotoxin-sensitive serine protease of the limulus coagulation cascade, binds and neutralizes LPS activity. Fluorescent tagged-S3 is shown to detect LPS-containing bacteria. For large-scale production of S3 and to mimic other pathogen-recognizing molecules, tandem multimers of the S3 gene were constructed and expressed in E. coli. Tetramer of S3 for example is shown to display an enhanced inhibitory effect on LPS-induced activities. An affinity matrix based on tetramer of S3 is also shown to be particularly efficient at removing LPS.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
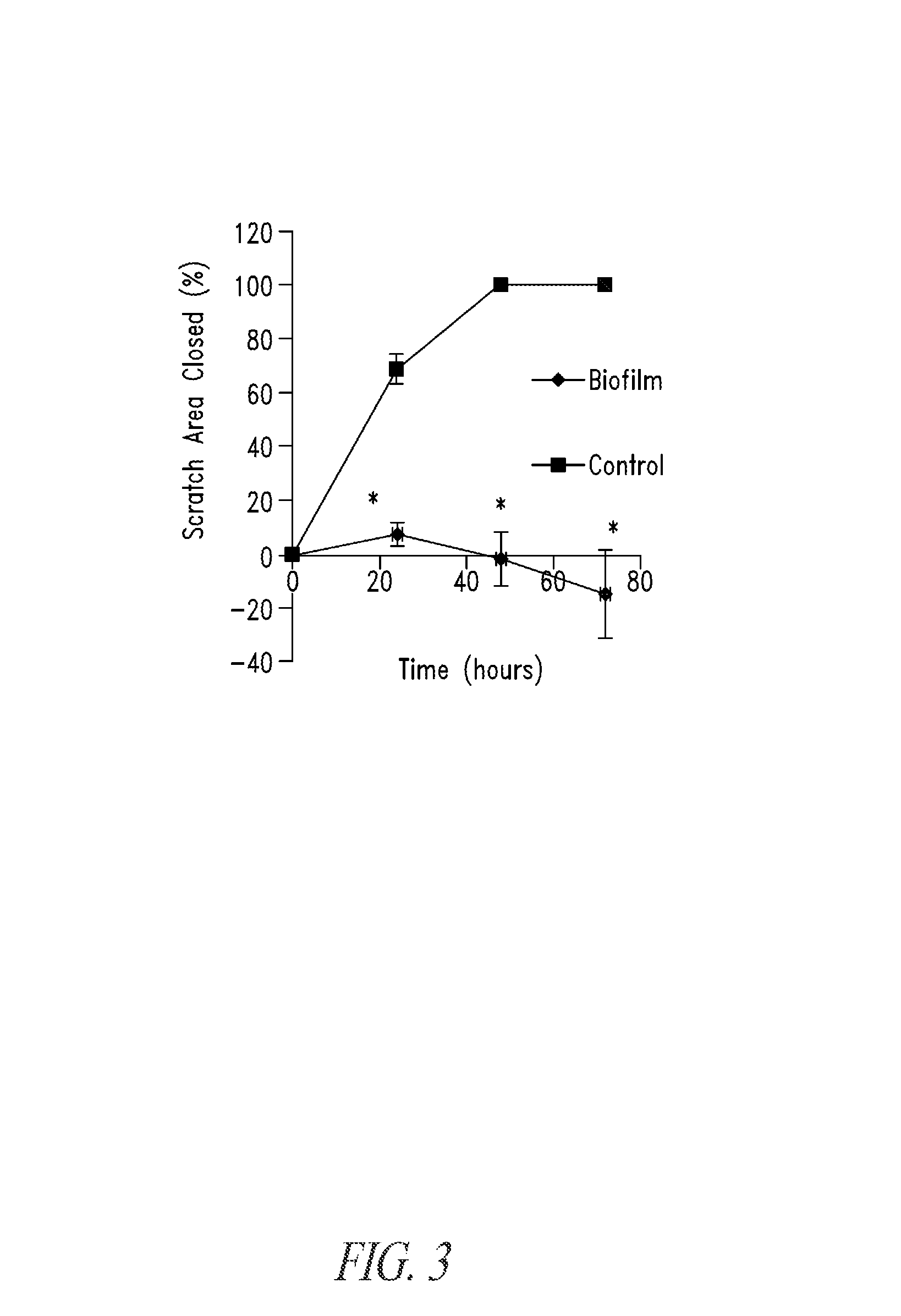
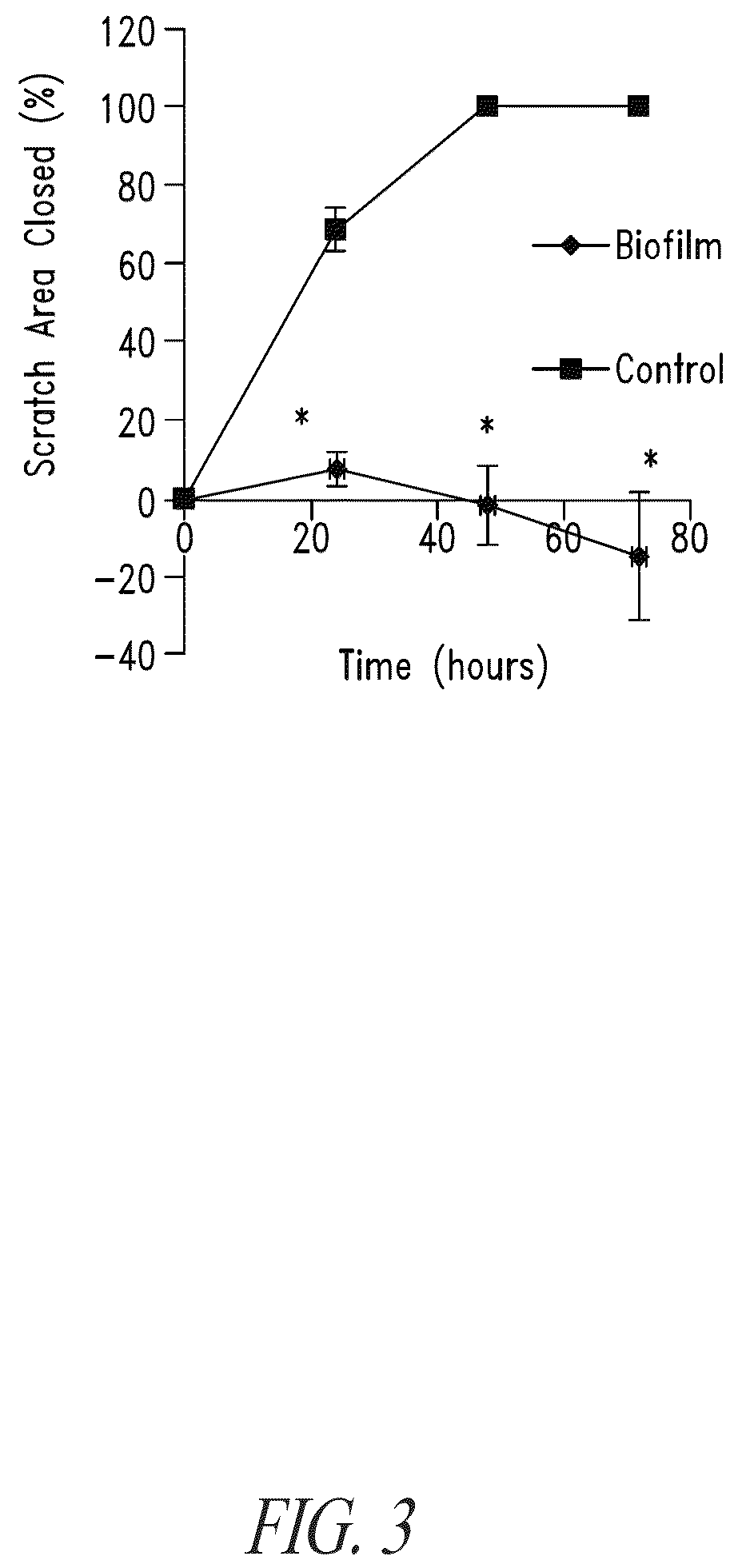
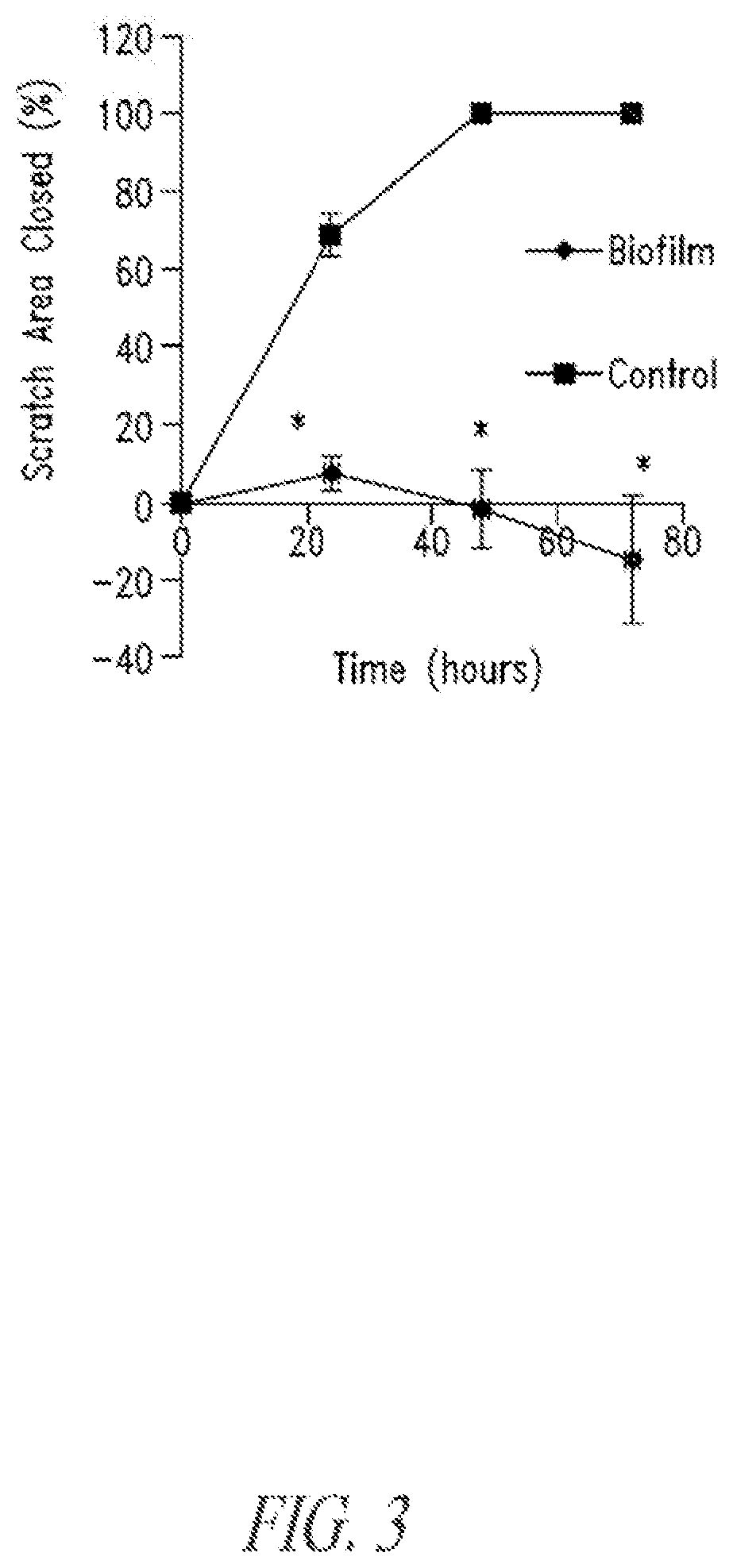
Bismuth-thiols as antiseptics for epithelial tissues, acute and chronic wounds, bacterial biofilms and other indications
ActiveUS8389021B2Reduce in quantityLow costAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBacteroidesInjury mouth
Compositions and methods, including novel homogeneous microparticulate suspensions, are described for treating acute wounds, chronic wounds and / or a wound or epithelial tissue surface that contains bacterial biofilm, including unexpected synergy between bismuth-thiol (BT) compounds and certain antibiotics, to provide topical formulations including antiseptic formulations, for management and promotion of wound healing and in particular infected wounds. Previously unpredicted antibacterial properties and anti-biofilm properties of disclosed BT compounds and BT compound-plus-antibiotic combinations are also described, including preferential efficacies of certain such compositions for treating gram-positive bacterial infections, and distinct preferential efficacies of certain such compositions for treating gram-negative bacterial infections.
Owner:MICROBION
Application of substituted benzene guanidine derivative serving as polymyxins antibiotic potentiator
ActiveCN105030744AGood synergyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsGuanidine derivativesCompounding drugs
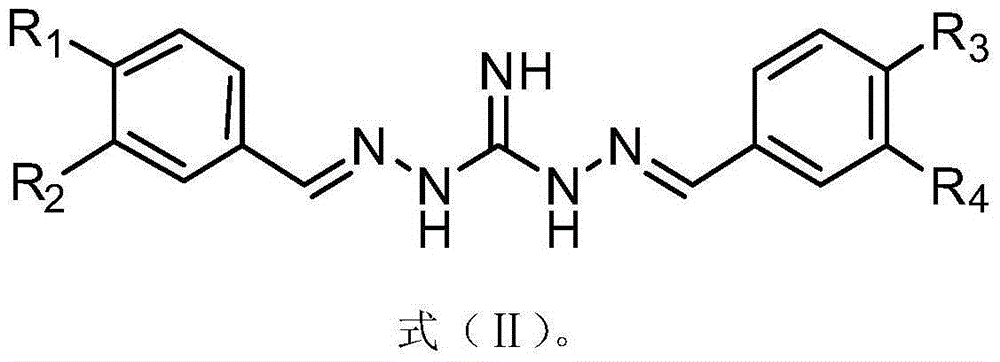
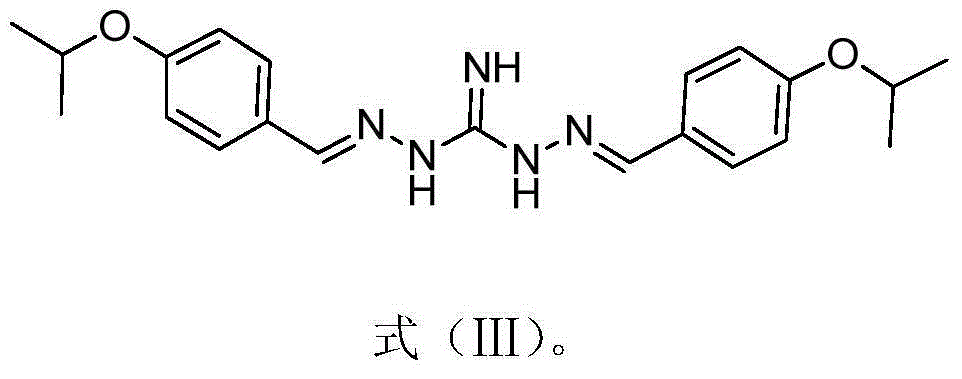
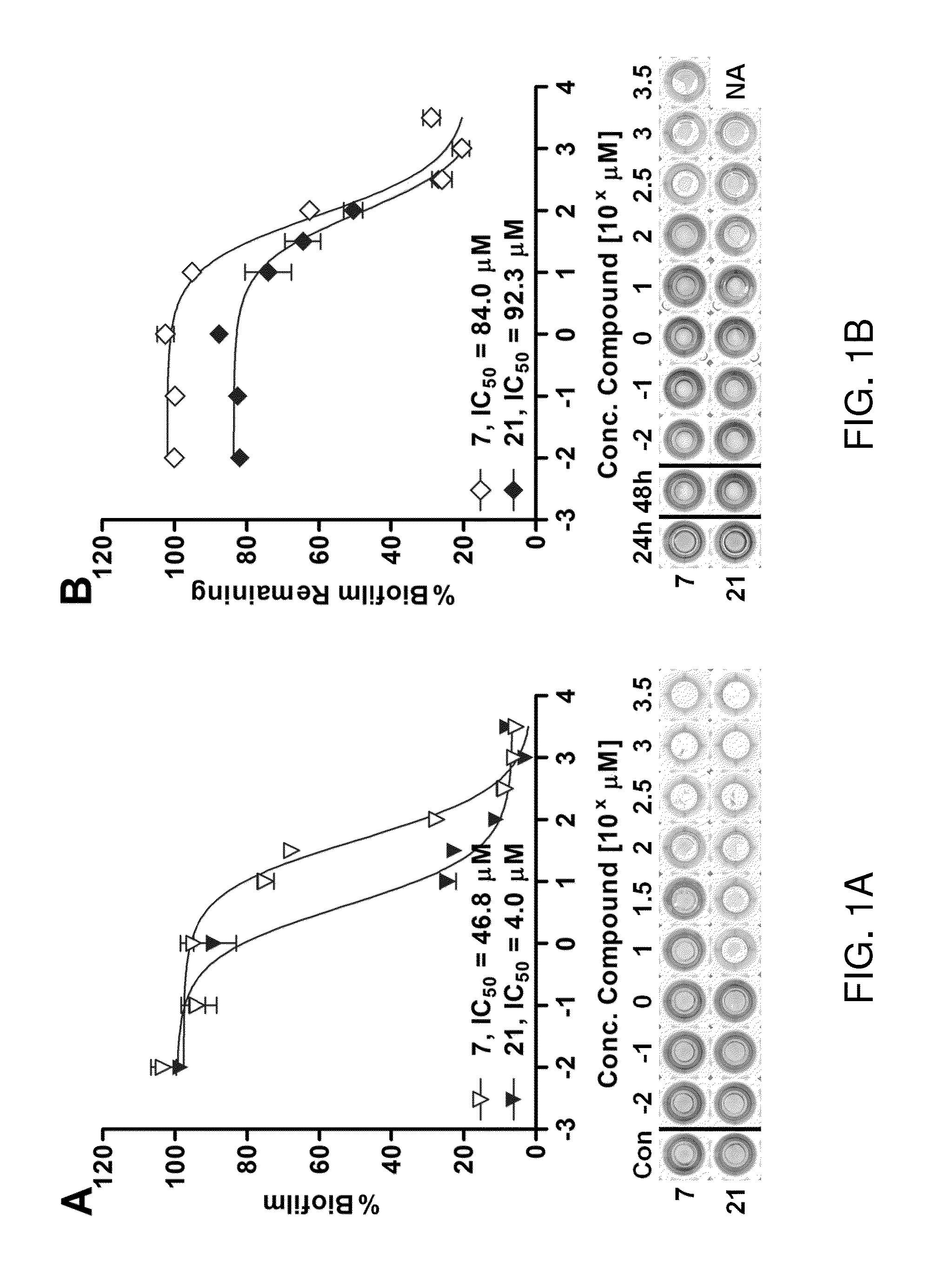
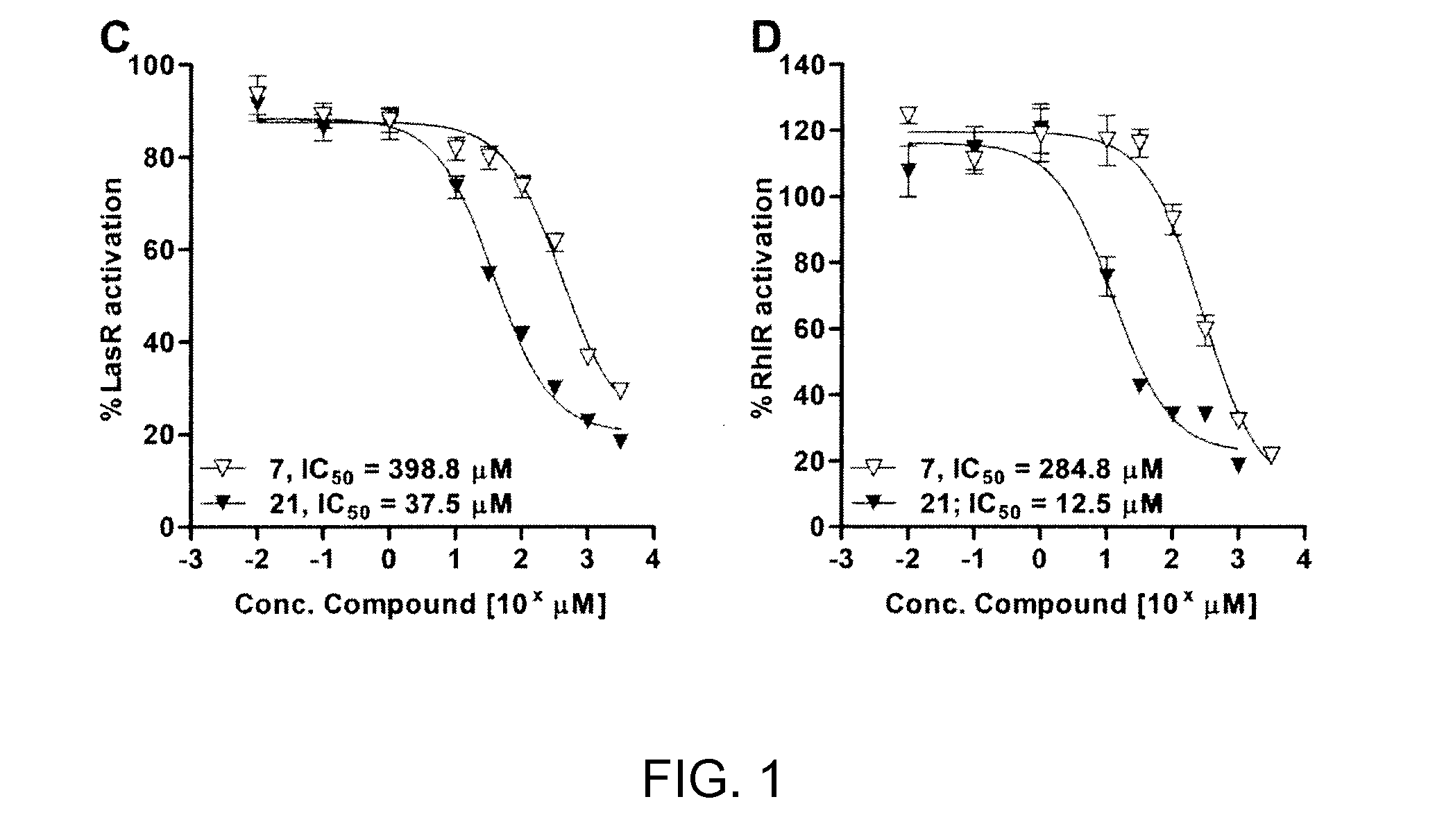
The invention discloses application of a substituted benzene guanidine derivative serving as a polymyxins antibiotic potentiator. For the first time, the substituted benzene guanidine derivative is found to be capable of serving as the polymyxins antibiotic potentiator, especially serving as a synergist of a polymyxins antibiotic to inhibit sensitive strains and a drug resistance reversal agent of the polymyxins antibiotic. The invention further provides combined application of the substituted benzene guanidine derivative or a combination containing the same and the polymyxins antibiotic in preparation of compound drug preparations for people or animals to treat diseases caused by gram-negative bacterial infection. The invention further provides combined application of the substituted benzene guanidine derivative or a combination containing the same and the polymyxins antibiotic in preparation of forage-use growth-promoting feed additives for animal breeding in animal husbandry.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INSIGHER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Inhibition and Dispersion of Bacterial Biofilms with 2-Aminobenzimidazole Derivatives
InactiveUS20130136782A1Reducing bacterial virulenceIncreased susceptibilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideControlled release2-aminobenzimidazole
Compounds described herein inhibit biofilm formation or disperse pre-formed biofilms of Gram-negative bacteria. Biofilm-inhibitory compounds can be encapsulated or contained in a polymer matrix for controlled release. Coatings, films, multilayer films, hydrogels, microspheres and nanospheres as well as pharmaceutical compositions and disinfecting compositions containing biofilm-inhibitory compounds are also provided. Methods for inhibiting formation of biofilms or dispersing already formed biofilms are provided. Methods for treating infections of gram-negative bacteria which form biofilms, particularly those of Pseudomonas and more particularly P. aeruginosa.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Bismuth-thiols as antiseptics for agricultural, industrial and other uses
ActiveUS20130224258A1Low costBiocideSurgical adhesivesGram-positive bacterial infectionsAntibiotic Y
Compositions and methods, including novel homogeneous microparticulate suspensions, are described for treating natural and artificial surfaces that contain bacterial biofilm, including unexpected synergy or enhancing effects between bismuth-thiol (BT) compounds and certain antibiotics, to provide formulations including antiseptic formulations. Previously unpredicted antibacterial properties and anti-biofilm properties of disclosed BT compounds and BT compound-plus-antibiotic combinations are also described, including preferential efficacies of certain such compositions for treating certain gram-positive bacterial infections, and distinct preferential efficacies of certain such compositions for treating certain gram-negative bacterial infections.
Owner:MICROBION
Bismuth-thiols as antiseptics for biomedical uses, including treatment of bacterial biofilms and other uses
Owner:MICROBION
Antimicrobial agents
The application relates to antimicrobial agents against Gram-negative bacteria, in particular to fusion proteins composed of an enzyme having the activity of degrading the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria and a peptide stretch fused to the enzyme at the N- or C-terminus, as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same. Moreover, it relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such a fusion protein, vectors comprising said nucleic acid molecules and host cells comprising either said nucleic acid molecules or said vectors. In addition, it relates to such a fusion protein for use as a medicament, in particular for the treatment or prevention of Gram-negative bacterial infections, as diagnostic means or as cosmetic substance. The application also relates to the treatment or prevention of Gram-negative bacterial contamination of foodstuff, of food processing equipment, of food processing plants, of surfaces coming into contact with foodstuff, of medical devices, of surfaces in hospitals and surgeries.
Owner:LYSANDO +1
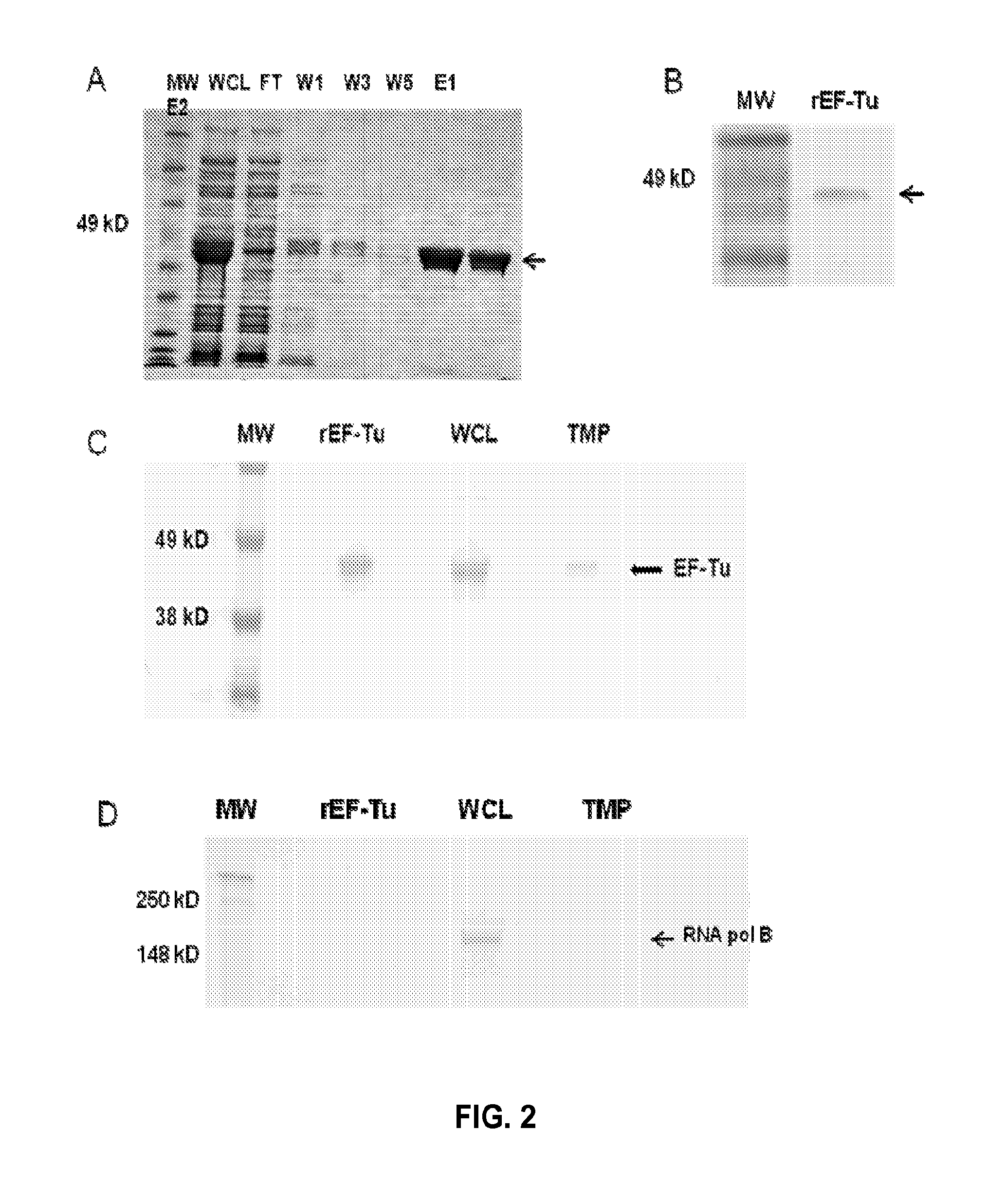
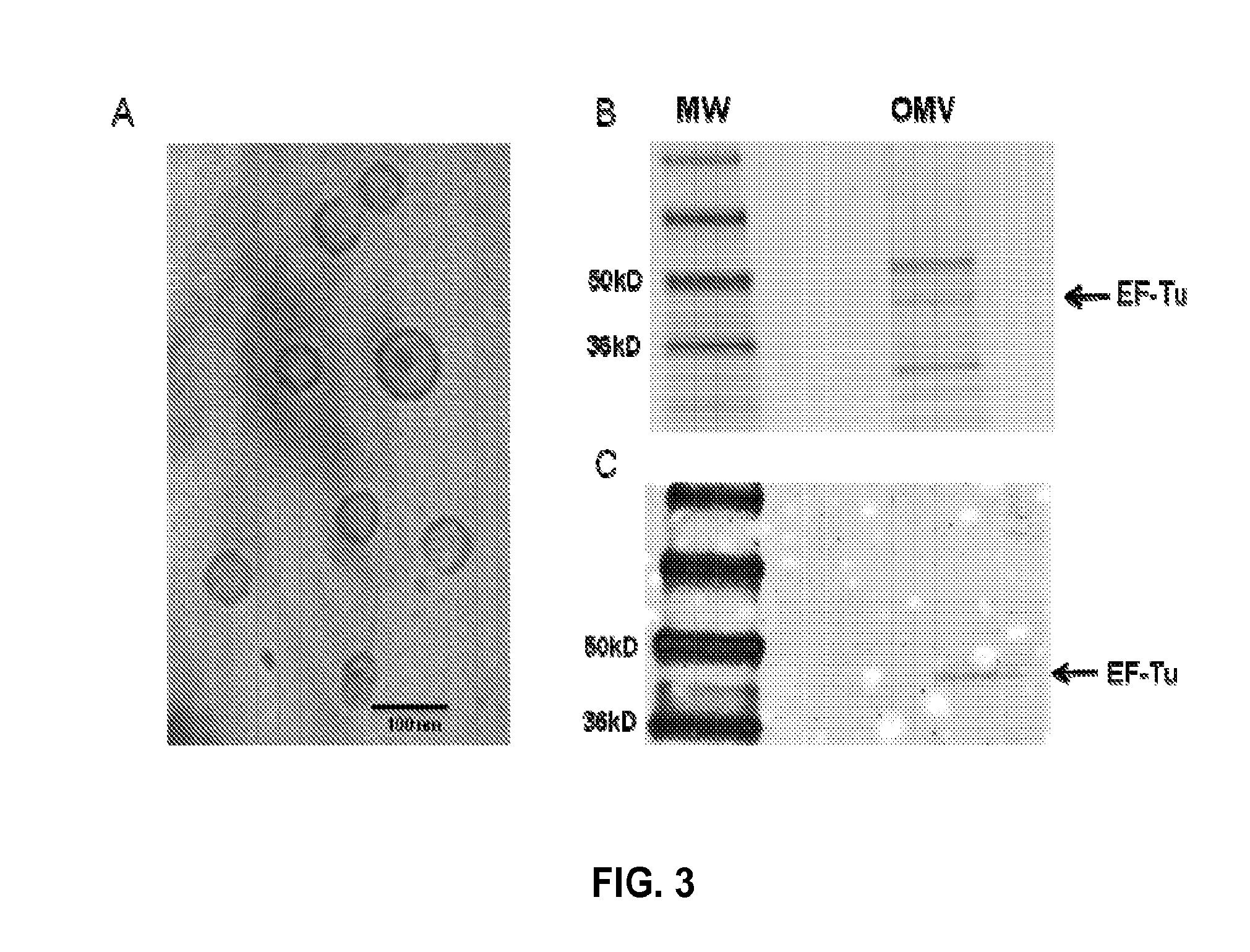
Omv vaccine against burkholderia infections
InactiveUS20140004178A1Provide protectionAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMedicineGram-negative bacterial infections
The present disclosure relates to vaccine compositions and methods of using the vaccine compositions to provide protection against various Gram-negative bacterial infections, including Burkholderia infections.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Vancomycin derivative, preparation method and antibacterial application thereof
ActiveCN105085636AGood in vitro antibacterial activityNovel structureAntibacterial agentsSaccharide peptide ingredientsDiseaseGram-negative bacterial infections
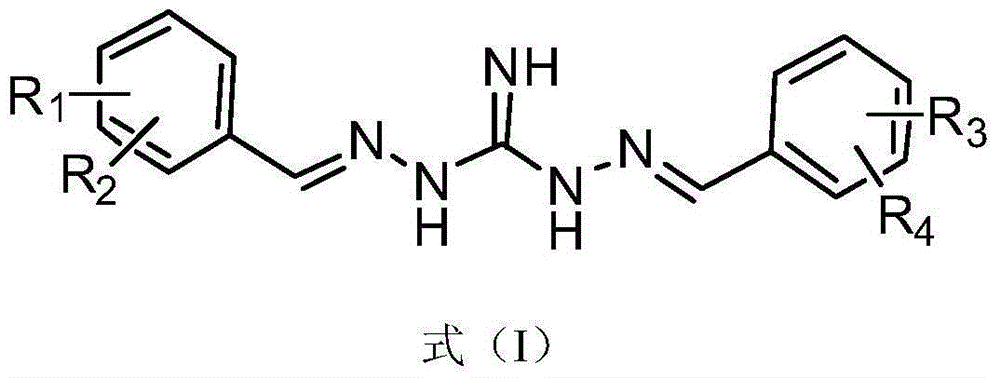
The invention relates to a vancomycin derivative as shown in the formula (I) and a stereisomer, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, a preparation method of the vancomycin derivative and its application in treating and / or preventing diseases or symptoms related to gram negative bacterial infections.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
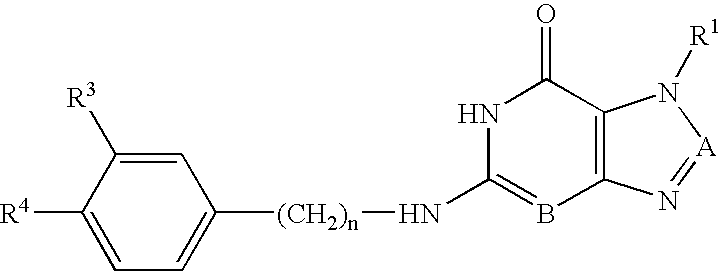
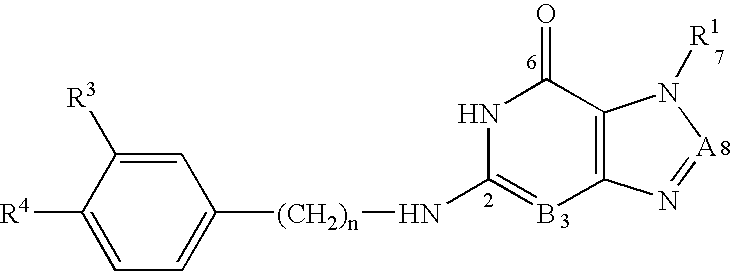
Purine and isosteric antibacterial compounds
InactiveUS6926763B2Relieve symptomsInhibit and reduce likelihoodAntibacterial agentsFireproof paintsPurineGram-negative bacterial infections
The invention features compounds of the formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein A is CR2 and B is N; wherein n is 0-3; wherein R1 is (CH2)m—{(G)o—(CH2)p}q—L, in which G is CH2, CH═CH, C≡C, CO, O, S, or NR5, where R5 is H or C1-6 alkyl, CHR6, where R6 is OH or C1-6 alkyl, CH(CR7R8), where each of R7 and R8 is, independently, H, halo, or C1-6 alkyl, OCO, CONR9, NR10CO, where each of R9 and R10 is, independently, H or C1-6 alkyl, SO2NH, or NHSO2; in which m is 1-4, o is 0-4, p is 0-4, and q is 0-4. The compounds disclosed herein have potent anti-microbial, e.g., both Gram-positive and Gram-negative anti-bacterial properties. The compounds inhibit DNA polymerase IIIC and DNA polymerase IIIE enzymes and thus act therapeutically by inhibiting the growth of a broad array of bacteria. The compounds can be administered to prevent or to treat Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacterial infections, e.g., in eukaryotic cell cultures, animals, or humans.
Owner:ACURX PHARMA LLC
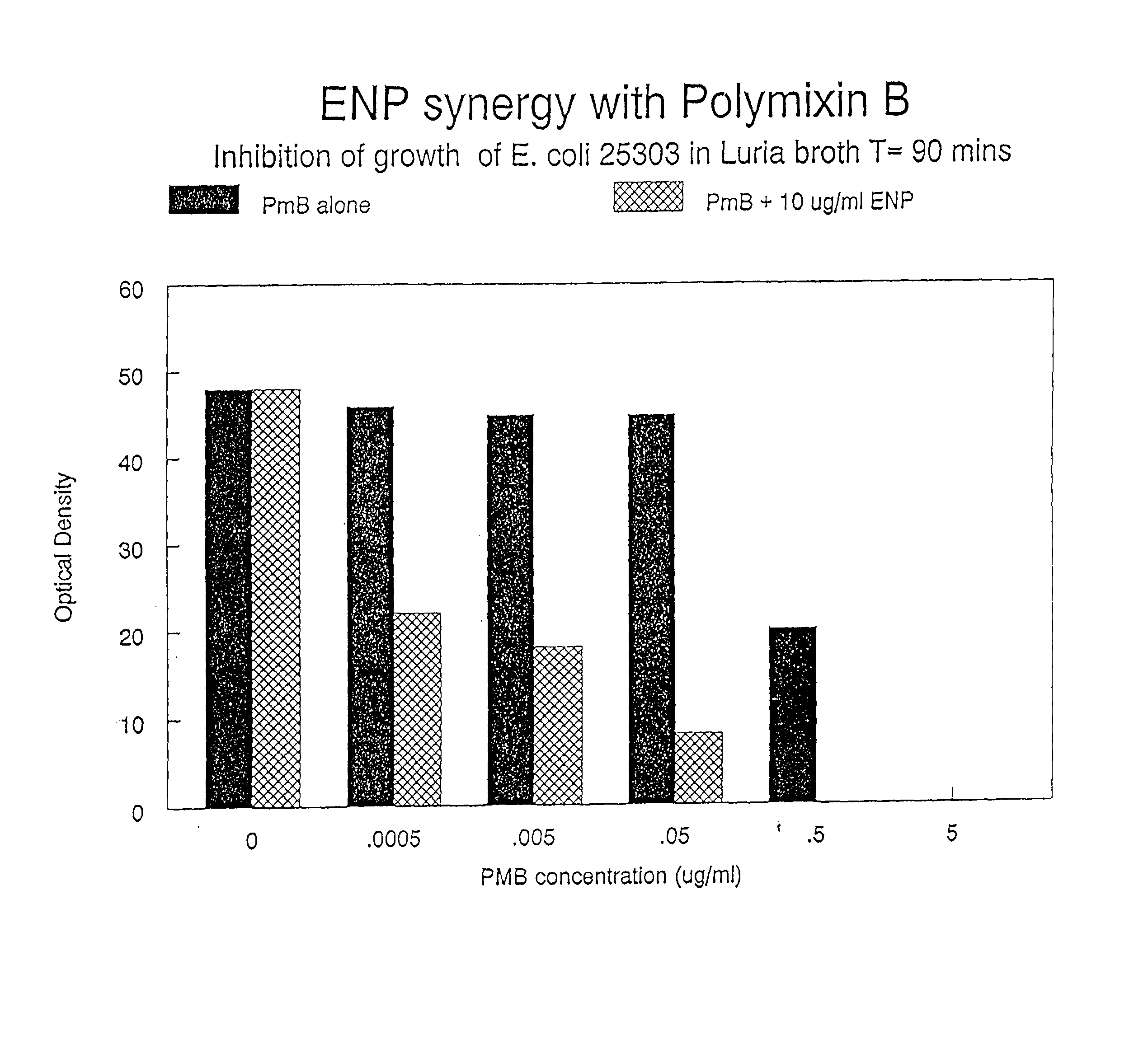
Composition comprising endotoxin neutralizing protein and derivatives and uses thereof
InactiveUS20020107174A1Prevent and inhibit growth of bacteriaAntibacterial agentsBiocidePersonal careGram-positive bacterial infections
The present invention relates to the use of endotoxin neutralizing protein (ENP) and derivatives thereof as stand alone microbial inhibitors or as synergistic enhancers of antibiotics and preservatives. Compositions comprising ENP or alone or in combination with an antibiotic may be used to prevent or treat gram-negative bacterial infections, endotoxemia, septic shock, gram-positive bacterial infections, yeast infections and fungal infections. Compositions comprising ENP alone or in combination with a conventional preservative may be used as antimicrobial preservative in cosmetic or personal care preparations.
Owner:ASSOCS OF CAPE COD
Polymyxin E2 composition, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and particularly relates to a polymyxin E2 composition, and a preparation method and application thereof. The composition mainly contains polymyxin E2, and also comprises E1, E3, E1-1, E1-7M0A and the like. The application provided by the invention is the application of the composition in preparation of medicaments for treating gram-negative bacterial infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Method for using novel hydroxamic acid derivative and antibacterial substance in combination
InactiveUS20170296503A1High antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHydroxamic acidGram-negative bacterial infections
Owner:FUJIFILM TOYAMA CHEMICAL CO LTD
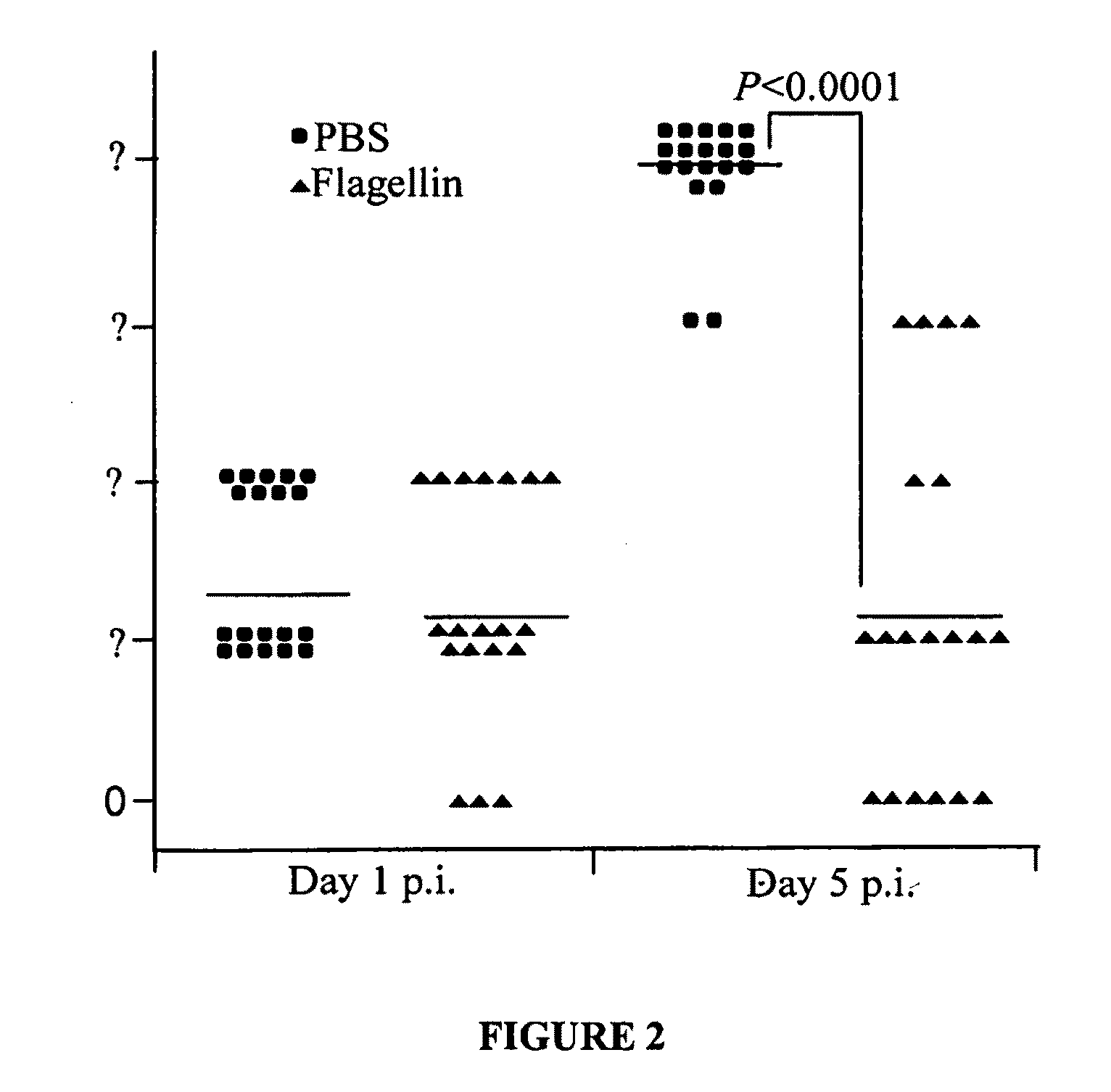
Use of flagellin to prevent and treat gram negative bacterial infection
The disclosure describes use of flagellin polypeptides to induce tolerance to gram negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, in order to alleviate the effects of the inflammatory response to bacterial infection in a patient. Also described are methods and compositions for treating and preventing keratitis, cystic fibrosis, asthma, and other diseases and conditions in which inflammation contributes to the pathology and symptoms.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
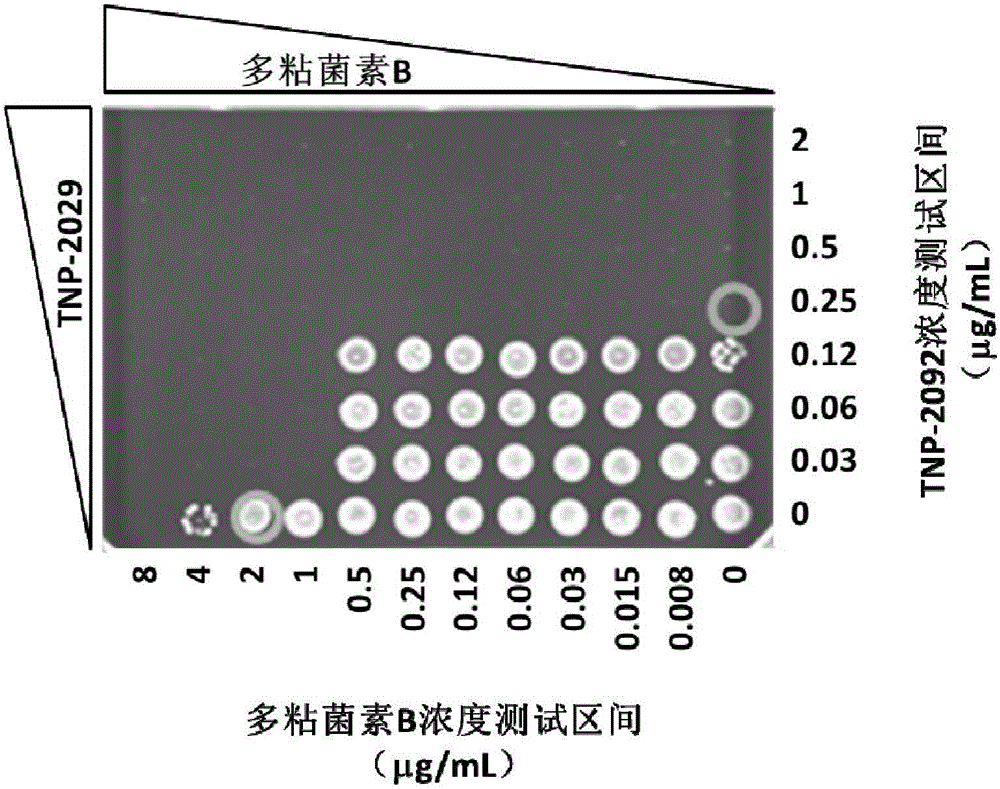
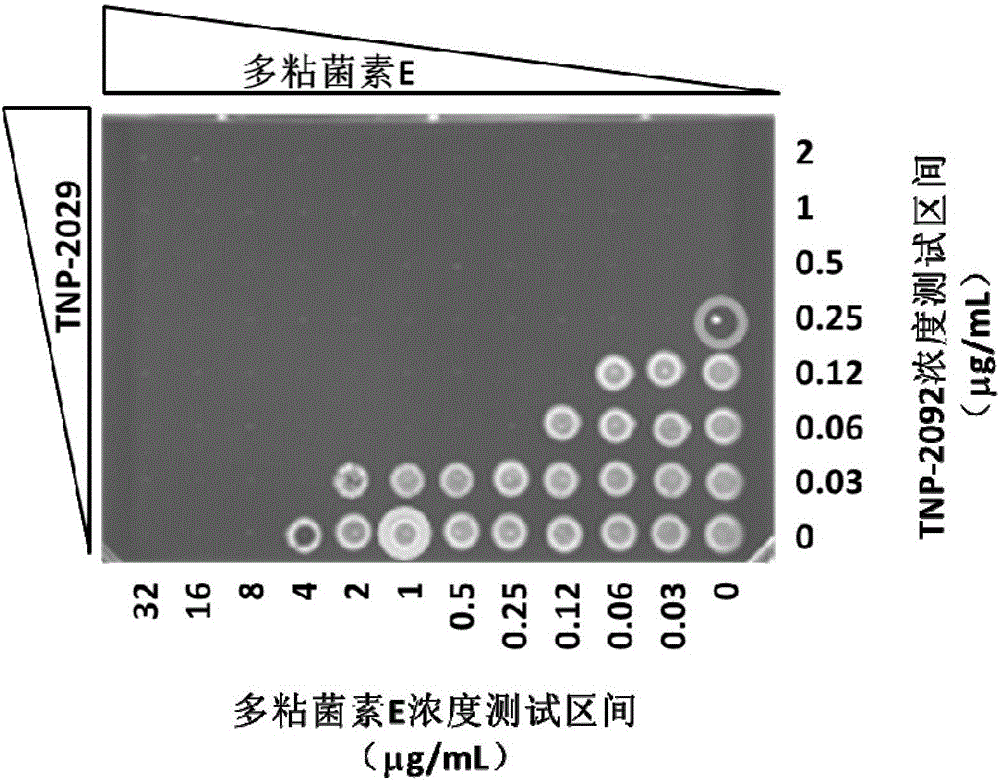
Antibacterial drug composition for treating Gram-negative bacterial infections
InactiveCN105879009AHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntimicrobial drugPolymixin E
The invention discloses an antibacterial drug composition for treating Gram-negative bacterial infections. The composition is prepared from TNP-2092 and a cell membrane penetrant, wherein the cell membrane penetrant is polymyxin B or polymyxin E. According to the antibacterial drug composition for treating Gram-negative bacterial infections, the Gram-negative bacterial infections are treated through the combined use of TNP-2092 and the cell membrane penetrant, the antibacterial activity of the composition is enhanced compared with the use of TNP-2092 or the cell membrane penetrant alone, and the composition has an antibacterial synergistic effect and can be used for treating the Gram-negative bacterial infections, including drug-resistance bacterial infections.
Owner:TENNOR THERAPEUTICS (SUZHOU) LTD
Polymyxin E composition and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102190711AGuaranteed Quality ControlAntibacterial agentsPolymyxinsPolymixin EGram-negative bacterial infections
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and in particular relates to a polymyxin E composition and a preparation method and application thereof. In the composition, total content of polymyxins E1, E2, E3, E1-1 and E1-7MOA is more than or equal to 80 percent, wherein the polymyxin E is preferably polymyxin E sulfate or polymyxin E sodium mesylate, and is particularly preferably polymyxin E sodium mesylate. The polymyxin E composition can be used for preparing medicines for treating Gram-negative bacterial infections.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Pyridinones to treat and prevent bacterial infections
Novel pyridinones and their derivatives which are effective in treating or preventing Gram-negative bacterial infections are provided. The pyridinones are stable and easily derivatized; the methods by which these derivatizations occur is described. Two regioselective and functional group tolerant methods for the synthesis of the novel pyridinones are also provided. One such synthetic method involves reacting an imine and a Meldrum's acid derivative in solution. The other synthetic method is a solid phase synthesis of the pyridinones in which an imine is prepared bound to a solid support and a Meldrum's acid derivative is reacted with the imine. Novel imine intermediates useful in the solid phase and solution methods of synthesizing the pyridionones are also described.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Lysin polypeptides active against gram-negative bacteria
ActiveUS20190070269A1Reduce the populationGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryLysinGram-negative bacterial infections
The present disclosure provides methods and compositions useful for the prophylactic and therapeutic amelioration and treatment of infections caused by Gram negative bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The disclosure further provides compositions and methods of incorporating and utilizing lysin polypeptides of the present disclosure for augmenting the efficacy of antibiotics generally suitable for the treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infection.
Owner:CONTRAFECT CORP
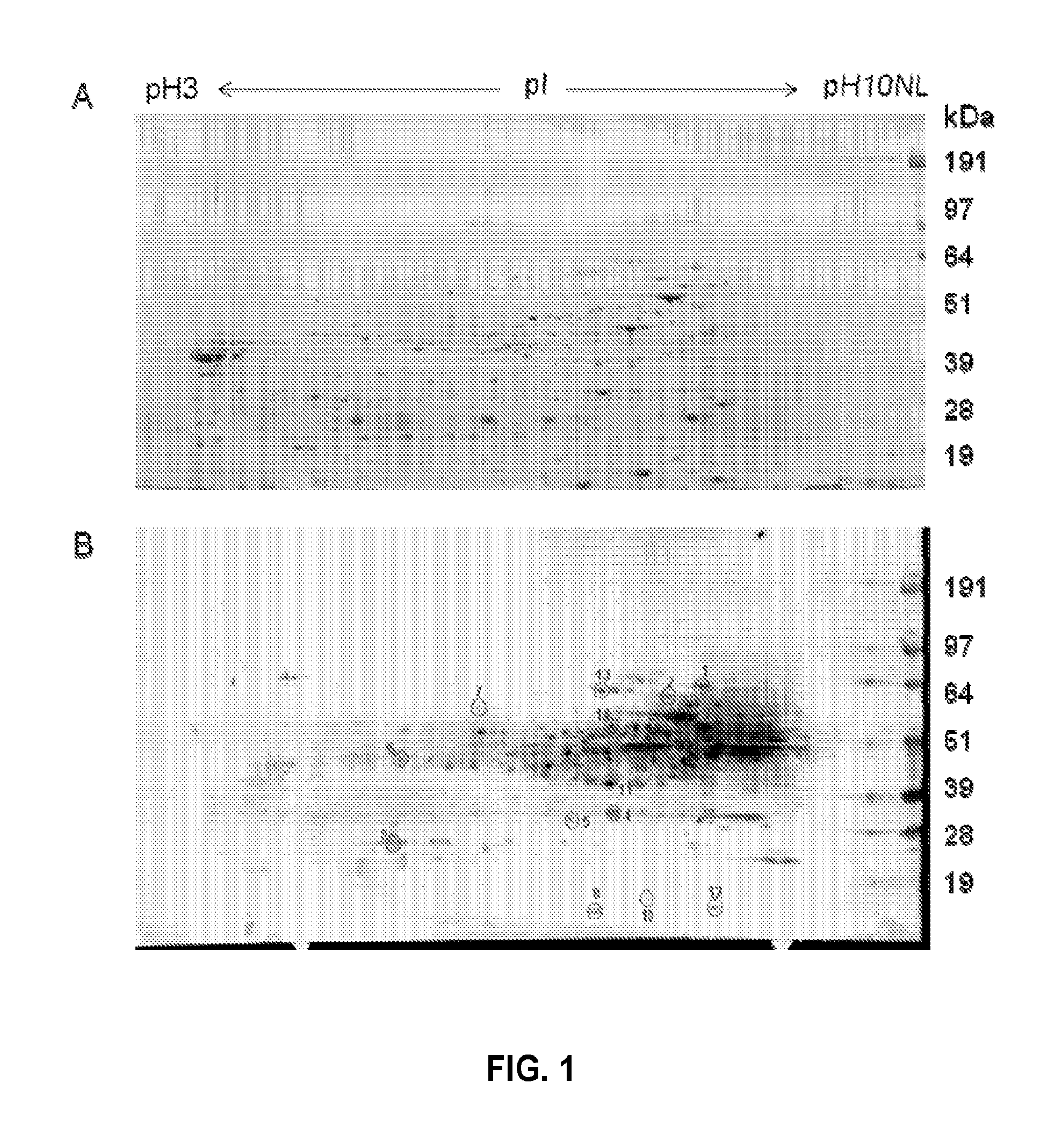
Factor c for treating gram-negative bacterial infection
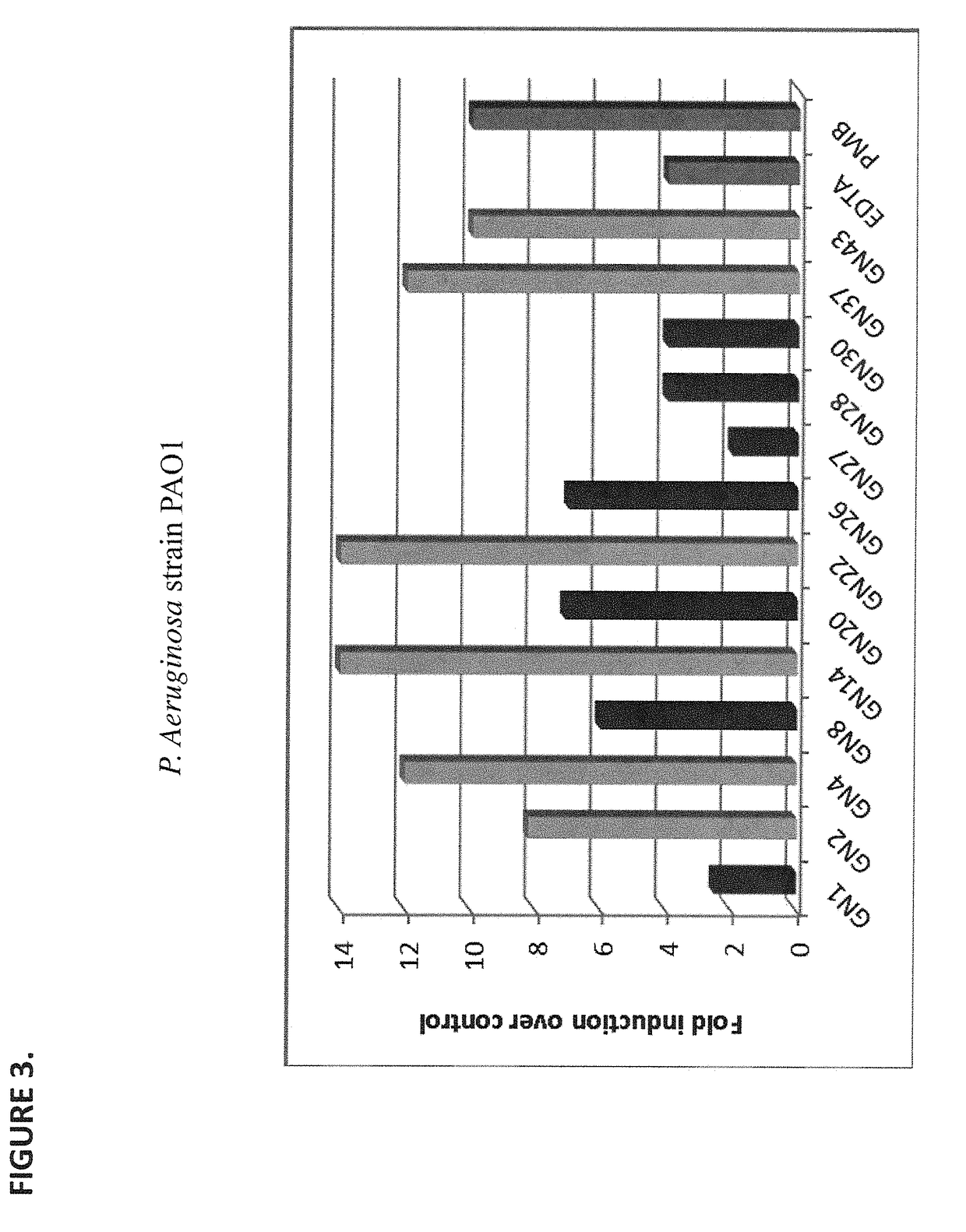
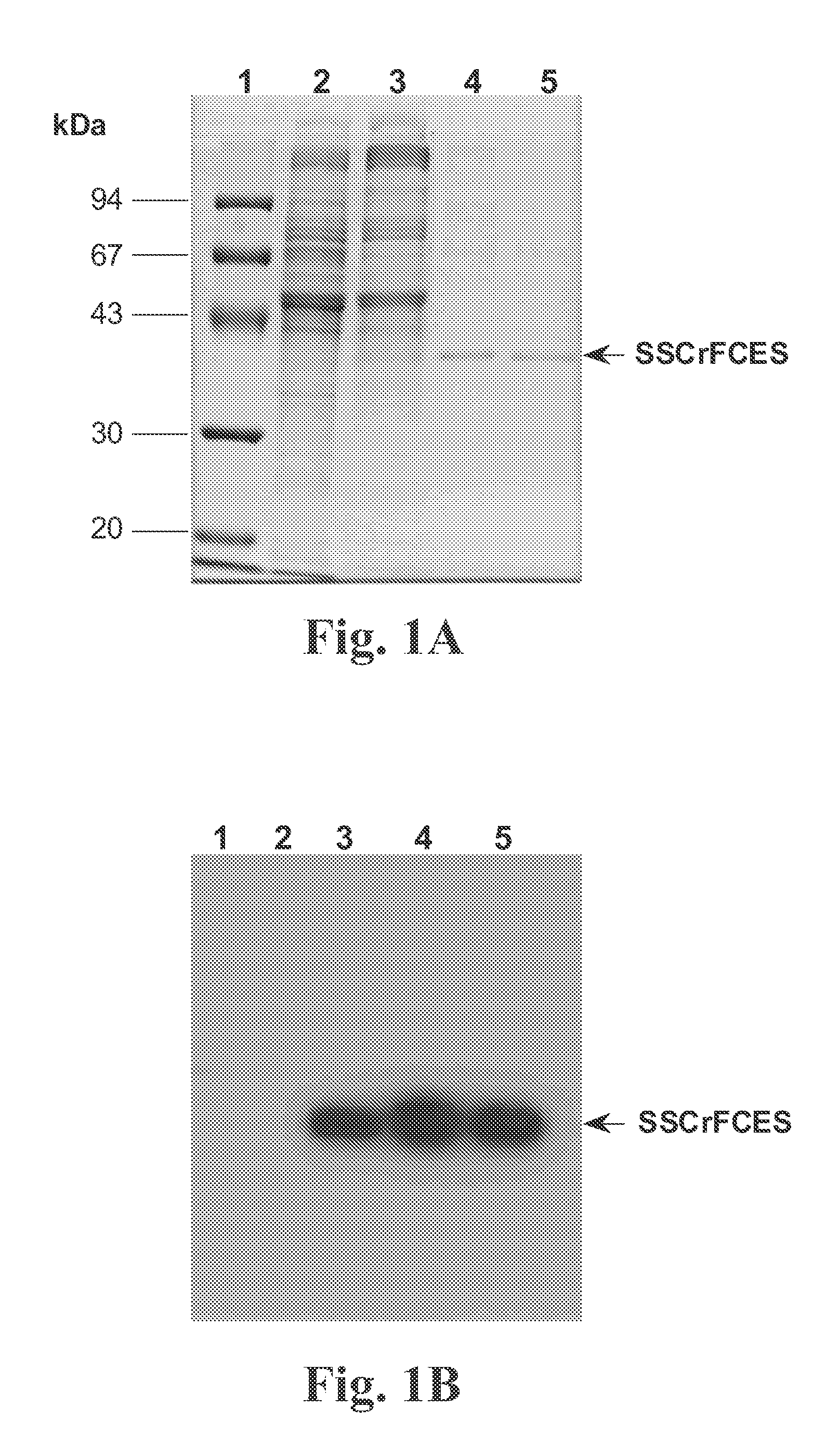
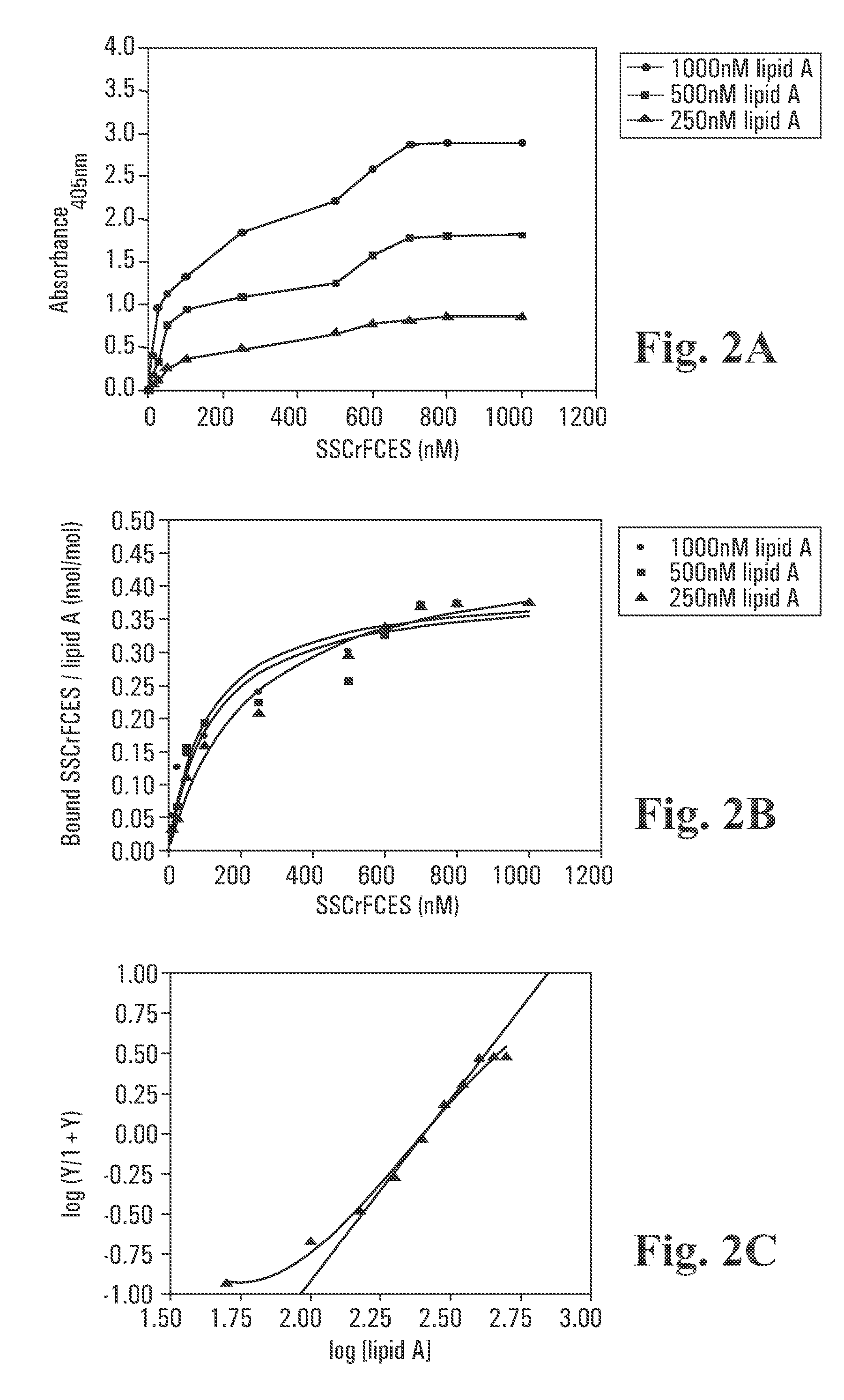
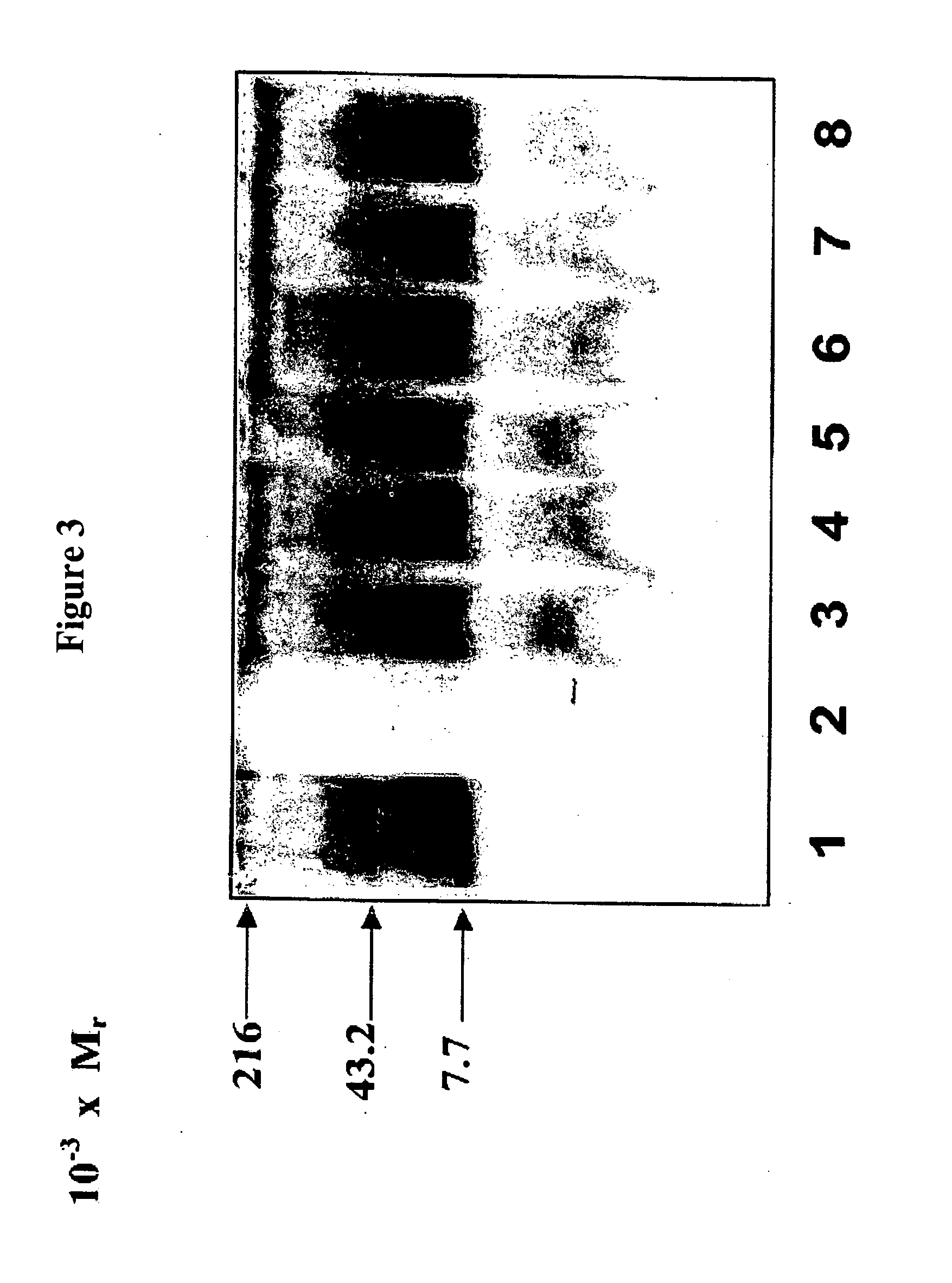
InactiveUS20080085865A1Strong antibacterial effectSuppress LPS-induced cytokinesAntibacterial agentsBiocideEndotoxin removalClearance rate
Recombinant fragments of Factor C are disclosed. These proteins and peptides show great potency in recognizing, binding to, neutralizing and removing endotoxin. These molecules can thus be used for anti-microbial, anti-endotoxin, and anti-sepsis therapy. SSCrFCES is a 38 kDa protein representing the LPS-binding domain of Factor C. The ability of SSCrFCES to bind lipid A was analyzed using an ELISA-based assay as well as surface plasmon resonance. Surface plasmon resonance similarly carried out for SSCrFC-sushi-1,2,3-GFP, SSCrFC-sushi-1GFP, and SSCrFC-sushi-3GFP confirmed their superior affinity for endotoxin. The 50% endotoxin-neutralizing concentration of SSCrFCES against 200 EU of endotoxin is 0.069 μM, suggesting that SSCrFCES is an effective inhibitor of LAL coagulation cascade. Although partially attenuated by human serum, as low as 1 μM of SSCrFCES inhibits the LPS-induced secretion of hTNF-α and hIL-8 by THP-1 and human pheripheral blood mononuclear cells with a potency more superior than polymyxin B. SSCrFCES is non-cytotoxic, with a clearance rate of 4.7 ml / minute. The LD90 of SSCrFCES for LPS lethality in mice is achieved at 2 μM. These results demonstrate the endotoxin-neutralizing capability of SSCrFCES in vitro and in vivo, as well as its potential for use in the treatment of endotoxin-induced septic shock. Also embodied in this application is the use of the sushi peptides and their mutant derivatives as potent antimicrobials.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Use of platelets in treating infections
PendingUS20210100846A1Reduce the amount requiredAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryProtozoaEbola virus
Provided herein in some embodiments is a method of treating a disease or condition such as an antibiotic resistant bacterial infection, a gram negative bacterial infection, a gram positive bacterial infection, a fungal infection, protozoa, a hemorrhagic virus, such as Ebola or Dengue, or a non-hemorrhagic virus, such as a coronavirus, in a subject, comprising administering to the subject in need thereof an effective amount of a composition comprising platelets or platelet derivatives, such as freeze-dried platelets; and an incubating agent comprising one or more salts, a buffer, optionally a cryoprotectant, and optionally an organic solvent.
Owner:CELLPHIRE INC
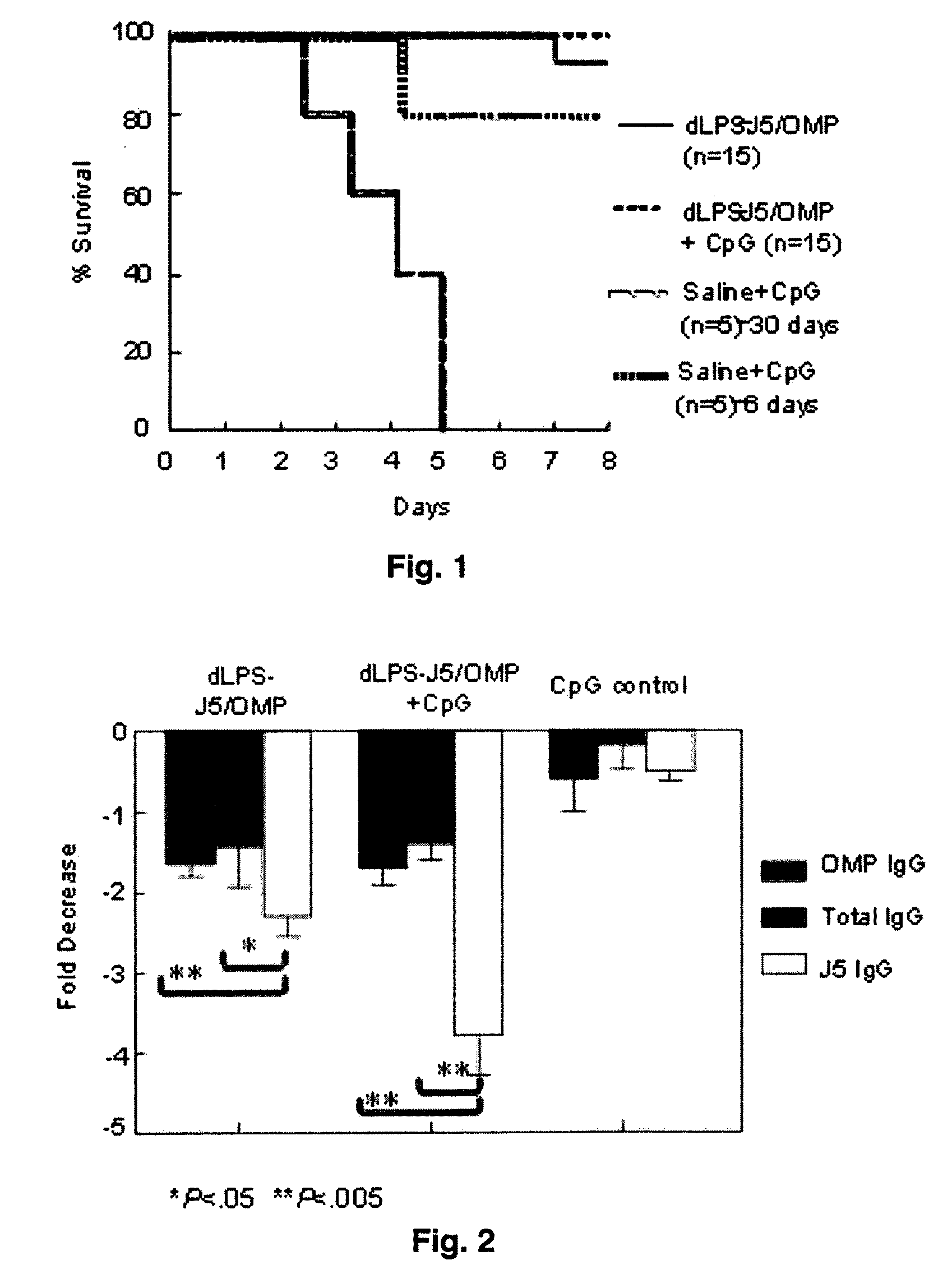
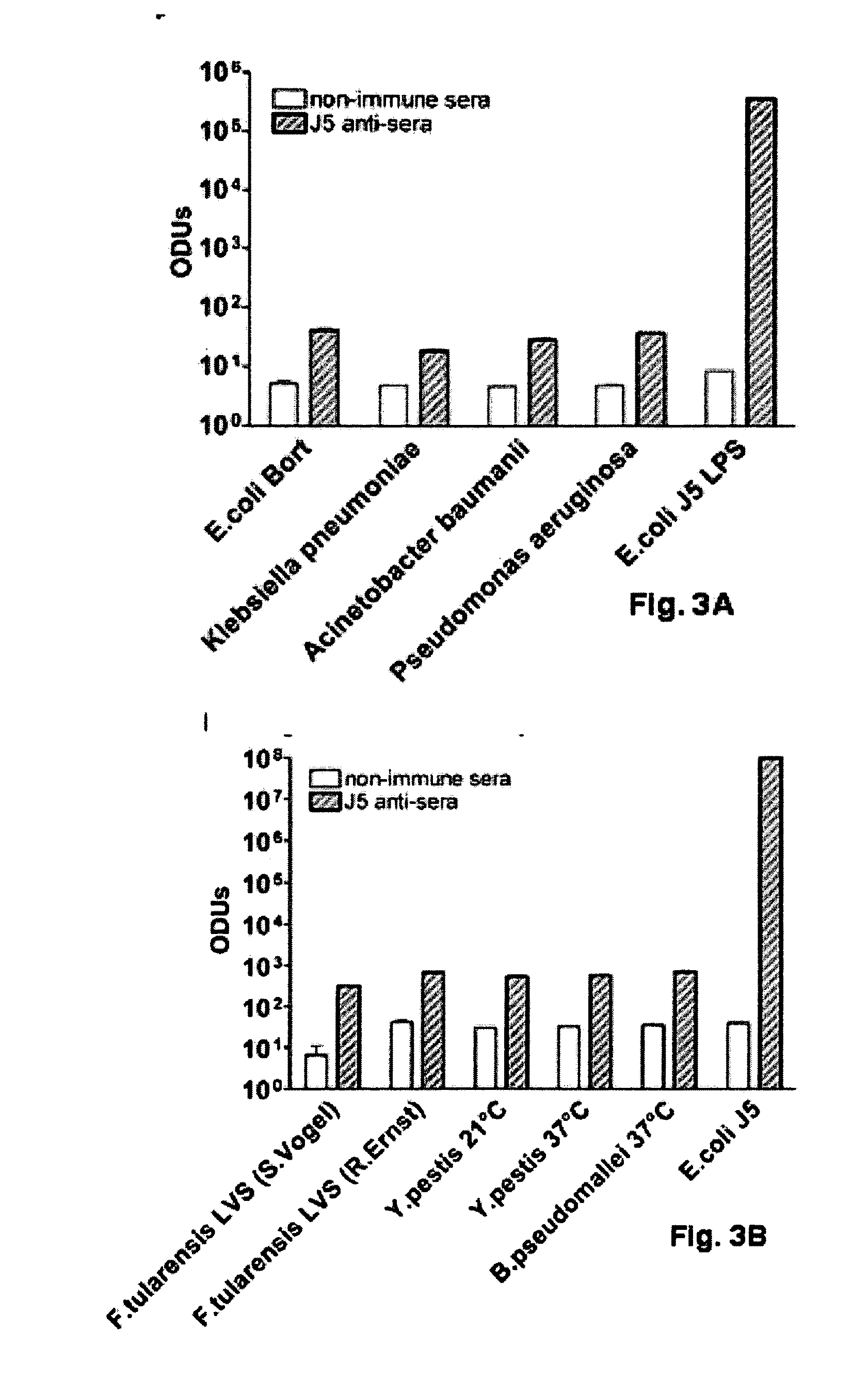
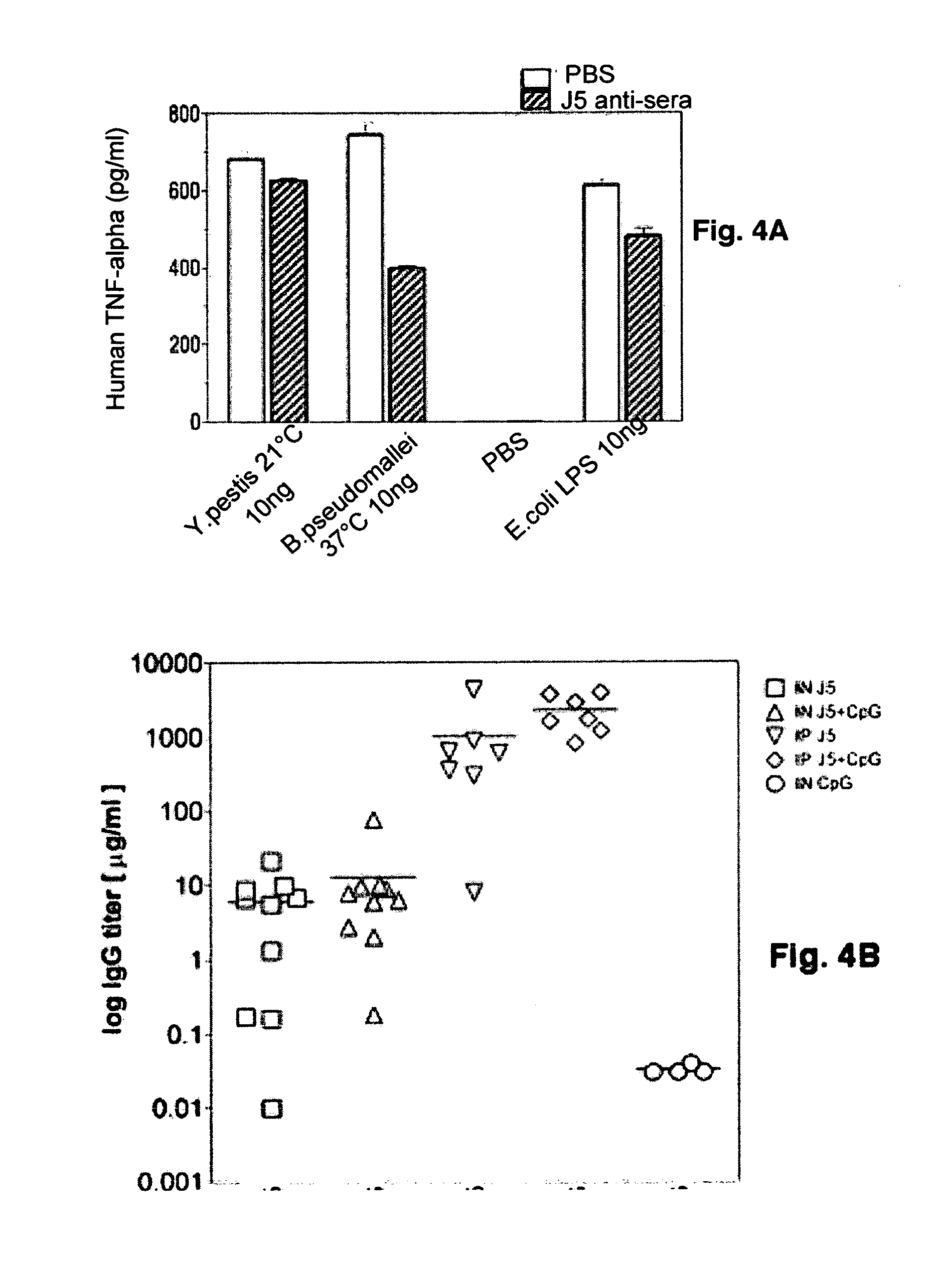
Detoxified Endotoxin Vaccine and Adjuvant and Uses thereof
InactiveUS20090220522A1Avoid infectionSnake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAdjuvantMammal
The present invention describes a detoxified Gram negative J5 core lipopolysaccharide / group B meningococcal outer membrane protein complex vaccine given in conjunction with CpG 7909 adjuvant. This vaccine composition can be used for either active or passive immunization of mammals for the prevention or treatment of sepsis and infection with Gram negative bacteria. The addition of CpG to the vaccine was shown to markedly increase the antibody response in mice. Furthermore, the ability of the endotoxin vaccine in protecting against Gram-negative bacteria such as Francisella tularensis in vivo is also demonstrated herein.
Owner:COLEY PHARM GRP INC +1
Bismuth-thiols as antiseptics for agricultural, industrial and other uses
Compositions and methods, including novel homogeneous microparticulate suspensions, are described for treating natural and artificial surfaces that contain bacterial biofilm, including unexpected synergy or enhancing effects between bismuth-thiol (BT) compounds and certain antibiotics, to provide formulations including antiseptic formulations. Previously unpredicted antibacterial properties and anti-biofilm properties of disclosed BT compounds and BT compound-plus-antibiotic combinations are also described, including preferential efficacies of certain such compositions for treating certain gram-positive bacterial infections, and distinct preferential efficacies of certain such compositions for treating certain gram-negative bacterial infections.
Owner:MICROBION
Polymyxin E composition and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and in particular relates to a polymyxin E composition and a preparation method and application thereof. The composition mainly comprises polymyxin E1, also comprises polymyxins of E2, E3, E1-1, E1-7MOA and the like. The composition is applied to preparing medicines for treating Gram-negative bacterial infections.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Compounds for inhibiting bacterial growth via phosphatidylglycerol binding
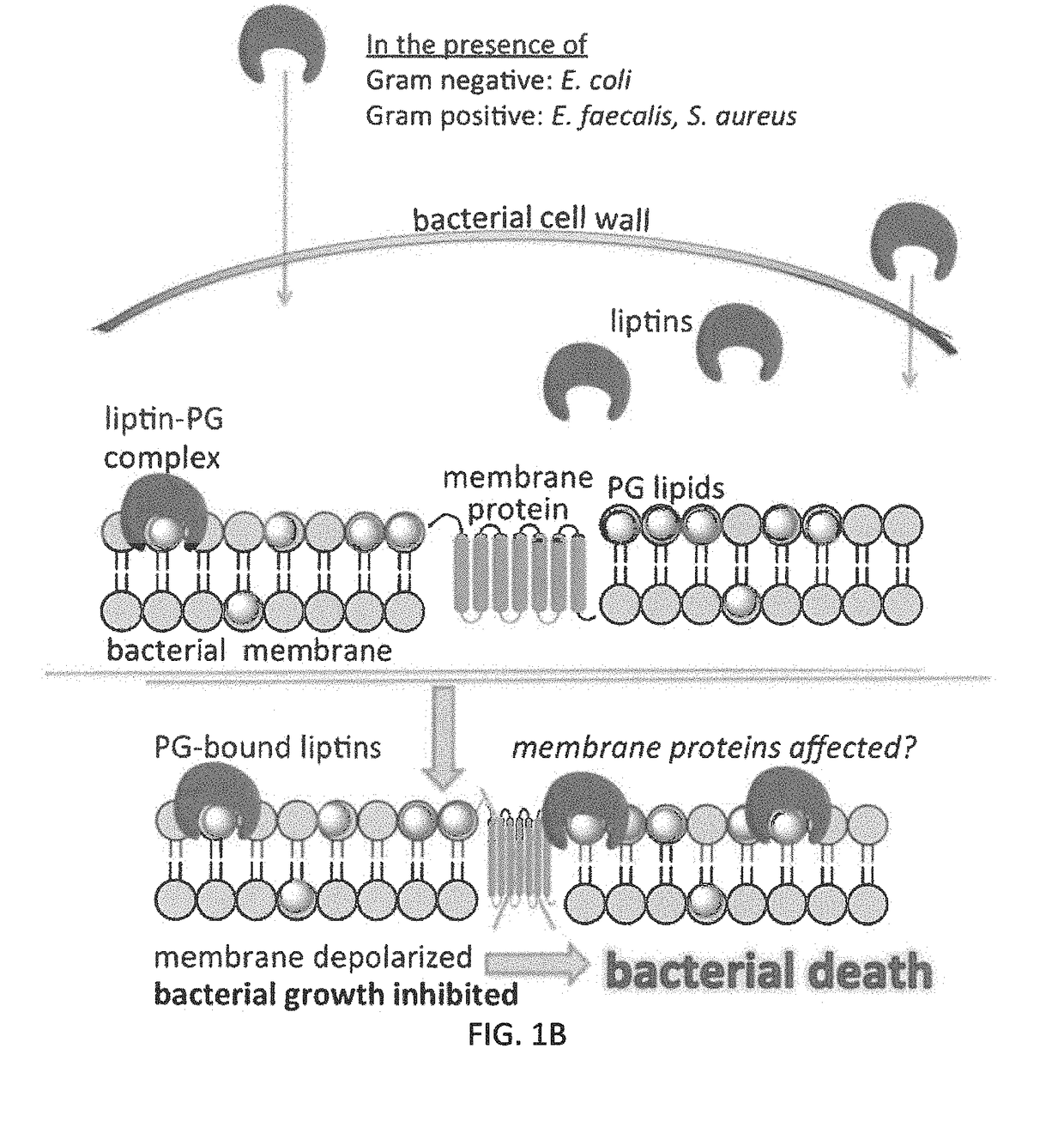
ActiveUS20190029998A1Fine control over directionalityHigh affinityAntibacterial agentsBiocideGramPhosphatidylglycerol binding
Antibacterial small molecule compounds, termed liptins, bind to phosphatidylglycerol in bacterial plasma membranes. The small molecule compounds comprise a three-dimensional complementary binding pocket for phosphatidylglycerol, disrupting membrane function in a bacteriostatic or bactericidal manner. Methods of inhibiting bacterial growth and / or treating Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacterial infection using such compounds are also disclosed.
Owner:WICHITA STATE UNIVERSITY
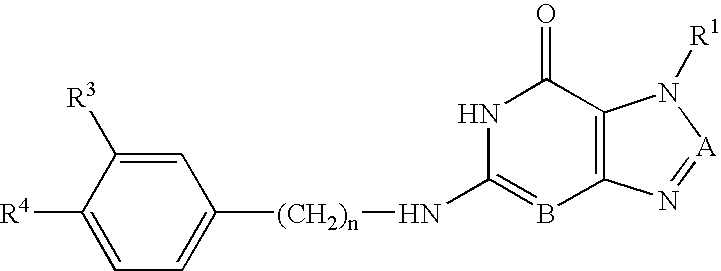
Organic compounds and their uses
InactiveUS8372885B2Improve throughputLimit deliveryAntibacterial agentsBiocideChemical compoundGram-negative bacterial infections
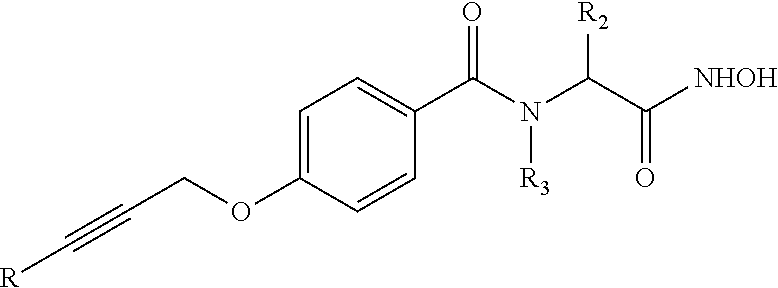
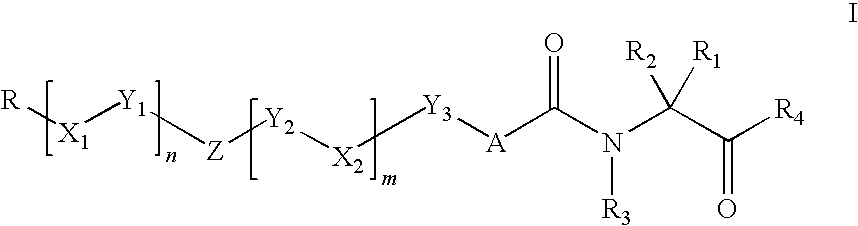
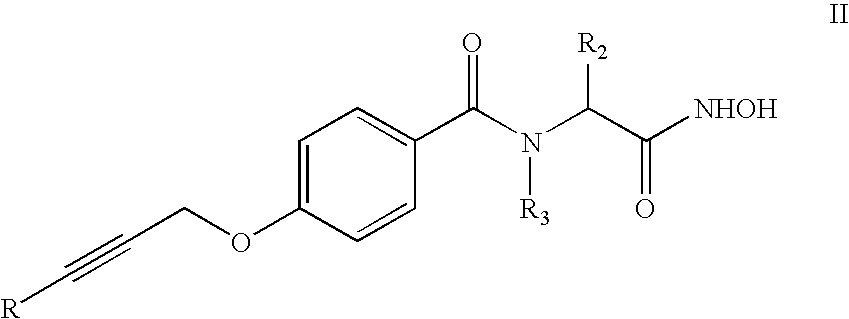
The present application describes organic compounds of a general formula:and salts, and isomers thereof, wherein R, R2 and R3 are defined in the specification. The compounds are useful for treating a gram-negative bacterial infection.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Compositions and methods for eliciting an immune response to gram-negative bacterial infections
InactiveUS20060018916A1Strong and longer immune responseStrong immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAntigenGram-negative bacterial infections
Compositions for eliciting an immune response against Gram-negative bacterial infections and methods of making such compositions are provided. The composition comprises glycosylated pilin, the pilin being glycosylated with the O-antigen of a target Gram-negative bacteria of interest. Methods of eliciting an immune response by administration of such compositions are also provided.
Owner:DUQUESNE UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing charge modified lactoferrin
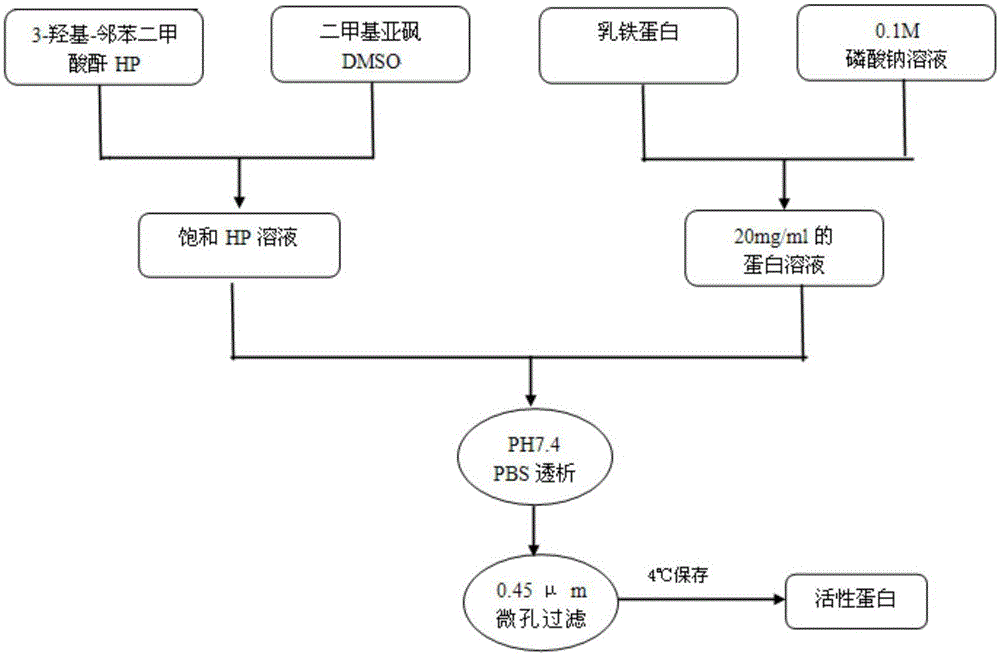
InactiveCN105031626AIncrease conversion rateGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsProtein solutionHuman papilloma virus infection
The invention discloses a method for preparing charge modified lactoferrin. The method comprises the following operation steps: dissolving 3-hydroxy-phtalic anhydride in dimethyl sulfoxide to prepare a saturated HP solution; dissolving lactoferrin in a 0.1M sodium phosphate solution to prepare a protein solution of 20mg / mL; uniformly mixing the saturated HP solution and the protein solution of 20mg / mL, regulating the pH to 10, standing at 25 DEG C for 1 hour, dialyzing by adopting PBS which has the pH of 7.4, and filtering and sterilizing with a 0.45mu m membrane to obtain the charge modified lactoferrin. The charge modified lactoferrin can be combined with carrageenan to prepare a composition medicine for preventing and treating infection of human papilloma virus of females and preventing and treating gynecological gram-negative bacterial infection of females.
Owner:NANJING LAKESEN BIOPHARM TECH CO LTD
Vaccine against Gram-negative bacterial infections
InactiveUS7025963B1Bacterial antigen ingredientsAntibody ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsColiform bacilli
A vaccine, effective in inducing the production of antibodies with which to immunize a second subject passively against infection by Gram-negative bacteria and LPS-mediated pathology, comprises a non-covalent polyvalent complex formed between purified, detoxified LPS derived from E. coli and purified outer membrane protein derived from N. meningitidis. The same vaccine will also actively immunize a host subject against Gram-negative bacterial infections and LPS-mediated pathology. Meningococcal infections are included among those Gram-negative bacterial infections protected against by the vaccine.
Owner:US ARMY MEDICAL RES MATERIEL COMMAND USAMRMC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com