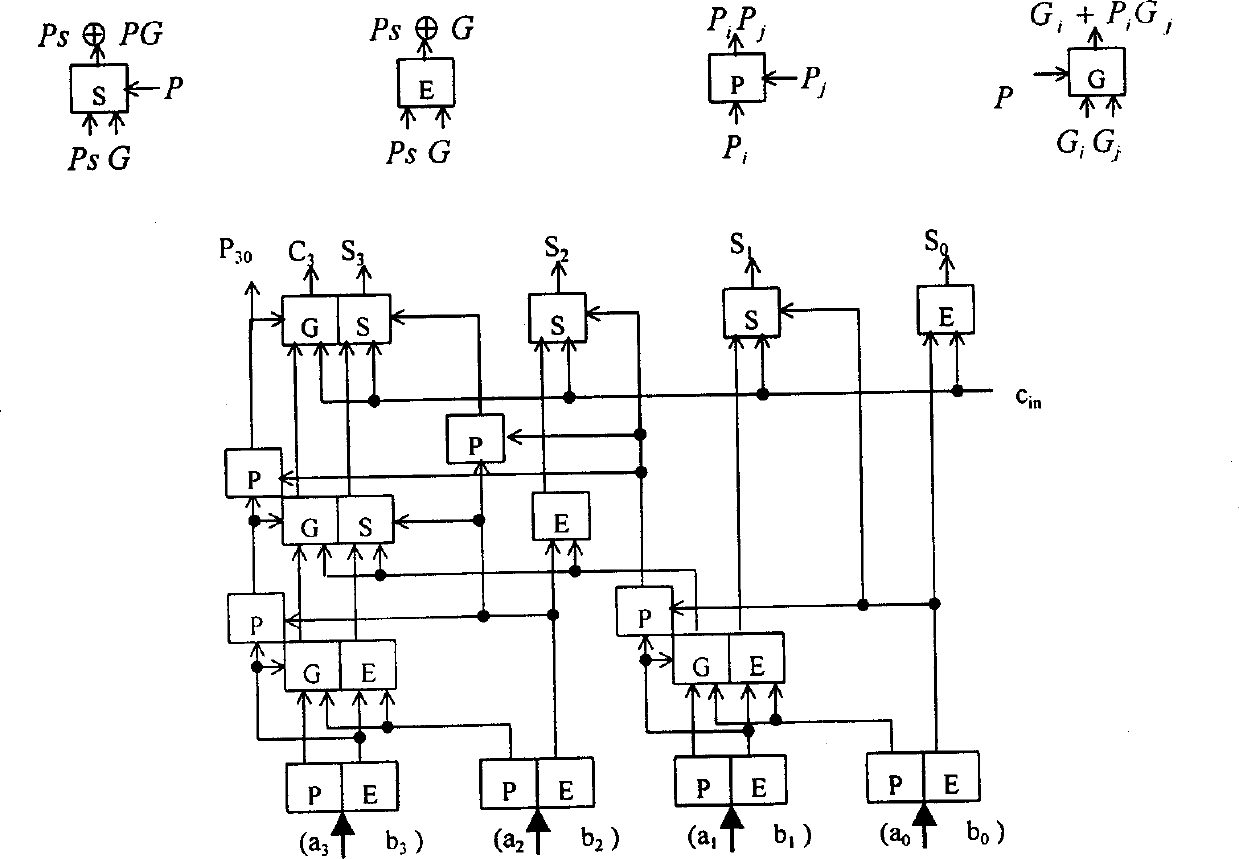
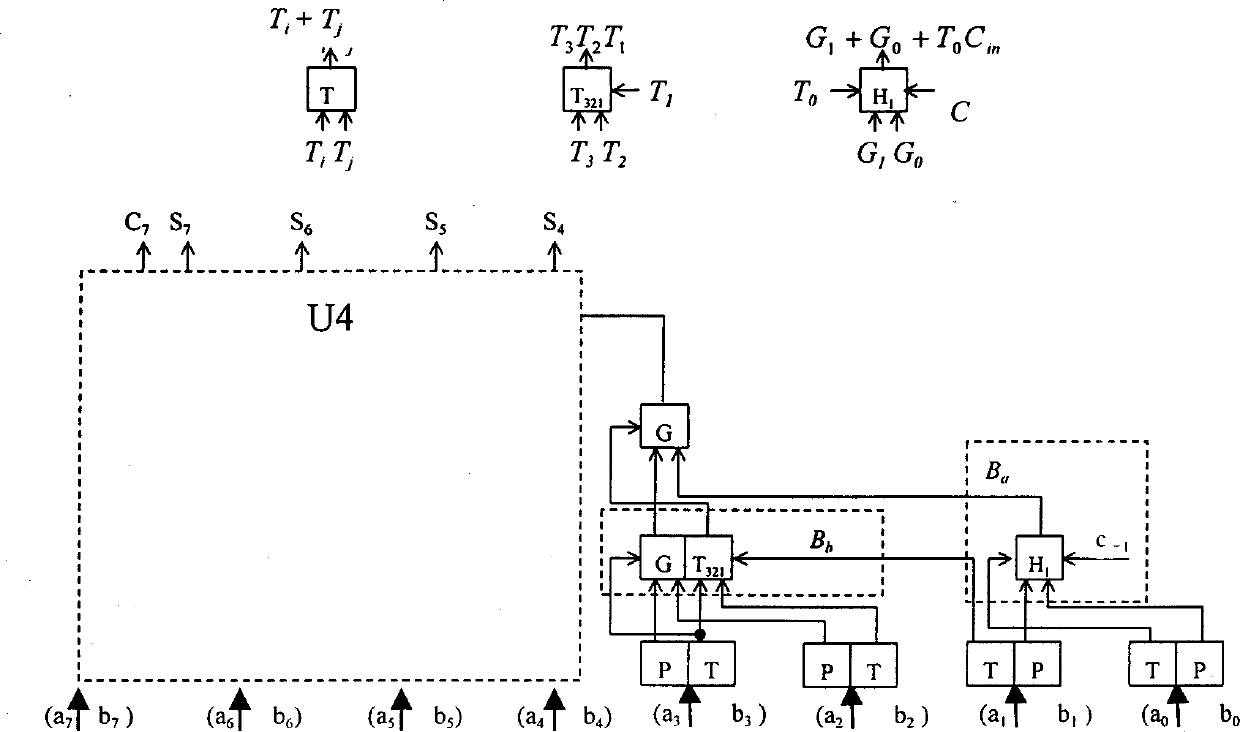
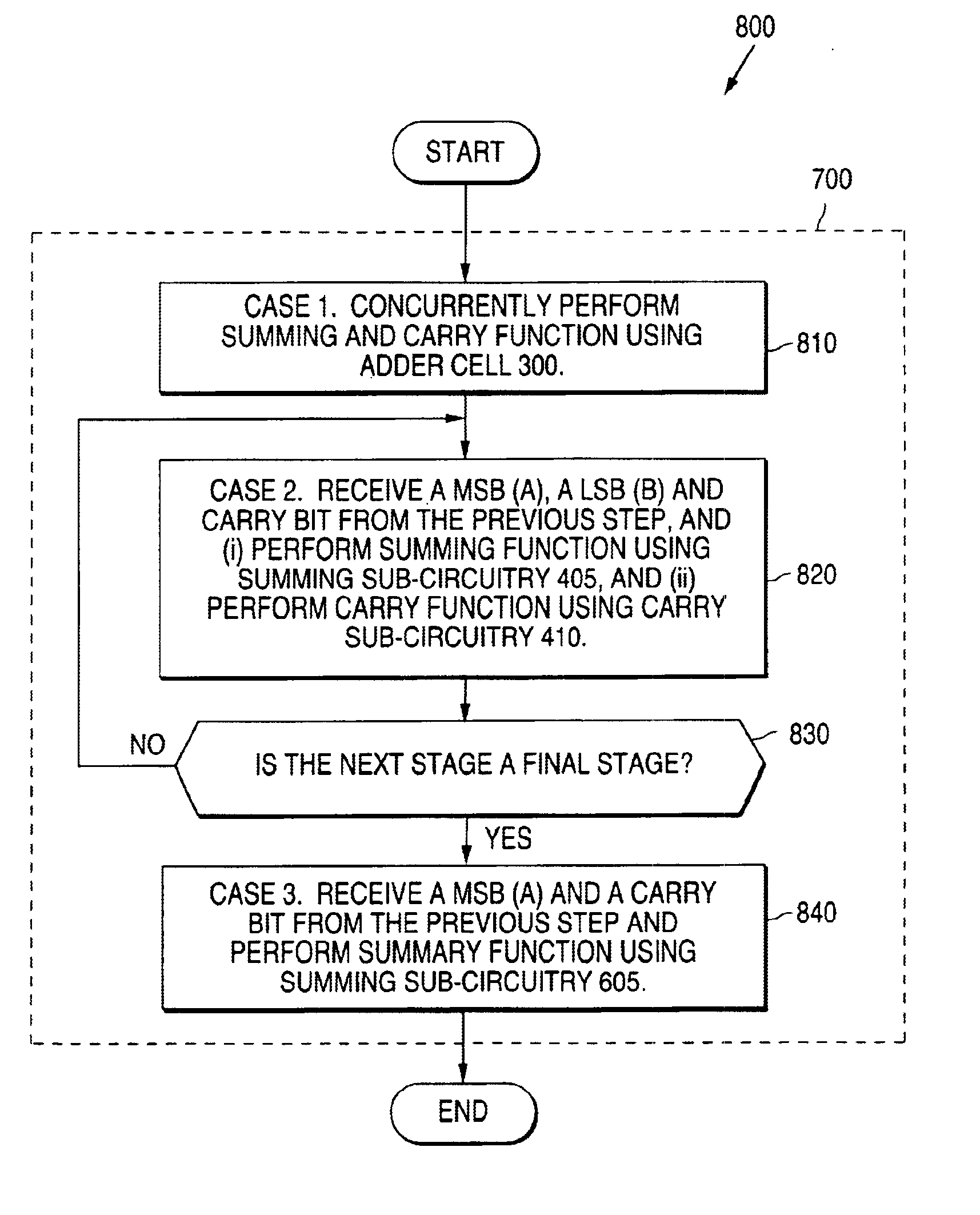
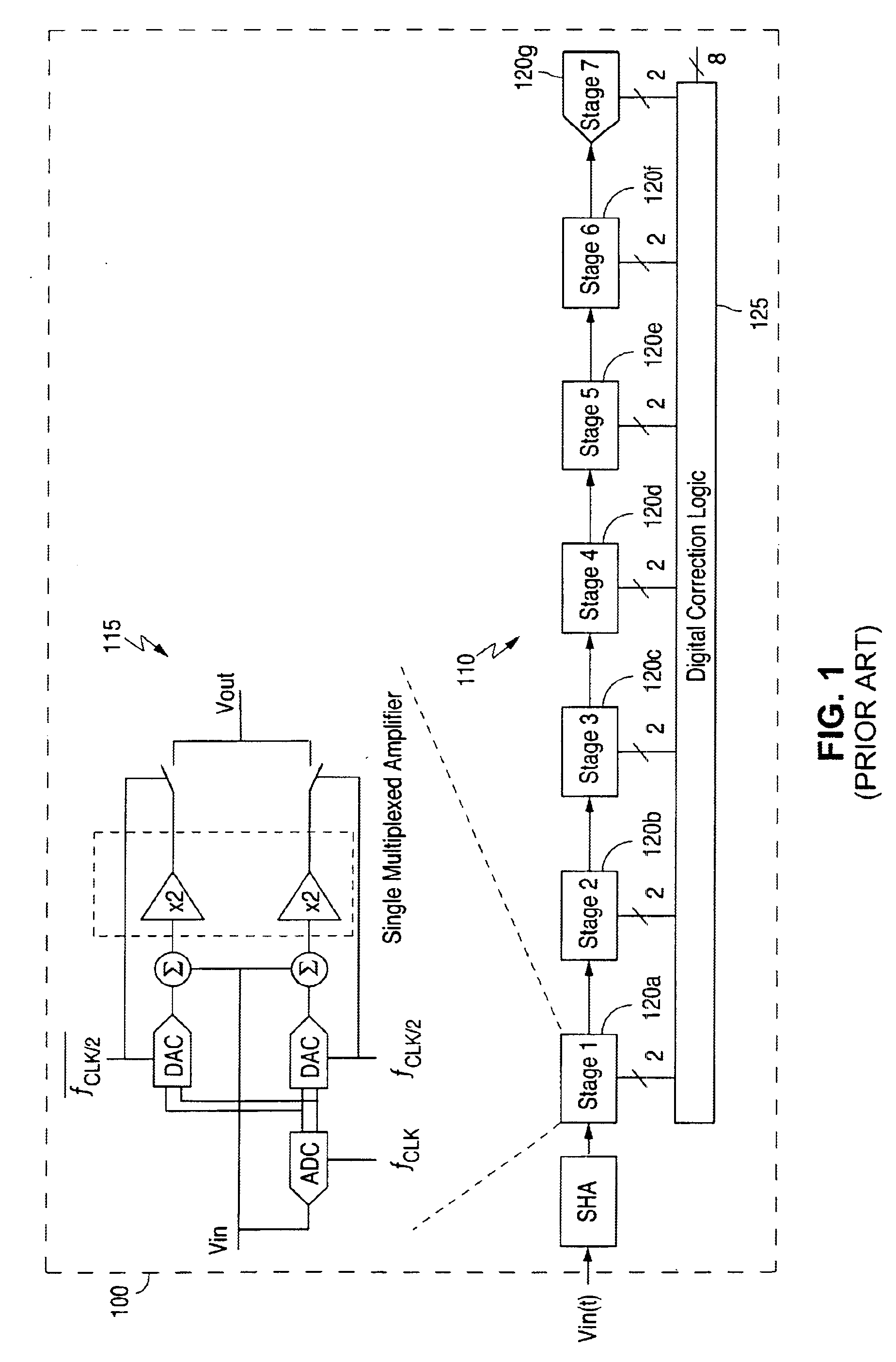
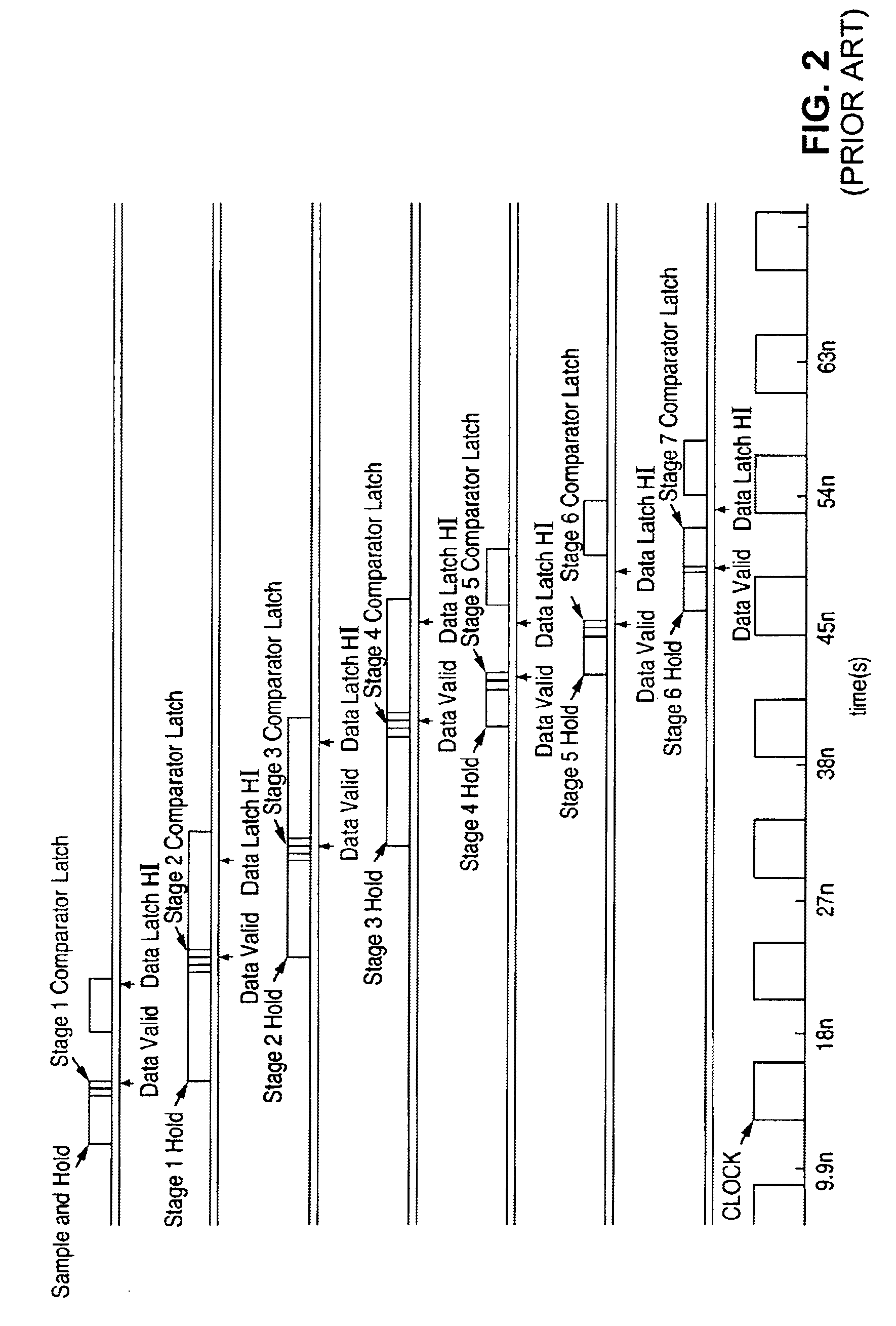
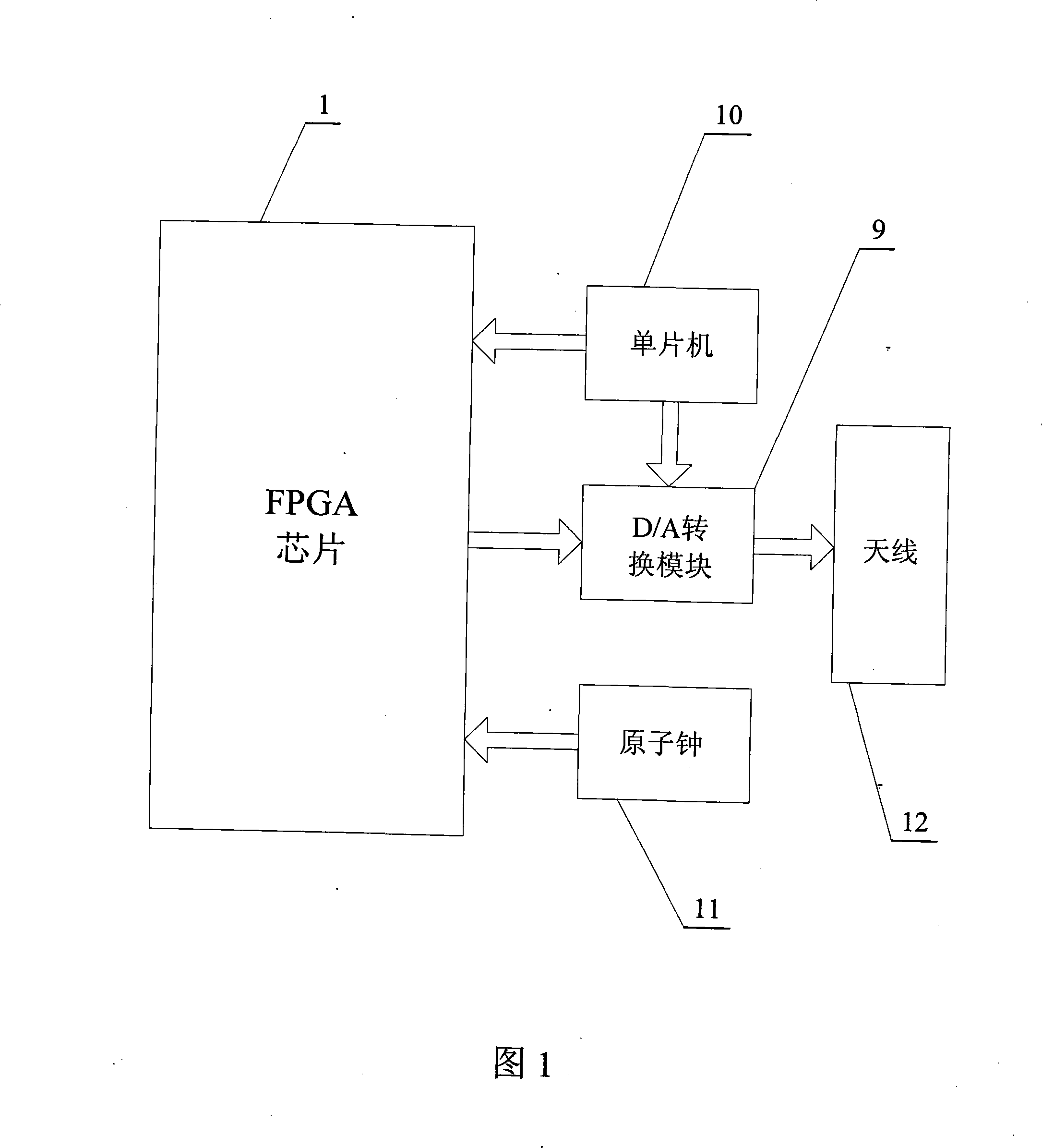
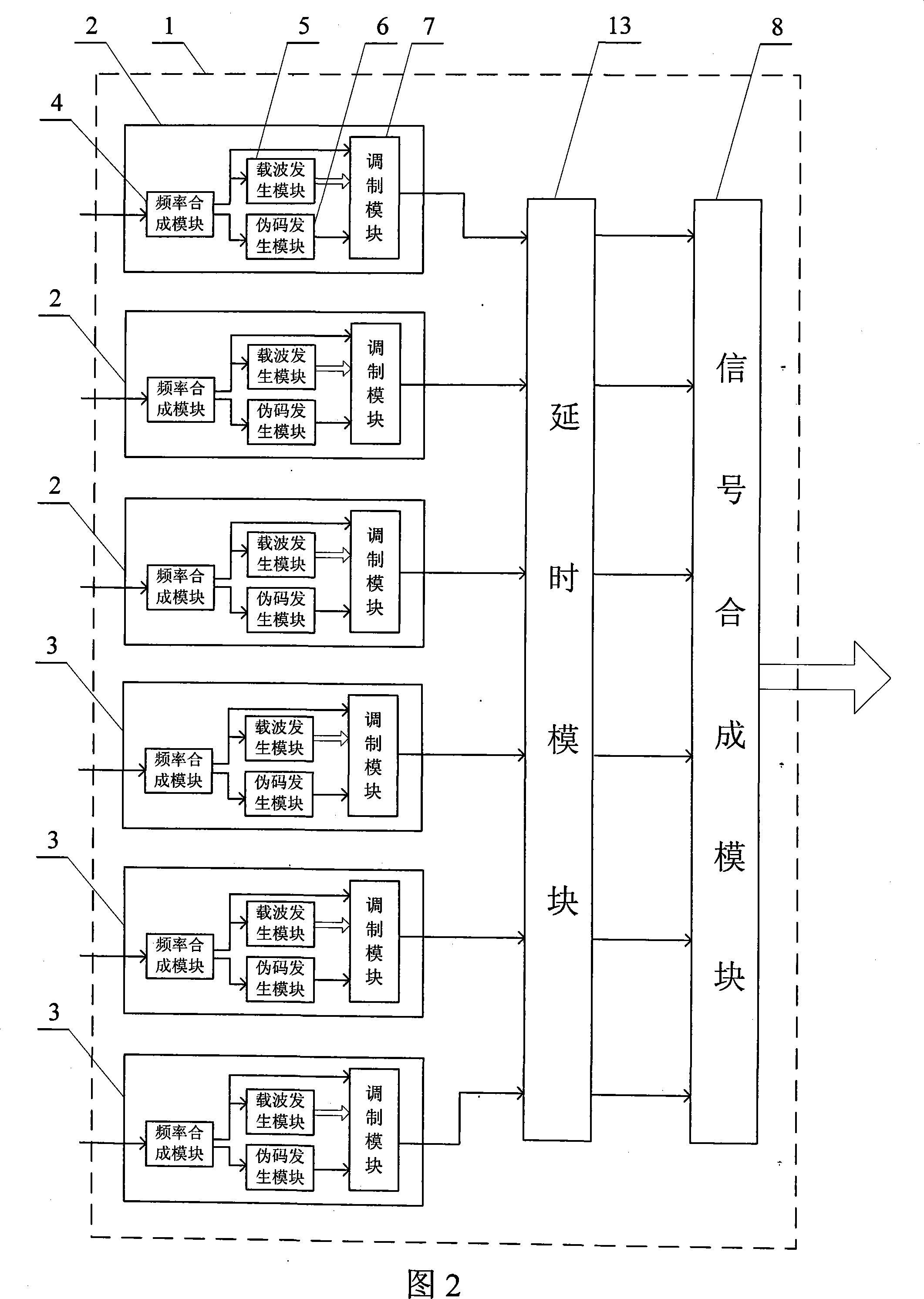
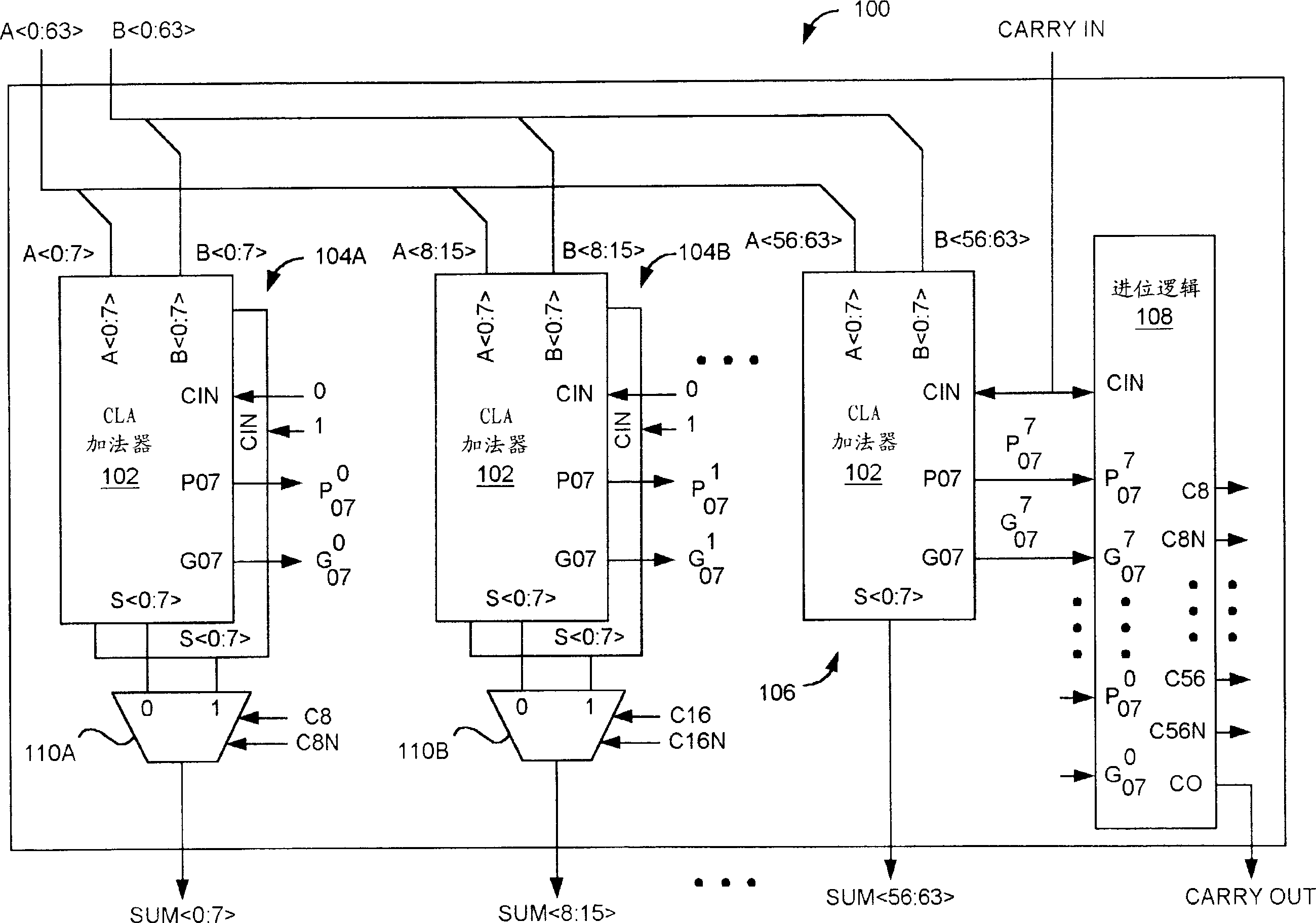
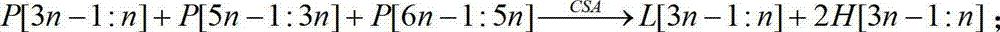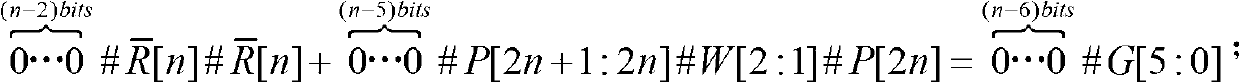Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117 results about "Binary addition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Efficient technique for matching hierarchies of arbitrary size and structure without regard to ordering of elements
InactiveUS7062493B1Efficient executionEasy to operateData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalElement OrderTheoretical computer science
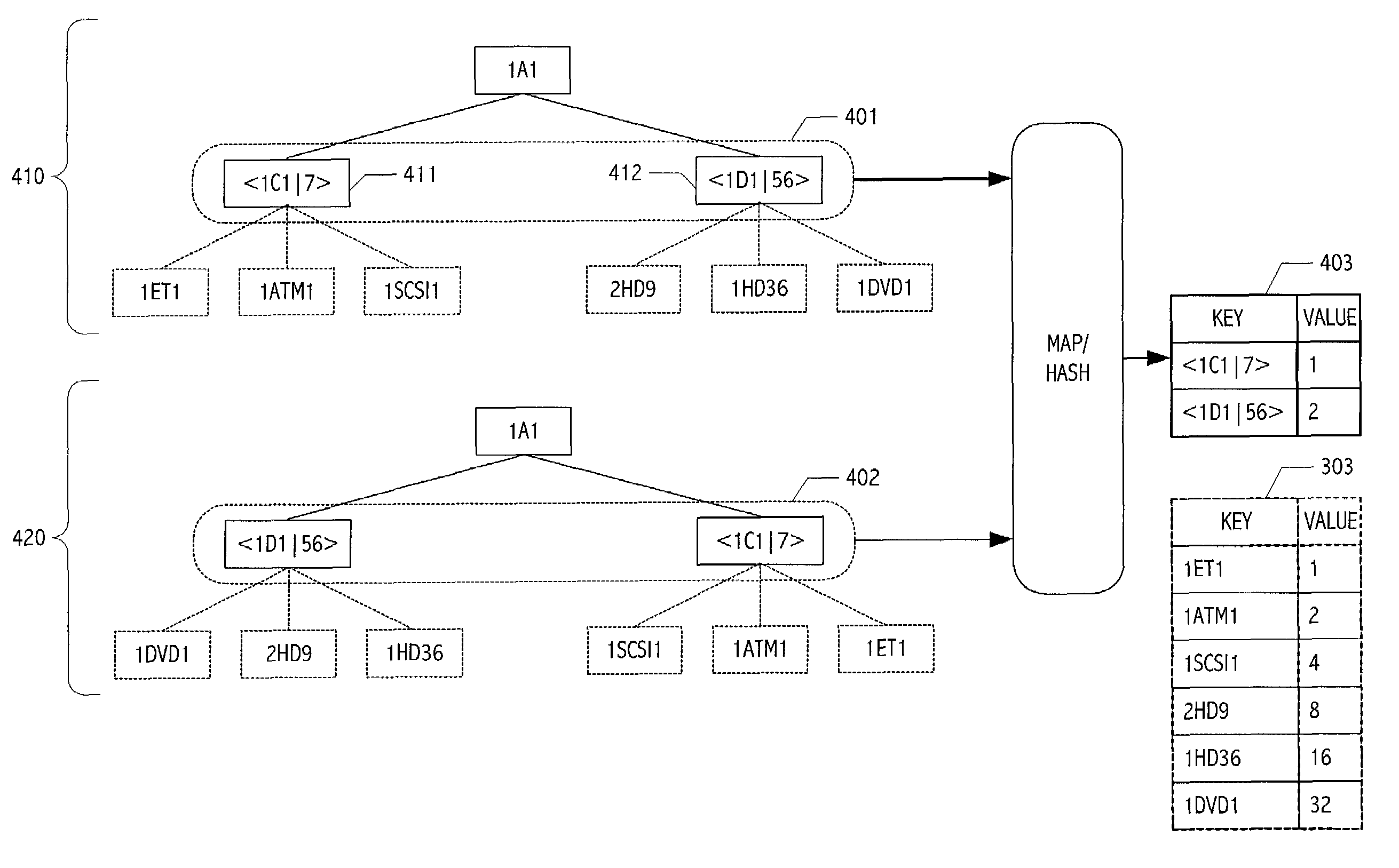
An element order independent comparison of hierarchically organized data structures may be performed efficiently using a transformation operation that orthogonally and recursively encodes child node information. In some implementations, a hash table is defined for which values are encoded as powers of two. Each value is therefore orthogonal when combined using simple binary addition. At any particular node, a concatenation of node-specific information with a sum of child-node hashes is, itself, hashed and associated with the node. Orthogonal encodings ensure that a combination (e.g., an additive combination) of values corresponding to elements of a sub-hierarchy is insensitive to ordering of the elements. Recursion can be employed to fold in information contributions at successive layers of an information hierarchy.
Owner:VERSATA DEV GROUP
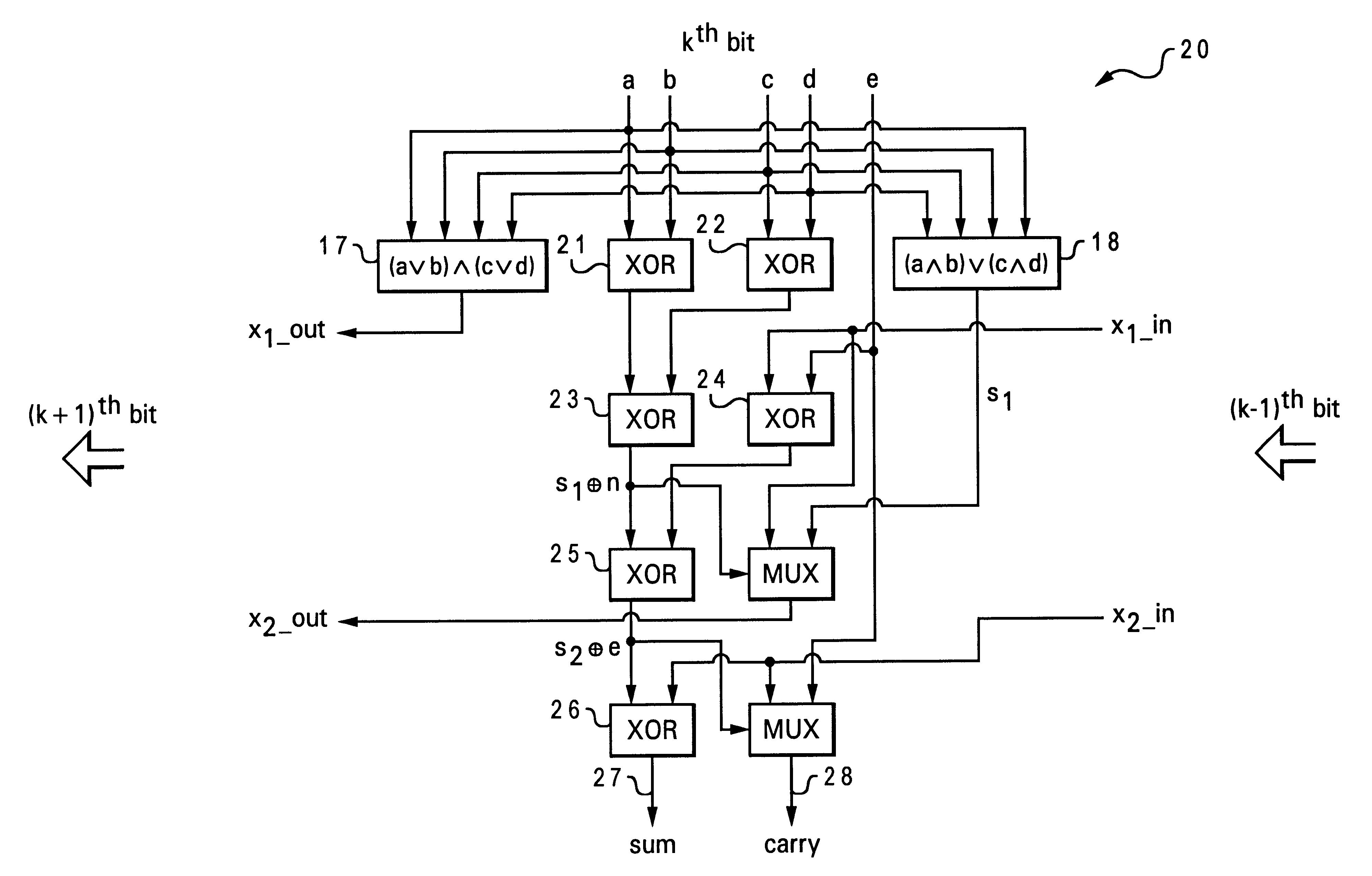
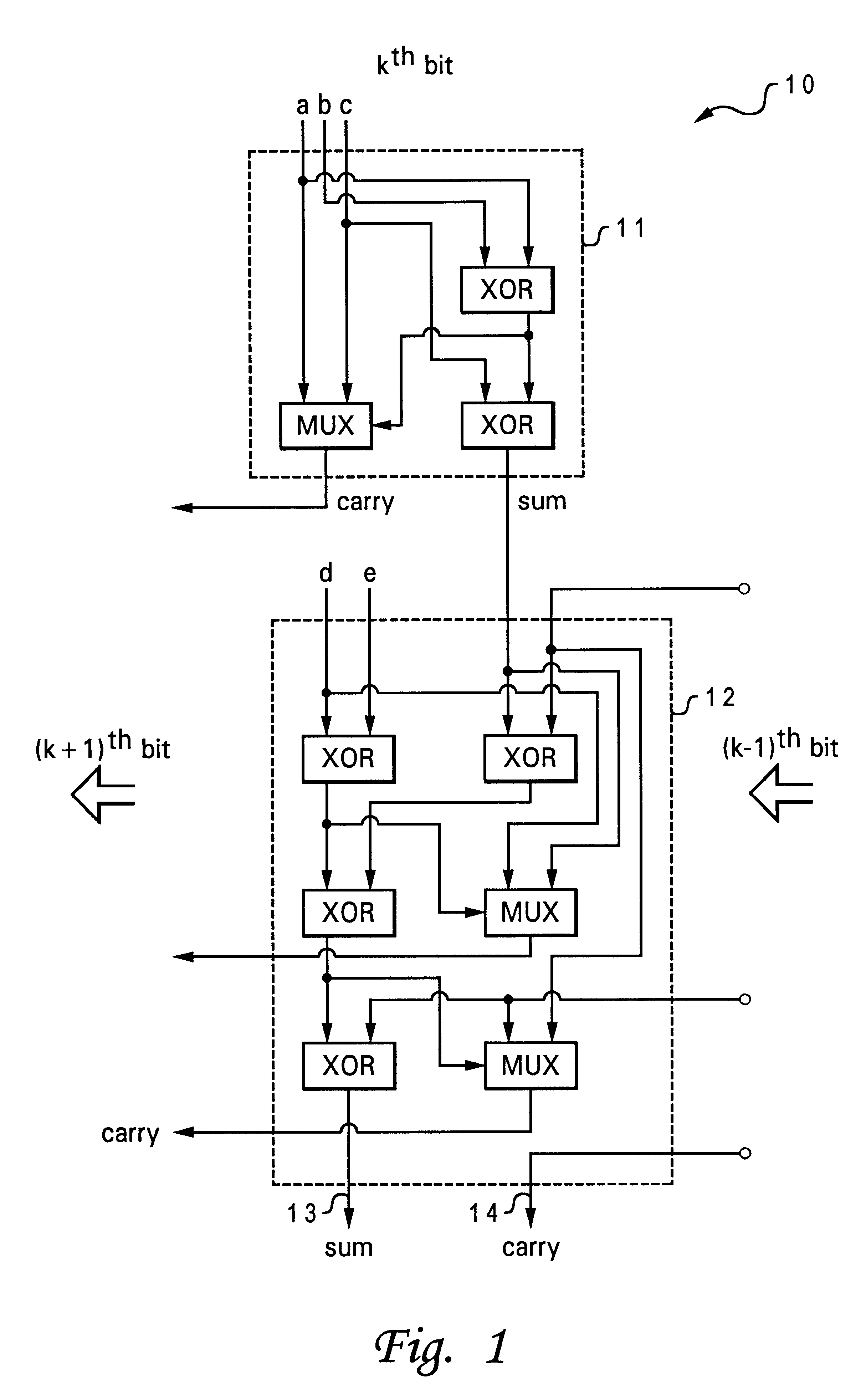
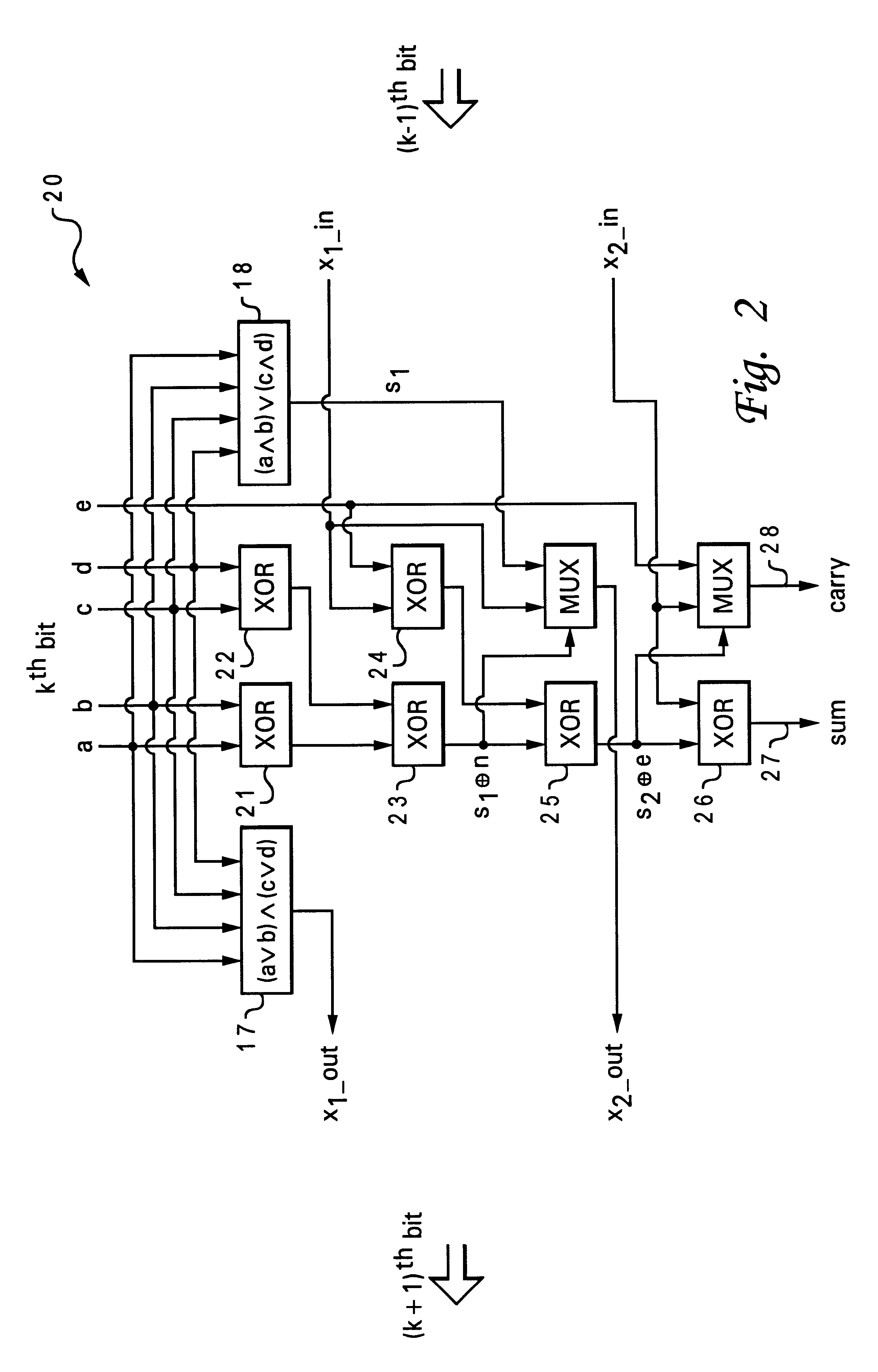
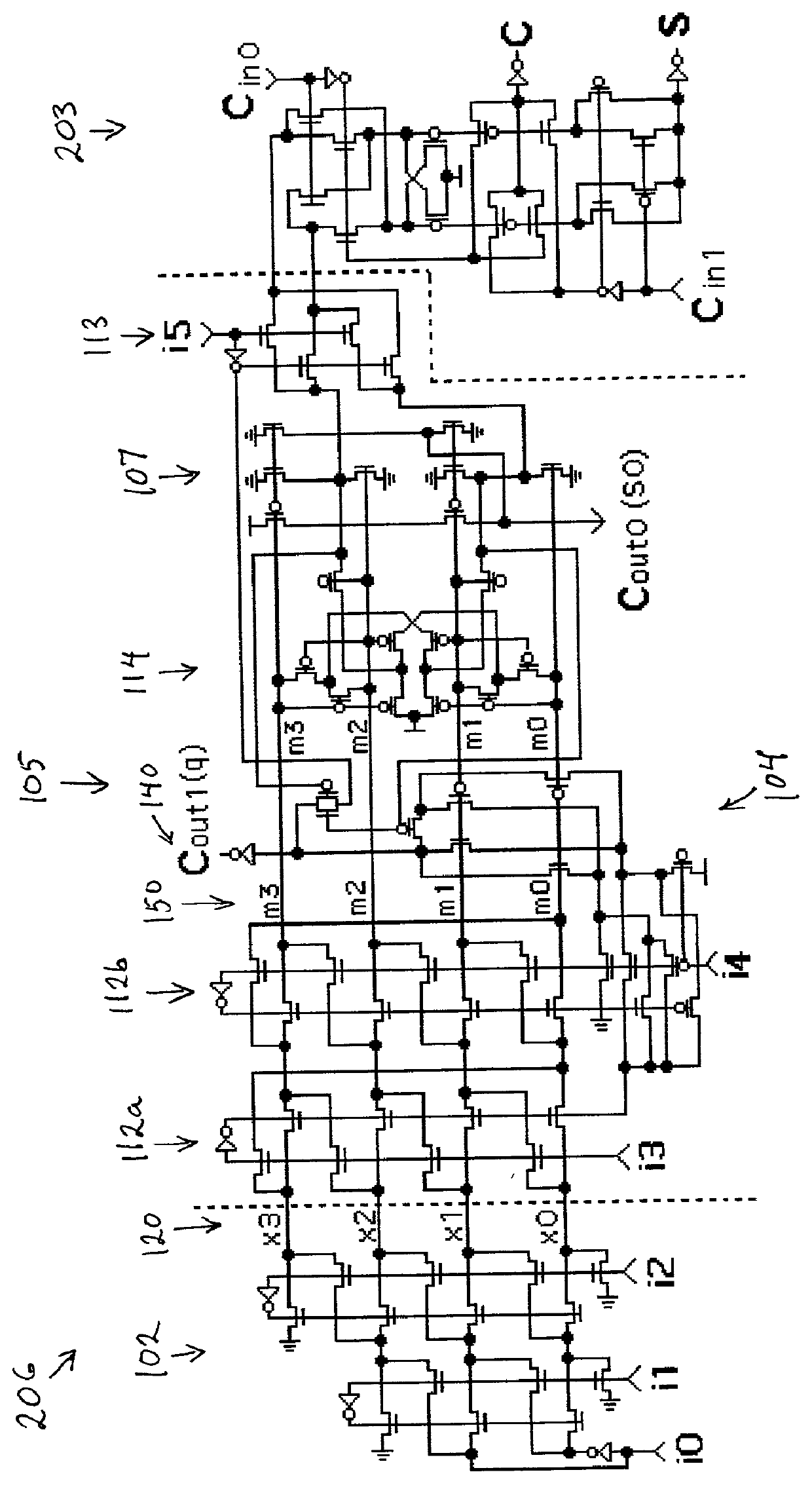
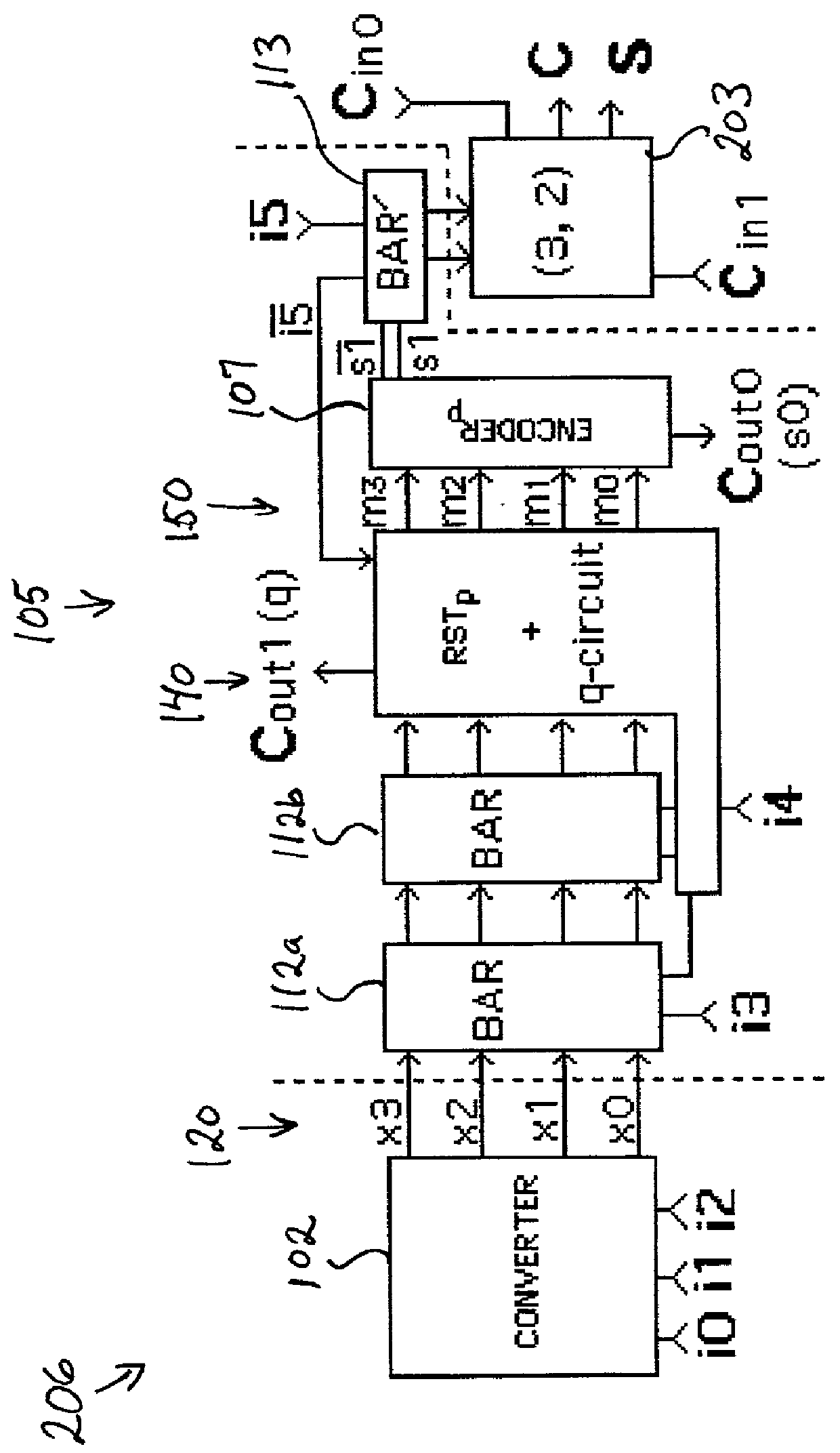
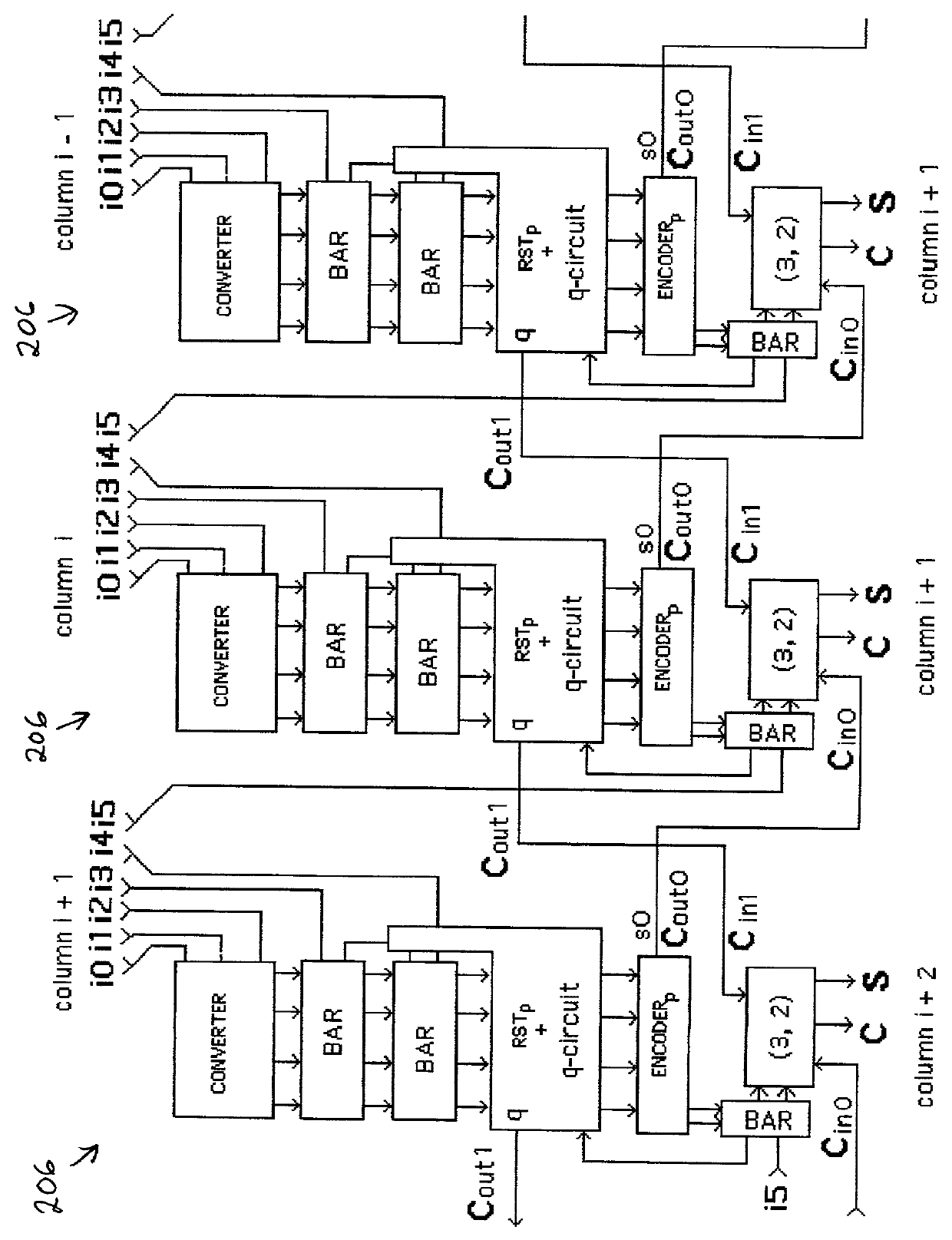
5-to-2 binary adder
A five-input / two-output binary adder is disclosed. The five-input / two-output adder includes five inputs and two outputs. Four levels of XOR logic gates are coupled between the five inputs and the two outputs for combining values received at the five inputs and generating a sum value and a carry value at the outputs.
Owner:IBM CORP
Quasi-cyclic LDPC serial encoder based on ring shift left
InactiveCN103248372ASimple structureReduce power consumptionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionShift registerBinary multiplier
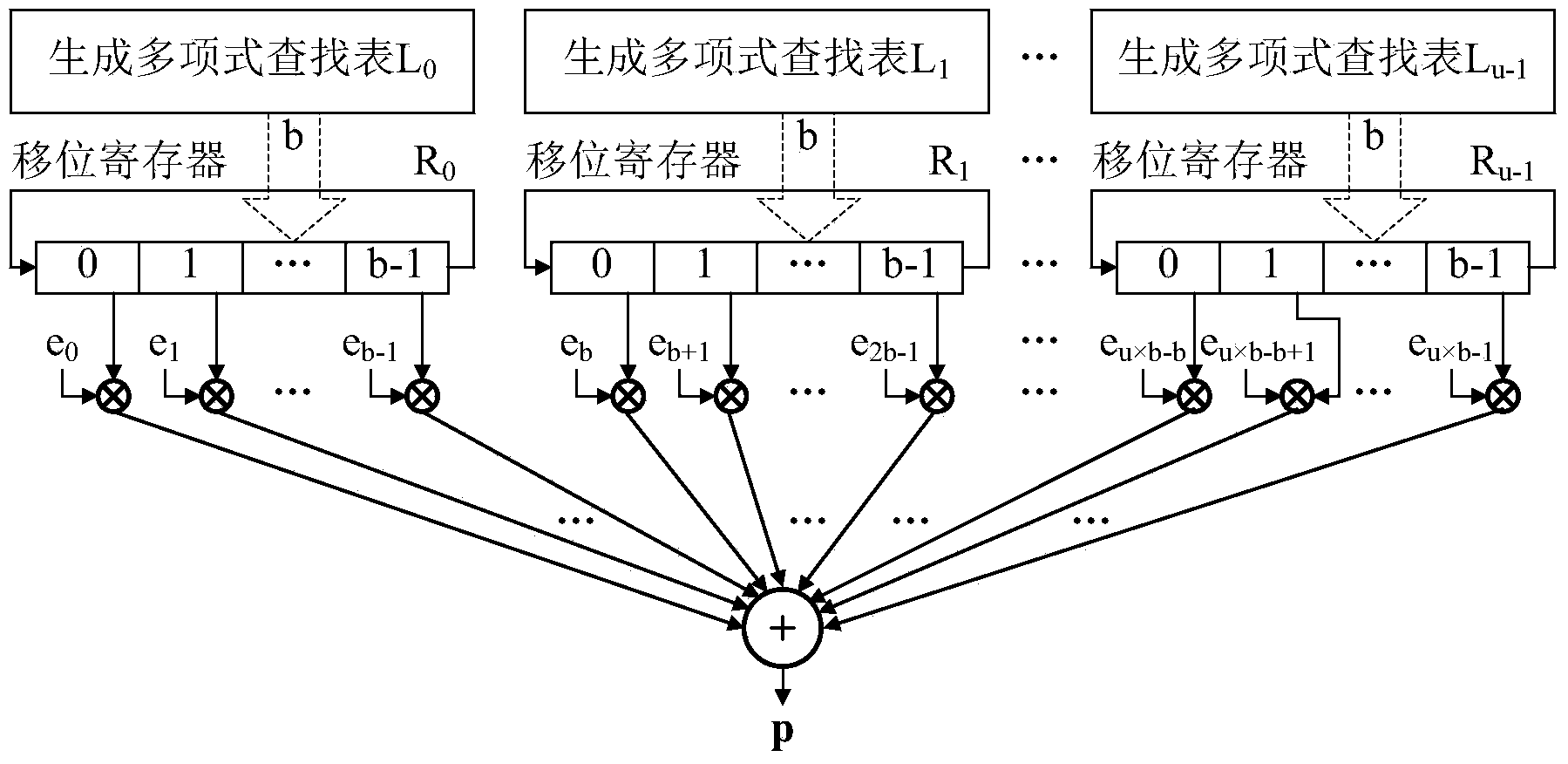
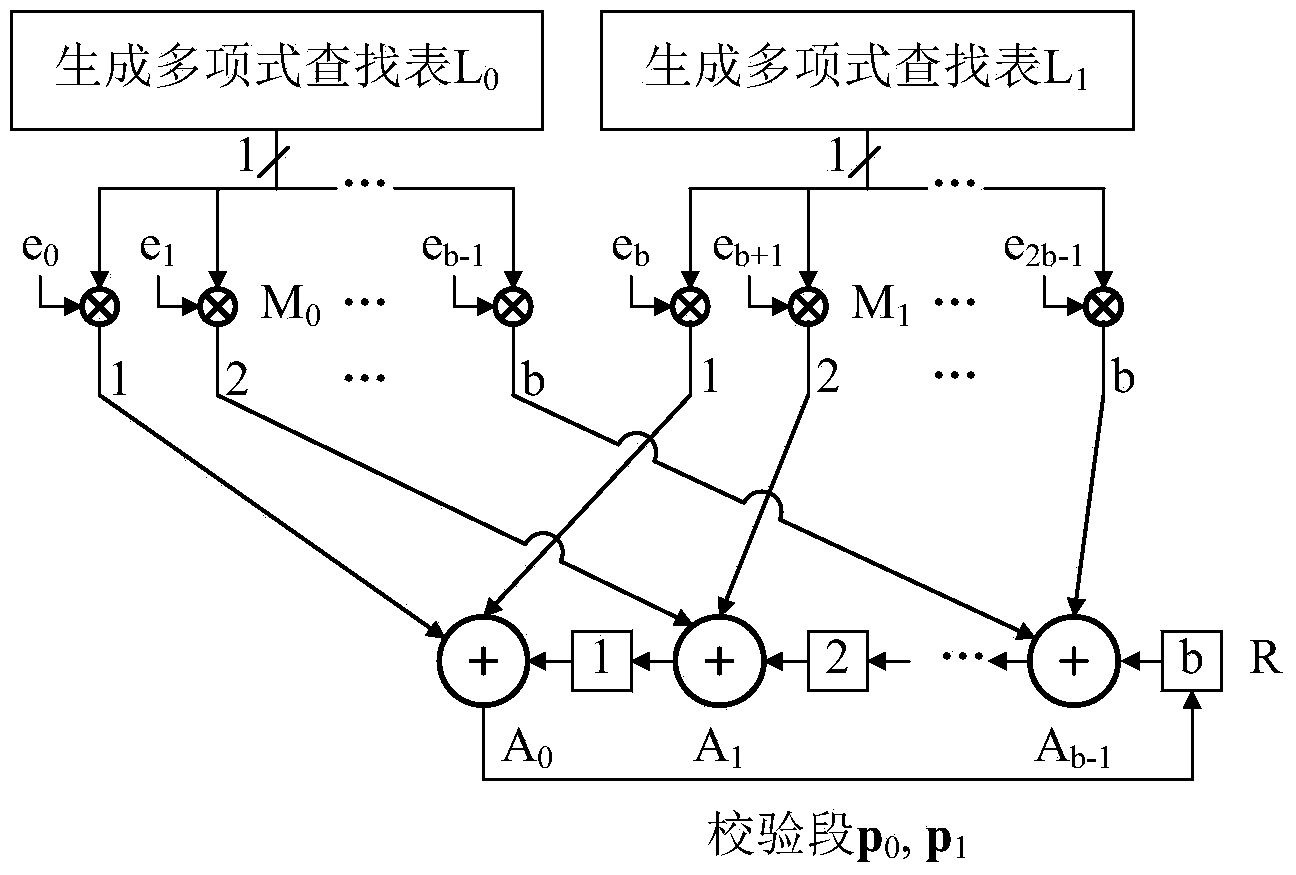
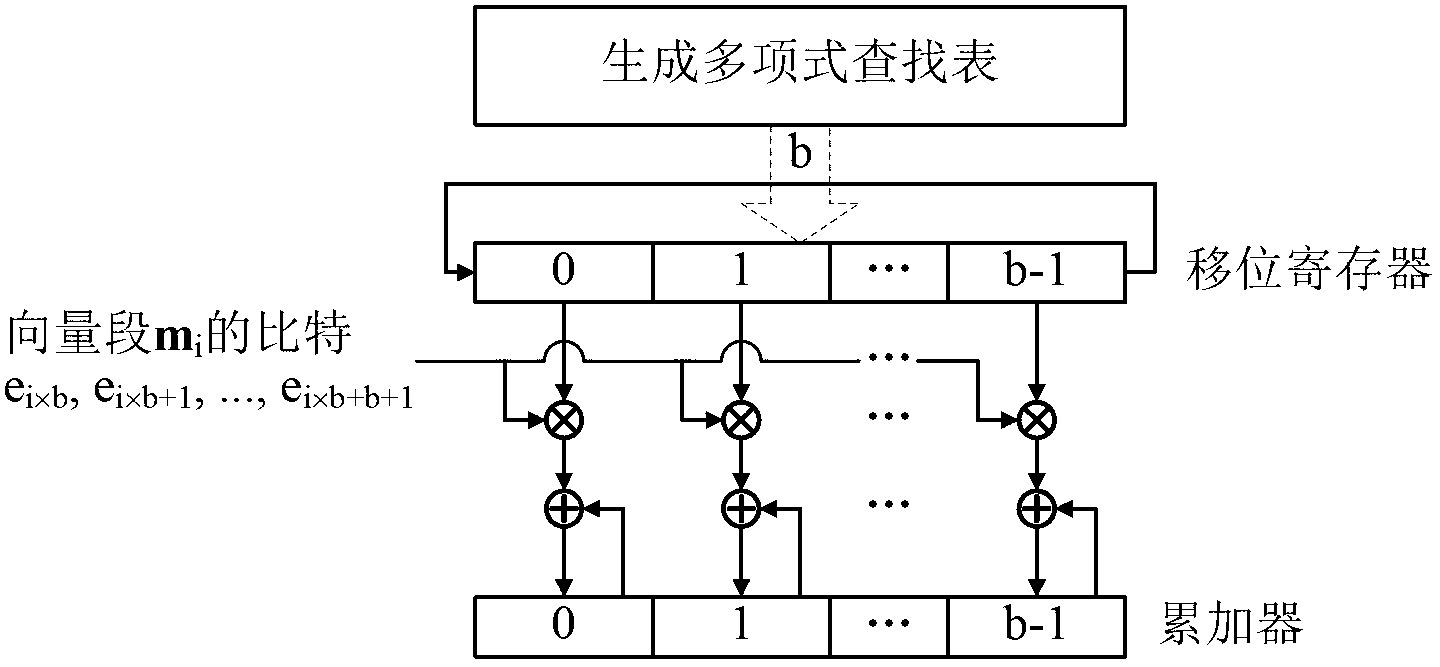
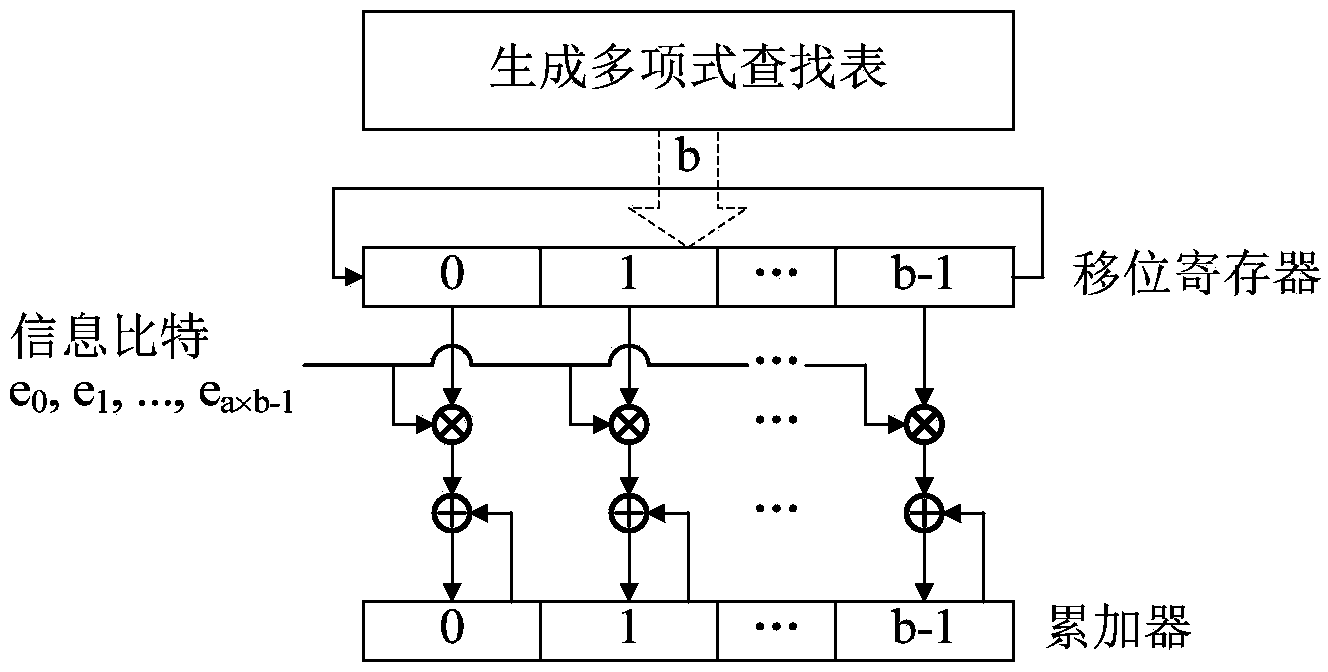
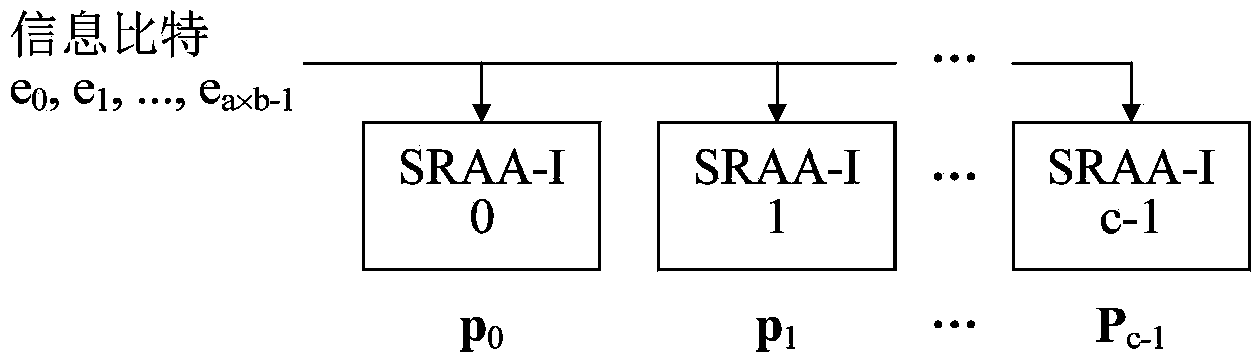
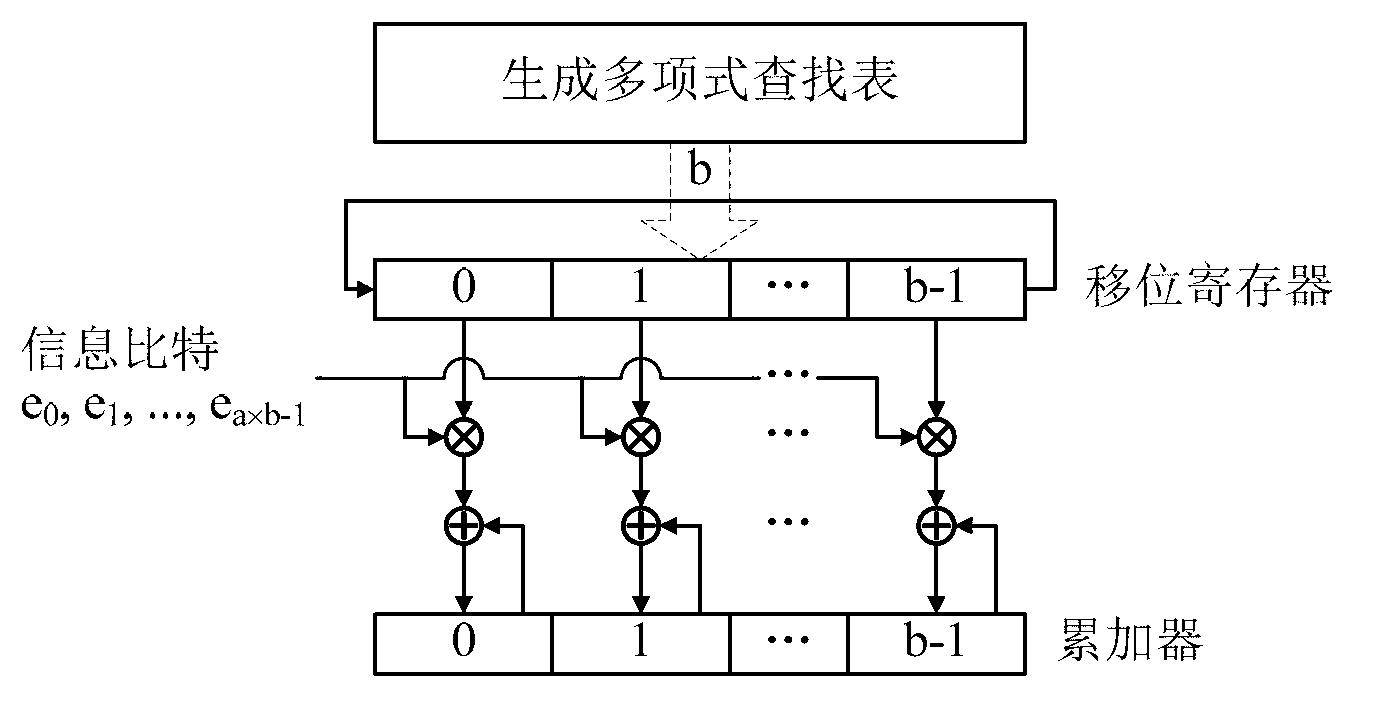
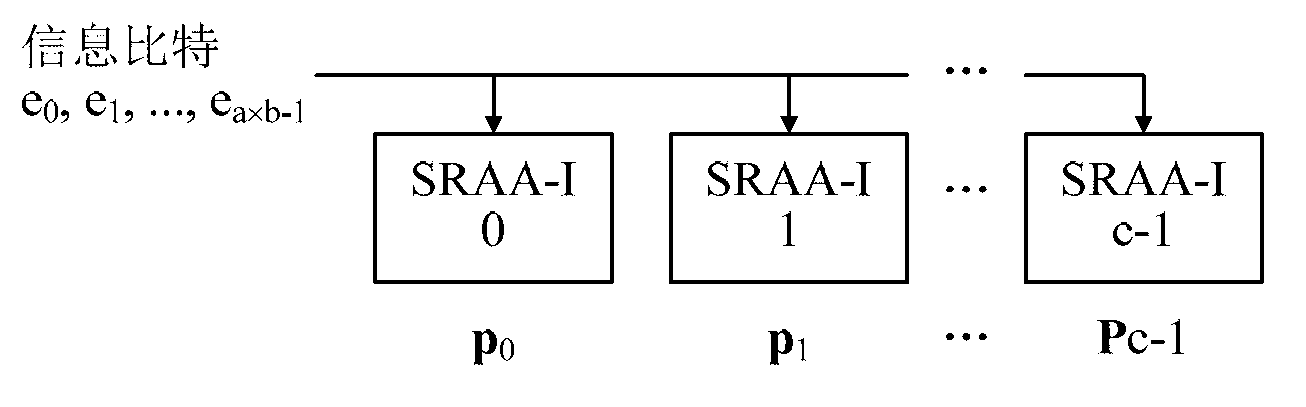
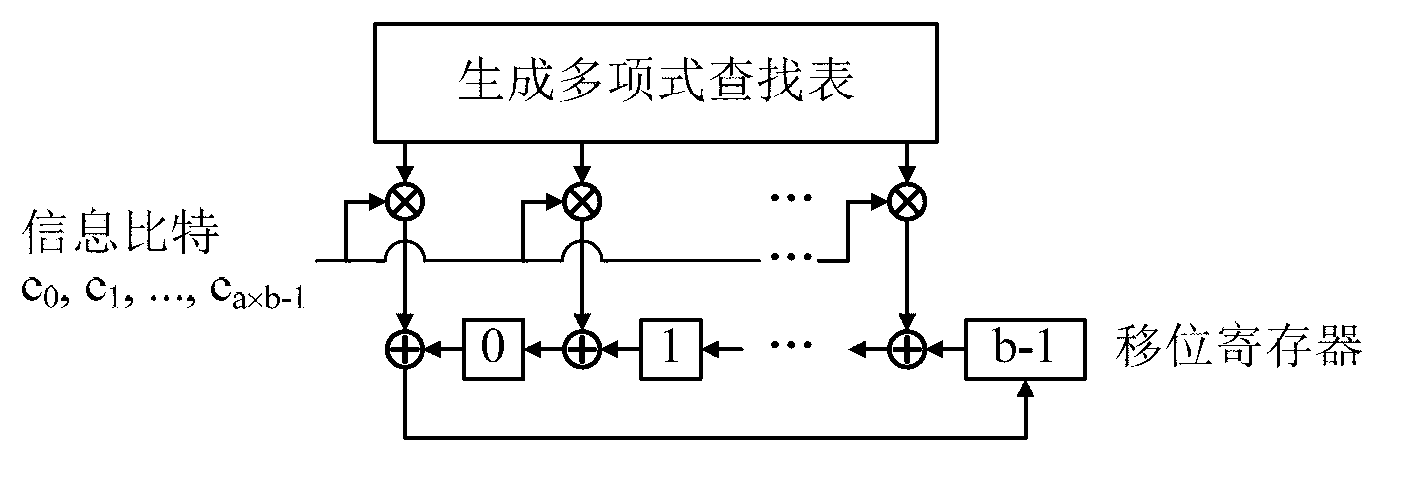
The invention provides a quasi-cyclic LDPC serial encoder based on ring shift left, which includes c generator polynomial lookup tables of all cyclic matrix generator polynomials in a prestored generated matrix, c b-bit binary multipliers for performing scalar multiplication to information bit and generator polynomials, c b-bit binary adders for performing modulo-2 adding to product and content of shifting registers, and c b-bit shifting registers for storing the sum of ring shift left for 1 bit, and finally, the checking data is stored in the c shifting registers. The serial encoder provided by the invention has the advantages of few registers, simple structure, low power consumption, low cost and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Dual cycle construction method suitable for high code rate quasi cyclic-low density parity check (QC-LDPC) code
ActiveCN104821831AImprove performanceImprove codeword performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsZero matrixLow density
According to a quasi-cyclic low density parity check code basis matrix construction method, node distribution acquired through optimization of a density evolution algorithm is used, then a stretch factor Z is set, the circle length of the LDPC code check matrix and external message scale of the circle are jointed optimized, finally, a QC-LDPC code basis matrix with excellent performances is generated through extension. Each element in the basis matrix is corresponding to one Z*Z dimensional all-zero matrix, a unit matrix or a cyclic shift matrix of the unit matrix. But in construction of high code rate QC-LDPC code, the contradiction of limitation of matrix row number and maximum line number usually occurs, namely, the maximum line number is greater than the row number. To solve the problem, the invention provides construction of the basis matrix through a method increasing line number through superposition of a plurality of cyclic shift matrixes, namely, multiple cyclic shift matrixes are embedded in a single block matrix. The "superposition" operation is binary addition, the constructed basis matrix not only guarantees the cycle performance of the QC-LDPC code, but also meets the requirement of optimization of codon performance through increase of minimum code distance.
Owner:南京融星智联信息技术有限公司
Quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier based on rotate left
InactiveCN103268217ASimple structureReduce power consumptionDigital data processing detailsShift registerBinary multiplier
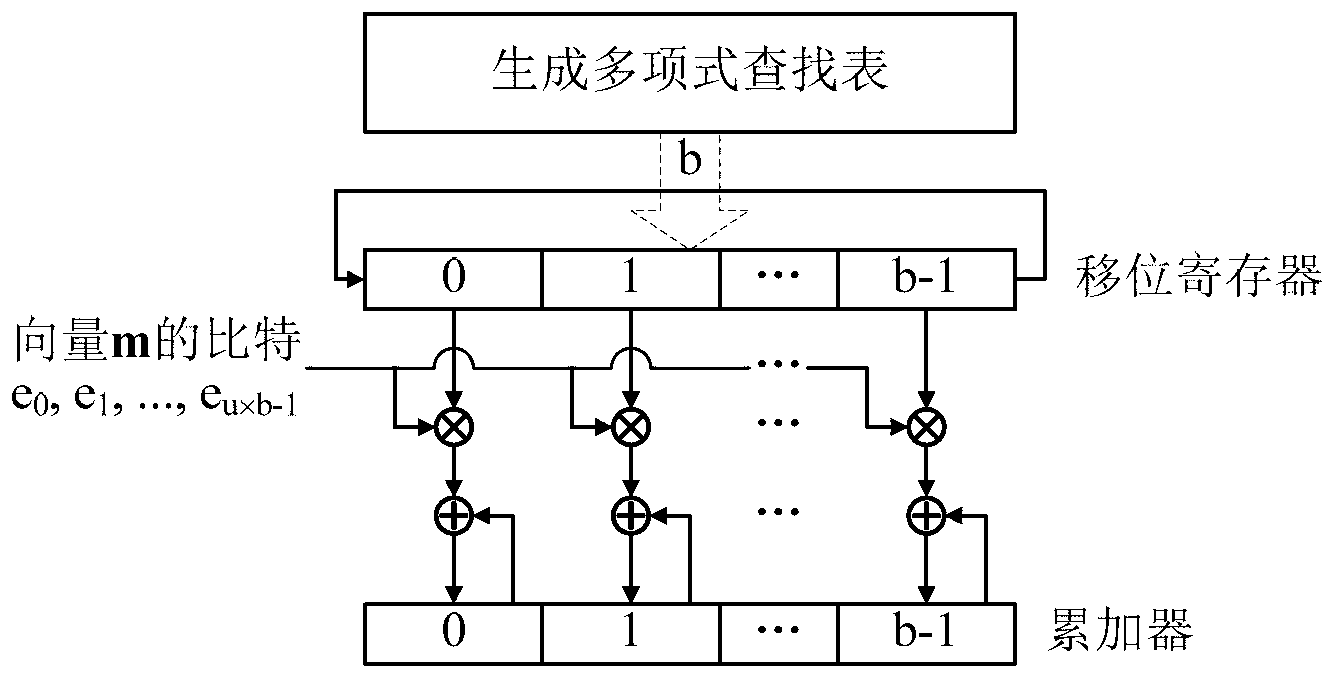
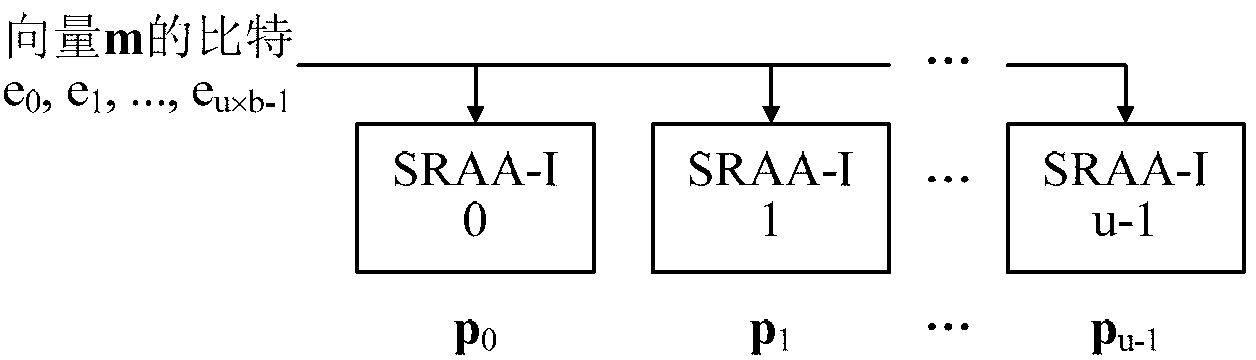
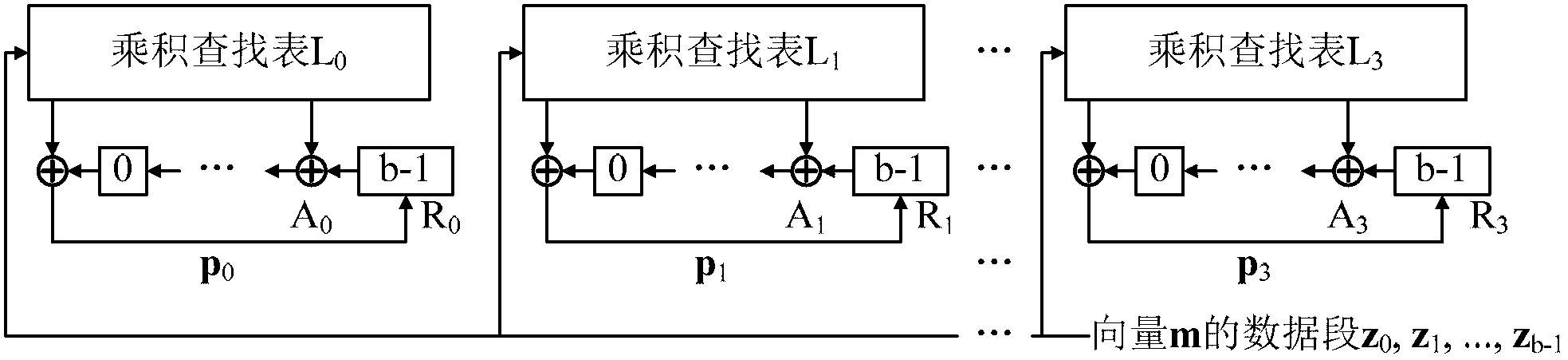
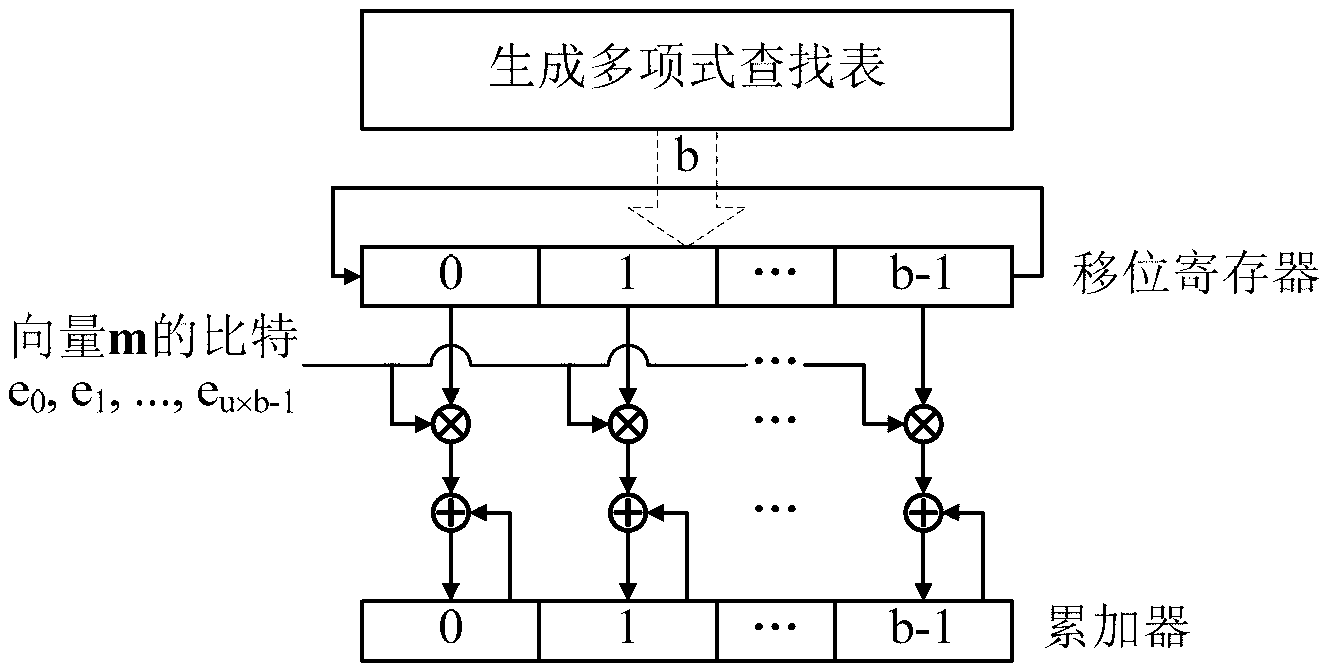
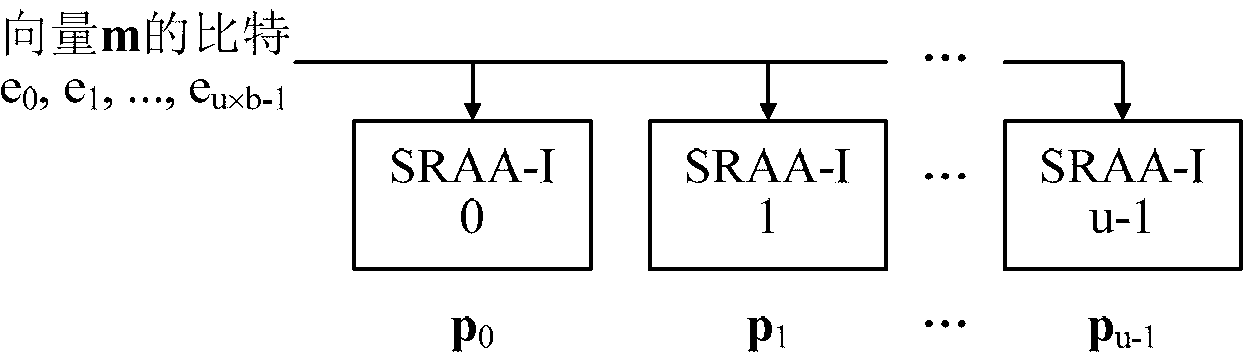
The invention provides a quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier based on rotate left. The quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier is used for implementing multiplication of a vector m and a quasi-cyclic matrix F in QC-LDPC (quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check) approximate lower triangular encodings. The multiplier comprises u generated polynomial lookup tables, u b-bit binary multipliers, u b-bit binary summators and u b-bit shift registers. The generated polynomial lookup tables are used for pre-storing quasi-cyclic matrix generated polynomial in the matrix F. The b-bit binary multipliers are used for performing scalar multiplication of the vector m data bit and the generated polynomial. The b-bit binary summators are used for performing modulo-2 adding of products and shift register contents. The b-bit shift registers are used for storing sums of 1-bit movements subjected to rotate left. The quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier has the advantages of small number of registers, simple structure, low power consumption and cost and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
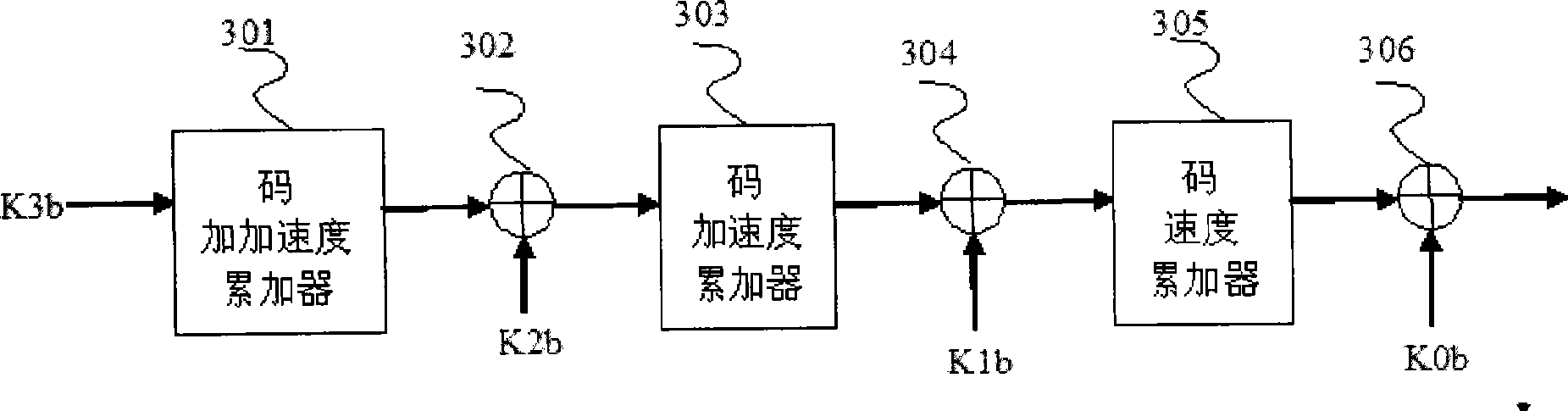
High dynamic high precision intermediate frequency simulation satellite signal generating method
InactiveCN101509968ASimple structureStable speedBeacon systems using radio wavesCarrier signalMedium frequency
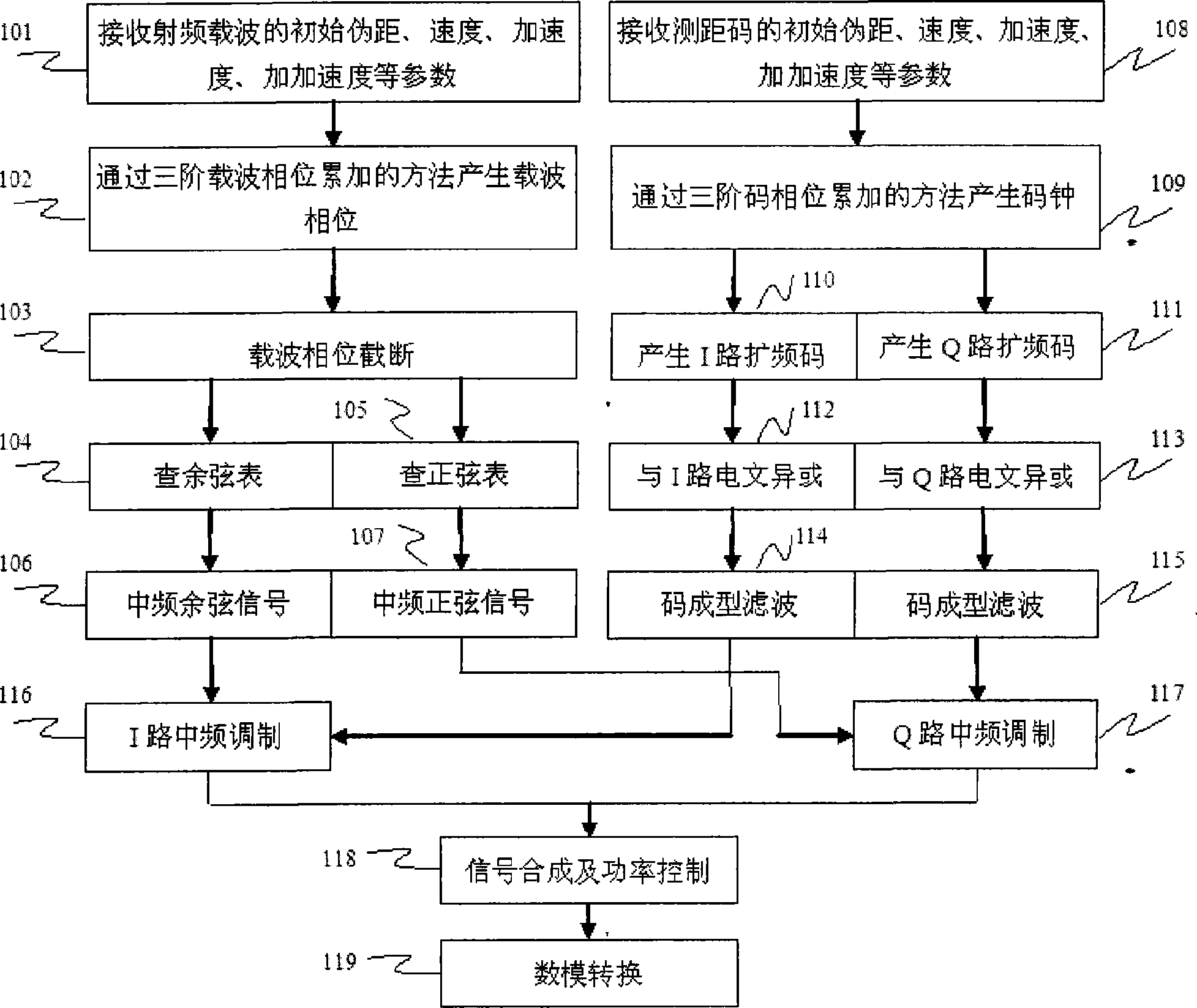
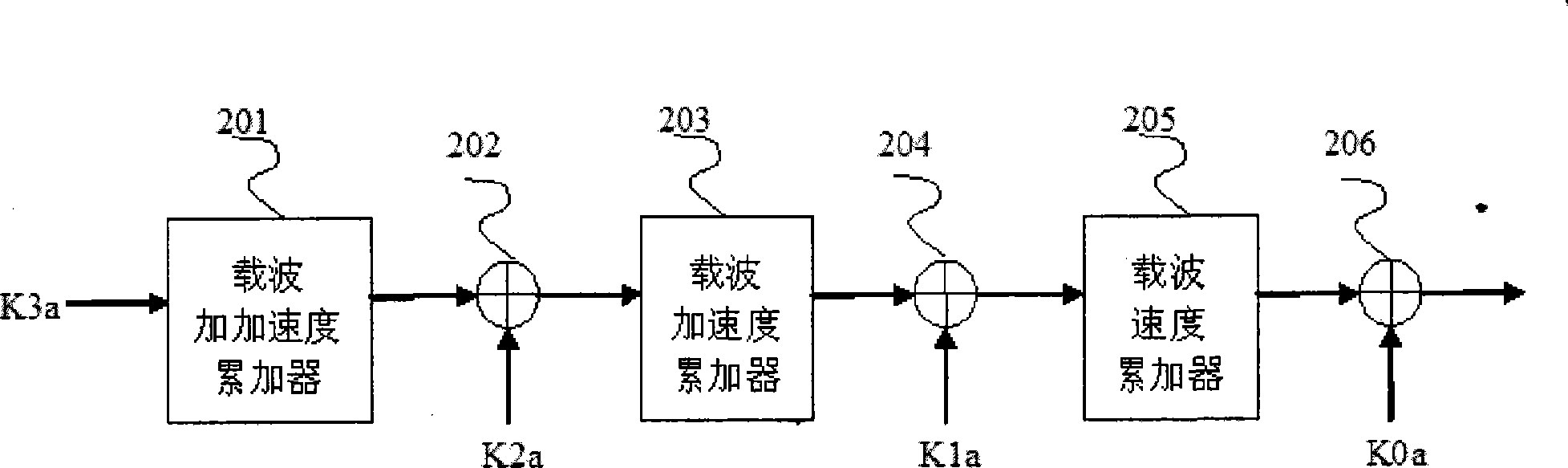
The invention relates to a method for generating medium-frequency satellite signals with high dynamic situation and high precision, and the method comprises the following steps: 1) parameters of a radio-frequency carrier are received, including the initial pseudo distance, the speed, the acceleration and the jerk; 2) the carrier phase with high precision and including Doppler frequency shift is generated by a method of three-phase carrier phase accumulation; 3) a medium-frequency carrier signal is obtained after carrier phase truncation by searching sine and cosine tables; 4) parameters of a ranging code are received, including the initial pseudo distance, the speed, the acceleration and the jerk; 5) a code clock with high precision is generated by a method of three-phase code phase accumulation; 6) under the action of the code clock, I-path and Q-path spreading codes are generated; 7) I-path and Q-path navigation messages are read and binary addition is carried out with the spreading codes; 8) the spreading codes are molded, filtered and modulated onto the medium carrier; 9) power control and digital-to-analog conversion are carried out to the spreading signals, thus obtaining the medium-frequency analogue satellite signals. The method has the advantages of simple structure, smooth speed without step and high precision.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Family of low power, regularly structured multipliers and matrix multipliers
InactiveUS20010056455A1Computation using non-contact making devicesNumber-of-one countersCircuit complexityPartial product reduction
A family of embodiments of a new class of CMOS VLSI computer multiplier circuits that are simpler to fabricate, smaller, faster, more efficient in their use of power, and easier to scale in size than the prior art. The normal binary adder circuit unit is replaced by the innovative shift switch circuit unit. Use of the shift switch circuit sharply reduces fluctuations of power caused by plurality variations in the bit representations of the input, intermediate and output numbers. Reduced-scale devices are used in shift-switch pass-transistor signal restoration circuits, significantly reducing the size, power demand, and power dissipation of internal circuitry, in contrast to ordinary multiplier design. The simplicity of the circuit design allows multiplier partial-product reduction in fewer logic stages than existing comparable designs allow, showing speed improvement over such designs. The circuit design simplicity and the use of reduced-scale devices require less VLSI area than existing designs need, facilitating integration in VLSI microprocessors. Modular circuit organization simplifies scaling for larger operands without the circuit complications of existing designs. The design includes a critical flip of the physical layout of the partial-product matrix at each size level, simplifying the layout of traces in the circuit at all size scales. Finally, the application of reconfigurable design principles to the easily-scaled layout reduces significantly the mean demand for computing resources over a wide range of multiplication bit-width scales, as compared to existing designs. Overall, the orchestrated integration of these diverse design innovations makes possible the implementation of simpler, faster, smaller, more efficient, more flexible, and easier-to-build VLSI multiplication circuits than the current art reveals.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Fixed-bit-width multiplier with high accuracy and low complexity properties
InactiveCN105183425AHigh compensation accuracyDigital data processing detailsBooth encodingBinary multiplier
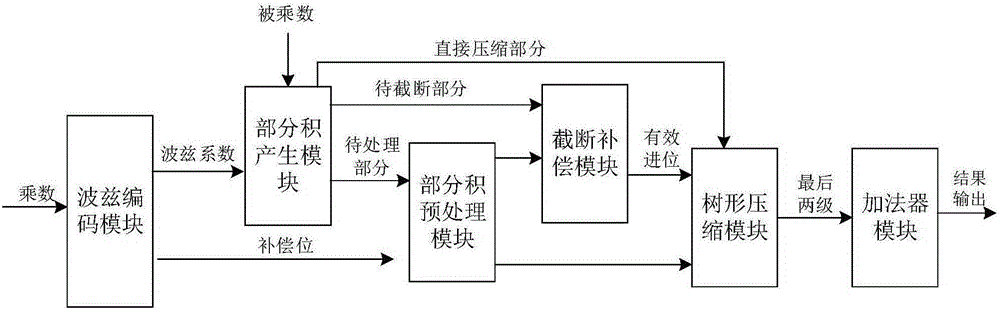
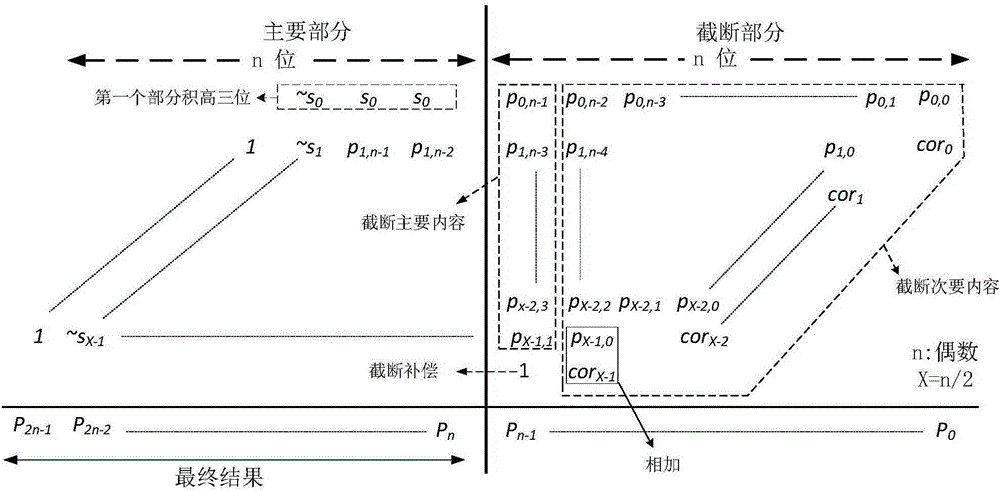
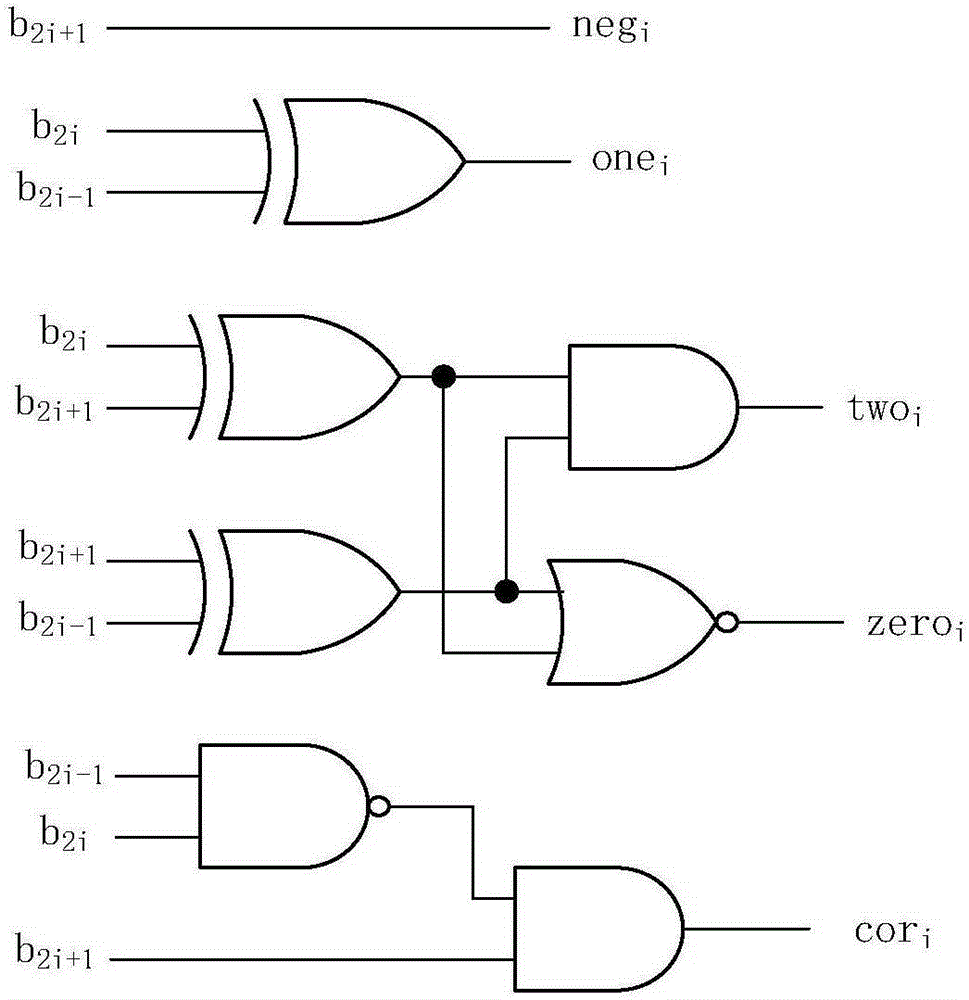
The present invention relates to the technical field of integrated circuits, and in particular to a fixed-bit-width multiplier with high accuracy and low complexity properties. The fixed-bit-width multiplier of the present invention comprises a Booth encoding module, a partial product generation module, a partial product preprocessing module, a cutoff compensation module, a tree-shaped compression module and a binary adder module. An input port of the Booth encoding module is connected to external input data, and an output port of the Booth encoding module is connected to the partial product generation module and the partial product preprocessing module; the partial product generation module is connected to the external input data, and an output port of the partial product generation module is connected to the partial product generation module, the cutoff compensation module and the tree-shaped compression module; an output port of the partial product preprocessing module is connected to the cutoff compensation module and the tree-shaped compression module; and an output port of the cutoff compensation module is connected to the tree-shaped compression module, and an output port of the tree-shaped compression module is connected to an input port of the adder module. The fixed-bit-width multiplier of present invention has the beneficial effect of being suitable for use in operation scenes with high calculation accuracy requirements and low hardware complexity requirements.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Rotate left-based quasi-cyclic (QC) matrix serial multiplier in deep space communication
InactiveCN103236850ASimple structureReduce power consumptionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsShift registerBinary multiplier
The invention provides a rotate left-based quasi-cyclic (QC) matrix serial multiplier in deep space communication, which is used for realizing the multiplication of a vector m and a quasi-cyclic matrix F in triangle coding under standard multi-code class QC-LDPC approximate in the deep space communication of consultative committee for space data systems (CCSDS). The multiplier comprises 4 generating polynomial lookup tables which prestore cyclic matrix generating polynomials of all code class matrixes F, 4 2048-bit binary multipliers which perform scalar multiplication on the data bit of the vector m and the generating polynomials, 4 2048-bit binary adders which perform modulo 2 addition on products and contents of shift registers, and 4 2048-bit shift registers which store the sums which are rotated left for one bit. The quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier provided by the invention is compatible with all code classes, and has the advantages of few registers, simple structure, low power consumption, low cost and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
ROL quasi-cyclic matrix multiplier for full parallel input in WPAN
InactiveCN103902509ASimple structureReduce registerComputation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsShift registerBinary multiplier
The invention provides an ROL quasi-cyclic matrix multiplier for full parallel input in a WPAN. The multiplier is used for multiplication of a vector m and a quasi-cyclic matrix F in standard QC-LDPC approximate triangle coding of the WPAN. The multiplier comprises two generating polynomial lookup tables for pre-storing all cyclic matrix cyclic generating polynomials in the matrix F, two 21-bit binary multipliers for performing scalar multiplication on the vector section and generating polynomial bits of the m, 21 three-bit binary adders for performing modulo-2 adding on content of a product sum shifting register and a 21-bit shifting register for storing the sum subjected to one-bit ROL. The multiplier for full parallel input is suitable for QC-LDPC codes in the WPAN standard and has the advantages of having fewer registers, being small in power consumption, low in cost, high in working frequency and large in throughput capacity, and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Modular (2<n>-3) multiplier
InactiveCN102253822AConsume less resourcesFast operationComputation using non-contact making devicesComputer architectureBinary multiplier
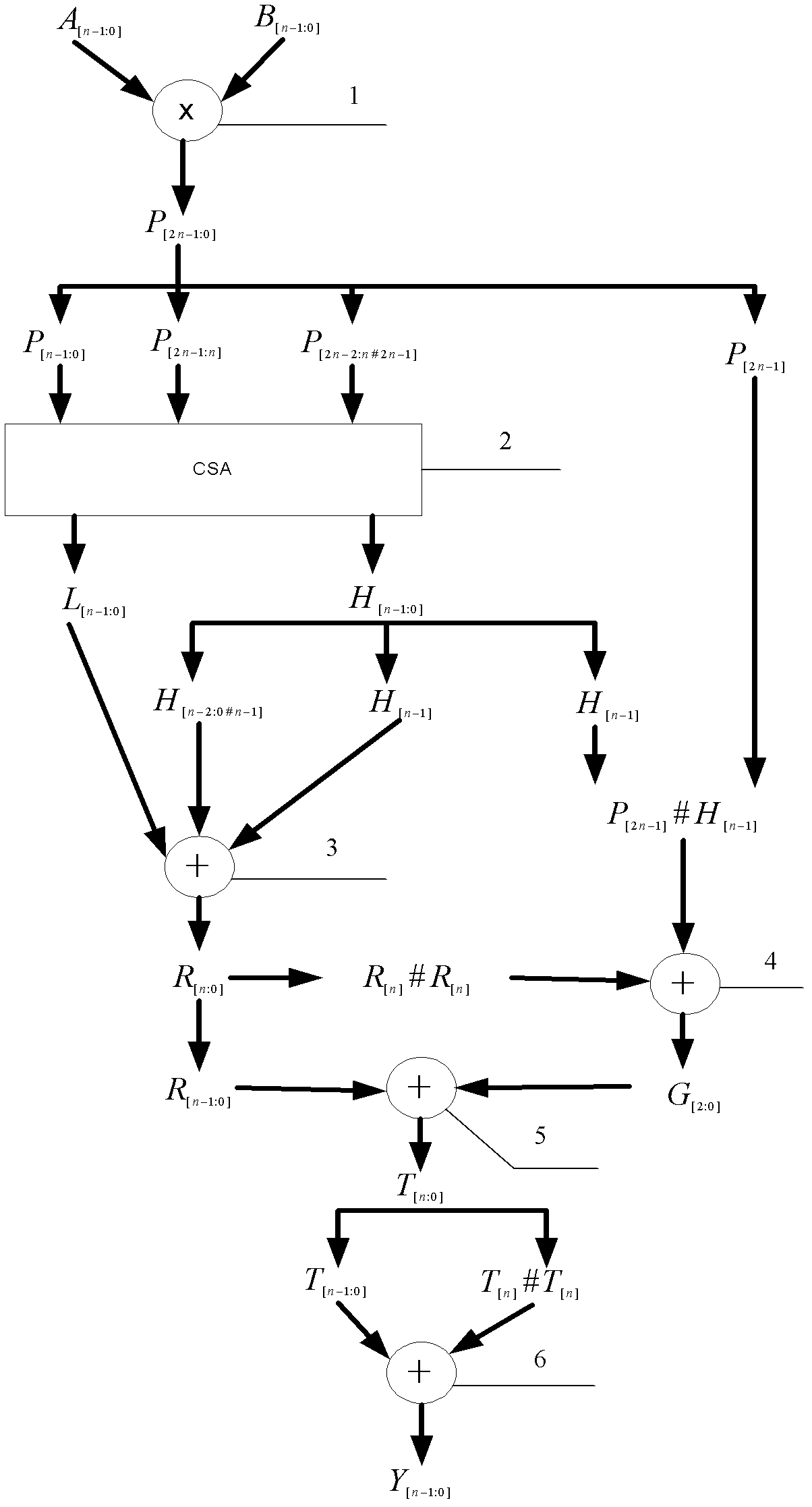
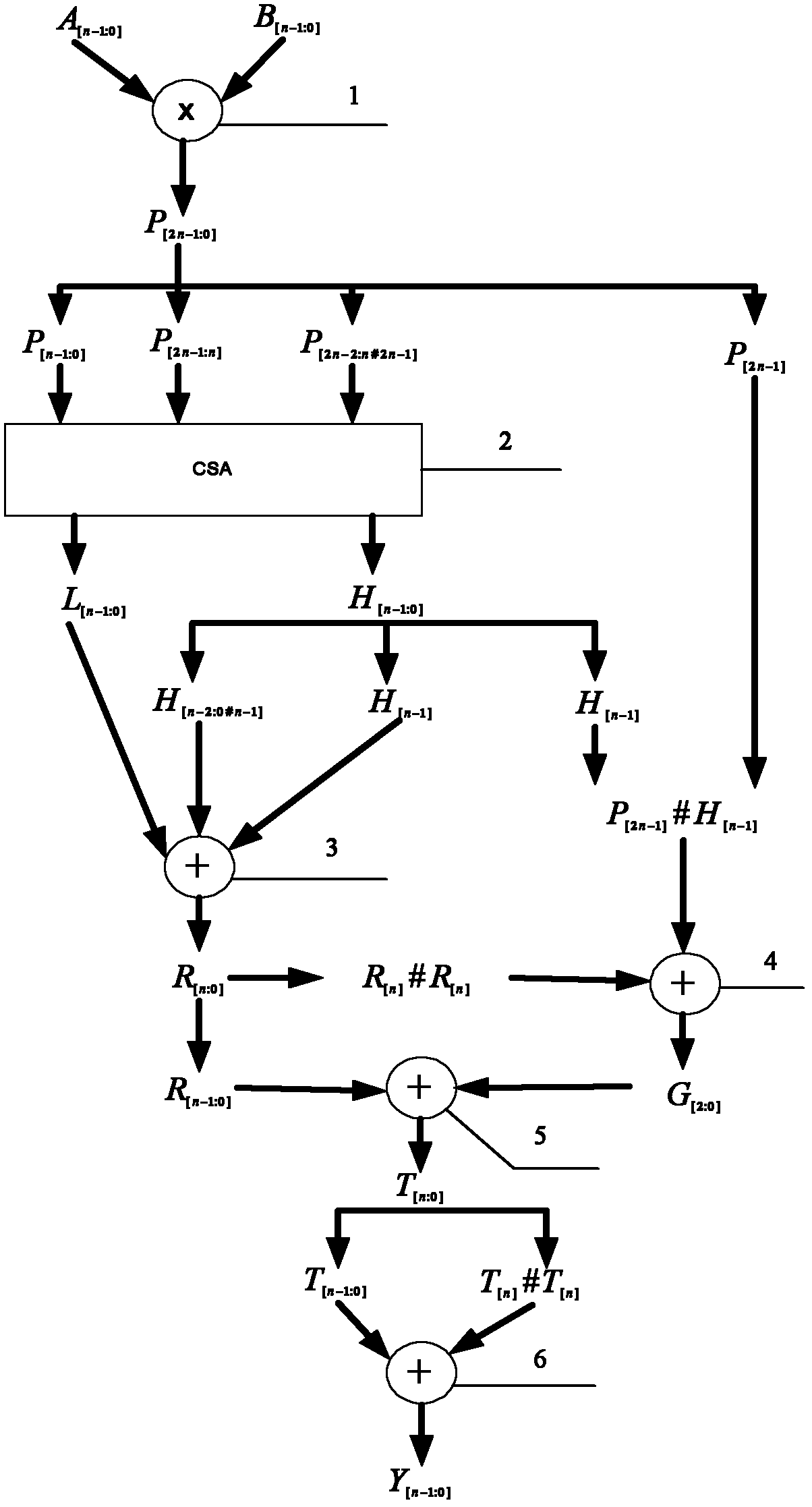
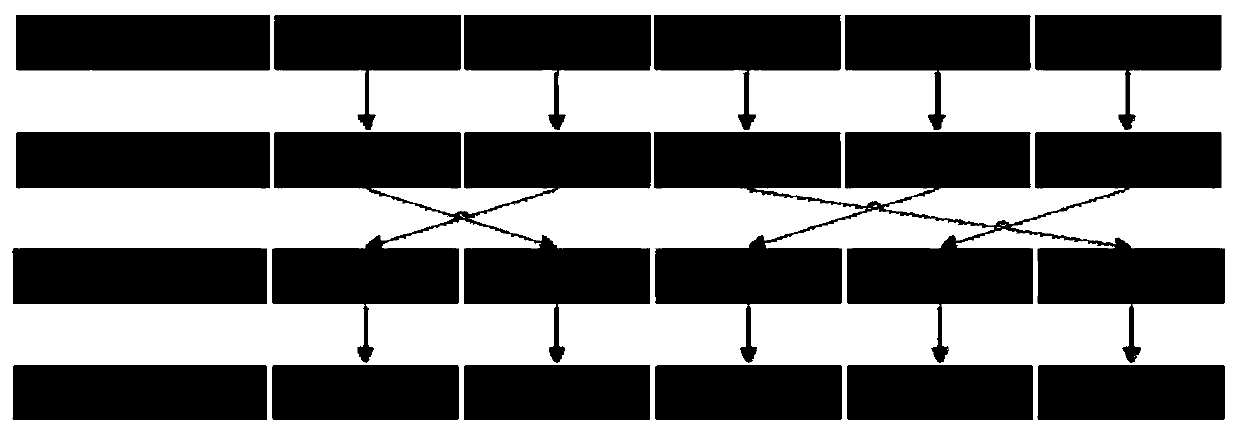
The invention belongs to the field of computers and integrated circuits and discloses a modular (2<n>-3) multiplier, which specifically comprises an n-bit binary multiplier (1), an n-bit carry save adder (CSA) compressor array (2), an n-bit binary adder (3) with carry input, a two-bit adder (4), a first n-bit binary adder (5) and a second n-bit binary adder (6). The modular (2<n>-3) multiplier reprocesses by using a result of binary multiplication as an operation number P, so multi-time modification of the conventional modular (2<n>-3) multiplier is changed into one-time modification, consumed resources of the modular (2<n>-3) multiplier are greatly reduced, and the operation speed of the modular (2<n>-3) multiplier is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
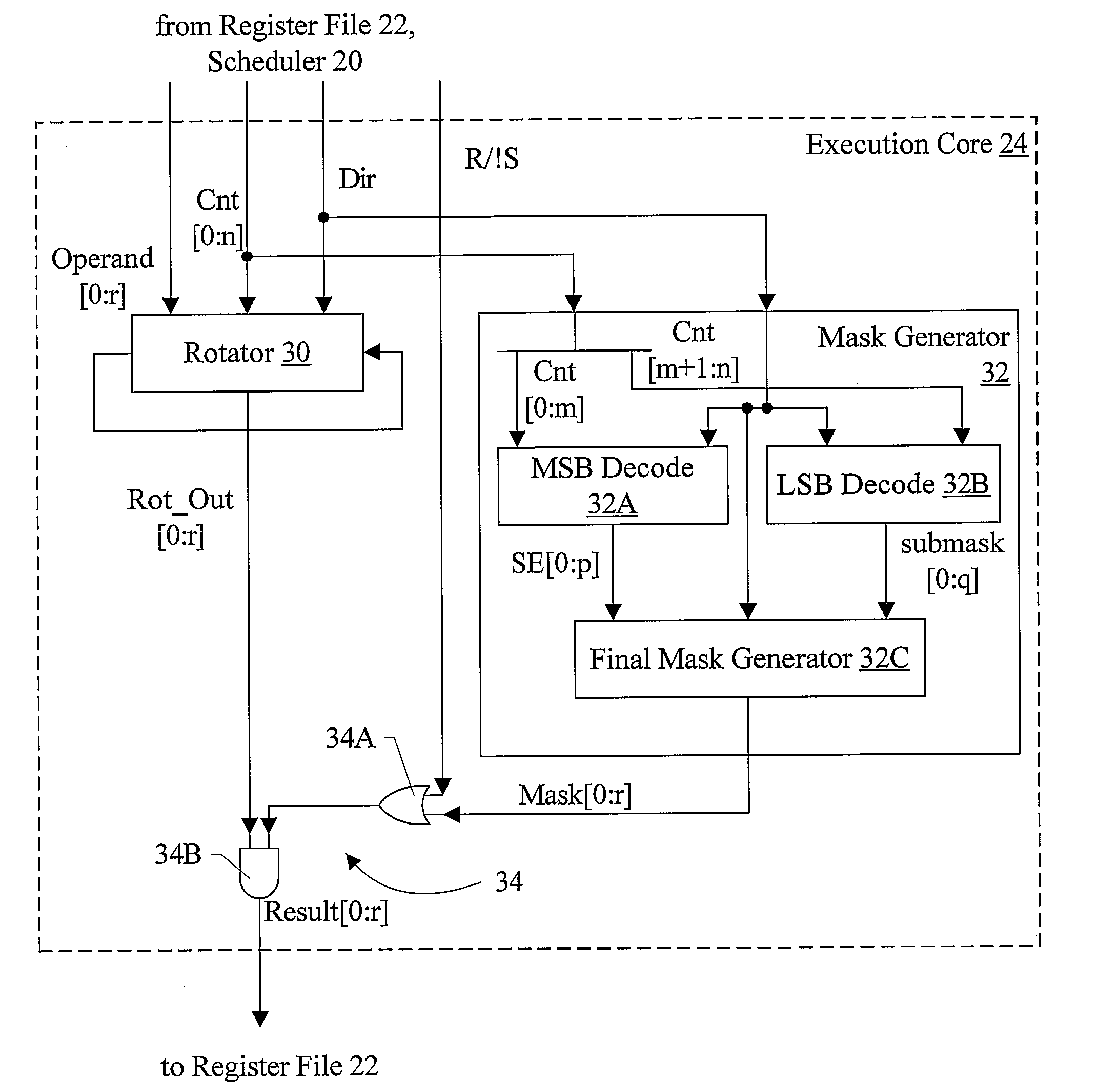
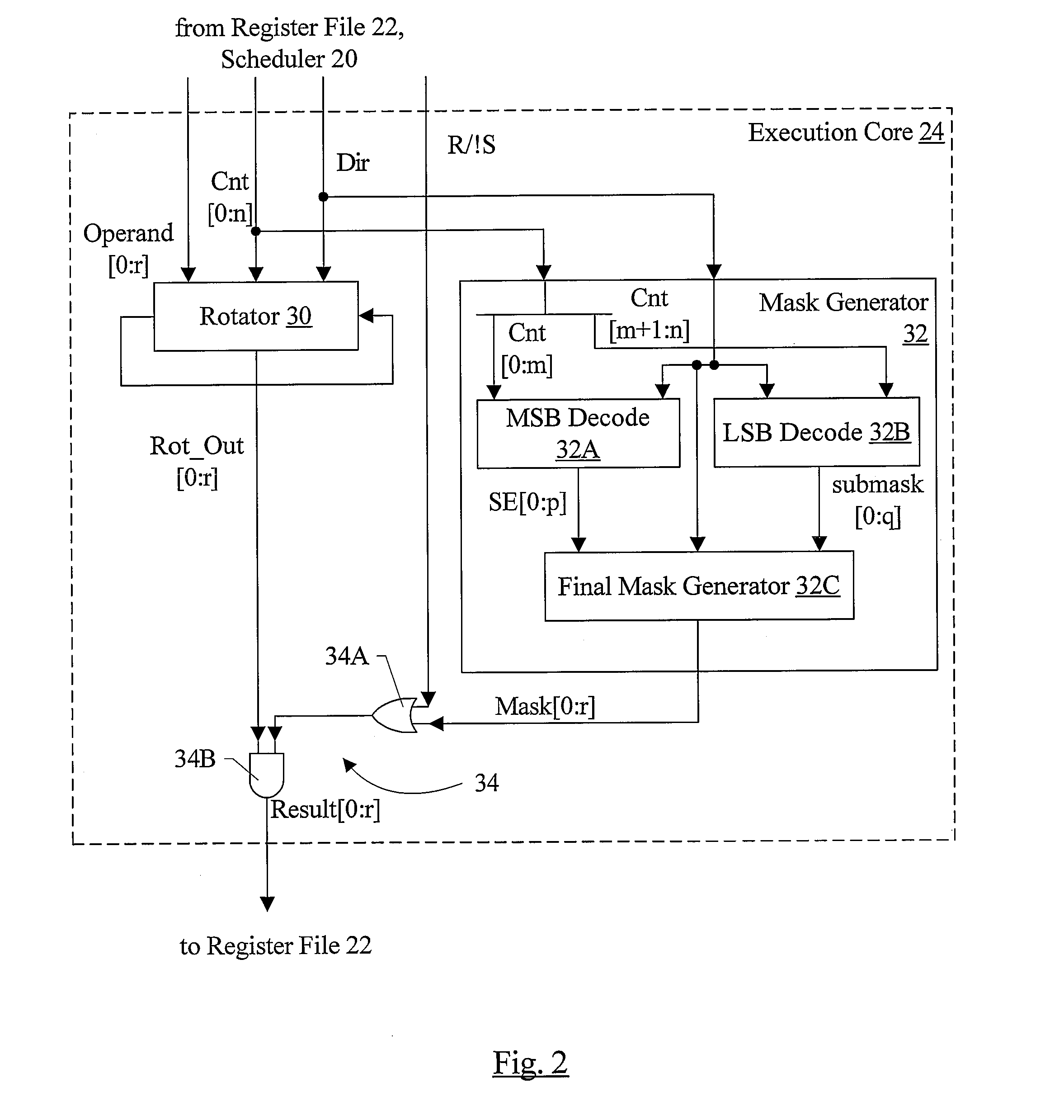
Fast Static Rotator/Shifter with Non Two's Complemented Decode and Fast Mask Generation
InactiveUS20080307204A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsLeast significant bitOperand
In one embodiment, a rotator, a mask generator, and circuitry configured to mask the rotated operand output by the rotator with the output mask generated by the mask generator perform a shift operation. Coupled to receive the input operand and the shift count, the rotator is configured to rotate the input operand by the shift count. Coupled to receive the shift count and the shift direction, the mask generator is configured to generate an output mask by decoding a most significant bit (MSB) field of the shift count to generate a first mask, decoding a least significant bit (LSB) field of the shift count to generate a second mask, logically ANDing the bits of the second mask with the corresponding bit of the first mask and logically ORing the result with an adjacent bit of the first mask that is selected responsive to the shift direction. Additionally, in one embodiment, the rotator may be configured to perform a right rotate / shift operation using a left rotate and without performing a two's complement operation on the rotate / shift count.
Owner:APPLE INC
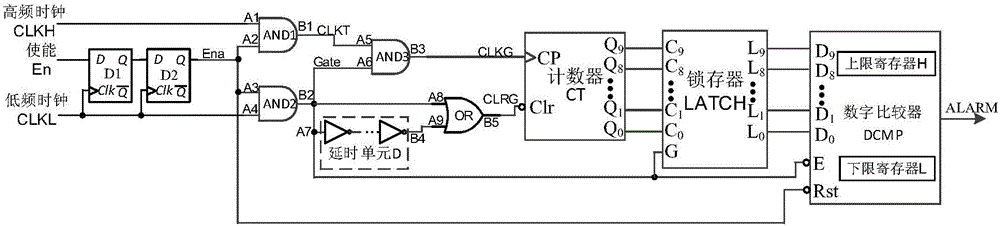
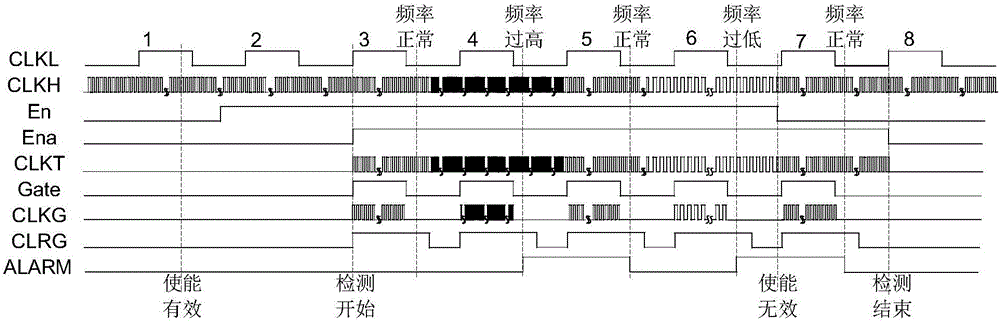
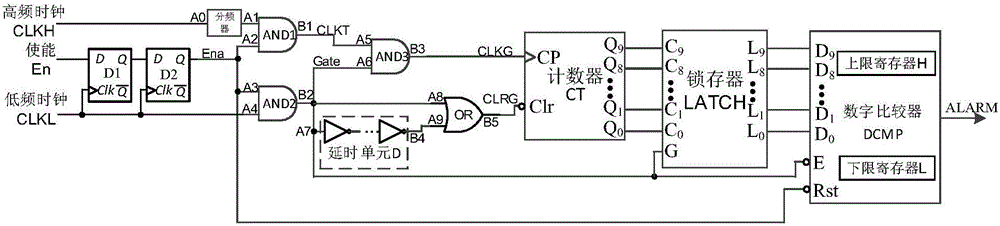
High-frequency clock frequency detection structure for resisting attack chip
ActiveCN106209034AFlexible changeReduce power consumptionPulse train pattern monitoringPlatform integrity maintainanceDelayed timeEngineering
The invention discloses a high-frequency clock frequency detection structure circuit for resisting an attack chip. The circuit comprises two D triggers which are connected in series and are triggered by a rising edge, three two-input AND gate, a delay unit D, an OR gate, a 10-bit asynchronous reset binary addition counter CT, a 10-bit latch and a 10-bit digital comparer DCMP. The two D triggers which are triggered by the rising edge, and the three two-input AND gate form a gate control clock structure. The delay unit D is formed by connecting the even number of phase inverters in series. Delay time is controlled by adjusting the number of the phase inverters. Two 10-bit registers, a frequency upper limit register H and a frequency lower limit register L, are contained in the10-bit digital comparer DCMP. The delay unit D or the OR gate forms a delay reset structure. An internal low-frequency clock is taken as a counting gate, the number of high-frequency clock periods is counted in fixed time, and the high-frequency clock frequency is deduced. When the obtained frequency exceeds a normal working frequency range, an alarm signal is generated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
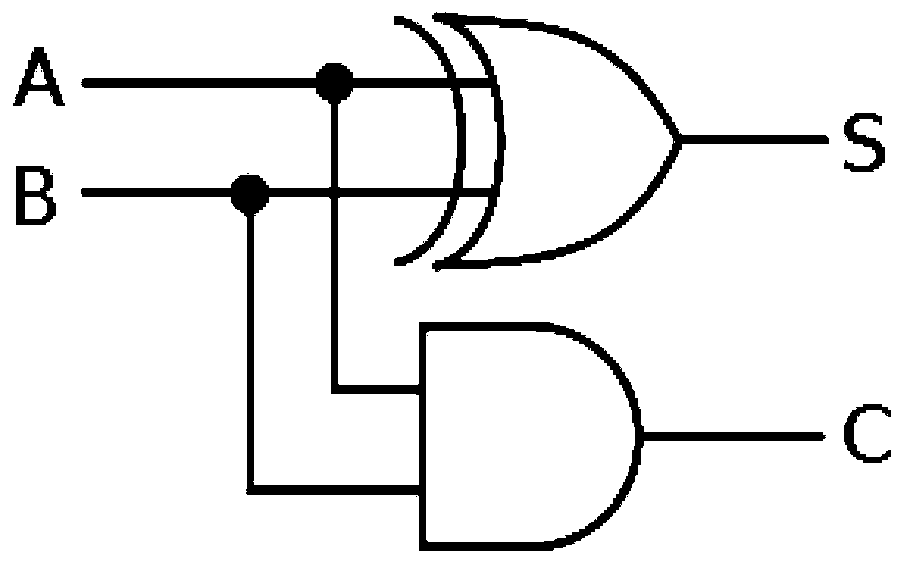
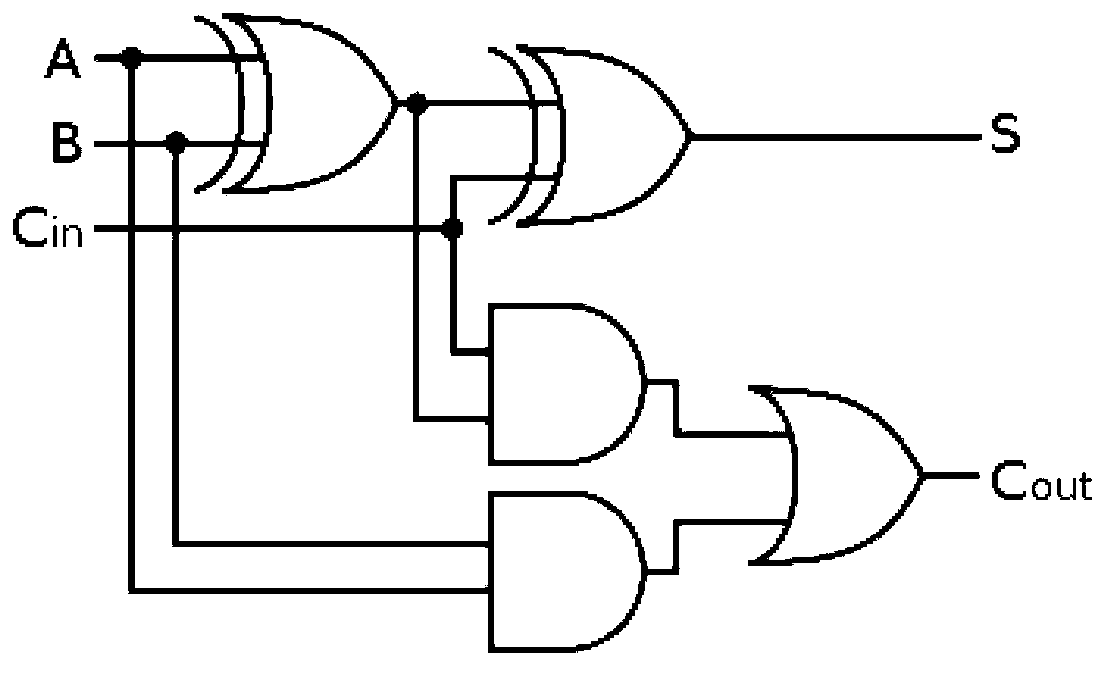
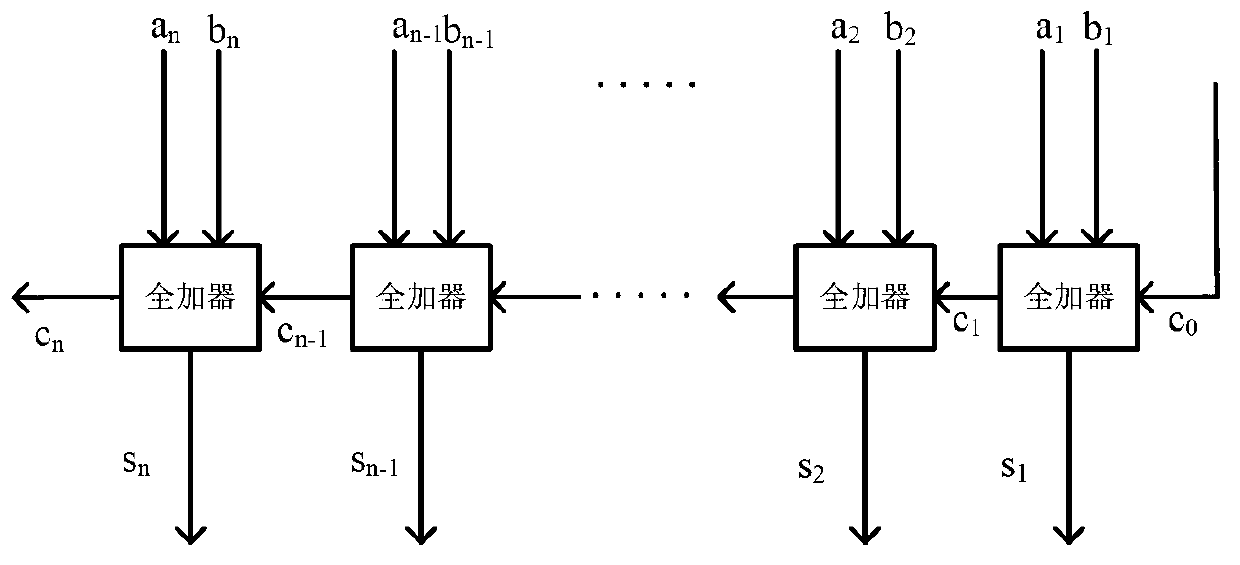
Adder
The invention discloses an adder and aims to solve the problem that multi-bit binary addition by a 1-bit full adder in the prior art is time-consuming. The adder comprises a plurality of one-bit full adders serially connected according to a first series rule to form a loop. Each full adder comprises a first addend input end, a second addend input end, a carry value input end, a sum output end, and a carry value output end, wherein the sum output end is used for outputting a sum of a first addend and a second addend, and the carry value output end is used for outputting a carry value obtained by adding the first addend and the second addend. The first series rule includes: the carry value output end of one of each two adjacent full adders is connected with the carry value input end of the other full adder.
Owner:RUIJIE NETWORKS CO LTD
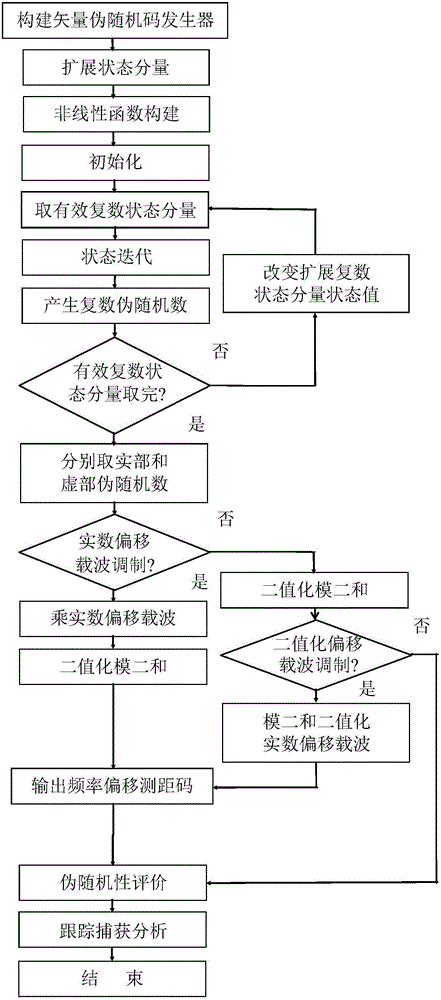
Spatiotemporal chaos vector pseudo-random code generator offset carrier modulation method and system
The invention discloses a spatiotemporal chaos vector pseudo-random code generator offset carrier modulation method and system, and the method comprises the steps: building a vector pseudo-random code generator; carrying out the functioning of the current state values of the current positions and offset positions of the component real parts and imaginary parts of a single complex stator vector through various types of nonlinear functions; taking a diffusion coefficient and a mutual coupling coefficient as weight values for the mixed calculation of addition, subtraction, multiplication or division; generating a complex pseudo-random number sequence, distributed along with time, through state iteration; extracting a real pseudo-random number sequence from the related component taps of the real and imaginary parts of a state component; carrying out binarization and binary addition through real offset carrier modulation, or carrying out the binary addition with a binarized real offset carrier after binarization; outputting and obtaining a range finding code with the needed frequency offset at a combined frequency through a bandpass filter. The method can be widely used for a satellite navigation system, and also can be used for various types of range finding systems, communication systems, broadcast and TV systems and control systems.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Approximating Functions
ActiveUS20150317126A1Computation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsApproximation functionBinary multiplier
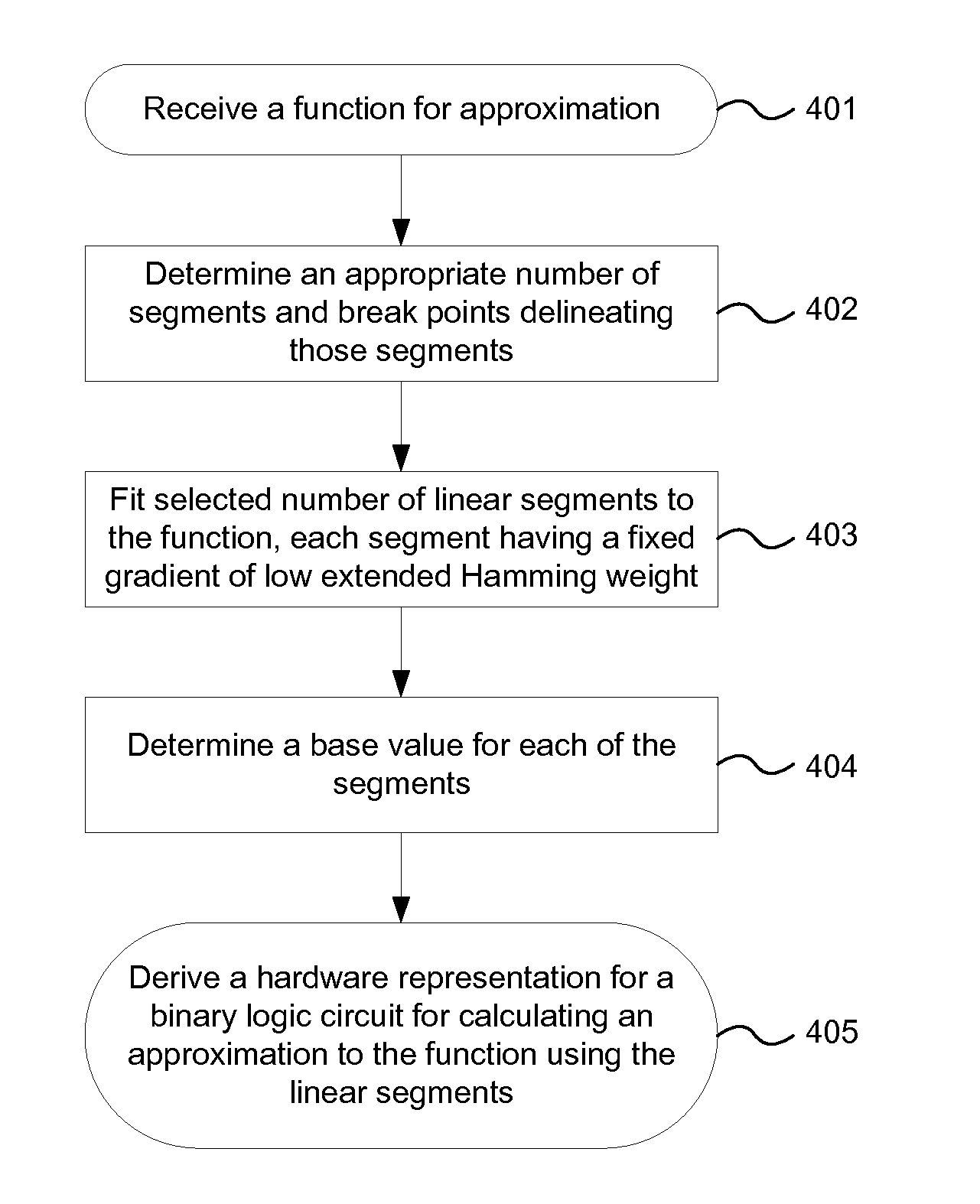
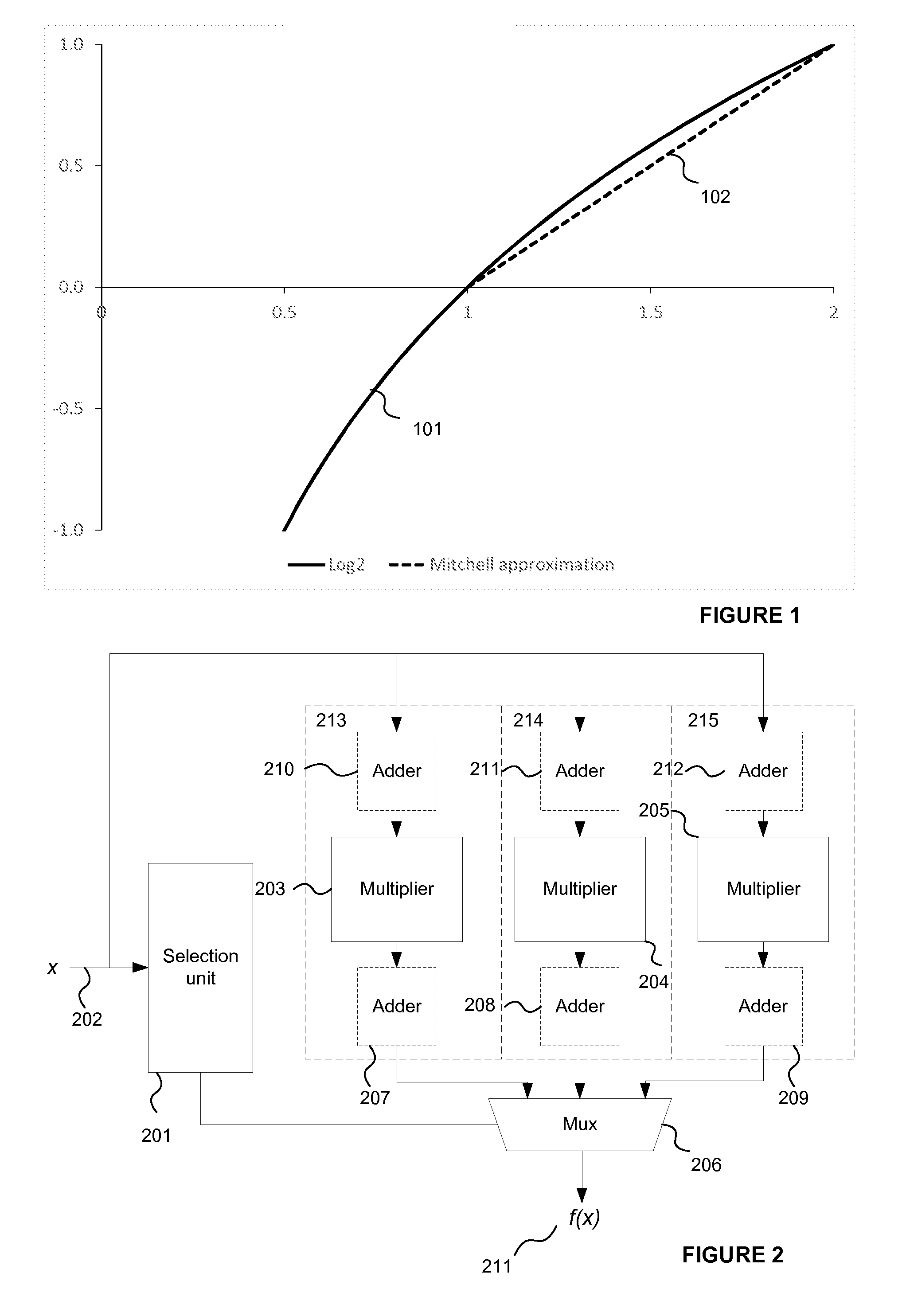
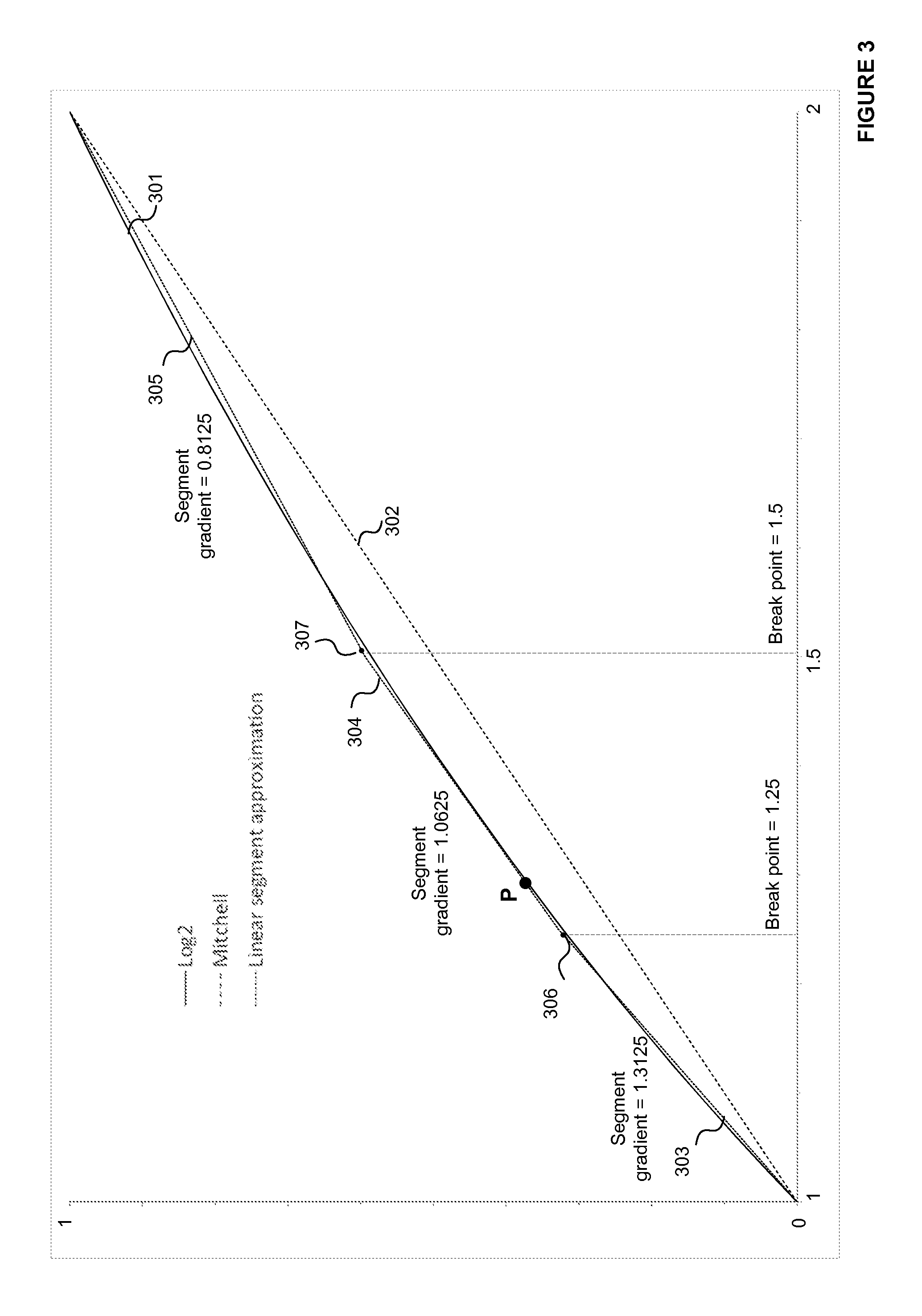
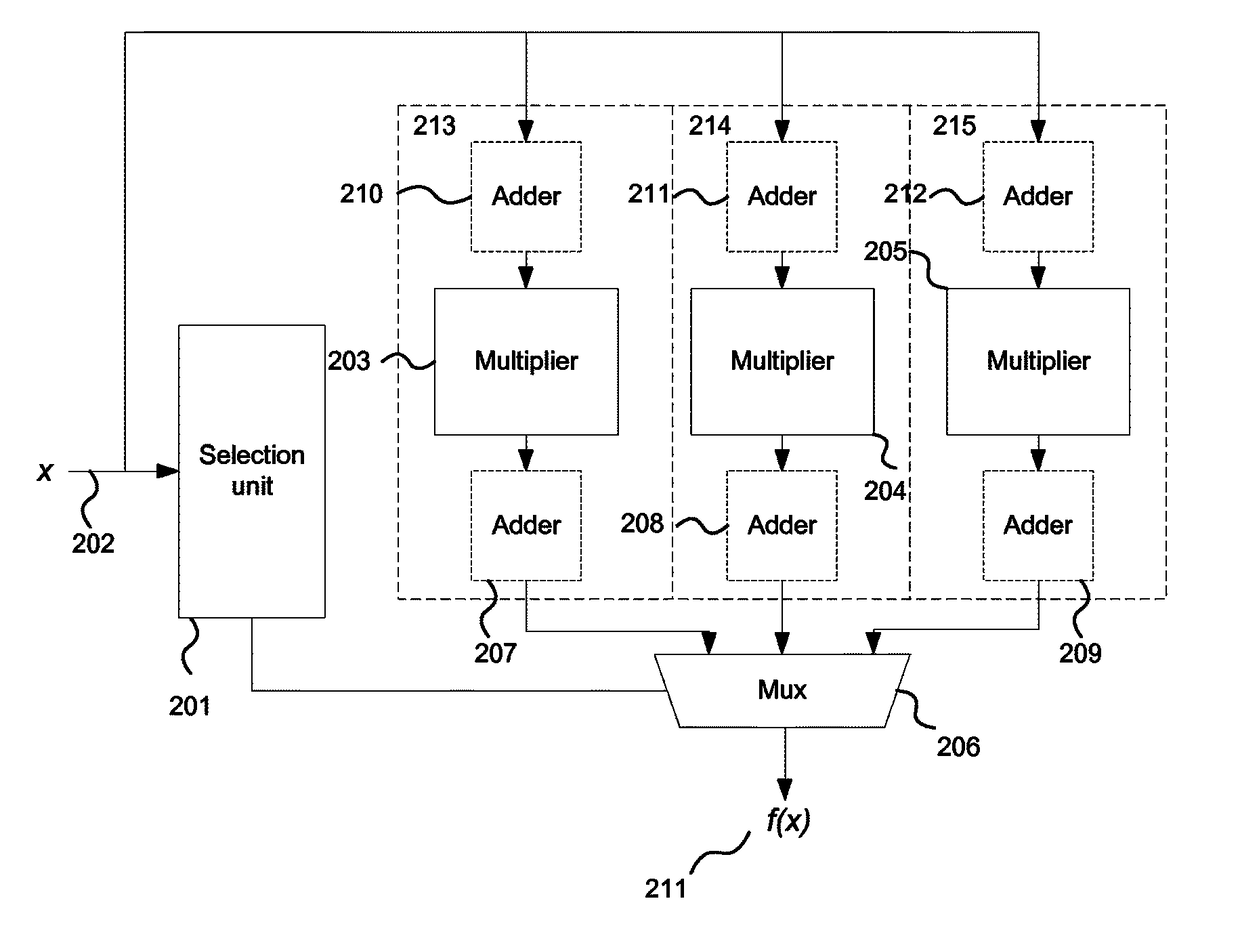
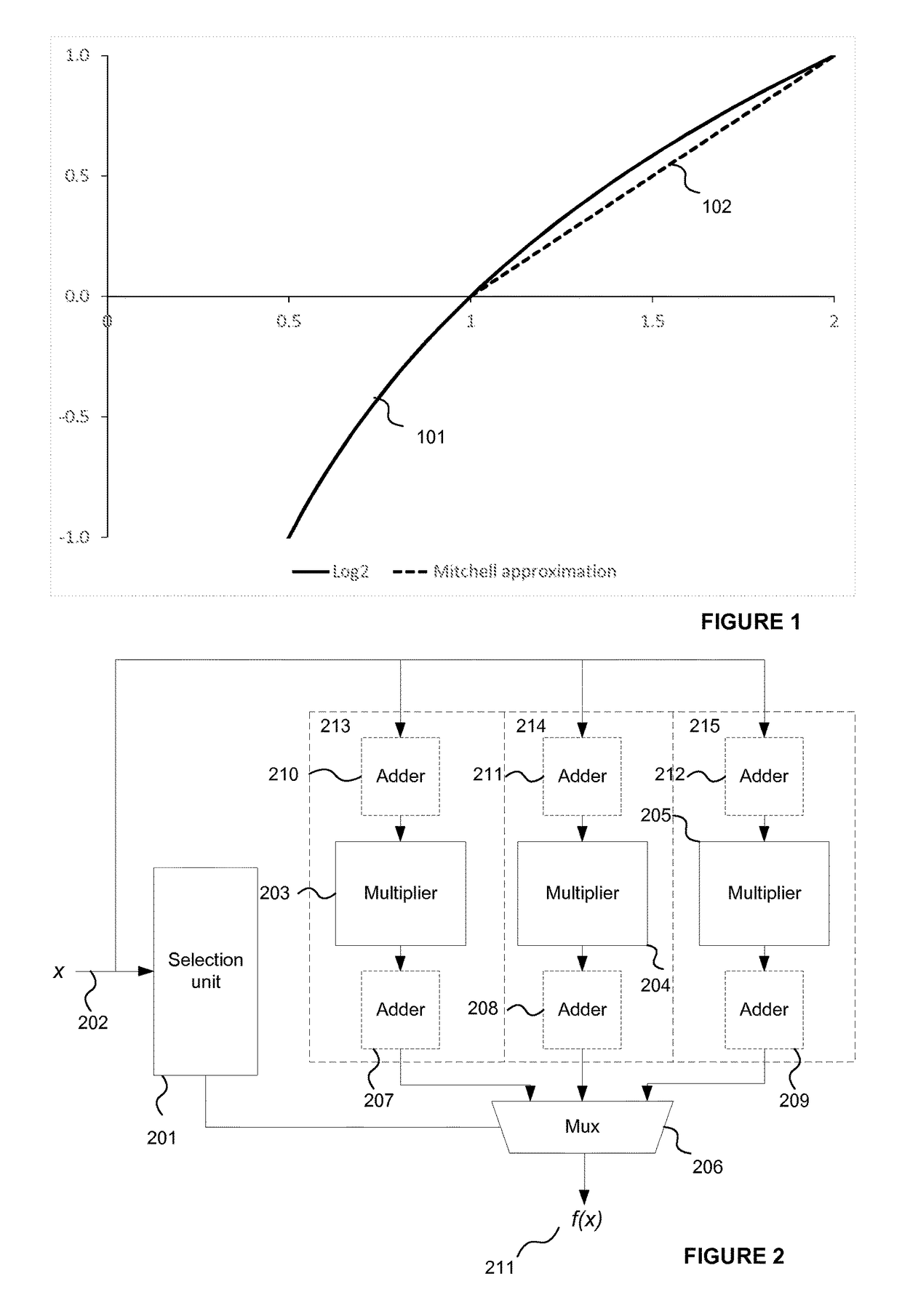
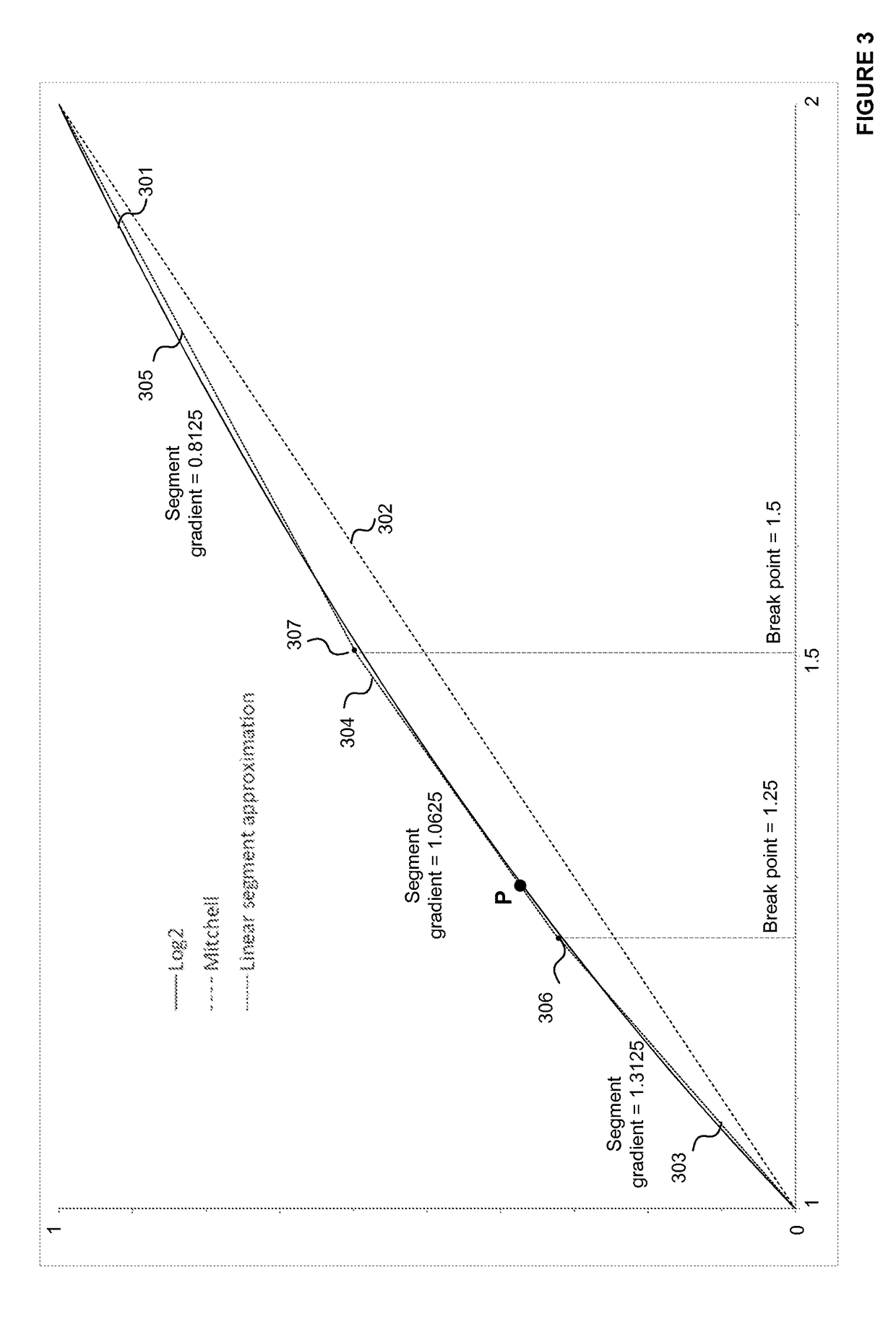
A binary logic circuit for approximating a mathematical function over a predefined range as a series of linear segments, each linear segment having one of a predetermined set of fixed gradients and a corresponding base value, the binary logic circuit comprising: an input for receiving an input variable in the predefined range; a plurality of logic chains each comprising: a binary multiplier adapted to perform multiplication by a respective one of the set of fixed gradients using h−1 binary adders, where h is the extended Hamming weight; and a binary adder adapted to add a base value to the input or output of the binary multiplier; and selection logic configured to select one of the logic chains in dependence on the input variable so as to provide, for the received input variable, an approximate value of the mathematical function.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Structure and circuit of logarithmic skip adder
InactiveCN1360348AHigh speedReduce areaDigital data processing detailsSolid-state devices16-bitCritical path delay
The invention relates to a circuit of digital adder in binary. The carry skipping algorithm is used between grups and the ELM tree type adding structure is used inside group in the circuit. Adopting new carry combination structure makes the initial carry embed into the carry chain so as to realize transferring parallel carry within group. The relationship between the delay of key path and number of bits within group is logarithmic. The invented circuit structure has advantages of the adder produced with small area and quick speed, simple connecting wire, easy to be integrated. The invention can implement binary add operation in 32 bits and 16 bits effectively.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Three-state binary adders and methods of operating the same
InactiveUS6859387B1Improve scalabilityReduce delaysElectric signal transmission systemsComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital signal processingAnalog-to-digital converter
Three-state binary adders are disclosed for use in pipelined analog-to-digital converters. According to one advantageous embodiment, a three-state binary adder is provided for use in a digital signal processing system. The three-state binary adder is operable to generate binary codes consisting of three states, namely, “00”, “01” and “10.”
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Digital heaven and ground wave signal synthesizer
InactiveCN101226234AEasy to modifyEasy to separateBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationSkyTransfer procedure
A digit sky-ground wave signal synthesizer relates to a sky-ground wave signal synthesizer of radio navigation system for resolving the problems of prior art as hard noise separation, noise transmission and amplification along with signal when uses analogue element to realize signal synthesizer to affect signal synthesis effect. The inventive frequency synthesis module according to standard sine signal synthesizes one path of carrier wave clock frequency and one patch of pseudo-code clock frequency, a carrier wave generating module receives the carrier wave clock frequency from the frequency synthesis module, extracts the amplitude of the carrier wave signal, generates and sends the carrier wave signal to a modulation module, a pseudo-code generating module receives the pseudo-code clock frequency from the frequency synthesis module and transmits the generated pseudo-code sequence to the modulation module, a modulation module processes binary addition on the carrier wave signal and pseudo-code sequence according to the carrier wave clock frequency of the frequency synthesis module and transmits the generated modulation signal to the signal synthesis module to process signal synthesis.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Binary adder circuit and method for producing carry logical circuit used by it
InactiveCN1497428AComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesNOR gateArrival time
A binary adder circuit including a carry logic circuit and selection logic. The carry logic circuit uses group generate and propagate signals to produce complementary carry signals. The selection logic produces one of two presums dependent on the complementary carry signals. In a method for producing a carry logic circuit, a group generate logic function GI, I+1=GI OR GI+1 AND PI is to be performed. When GI+1=CI+1, GI, I+1=CI, arrival times of generate signals GI and GI+1, are investigated. If GI arrives before GI+1, a complex AND-OR-INVERT gate is used, otherwise a cascaded pair of NAND gates is selected. To produce a complementary carry signal, a logic function GI, I+1'=GI' AND GI+1' OR PI' is to be performed. If the generate signal GI' arrives before GI+1', a complex OR-AND-INVERT gate is used, otherwise a cascaded pair of NOR gates is selected.
Owner:IBM CORP
Image encryption method based on hyper-chaotic system and variable step size Josepher problem
ActiveCN110086600AAdd scrambling methodAdd rules for traversing the Joseph ringSecuring communication by chaotic signalsCryptographic attack countermeasuresPattern recognitionPlaintext
The invention provides an image encryption method based on a hyper-chaotic system and a variable step size Josepher problem, which comprises the following steps of inputting an original image into a key generation function to generate a binary sequence, and calculating an initial value of the hyper-chaotic system; iterating by utilizing the hyper-chaotic system to generate four pseudo-random sequences X, Y, Z and W; inputting the sequence X as a secret key into a variable step size Josepher function to scramble each line in the original image to obtain an image I1; taking the element of the sequence Y as a secret key to perform Josepher ring-based pixel position scrambling on the image I1 to obtain an image I2; inputting the sequence Z as a secret key into the variable step size Josepher function to scramble each column of the image I2 to obtain an image I3; and carrying out two-bit binary addition / subtraction operation on the image I3 by using the element of the sequence W to obtain aciphertext image. According to the invention, the plaintext is linked with the key, so that the method has plaintext sensitivity and can resist selection plaintext attacks and has a strong key spaceand the acute key sensitivity.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Modular multiplier
InactiveCN102955682AFast operationDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierModular multiplier
The invention discloses a modular (2<3n>-2<n>) multiplier, which comprises a 3n-bit binary multiplier, a 2n-bit CSA (Carry Save Adder) compressor array, a first 2n-bit binary adder, a one-bit phase inverter and a second 2n-bit binary adder. In the modular (2<3n>-2<n>) multiplier disclosed by the invention, the result P of binary multiplication is taken as an operand for reprocessing, and modulo addition operation is corrected in a way of adding 1 in advance, so that the operation speed is increased greatly. Compared with the prior art, the modular (2<3n>-2<n>) multiplier has the advantages that a multiplier and a combined logic circuit are reduced on resource cost; and on a key path, a multiplier is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Quasi-cyclic matrix high-speed multiplier in deep space communication based on lookup table
InactiveCN103268214ASimple structureReduce memoryDigital data processing detailsBinary additionShift register
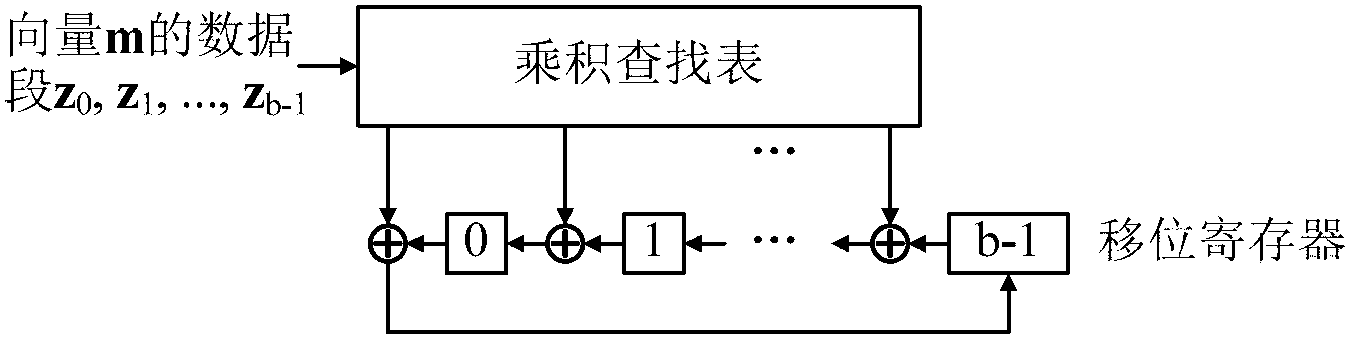
The invention provides a quasi-cyclic matrix high-speed multiplier in deep space communication based on a lookup table, and is used for realizing multiplication of a vector m and a quasi-cyclic matrix F in triangular encoding under multi-code quasi-cyclic low density parity check (QC-LDPC) approximation in the consultative committee for a space data system (CCSDS). The multiplier comprises four product lookup tables which are used for pre-storing possible algebraic sum of all generated polynomials in a binary field in block rows of all code matrixes F, four 2,048-bit binary summators for performing modulo-2 adding on outputs of the product lookup tables and contents of shift registers, and four 2,048-bit shift registers for storing the sum which is cyclically shifted 1 bit leftwards. The quasi-cyclic matrix high-speed multiplier is compatible with all the code types, so that the number of storage devices and logic resources are reduced; and the quasi-cyclic matrix high-speed multiplier has the advantages of simple structure, low power consumption, low cost and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Partial parallel input left shift accumulation QC-LDPC encoder in near-earth communications
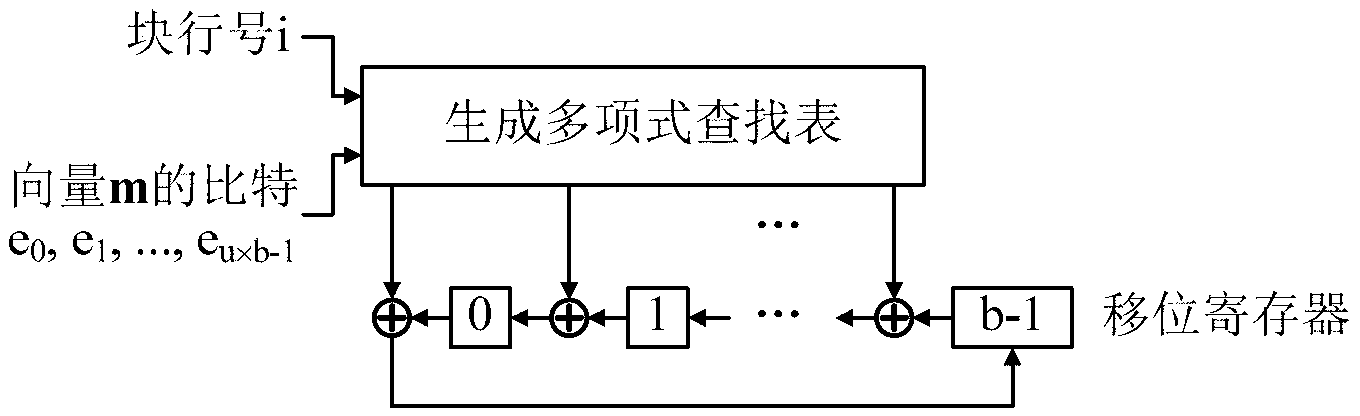
InactiveCN103929189ASimple structureMaintain encoding speedError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsShift registerParallel computing
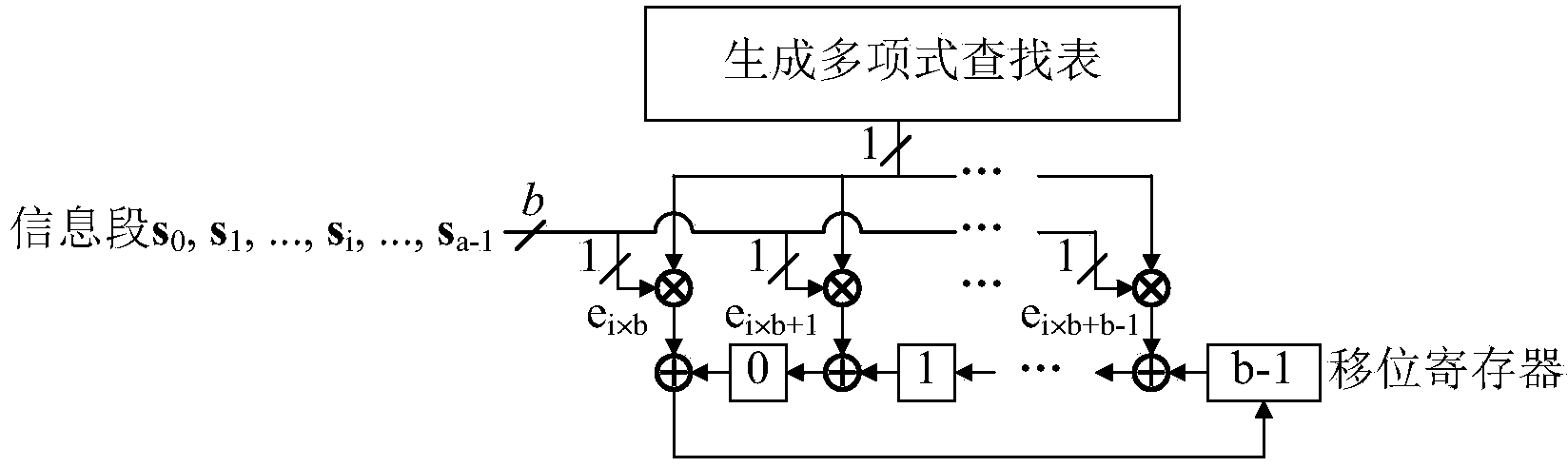
The invention provides a partial parallel input left shift accumulation QC-LDPC encoder in near-earth communications. The partial parallel input left shift accumulation QC-LDPC encoder comprises two generator polynomial lookup tables which prestores all circulant matrix generator polynominals in a generated matrix, two 511-bit binary multipliers which are used for conducting scalar multiplication on information segments and generator polynomial bits, two 511-bit binary adders which are used for conducting modulo 2 addition on products and the content of shifting registers, and two 511-bit shifting registers which are used for storing the sum of bits which are rotated once to the left. Finally, calibration data are included in the two shifting registers. The partial parallel input encoder is suitable for QC-LDPC codes in a CCSDS near-earth communication system, and has the advantages of being few in register, simple in structure, small in power consumption, low in cost, high in working efficiency, large in throughput capacity and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
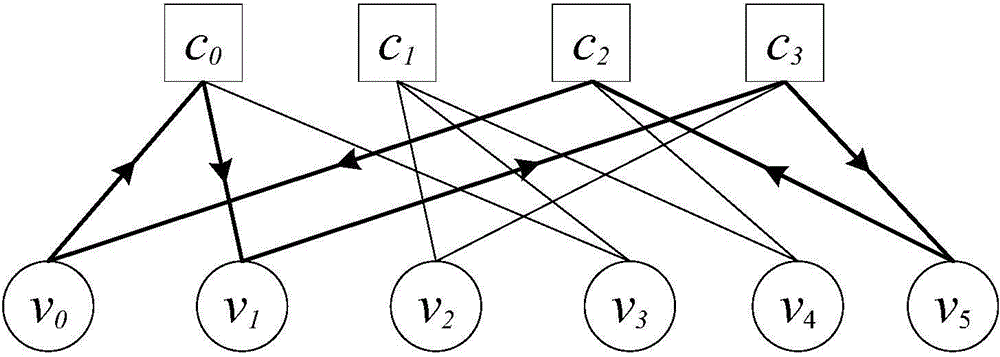
LT code coding/decoding method
ActiveCN106788886ALower success rateImprove operational efficiencyChannel coding adaptationDecoding methodsProgramming language
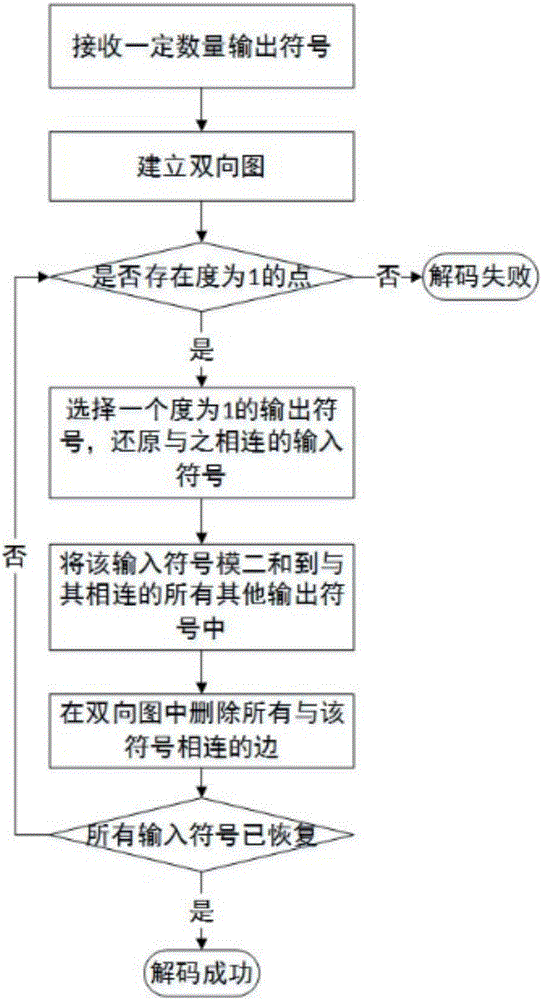
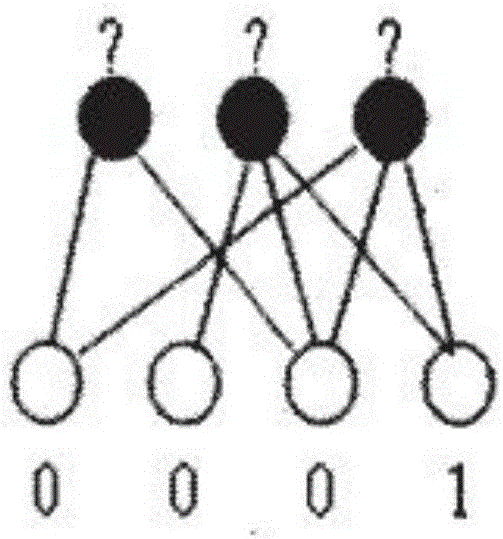
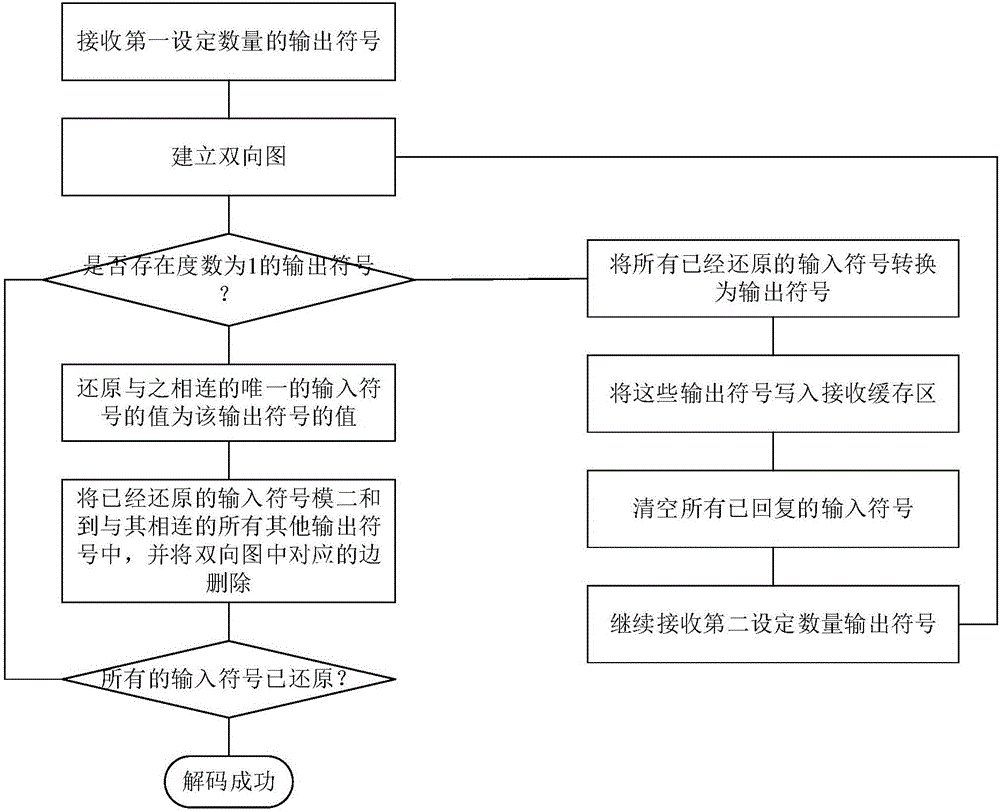
The invention relates to an LT code coding / decoding method. The method comprises the following steps: step S1, uniformly dividing a file into K input symbols; and step S2, performing LT coding; the method further comprises the step S3, receiving a certain amount of output symbols; step S4, establishing a bidirectional chart according to a corresponding relation between the output symbol and the input symbol; step S5, judging whether the output symbol with degree of 1 is existent, restoring a value of the unique input symbol connected with the output symbol and executing the step S7 if the output symbol with degree of 1 is existent, otherwise, executing the step S6; step S6, saving the restored input symbol as the output symbol, continuously receiving a small amount of output symbols, and returning to step S4; step S7, saving the restored input symbol binary addition to all other output symbols connected with the input symbol, and deleting the corresponding side in the bidirectional chart; and step S8, judging whether all input symbols have been restored, ending the decoding if all input symbols have been restored, otherwise, returning to the step S5. Compared with the prior art, the working efficiency is improved by use of the method disclosed by the invention.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
LDPC encoder based on DVB-S2 standard multi-rate compatibility
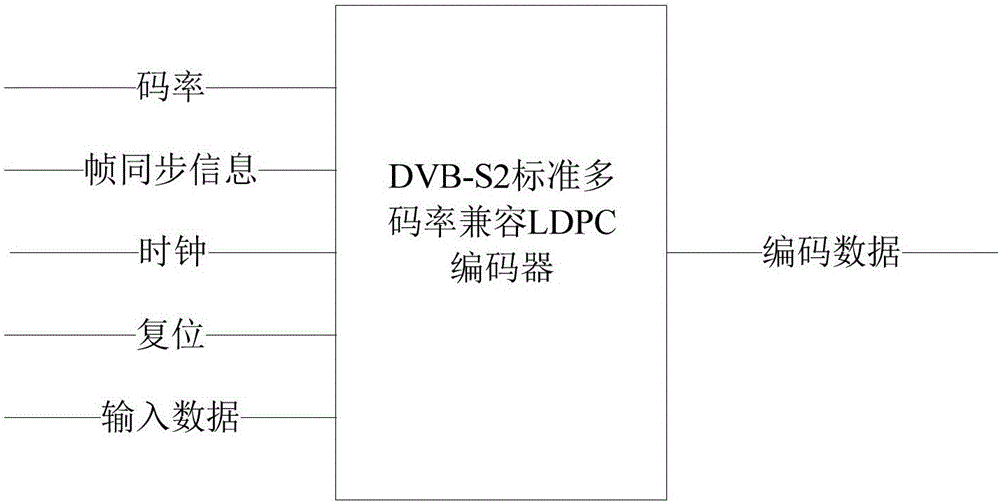
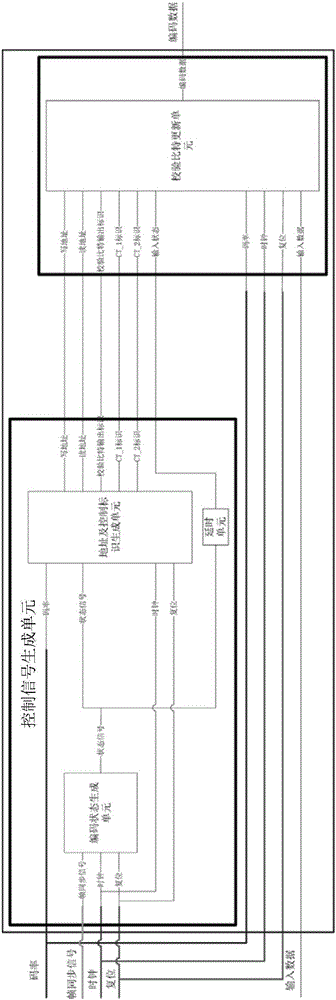
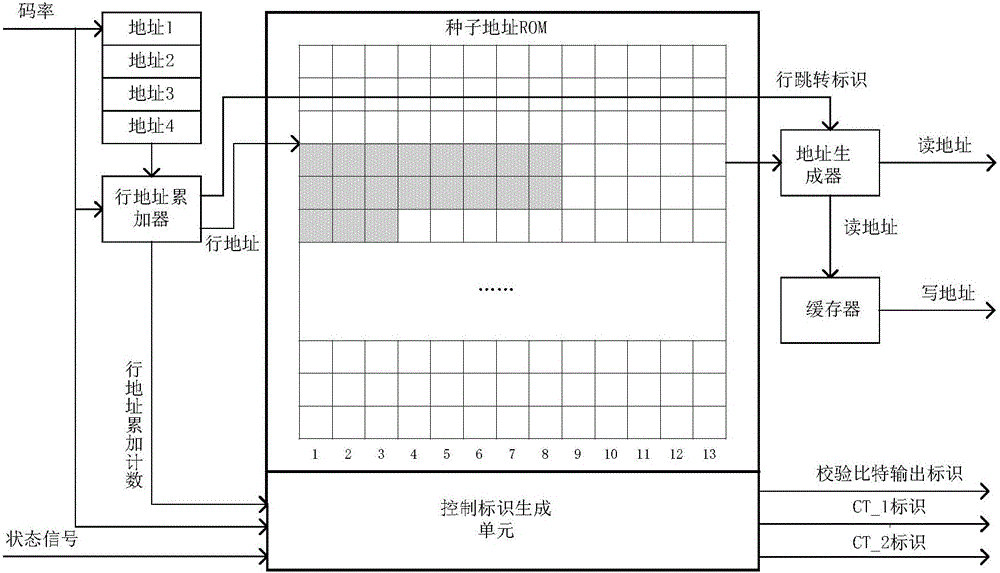
ActiveCN106506010AQuick buildReduce occupancyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionControl signalDVB-S2
The invention provides an LDPC encoder based on DVB-S2 standard multi-rate compatibility, which comprises a control signal generation unit and a check bit updating unit. The control signal generation unit generates, according to set encoding rates and an encoding initial identifier signal, a state control signal for controlling operation of the entire encoder, a plurality of addresses of corresponding rows in an address table, which are provided by easy input information bit to be encoded correspondingly to a DVB-S2 standard, and control identifier signals corresponding to the encoding rates, and outputs the state control signal, the addresses and the control identifier signals to the check bit updating unit; the check bit updating unit carries out binary addition operation on the information bits to be encoded and check bits read from the plurality of addresses corresponding to the information bits to be encoded, and writes an operation result into an original address. According to the LDPC encoder provided by the invention, by separately designing a control unit and an operation unit, the LDPC encoder compatible to various code rates is implemented; and encoding operation of the corresponding code rates can be completed only by setting the corresponding encoding rates at an external interface.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Rotate left-based quasi-cyclic low density parity check (LDPC) serial encoder in near field communication
InactiveCN103236855ASimple structureReduce power consumptionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsShift registerScalar multiplication
The invention provides a rotate left-based quasi-cyclic low density parity check (LDPC) serial encoder in near field communication. The encoder comprises 2 generating polynomial lookup tables which prestore cyclic matrix generating polynomials of the generating matrixes, 2 511-bit binary multipliers which perform scalar multiplication on information bit and the generating polynomials, 2 511-bit binary adders which perform modulo 2 addition on products and contents of shift registers, and 2 511-bit shift registers which store the sums which are rotated left for one bit. Finally, calibration data are contained in the 2 shift registers. The serial encoder provided by the invention is applicable to a near field communication system of consultative committee for space data systems (CCSDS), and has the advantages of few registers, simple structure, low power consumption, low cost and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Quasi cyclic matrix serial multiplier free of multiplication
InactiveCN103257843ASimple structureSave logic resourcesDigital data processing detailsShift registerBinary multiplier
The invention provides a quasi cyclic matrix serial multiplier free of multiplication. The quasi cyclic matrix serial multiplier free of the multiplication is used for realizing multiplication of a vector m and a quasi cyclic matrix F in QC-LDPC approximate lower triangular codes. The multiplier comprises u cyclic matrix generator polynomials pre-stored in a matrix F, a generator polynomial lookup table of a b-position null vector, u b-position binary adders outputting the generator polynomial lookup table and conducting analog 2 adding on contents of a shifting register, and u b-position shifting registers for storing results of cyclic shift left one position. The quasi cyclic matrix serial multiplier removes the multiplication, and has the advantages of being few in logic resource, simple in structure, low in consumption, low in cost, and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Modular multiplier
InactiveCN102929575AConsume less resourcesFast operationDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierResource consumption
The invention discloses a modular multiplier, which comprises (n+1)-bit binary multiplier, an n-bit inverter array, an n-bit CSA compressor array, a first n-bit binary adder, a 1-bit full adder, a 5-bit adder, a first 1-bit inverter, a second 1-bit inverter, a third 1-bit inverter, a second n-bit binary adder and a third n-bit binary adder. According to a modular (2n+3) multiplier, the result of binary multiplication serves as an operation number and is reprocessed, so that repeated correction of the traditional modular (2n+3) multiplier is changed into one-step correction, the resource consumption of the modular (2n+3) multiplier is greatly reduced, and the operation speed is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Approximating functions
ActiveUS9785406B2Digital function generatorsComplex mathematical operationsApproximation functionBinary multiplier
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com