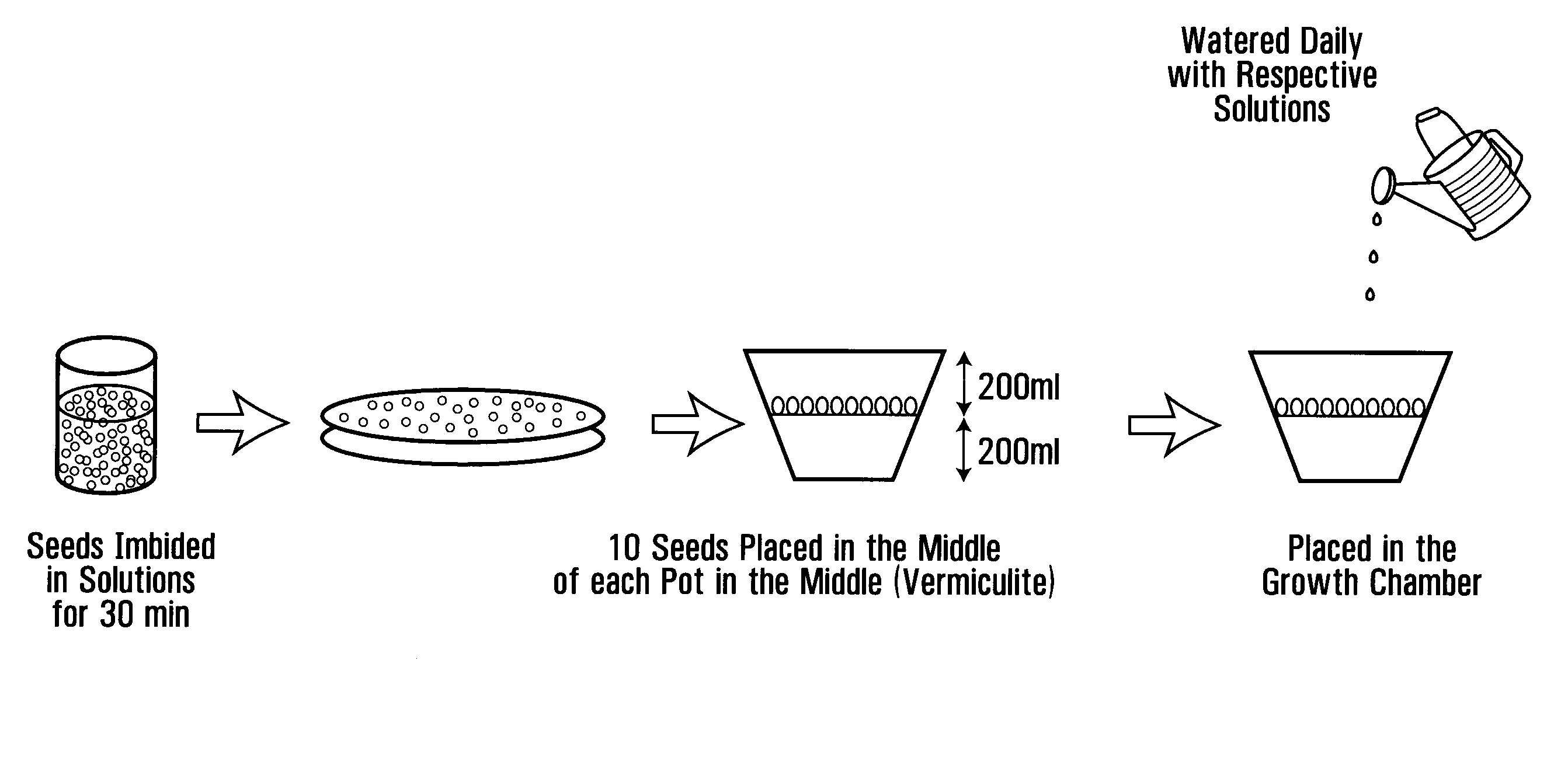
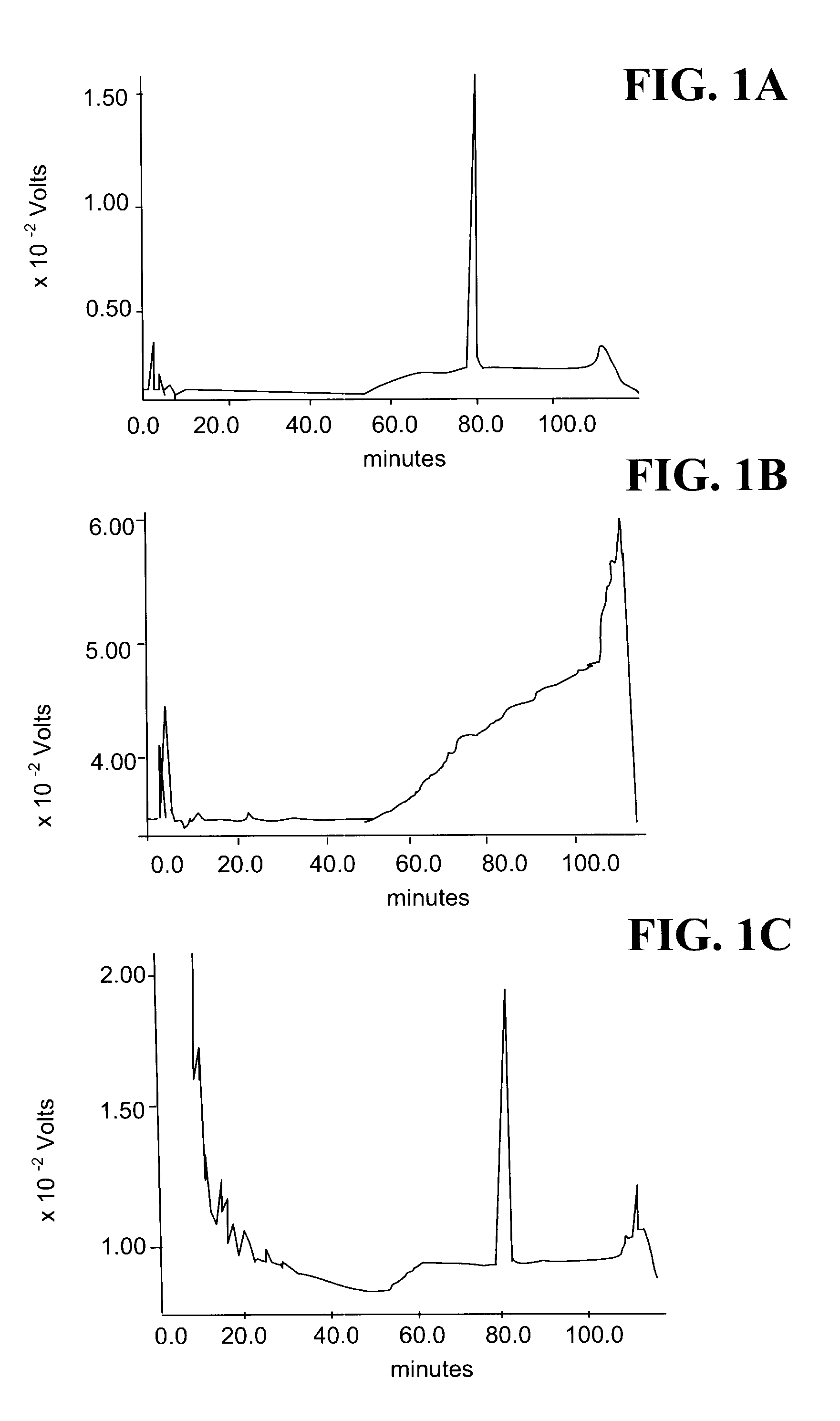
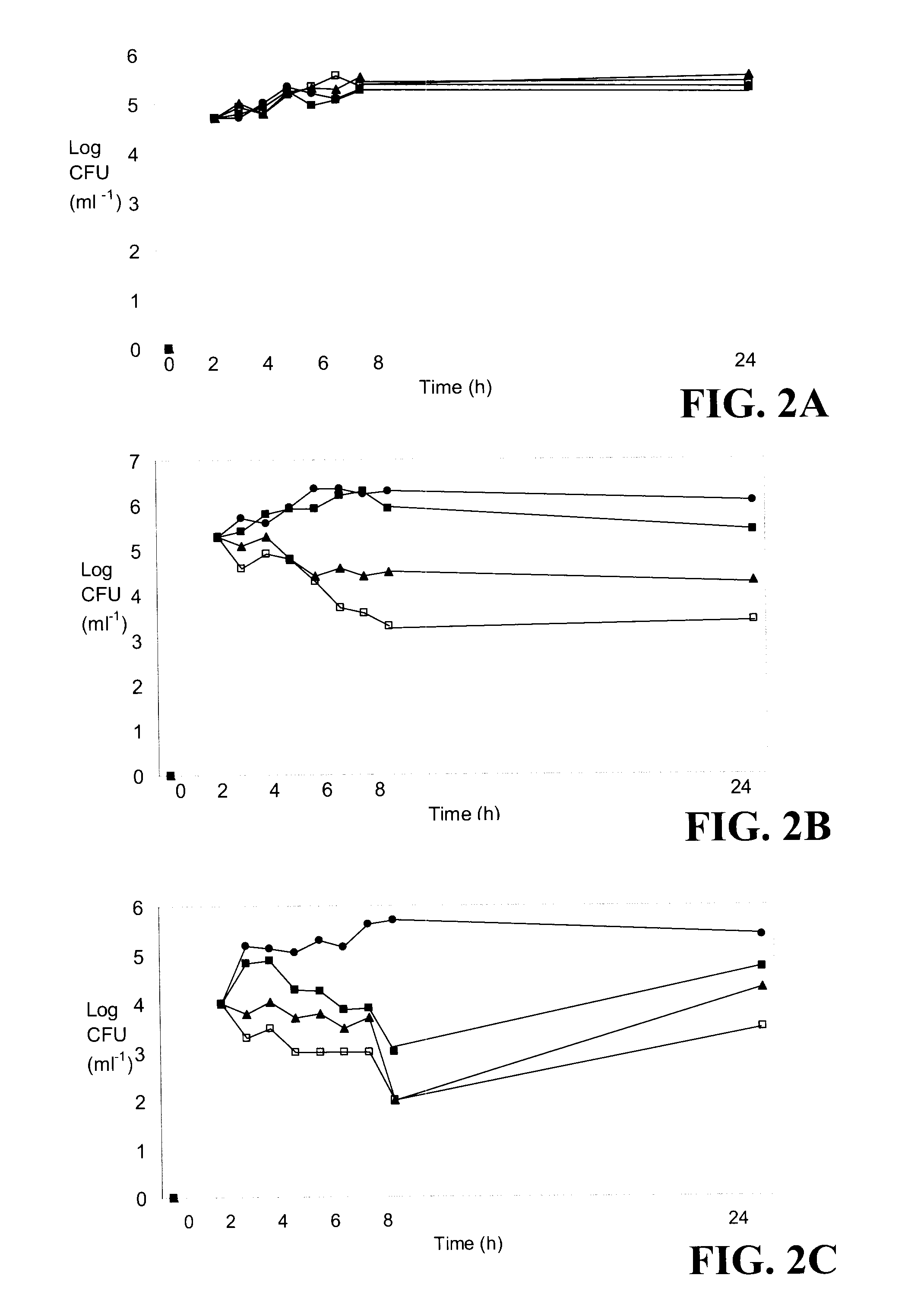
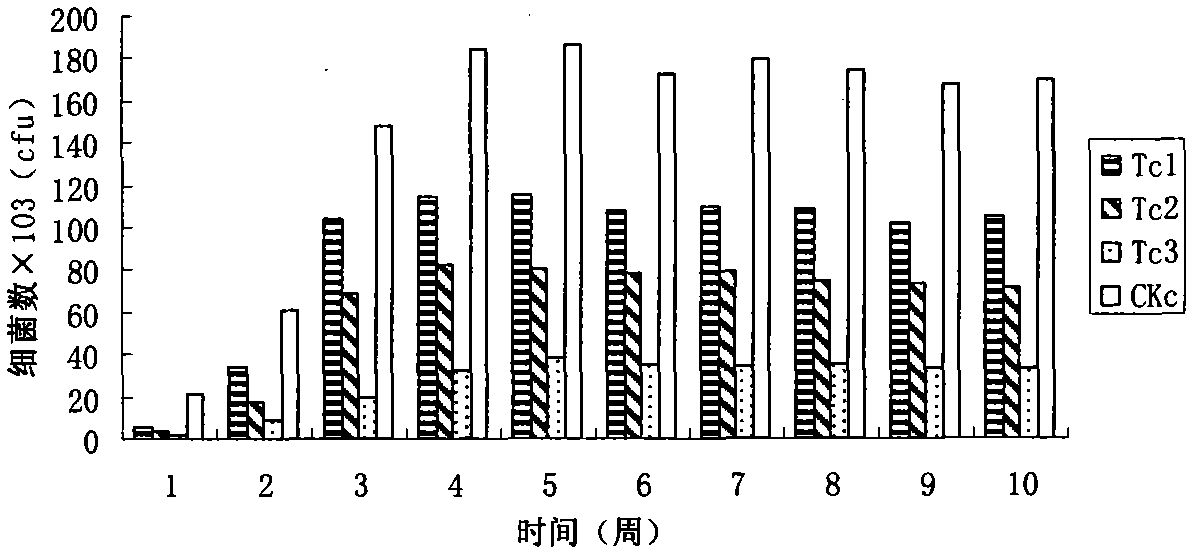
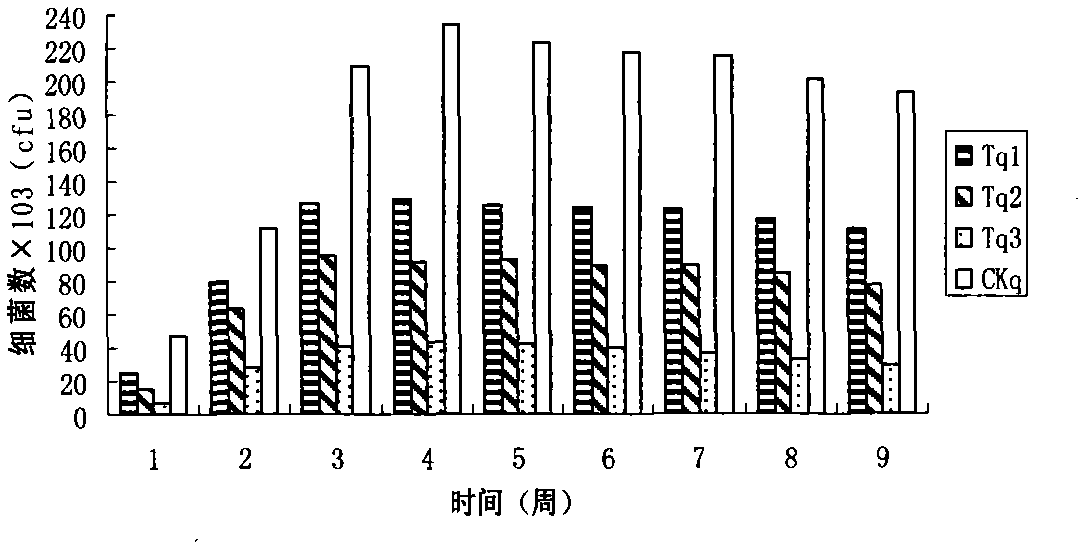
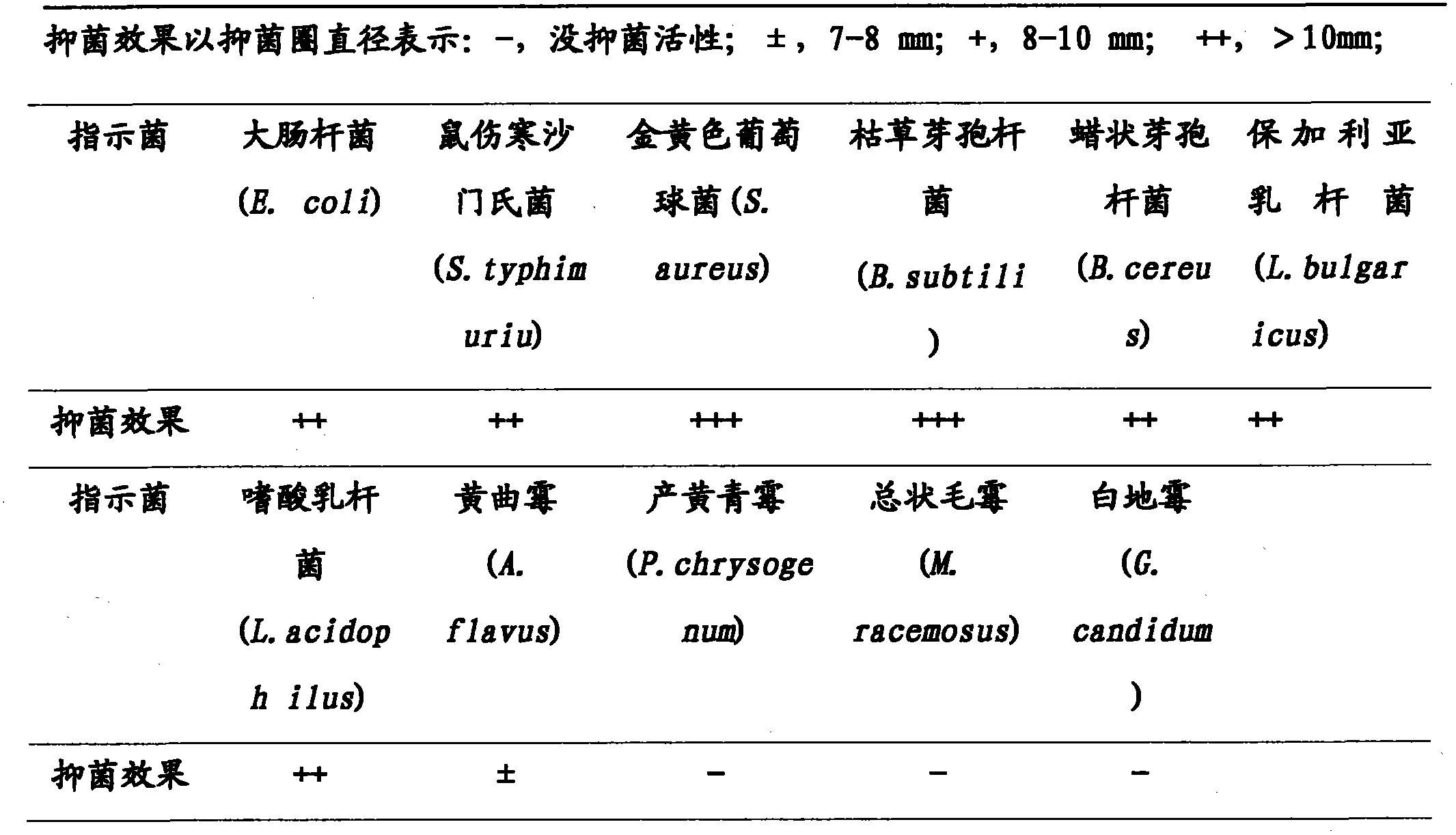
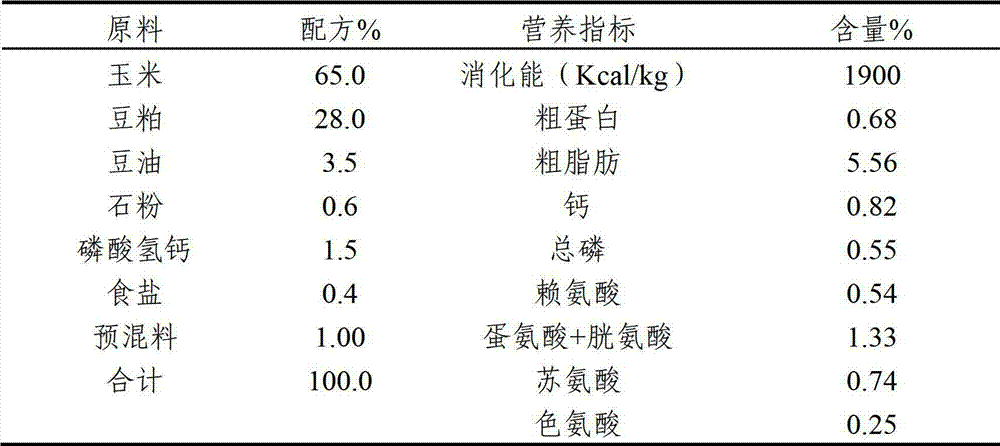
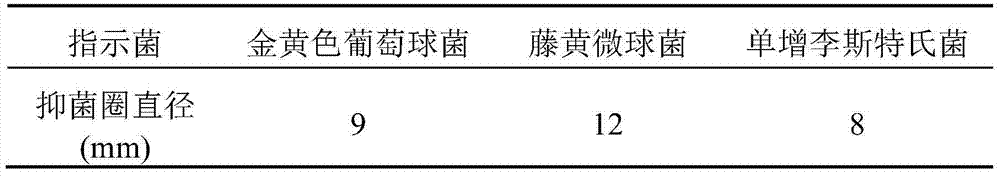
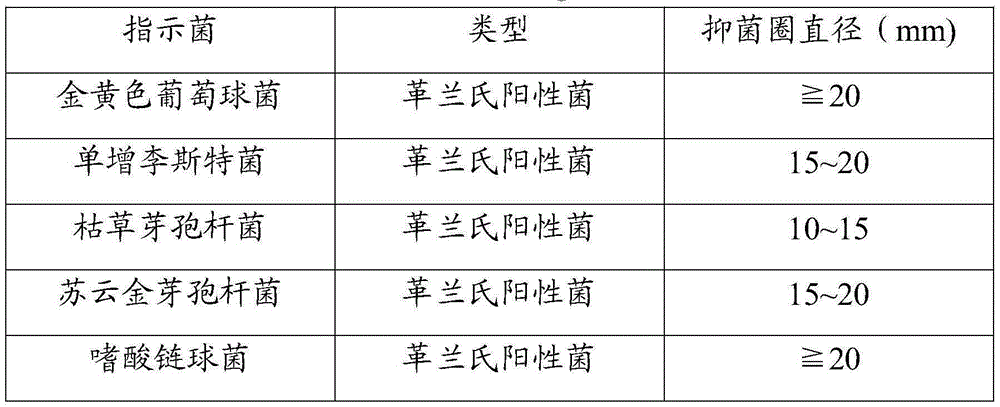
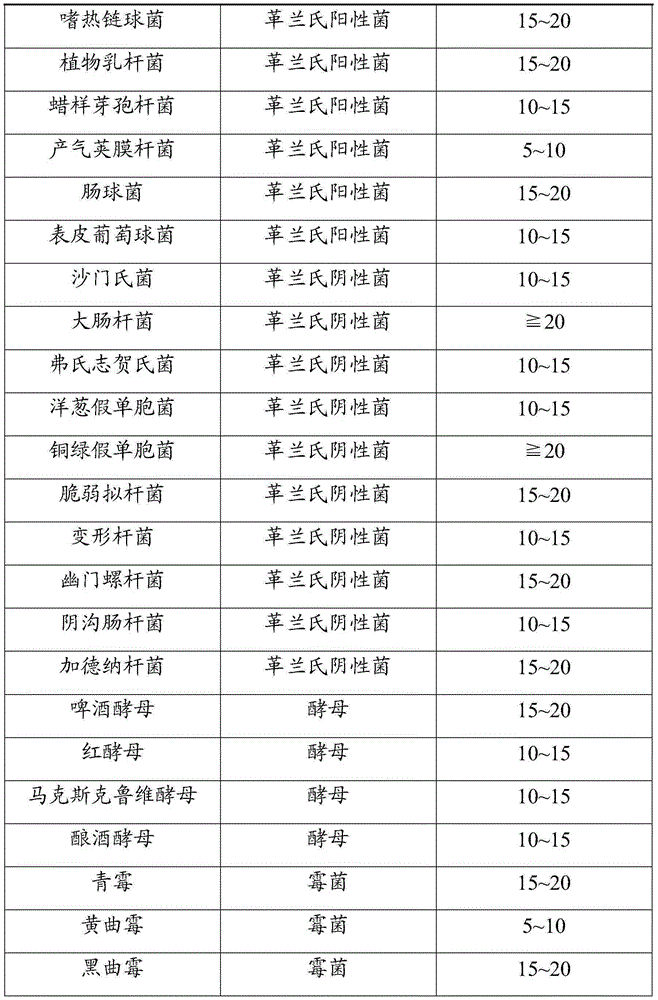
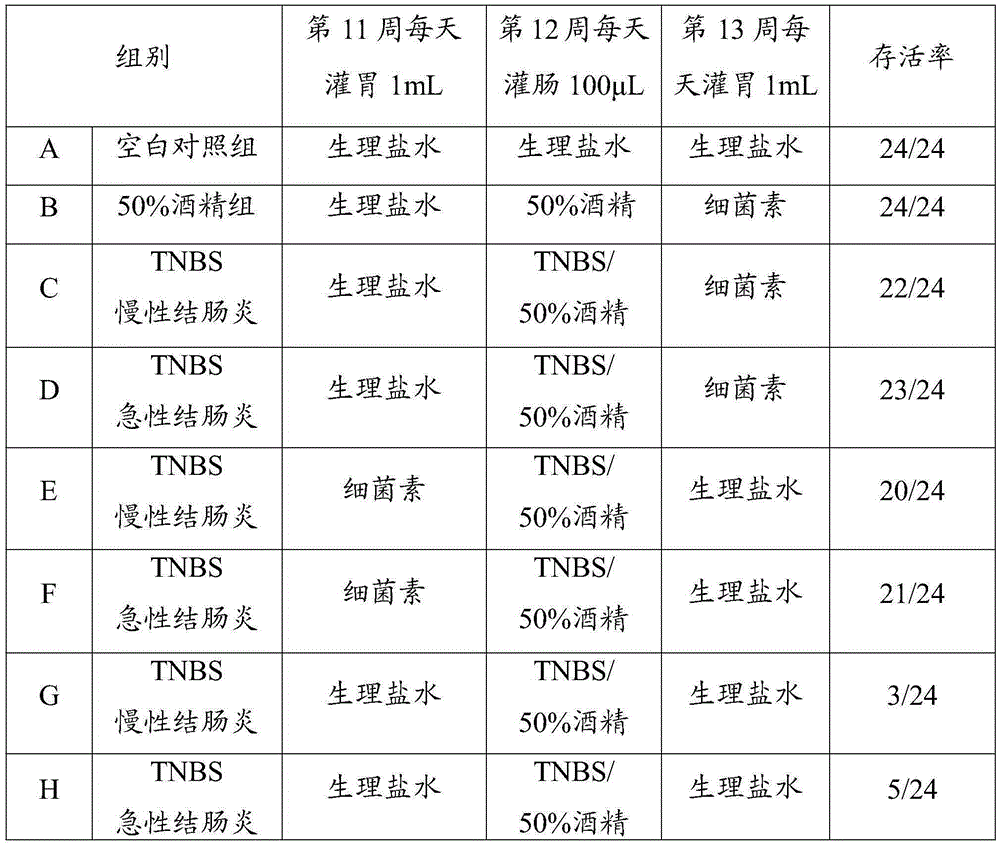
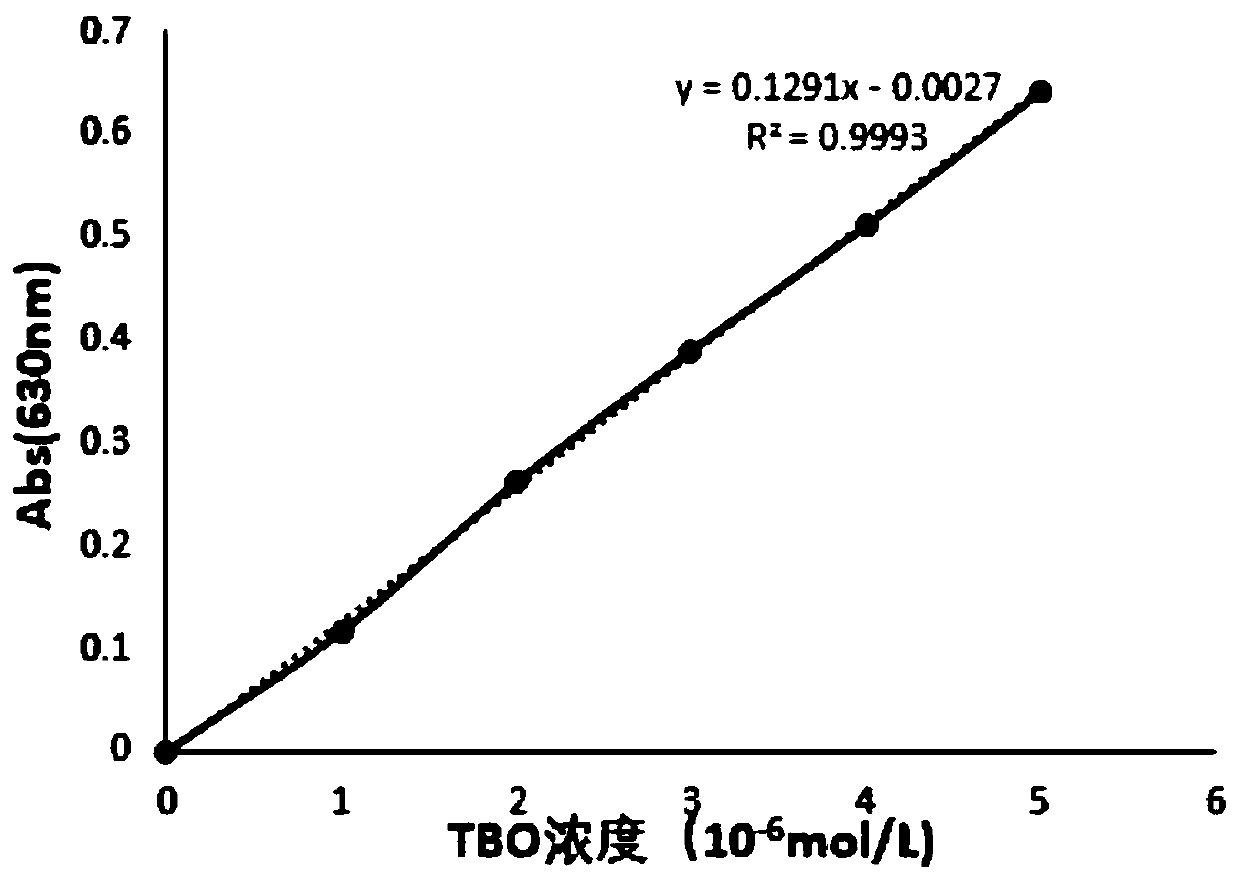
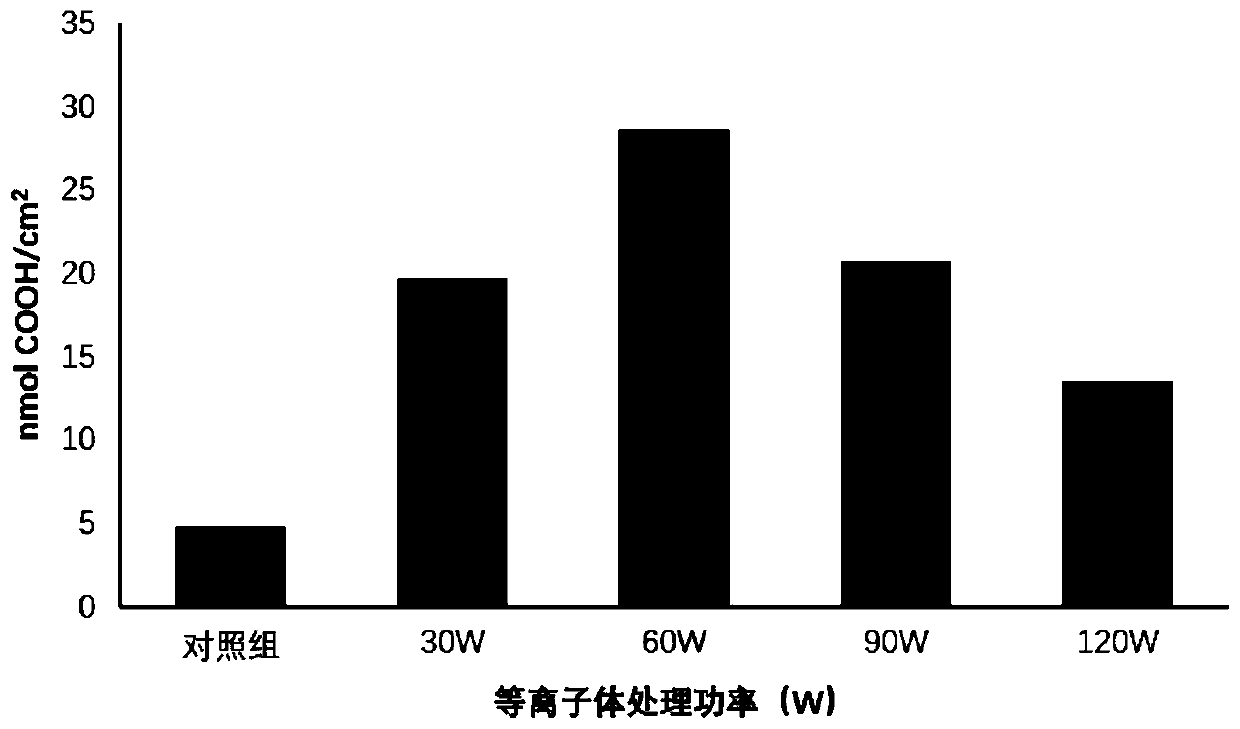
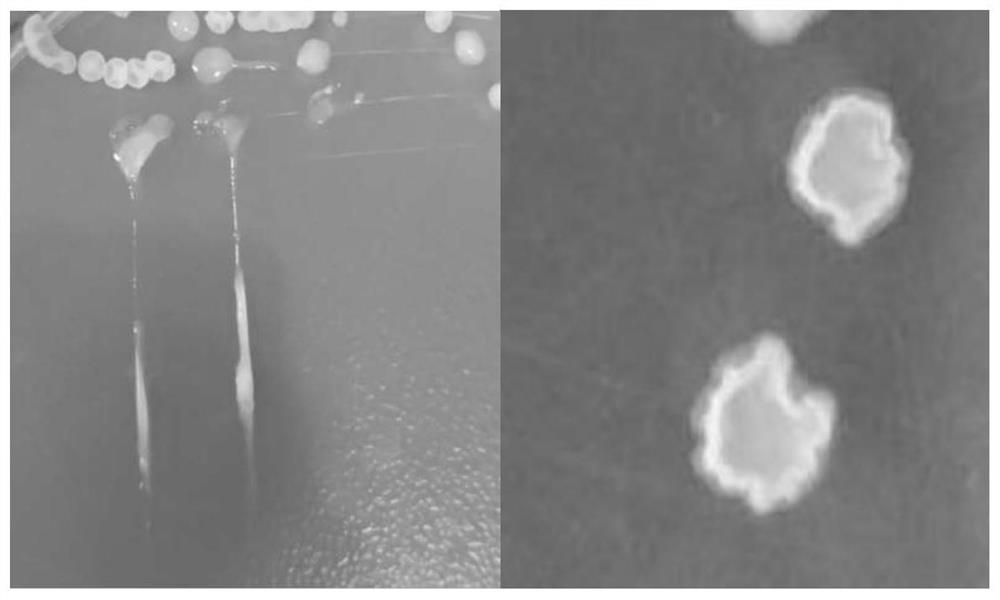
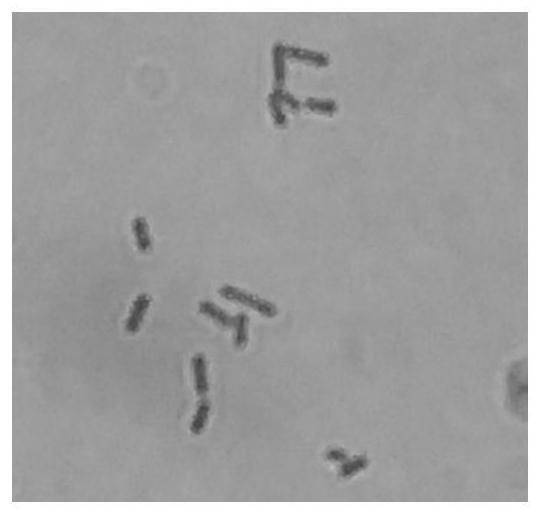
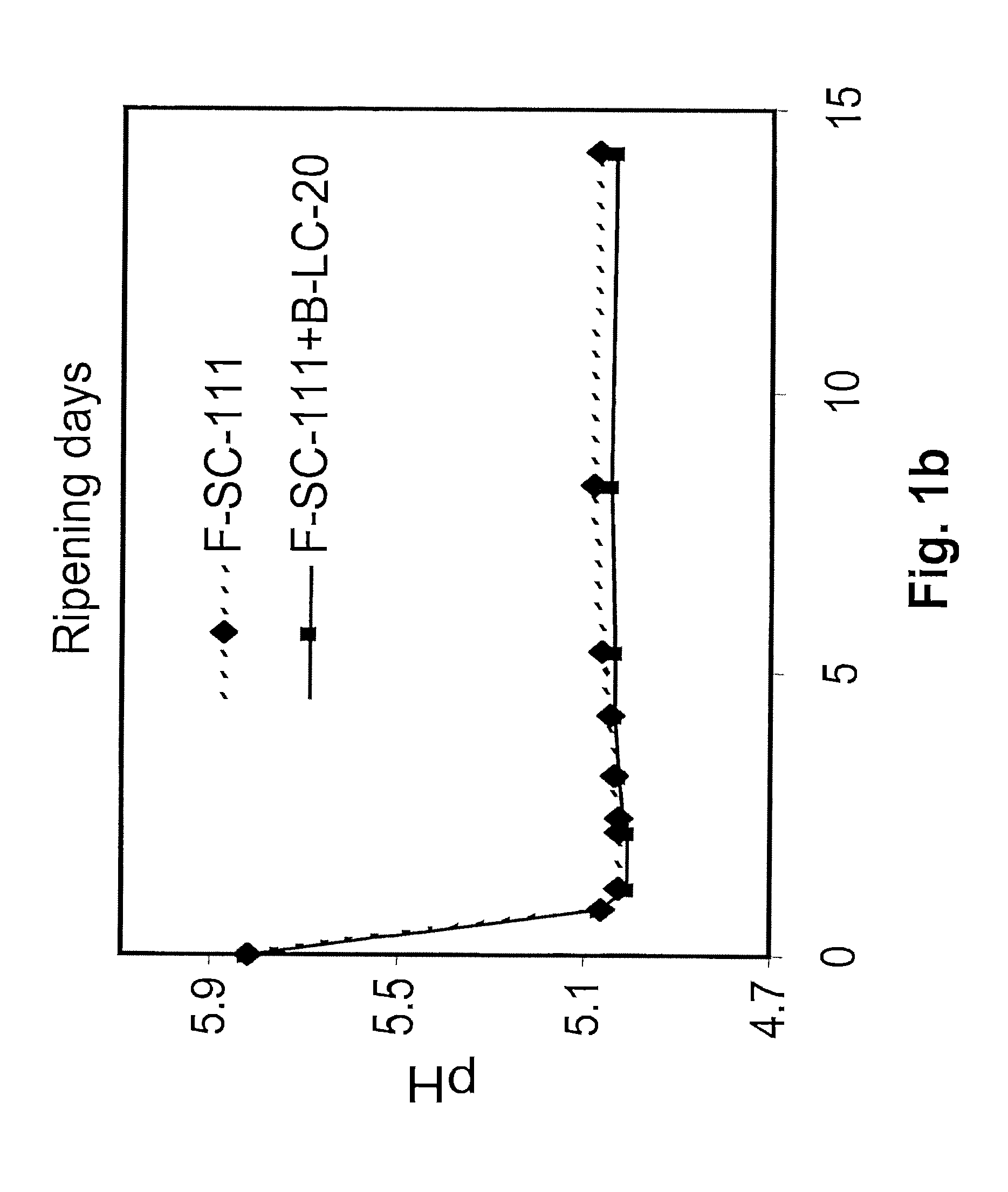
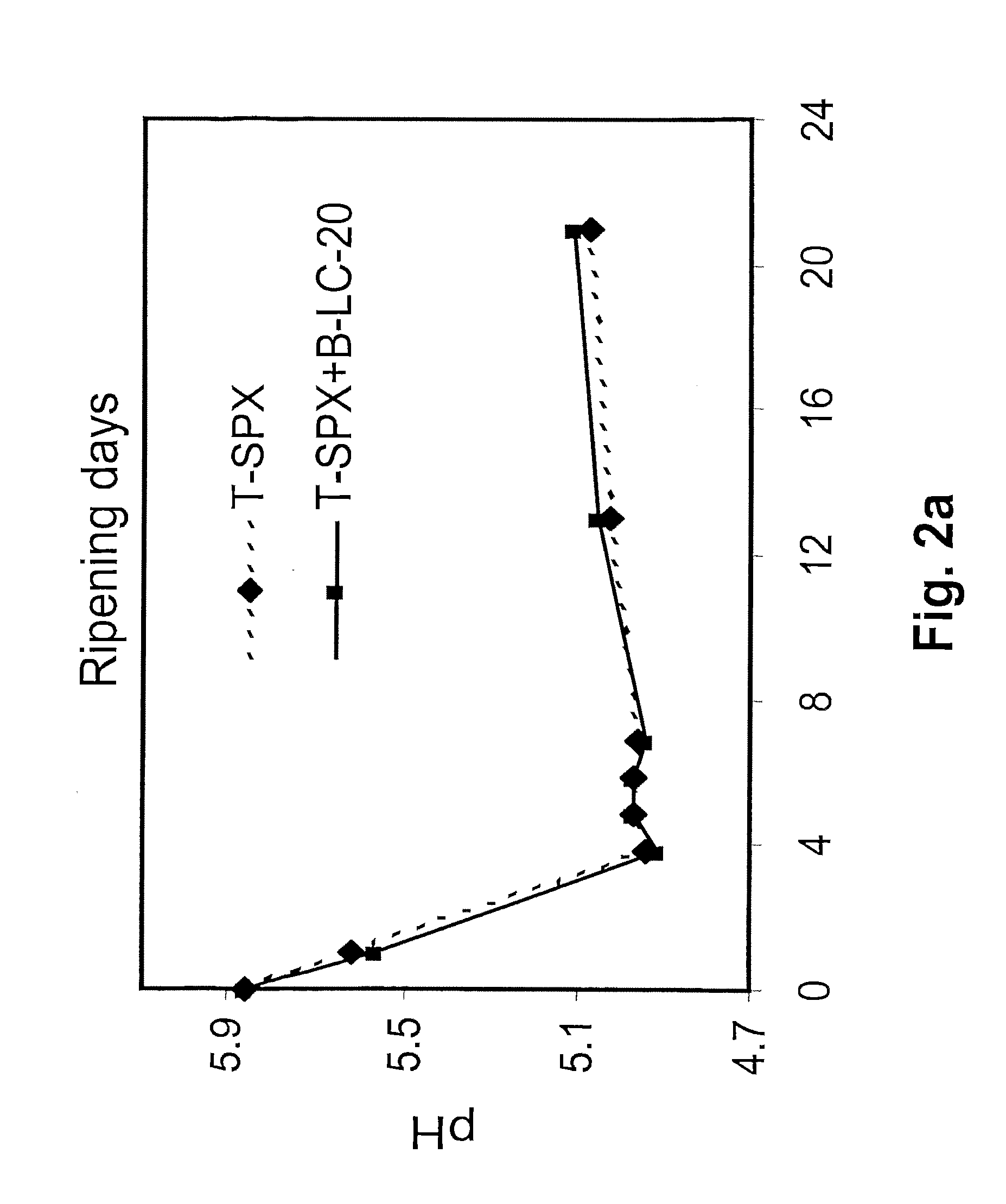
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
151 results about "Bactericin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
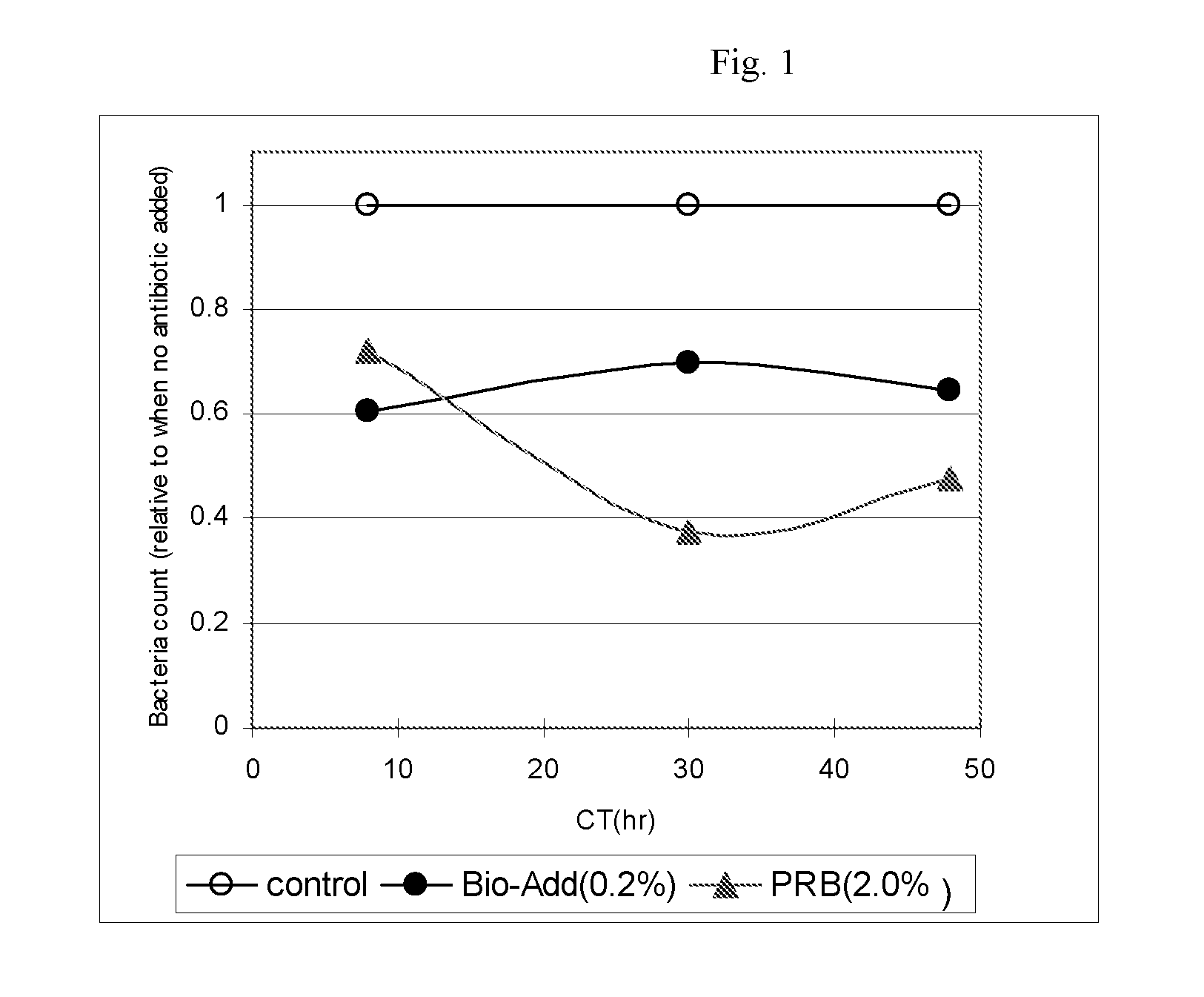
Antimicrobial compositions and methods
InactiveUS20050053593A1Easy to handleReduce Microbial ContaminationAntibacterial agentsBiocideLipid formationAlcohol sugars
The present invention is generally related to a product and process to reduce the microbial contamination on organic matter, such as processed meat, fruits and vegetables, plant parts, inanimate surfaces such as textiles and stainless steel, and in the mouth or on dental products. In particular, the invention is related to a product and process to disinfect surfaces using an antimicrobial composition containing an antimicrobial lipid, an enhancer selected from the group consisting of bacteriocins, antimicrobial enzymes, sugars, sugar alcohols, iron-binding proteins and derivatives thereof, siderophores, and combinations thereof, and optionally a surfactant.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Recombinant bacteriophage and methods for their use
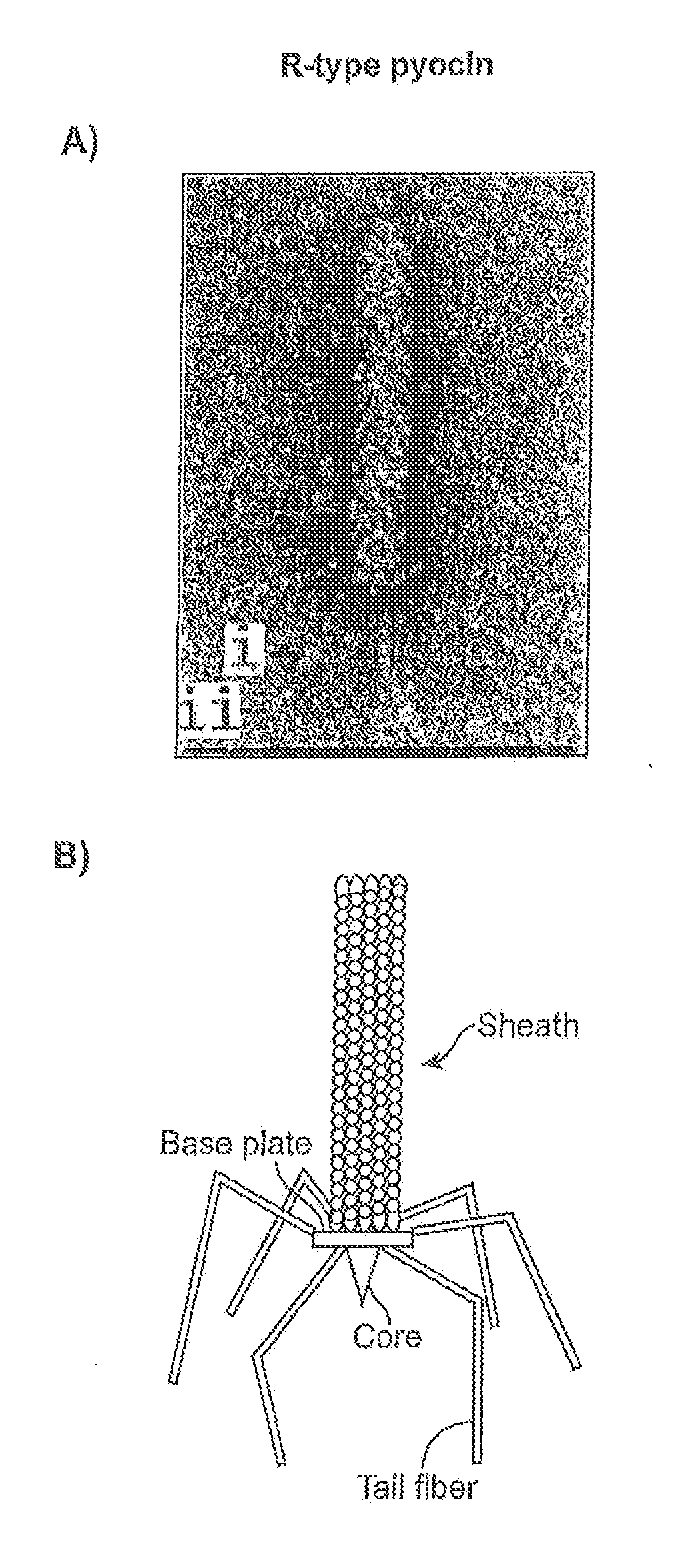
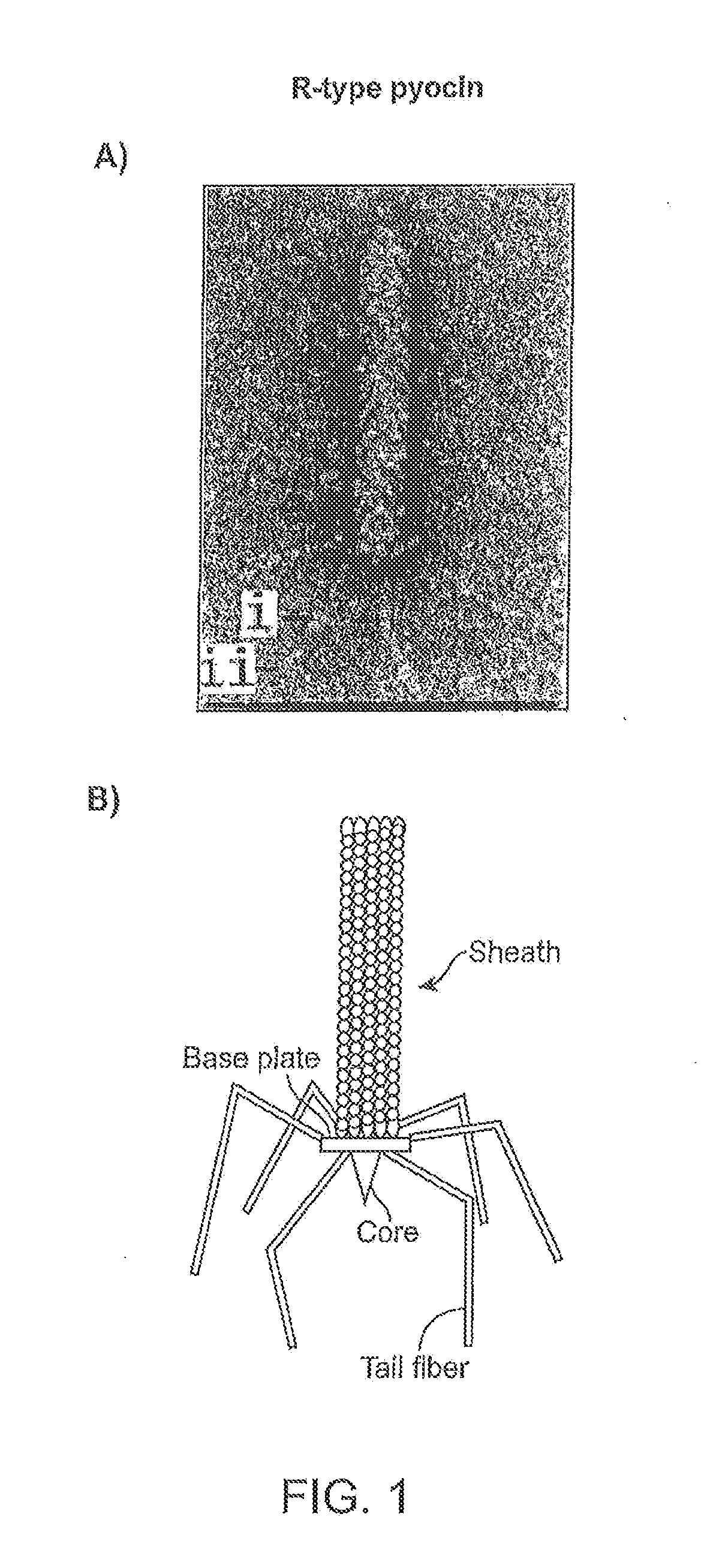
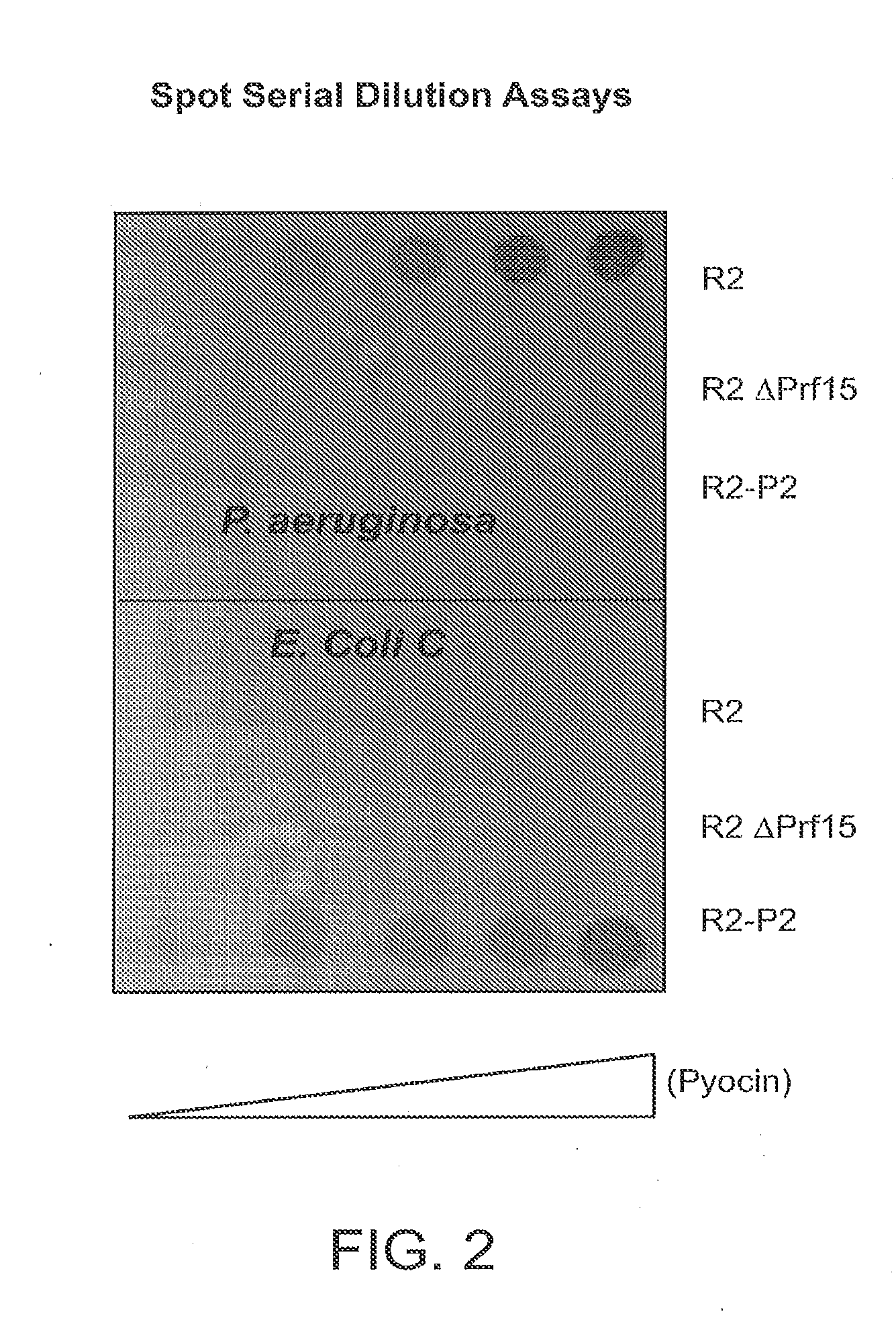
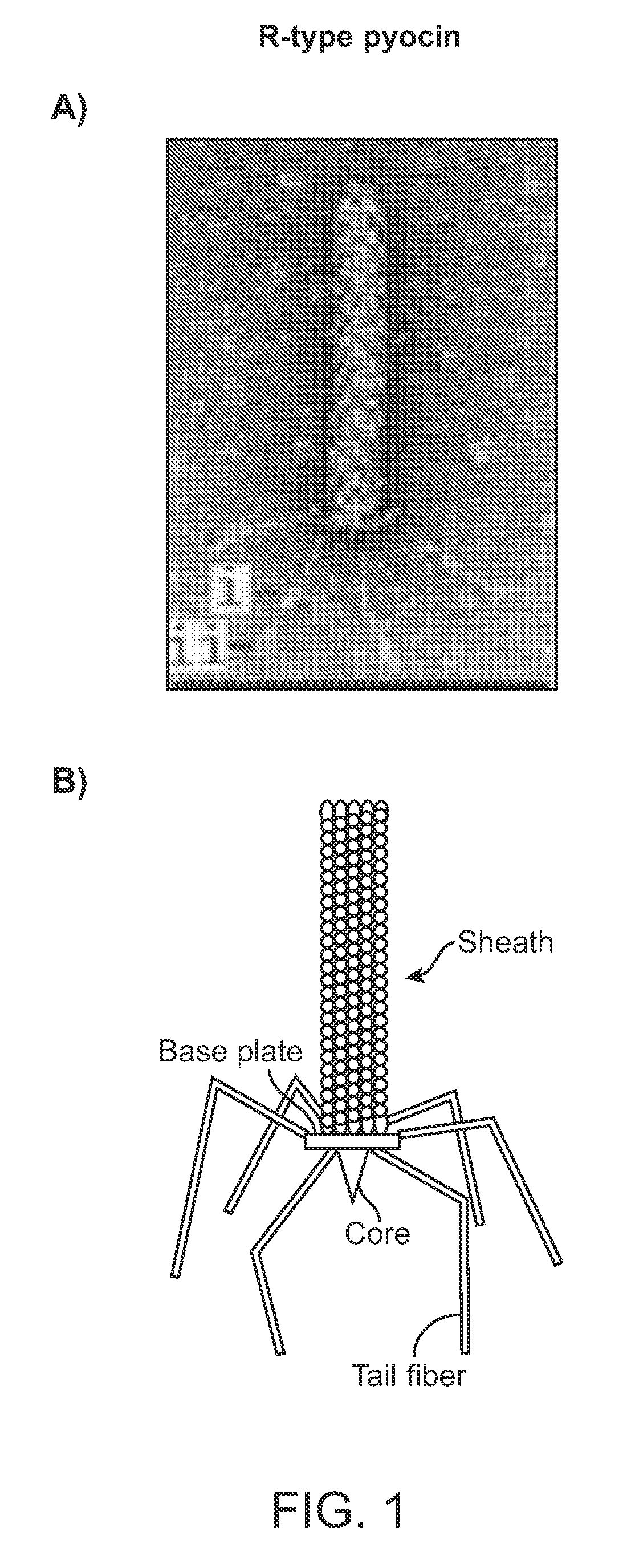
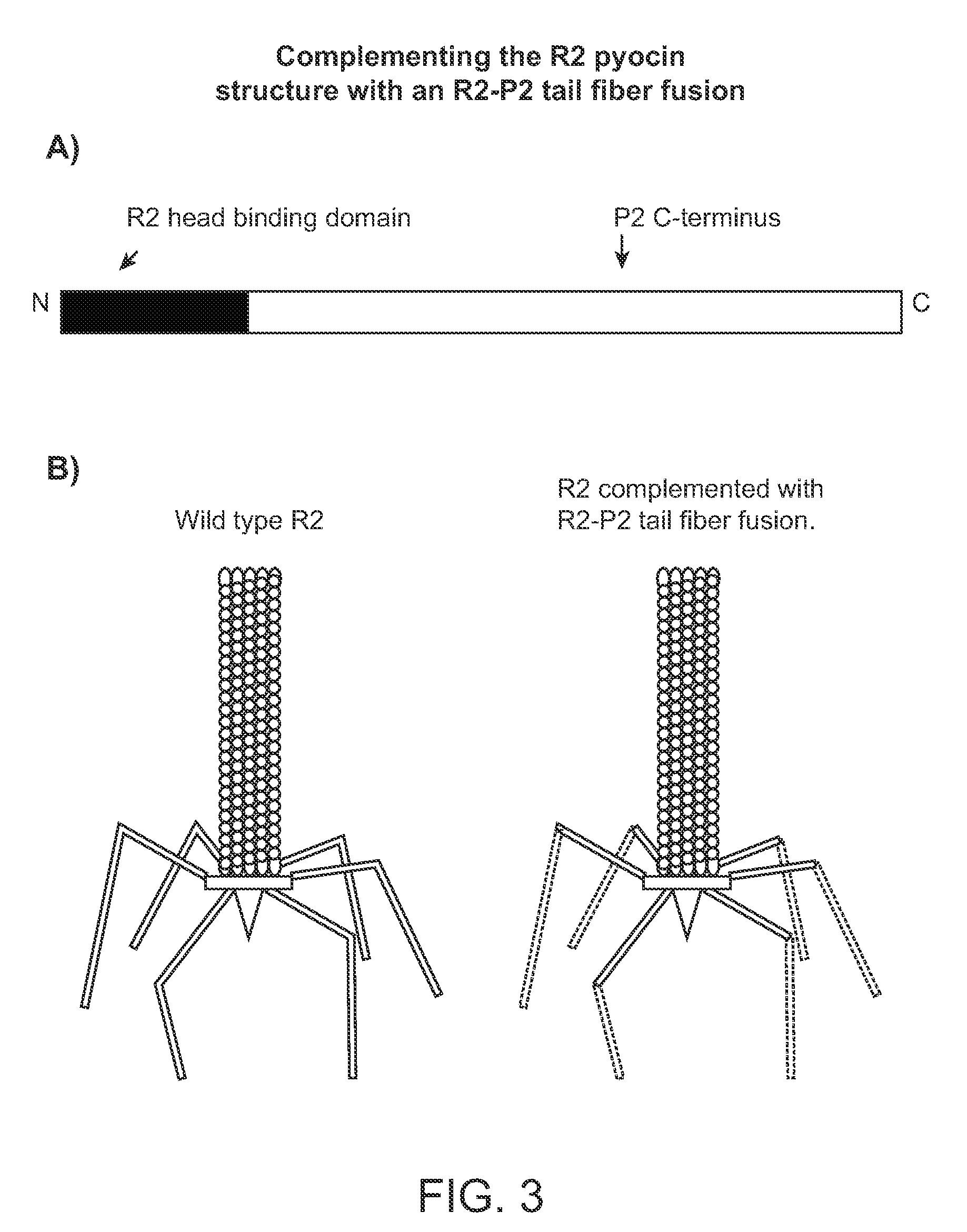
Modified forms of naturally occurring bacteriocins, such as the R-type pyocins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, are disclosed as are methods for producing them in GRAS organisms. The bacteriocins are modified at the ends of their tail fibers in a region responsible for binding specificity and affinity to their cognate binding partners, or receptors, such as those on the surface of bacteria. Methods for the use of the modified bacteriocins, such as to bind receptors, including virulence or fitness factors, on the surfaces of bacteria, are also described.
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Biocompatible compositions as carriers or excipients for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical formulations and for food protection
InactiveUS20050226905A1Reduce solubilityImprove hydrophobicityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyActive agent
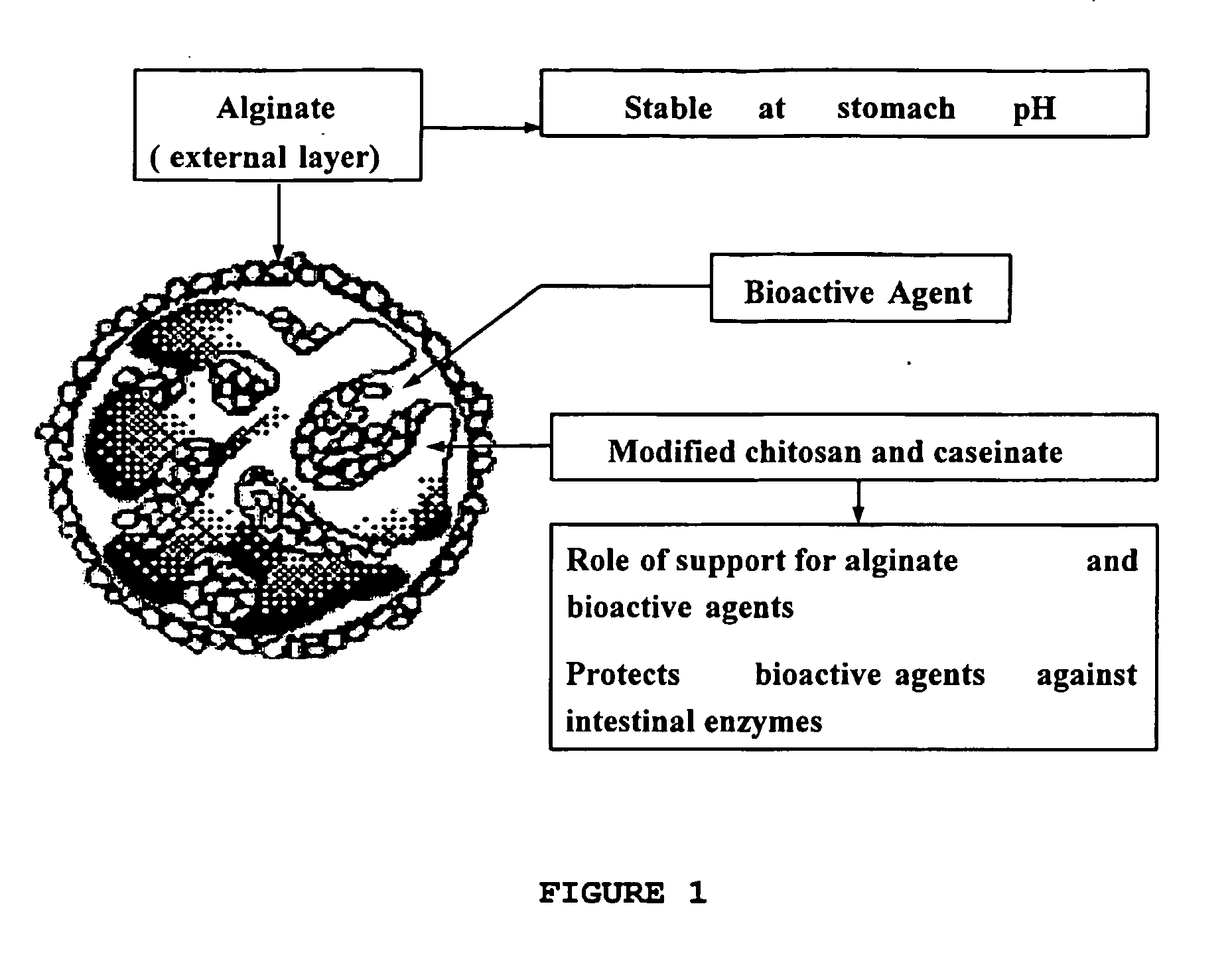
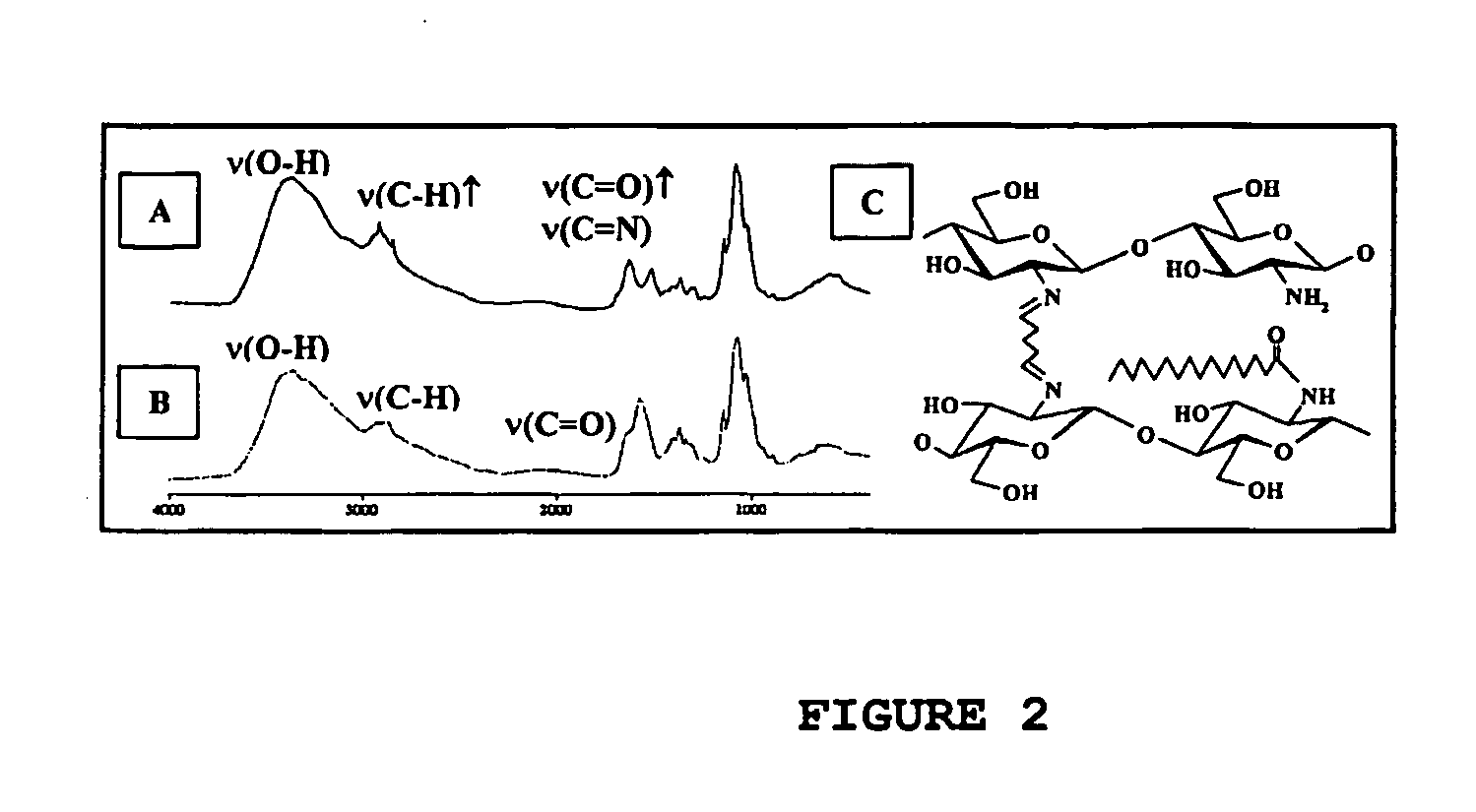
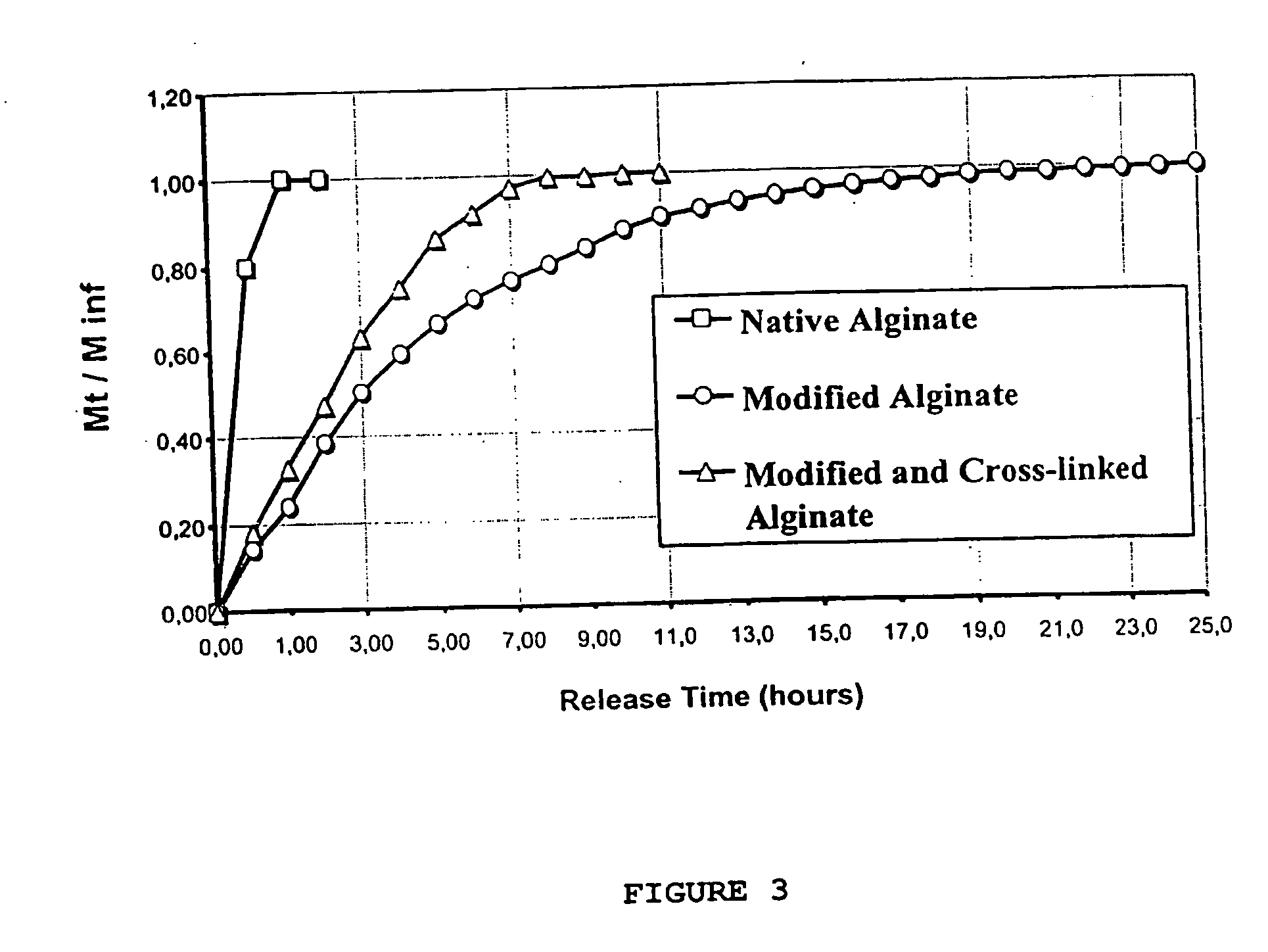
This invention refers to biocompatible carbohydrate polymers such as modified polysaccharides (e.g. chitosan, alginate), associated with milk protein (e.g. caseinate and / or whey proteins) designed to carry bioactive agents. The formulations may be used in various delivery systems including beads, tablets, microencapsulating agents and coatings for oral dosage forms, implants for subcutaneous devices and films for topic administration and food protection. These formulations present improved chemical resistance and exert their activity for prolonged time into gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and blood circulation as well as for preserving food qualities over long period. The association of modified chitosan, modified alginate with milk proteins results in a stabilized structure able to control the release of drugs, bacteria, bacteriocines, enzymes, nutraceutics, etc. into enteric, topic or systemic route.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE +1
Anti-listerial mixed culture and method for producing cheese
ActiveUS20130011516A1Highly effective against ListeriaGreat tasteMilk preparationBacteriaMixed cultureBiotechnology
The present invention discloses a method for producing a fermented dairy product, preferably cheese, comprising inoculating milk with lactic acid bacteria capable of producing a Class IIa type bacteriocin; and lactic acid bacteria capable of producing a Class I type bacteriocin.
Owner:CSK FOOD ENRICHMENT
Modified bacteriocins and methods for their use
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Lactobacillus casei bacteriocin and use thereof in feed
The invention discloses lactobacillus casei bacteriocin and use thereof in feed. The lactobacillus casei provided by the invention is separated from Tibet plateau traditional fermented yak yogurt, and the produced bacteriocin is obtained by ammonium sulfate precipitation, Sephadex G-100 gel filtration and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). The bacteriocin has thermal and acid stability, can be degraded by protease and has a wide antibacterial spectrum. When the bacteriocin is added into feed, and the growth of bacteria can be inhibited. The bacteriocin has a bright prospect in use as a feed additive.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method of bacillus subtilis HJDA32 and bacteriocin generated by bacillus subtilis HJDA32
ActiveCN103013861ABroad antibacterial spectrumImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHydrolysis
A bacillus subtilis HJDA32 strain is preserved on September 25, 2012 with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.6624, which is separated from solid fermentative substrate of vinegar in the Shanxi province Qingxu mature vinegar plant. The strains are cultured in a beef extract peptone basic medium and arranged in pole, single, paired or chained shape with the size between 0.6-0.85mu m*1.5-3.5mu m, and have capsules; elliptical spores are cultured on a raw spore culture medium; the strain is identified to be bacillus subtilis through catalase and carbon source utilization test, gelatin hydrolysis, starch hydrolysis, ethanol oxidation, acetic acid oxidation and other physiological and biochemical identifications and 16SrDNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) phylogenetic analysis; and the bacillus subtilis HJDA32 strain is used as a production strain, cultured with fermenting culture fluid, and subjected to centrifuge, ammonium sulfate powder salting out and centrifuge to obtain the bacteriocin. The bacteriocin is wide in antimicrobial spectrum and high in bacteriostatic activity, can inhibit various food-borne pathogenic bacteria, as well as gram positive and gram negative bacteria causing food spoilage, and can be used in food preservatives.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Secretory expression method of bacteriocin lacticin Q
InactiveCN103214583AEasy to separate and purifyIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSecretion expressionAntibacterial activity
The invention provides a secretory expression method of bacteriocin lacticin Q. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning lacticin Q and an SUMO fusion gene SUMO-lacticin Q to pWB980; transferring to bacillus subtilis; expressing the SUMO fusion gene SUMO-lacticin Q in a secretory manner in a culture medium; separating and purifying the SUMO fusion gene SUMO-lacticin Q I; and digesting and releasing the lacticin Q to further purify and obtain the lacticin Q. The activity detection confirms that the obtained recombinant protein is good in antibacterial activity which is equivalent to that of natural lacticin Q. According to the method provided by the invention, not only can the separating and purifying process of the lacticin Q be simplified, but also the yield of the lacticin Q is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Feed additive, premix and mixture containing like-bacteriocin and pediococcus acidilactici
ActiveCN102965316AImprove conversion efficiencyReduce or avoid the use ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySynechococcus
The invention discloses a new strain HT of pediococcus acidilactici and a feed additive containing bacillus like-bacteriocin and pediococcus acidilactici. The collection number of the new strain of pediococcus acidilactici is CGMCC No.6500. The freeze-dried powder of the like-bacteriocin of bacillus subtilis CGMCC No.6511 is sufficiently mixed with the powder of pediococcus acidilactici HT according to a proportion to obtain the feed additive. The feed additive is a green feed additive which improves the feed conversion rate, enhances the productivity and immunity of animals, prevents diarrhea, and realizes an effect of improving the quality of animal products.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Lactobacillus plantarum SWUN5815 for high-yield bacteriocin and application of lactobacillus plantarum SWUN5815
The invention discloses a lactobacillus plantarum SWUN5815 for high-yield bacteriocin and an application of the lactobacillus plantarum SWUN5815. The strain is preserved at the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCCTCC) on August 2, 2016 and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2016419; and the strain is separated from yak dung. The bacteria generated by the strain can be degraded by protease; the strain has a very high inhibition effect on salmonella and escherichia coli and has good acid resistance and relatively high cholate tolerance; the survival rate after 3h in artificial gastric juice of which the pH is 3.0 is 93.36+ / -4.06%; the strain can slowly grow in 1.0% cholate; and the growth efficiency reaches 15.26+ / -1.19% of that of the strain which is cultivated under the condition free of the cholate. The bacteriocin is capable of effectively inhibiting growth of salmonella, escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. Therefore, the lactobacillus plantarum SWUN5815 for the high-yield bacteriocin has the potential of being applied to yak intestinal tracts as a microecological preparation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
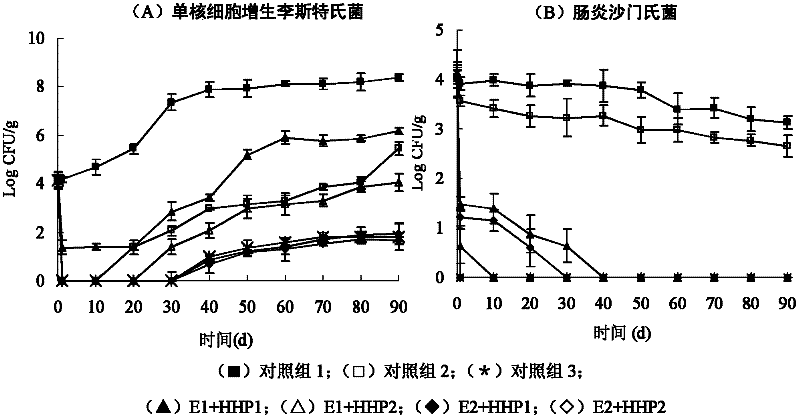
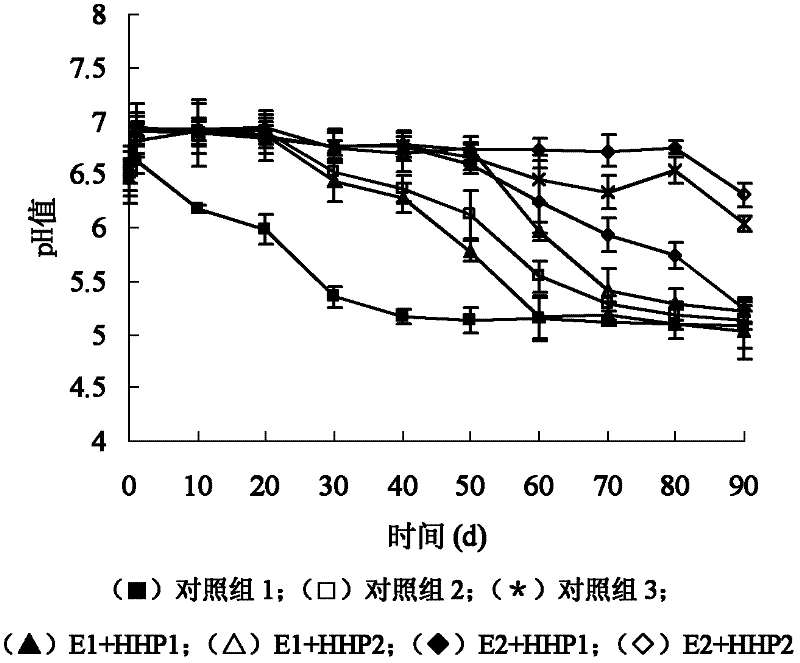
Bacteriocin and ultra-high pressure joint antiseptic preservation technology and its application
The invention discloses a bacteriocin and superhigh pressure joint antiseptic preservation technology and an application thereof. The invention provides a bacteriostasis and / or sterilization method for food. The bacteriostasis and / or sterilization method for the food provided by the invention comprises the following steps: adding the bacteriocin enterocin P into the food, and performing superhighpressure treatment on the food added with the bacteriocin enterocin P, wherein the pressure for the superhigh pressure treatment is 100-600 MPa. According to the invention, under the condition of notadding any chemical preservative, the defects of relatively poor bacteriostasis activity of nisin against Gram-negative bacteria and influence of 600 MPa superhigh pressure treatment on the sensory quality of food are overcome by combining the bacteriocin enterocin P with the superhigh pressure technology, and an efficient, environmentally-friendly and safe antiseptic preservation technology is provided for low-temperature meat products.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Antibiotic, Compositions Containing the Antibiotic, and Methods for Administering the Antibiotic and/or Said Compositions to Livestock
InactiveUS20070009503A1Growth inhibitionEfficient growth processAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBiotechnology
An antibiotic comprising a protease-resistant bacteriocin derived from a lactic acid bacterium, and compositions thereof, are disclosed. A feed composition for livestock comprising the antibiotic comprising a protease-resistant bacteriocin derived from a lactic acid bacterium is also disclosed. A method for preventing the growth of human food poisoning-causing bacteria in the stomach and / or intestines of livestock comprising administering the feed composition comprising a protease-resistant bacteriocin derived from a lactic acid bacterium to livestock is disclosed.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing lactic acid bacterium culture containing bacteriocin and a method for preserving food products for by using it
InactiveUS20060270019A1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyLactic acid bacterium
The present invention provides a lactic acid bacterium culture containing protease-resistant bacteriocin, which can be produced by cultivating lactic acid bacteria (e.g., from the genus Weissella). As such, the shelf stability of a food can be improved by incorporating the culture of the present invention therein.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Probiotic propionibacterium
InactiveUS7427397B2Promote growthGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesPropanoic acid
The present invention relates to probiotic Propionibacterium strains and their use in the preparation of probiotic supplements and foods. The invention relates to the provision of Vitamin B12, propionic acid, folacin and bacteriocins by probiotic strains, stimulation of bifidobacteria growth, production of favourable effects on the lipid metabolism and on the immune system of hosts through immunostimulation, immunomodulation or use of a probiotic strain as an adjuvant, reduction of homocysteine and β glucuronidase and the prevention, treatment or amelioration of conditions associated with a need for these activities. The probiotic bacteria of the invention can be used in humans or other animals. In at least some applications, the bacteria can be used dead and parts rather than whole cells may be used. The present invention also relates to the preparation of vaccines for use in protecting patients from infectious diseases, in particular tuberculosis.
Owner:UNIV OF NEWCASTLE RES ASSOCS
Probiotic strains from Lactobacillus salivarius and antimicrobial agents obtained therefrom
A strain of Lactobacillus salivarius isolated from resected and washed human gastrointestinal tract inhibits a broad range of Gram positive and Gram negative microorganisms and secretes a product having antimicrobial activity into a cell-free supernatant. The activity is produced only by growing cells and is destroyed by proteinase K and pronase E, the inhibitory properties of the strain and its secretory products being maintained in the presence of physiological concentrations of human bile and human gastric juice. The strain exhibits a broad-spectrum of activity against bacteria including Listeria, Staphylococcus, including methocillin resistant St. aureus (MRSA), and Bacillus, but does not inhibit many closely related lactobacilli. An antimicrobial agent is obtained from the strain which has bacteriocin-like properties.
Owner:ENTERPRISE IRELAND & UNIV COLLEGE CORK +1
Bacteriocin crude extract with bacteriostatic action, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104762351ASolve the current situation of narrow sourcesStable in natureFood preservationMicroorganism based processesPutrefying bacteriaFood safety
The invention discloses a bacteriocin crude extract with bacteriostatic action, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the bacteriocin crude extract comprises the following steps: (1) inoculating Paenibacillus sp. into a culture medium for culturing Paenibacillus sp., and carrying out shake fermentation and culture to obtain a fermentation liquid; and (2) centrifuging the fermentation liquid obtained in the step (1), taking the precipitate, adding acetone, evenly mixing, leaching, centrifuging, taking the supernatant, and removing acetone. The method solves the problem of narrow bacteriocin sources at present. Compared with the traditional bacteriocin, the bacteriocin crude extract prepared by the method has stabler properties, and thus, has higher food safety. The bacteriocin crude extract can be directly used for food production, thereby achieving the goals of inhibiting putrefying bacteria and prolonging the shelf life of food, and further lowering the application cost.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
Lactococcus garviea bacteriocin, preparing method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN105385729AStrong broad-spectrum antibacterial abilityIncrease productionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFood spoilageHuman disease
The invention relates to a lactococcus garviea bacteriocin, a preparing method thereof and an application thereof. The high-yield actococcus garviea bacteriocin can be obtained in the mode that lactococcus garviea is subjected to fermented cultivation, and then the bacteriocin in the cultivating-fermenting liquid is extracted with a pH adsorption method; more than 800 mg of the lactococcus garviea bacteriocin can be prepared through 1 L of the fermenting liquid. The lactococcus garviea bacteriocin has quite high broad-spectrum bacteriostasis capacity and has a quite high inhibiting effect on some gram negative bacteria, some gram positive bacteria, yeast and mould causing human diseases and food spoilage. The lactococcus garviea bacteriocin has the effect of treating and preventing acute and chronic enteritis.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGYOUYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Bifidobacterium adolescentis bacteriocin as well as production method and special production strain of bifidobacterium adolescentis bacteriocin
ActiveCN104046584AGood food processing properties and safetyBroad antibacterial spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAmmonium sulfateBifidobacterium adolescentis
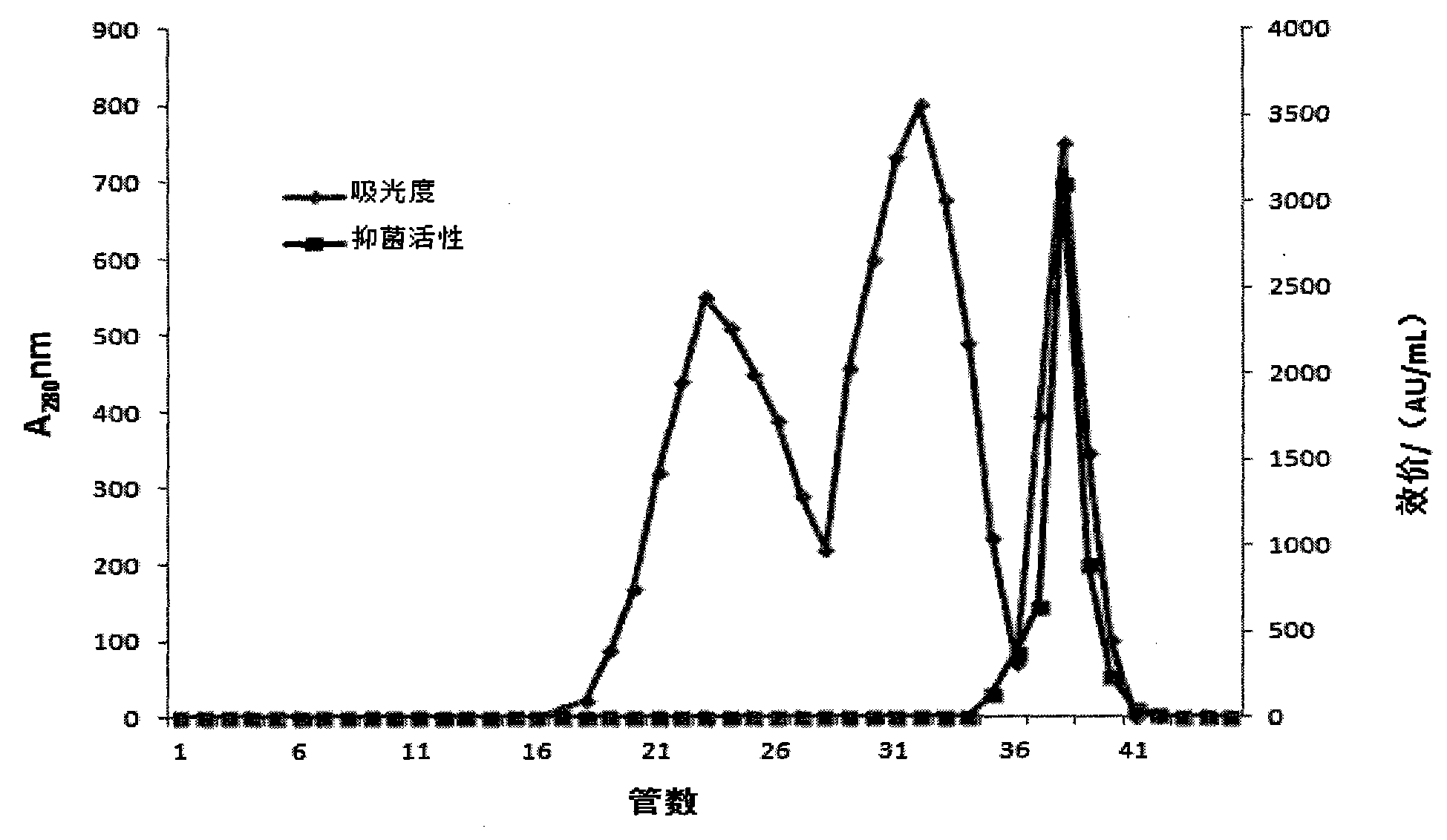
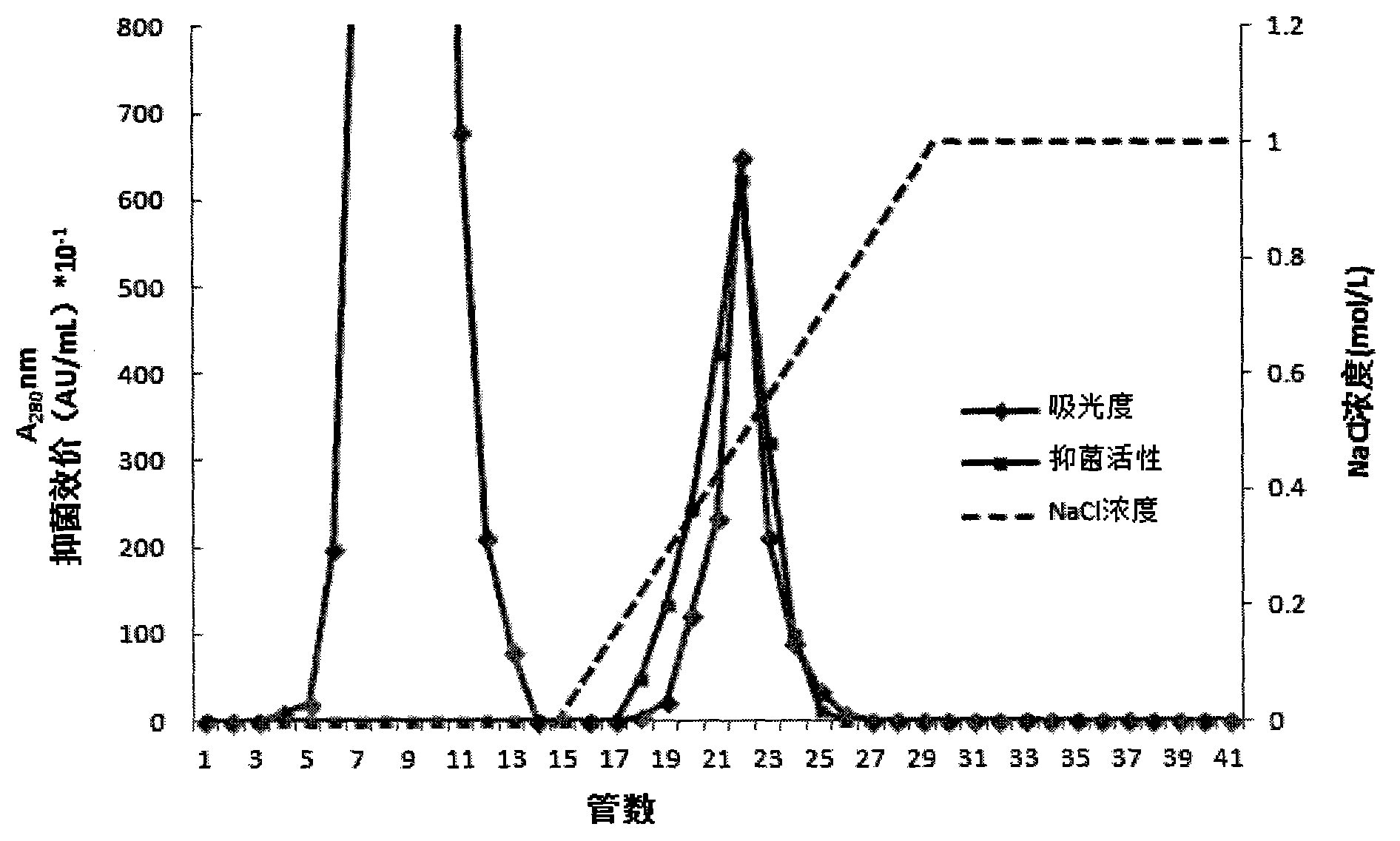
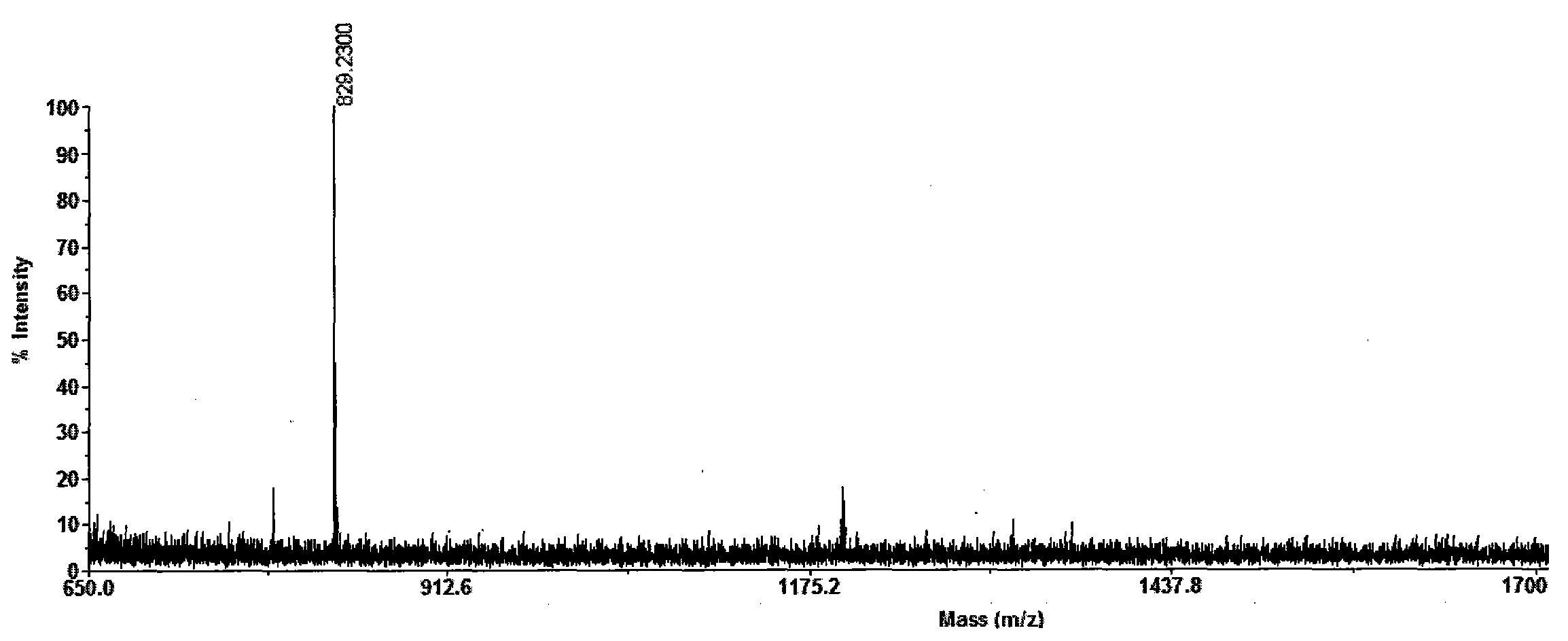
The invention discloses bifidobacterium adolescentis bacteriocin as well as a production method and a special production strain of the bifidobacterium adolescentis bacteriocin. The bifidobacterium adolescentis bacteriocin provided by the invention is obtained by fermenting bifidobacterium adolescentis BL-8 CGMCC No.7791. The invention provides an optimal culture medium component and a culture condition of bacteriocin generated by metabolism of bifidobacterium adolescentis and also provides an extraction and purification method of the bifidobacterium adolescentis bacteriocin. The extraction and purification method comprises the steps of: crude extraction through ammonium sulfate salting and precipitating; gel filtration chromatography; cation exchange resin chromatographic purification to obtain pure bacteriocin. The bifidobacterium adolescentis bacteriocin provided by the invention has the molecular weight of 829.23Da, is novel bifidobacterium adolescentis bacteriocin, is very good in food processing property, wide in antibacterial spectrum and high in safety and can be used for developing natural biological preservatives for foods.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
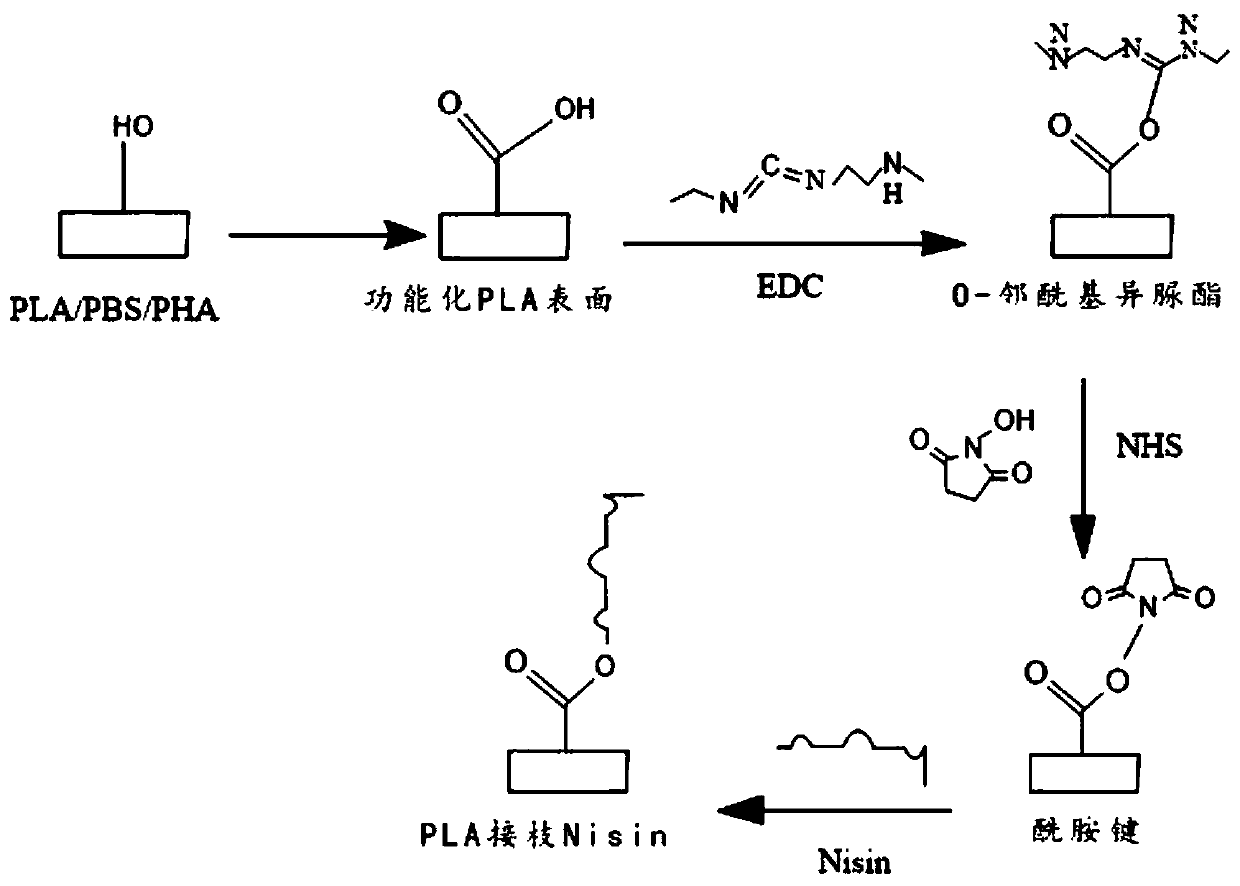
Grafted antibacterial degradable fresh-keeping film, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a grafted antibacterial degradable fresh-keeping film, and a preparation method and an application thereof. One or more of degradable materials which are polylactic acid (PLA),butenesuccinic acid (PBS) and polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) are used as a base film of a packaging material, the base film is subjected to surface modification by adopting plasma treatment to make activegroups such as a carboxyl group generated on the surface, bacteriocin is connected to the surface of the plasma-treated film through an EDC-NHS coupling technology, and an amino group on an active antibacterial agent and the carboxyl group, generated on the film subjected to plasma and coupling agent treatment, are stably combined in a mode of forming an amido bond. The grafted antibacterial degradable fresh-keeping film has a hydrophilic antibacterial activity, is an environmentally-friendly, safe and reliable novel antibacterial packaging material, and can be applied to food preservation.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Multi-effect bacillus subtilis for high yield of immune polysaccharide and bacteriocin and application
ActiveCN111961617AExcellent bacteriocin producing abilityIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention provides multi-effect bacillus subtilis for high yield of immune polysaccharide and bacteriocin and application. The preservation number of the bacillus subtilis provided by the invention is CGMCC NO.20463. The strain has excellent extracellular immune polysaccharide production capability; after fermentation by a conventional method, fermentation liquor is purified, and the yield ofthe exopolysaccharide is as high as 8203.64 mg / L; and the strain has excellent bacteriocin production capacity and endotoxin digestion capacity, and can effectively inhibit pathogenic or harmful bacteria such as salmonella, escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, listeria monocytogenes, sarcina lutea, streptococcus, clostridium perfringens and the like. The bacillus subtilis disclosed by the invention can be used as a food additive or a feed additive, has good immunoregulation, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capacities, and has a wide application prospect in the aspects of disease resistance, disease prevention and livestock and poultry antibiotic substitution.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Screening method and application of lactobacillus plantarum
InactiveCN104877986AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove thermal stabilityMutant preparationFood preservationFood additiveMononucleosis
The invention discloses a mutation breeding method of lactobacillus plantarum and application of a strain of the lactobacillus plantarum. The collection number of the lactobacillus plantarum in China general microbiological culture collection center is CGMCC No 5297. The lactobacillus plantarum can generate bacteriocin which has a better inhibiting effect on multiple gram-positive bacteria and especially has great a high inhibiting effect on listeria monocytogenes, and the bacteriocin has the advantages of better heat stability, acid stability and the like and can be applied as a food additive and a feed preservative agent which have wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Natural composite preservative special for chilled fresh meat
ActiveCN106479941AWith antibacterial functionAntioxidantBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPreservativeGingerol
The invention discloses a natural composite preservative special for chilled fresh meat. The invention provides Lactobacillus plantarum b-2 collected under CGMCC No. 13413. The invention also claims bacteriocin produced by the Lactobacillus plantarum b-2. The bacteriocin produced by the Lactobacillus plantarum b-2 is blended with ginger juice to prepare the natural composite preservative; the natural composite preservative is good in safety and zero in toxicity, has antibacterial, anti-oxidization and health functions, can be added to prevent chilled fresh meat from spoiling, significantly extend the shelf life of chilled fresh meat and improve the safety of the chilled fresh meat, may extend the shelf of chilled fresh meat for 4 days, and has a promising application prospect.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS
Bacterocide compositions and their preparation from micrococcus varians
A bacteriocin having activity against bacteria including Listeria monocytogenes is obtained by culturing cells of a strain of Micrococcus varians, particularly cells of deposited strains CNCM I-1586 and CNCM I-1587, to obtain cultured cells and a supernatant and by separating the supernatant from the cultured cells to obtain the supernatant which contains the bacteriocin which, in turn, may be isolated from the supernatant.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Bacteriocin bacteriostatic fresh-keeping biological composite film
The invention discloses a bacteriocin bacteriostatic fresh-keeping biological composite film. The biological composite film is prepared by preparing a film matrix from 94-97wt% of polylactic acid and 3-6wt% of sawdust particles and adsorbing a trace amount of bacteriocin on the film surface. A manufacturing method comprises the following steps of stirring and mixing the pretreated sawdust particles and polylactic acid, extruding and blowing the film; carrying out dry heat treatment on the biological composite film and implanting the bacteriocin into the film by virtue of a diffusion coating method. The manufacturing method is simple and low in production cost, the bacteriocin can be effectively adsorbed on the surface of the biological composite film and the industrial production can be realized. The prepared bacteriocin bacteriostatic fresh-keeping biological composite film has the advantages of stronger effects on inhibiting activities of multiple food-borne pathogenic bacteria and food spoilage bacteria, very low solubility in water and complete biodegradability and is especially suitable for fresh-keeping preservation of fresh meat and other high-moisture foods.
Owner:安徽民祯生物工程有限公司
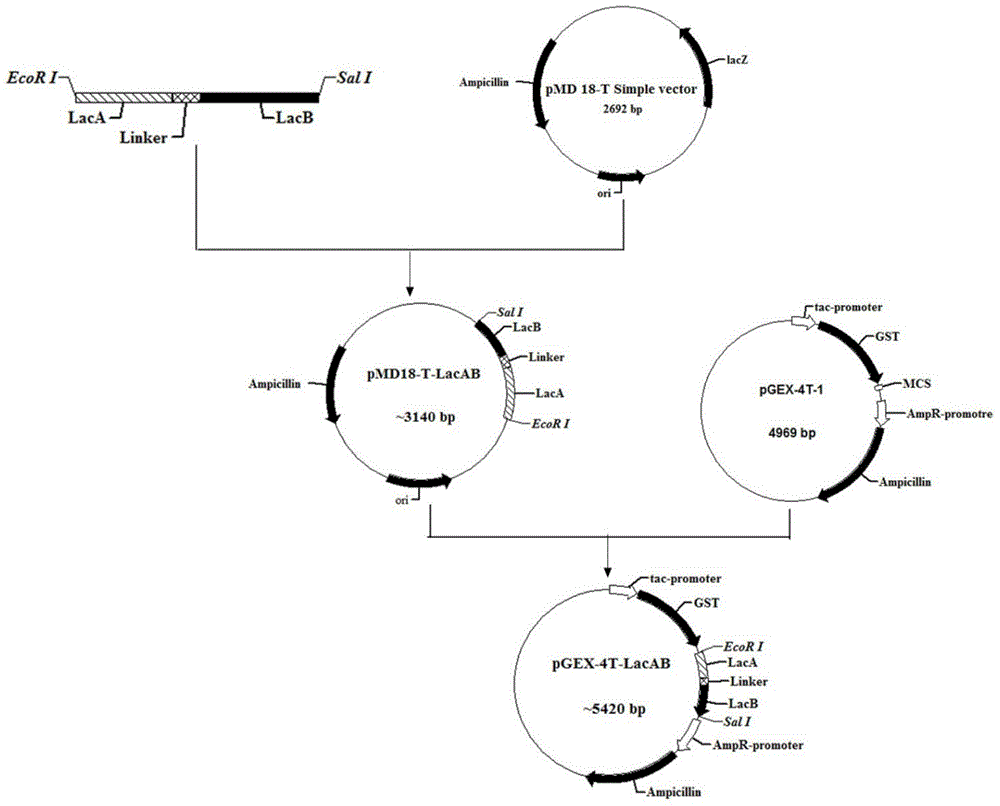
Recombinant bacteriocin and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104962566AHigh yieldHigh antibacterial activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliProtein solution
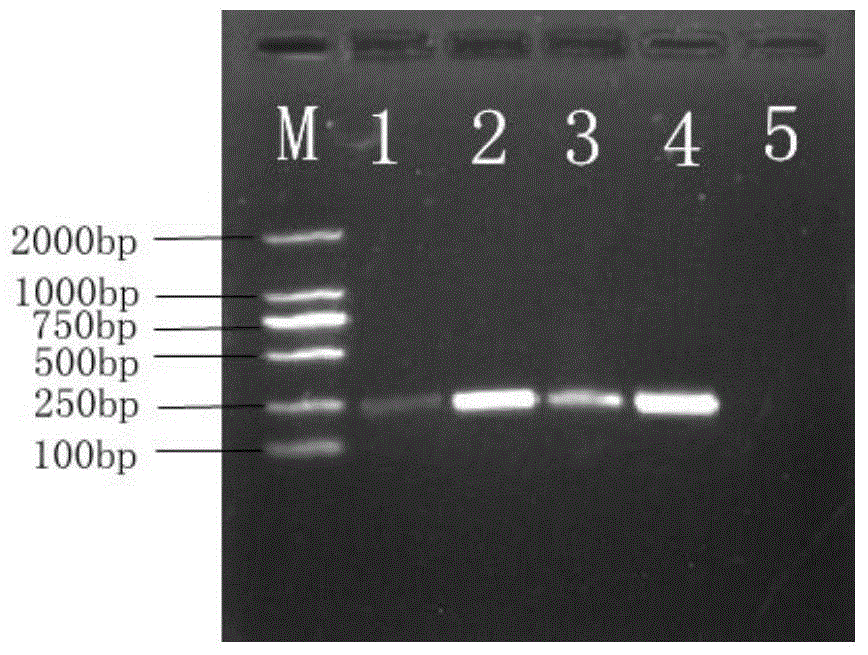
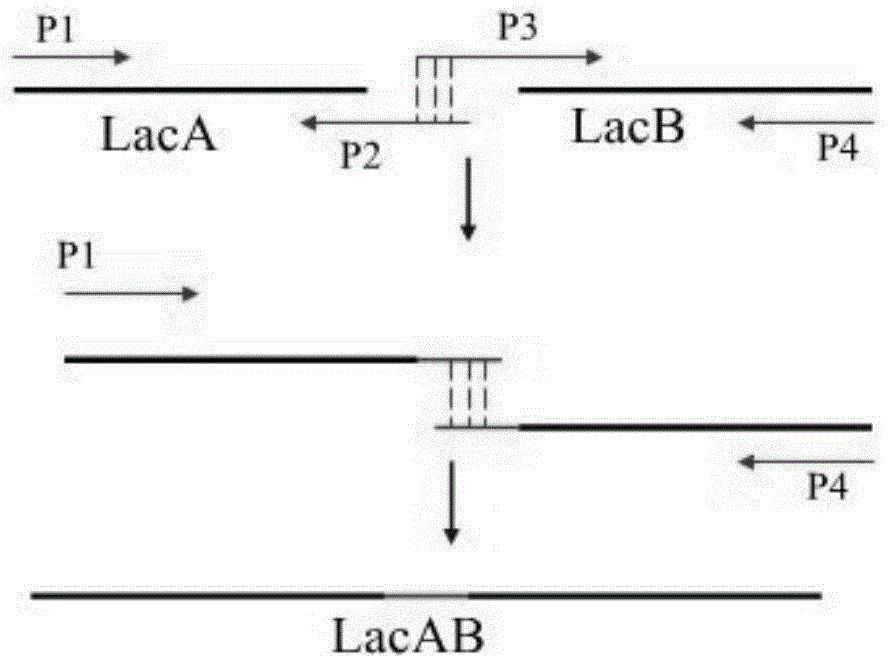
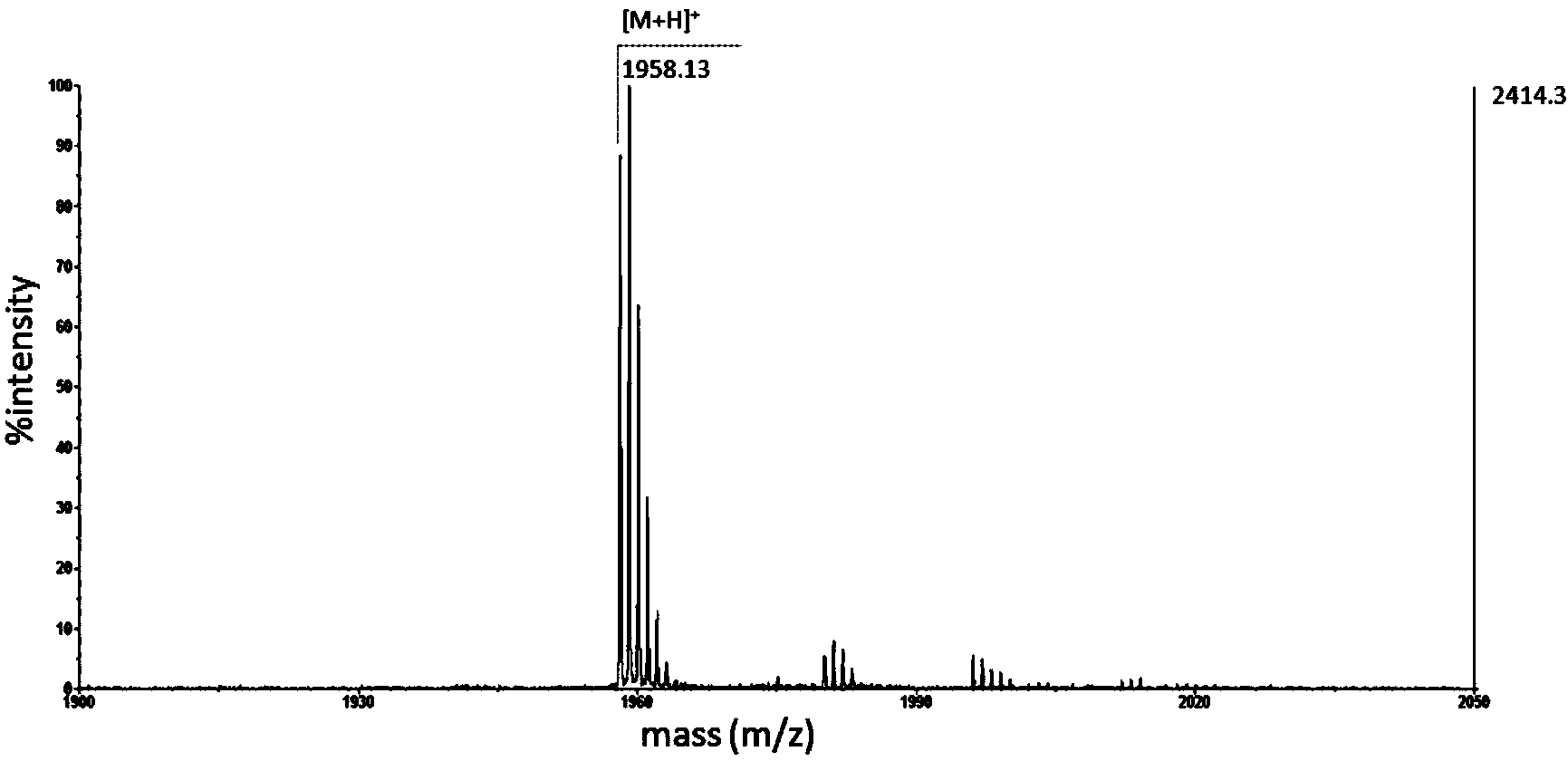
The invention relates to a recombinant bacteriocin and a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. A nucleotide sequence of a LacAB gene of the recombinant bacteriocin is shown in an SEQ ID NO:1, and a recombinant expression vector pGEX-4T-1-LacAB comprises the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO:1. Escherichia coli BL21 containing the recombinant expression vector pGEX-4T-1-LacAB is induced by IPTG to express objective protein, and a bacterium solution is collected, recombinant protein in the bacterium solution is extracted; an obtained recombinant protein solution passes through a GST purification column, a GST label is combined with GST rabphilin rab on the column, and purified GST-LacAB protein is obtained through an eluant; the GST label is cut and removed by thrombin, purification is conducted through a GST purification kit, and the single recombinant bacteriocin LacAB is obtained. According to the recombinant bacteriocin and the preparation method and the application thereof, the antimicrobial activity and the stability of the recombinant bacteriocin are good, the antimicrobial spectrum is wide, and the recombinant bacteriocin can serve as an ideal antibiotic succedaneum, a human and animal biological drug, a feed supplement, an antiseptic substance, a disinfection agent and the like.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
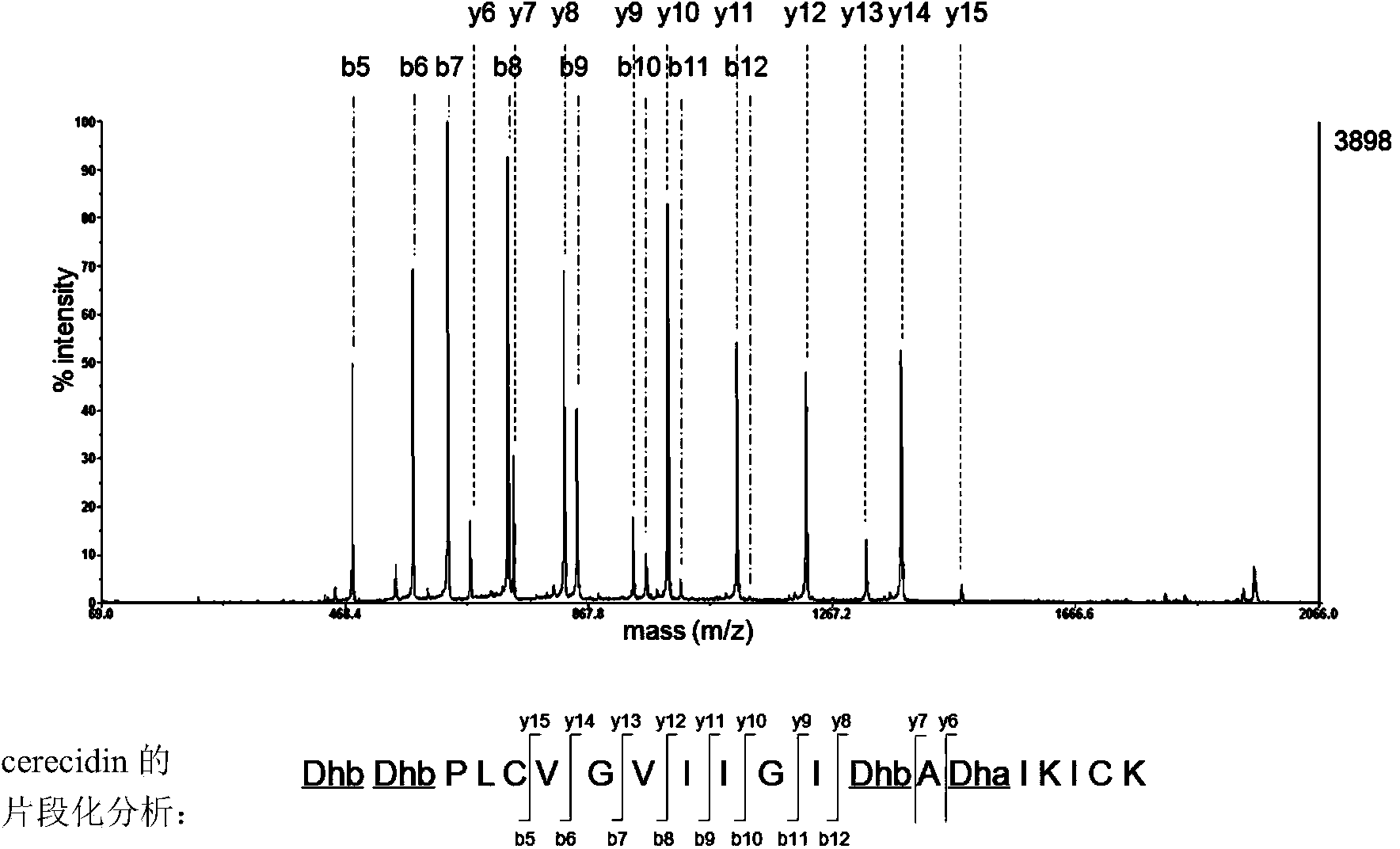
Novel effective cerecidin and application thereof
ActiveCN103483433AIncrease productionThe synthesis method is simpleAntibacterial agentsFungiAntibacterial activityVancomycin
The invention discloses novel effective cerecidin and an application thereof. The cerecidin disclosed by the invention is a modified polypeptide. A synthetic method of the cerecidin disclosed by the invention is simpler compared with the conventional method. Meanwhile, the synthesized cerecidin has relatively high antibacterial activity, the antibacterial effect of the cerecidin for resisting vancomycin enterococcus faecalis V583(VRE) is better than that of nisin, and under a relatively wide pH condition and a high temperature, the cerecidin is relatively stable.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lactobacillus paracasei producing bacteriocin and application thereof
ActiveCN110205266AEnhanced inhibitory effectWon't accumulateBacteriaFood preservationEscherichia coliMinimum inhibitory concentration
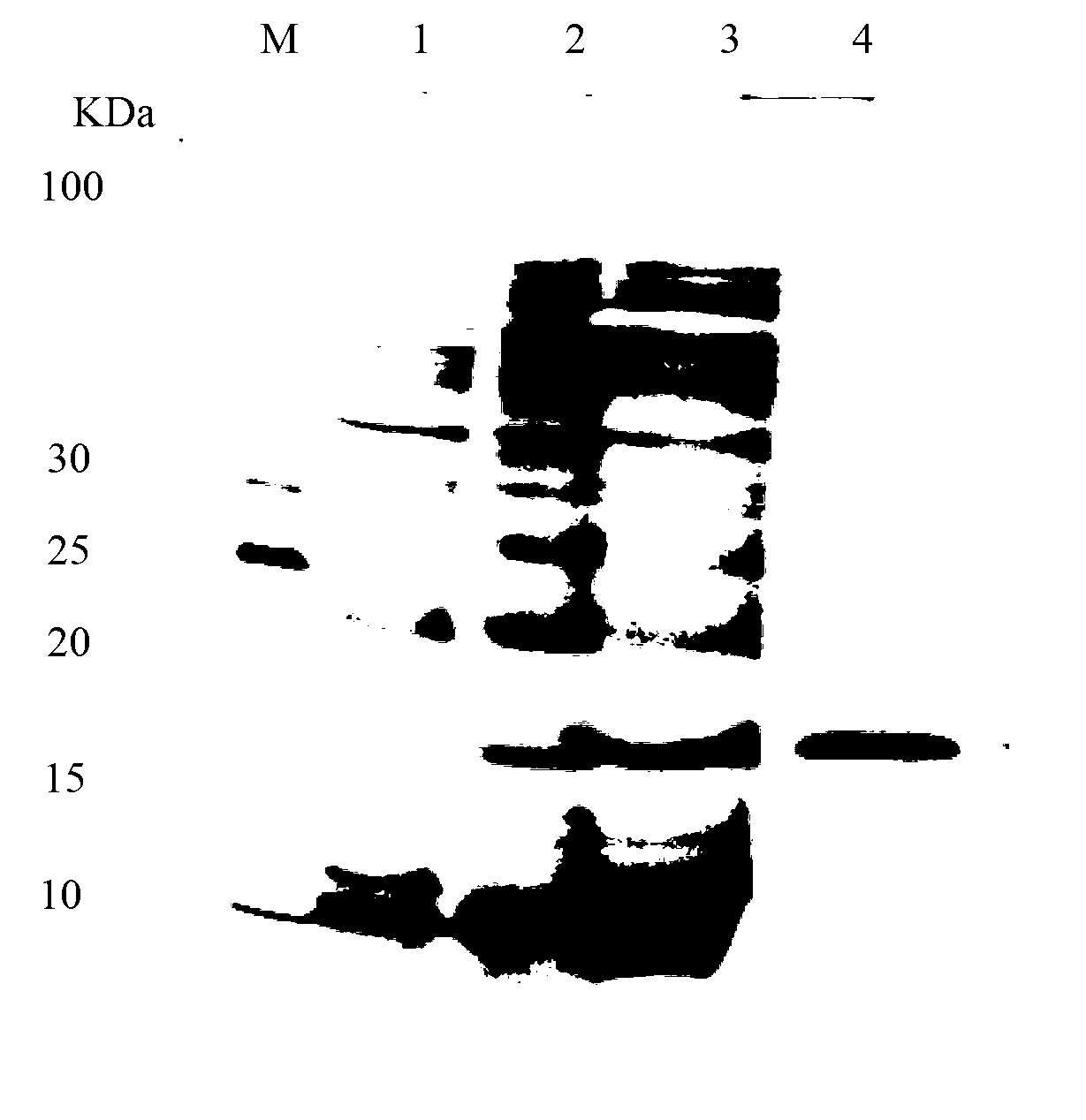
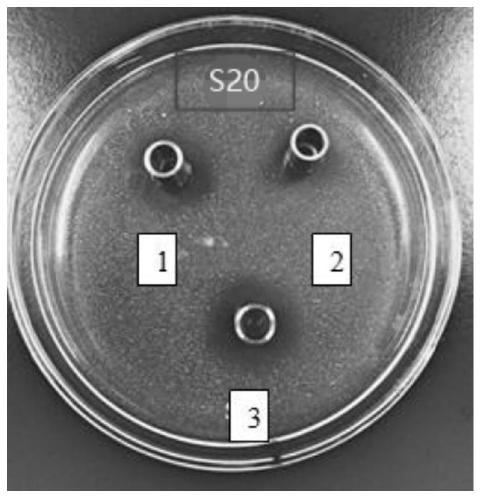
The invention provides a lactobacillus paracasei producing bacteriocin and an application thereof. The present invention relates to a Lactobacillus paracasei S20 strain with a preservation number of CGMCC NO. 17120, The strain is isolated from a Tibetan traditional fermented food-milk block. A crude bacteriocin extract is obtained by extracting from a MRS fermentation supernatant of the strain byusing ammonium sulfate grading deposition. The experiment proves that the bacterial extract produced by the strain has a strong inhibitory effect against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, and the minimum inhibitory concentration measured by a double dilution method is 312 and 625 [mu]g / mL, respectively. The bacteriocin produced by the strain can be hydrolyzed by proteases such as neutralprotease and trypsin, and does not accumulate in the body. The Lactobacillus paracasei and its bacteriocin screened by the invention have broad application prospects in fermented foods.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method for reducing the content of pathogenic organisms present in food materials
ActiveUS20120114790A1Significantly affecting the acidification profile of the fermentationImprove securityMilk preparationDough treatmentMicroorganismMicrobial safety
The present invention relates to a method for reducing the concentration of pathogenic organisms such as Listeria spp. in fermented food products. The method comprises the steps of: (i) providing a food material, (ii) mixing said food material with a starter culture, (iii) mixing the food material with at least one adjunct culture in form of a bacteriocin-producing Pediococcus species, (iv) subjecting the mixture provided in step (iii) to a fermentation process, said fermentation process being conducted at conditions that are sub-optimal for growth of the bacteriocin-producing Pediococcus species in order to provide a limited acidification and allow for a high production of bacteriocin, and obtain a fermented food product. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of bacteriocin-producing Pediococcus species as an adjunct culture for securing microbial safety of fermented food products.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
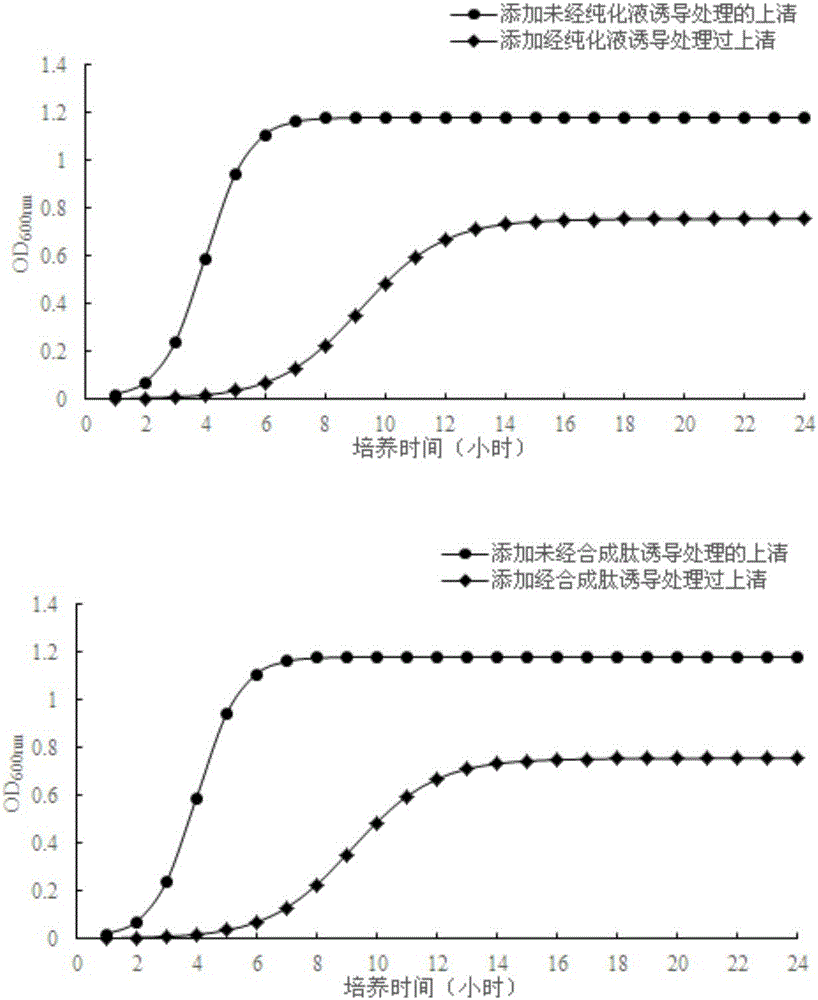
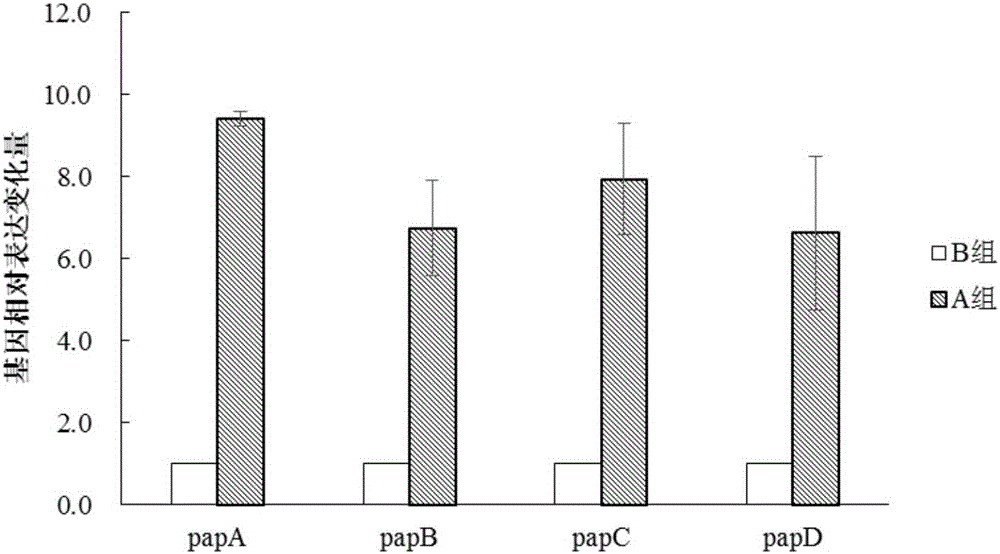
Polypeptide and lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite, application thereof, method for inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin and identification method
ActiveCN106188252AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Relating to the field of microorganism, the invention discloses a polypeptide and a lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite, application thereof, a method for inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin and an identification method. The invention specifically relates to a polypeptide shown as SEQ ID NO:1, a lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite containing the polypeptide and a preparation method, application of the polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite in inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin, a method for inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin and an identification method of bacteriocin-producing lactobacillus plantarum. The polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite can induce lactobacillus plantarum to express bacteriocin, the expression levels of the four genes papA, papB, papC gene and papD related to bacteriocin production in a lactobacillus plantarum gene are respectively increased by 9.41, 6.75, 7.94 and 6.63 times, thus indicating that adding of the polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite can induce the expression of related genes in lactobacillus plantarum.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com