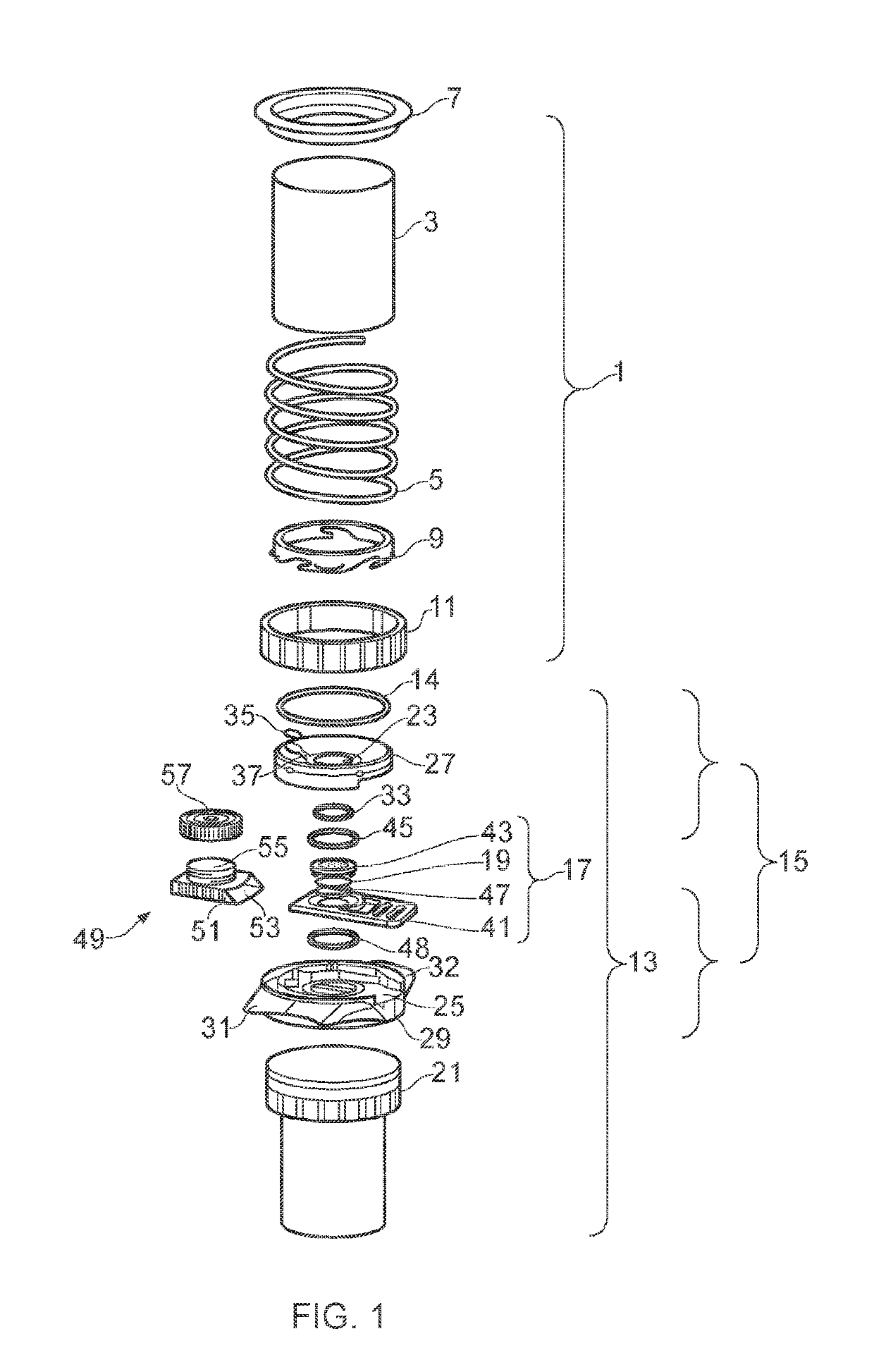
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Easy and low cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
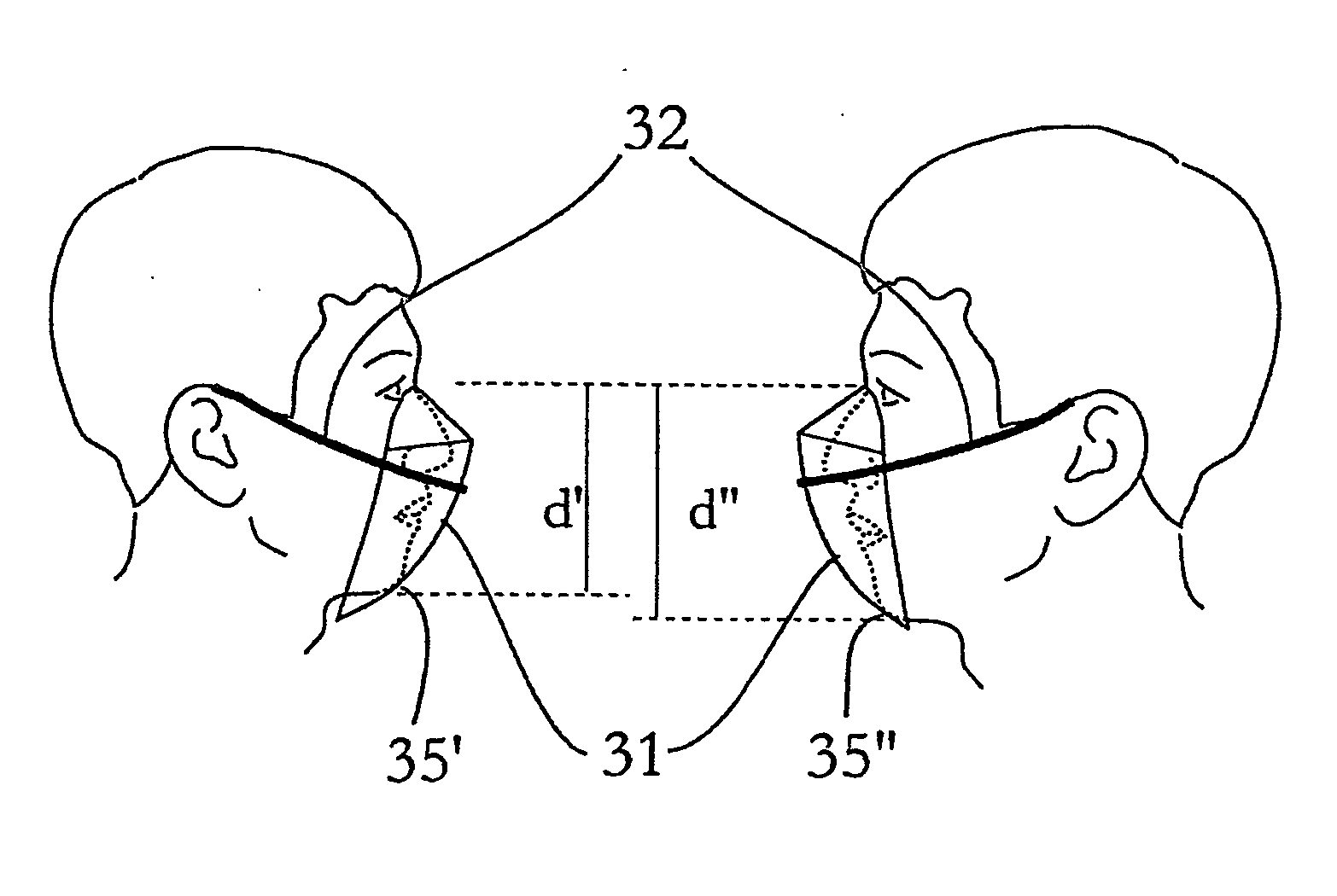
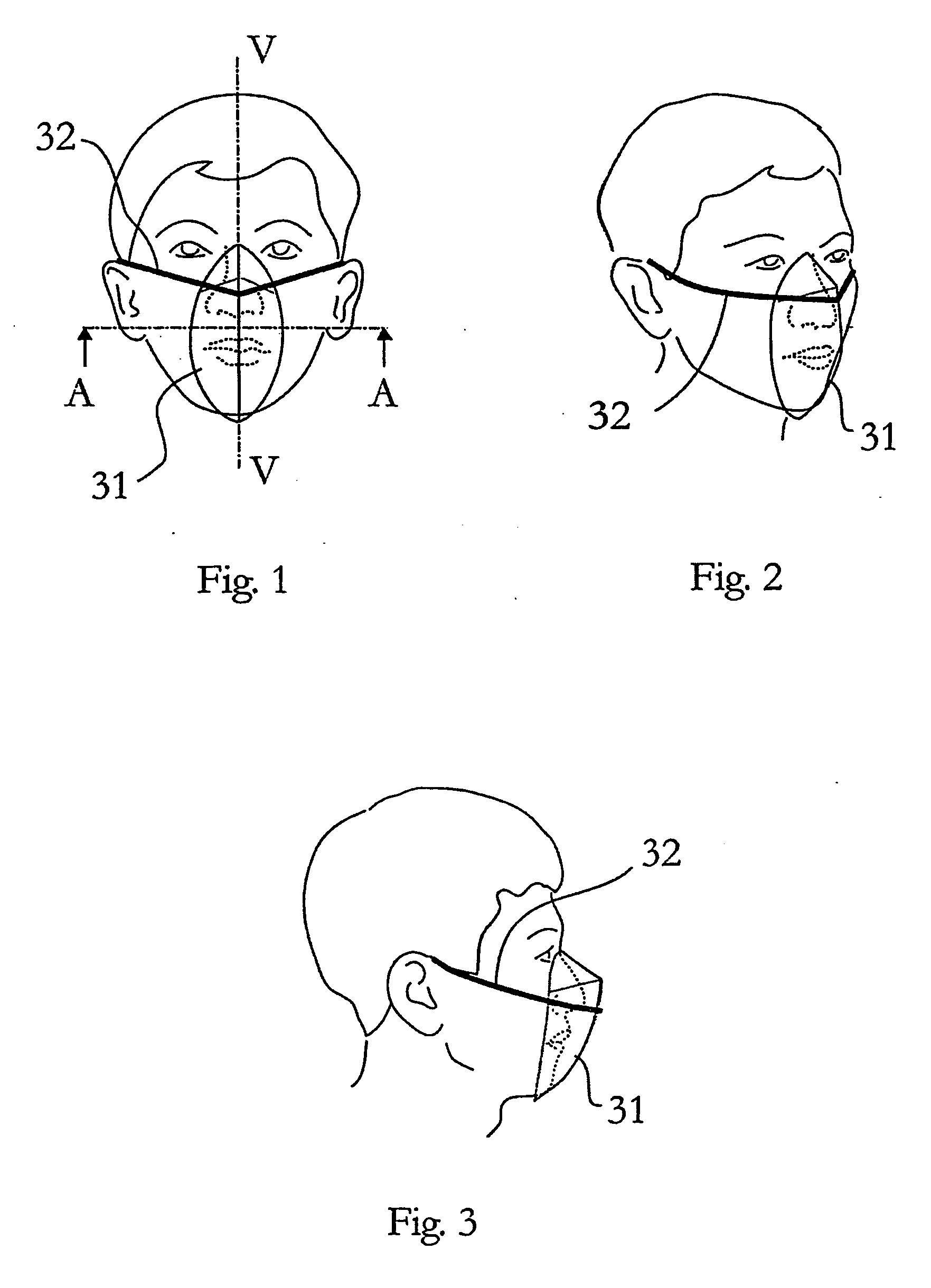
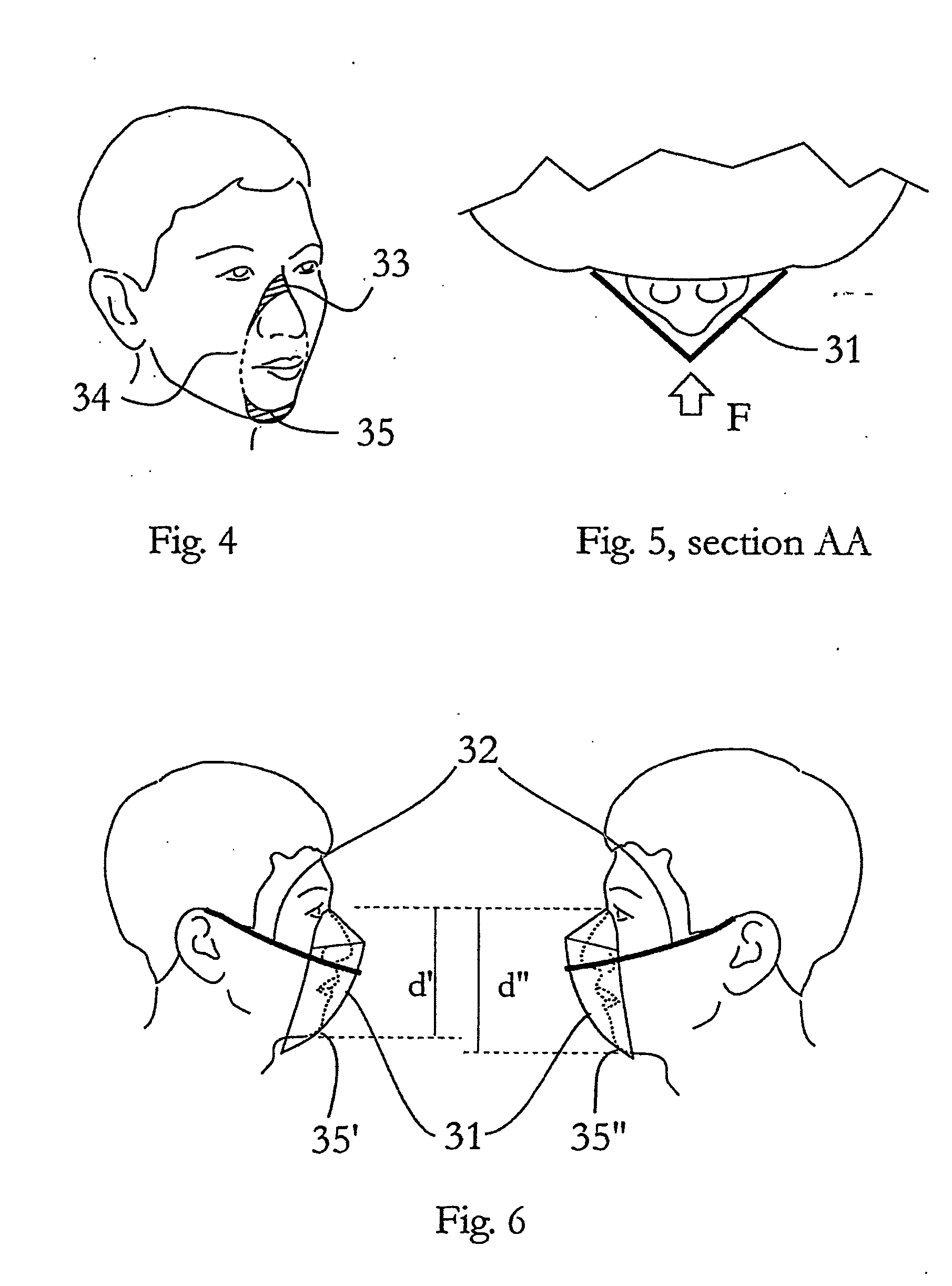
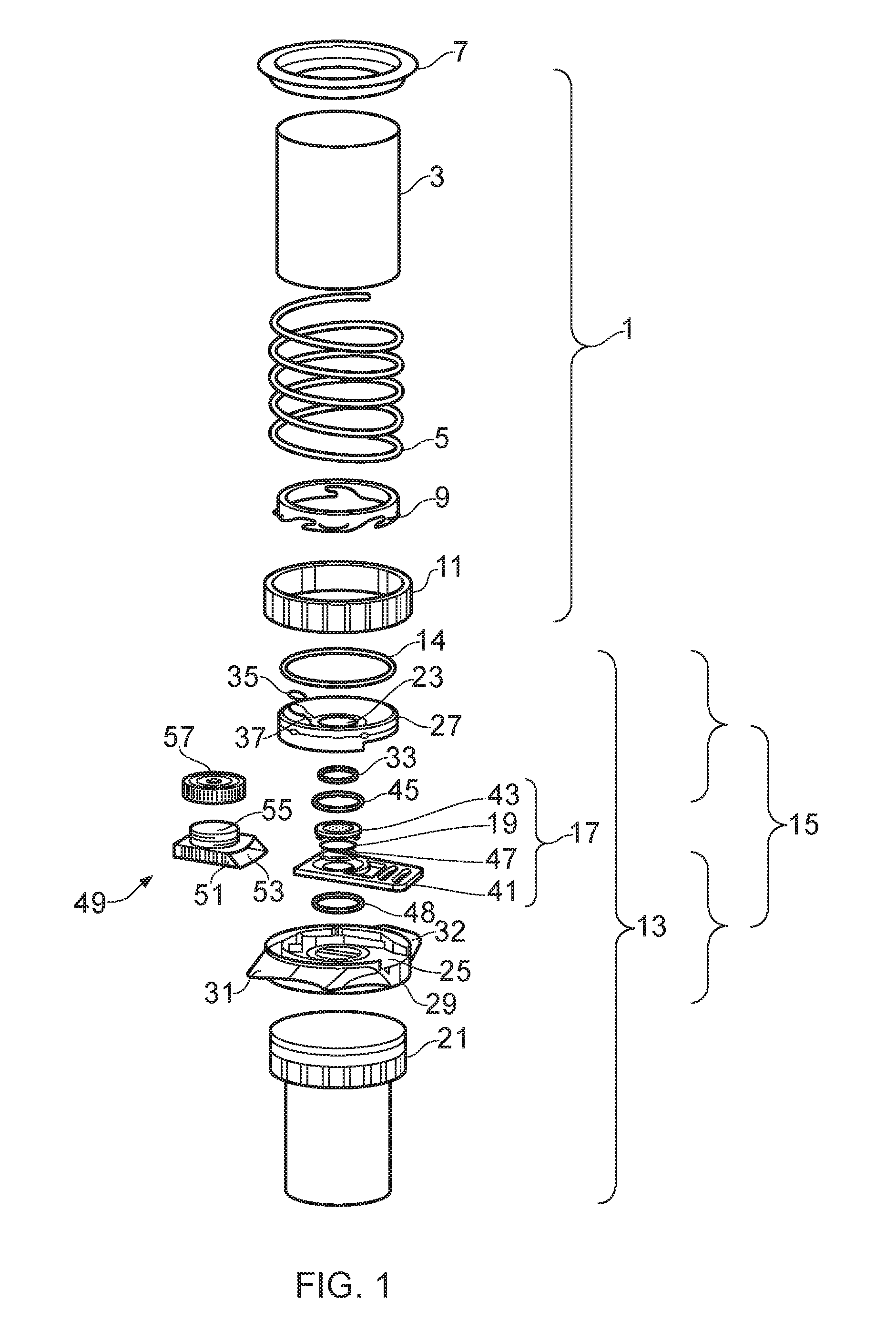
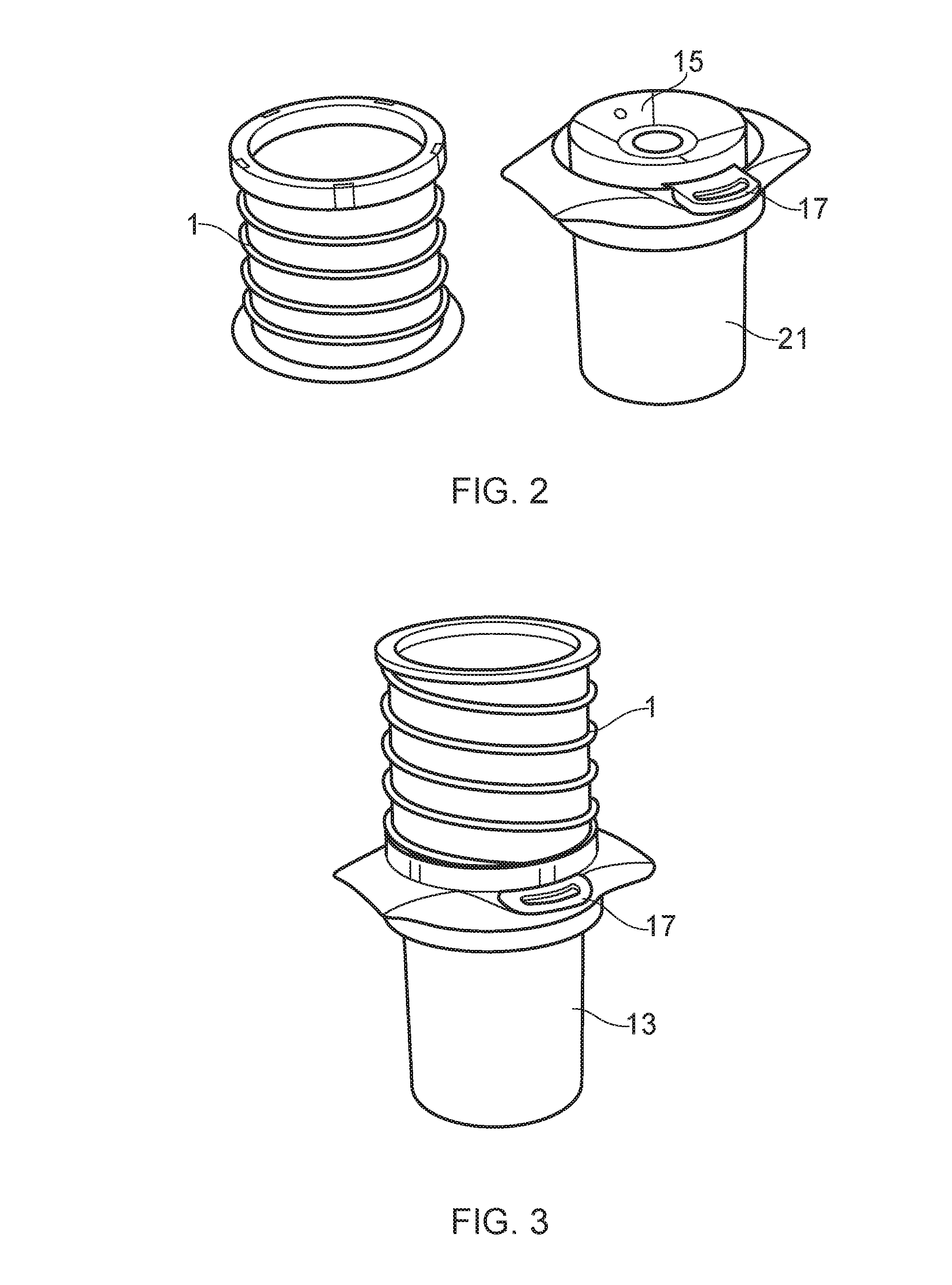
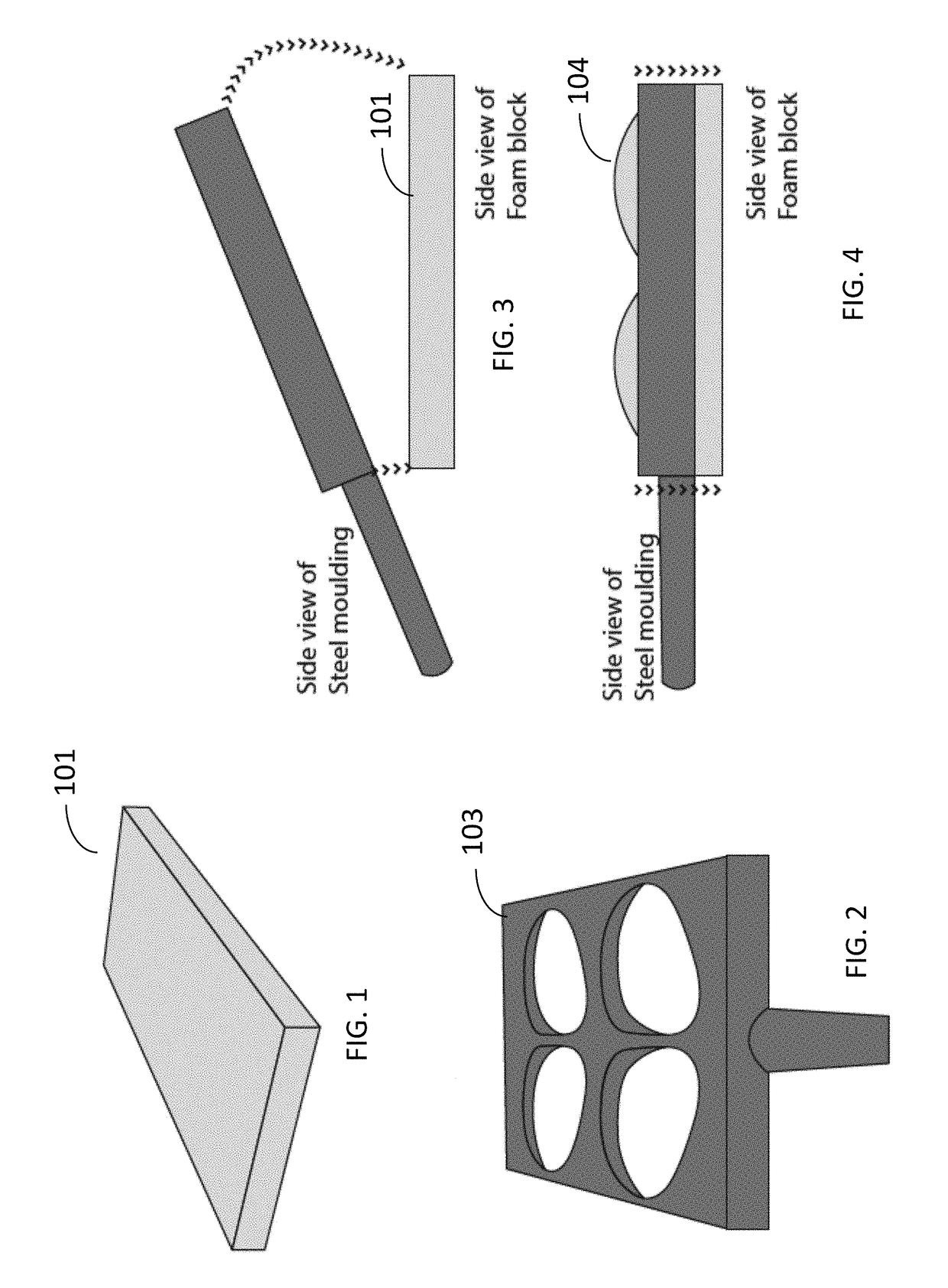
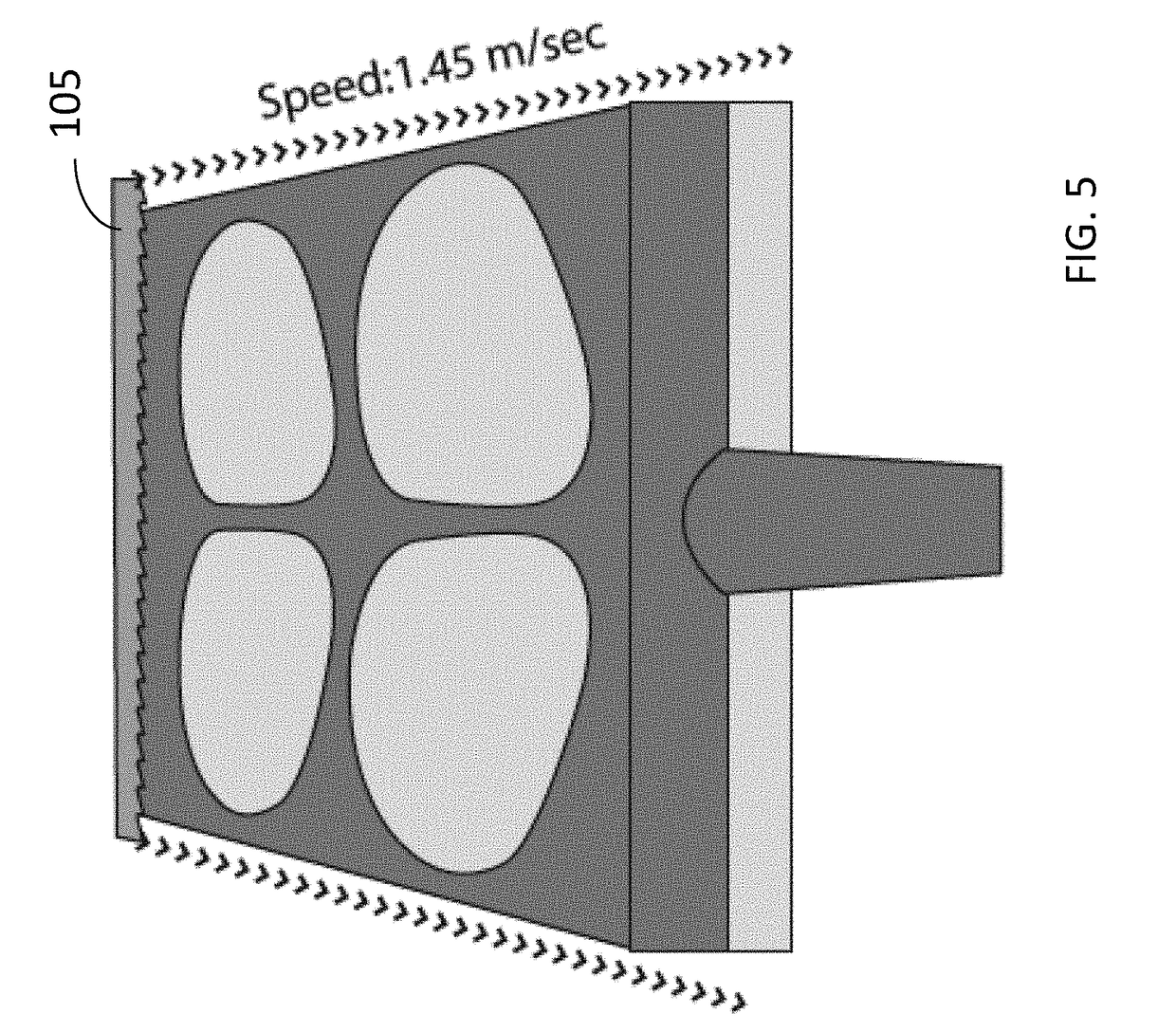
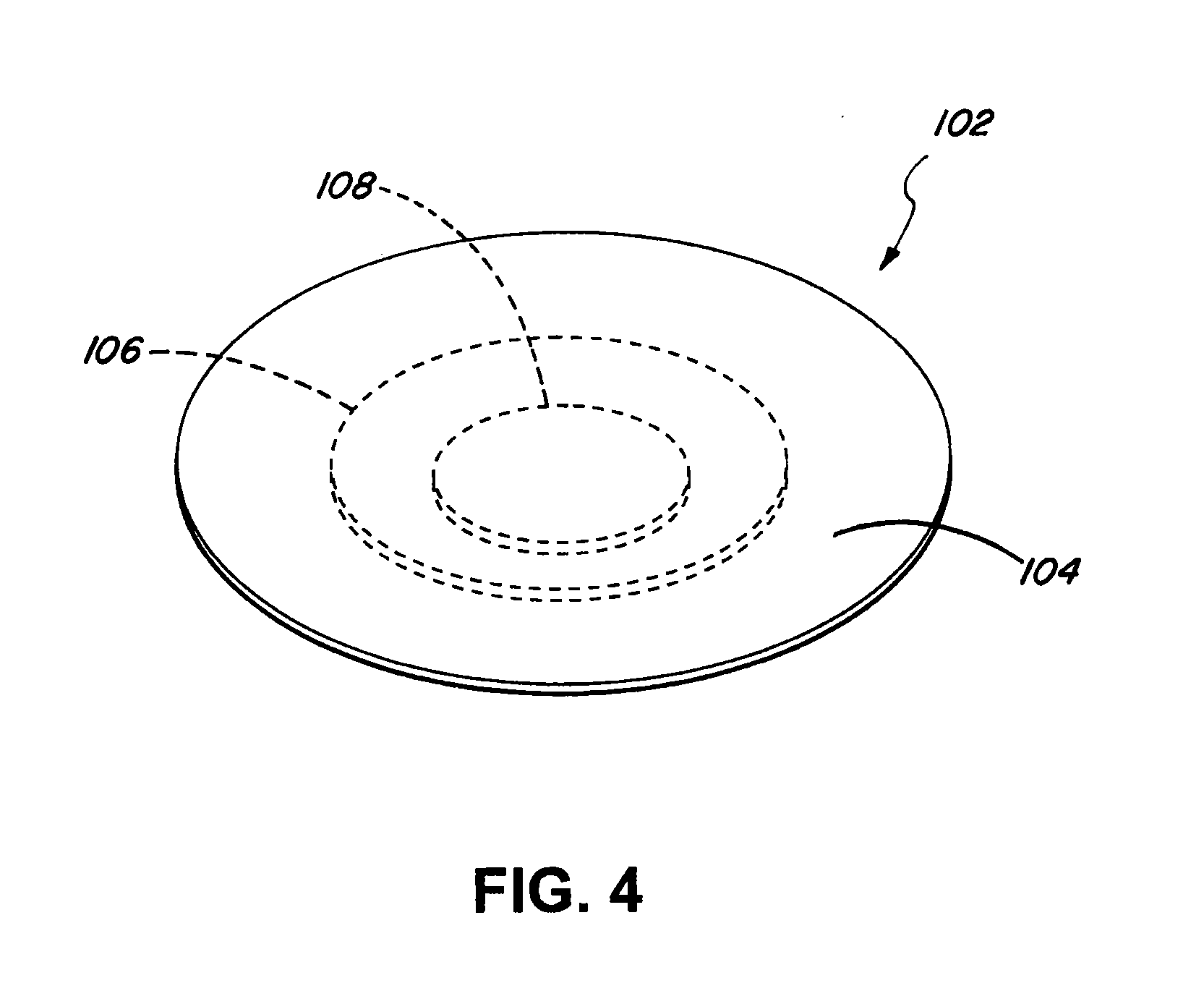
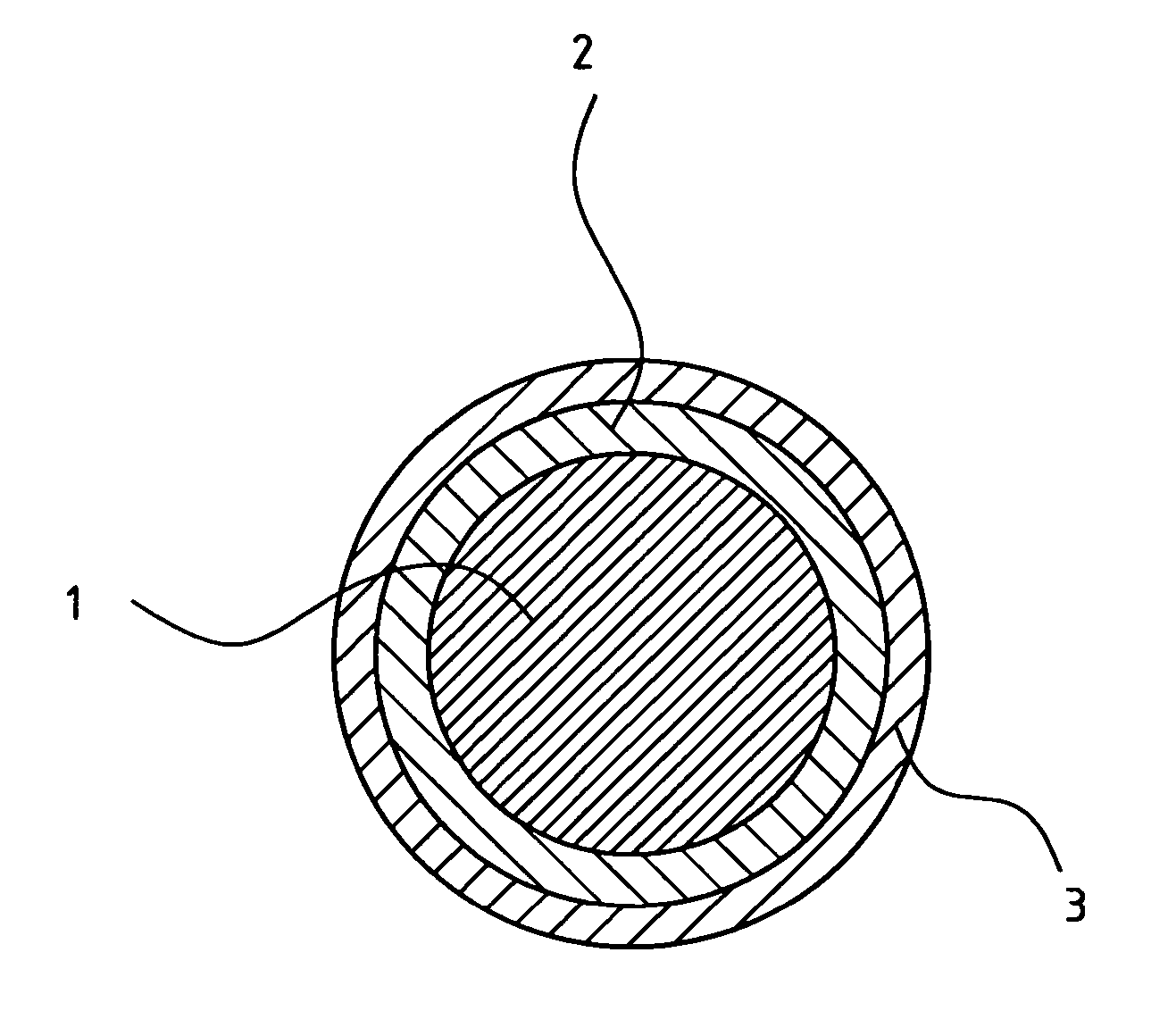
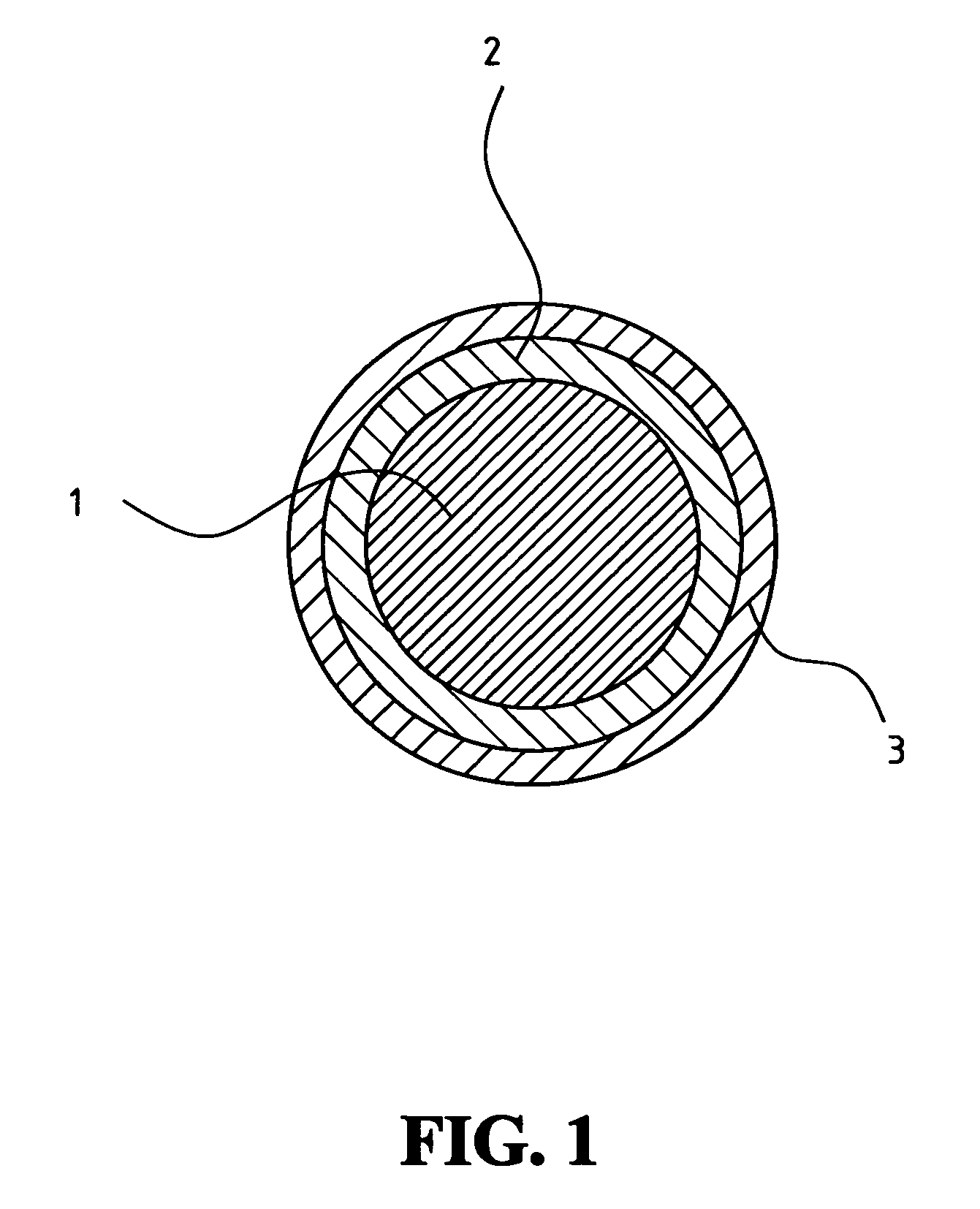
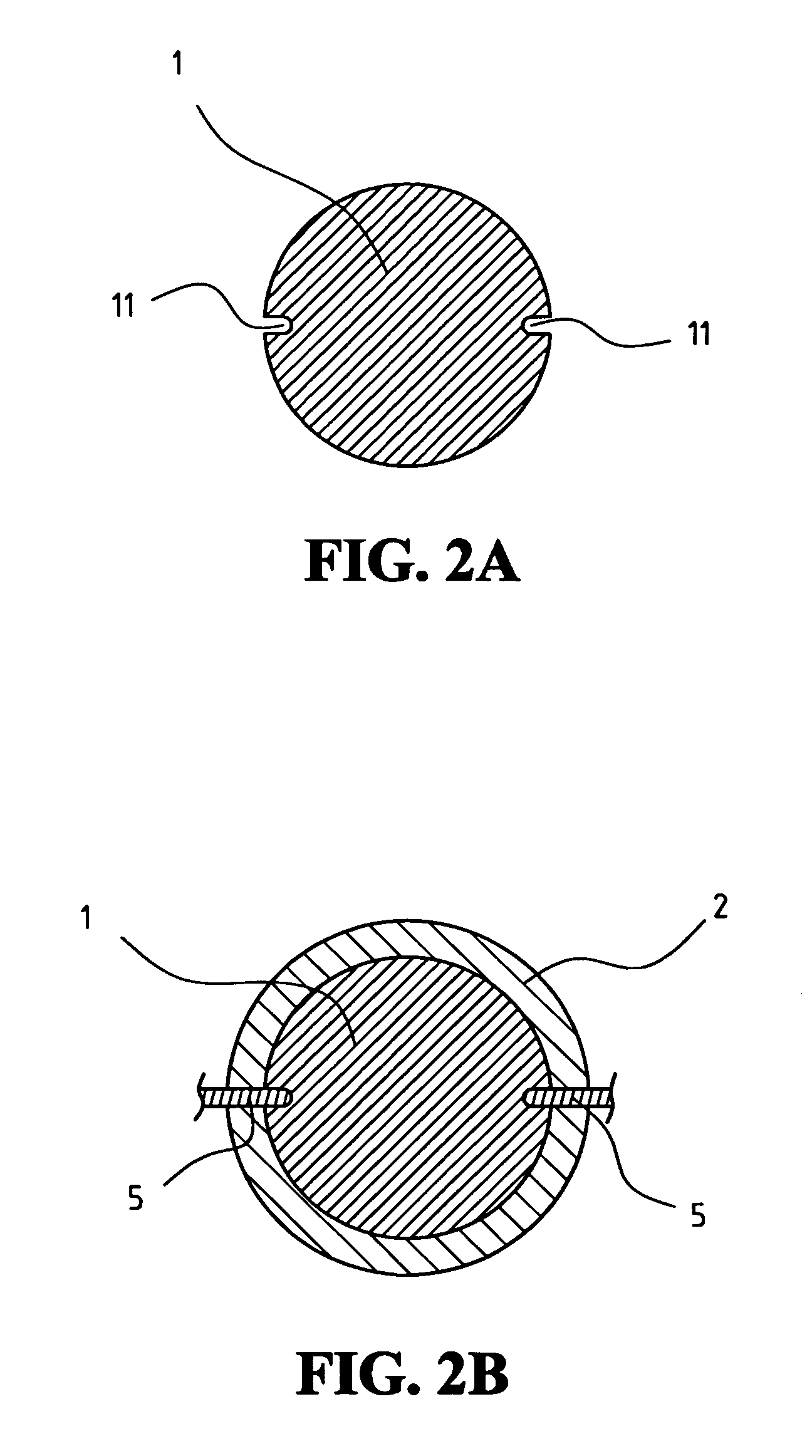
Flat-foldable face-mask and process of making same
InactiveUS20060201513A1Easy to carry and storeEasy to carryBreathing filtersBreathing masksEngineeringBreathing cycle
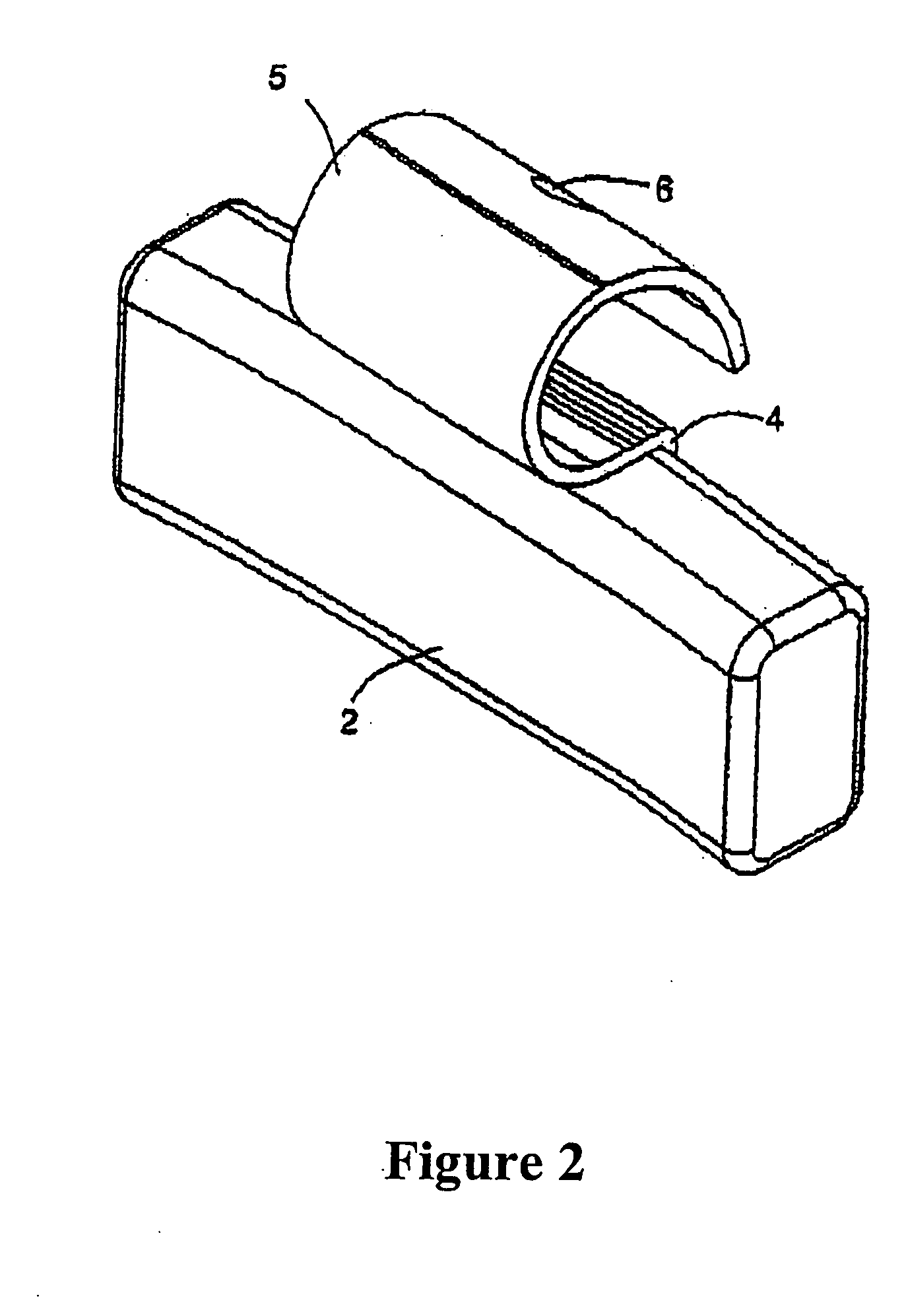
Flat-folded personal respiratory device or a face-mask with a first portion and a second portion (31), connecting with each other along at least one common edge, flat-foldable along the common edge(s), a securing mean (32) responsive to the breathing cycle thereby forming an effective respiratory seal as the wearer inhale and release the respiratory seal as the wearer exhale, and a filtering mean (40) to filter inhaling air. A preferred embodiment includes the securing mean includes an elastic headband providing holding force (F) at a location substantially away from the periphery of the face-mask.
Owner:CHU WA
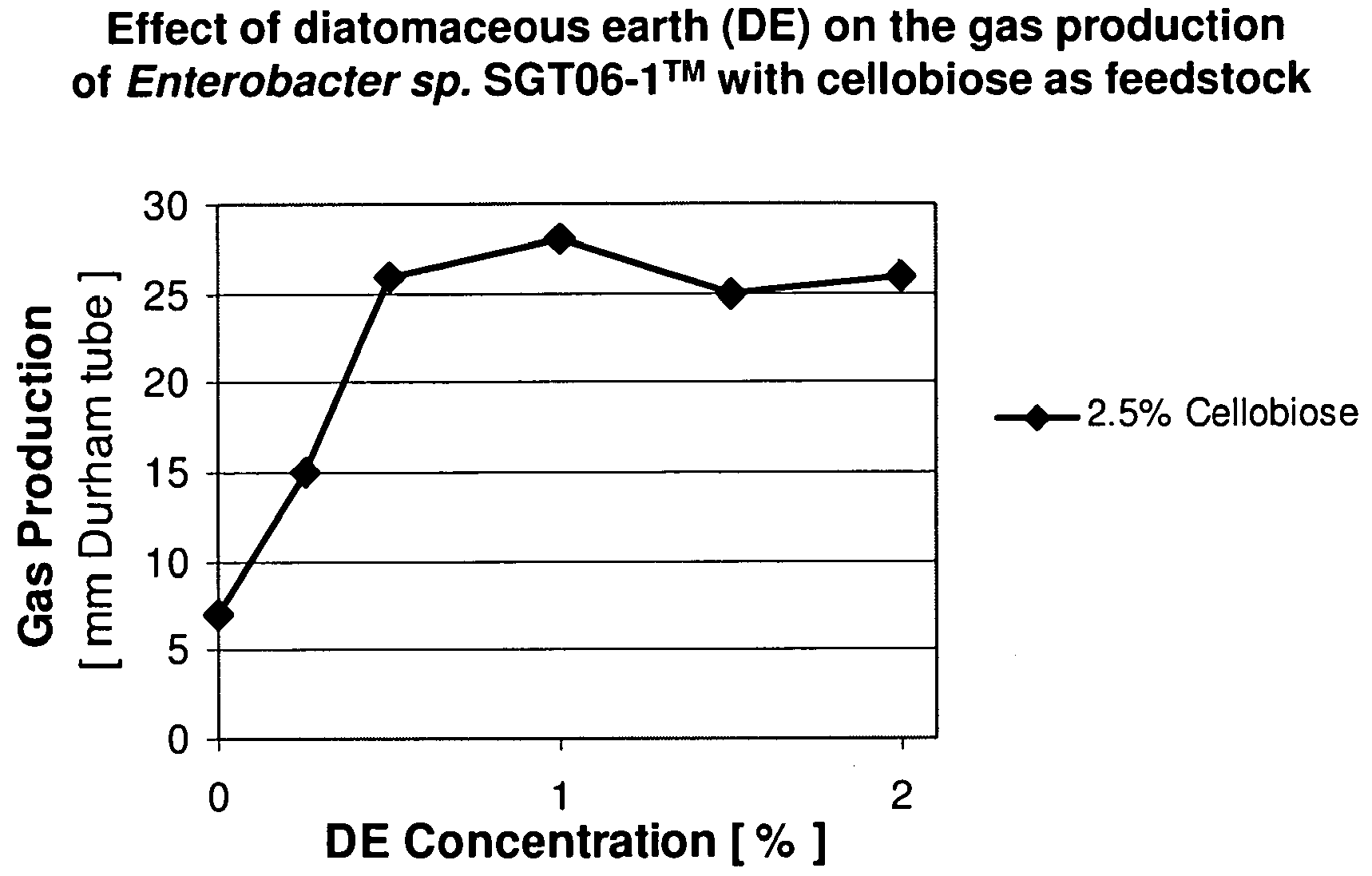
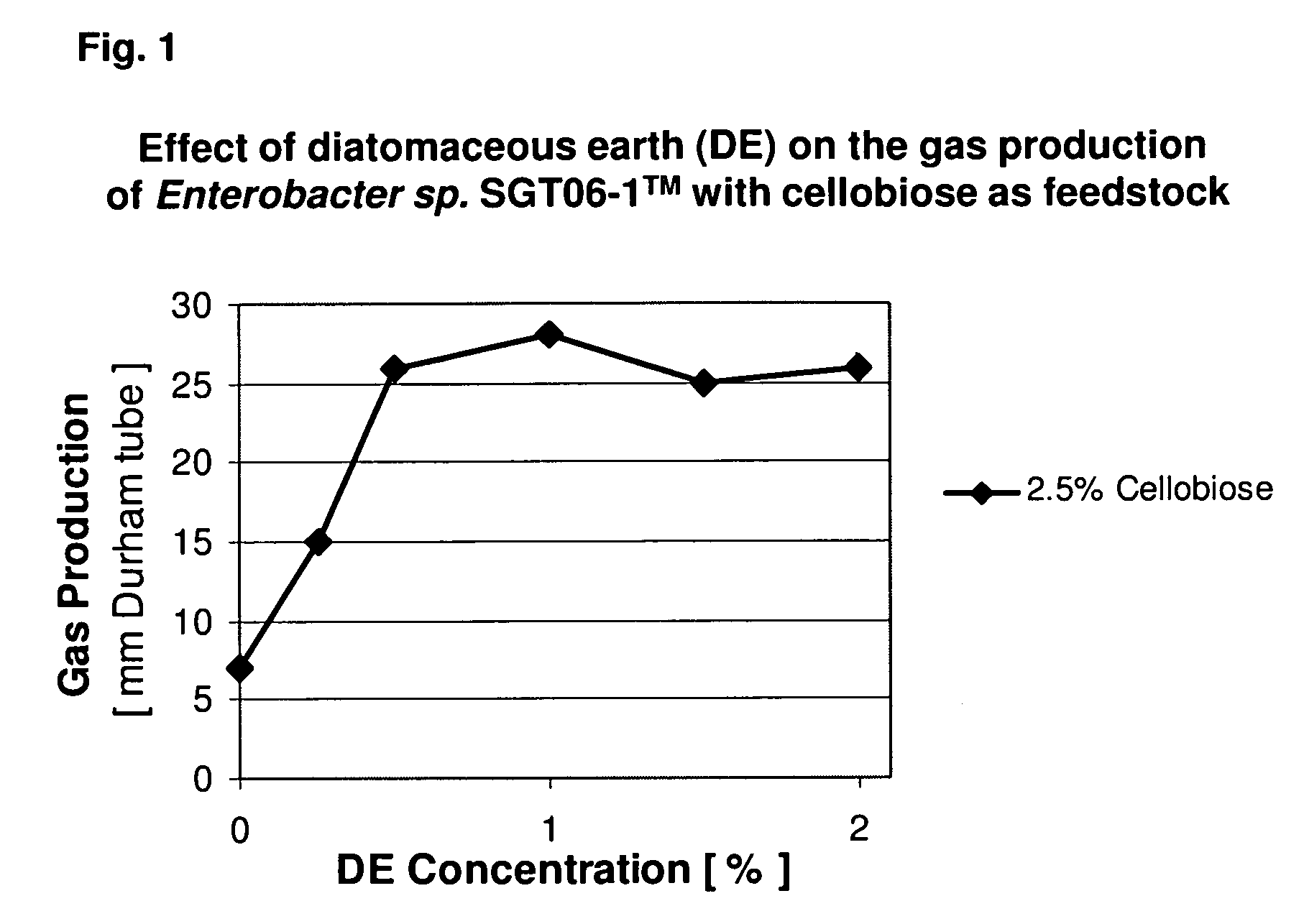
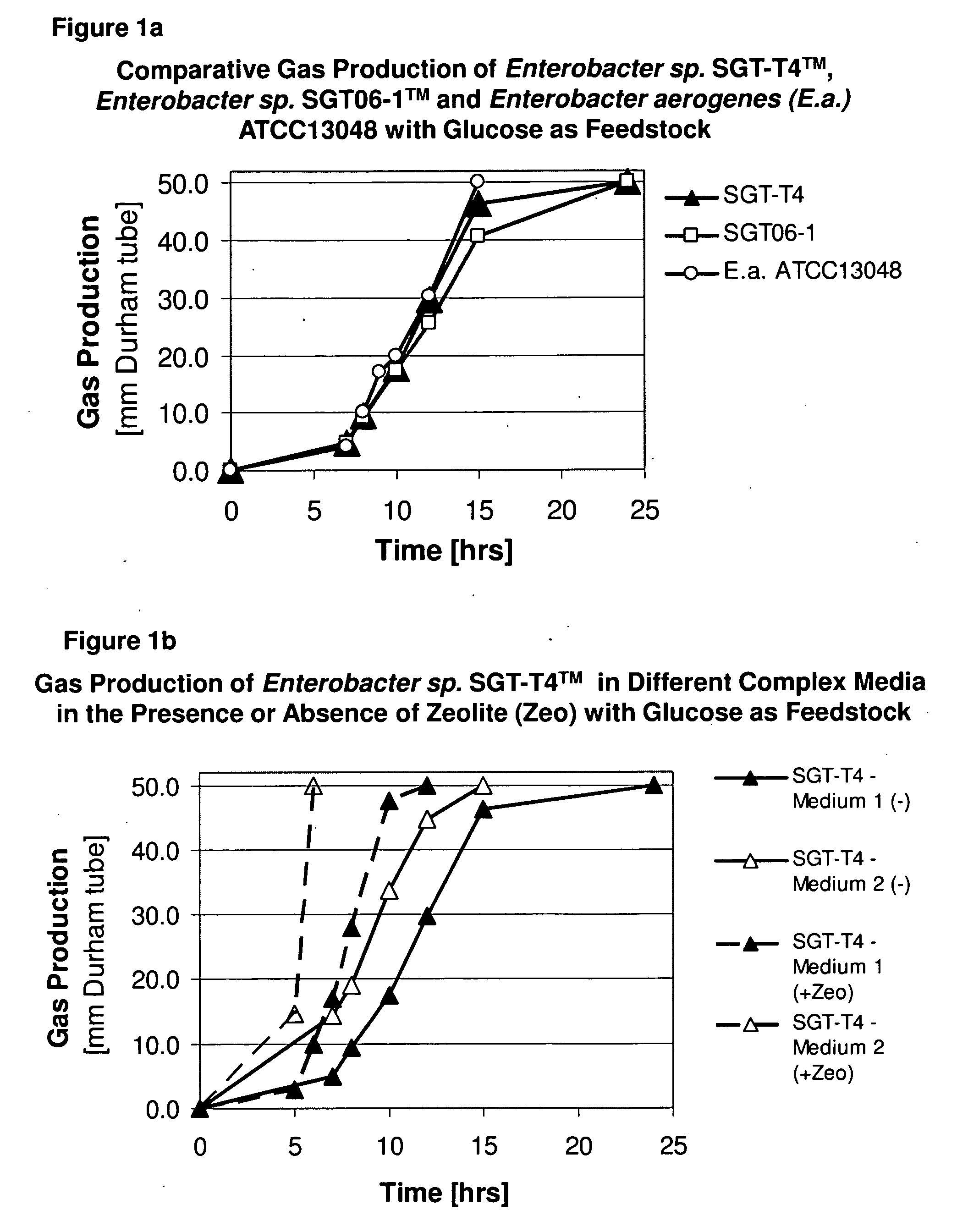
Microorganisms and methods for increased hydrogen production using diverse carbonaceous feedstock and highly absorptive materials
The disclosed invention relates to an isolated hydrogen gas producing microorganism, termed Enterobacter sp. SGT-T4™ and derivatives thereof. Compositions and methods comprising the disclosed microorganisms are also provided. The disclosed invention also relates to a method to increase the hydrogen production rate and yield of hydrogen gas producing microorganism in the presence of diatomaceous earth and other absorptive materials. Further, the disclosure relates to the production of high microalgal biomass and microalgal oils suitable for economical industrial scale bio-diesel production from processed bacterial fermentation wastes as feedstock using the green microalga Chlorella protothecoides.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE GREEN TECH
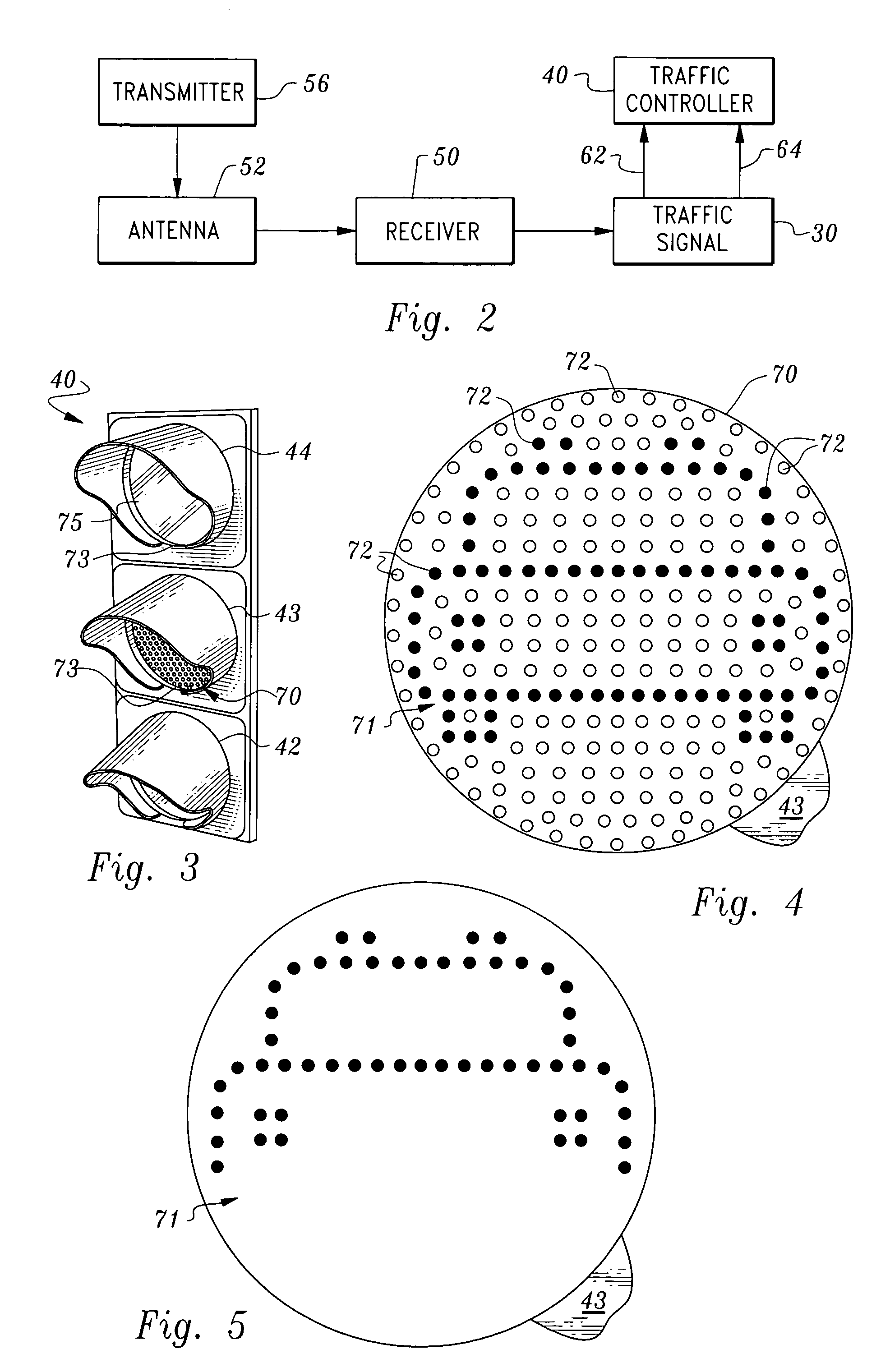
Automated traffic control system having an interactive emergency vehicle warning therein
InactiveUS6987464B2Easy and low-costControlling traffic signalsDetection of traffic movementAir traffic controlColored light
Owner:PEARSON JEREMIAH W
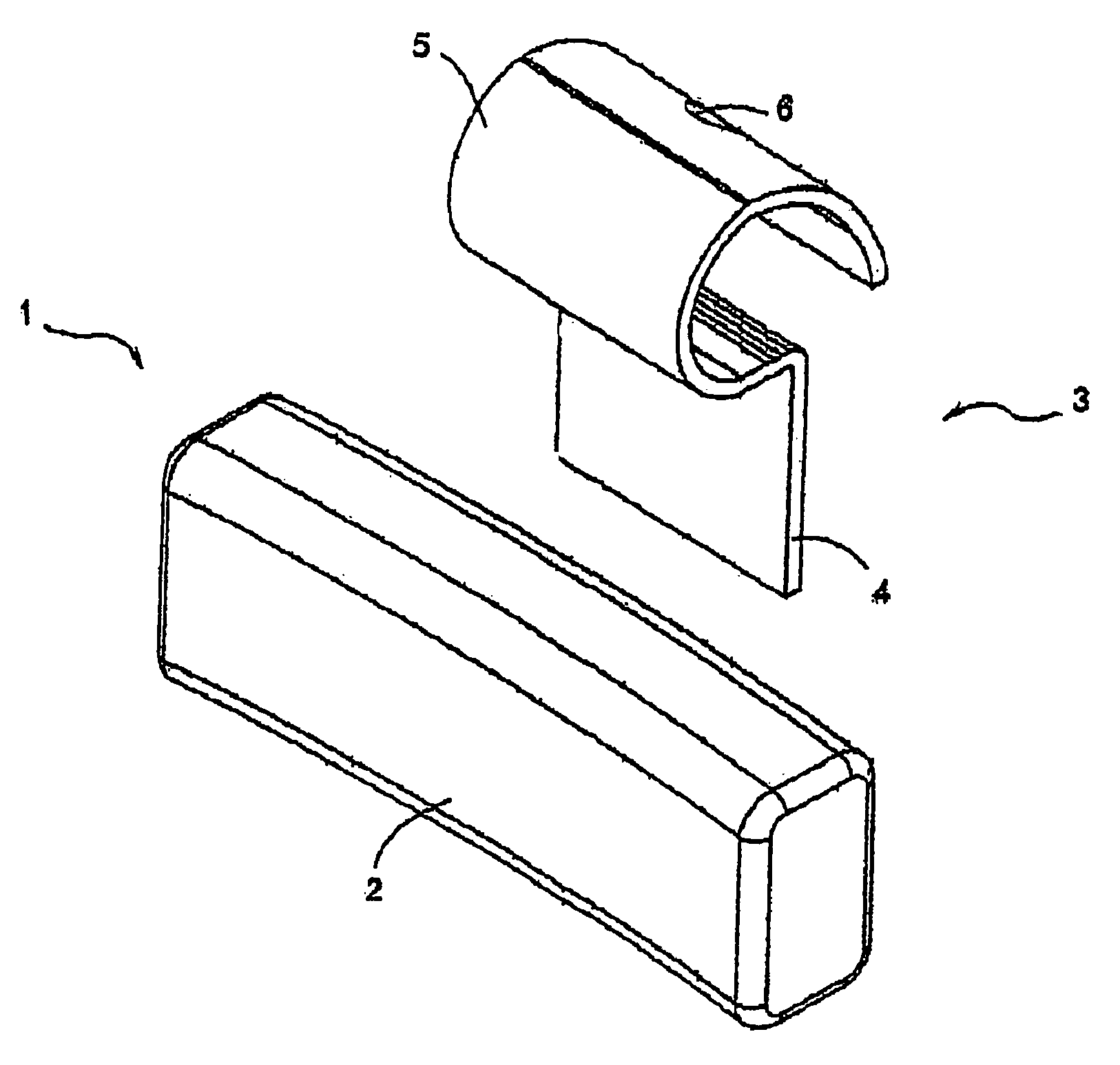
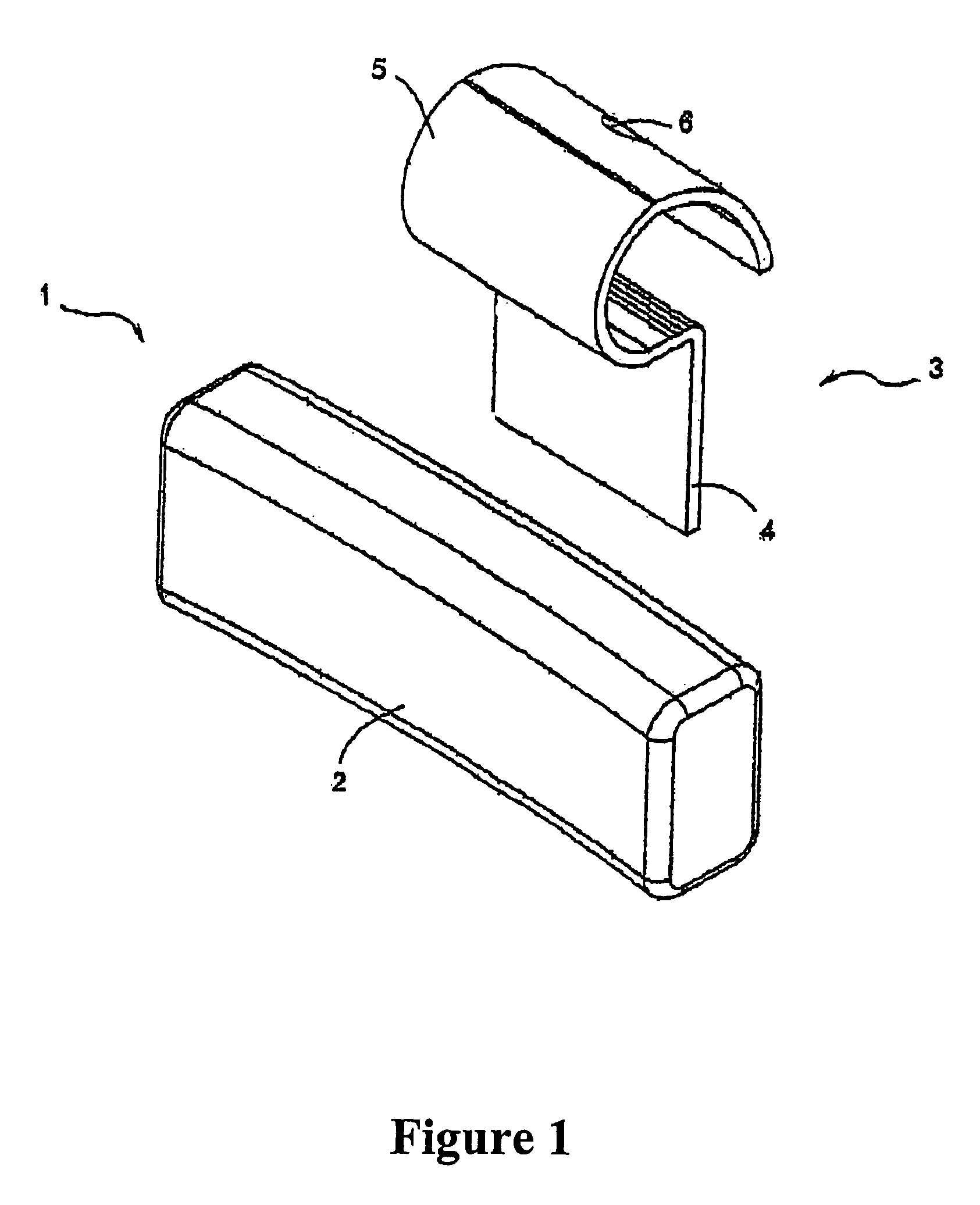
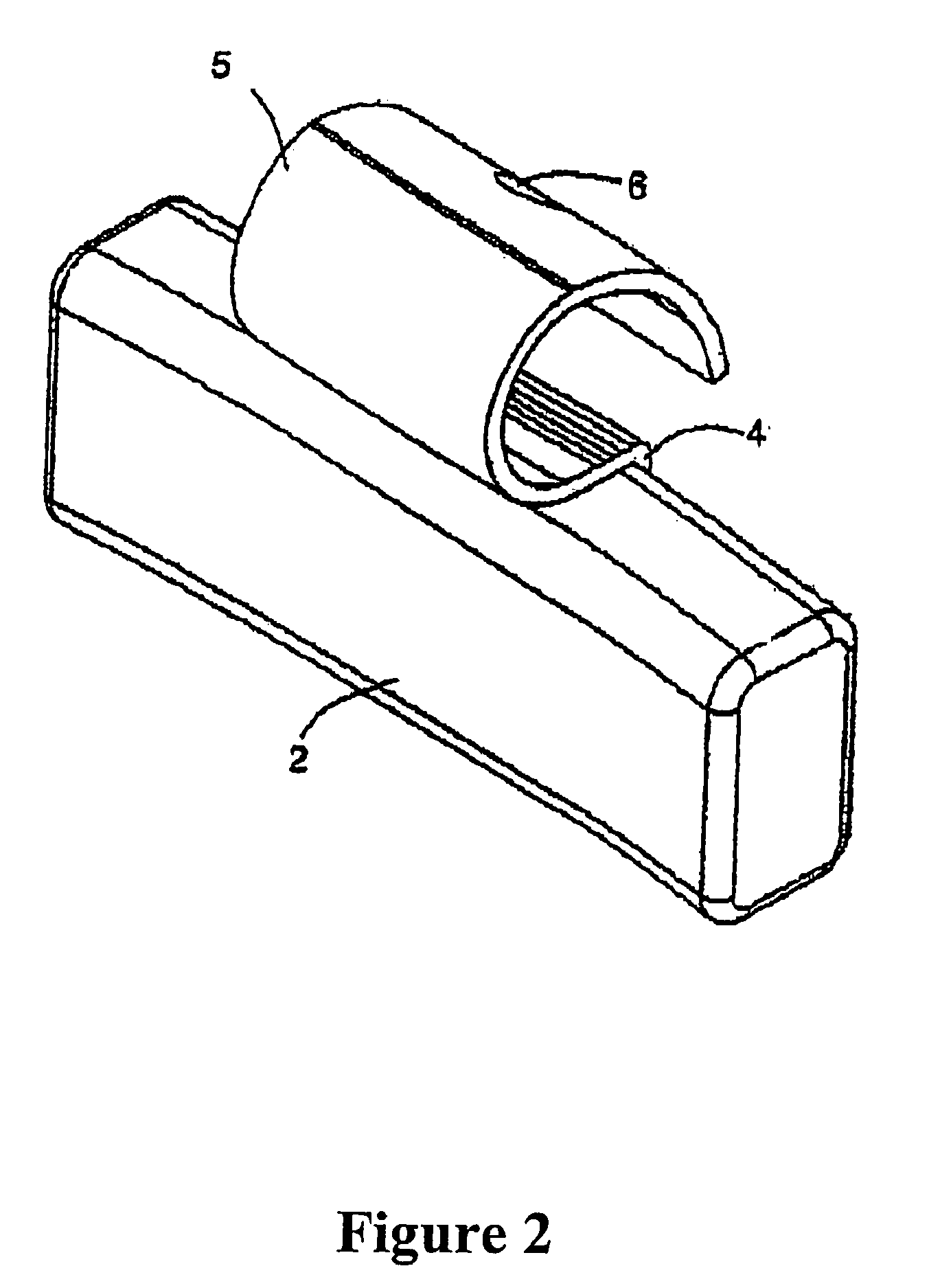
Wheel balancing device
A wheel balancing device of this invention comprising a wheel balancing body having a wheel rim engaging bar made of iron metal or iron-based metal component to be formed in any shape as required. Being provided on one side of the wheel balancing body is an engaging part fixed thereto. The engaging part is composed of an engaging plate having one end engaged and fixed to one end of the wheel rim engaging bar by a locking means and the other end is bent as an upper curve to be locked and fixed to a wheel rim of an automobile. The wheel rim engaging bar and a part of engaging plate are enwrapped by the outer cover plate made of plastic or plastic-contained composition.
Owner:P C PRODS INT
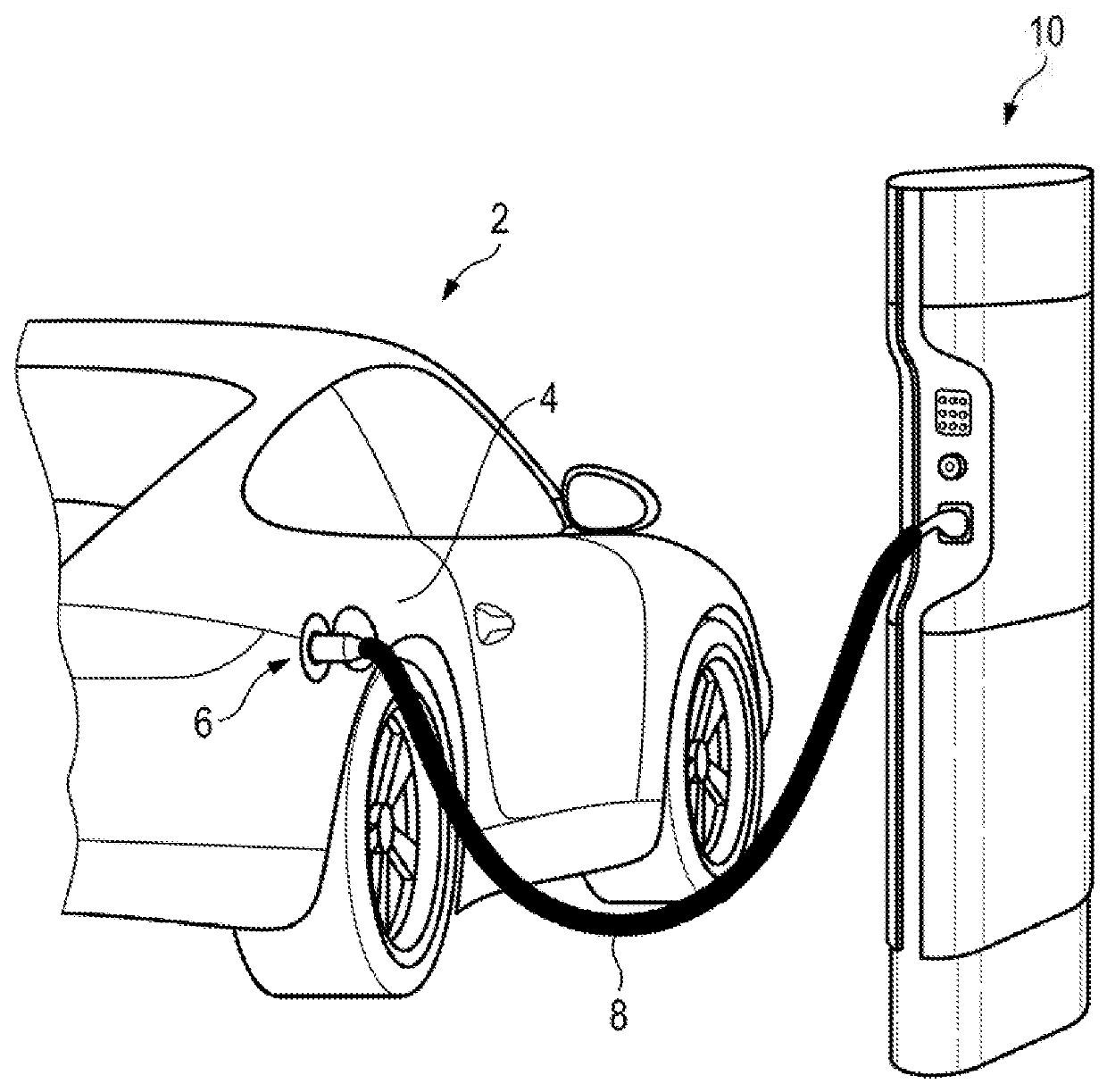
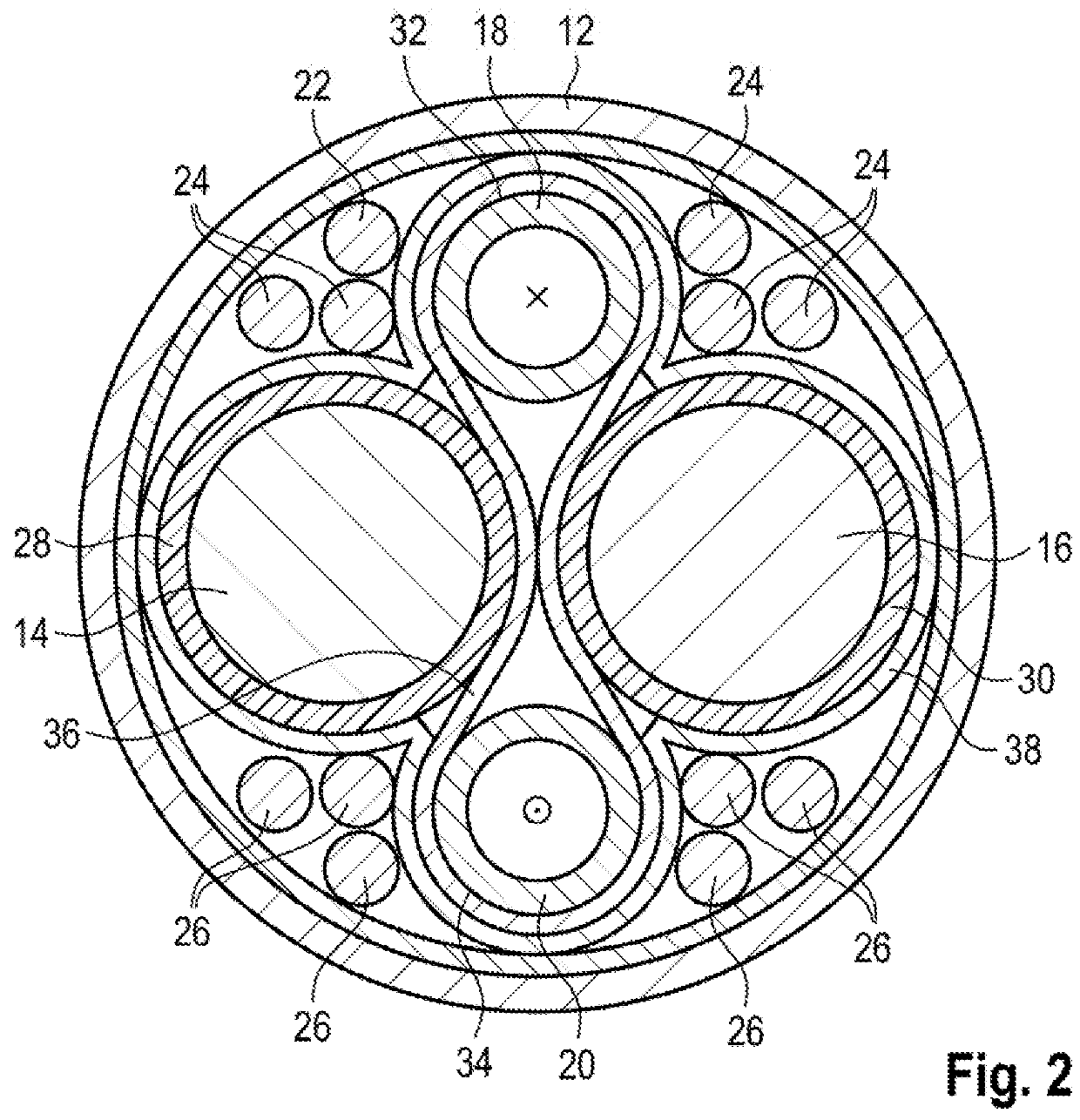
Charging cable assembly
ActiveUS20180277283A1Easy and low-costImprove cooling effectCharging stationsMagnetic/electric field screeningPower flowElectrical conductor
A charging cable assembly for transmitting electrical energy between a power supply station and an electrically drivable vehicle with a charging cable outer sheathing, in which at least one current conductor cable with a current conductor outer sheathing and at least one coolant line with a heat transfer surface are arranged, there being provided at least one heat transfer layer, which lies at least partially against the heat transfer surface and the current conductor outer sheathing.
Owner:DR ING H C F PORSCHE AG
Antireflection structure and optical material comprising the same
An antireflection structure having on its surface an antireflection face having fine concaves or convexes, wherein 10 to 90% of the effective area of the antireflection face is accounted for by the concaves or convexes. The concaves or convexes include basic forms which may be connected to each other. The basic forms have an average length of 30 nm to 200 nm and an average diameter of 80 nm to 400 nm, and the basic forms are substantially irregularly arranged on the antireflection face. The antireflection structure can be used as an optical member to effectively prevent light reflection. For example, in the case of an optical member for information display such as display devices, the visibility can be improved, and, in the case of a light receiving optical member such as solar battery panels, the efficiency for light utilization can be improved.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Thermoplastic resin composition, cellulose-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition, method for producing cellulose-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition, cellulose-reinforced resin molded article, and method for producing cellulose-reinforced resin molded article
PendingCN108834420AEasy and uniform dispersionHigh mechanical strengthCelluloseUltimate tensile strength
Provided are: a thermoplastic resin composition containing 10-70 parts by mass of cellulose per 100 parts by mass of a thermoplastic resin and containing an organic peroxide, wherein the resin comprising the thermoplastic resin composition has a tensile strength of 40 MPa or higher as measured in accordance with JIS K7161; a cellulose-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition; a cellulose-reinforced resin molded article; and a method for producing a cellulose-reinforced resin composition or molded article.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
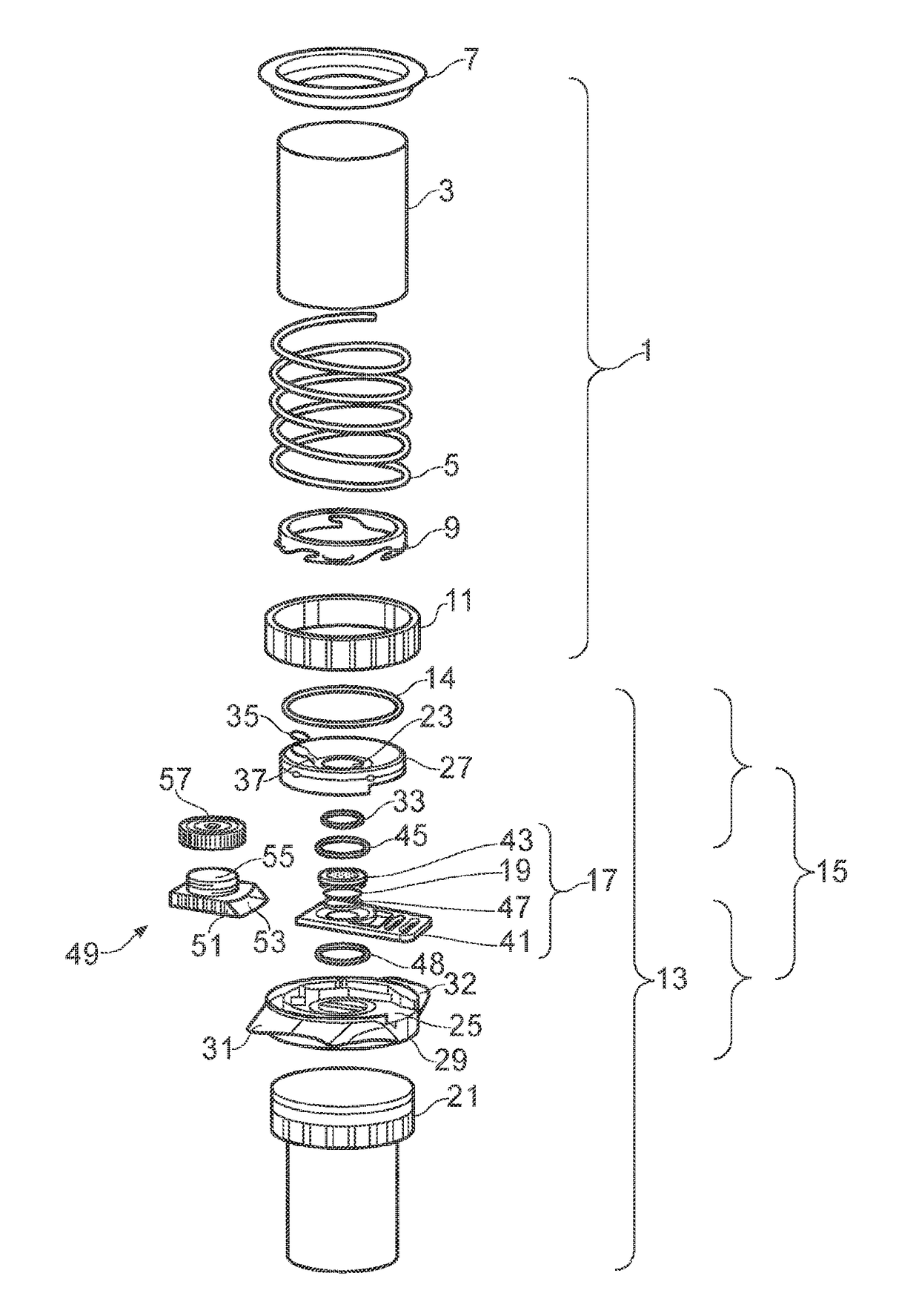
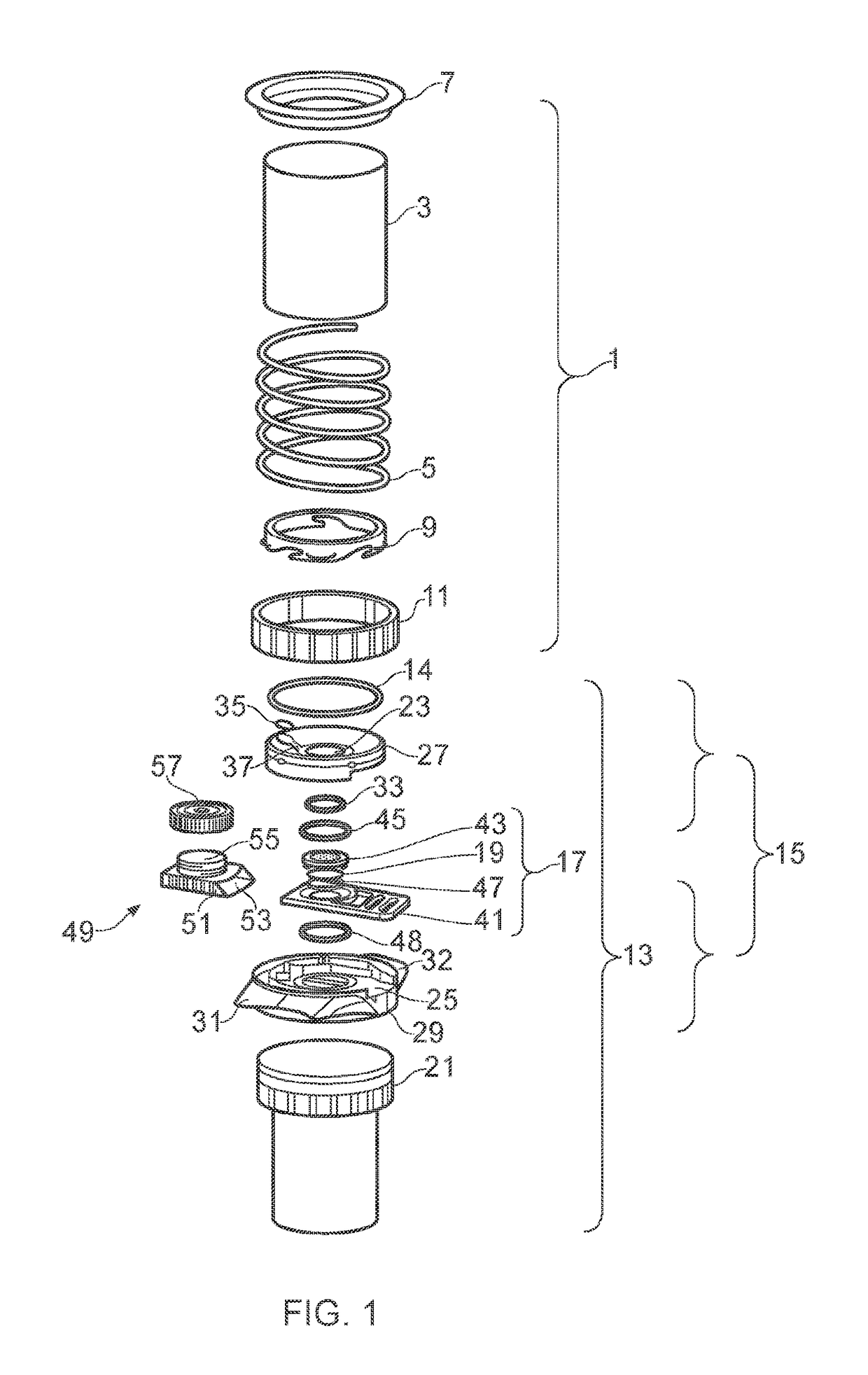
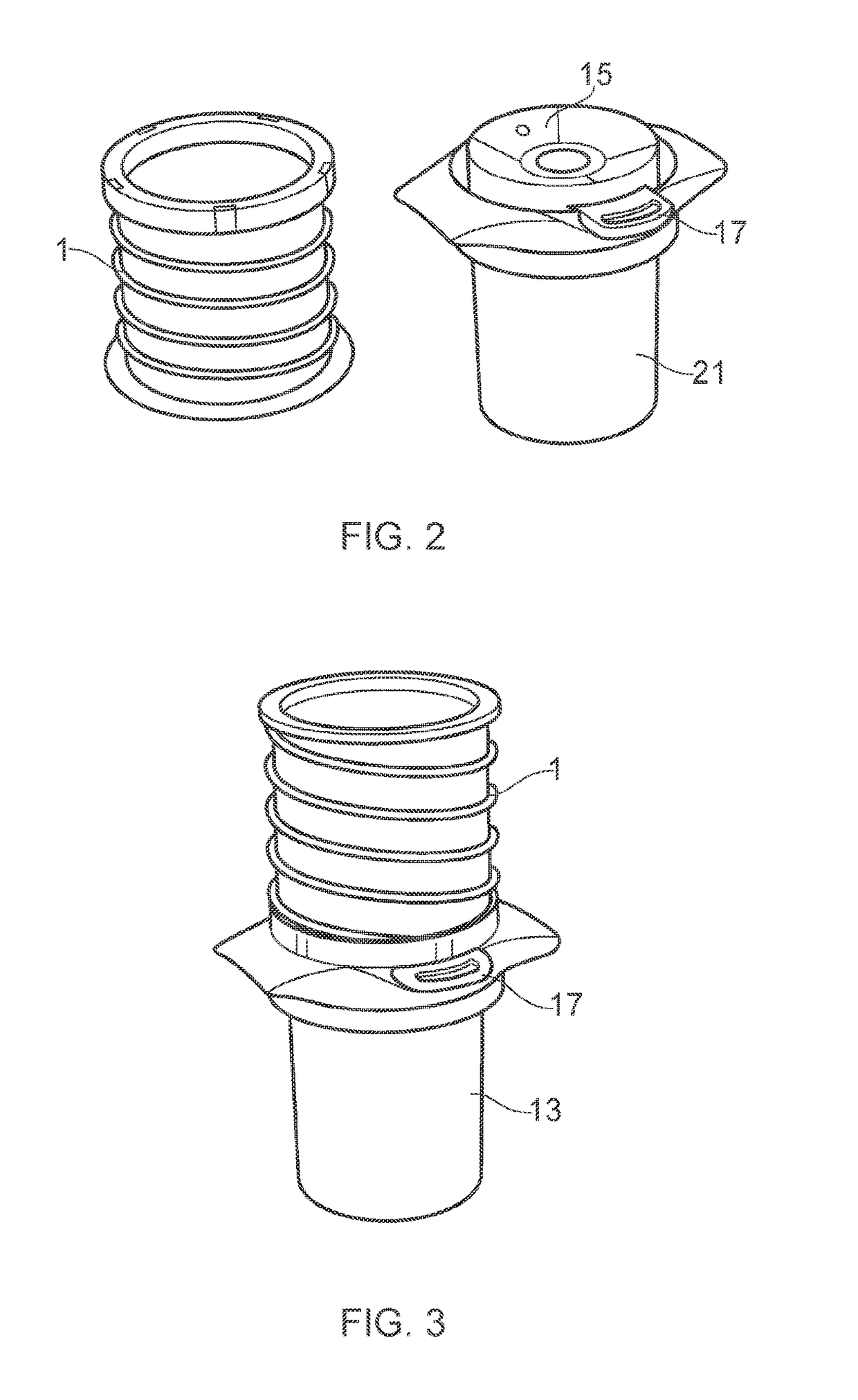
Biological fluid filtration assembly
InactiveUS20160223442A1Easy and efficient assemblyEasy and low-cost collectionMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFiltrationBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to biological fluid filtration assemblies and to methods of using such assemblies. The biological fluid filtration assembly has a filtration device for filtering a biological fluid sample and a storage unit, the storage unit having a body configured to engage with a removable filter cartridge of the device such that, when engaged, the filter of the filter cartridge is sealed within the body of the storage unit.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Wear indicator for a roller
InactiveUS7175580B2Low costEasy to processTobacco preparationLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringFilter material
A roller for a device for processing a filter material ribbon in the tobacco-processing industry. The roller comprises a roller core and a covering for the roller core. The roller has at least one wear indicator operatively arranged for indicating wear of the covering.
Owner:HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG
Thermal interface material
ActiveUS20150036363A1Robust in useFacilitate increase of thicknessPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesContact pressureHeat conducting
There is provided a thermal interface material, TIM, a thermal interface application comprising such a TIM, and corresponding methods for providing the material and the thermal interface. The TIM comprises a TIM layer in which an activable shrinkage material is distributed, such that upon activation of the shrinkage material the thickness of the TIM layer is increased. In the thermal interface application, where the TIM (400) is arranged between a heat generating component (20) and a heat conducting element (30), the increase in thickness of the TIM layer is utilized to increase the contact pressure on mating surfaces. The TIM is sandwiched between the heat generating component and the heat conducting element before the activation of the shrinkage material, and the distance (h) between the heat generating component and the heat conducting element is restricted such upon activation of the shrinkage material, the restricted maximum height (h) between the heat generating component and the heat conducting element in combination with the TIM increasing the thickness of the TIM layer, the contact pressure on the mating surfaces is increased.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Device and method for printing a thixotropic medium onto a PCB
InactiveUS20150283637A1Avoid quality problemsImprove statusWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesElectrical and Electronics engineeringHead parts
Owner:ASM ASSEMBLY SYST SINGAPORE PTE LTD
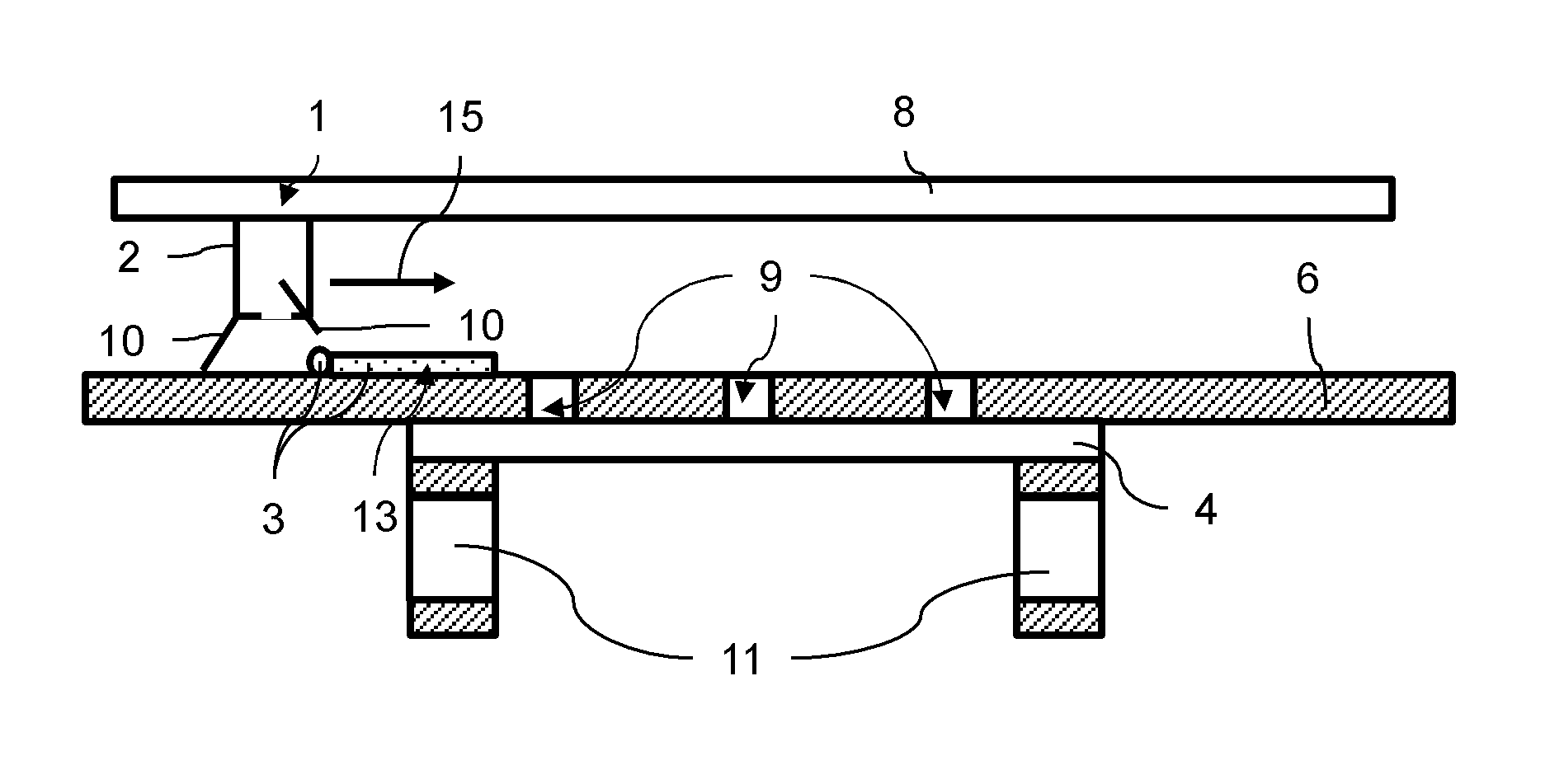
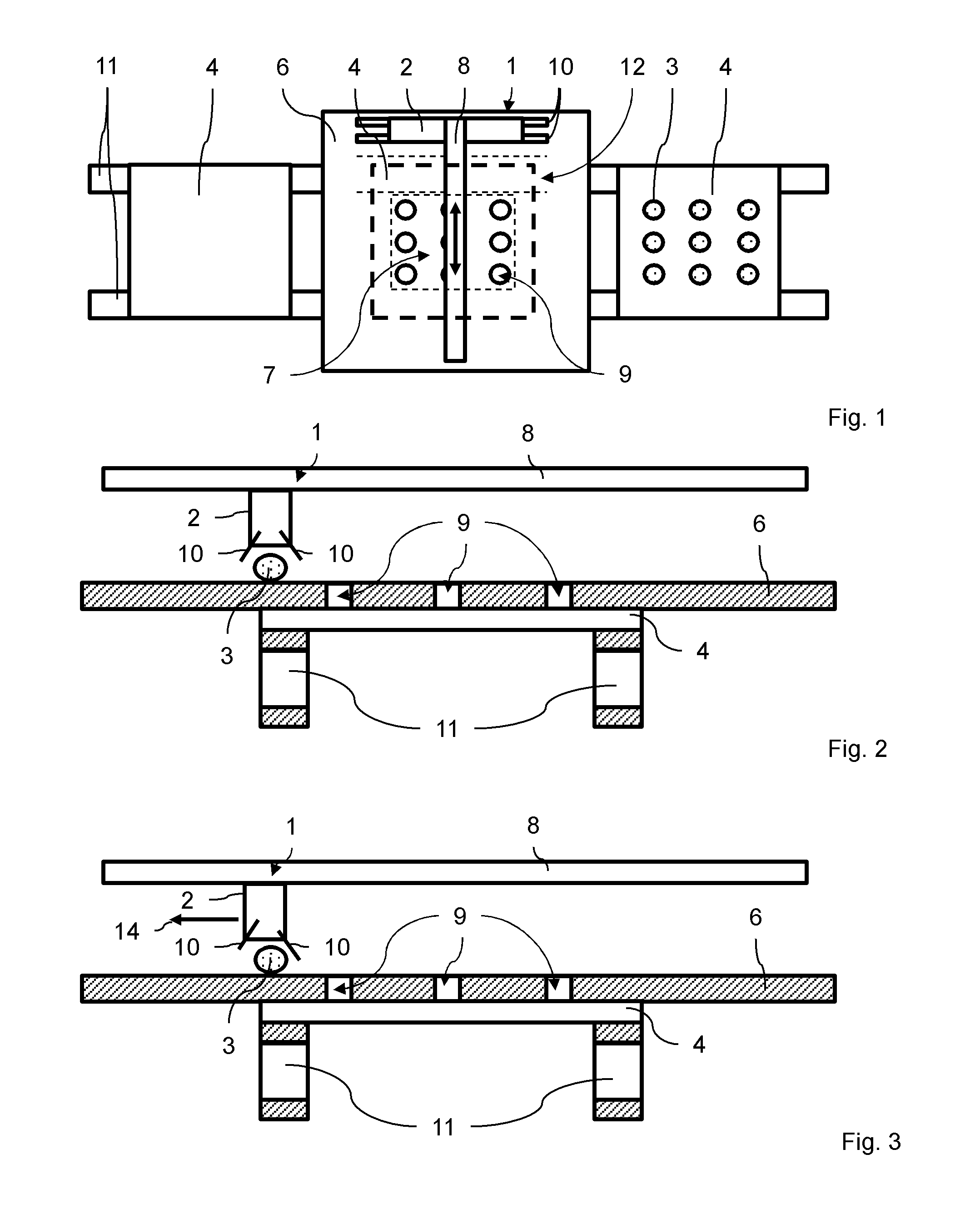
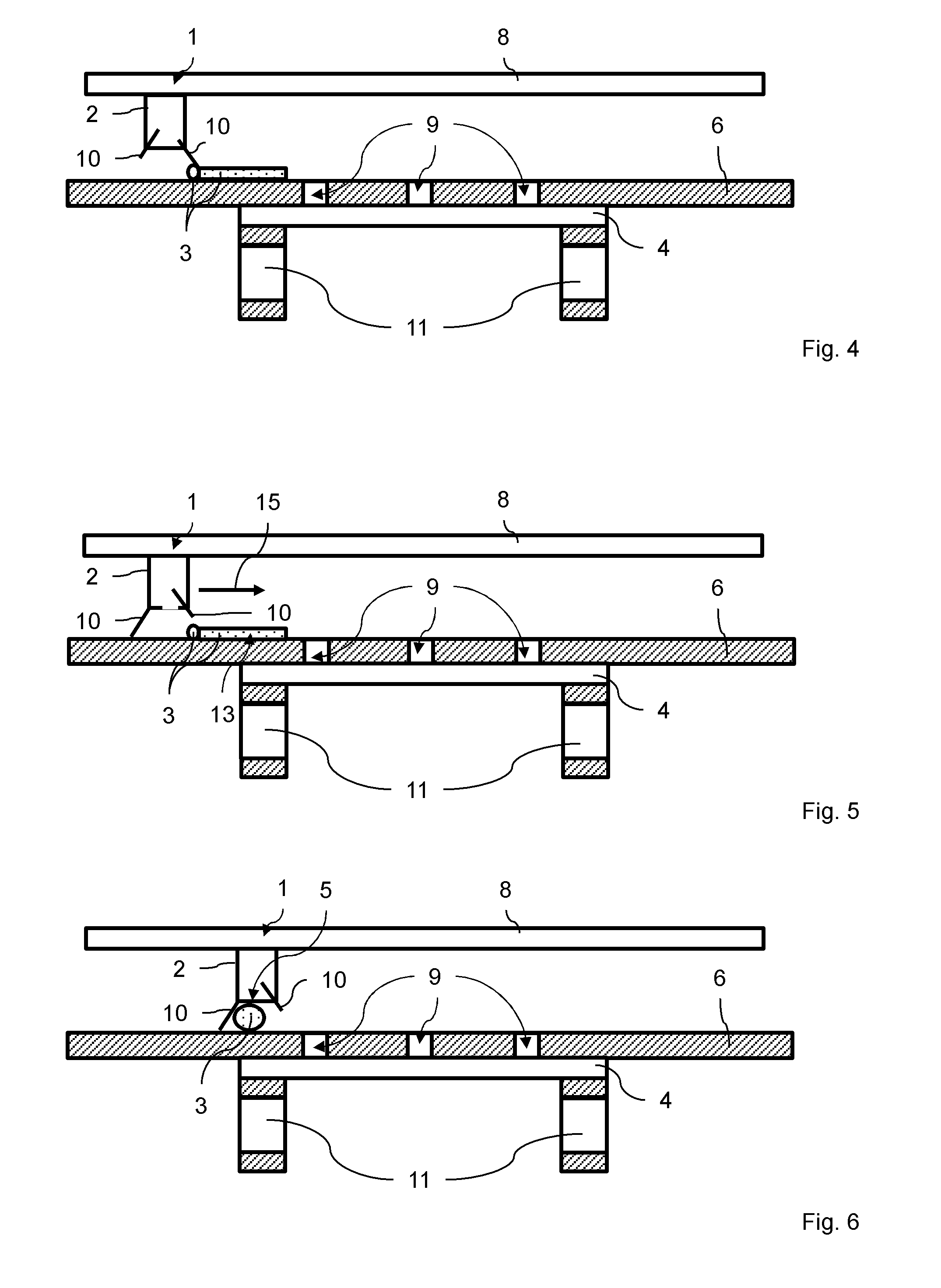
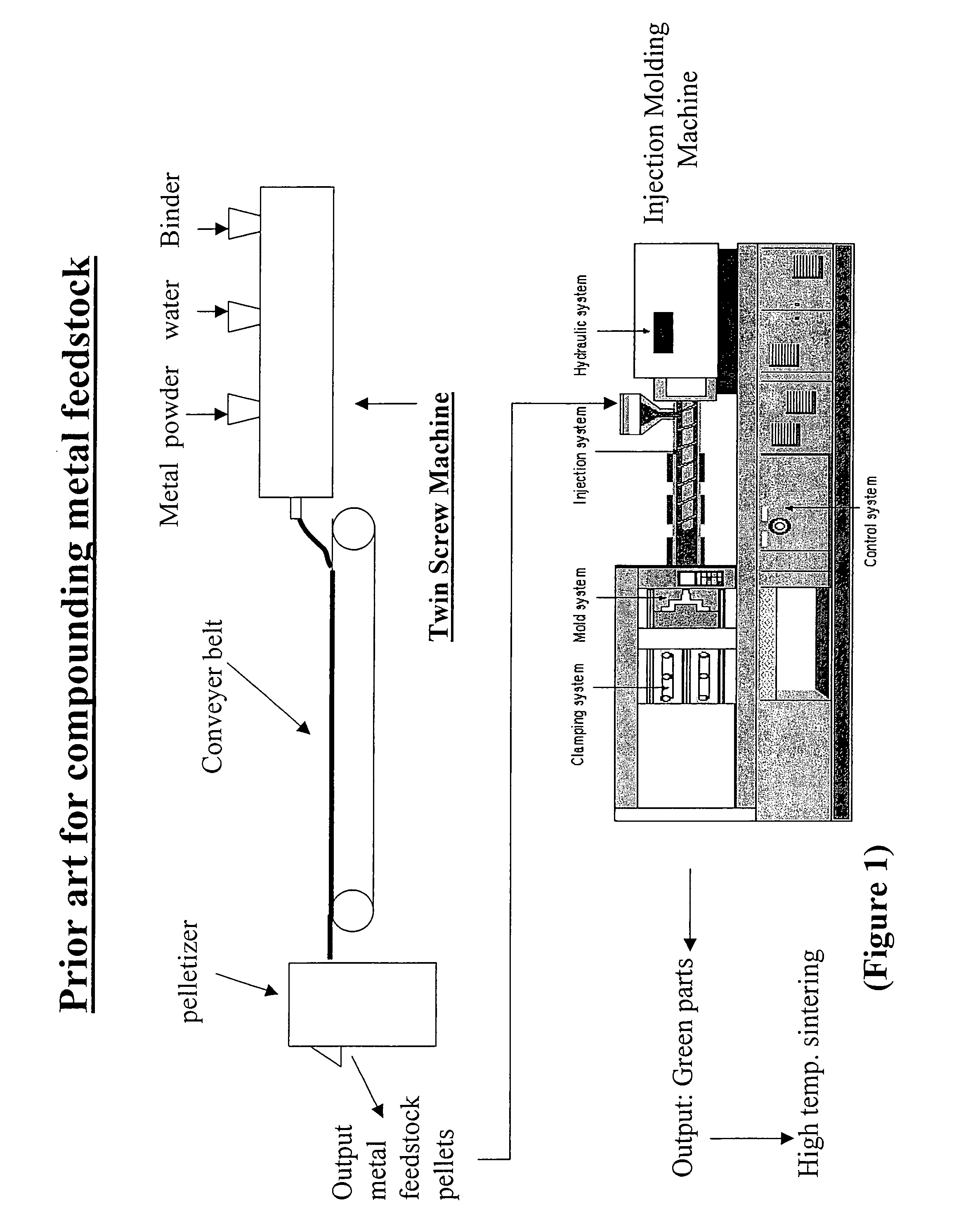
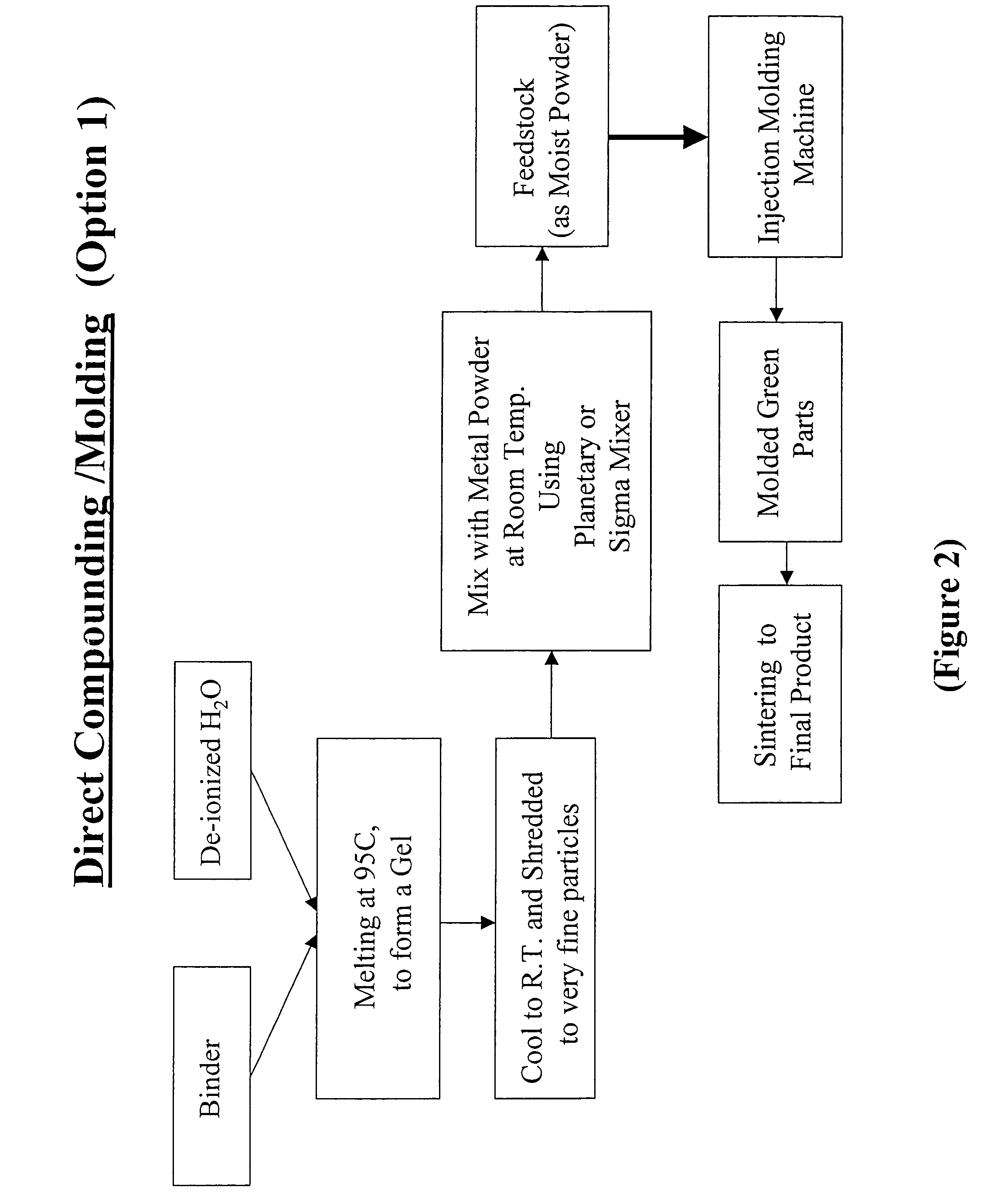
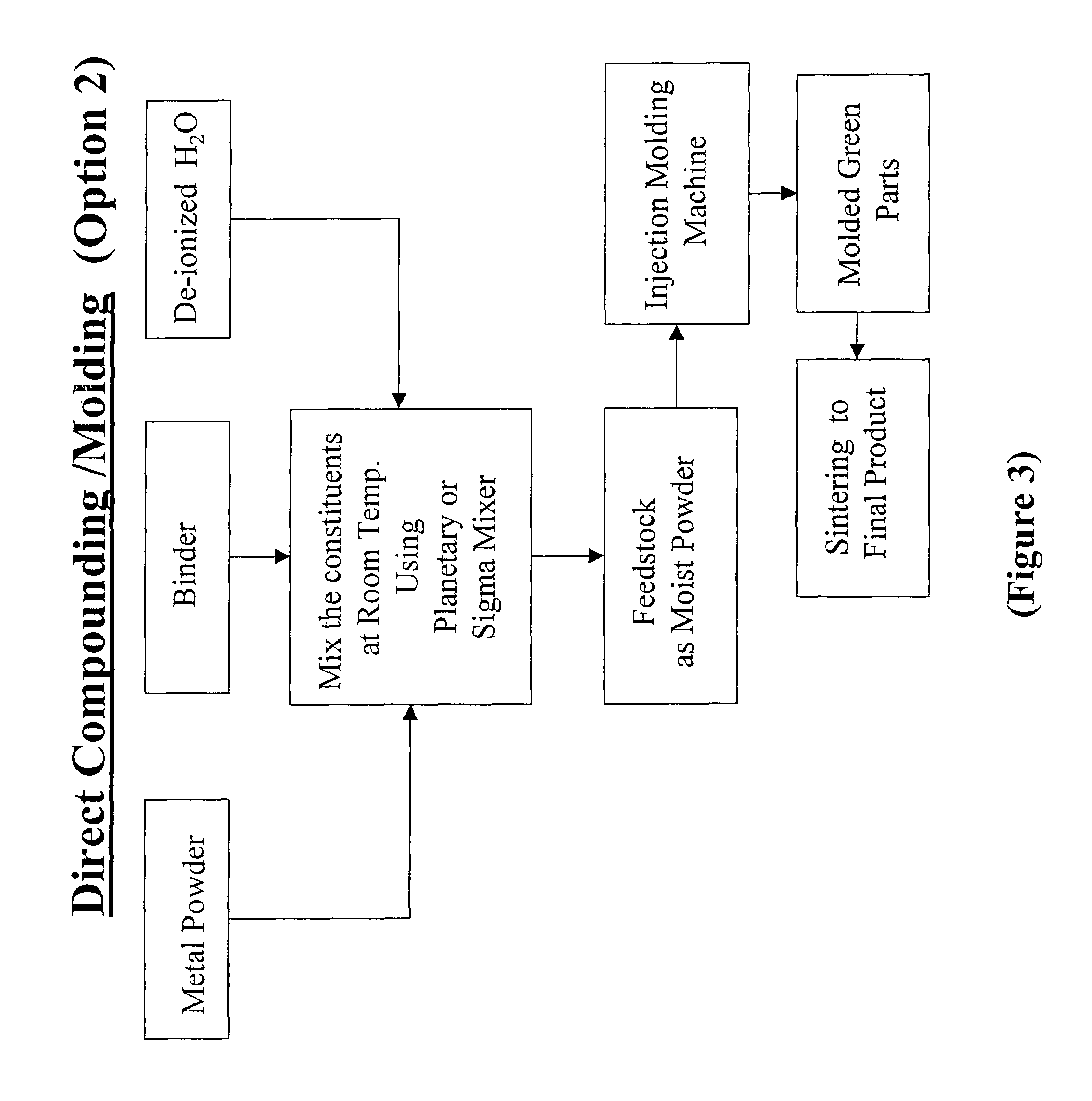
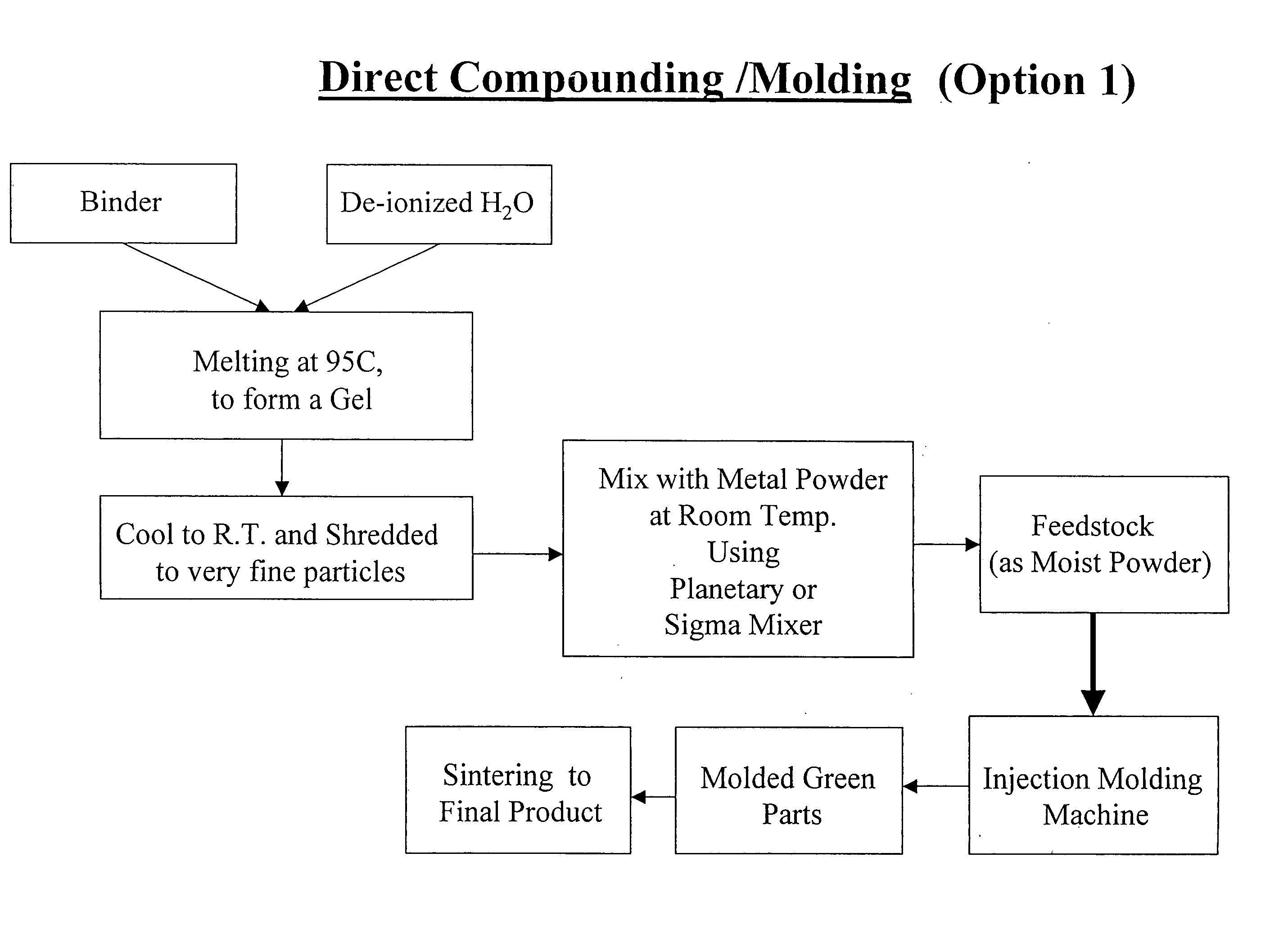
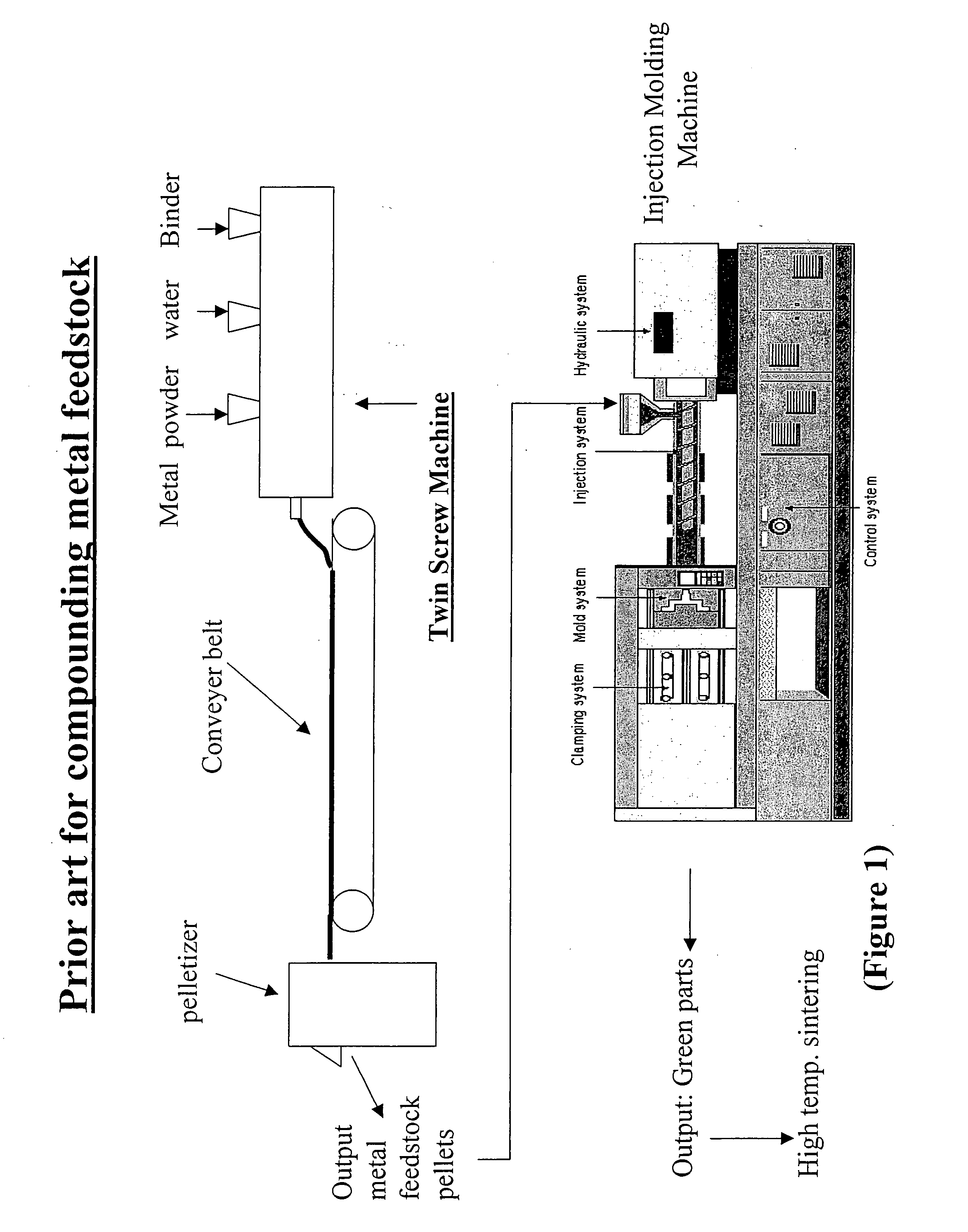
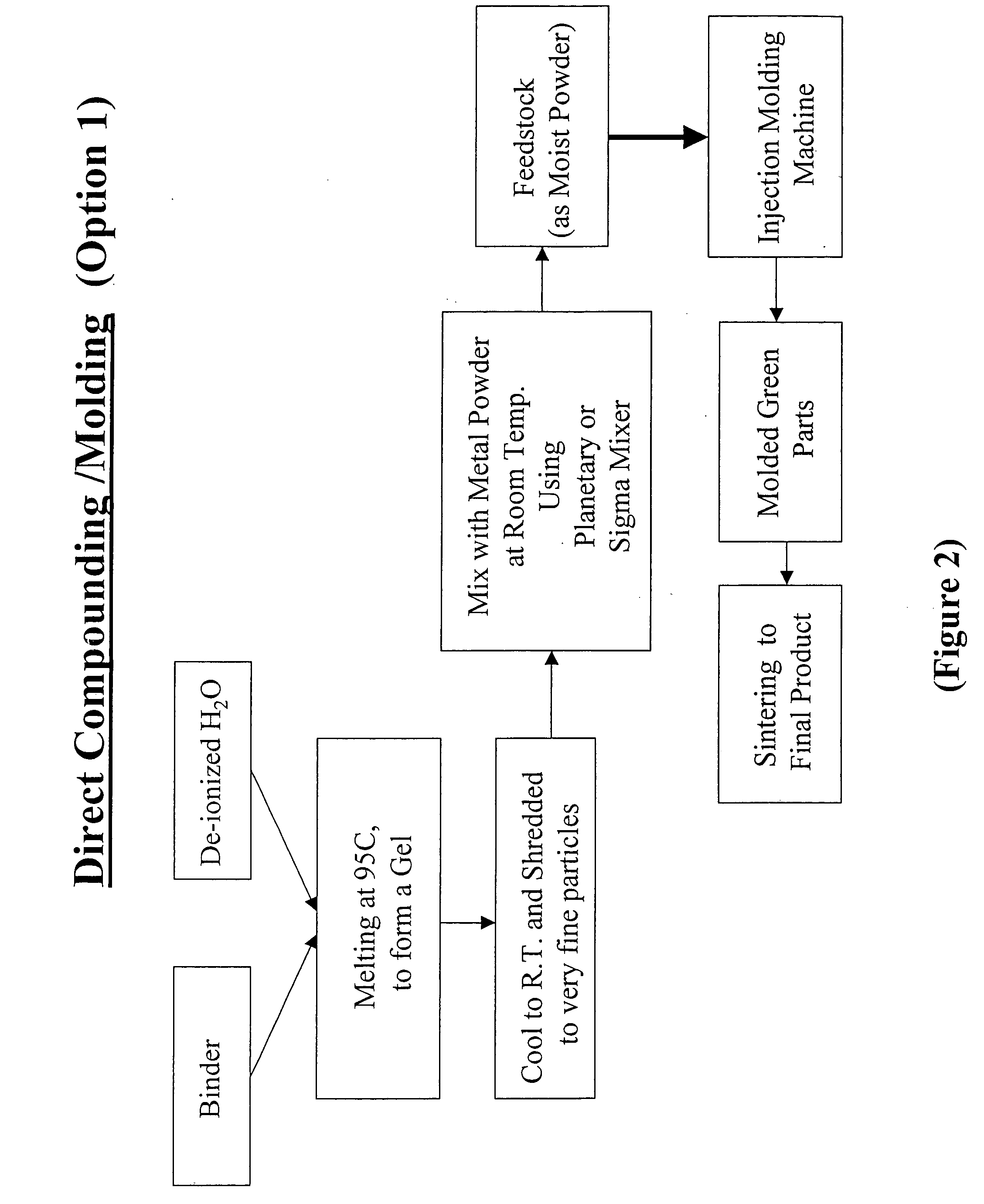
Aqueous binder formulation for metal and ceramic feedstock for injection molding and aqueous coating composition
Low cost water based binder system was developed for shaping ferrous, nonferrous metals and / or ceramics parts by injection molding processes. The process comprises the steps of preparing a mixture containing a gel-forming powder comprising carrageenan, metal and / or ceramic powders, de-ionized water and a gel-strengthening additive. The mixture is injection molded to produce self-supporting articles. The present invention provides a direct compounding and molding of metal and / or ceramic feedstock. Additionally, a coating composition comprising gelatine, water and a metal and / or ceramic powder is used to form coating layers on selected materials.
Owner:UNITED MATERIALS TECH
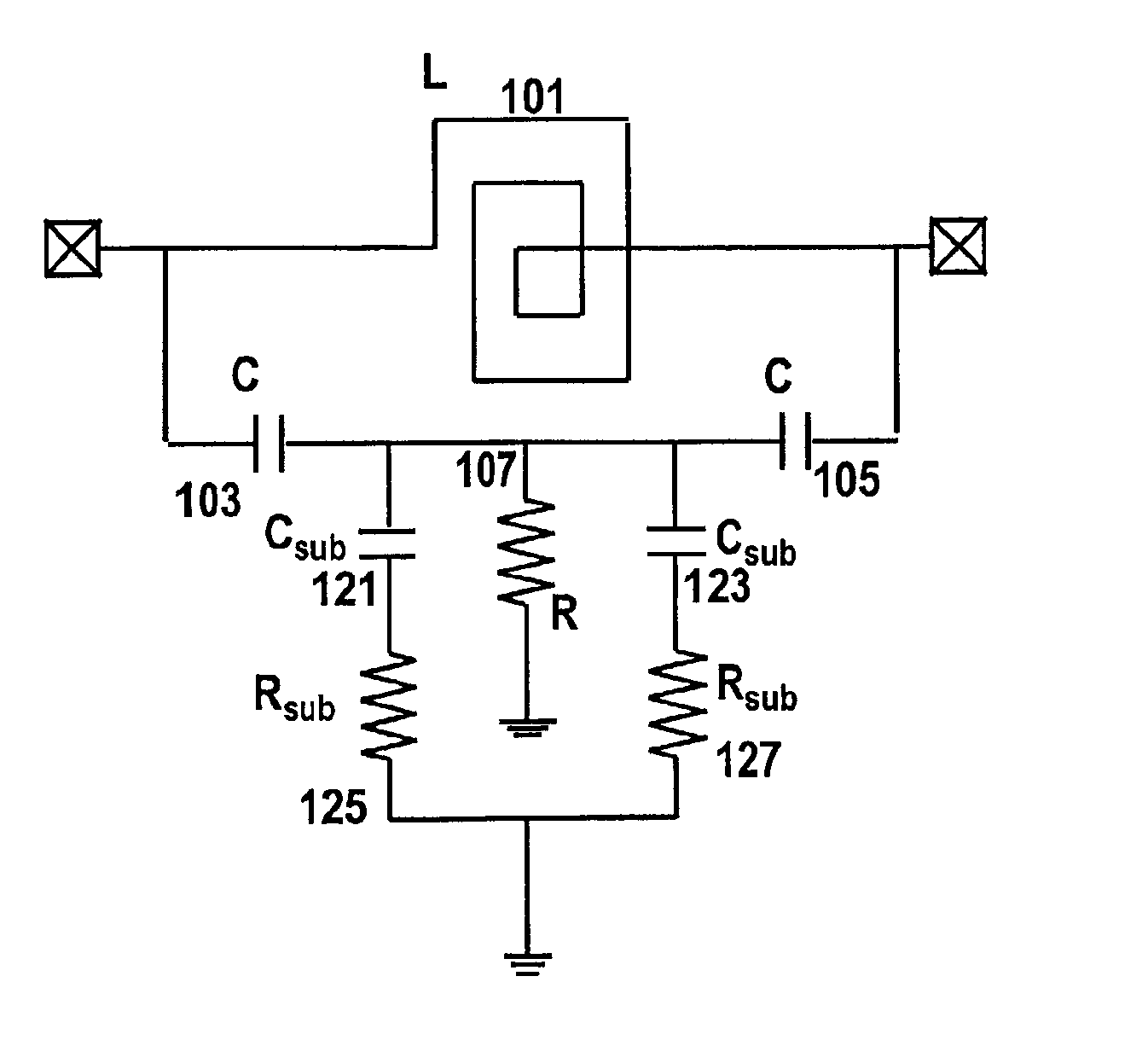
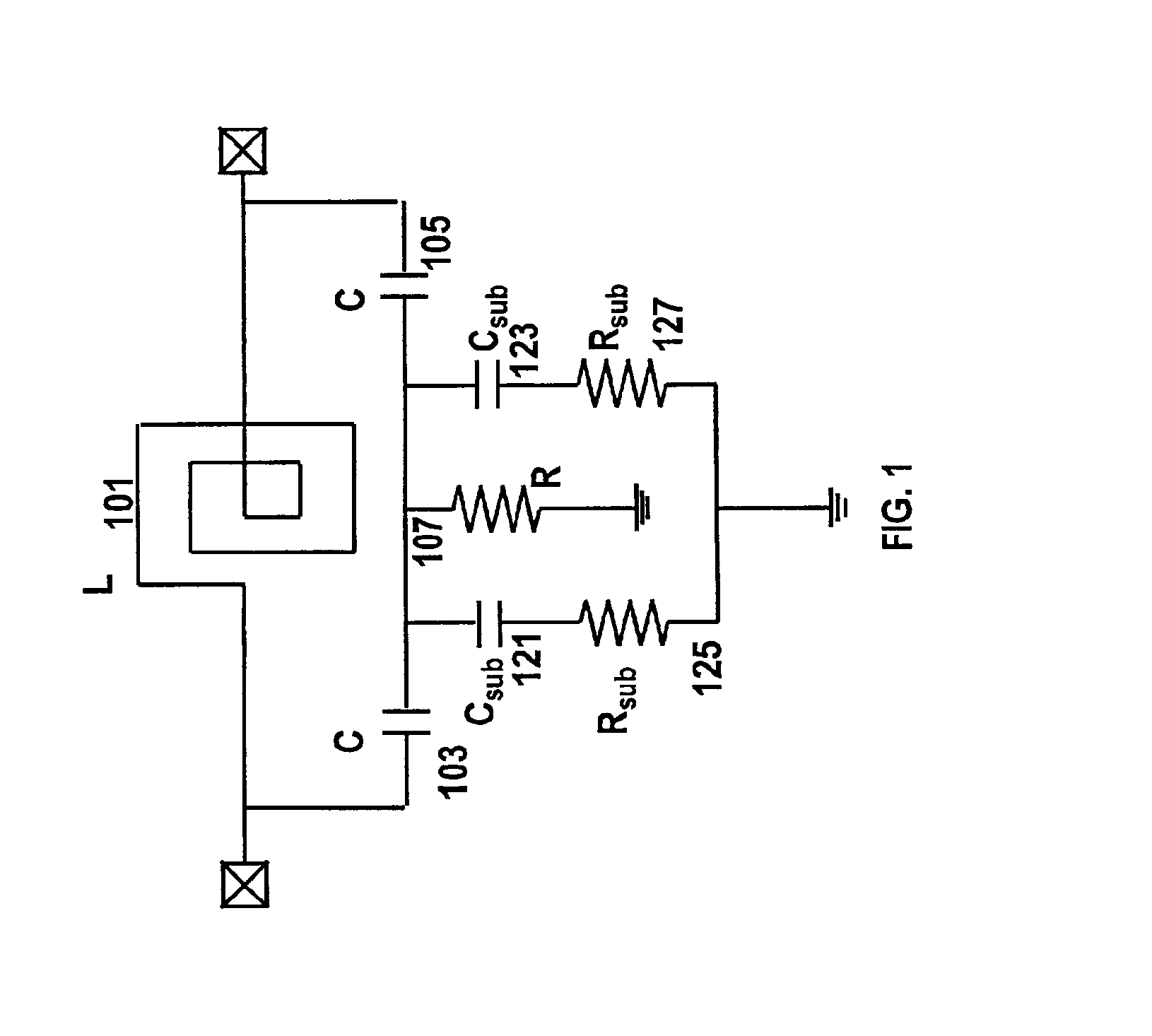
Filters implemented in integrated circuits
InactiveUS6867665B2High-Q filterCompact structureMultiple-port networksSolid-state devicesInductorRf filters
An integrated RF filter for use at microwave frequencies comprising: an integrated circuit inductor with connected integrated circuit capacitors, arranged as a tank circuit, and an integrated circuit shunt resistor; the inductor, capacitors and resistor being interconnected in a bridge-T filter arrangement.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
Rolling guide device and method of manufacturing the same
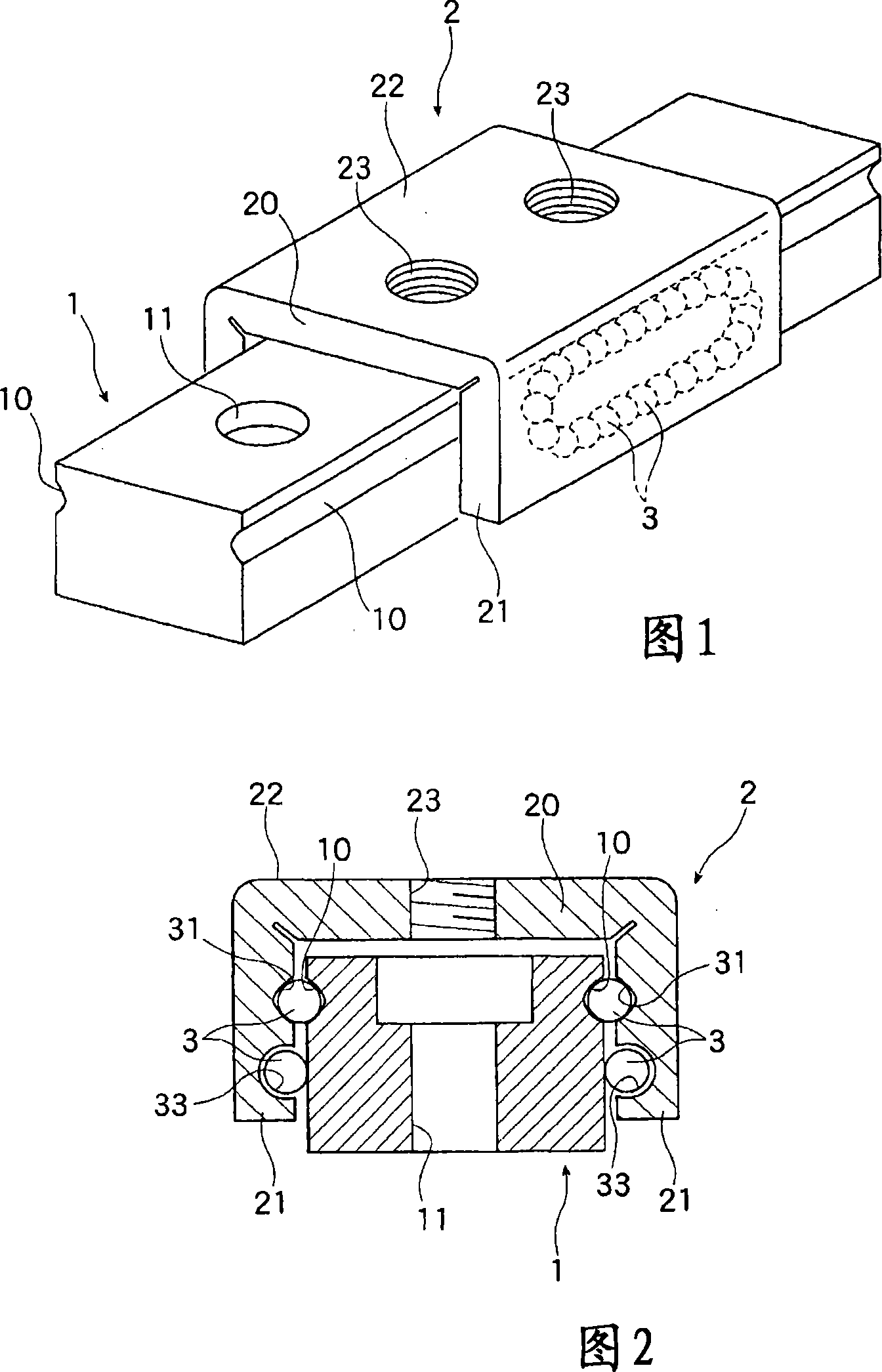
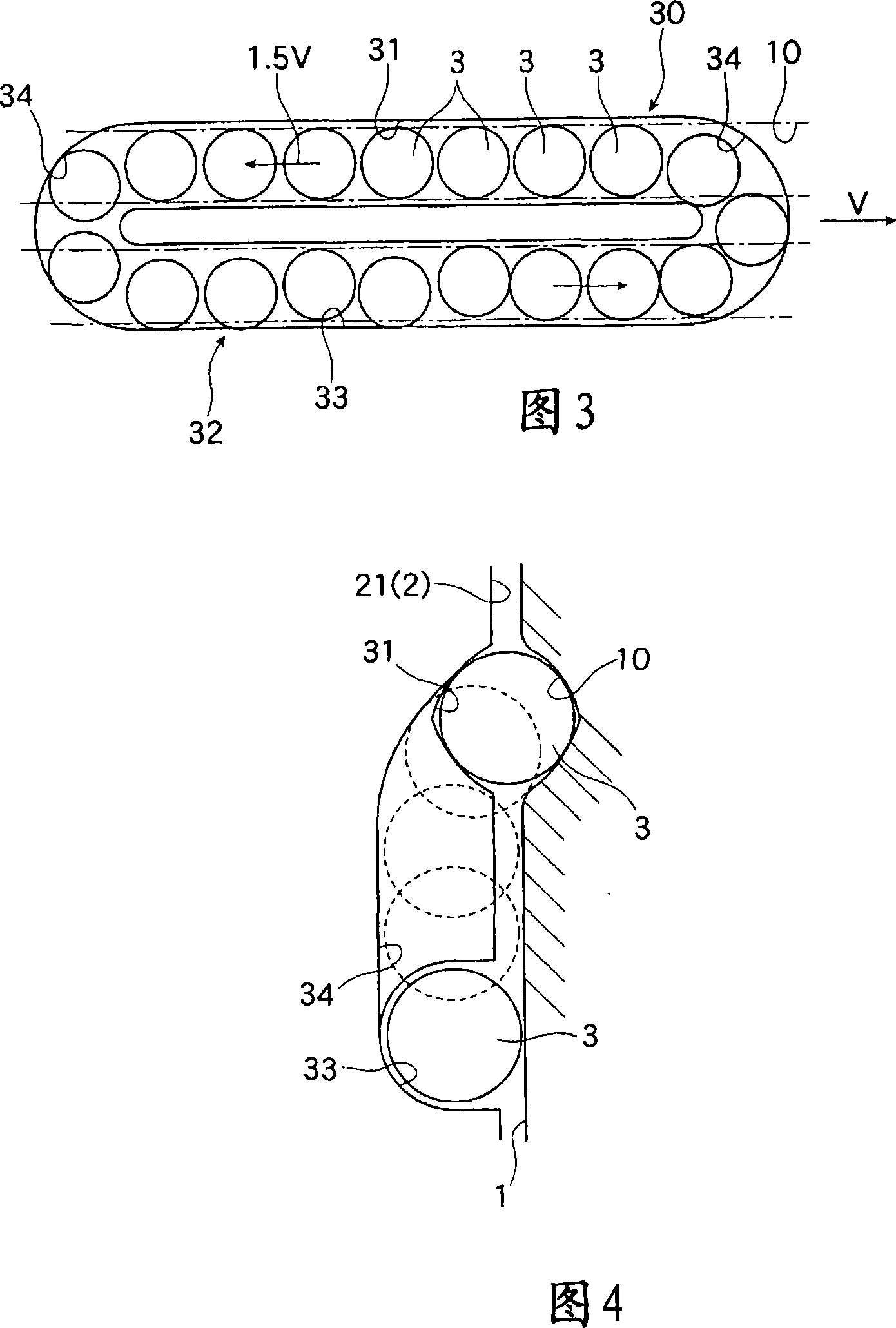
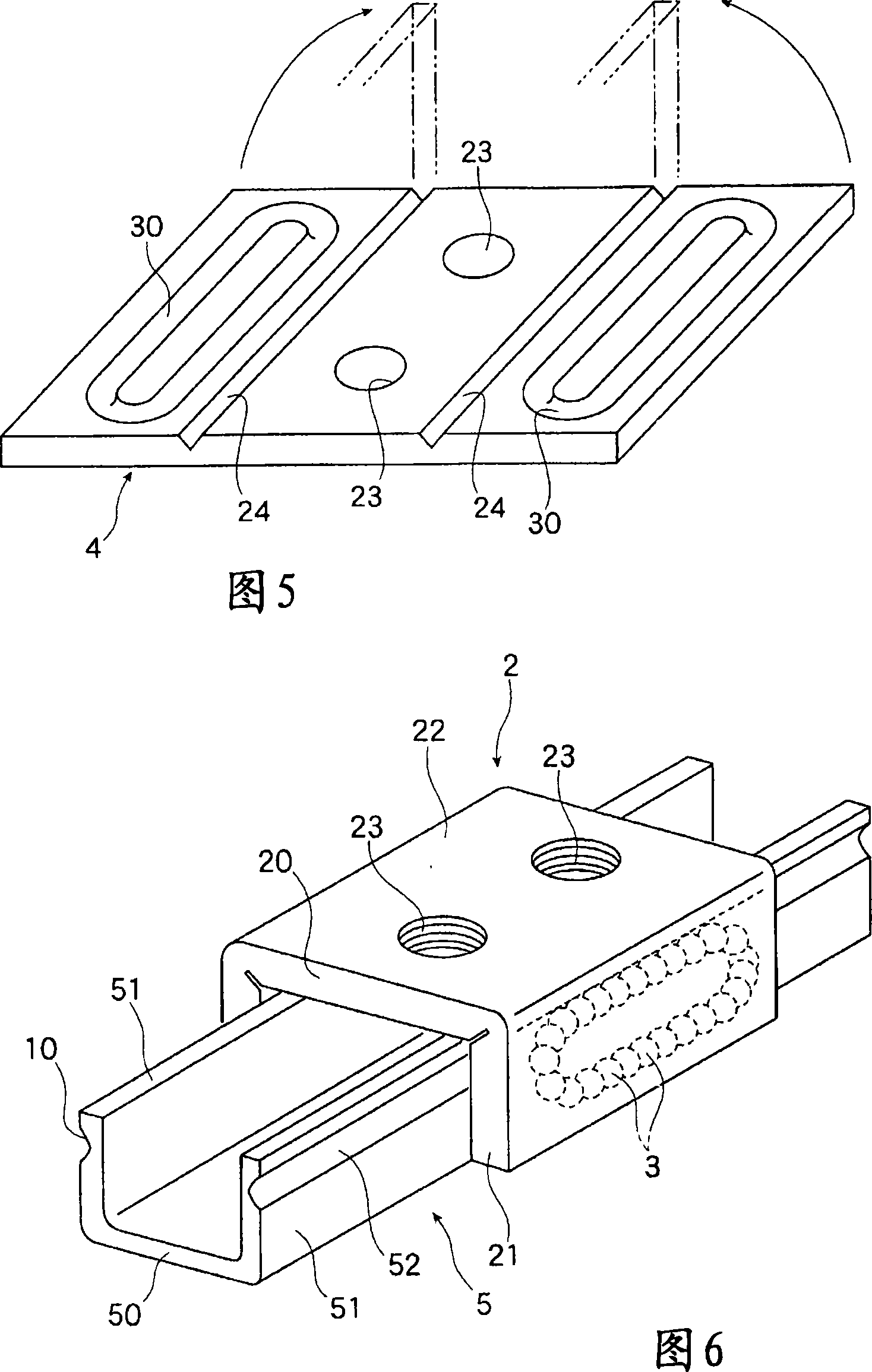
InactiveCN101213383AEasy and low costReduce processing timeLinear bearingsBearing unit rigid supportEngineeringMetal
The rolling guide device of the present invention can reduce the number of parts and components when forming the sliding part (2), reduce the processing man-hours, and be manufactured easily and at low cost. It is assembled on the track guide rail (1) and the track guide rail ( The sliding part (2) on 1) is formed, and the sliding part (2) is formed by bending the metal plate part (5), and has a transverse web (20) and a pair of flange parts (21) formed in a tunnel shape, and each wing A track groove (30) for the ball (3) to circulate is formed on the edge (21), and the track groove (30) includes: a load linear groove (31) where the ball (3) rolls while bearing a load, and a handle on the load line The ball (3) rolling over in the groove (31) is released from the load state and a pair of ball deflection grooves (34) that make its direction change, and the ball (3) is transferred from one ball deflection groove (34) to The other side of the ball deflection groove (34) is constituted by an unloaded linear groove (33).
Owner:THK CO LTD
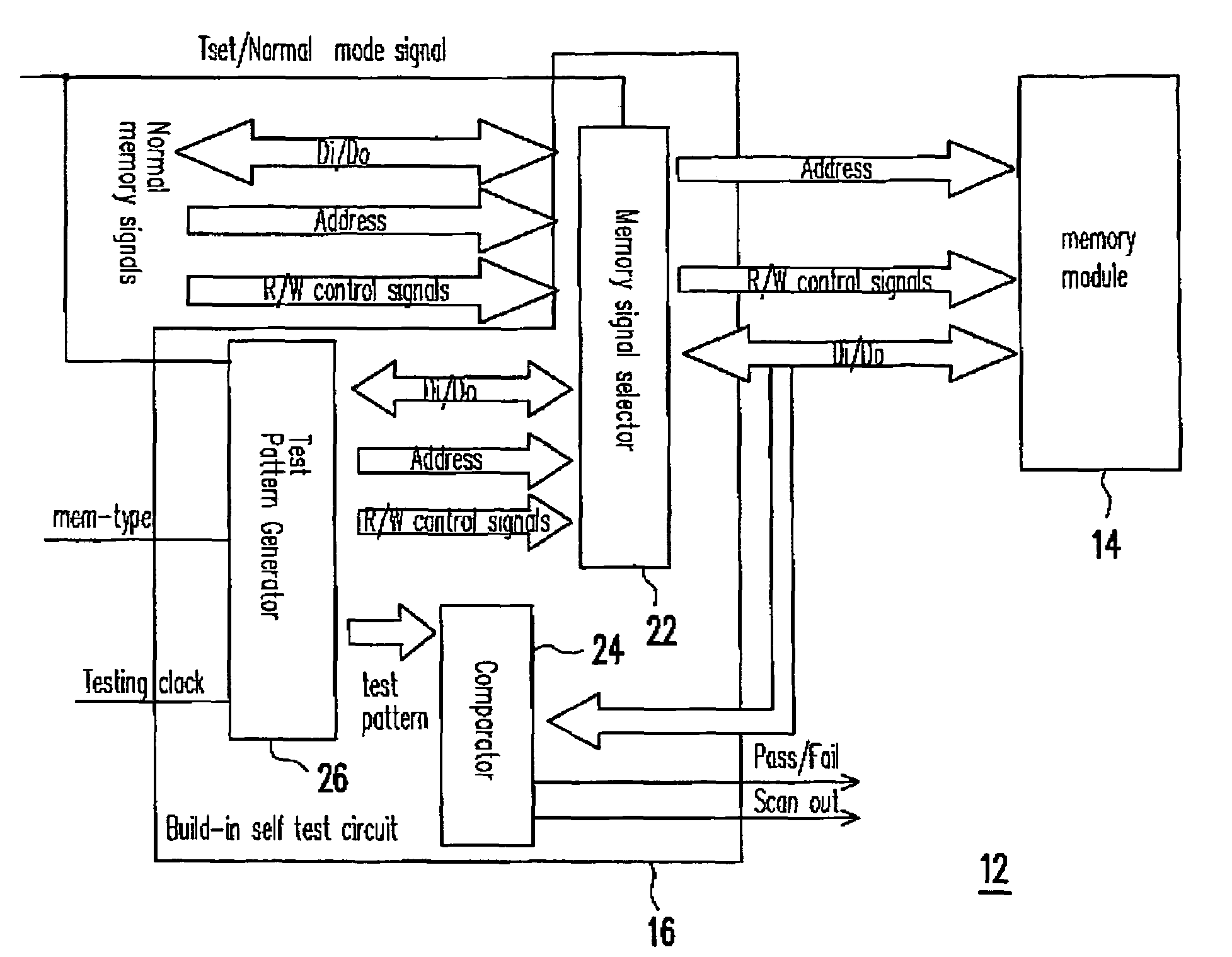
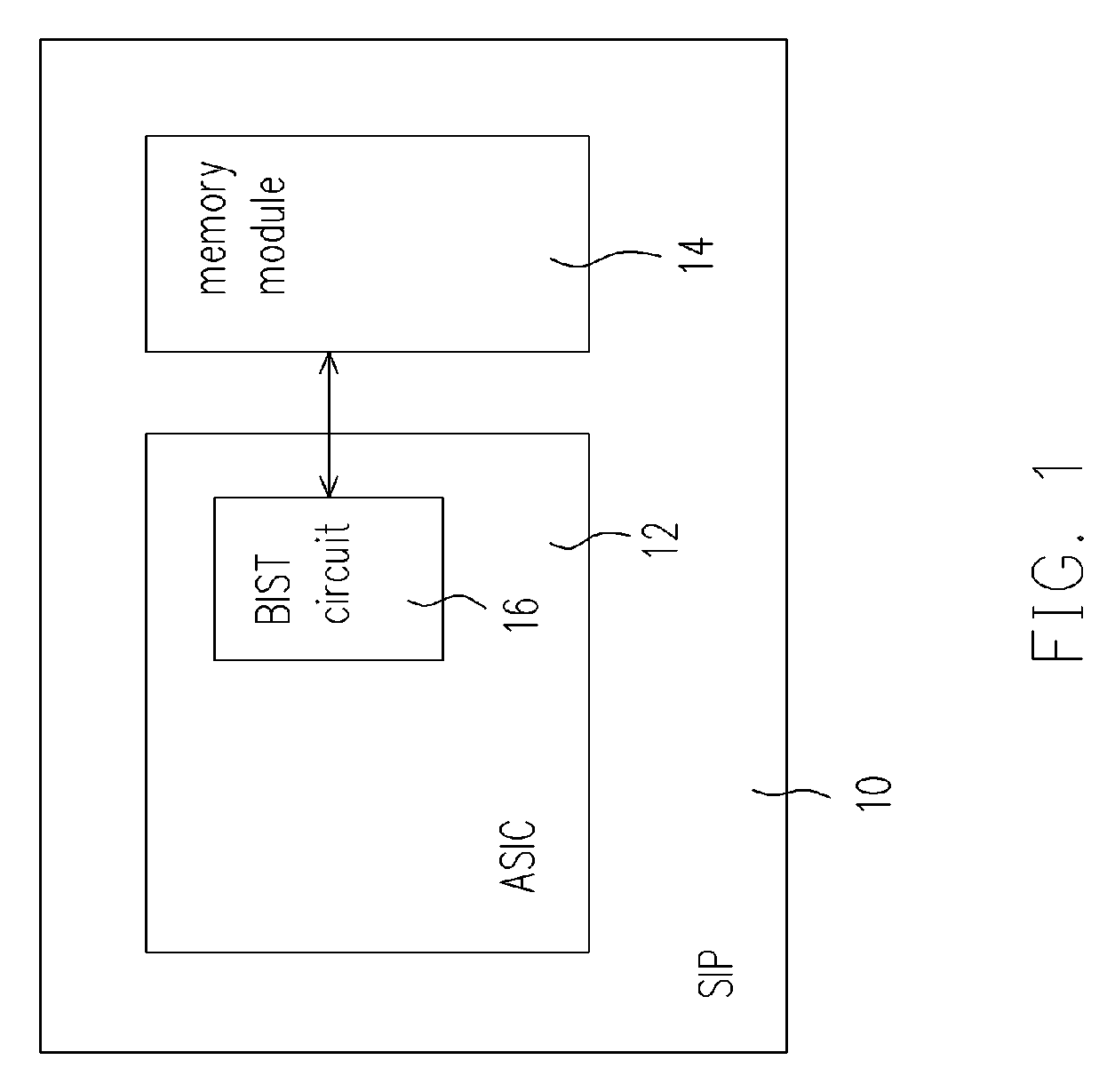
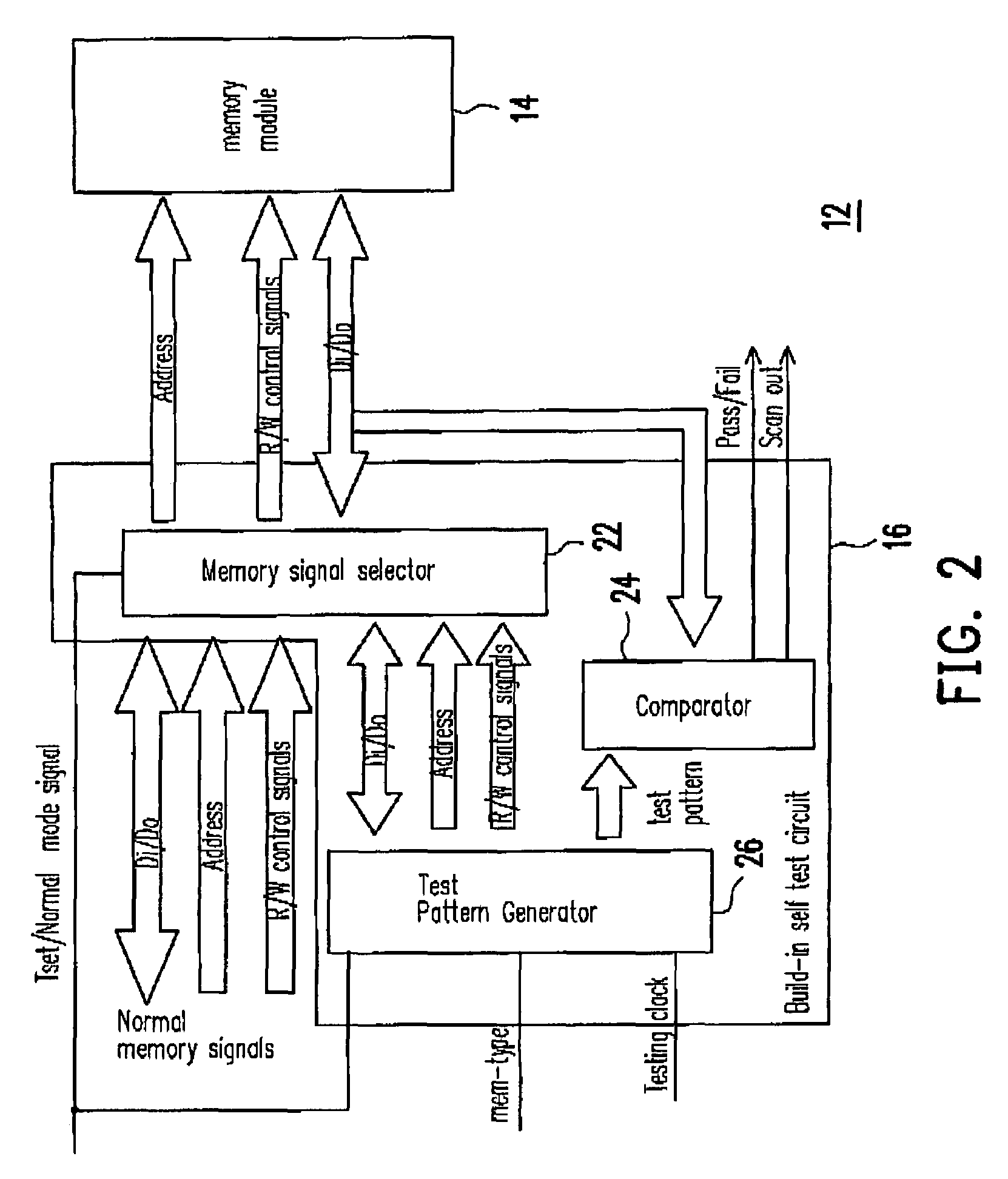
Built-in self test for system in package
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Aqueous binder formulation for metal and ceramic feedstock for injection molding and aqueous coating composition
InactiveUS20060054856A1Low costHigh green strengthStarch adhesivesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionWater basedCarrageenan
Low cost water based binder system was developed for shaping ferrous, nonferrous metals and / or ceramics parts by injection molding processes. The process comprises the steps of preparing a mixture containing a gel-forming powder comprising carrageenan, metal and / or ceramic powders, de-ionized water and a gel-strengthening additive. The mixture is injection molded to produce self-supporting articles. The present invention provides a direct compounding and molding of metal and / or ceramic feedstock. Additionally, a coating composition comprising gelatine, water and a metal and / or ceramic powder is used to form coating layers on selected materials.
Owner:UNITED MATERIALS TECH
Wheel balancing device
A wheel balancing device of this invention comprising a wheel balancing body having a wheel rim engaging bar made of iron metal or iron-based metal component to be formed in any shape as required. Being provided on one side of the wheel balancing body is an engaging part fixed thereto. The engaging part is composed of an engaging plate having one end engaged and fixed to one end of the wheel rim engaging bar by a locking means and the other end is bent as an upper curve to be locked and fixed to a wheel rim of an automobile. The wheel rim engaging bar and a part of engaging plate are enwrapped by the outer cover plate made of plastic or plastic-contained composition.
Owner:P C PRODS INT
Built-in self test for system in package
ActiveUS20070159201A1Easy and low-costStatic storageIndividual semiconductor device testingIntegration testingSystem in package
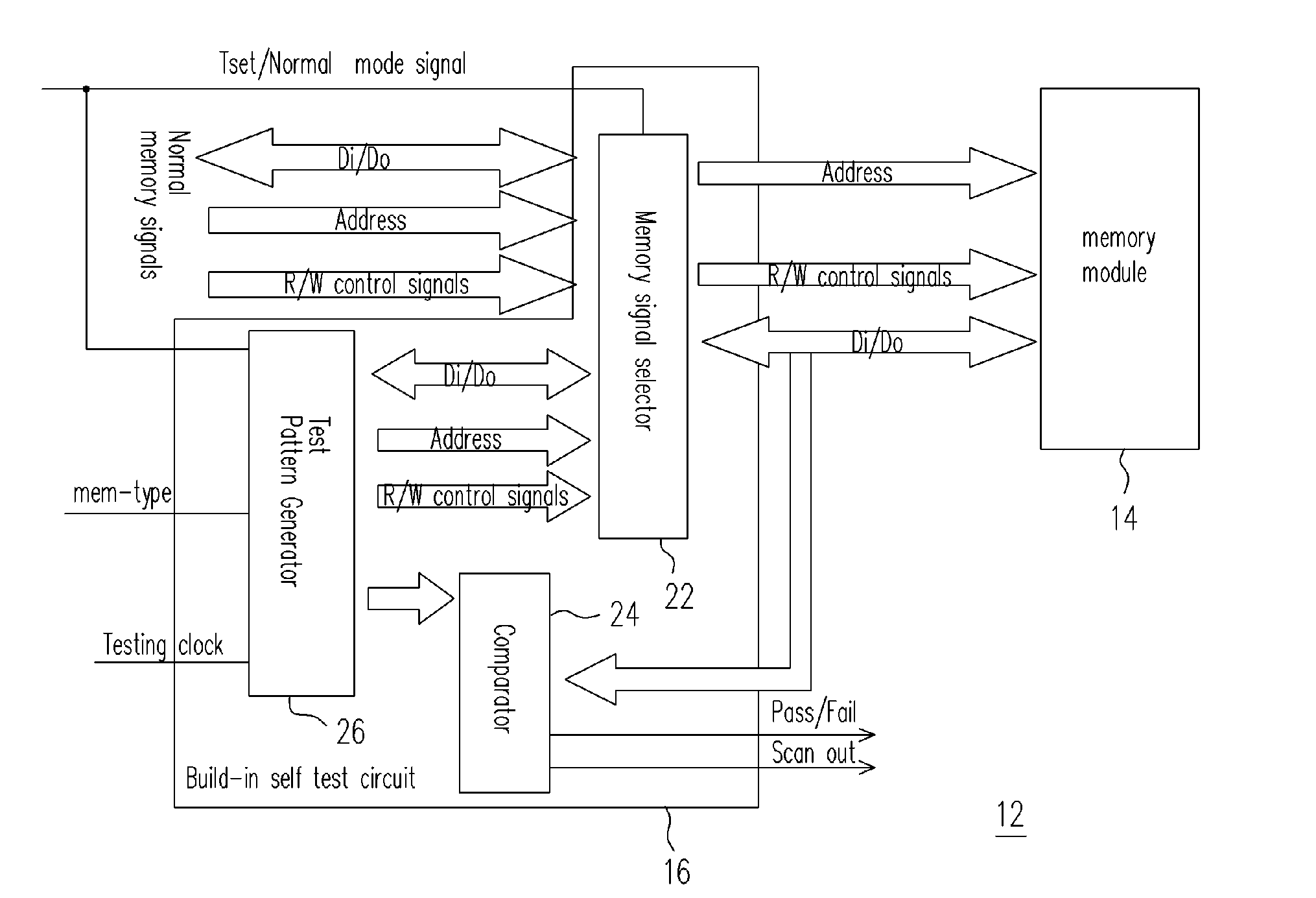
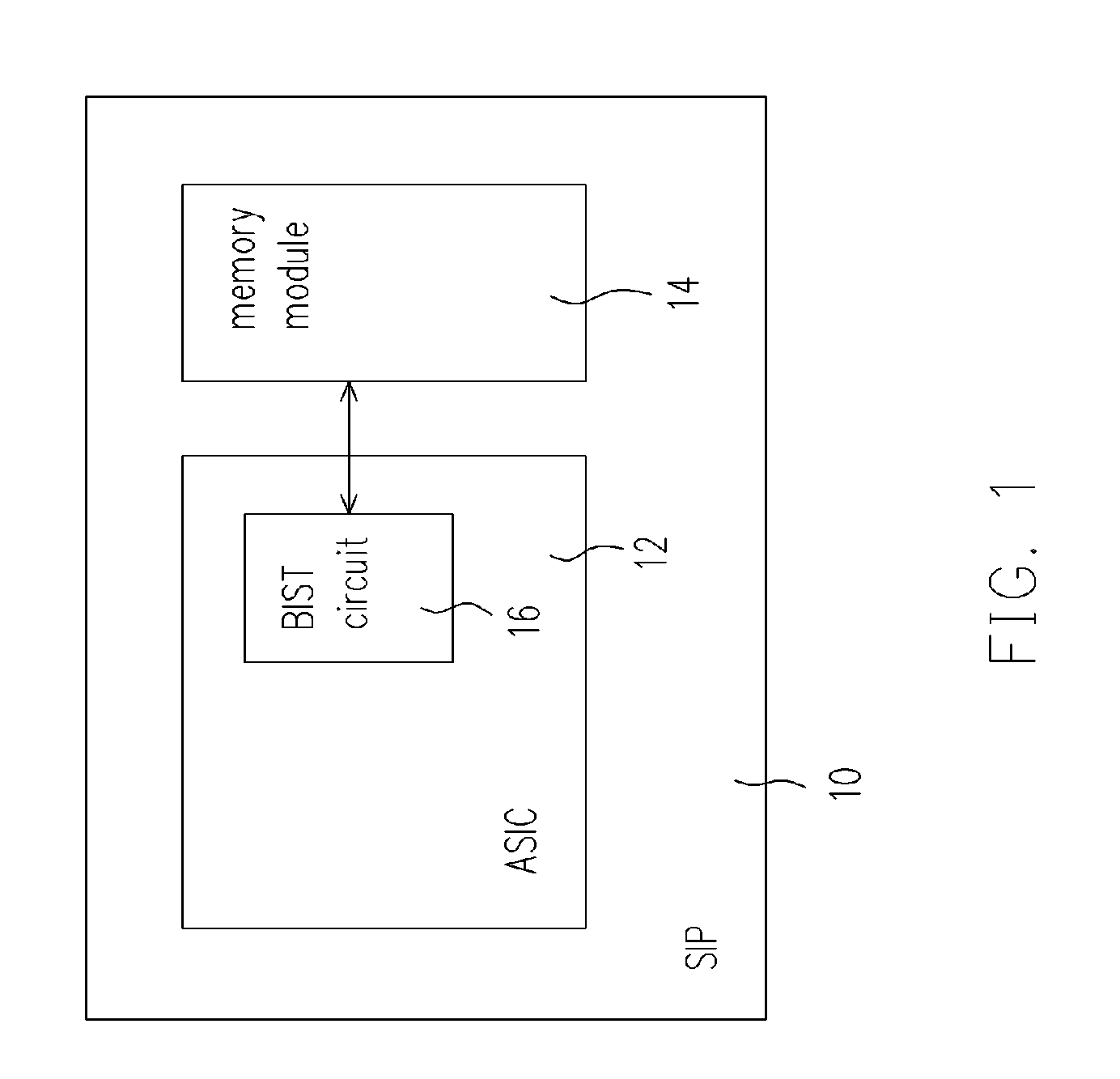
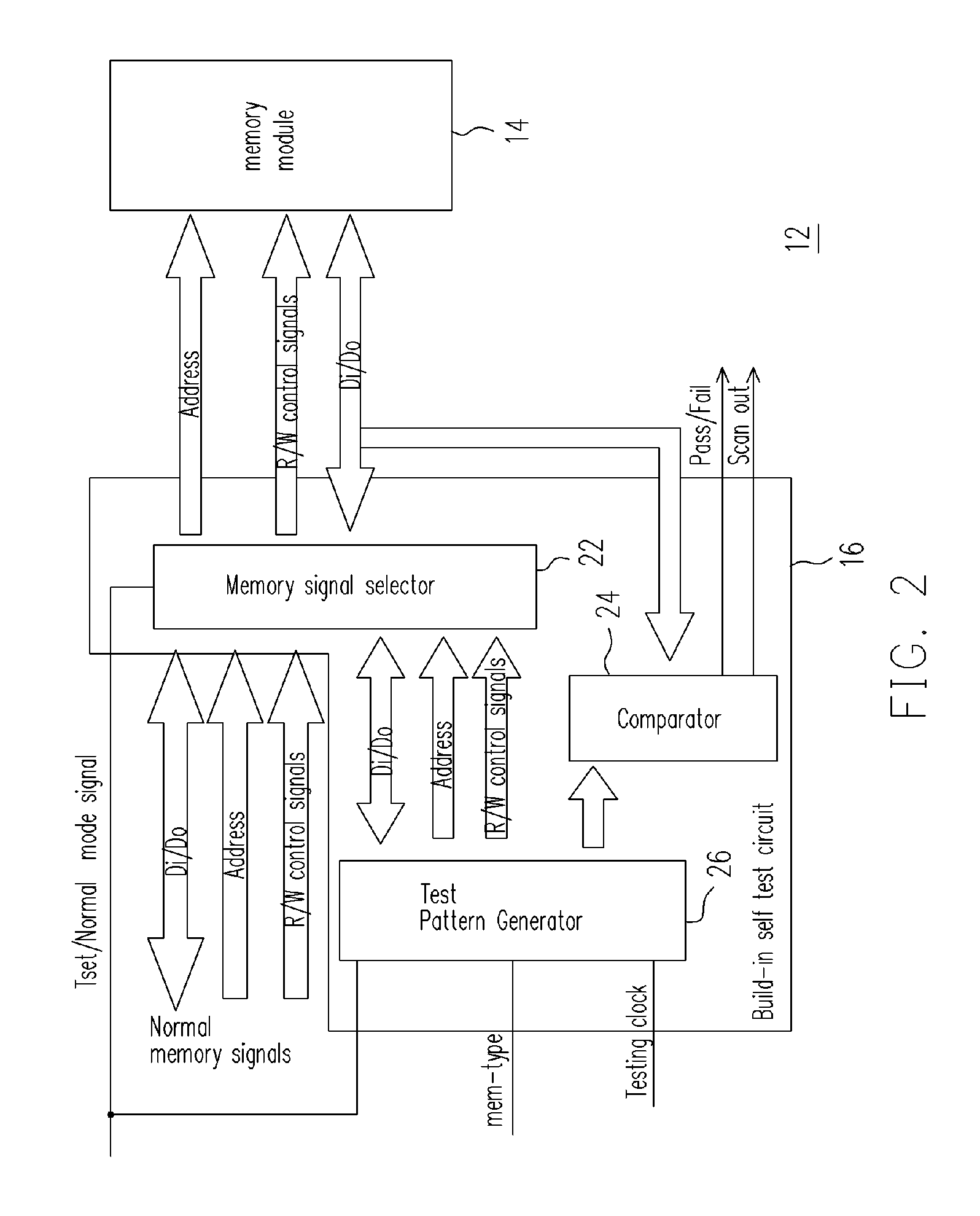
A SIP (system in package) with a chip and a memory mode, capable of performing integration test on the memory module even if the memory module does not include any scan chain is provided. The chip has a built-in self-test (BIST) circuit, which generates test pattern signals to test the memory module in response to a mode signal. Under a test mode, after the memory module receives the test pattern signals, the memory module outputs responsive readout signals to the BIST circuit and the BIST circuit determines and outputs a test result and a test record in response to the readout signals. If the test fails, conditions of the faulty memory module are recognized from the test record.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
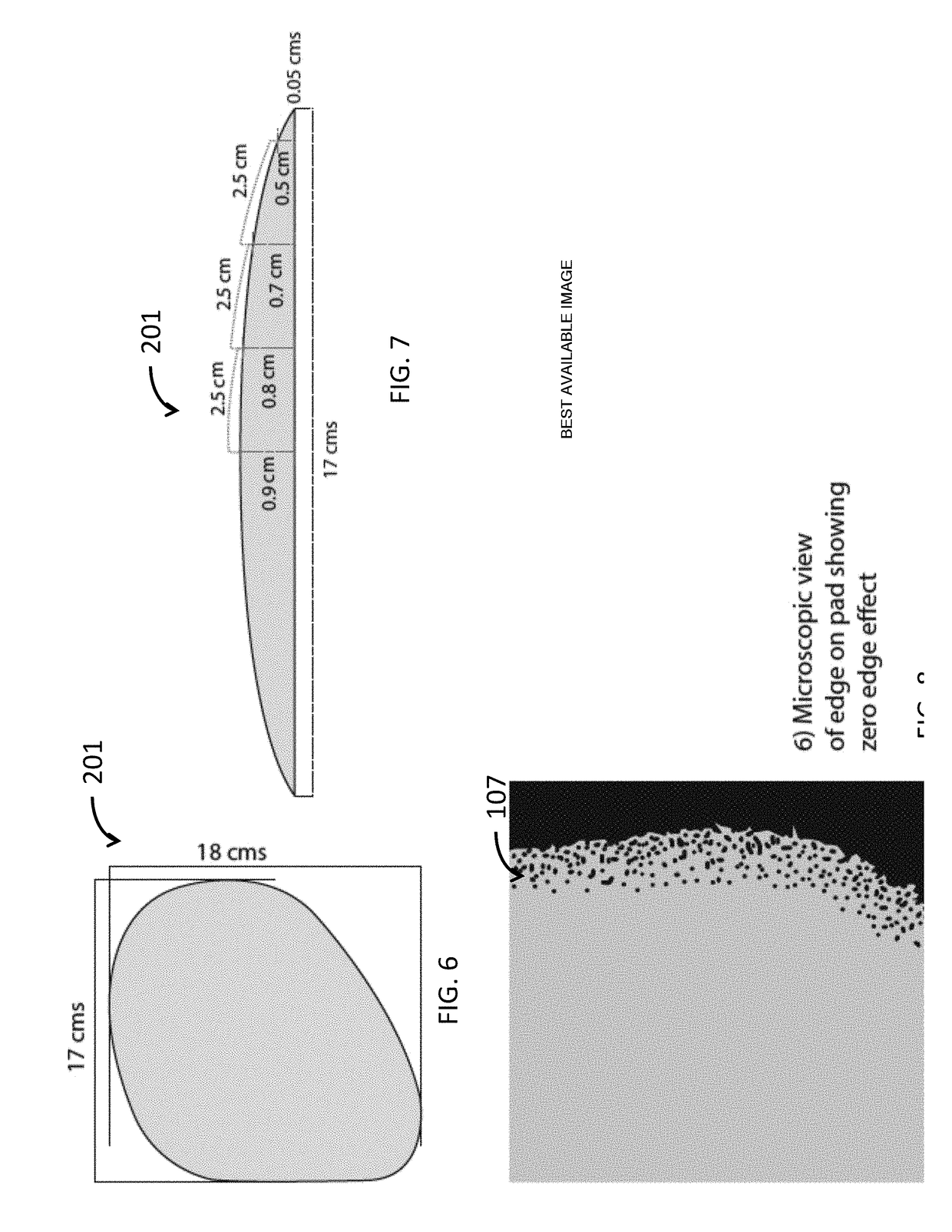
Garments having muscle enhancement device and method of the making the same
ActiveUS20190075867A1Comfortable to wearLight weightGarment special featuresMetal sawing toolsEngineering
The present invention describes a muscle enhancement device comprises a pad sandwiched between two pieces of fabric. The pad is surround by a transitional edge. When muscle enhancement device is being worn properly, the muscle enhancement device is changed from a relaxed state to a stretched state and pad provides a soft, comfortable diffused and obscure edge.
Owner:ROUNDERBUM LLC
Apparatus and methods for liquid separation and capture of biologics
ActiveUS10533932B2Easy and efficient assemblyEasy and low-cost collectionMembranesMicrobiological testing/measurementPoint of careProcess engineering
The present disclosure provides apparatus and methods for processing liquids or fluids. Such apparatus and methods are convenient and efficient for low-cost separation, filtration, capture, collection, and / or storage of biologics and related materials. Provided apparatus and methods are designed for point-of-care use and offer advantages for patients and medical practitioners, including advantages in diagnosis and long-term monitoring of conditions.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Low cost parabolic solar concentrator and method to develop the same
ActiveUS20120204862A1Low costEasy and low costSolar heating energyMirrorsEngineeringSolar concentrator
The present invention relates to a low cost parabolic solar concentrator and method to develop the same. The parabolic solar concentrator can be formed by deforming a hybrid plate. Force can be placed on an edge portion of the hybrid plate and / or a middle portion of the hybrid plate. The selective application of the force deforms the hybrid plate into a parabolic solar concentrator, instead of a sinusoidal shape. The hybrid plate can be formed from a first plate, a second plate, and a third plate attached to each other. The characteristics of the first plate, the second plate, and the third plate, can be chosen to allow the hybrid plate to be deformed into the parabolic shape with the selective application of forces.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Apparatus and methods for liquid separation and capture of biologics
ActiveUS20180224362A1Easy and efficient assemblyEasy and low-cost collectionMembranesMicrobiological testing/measurementPoint of careFiltration
The present disclosure provides apparatus and methods for processing liquids or fluids. Such apparatus and methods are convenient and efficient for low-cost separation, filtration, capture, collection, and / or storage of biologics and related materials. Provided apparatus and methods are designed for point-of-care use and offer advantages for patients and medical practitioners, including advantages in diagnosis and long-term monitoring of conditions.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Bocce ball
A Bocce ball includes, sequentially from outside to inside, a body layer, a medium layer, and a core layer. The body layer and the medium layer are made of different materials. For example, the body layer is made of unsaturated polyester resin, while the medium material is made of acrylic material. The body layer and the medium layer are securely combined with each other. The core layer is made heavy and is enclosed by the medium layer.
Owner:LIAO GRACE
Method of Packaging a Continuous Length of Product on a Spool using Indexed Layers
InactiveUS20130214077A1Reduce setup timeMinimizing interruptionFilament handlingWebs handlingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method is provided for packaging a continuous thread of a woven material or finished product, such as an absorbent food pad, onto a spool, spindle, or other large roll in indexed layers forming rows, for efficient loading and unloading of the product from the spool. A finished spool formed by rows of indexed layers of a continuous thread of the product is also provided.
Owner:PAPER PAK IND
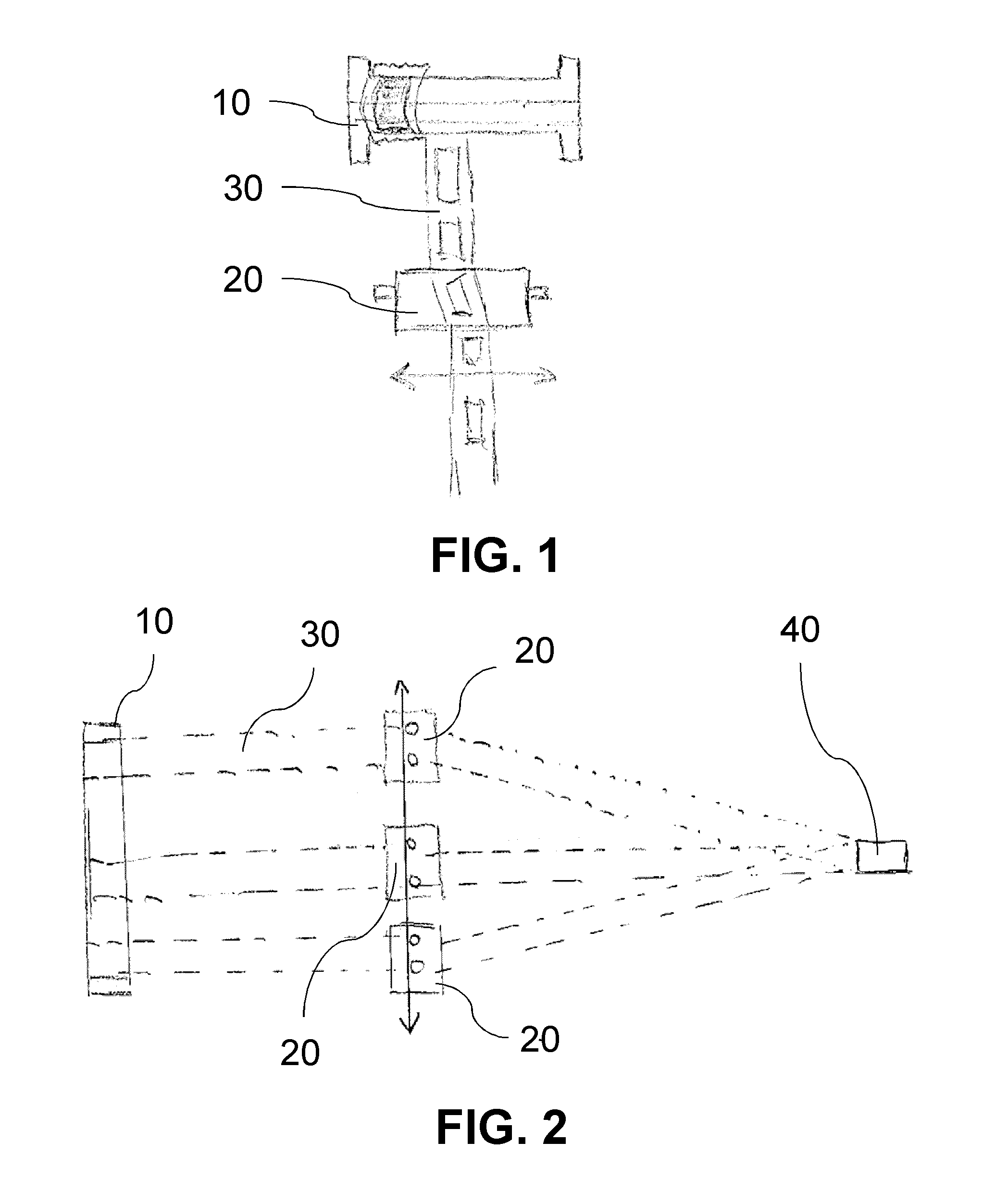
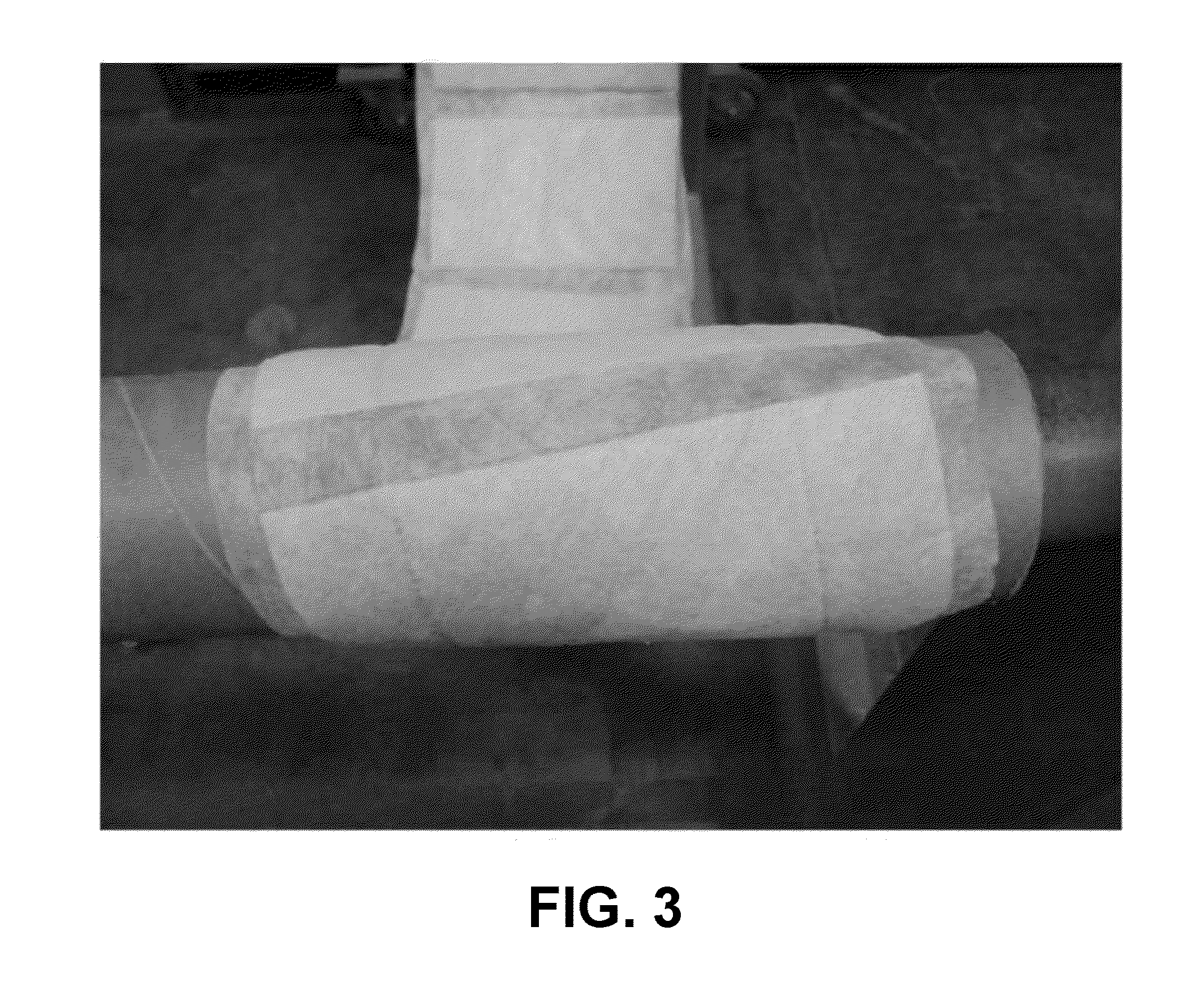
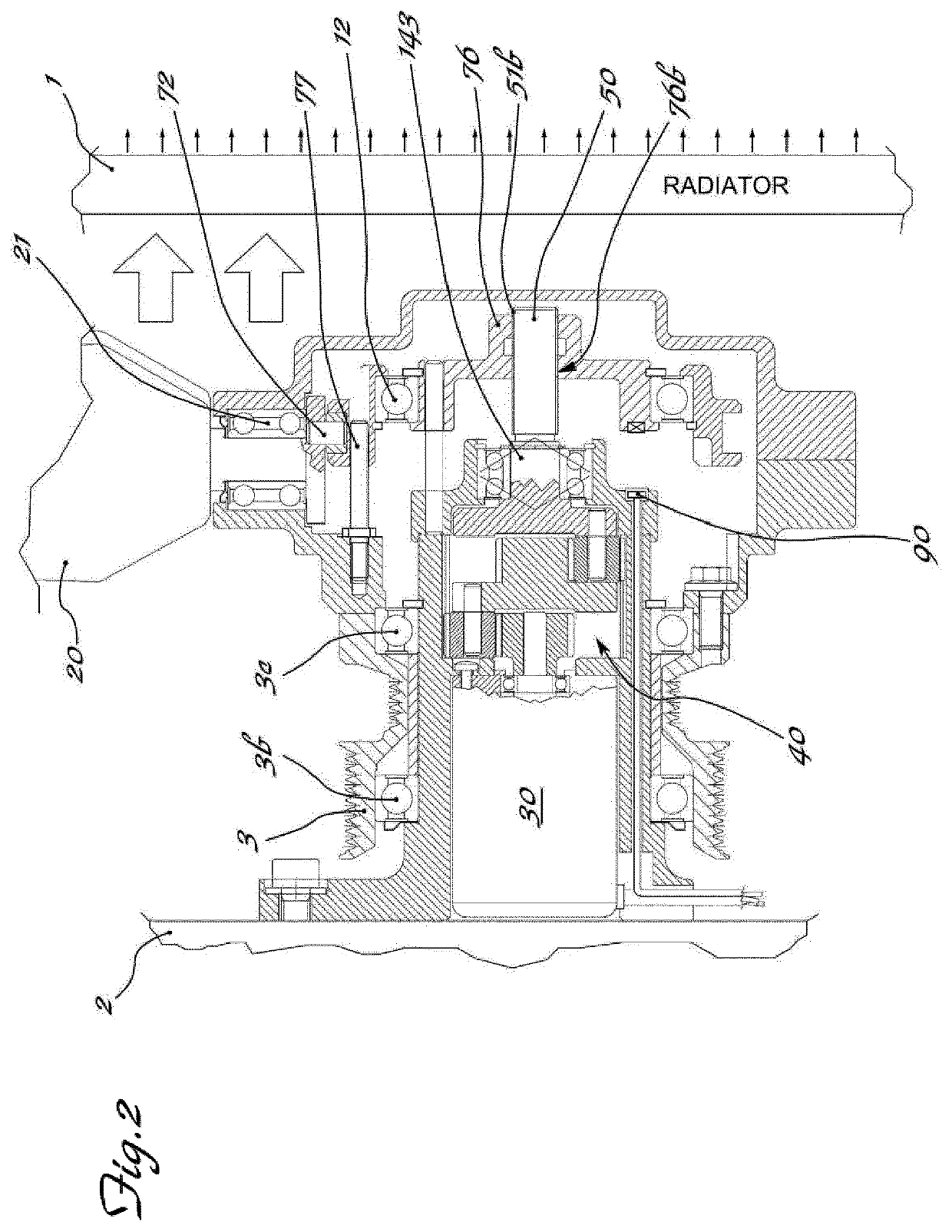
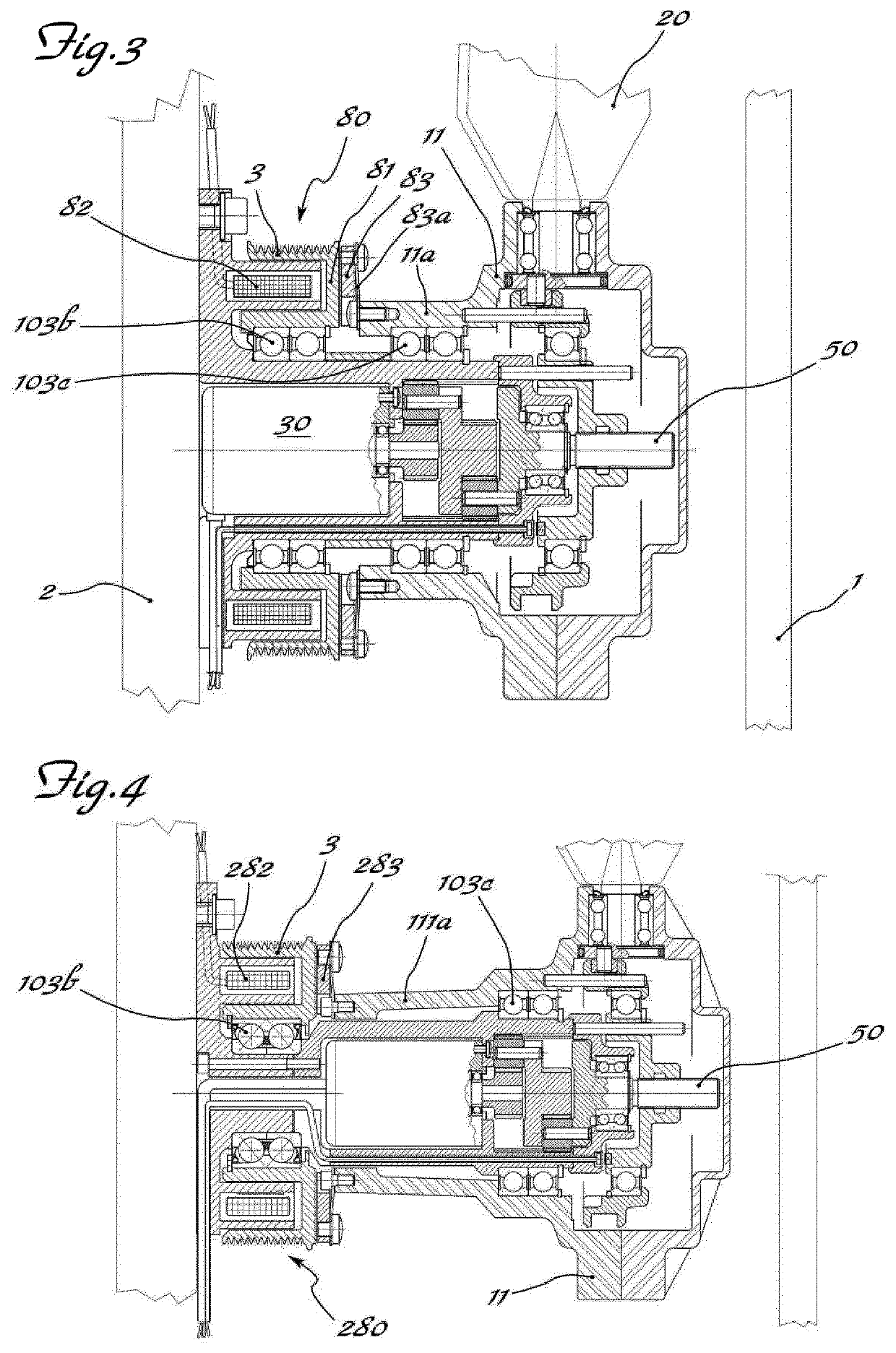
Apparatus for actuating and controlling the rotation of blades of fans for cooling the coolant in machines/vehicles
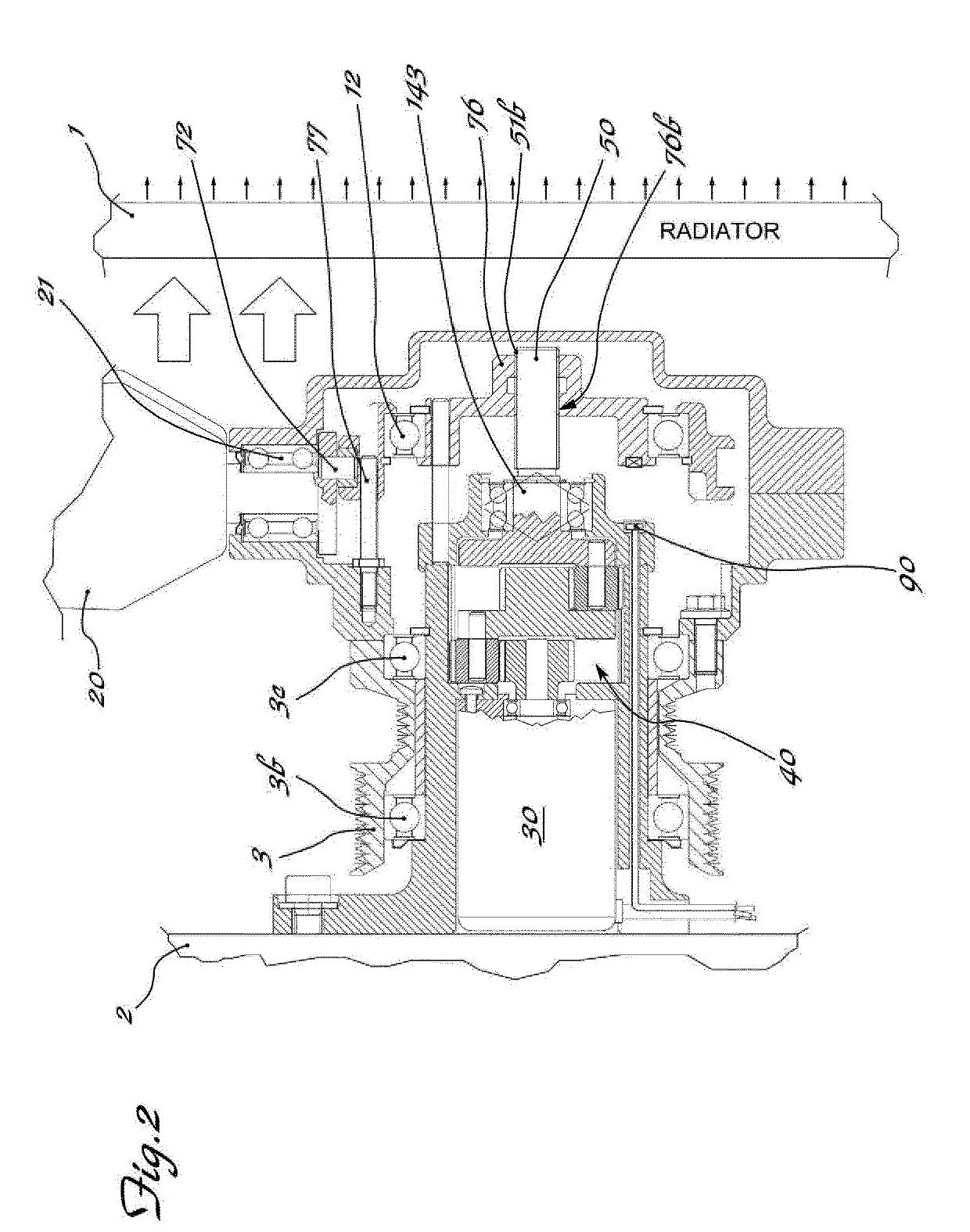
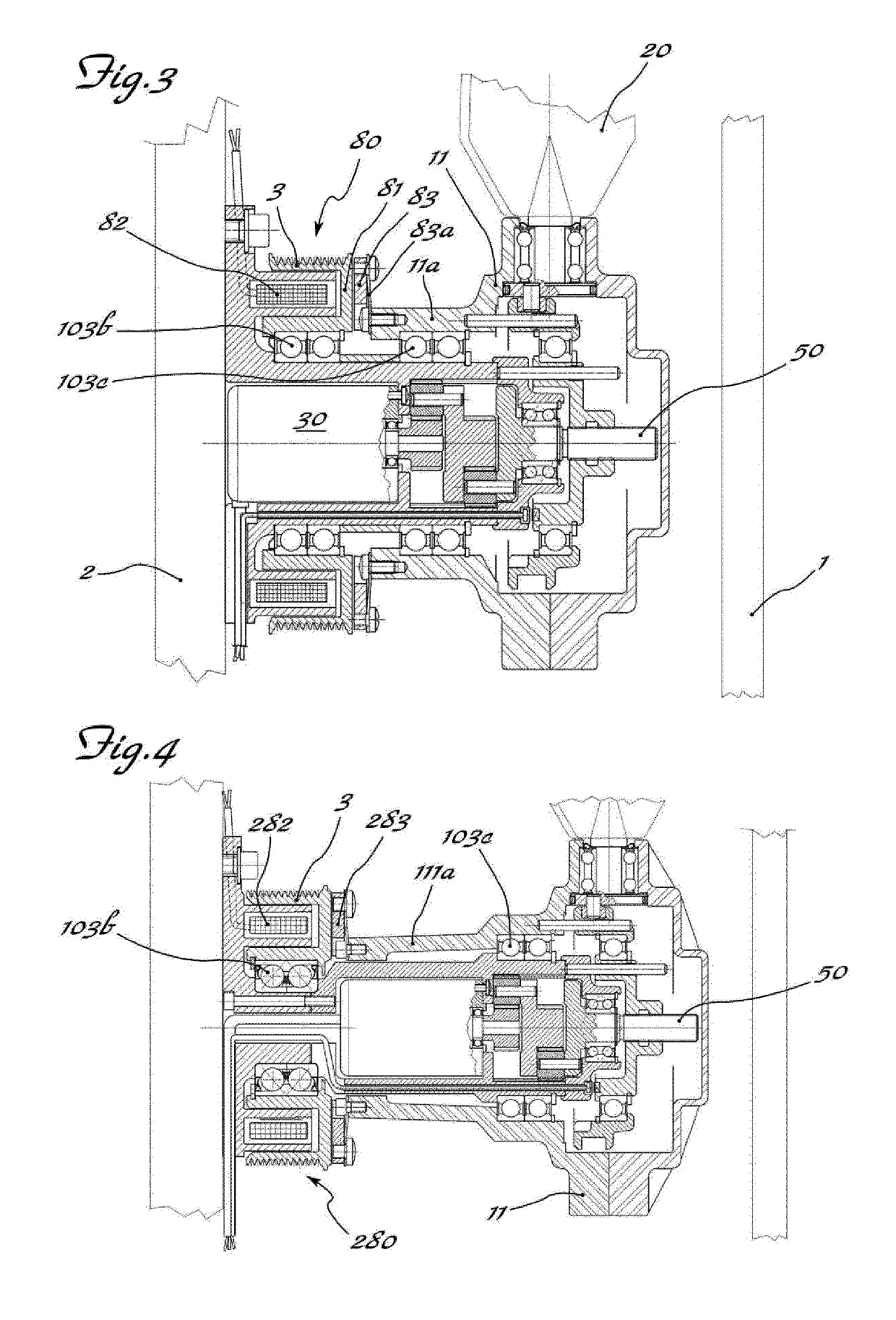
ActiveUS10738681B2Avoid power consumptionEasy and low-costCoolant flow controlPump componentsGear wheelElectromagnetic clutch
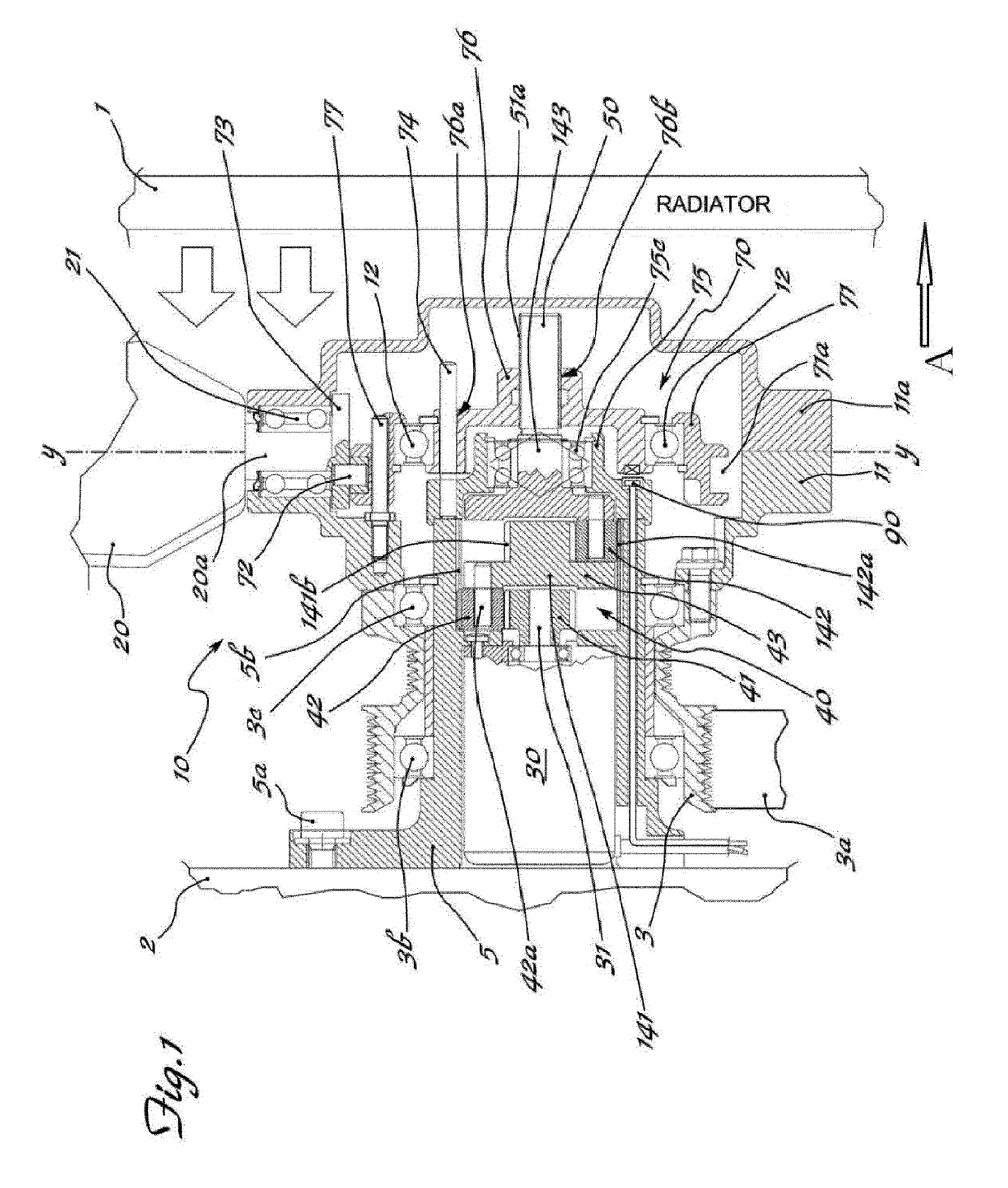
Apparatus for actuating and controlling the rotation, about their longitudinal axis (Y-Y), of blades (20) of cooling fans (10) for operating machines and / or vehicles, in particular agricultural tractors and off-road vehicles, said fan being mounted on a hub (11) which can be rotationally driven about its axis (X-X) by associated driving means (3,3a) suitable for connection to the heat engine (1) and mounted on a fixed support (5) by means of a bearing (3b) the apparatus comprising a ring (71) provided with a radial seat (71a) inside which a radial pin (72), eccentrically engaged in a base (73) integral with the shank (20a) of the blade (20), is inserted; an electric motor (30) which is coaxial with the axis (X-X) of the hub (11) and the shaft (31) of which is coaxially connected to a reduction gear (40), the kinematic output element (143) of which is coaxially connected by means of a screw (51a) / female thread (76a) coupling to a slider (76) displaceable in both directions along the axis (X-X) and kinematically connected to the ring (71) with an eccentric pin (72) driving the base (73) of the shank of the blade, an electromagnetic clutch (80; 180; 280) being arranged between the pulley (3) and the hub (11) of the fan.
Owner:BARUFFALDI
Side paneling system
ActiveCN103158663AEasy and low costLow costPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVehiclesEngineeringAirbag
A side paneling system 1 for a pillar 7 of a motor vehicle, comprises a side paneling part 2 for covering the pillar and an airbag 10 arranged between the side paneling part and the pillar, at least one connecting element 14, 17 for releasably connecting the side paneling part to the pillar so that as the airbag is activated the side paneling part can move away from the pillar with the airbag, and a catch band or strap 11 that is indirectly or directly connected to the side paneling part, so that the side paneling part is indirectly or directly fastened to the pillar with the catch band even when the airbag is activated and the connecting element 14 is released, wherein the side paneling part has a first part 3 and a second part 4, and only the second part can move away from the pillar with the airbag. The airbag may be for protecting a persons head, and may be located adjacent an A or C pillar. A method of securing the paneling system in a vehicle is also disclosed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Penetration part fireproof coating material
ActiveUS20200299956A1Increase production costForming accuratelyNuclear energy generationPipesStructure buildingFastener
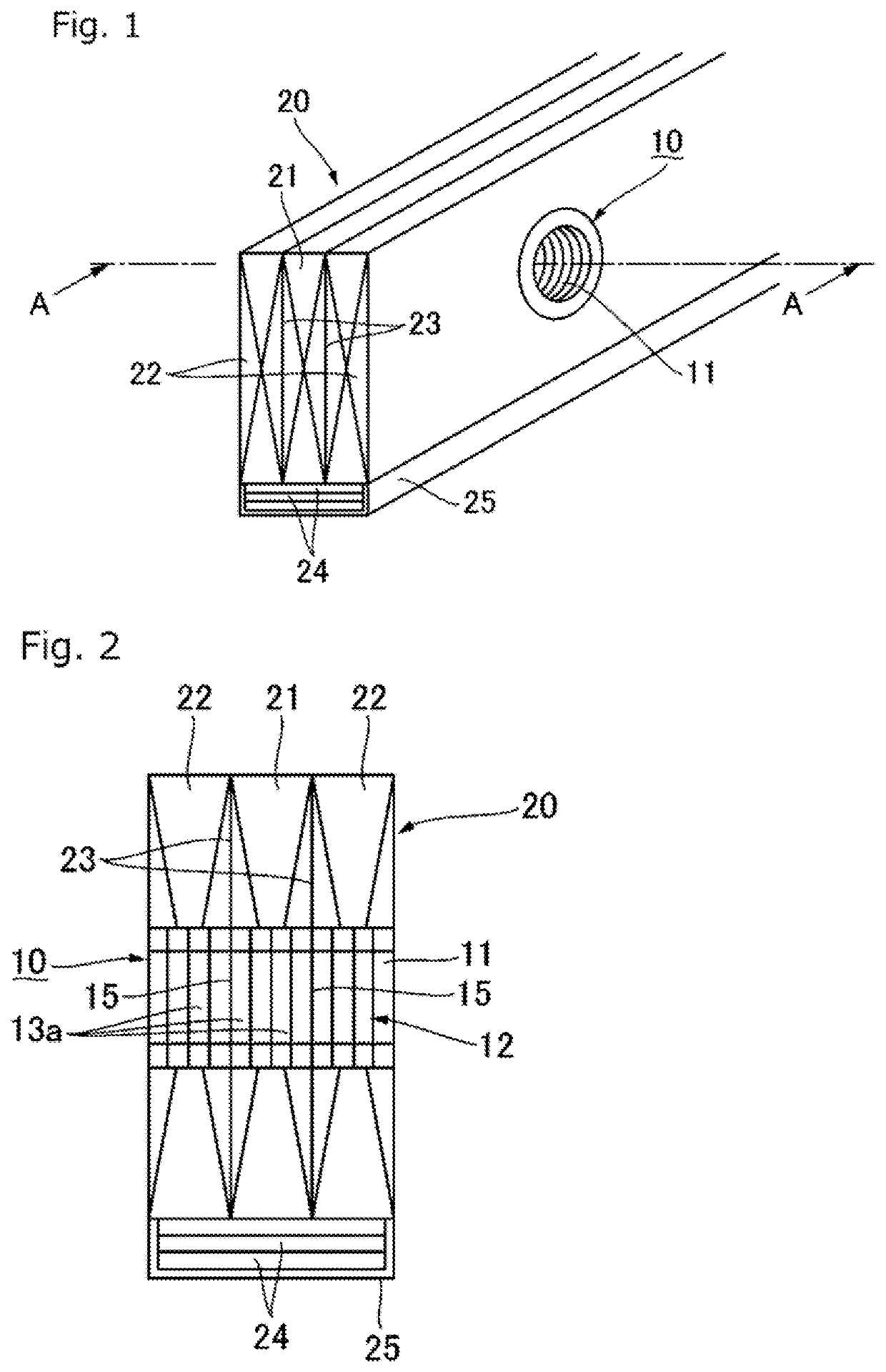
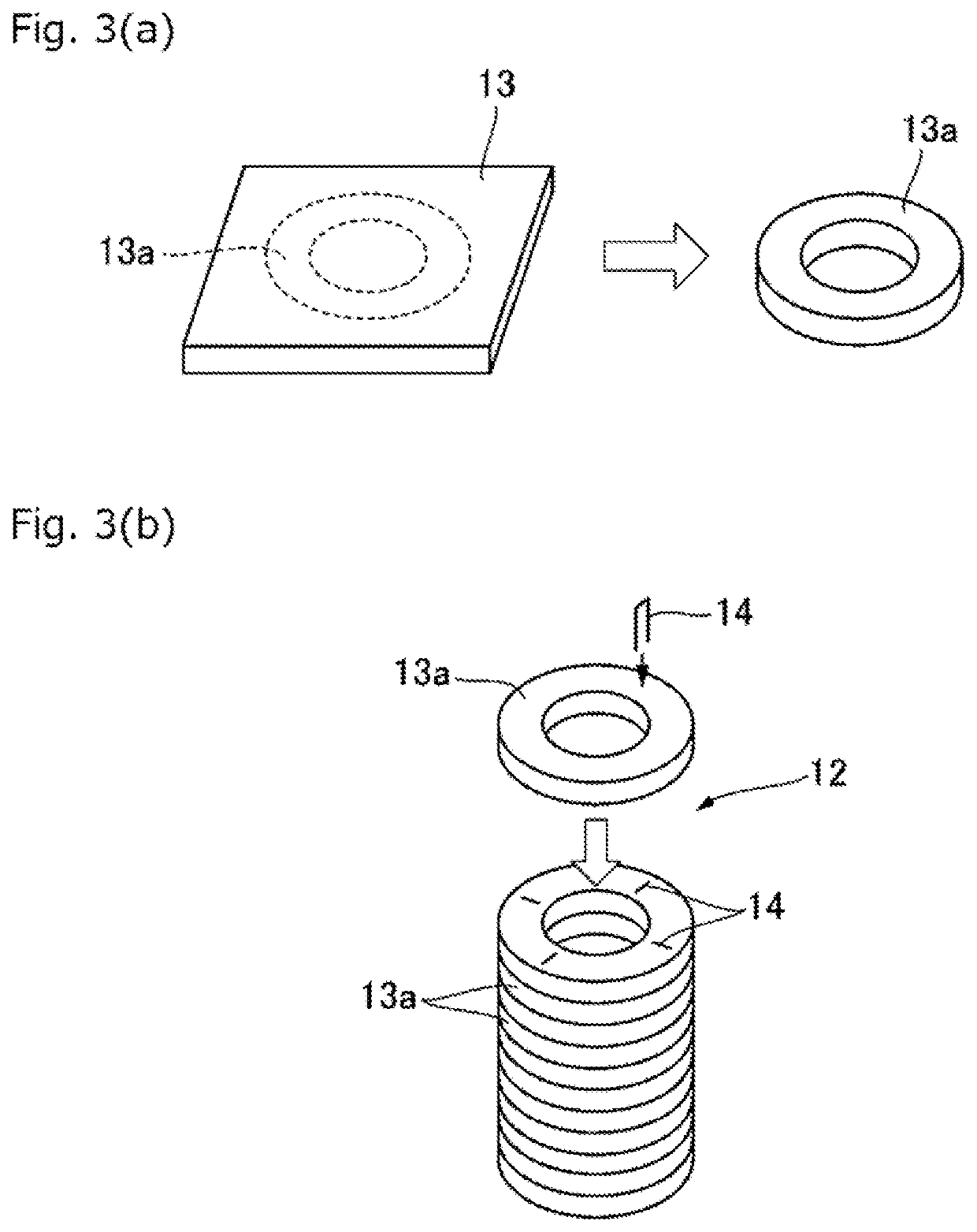
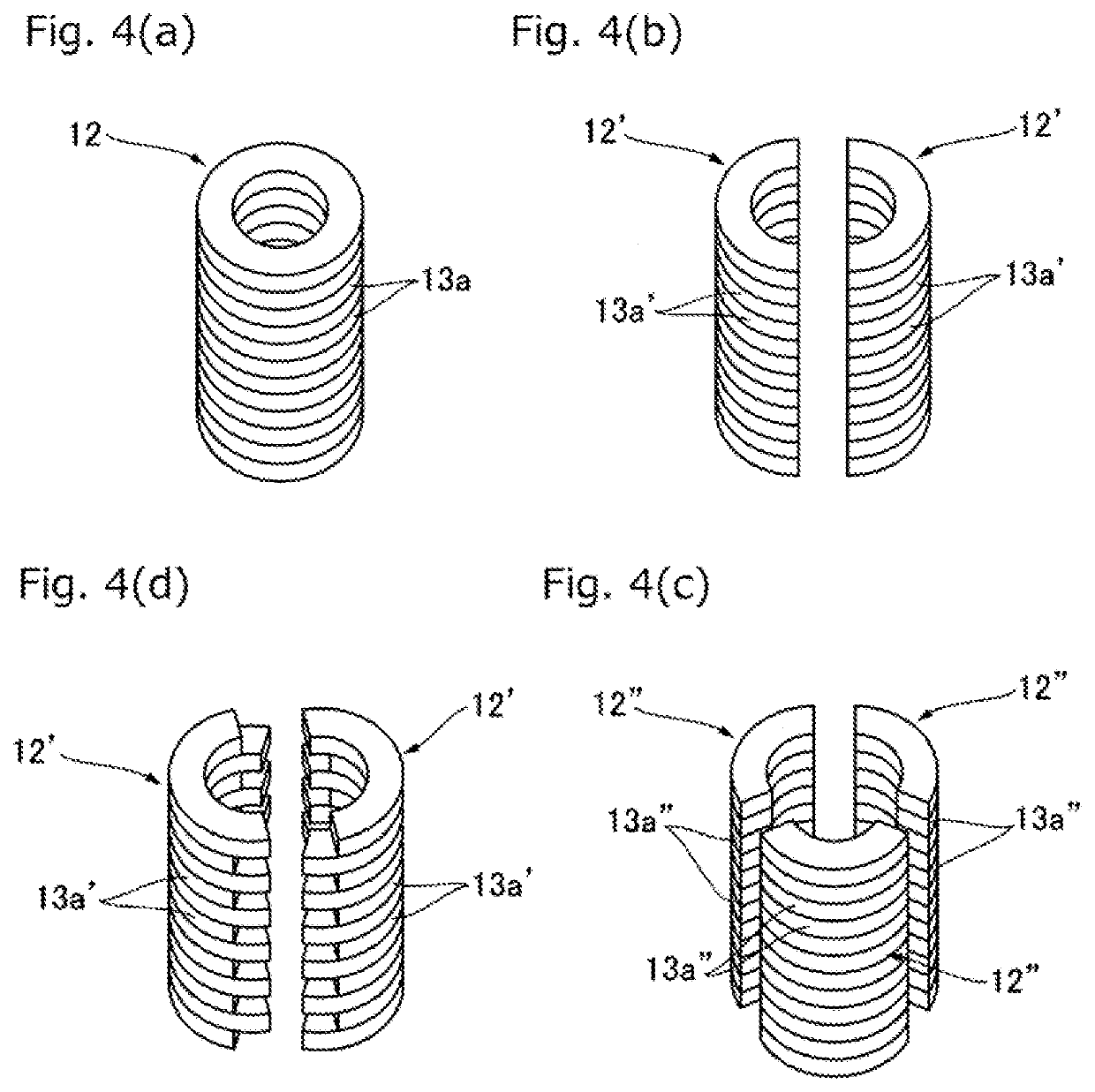
A penetration part fireproof covering material used when a penetration part covered for fireproof is formed in a fireproof beam that is a fireproof constructional member that constitutes a wooden building, wherein the penetration part fireproof covering material is formed to have a tubular shape by stacking a plurality of gypsum board pieces (13a) formed from gypsum boards in a thickness direction and unitarily connecting the plurality of gypsum board pieces. The penetration part fireproof covering material is formed to have the tubular shape by stacking the plurality of gypsum board pieces that preferably have an annular shape and are cut out from commercially available gypsum boards having thicknesses of 9.5 mm to 25.5 mm while fixing the plurality of gypsum board pieces to each other preferably using metal fasteners such as staples, and unitarily connecting the plurality of gypsum board pieces.
Owner:YOSHINO GYPSUM CO LTD
Apparatus for actuating and controlling the rotation of blades of fans for cooling the coolant in machines/vehicles
ActiveUS20190162105A1Prevent any residual power consumptionEasy and low-cost mannerCoolant flow controlPump componentsElectromagnetic clutchEngineering
Apparatus for actuating and controlling the rotation, about their longitudinal axis (Y-Y), of blades (20) of cooling fans (10) for operating machines and / or vehicles, in particular agricultural tractors and off-road vehicles, said fan being mounted on a hub (11) which can be rotationally driven about its axis (X-X) by associated driving means (3,3a) suitable for connection to the heat engine (1) and mounted on a fixed support (5) by means of a bearing (3b) the apparatus comprising a ring (71) provided with a radial seat (71a) inside which a radial pin (72), eccentrically engaged in a base (73) integral with the shank (20a) of the blade (20), is inserted; an electric motor (30) which is coaxial with the axis (X-X) of the hub (11) and the shaft (31) of which is coaxially connected to a reduction gear (40), the kinematic output element (143) of which is coaxially connected by means of a screw (51a) / female thread (76a) coupling to a slider (76) displaceable in both directions along the axis (X-X) and kinematically connected to the ring (71) with an eccentric pin (72) driving the base (73) of the shank of the blade, an electromagnetic clutch (80; 180; 280) being arranged between the pulley (3) and the hub (11) of the fan.
Owner:BARUFFALDI
Device for polishing and cooling plastic tapes from gas nozzles
Owner:REIFENHAUSER GMBH & CO MASCHFAB
Explosion-proof inductive voltage transformer
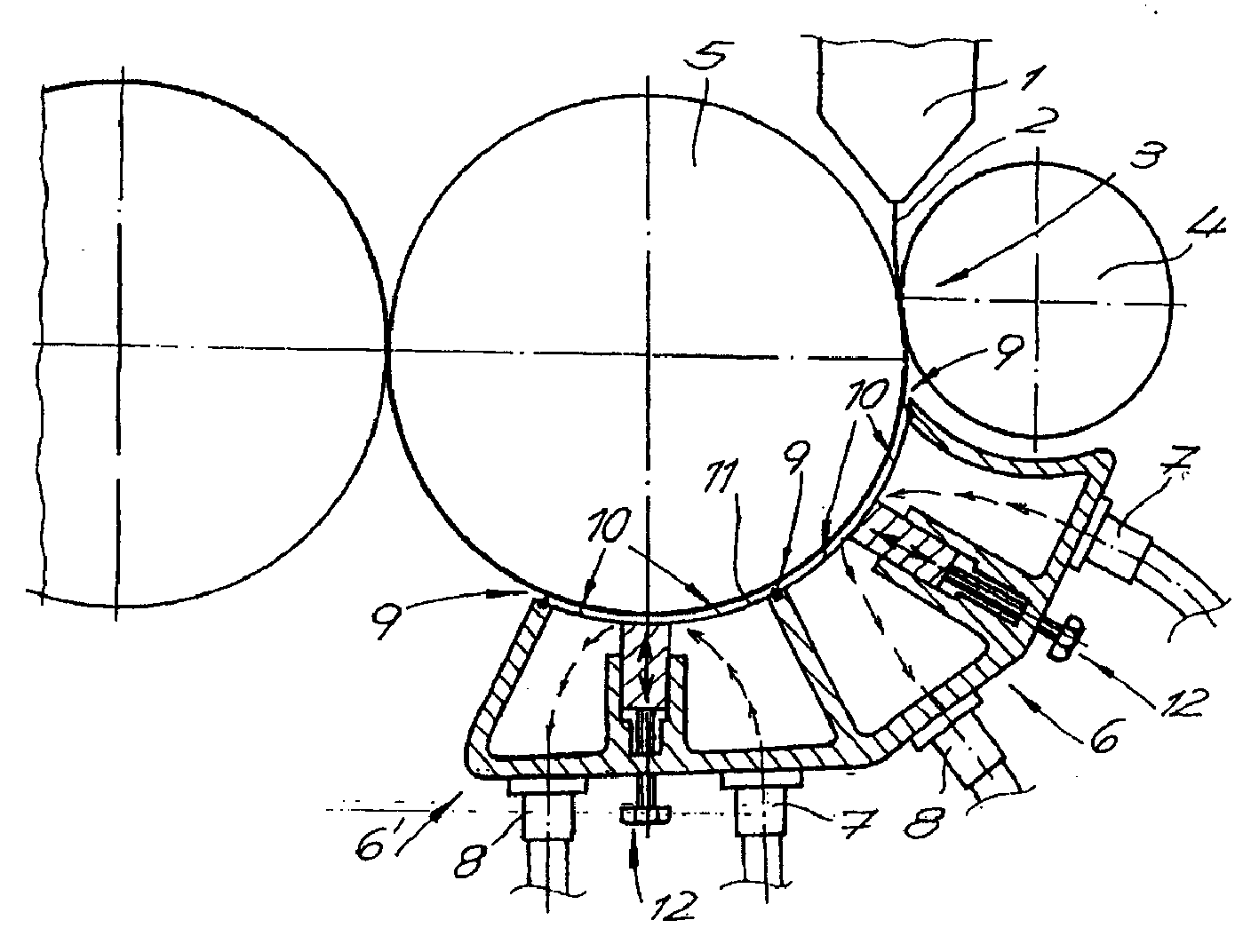
ActiveUS20190355513A1Easy and low cost approachPrevent and reduce damageTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionTransformersElectrical FailureLow voltage
An explosion-proof inductive voltage transformer (IVT) of the type comprising: i) a high voltage section that receives a high voltage current, limits and insulates the high voltage current to be transformed and reduces its electrical stress; and, ii) a voltage transforming section connected to the high voltage section and contained in an insulation body in order to protect the elements of the voltage transforming section and reduce the impact of explosions in case of electrical failure, wherein the voltage transforming section comprises means for reducing the voltage of the high voltage current to a low voltage and electric transmission means that transmit a resulting low voltage current to a low voltage distribution line; wherein the voltage transforming section of the IVT further comprises shock mitigation means comprising at least one hollow section located opposite the high voltage section that, during an electrical failure causing an explosion, direct the gases and shockwave of the explosion towards the hollow section, thereby reducing the damage caused by the explosion to the IV transformer and its surroundings; provides an explosion-proof inductive voltage transformer easy to install and with a low cost manufacture.
Owner:ARTECHE NORTH AMERICA S A DE CV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com