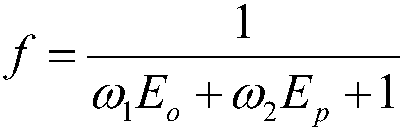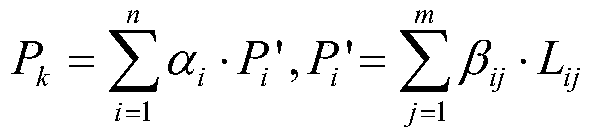Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Continuum function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the continuum function is , i.e. raising 2 to the power of κ using cardinal exponentiation. Given a cardinal number, it is the cardinality of the power set of a set of the given cardinality.
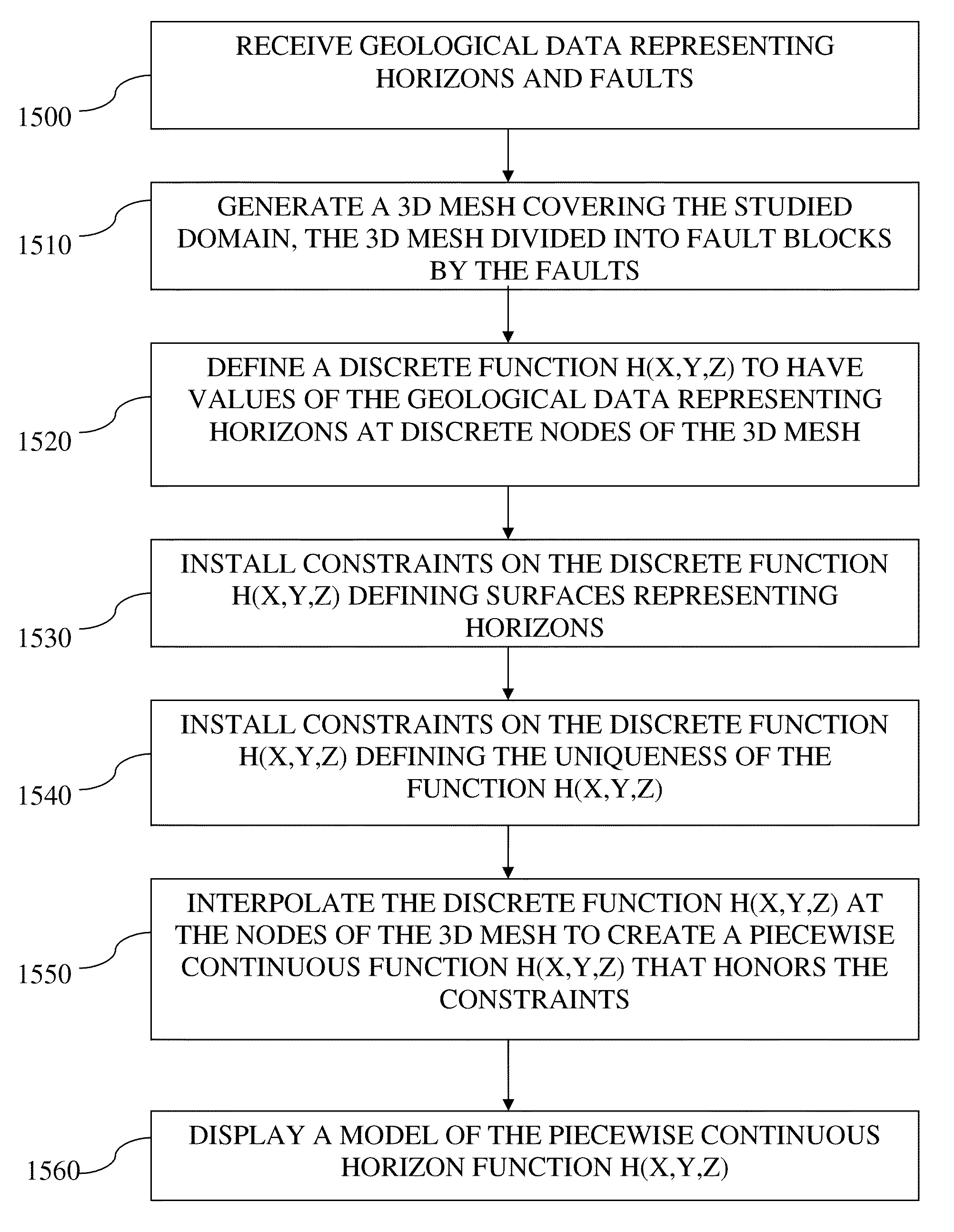
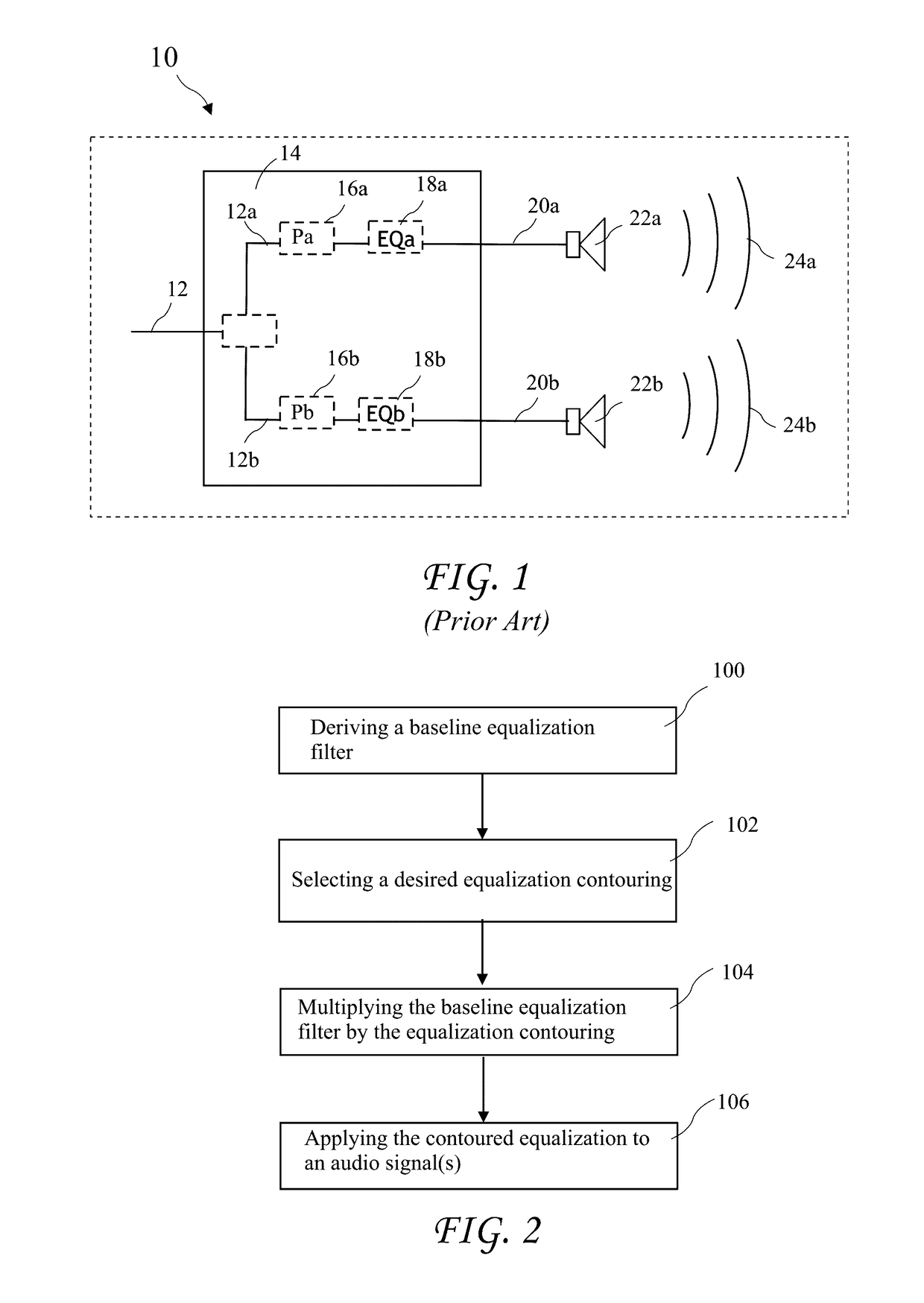
System and method for generating an implicit model of geological horizons
ActiveUS20130262052A1Ensure uniquenessSeismologyComputation using non-denominational number representationHorizonDiscrete functions
A method and system for generating a model function h(x,y,z) implicitly representing geologic horizons. Geological data representing a fault network and horizons automatically extracted from seismic data may be received. A 3D mesh may be generated and divided into a plurality of fault blocks by the fault network. A discrete function h(x,y,z) may be defined having values of the geological data representing horizons at discrete nodes of the mesh. Constraints may be installed on the discrete function h(x,y,z) defining surfaces representing horizons. Constraints may be installed on the discrete function h(x,y,z) to ensure the uniqueness of the function h(x,y,z). The discrete function h(x,y,z) may be interpolated at the nodes of the mesh to create a piecewise continuous function h (x,y,z) while honoring the constraints. The piecewise continuous horizon function h(x,y,z) may be synchronized across multiple fault blocks. A model of the piecewise continuous horizon function h(x,y,z) may be displayed.
Owner:ASPEN PARADIGM HLDG LLC
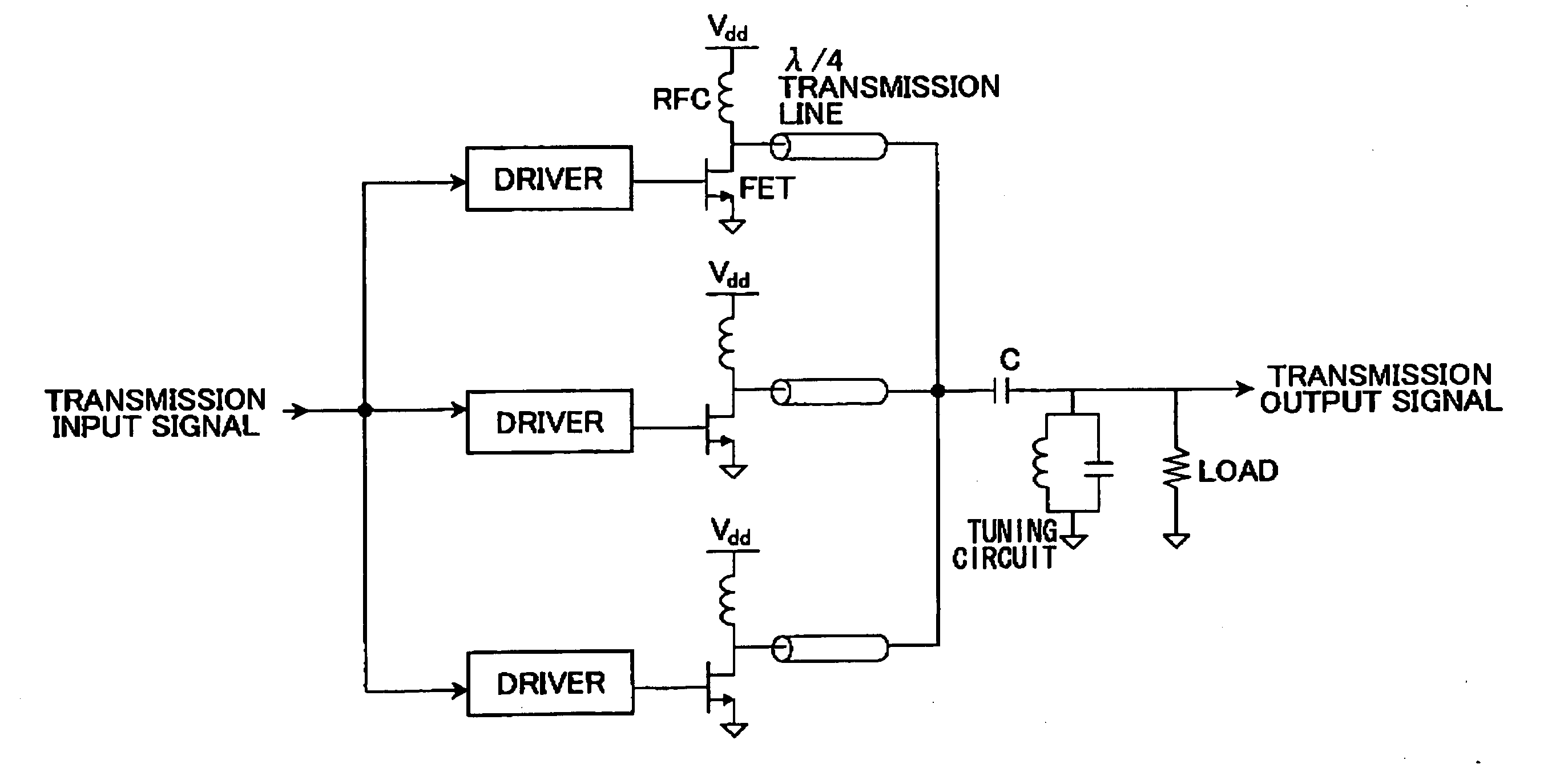
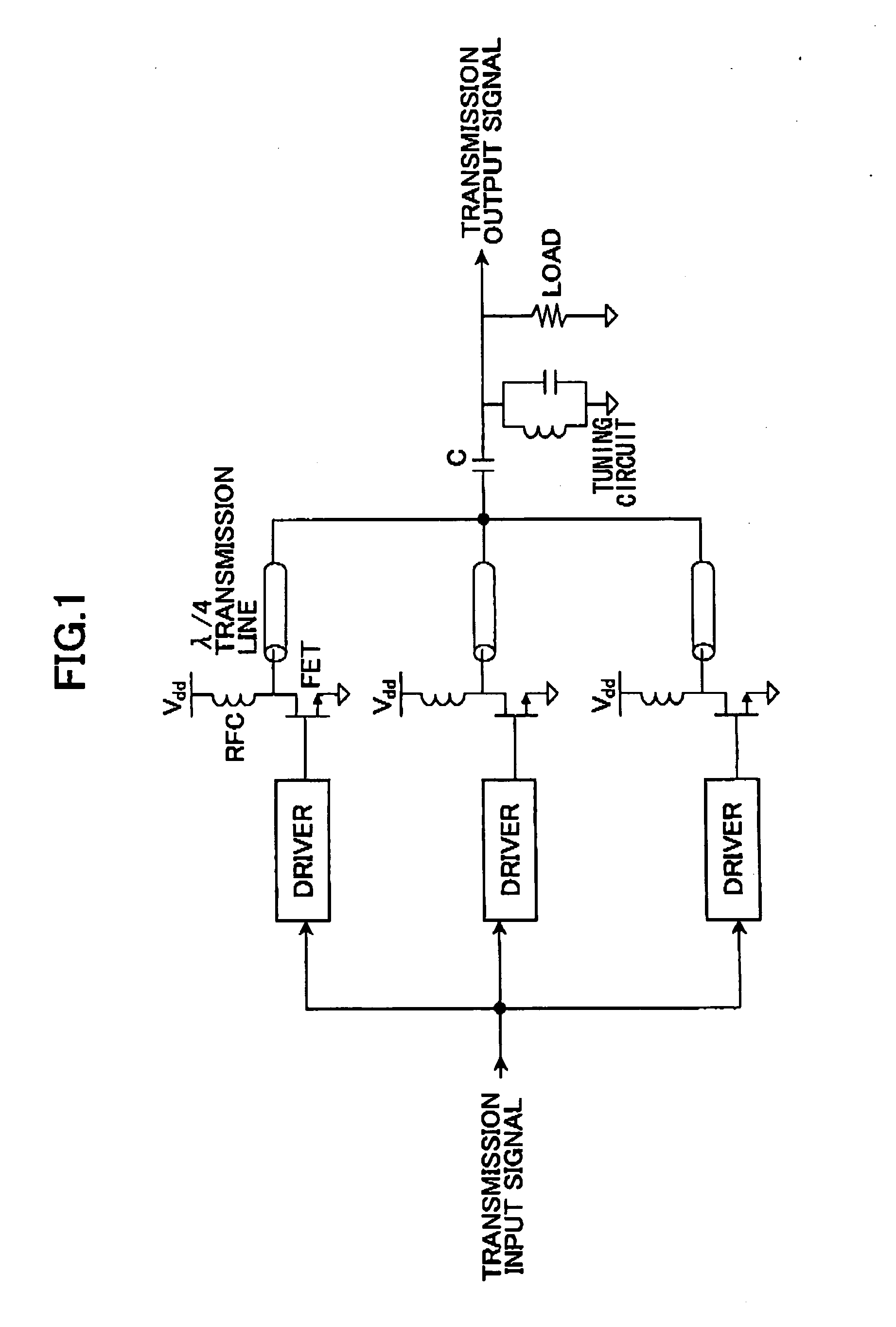
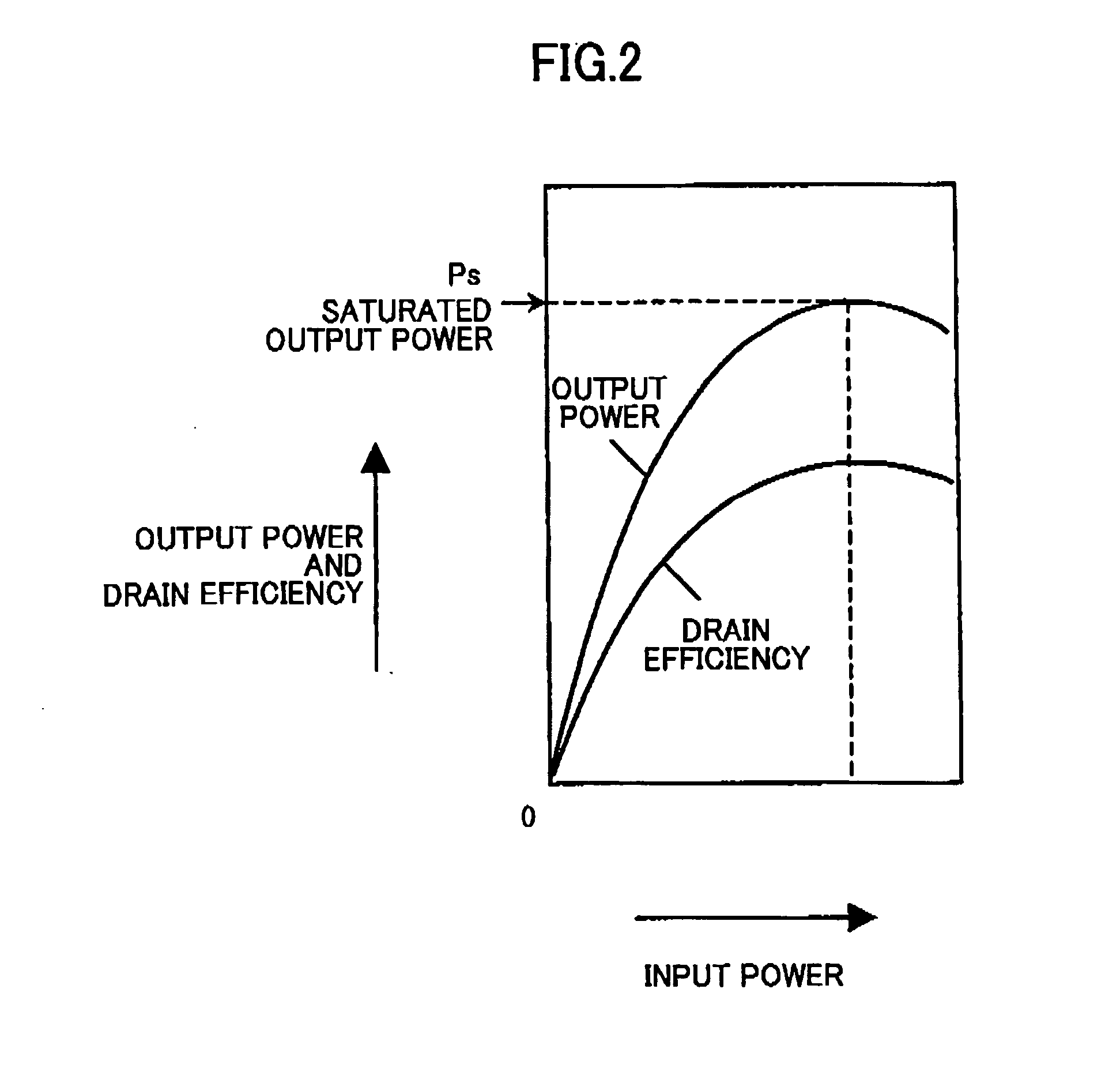
Power amplifier
InactiveUS20050030104A1Highly efficiently controlled transmission powerContinuous levelAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
A power amplifier (1) for receiving and amplifying an input signal (10) and outputting an output signal (11) is disclosed. The power amplifier comprises: N power amplifying units (12) (N is an integer larger than 1) connected in parallel so as to output amplified signals in response to the input signal (10); an output combining unit (14) for combining the output signals from the N power amplifying units (12) and outputting a combined signal as the output signal (11) of the power amplifier; and an amplitude controlling unit (15) for selectively turning ON each of the N power amplifying units (12) based on an amplitude of the input signal (10). In the power amplifier, the amplitude controlling unit (15) may comprise N amplitude adjusters (113) connected in parallel for adjusting the amplitude of the input signal (110) of the power amplifier; and a controller (115) for selectively turning ON each of the N power amplifying units (112) and controlling the amplitude adjusters (113) so that an amplitude of the output signal (111) becomes a substantially continuous function with respect to the amplitude of the input signal (110). The power amplifier may further comprise a local oscillator (222) outputting an constant envelope signal, receiving a modulation signal (210) as the input signal of the power amplifier and outputting an amplified modulated signal (211) as the output signal of the power amplifier; wherein the N power amplifying units comprise N saturation amplifying units connected in parallel so as to amplify the constant envelope signal from the local oscillator; and the amplitude controlling unit comprises an amplifying controller (215) for selectively turning ON each of the N saturation amplifying units (212) based on an amplitude of the modulation signal (210).
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
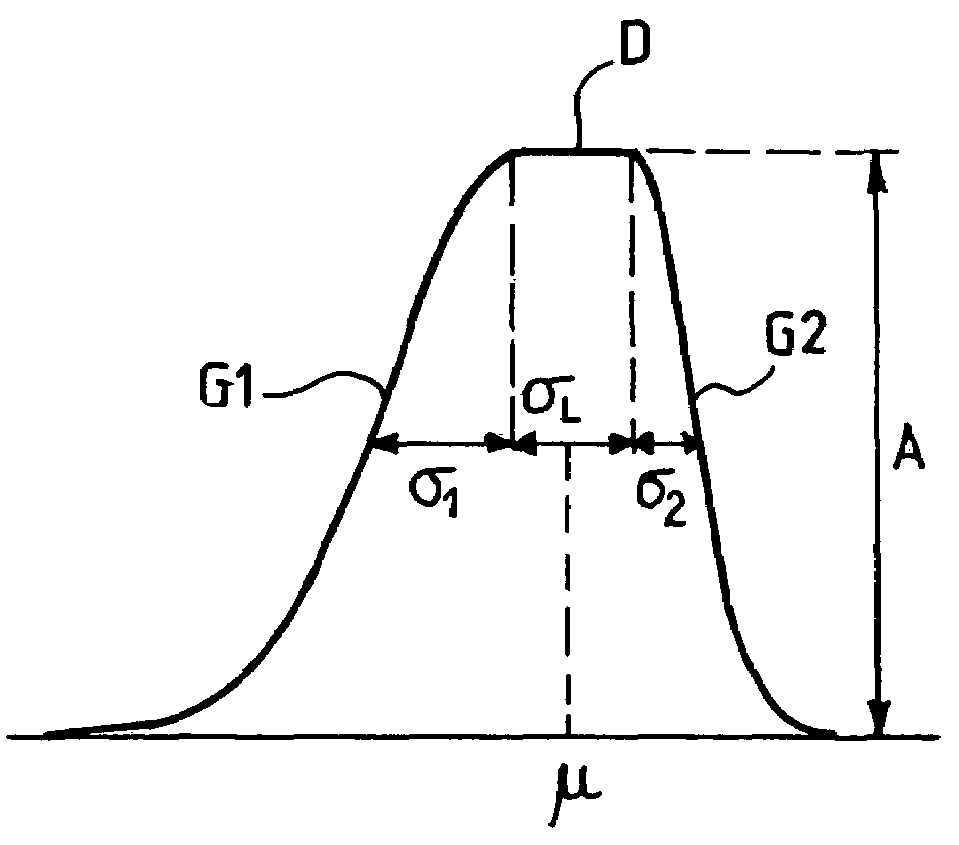
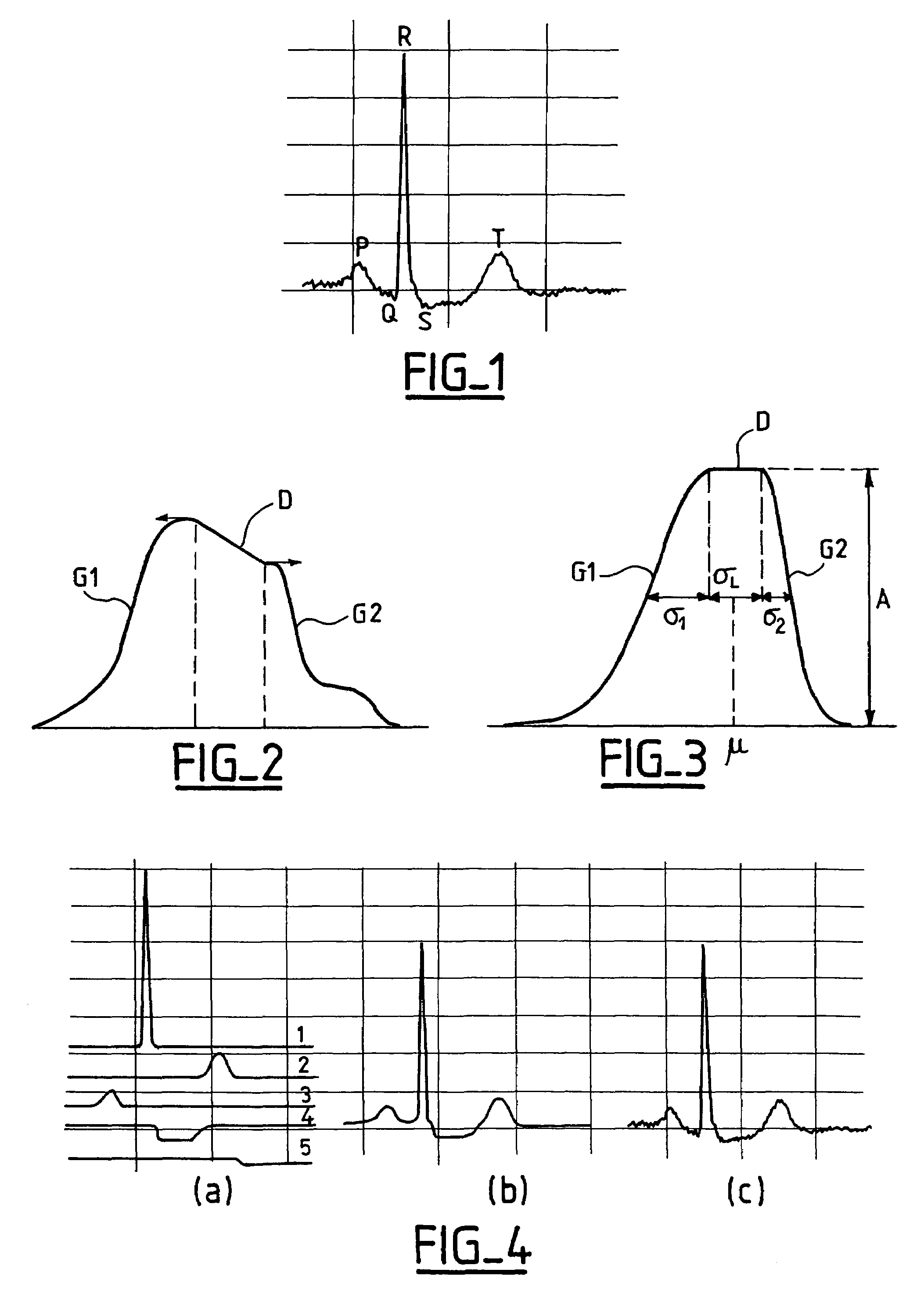
Device for analysis of a signal, in particular a physiological signal such as an ECG signal
InactiveUS7359749B2Reduce disadvantagesLimited data-processing resourceElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisEcg signalGaussian function
A device for analyzing a physiological signal, such as an electrocardiogram or electrogram, that was previously collected, filtered, sampled and digitized. The device memorizes the digitized signal and analyzes it by decomposing the signal into a plurality of N parameterized bump functions, where each bump function is a continuous function defined by three successive intervals, respectively, a first monotonic parameterized function, an affine function, and a second monotonic parameterized function, with one of the monotonic parameterized functions being increasing and the other decreasing. The parameterized functions are preferably half-Gaussian functions, and the affine function preferably has a null slope. Each N bump function is classified by recognizing at least one parameter characteristic of each wave, and allotting a standardized label, selected among a plurality of predetermined labels, according to one or to more of the characteristic parameters thus recognized.
Owner:ELA MEDICAL
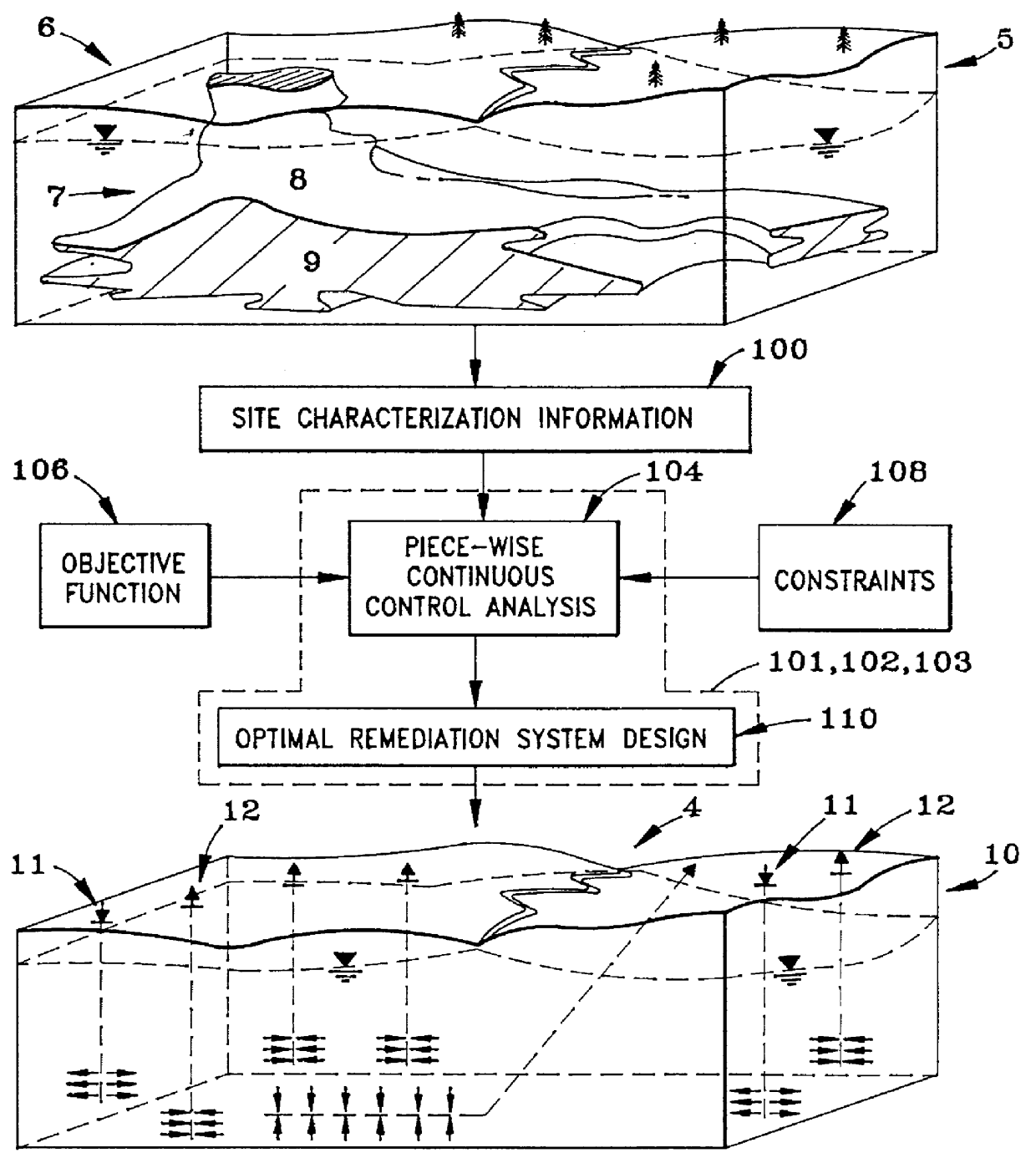
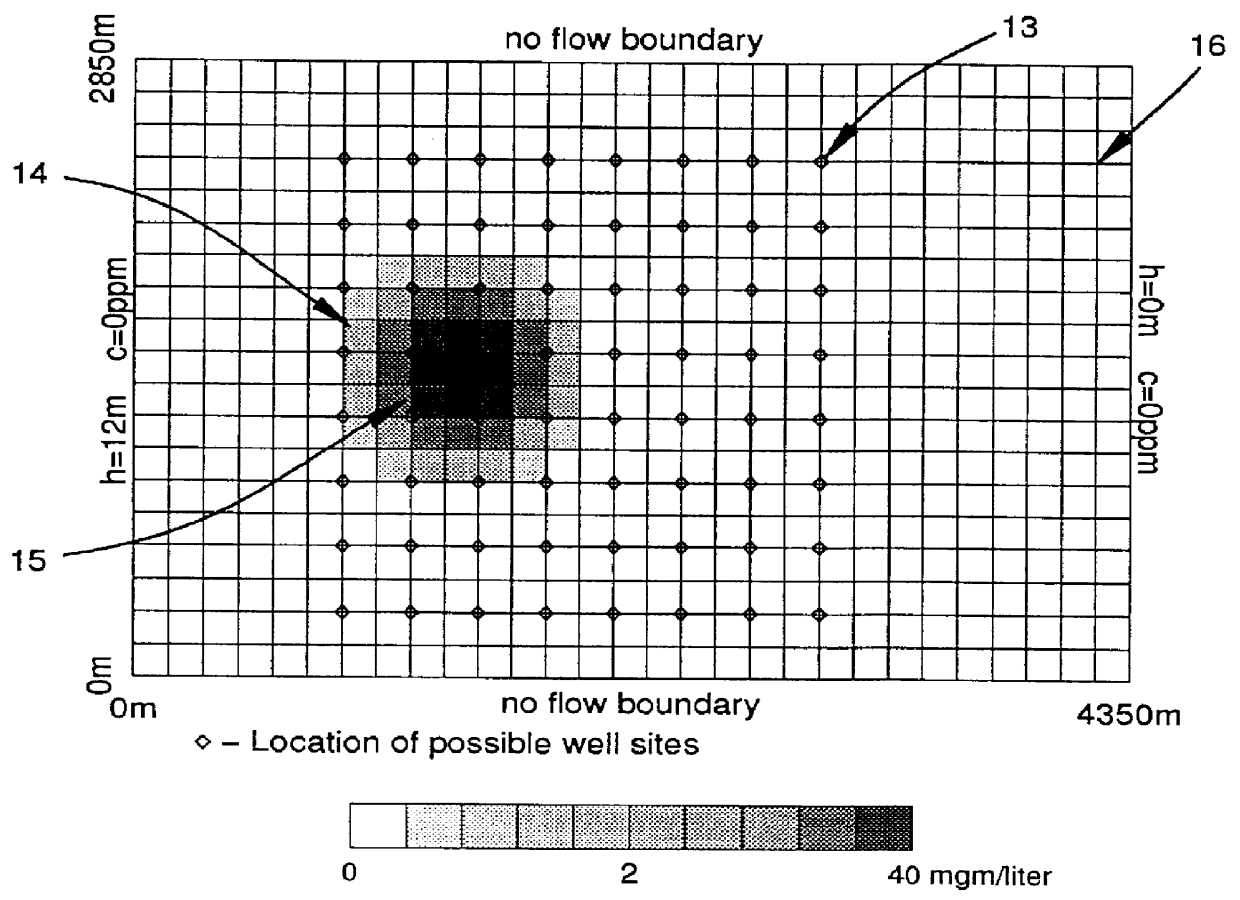
Piecewise continuous control of groundwater remediation
InactiveUS6151566AGood flexibilityMaximize efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationAnalogue computers for heat flowTime functionGroundwater remediation
A piecewise continuous-time dynamic control method and apparatus for optimizing remediation of groundwater is disclosed. The piece-wise continuous control process is used to generate efficient designs for rededication systems based on differentiable groundwater models. The remediation strategies generated are characterized by piece-wise continuous functions of time which dictate the operation of remediation devices. The piece-wise continuous functions may change discontinuity at the end of each management period, or optionally, a finite number of times during each management period. The duration and number of management periods covering a groundwater cleanup may be selected by the user of the invention to maximize the contamination removal efficiency and reflect the mechanical limitations of the specific rededication devices chosen. The continuous-time property of piece-wise continuous control requires simpler (usually sparse) derivatives of a groundwater model than the derivatives required by static and discrete-time control of groundwater remediation.
Owner:WHIFFEN GREG
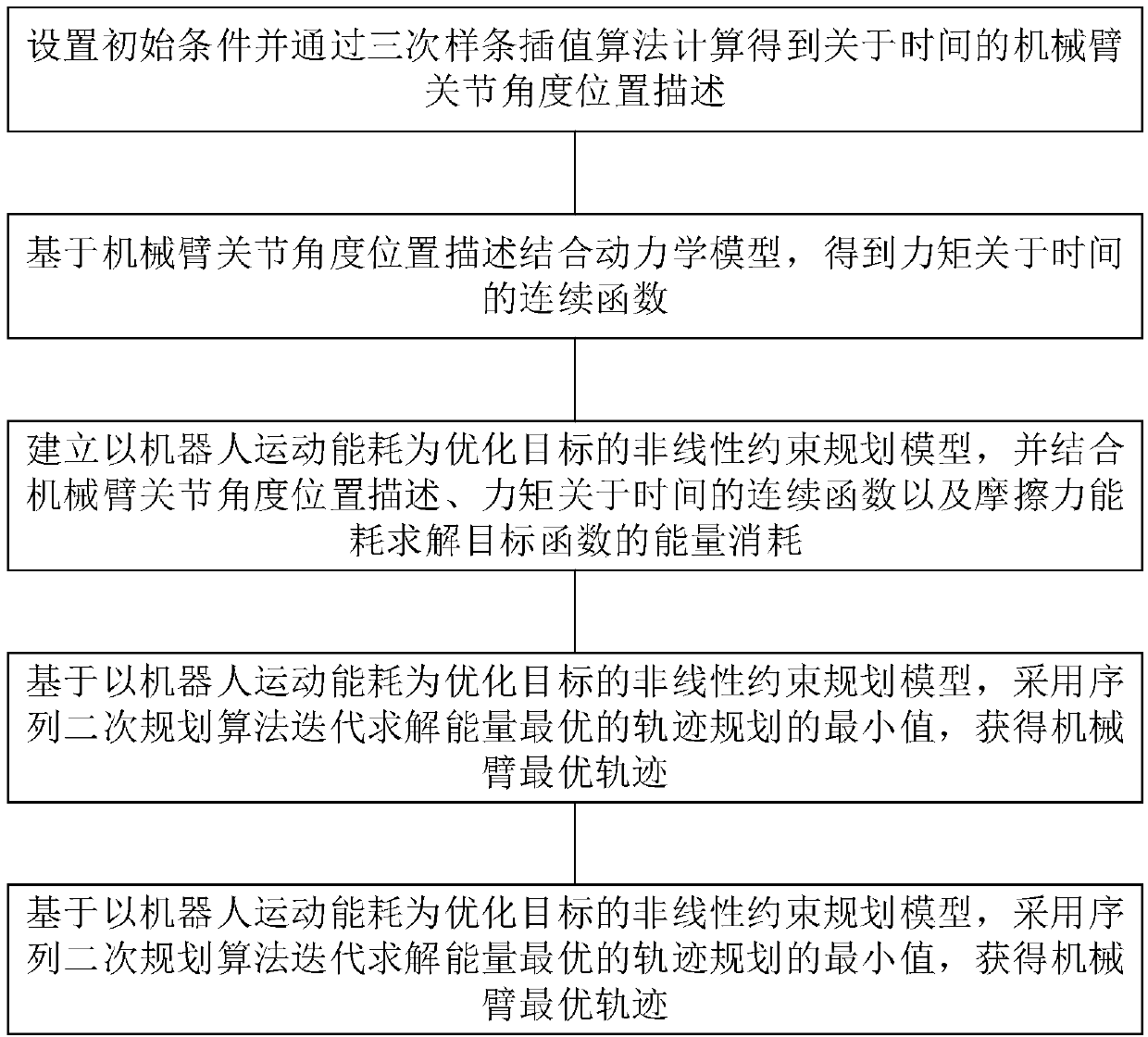
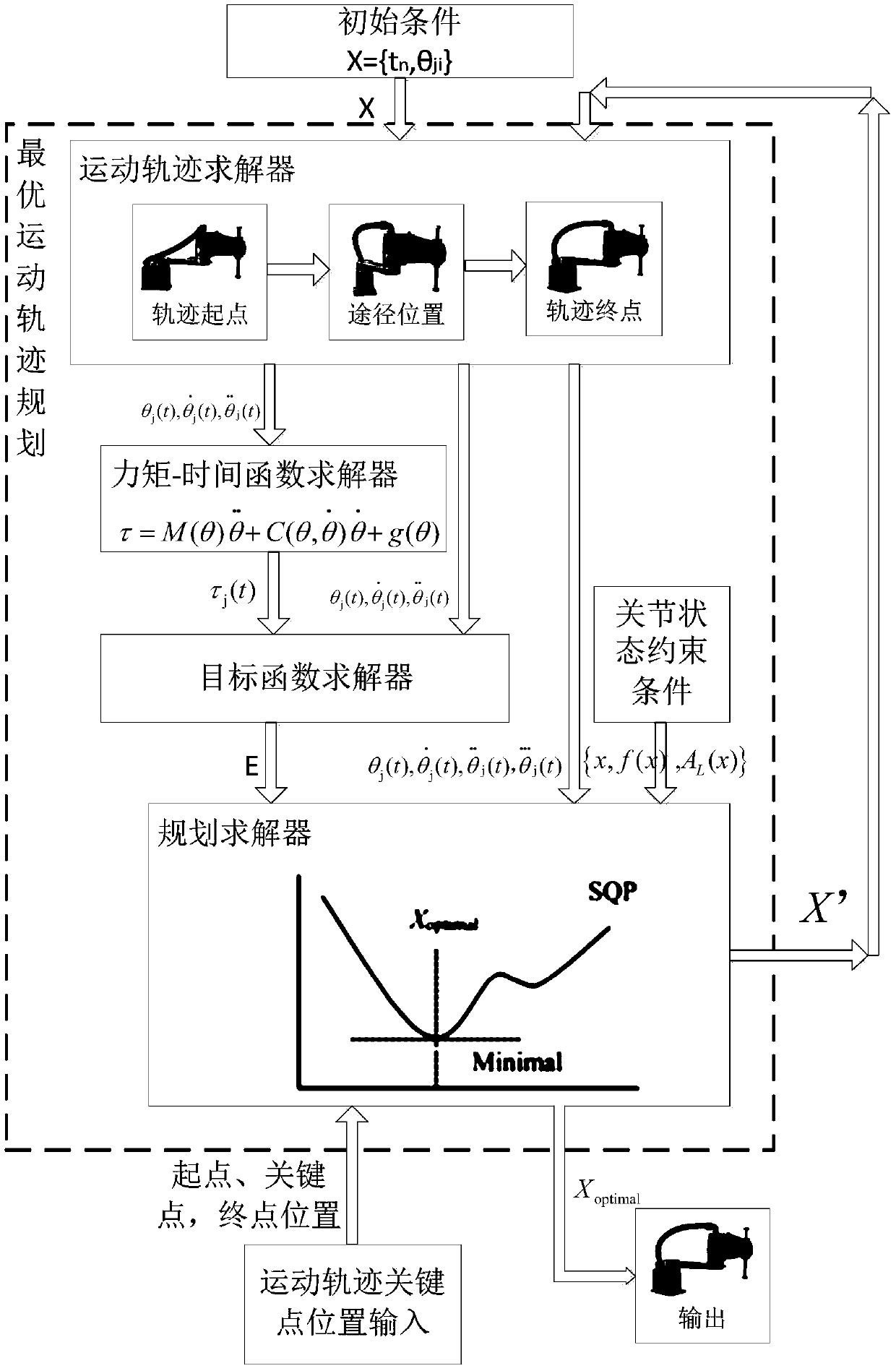
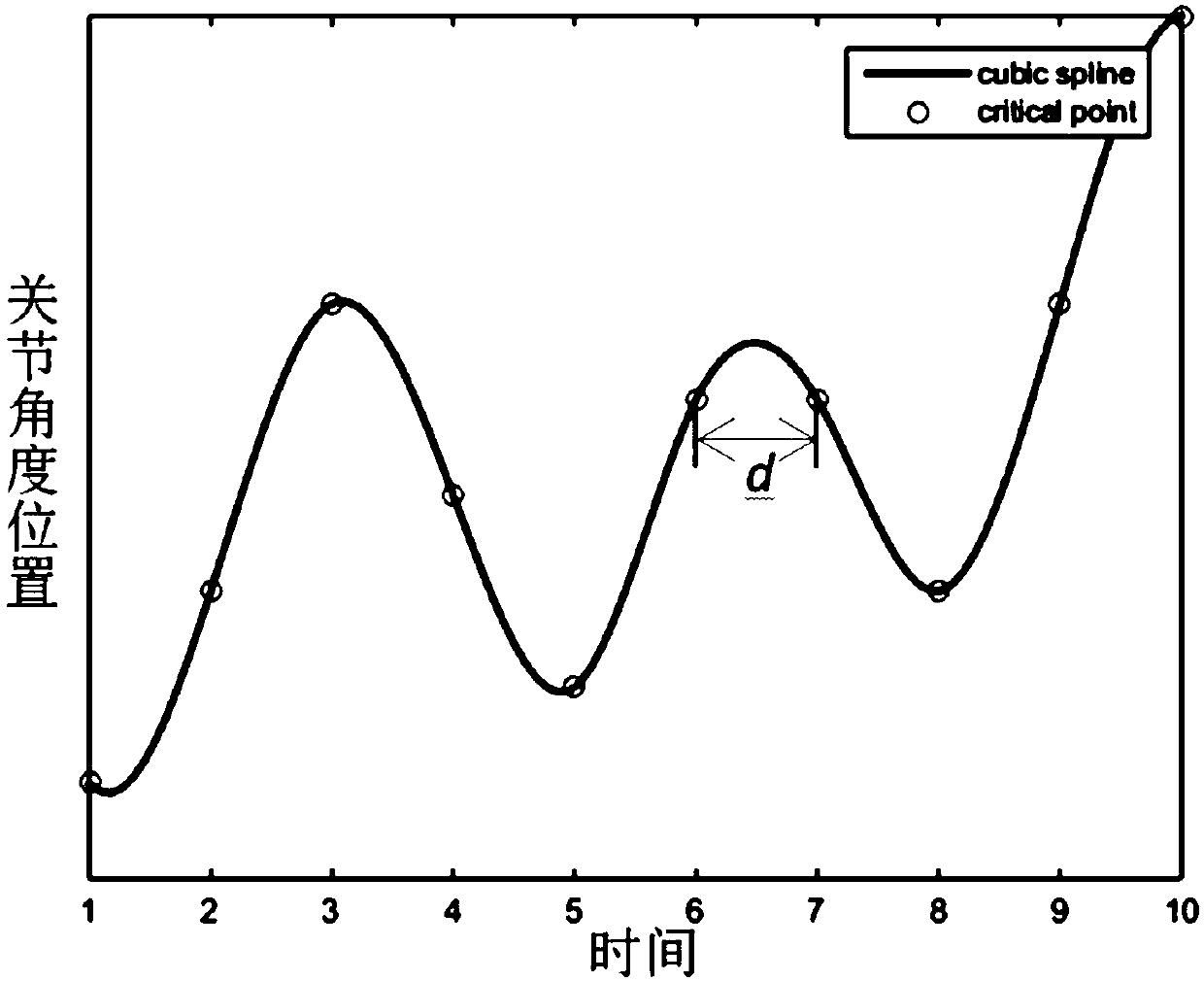
Model-constraint-based mechanical arm energy optimal trajectory planning control method and device
PendingCN108621157AReduce consumptionImprove real-time performanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDynamic modelsEngineering
The invention relates to a model-constraint-based mechanical arm energy optimal trajectory planning control method and device. The model-constraint-based mechanical arm energy optimal trajectory planning control method comprises the steps that initial conditions are set and mechanical arm joint angle position description with respect to time is calculated and obtained through a cubic spline interpolation algorithm; on base of the mechanical arm joint angle position description and in combination with a dynamics model, a continuous function of moment with respect to time is obtained; a nonlinear constrained planning model taking mechanical arm movement energy consumption as the optimizing target is established, and in combination with the mechanical arm joint angle position description, thecontinuous function of the moment with respect to time and friction force energy consumption, energy consumption of a target function is solved; and on base of the nonlinear constrained planning model taking mechanical arm movement energy consumption as the optimizing target, the minimum value of energy optimal trajectory planning is iteratively solved adopting a sequential quadratic planning algorithm, and a mechanical arm optimal trajectory is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the model-constraint-based mechanical arm energy optimal trajectory planning control method and device do notneed a large number of complex calculation and have good real-time performance, and energy consumption is least.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and apparatus based on coplanar striplines
ActiveUS20050068116A1Overcome coplanar stripline lossFacilitate low loss single mode operationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMode controlClosed loop
Methods and apparatus for implementing standing wave oscillators (SWOS) using coplanar striplines (CPS). One example is given by a quarter-wavelength (λ / 4) coplanar stripline standing wave oscillator (SWO), while another implementation utilizes a closed-loop coplanar stripline configuration. In various aspects, SWOs are configured to optimize sinusoidal performance at high frequencies with low power dissipation by incorporating various features that dramatically increase the quality factor Q of the oscillator. In particular, in one aspect, an amplitude-dependent tailored distributed amplification scheme is employed as a mode control technique using multiple amplifiers having different gains along the length of the coplanar stripline. In another aspect, a coplanar stripline configured such that its resistance per unit length R and conductance per unit length G are discreet or continuous functions of position along the coplanar stripline is employed to reduce SWO losses. In another aspect, an enhancement of the quality factor Q is achieved while at the same time reducing the phase velocity of waves propagating in the SWO, thereby also facilitating the fabrication of relatively smaller devices. In yet another aspect, SWOs are configured with frequency adjustability that is again optimized to reduce power dissipation while facilitating significant adjustments of oscillator frequency.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Realistic video color display
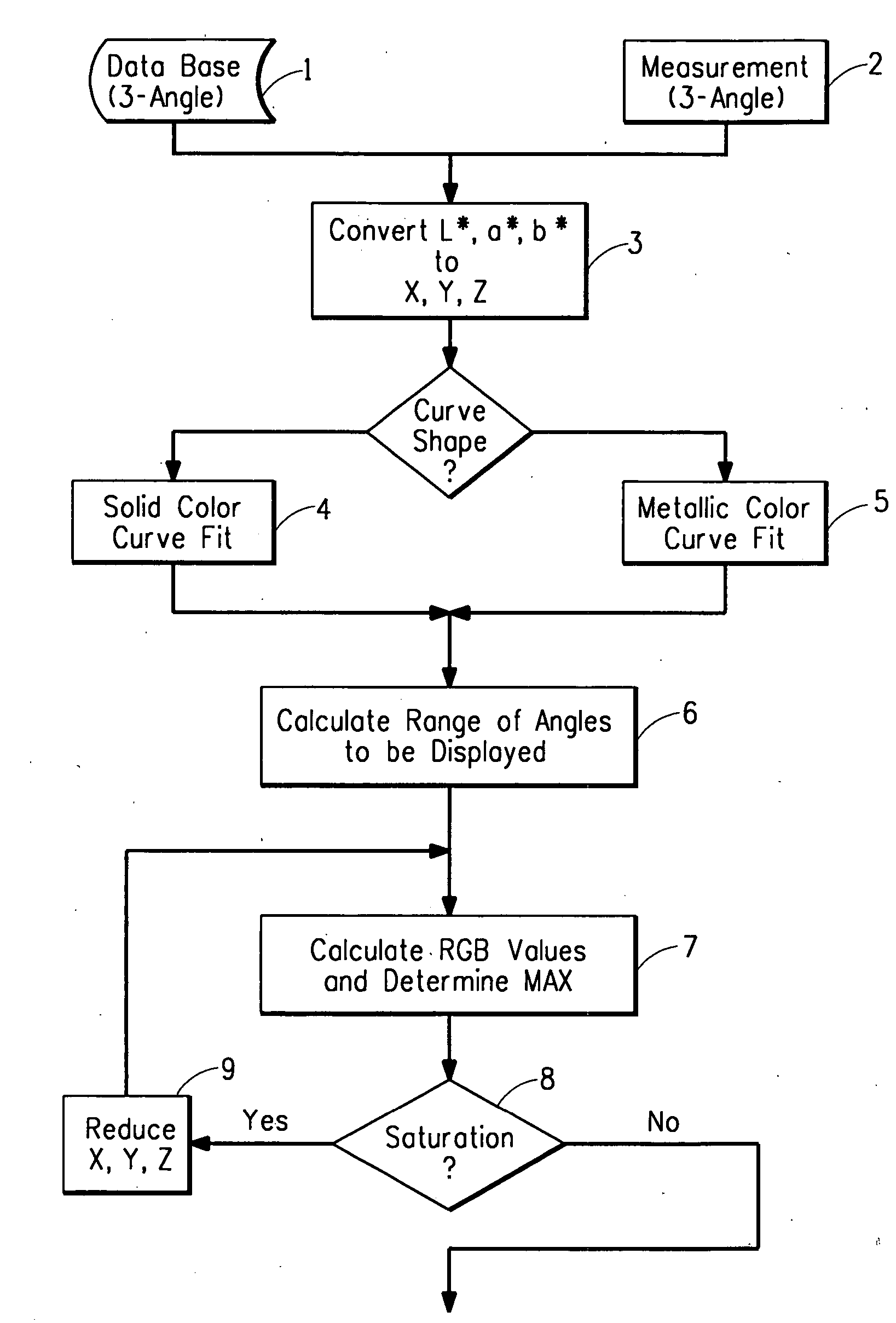
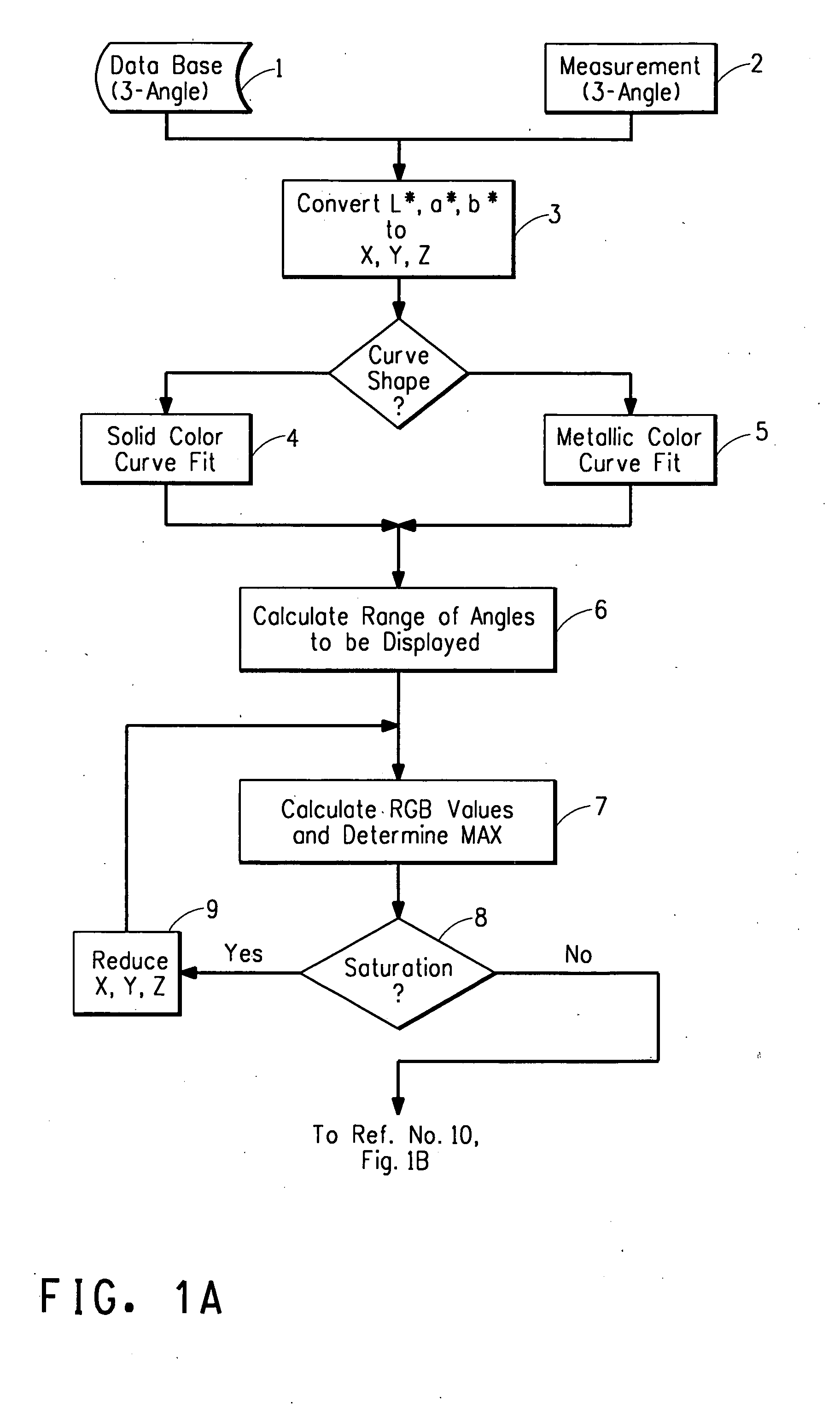
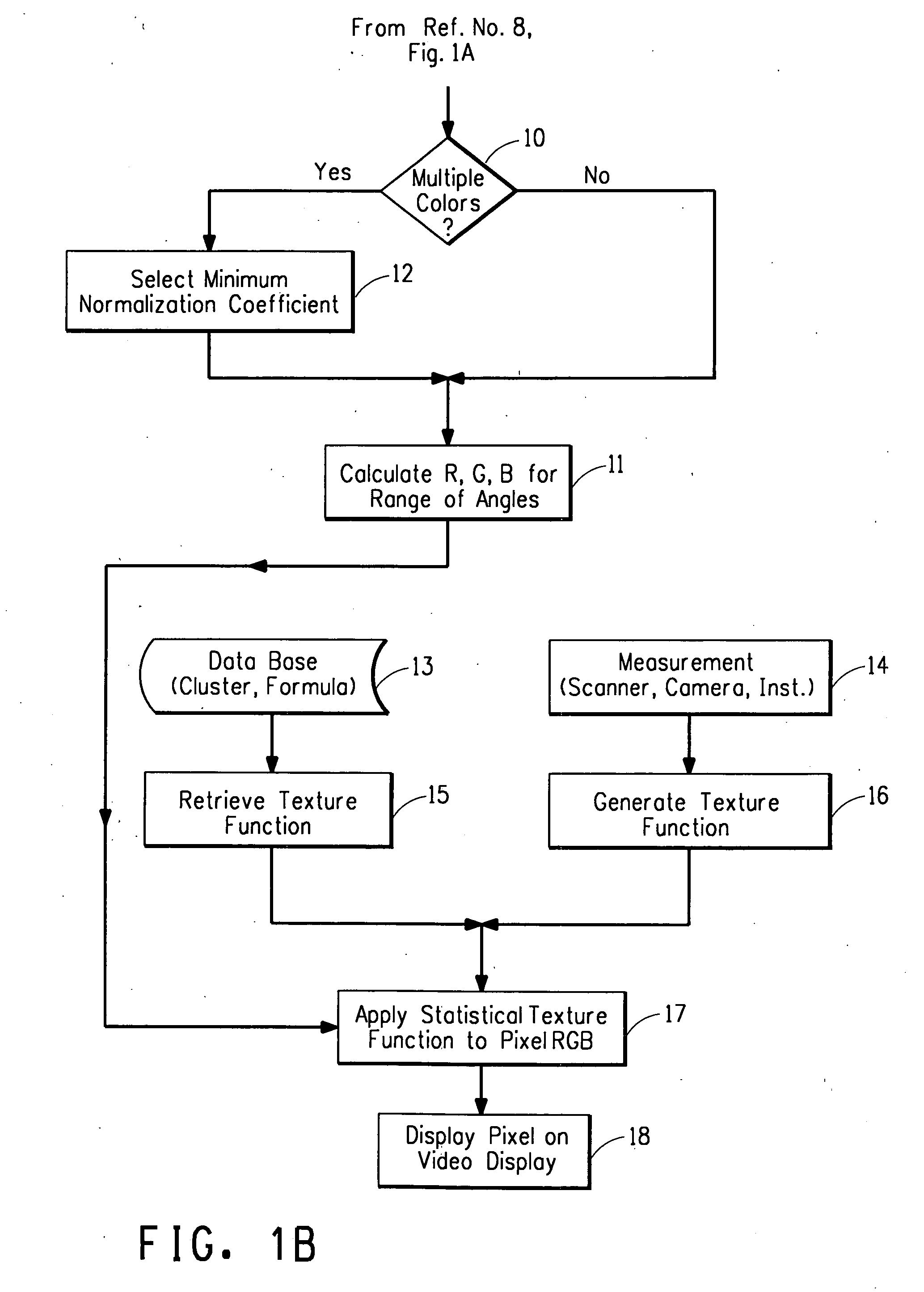
A computer-implemented method for displaying on a color display device a realistic color of a paint coating comprising the following steps: (A) identify L*, a* b* color values at at least three different angles for a paint coating from a data base; (B) convert the at least three angle L*, a* b* color values to tristimulus X, Y, Z values; (C) develop continuous function equation for each tristimulus X, Y, Z values vs. aspecular angle via computer implementation and calculate the range of angles to be displayed; (D) calculate a range of aspecular angles required to display the object; (E) calculate R,G,B values from tristimulus values over the range of aspecular angles and determine maximum saturation of R,G,B values and bring into range allowed by color display device; (F) determine statistical texture function of paint coating to be simulated; and (G) apply statistical texture function to the R,G,B values of step (E) and display color pixels on color display device to show realistic color of paint coating.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Real-time computing method for theoretical line loss of low-voltage distribution room
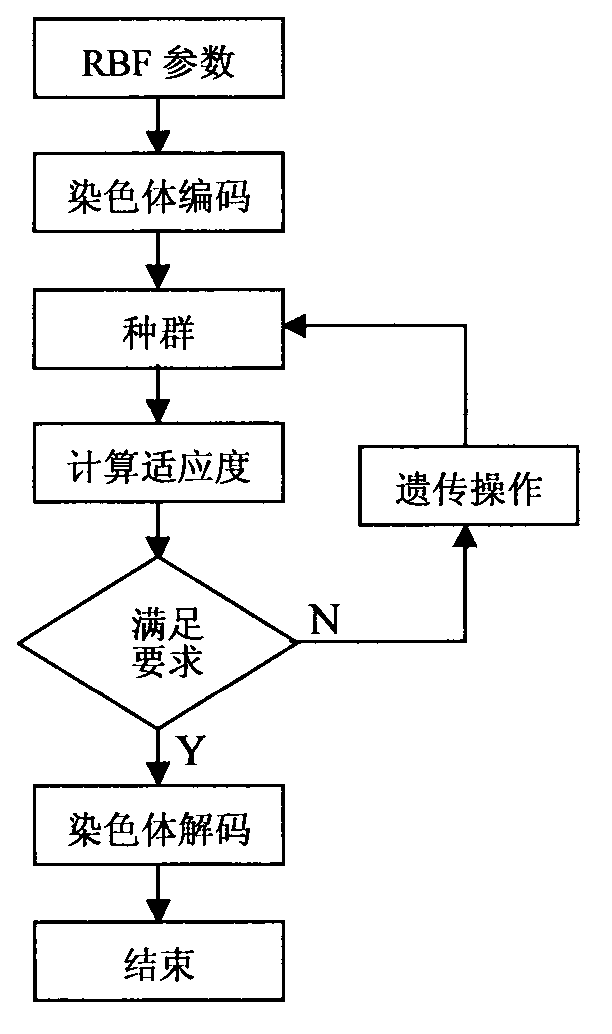
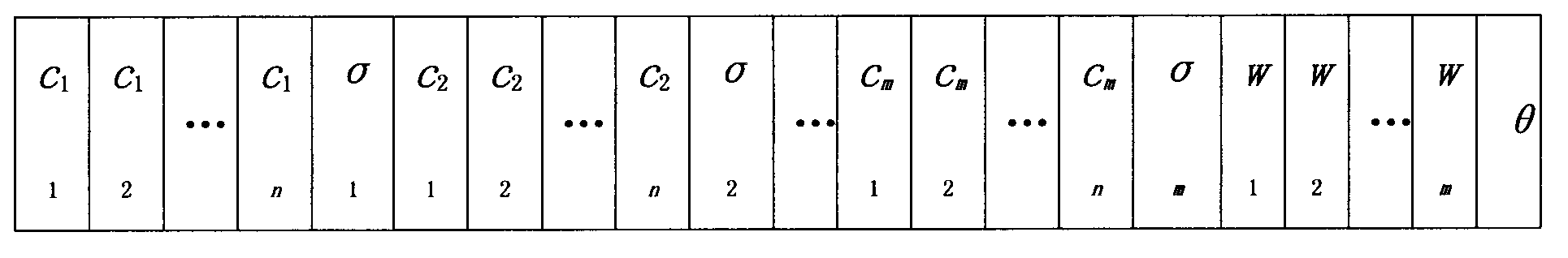
InactiveCN103577679AEasy to implementImprove calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsLow voltage
The invention discloses a real-time computing method for the theoretical line loss of a low-voltage distribution room with dynamic change of the number of users and the power consumption. The real-time computing method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting the type of a model, utilizing the unique optimal approximation character of an RBF (Radial Basis Function) neural network, i.e., any continuous function can be approximated by any precision, adopting the RBF neural network with an online learning function to establish a dynamic model for a power supply and distribution system in the low-voltage distribution room; (2) determining the structure of the model, and determining the structure of the neural network model (neuron) according to the number of the users and the power consumption characteristic in the low-voltage distribution room; (3) identifying parameters of the model; (4) carrying out computation on the theoretical line loss by utilizing the model. The real-time computing method has the advantages that the implementation method is simple, and the neuron network is adopted for constructing the system model, so that the influence of external factors on results is reduced, and further the computing precision is high.
Owner:深圳龙电华鑫控股集团股份有限公司 +1
Robust detection and classification of objects in audio using limited training data
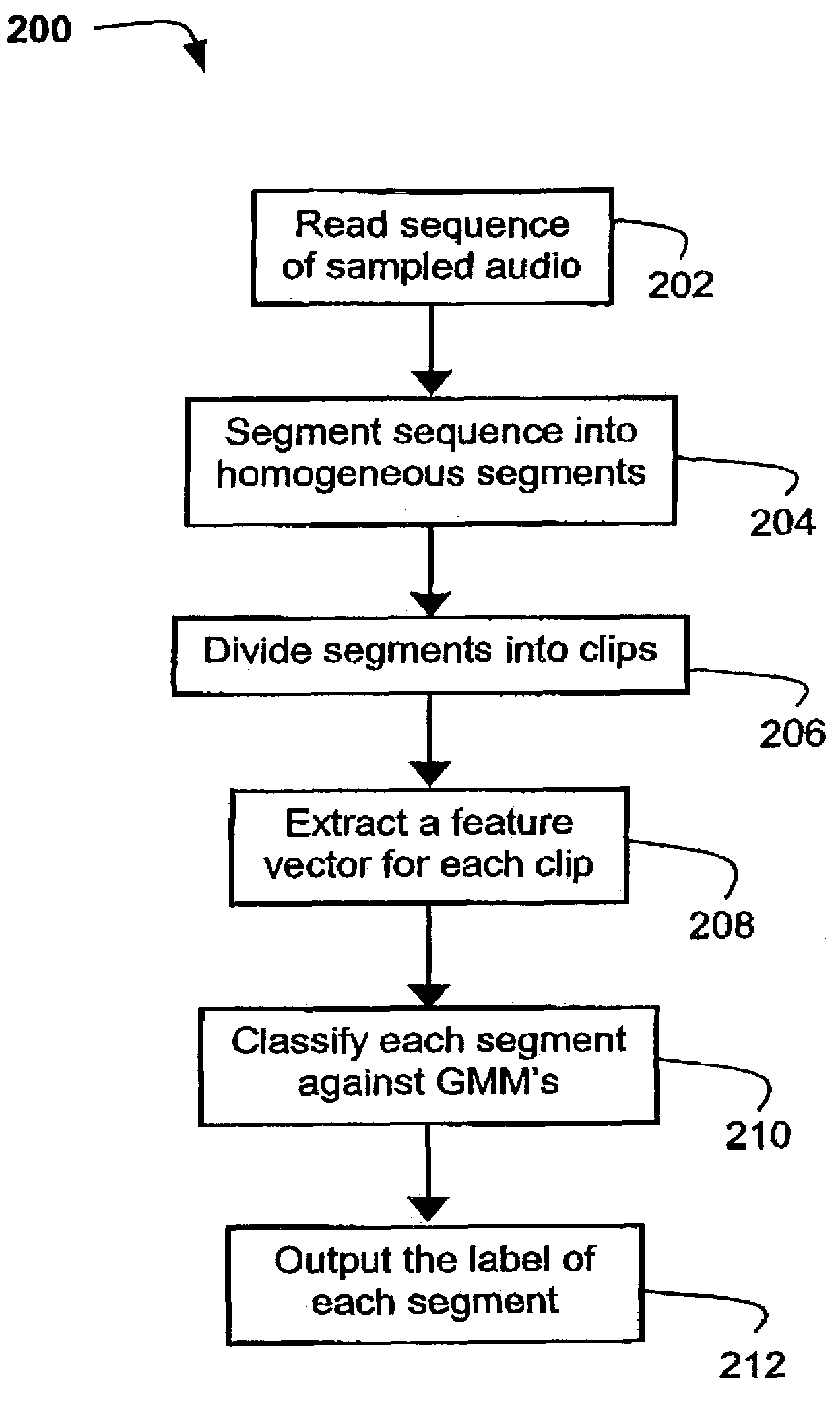
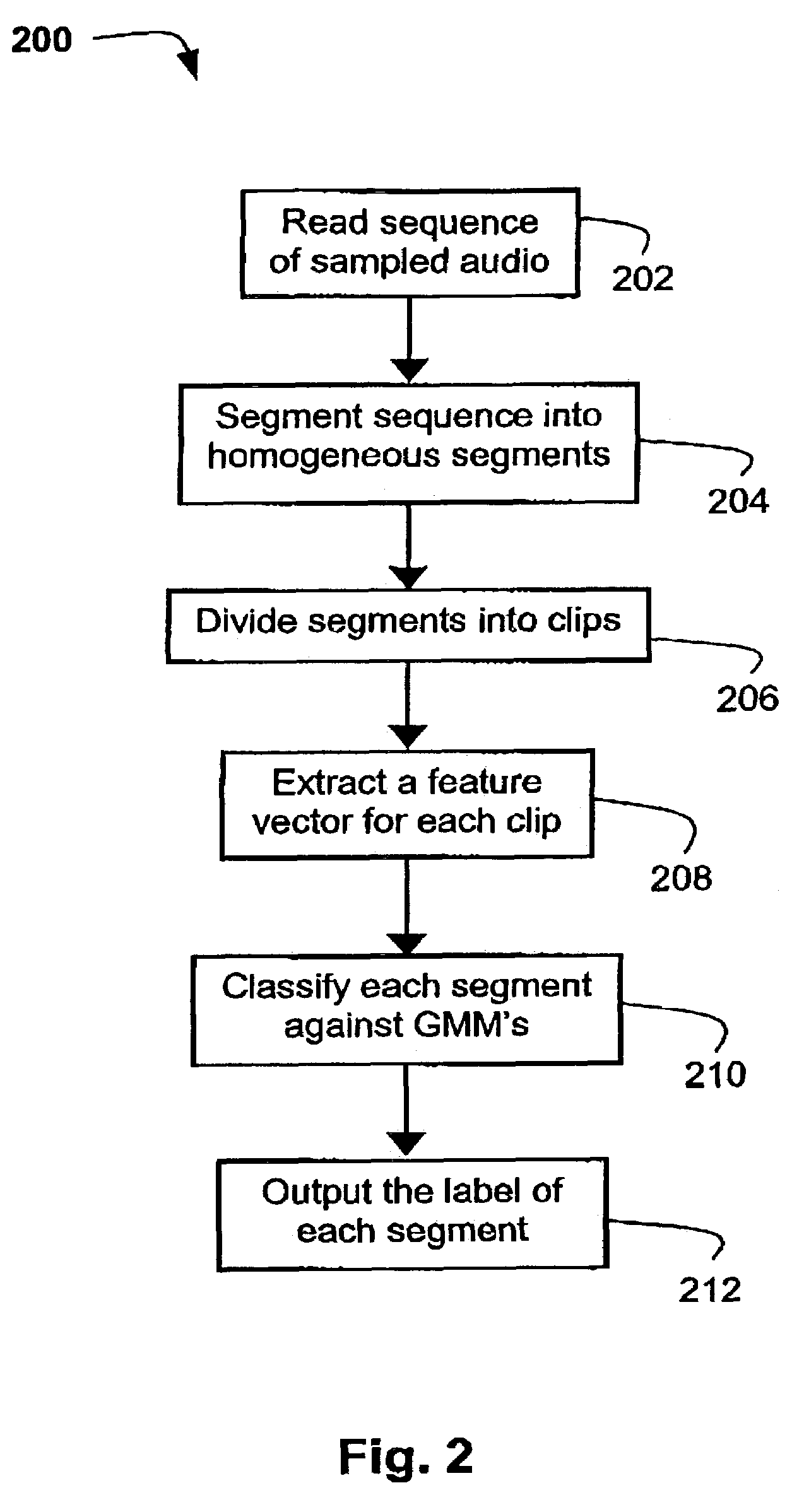
InactiveUS7263485B2More disadvantageSpeech recognitionVolume compression/expansionFeature vectorContinuum function
A method (200) and apparatus (100) for classifying a homogeneous audio segment are disclosed. The homogeneous audio comprises a sequence of audio samples (x(n)). The method (200) starts by forming a sequence of frames (701-704) along the sequence of audio samples (x(n)), each frame (701-704) comprising a plurality of the audio samples (x(n)). The homogeneous audio segment is next divided (206) into a plurality of audio clips (711-714), with each audio clip being associated with a plurality of the frames (701-704). The method (200) then extracts (208) at least one frame feature for each clip (711-714). A clip feature vector (f) is next extracted from frame features of frames associated with the audio clip (711-714). Finally the segment is classified based on a continuous function during the distribution of the clip feature vectors (f).
Owner:CANON KK
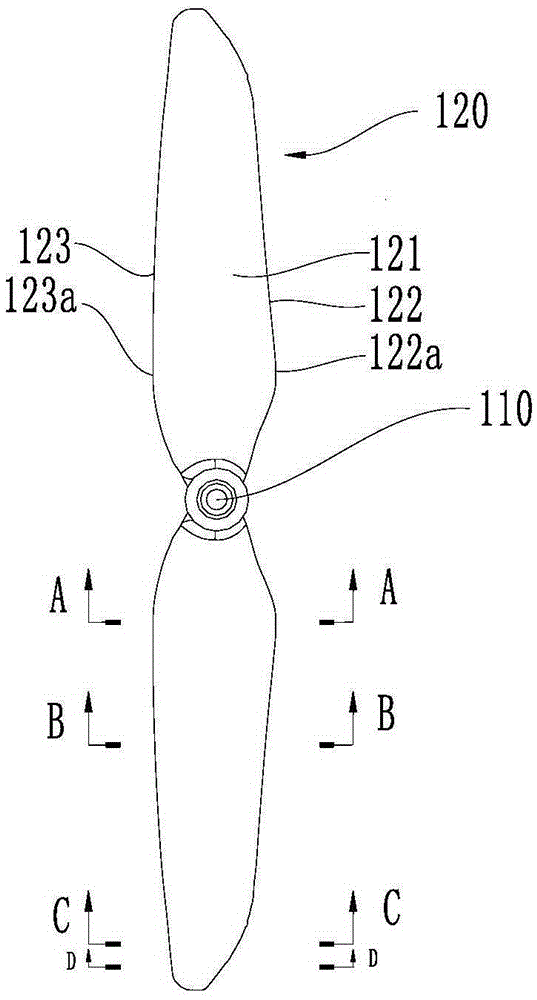
Screw propeller and aerocraft
The invention relates to the technical field of an aerocraft, in particular to a screw propeller and the aerocraft. The screw propeller comprises an oar hoop and at least two blades which are connected with the oar hoop, wherein at a position (the proportion of the distance from the position to the center of the oar hoop to the radius of the screw propeller is P), the attack angle of the blades is beta, beta is the continuous function of the radius proportion P and satisfies the following conditions that when P is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 25 percent, beta is more than or equal to 10 degrees and less than or equal to 12 degrees; when P is more than 25 and less than or equal to 90 percent, beta is more than or equal to 8.75 degrees and less than 12 degrees; when P is more than 90 percent and less than or equal to 100 percent, beta is more than or equal to 8 degrees and less than or equal to 9 degrees. Due to the fact that different attack angles are arranged at different positions of the blades of the screw propeller, the air resistance is reduced, the efficiency is improved, and the flying speed and the flying distance of the aerocraft are increased; due to the fact that the attack angle beta of the screw propeller is continuously changed, the stability of the screw propeller is improved, and the flying performance of the aerocraft is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUTEL INTELLIGENT AVIATION TECH CO LTD
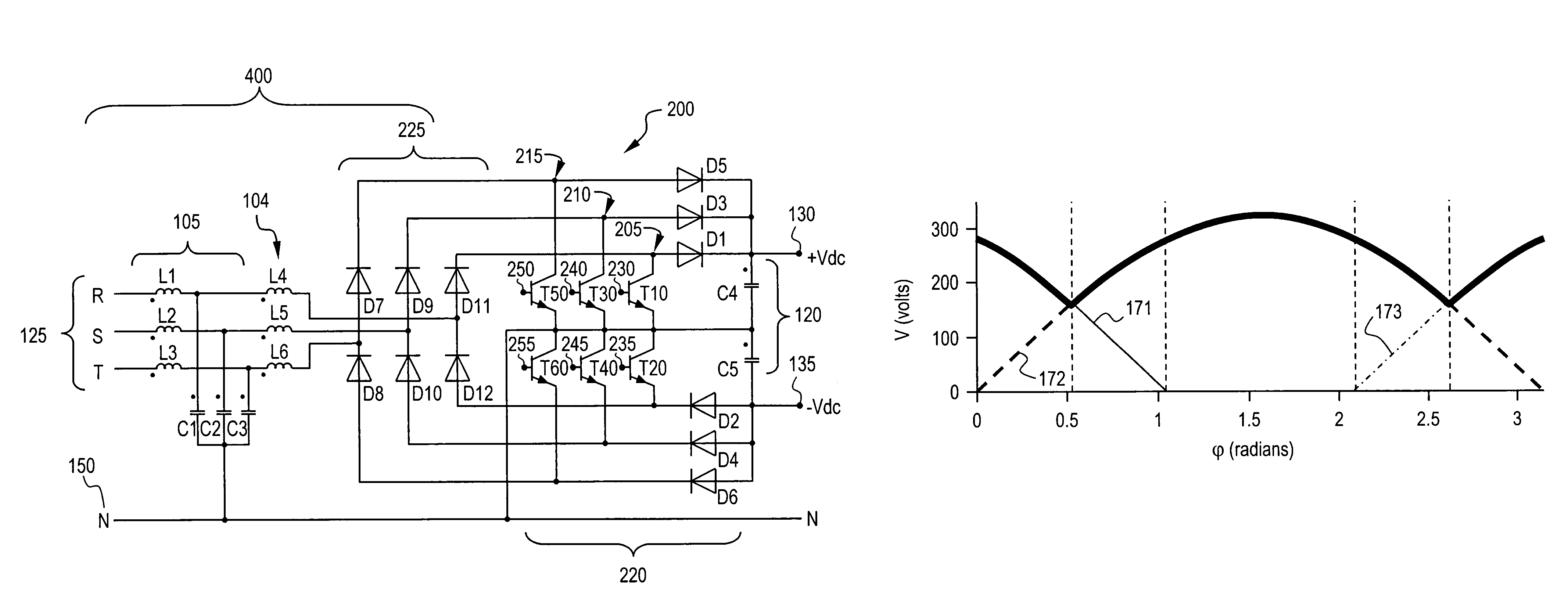
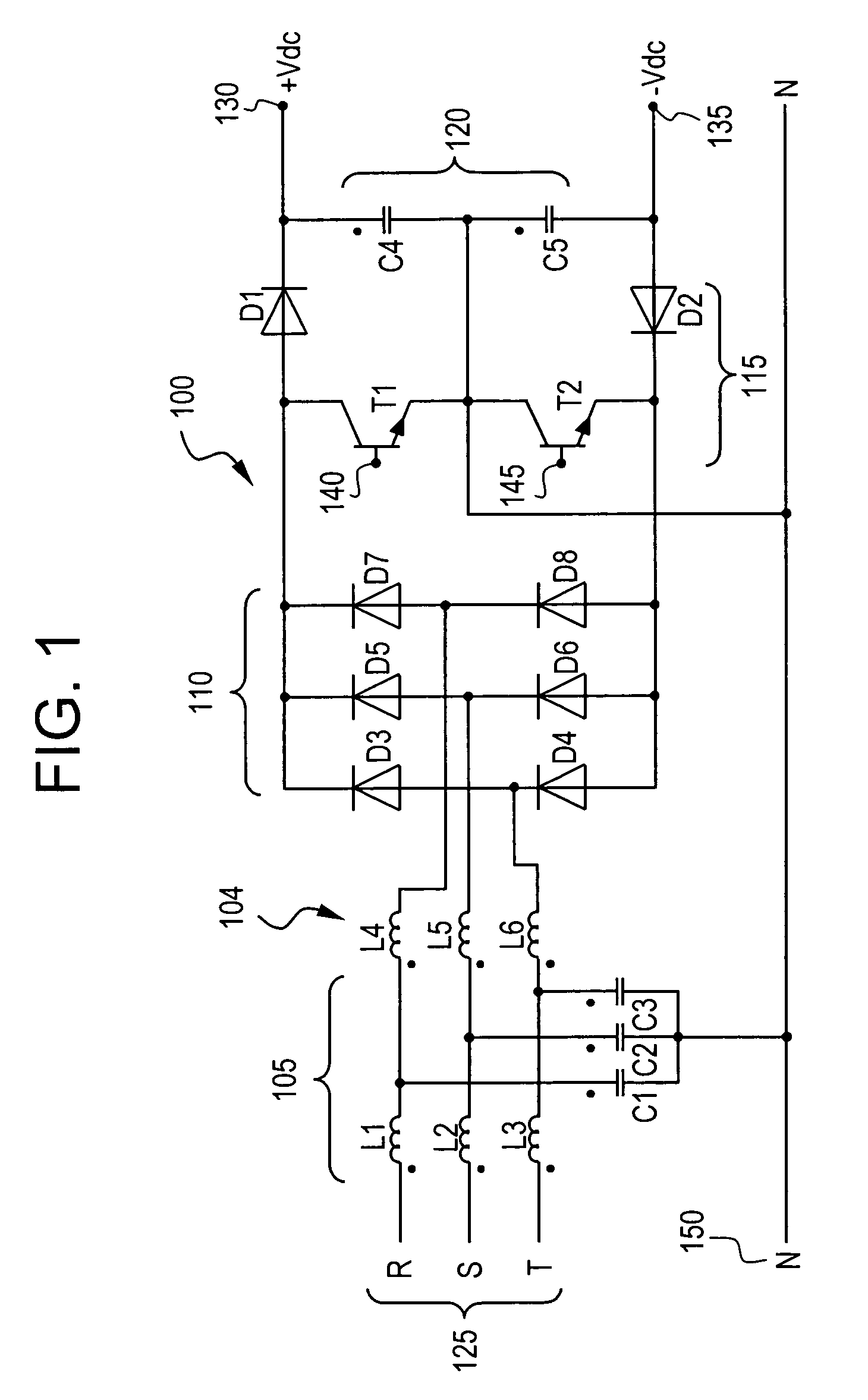
AC/DC converter and method of modulation thereof
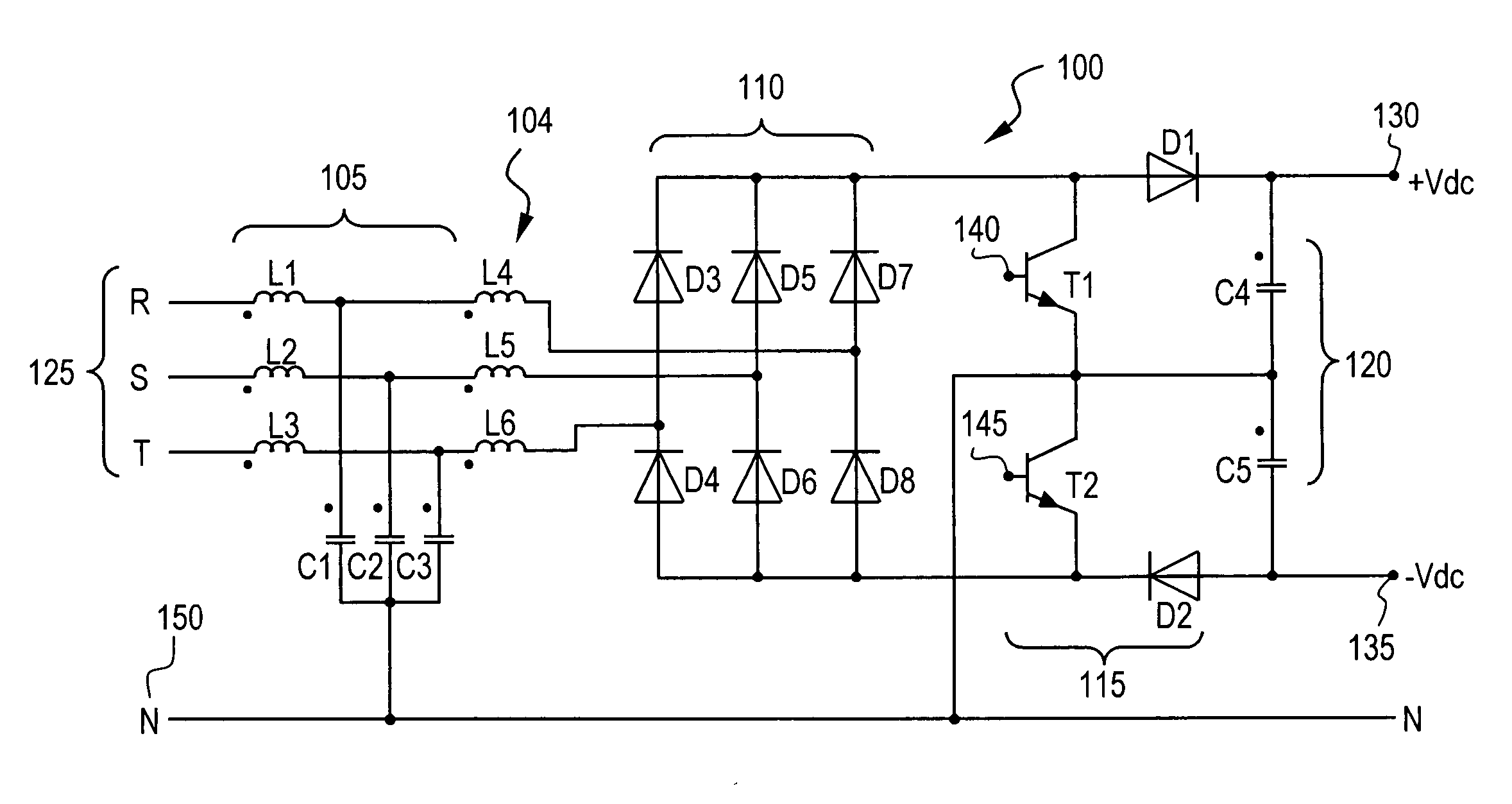
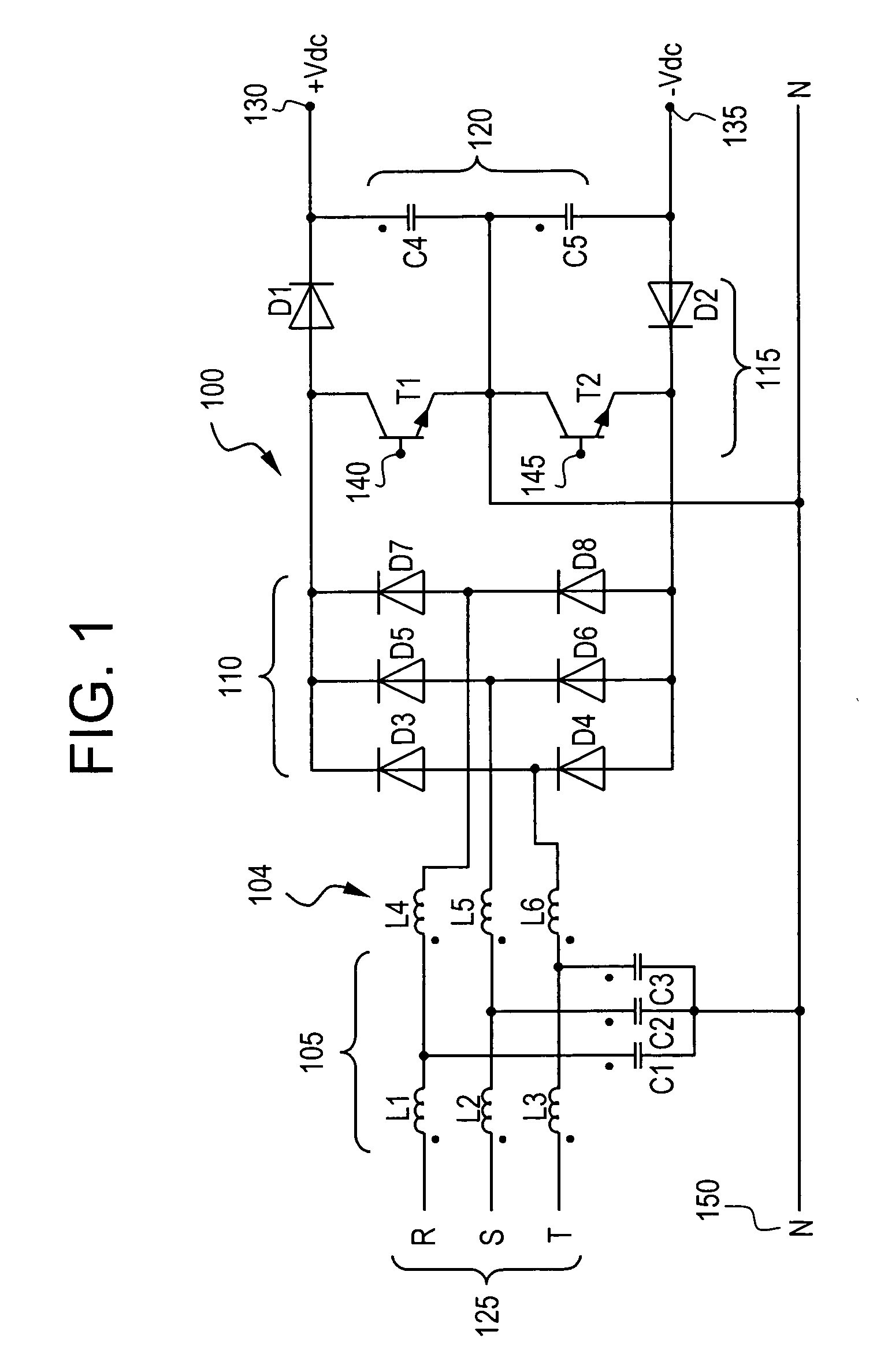
ActiveUS7375989B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcBoost rectifierEngineering
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
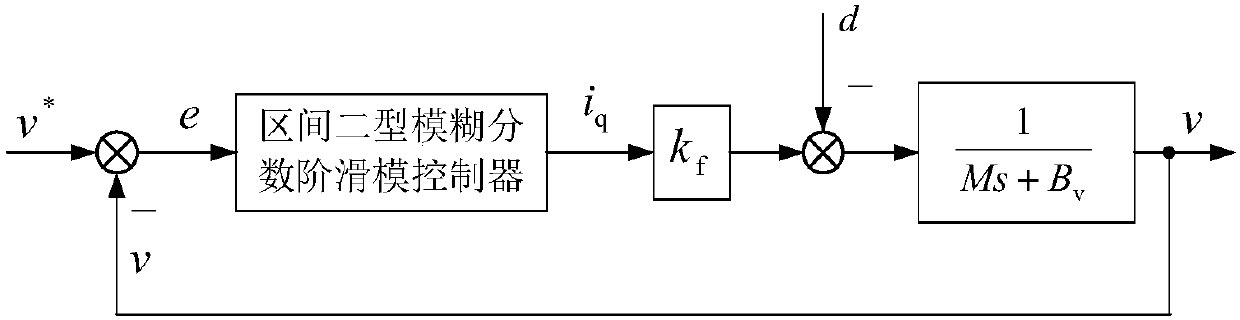
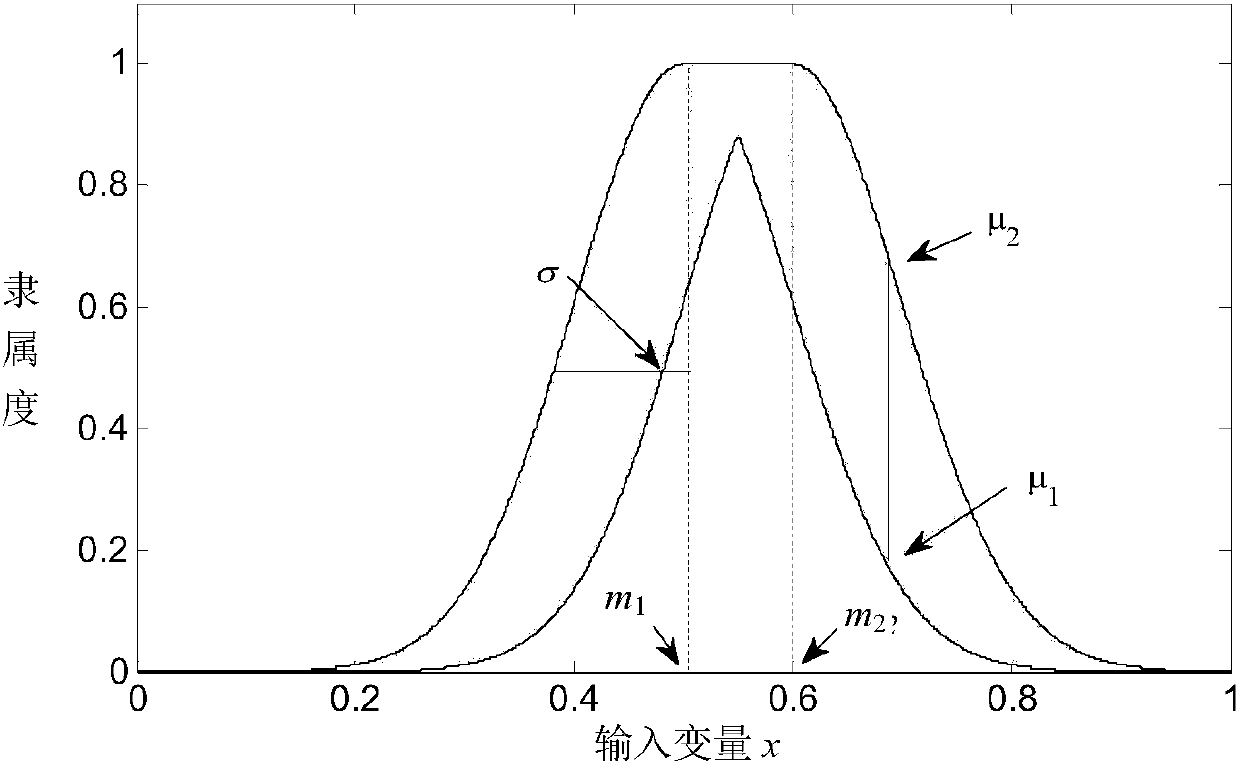
Permanent magnet linear synchronous motor second type fuzzy fractional order sliding mode control system and method
ActiveCN107070336AReduce buffetingResolve uncertaintyElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlFuzzy ruleControl system
The invention provides a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor second type fuzzy fractional order sliding mode control system and method. According to the control technology, error amount is obtained according to subtracting of the given speed signals and the feedback speed signals of a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor servo system, a fractional order sliding mode surface is designed according to the error amount, a sliding mode control switching item is designed based on the fractional order theory, the product of the gain and the discontinuous function in the switching item is replaced by using an interval second type fuzzy controller, and the system is verified to be stable according to the Lyapunov function. The interval second type fuzzy controller and the fractional order sliding mode surface are introduced in the design, and the switching item based on the fractional order differential and integral theory is adopted so that buffeting can be effectively reduced. Meanwhile, the uncertainty problem existing in the fuzzy rules of the first type fuzzy system can also be solved so that the robustness of the system can be enhanced. Finally the robustness of the system can be enhanced by the method and the buffeting phenomenon of the system can be weakened.
Owner:东能(沈阳)能源工程技术有限公司
AC/DC converter and method of modulation thereof
ActiveUS20060164873A1Minimize cost functionAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcBoost rectifierContinuum function
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
X-ray source arrangement for generating x-ray radiation
ActiveUS20190387602A1Improved and stable and reliably and arrangementImprove output characteristicsX-ray tube structural circuit elementsEfficient power electronics conversionMathematical modelControl signal
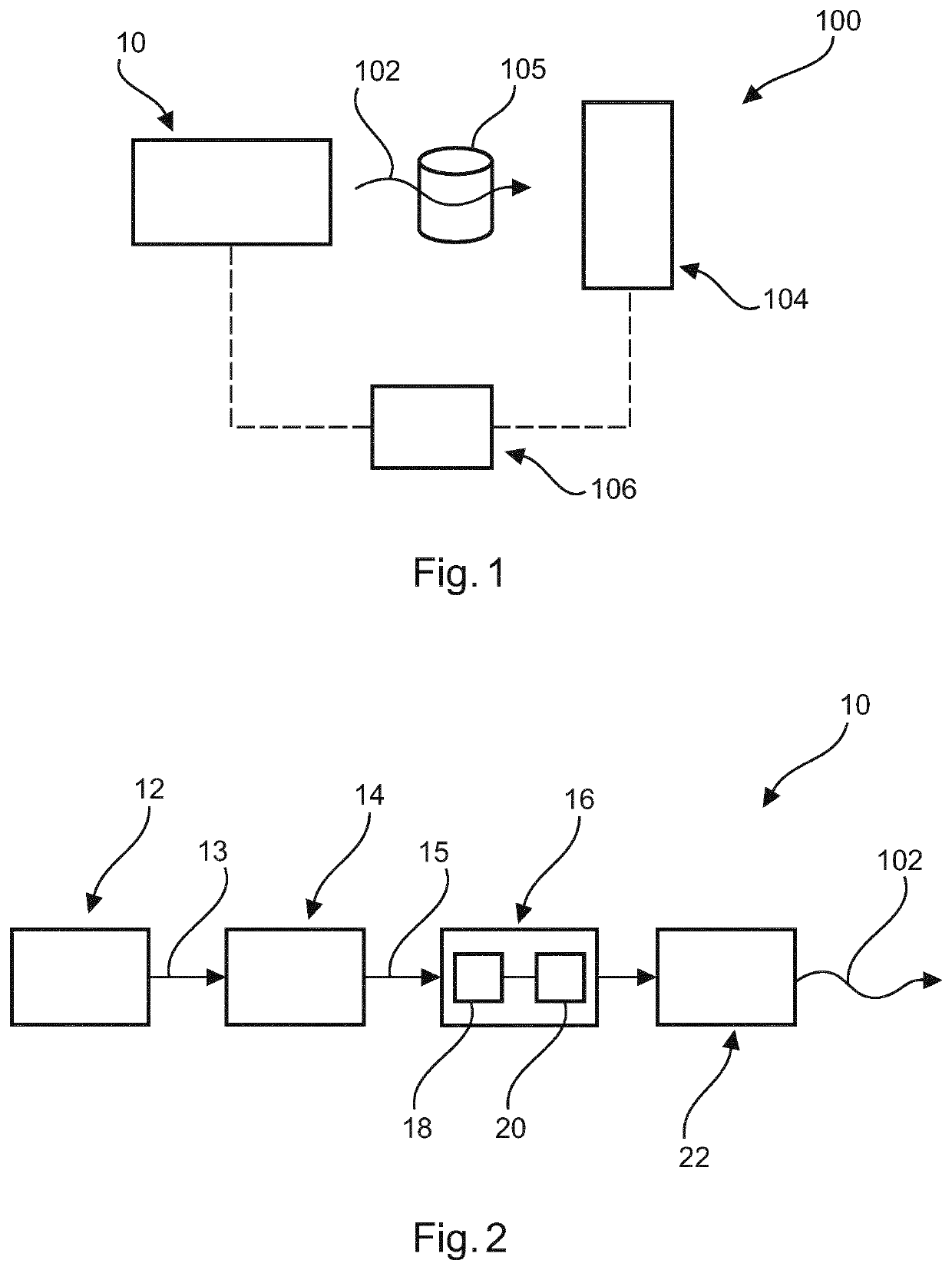
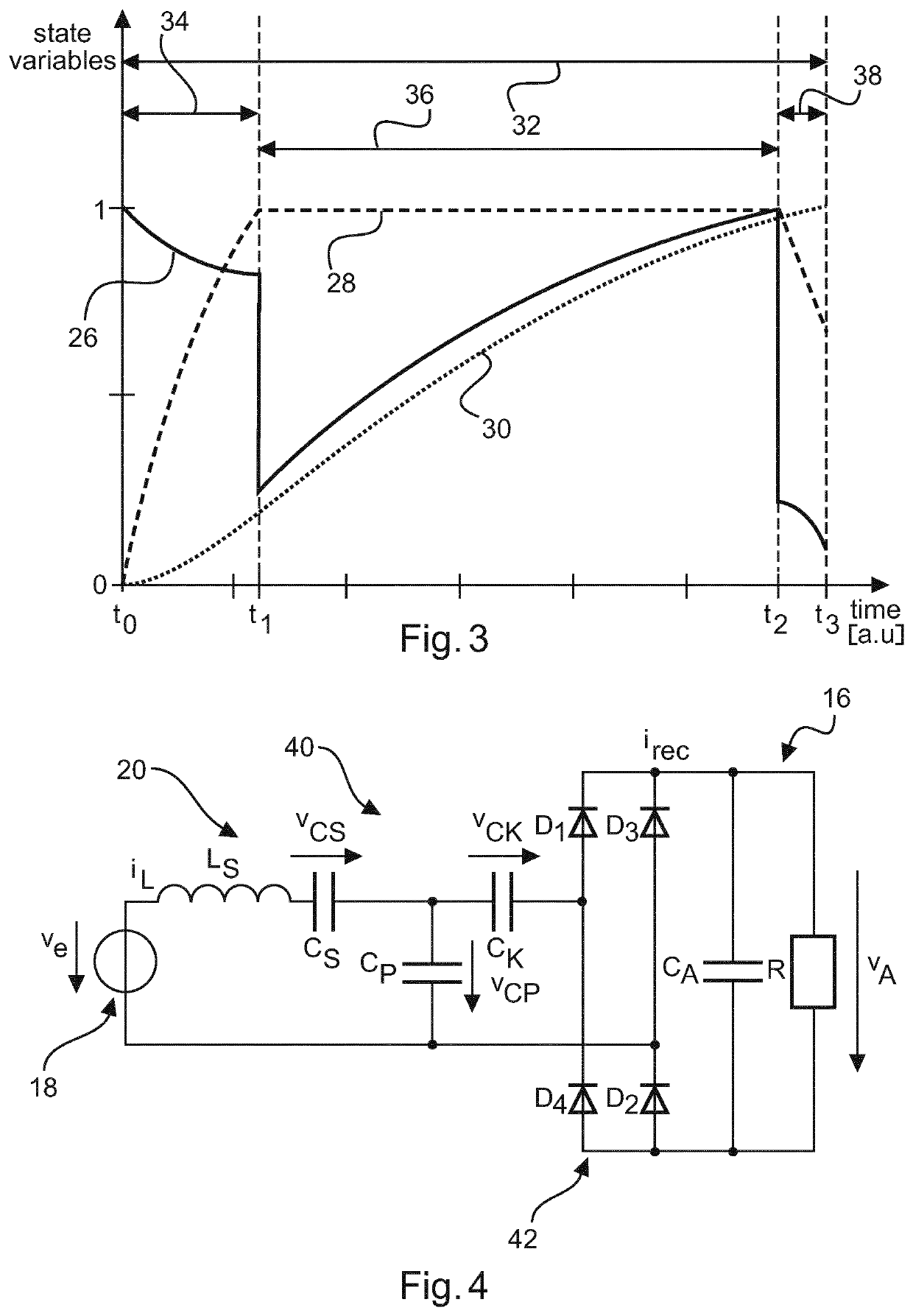
An X-ray source arrangement (10) for generating X-ray radiation (102), a method for operating the X-ray source arrangement (10), and an X-ray imaging apparatus (100) are provided. The X-ray source arrangement (10) comprises an X-ray tube (22), a converter arrangement (16) with an inverter (18) and a resonant converter (20) for providing a source voltage to the X-ray tube (22), a pre-controller (12), and a modulator (14). The pre-controller (12) is configured for determining a reference duty ratio (r, 26) of the resonant converter (20) as a continuous function of time based on a mathematical model of the resonant converter (20), and for providing a control signal (13) correlating with the reference duty ratio (r, 26) to the modulator (14). The modulator (14) is configured for determining a switching signal (15) based on the control signal (13), and for providing the switching signal (15) to the inverter (18) of the converter arrangement (16) for actuating the inverter (18).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Inverse kinematics solving method and device for service robot in intelligent space
InactiveCN108255058AImprove controlPrevent inversionAdaptive controlGenetic algorithmsDiscretizationContinuum function
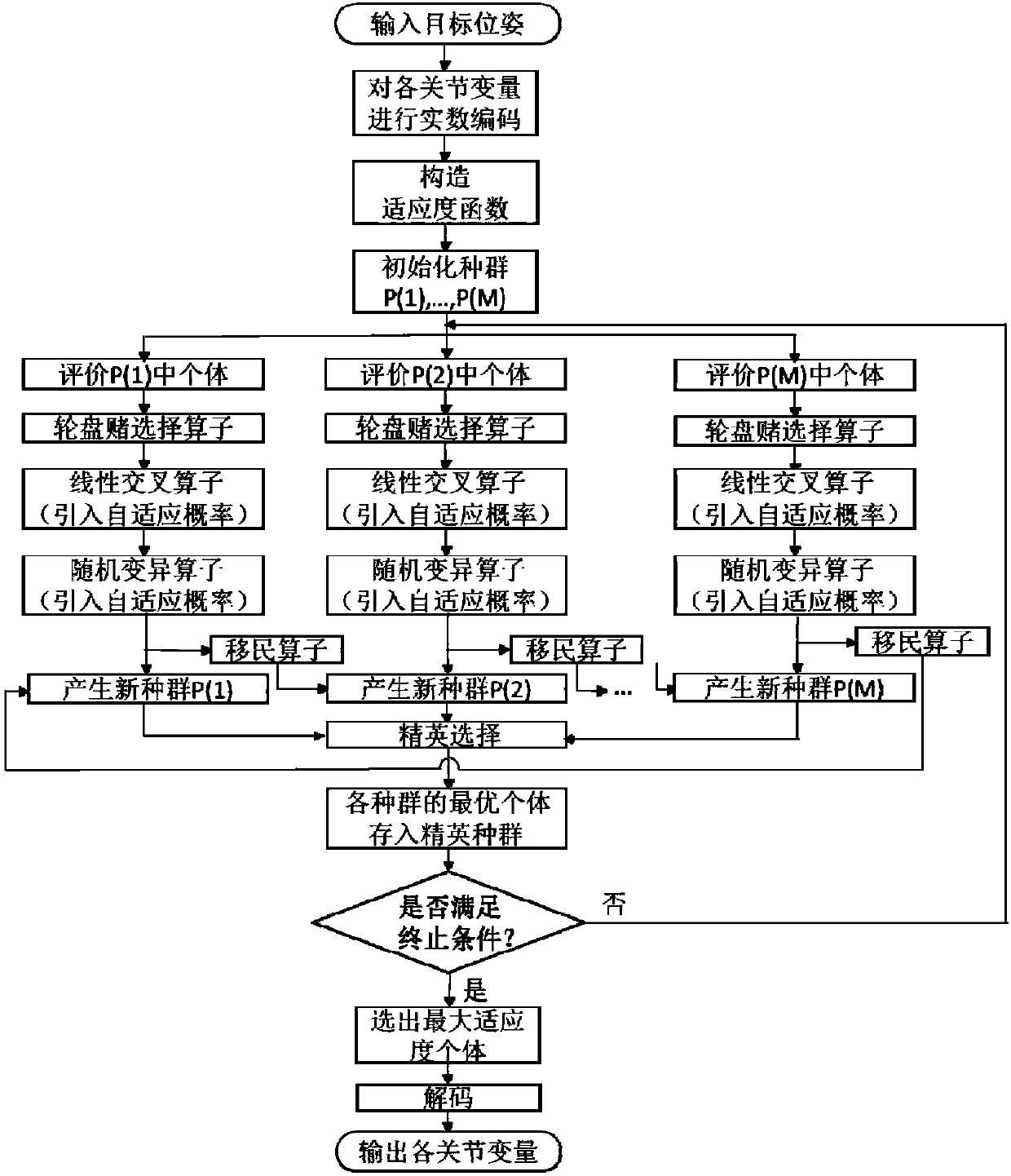
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics solving method and device for a service robot in a smart space. The method includes the following steps that: the forward kinematics model of the robot isestablished by using a D-H parameter method; real number coding is performed on the joint variables of the robot; an adaptive function is constructed with difference between a current pose and a target pose adopted as an optimization objective; and a genetic algorithm is used to perform optimization solution on the joint variables, so that the optimal solution of the inverse kinematics problem isobtained. The method of the invention does not need to be limited to robot configurations, and a plurality of populations are introduced, so that parallel optimization search can be realized, and therefore, the method can cope with the increase of the degree of freedom of the robot; the real number coding is adopted for the individuals, and mapping errors occurring during continuous function discretization when binary coding is adopted can be avoided; and on the basis of the real number coding, crossover operation adopts a linear crossover mode, mutation operation adopts a random mutation mode, and adaptive crossover and mutation probabilities are introduced, and therefore, a better solution can be effectively protected in the later stage of evolution, and convergence speed and precisioncan be guaranteed.
Owner:山东大学深圳研究院
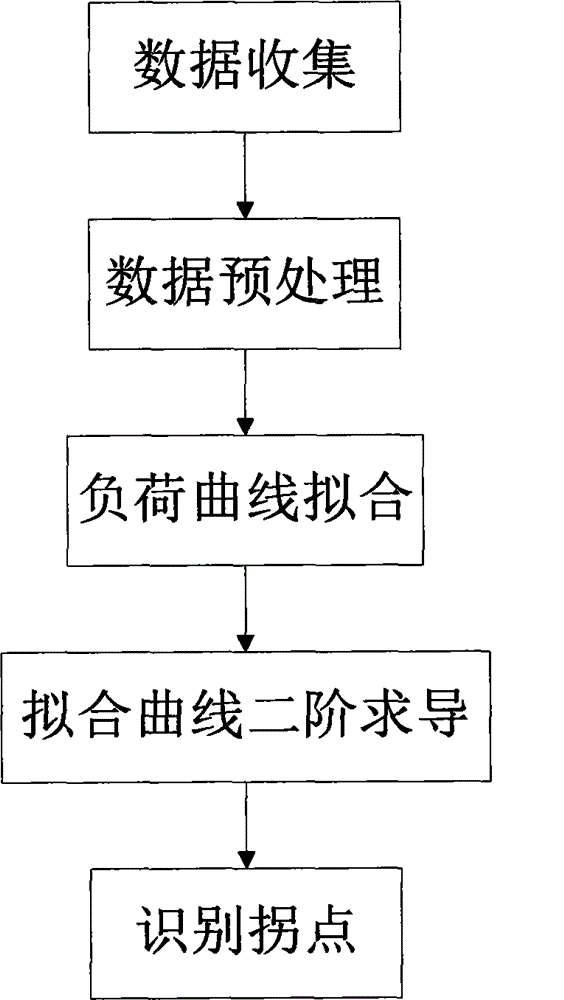
Load curve convergence optimal inflection point recognition method
InactiveCN105988974AImprove safety and reliabilityComplex mathematical operationsOriginal dataMATLAB
A load curve convergence optimal inflection point recognition method includes the following steps: S1, data collection; S2, data pretreatment including S2-1 data filling and S2-2 data correction through a wavelet de-noising method; S3, achievement of approximate fitting of a load curve based on a data pretreatment technique; and S4, performing mathematical treatment on the obtained fitting daily load curve to determine an optimal inflection point. After pretreatment is performed on the original data through data filling and the wavelet de-noising method, Matlab software is called to perform approximate fitting on polynomial, and in this way, a smooth continuous function format is obtained; an inflection point definition of the mathematics field is applied to the power load curve, the inflection point of the load curve can be rapidly found, and then power dispatching workers can timely determine the present inflection point and can make ready for corresponding dispatching works, and the stability and the reliability of power grid operation can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Ecological risk evaluation method combining landscape pattern and regional ecological risk factor
InactiveCN110188986AMaintain ecological securityAccurate predictionResourcesStructural vulnerabilityEcological risk
The invention discloses an ecological risk evaluation method combining a landscape pattern and a regional ecological risk factors. The method comprises the following steps: 1) dividing a to-be-evaluated region into risk evaluation units; 2) determining a risk receptor and an ecological endpoint, analyzing a risk source, and reflecting the hazard degree of the risk source to the receptor accordingto the probability and the intensity to obtain the hazard degree (P) of the risk source; 3) researching the contact exposure relation between the risk source and the receptor in the drainage basin, measuring the vulnerability of the ecosystem, representing the external disturbance degrees of different types of ecosystems by landscape disturbance degree indexes, and reflecting the structural vulnerability in the ecosystem by the vulnerability degree indexes to obtain the vulnerability (D) of the ecosystem; 4) representing the potential loss degree of the risk receptor by adopting ecological assets to obtain the loss degree (L) of the risk receptor, and 5) constructing an ecological risk evaluation model, and regarding the ecological risk (ER) as a continuous function of the risk degree (P)of the risk source, the vulnerability (D) of the ecosystem and the loss degree (L) of the risk receptor.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
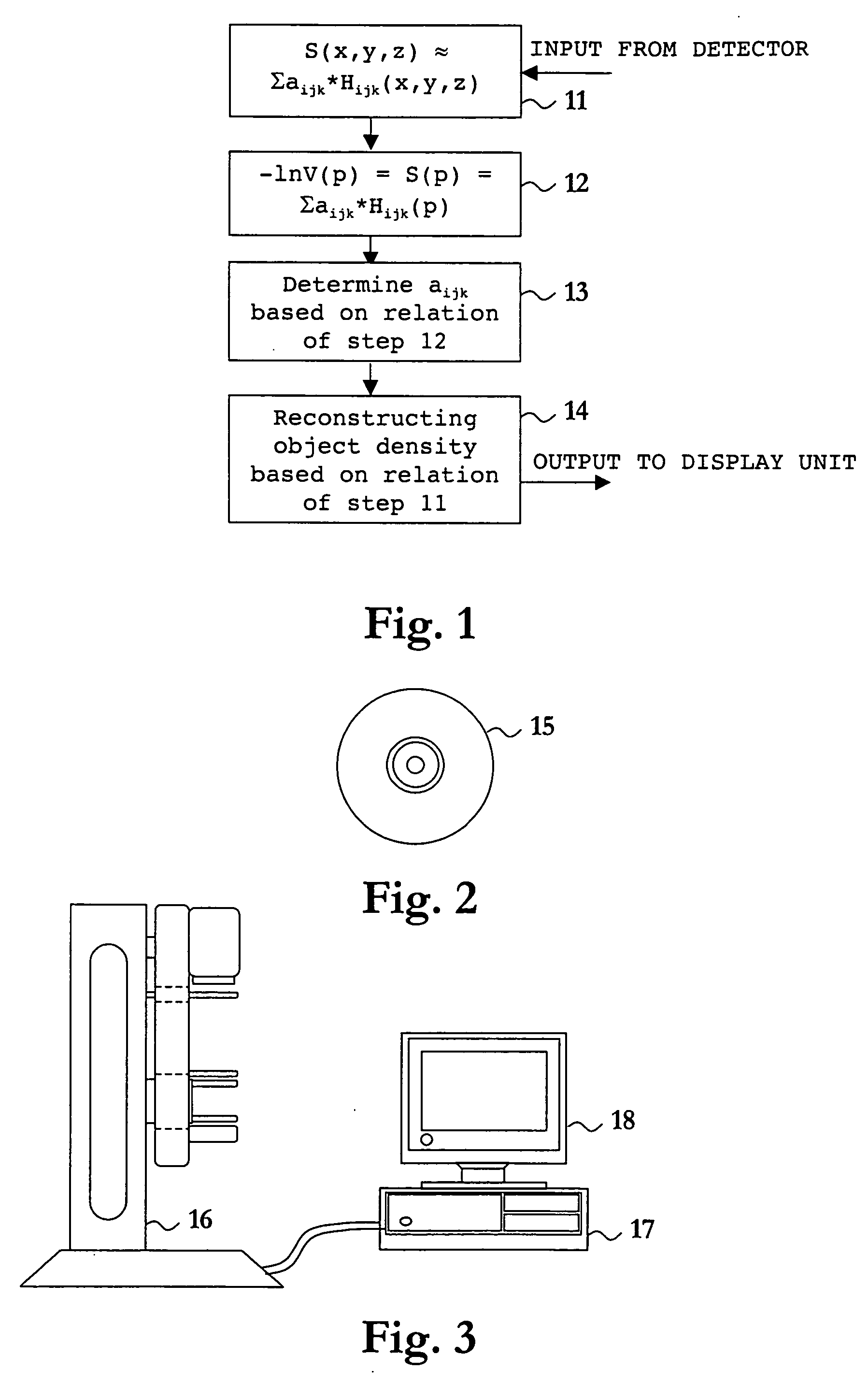
Method and apparatus for reconstruction of the attenuation density of an object from x-ray projection image data
InactiveUS20050152505A1Accurate and reliable processImprove signal-to-noise qualityReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingUltrasound attenuationProjection image
A method for reconstruction of object attenuation density (S(x,y,z)) from X-ray projection image data values (V(pq)) comprises the steps of: representing (11) the object attenuation density by a sum of predetermined continuous harmonics (Hijk(x,y,z)) with unknown coefficients (aijk); relating (12) each of the projection image data values to an integral (S(pq)) of the object attenuation density, and thus to a corresponding sum of sums (aijk*Hijk(pq)) of the predetermined continuous harmonics with unknown coefficients; determining (13) the unknown coefficients (aijk) from the above relation; and reconstructing (14) the object attenuation density by said sum of predetermined continuous harmonics with said determined coefficients. The spatial three-dimensional object attenuation density is found as a continuous function with uniform resolution over all its volume and is shown as a solid three-dimensional body, which can be cut in arbitrary way and shown in continuous motion.
Owner:XCOUNTER
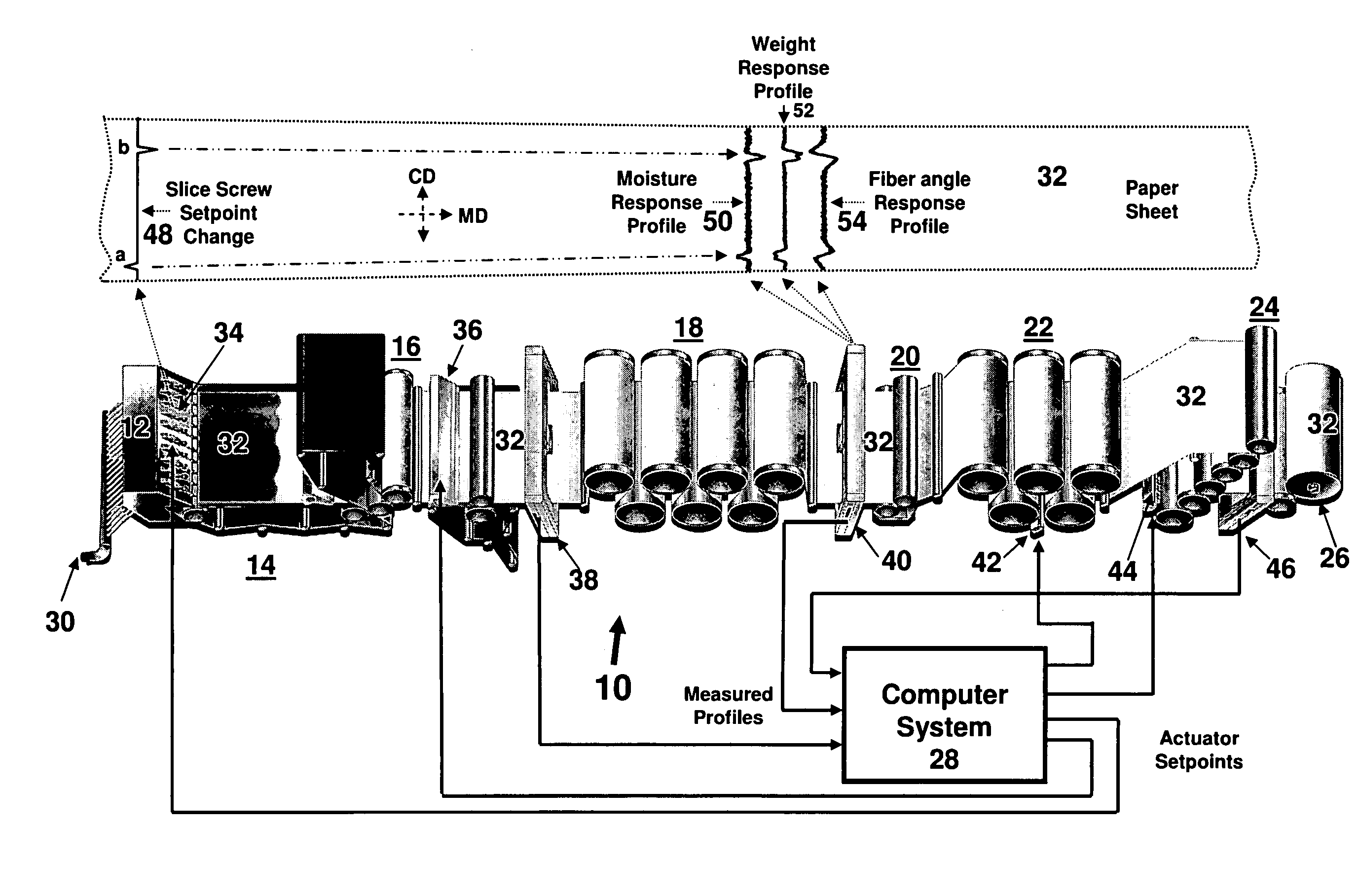
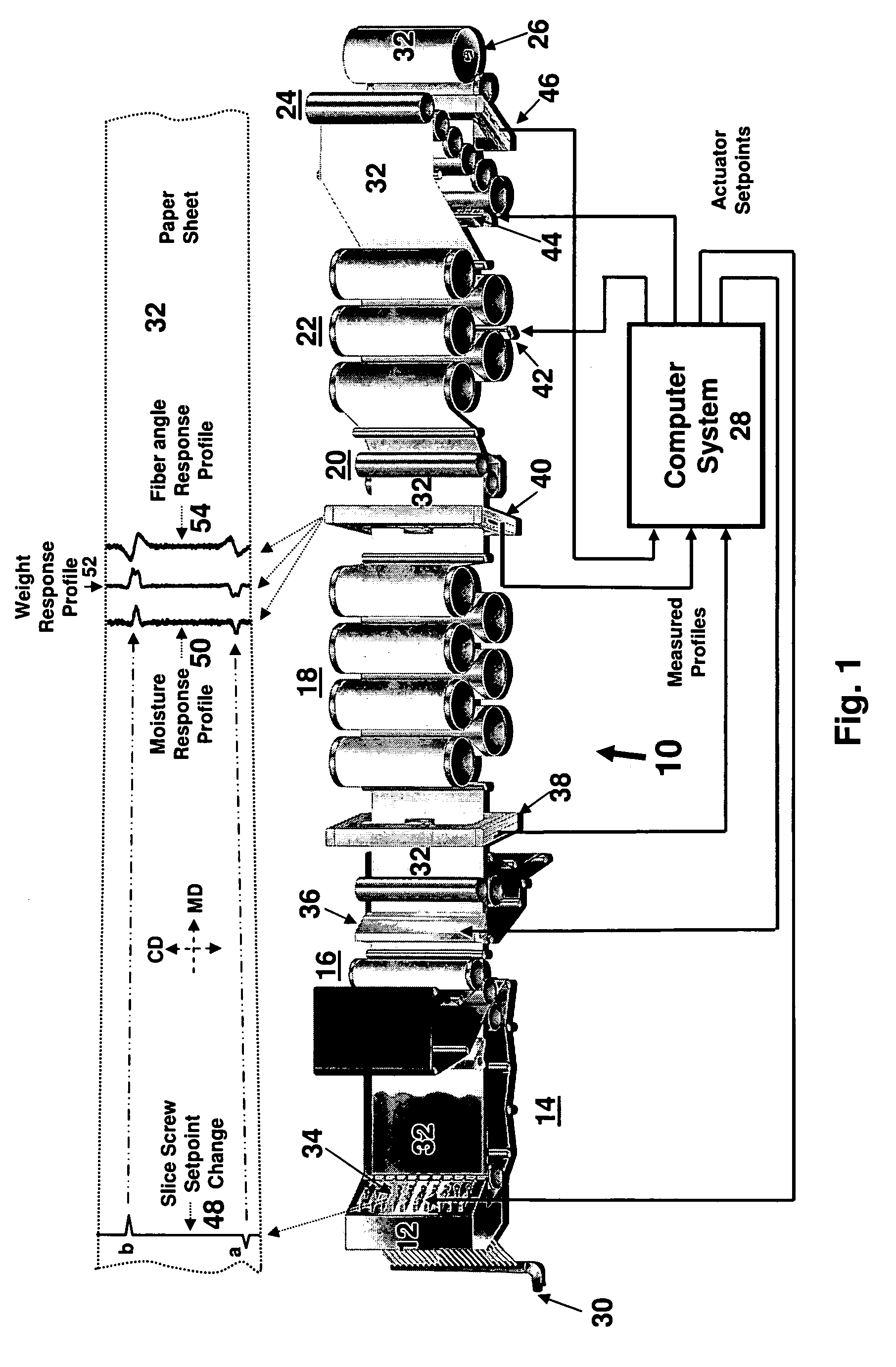
Method and apparatus for creating a generalized response model for a sheet forming machine
Owner:ABB AUTOMATION GMBH +1
Perpetually decreasing group pricing system and method
InactiveUS20140089053A1Address rising pricesIncrease the amount of controlMarket predictionsEngineeringContinuum function
The present invention takes an input of the acceptable pricing to volume points from a business and outputs a continuous function which interpolates the pricing information for the entire range of customer volumes. As each consumer agrees to purchase an offer, they are added to the group, and the price decreases as defined by the output function. The result of this model is that of consumer collusion; it is in each consumer's best interest to increase the volume of purchases for the offer by the business. This yields lower prices for the individual, incentivizing each consumer to advertise for the business making the offer.
Owner:IORGA DAN
Bi-helical toothed wheel with variable helix angle and non-encapsulating tooth profile for hydraulic gear apparatuses
ActiveCN107642592AMaintain shape continuityPortable liftingEngine of intermeshing engagement typeDrive wheelAngular point
The invention relates to a bi-helical toothed wheel (1) with non-encapsulating profile (4) for hydraulic gear apparatuses (2), of the type bound to a support shaft (5) to form a driving or driven wheel of said hydraulic apparatus and comprising a plurality of teeth (6) extended with variable helix angle with continuous function in the longitudinal direction, wherein the teeth profile (4) keeps a shape continuity in each cross section thereof. More particularly, each tooth of the toothed wheel is longitudinally split in three zones: initial (A), central (B) and terminal (C) zones, and the central zone (B) has a variable helix angle, while the initial (A) and terminal (C) zones have a constant helix angle. The invention allows to manufacture contra-rotating rotors, having a non-encapsulatingprofile and a helix shape such as to suppress the angular point at the center of the rotors themselves and therefore all the problems related to their machining.
Owner:SETTIMA FLOW MECHANISMS SRL
A microgrid economic dispatching method based on particle swarm optimization algorithm
InactiveCN109217354ATo achieve the purpose of economic dispatchSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsArtificial lifeMathematical modelPower grid
The invention discloses a microgrid economic dispatching method based on a particle swarm optimization algorithm. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm makes full use of its own experience and swarm experience to adjust the state of particles, which can effectively optimize the system parameters. Its advantage lies in solving some optimization problems of continuous functions. In view of theabove situation, particle swarm optimization algorithm is applied to the economic dispatching of micro-grid. Firstly, the mathematical model of micro-power generation is established, and then the economic dispatching model of micro-power grid is established according to the dispatching criterion, and the economic optimal dispatching strategy is put forward. According to the constraint conditions,a micro-grid economic dispatching program based on particle swarm optimization algorithm is compiled. The results show that this algorithm can be used in micro-grid economic dispatching effectively and reasonably to allocate the output of micro-generators and achieve economic dispatching.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method for controlling optimization through self-organized extremum optimization process
InactiveCN104361204ASolve the problem that the entire solution space cannot be searchedSpecial data processing applicationsControl objectiveExtremal optimization
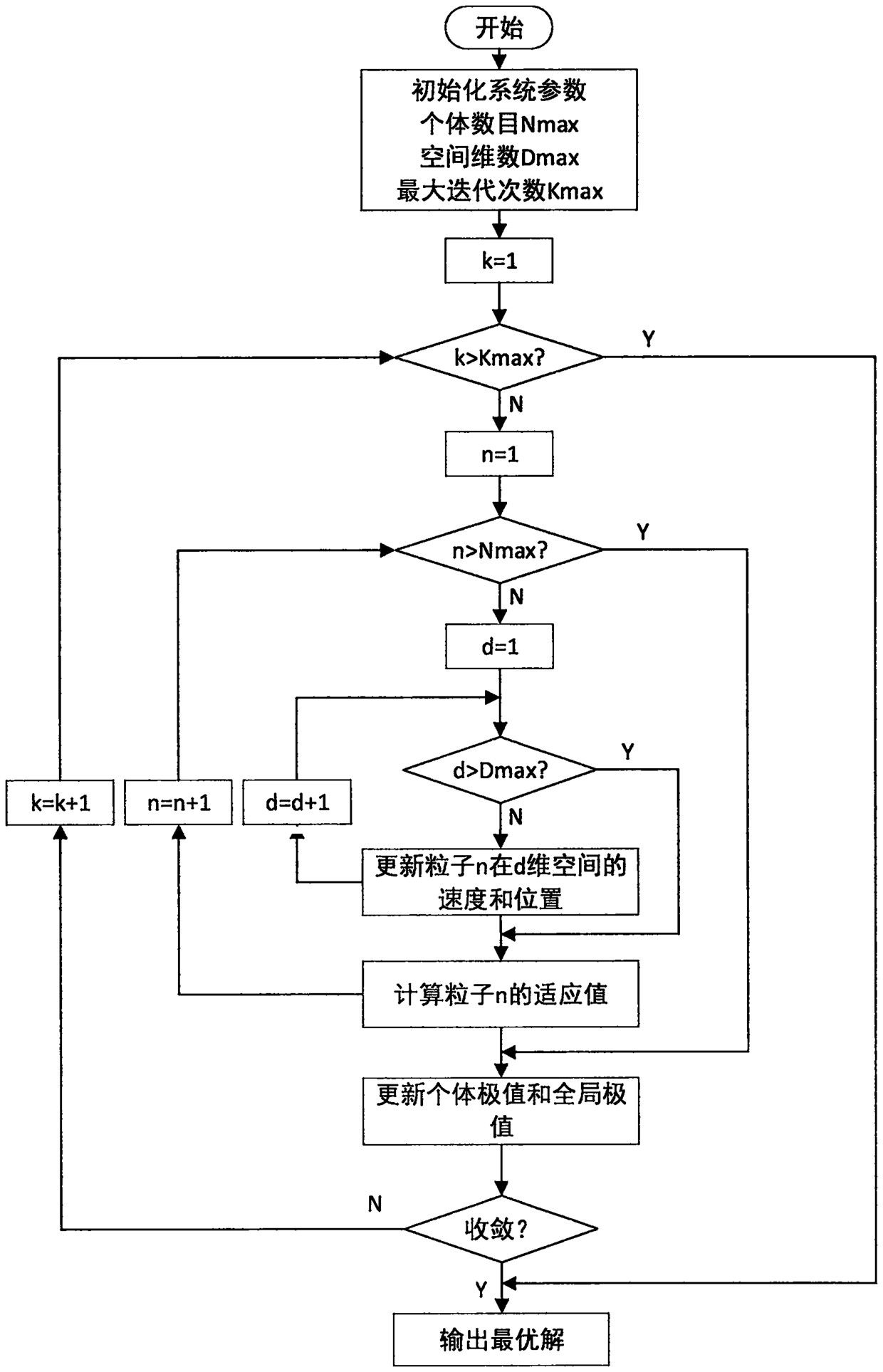
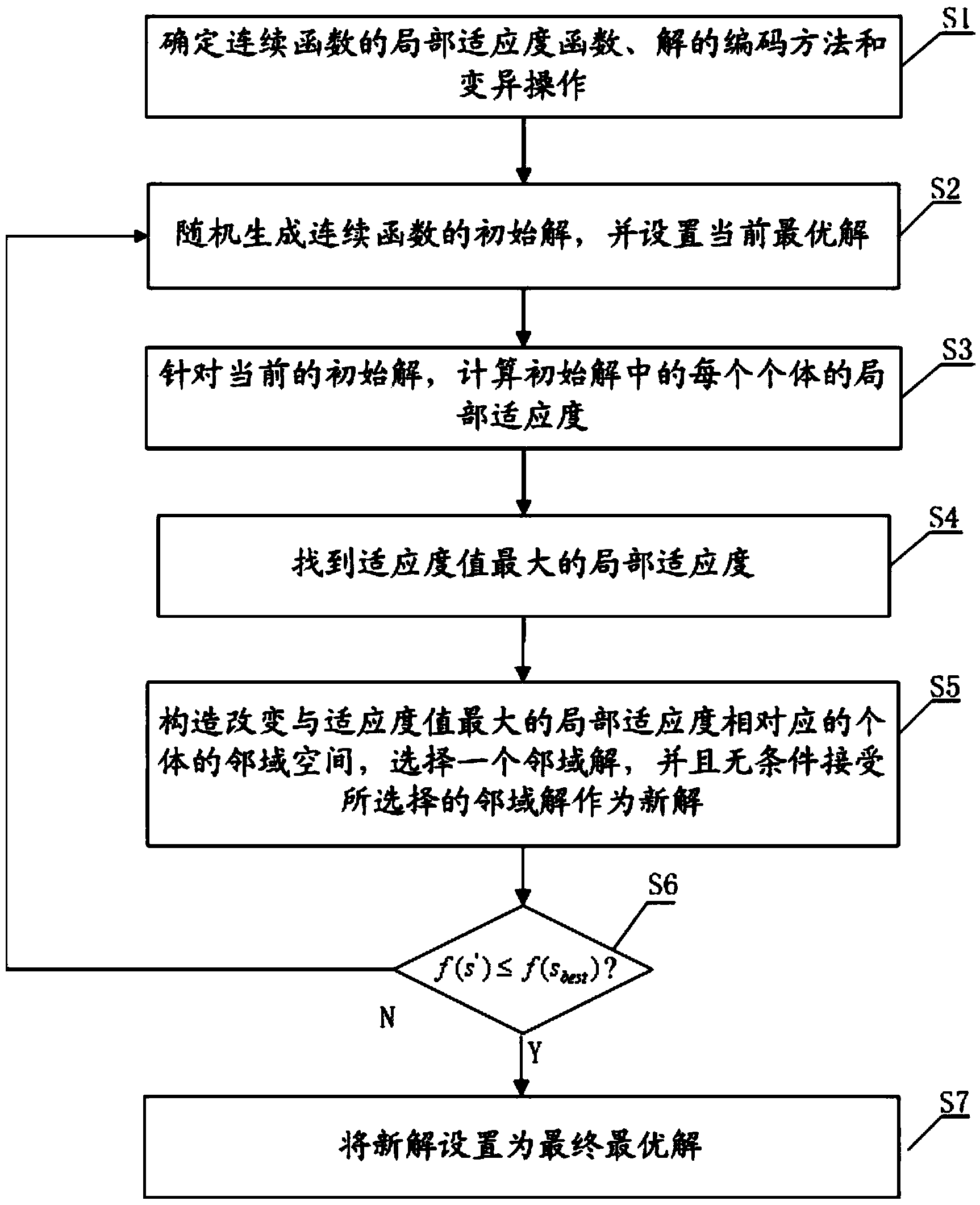
A method for controlling optimization through self-organized extremum optimization process is used for solving continuous function optimization through the self-organized extremum optimization process, and the solved optimum solution is used as control parameters. The self-organized extremum optimization process comprises the following steps: step 1, determining the local fitness function of a continuous function f(x) according to a control objective; step 2, generating the initial solution s of the continuous function f(x) at random and setting the current optimum solution sbest; step 3, working out the local fitness of each individual si (i equals to 1, ..., m) aiming at the current initial solution; step 4, finding out the local fitness with the maximum fitness value; step 5, structurally changing the neighbourhood space N(s) of the individual sj corresponding to the local fitness with the maximum fitness value, selecting a neighbourhood solution s' belonging to N(s), and taking the selected neighbourhood solution as a new solution unconditionally; step 6, substituting the new solution and the current optimum solution sbest into the continuous function respectively so as to judge that whether the formula that f(s') is less than or equal to f(sbest) is workable or not, if the formula that f(s') is less than or equal to f(sbest) is workable, setting the new solution to be the final optimum solution, and if the formula that f(s') is less than or equal to f(sbest) is not workable, returning to step 2.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
Tool radius directional compensation algorithm for slow slide servo turning of complex curved surface
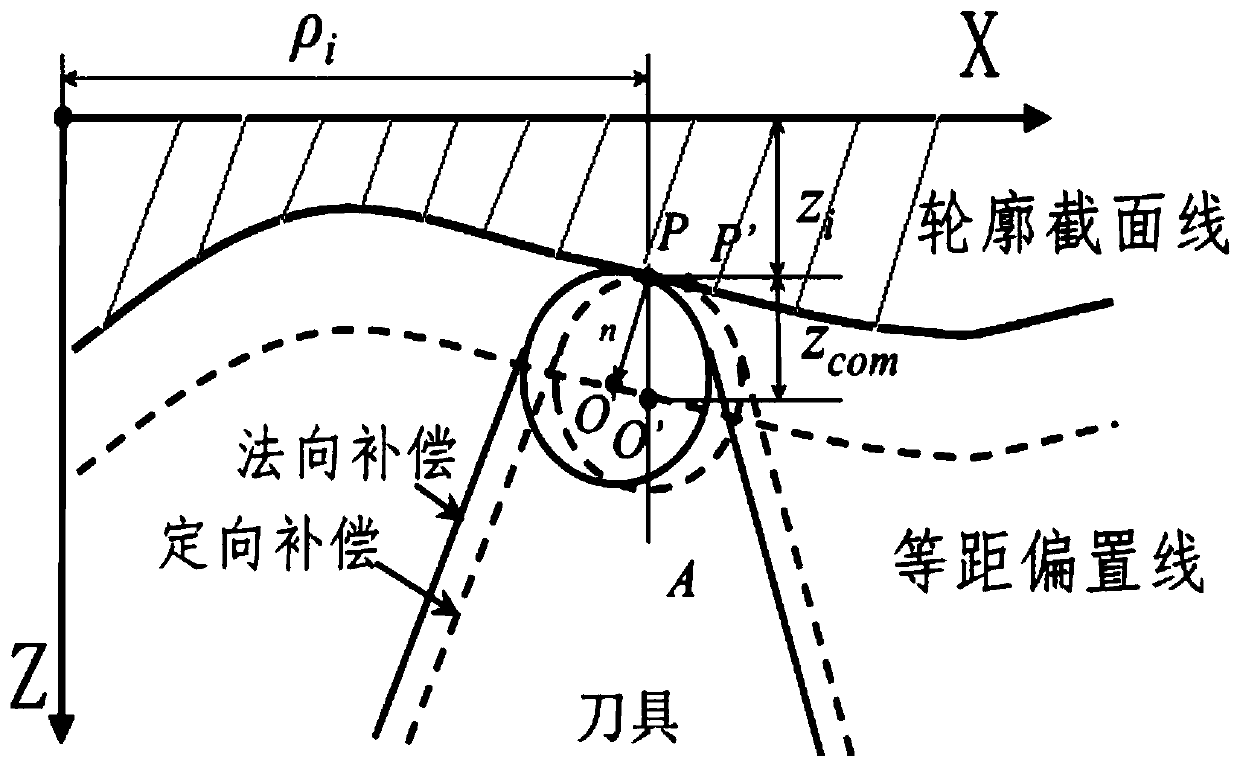
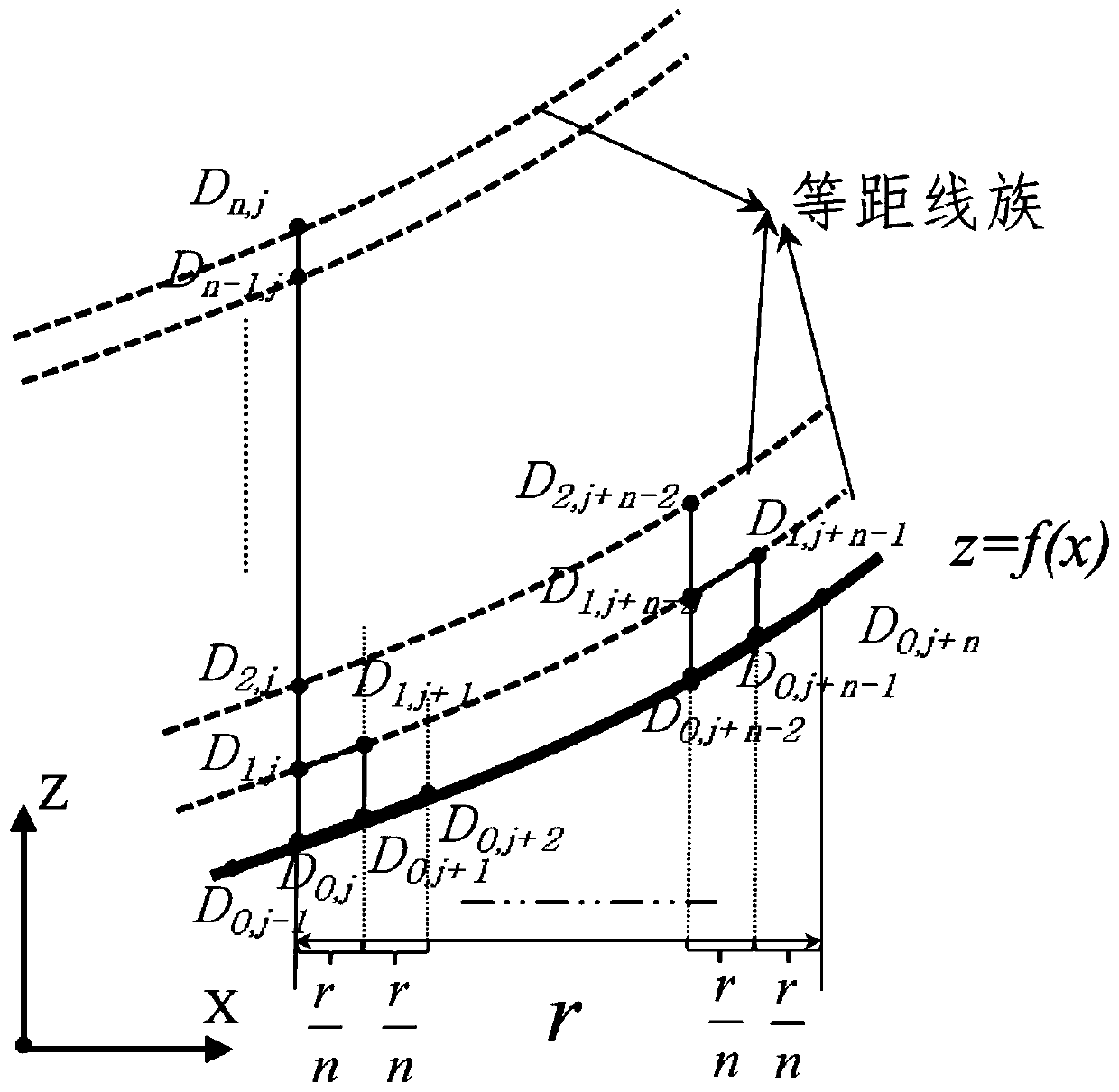
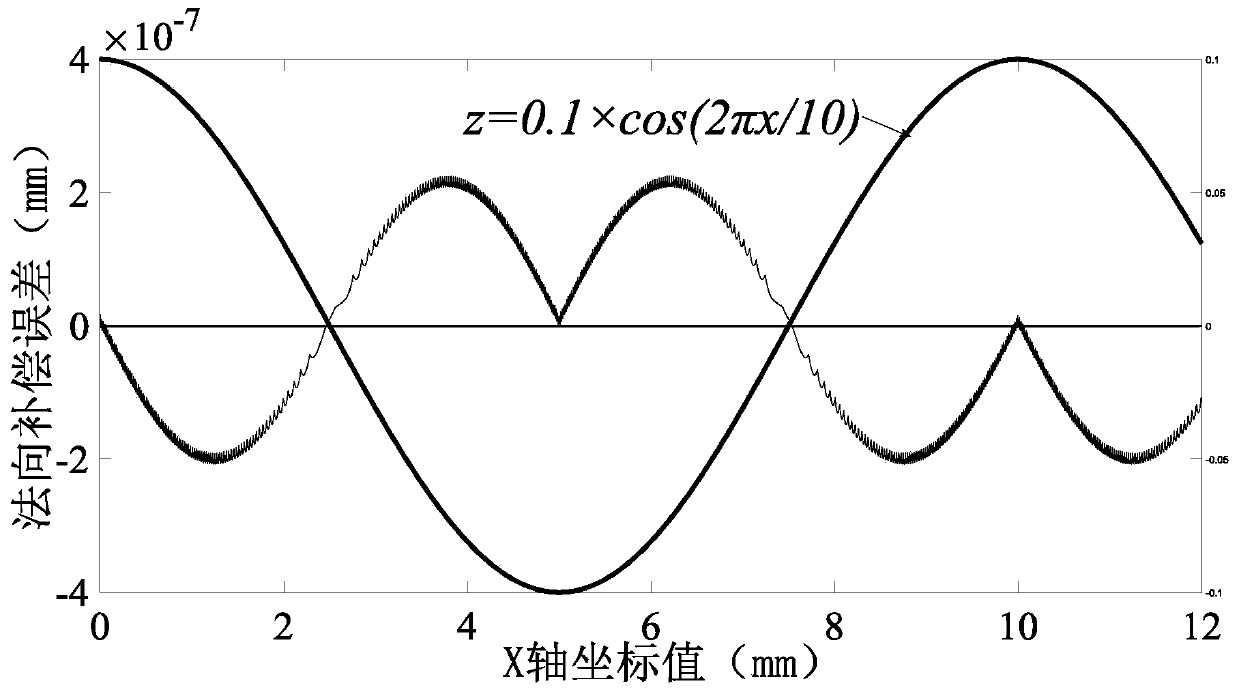
ActiveCN110209113ASolve solution efficiencySolve solution accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlPoint sequenceEngineering
The invention discloses a tool radius directional compensation algorithm for slow slide servo turning of a complex curved surface. The tool radius directional compensation algorithm comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing an XZ coordinate system on a contour section curve; carrying out point position discrete processing on the contour section curve to obtain discrete point positions, representing a Z coordinate value with Di,j, wherein in subscripts, i represents times of compensation and j represents a point sequence; then obtaining a subdivided radius compensation point D1,jat a compensated point D0,j; repeating the steps until obtaining a final compensated point Dn,j; and finally, obtaining the Z coordinate value of Dn,j at D0,j. according to the invention, the curve isdirectly subject to discrete subdivision, and the compensated point is obtained on the basis of the rapid directional compensation algorithm; and compared to existing algorithms in the current literature, the tool radius directional compensation algorithm only needs to carry out square and radication operations without carrying out equation solution or curve reconstruction, meanwhile, is also applicable to directional compensation of a first-order discontinuous function, meets the requirements of actual ultraprecision machining engineering application and solves problems of solving efficiencyand solving accuracy.
Owner:INST OF MACHINERY MFG TECH CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
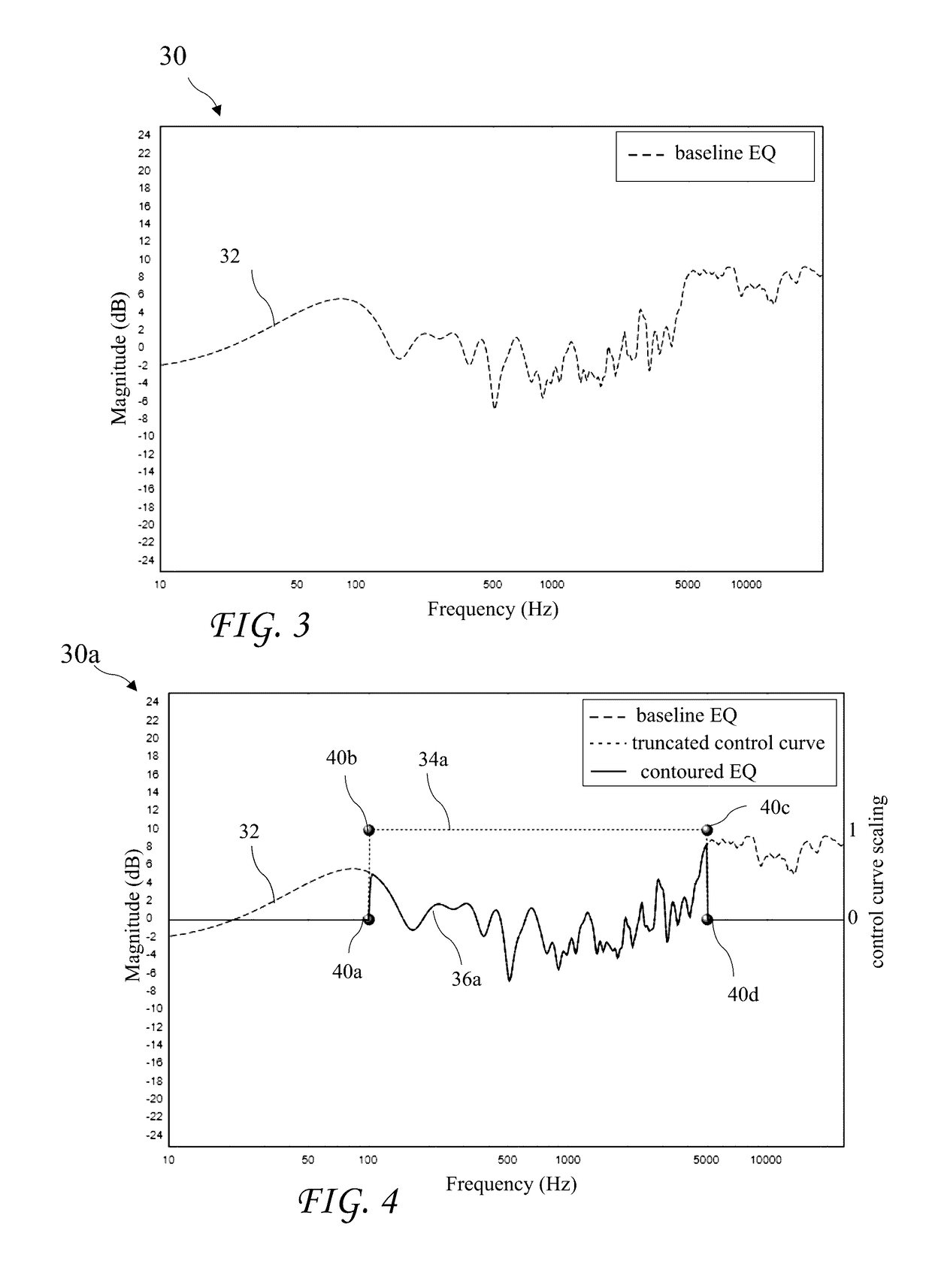
Equalization contouring by a control curve
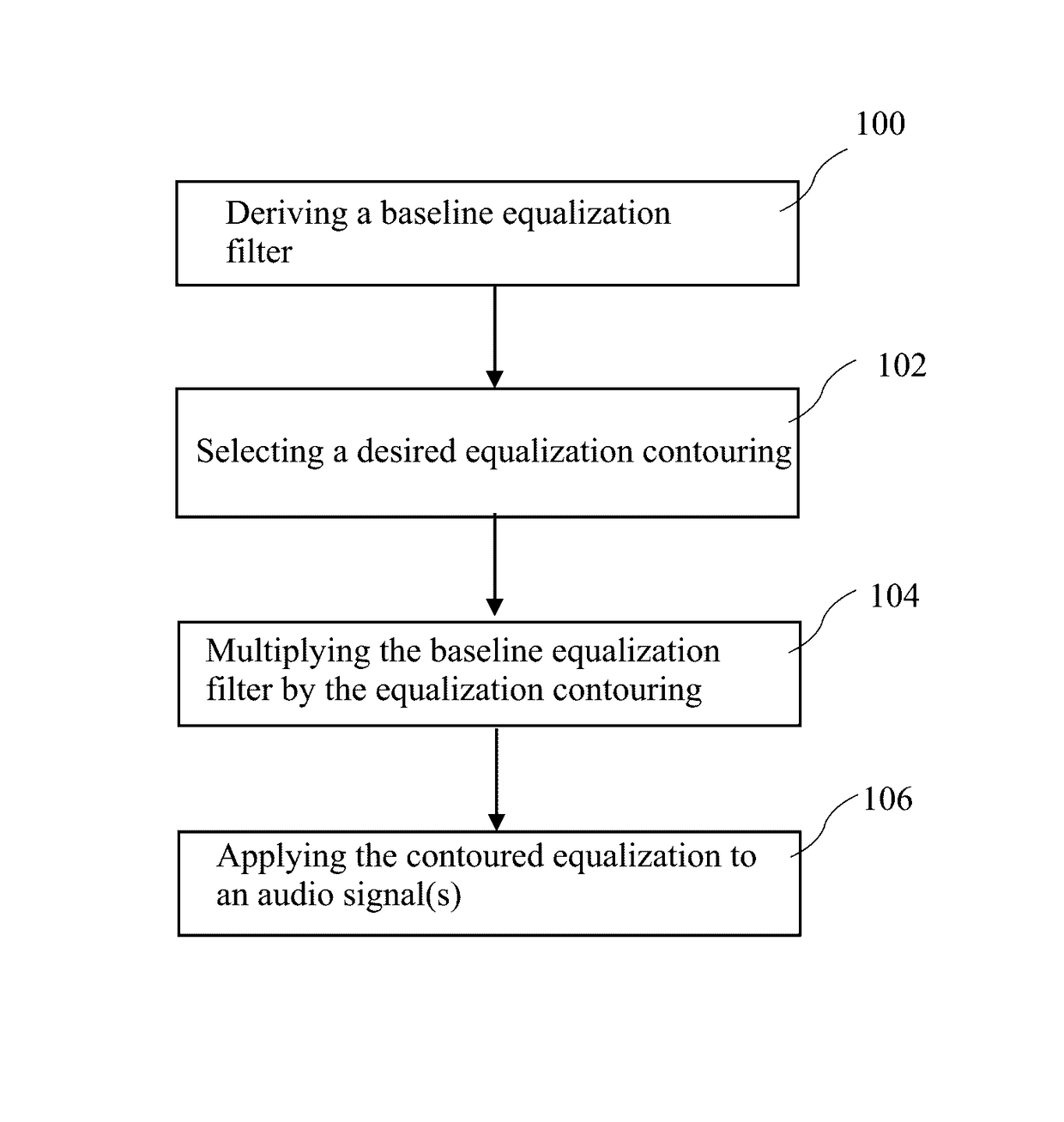
ActiveUS9680437B2Smoothly scales magnitude of equalizationReduction of equalizationAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlFrequency response correctionEngineeringContinuum function
A method for equalization contouring provides a reduction of equalization in certain frequency regions either by user control or by automated selection of frequency, without introducing artifacts. A control curve smoothly scales the magnitude of the equalization in the areas where less equalization is desired to obtain a contoured equalization. The control curve varies by frequency and may be defined specifically for every sampled frequency value of the equalization, may be a continuous function of frequency, or may be a function of control points at a select number of frequency points. The control curve may also have automatic inputs, e.g. a machine-detected cutoff frequency of a speaker may be used to determine a control point in the control curve. As another example, the reverberation time (e.g. RT60) may be used to determine a control point in the control curve. The result is a contoured equalization curve without sudden steps.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
Geostatistical method for variation function simulation of surface spatial data of seas and mountains
The invention discloses a geostatistical method for variation function simulation of surface spatial data of seas and mountains. The geostatistical method includes: defining 3D-Surface regionalized variables; calculating according to a variation function based on 'distance-gradient' or 'distance-relative water depth' to fit a range to a gradient continuous function; performing KRIGING valuation.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
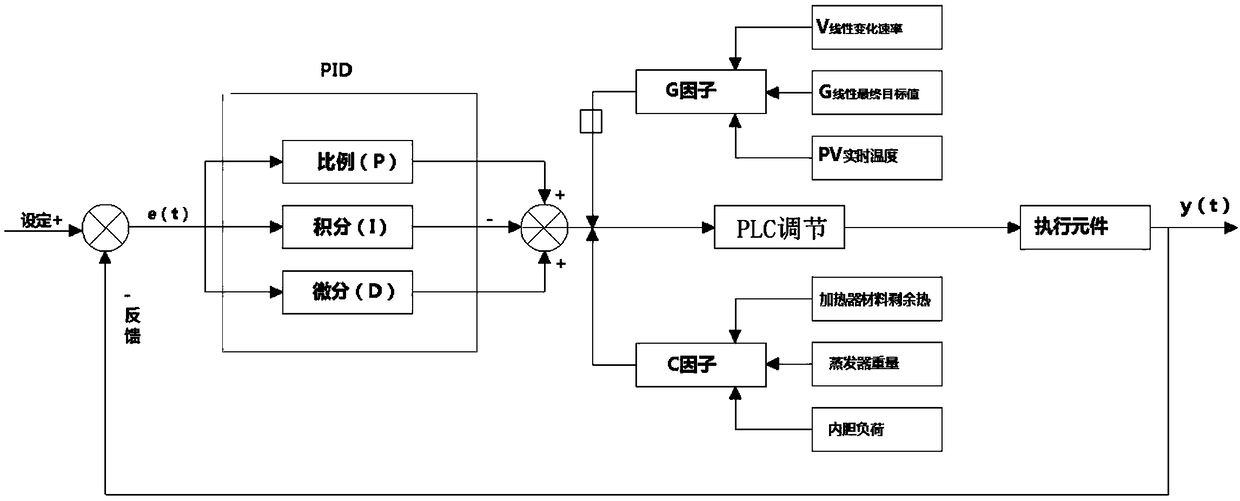
Dynamic braking control method for electronic expansion valve
The invention relates to a dynamic braking control method for an electronic expansion valve. The method comprises the following steps: 1) setting e (t) and carrying out PID operation of a continuous function; 2) setting a G factor, wherein the G factor comprises a V linear variation factor, a G linear final target value and a real-time temperature of the PV; 3) setting the C factor, wherein the Cfactor comprises the residual heat of the heating material, the weight of the evaporator and the load of the inner container; 4) setting e (t), carrying out PID operation of a continuous function, andsubstituting the PID operation of the continuous function into a PLC system for PID adjustment of the analog quantity; the real-time PLC error elimination regulation is carried out in the same time into the G factor and the C factor, and the overshoot is kept within the standard by executing the original output; 5) while the output data is again fed back to e (t).
Owner:JIANGSU TUOMILUO ENVIRONMENTAL TEST EQUIP CO LTD
Optical recording medium, recording method thereof and evaluation method of optical recording medium
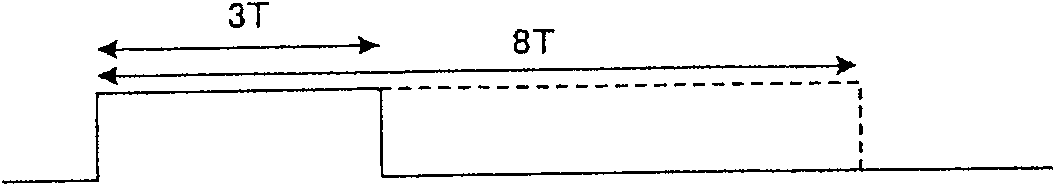
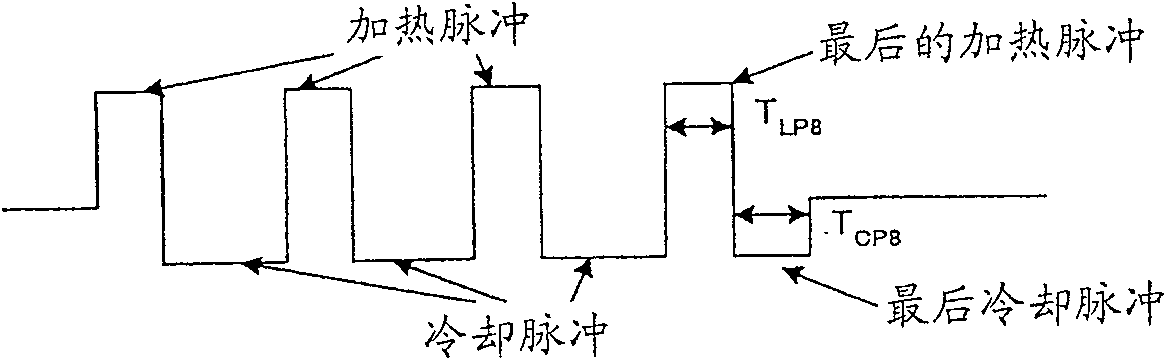
A recording method for an optical recording medium, comprising: irradiating the medium with a laser light having m pulse groups, wherein each pulse group includes a heating pulse and a cooling pulse, wherein m is a natural number; The above medium is used to record marks with a length of nT, wherein n is a natural number of 3 or more, and T is a clock period, wherein the length TCPn of the last cooling pulse is determined according to the scanning speed v using the following function: when v<v0, TCPn / T=f1, n(v); when v≥v0, TCPn / T=f2, n(v), where f1, n(v) and f2, n(v) all represent continuous functions of scanning speed v , and satisfy the condition that the presence ratio of abnormal markers is 1.0×10-4 or less, and v0 is a selectable scanning speed.
Owner:RICOH KK
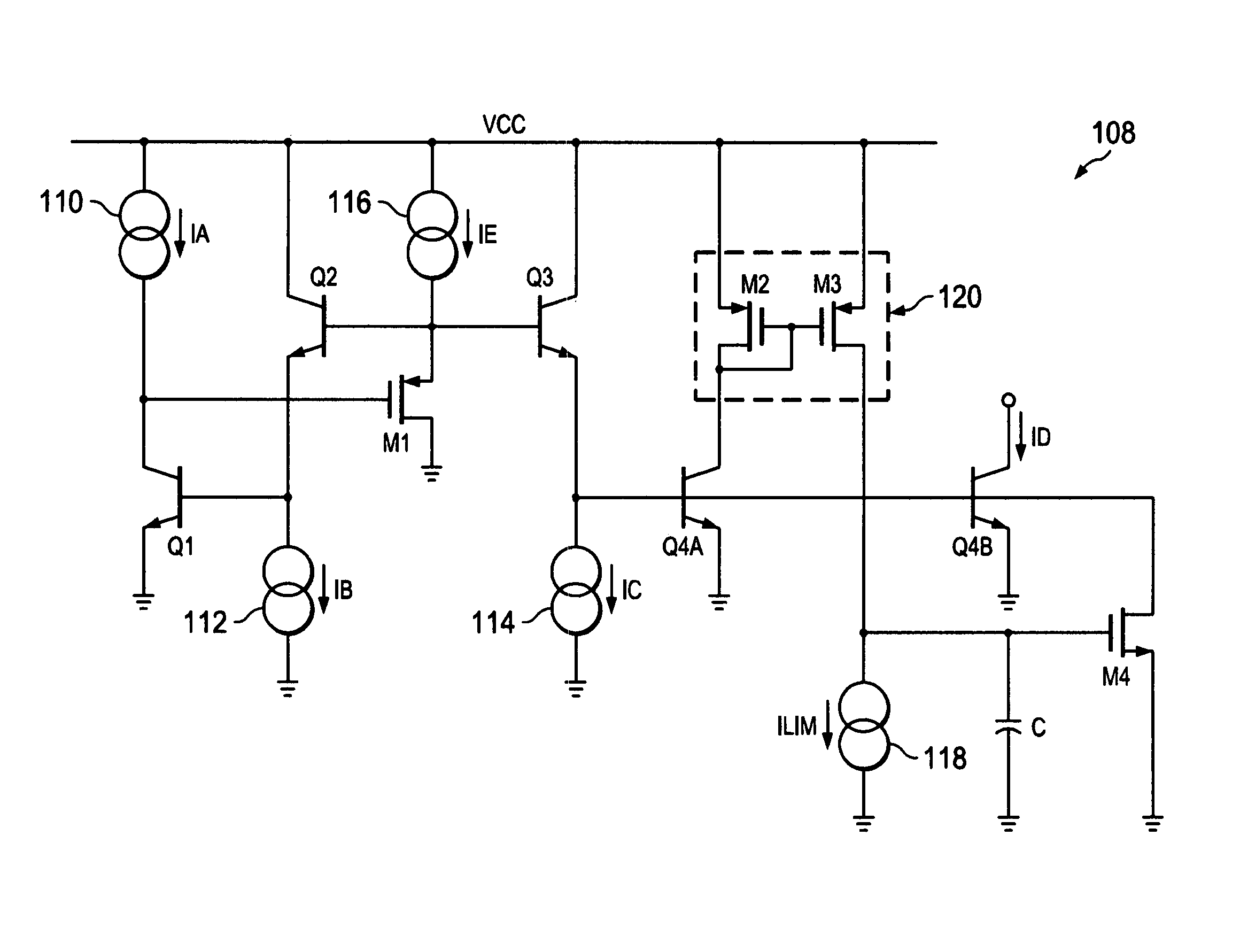
Implementing a piecewise-polynomial-continuous function in a translinear circuit
ActiveUS8305133B2Pulse automatic controlComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsLoop controlTranslinear circuit
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
GPS single epoch deformation monitoring sidereal day cycle error elimination method
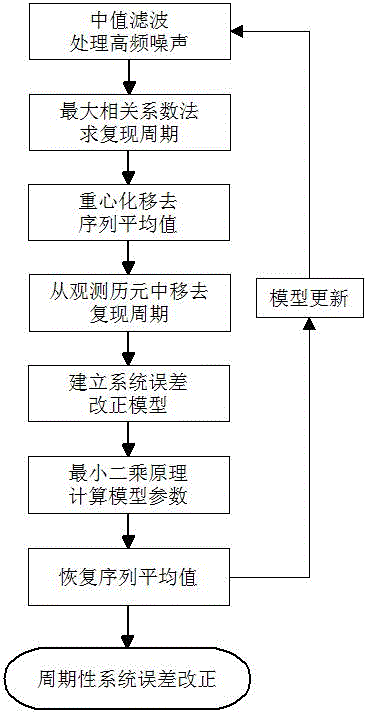
InactiveCN106323205ASatellite radio beaconingUsing wave/particle radiation meansDeformation monitoringContinuum function
The invention discloses a GPS single epoch deformation monitoring sidereal day cycle error elimination method, which belongs to the field of surveying and mapping science and technology. The geometric position relationship between a GPS satellite and a ground monitoring station is repeated with a sidereal day as a cycle, and a GPS system error has whole-cycle day features. In the existing system error elimination method, prolonging of observation time is impractical for the single epoch. An error model is established based on a satellite altitude angle and an azimuth angle, which is complicated and is not practical. Discrete sidereal day filter does not adopt a continuous correction function, and a time point is hard to be aligned. A time series maximum correlation coefficient is adopted to determine a recurrence cycle, high-frequency noise is filtered through median filtering, a correction model is built for the system error by using the continuous function and is dynamically updated, different recurrence cycles in three directions of NEU can be determined, high-frequency noise and cycle errors can be eliminated, and the GPS single epoch deformation monitoring precision is improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com