Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "DVB-S2" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
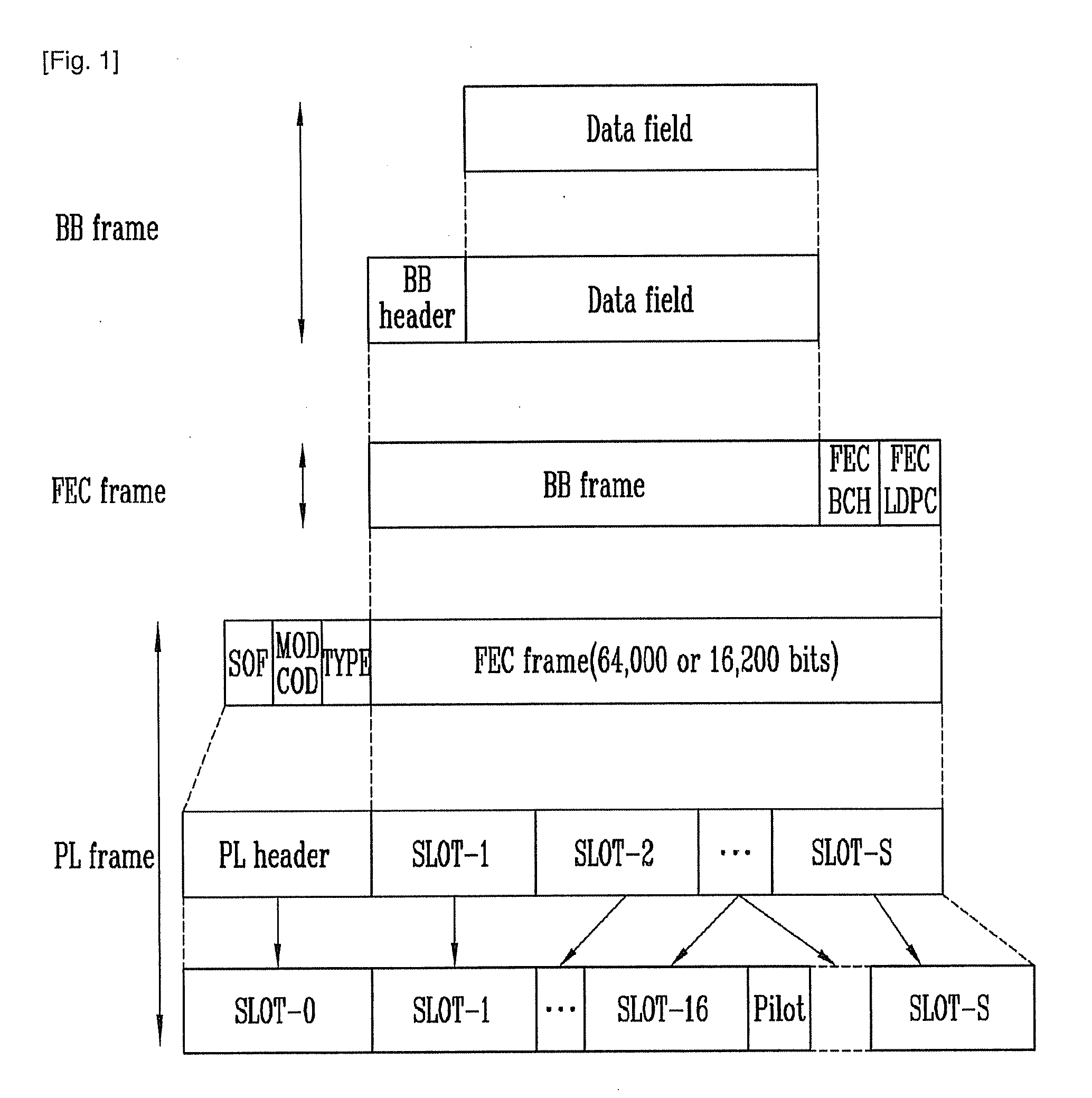
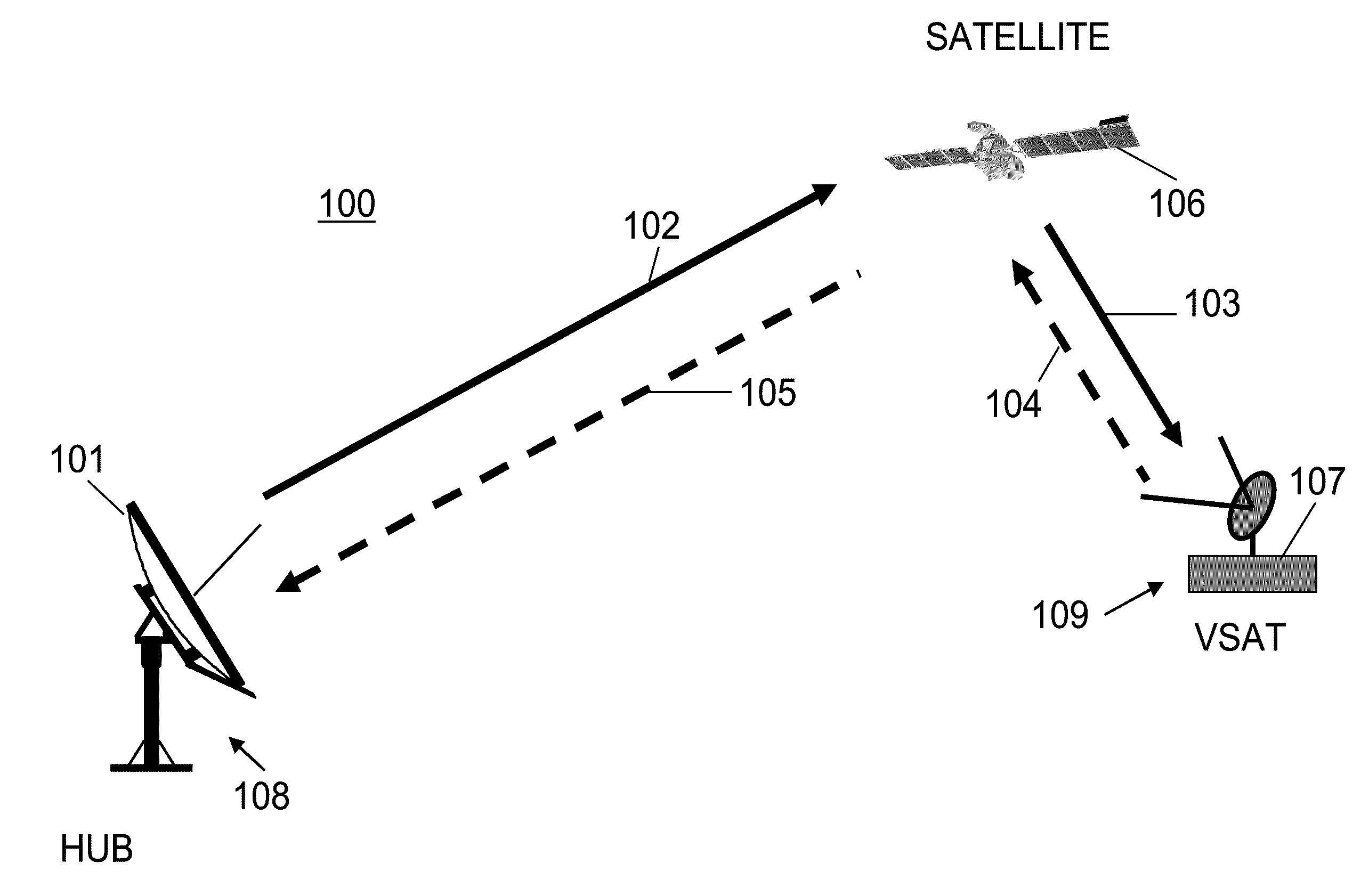
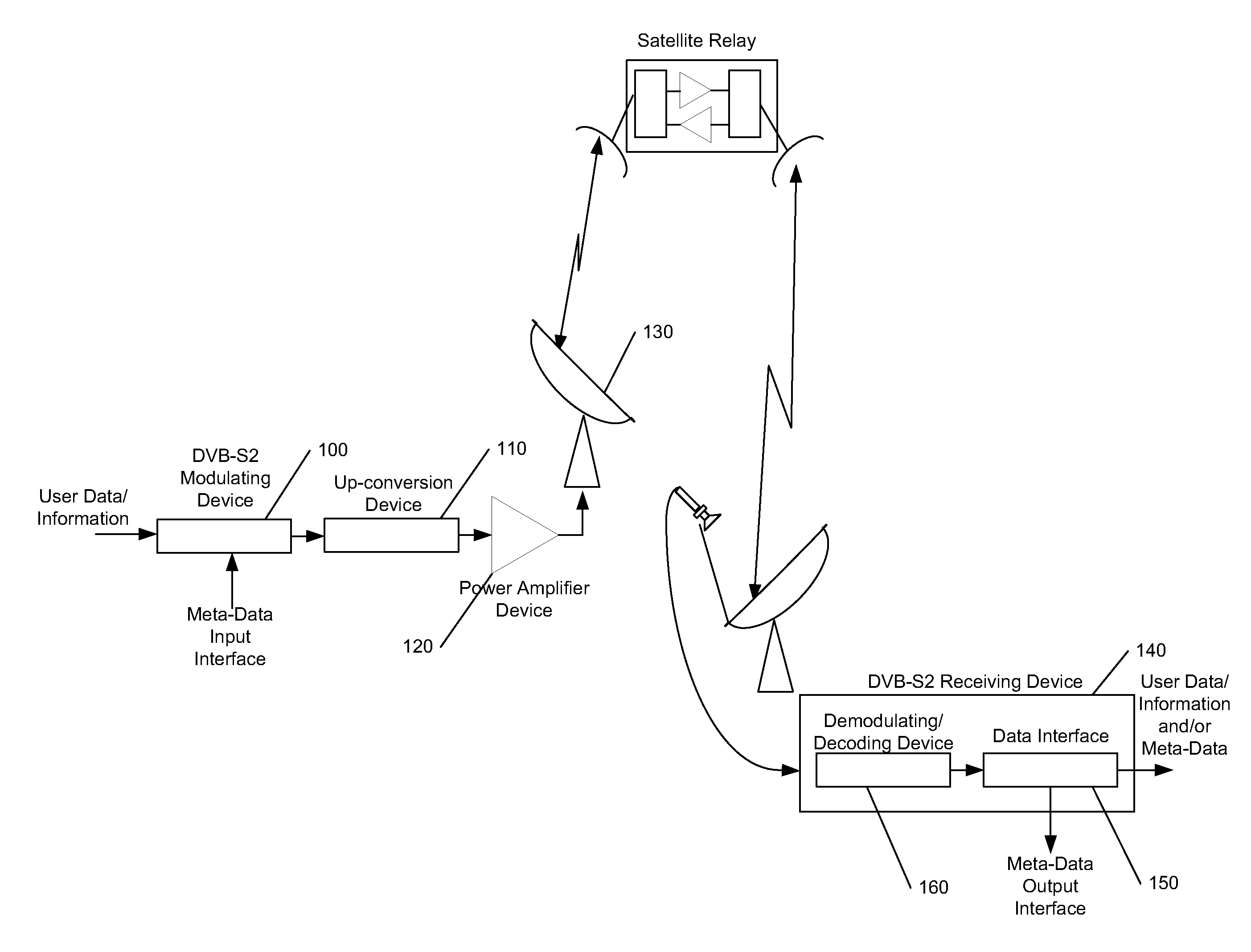
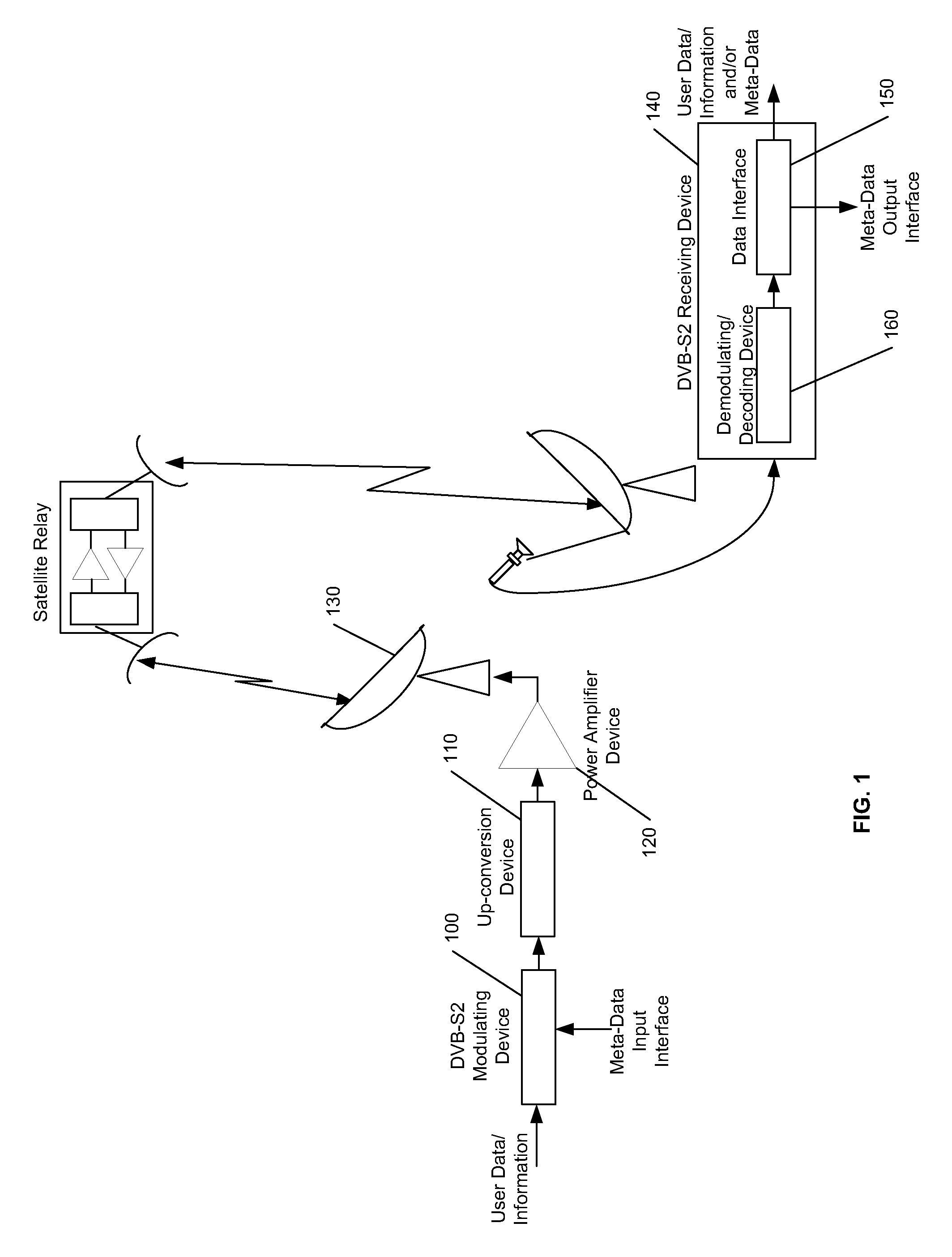
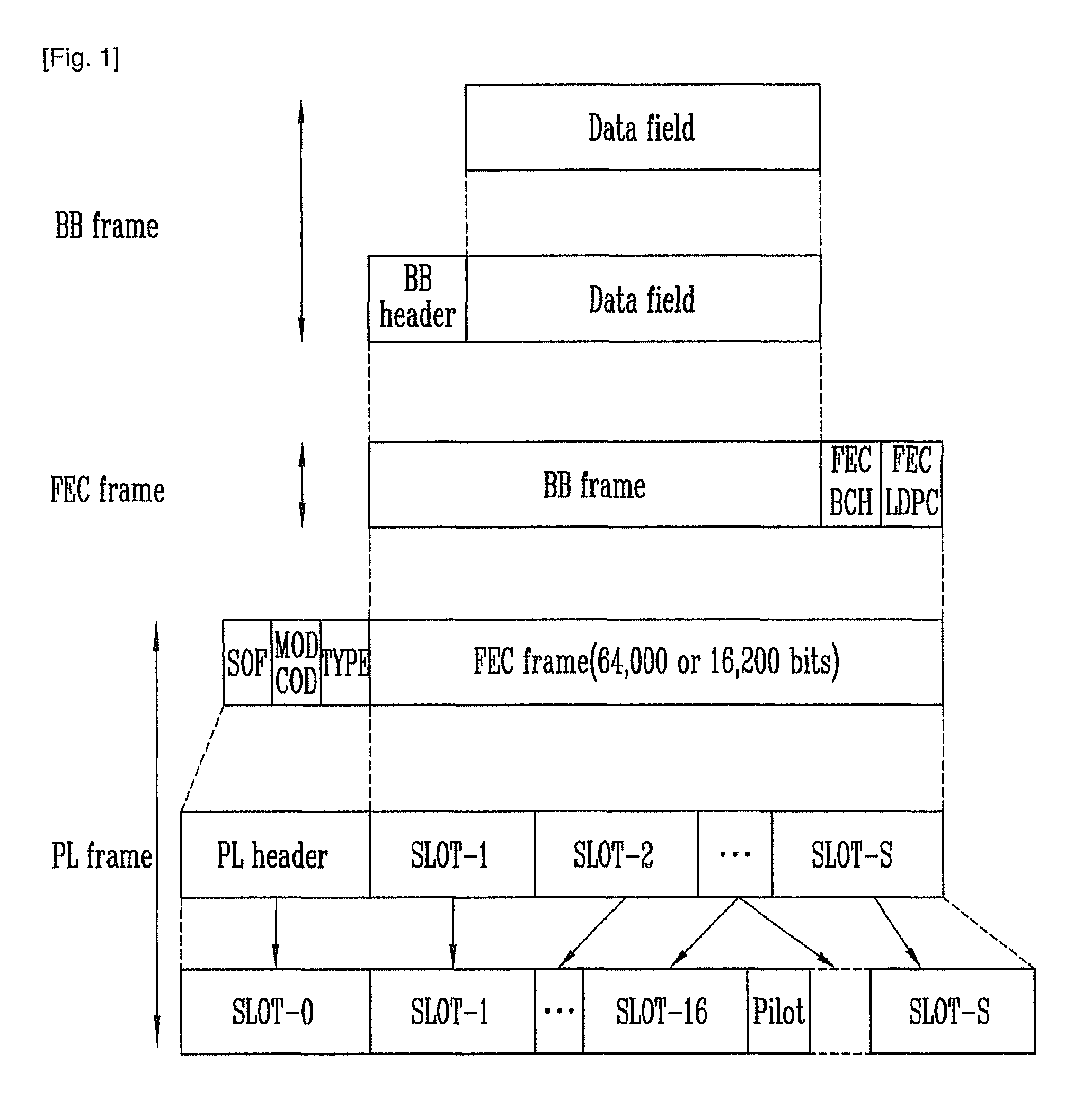
Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI (EN 302307) in March 2005. The standard is based on, and improves upon DVB-S and the electronic news-gathering (or Digital Satellite News Gathering) system, used by mobile units for sending sounds and images from remote locations worldwide back to their home television stations.
Packing Data Over An Adaptive Rate Link
ActiveUS20080049659A1Prevent overflowEnabling useTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexComputer networkDVB-S2
Owner:GILAT SATELLITE NETWORKS
Transmodulator for very small aperture terminals employing internet protocol based communications
ActiveUS20080064323A1Promote migrationQuick exchangeBroadcast transmission systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTTEthernetTelecommunications
DVB-S / S2 transmodulator for VSAT units employing IP based communication. The transmodulator is optimized for VSAT networks, enabling legacy VSAT units to benefit from the developments of the advanced DVB-S2 standard. The transmodulator appears transparent to the legacy VSAT unit that is configured to operate with the older DVB-S standard. Some embodiments offer a unique feedback channel allowing the transmodulator to send messages and information to the ground station via the VSAT itself.
Owner:AYECKA COMM SYST
Low density parity check (ldpc) decoder
InactiveCN101032084AError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionLow densityDVB-S2
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Method and system for effective adaptive coding and modulation in satellite communication system
InactiveUS20100046415A1Efficiently transmitting signalKeep in syncFrequency-division multiplex detailsCode conversionDigital videoAdaptive coding
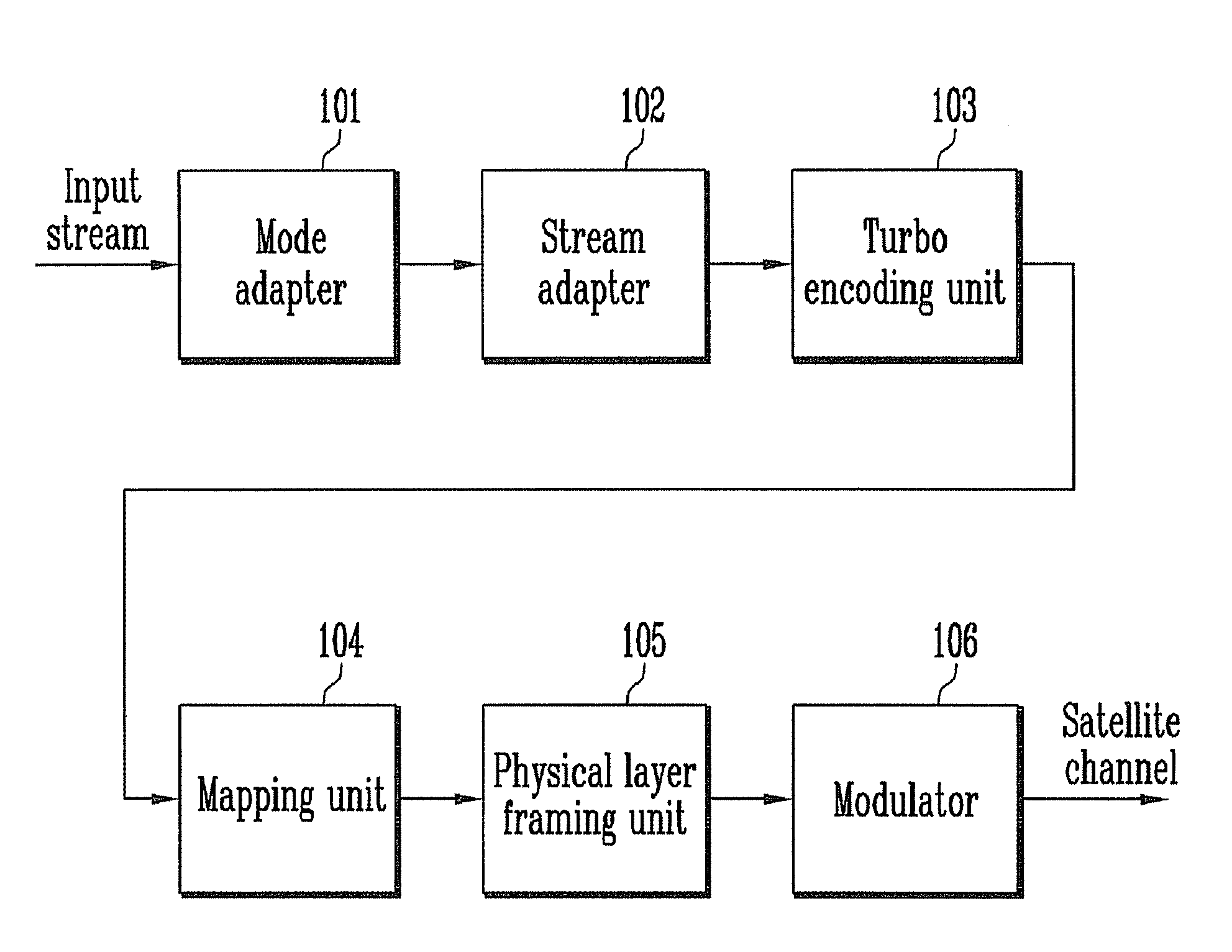
A Second Generation Digital Video Broadcasting via Satellite (DVB-S2) system is provided. More particularly, a method and apparatus for maintaining synchronization of a signal by changing an Adaptive Coding and Modulation (ACM) method that is used for a conventional DVB-S2 system are provided. In the apparatus and method, an FEC frame of a variable length is formed by turbo encoding rather than Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) and Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) encoding, and a Physical Layer (PL) frame of a specific length is formed regardless of a modulation method, so that a satellite terminal receives a signal transmitted at a specific length regardless of a modulation method or a coding rate to easily maintain synchronization without interruption and efficiently transmit the signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for synchronizing DVB-S2 system receiver full-mode physical layer frame
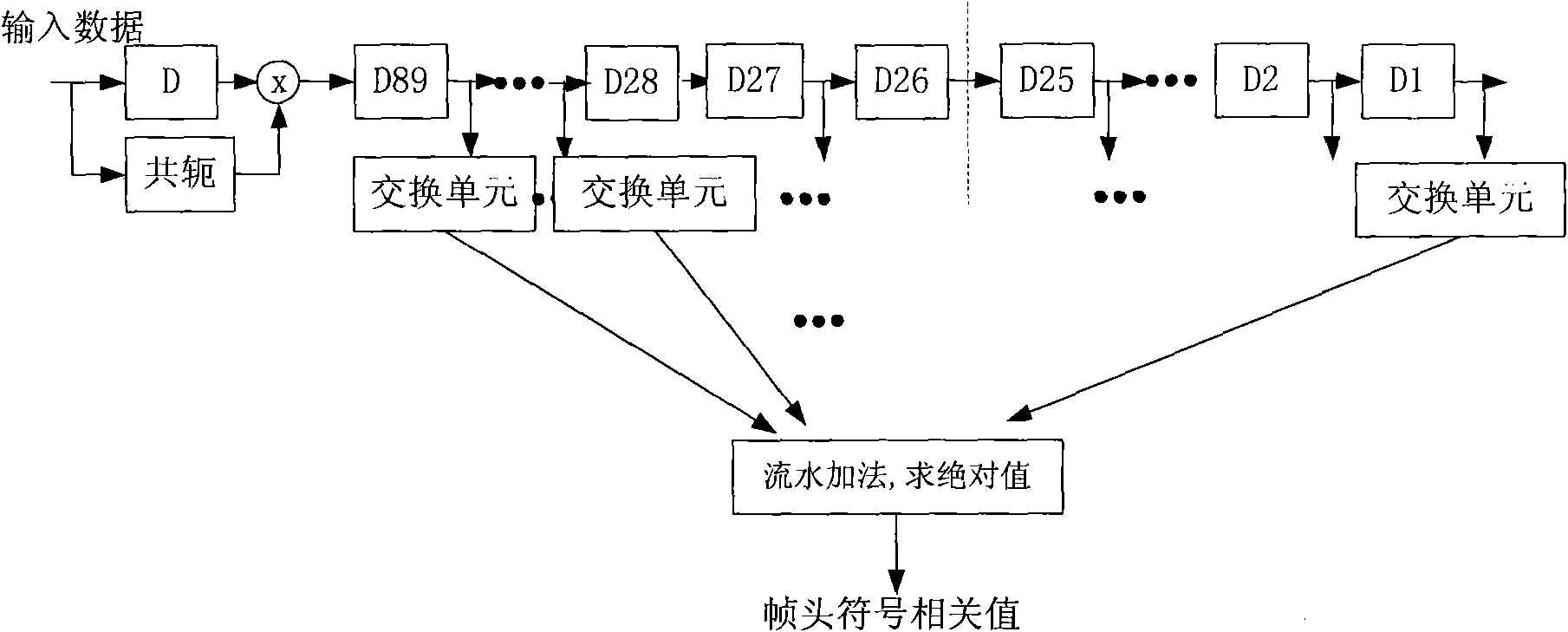
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital communication and transmission synchronization, in particular relates to a method for synchronizing a DVB-S2 system receiver full-mode physical layer frame. The invention fully utilizes the characteristics of a physical layer frame structure, after carrying out differential relevant processing, the information obtained by extracting 90 signs of a frame header after pilot frequency information is extracted in a pilot frequency mode and the information obtained by extracting 90 signs of the frame header in a non-pilot frequency mode enter parallel sliding peak value detection windows; when the peak value detection judgment is carried out in each window, a double-peak value detection scheme is introduced, and the corresponding judgment is made. The invention can accelerate the speed of the frame synchronization capturing frame header, obviously improve the performance of frame synchronization relevant peaks when a system is operated in low signal-to-noise ratio and larger frequency deviation and accurately give frame synchronization and initial position information, and in addition, a multiplier during differential relevant processing is replaced by a simple control exchange unit so as to lead the method to have lower complexity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Channel Estimation
InactiveUS20090135789A1Reduce system marginLarge system marginSatellite broadcast receivingBroadcast transmission systemsDVB-S2Telemetry
To allocate a VSAT to a MODCOD in a DVB-S2 ACM system, the HUB periodically transmits pilot frames of alternating MODCODs, which is identified by the VSAT. An FPGA at a VSAT site maintains telemetry of good and bad frames. A processor polls this telemetry to determine the optimal MODCOD to be allocated to the VSAT.
Owner:GILAT SATELLITE NETWORKS
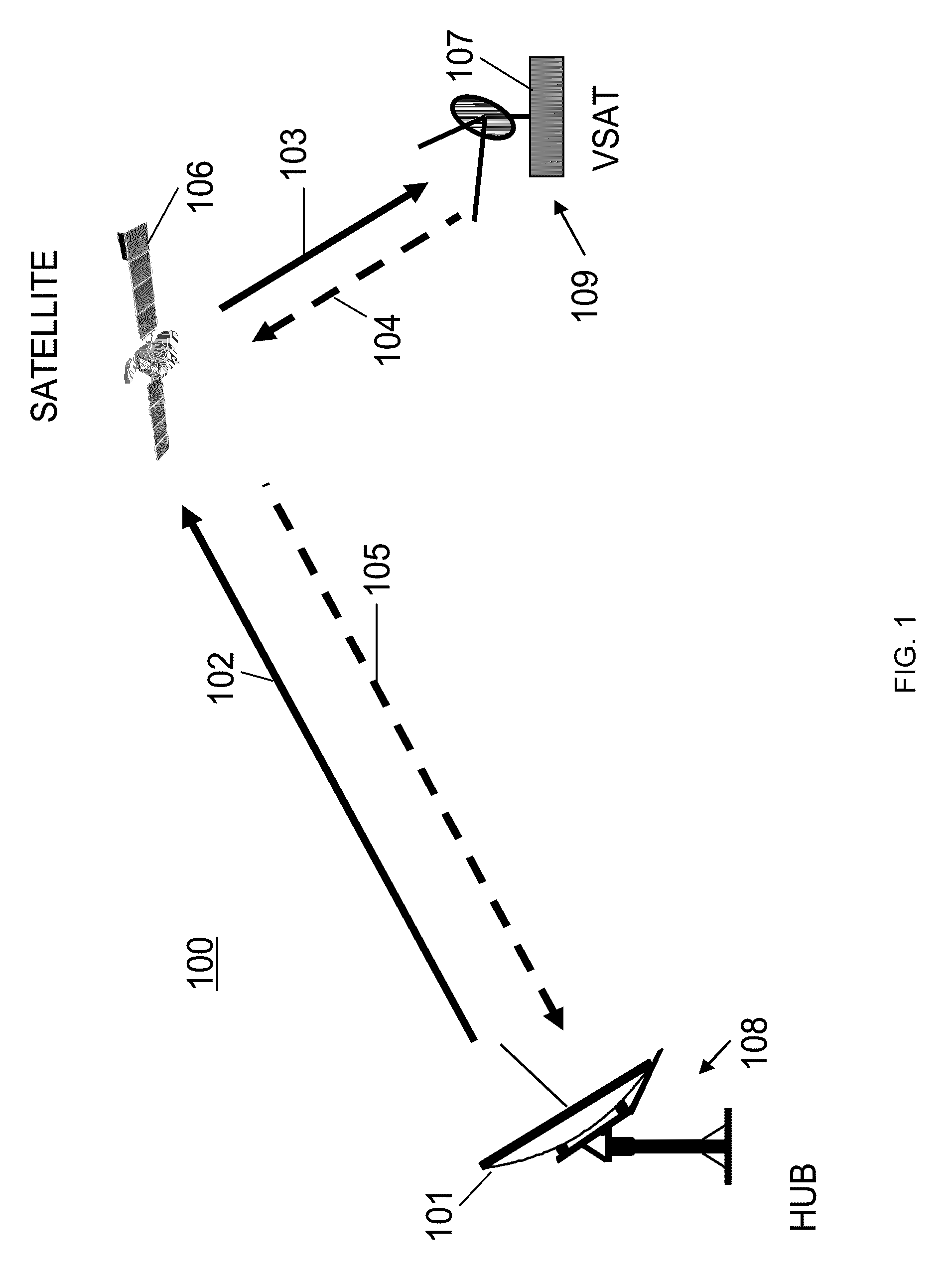
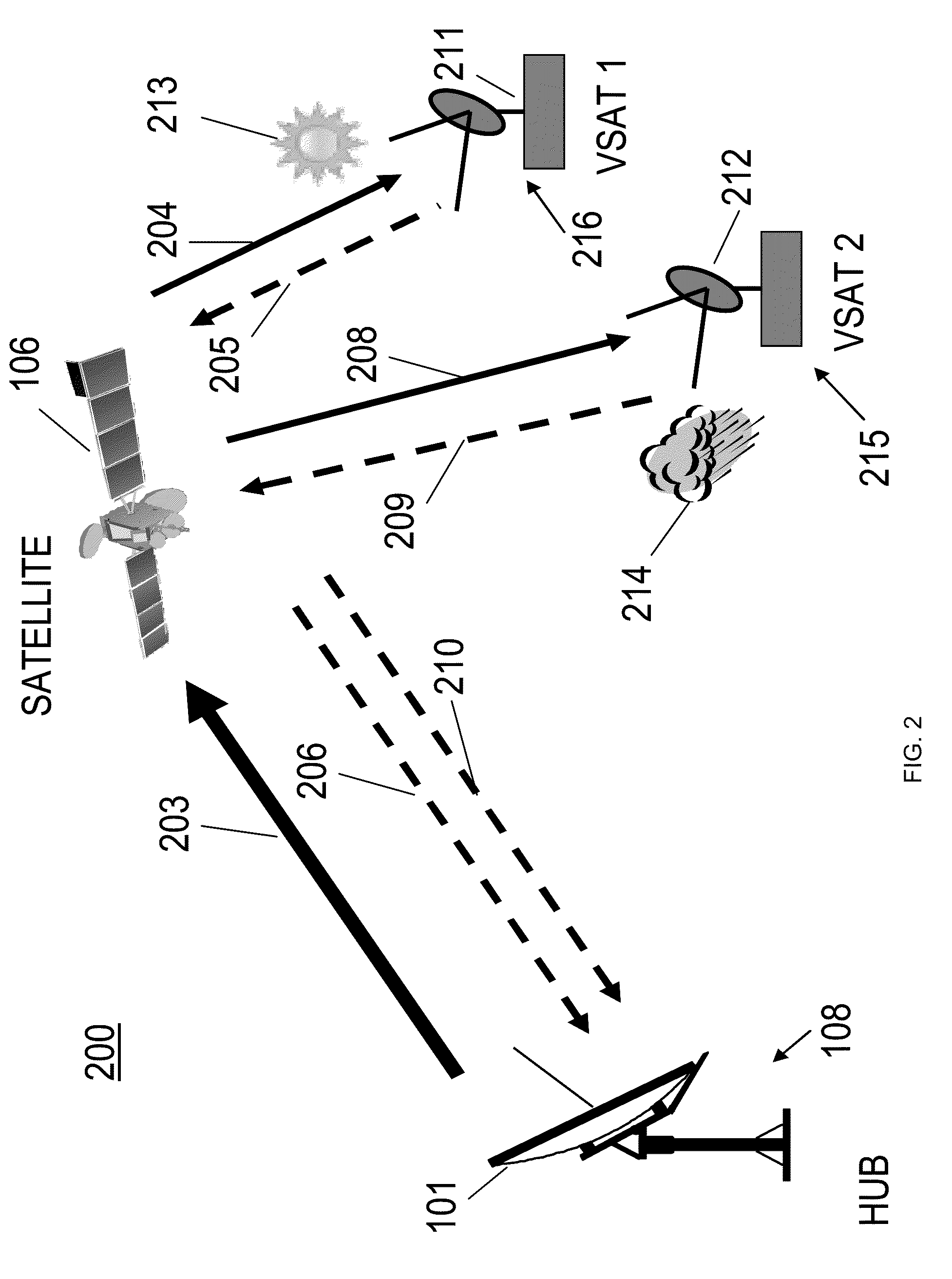
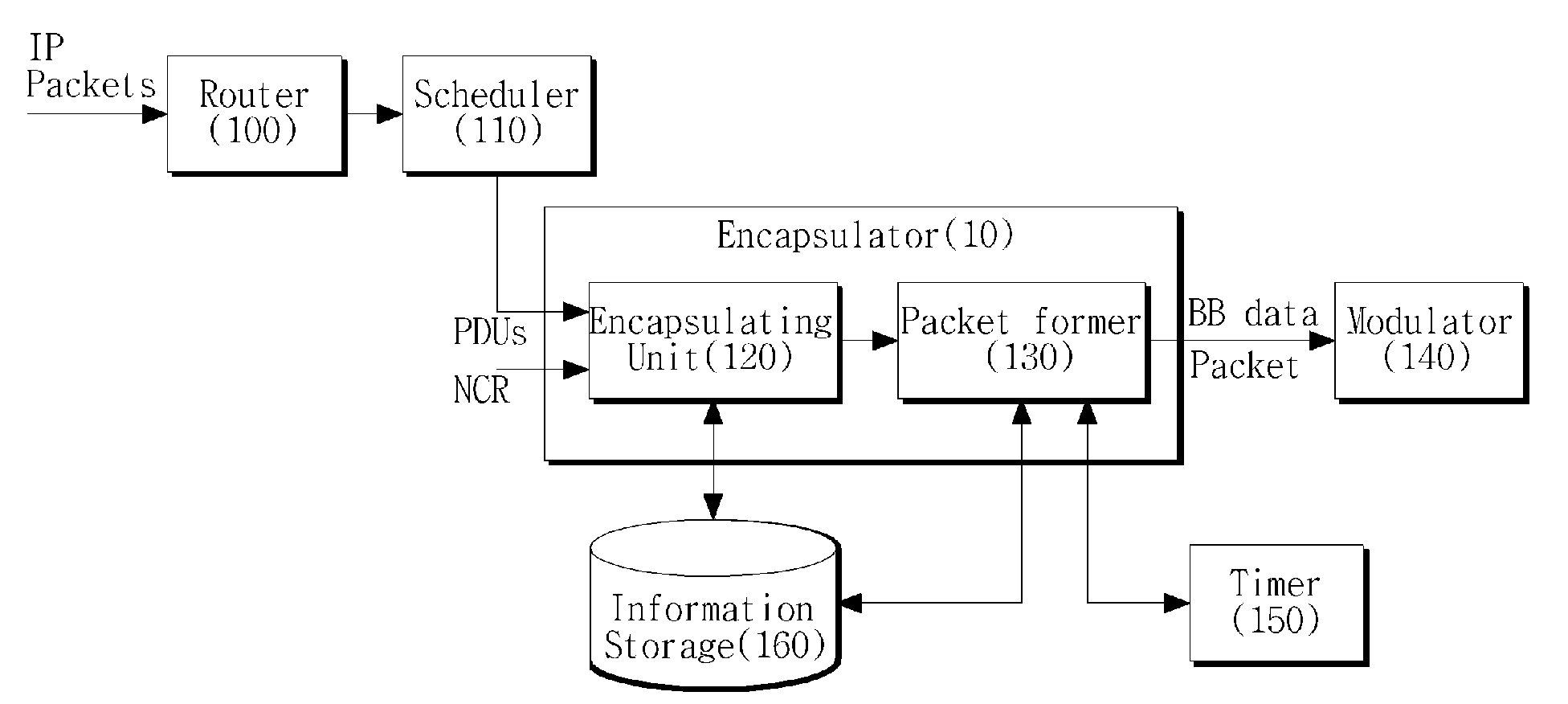
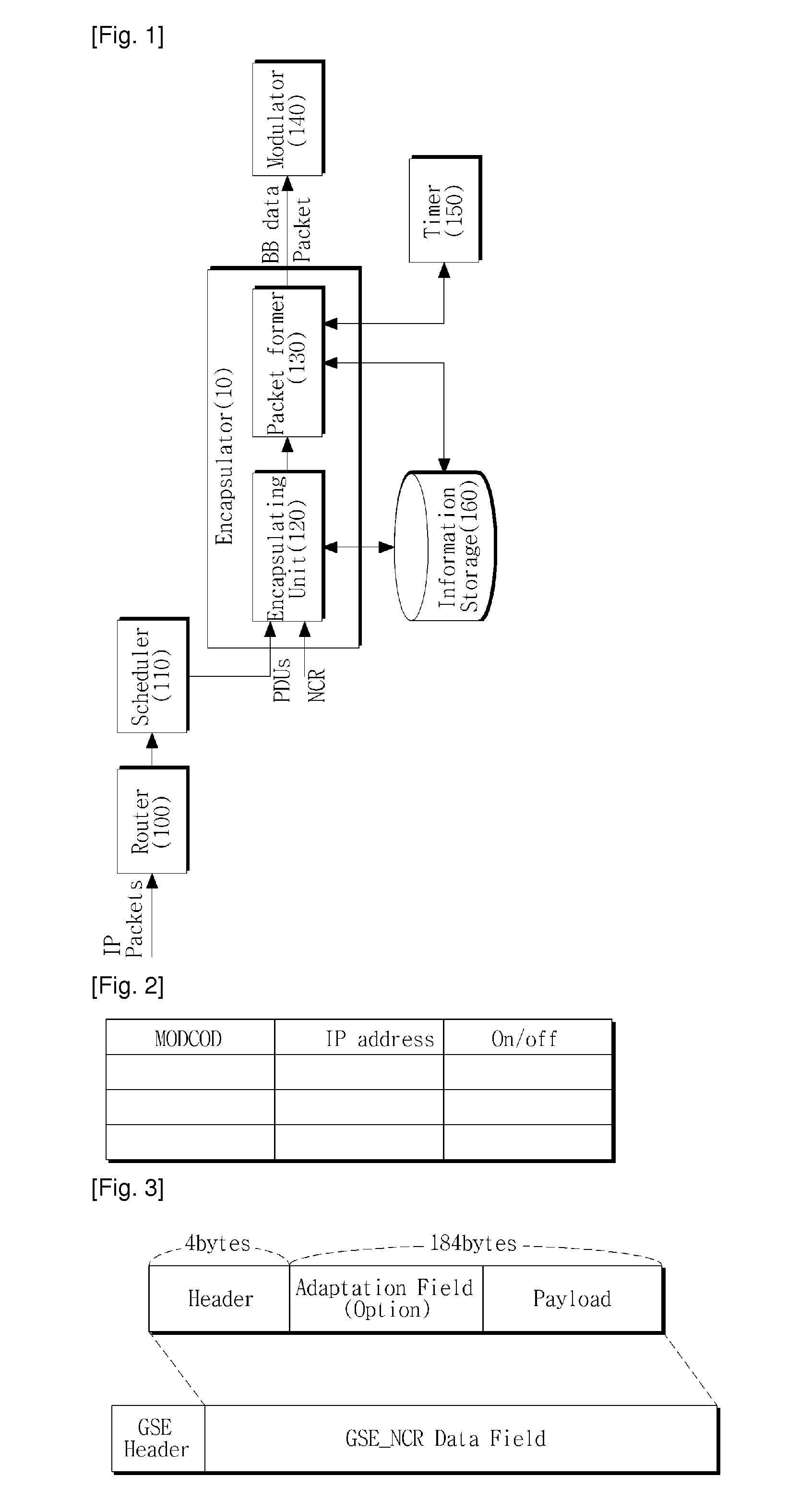
Method of encapsulating data in digital satellite communication system, and data transmission apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20110051745A1Reduce overheadImprove throughputPulse modulation television signal transmissionInformation formatDigital videoTime information
Provided is a satellite network communication system based on Second Generation Digital Video Broad-casting via Satellite (DVB-S2). A method for encapsulating transmission data in a digital satellite communication system includes: determining whether a time at which a reference time information packet has to be inserted into a packet data unit is arrived, in the digital satellite communication system; and if the time at which the reference time information packet has to be inserted into the packet data unit is arrived, transforming the packet data unit in the form of a baseband data packet including the reference time information packet. Therefore, by allowing transmission of Network Clock Reference (NCR) information in a satellite communication environment based on Generic Steam Encapsulation (GSE), bidirectional satellite communications are possible.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and device for decoding DVB-S2 LDPC encoded codewords
ActiveUS20060206779A1Reduce in quantityImprove communication performanceCode conversionCoding detailsDVB-S2Distributed computing
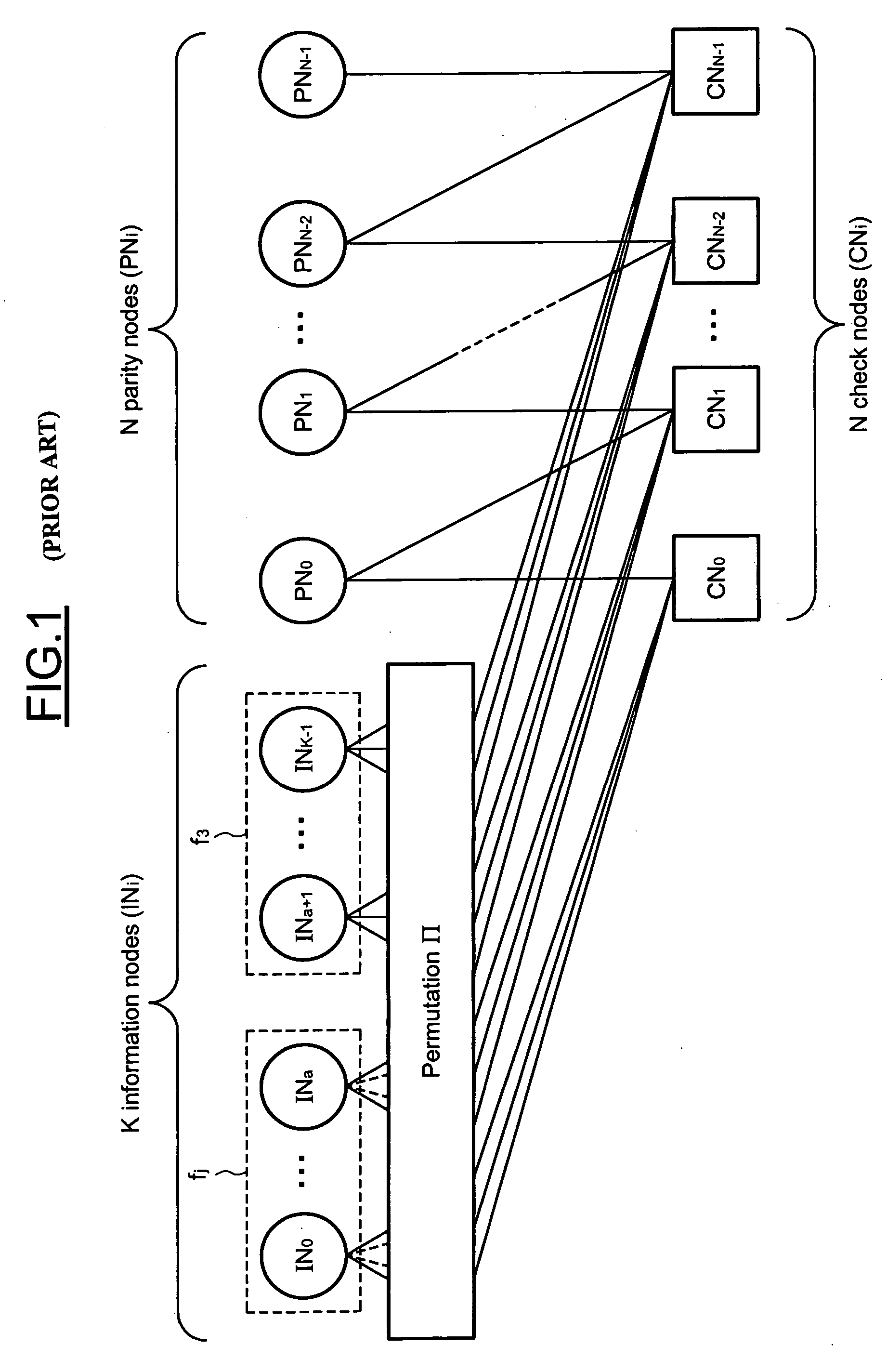
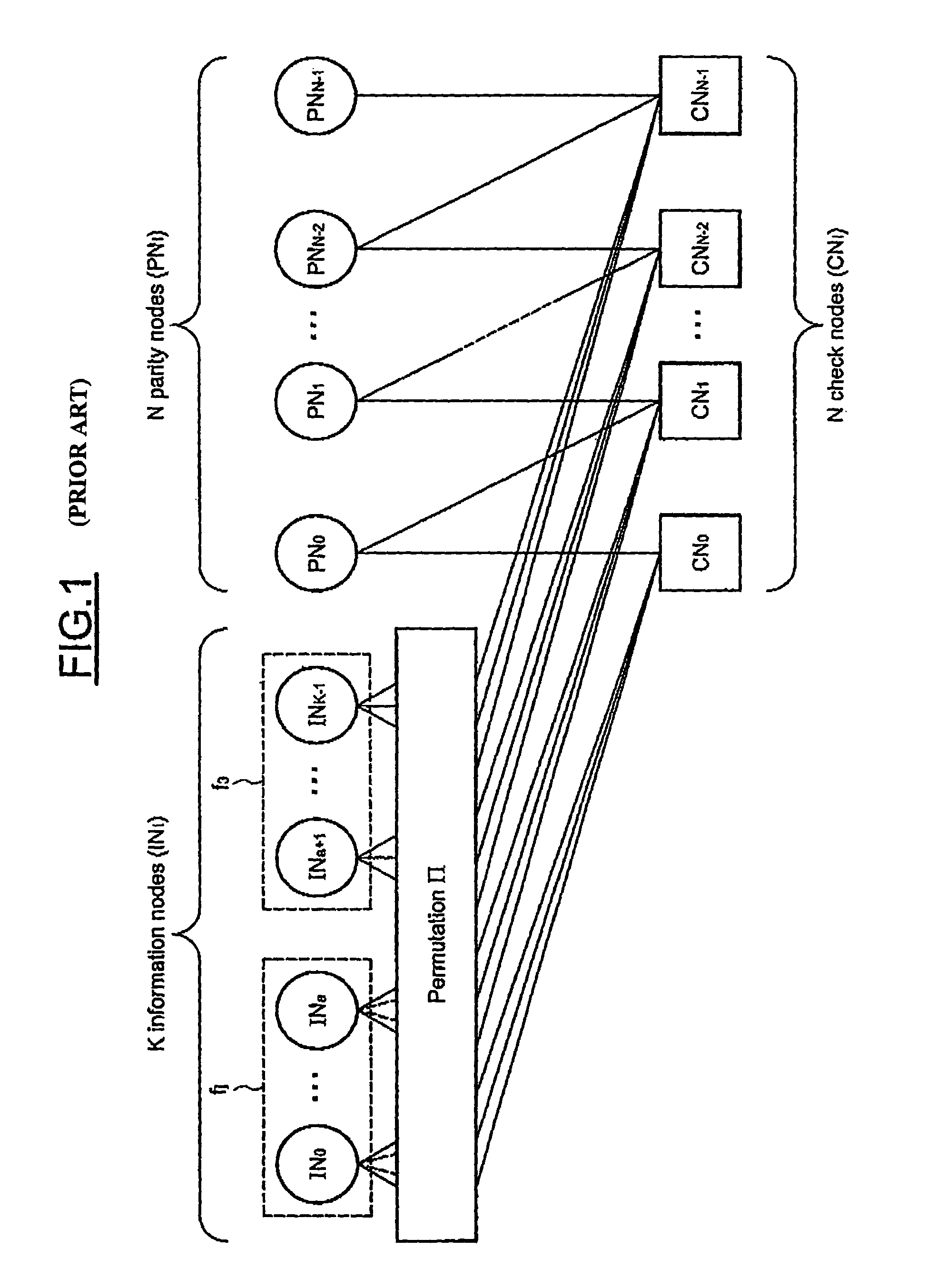
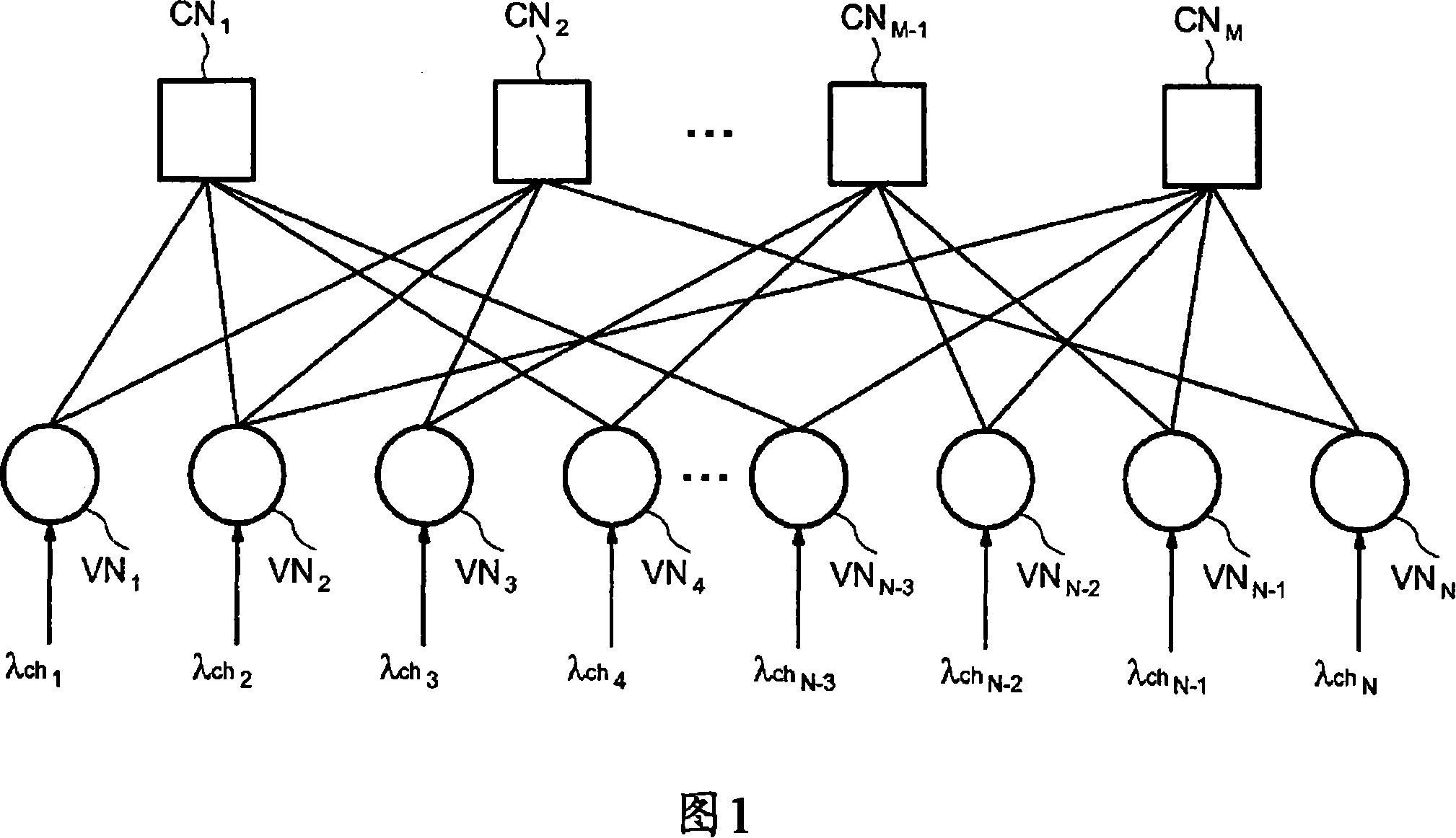
The method is for decoding an LDPC encoded codeword, the LDPC code being represented by a bipartite graph between check nodes and variable nodes including first variable nodes and second variable nodes connected to the check nodes by a zigzag connectivity. The method includes updating messages exchanged iteratively between variable nodes and check nodes including a first variable processing phase during which all the messages from the first variable nodes to the check nodes are updated and a check nodes processing phase during which all the messages from the check nodes to the first variable nodes are updated. The check nodes processing phase further includes updating all the messages from the second variable nodes to the check nodes, and directly passing an updated message processed by a check node to the next check node through the zigzag connectivity.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Transmodulator for very small aperture terminals employing internet protocol based communications
ActiveUS7603075B2Low implementation costPromote migrationBroadcast transmission systemsRadio transmissionInternet protocol suiteTTEthernet
DVB-S / S2 transmodulator for VSAT units employing IP based communication. The transmodulator is optimized for VSAT networks, enabling legacy VSAT units to benefit from the developments of the advanced DVB-S2 standard. The transmodulator appears transparent to the legacy VSAT unit that is configured to operate with the older DVB-S standard. Some embodiments offer a unique feedback channel allowing the transmodulator to send messages and information to the ground station via the VSAT itself.
Owner:AYECKA COMM SYST
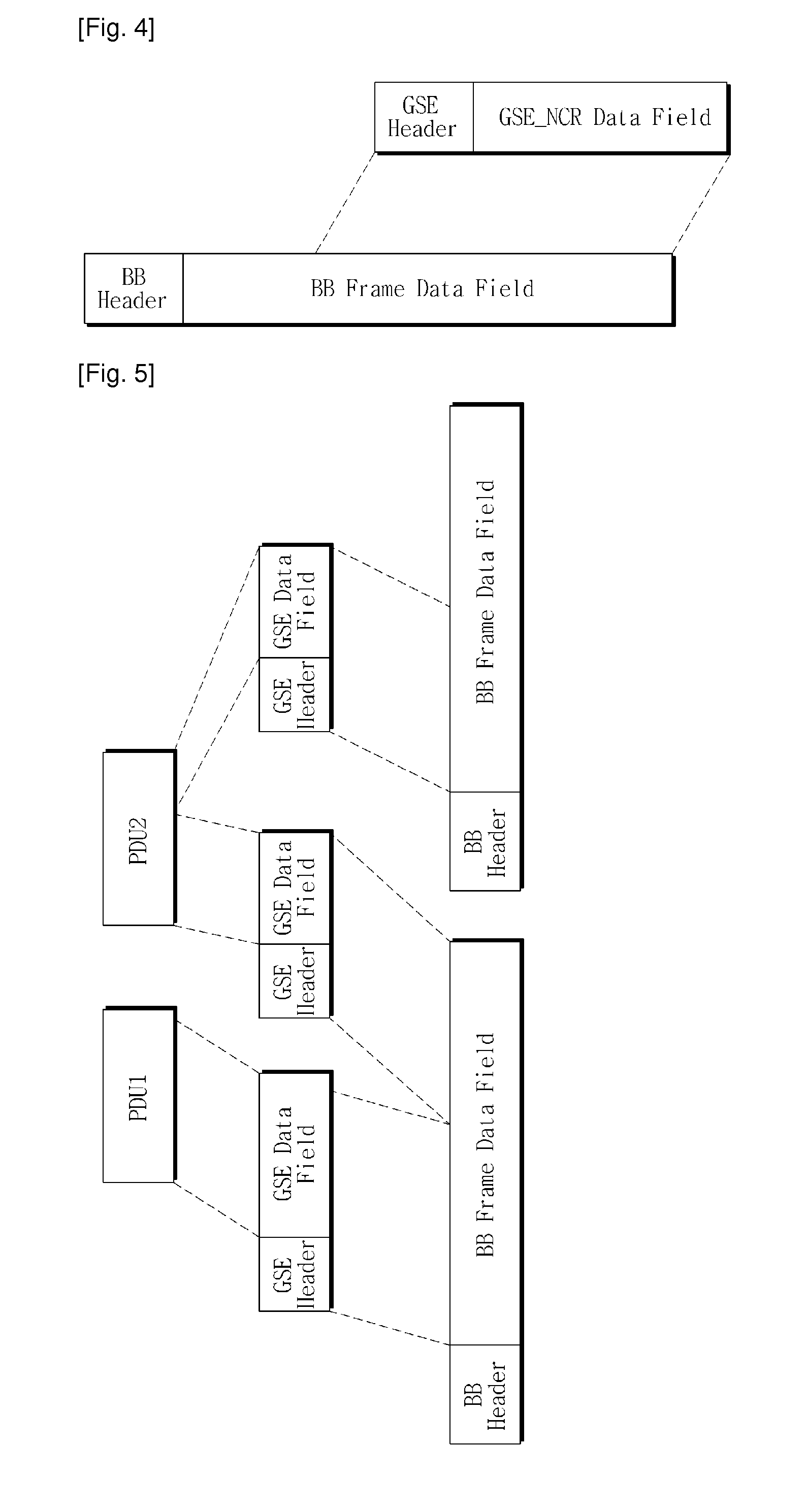
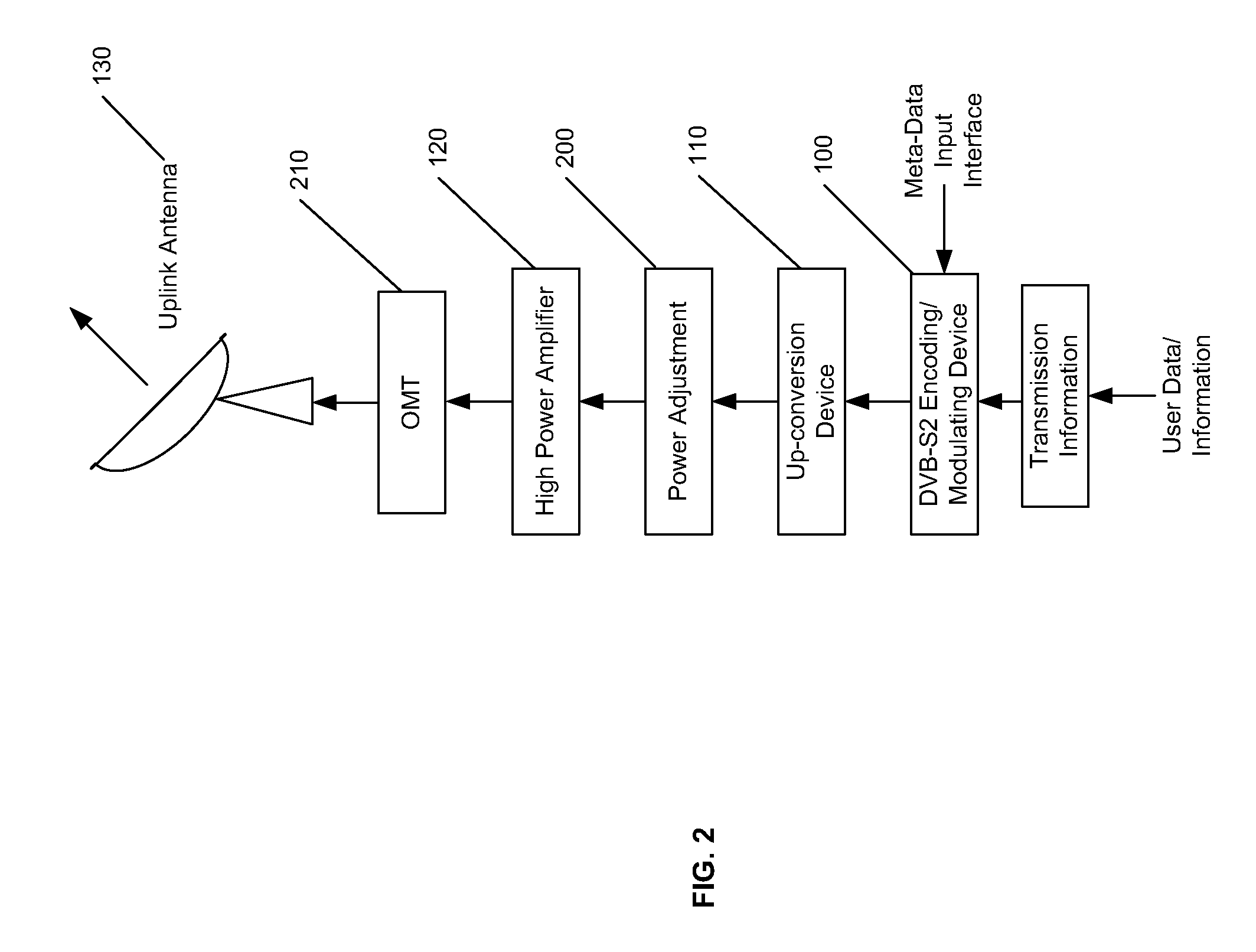
Method for carrying meta-data over digital video broadcasting-satellite second generation (dvb-s2) streams over the physical-layer framing structure
InactiveUS20110176603A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDigital videoStructure of Management Information
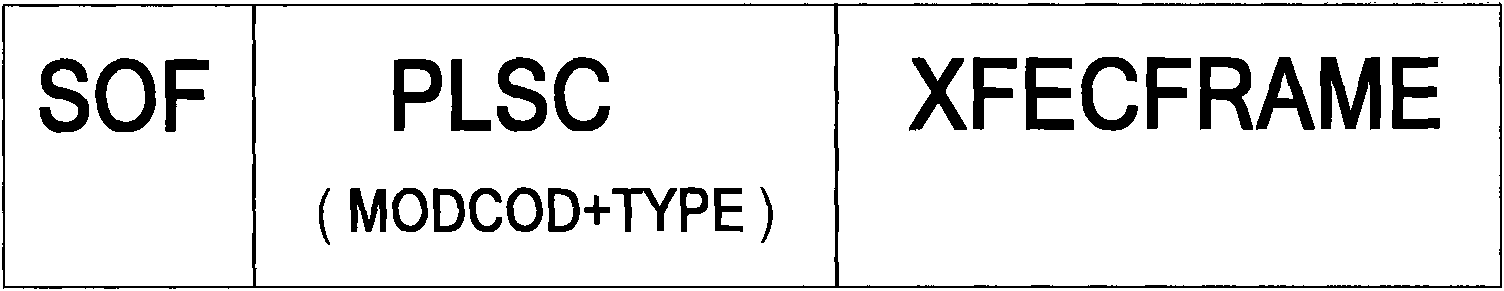
A method of inserting meta-data into a physical layer framing structure of a Digital Video Broadcast Satellite-Generation 2 (DVB-S2) comprising encoding meta-data and an original carrier signal using an encoder, the original carrier signal having a pilot sequence, replacing, by a meta-data insertion device, at least a portion of the pilot sequence with at least a portion of the meta-data to form a meta-pilot carrier signal, modulating, using a modulator, the meta-pilot carrier signal to form a modulated meta-pilot carrier signal, and transmitting, using a transmitting device, the modulated meta-pilot carrier signal. Additionally, the meta-data may be inserted by a meta-data insertion device into at least a portion of the XFECFRAME structure when dummy-PL Frames are available when VCM and ACM operation is used.
Owner:COMTECH EF DATA
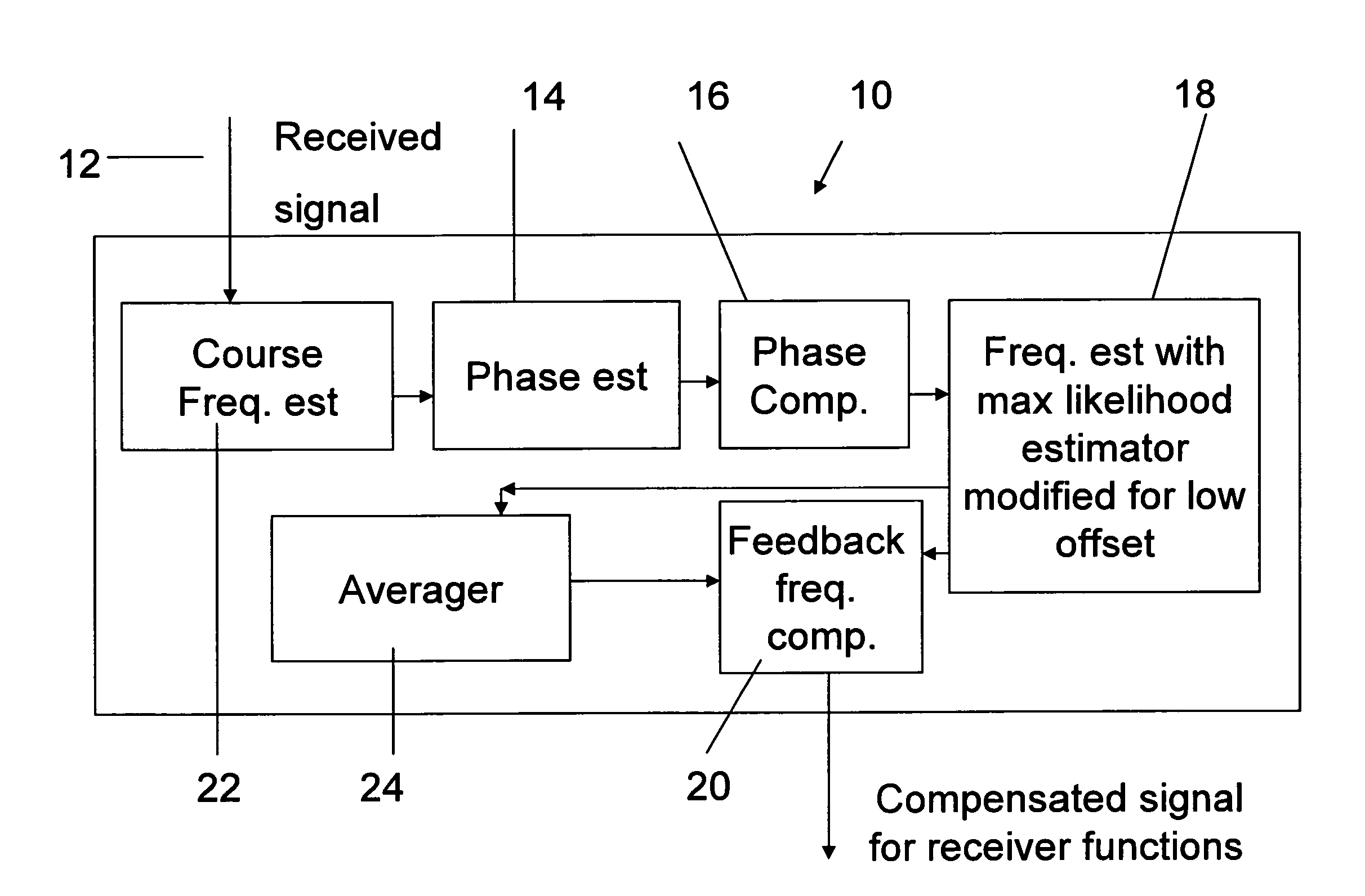
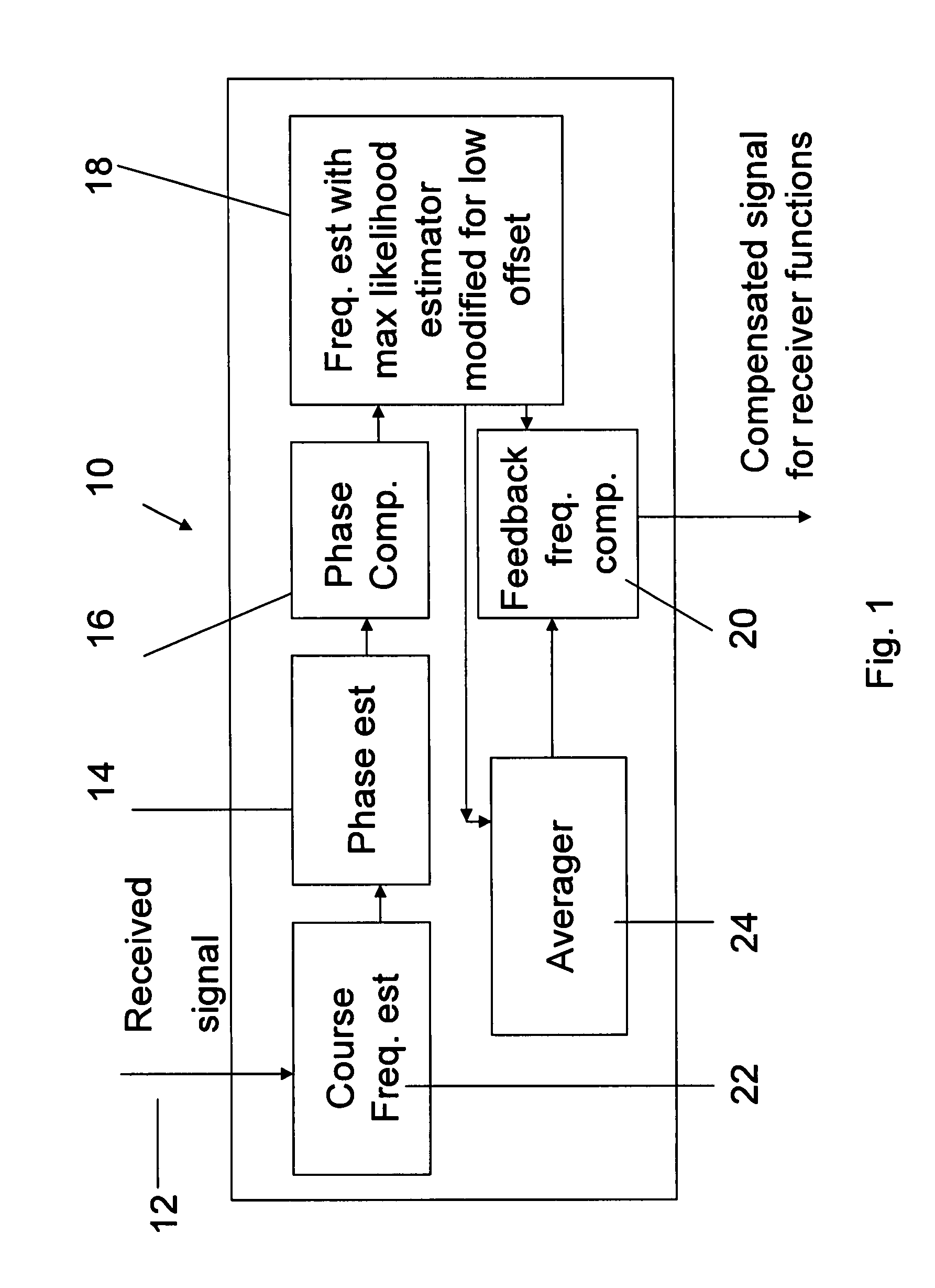
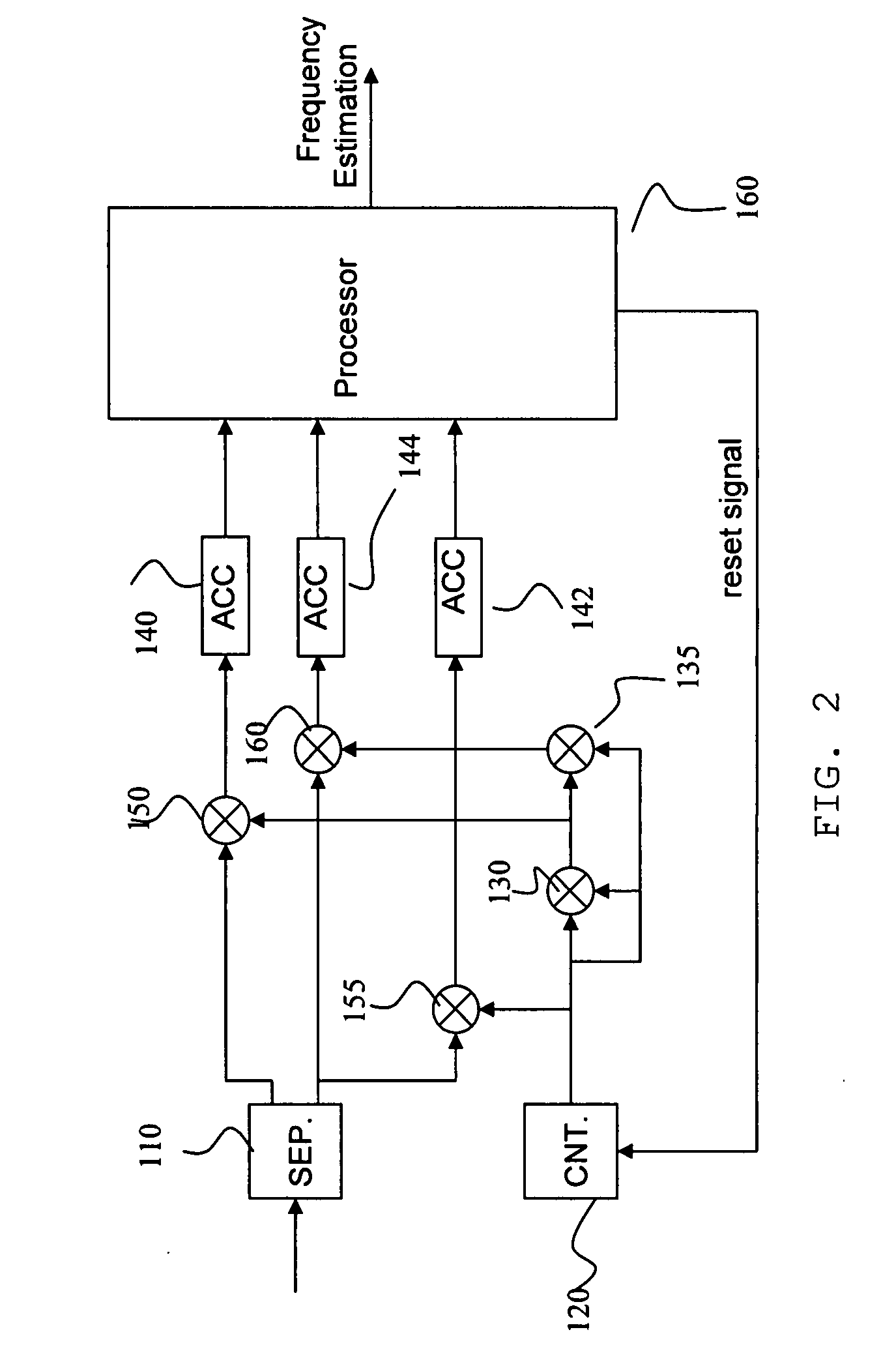
Accurate data-aided frequency tracking circuit
InactiveUS20090129514A1Carrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency compensationData aided
A frequency compensation circuit for compensating for a frequency offset in a received signal, the received signal including a periodically repeated pilot sequence for phase locking. The circuit comprises a phase estimator for estimating a phase of the received signal; a phase compensator, associated with the phase estimator, for compensating for the phase; a frequency estimator, comprising a maximum likelihood estimator comprising a first modification for estimating a frequency offset which is small relative to a symbol time, from the pilot sequence, the frequency estimator being connected downstream of the phase compensator; and a frequency compensator for applying a compensation to the signal, thereby to compensate for the frequency offset. The compensator is suitable for the exacting conditions of the DVB-S2 standard.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS CORP INT
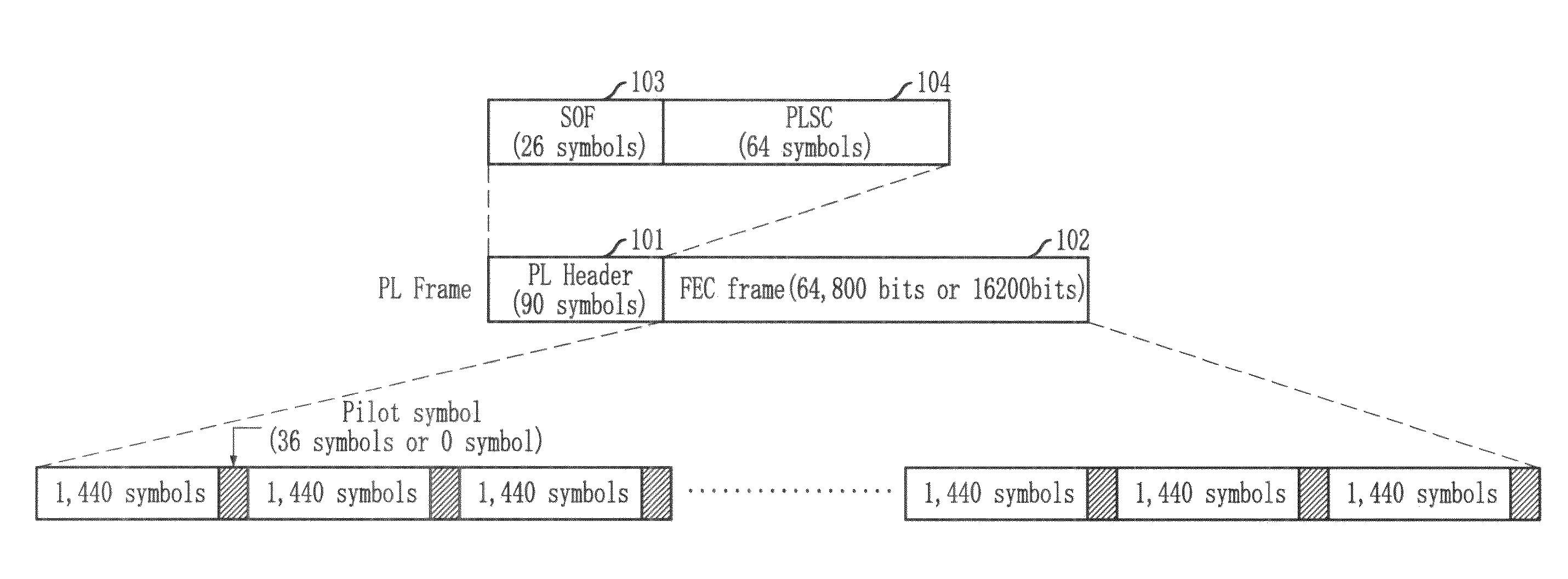
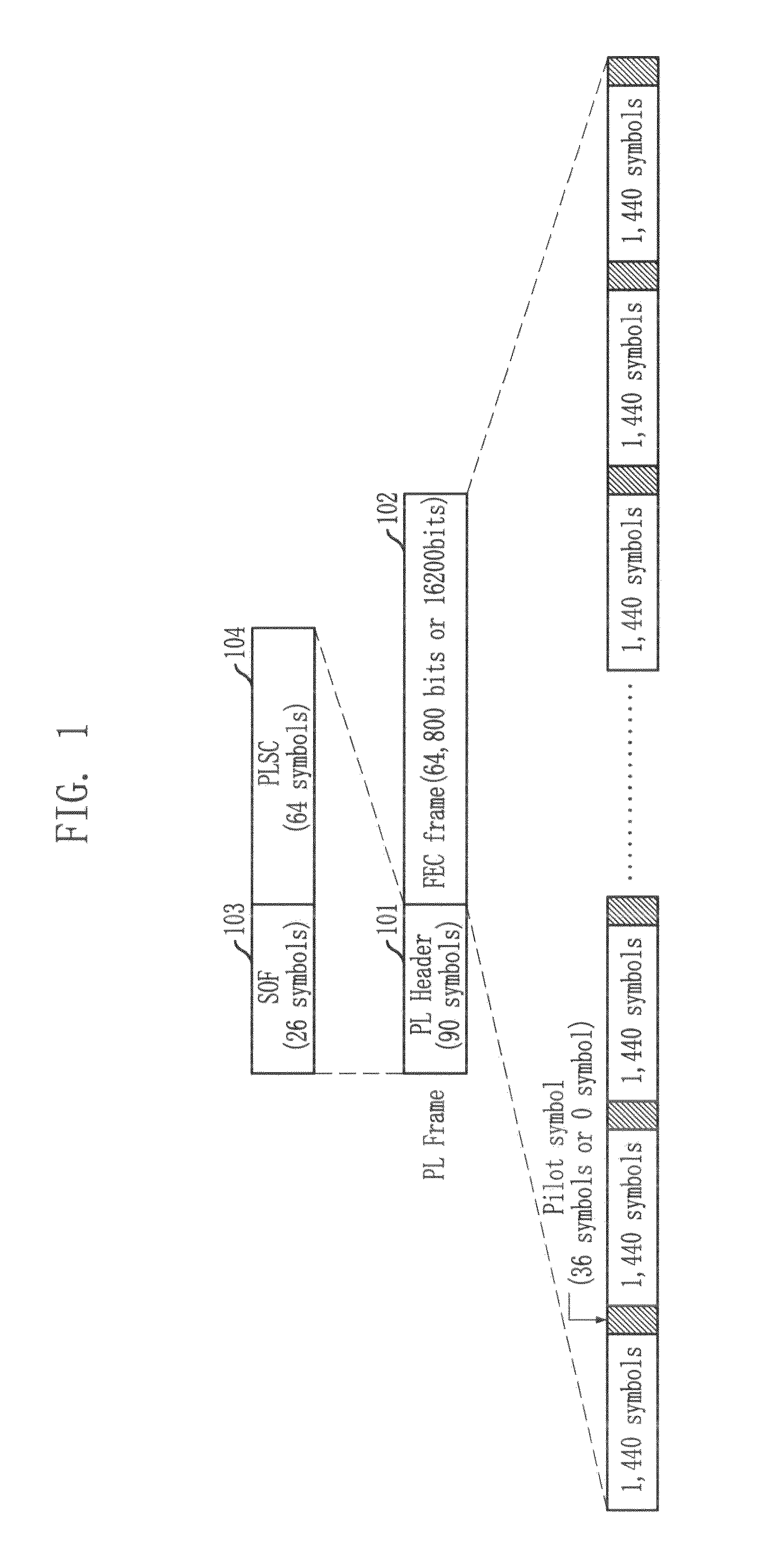
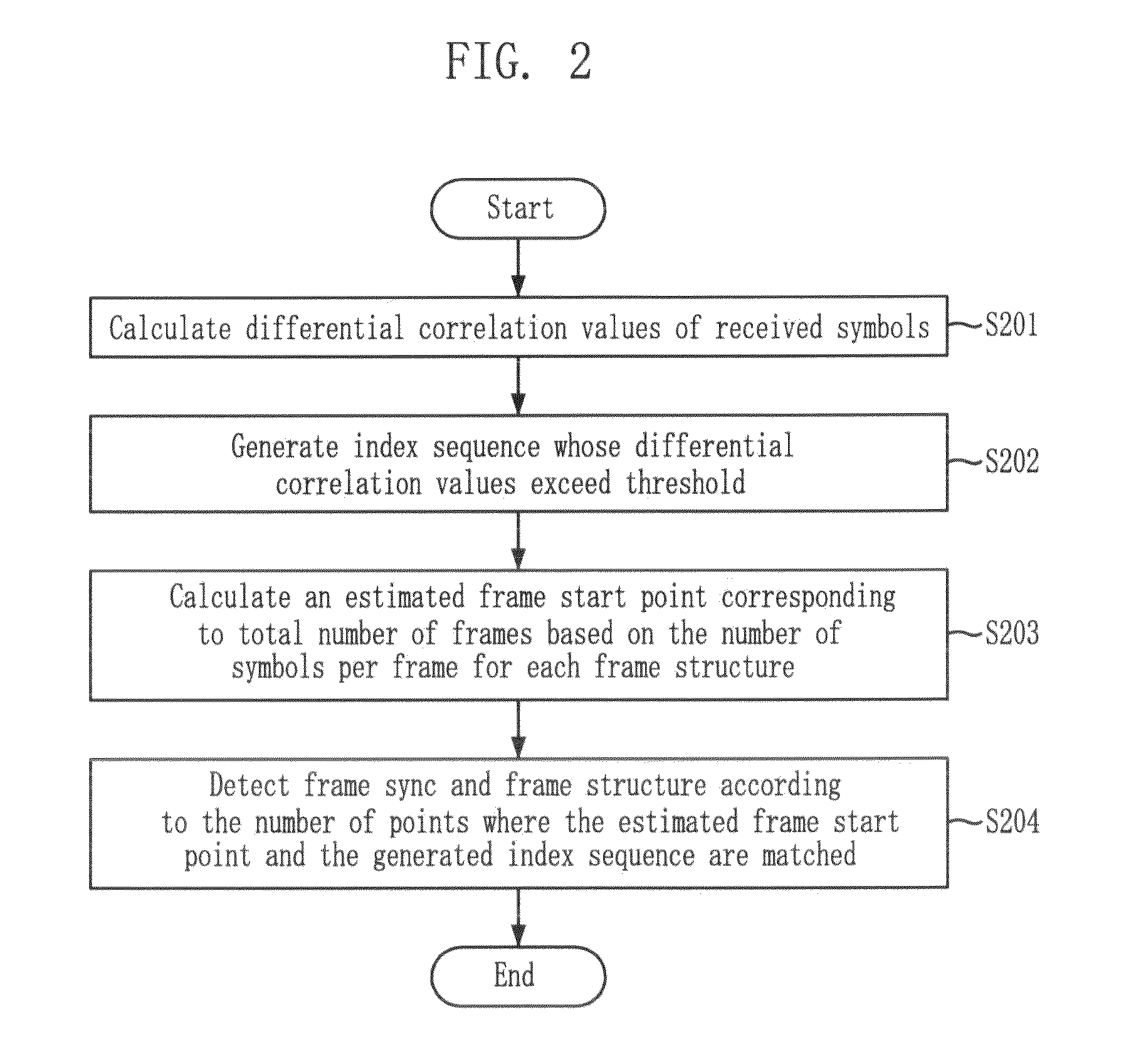
Frame synchronization and structure detection method in dvb-s2 system
InactiveUS20100007743A1Reduce complexitySmall memory capacityTelevision system detailsSatellite broadcast receivingSatellite broadcastingDVB-S2
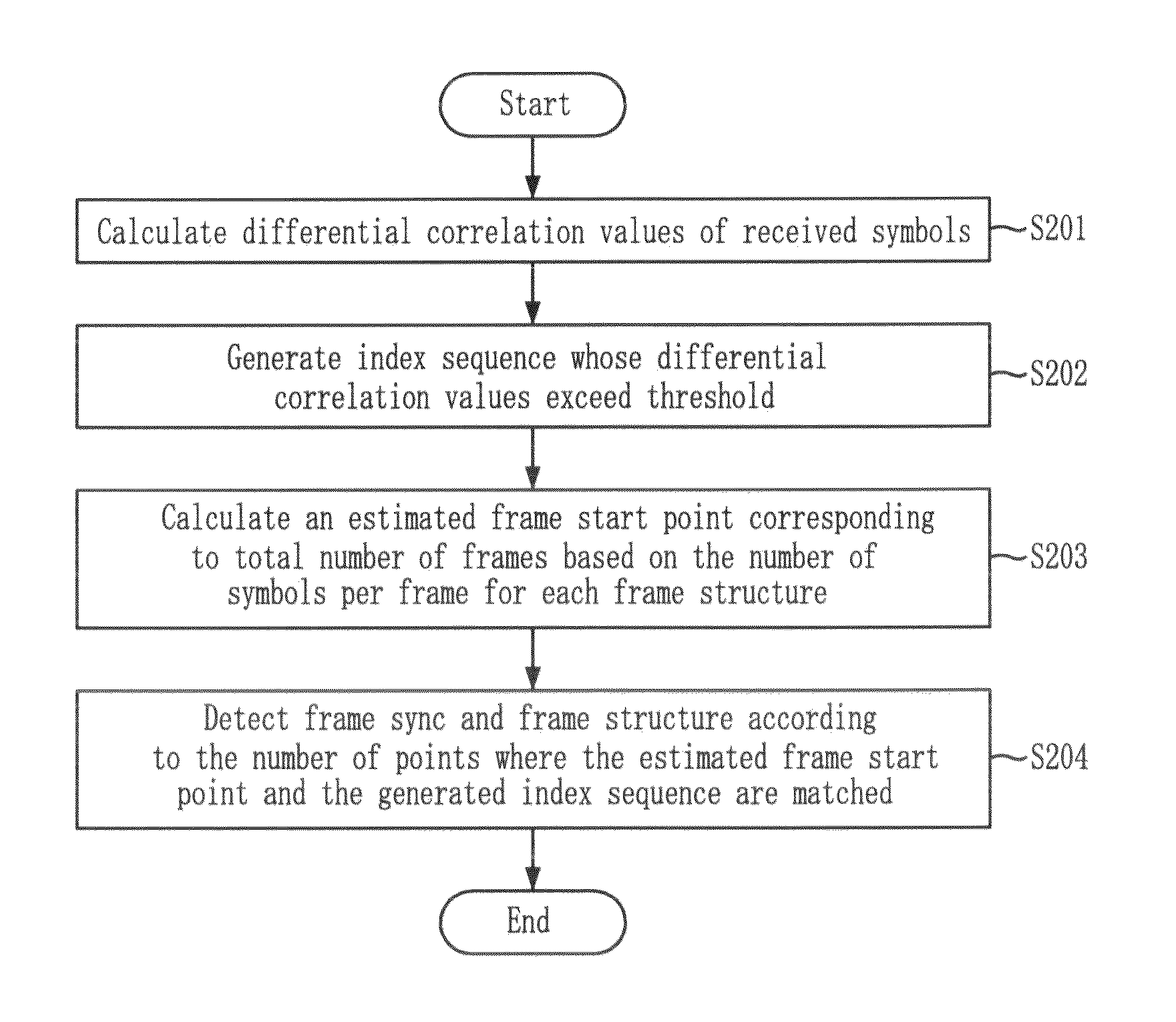
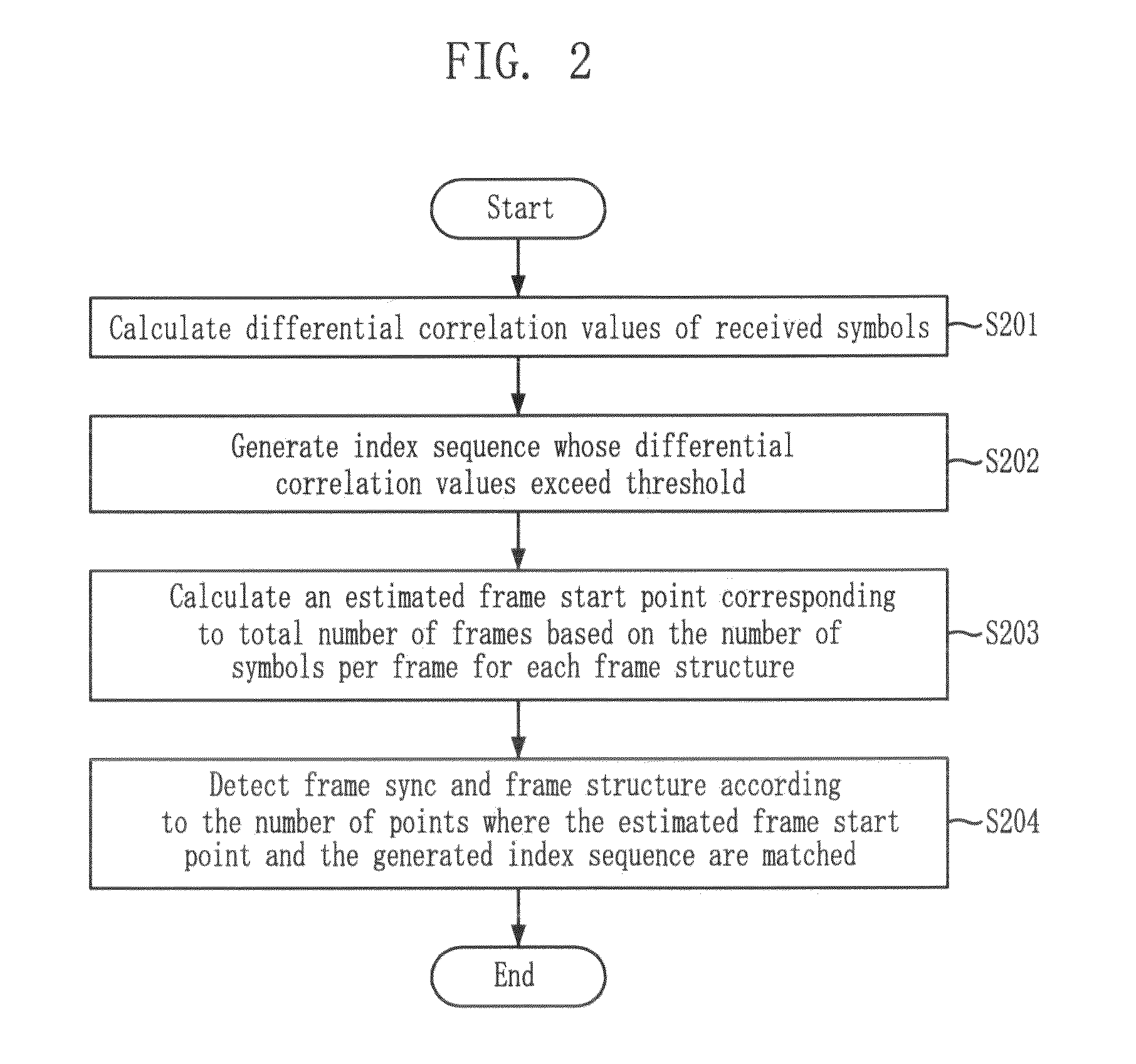
Provided is a method for detecting frame sync and frame structure in a satellite broadcasting system. The method for detecting frame sync and frame structure includes the steps of: calculating differential correlation values of reception symbols; generating index sequences of reception symbols whose differential correlation values calculated above exceed a threshold value; calculating positions estimated as frame start points which correspond to a total frame number based on the number of symbols per frame for each frame structure; and detecting frame sync and frame structure based on the umber of positions where the above-calculated frame start point estimated positions and the above-generated index sequences are matched.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
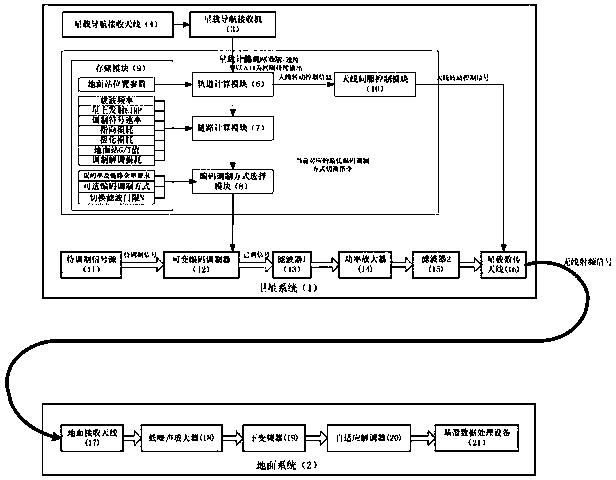
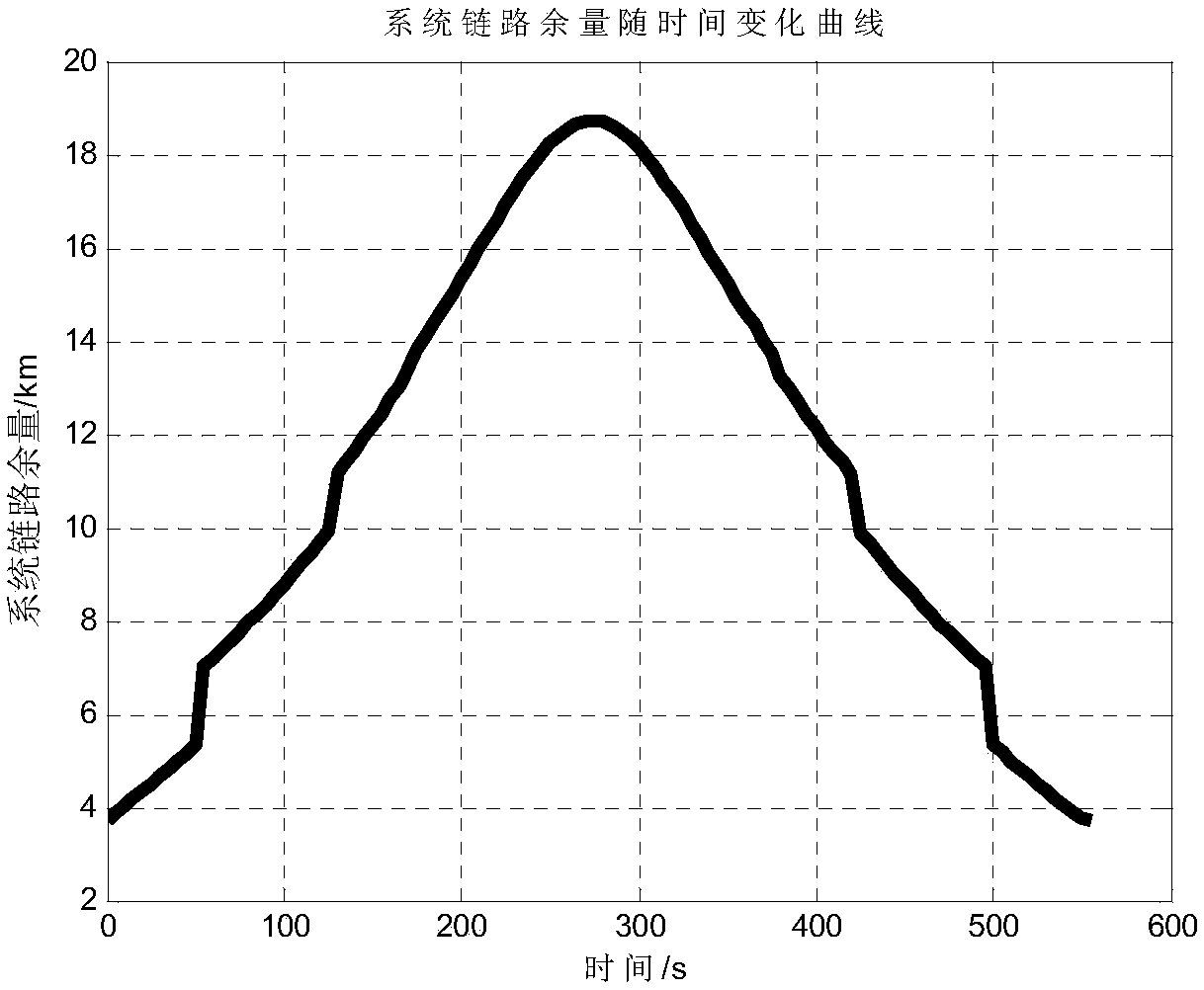
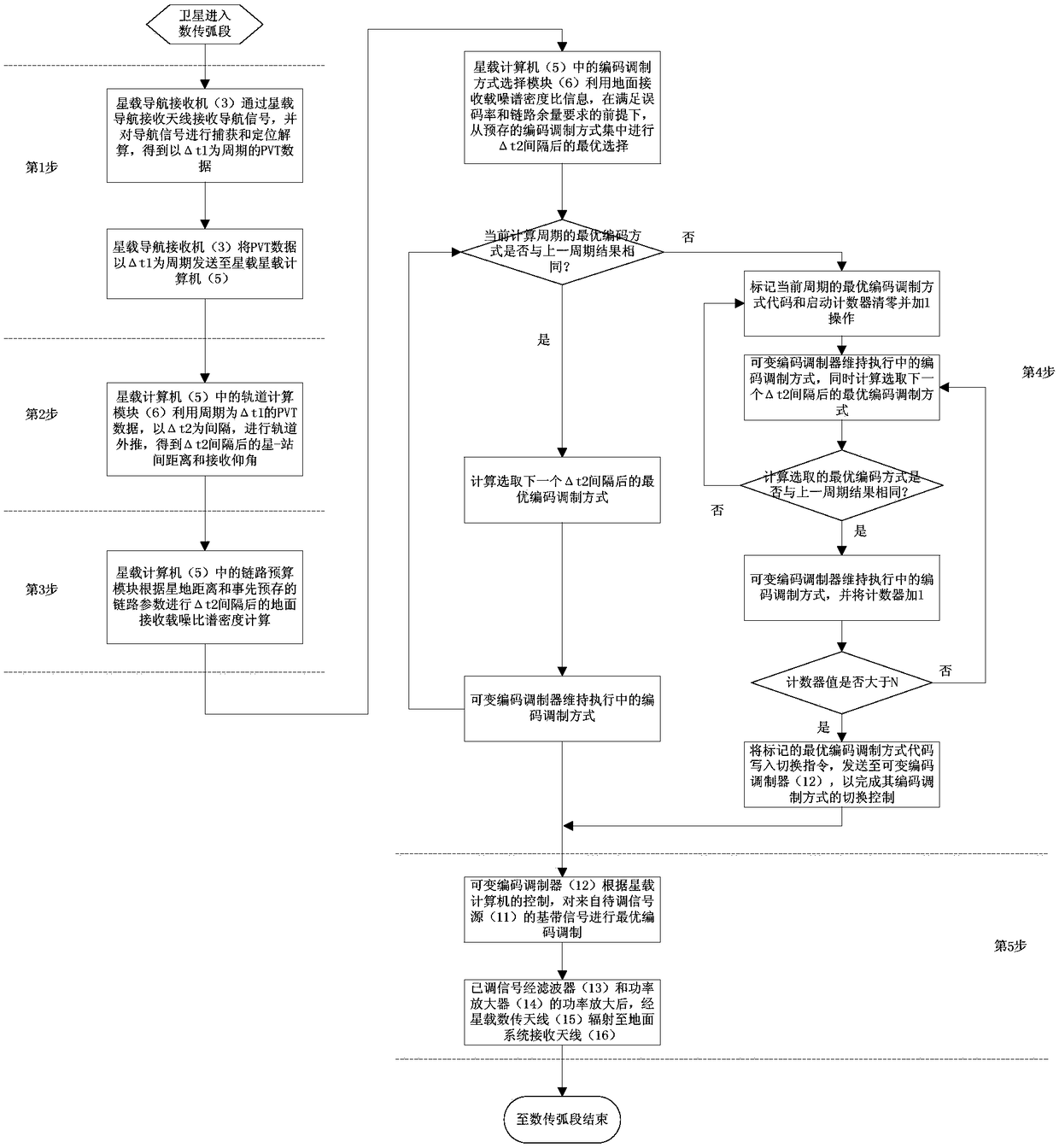
Near-earth remote sensing satellite self-adaptive variable code modulation data transmission system and method
ActiveCN109379167AImprove data transfer performanceIncrease the amount of effective informationRadio transmissionChannel coding adaptationFrequency spectrumTransport system
The invention discloses a near-earth remote sensing satellite self-adaptive variable code modulation data transmission system and method, belonging to the field of satellite overall design. The invention provides a variable code modulation data transmission system and method based on a DVB-S2 protocol, which fully utilizes link resources for the near-earth remote sensing satellite data transmission, adopts a variable code modulation (VCM) system, fully utilizes the system link margin, and improves the satellite star-ground data transmission efficiency; and the optimal code modulation mode is selected by means of the DVB-S2 protocol under the condition of satisfying a bit error rate and the link margin, so that the amount of effective information transmitted per unit time is the largest. The near-earth remote sensing satellite self-adaptive variable code modulation data transmission method provided by the invention can maximize the adaptation to changing channel conditions and channel capacity due to orbital changes of the near-earth remote sensing satellite, and transmit more data information on a limited spectrum resource, which is very suitable for the data transmission of the near-earth remote sensing satellite to the ground.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
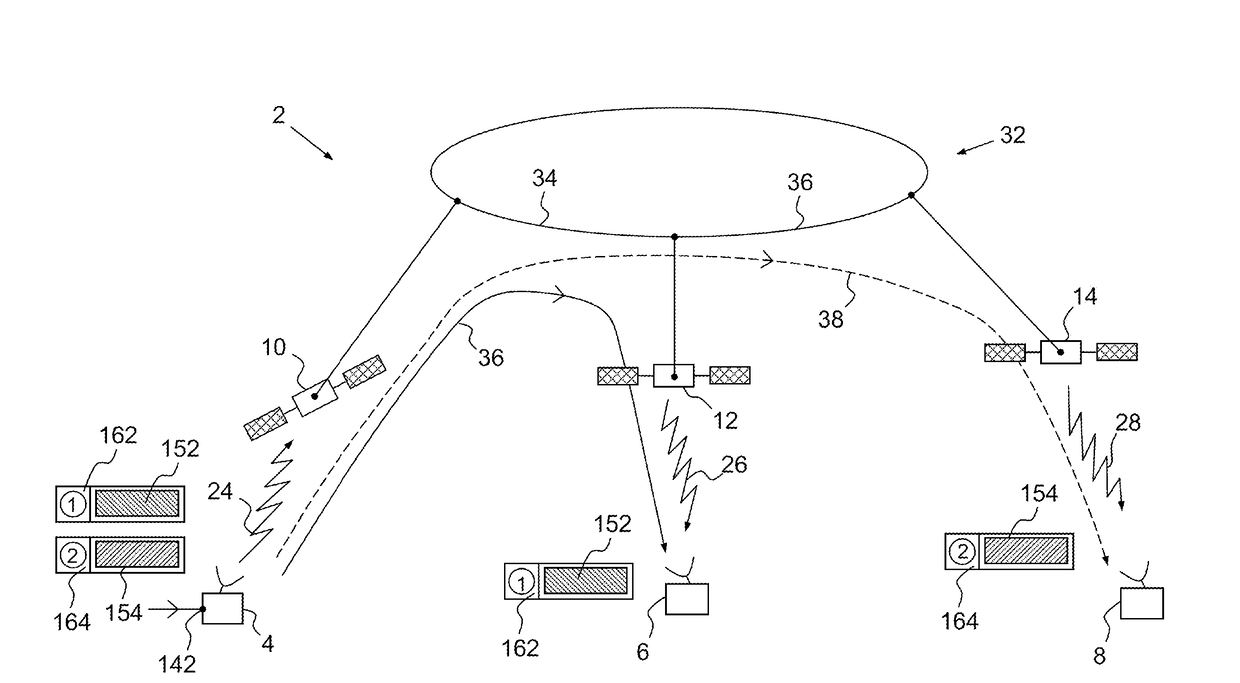
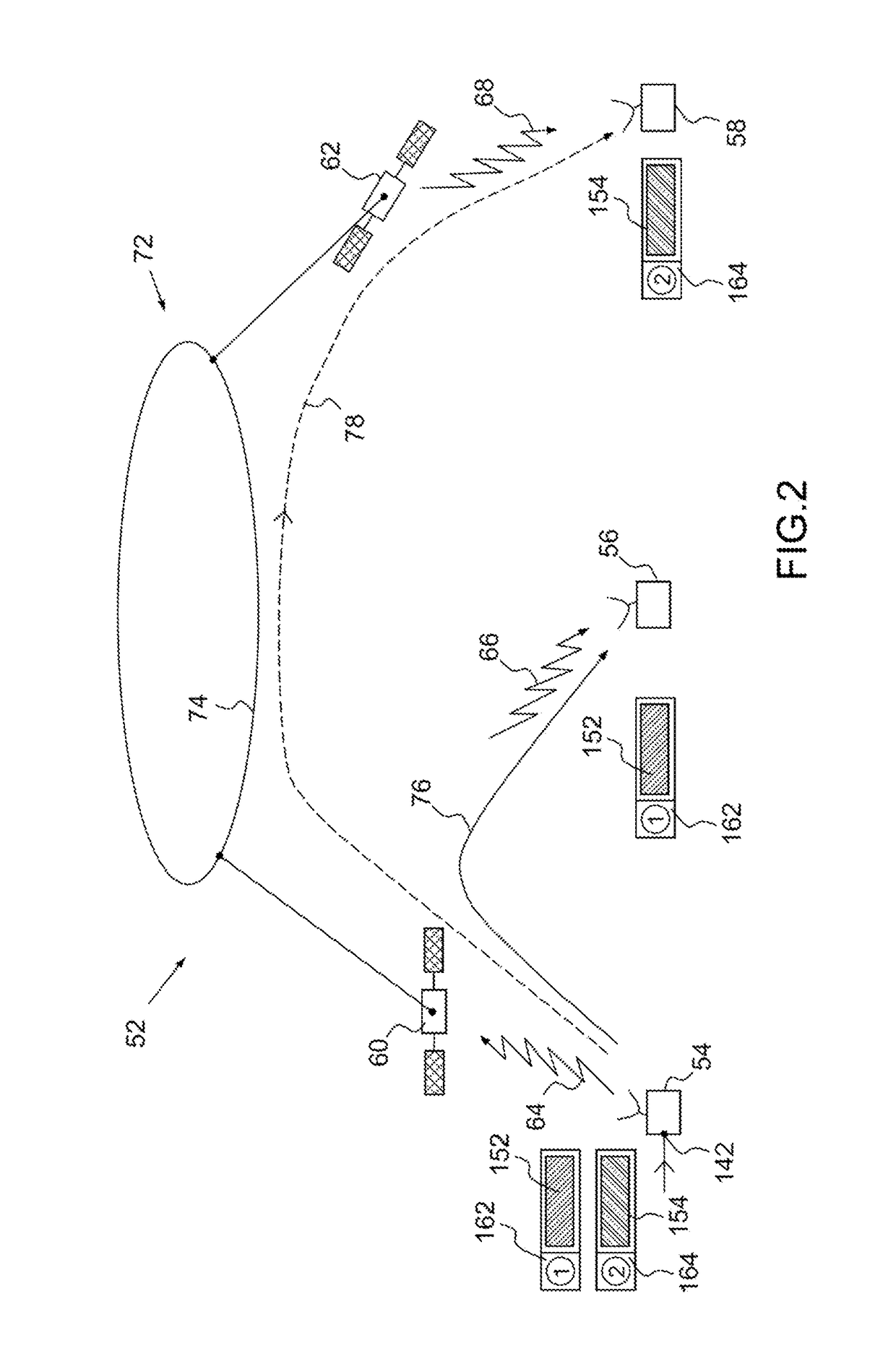
Method for transparent on-board routing of data packets at very high bit rate in a space telecommunication system using a network of at least one regenerative satellite(s)
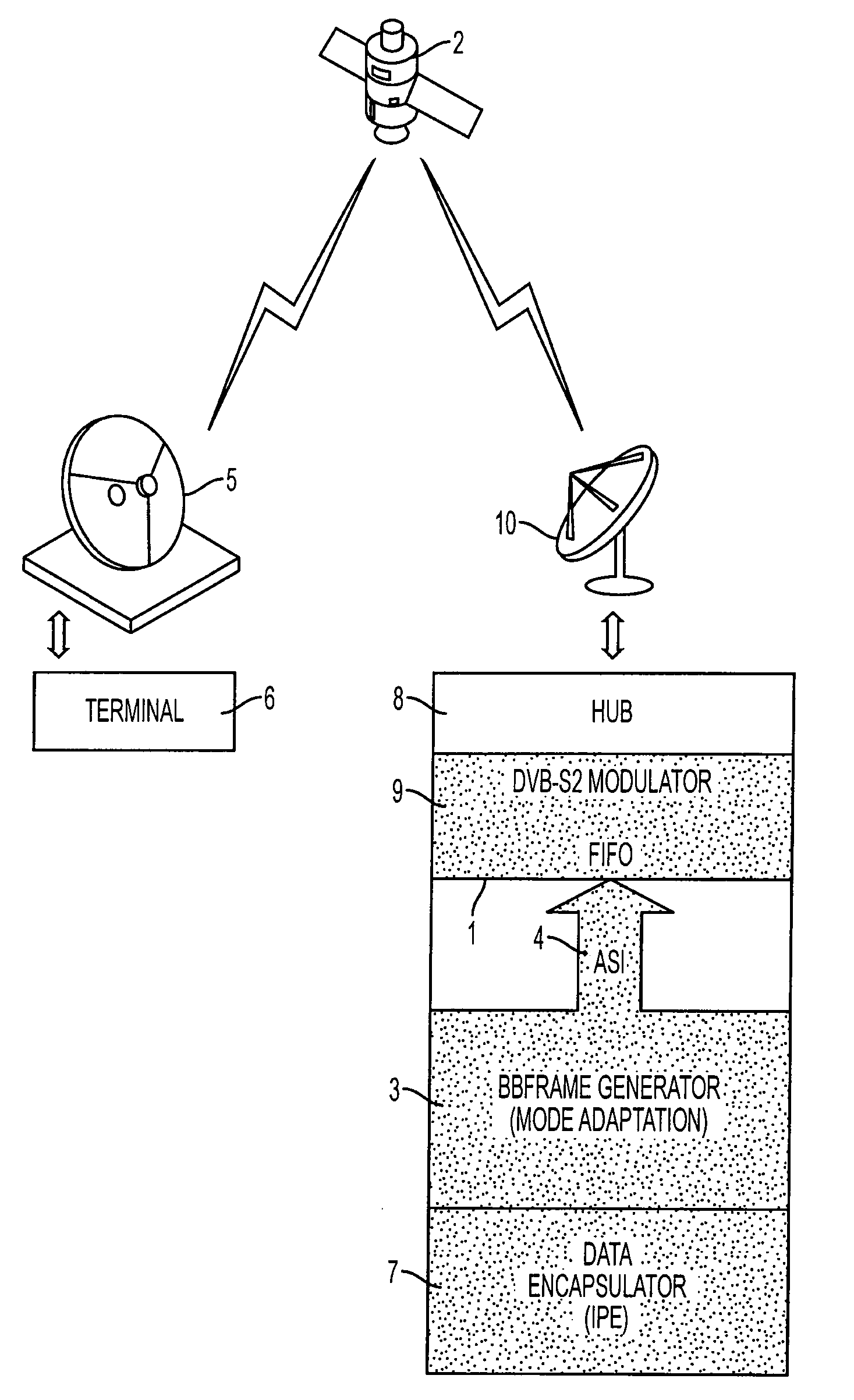
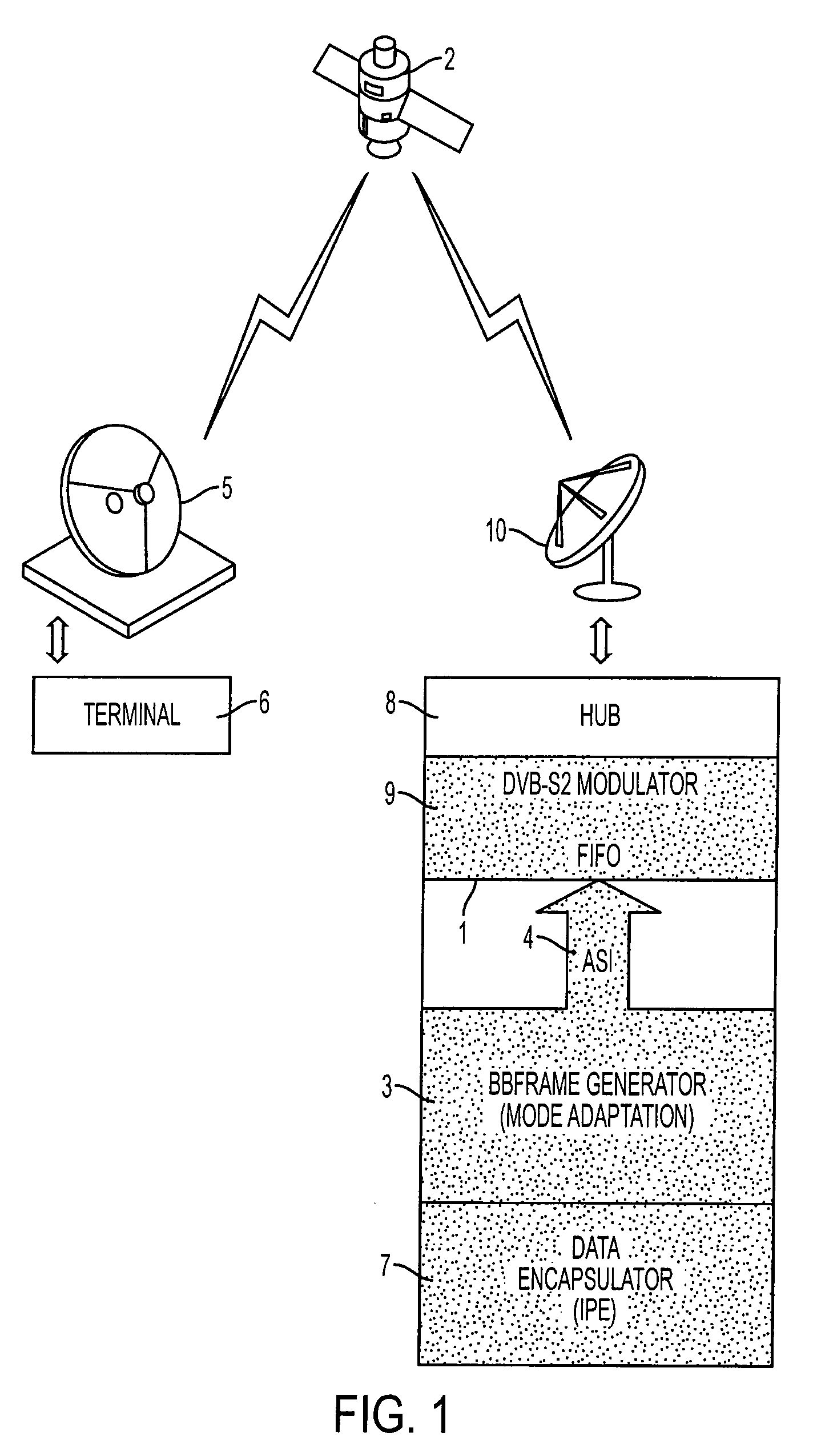
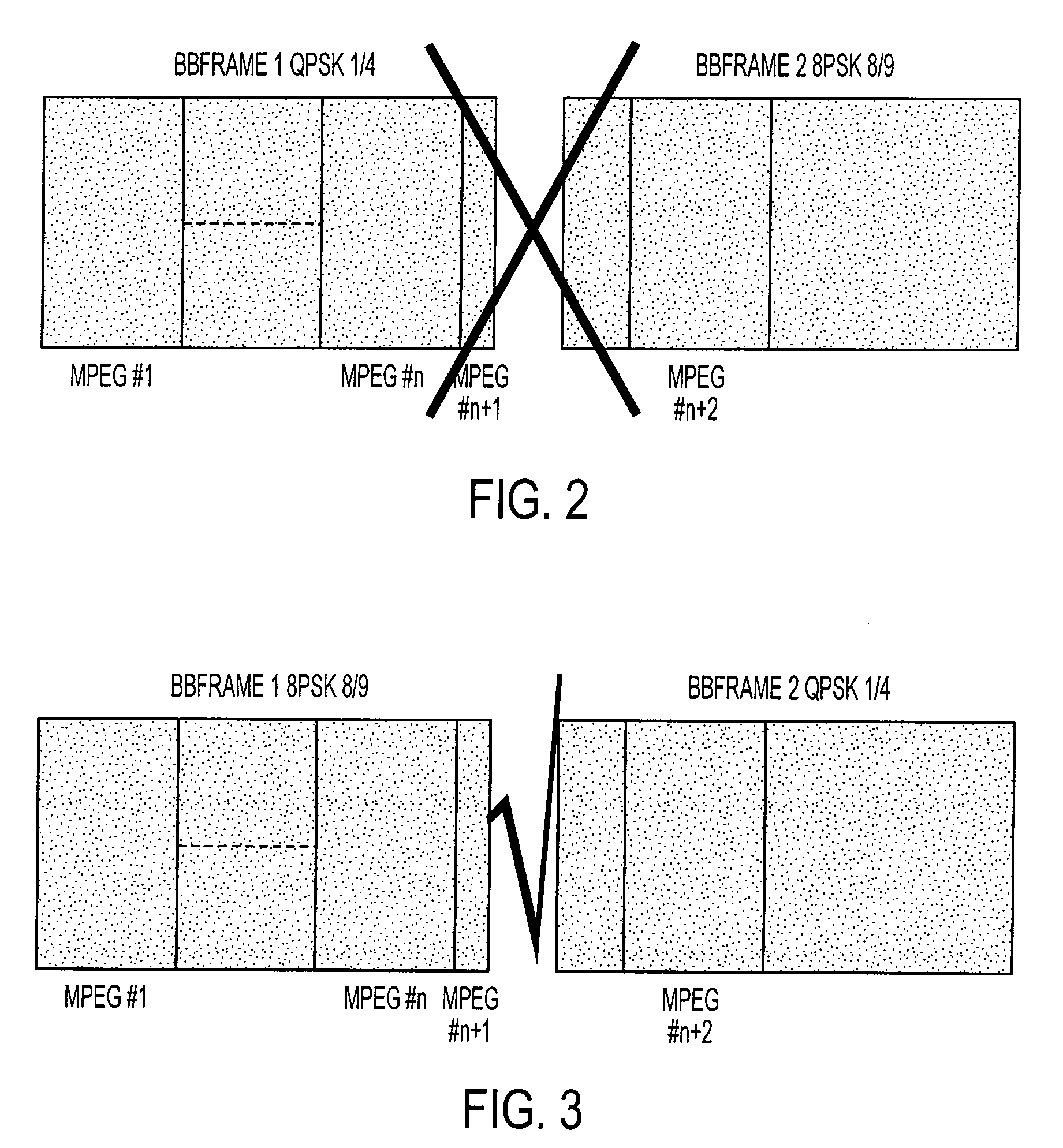
A method for transparent on-board routing of data packets at high bit rate is implemented by a telecommunication system comprising an origin transmitting station, a first destination receiving station, a second destination receiving station, and a plurality of at least two satellites. The origin transmitting station segments high bit rate data streams into coded or uncoded packets each having the structure of a coded or uncoded DVB-S2 baseband frame BBFRAME; and the origin transmitting station inserts, for each segmented BBFRAME packet, coded or uncoded, an on-board routing label of a single piece respectively associated with the coded or uncoded BBFRAME packet. The on-board routing label contains an identifier of the destination receiving station associated with the coded BBFRAME packet, out of the first destination receiving station and the second destination receiving station.
Owner:THALES SA
Multi-standard television receiver and television signal receiving method thereof
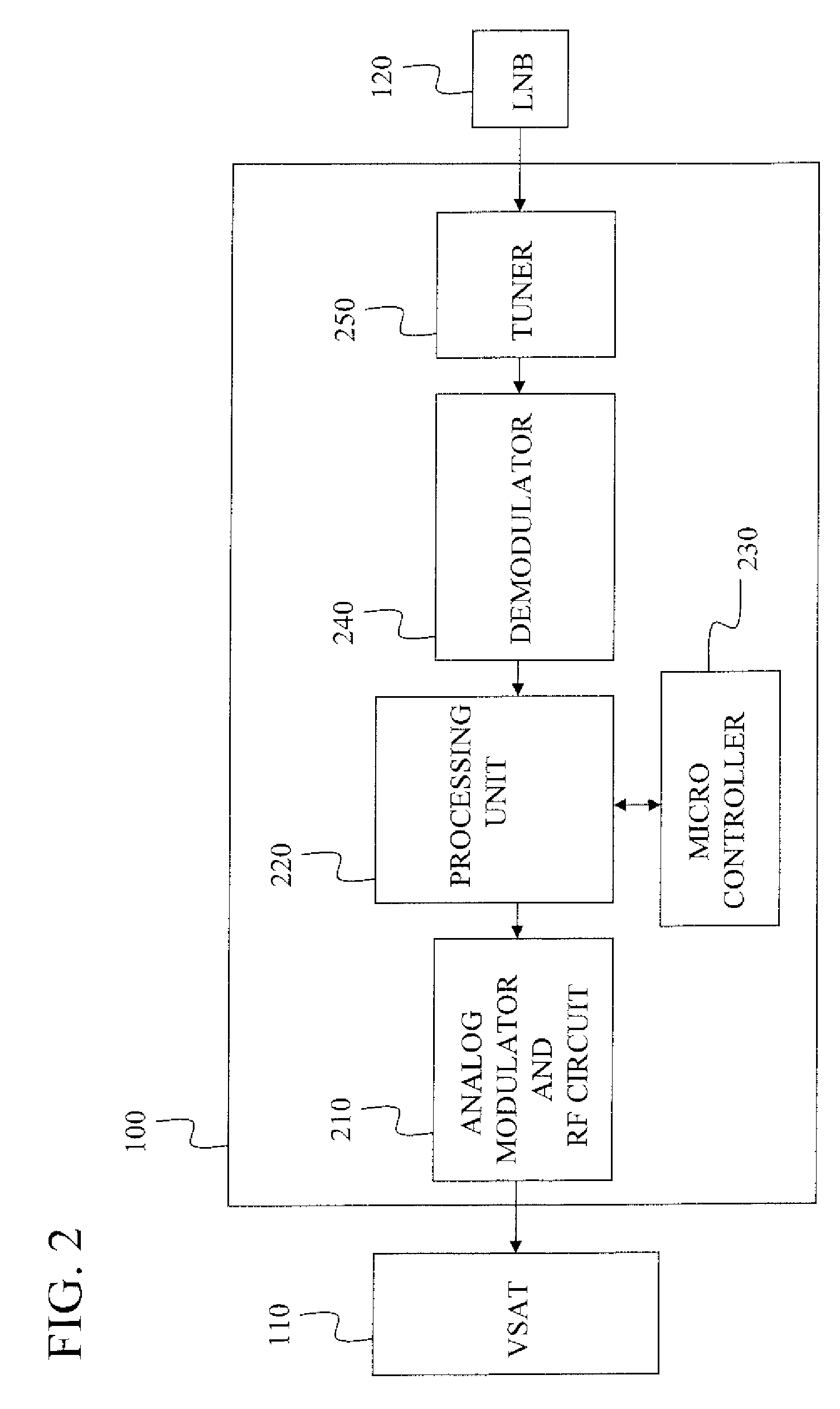
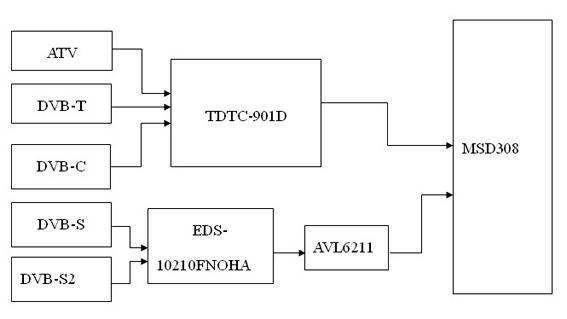
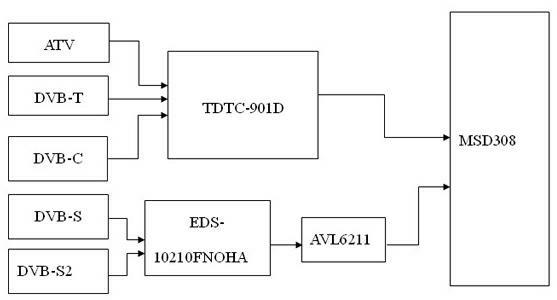
The invention discloses a multi-standard television receiver, comprising receiving ports, tuners and a main processor, wherein the receiving ports receive different television standard signals; the tuners modulate the different television standard signals into intermediate-frequency signals and output the intermediate-frequency signals to the main processor for processing; the receiving ports comprises an SATELLITE port for receiving DVB-S (Digital Video Broadcasting-Satellite) and DVB-S2 television signals, an AIR port for receiving DVB-T (Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial) television signals, a CABLE port for receiving DVB-C (Digital Video Broadcasting-Cable) television signals and an ATV (Analog Television) port for receiving analog signals. The technical scheme of the invention contains ATV, DVB-T, DVB-C, DVB-S and DVB-S2 so that almost all European basic television standards are supported. With the five-in-one design, the requirements of different people in most European countries can be satisfied.
Owner:SHENZHEN CULTRAVIEW DIGITAL TECH
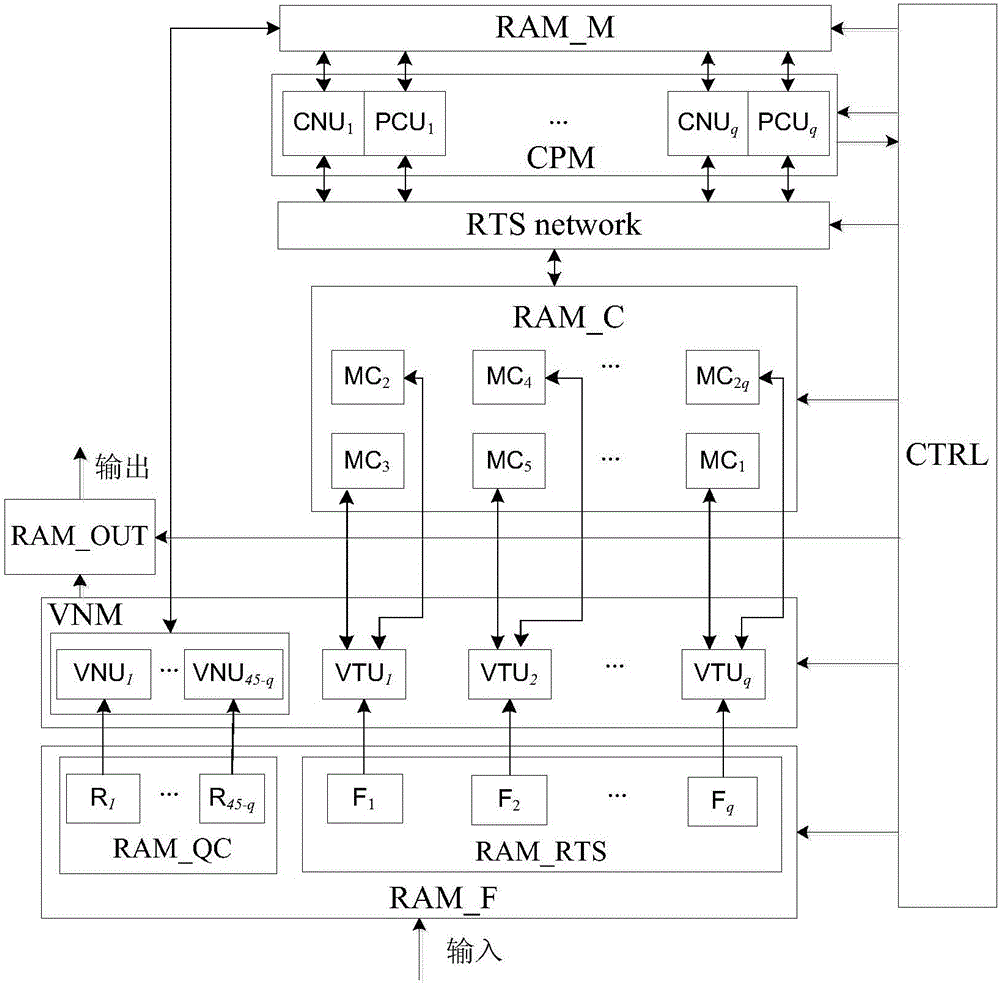
FPGA-based high-speed adaptive DVB-S2 LDPC decoder and decoding method
ActiveCN106571829AReduce complexityDoes not affect decoding performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDVB-S2Decoding methods
The invention relates to an FPGA-based high-speed adaptive DVB-S2 LDPC decoder and a decoding method. the method comprises steps: (1) matrix transformation is carried out, the generated left matrix has a quasi-cyclic structure, and the right matrix is a new matrix for a triangle-to-dual-diagonal (RTS) sub matrix; (2) RAM and iteration times are initialized; (3) the two parts of matrixes complete variable node information updating and data write back; (4) node information updating and write back are verified, a syndrome vector s is calculated, and one is added to the iteration times iter; (5) if the syndrome vector s is equal to 0 or the maximum iteration times are reached, a sixth step is carried out, or otherwise, the third step is carried out for next-round iteration processing; and (6) a decoding judgment bit is read, and a decoding codeword is outputted.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Method for detecting frame synchronization and structure in dvb-s2 system
InactiveUS20100322366A1Overcoming distortionReduce signal to noise ratioTelevision system detailsGHz frequency transmissionCorrelation analysisSatellite broadcasting
Provided is a method for detecting frame sync and frame structure in a satellite broadcasting system, which acquires an estimated value for detecting frame structure and frame sync and overcomes distortion of correlation analysis values by summing differential correlation values for SOF positions in consideration of the variable frame length, and selecting a maximum value in a channel environment with low signal-to-noise ratio and high frequency error. SOF is a sync word indicating the start point of a frame. The method includes the steps of: acquiring SOF differential correlation value sequences; acquiring sums (di,t) of the correlation values normalized for SOF positions based on the number of symbols per frame by using the above-generated SOF differential correlation value sequences; and selecting a maximum value (dz,x) among the sums of correlation values, detecting z as a frame sync position, and detecting x as a frame structure index.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Digital video broadcasting - satellite - second generation (dvb-s2) based transmission and reception apparatus and method operable in circumstances of low signal to noise ratio (SNR)
InactiveUS20140082675A1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsGHz frequency transmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Spread factor
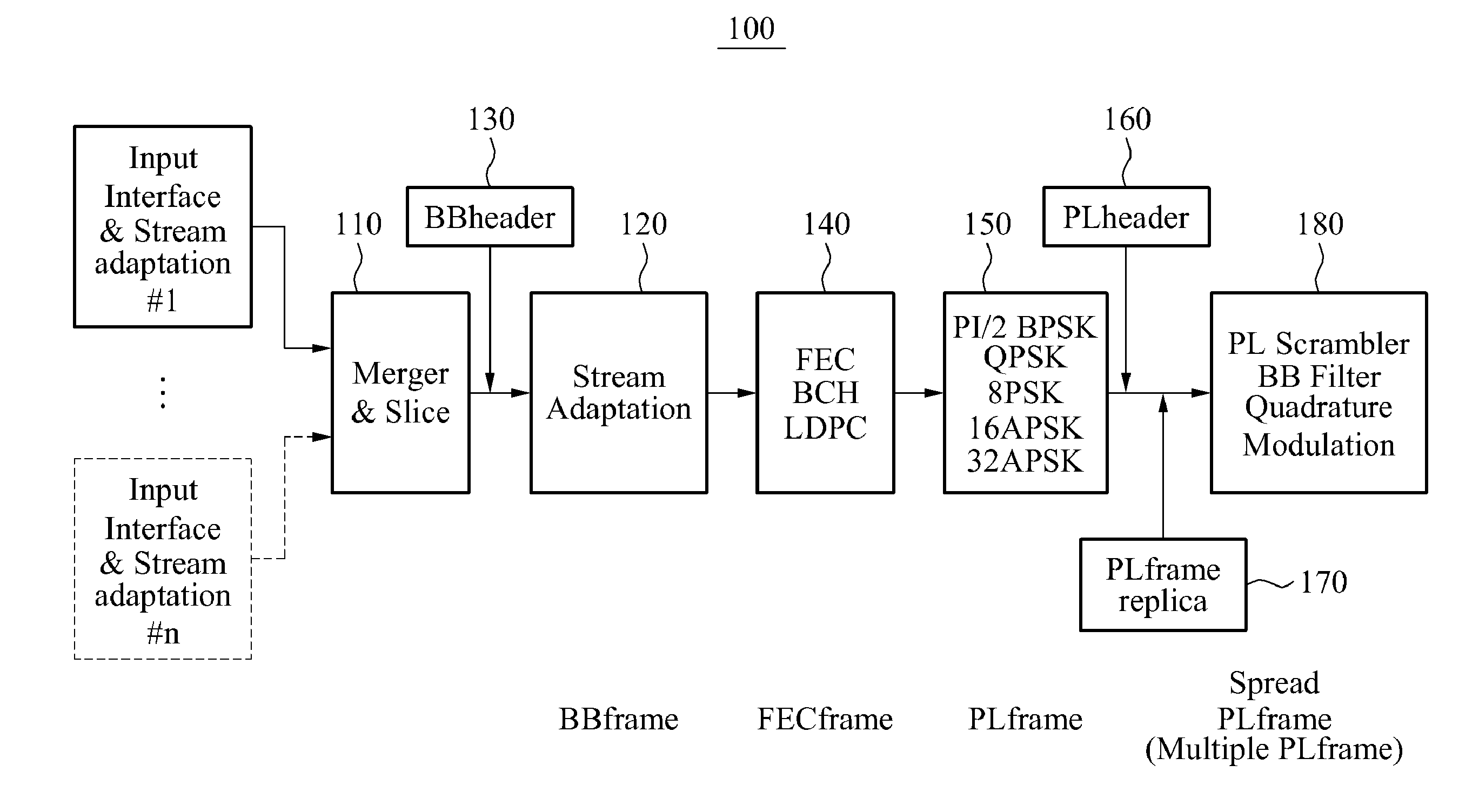
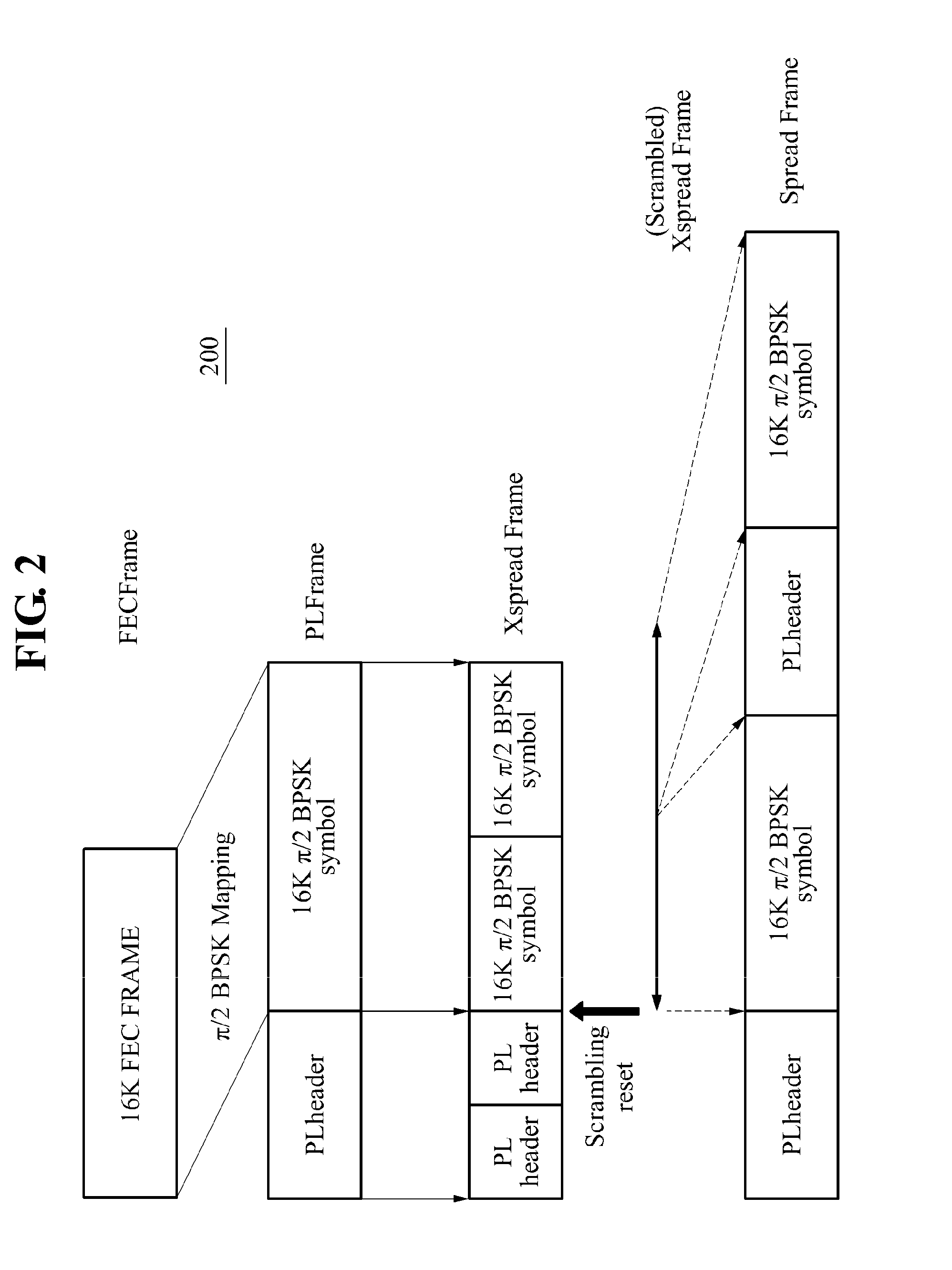
Provided is a digital video broadcasting-satellite-second generation (DVB-S2) based transmission and reception apparatus and method operable in circumstances of a low signal to noise ratio (SNR), the DVB-S2 based transmission and reception apparatus including a DVB-S2 based transmitter, a mapping unit to determine bit mapping based on at least one of a state of a transmission channel and an area to be applied, and a physical layer frame (PLframe) replica processing unit to repeat a PLframe in which a physical layer header (PLheader) corresponding to a spreading factor (SF) is inserted.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Modulation and demodulation method for satellite communication using widespread signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
InactiveUS20130195148A1Phase-modulated carrier systemsSelective content distributionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Spread factor
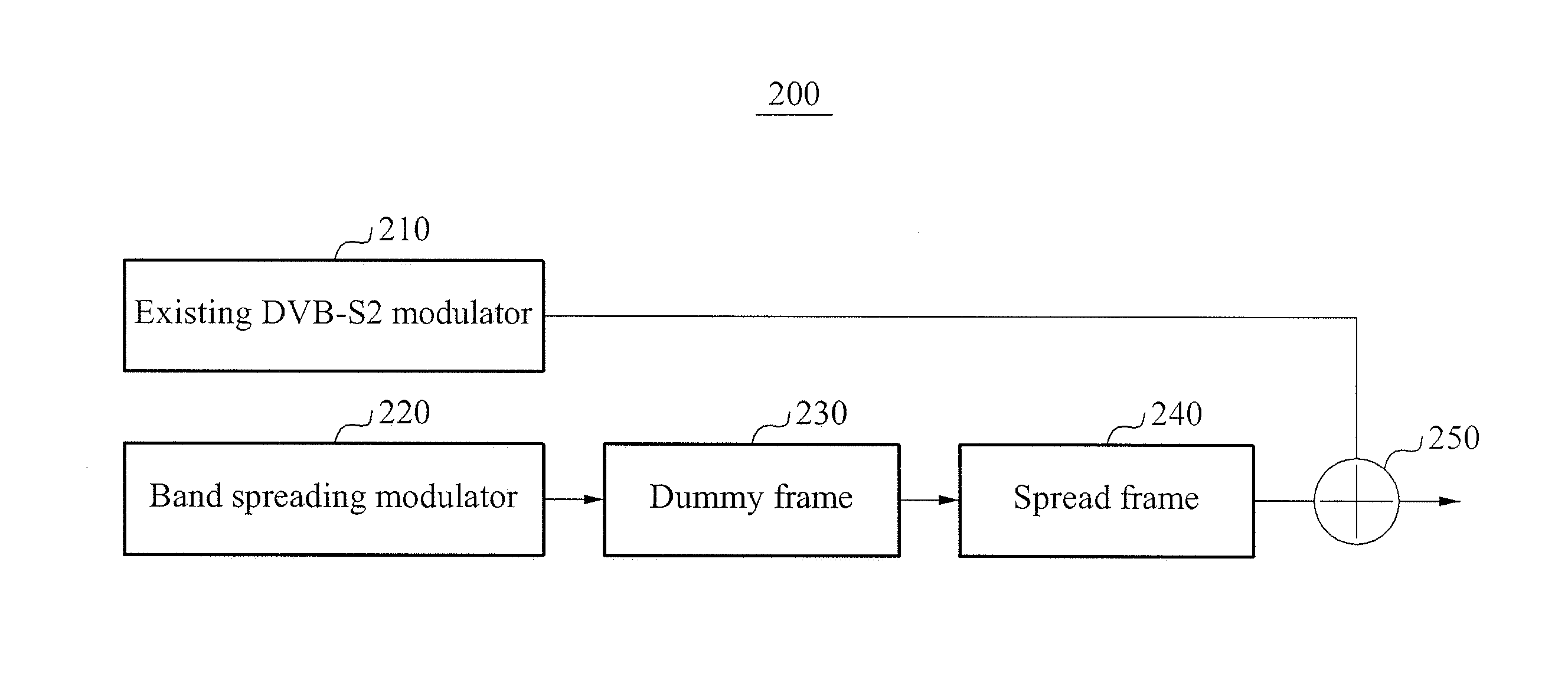
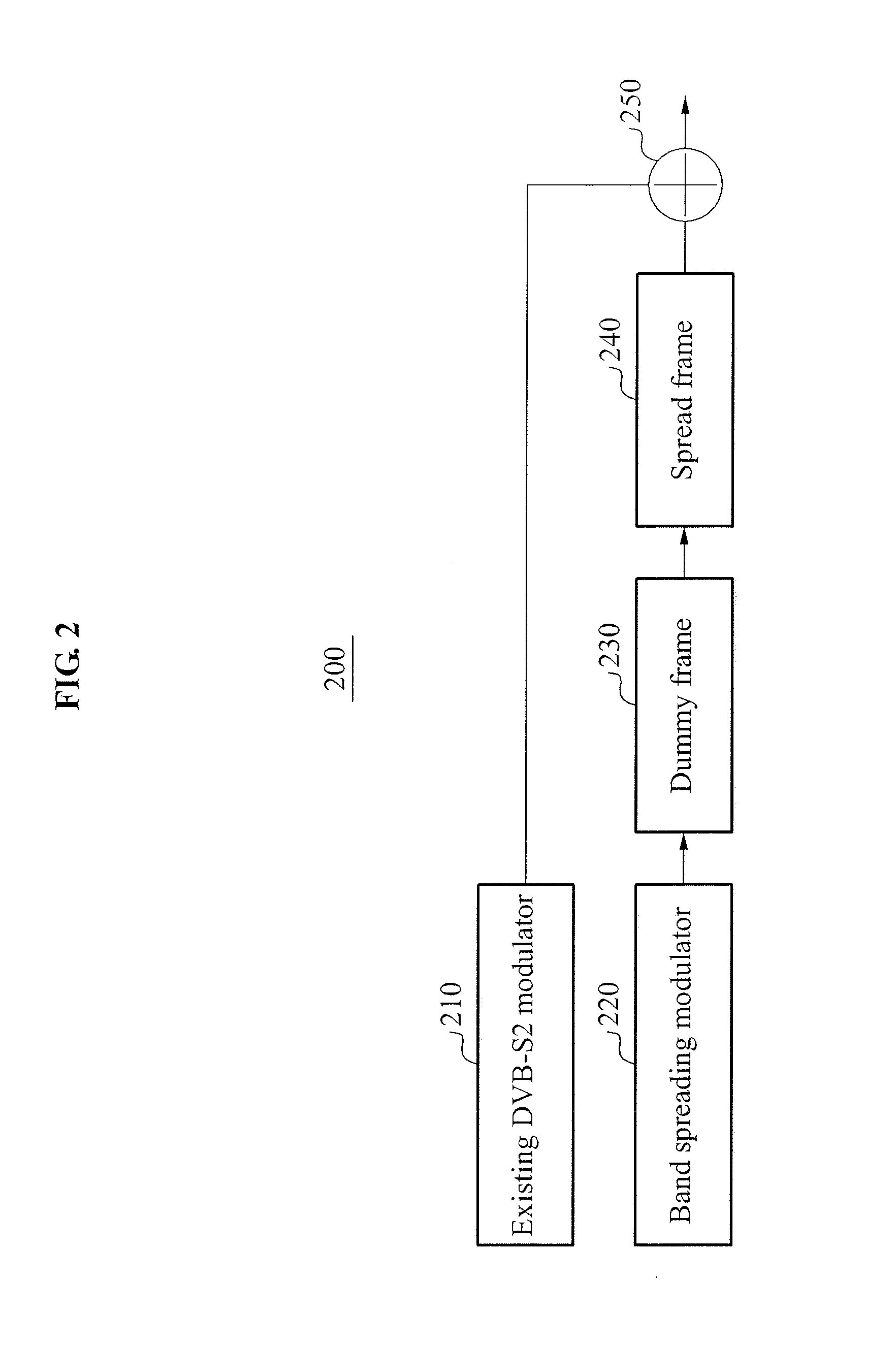
Provided are a modulation method and a demodulation method for satellite communication using a widespread signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), the method including: adding a dummy frame to a broadcasting / communication signal frame for signal transmission of a digital video broadcasting-satellite second generation (DVB-S2) modulator; verifying a spreading factor; adding the same physical layer header to the broadcasting / communication signal frame to which the dummy frame is added, repeatedly the number of times corresponding to the verified spreading factor; and repeating the same data, for example, PL frame data as the physical layer header.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
LDPC decoder for DVB-S2 decoding
ActiveUS7774674B2Reduce the numberSmall sizeRead-only memoriesDigital computer detailsMemory bankParallel computing
The LDPC decoder includes a processor for updating messages exchanged iteratively between variable nodes and check nodes of a bipartite graph of the LDPC code. The decoder architecture is a partly parallel architecture clocked by a clock signal. The processor includes P processing units. First variable nodes and check nodes are mapped on the P processing units according to two orthogonal directions. The decoder includes P main memory banks assigned to the P processing units for storing all the messages iteratively exchanged between the first variable nodes and the check nodes. Each main memory bank includes at least two single port memory partitions and one buffer the decoder also includes a shuffling network and a shift memory.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Frame synchronization and structure detection method in DVB-S2 system
InactiveUS8085818B2Reduce complexitySolve large capacityTelevision system detailsSatellite broadcast receivingSatellite broadcastingDVB-S2
Provided is a method for detecting frame sync and frame structure in a satellite broadcasting system. The method for detecting frame sync and frame structure includes the steps of: calculating differential correlation values of reception symbols; generating index sequences of reception symbols whose differential correlation values calculated above exceed a threshold value; calculating positions estimated as frame start points which correspond to a total frame number based on the number of symbols per frame for each frame structure; and detecting frame sync and frame structure based on the umber of positions where the above-calculated frame start point estimated positions and the above-generated index sequences are matched.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Satellite communication transmitter and receiver for reducing channel interference
Satellite communication transmitter and receiver in a DVB-S2 system are provided. The satellite communication transmitter includes a modulator to modulate a satellite communication signal to be transmitted, and a spread spectrum unit to spread the modulated signal and transmit the spread signal. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce interference with a neighboring channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and device for controlling the decoding of a ldpc encoded codeword, in particular for dvb-s2 ldpc encoded codewords
ActiveCN101156321AOther decoding techniquesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsDigital dataDVB-S2
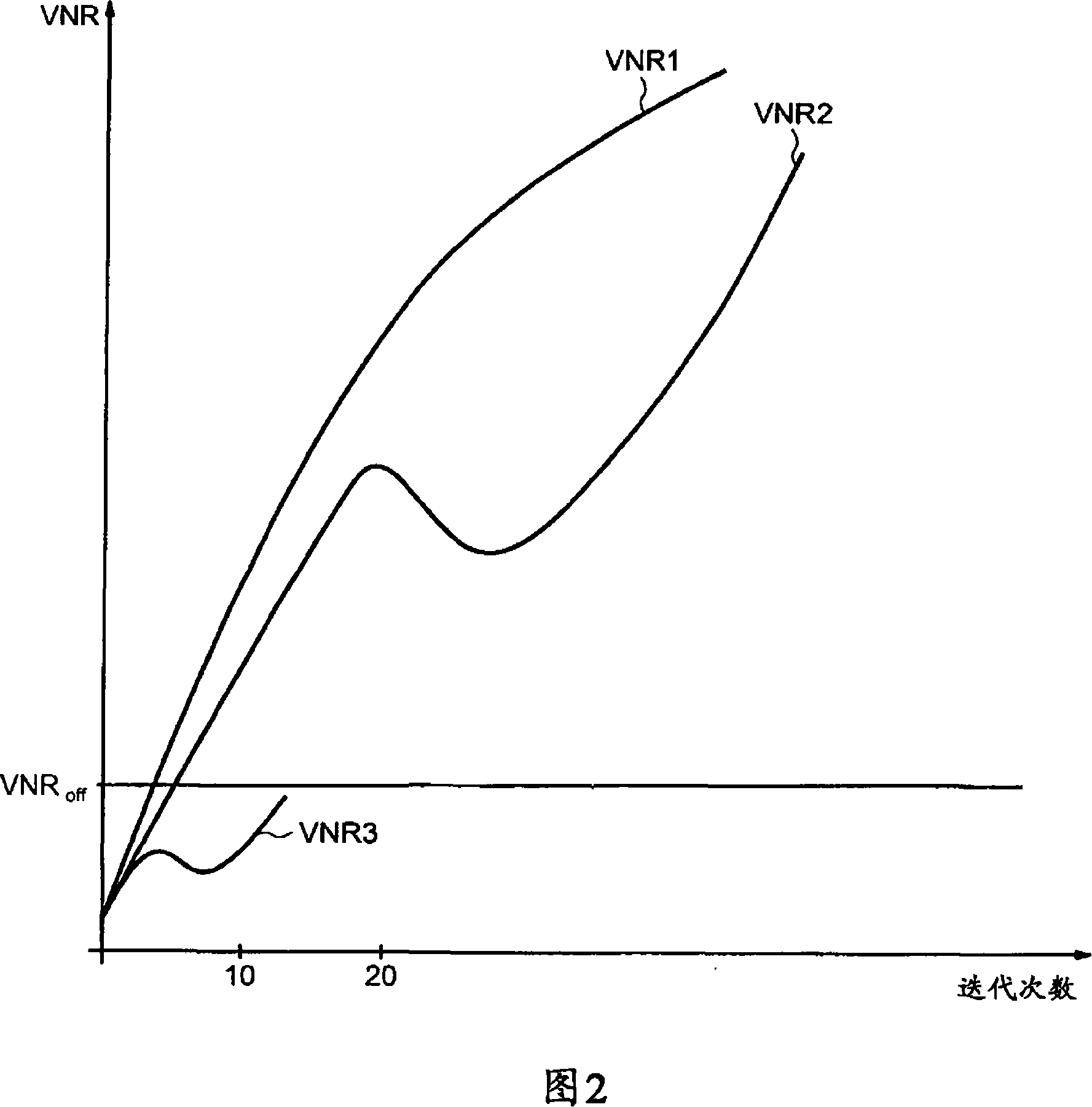
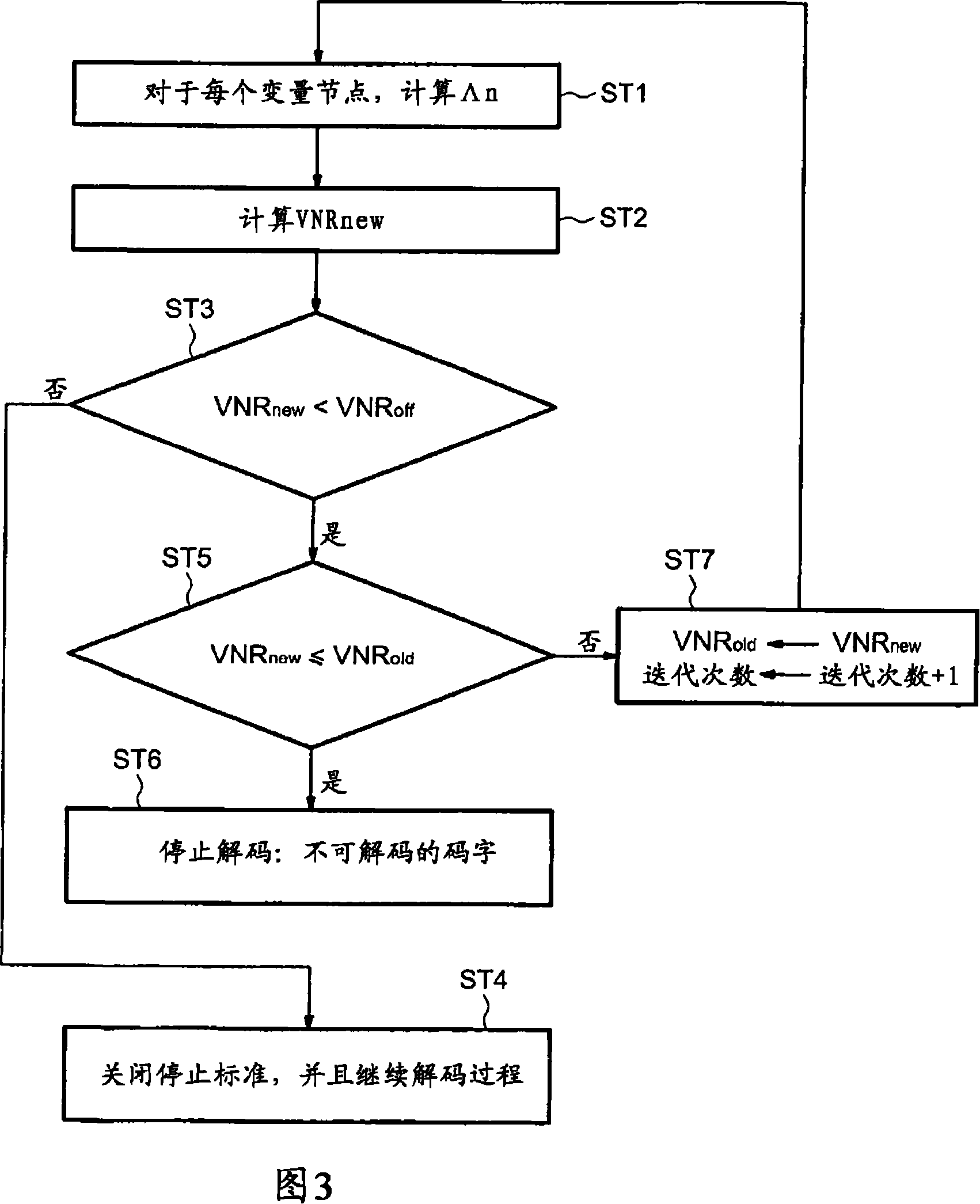
This is a method for controlling decoding of an LDPC encoded codeword composed of several digital data represented by a bipartite graph between check nodes (CNi) and variable nodes (VNi). The method comprises updating messages iteratively exchanged between variable nodes (VNi) and check nodes (CNi). The method comprises: in each iteration, for each variable node, computing a first sum (Λn) of all incoming messages (λi) and corresponding digital data (λch) received by said variable node, and computing a first sum (Λn) of A second sum (VNRnew) of all absolute values of the sum (Λn), if said second sum (VNRnew) does not change or decreases in two consecutive iterations, and if a predetermined threshold condition is met, stop the Describe the decoding process.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
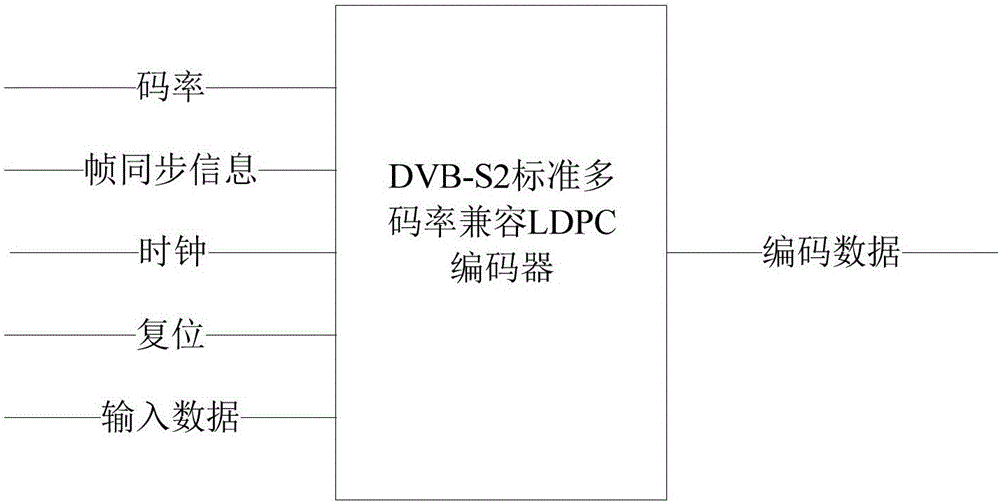
LDPC encoder based on DVB-S2 standard multi-rate compatibility
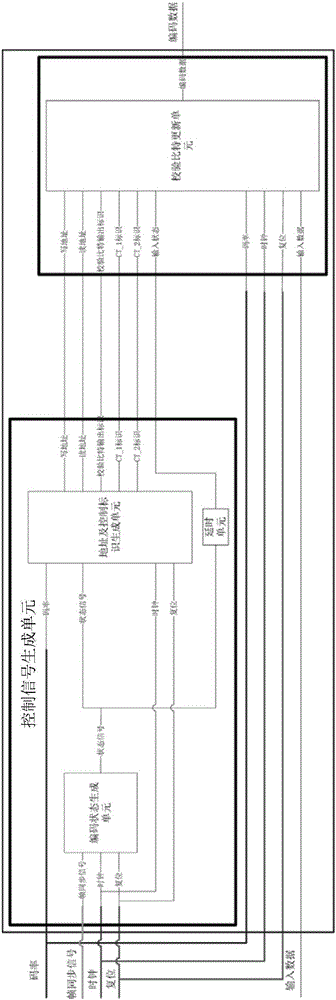
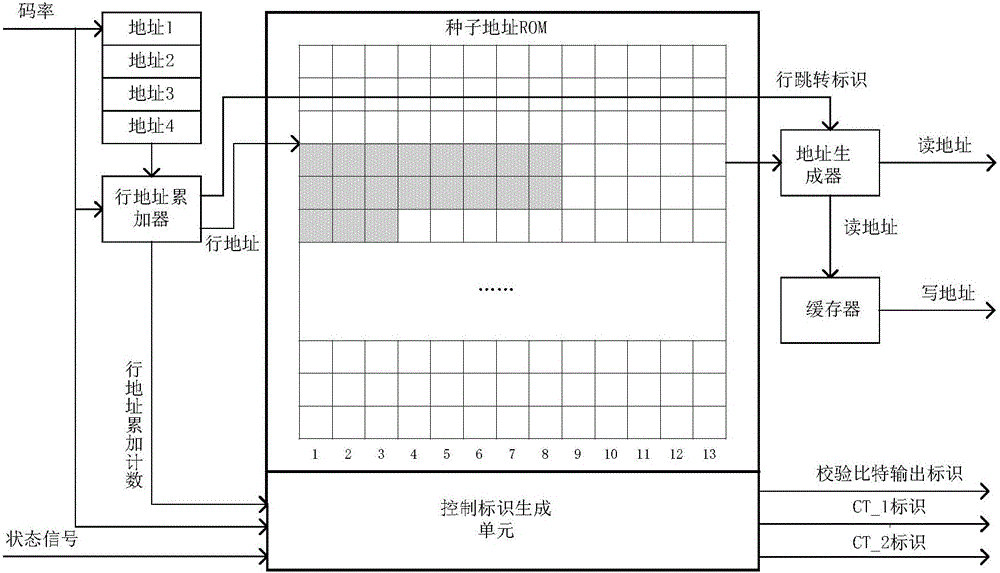
ActiveCN106506010AQuick buildReduce occupancyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionControl signalDVB-S2
The invention provides an LDPC encoder based on DVB-S2 standard multi-rate compatibility, which comprises a control signal generation unit and a check bit updating unit. The control signal generation unit generates, according to set encoding rates and an encoding initial identifier signal, a state control signal for controlling operation of the entire encoder, a plurality of addresses of corresponding rows in an address table, which are provided by easy input information bit to be encoded correspondingly to a DVB-S2 standard, and control identifier signals corresponding to the encoding rates, and outputs the state control signal, the addresses and the control identifier signals to the check bit updating unit; the check bit updating unit carries out binary addition operation on the information bits to be encoded and check bits read from the plurality of addresses corresponding to the information bits to be encoded, and writes an operation result into an original address. According to the LDPC encoder provided by the invention, by separately designing a control unit and an operation unit, the LDPC encoder compatible to various code rates is implemented; and encoding operation of the corresponding code rates can be completed only by setting the corresponding encoding rates at an external interface.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Frame synchronization method for overcoming low signal-to-noise ratio and carrier frequency offset of receiver
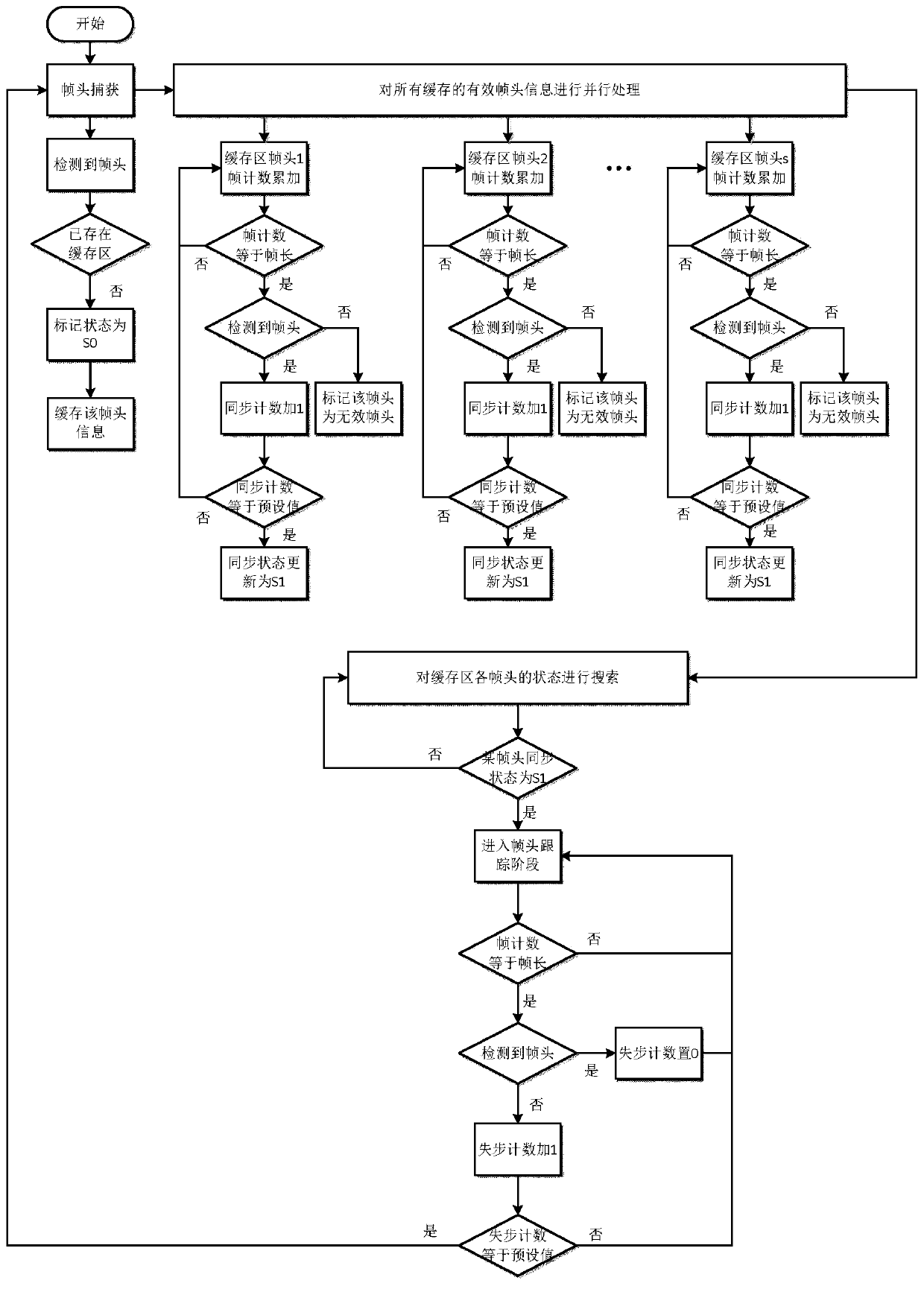
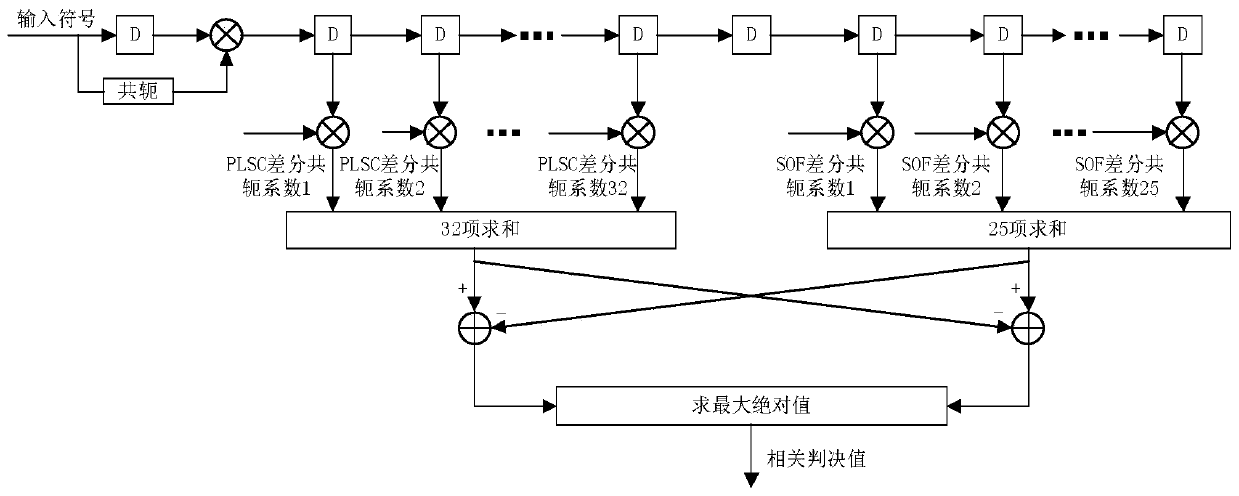
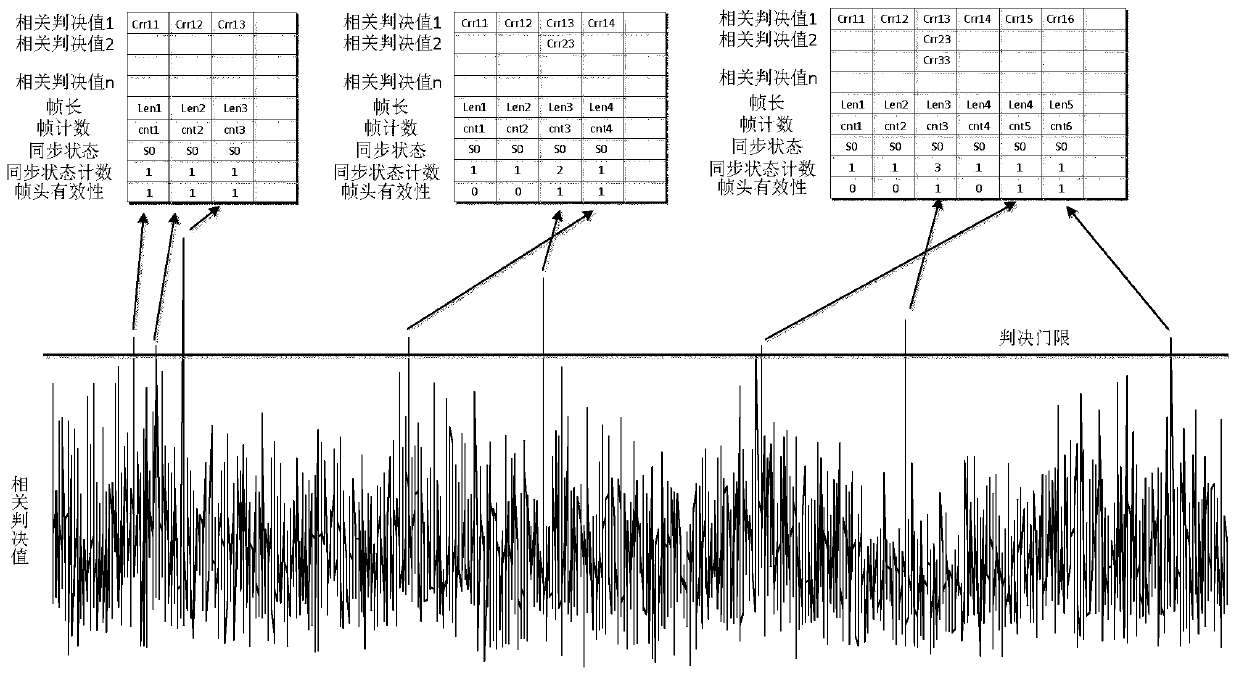
ActiveCN110034914ASync fastHigh synchronization accuracyTelevision system detailsGHz frequency transmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Multiple frame
The invention provides a frame synchronization method for overcoming low signal-to-noise ratio and carrier frequency offset of a receiver, and aims to provide a frame synchronization method which canwork at an extremely low signal-to-noise ratio and is suitable for DVB-S2 protocol. The method is realized through the following technical scheme: DVB-S2 receiver frame synchronization is divided intoa frame header capturing stage and a frame header tracking stage, and multi-frame frame header segment data is combined in the frame header capturing and tracking stage to carry out combined frame header judgment; the DVB-S2 receiver adopts an SOF+PLSC algorithm to obtain related decision values, the related decision values are averaged with a plurality of related decision values cached before the frame header, an average result is compared with a preset decision threshold, if the average result is greater than the decision threshold, one is added to the synchronous state count, otherwise, the effectiveness is set to be 0, and the frame header is marked as an invalid frame header; and for all valid frame header information of the cache region, parallel operation is carried out to quicklycapture correct frame headers.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Method and system for effective adaptive coding and modulation in satellite communication system
InactiveUS8179778B2Guaranteed normal transmissionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCode conversionDigital videoAdaptive coding
A Second Generation Digital Video Broadcasting via Satellite (DVB-S2) system is provided. More particularly, a method and apparatus for maintaining synchronization of a signal by changing an Adaptive Coding and Modulation (ACM) method that is used for a conventional DVB-S2 system are provided. In the apparatus and method, an FEC frame of a variable length is formed by turbo encoding rather than Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) and Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) encoding, and a Physical Layer (PL) frame of a specific length is formed regardless of a modulation method, so that a satellite terminal receives a signal transmitted at a specific length regardless of a modulation method or a coding rate to easily maintain synchronization without interruption and efficiently transmit the signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Satellite searching system and satellite searching method with satellite signal mistake-locking prevention function
ActiveCN107799898ASolve the problem of easy false lock (satellite antenna antenna surface is not aligned with the corresponding satellite)Reduce use costRadio transmissionAntennasFrequency changerSignal quality
The invention provides a satellite searching system and a satellite searching method with a satellite signal mistake-locking prevention function, and relates to the communication field of the satellite. The satellite searching system comprises a microprocessor MCU unit, a high frequency head, a frequency converter, a demodulator and a positioning module; the high frequency head receives a satellite signal transmitted by an antenna feed source; the frequency converter performs amplifying and down conversion on the signal output by the high frequency head; the demodulator demodulates the signaloutput by the frequency converter into a standard transmission signal according to the transmission standard (DVB-S, DVB-S2, ABS-S) of the satellite signal; and the MCU unit obtains a signal quality value of the current satellite signal from the demodulator and drives the positioning module according to the signal quality value to enable the antenna to search the satellite automatically so as to complete satellite signal locking. By virtue of the satellite searching system, the problem of easy mistake locking (the antenna plane of the satellite antenna is not aligned to the corresponding satellite) of the automatically tacking satellite antenna can be solved, so that the satellite searching system can be applicable to a vehicle platform and a shipborne platform, and is low in use cost, simple in control, convenient to operate and high in stability.
Owner:XIAMEN DBS ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
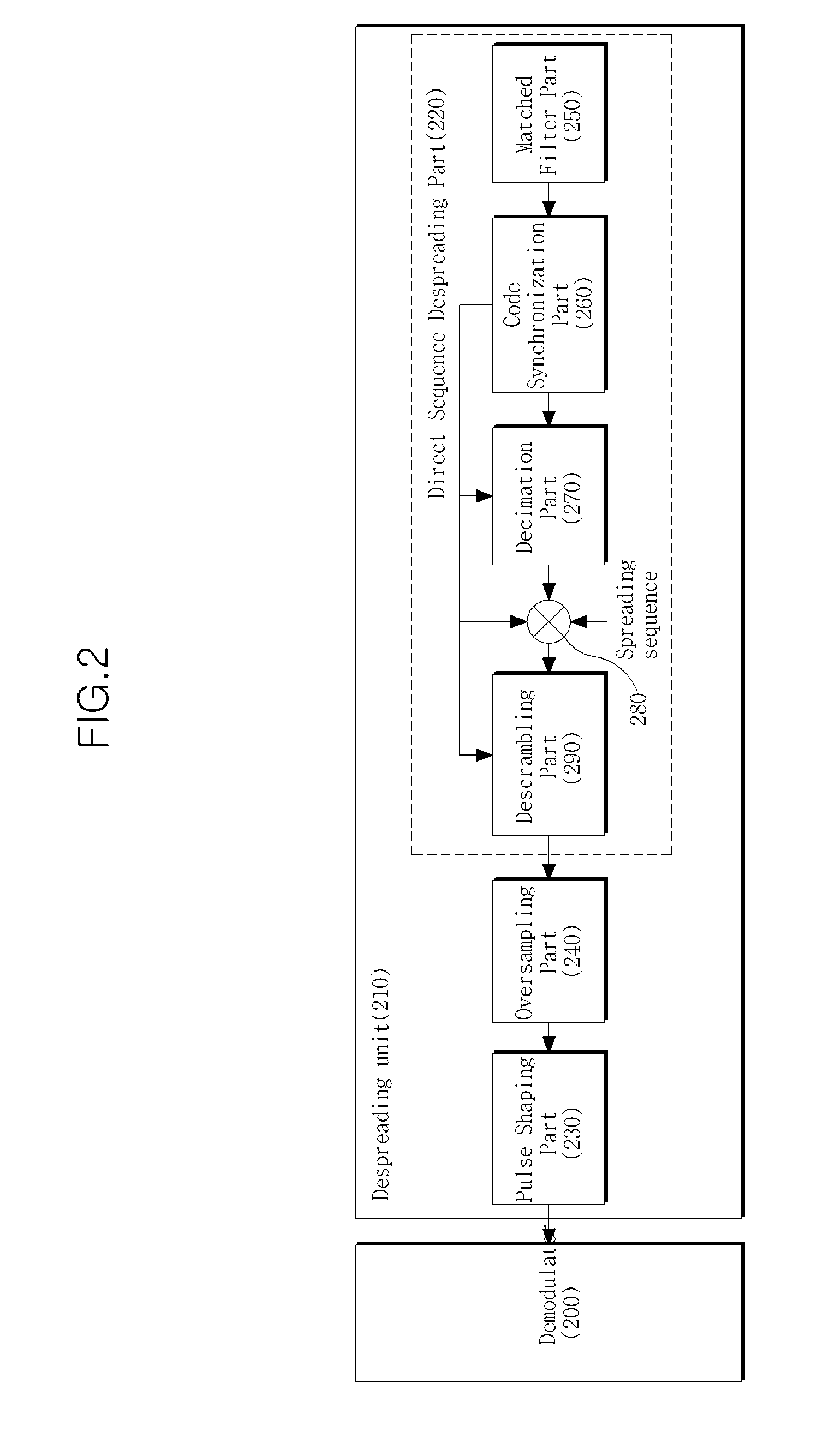
Signal demodulation method based on dvb-s2
InactiveUS20100128821A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsComputer hardwareCarrier signal
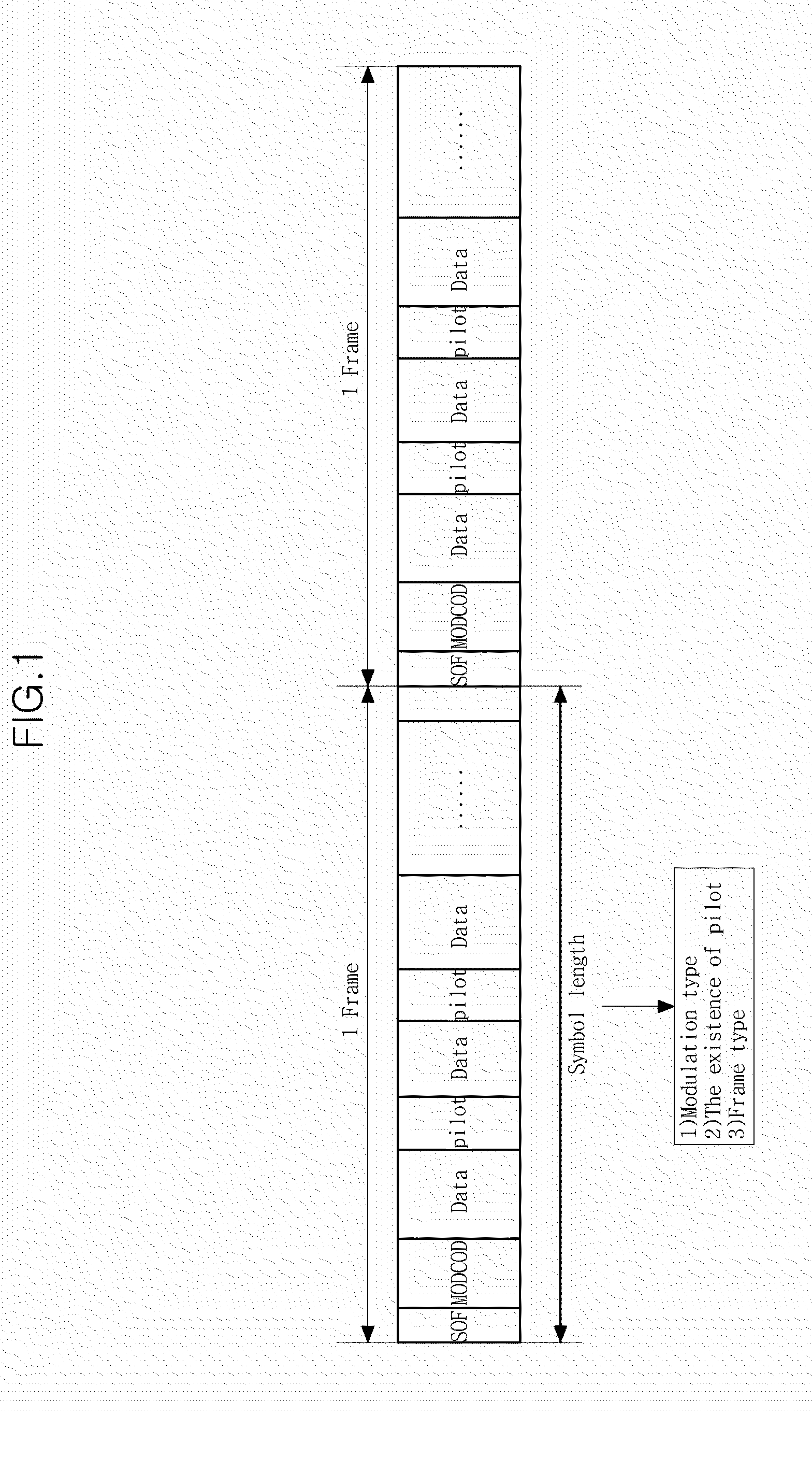
A satellite broadcasting frame signal demodulation method is disclosed. A demodulation method of a demodulator that demodulates a Digital Video Broadcasting-Satellite—Second Generation (DVB-S2) standard satellite broadcasting frame signal includes: performing symbol synchronization; performing frame synchronization after symbol synchronization; recovering a carrier wave after frame synchronization; and decoding mode code (MODCOD) information to obtain frame configuration information after recovering the carrier wave. This method ensures rapid demodulation and reliable demodulated data.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Decoding method and apparatus
ActiveCN106160927AAddresses Susceptibility to Phase DeviationDecoding is fast and preciseError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsComputer hardwareDecoding methods
The invention relates to a decoding method and an apparatus, which particularly relates to a decoding method and an apparatus capable of relying on phase deviation effects on a SOF (Start of Frame) sequence in a frame header signal in second-generation digital satellite broadcasting (DVB-S2) to further decode information of seven bits in a physical layer signaling code in the second-generation digital satellite broadcasting system.
Owner:ALICORP
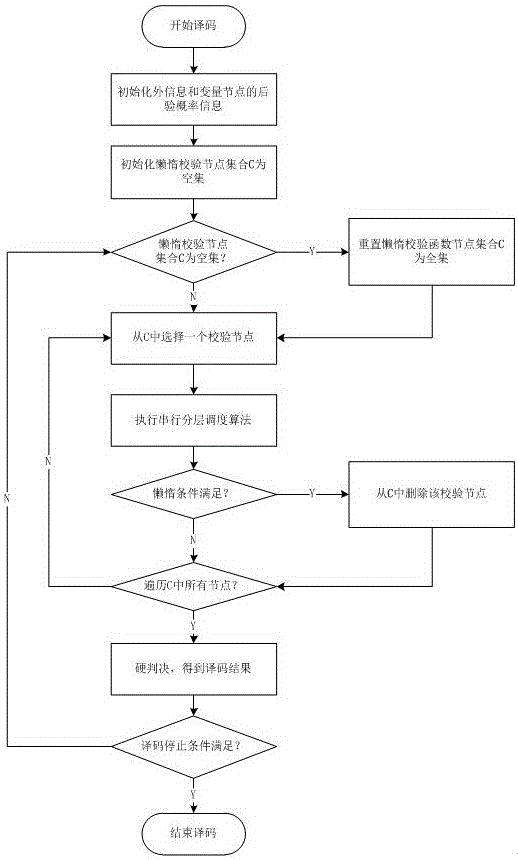
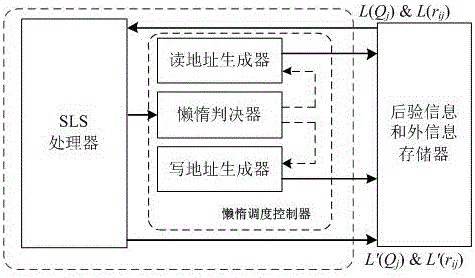
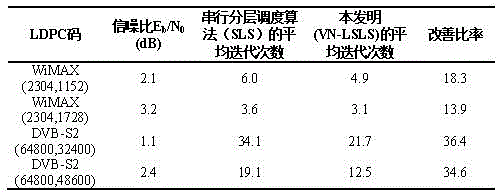
LDPC (Low-Density Parity-Check) decoding algorithm based on variable-node lazy serial layered scheduling
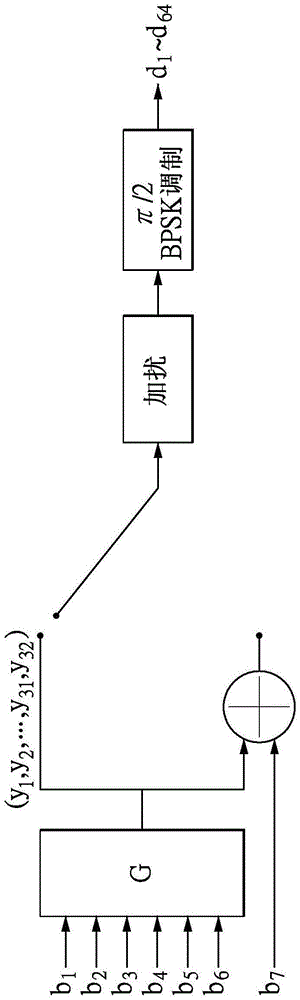
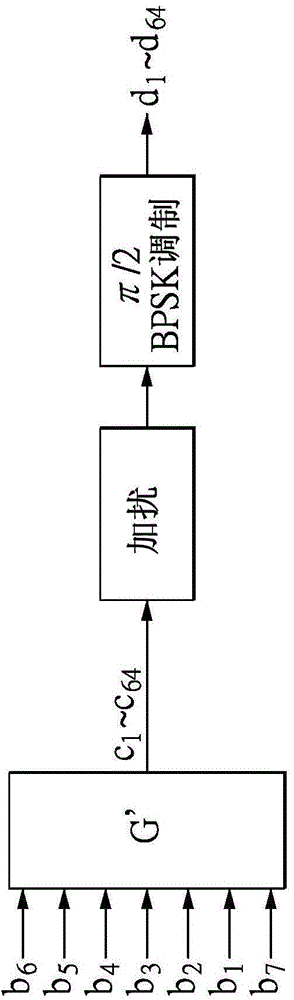
InactiveCN106788461AReduce complexityReduce power consumptionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionRound complexityCoding decoding
The invention relates to an LDPC (Low-Density Parity-Check) decoding algorithm based on variable-node lazy serial layered scheduling. A lazy serial layered scheduling algorithm based on variable-node belief degree is employed, and the algorithm is realized based on an FPGA platform. Specifically, according to the decoding algorithm, in a serial layered scheduling algorithm execution process, if the belief degree of all variable nodes adjacent to certain check function node is very reliable, the check function node is set as a lazy node and does not participate in a follow-up iterative decoding process, so the complexity of the LDPC code decoding algorithm is reduced, and the time delay and power consumption of a decoder are reduced. For the LDPC decoders in WiMAX and DVB-S2, according to the algorithm, the time delay and power consumption can be reduced by 13.9%-36.4%.
Owner:TOEC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com