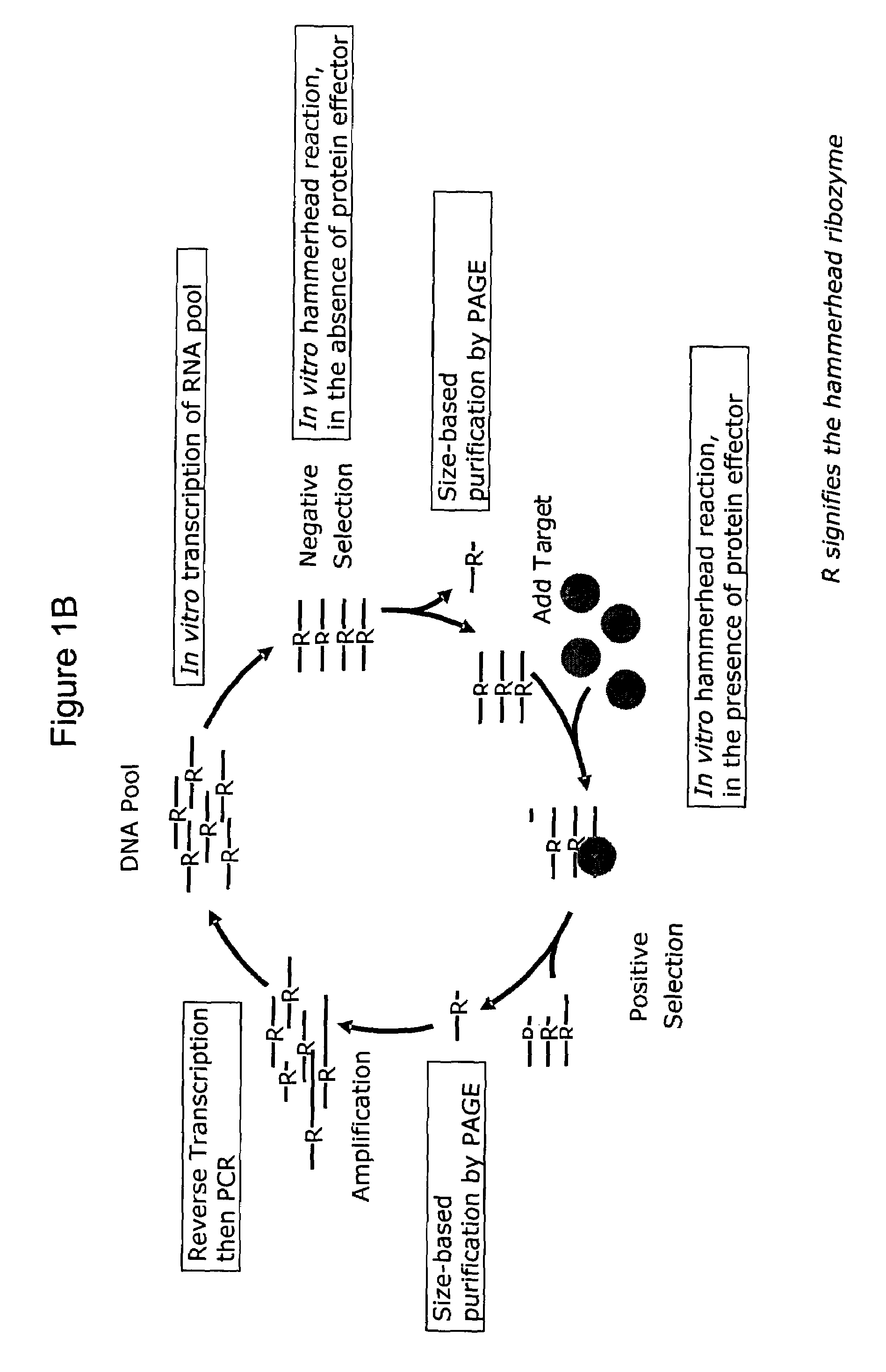
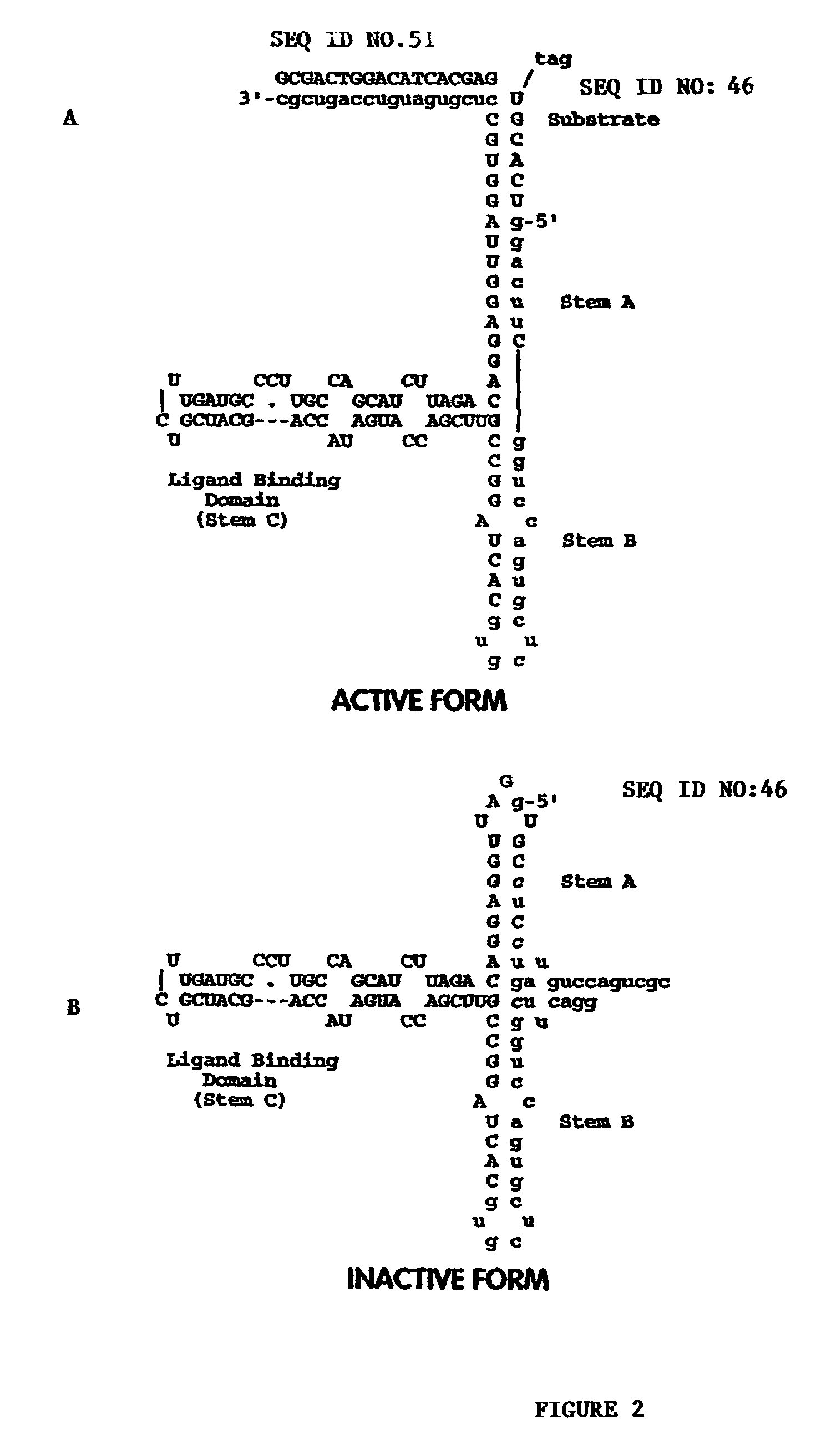
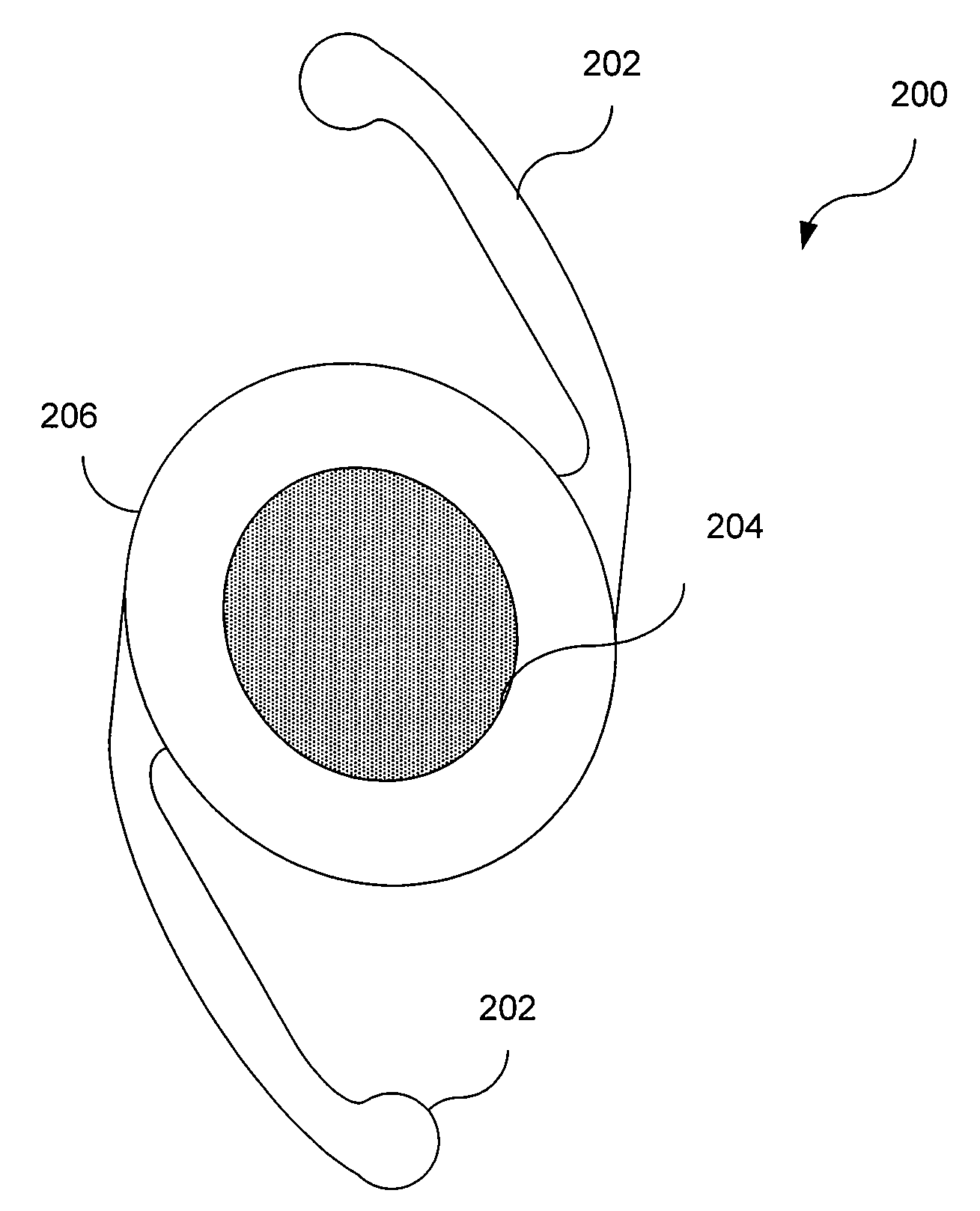
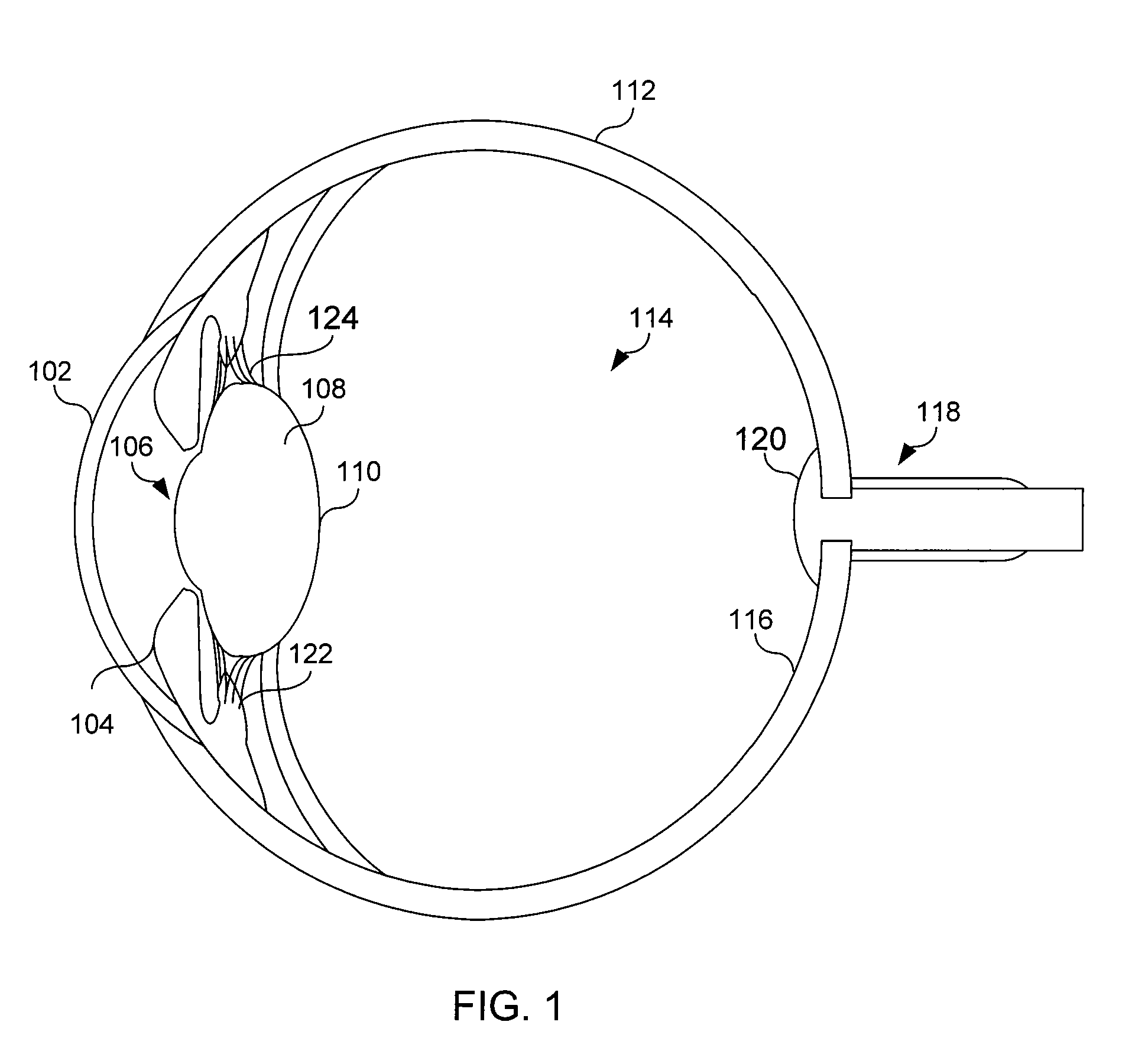
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107results about How to "Change optical properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
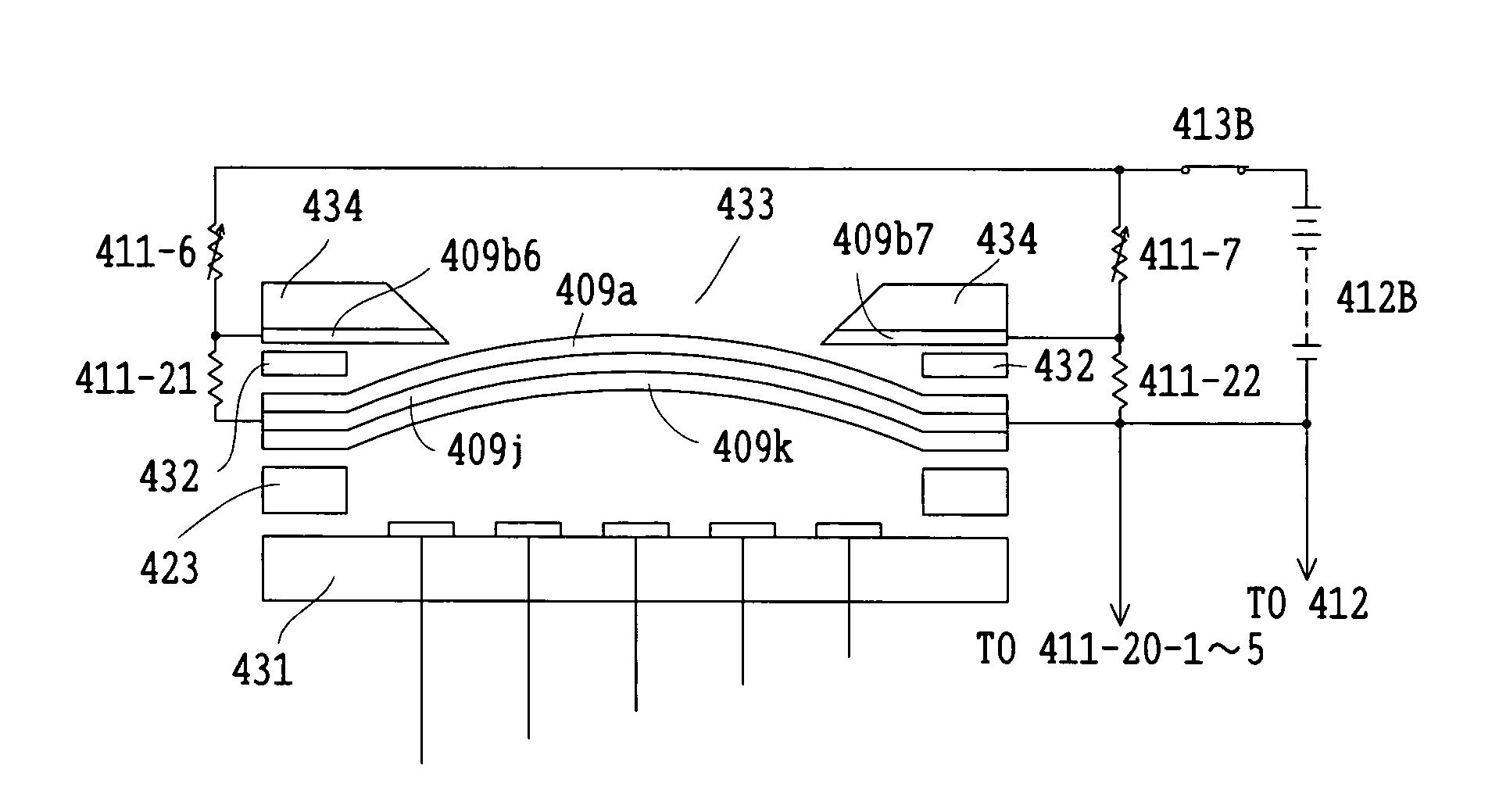
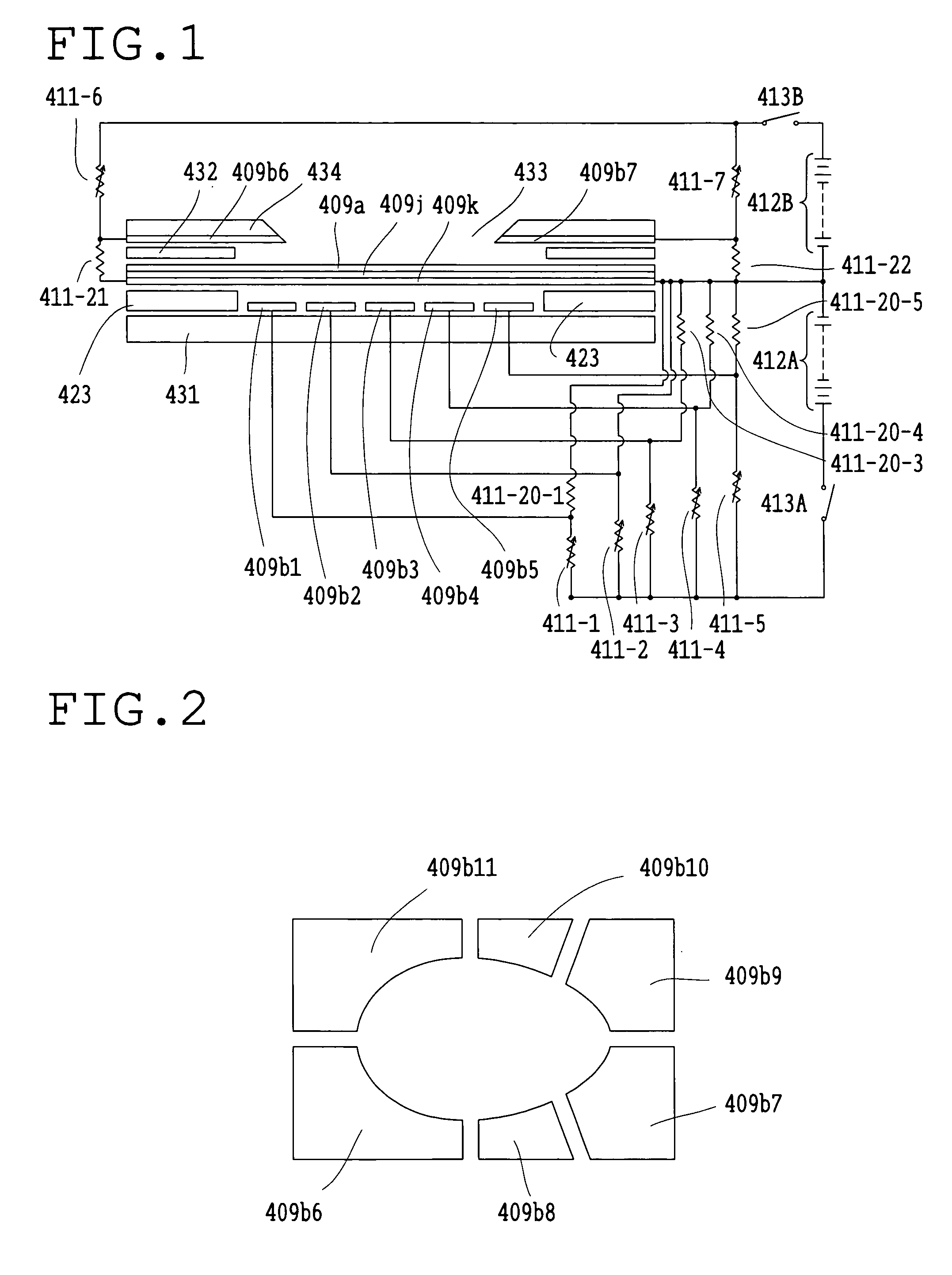
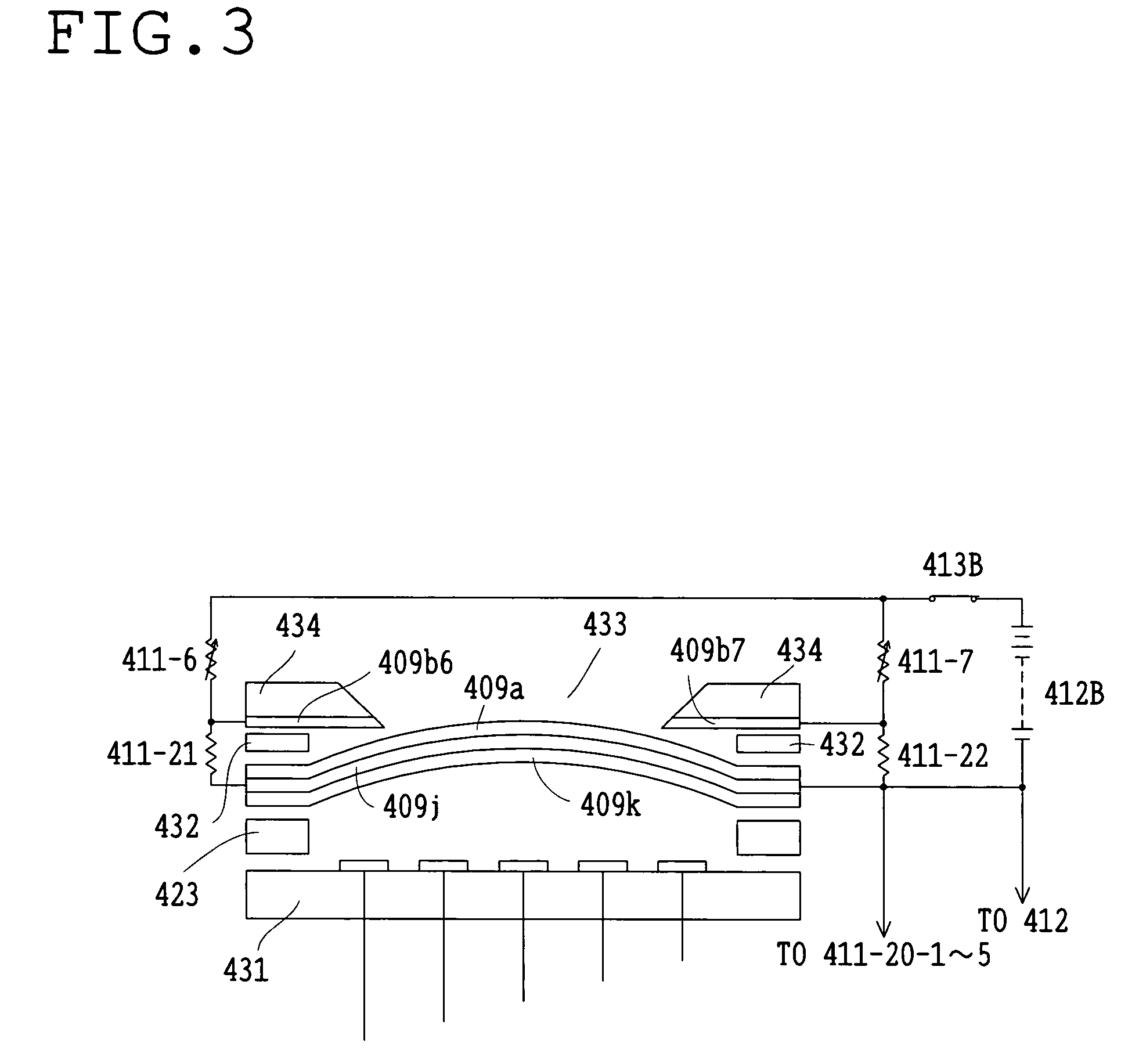
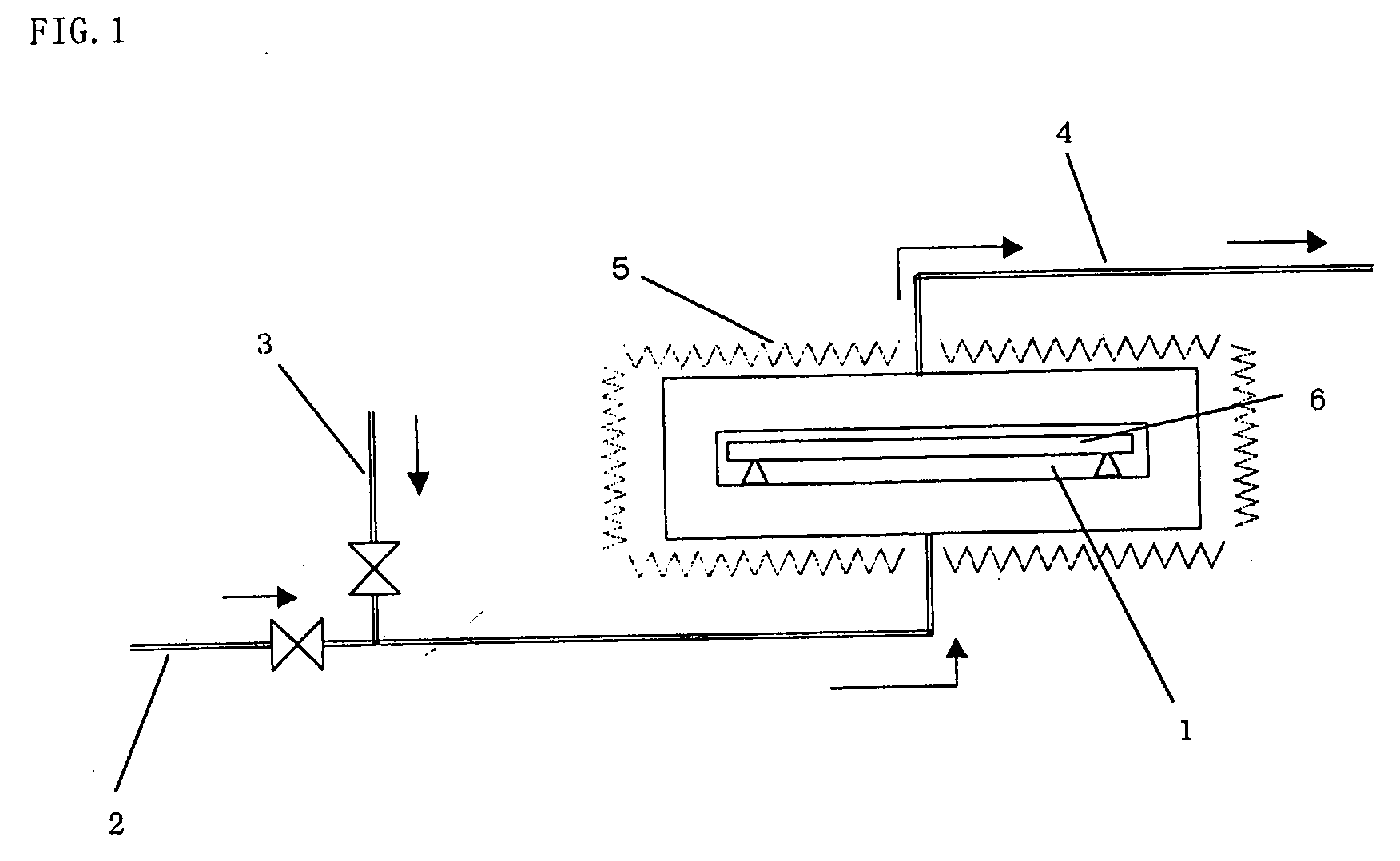
Variable optical-property element
InactiveUS20050030438A1Change optical propertiesChange propertiesMirrorsStatic indicating devicesElectric forceOptical property
A variable optical-property element includes a plurality of electrodes, a substrate which is driven by an electric force and can be deformed into a convex shape, an electrode constructed integrally with the substrate, an optical surface provided on the substrate, and a driving circuit connected to the electrodes.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Nucleic acid sensor molecules and methods of using same
InactiveUS7125660B2Easy to detectChange optical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesOptical propertyDNA
Methods for engineering a nucleic acid sensor molecule are provided. Biosensors comprise a plurality of nucleic acid sensor molecules labeled with a first signaling moiety and a second signaling moiety. The nucleic acid sensor molecules recognizes target molecules which do not naturally bind to DNA. Binding of a target molecule to the sensor molecules triggers a change in the proximity of the signaling moieties which leads to a change in the optical properties of the nucleic acid sensor molecules on the biosensor. Reagents and systems for performing the method are also provided. The method is useful in diagnostic applications and drug optimization.
Owner:ARCHEMIX CORP
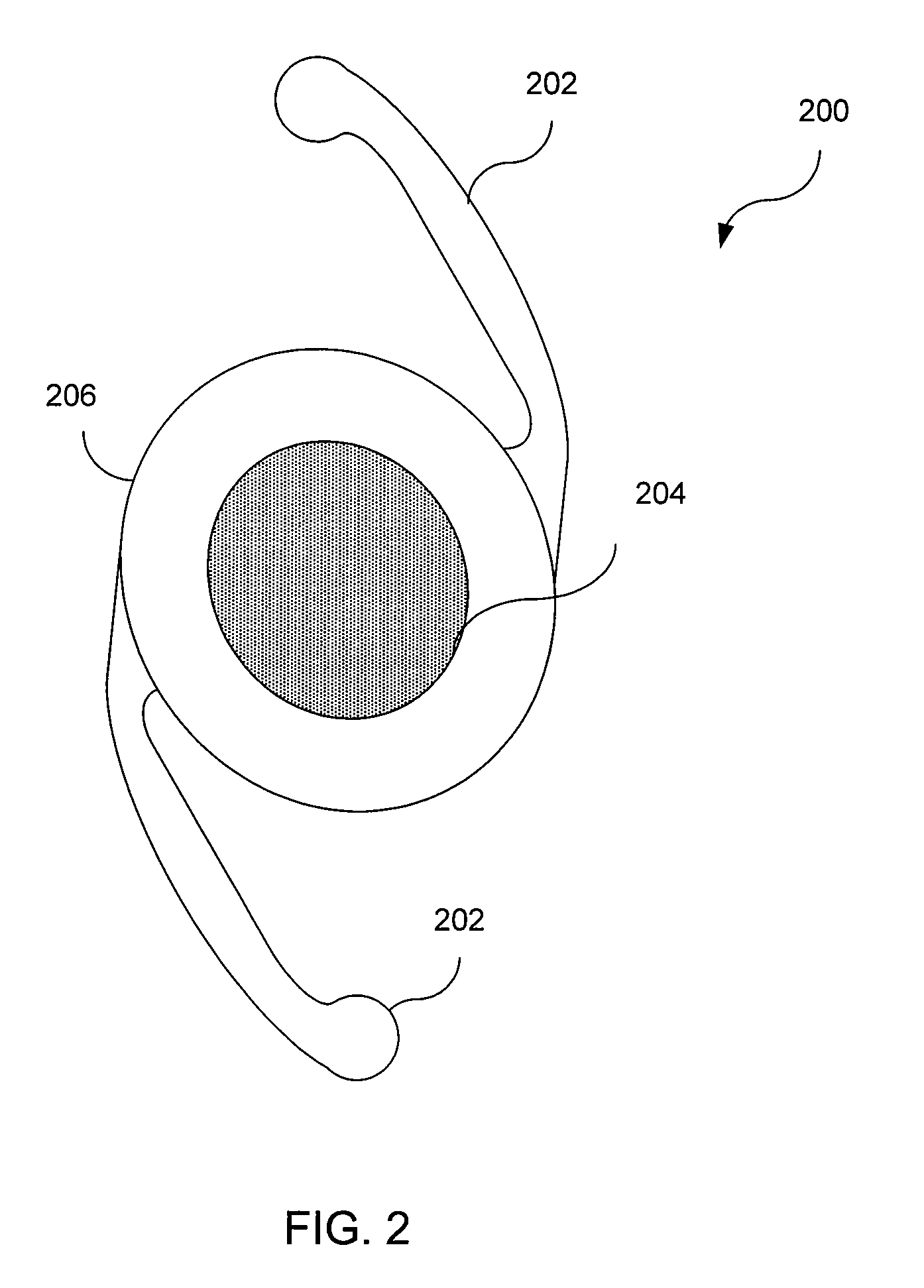
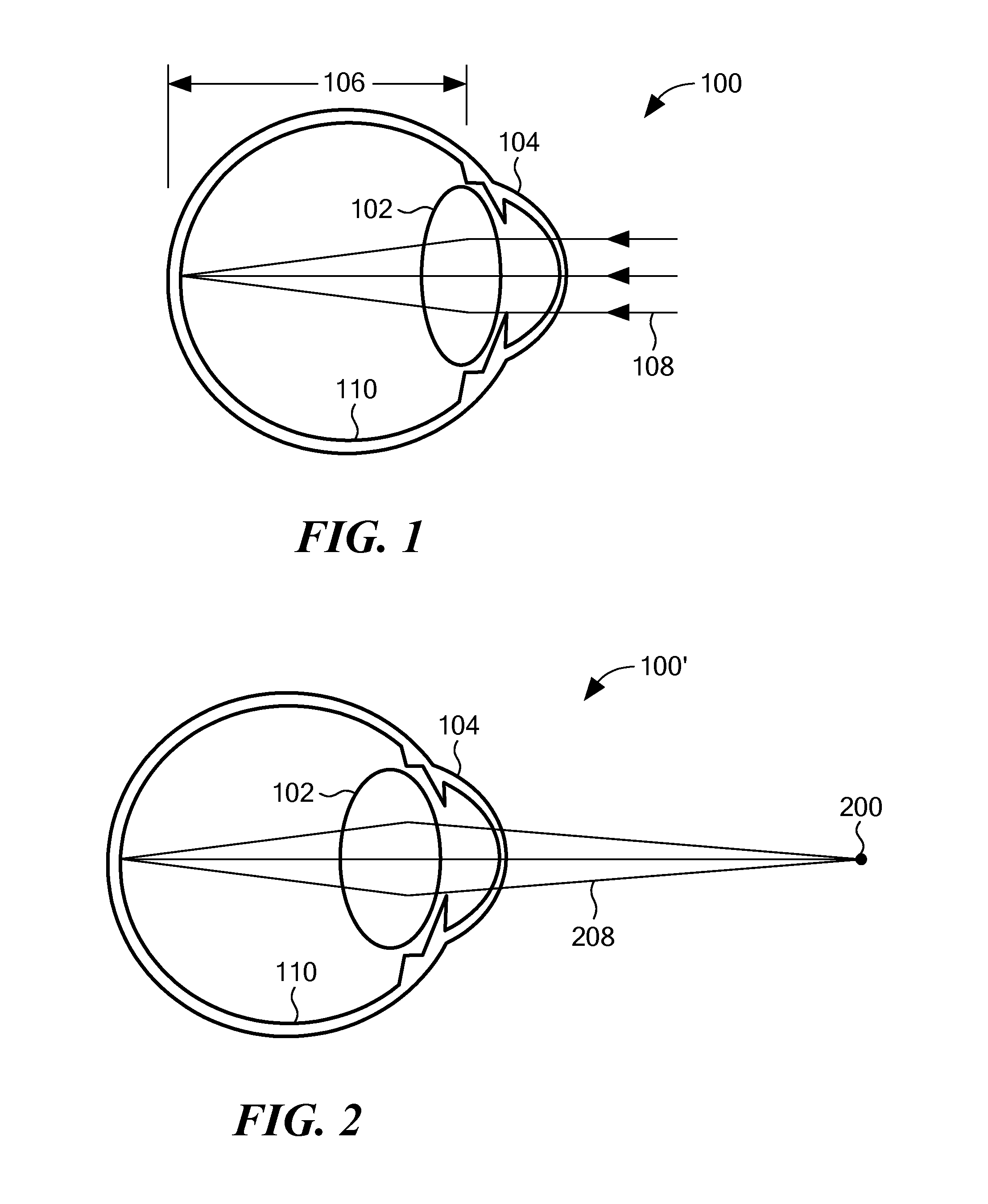
Accommodating intraocular lens
InactiveUS20100094412A1Correct visual impairmentImproved ocular implantEye surgeryIntraocular lensLiquid ChangeHigh surface
An improved multifocal design for an ocular implant is provided. This ocular implant can include an accommodating intraocular lens (IOL) and a number of haptics. The accommodating IOL includes a liquid suspended between two optically transparent plates or membranes to form a pressure lens that passes optical energy. The haptics mechanically couple to the IOL in order to position and secure the IOL within the eye. The IOL achieves accommodation by using the eye's ciliary muscles to vary the surface curvature of the liquid. The liquid may have a high surface tension and be surrounded by phobic liquid. Pressure from the ciliary muscles causes fluid to be added from or withdrawn to a reservoir. Increasing / decreasing the internal pressure of the liquid changes the angle (curvature) of the surface thus changing the optical properties of the lens. When the pressure is released the liquid returns to the reservoir. The whole system may be sealed off from the interior of the eye by a membrane / transparent lens.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
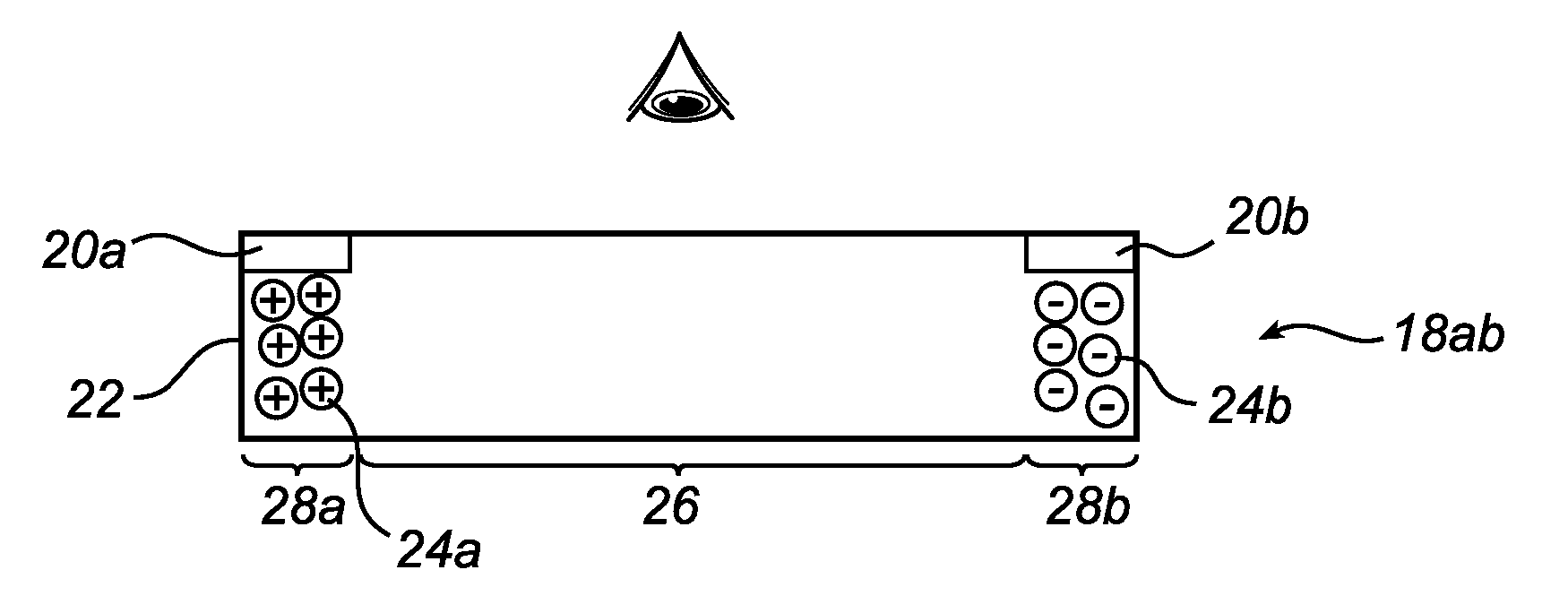
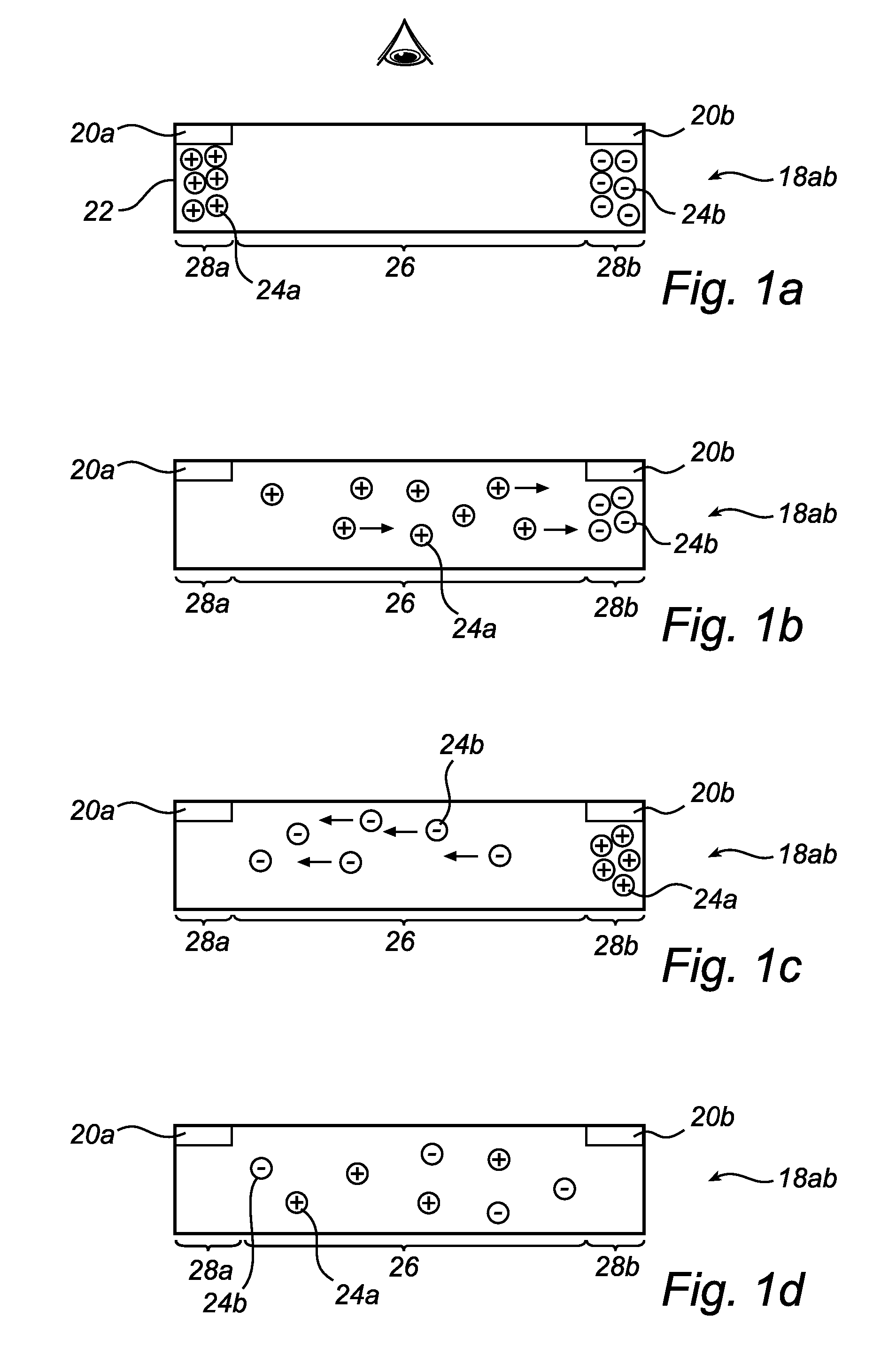
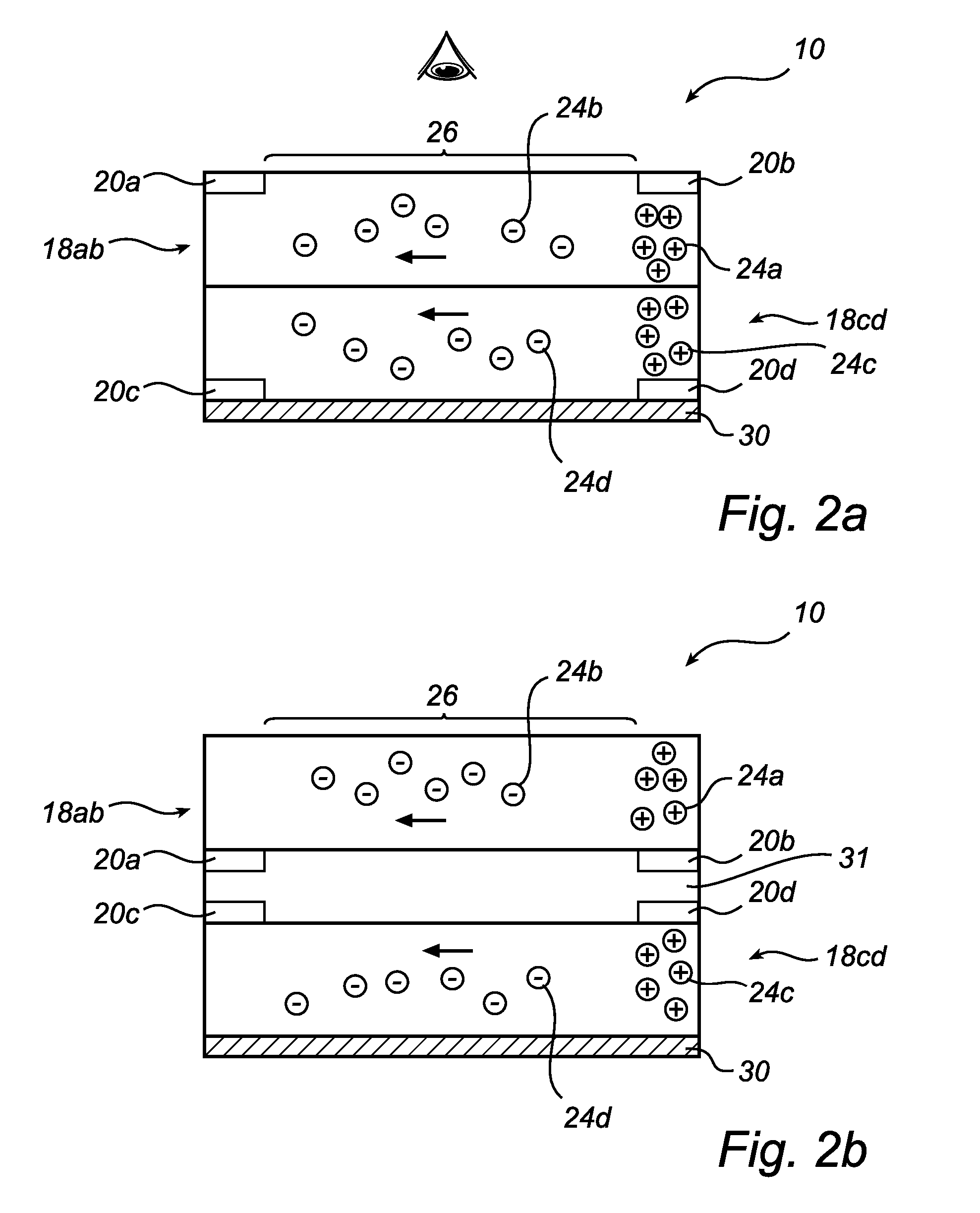
In-plane switching electrophoretic colour display
InactiveUS20100060628A1Improved electrophoreticImprove color displayCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsIn planeOptical property
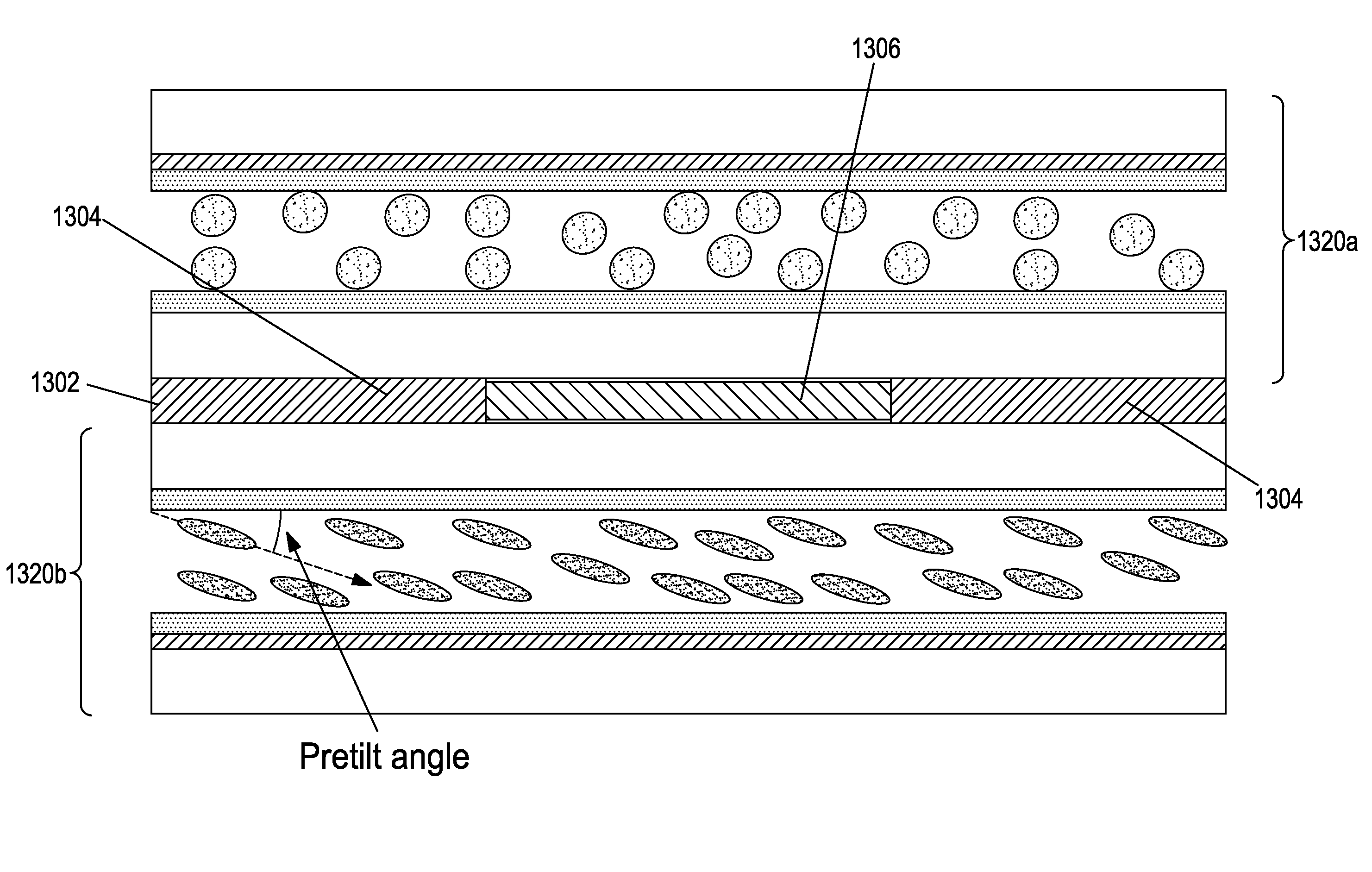
The invention relates to an electrophoretic color display panel, the display panel comprising at least one pixel (10, 12), the at least one pixel (10, 12) comprising a layer cavity (18ab) containing a suspension with a first set of charged particles (24a) having a first optical property and a second set of charged particles (24b) having a second optical property, and a pair of control electrodes (20a, 20b) arranged adjacent to the layer cavity (18ab), such that charged particles (24a, 24b) are essentially in-plane displaceable in an in-plane direction within the layer cavity (18ab) upon application of a control voltage over the electrode pair, wherein the in-plane distribution of charged particles (24a, 24b) having first and second optical properties in the layer cavity (18ab) depends on at least one of a differing control property additional to any polarity difference of the charged particles (24a, 24b) for each set of charged particles, or at least one additional electrode arranged adjacent to the layer cavity, wherein the electrode pair (20a, 20b) and the at least one additional control electrode are arranged essentially outside of a viewing area (26) of the at least one pixel (10, 12), such that a composite optical property of at least a portion of the at least one pixel (10, 12) is controllable. According to the invention, the control electrodes will be arranged at essentially the outer ends, or arranged in-plane, at a peripheral, of a prolonged layer cavity, such that the particles move in an in-plane direction within the layer cavity when the control voltage is applied. This facilitates the handling of the pixel since the layer cavity can be reached from essentially the outside of the pixel. Another advantage is that since only a minor part of the pixel area has to be covered with an electrode material the total transmission and thus the brightness of the pixel can be optimized.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Authenticatable media and method of authenticating
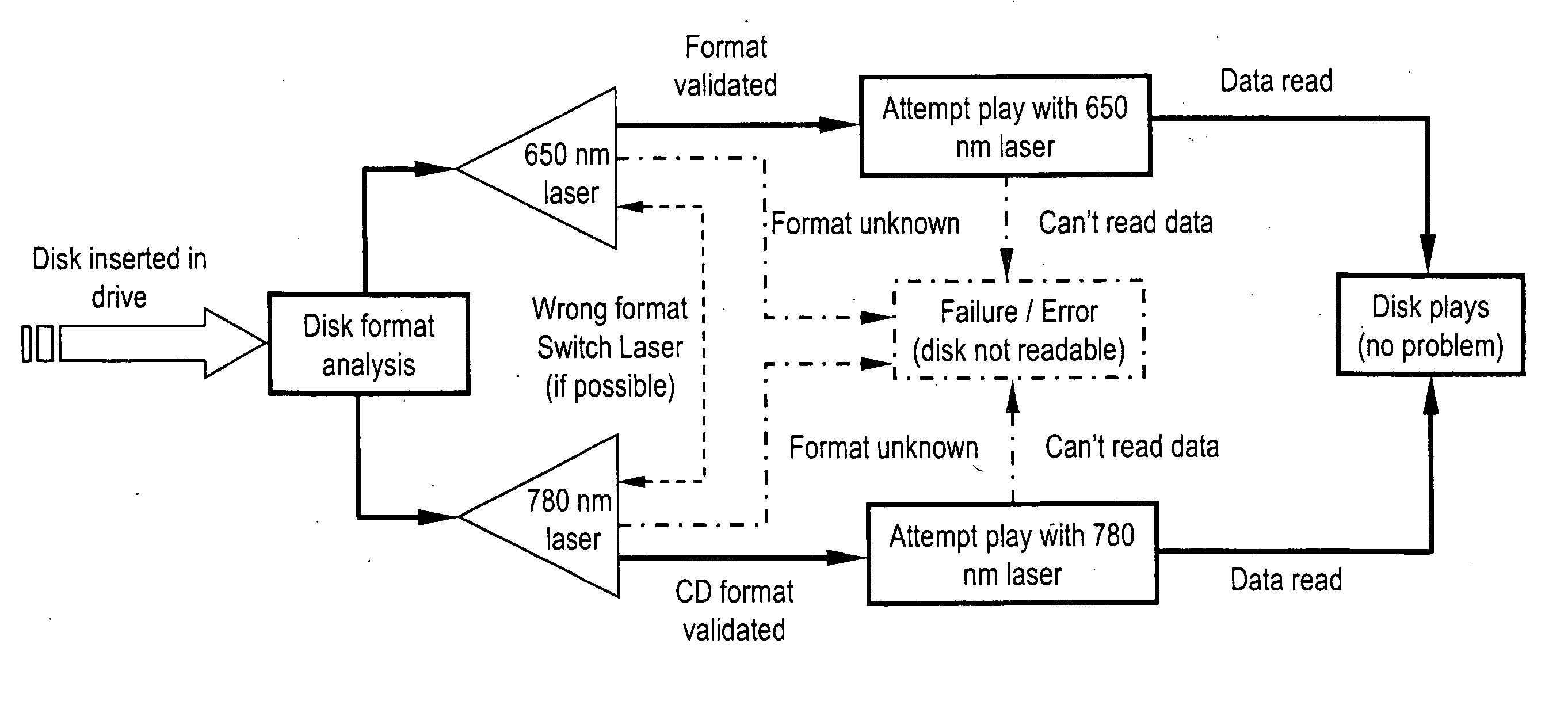
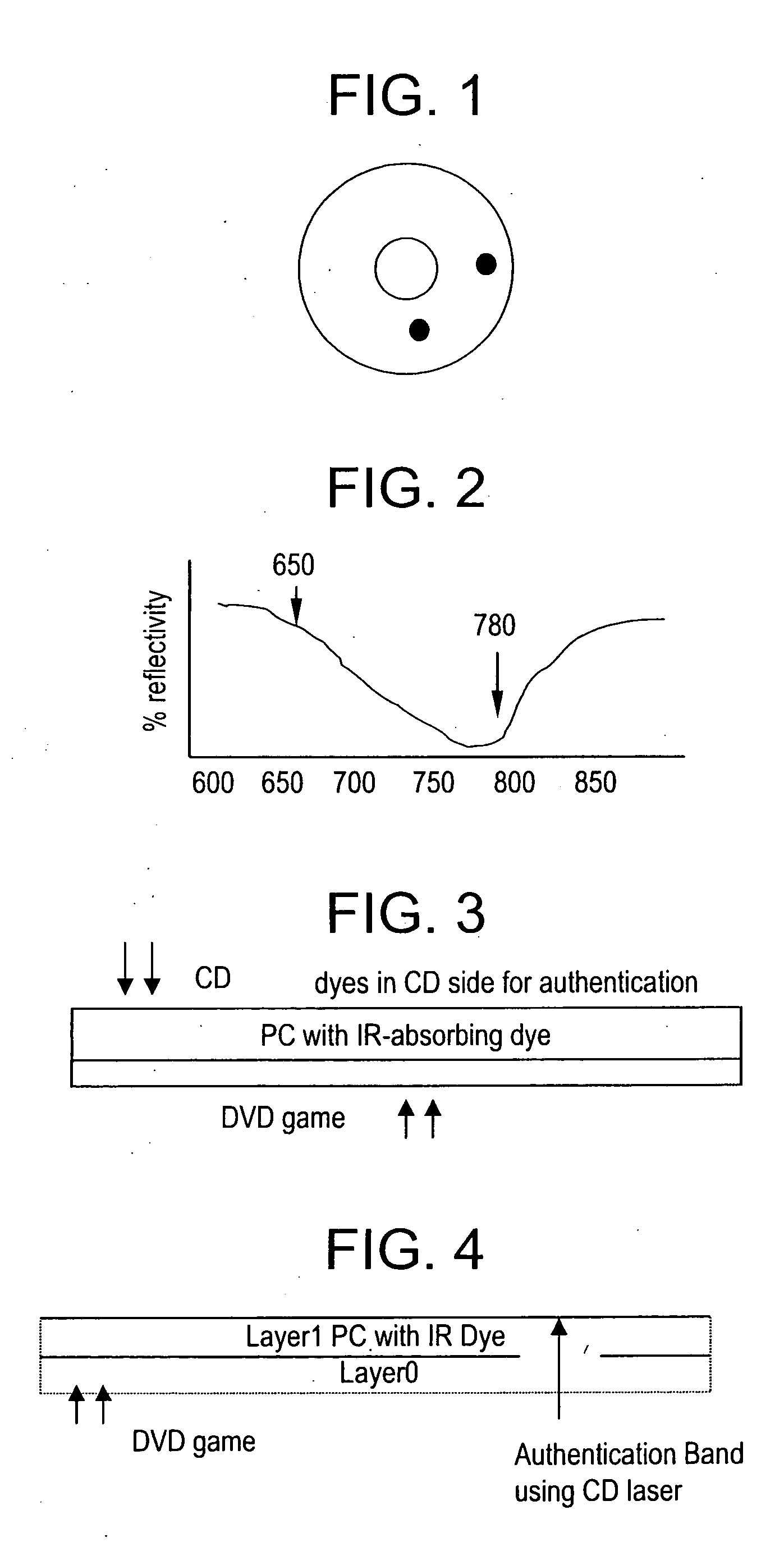
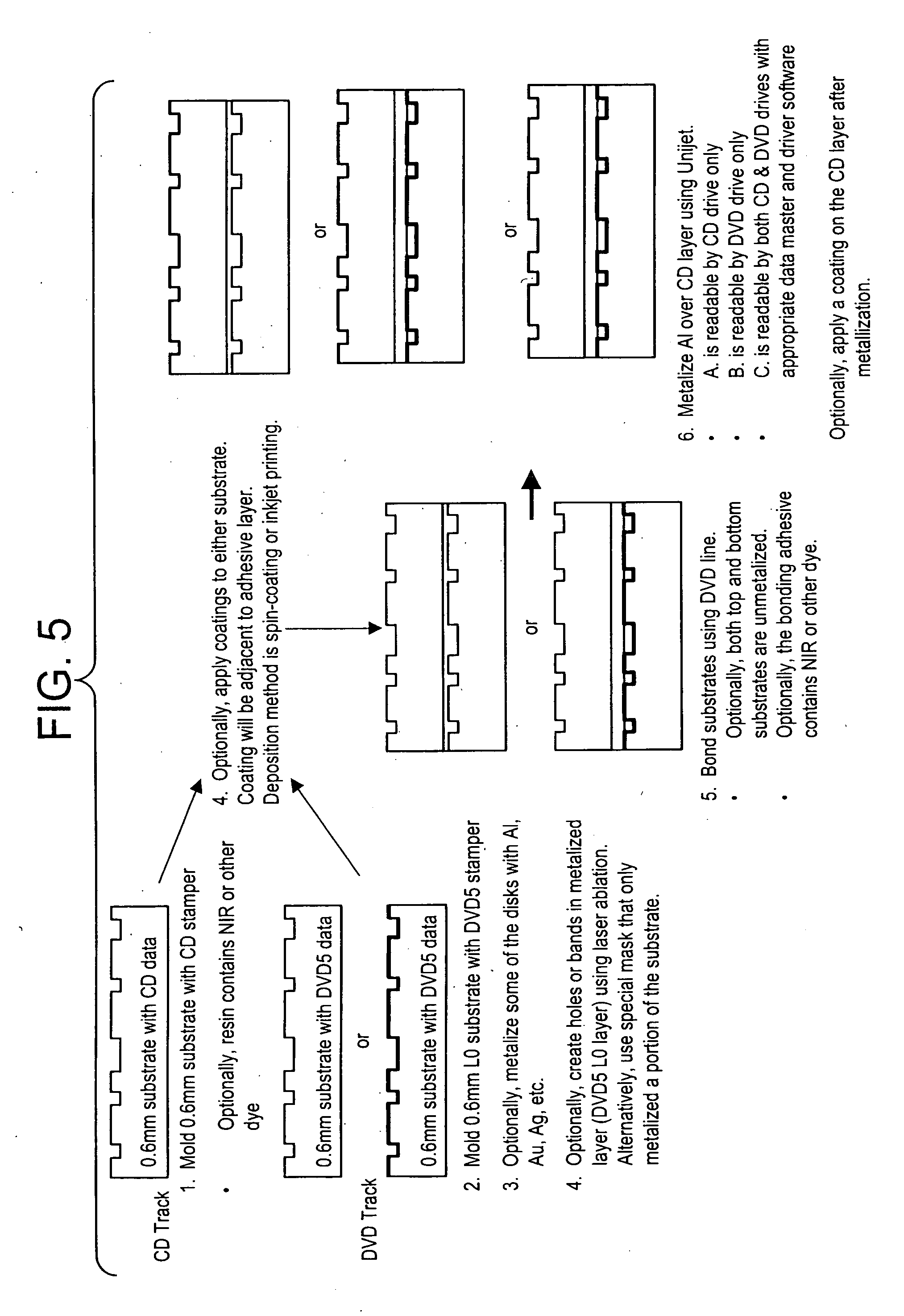
InactiveUS20060104172A1Change optical propertiesCombination recordingPaper-money testing devicesValidation methodsLength wave
One method for playing a disk, comprises illuminating a first portion of the optical article with a first laser to obtain a first optical signal, wherein the first laser has a first wavelength, illuminating a second portion with a second laser to obtain a second optical signal, wherein the second laser has a second wavelength that is different from the first wavelength, and determining if the optical article is authentic by comparing the first optical signal and the second optical signal.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Apparatus and method comprising deformable lens element
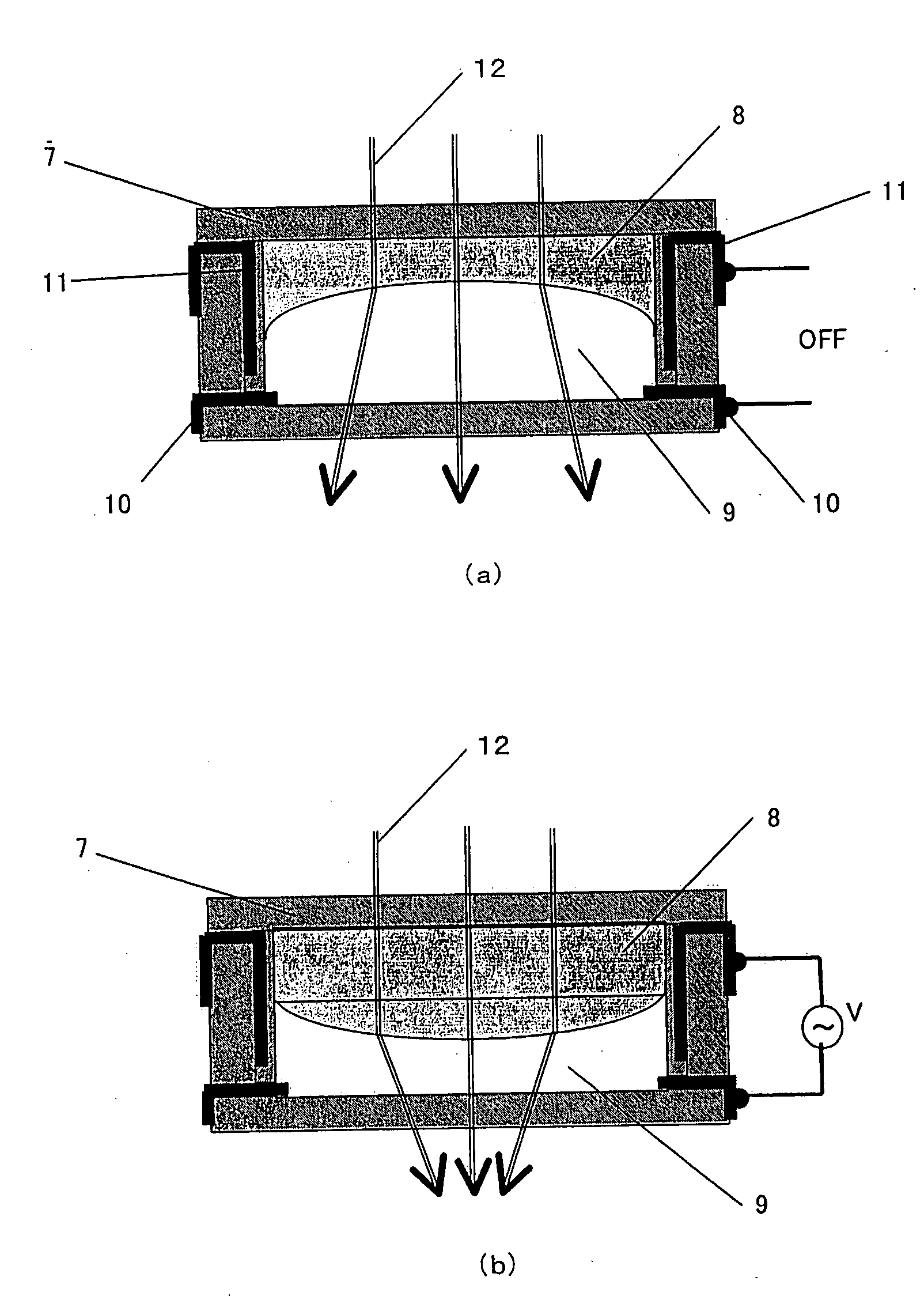
ActiveCN101632030AChange optical propertiesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPull forceEngineering
An apparatus for use in a lens assembly, the apparatus comprising a deformable lens element having an axis and a deformable surface, at least part of which transmits image forming ligth rays, and a force imparting structural member disposed to impart a force to said deformable surface, wherein the apparatus is adapted so that said force imparting structural member is capable of imparting at least one of a pushing force or a pulling force to the deformable surface.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
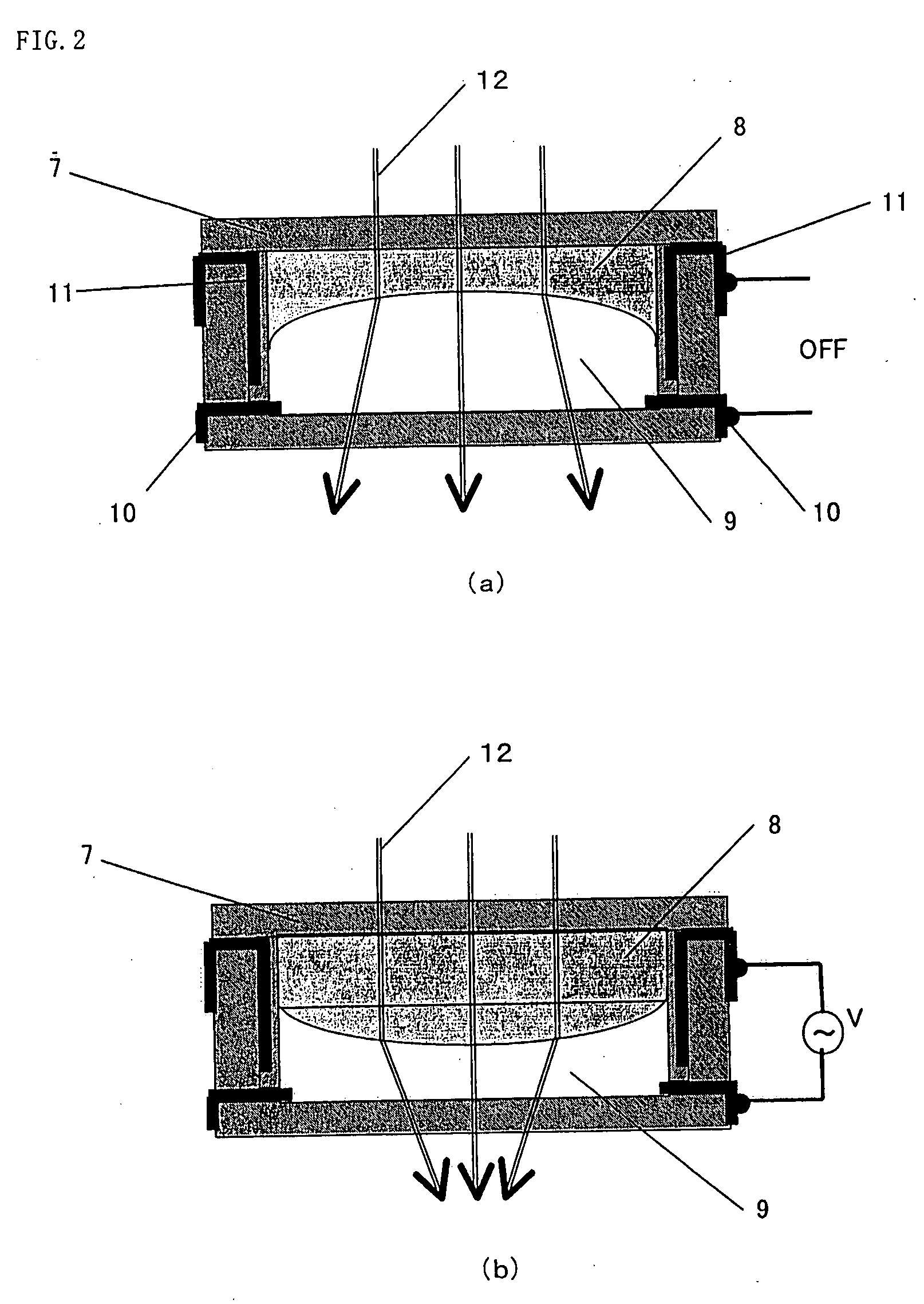
Electro-optical devices using dynamic reconfiguration of effective electrode structures
ActiveUS20110109824A1Reduce aberrationImprove performance of lensLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesElectric fieldLiquid crystal devices
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device may be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and may be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Electro-optical devices using dynamic reconfiguration of effective electrode structures
ActiveUS20110216257A1Reduce aberrationImprove performance of lensStatic indicating devicesFixed grillesOptical propertyElectric field
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device may be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and may be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Image stabilization and shifting in a liquid crystal lens
InactiveUS20120257131A1Easy to controlEnhanced electric field controlStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical propertyImage stabilization
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device can be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and can be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Discrimination Medium And Discrimination Method Therefor
InactiveUS20080090029A1Reliable performanceChange in optical propertyScattering properties measurementsOptical articlesCholesteric liquid crystalSelective reflection
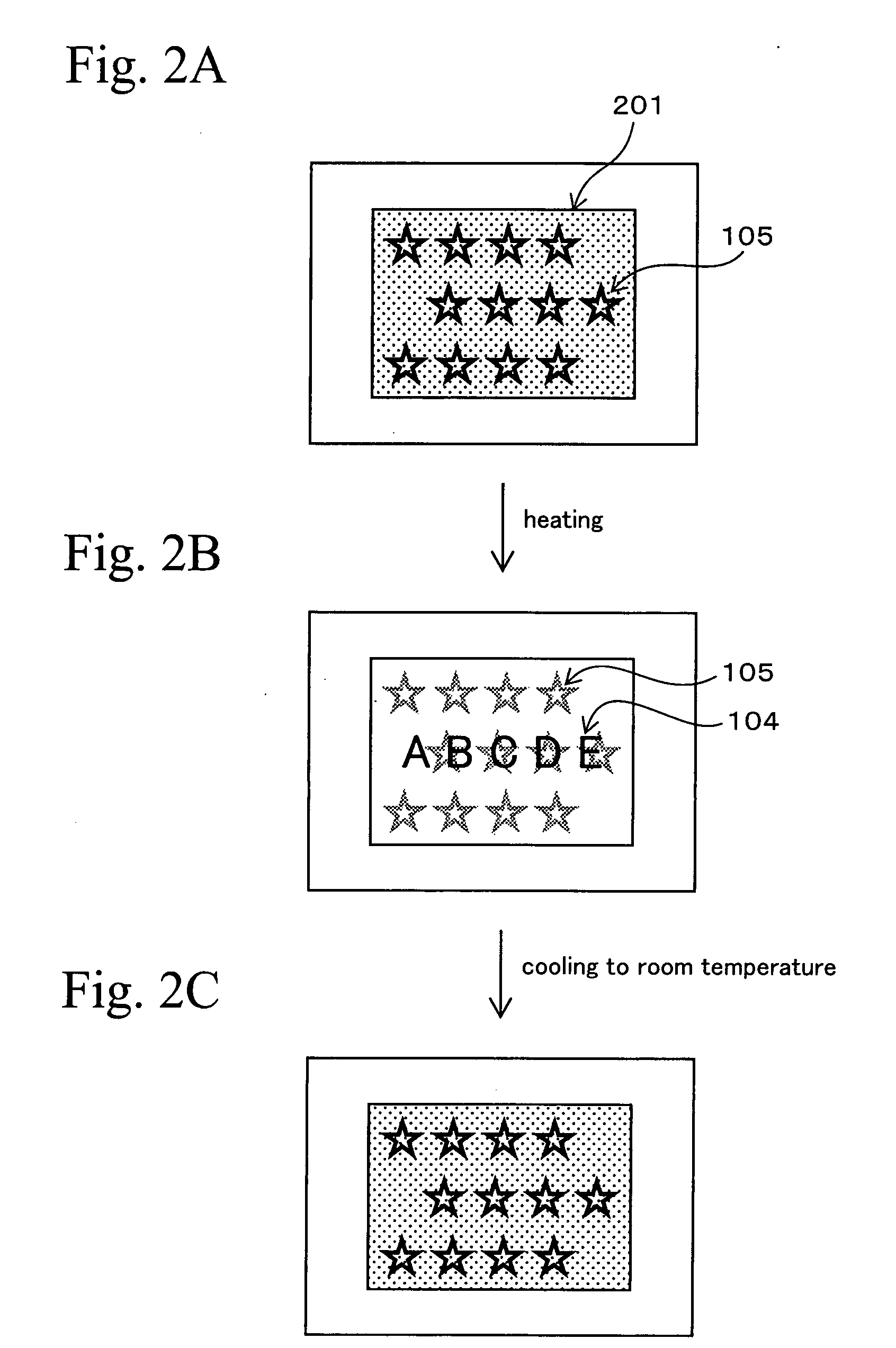
A thermal ink layer (102) formed by a thermochromic material changing from a black color to a transparent state when heated is arranged on a base (101) which is a PET film. A cholesteric liquid crystal layer (103) in which an appropriate pattern of hologram (105) is formed is arranged on the thermal ink layer (102). At room temperature, the thermal ink layer (102) exhibits the light absorption characteristic and the selective reflection characteristic and it is possible to observe the color shift characteristic of the cholesteric liquid crystal layer (103). When heated, the thermal ink layer (102) becomes transparent and the pattern (104) on the base (101) is further observed in the superimposed state. By utilizing the change of the view, it is possible to authenticate a commodity. This realizes a higher level for preventing forgery than the conventional discrimination technique and enables a user to easily and surely judge whether a commodity is a forged one.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
3D printing device of biological tissue optical simulation
InactiveCN104908324AMeet the calibrationQuickly adjust the supply ratioAdditive manufacturing apparatusMedical treatmentBiological tissue
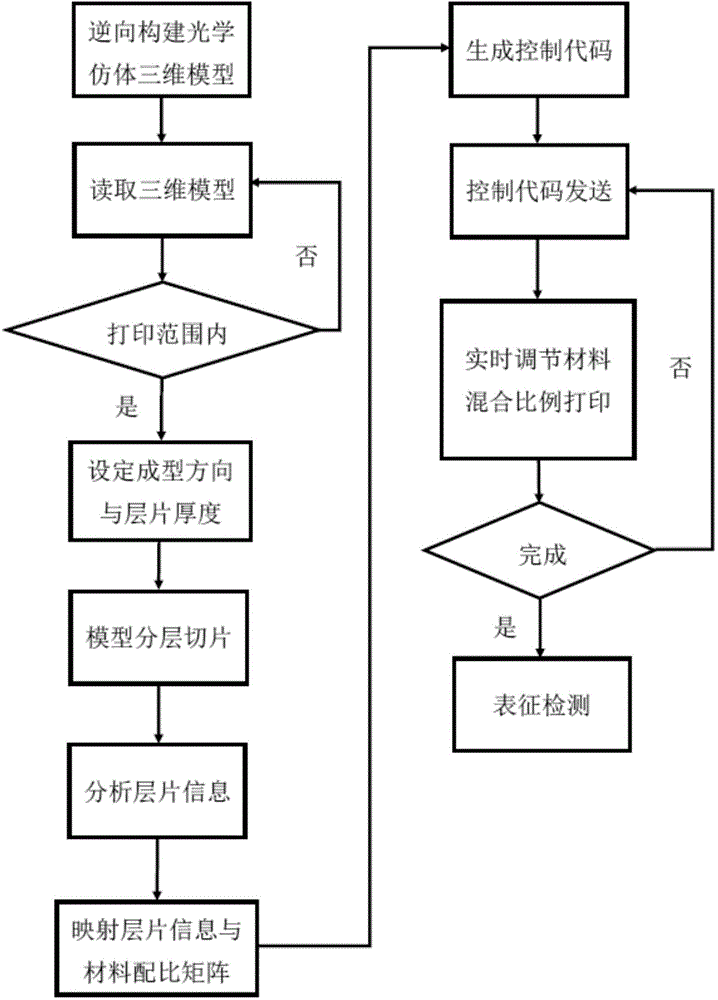
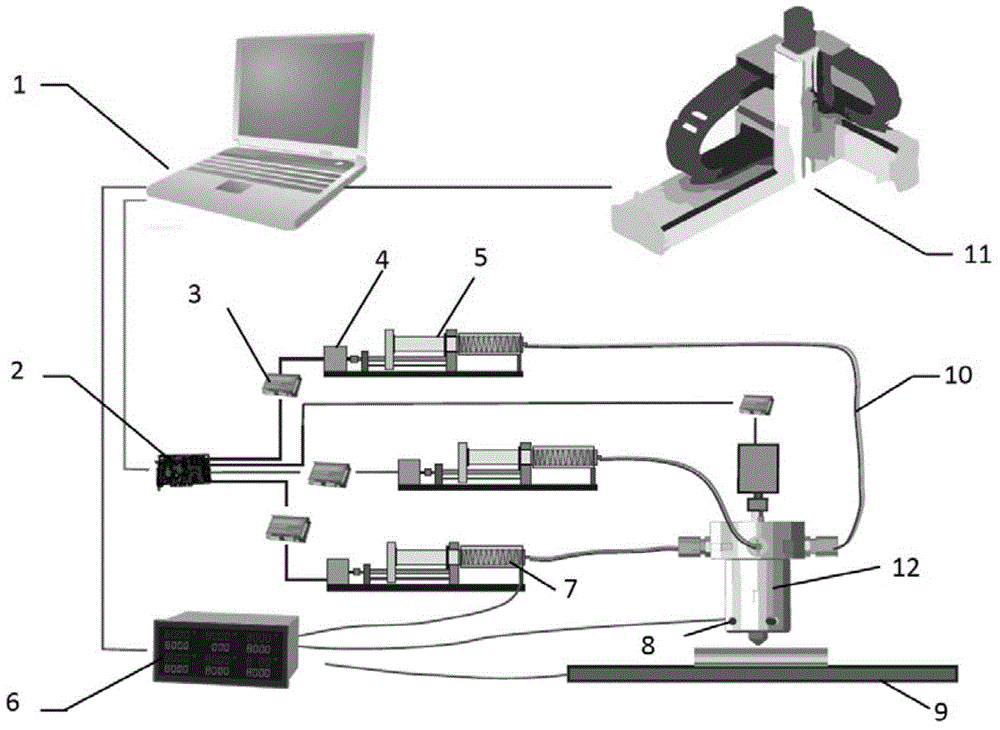
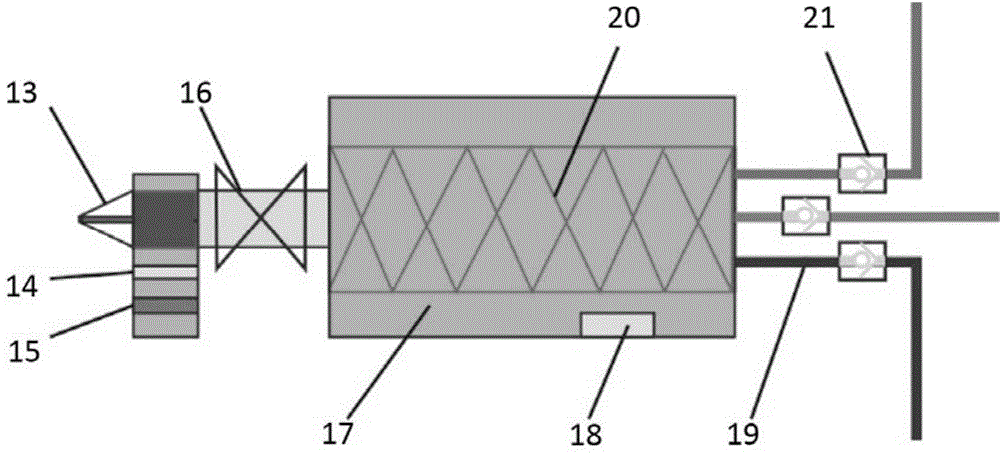
The invention relates to a 3D printing device and method of biological tissue optical simulation. By mainly employing the 3D printing principle and based on a multi-channel melting and depositing nozzle, a heterogeneous optical simulation capable of accurately simulating the optical characteristics of a biological tissue can be rapidly prepared and the calibration of various optical medical image instruments can be met.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Electro-optical devices using dynamic reconfiguration of effective electrode structures
ActiveUS8028473B2Increase charge mobilityReduce conductivityStatic indicating devicesFixed grillesOptical propertyElectric field
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device may be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and may be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Optical Element
An optical element includes a first liquid, a second liquid, and a container, wherein the first liquid and the second liquid substantially differ in refractive index and are immiscible, the first liquid and the second liquid are hermetically placed in the container so that an interface between the first liquid and the second liquid forms a specific shape, the shape of the interface between the first liquid and the second liquid is changed by applying a voltage between the first liquid and the second liquid through electrodes formed in the container, and the container is (1) a resin container of which an inner surface portion of a container wall has a resin phase with a fluorine atom content higher than that of an internal portion of the container wall, (2) a container of which a top portion and a bottom portion are formed of a resin composition including a resin and a hindered amine compound having a transmittance of light with a wavelength of 400 nm measured for a 5 wt % chloroform solution using a cell with 10-mm optical path of 90% or more and a molecular weight of 1500 or more, or (3) a container of which an inner surface is coated with a CVD film formed of a fluorocarbon compound. According to the present invention, an optical element can be provided of which the refractive power for light passing therethrough can be efficiently controlled with a small configuration utilizing an electrowetting phenomenon and which allows continuous transmission or concentration of light from a blue laser (short-wavelength laser).
Owner:ZEON CORP
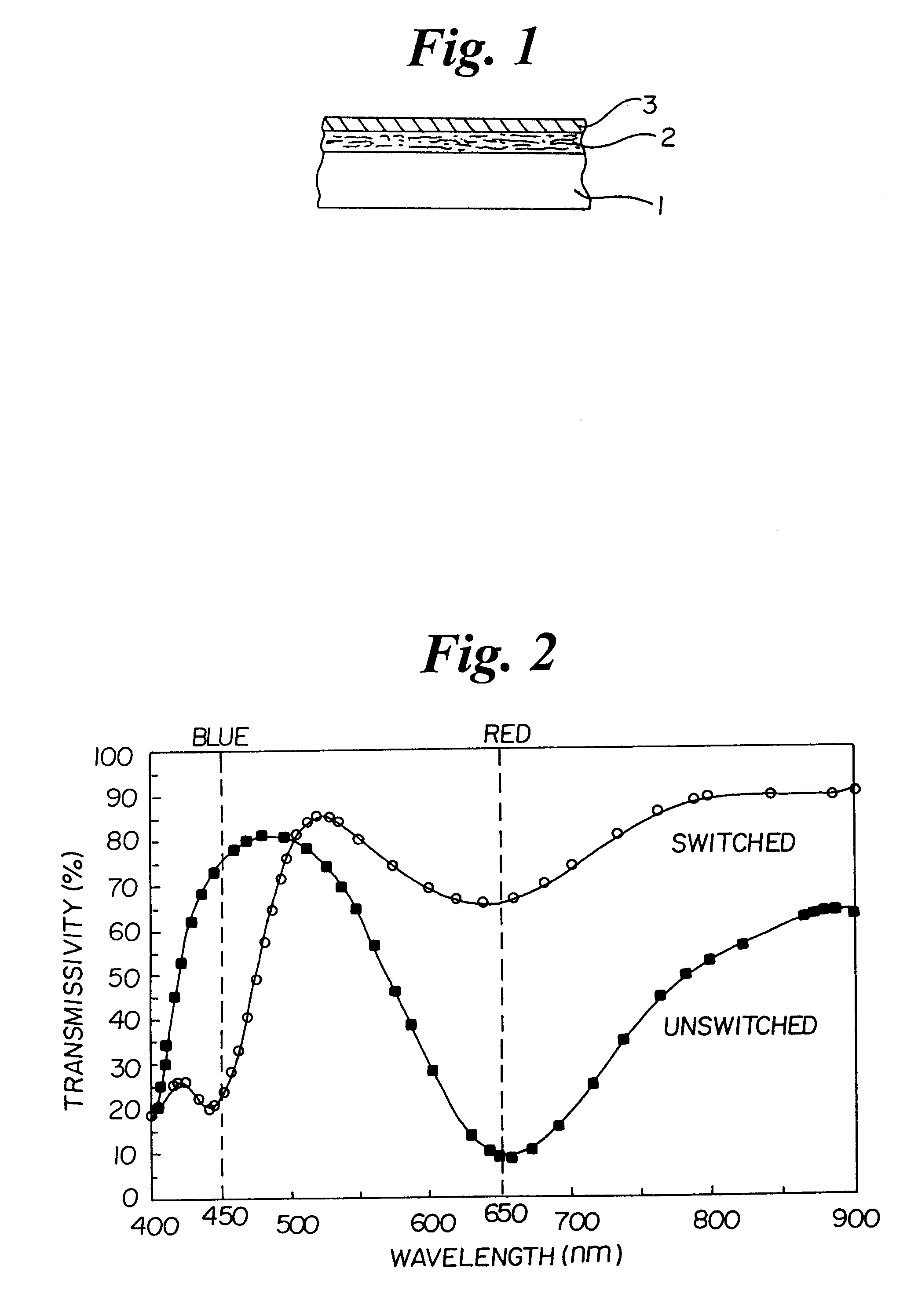
Optical data storage materials for blue-light DVD-R
InactiveUS6214431B1Improve behaviorRaise the ratioPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsPhysicsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The present invention provides a new category of information storage material, nonstoichiometric metal-organic complex Ag1-beta(TCNQ), which is particularly suitable for digital video disc (DVD-R) operated by blue laser (wavelength 450 nm) or red laser (wavelength 650 nm), wherein, Ag is silver, TCNQ is tetracyano-p-quinodimethane C12H4N4, beta is a parameter chosen by its performance and beta<=0.4. The material can produce apparent absorption change under the incidence of the above-mentioned two different lasers. When used as optical recording medium, it has the advantages of high signal-to-noise ratio, fast response and low cost. The actual number of write-erase cycles can be larger than 20. Therefore, its performance is better than a conventional DVD-R.
Owner:HUA ZHONGYI +1
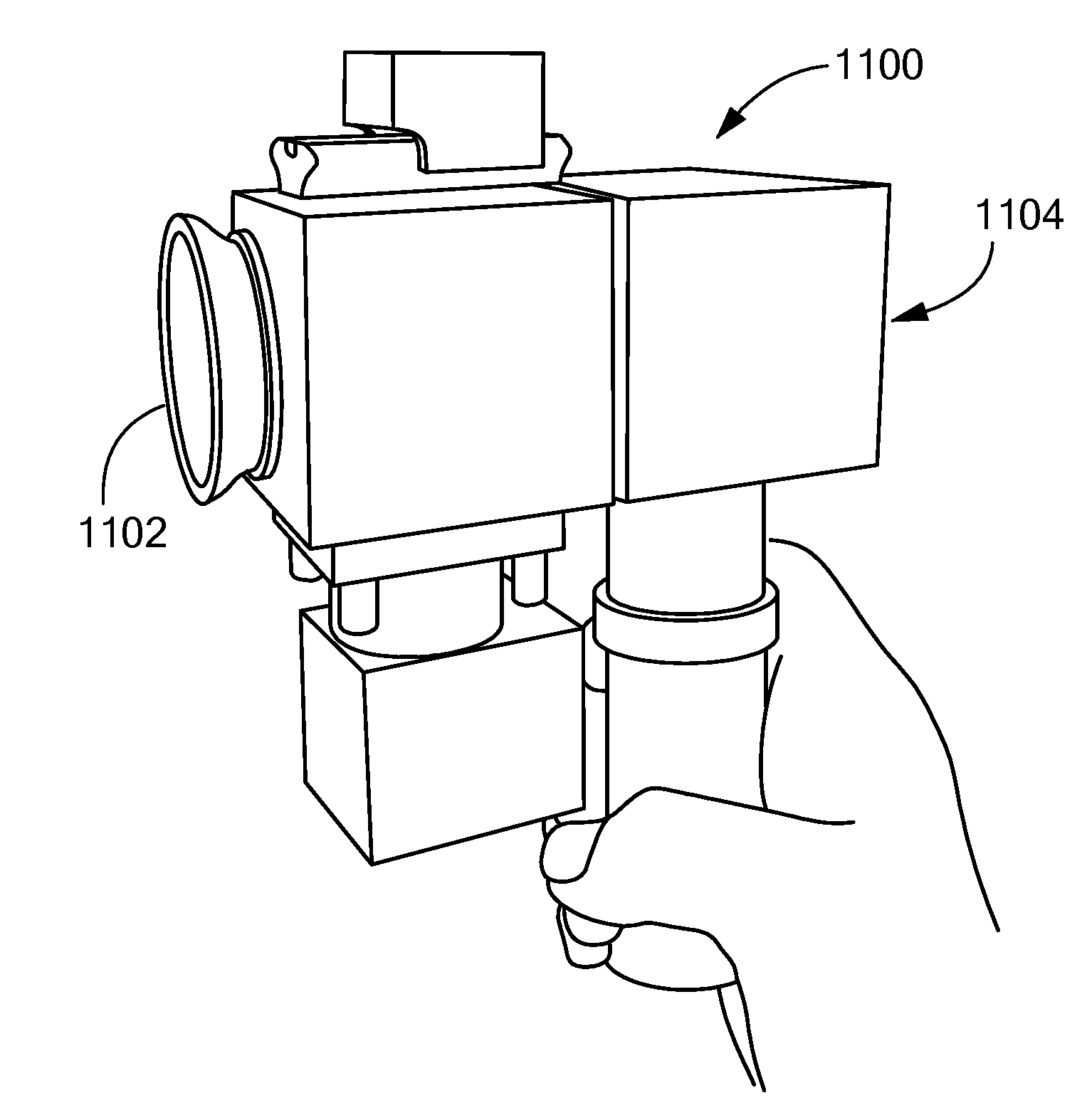
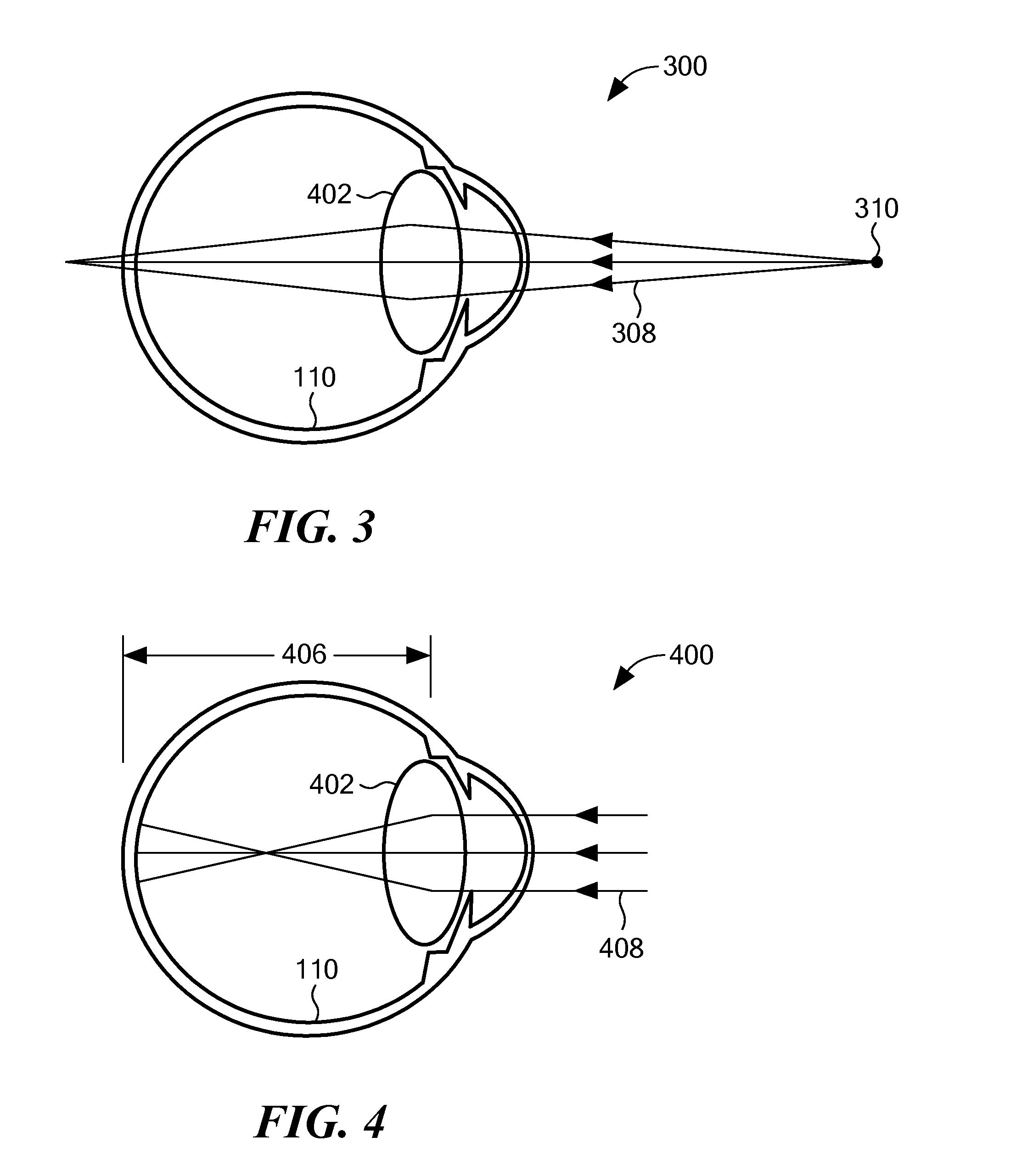
Apparatus and Method of Determining an Eye Prescription
ActiveUS20160128566A1Reduce noiseChange optical propertiesLaser surgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical prescriptionComputer science
Eye prescriptions may be determined by providing a simple, easy to use, portable device with a specially configured targeting light source that aligns the eye, mitigates accommodation, and provides accurate results. Unlike stationary, closed view autorefractors, this device typically is portable, self-usable, relatively inexpensive, enabling more widespread use across the world.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Tempering low-emissivity coated glass containing silver alloy
ActiveCN103802379AGrain refinementHigh hardnessGlass/slag layered productsMetal layered productsLow emissivityHardness
The invention provides tempering low-emissivity coated glass containing silver alloy. The glass comprises a glass substrate and a coating layer deposited on the glass substrate, and is characterized in that the coating layer comprises two or more functional layers, at least one of the functional layers is a silver alloy layer, and the silver alloy layer is made from one of Ag-Cu-Ni or Ag-Cu-Al or Ag-Cu-Pt. According to the tempering low-emissivity coated glass containing the silver alloy provided by the invention, a traditional Ag layer is substituted by the silver alloy layer, a small quantity of alloy metal elements are doped in the Ag layer, Ag crystal particles are refined, the hardness, the abrasive resistance and the burning loss resistance of silver are improved, the optical performance of Ag is changed, the overall glass is perspective and grey, the outdoor color is neutral and is close to natural color which is real and beautiful, and thus the demand of people on the color is satisfied; meanwhile, the processability of the glass is improved, and the oxidation resistance of the glass is enhanced.
Owner:CHANGJIANG GLASS TAIBO
Electro-optical devices using dynamic reconfiguration of effective electrode structures
ActiveUS8033054B2Efficient configurationChange optical propertiesLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesLiquid crystallineOptical property
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device may be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and may be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Photon crystal gel material for detecting glucose and glucose detection method
ActiveCN107056981AStrong specificityHigh selectivityColor/spectral properties measurementsPhenylboronic acidPhotonic crystal
The invention provides a photon crystal gel material for detecting glucose, which comprises polyacrylamide-acrylic acid gel and a photon crystal embedded in the gel, wherein the gel is directly or indirectly chemically grafted with phenylboronic acid groups, and the photon crystal is two-dimensional photon crystal or three-dimensional photon crystal. The invention also provides a glucose detection method based on the photon crystal gel material, and the color information displayed after the photon crystal gel material detects a glucose solution is converted into glucose concentration information. The glucose detection method provided by the invention can qualitatively or quantitatively detect glucose concentration with high selectivity, sensitivity, convenience and visualization, and provide a novel non-invasive detection method for urine glucose monitoring of diabetics.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Tungsten trioxide/polymer nano core-shell microsphere and preparing process thereof
InactiveCN1634647AChange optical propertiesChange thermal propertiesMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationOrganic solventMicrosphere
This invention relates to a tungsten trioxide and polymer nanometer shell micro ball and the process method, which belongs to organic and inorganic, compound materials technique field and are processed by emulsion polymerization on the surface of tungsten trioxide particles. It covers macromolecule materials on the tungsten trioxide nanometer particles to avoid the reaction between outer environments with the particles and to alter the particles optics properties and it together with other organic semi-conductor makes effective compound to improve its photoelectricity property or process property.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHANGE ORGANIC SILICON MATERIAL
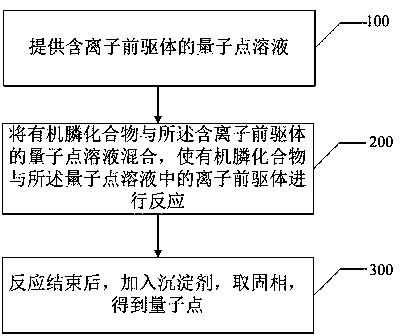
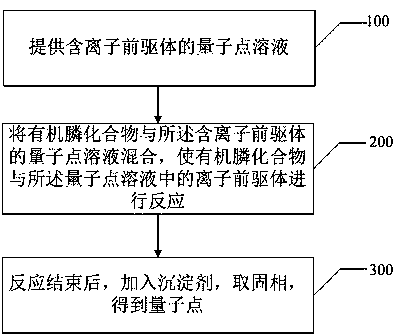
Quantum dot purification method
InactiveCN109971458AThe purification process is simpleEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsIonSolid phases
The invention discloses a quantum dot purification method. The method includes the steps of: providing a quantum dot solution containing an ion precursor; mixing an organic phosphine compound with thequantum dot solution containing the ion precursor to react the organic phosphine compound with the ion precursor in the quantum dot solution; and adding a precipitant at the end of the reaction, andtaking the solid phase, thus obtaining the quantum dot. The method provided by the invention can effectively remove a large number of residual cationic precursors in the quantum dot solution completely. More importantly, the optical properties of the quantum dot itself do not change significantly. The method has the characteristics of simple purification process and easily repeatable operation, solves the shortcomings of quantum dot related applications in the prior art, and provides more possibilities for preparation of high-efficiency QLED devices.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL IND RES INST
Image stabilization and shifting in a liquid crystal lens
ActiveUS20150309342A1Easy to controlEnhanced electric field controlStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical propertyImage stabilization
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device can be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and can be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:LENSVECTOR
Image stabilization and shifting in a liquid crystal lens
InactiveUS9036102B2Easy to controlEnhanced electric field controlStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical propertyImage stabilization
Variable liquid crystal devices for controlling the propagation of light through a liquid crystal layer use a frequency dependent material to dynamically reconfigure effective electrode structures in the device. The frequency of a drive signal that generates an electric field in the device can be varied, and the frequency dependent material has different charge mobilities for the different frequencies. At a low charge mobility, the frequency dependent material has little effect on the existing electrode structures. However, at a high charge mobility, the frequency dependent material appears as an extension of the fixed electrodes, and can be used to change the effective electrode structure and, thereby, the spatial profile of the electric field. This, in turn, changes the optical properties of the liquid crystal, thus allowing the optical device to be frequency controllable.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
Apparatus and method of determining an eye prescription
ActiveUS9854965B2Reduce high frequency noiseImprove signal-to-noise ratioLaser surgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringOphthalmologyAccommodation
Eye prescriptions may be determined by providing a simple, easy to use, portable device with a specially configured targeting light source that aligns the eye, mitigates accommodation, and provides accurate results. Unlike stationary, closed view autorefractors, this device typically is portable, self-usable, relatively inexpensive, enabling more widespread use across the world.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Perovskite solar cell device and method for manufacturing same
PendingCN110112258AChange optical propertiesChange electrical propertiesFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPerovskite solar cellHigh energy
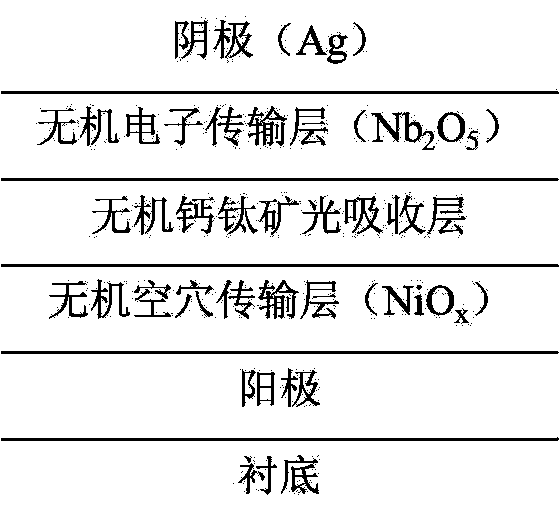
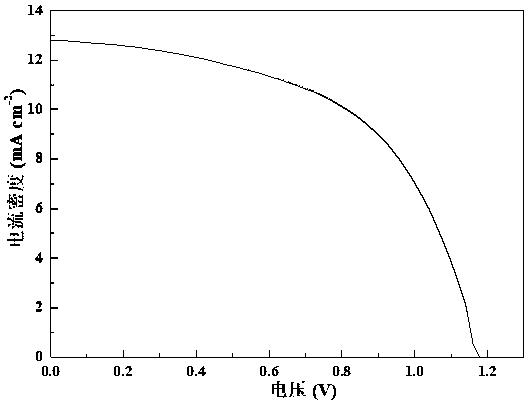
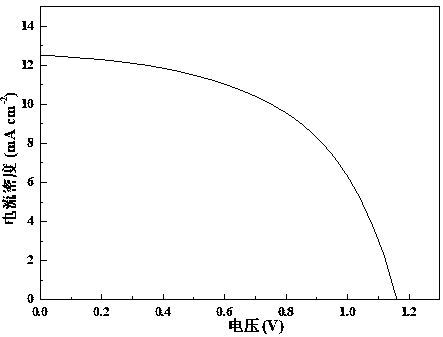
The embodiment of the invention discloses a perovskite solar cell device and a method for manufacturing the same. The perovskite solar cell device comprises a substrate, an anode (ITO), an electron beam evaporation inorganic hole transport layer (NiOx), an inorganic perovskite light absorbing layer, an electron beam evaporation inorganic electron transport layer (Nb2O5), and an electron beam evaporation cathode (Ag) which are successively stacked. The all-inorganic perovskite solar cell device and the manufacturing method thereof obtain high energy conversion efficiency, and the hole transportlayer nickel oxide can achieve doping of different elements and different concentrations by double-source electron beam co-evaporation so as to improve optical and electrical properties. The all-inorganic perovskite cell device has a low processing cost and can achieve large-area processing, and has a good application prospect in the field of solar cells.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Light path interchange device based on total reflection
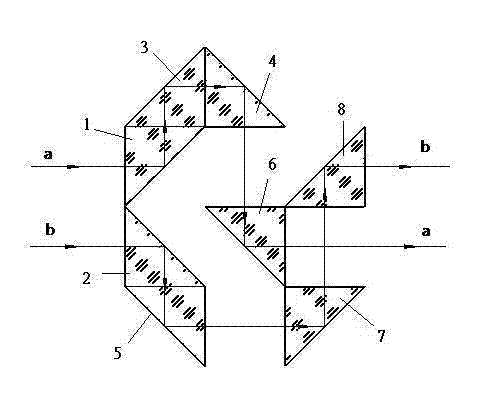
InactiveCN102519356AChange optical propertiesBeam polarization state has no effectUsing optical meansOptical elementsOptical propertyControl system
The invention relates to a light path interchange device based on total reflection, which consists of eight isosceles right-angle prisms with the same specification; a light path structure control system between an incident light beam and an outgoing light beam is formed by the eight prisms; and two parallel incident light beams are totally reflected by the system for four times and are then emitted in parallel, so that position interchange can be realized, but the interval and the optical property of the two light beams are not changed. The light path interchange device is small in volume, simple in structure, stable in control and free from the influence for light beam polarization state.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Laser bar and cavity integrating method and structure
InactiveCN1466251AChange optical propertiesMeet the design requirementsActive medium materialResonant cavityIon laser
This invention discloses an integral method and its structure for a laser rod cavity including bonding common host crystals of unmixed laser active ion on one or two ends of mixed laser active ion laser crystal by heat to form two end caps to be filmed after optical process. The common host crystal of mixed laser rod crystal and unmixed laser active ions can be: Nd: YAG and unmixed YAG, Yb: YAG and unmixed YAG, Nd, GdVO4 and unmixed GdVO4, Yb:GdVO4 a and unmixed GdVO4, Lateral pump rod-cavity integral laser elements and end face pump rod-cavity integral laser elements can be processed according to different needs by filming, realizing the integral of resonant cavity and its working subjects.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing a glass ceramic element with patterned coating
InactiveCN105693109AChange optical propertiesChange designLayered product treatmentStoves/ranges topsMetallurgyVisible spectral range
The invention is based on the object to improve the creation of patterned coatings on glass ceramic substrates so as to provide for more flexibility in patterning. A method is provided for producing a glass ceramic element (1) with a patterned coating is provided. The method includes: providing a glass ceramic element (1) with a coating which is at least partially light-blocking and preferably opaque in the visible spectral range; irradiating the glass ceramic element (1) with a pulsed laser beam (71) on the face provided with the coating (5) so that the coating (5) is removed by ablation; during irradiating the laser beam is directed over the surface of the glass ceramic element (1) so that a portion of the coating (5) is removed which has a greater lateral extent than the diameter of the laser beam; and once the coating (5) has been removed, irradiating the glass ceramic with the laser (7) in the region where the coating (5) has been removed, thereby optically modifying the glass ceramic in the irradiated region.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Inter-Chip Alignment
ActiveUS20170179093A1Low costEasy to detectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEdge surfaceEngineering
First and second integrated devices each have an optical component and a plurality of interconnect structures disposed one edge thereon. The first edge surface of the second integrated device is positioned contiguous to the first edge surface of the first integrated device. The interconnect structures disposed on the first integrated device are in physical contact with the interconnect structures disposed on the edge surface of the second integrated device so as to provide alignment for conveying at least one signal between the optical components on the first and second integrated devices.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC +1
Method for producing a toughened glass article with a durable functional coating and a toughened glass article with a durable functional coating
ActiveCN108025962AChange optical propertiesEasy to produceGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsSurface layerSol gel coating
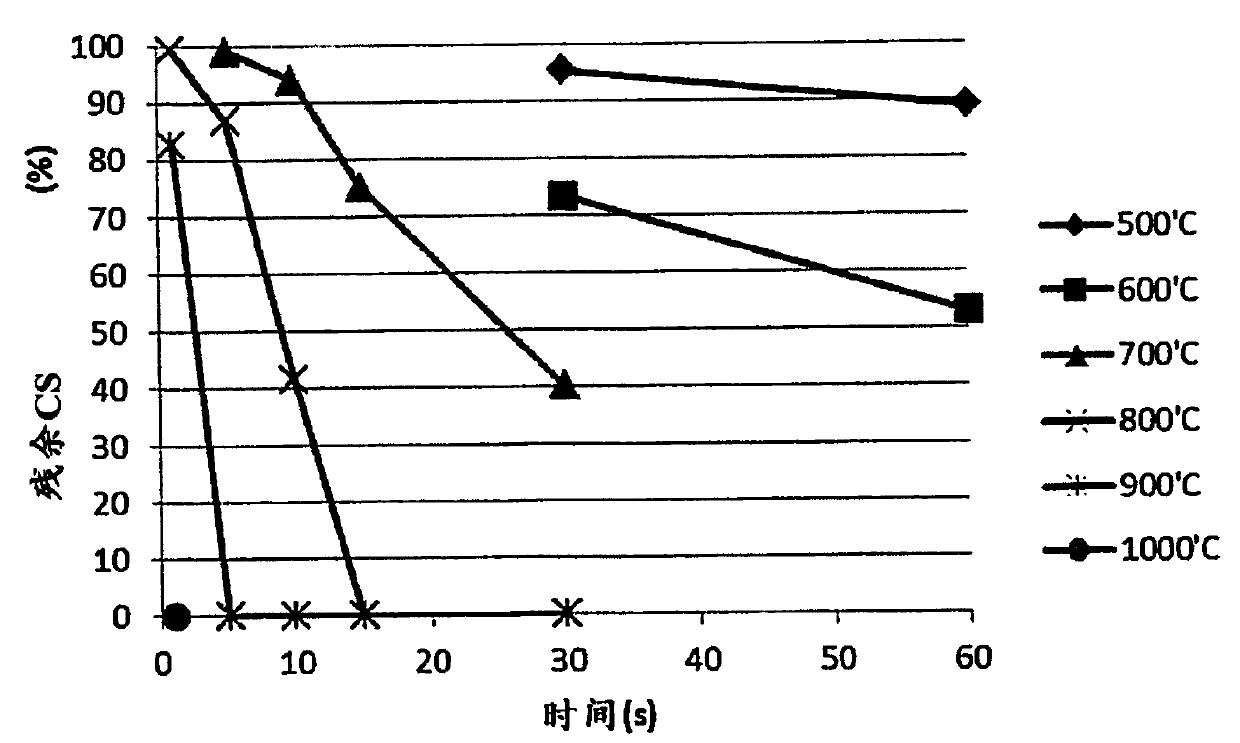
A method for producing a toughened glass article with a functional coating comprises providing a chemically toughened glass substrate with a first and a second face and a thickness (t) there between.The glass substrate has a surface layer with a compressive stress (CS) extending to a depth-of-layer (DoL) below the first and / or second face. The method further comprises applying a sol-gel coating to the first and / or the second face of said glass substrate and curing the sol-gel coating by heating it to curing temperatures above T a-200 DEG C during a curing time t c to produce the durable functional coating. The curing time t c satisfies formula (I) wherein T a is the temperature at the annealing point of the glass material of the glass substrate and T c is the maximum curing temperature, where T a and T c are given in DEG C. Further provided is a toughened glass article with a durable functional coating, in particular produced by the method according to the invention.
Owner:SCHOTT GLASS TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
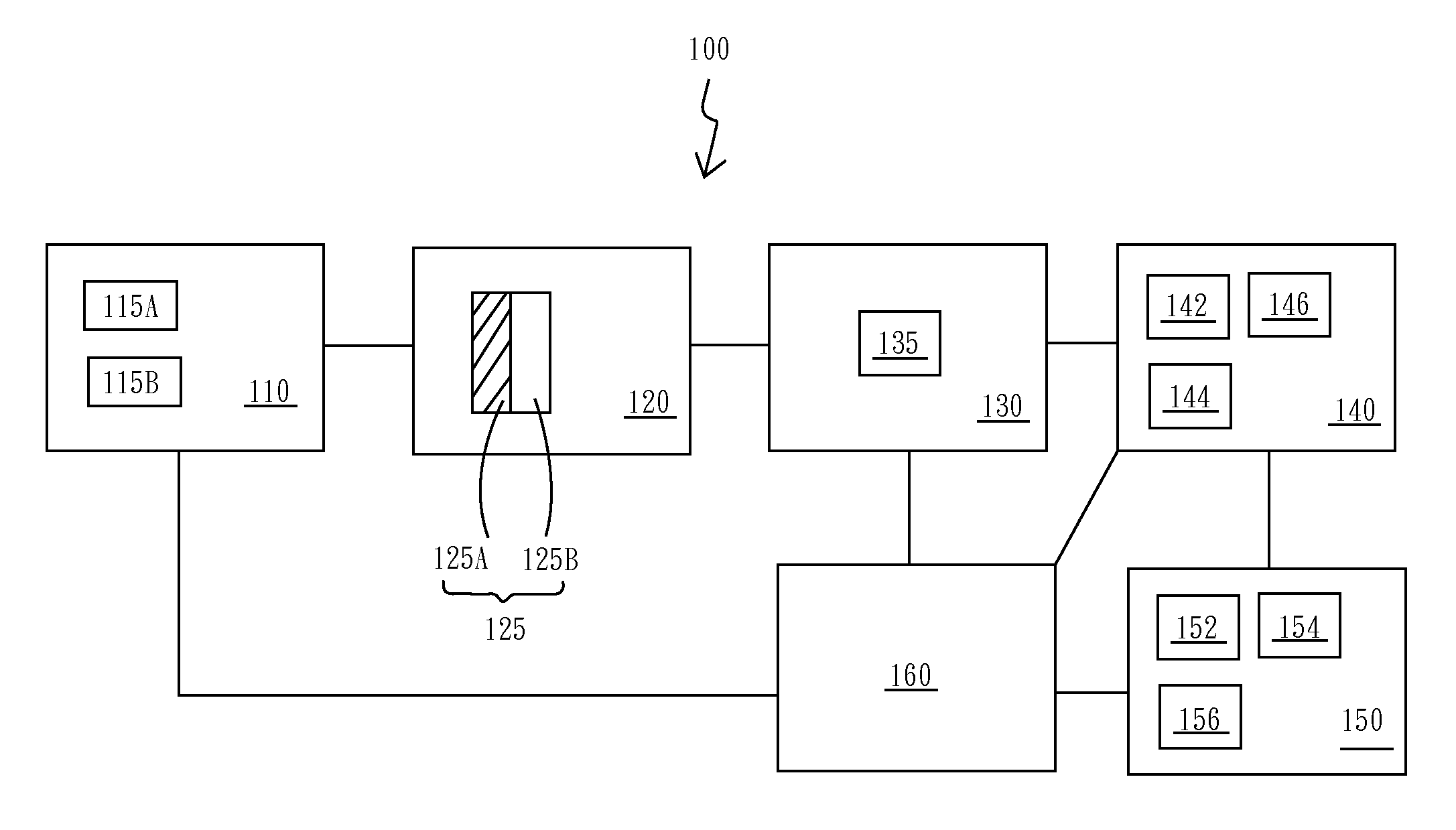
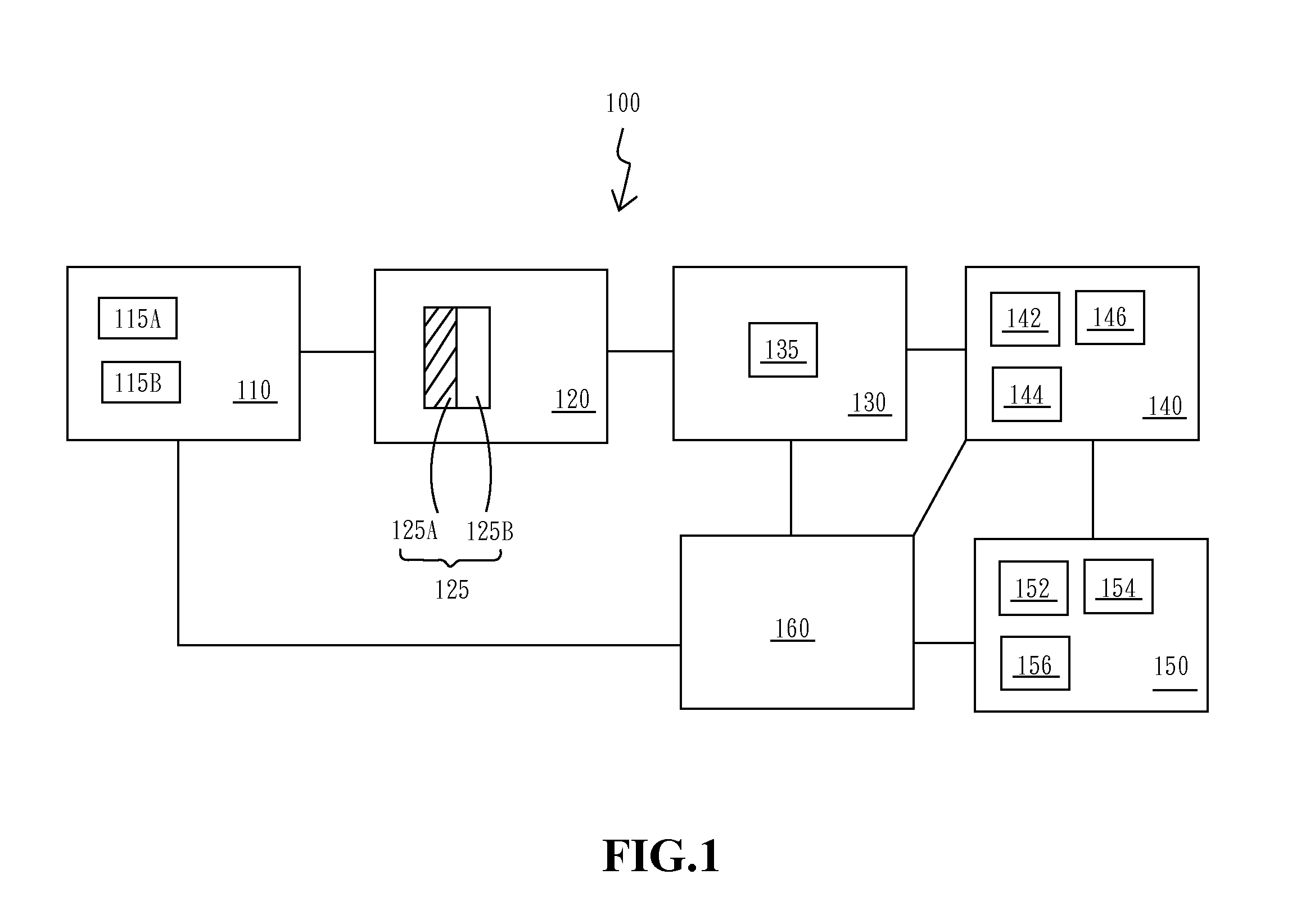
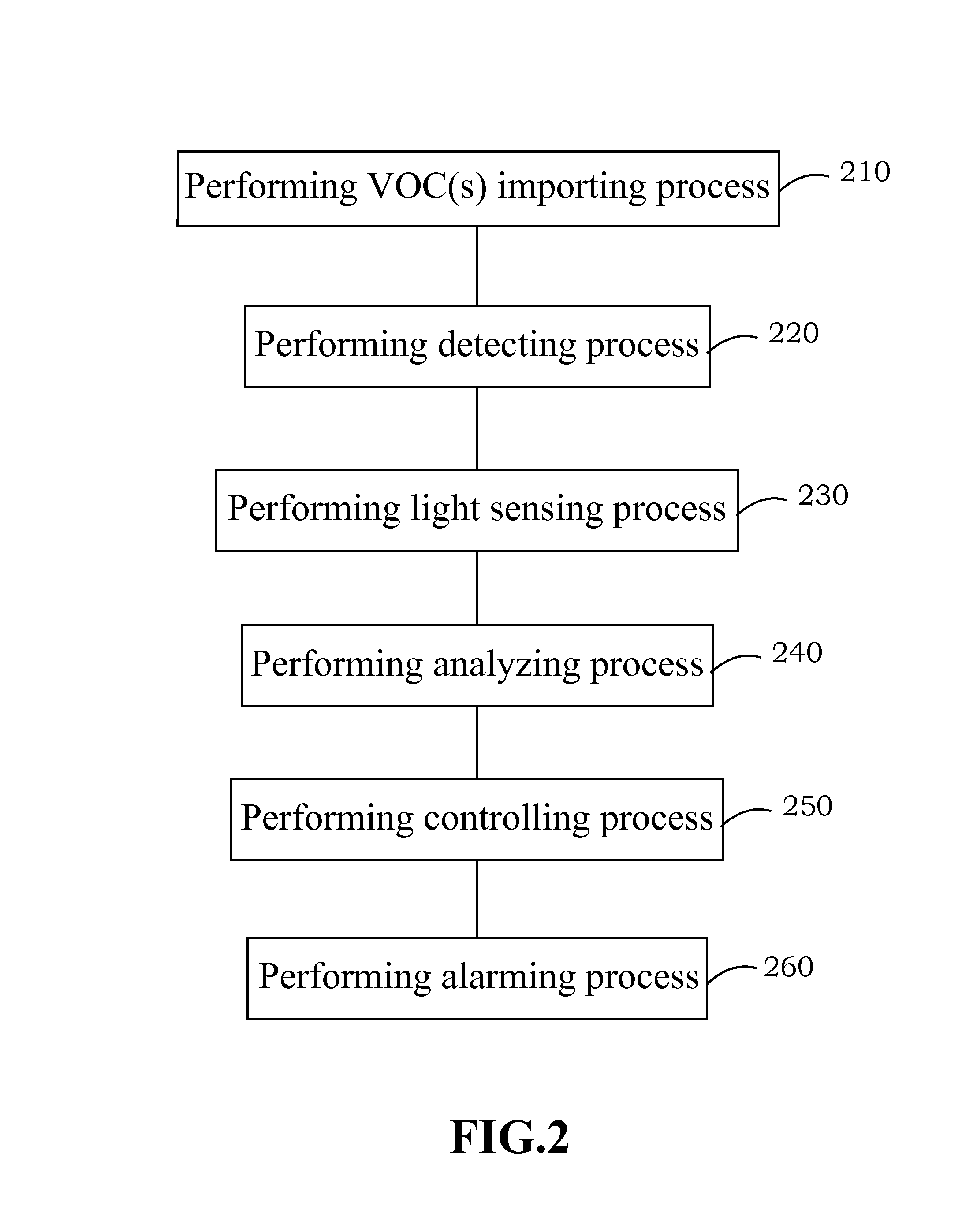
System for detecting volatile organic compounds and the method for forming the same and utility thereof
InactiveUS9146222B2Easily be damaged and pollutedChange optical propertiesMaterial capacitanceConductive polymerEngineering
The system for detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) of this present invention comprises a detecting material made by blending a nano-material and a conductive polymer. The system for detecting VOCs presents the property of high sensitivity, high sensing accuracy, quick response, and real-time VOC detecting, and is demonstrated in the present work for commercialization usage. The system for detecting VOCs can be easily operated to detect VOC without electronic detecting method, and hence this invention can reduce a lot of operation energy and procedure. Furthermore, when adding inorganic nanoparticles, the area of VOC exposure of this invention is increased and the molecular morphology variation of the detecting material is enhanced, and hence the detecting activity of the system for detecting VOCs is improved.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com