Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134 results about "Conventional memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
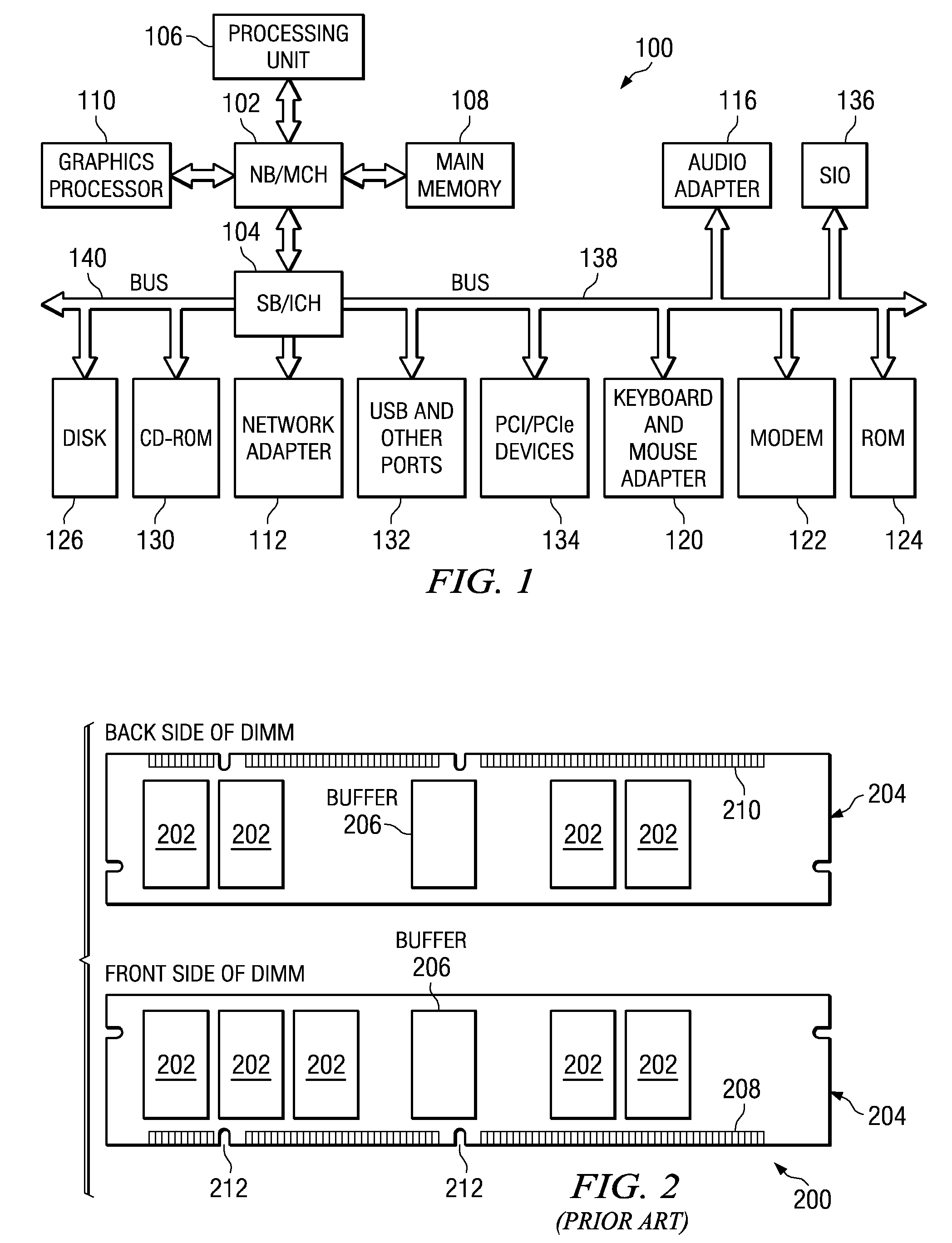
In DOS memory management, conventional memory, also called base memory, is the first 640 kilobytes (640 × 1024 bytes) of the memory on IBM PC or compatible systems. It is the read-write memory directly addressable by the processor for use by the operating system and application programs. As memory prices rapidly declined, this design decision became a limitation in the use of large memory capacities until the introduction of operating systems and processors that made it irrelevant.
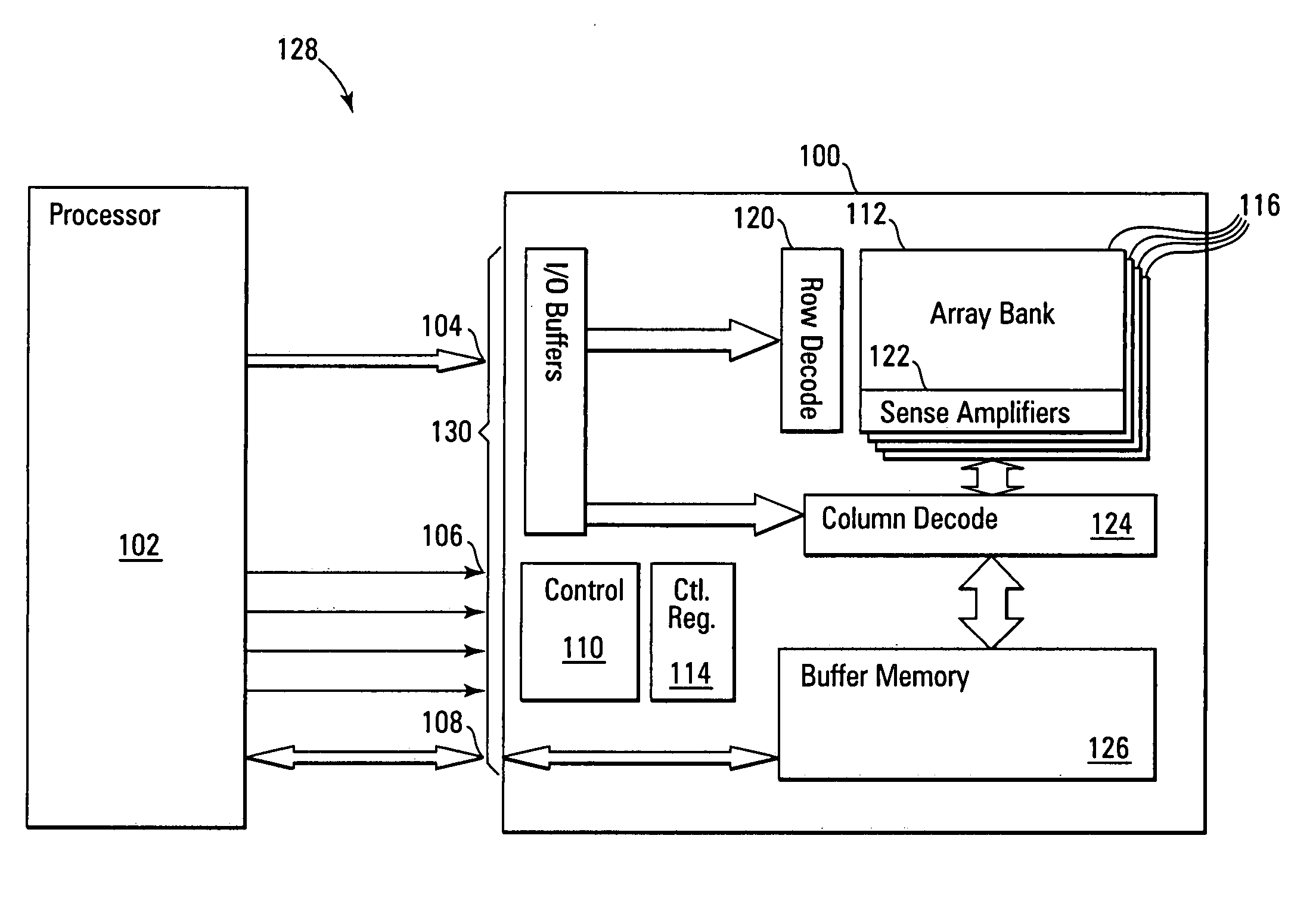
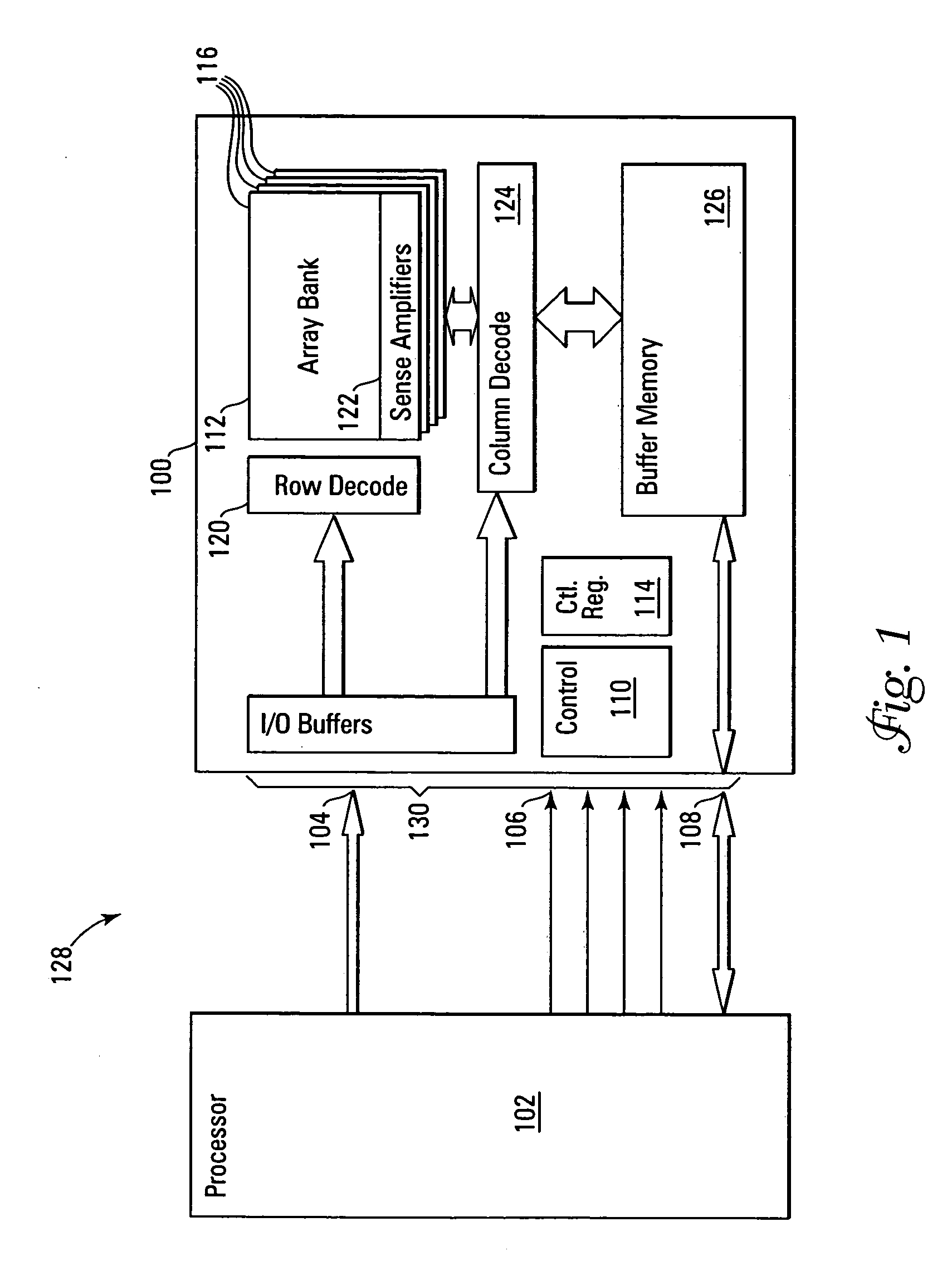
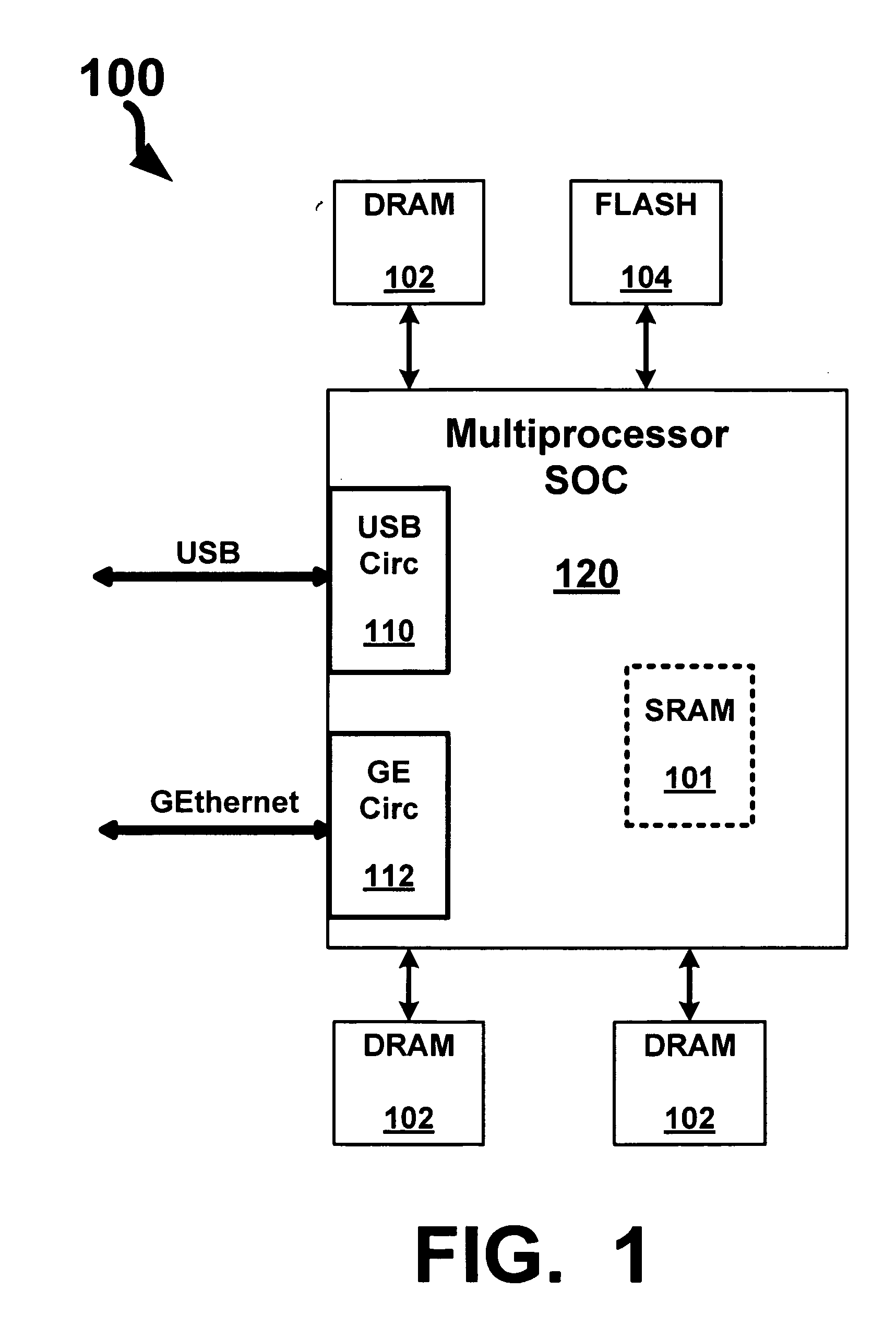
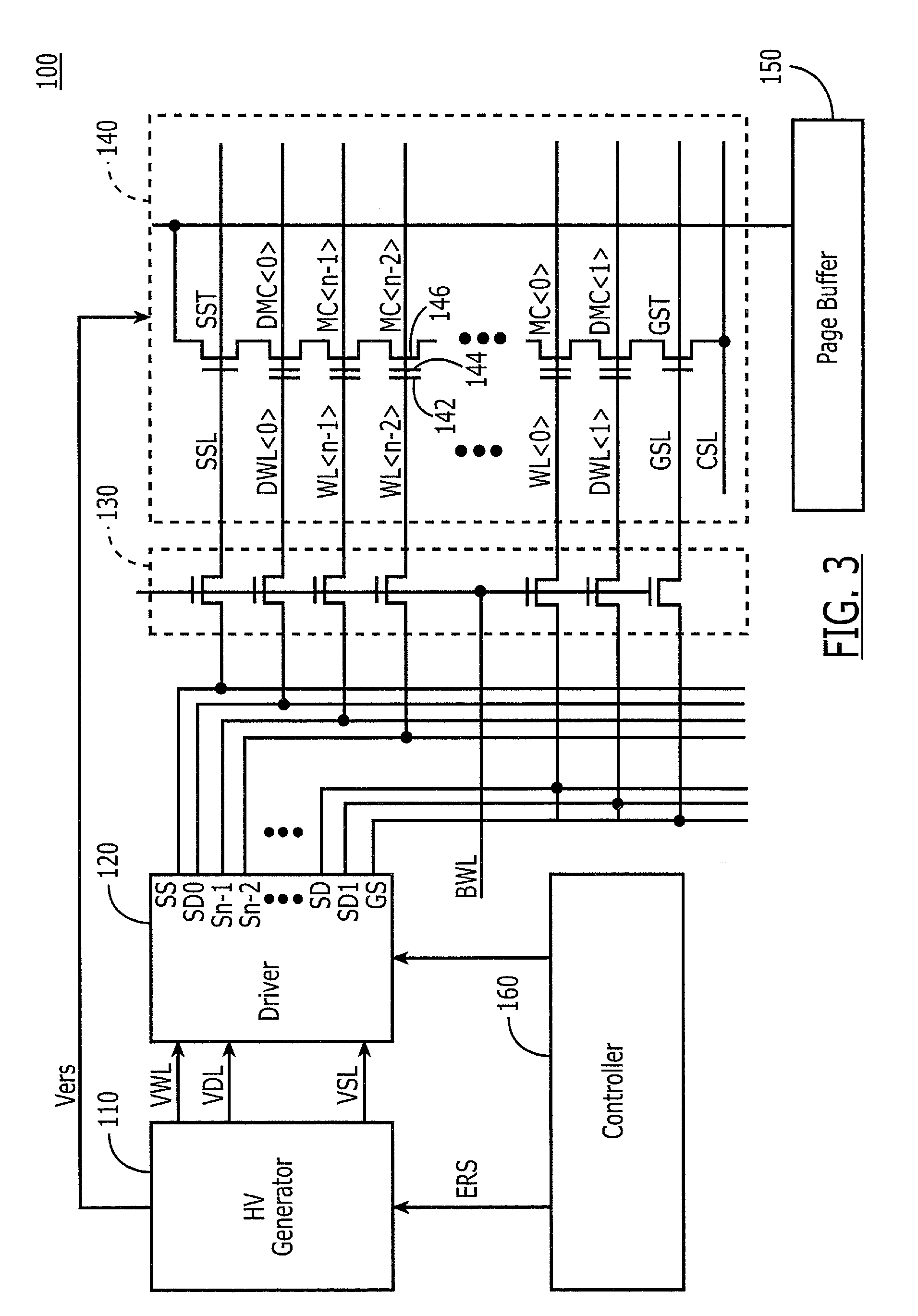
Non-volatile memory with synchronous DRAM interface
InactiveUS20050204091A1Easy accessSimplifies design effortMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageConventional memoryHigh density
A high density non-volatile memory system, card, and device is described that incorporates a synchronous interface. This is accomplished through use of an external or embedded controller and / or memory buffer to manage the high density non-volatile memory device(s) to present it as a conventional memory device having a synchronous interface that is accessible by row and column address. This allows the high density non-volatile memory to support in-place code execution and allows it to be booted from. Additionally, this incorporation eliminates the overhead of drivers and / or operating system support required to utilize and present conventional high density non-volatile memory devices and moves it internal to the memory device. This simplifies the use and design effort in the overhead and specialized interfacing of high density non-volatile memories and in particular, NAND architecture Flash memories, while reducing the production cost through use of less expensive high density non-volatile memory.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
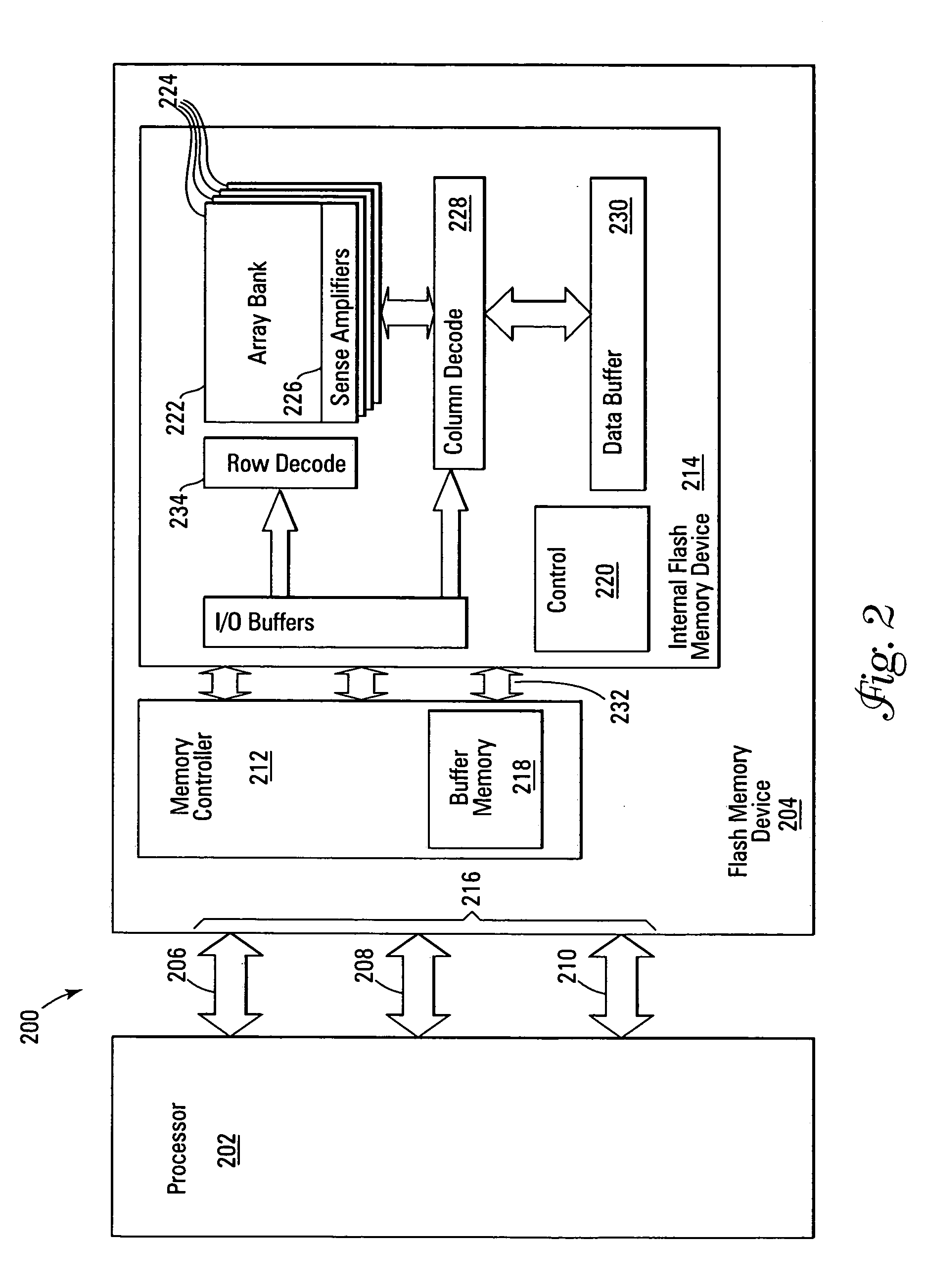
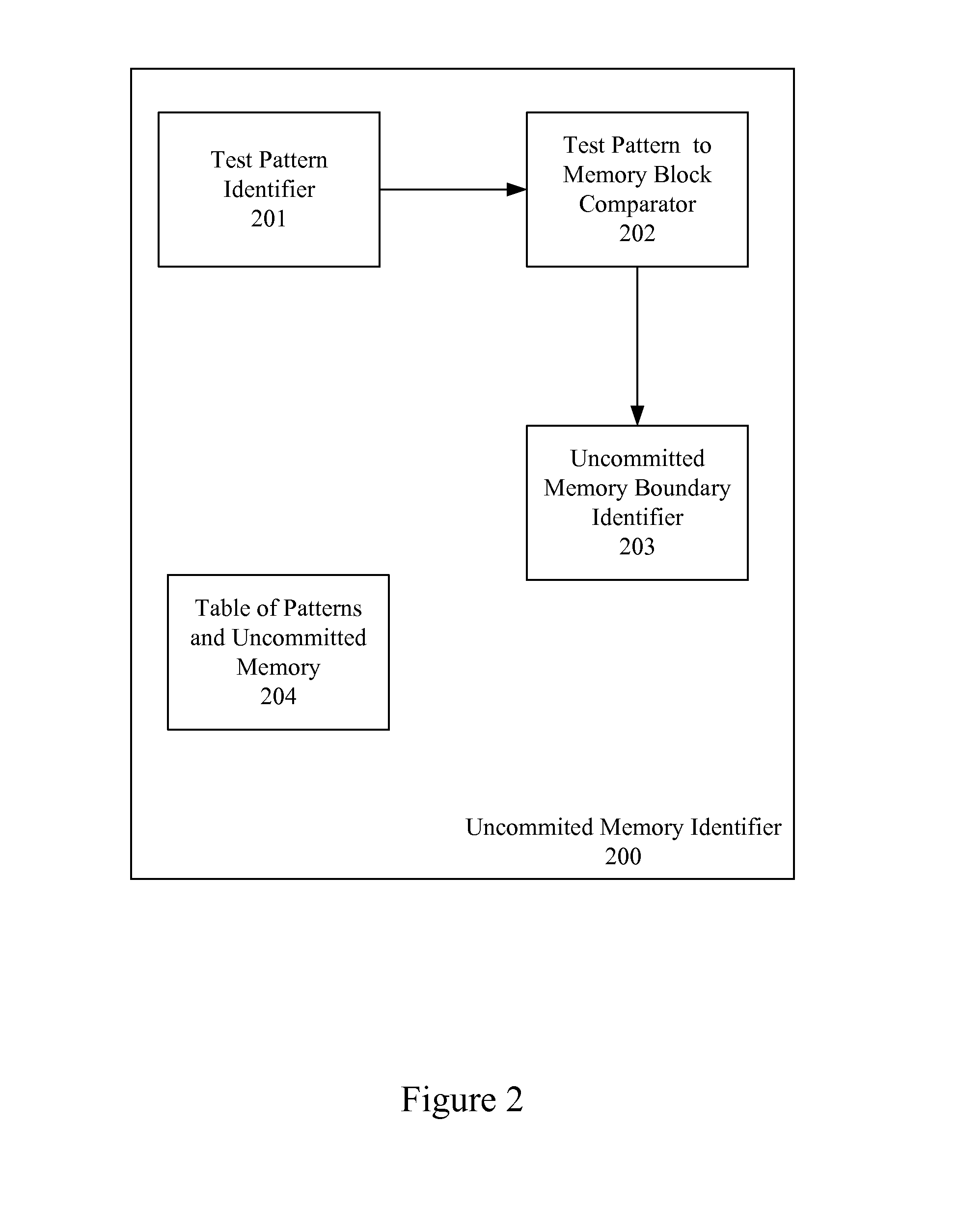
Identification of Uncommitted Memory Blocks During an Initialization Procedure
InactiveUS20080065852A1Easy to useDigital computer detailsProgram controlConventional memoryOption ROM
An apparatus and method are described for identifying uncommitted memory in a system RAM during an initialization process of a computer system, such as a boot procedure or power-on self test, during which memory management is uncontrolled. In various embodiments of the invention, repeating patterns that are indicative of uncommitted memory blocks are identified within a conventional memory area of the system RAM. At least some of the uncommitted memory blocks are allocated for use by an option ROM or other BIOS data and a table is created identifying these uncommitted memory blocks. After the BIOS code exits the system RAM, the table is used to restore the uncommitted memory blocks into their previous data states.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
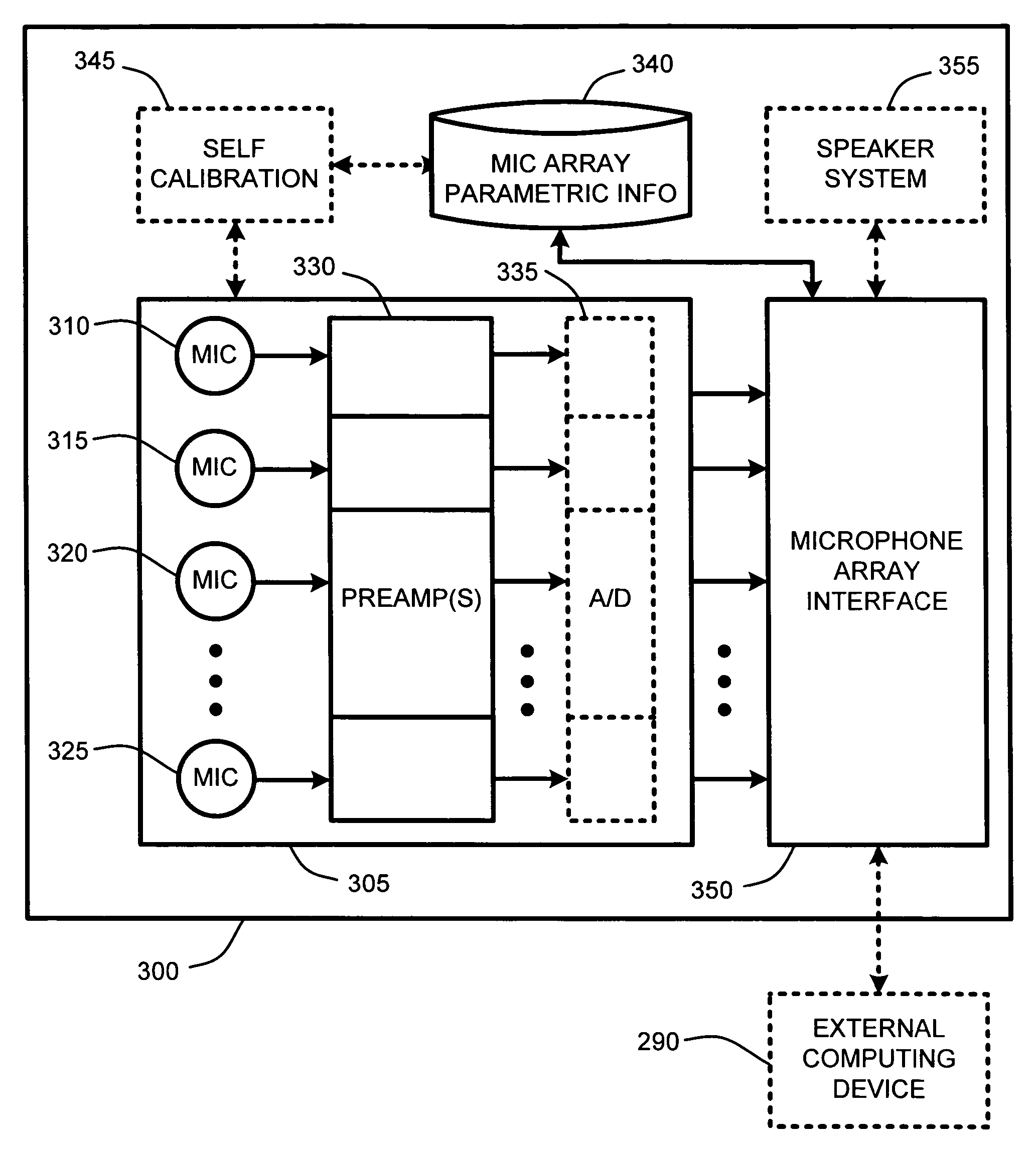
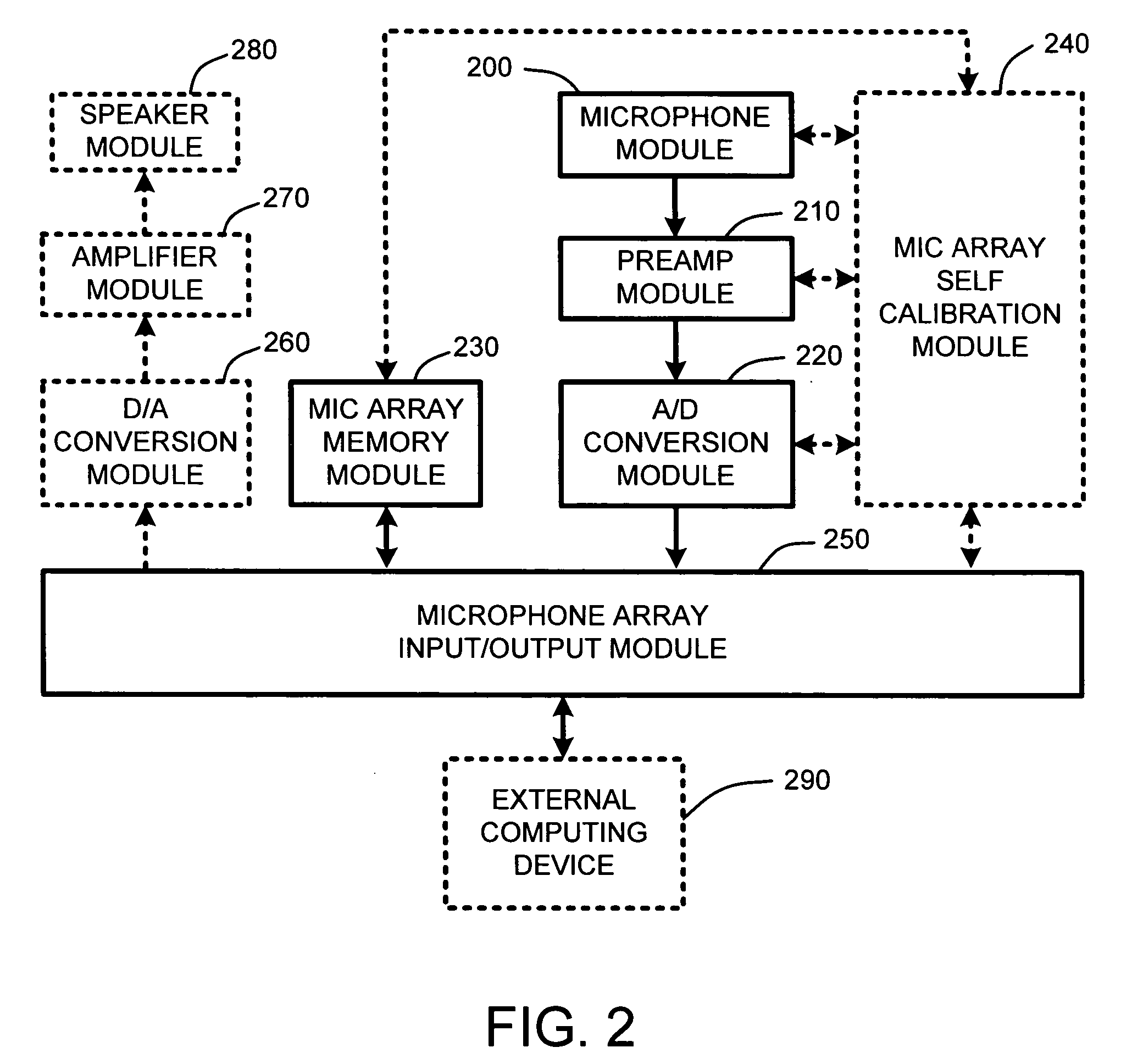
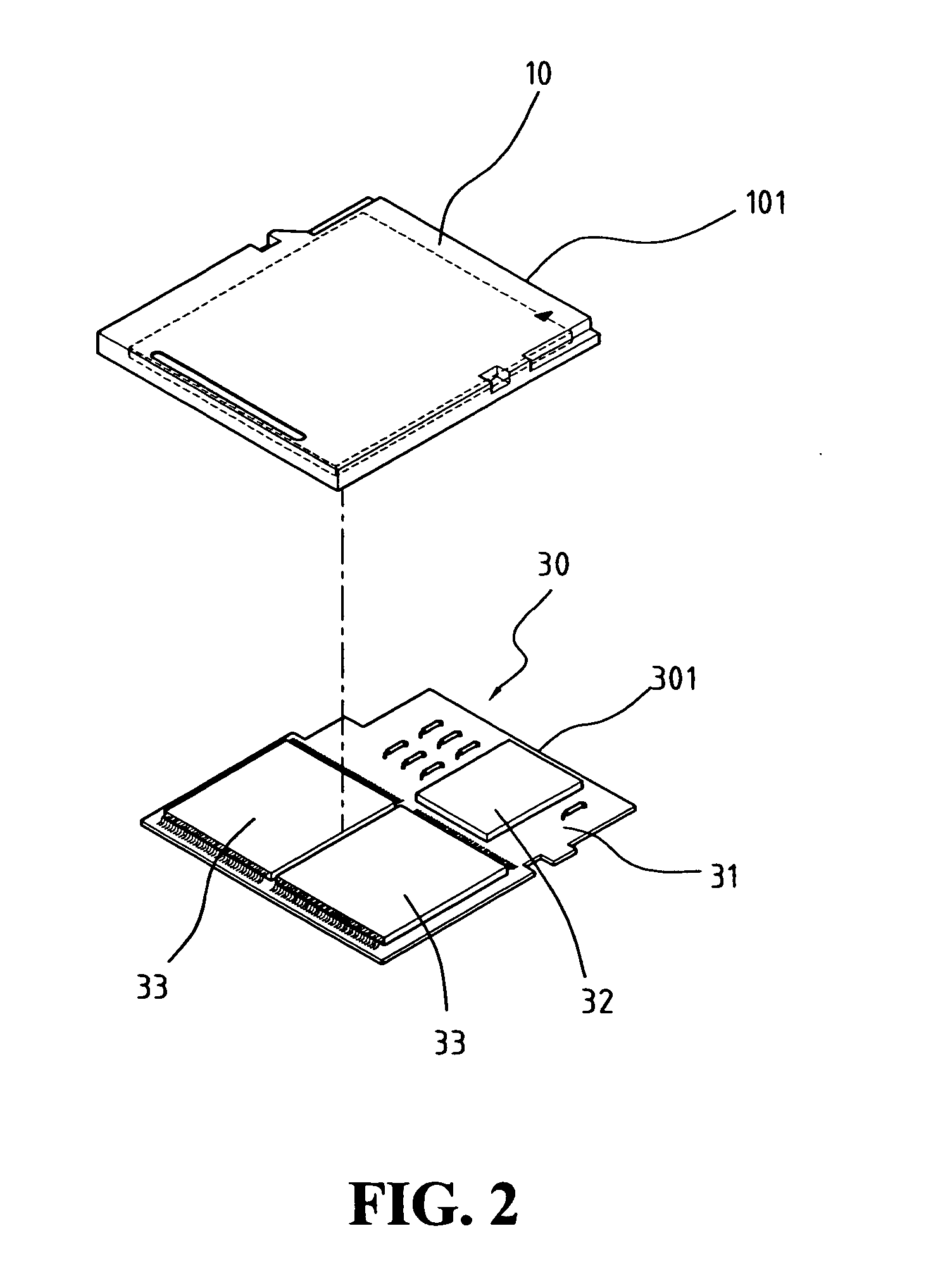
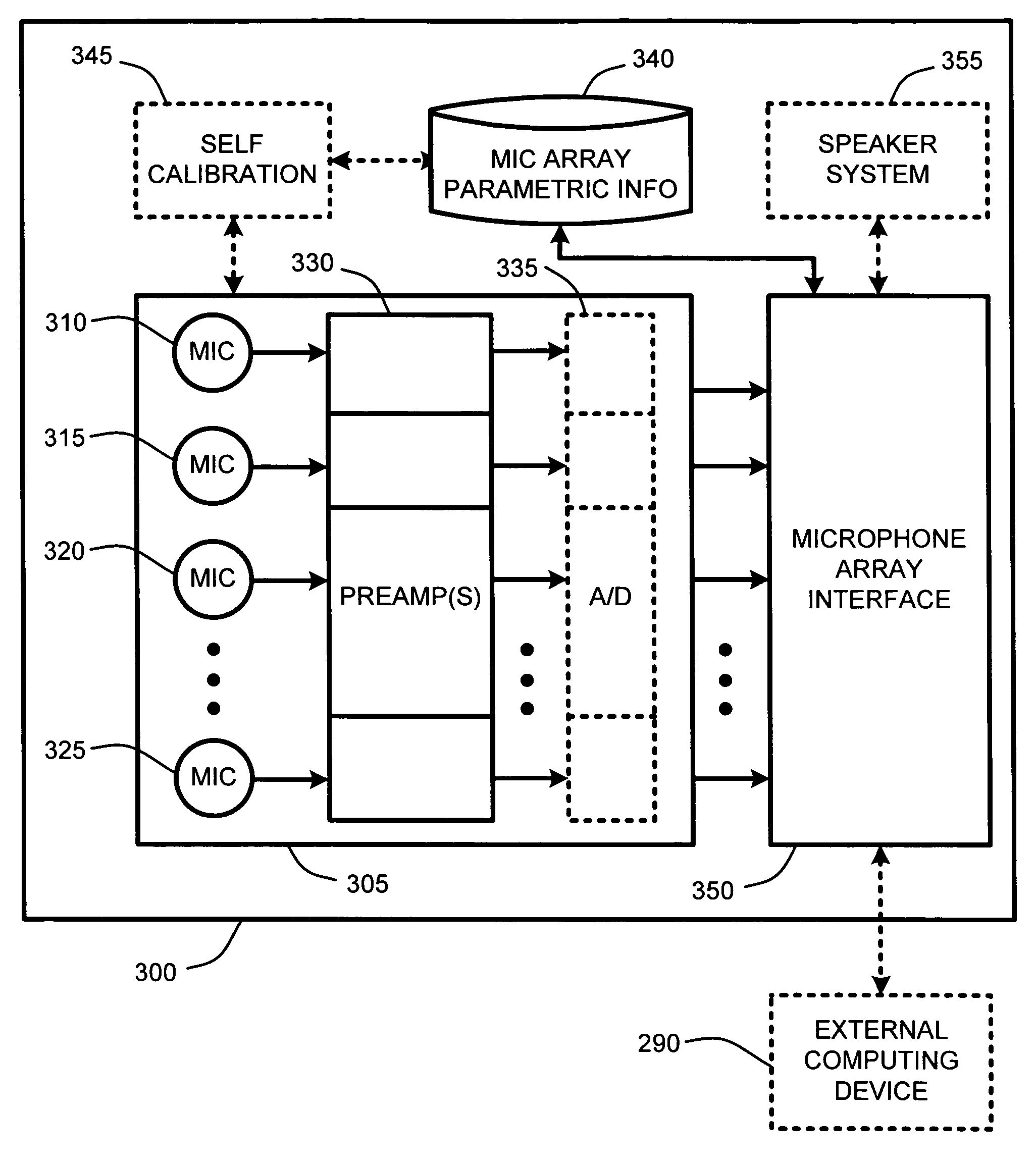
Self-descriptive microphone array
ActiveUS20050175190A1Reduce manufacturing costReducing microphone array costMicrophones signal combinationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsConventional memoryUSB
A self-descriptive microphone array includes a microphone array memory, such as, for example a ROM, EEPROM, or other conventional memory, which contains a microphone array device description. This device description includes parametric information which defines operational characteristics and configuration of the microphone array. In further embodiments, the microphone array uses any of a variety of conventional wired or wireless computer interfaces, including serial, IEEE 1394, USB, Bluetooth™, etc., to connect to a computing device. Once connected, the microphone array provides its device description to the computing device. Sound processing software residing within the computing device is then automatically configured for optimally interacting with one or more analog or digital audio signals provided by the microphone array. In another embodiment, the microphone array performs integrated self calibration for automatically updating the device description. The self calibration is performed either upon connection to the computing device, or upon regular or user-specified intervals.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
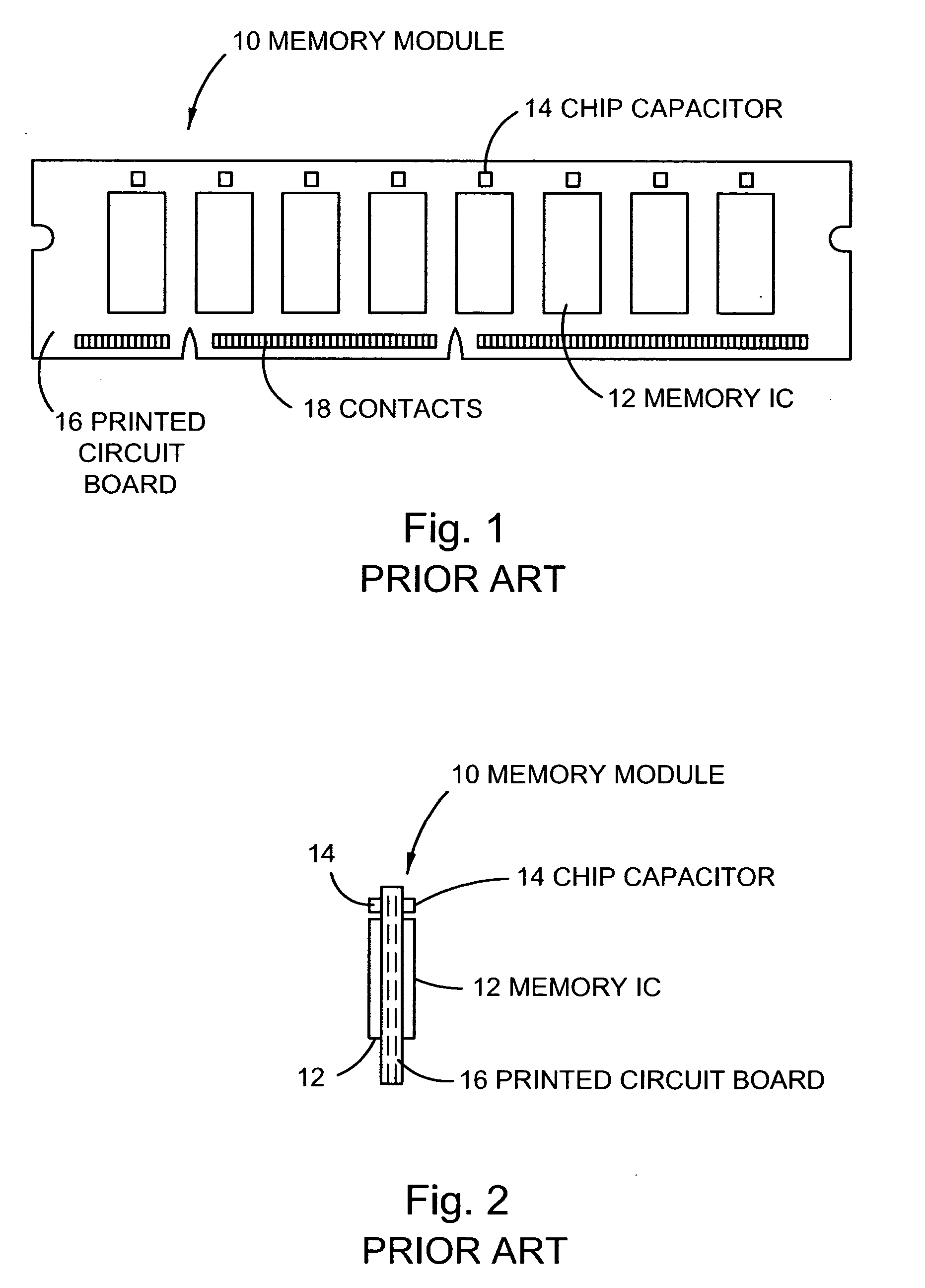
Molded memory module and method of making the module absent a substrate support
InactiveUS6843421B2Avoid restSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConventional memoryElectrical conductor
An improved memory module and method of manufacture are presented. The memory module takes on the same outer dimensions as conventional memory cards. The memory module includes an integrated circuit and a conductor encased within molded resin. The conductor can be taken from a tape or a lead frame, and can include bumps or wires extending from the conductor to corresponding bonding pads on the integrated circuit. The bonded integrated circuit can thereafter be placed within a cavity formed inside a mold housing, where resin may be injected to form the memory module. The conductor can also be shaped so as to extend on multiple planes from the connection point on or near the bonding pad to an edge connector residing near one edge only of the memory module. The conductor is thereby connected to the integrated circuit and provides slide-in, releasable coupling to a receptor.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
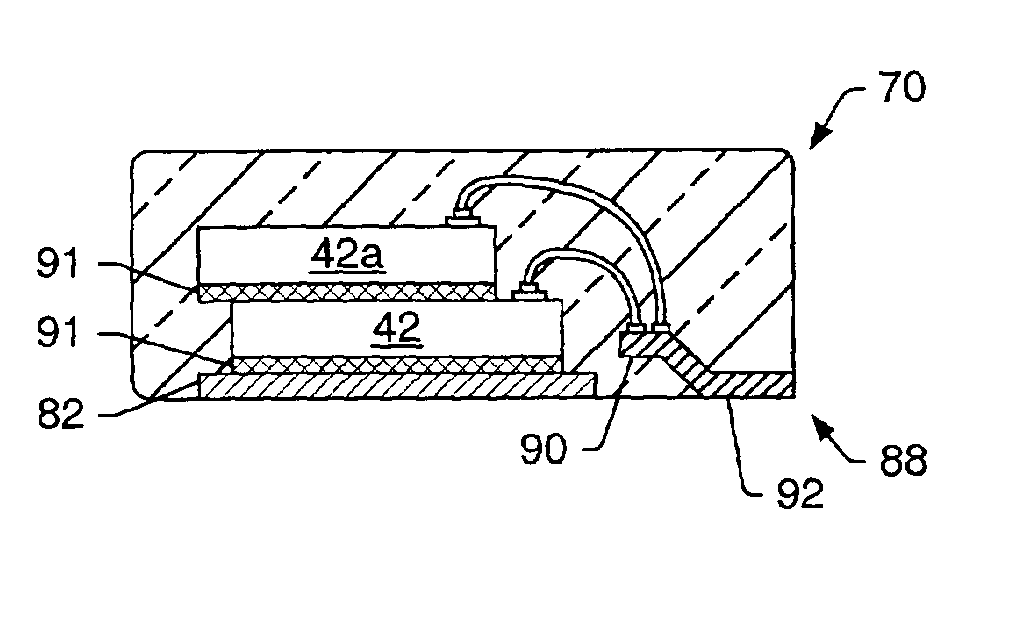
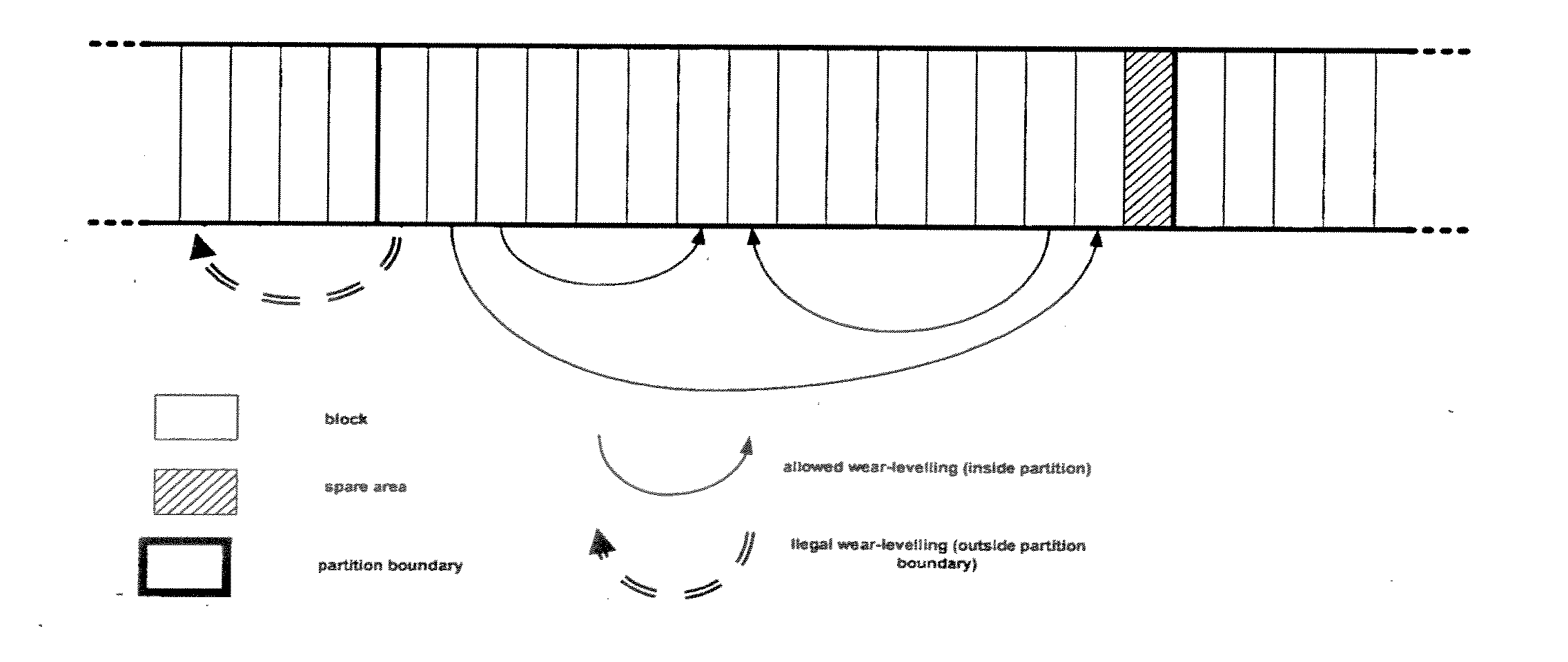
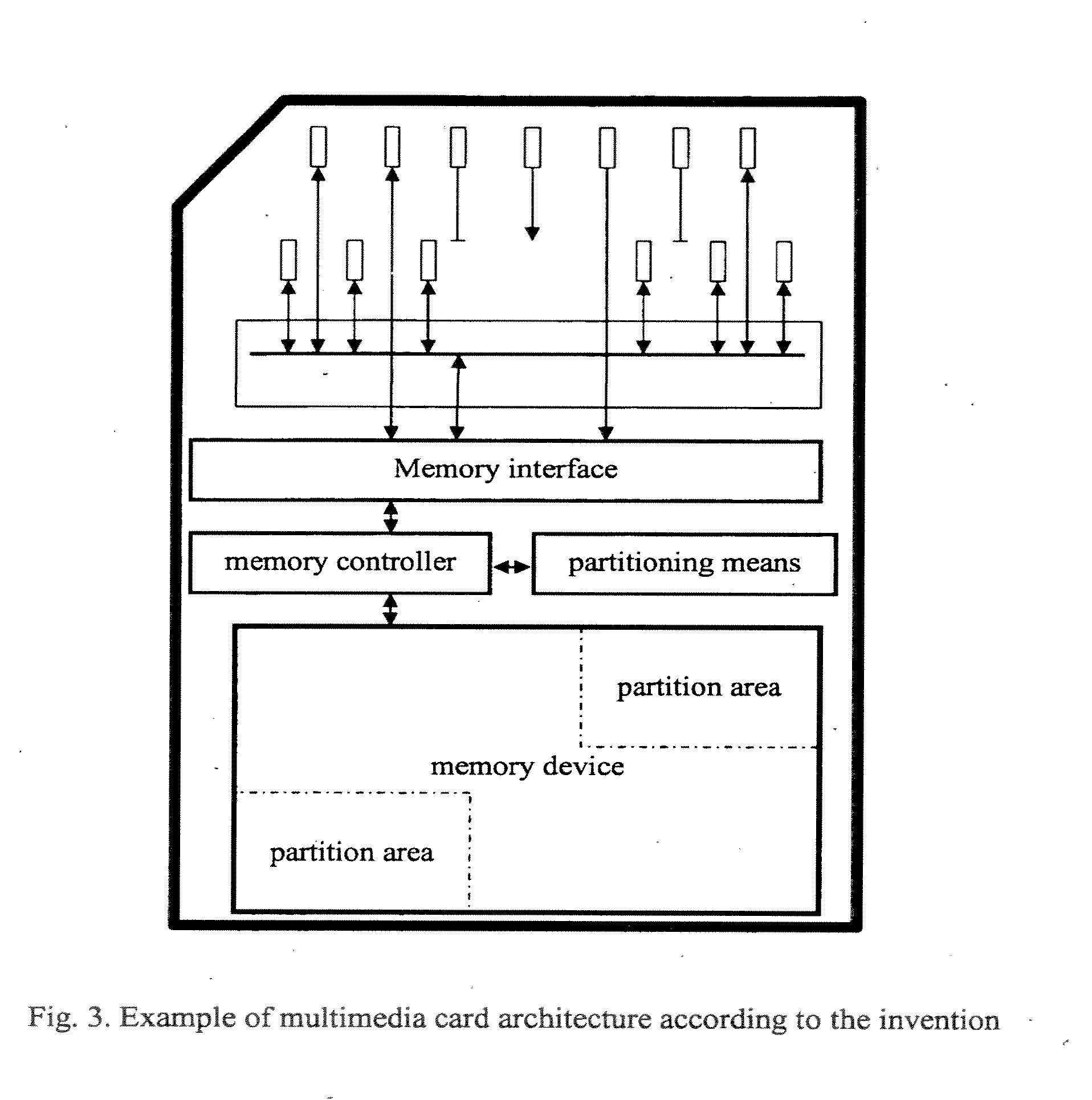
Method For Utilizing A Memory Interface To Control Partitioning Of A Memory Module
ActiveUS20130124793A1Easy accessMinimize data interferenceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationConventional memoryMemory interface
Apparatuses and methods for implementing partitioning in memory cards and modules where conventional memory cards or modules have only a single partition. A representative memory card / module in accordance with the invention includes a memory device(s), and a memory interface which includes a data bus, a command line and a clock line. The memory card / module further includes a memory controller coupled to the memory device(s) and to the memory interface. The memory card / module includes means for controlling the partitioning of the memory device(s), and the memory controller is configured to operate the memory device(s) in accordance with the partition information.
Owner:MEMORY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
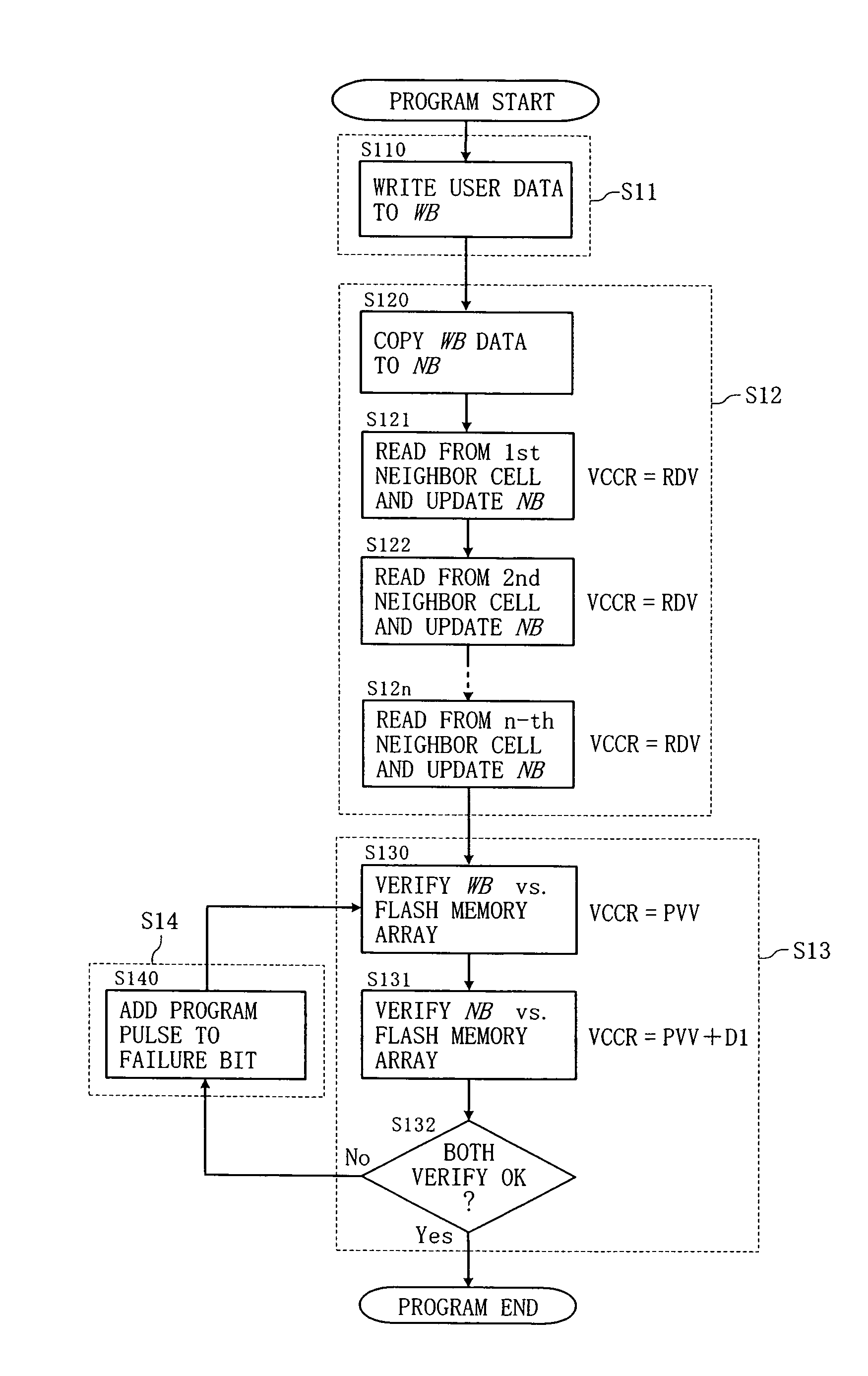
Flash memory and program verify method for flash memory
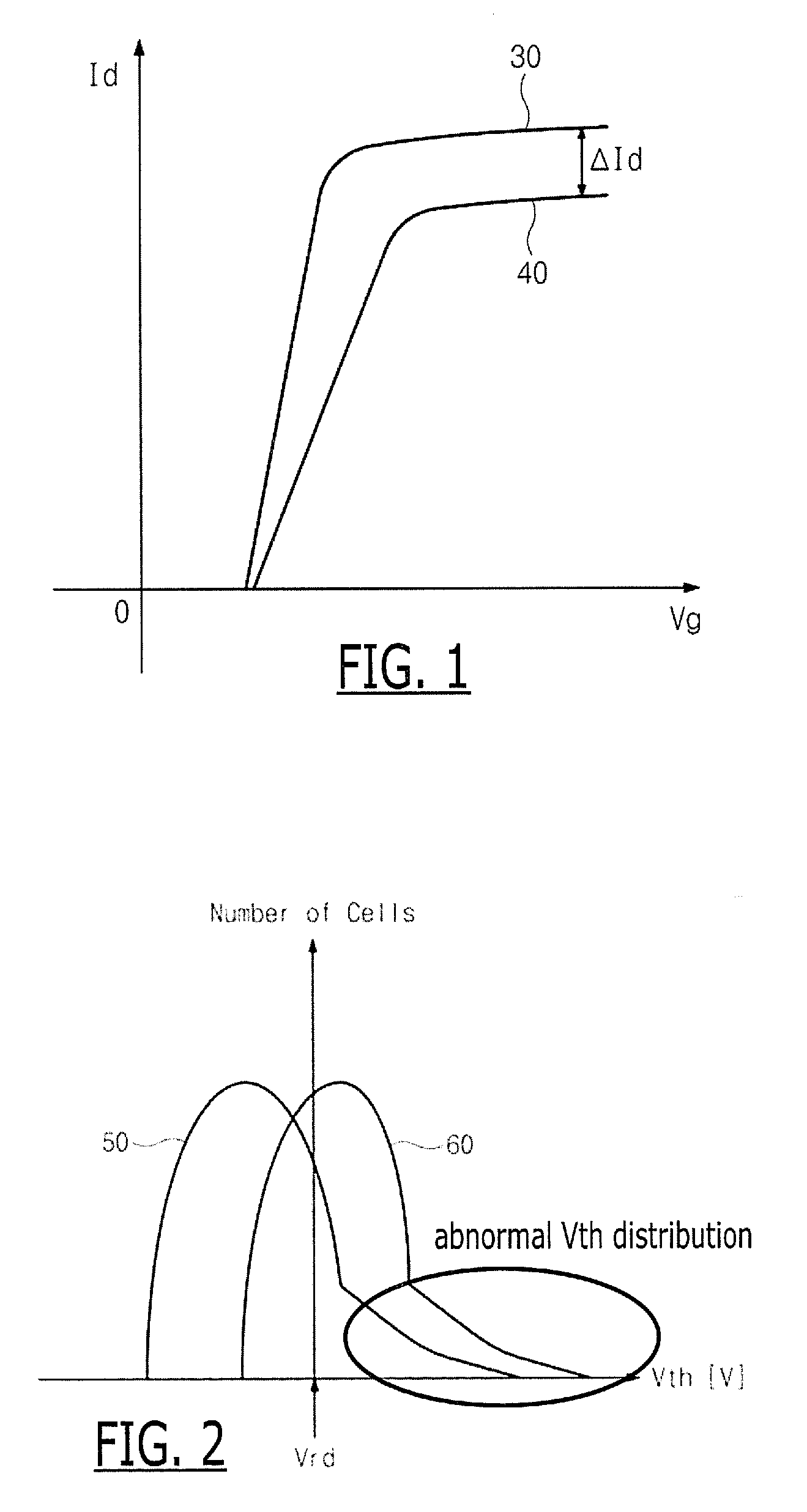
ActiveUS20050286299A1Improve reliabilityExclude influenceRead-only memoriesDigital storageConventional memoryBit line
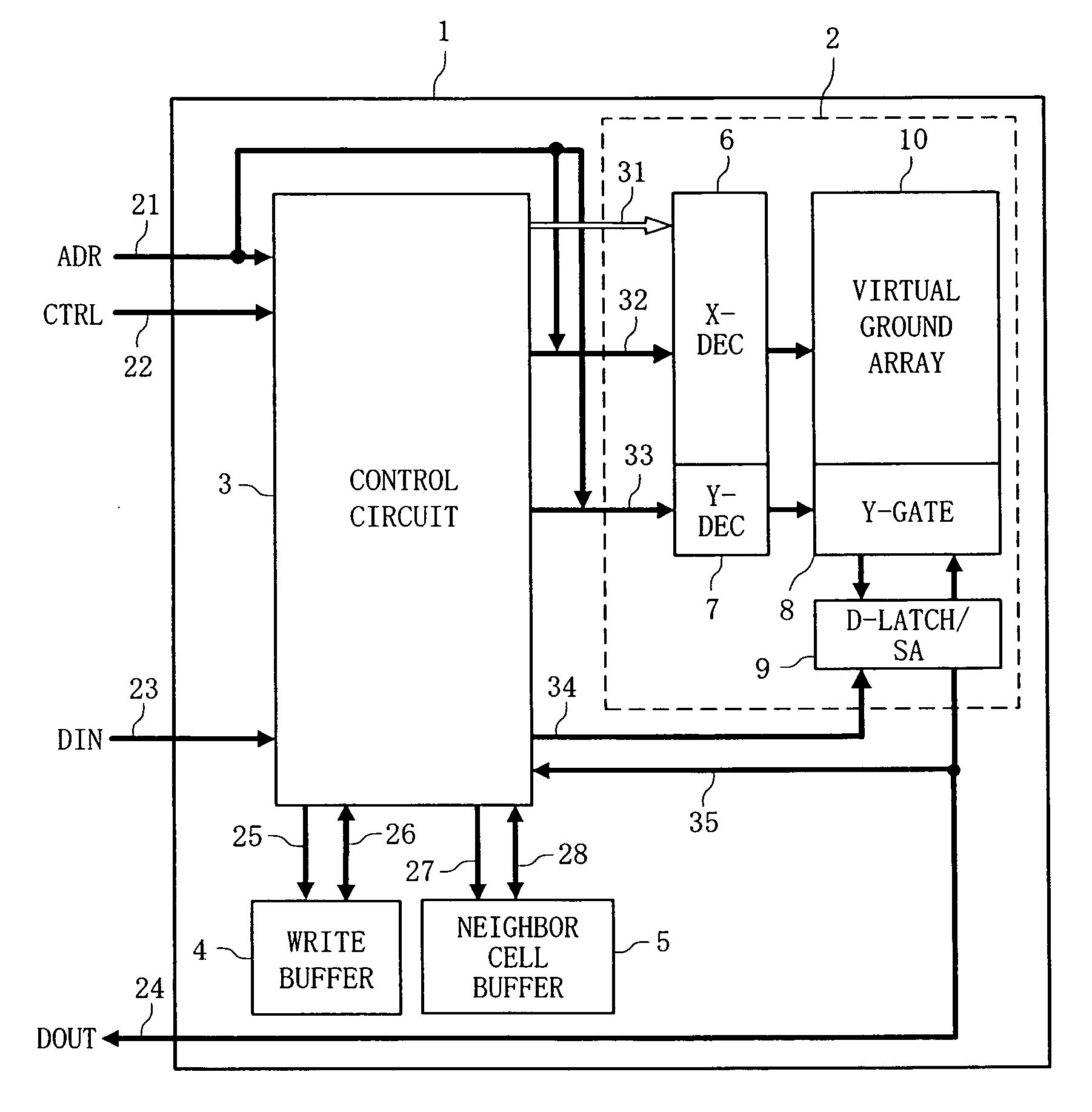
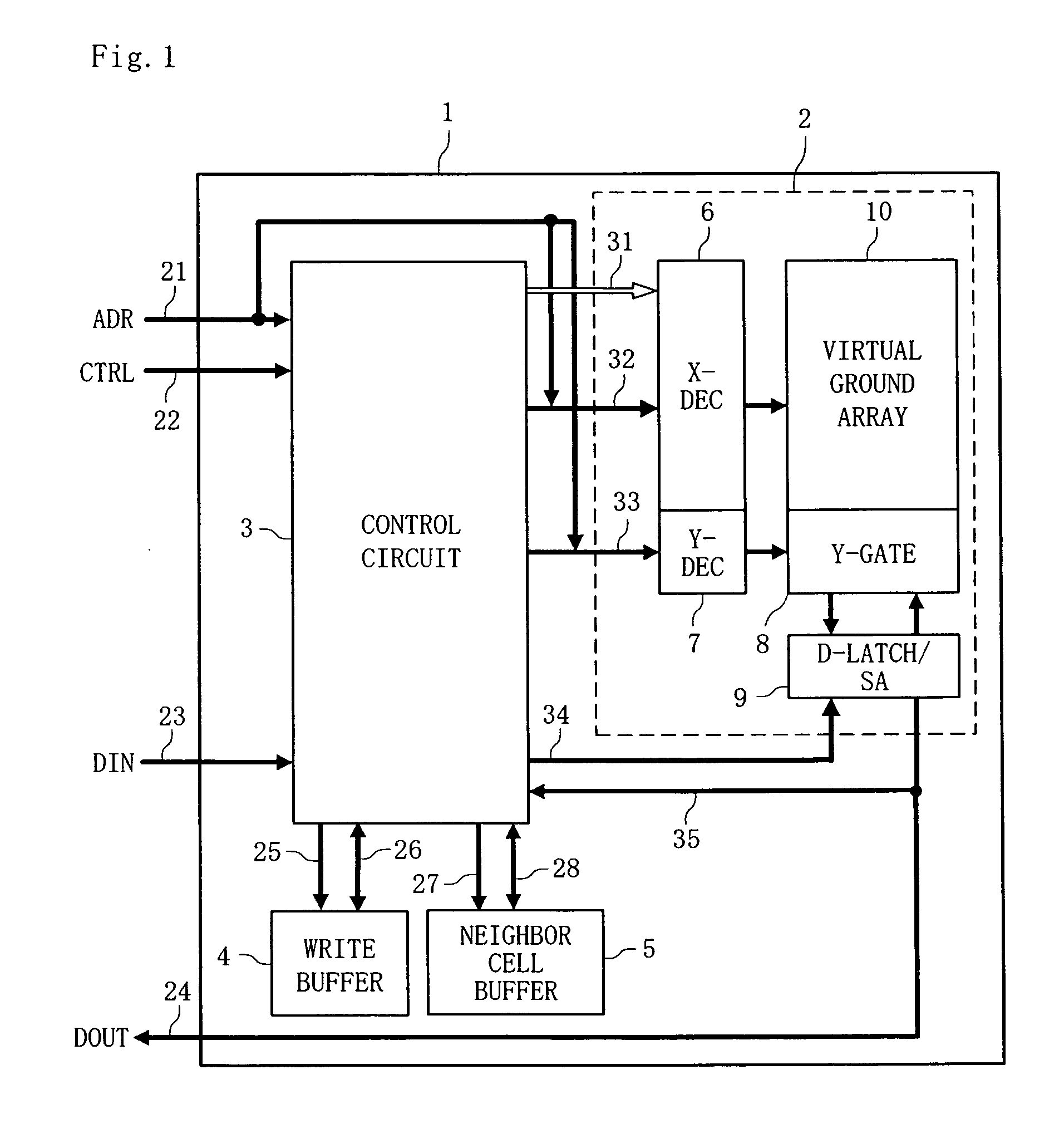
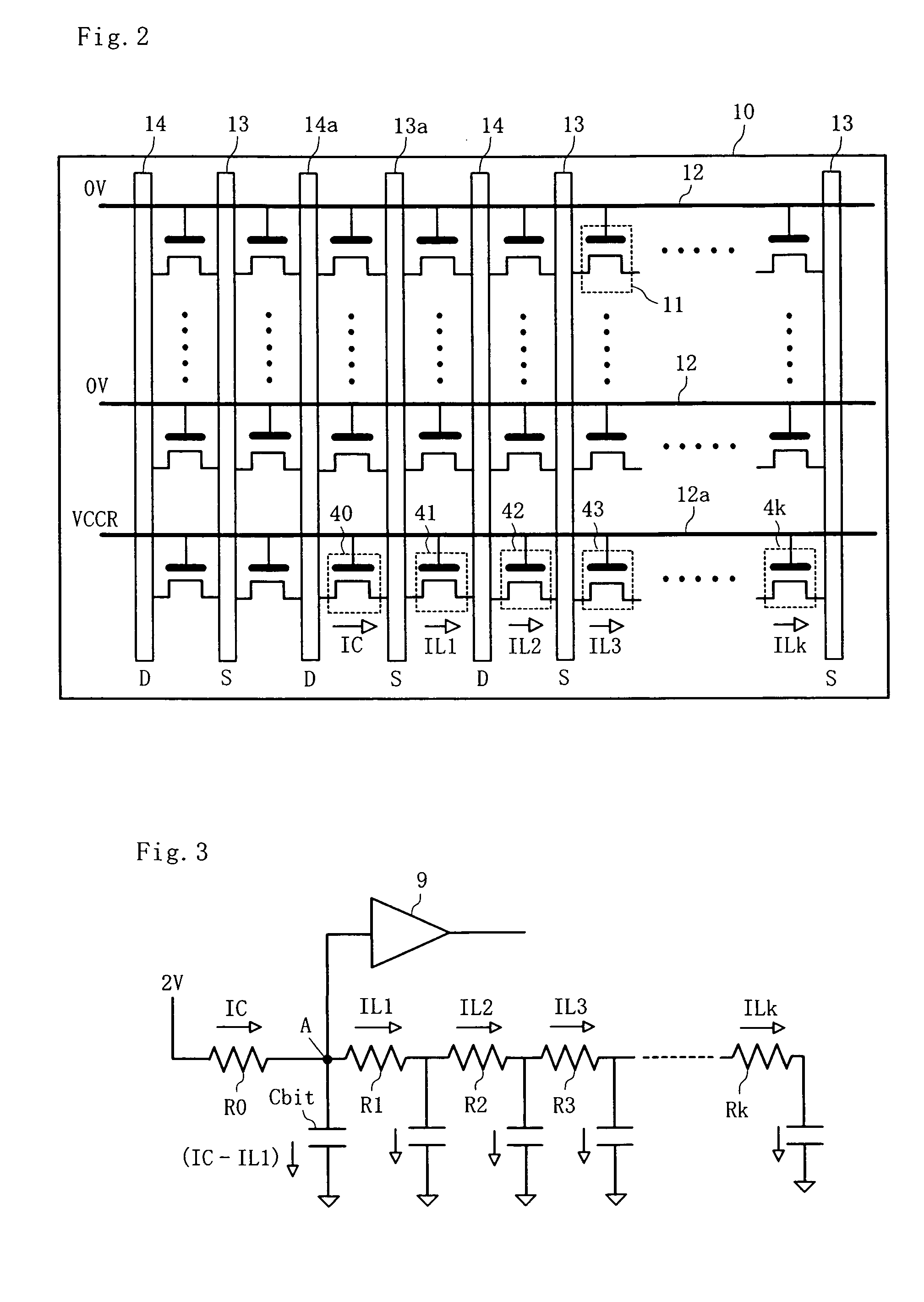
In conventional memory arrays in which a bit line is shared by memory cells, a cell current flows over into neighbor cell(s) in a program verify process, and therefore, the threshold of a memory cell to be programmed is erroneously determined to be lower. Therefore, in a program verify process, a control circuit 3 writes a fail value to a neighbor cell buffer 5 when all neighbor cell(s) having an offset of n or less from a memory cell to be programmed are in the erased state, and when otherwise, writes a pass value to the neighbor cell buffer 5. The control circuit 3 verifies input write data and also verifies data stored in the neighbor cell buffer(s). In the latter verify process, a verify voltage higher than an ordinary one is used to compensate for the leakage of cell current.
Owner:TOWER SEMICONDUCTOR +1
Buffered Memory Module Supporting Double the Memory Device Data Width in the Same Physical Space as a Conventional Memory Module
InactiveUS20090063785A1Increased memory bandwidthDouble storage capacityFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsConventional memoryPhysical space
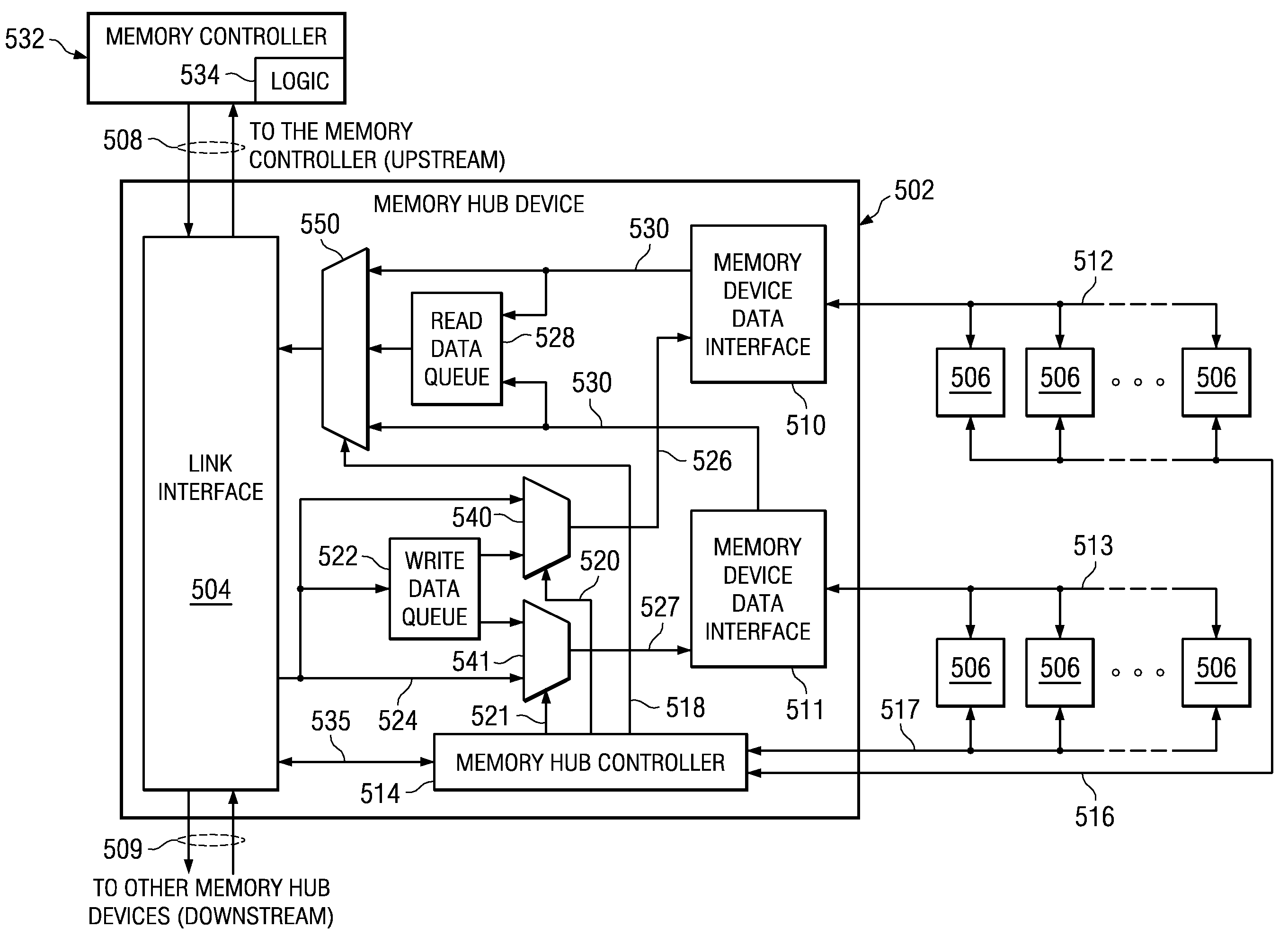
A memory system is provided that enhances the memory bandwidth available through a memory module. The memory system includes a memory hub device integrated into a memory module, a first memory device data interface integrated that communicates with a first set of memory devices and a second memory device data interface integrated that communicates with a second set of memory devices. In the memory system, the first set of memory devices are spaced in a first plane and coupled to a substrate of the memory module and the second set of memory devices are spaced in a second plane above the first plane and coupled to the substrate. In the memory system, data buses of the first set of memory devices are coupled to the substrate separately from data buses of the second set of memory devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
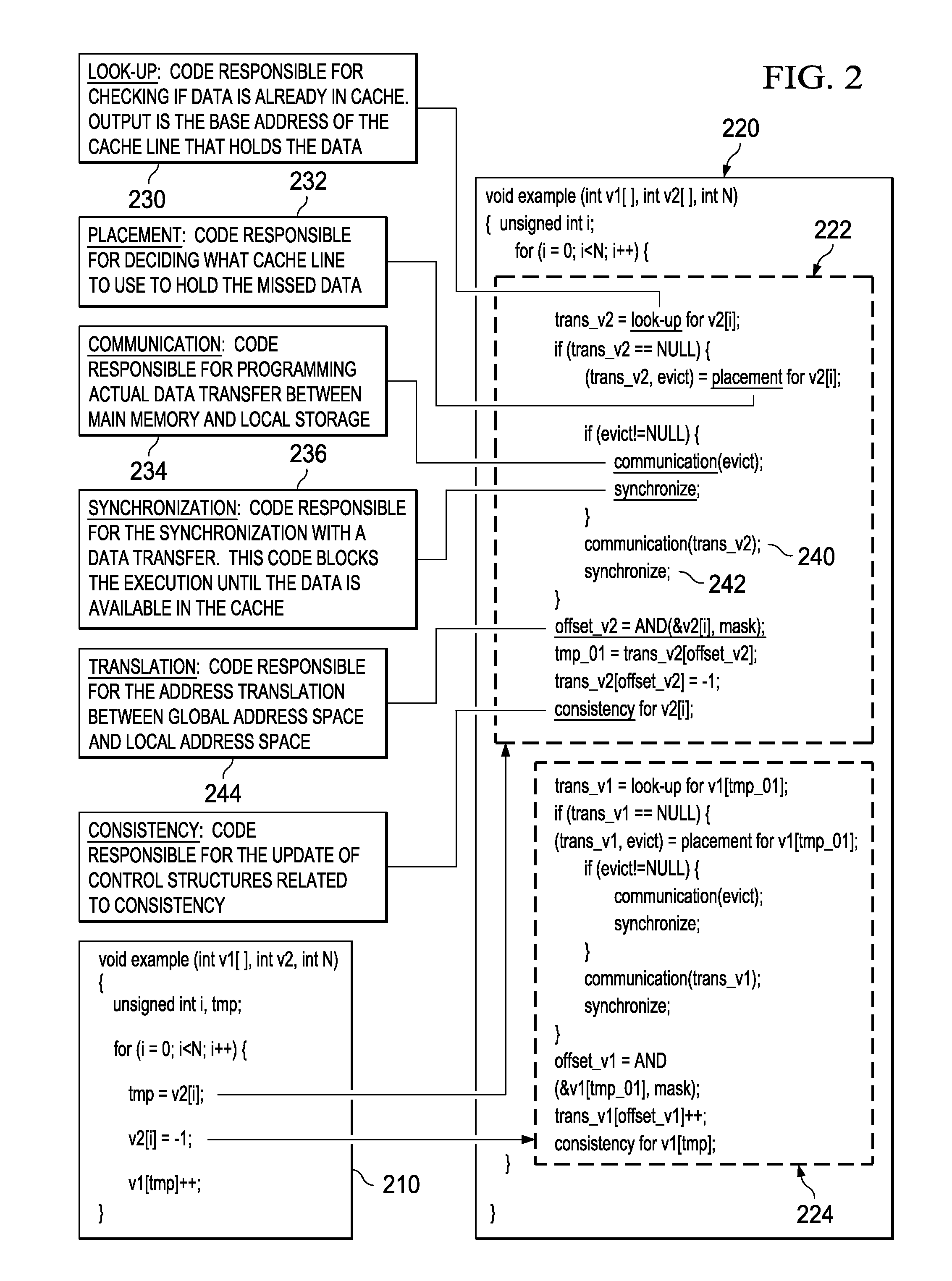
Optimized Code Generation Targeting a High Locality Software Cache
InactiveUS20100088673A1Error preventionError detection/correctionConventional memoryParallel computing
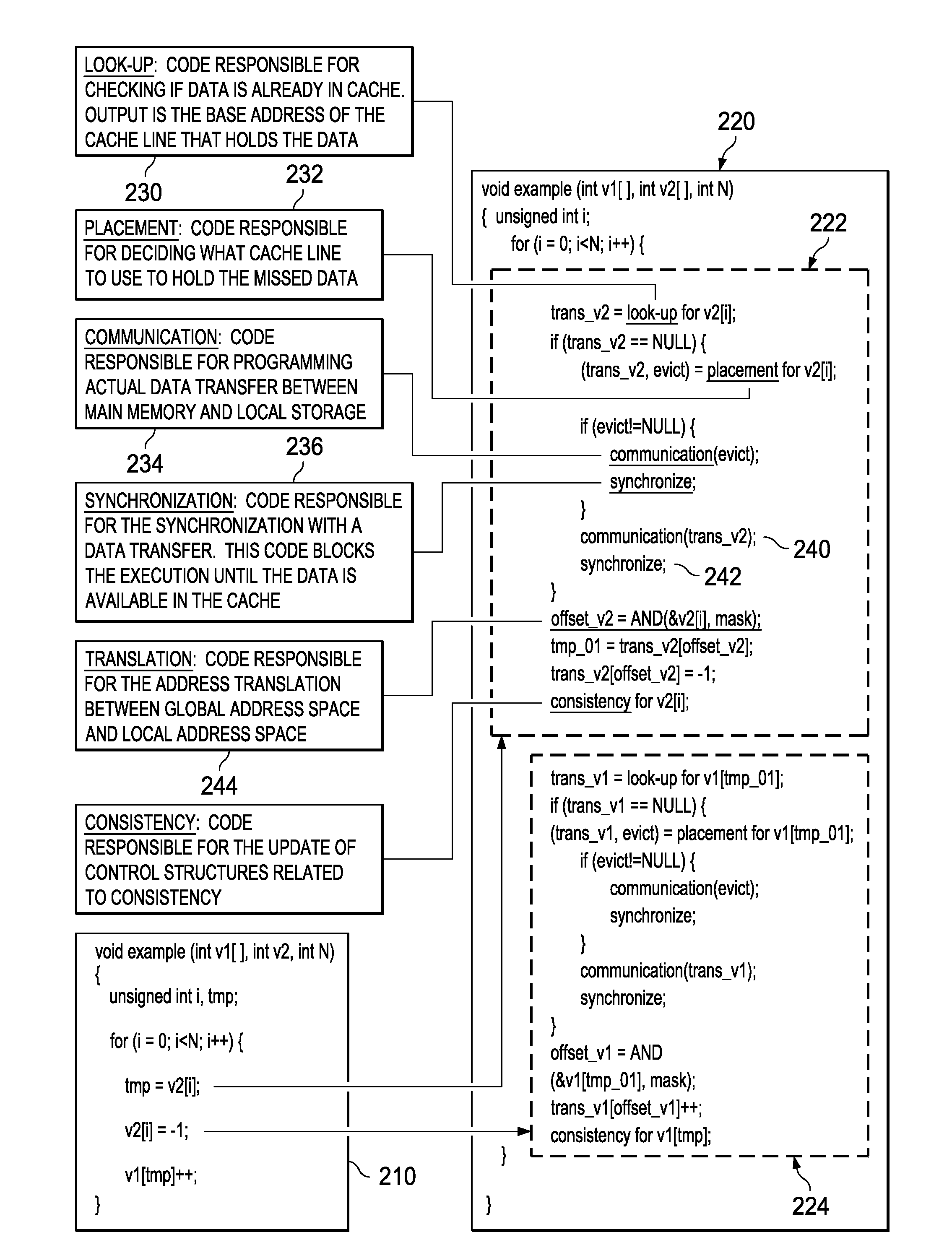
Mechanisms for optimized code generation targeting a high locality software cache are provided. Original computer code is parsed to identify memory references in the original computer code. Memory references are classified as either regular memory references or irregular memory references. Regular memory references are controlled by a high locality cache mechanism. Original computer code is transformed, by a compiler, to generate transformed computer code in which the regular memory references are grouped into one or more memory reference streams, each memory reference stream having a leading memory reference, a trailing memory reference, and one or more middle memory references. Transforming of the original computer code comprises inserting, into the original computer code, instructions to execute initialization, lookup, and cleanup operations associated with the leading memory reference and trailing memory reference in a different manner from initialization, lookup, and cleanup operations for the one or more middle memory references.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method for utilizing a memory interface to control partitioning of a memory module
InactiveUS20070174549A1Minimal amountMinimize data interferenceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesConventional memoryMemory interface
Apparatuses and methods for implementing partitioning in memory cards and modules where conventional memory cards or modules have only a single partition. A representative memory card / module in accordance with the invention includes a memory device(s), and a memory interface which includes a data bus, a command line and a clock line. The memory card / module further includes a memory controller coupled to the memory device(s) and to the memory interface. The memory card / module includes means for controlling the partitioning of the memory device(s), and the memory controller is configured to operate the memory device(s) in accordance with the partition information.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
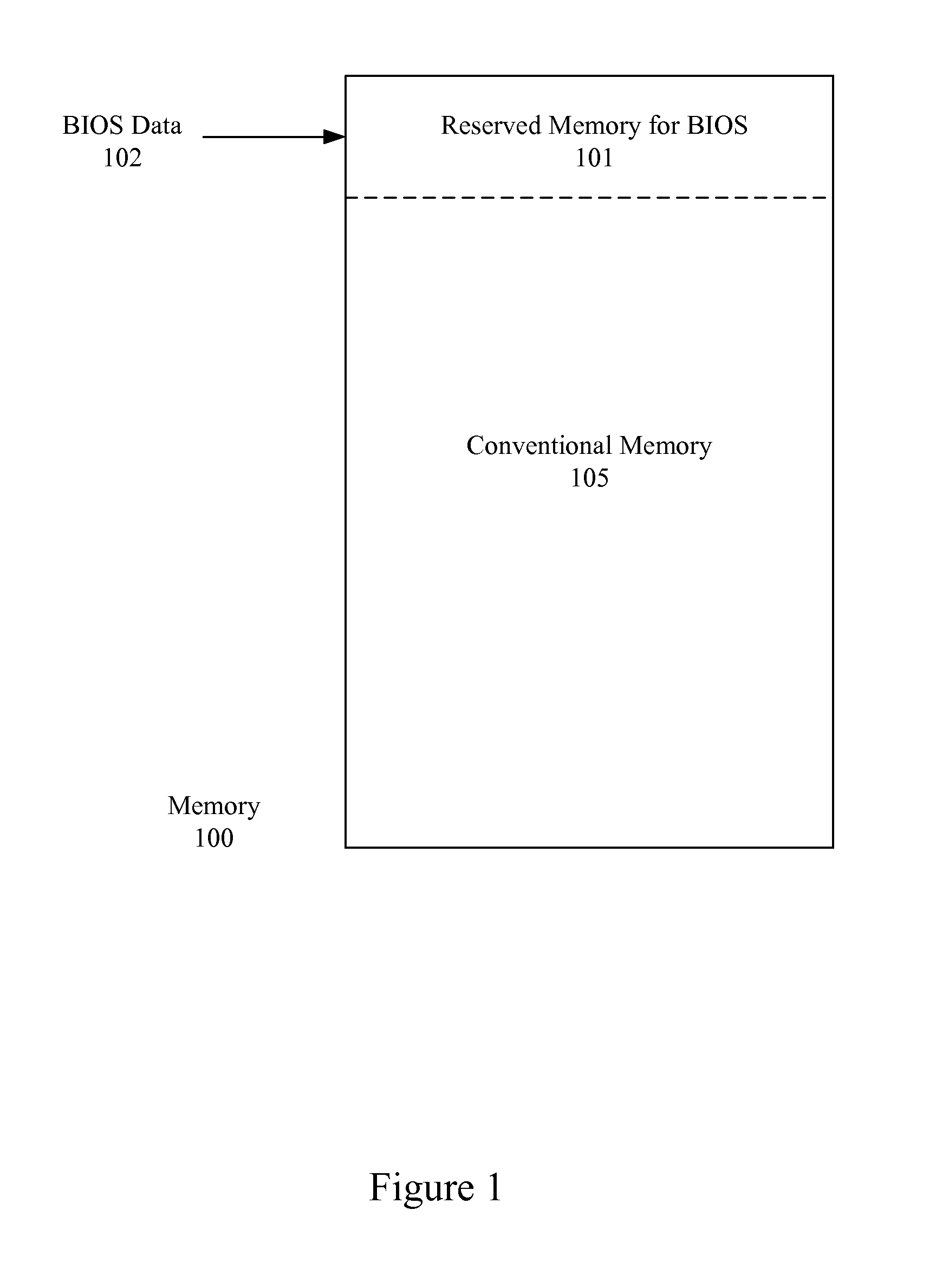
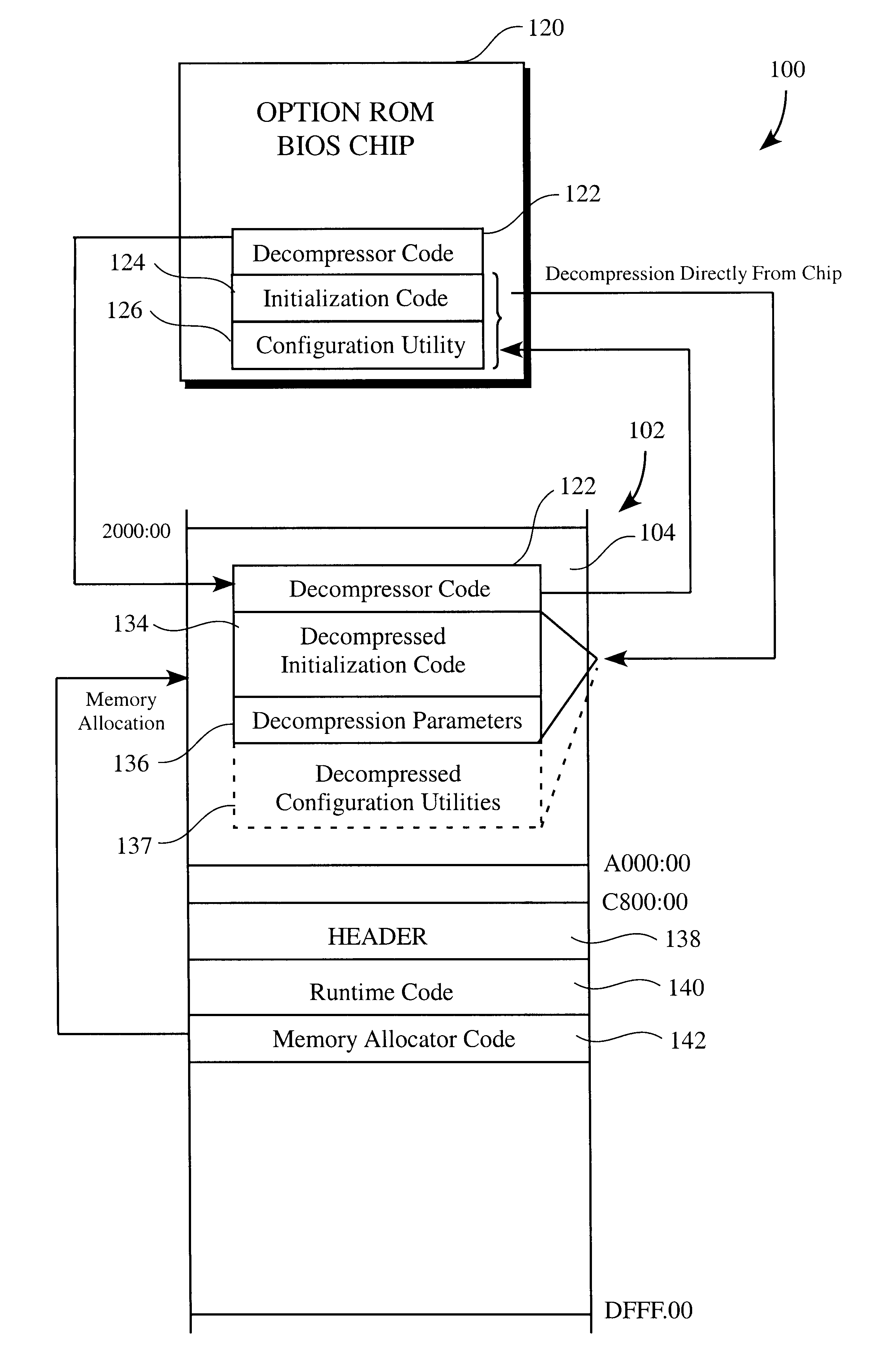
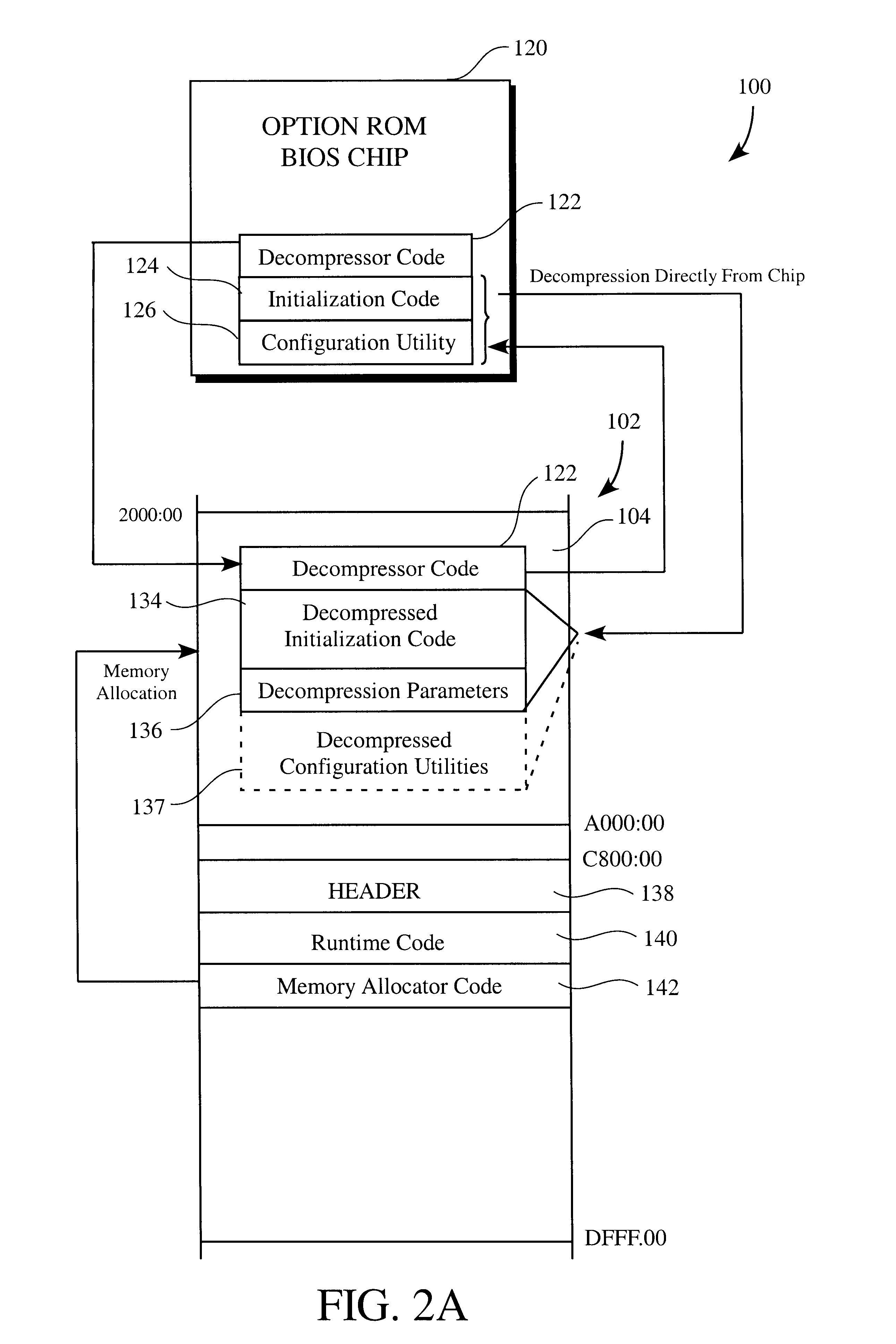
Method of conserving memory resources during execution of system BIOS
Methods of conserving memory resources available to a computer system during execution of a system BIOS are provided. The method includes (a) executing the system BIOS; (b) loading the header, runtime code, and memory allocator code associated with the option ROM BIOS chip into the option ROM memory space; (c) passing control to the memory allocator code; (d) executing the memory allocator code to allocate conventional memory of the system RAM; (e) copying the decompressor code from the option ROM BIOS chip to the allocated conventional memory; (f) passing control to the decompressor code; (g) executing the decompressor code to decompress the compressed initialization code directly from the option ROM BIOS chip and thus loading the decompressed initialization code into the conventional memory; and (h) executing the decompressed initialization code to initialize the adapter card or controller.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
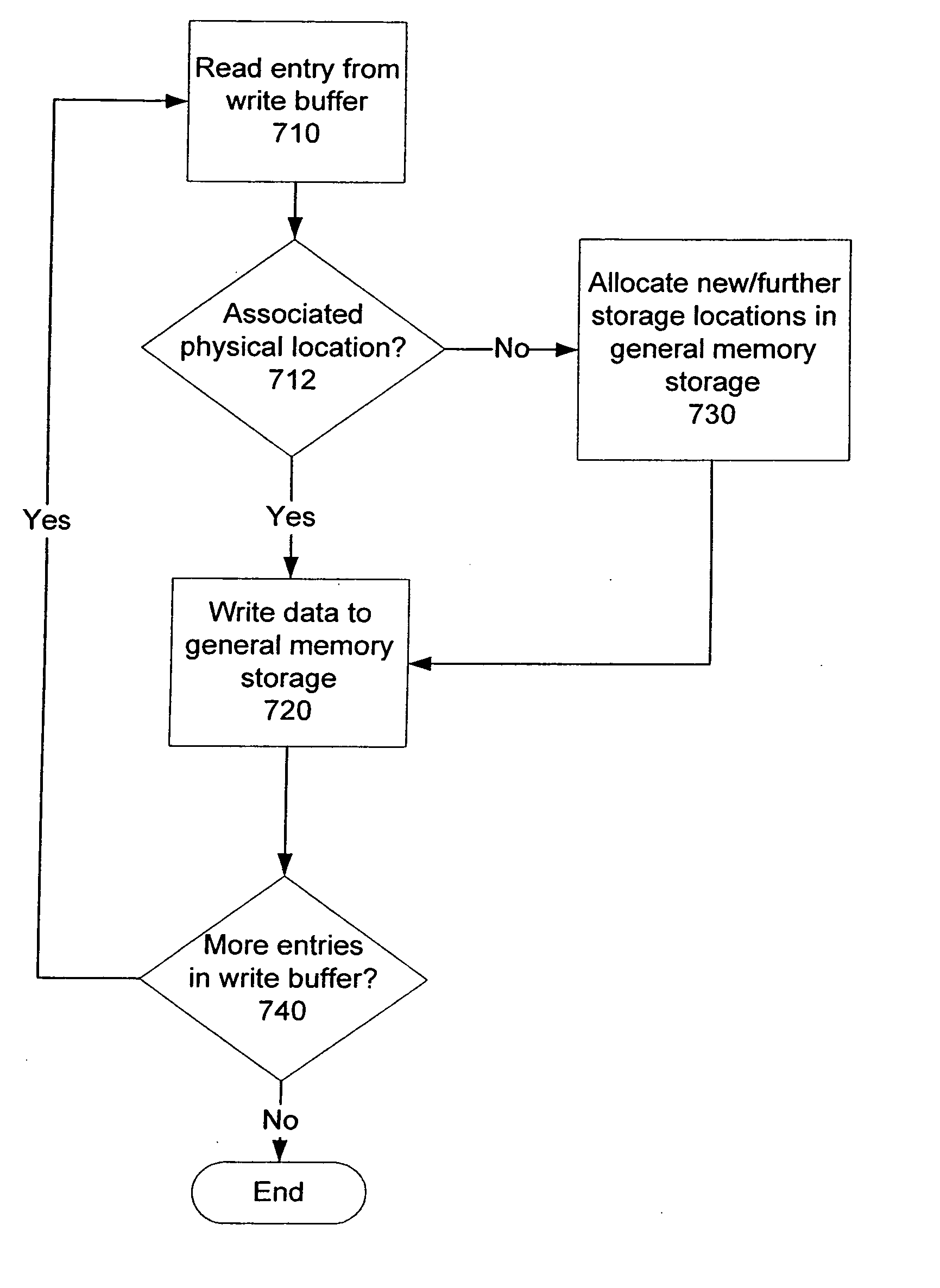
Computer system having logically ordered cache management
ActiveUS20070005894A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationConventional memoryFile system
A computer system is set forth that includes a processor, general memory storage, and cache memory for temporarily storing selected data requested from the general memory storage. The computer system also may include file system software that is executed by the processor. The file system software may be used to manage the file data and the structure of the file system for files stored on the general memory storage. Management of the cache memory is placed under the control of cache management software. The cache management software is executed by the processor to manage the contents of the cache memory pursuant to cache hit and cache miss criterion. Sections of the cache memory are organized by the cache management software based on logical addresses of file data requested from the general memory storage.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
CMOS sensor array with a memory interface
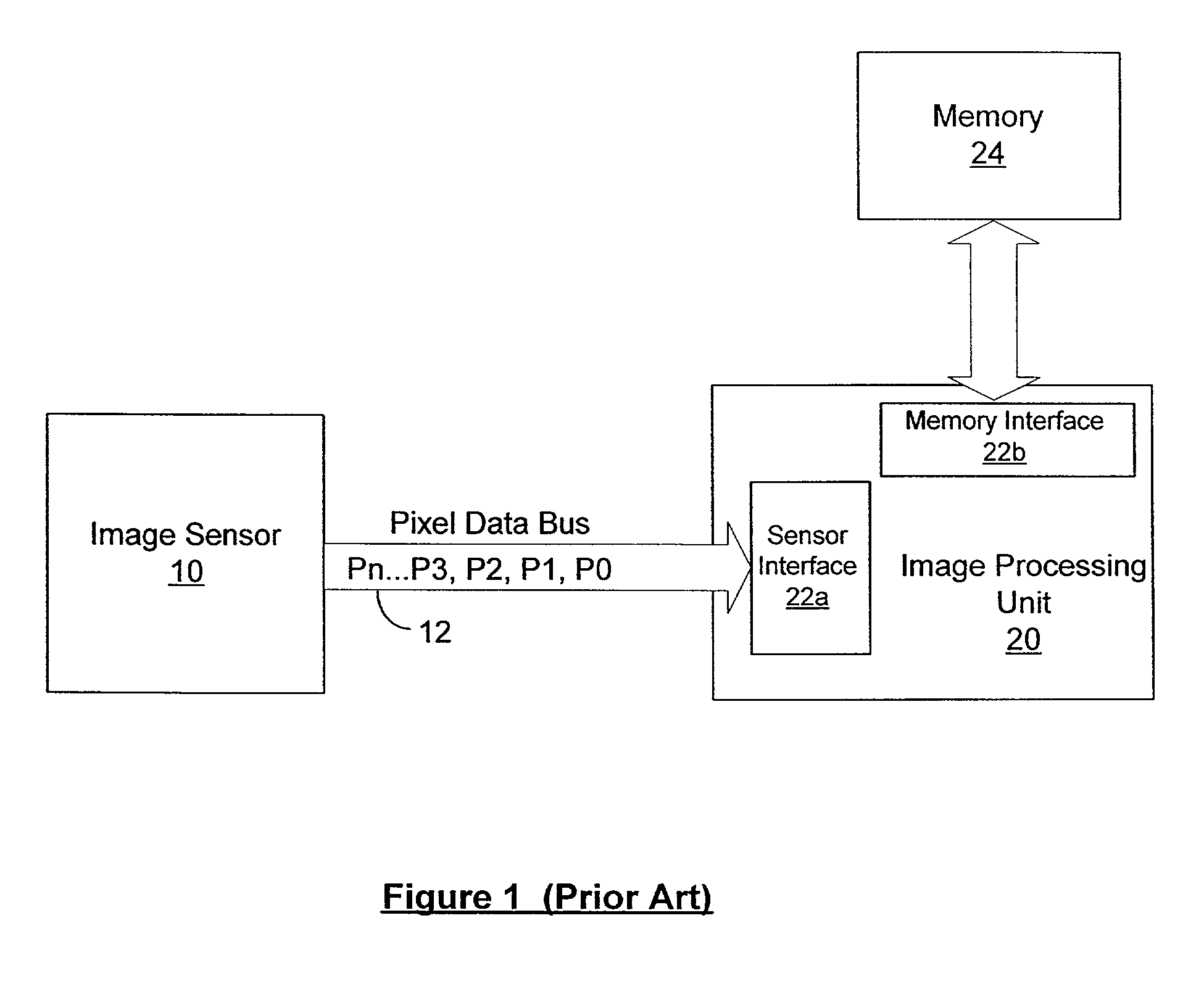
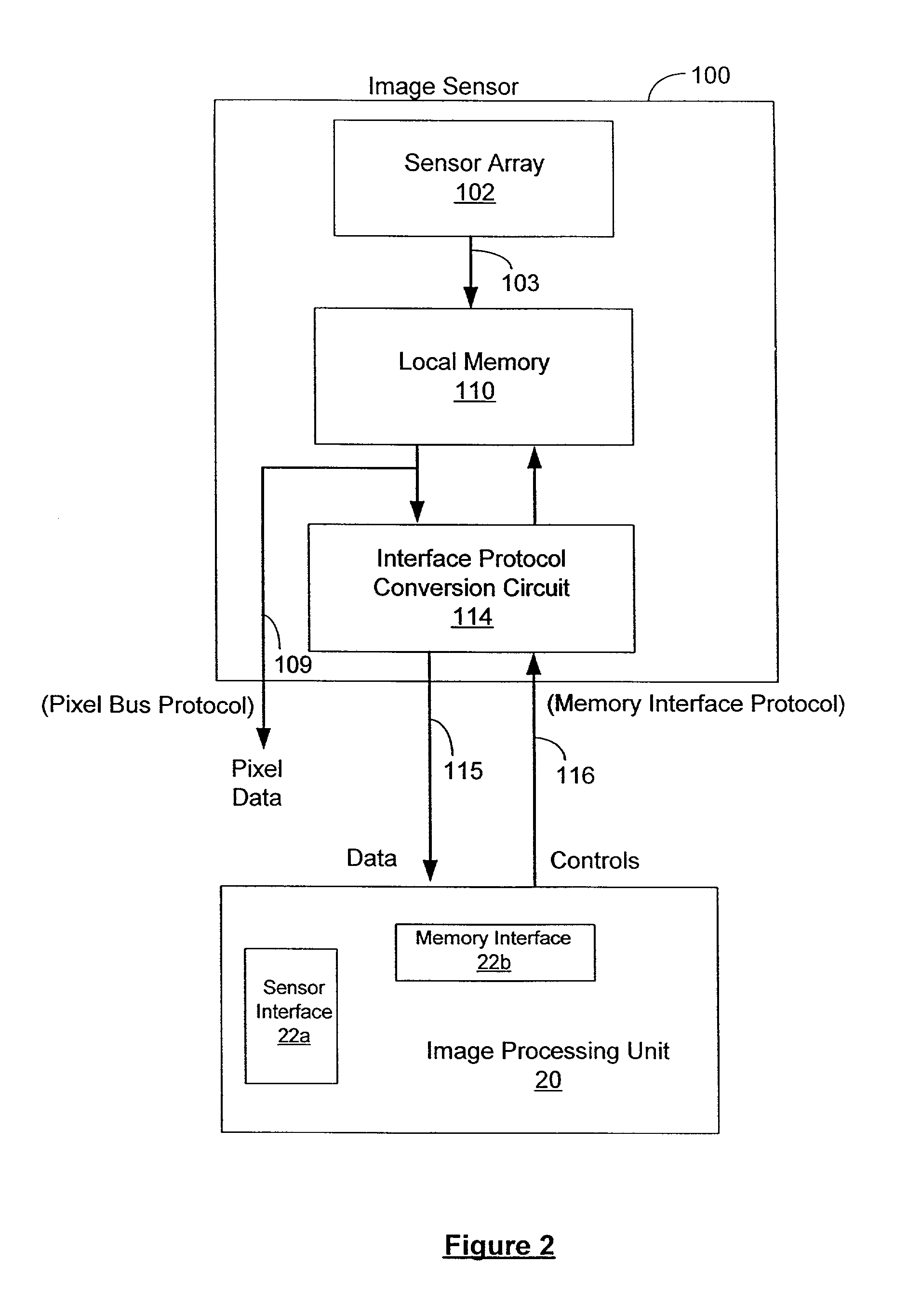
InactiveUS6985181B2Improve efficiencyOperation complexity can be reducedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsConventional memorySensor array
An image sensor includes a sensor or a pixel array, a data memory, and a logic circuit, all fabricated on the same integrated chip. The sensor or pixel array outputs digital signals as pixel data representing an image of a scene. The data memory is coupled to the sensor or pixel array for storing the pixel data. The logic circuit is coupled to the data memory and provides a memory interface for exporting the pixel data. The memory interface can be one of a SRAM, a DRAM or a packet protocol synchronous DRAM interface. Including a memory interface in the image sensor allows the image sensor to be coupled directly to the memory interface port of an external image processing unit. The image processing unit can access the image sensor using conventional memory access protocols, thus improving the efficiency and reducing the operational complexity of the image processing unit.
Owner:PIXIM
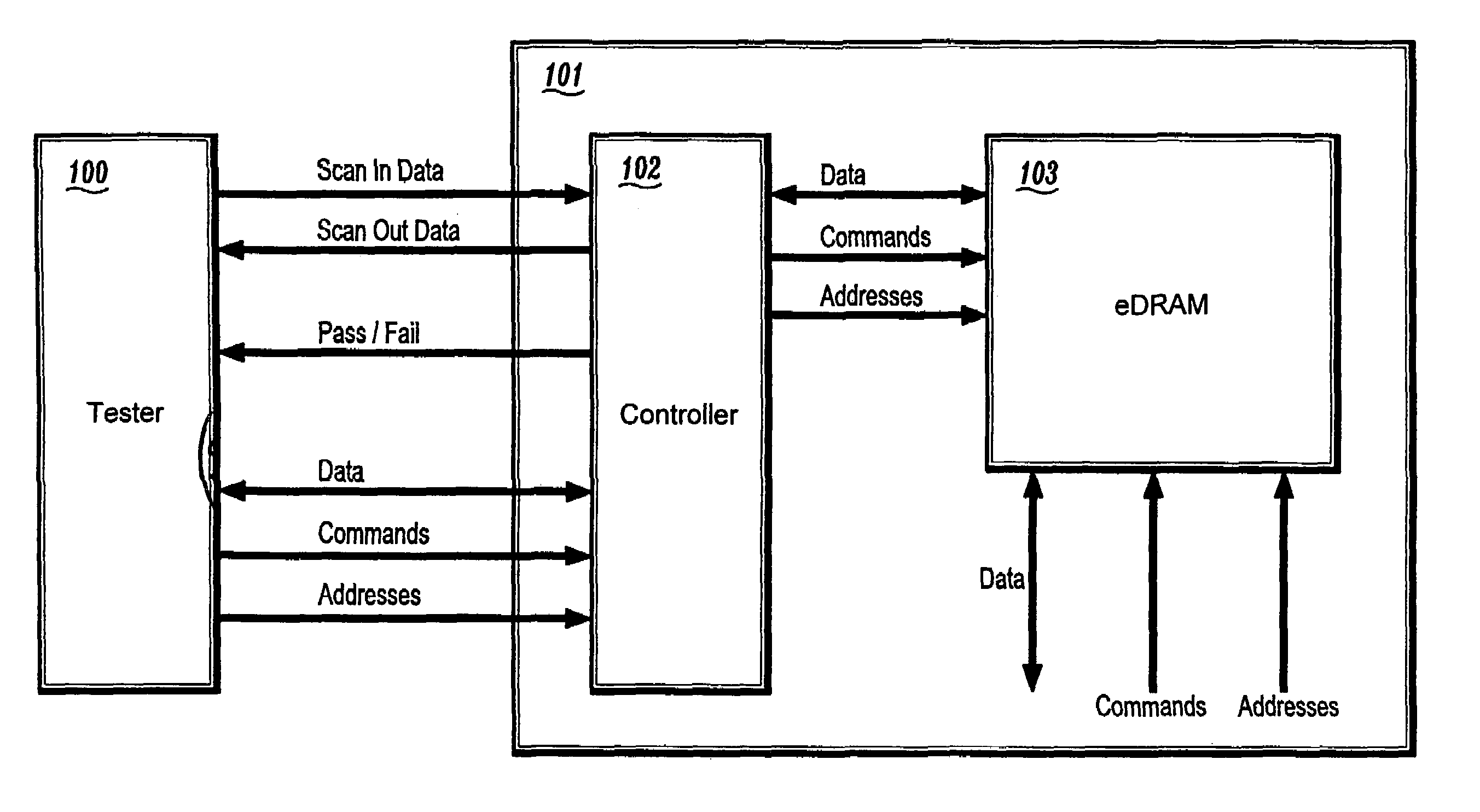
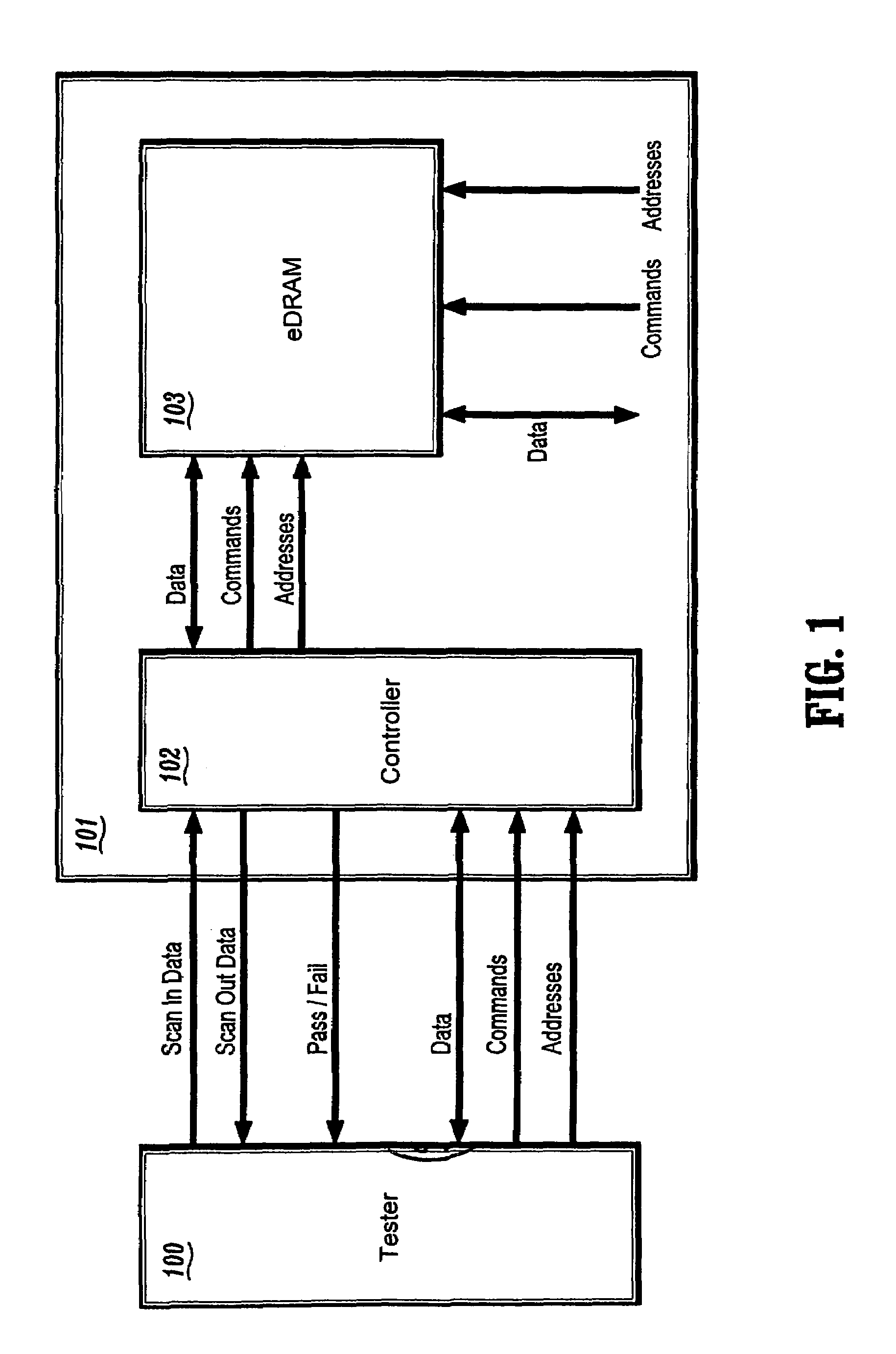
Circuit and method for testing embedded DRAM circuits through direct access mode
A circuit and method for testing an eDRAM through a test controller with direct access (DA) mode logic is provided. The circuit and method of the present invention allows the testing of eDRAMs with a conventional memory tester. The present invention provides a semiconductor device including an embedded dynamic random access memory (eDRAM) for storing data, the eDram including a plurality of memory cells, and a test controller for testing the plurality of memory cells to determine if the cells are defective, the test controller including built-in self-test (BIST) logic circuitry for performing tests and for interfacing to a logic tester, and direct access mode logic circuitry for interfacing the eDRAM with an external memory tester. The test controller further comprises a multiplexer for multiplexing data, commands, and addresses from the BIST logic circuitry and the direct access mode logic circuitry to the eDRAM.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
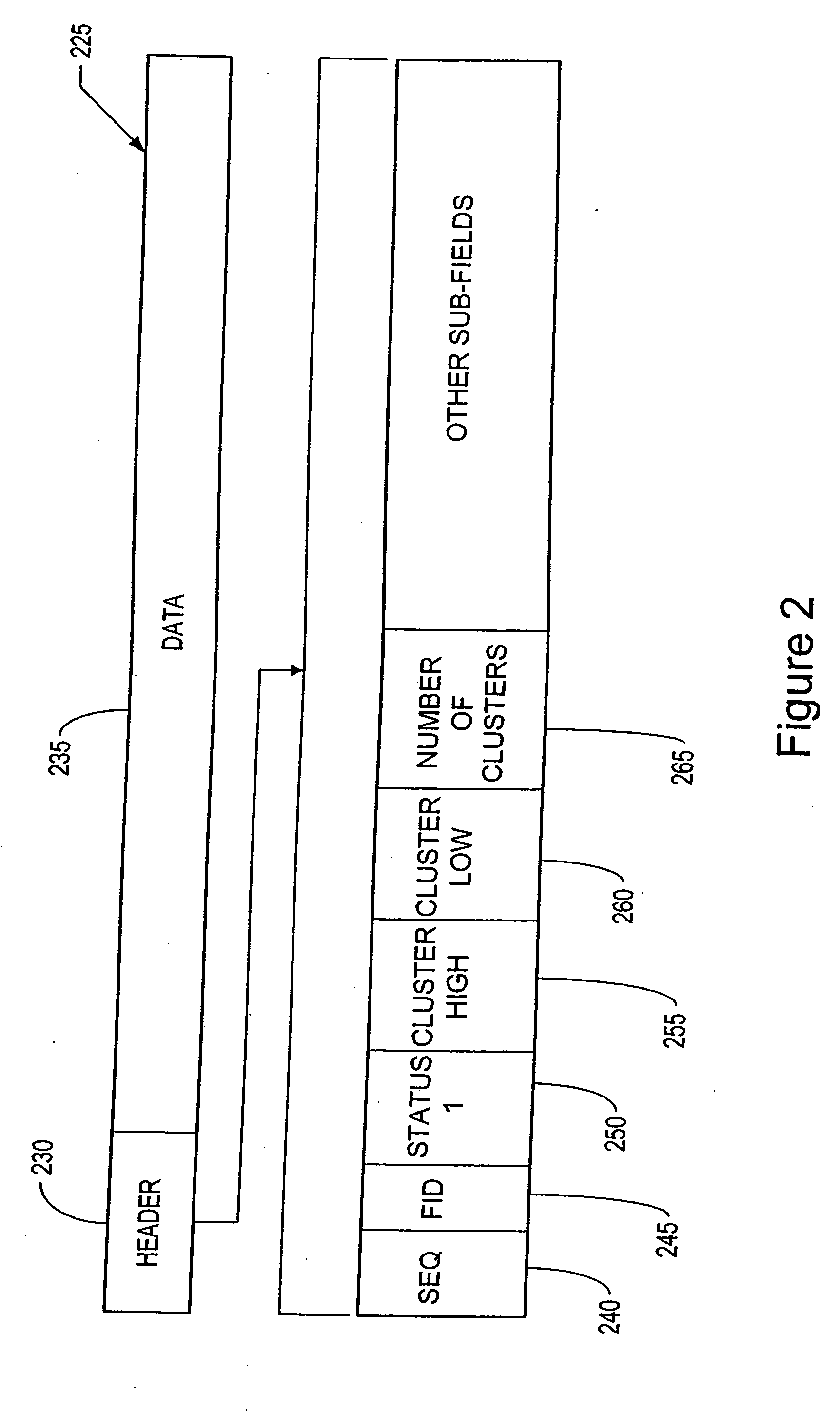
Data bus inversion using spare error correction bits
In a memory system, a spare error correction bit is produced by processing data to be stored in sufficiently large chunks that the number of error correction bits required to protect each chunk are fewer than the available error correction signal lines on a memory bus and storage device. The spare bit is then used for an inversion bit in a parallel data bus inversion scheme, wherein data is selectively inverted to minimize bus switching. The transmission of data and error correction bits are spread over multiple phases, wherein parallel data bus inversion is applied to each phase. Alternatively, the transmission of data and error correction bits may be transmitted and stored in a single transaction. In either case, the spare bit is transmitted on a conventional memory bus and stored in a conventional memory module along with data and error correction bits.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
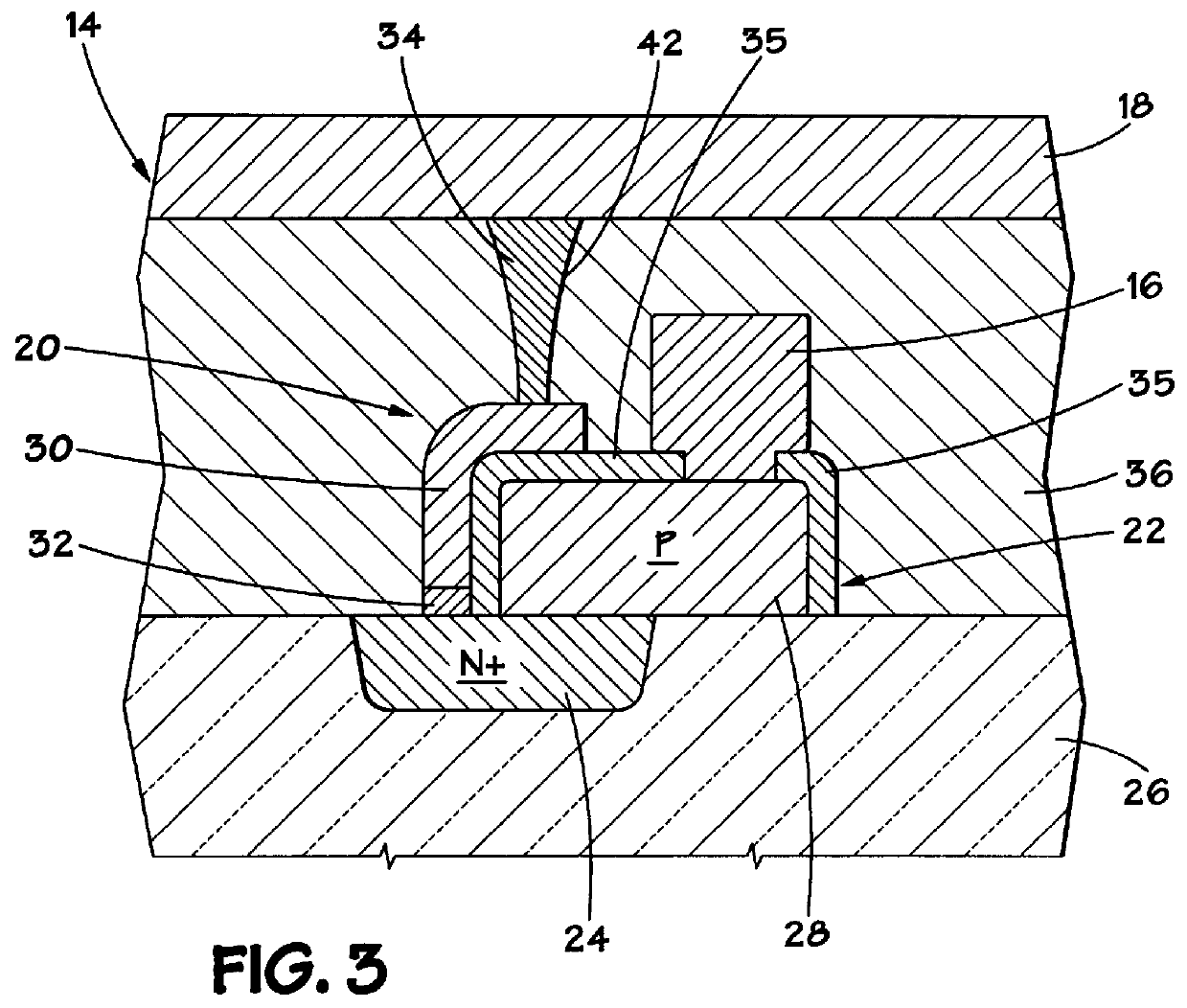
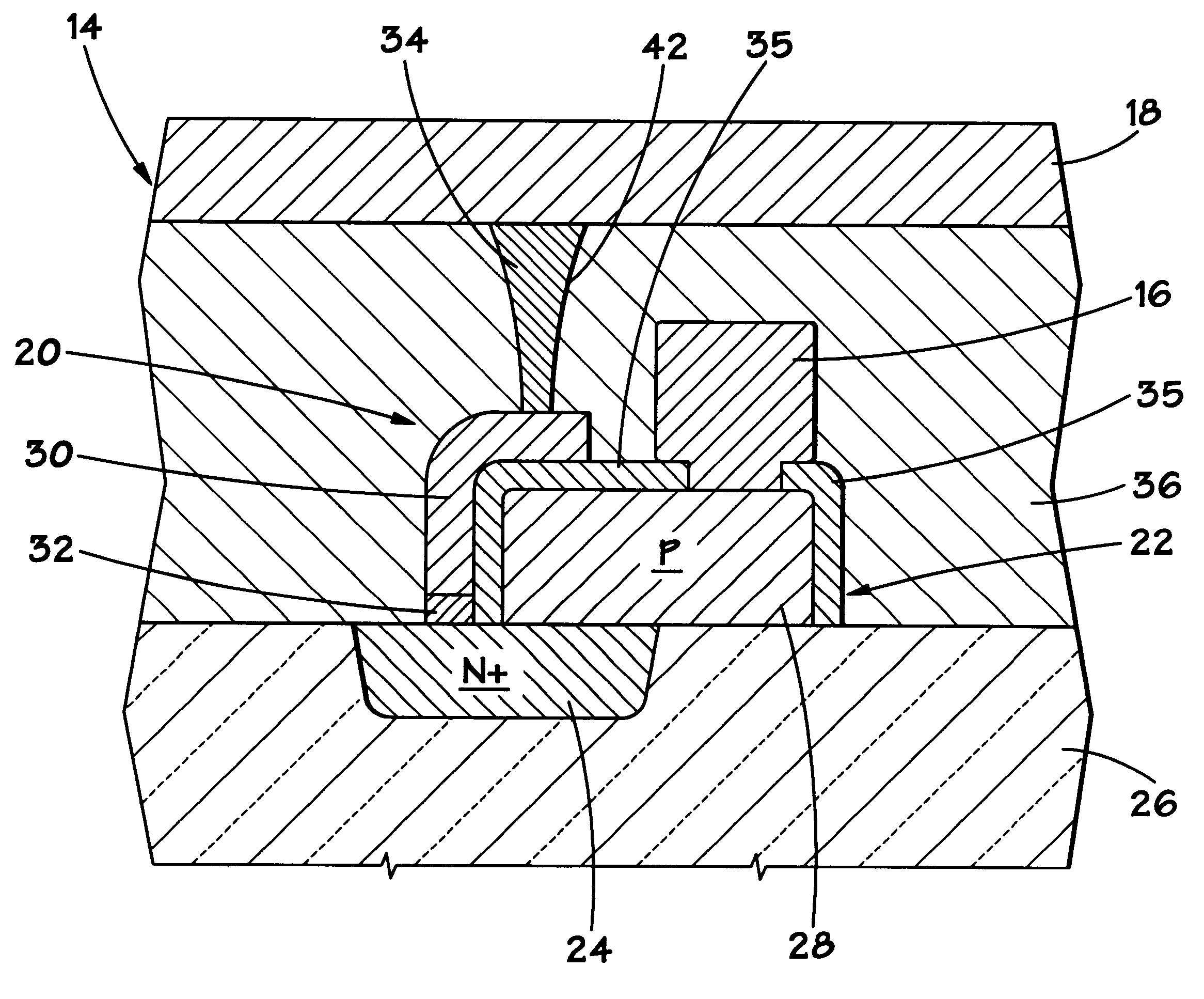
Memory cell having a reduced active area and a memory array incorporating the same
There is disclosed a memory cell having a reduced active area. The memory cell may be incoporated into a memory array. A method of fabricating the memory cell and the memory array includes the fabrication of an access device, such as a diode, that protrudes above the semiconductor substrate. The memory element, such as a memory element formed of chalcogenide material, is disposed on the side of the protrusion to reduce the active area of the memory element as compared with conventional memory elements.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
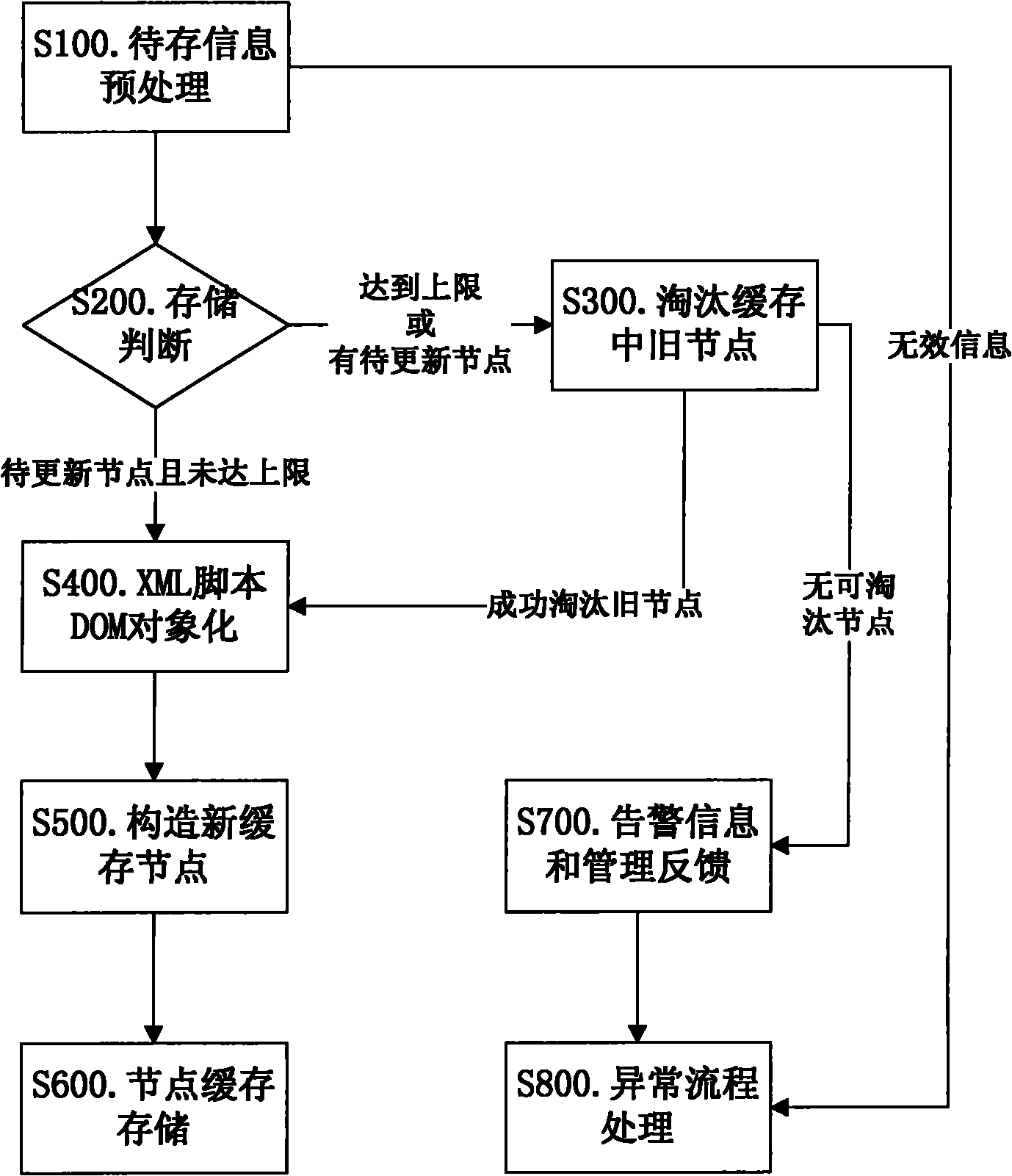
Memory-based XML script buffer
The invention discloses a memory-based XML script buffer. An XML resolution interface is arranged in the buffer, and an external XML resolver can be called. Core information stored in the buffer is not an XML script in a text form but a DOM object obtained by resolving the XML script. The buffer per se comprises a buffer algorithm, so that the buffer can be accessed at a high speed on the premise of a limited volume and can dynamically weed stored obsolete information out. The memory-based XML scrip buffer of the invention provides the interface of the XML resolver embedded into the buffer per se, caches contents which are not pure XML scrip texts but the DOM objects of the XML scripts, has the characteristics of the tracking, reentry, weeding out, dynamic backup and recovery and update of the DOM objects, and can completely recover the functions of the conventional memory buffers by realizing the fluidization and structuring of the objects in fit with the external XML resolver.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for archiving digital content
ActiveUS20080162797A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationConventional memoryDigital content
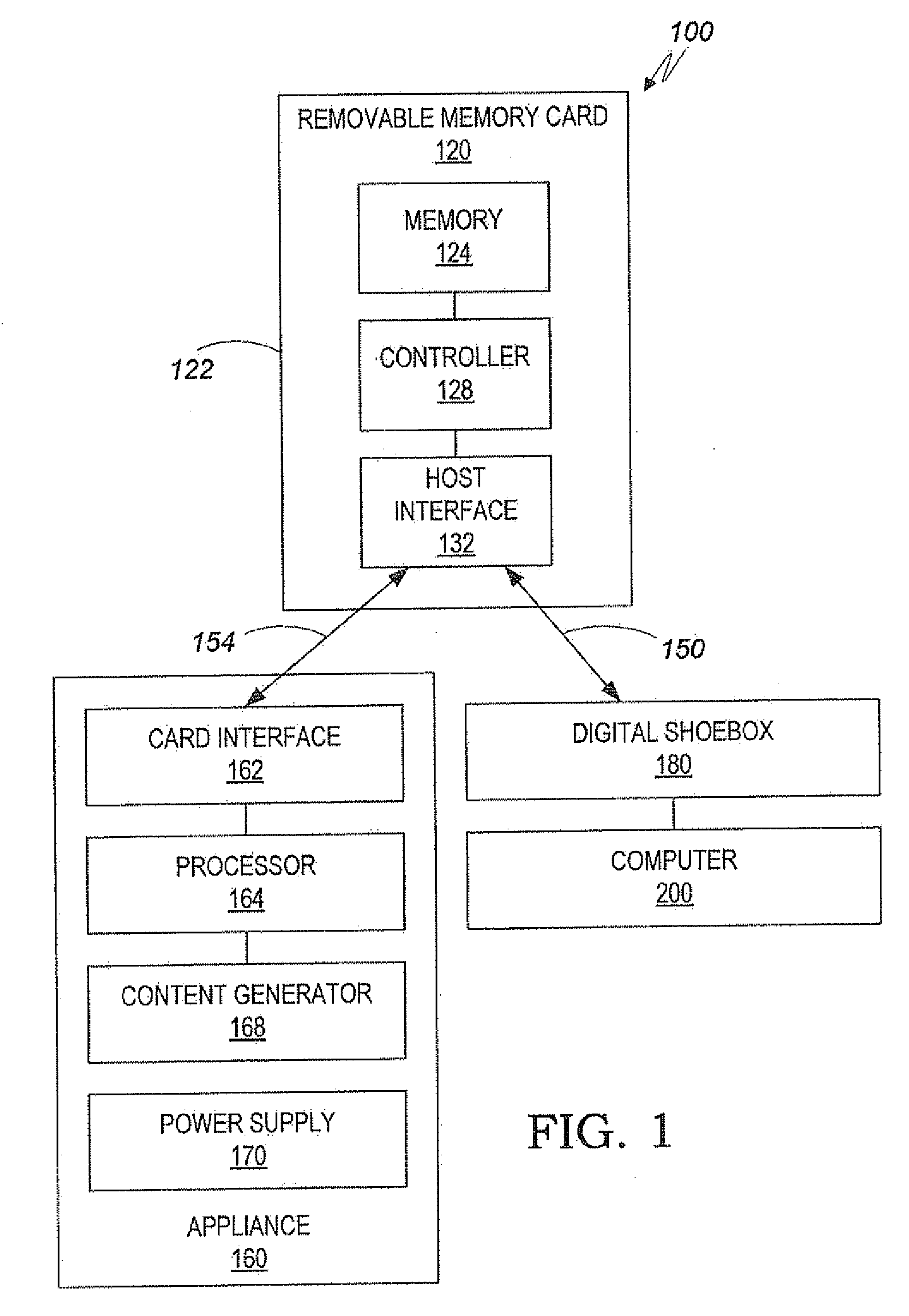
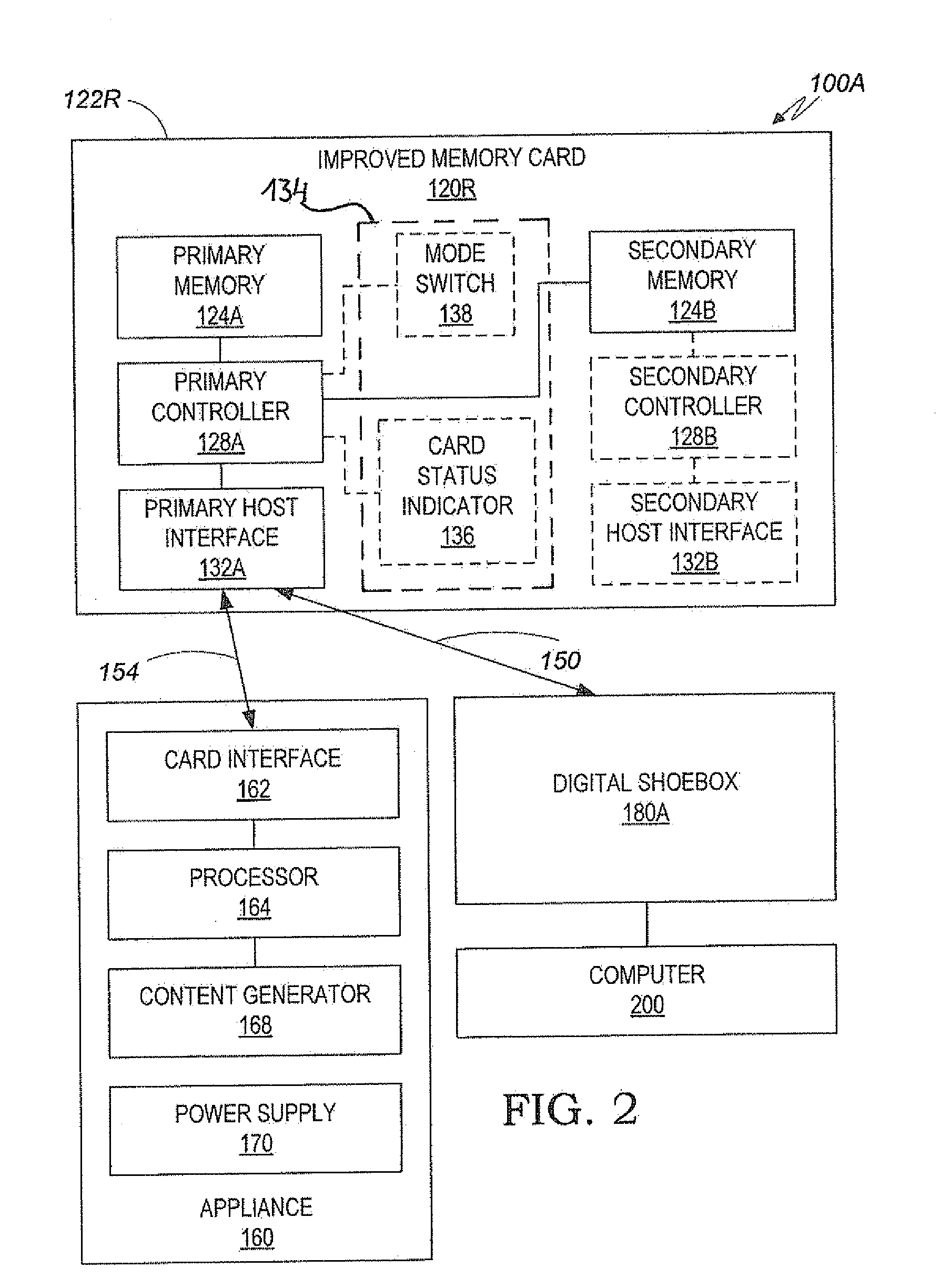
An improved memory card includes an interface for receiving content from an appliance, a primary memory, a secondary memory, and primary controller. The primary controller is configured to selectively write the content only on the primary memory card, or only on the secondary memory card, or on both memories. The improved memory card also includes an enclosure for enclosing the primary memory, the secondary memory, the primary host interface and the primary controller. The improved memory card also includes a user interface that includes a user-operable mode switch that is switchable between a “full capacity” mode and a “fall redundancy” mode. In the “full capacity” mode the secondary memory is used for recording genuine content, whereas in the “full redundancy” mode the secondary memory is used for backing up content that has been recorded on the primary memory. A digital shoebox is also provided, which can use improved memory cards and conventional memory cards alike for archiving content.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
Content-based information retrieval architecture
InactiveUS20050174272A1Easy constructionReadily implemented in hardwareDigital data information retrievalCode conversionConventional memoryContent based information retrieval
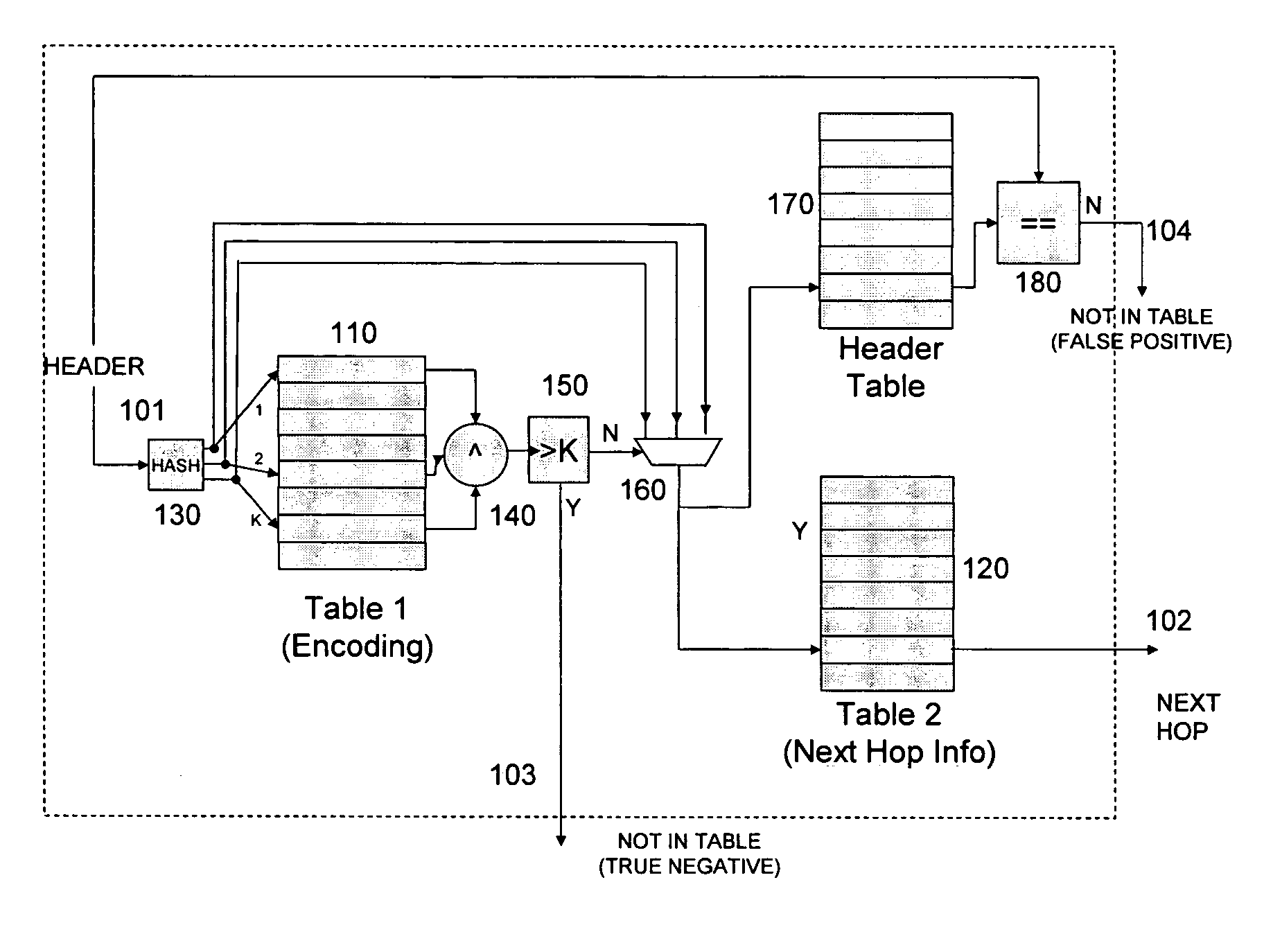
A content-based information retrieval architecture is herein disclosed that can achieve correct and predictable high speed lookups while taking advantage of inexpensive conventional memory components.
Owner:NEC CORP
Digital remote store
Expanded storage is provided to portable electronic devices of the type that typically incorporate compact flash memory cards or a similar local replaceable memory device. A transceiver assembly is provided within the form factor of the local replaceable memory normally used in the local storage device. The transceiver assembly communicates with the portable electronic device over the connections and using the same communication protocol as the portable electronic device conventionally uses to communicate with the local replaceable memory device. Data are written to the transceiver assembly as if the transceiver were the conventional memory device. The data are buffered and transmitted over a wireless link to a corresponding wireless link associated with a remote mass storage device. Data transferred across the wireless link are stored in the remote mass storage device as if the mass storage were provided within the portable electronic device, thereby providing greatly expanded storage to the portable electronic device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Memory test device and method capable of achieving fast memory test without increasing chip pin number
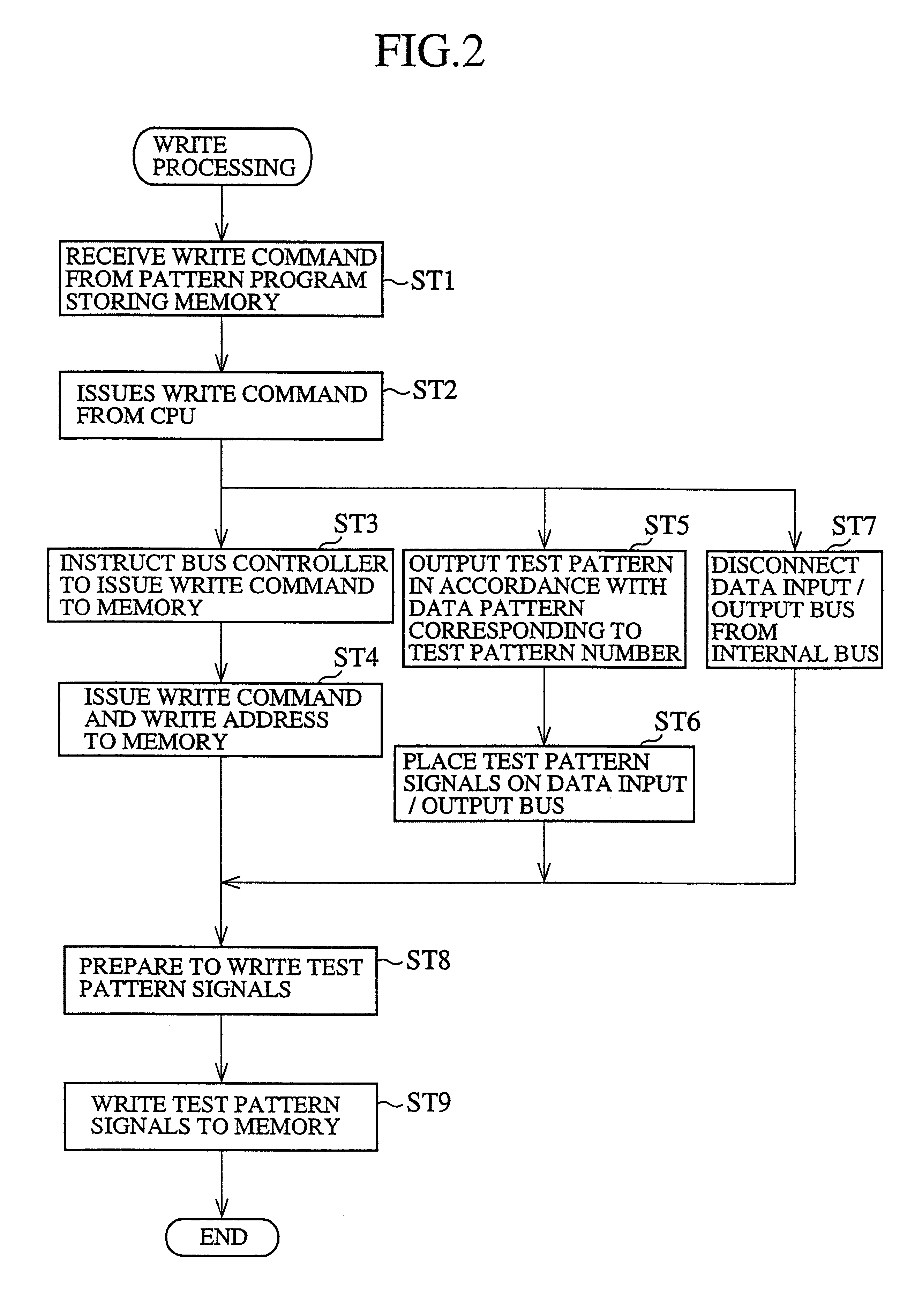
InactiveUS6324666B1Digital circuit testingError detection/correctionConventional memoryBus mastering
A memory test device that issues a test pattern read request to a memory, captures test pattern signals placed by the memory on a data input / output bus in response to the test pattern read request, and compares the test pattern signals with their expected values. This can solve a problem involved in a conventional memory test device in that because the pin width of data pins is narrower than the bus width of the data input / output bus that connects a memory and a data bus controller, even if the memory reads test pattern signals in accordance with the width of the data input / output bus, the test pattern signals cannot be sent to the tester without being divided, and hence the tester cannot achieve the quick test of the memory.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Multiple layers of memory implemented as different memory technology
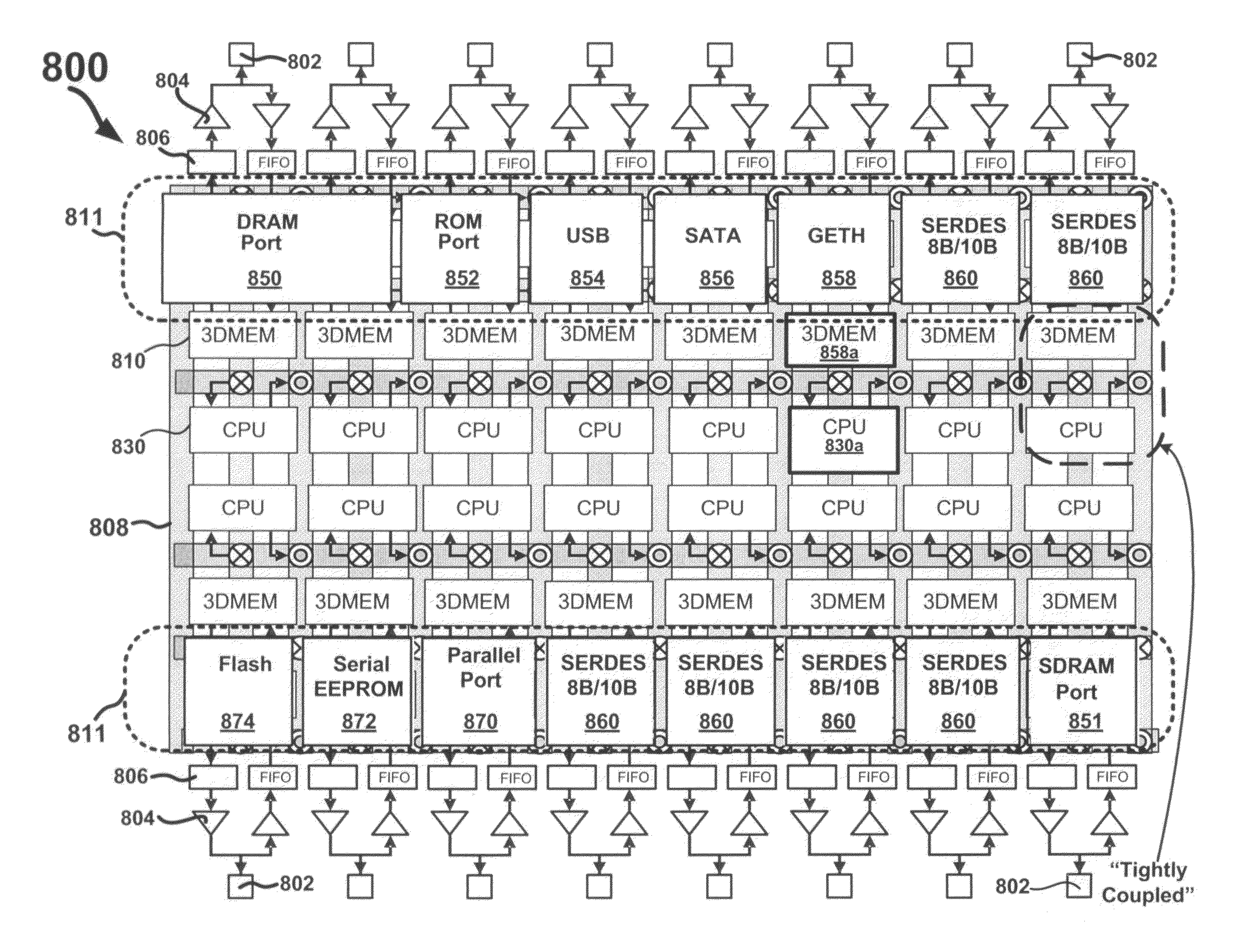
InactiveUS20100195363A1Printed circuit assemblingDigital storageComputer hardwareConventional memory
Circuits and methods that use third dimension memory as a different memory technology are described. The third dimension memory can be used for application specific data storage and / or to emulate conventional memory types such as DRAM, FLASH, SRAM, and ROM or new memory types as they become available. A processor-memory system implements a memory operable as different memory technologies. The processor-memory system includes a logic subsystem and a memory subsystem, which includes third dimension memory cells. The logic subsystem implements memory technology-specific signals to interact with the third dimension memory cells as memory cells of a different memory technology. As such, the memory subsystem can emulate different memory technologies. The logic subsystem can be fabricated FEOL on a substrate and the memory subsystem can be fabricated BEOL directly on top of the substrate. An interlayer interconnect structure can electrically couple the logic subsystem with the memory subsystem.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
Miniature flash memory card with mini-SD and RS-MMC compatibility
InactiveUS20060226241A1Easy to addEasy to replaceRecord carriers used with machinesConventional memoryHigh density
Miniature flash memory card with mini-SD and RS-MMC compatibility is provided. This is accomplished by a special circuit layout of the module substrate, so that the memory controller is attached on the front end of the module substrate, and two or more memory dies can be fitted in the memory block toward the back end of the module substrate, using smaller and higher density memory, whereas the conventional memory card has to use monolithic memory module. In the present design, the memory ICs are built into the memory module, but the memory can be easily replaced or added for memory expansion.
Owner:TEC TECH INT
Methods for optimizing memory resources during initialization routines of a computer system
InactiveUS6865669B1Improve abilitiesIncrease capacityData resettingMultiple digital computer combinationsConventional memoryOperational system
Methods for optimizing of memory resources during an initialization routine of a computer system which prepares the computer system for loading of an operating system is disclosed. One exemplary method includes receiving a request from a system BIOS to locate an amount of conventional memory where the amount of conventional memory accommodates at least a decompressed version of data located in an option ROM BIOS. Then the amount of conventional memory requested by the system BIOS is determined. If the amount of conventional memory requested by the system BIOS is not available, the method continues and system BIOS data located within the conventional memory is read where the system BIOS data occupies at least the amount of conventional memory requested by the system BIOS. After the system BIOS data is read, the system BIOS data is written from the conventional memory to an extended memory, and the system BIOS data located in the conventional memory that has been written into the extended memory is deleted.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
Self-descriptive microphone array
ActiveUS7515721B2Reduce manufacturing costLow costMicrophones signal combinationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsConventional memoryWireless computing
A self-descriptive microphone array includes a microphone array memory, such as, for example a ROM, EEPROM, or other conventional memory, which contains a microphone array device description. This device description includes parametric information which defines operational characteristics and configuration of the microphone array. In further embodiments, the microphone array uses any of a variety of conventional wired or wireless computer interfaces, including serial, IEEE 1394, USB, Bluetooth™, etc., to connect to a computing device. Once connected, the microphone array provides its device description to the computing device. Sound processing software residing within the computing device is then automatically configured for optimally interacting with one or more analog or digital audio signals provided by the microphone array. In another embodiment, the microphone array performs integrated self calibration for automatically updating the device description. The self calibration is performed either upon connection to the computing device, or upon regular or user-specified intervals.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
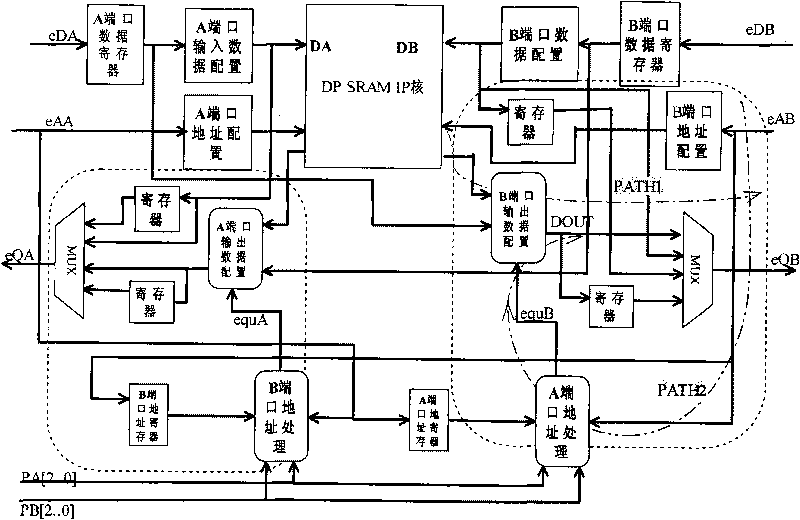
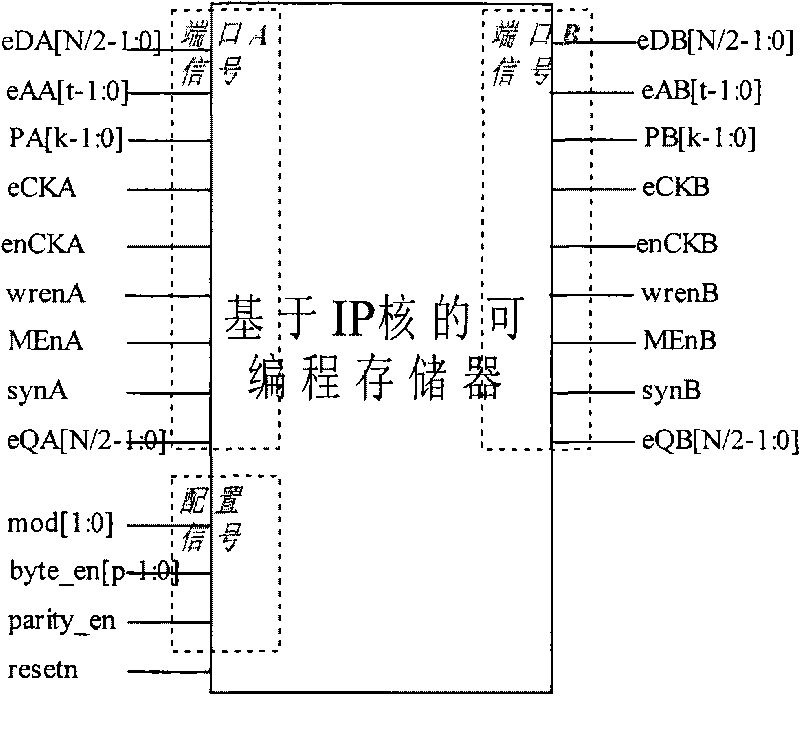
Embedded programmable memory based on memory IP core
ActiveCN101751980ASupport Programmable DesignWork fasterDigital storageConventional memoryProcessor register
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Interposable heat sink for adjacent memory modules
InactiveUS20060221578A1Improve cooling effectDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConventional memoryPrinted circuit board
A h9eat sink device for conventional memory modules, such as DIMMs, that is configured to be positioned between adjacent memory modules mounted in substantially parallel connectors on a printed circuit board. Each heat sink device includes thermally conductive first and second members configured to thermally couple with electronic components of a conventional memory module. The first and second members may be resiliently biased away from one another so that the resilient bias causes the members to abut respective electronic components when placed between adjacent memory modules. A separate wedge, or a lever-mounted wedge, may be provided for insertion between the members to urge them away from one another and into abutting relationship with electronic components on facing surfaces of the adjacent memory modules. When abutting opposing electronic components, a single heat sink device facilitates heat dissipation from both of the adjacent memory modules.
Owner:IBM CORP
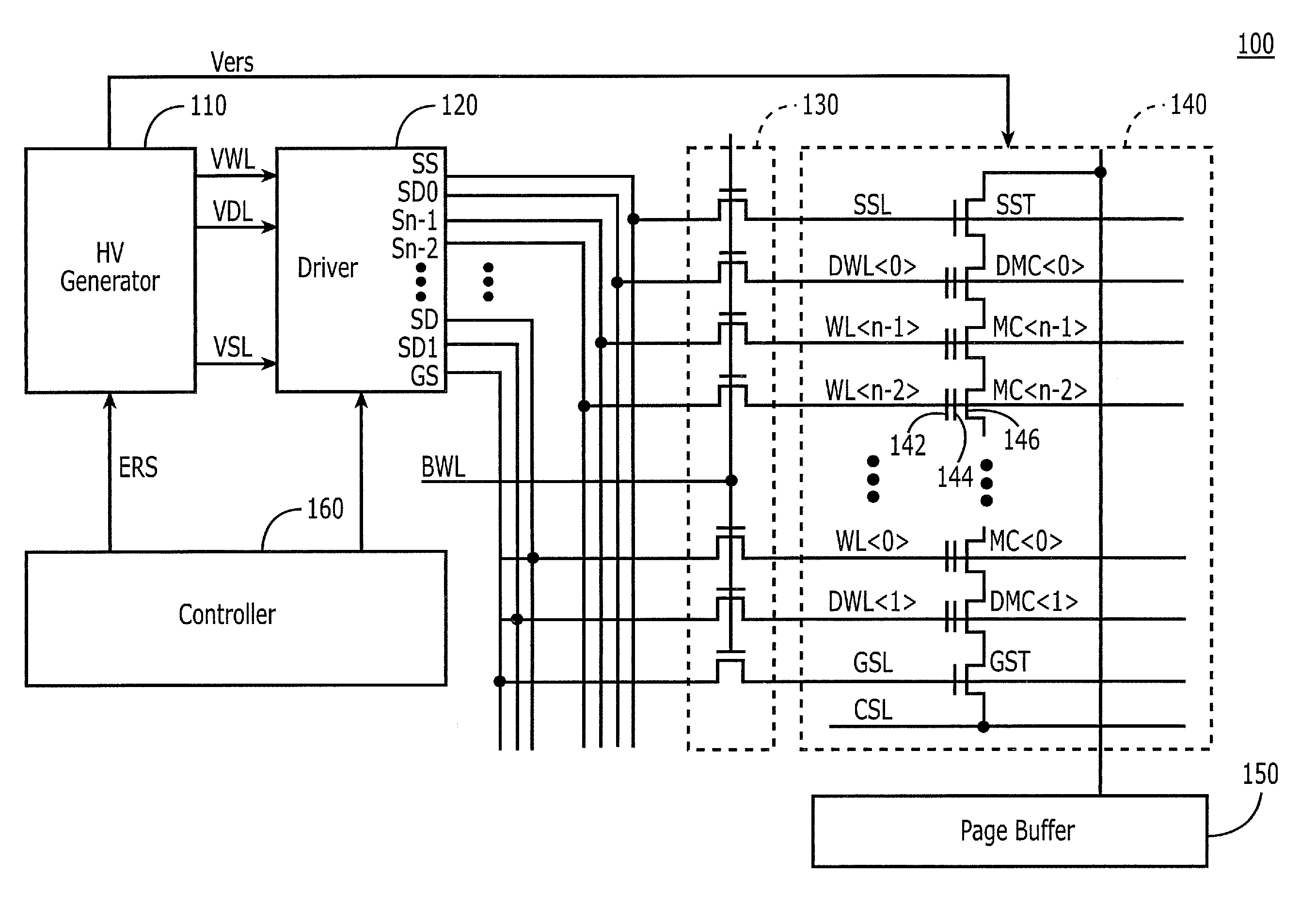
Flash memory devices and operating methods that concurrently apply different predetermined bias voltages to dummy flash memory cells than to regular memory cells during erase
Integrated circuit flash memory devices, such as NAND flash memory devices, include an array of regular flash memory cells, an array of dummy flash memory cells and an erase controller. The erase controller is configured to concurrently apply a different predetermined bias voltage to the dummy flash memory cells than to the regular flash memory cells during an erase operation of the integrated circuit flash memory device. Related methods are also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Memory cell having a reduced active area and a memory array incorporating the same
There is disclosed a memory cell having a reduced active area. The memory cell may be incorporated into a memory array. A method of fabricating the memory cell and the memory array includes the fabrication of an access device, such as a diode, that protrudes above the semiconductor substrate. The memory element, such as a memory element formed of chalcogenide material, is disposed on the side of the protrusion to reduce the active area of the memory element as compared with conventional memory elements.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
According to one embodiment, a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array including regular memory cells and permanent memory cells and a control circuit. The regular memory cells are capable of switching between a first data storage state and a second data storage state. The permanent memory cells are fixed in a third data storage state that is read as the same logic level data as the first storage state. Data is stored in at least one of the regular memory cells and at least one of the permanent memory cells. The control circuit rewrites at least one of the regular memory cells from the second data storage state to the first data storage state at the time of data holding. The control circuit performs a reading operation after rewriting the regular memory cells from the first data storage state to the second data storage state.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Flash memory and program verify method for flash memory
ActiveUS7313649B2Exclude influenceImprove reliabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineConventional memory
Owner:TOWER SEMICONDUCTOR +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com