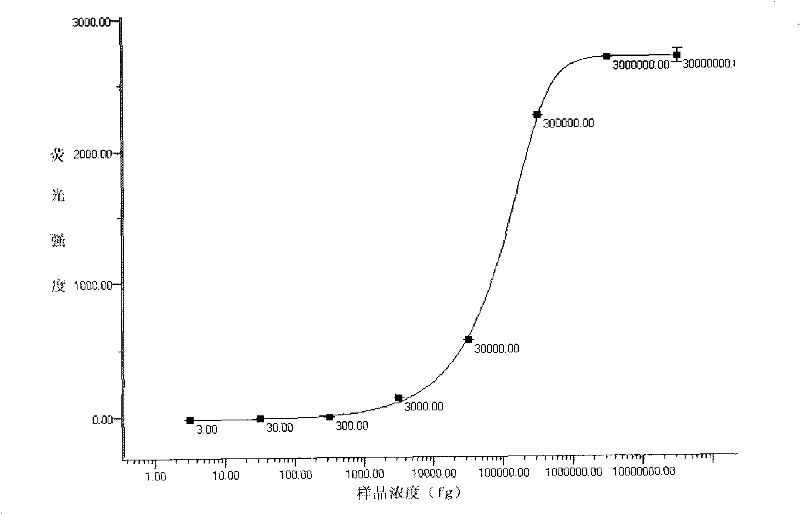
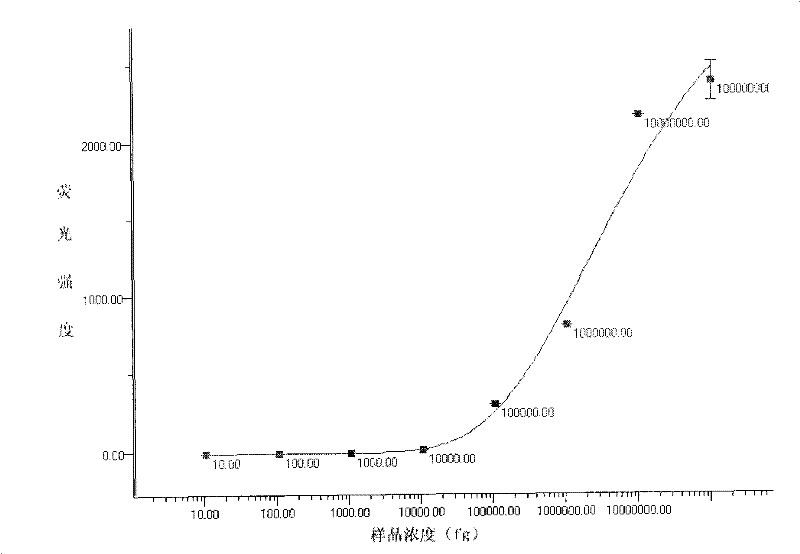
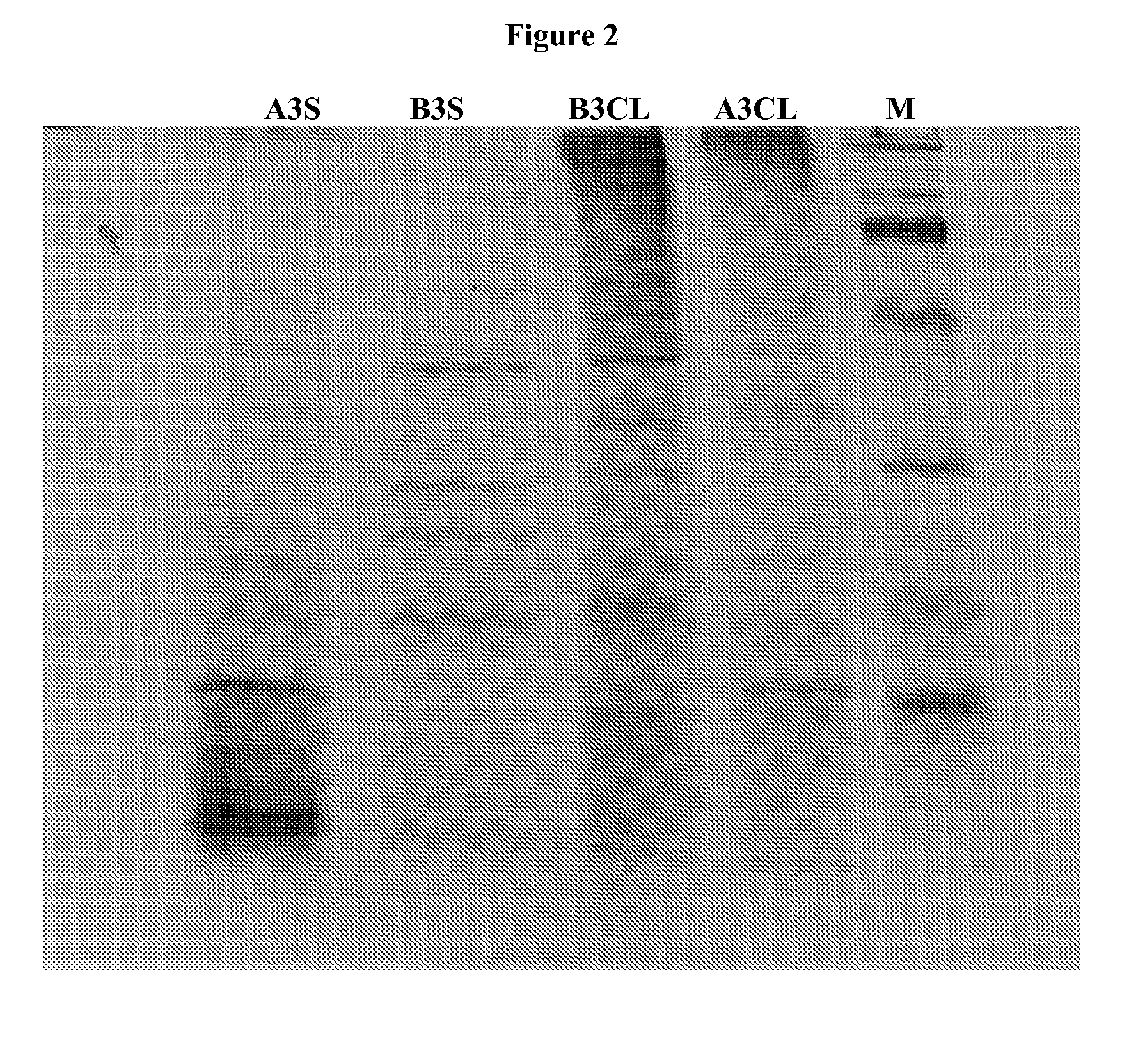
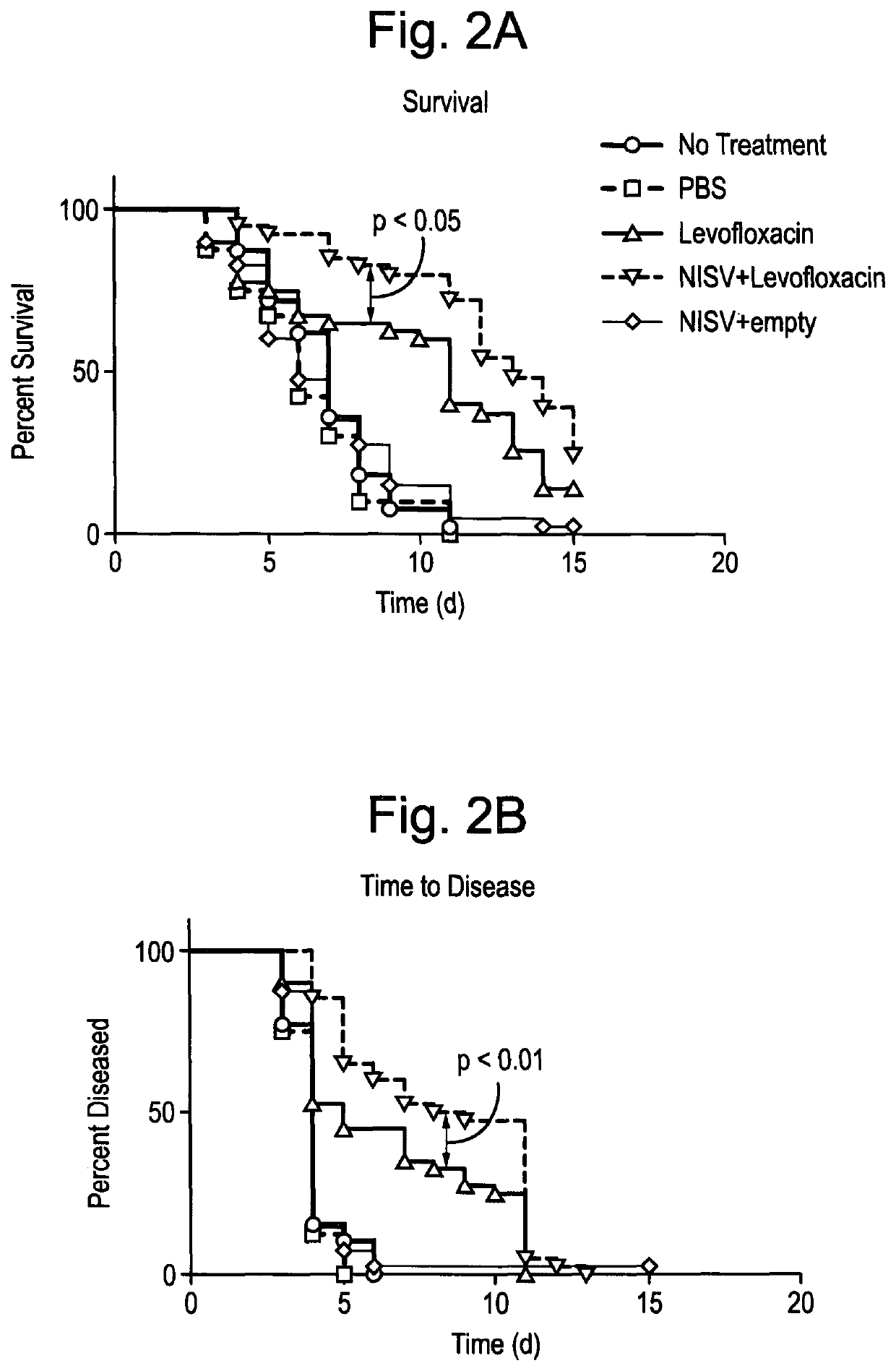
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Francisella tularensis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Francisella tularensis is a pathogenic species of Gram-negative coccobacillus, an aerobic bacterium. It is nonspore-forming, nonmotile, and the causative agent of tularemia, the pneumonic form of which is often lethal without treatment. It is a fastidious, facultative intracellular bacterium, which requires cysteine for growth. Due to its low infectious dose, ease of spread by aerosol, and high virulence, F. tularensis is classified as a Tier 1 Select Agent by the U.S. government, along with other potential agents of bioterrorism such as Yersinia pestis, Bacillus anthracis, and Ebola virus. When found in nature, Francisella tularensis can survive for several weeks at low temperatures in animal carcasses, soil, and water. In the laboratory, F. tularensis appears as small rods (0.2 by 0.2 µm), and is grown best at 35-37°C.
Novel purified FabI polypeptides from fransicella tularensis
The present invention relates to novel drug targets for pathogenic bacteria. Accordingly, the invention provides purified protein comprising the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also provides biochemical and biophysical characteristics of the polypeptides of the invention.
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
Genetic liquid phase chip for joint detection of five drastic pathogenic bacteria and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101560557AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesYersinia pestisPathogenic bacteria
The invention discloses a genetic liquid phase chip for rapid detection of five drastic pathogenic bacteria of bacillus anthracis, yersinia pestis, brucella bacteria, francisella tularensis and burkholderia pseudomallei. The liquid phase chip for detecting the five drastic pathogenic bacteria has the advantages of large flux, less required sample capacity, strong specificity, high sensitivity, accuracy, high efficiency, and the like.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
CRISPR-Cas12a detection primer group for francisella tularensis and application thereof
ActiveCN111394490AShort detection timeHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGeneticsNucleotide sequencing
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Method and kit for detecting multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN102796810AImprove throughputAddresses issues with reduced sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesHighly pathogenic
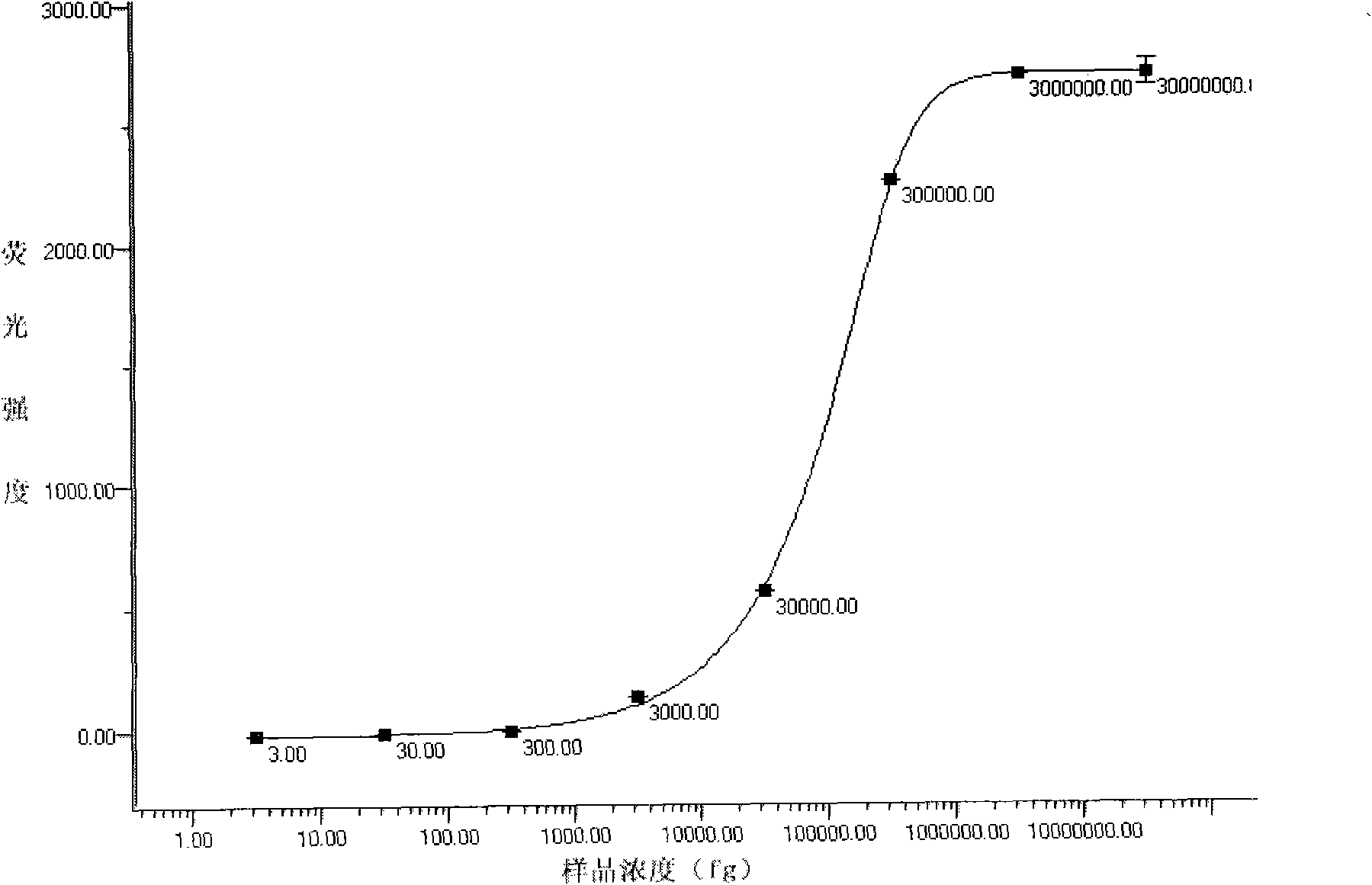
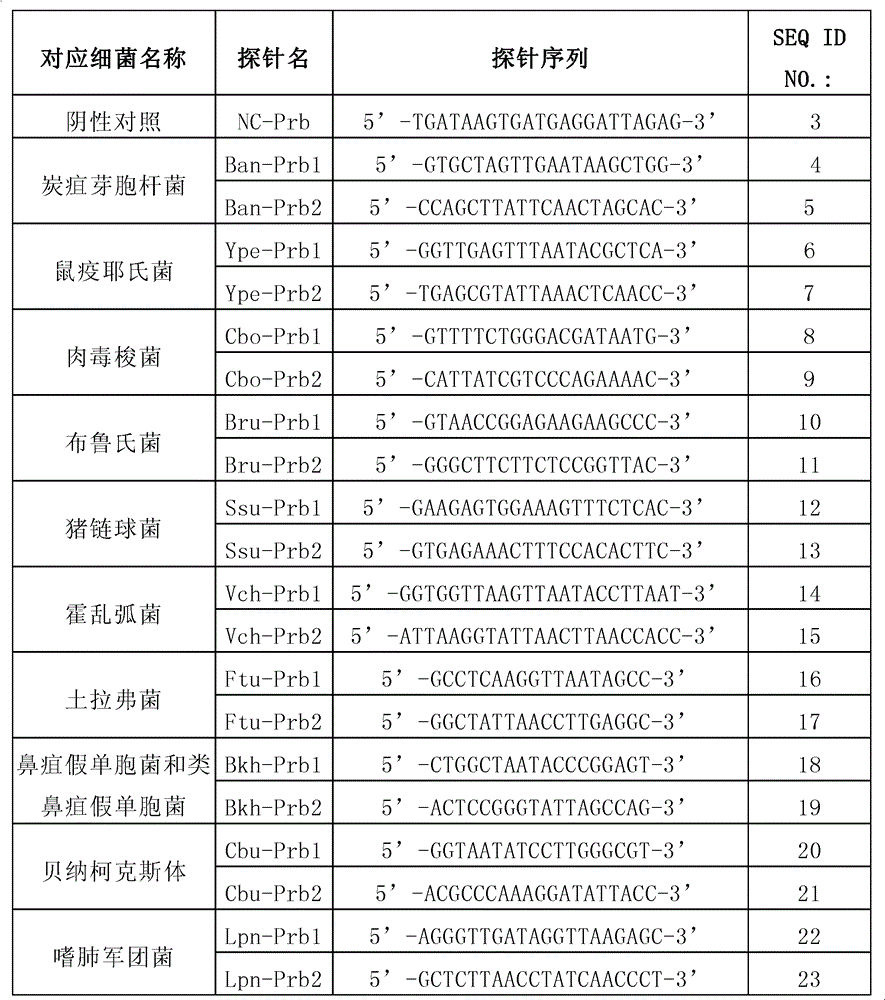
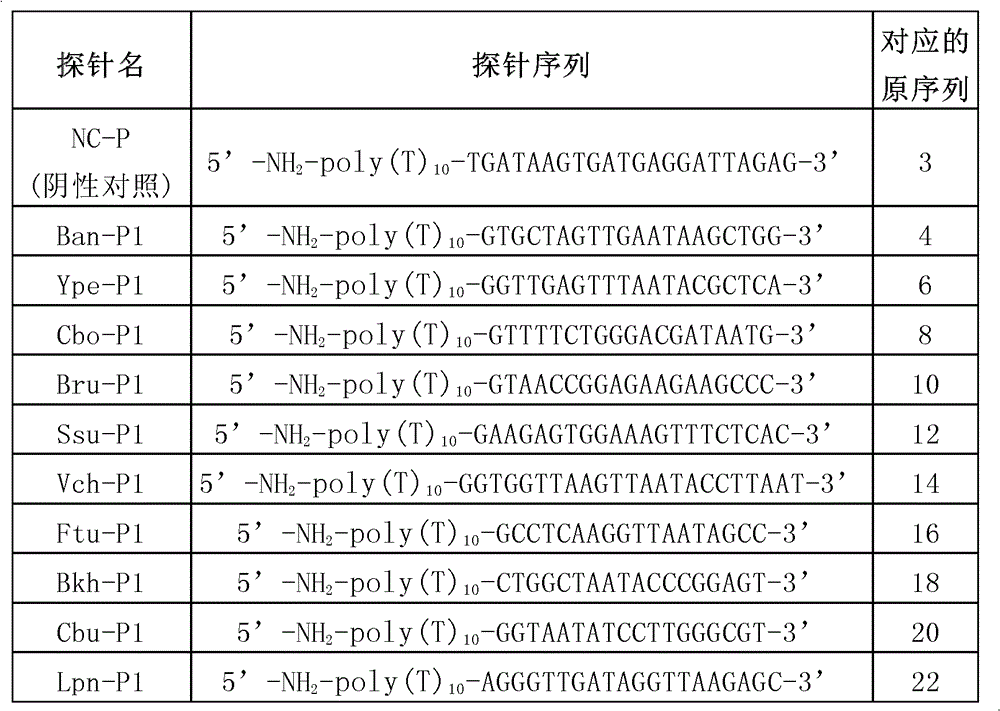
The invention provides a method and kit for detecting multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria, particularly a method for simultaneously detecting multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria, which comprises the following steps: in a polymerase reaction system, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) on high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria by using a specific primer set, thereby obtaining an amplification product; and detecting with a specific probe or probe microsphere. The invention also provides a corresponding kit. The invention can sensitively and conveniently detect and identify multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria, including Bacillus anthracis, Yersinia pestis, Clostridium botulinum, Brucella, Streptococcus suis, Vibrio cholerae, Francisella tularensis, Pseudomonas mallei (or Pseudomonas pseudomallei), Coxiella burnetii and Legionella pneumophila.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELLGEN LIFE SCI CO LTD
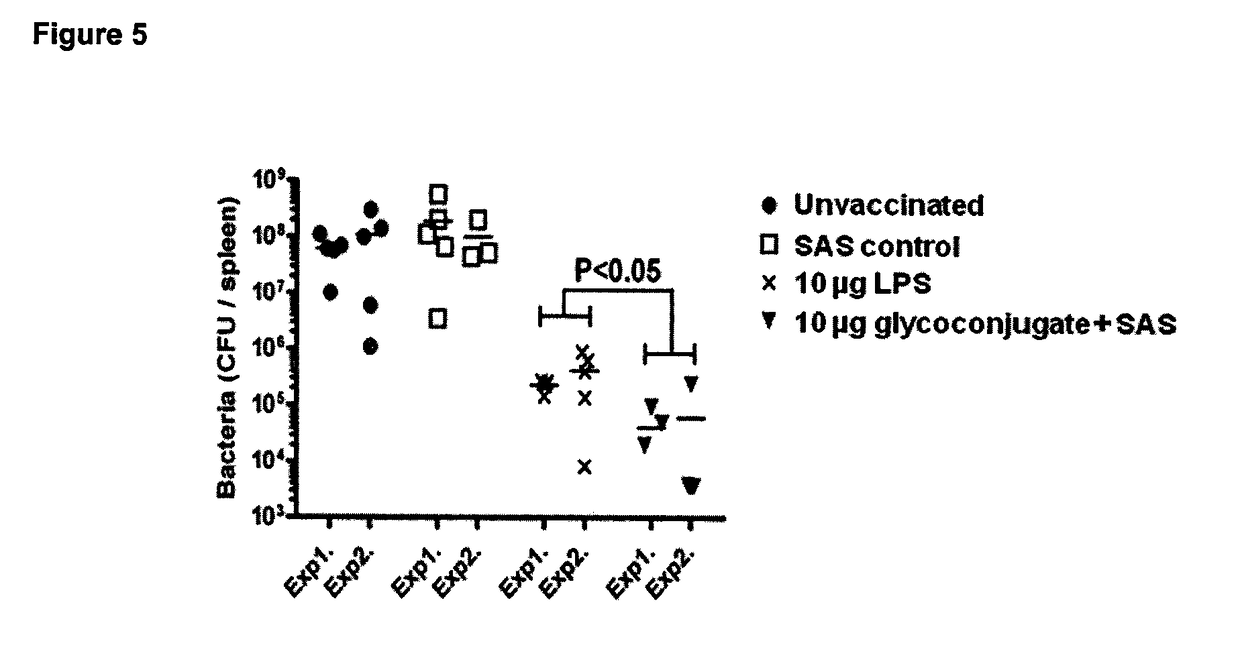
Glycoconjugate vaccines
ActiveUS20150328301A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenGlycoconjugate
The disclosure relates to a glycoconjugate vaccine conferring protection against Francisella tularensis infections and a method to manufacture a glycoconjugate antigen.
Owner:LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE
Immunological chromatographic test paper for testing francisella tularensis and its prpearation method
InactiveCN101000347ASuitable for useSimple specimen handlingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiochemistryMonoclonal antibody agent
An immune chromatographic test paper for testing francisella tularensis is prepared as series-connecting sample pad, golden labeled pad with collaurum probe containing francisella tularensis single clone antibody label, fiber membrane nitrate and water absorption pad; enveloping a detection line and a quality control line being separated to each other on fiber membrane nitrate; using francisella tularensis single clone antibody as detection line and using anti-antibody of anti-mouse as quality control line.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Reagent for detecting francisella tularensis and complex probe and fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for detecting francisella tularensis
InactiveCN102154487AShorten detection timeGuaranteed specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescencePcr method
The invention provides a reagent for detecting francisella tularensis. The reagent comprises an upstream primer, a downstream primer, a fluorescent probe and a quenching probe, wherein the gene sequence FTF1 of the upstream primer is 5'-aagcaagtgttgactacagat-3', the gene sequence FTR1 of the downstream primer is 5'-caccaaagaaccatgttaaac-3', the gene sequence FPFT1 of the fluorescent probe is 5'-FAM-aatcatgttagtacccgctctgcca-p-3', and the gene sequence QPFT1 of the quenching probe is 5'-agcgggtactaacatgat-Dabcyl-3'. The invention also provides a complex probe and fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting the francisella tularensis by using the reagent. Compared with the traditional francisella tularensis detecting technology, the invention has the advantages of simple operation, high efficiency, quickness and high specificity.
Owner:浙江国际旅行卫生保健中心
Method for detecting Francisella tularensis using multiple PCR technology
InactiveCN101372713ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisComplete sequence
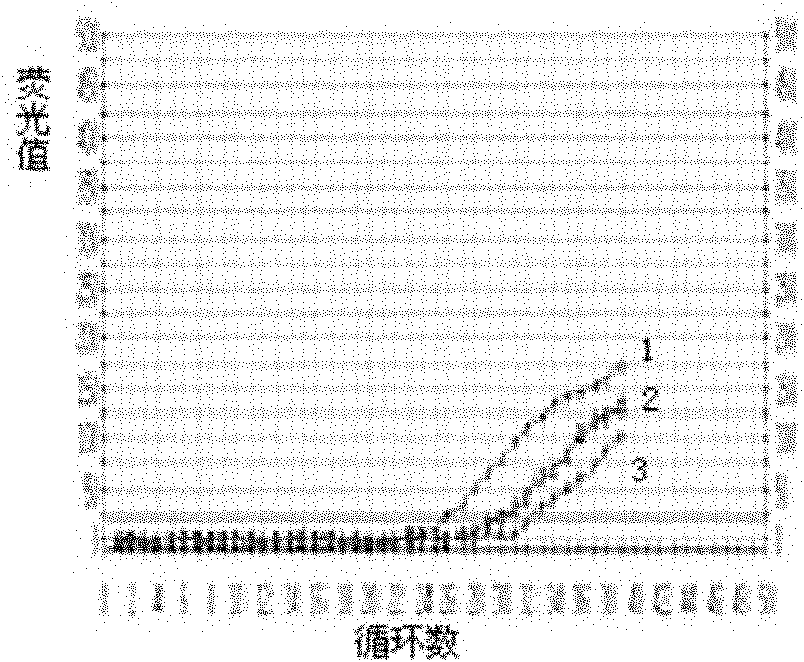
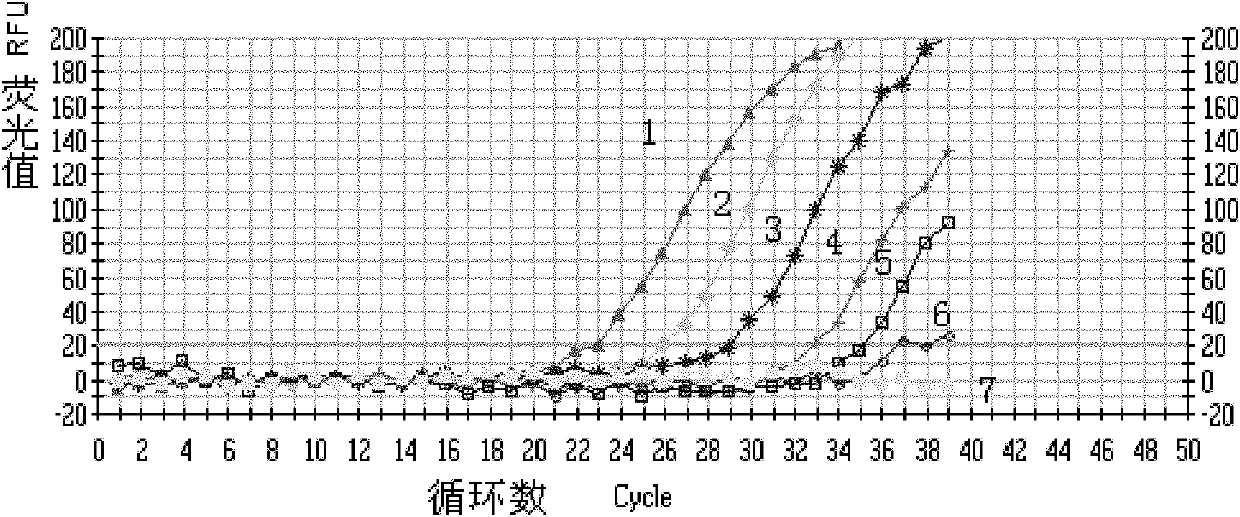
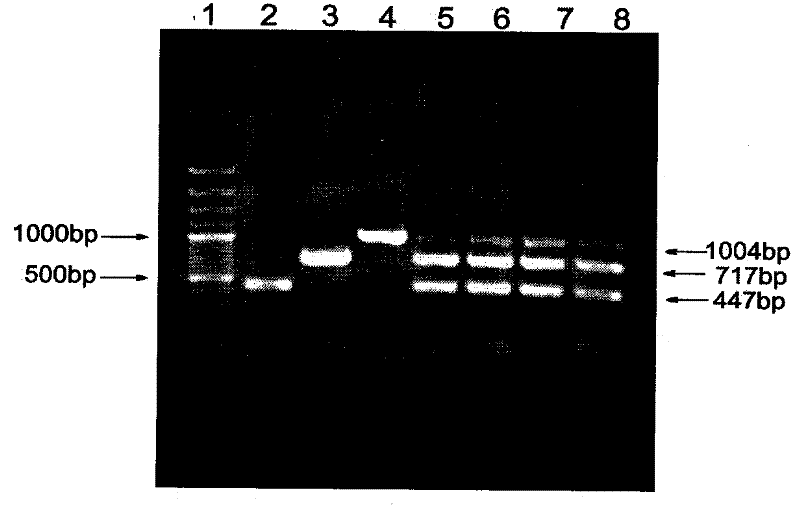
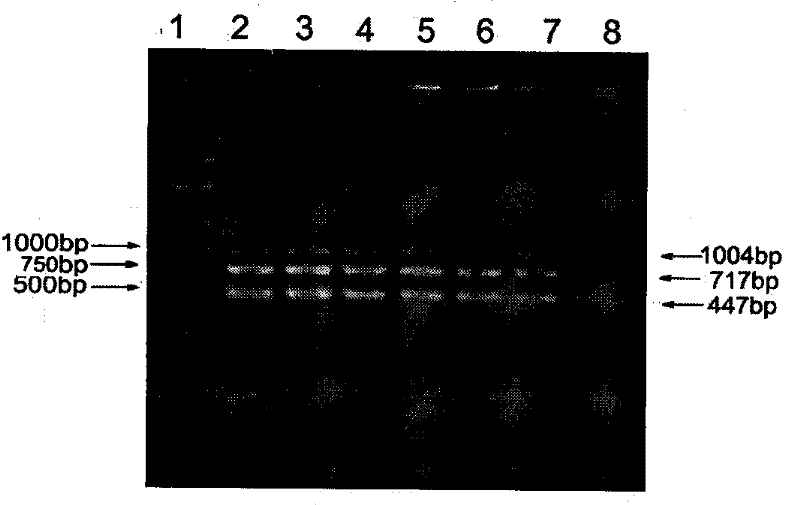
The invention relates to a method of detecting Francisella tularensis by a multiple PCR technique, belonging to the technical field of detecting biological agent. The invention comprises steps of: using the related genes lpxF, lpxE and flmK of the endotoxin of the Francisella tularensis as the specificity targets, carrying out comparison by complete sequence Blastp of NCBI microbial genome to determine the specificities of the three genes, designing the related primer and conducting detection by the multiple PCR technique; after three strips, which are 447bp,717bp and 1004bp in turn, appear in the electrophoresis detection, judging the strips to be masculine according to the appearance of three specificity strips, otherwise, judging the strips to be feminine. The invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, easy promotion and application, short detecting cycle, high sensitivity, good specificity and higher detecting rate, wherein, with respect to 5 to 7 days needed to obtain the result by the traditional detecting method, the detecting cycle of the method, which is 3 hours, is much shorter than that of the traditional method, thus greatly improving the detecting efficiency; moreover, the detecting limit, which is 0.01ng / [mu]L and 5X10<5>cfu / mL, reaches or exceeds that of the traditional detecting method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Detoxified Endotoxin Vaccine and Adjuvant and Uses thereof
InactiveUS20090220522A1Avoid infectionSnake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAdjuvantMammal
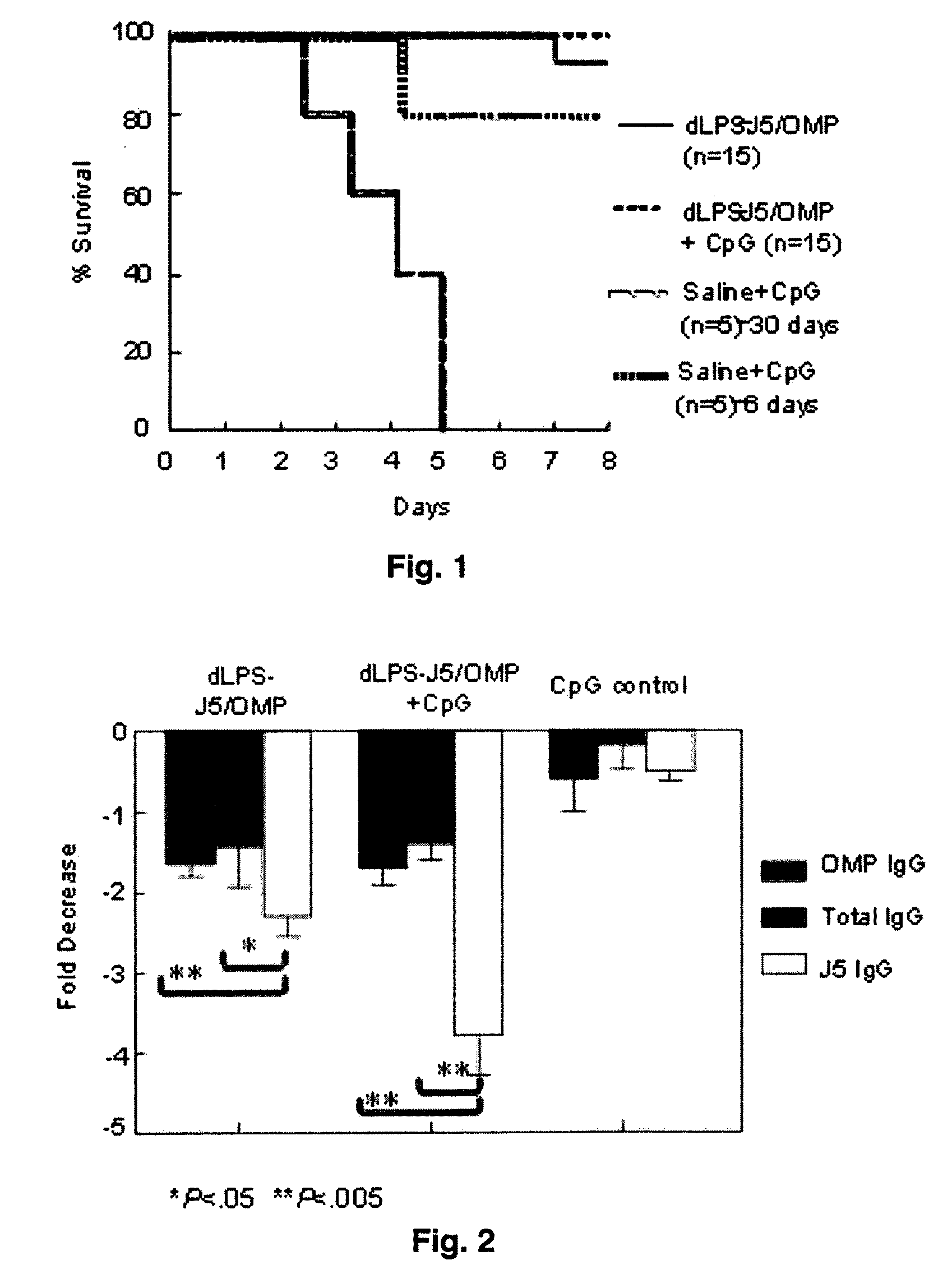
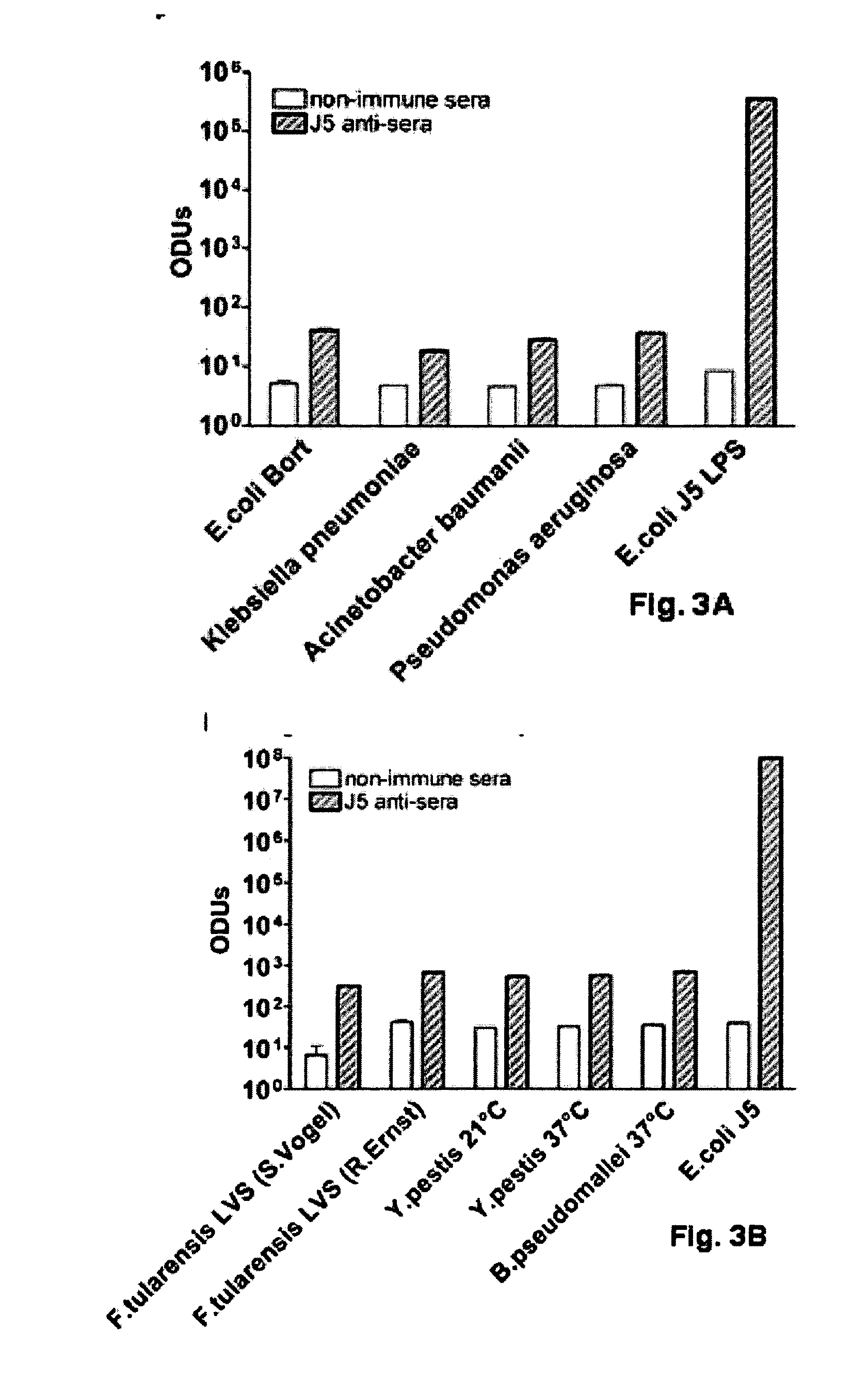
The present invention describes a detoxified Gram negative J5 core lipopolysaccharide / group B meningococcal outer membrane protein complex vaccine given in conjunction with CpG 7909 adjuvant. This vaccine composition can be used for either active or passive immunization of mammals for the prevention or treatment of sepsis and infection with Gram negative bacteria. The addition of CpG to the vaccine was shown to markedly increase the antibody response in mice. Furthermore, the ability of the endotoxin vaccine in protecting against Gram-negative bacteria such as Francisella tularensis in vivo is also demonstrated herein.
Owner:COLEY PHARM GRP INC +1
Glycoconjugate vaccines
ActiveUS9642902B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenGlycoconjugate
The disclosure relates to a glycoconjugate vaccine conferring protection against Francisella tularensis infections and a method to manufacture a glycoconjugate antigen.
Owner:LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE
PCR primer pair and kit for rodent-borne disease pathogenic microorganisms and application thereof
InactiveCN110218803AEfficient detection methodFast detection methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPathogenic microorganismBartonella
The invention discloses a PCR primer pair for rodent-borne disease pathogenic microorganisms. The primer pair is used for amplifying specific genes of leptospira interrogans, Rickettsi Mooseri, Orientia tsutsugamushi, anaplasma phagocytophilum, francisella tularensis, Coxiella burnetii and Bartonella. By adopting the PCR primer pair, on the basis of the TSP principle, the method for high-sensitiveand specific independent or combined detection of the seven kinds of pathogene.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
PCR detection method and kit for francisella tularensis and subspecies of francisella tularensis
ActiveCN109337995ALower skill requirementsSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEtiologyBacteroides
The invention provides a PCR detection method and kit for francisella tularensis and subspecies of francisella tularensis. The kit contains at least a universal primer (SEQ ID NO:1-2) for detecting francisella tularensis and a specific PCR primer (SEQ ID NO:3-10) for detecting the subspecies of francisella tularensis, namely F.m, F.n, F.Tu and F.h. By adopting the PCR detection method provided bythe invention, francisella tularensis can be quickly determined, the subspecies of francisella tularensis can be determined, an etiology can be directly detected, complicated processes of conventionalbacterial isolation, culture and biochemical identification can be avoided, the detection time is shortened, the operation is convenient, the detection method can be skillfully used after simple training, at the same time, an operator can be avoided from contacting with pathogens directly, thereby improving the safety of an inspection process. The method is high in sensitivity, strong in specificity, and capable of distinguishing the subspecies of francisella tularensis from other subspecies without any cross reaction. The method provides a powerful technical support for the detection of a base layer analysis unit.
Owner:SHANDONG BINZHOU ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE ACADEMY +1
Diagnostic method and products useful therein
InactiveUS20110117543A1Shorten analysis timeReduce analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayYersinia pestis
A method for simultaneous detection and identification of Bacillus anthracis, Yersinia pestis and Francisella tularensis, in a single real time PCR assay using species-specific primers and Taqman MGB probes. Also, a kit for the diagnosis of bacterial bioterrorism agents. In addition, an infection-free control plasmid to verify the result of the real time PCR analysis method.
Owner:THE FINNISH DEFENCE FORCES
Nucleotide sequences specific to Francisella tularensis and methods for the detection of Francisella tularensis
InactiveUS7172868B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesHybridization probe
Described herein is the identification of nucleotide sequences specific to Francisella tularensis that serves as a marker or signature for identification of this bacterium. In addition, forward and reverse primers and hybridization probes derived from these nucleotide sequences that are used in nucleotide detection methods to detect the presence of the bacterium are disclosed.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Use Of 5,6-Dimethylxanthenone-4-Acetic Acid as an Antimicrobial Agent
The invention relates to the areas of therapeutics, pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, and immunotherapy. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods of stimulating the immune system through the administration of flavone acetic acid [FAA] analogues, and in particular, the flavone acetic acid analogue, 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA) so as to comprise an antimicrobial therapeutic agent for the treatment of viral, fungal, bacterial or parasitic infections in humans and non-human animals. The invention is especially suitable for use in a process of treating and preventing infection by viruses (for example, rhinoviruses, enteroviruses, and influenza viruses, etc.) and bacteria (especially intracellular bacterial pathogens such as Francisella tularensis).
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Diagnostic method and products useful therein
InactiveUS7960106B2Reduce analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayYersinia pestis
A method for simultaneous detection and identification of Bacillus anthracis, Yersinia pestis and Francisella tularensis, in a single real time PCR assay using species-specific primers and Taqman MGB probes. Also, a kit for the diagnosis of bacterial bioterrorism agents. In addition, an infection-free control plasmid to verify the result of the real time PCR analysis method.
Owner:THE FINNISH DEFENCE FORCES
Nucleotide sequences specific to Francisella tularensis and methods for the detection of Francisella tularensis
InactiveUS20060040268A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeNucleotide sequencing
Described herein is the identification of nucleotide sequences specific to Francisella tularensis that serves as a marker or signature for identification of this bacterium. In addition, forward and reverse primers and hybridization probes derived from these nucleotide sequences that are used in nucleotide detection methods to detect the presence of the bacterium are disclosed.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Methods of detecting and typing pathogenic strains of francisella tularensis
ActiveUS20200332345A1Improve accuracyImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic bacteriaVirology
A method of detecting a presence of Francisella tularensis (F. tularensis). The method includes amplifying a first nucleic acid from said specimen using a first plurality of primers, said first plurality of primers comprising SEQ ID NO 4 and SEQ ID NO 5. When the first nucleic acid is detected, then the presence of F. tularensis is determined.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRSENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE AIR FORCE
Genetic liquid phase chip for joint detection of five drastic pathogenic bacteria and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101560557BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesYersinia pestisBrucella
The invention discloses a genetic liquid phase chip for rapid detection of five drastic pathogenic bacteria of bacillus anthracis, yersinia pestis, brucella bacteria, francisella tularensis and burkholderia pseudomallei. The liquid phase chip for detecting the five drastic pathogenic bacteria has the advantages of large flux, less required sample capacity, strong specificity, high sensitivity, accuracy, high efficiency, and the like.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
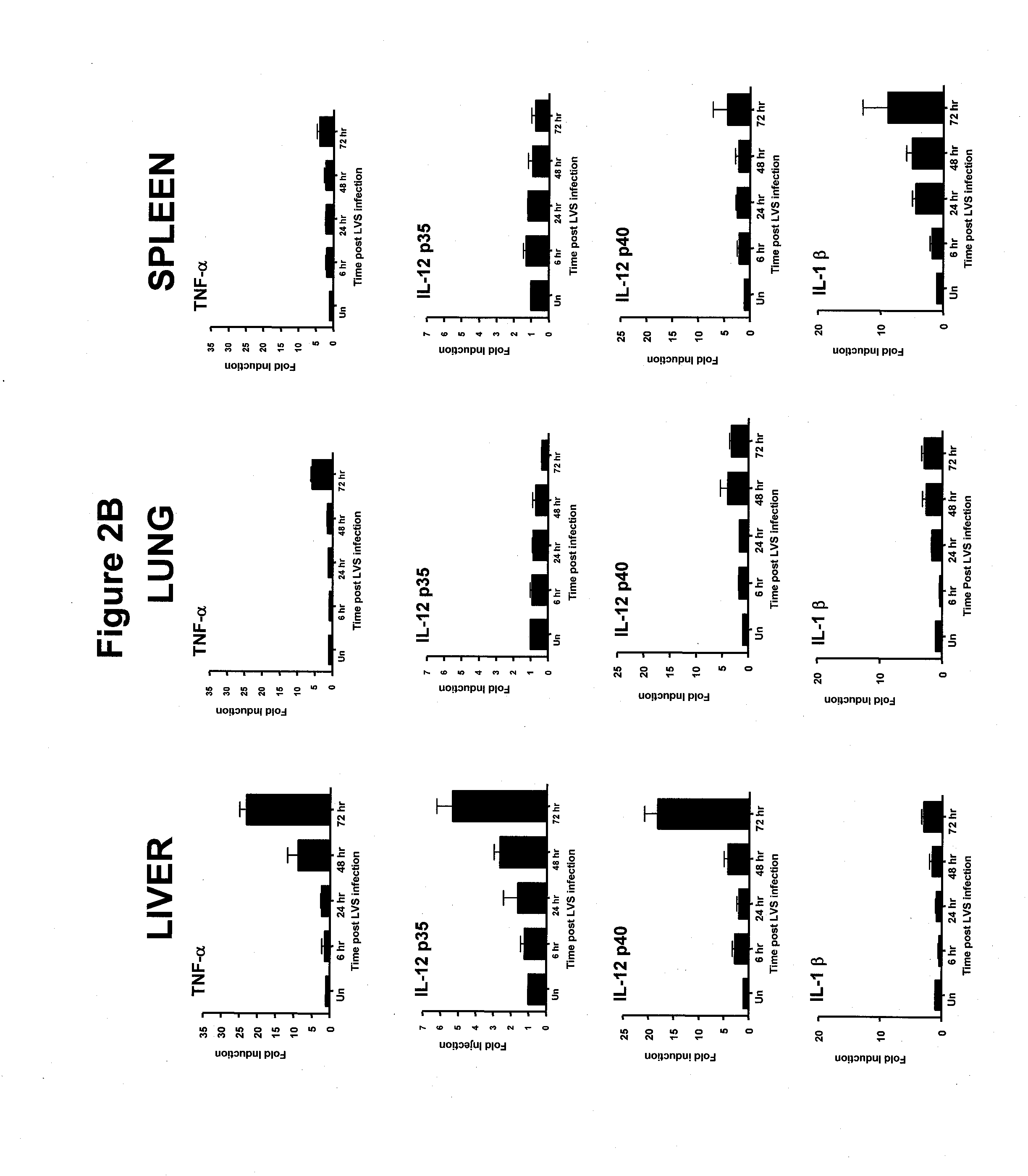
Methods of Treating A Bacterial Infection using F. Tularensis Lipopolysaccharide
InactiveUS20070042004A1Avoid bacterial infectionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPolysaccharideImmune reaction
The present invention relates to the ability of Francisella tularensis LVS lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to confer protection in a subject against a subsequent bacterial infection. Accordingly, the invention provides methods of treating and preventing bacterial infection in a subject by administering F. tularensis LPS to the subject. The invention also relates to methods of modulating the immune response in a subject comprising administering F. tularensis LPS to the subject.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
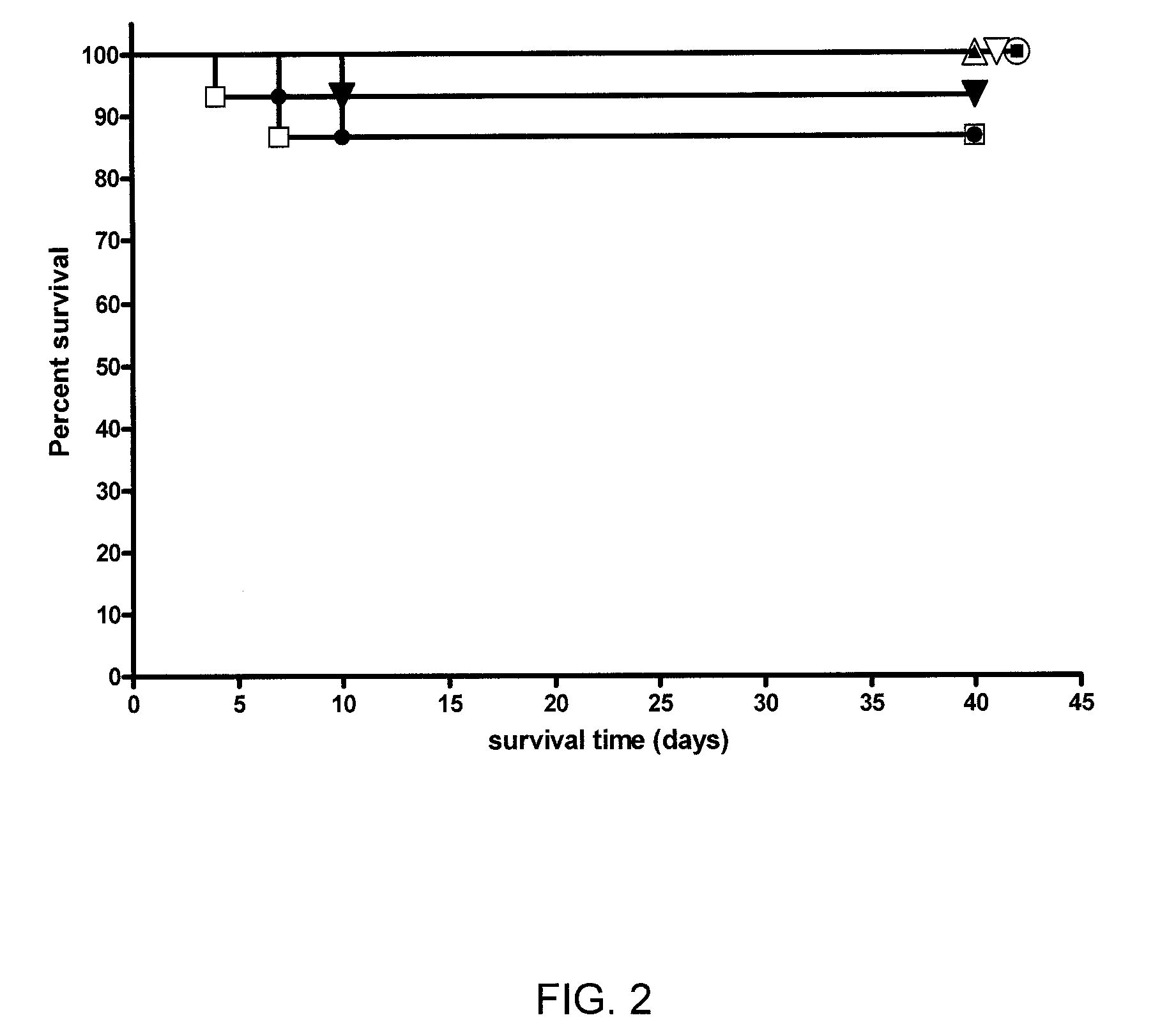
Mutants of Francisella tularensis and uses thereof
ActiveUS8993302B2Less virulentProtects mice more effectivelyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMutantBiology
The present invention relates to a mutant Francisella tularensis strain comprising an inactivated clpB gene and compositions comprising such mutant. Methods of producing the mutant are also described. The present invention also encompasses a method of conferring immunity against F. tularensis in a host, comprising administering the described mutant F. tularensis strain.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Methods for therapeutic or prophylactic treatment of melioidosis and/or associated diseases
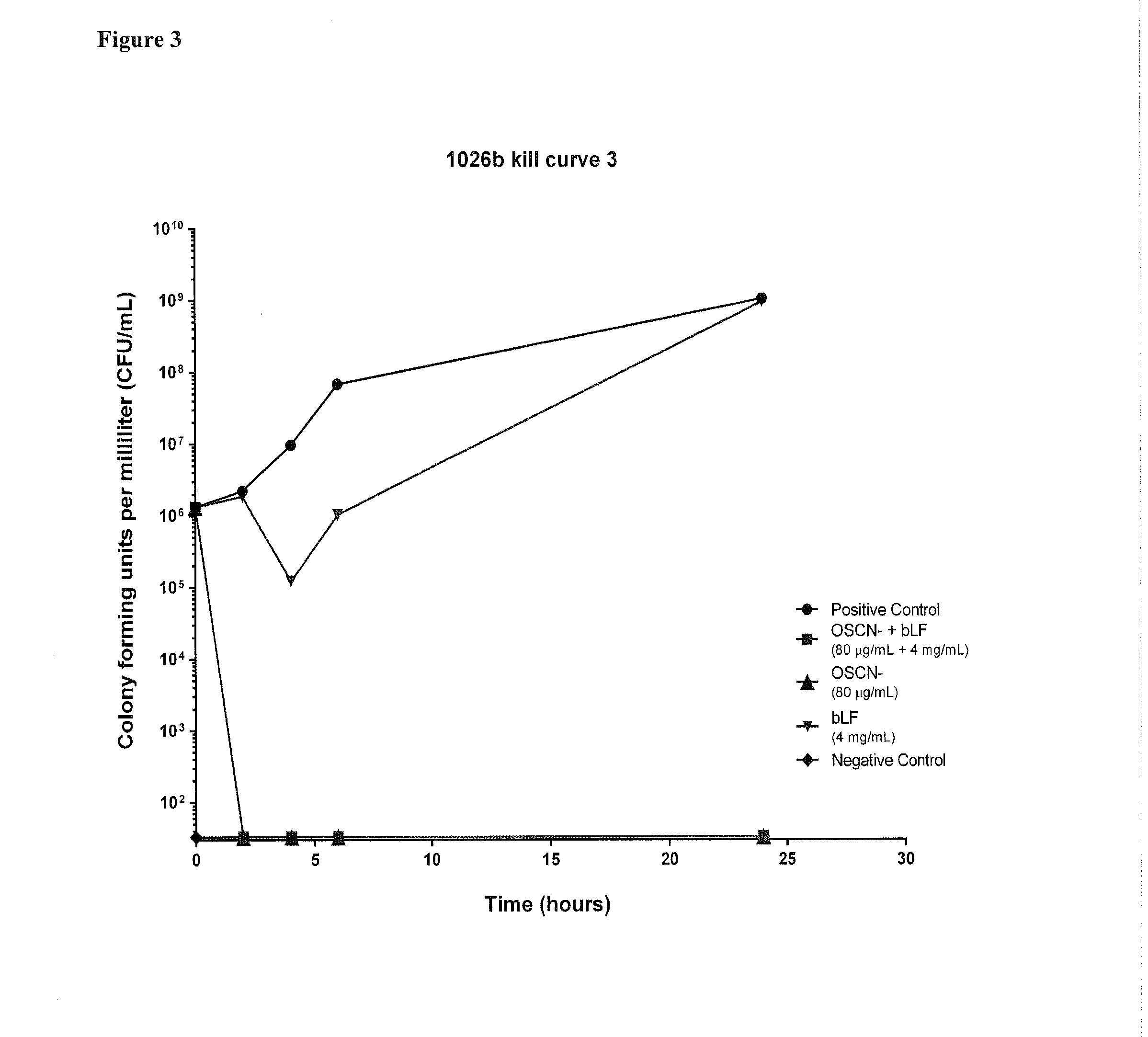
The present invention generally relates to a method for therapeutic or prophylactic treatment of melioidosis and / or associated diseases in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to said subject an effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising either one ion selected from the group of the hypothiocyanites (OSCN−) and / or hypohalites and / or lactoferrin or a combination thereof.The present invention also generally relates to methods of treating or preventing various bacterial infections selected from the group consisting of Burkholderia pseudomallei, Burkholderia mallei, bacillus anthracis, Yersinia pestis, and francisella tularensis infections.
Owner:STRAGEN PHARMA +1
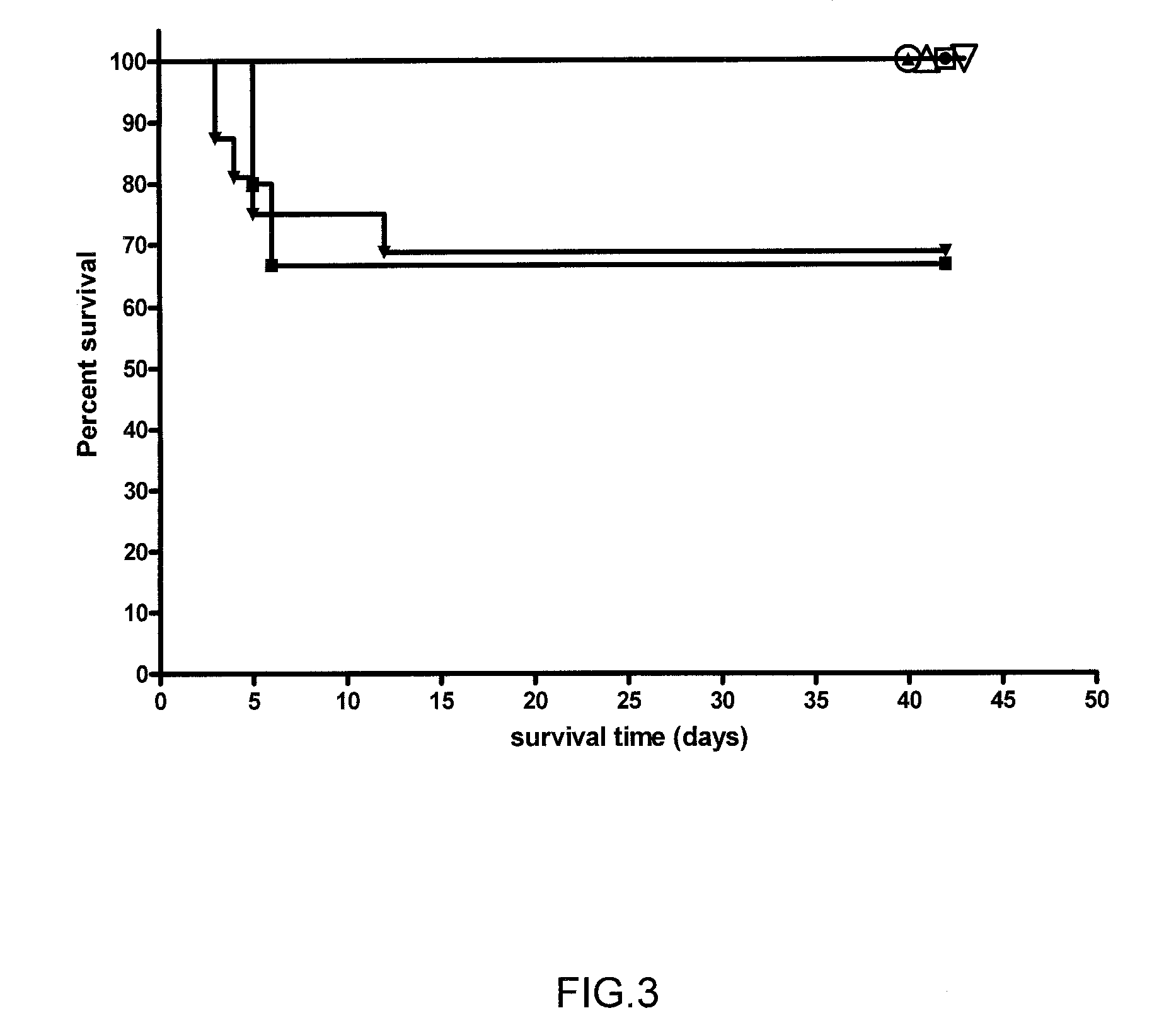
Mutant F. turlarensis strain and uses thereof
InactiveUS7910351B2Lack of functionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPeroxynitriteVirulent characteristics
A mutant strain of Francisella tularensis has attenuated virulence and has a mutation in the gene coding for a putative peroxynitrite resistance protein A (prpA) which prevents normal function of the protein. The mutant is useful as a vaccine against type A and B virulent strains of F. tularensis, and is produced by obtaining a virulent F. tularensis strain and mutating the gene, FTT0918, that codes for prpA.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Live Attenuated Vaccine Strain for Prevention of Tularemia
The invention provides live attenuated avirulent strains of Francisella tularensis, as well as methods for their preparation and use in protecting a mammal against infection with F. tularensis and against tularemia.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Use of cross-protection to identify novel vaccine candidates for infectious agents
InactiveUS7323180B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsHigh concentrationEnzyme digestion
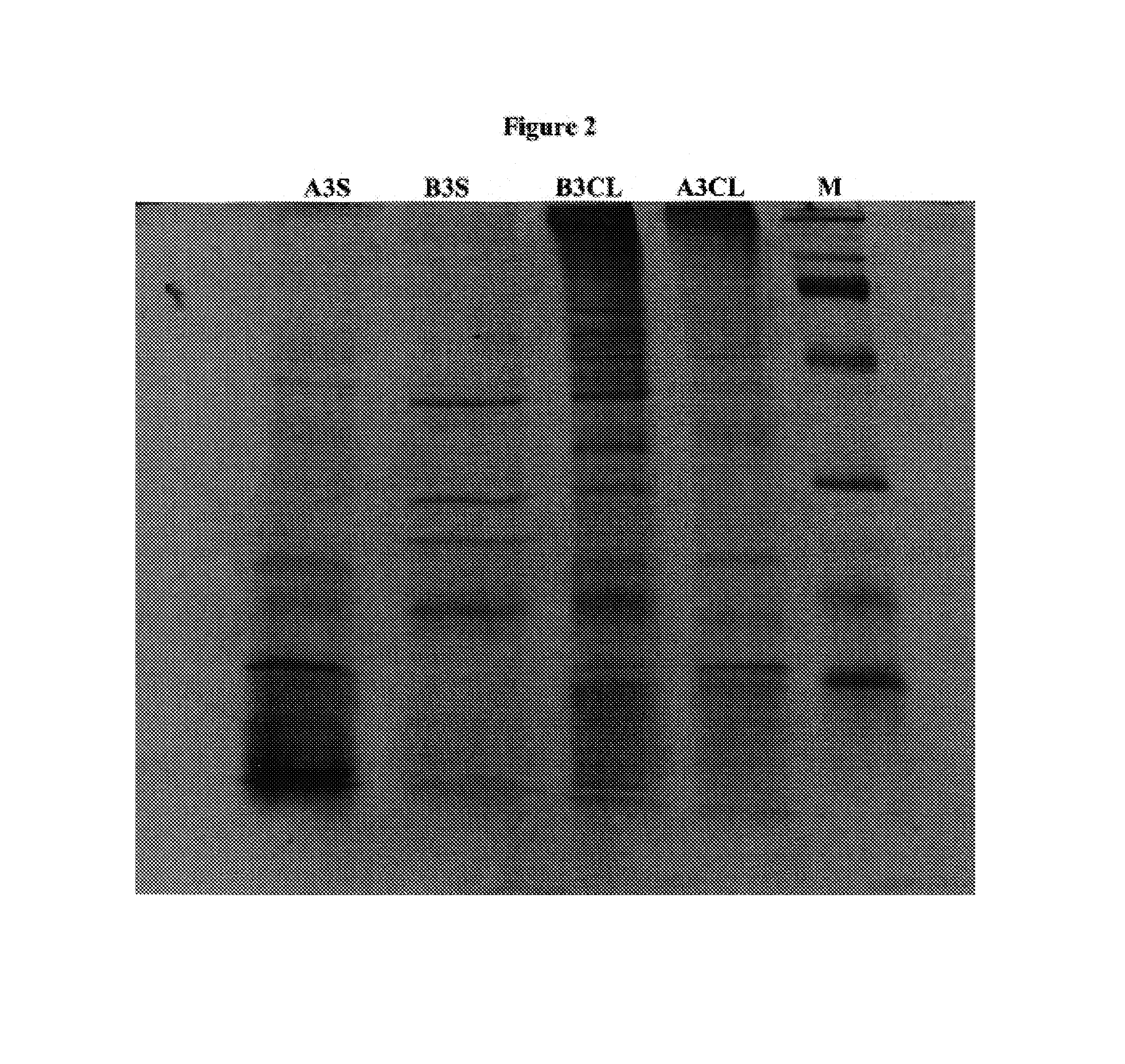
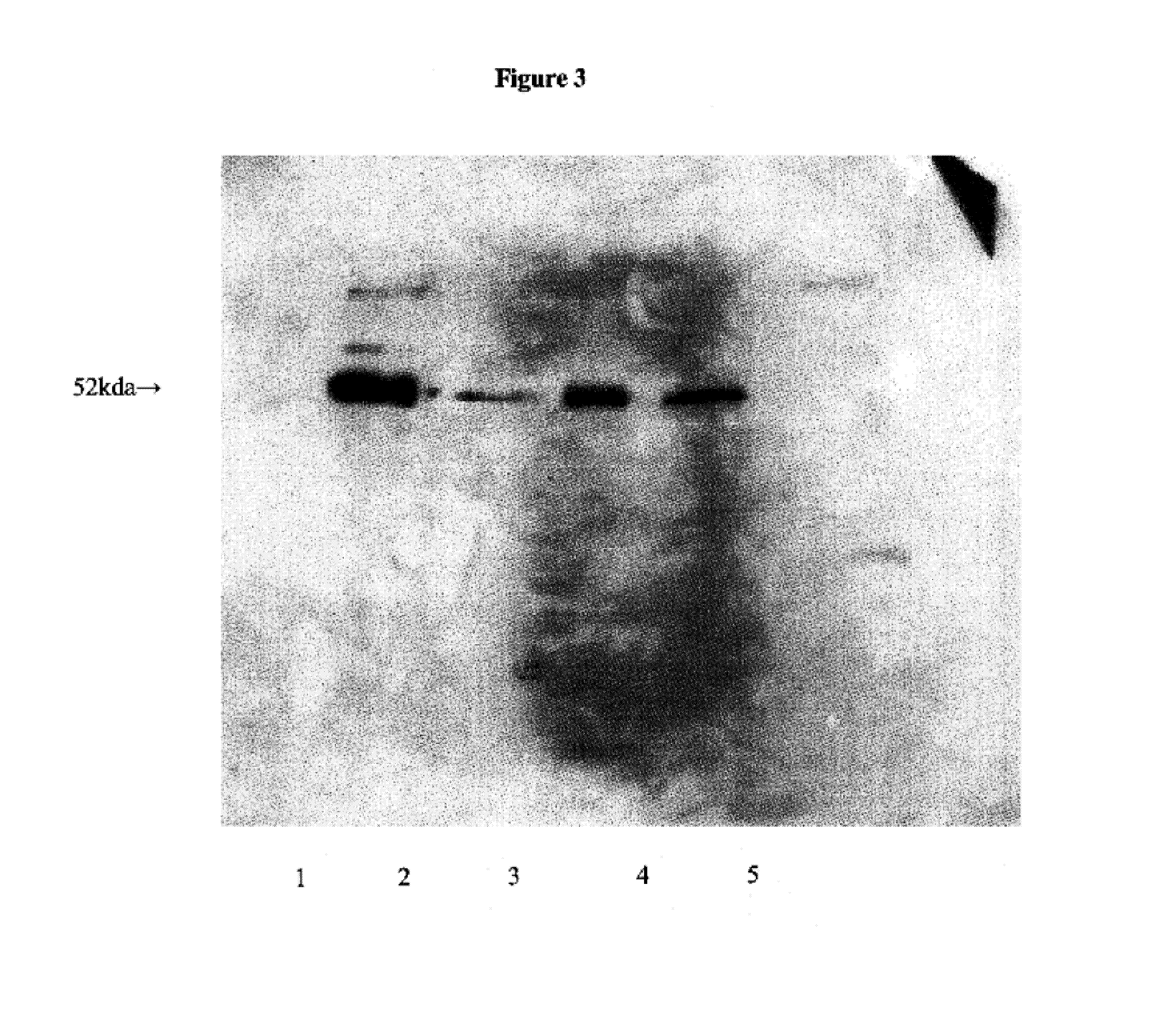
This invention discloses methods for identifying Francisella tularensis vaccine candidates. It enables identification of novel vaccine candidates and quality assurance for vaccine batches, assessment of protection in vaccinates and identification of the infecting agent in vaccinates. Mice were first vaccinated with Brucella abortus O-polysaccharide (OPS) vaccine. These animals were then given 10 LD50s of F. tularensis live vaccine strain (LVS). Sixty percent (60%) of the vaccinated mice survived the multiple lethal doses. Sera were collected from these surviving mice and the antibodies were used to probe supernatant and cell lysates of live F. tularensis LVS cultures. Several F. tularensis components were identified only by the noted “survivor” antisera. Of these identified proteins, enzyme digestions and chemical oxidation suggest post-translational modifications of some proteins e.g. a 52 kDa glycoprotein, a 45 kDa lipoprotein and a 19 kDa nucleoprotein. The 52 kDa component caused nitrous oxide induction in tissue cultures at low concentrations, cell death at high concentrations. Vaccination with this gave partial protection while addition of other components acted synergistically to give enhanced protection from 250 LD50s of F. tularensis LVS.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Use of cross-protection to identify novel vaccine candidates for infectious agents
This invention discloses methods for identifying Francisella tularensis vaccine candidates. It enables identification of novel vaccine candidates and quality assurance for vaccine batches, assessment of protection in vaccinates and identification of the infecting agent in vaccinates. Mice were first vaccinated with Brucella abortus O-polysaccharide (OPS) vaccine. These animals were then given 10 LD50s of F. tularensis live vaccine strain (LVS). Sixty percent (60%) of the vaccinated mice survived the multiple lethal doses. Sera were collected from these surviving mice and the antibodies were used to probe supernatant and cell lysates of live F. tularensis LVS cultures. Several F. tularensis components were identified only by the noted “survivor” antisera. Of these identified proteins, enzyme digestions and chemical oxidation suggest post-translational modifications of some proteins e.g. a 52 kDa glycoprotein, a 45 kDa lipoprotein and a 19 kDa nucleoprotein. The 52 kDa component caused nitrous oxide induction in tissue cultures at low concentrations, cell death at high concentrations. Vaccination with this gave partial protection while addition of other components acted synergistically to give enhanced protection from 250 LD50s of F. tularensis LVS.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Methods for the preparation of a pharmaceutical-vesicle formulation and associated products and uses
ActiveUS20210316009A1Enhancing cellular uptake of a pharmaceutical agentInexpensive to synthesizeAntibacterial agentsDispersion deliveryEncephalitisPharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to methods for the preparation of a pharmaceutical-vesicle formulation comprising steps of: preparing and processing vesicle components and a pharmaceutical agent to entrap the pharmaceutical agent in the vesicle and form a pharmaceutical-vesicle formulation, wherein the pharmaceutical-vesicle formulation is reconstituted in a known quantity of the pharmaceutical agent dissolved in a pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier to provide a biphasic pharmaceutical-vesicle formulation. The invention also relates to the associated pharmaceutical-vesicle formulations, pharmaceutical kits and uses as a medicament, in particular for the prevention or treatment of infection by bacteria such as Burkholderia pseudomallei and Francisella tularensis, and viruses such as Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus (VEEV).
Owner:UNIV OF STRATHCLYDE +1
CRISPR-Cas12a detection primer set and its application for tularensis
ActiveCN111394490BShort detection timeHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGeneticsNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a CRISPR-Cas12a detection primer group for francisella tularensis and an application thereof. The invention provides the primer group for detecting francisella tularensis and is composed of an RPA primer pair and crRNA; the RPA primer pair is designed according to the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in the francisella tularensis genome; the crRNA comprises an anchoring sequence and a guide sequence, wherein the anchoring sequence can be combined with a cas protein, and the guide sequence is matched with an amplification product sequence of an RPA primer pair. The detection primer group has the characteristics of short detection time, high amplification efficiency, high sensitivity, strong specificity and the like, and the detection sensitivity on francisella tularensis positive plasmids can reach 900 copy / ml, and the detection sensitivity on the francisella tularensis genome can reach 1260 fg / mL. The francisella tularensis onsite diagnosis method has awide application prospect.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Method for detecting Francisella tularensis using multiple PCR technology
InactiveCN101372713BSimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisComplete sequence
The invention relates to a method of detecting Francisella tularensis by a multiple PCR technique, belonging to the technical field of detecting biological agent. The invention comprises steps of: using the related genes lpxF, lpxE and flmK of the endotoxin of the Francisella tularensis as the specificity targets, carrying out comparison by complete sequence Blastp of NCBI microbial genome to determine the specificities of the three genes, designing the related primer and conducting detection by the multiple PCR technique; after three strips, which are 447bp,717bp and 1004bp in turn, appear in the electrophoresis detection, judging the strips to be masculine according to the appearance of three specificity strips, otherwise, judging the strips to be feminine. The invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, easy promotion and application, short detecting cycle, high sensitivity, good specificity and higher detecting rate, wherein, with respect to 5 to 7 days neededto obtain the result by the traditional detecting method, the detecting cycle of the method, which is 3 hours, is much shorter than that of the traditional method, thus greatly improving the detecting efficiency; moreover, the detecting limit, which is 0.01ng / [mu]L and 5X10<5>cfu / mL, reaches or exceeds that of the traditional detecting method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
PCR primer pair, kit and use thereof for pathogenic microorganisms with comonbid diseases in humans and mice
InactiveCN110218803BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseAnaplasma phagocytophilum DNA
The invention discloses a PCR primer pair for rodent-borne disease pathogenic microorganisms. The primer pair is used for amplifying specific genes of leptospira interrogans, Rickettsi Mooseri, Orientia tsutsugamushi, anaplasma phagocytophilum, francisella tularensis, Coxiella burnetii and Bartonella. By adopting the PCR primer pair, on the basis of the TSP principle, the method for high-sensitiveand specific independent or combined detection of the seven kinds of pathogene.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com