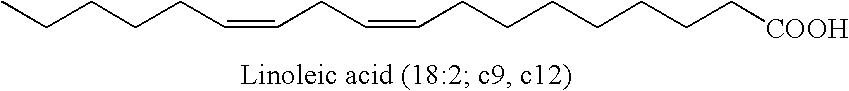Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87results about "Organic isomerisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
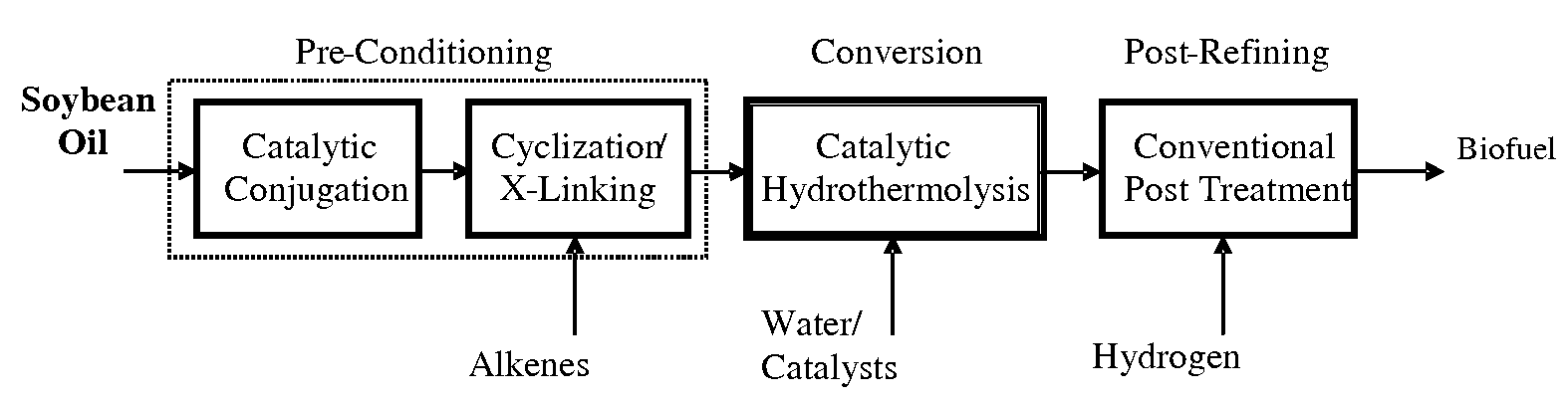
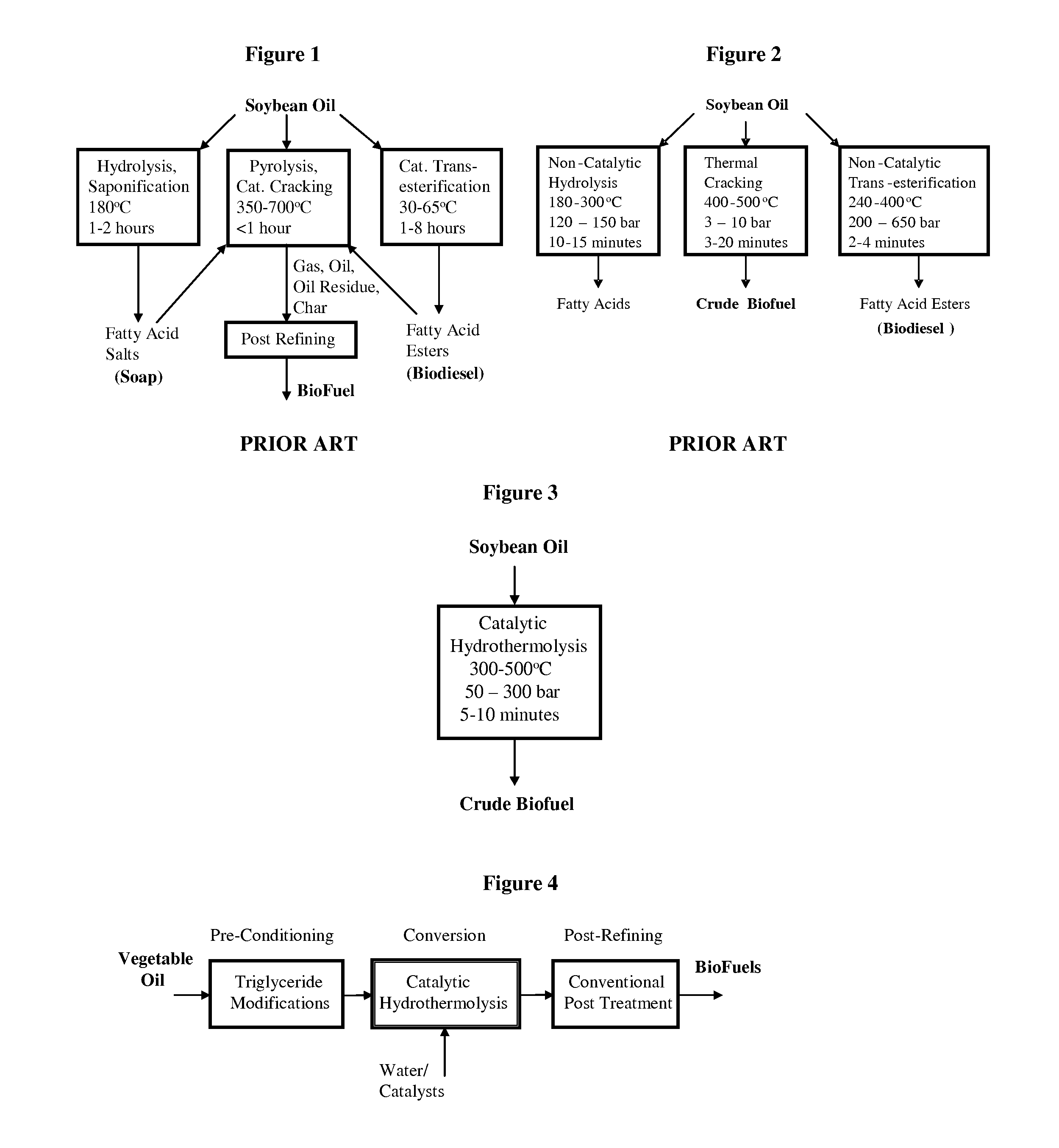
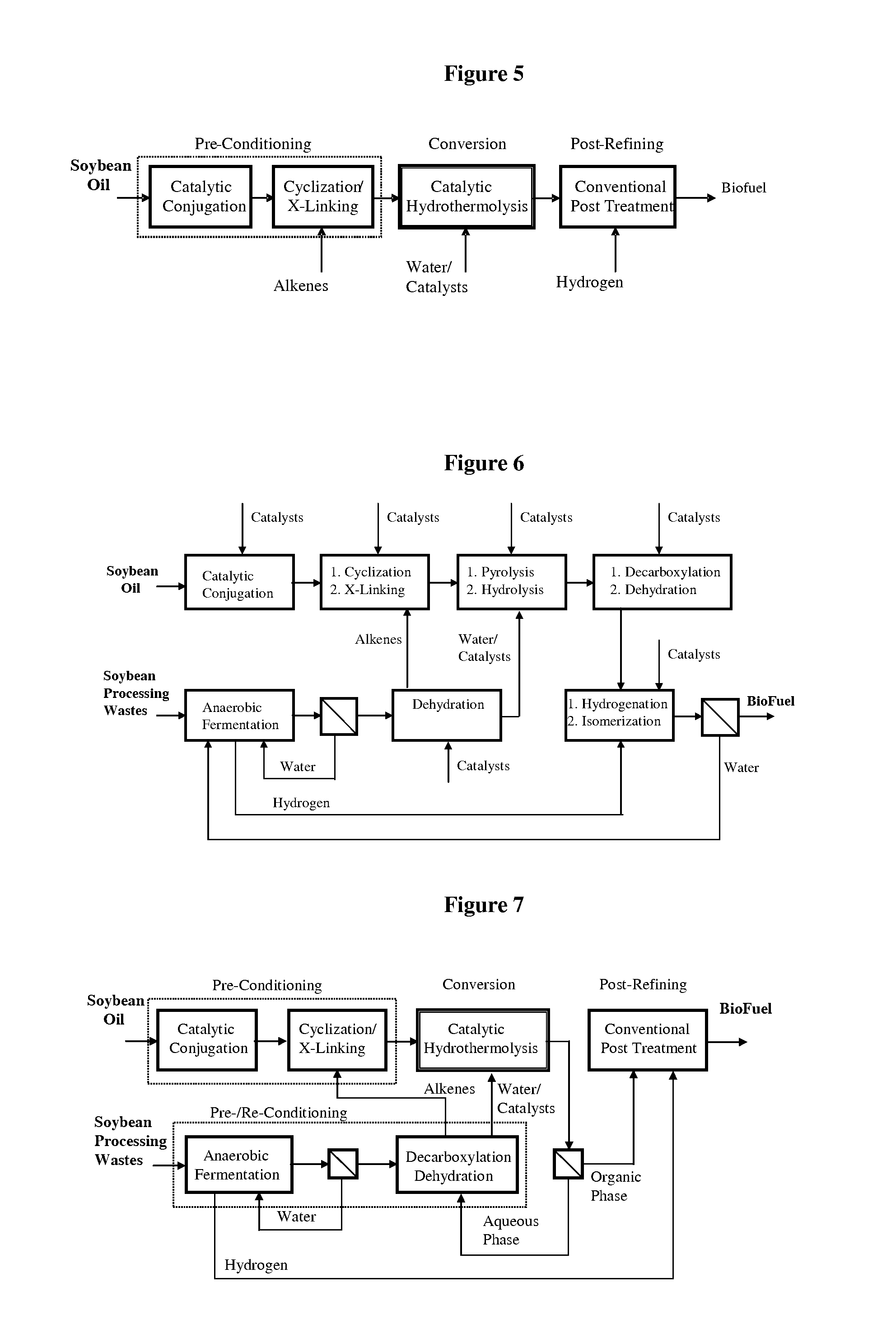
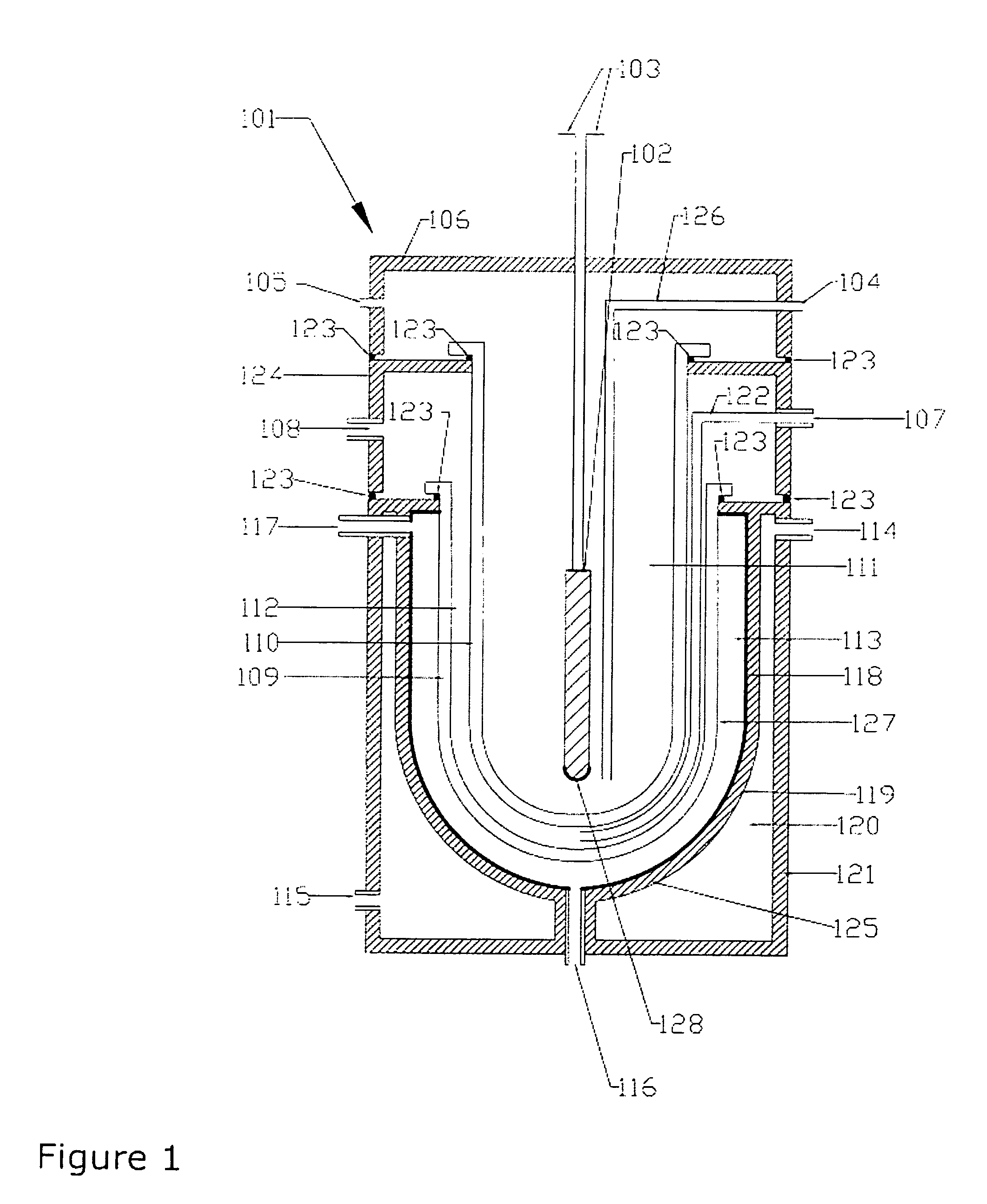
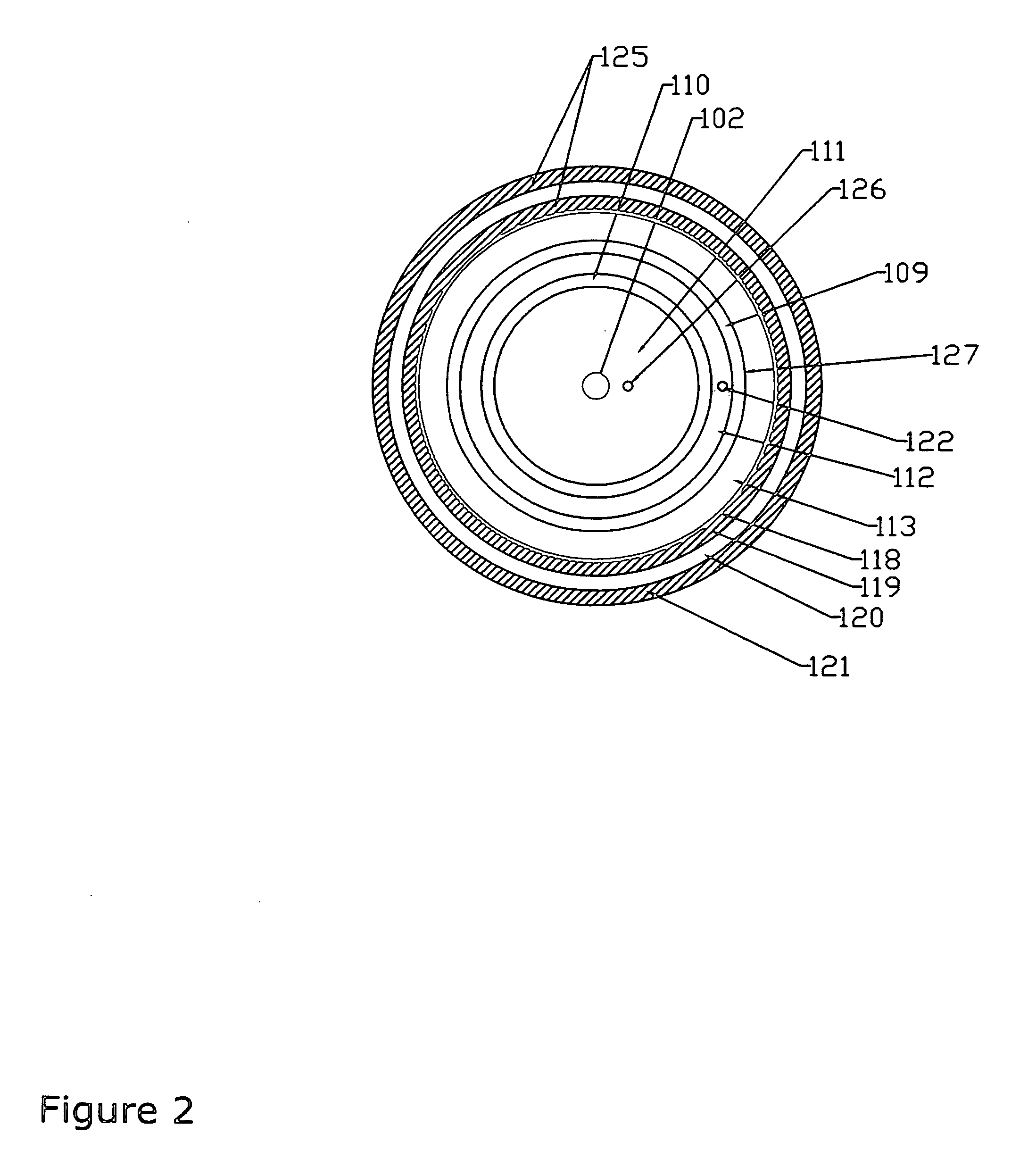
Method of converting triglycerides to biofuels
ActiveUS7691159B2Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationCross-linkIsomerization
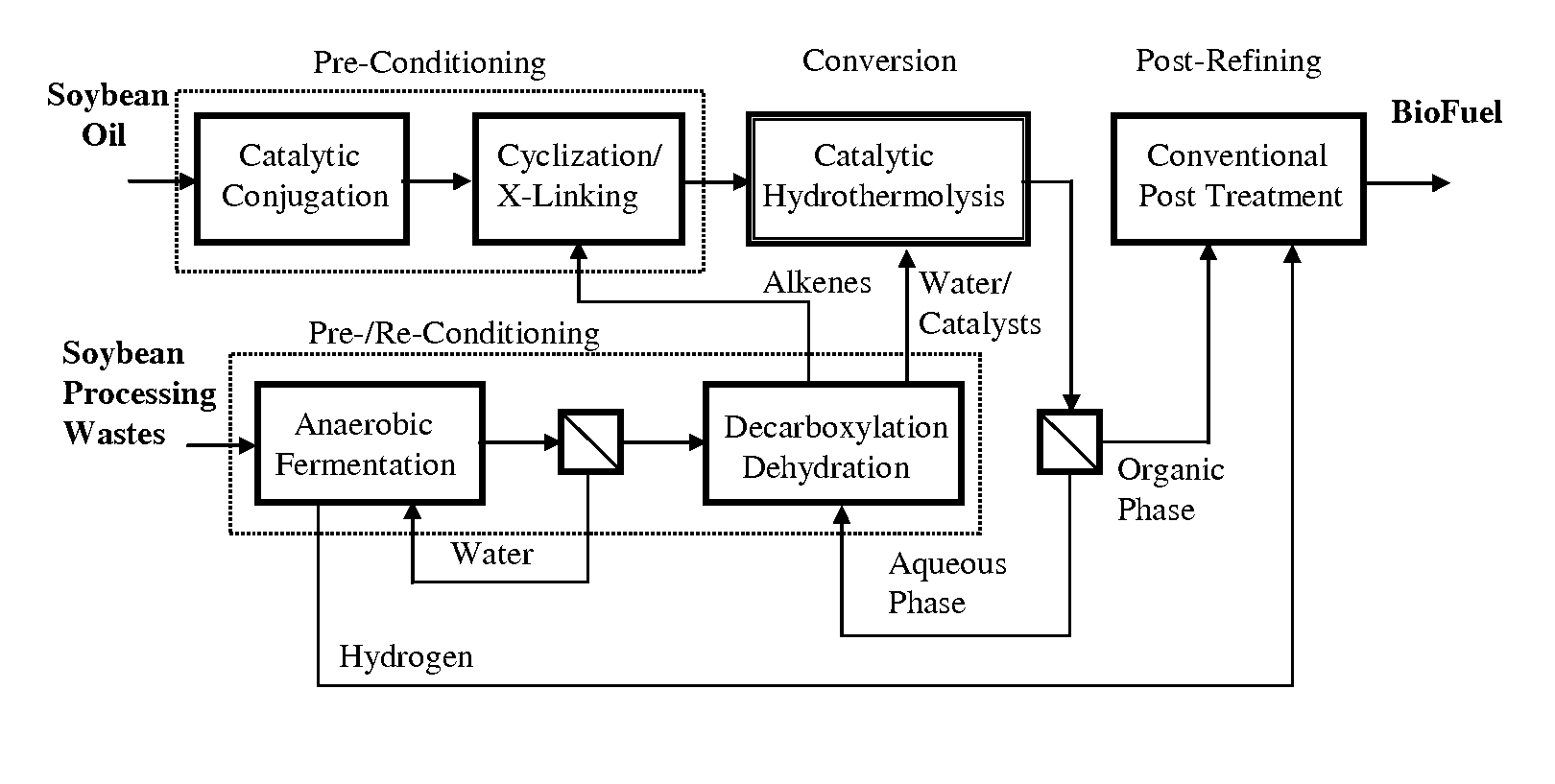
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Method of Converting Triglycerides to Biofuels
ActiveUS20080071125A1Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationBiofuelsIsomerizationPtru catalyst
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Alkane hydroisomerization catalyst, its preparation method and application
The alkane hydroisomerization catalyst comprises: the composite molecular sieve formed by silica-alumina structure and silicoaluminophosphate structure both of ten-membered ring and composed of ZSM-22 / SAPO-11, ZSM-23 / SAPO-11, ZSM-5 / SAPO-11, EU-1 / SAPO-11, and NU-87 / SAPO-11 composite sieves; and 0.05~5.0wt% one or two metal from Pt, Pd and Ir of VIII group noble metal. Compared with prior art, this catalyst has higher activity, selectivity, and yield.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Suppression of carcinoma using high purity conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
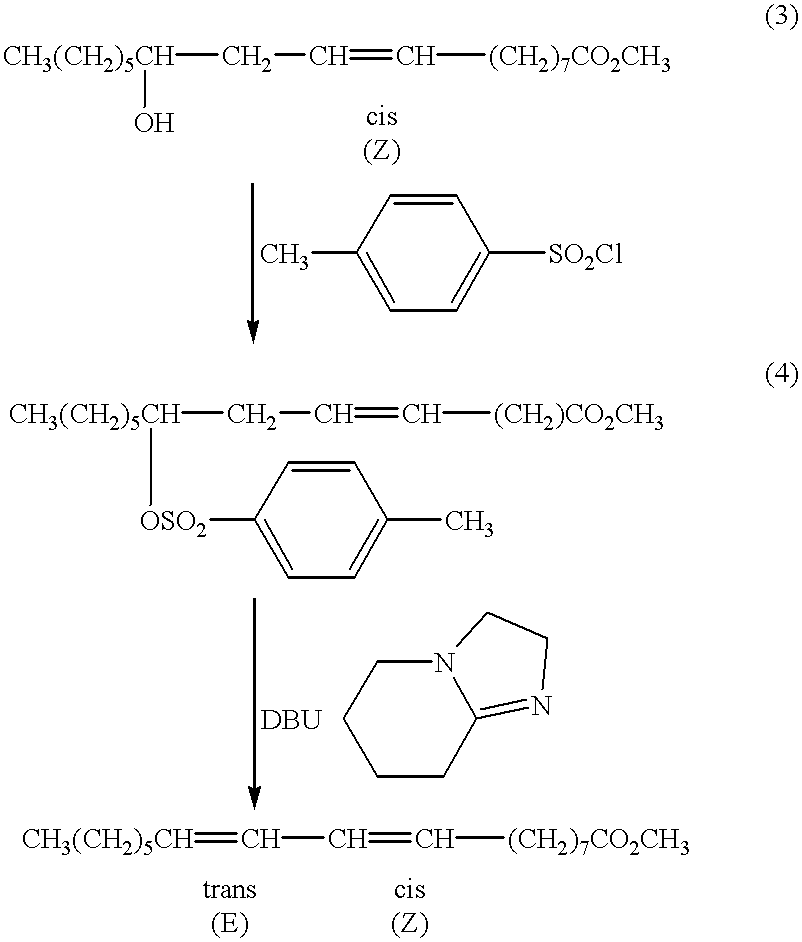
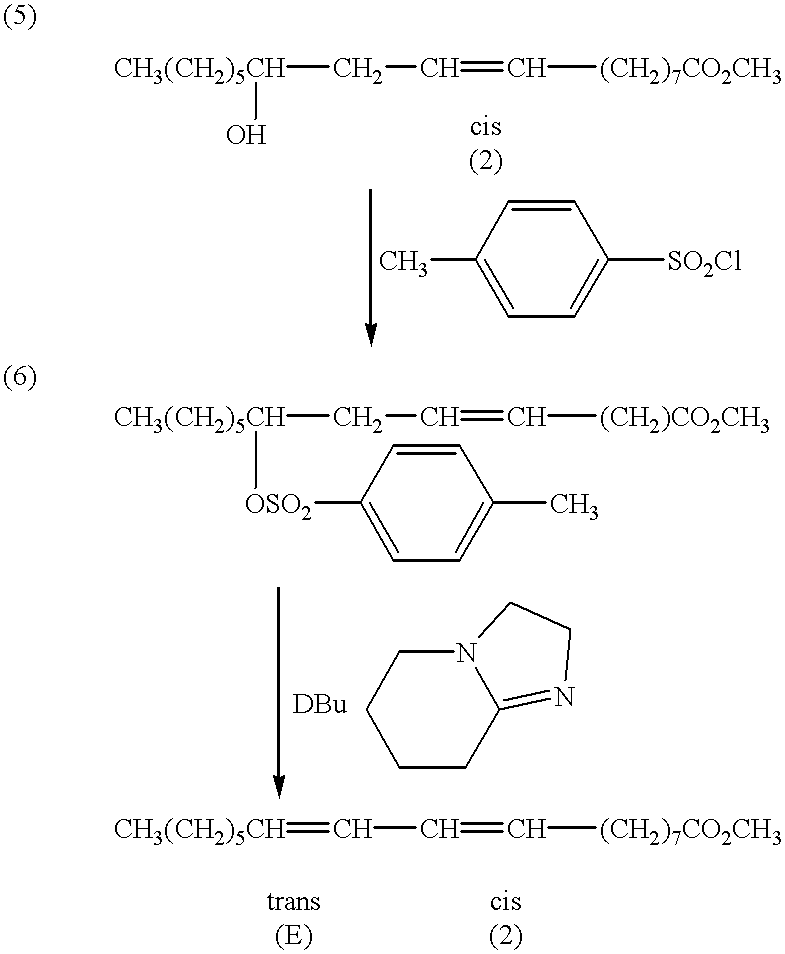
A method for the treatment of carcinoma in a human is disclosed, including administering to a human a therapeutically effective amount of 9-cis, 11-trans octadecadienoic acid formed by reacting an ester of ricinoleic acid with a tosyl chloride or a mesyl chloride to form a tosylate or mesylate of an ester of ricinoleic acid, and reacting the tosylate or mesylate of an ester of ricinoleic acid with diazabicyclo-undecene. The method includes administering to a human a purified conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) produced by a novel synthesis process for producing 9-cis, 11-trans octadecadienoic acid at room temperature in high yield including providing a tosylate or mesylate of a methyl ester of ricinoleic acid and providing a purified 9-cis, 11-trans octadecadienoic acid formed when the tosylate or mesylate reacts with diazabicyclo-undecene.
Owner:MATREYA
Method for producing conjugated linoleic acid glycerides
ActiveUS20050176977A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid isomerisationIsomerizationGlycerol
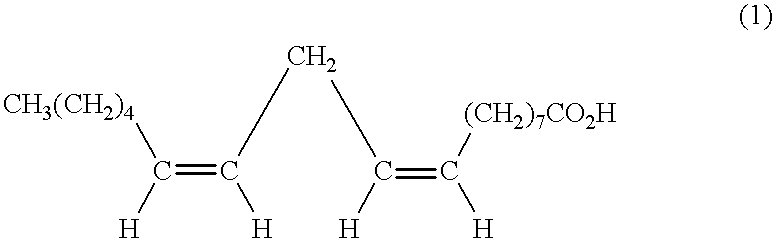
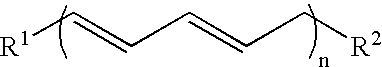
Processes for preparing conjugated fatty acid glycerides comprising: (a) isomerizing a fatty acid lower alkyl ester corresponding to the general formula (I) in the presence of a basic catalyst at a temperature of from 100 to 160° C., to form a conjugated fatty acid lower alkyl ester: R1CO—OR2 (I)wherein R1CO represents an acyl radical having from 16 to 22 carbon atoms and at least two carbon-carbon unsaturations and R2 represents an alkyl radical having from 1 to 4 carbon atoms; and (b) transesterifying the conjugated fatty acid lower alkyl ester with glycerol to form a conjugated fatty acid glyceride, wherein a lower alkanol corresponding to the general formula R2OH is formed, wherein R2 is as defined above, and the lower alkanol is continuously removed from the transesterification reaction; are described.
Owner:COGNIS DEUT GMBH & CO KG
Manufacture of conjugated linoleic salts and acids
InactiveUS6897327B2Delayed reaction timeIncrease productivityFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationIsomerizationDouble bond
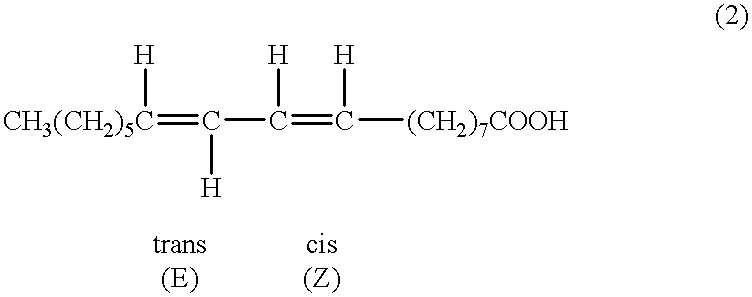
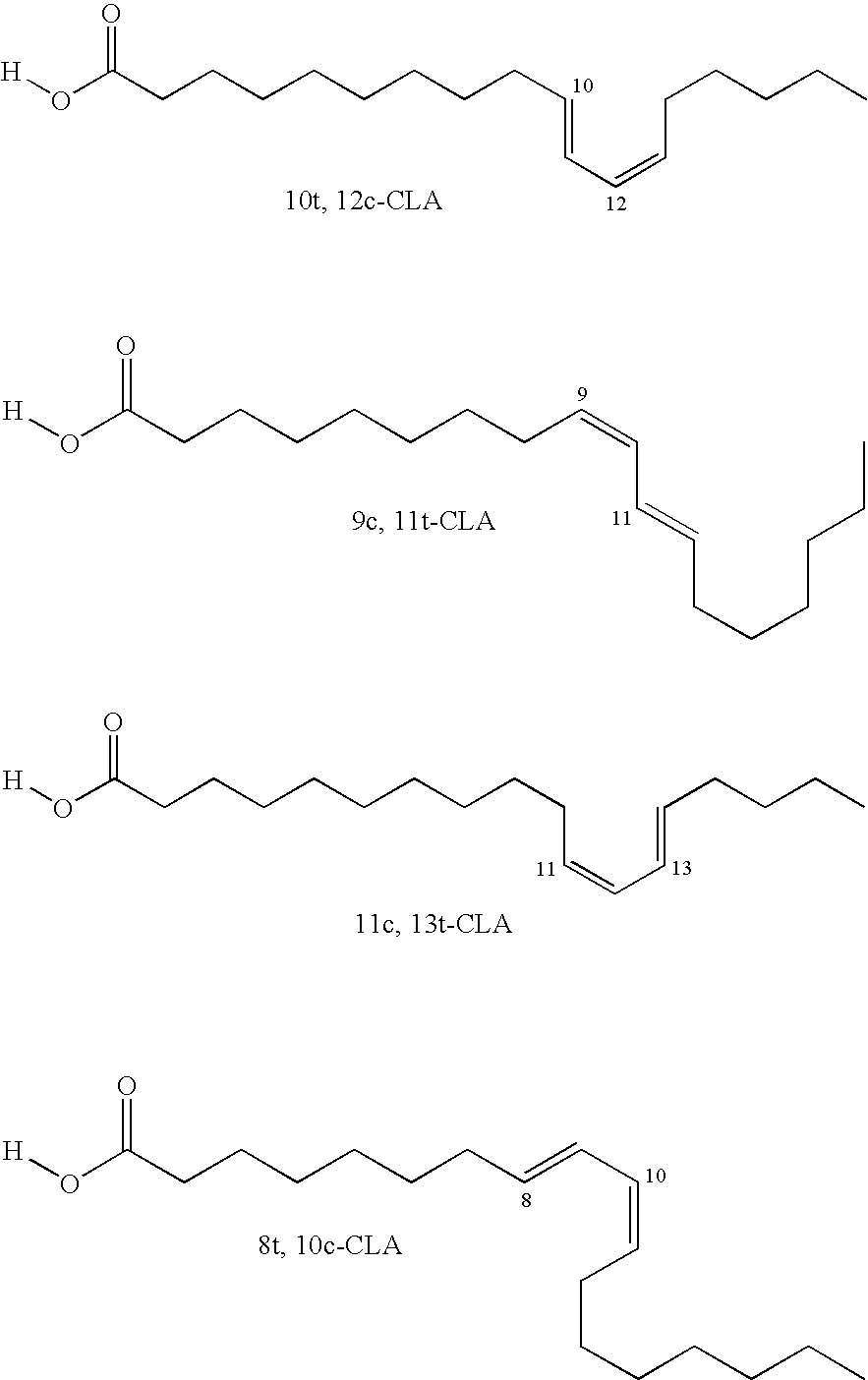
A process to manufacture conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)-containing materials such as conjugated linoleic salts and acids that are enriched in desirable cis-9, trans-11- and trans-10, cis-12-CLA isomers and are low in certain undesirable isomers. The process generally entails isomerization of an alkyl ester of a linoleic acid-containing material at a temperature typically between about 90 to 140° C. to effectuate conjugation of the double bonds, followed by saponification of the resultant CLA-containing fatty acid ester to produce a CLA-containing fatty acid salt, optionally followed by neutralization of the CLA-containing fatty acid salt with an acid source to produce a CLA-containing fatty acid.
Owner:STEPAN SPECIALTY PRODS
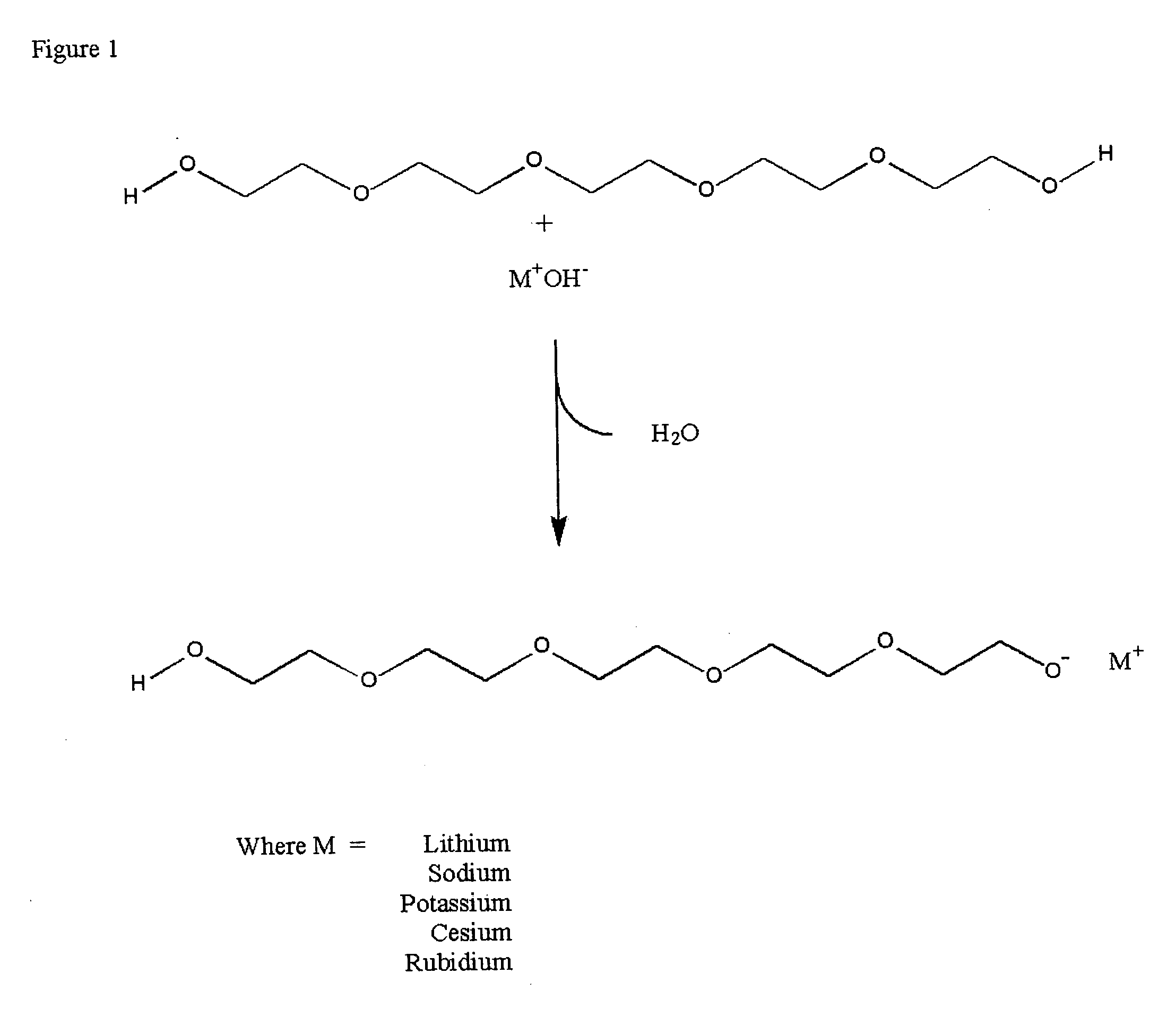
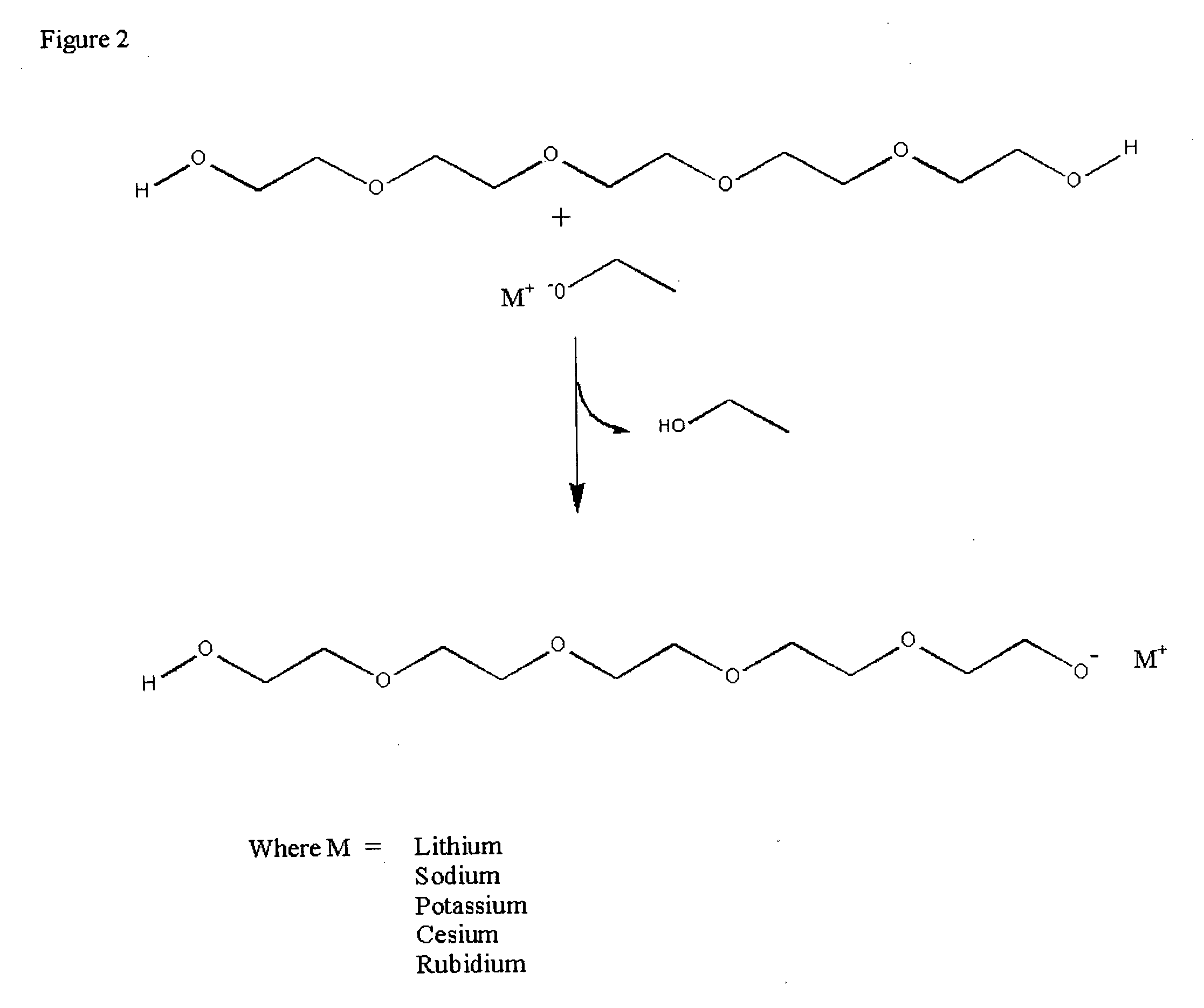
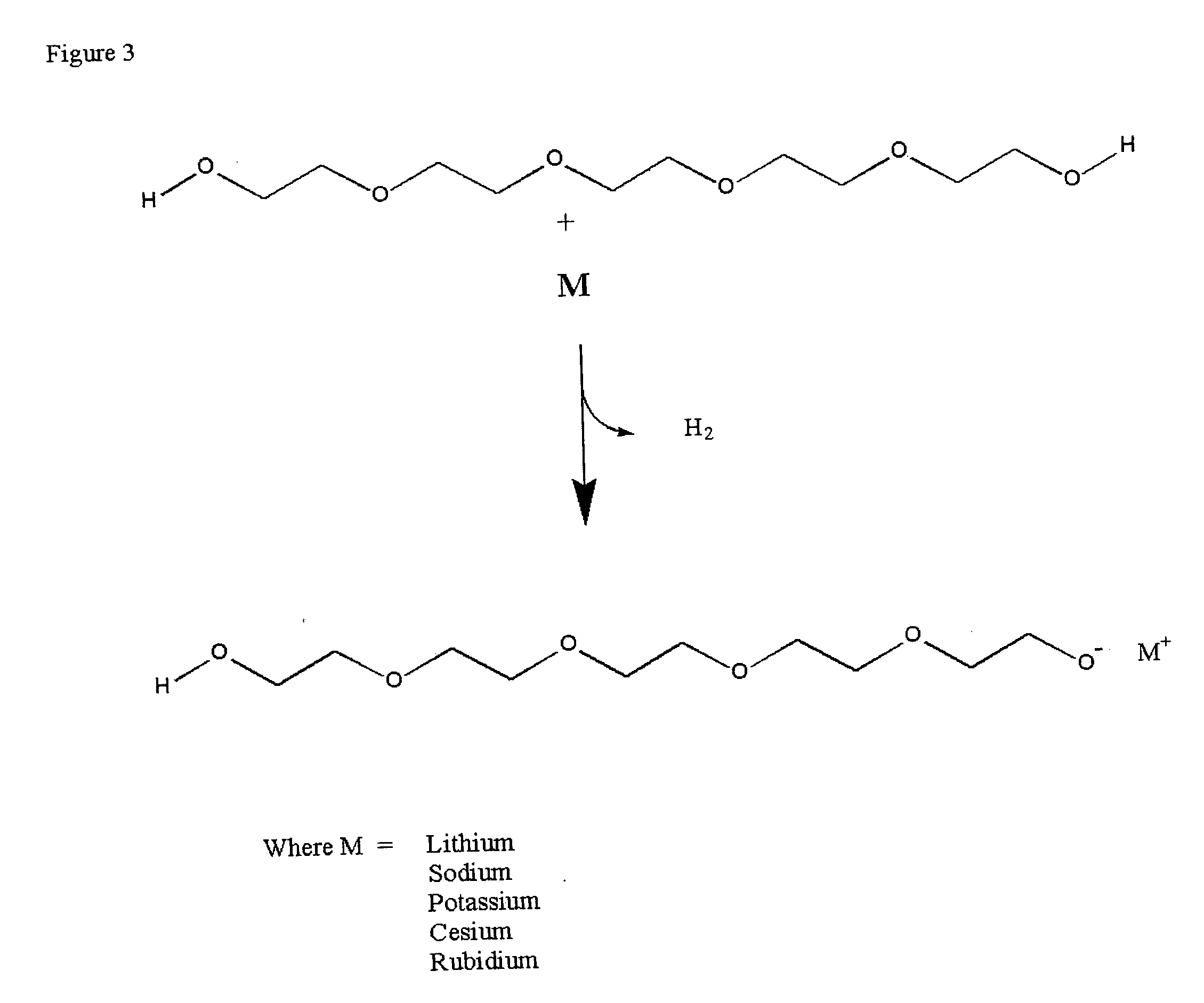
Methods for preparation and use of strong base catalysts
Methods for preparation of a unique superbase catalyst consisting of mixture of polyether alcohol and base in which a polyether alcohol superbase is produced by the removal of water or alcohol at elevated temperatures to form a polyether alcohol alkoxide. The superbase catalyst is useful in, but not limited to, quantitative isomerization of alkyl esters of vegetable oils containing interrupted double bond systems to yield esters with conjugated double bond systems.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Conjugated linolenic acids and methods of preparation and purification and uses thereof
InactiveUS7417159B2High selectivityShort timeFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteBiocidePurification methodsConjugated linoleic acid
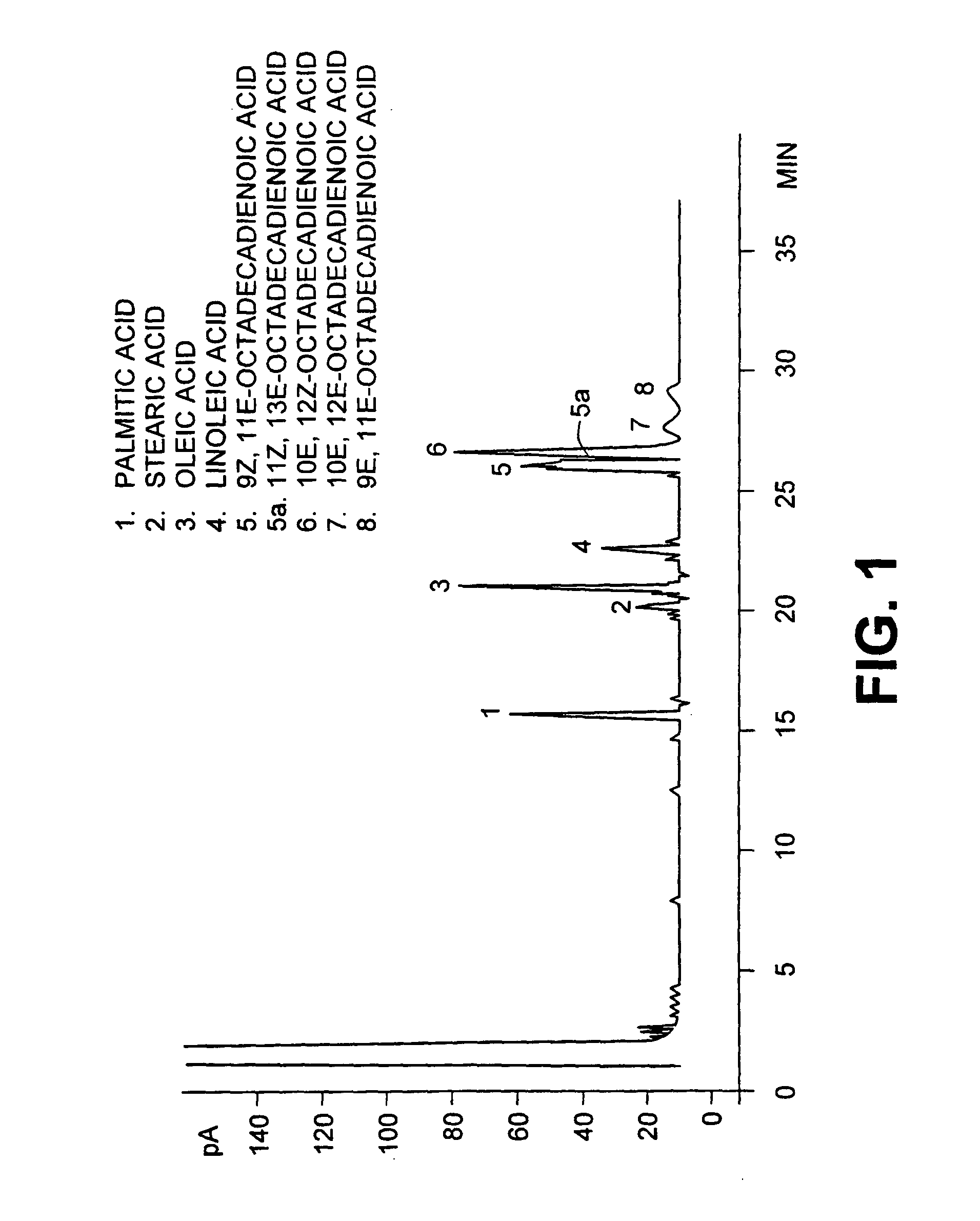
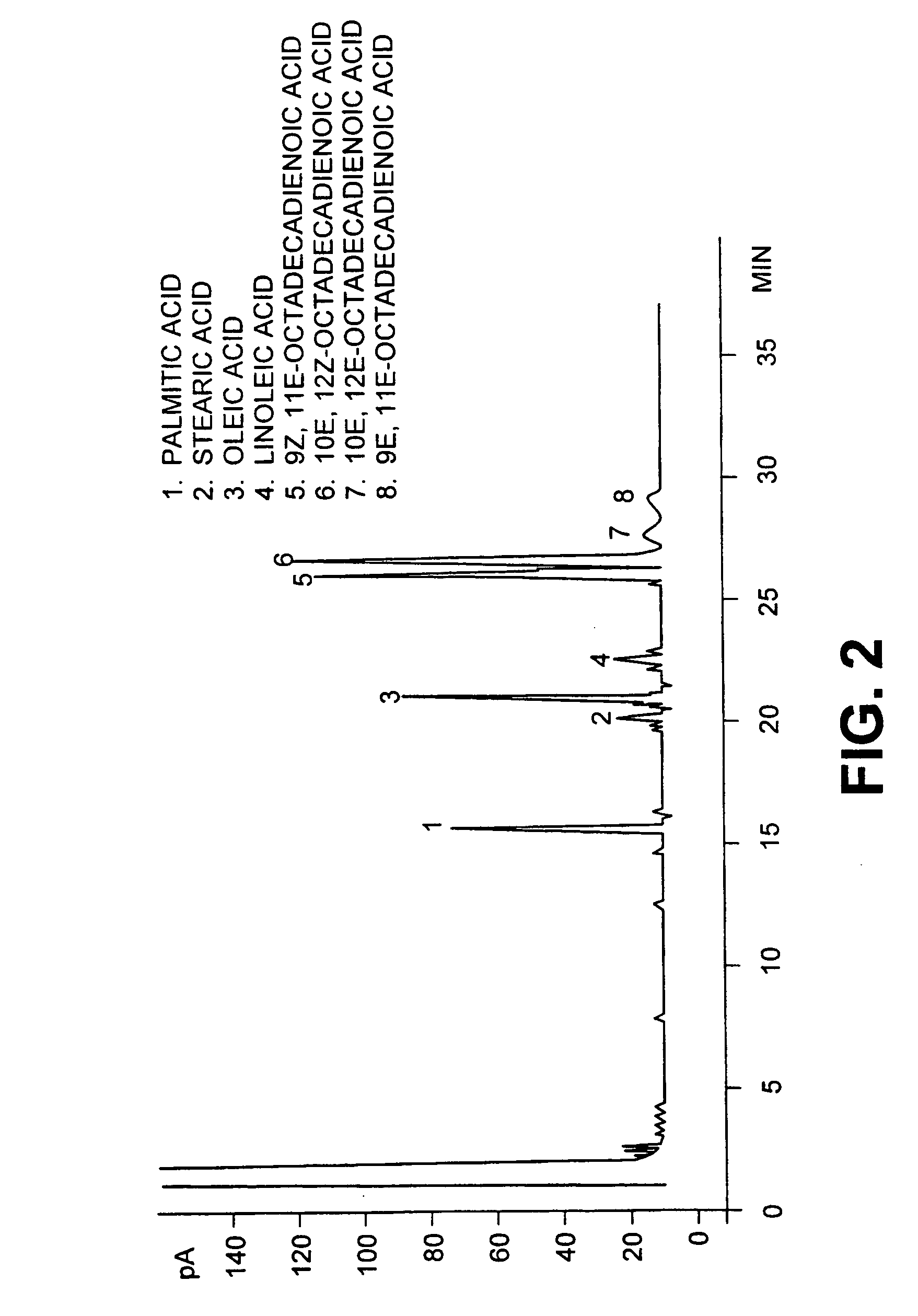
This invention relates to a new conjugated linoleic acids, a process for preparation thereof and method of use. Thus this invention is concerned with the preparation and purification of conjugated linoleic acids from materials rich in alpha or gamma linoleic acids. The reaction produces a mixture containing a 1:1 ratio of 9Z, 11E, 15Z-octadecatrienoic acid and 9Z, 13E, 15Z-octadecatrieonic acid. The mixture can be purified up to 90% by liquid chromatography, crystallization or urea crystallization. The mixture of 1:1 9Z, 11E, 15Z-octadecatrienoic acid and 9Z, 13E, 15E, 15Z-octadecatrienoic acid have anticancerous activities.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
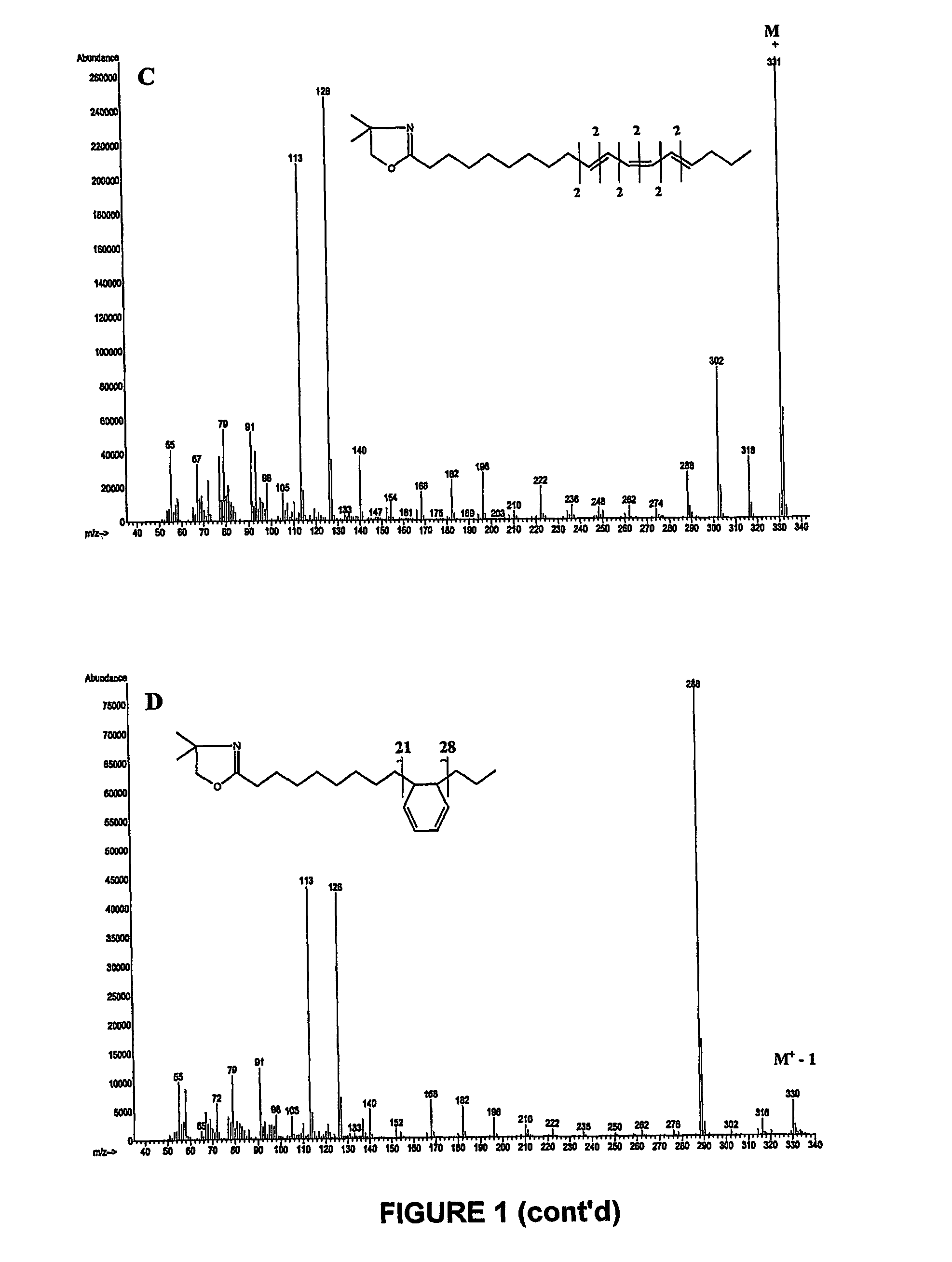
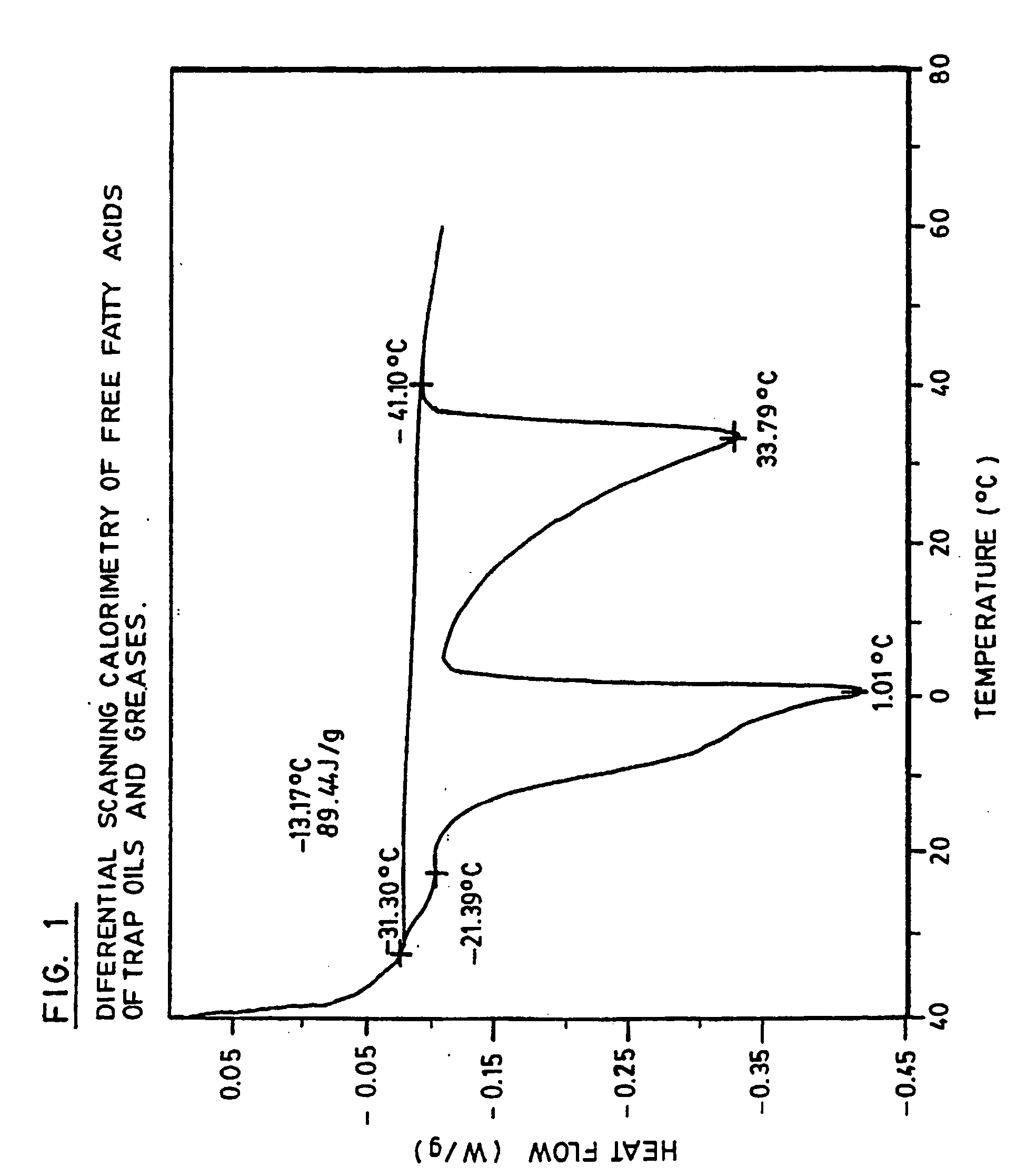
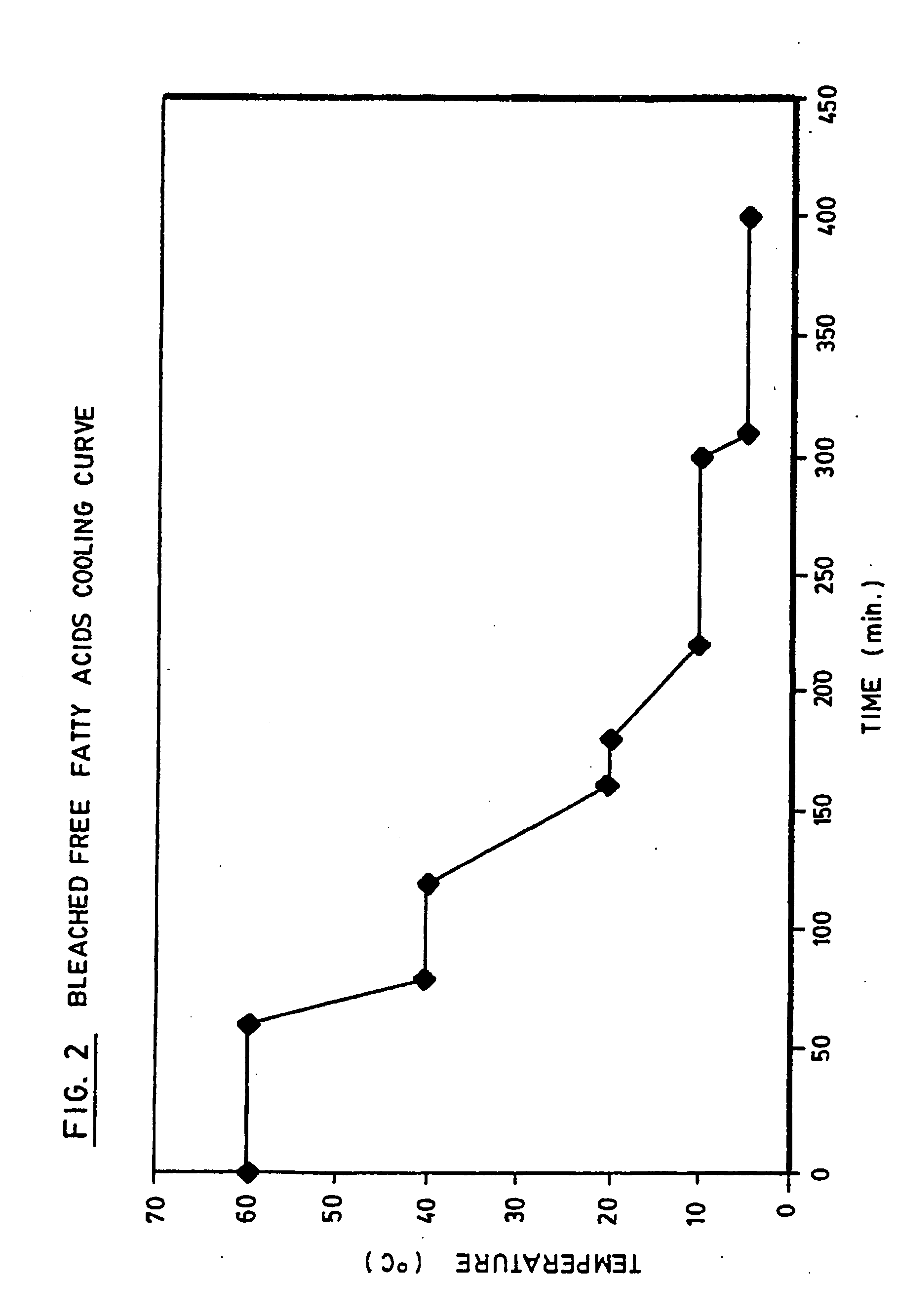
Production of high grade and high concentration of free fatty acids from residual residual oils, fats and greases
InactiveUS20050043555A1Inexpensive and simple to and concentrationInexpensive and simple to produceFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationHigh concentrationYellow grease
Owner:PROLAB TECH
Processes for the production of triglycerides of conjugated linoleic acid
InactiveUS7067684B2Increase productionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTransesterificationTG - Triglyceride
Processes for preparing conjugated linoleic acid triglycerides are described which comprise: (a) providing a conjugated linoleic acid alkyl ester, wherein the alkyl group is linear or branched and has from 1 to 5 carbon atoms; and (b) subjecting conjugated linoleic acid alkyl ester to transesterification with triacetin to provide a conjugated linoleic acid triglyceride.
Owner:COGNIS DEUT GMBH & CO KG
Gemini ionic liquid with fluorous biphasic property, and catalyst prepared by utilizing ionic liquid and application thereof
InactiveCN101781254ANo lossNot easy to loseOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic isomerisationIsomerizationIonic liquid
The invention discloses gemini ionic liquid with fluorous biphasic property. The molecular formula of the ionic liquid is [(R1N2C3H3)2R]2+.[2X-]. The structure of the ionic liquid is shown as the general formula (I) in the specification, wherein R1 represents hydrogen or C1-C8 alkyl; R represents ethylidene oxyl element, is selected from-(CH2CH2O)qCH2CH2- and is formed by polyethylene glycol 400-10000, and q is 6-250; and X represents HBF4, HPF6, HNO3 or halogenated hydrogen. A catalyst can be prepared immediately after adding palladium, rhodium or nickel catalyst into the gemini ionic liquid with fluorous biphasic property for coordination, and can be used in HECK reaction, C-C coupling reaction and isomerization reaction. The ionic liquid is not easy to volatilize, and the catalyst prepared by utilizing the ionic liquid is used in HECK reaction, C-C coupling reaction and isomerization reaction, has high catalytic efficiency and can be reused.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Isomerisation of pharmaceutical intermediates
InactiveUS20070215455A1High yieldIrradiation time can be shortenedGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsVitamins chemistryIsomerizationCalcipotriol monohydrate
The present invention relates to an isomerisation method of vitamin D analogues, such as compounds useful for the synthesis of calcipotriol, and to and to the use of a flow-through photoreactor or continuous flow photoreactor reactor for making said vitamin D analogues. The present invention relates further to the use of intermediates produced with said method for making calcipotriol or calcipotriol monohydrate, or pharmaceutical formulations thereof.
Owner:LEO PHARMA AS
Method for commercial preparation of preffered isomeric forms of ester free conjugated fatty acids with solvents systems containing polyether alcohol solvents
InactiveUS20040015001A1Fatty acid isomerisationOrganic compound preparationIodo fatty acidIsomerization
Methods for sequential saponification and quantitative isomerization of glyceride oils containing interrupted double bond systems, with alkali in a polyether alcohol solvent to yield soaps with conjugated double bond systems are disclosed. The novel properties f the polyether alcohols allow the removal of water added with the alkali by boiling. The preferred embodiment uses a vegetable oil rich in linoleic acid such as sunflower or safflower oil, potassium hydroxide, phosph ric acid to neutralize the soaps. The reaction forms equal quantities of 9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid and 10E,12Z-octadecadienoic acids.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Conjugated linoleic acid compositions
InactiveUS7115759B2High acid valueFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationDietary supplementTriglyceride
The present invention relates to the manufacture of conjugated linoleic acid, and in particular, to dietary supplements, feeds and food products containing conjugated linoleic acid. Accordingly, processes for producing conjugated linoleic acid of high purity and acid value are disclosed. These processes utilize alcoholate catalysts and esters of sunflower oil, safflower oil, or corn oil as the source of linoleic acid. The esters of conjugated linoleic acid produced by the process can be used in animal feeds and in food products suitable for human consumption. Furthermore, the esters can be converted into free fatty acids or incorporated into triglycerides.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ASA
Method for commercial preparation of conjugated linoleic acid from by-products of vegetable oil refining
InactiveUS6414171B1Increase volumeIncrease temperatureFatty acid isomerisationFatty acids production/refiningVegetable oilDouble bond
Methods for quantitative conversion of soapstock, lecithin gums, deodorizer distillate and other by-products of vegetable oil refining containing interrupted double bond systems, to products with conjugated double bonds, using a reduced amount of alkali. Less than one mole of alkali per mole of acyl group present is required, thereby greatly reducing the need for added caustic compared with methods using oils, fatty acids and esters as starting materials. The preferred starting materials are soapstocks derived from vegetable oils rich in linoleic acid.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Method for producing conjugated linoleic acid
InactiveUS20060189817A1Fatty acid isomerisationOrganic compound preparationIsomerizationCost effectiveness
Owner:COGNIS DEUT GMBH & CO KG
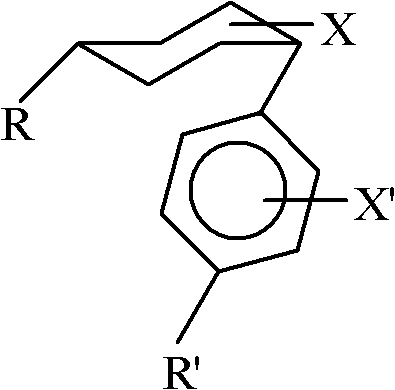
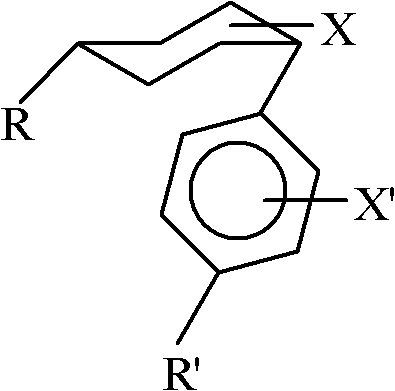
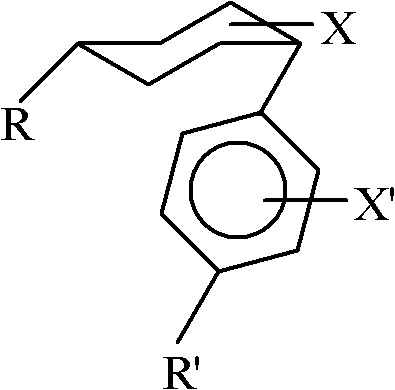
Method for converting cis-substituted cyclohexyl in organic molecules into trans-substituted cyclohexyl
ActiveCN102408284AWide applicabilityRich varietyHydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIsomerizationReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for converting cis-substituted cyclohexyl into trans-substituted cyclohexyl. The cis-substituted cyclohexyl has a structural formula shown in the specifications, wherein R and R' are the same or different and are an H atom, fatty hydrocarbyl with 1 to 10 carbon atoms, or aromatic hydrocarbyl with 1 to 10 carbon atoms; X and X' are the same or different and are an H element, 1 to 3 halogens, cyan, alkyl, alkoxy, trifluoromethyl or trifluoromethoxy; a catalyst converted from an isomer is weakened aluminum trichloride of which the activity is weakened by a weakening additive, or tetrachloroaluminate; and the reaction temperature is between -20 and +50 DEG C. The conversion method is simple and practicable, other isomerization side reactions in the cyclohexyl conversion process can be effectively inhibited when cyclohexyl conversion reaction is performed, a few isomerization byproducts are generated, yield is high, and a wide application prospect is achieved.
Owner:江苏广域化学有限公司
Synthesis of class of amino acid type amphoteric water-soluble chiral phosphine ligand and application thereof in asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation
InactiveCN101775035AHigh catalytic activityHigh stereoselectivityOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDehydrogenationHigh activity
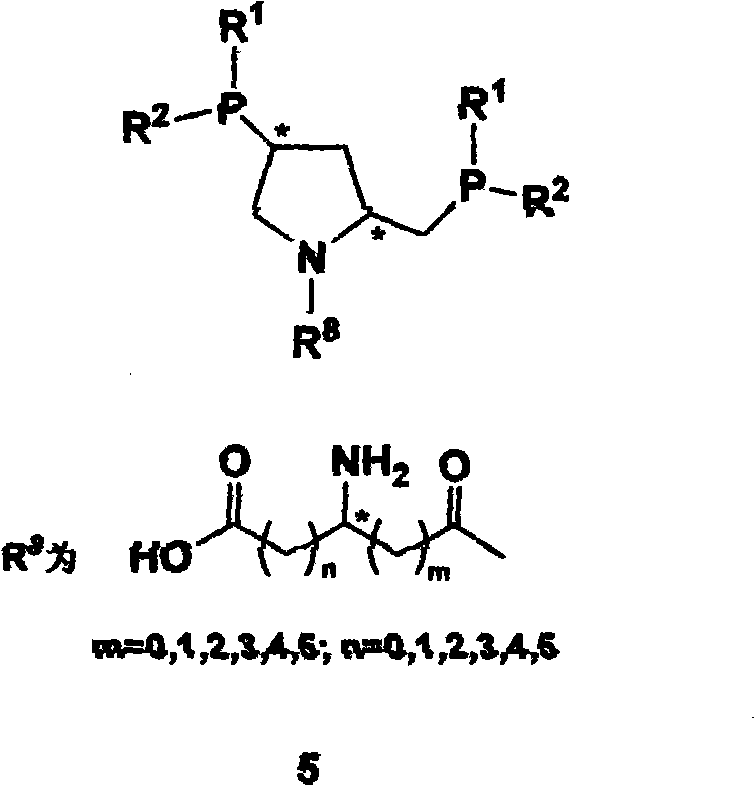
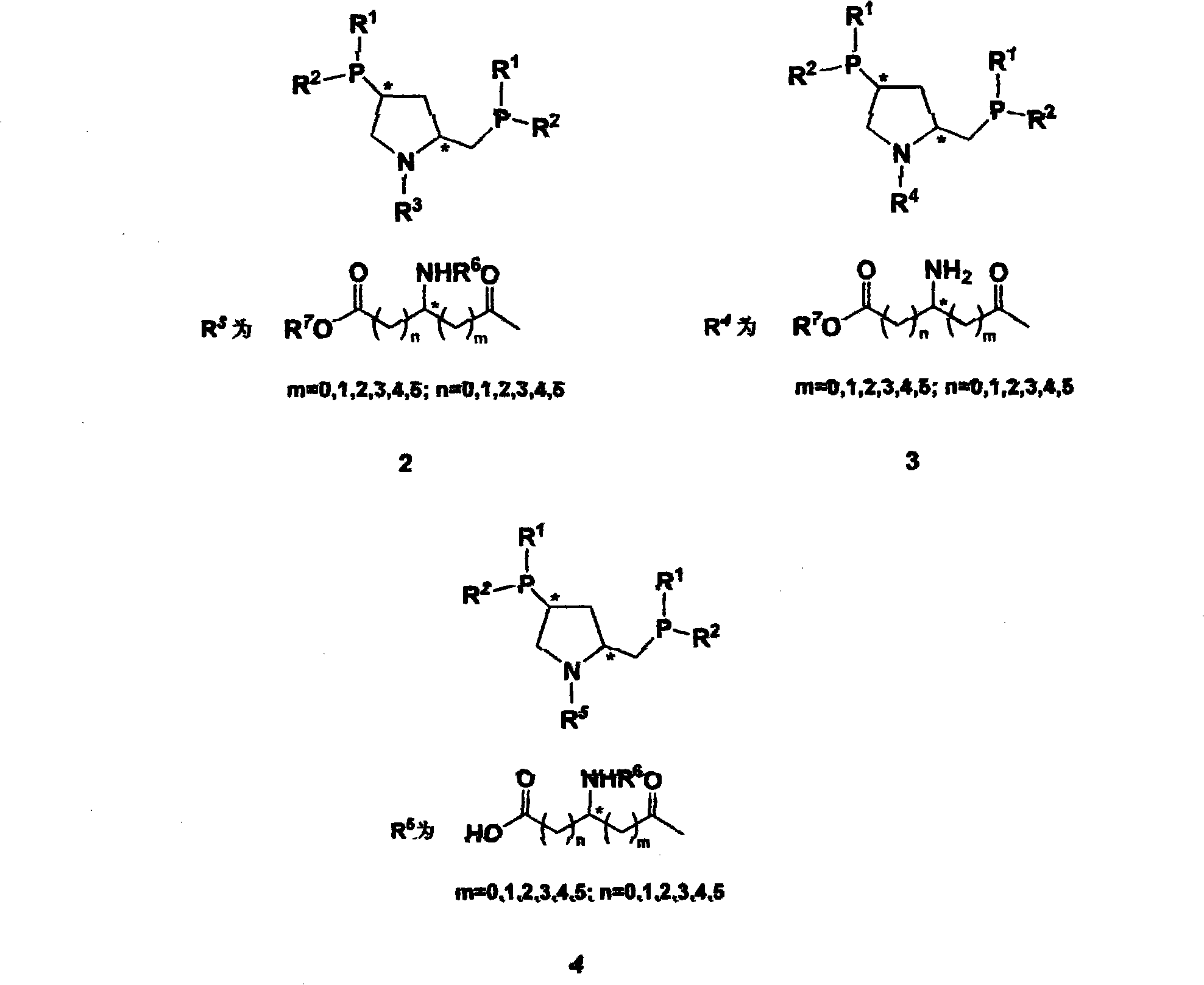
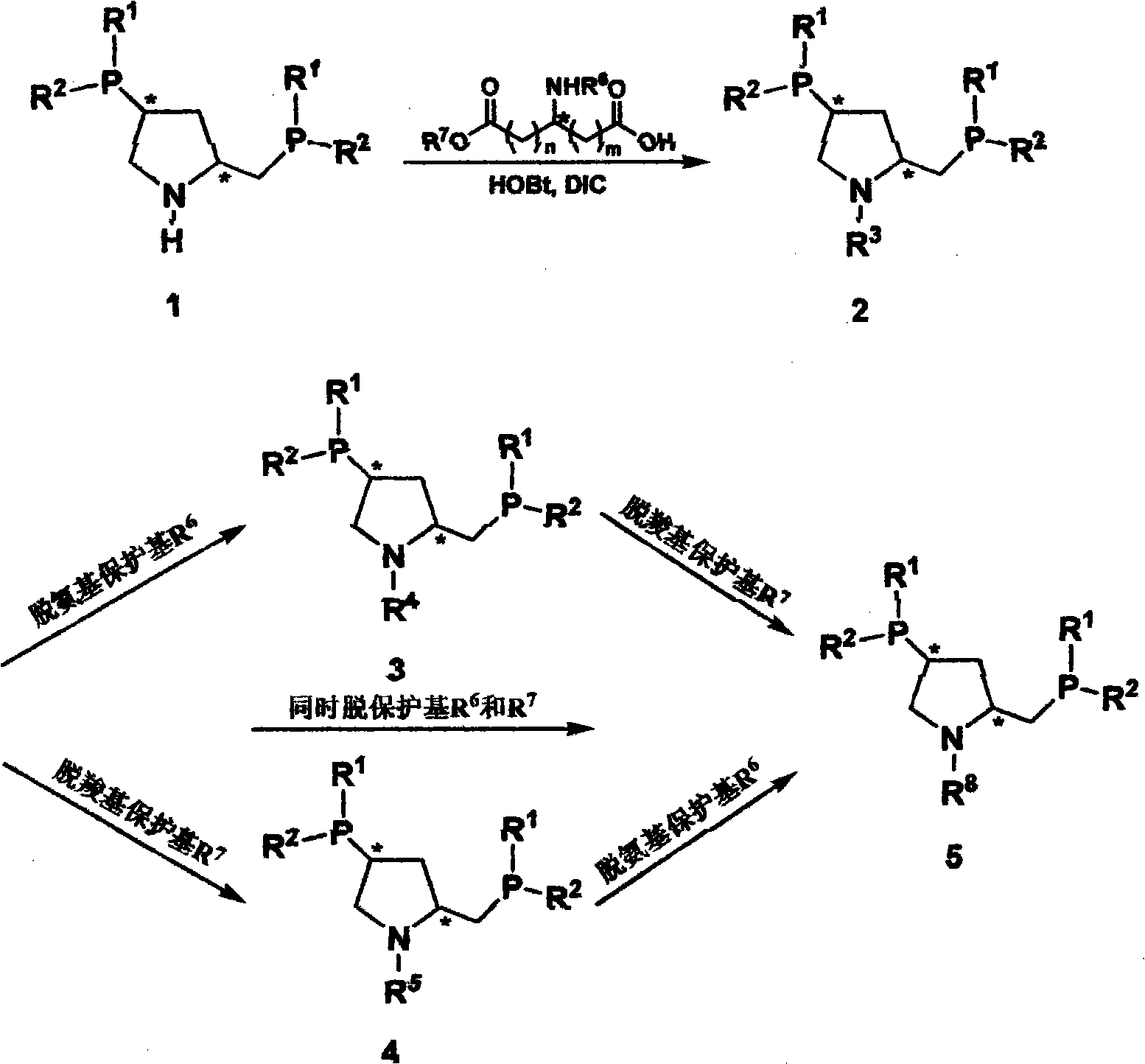
The invention relates to synthesis of class of amino acid type amphoteric water-soluble chiral phosphine ligand and application thereof in asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation. The class of ligand takes chiral phosphine ligand PPM as the matrix, amino acid molecules are introduced into PPM molecules, chiral dual phosphine ligands and synthesis midbody thereof are provided, the ligand designed into the invention can be applied to various asymmetric synthetic reactions catalyzed by metals, comprising asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation, hydrogen transfer, hydroformylation and the like, and especially has higher activity and stereoselectivity in asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation of alpha-dehydrogenation amino acid and derivatives thereof.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Suppression of carcinoma using high purity conjugated fatty acid
Treatment of carcinoma in a human is disclosed, including administering a therapeutically effective amount of a fatty acid having four carbons with two conjugated double bonds formed by reacting an ester of a fatty acid with a tosyl chloride or a mesyl chloride, the fatty acid having four carbon atoms such that carbon one bears one hydrogen and one hydroxyl group, carbon two bears two hydrogens, and a double bond is positioned between carbon three and four. The tosylate or mesylate of the ester of the fatty acid having the chain of four carbon atoms such that carbon one bears one hydrogen and one hydroxyl group, carbon two bears two hydrogens, and a double bond is positioned between carbon three and four is reacted with diazabicyclo-undecene. The method includes administering to a human a highly purified fatty acid in accordance with the present invention.
Owner:MATREYA
Method For The Production Of Conjugated Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids With Heterogenous Catalysts
ActiveUS20130245299A1Brønsted acidity of the heterogeneous catalyst is reduced or lowAluminium compoundsFatty acid isomerisationMetal catalystFatty acids.polyunsaturated
The present invention relates to an improved process for the production of conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), preferably conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), using finely dispersed heterogeneous metal catalysts on a mesoporous support, in the absence of Hg. The present invention also relates to a method to increase the large microporosity and (optionally) the small mesoporosity of a zeolite, thus obtaining a modified zeolite having a large and highly accessible internal surface.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Method for isomerization of light hydrocarbon
ActiveCN1840513AHigh activityIncrease the rate of isomerizationPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationAlkane2-methylbutane
The isomerization method for lighter hydrocarbons comprises: rectifying the material to remove water and isopentane; then, with carrring-SO42- ZrO2 as solid super acidic catalyst, taking hydroisomerization reaction. This invention can improve yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Conjugated linolenic acids and methods for commerical preparation and purification
InactiveUS20060281814A1High selectivityShort timeBiocideFatty acid isomerisationVegetable oilGeometric isomer
A method for the preparation and purification of conjugated linolenic acids is described. The method comprises blending a mixture of vegetable oils and or fats including various concentrations of alpha or gamma and or both linolenic acids with a base. The method transforms approximately over two thirds of α-linolenic acid (9Z,12Z,15Z-octadecatrienoic acid) into 9Z,11E,15Z-octadecatrienoic acid and 9Z,13E,15Z-octadecatrienoic acid. The method also transforms gamma-linolenic acid (6Z,9Z,12Z-octadecatrienoic acid) into 6Z,8E,15Z-octadeccatrienoic acid and 6Z,10E,12Z-octadecatrienoic acid. In all cases, geometrical isomers and fully conjugated isomers are also produced.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Process for isomerizing and converting (Z)-olefins to (E)-olefins
PendingCN110878001ARealize isomerization conversionImprove efficiencySilicon organic compoundsHydrocarbon by isomerisationIsomerizationPtru catalyst
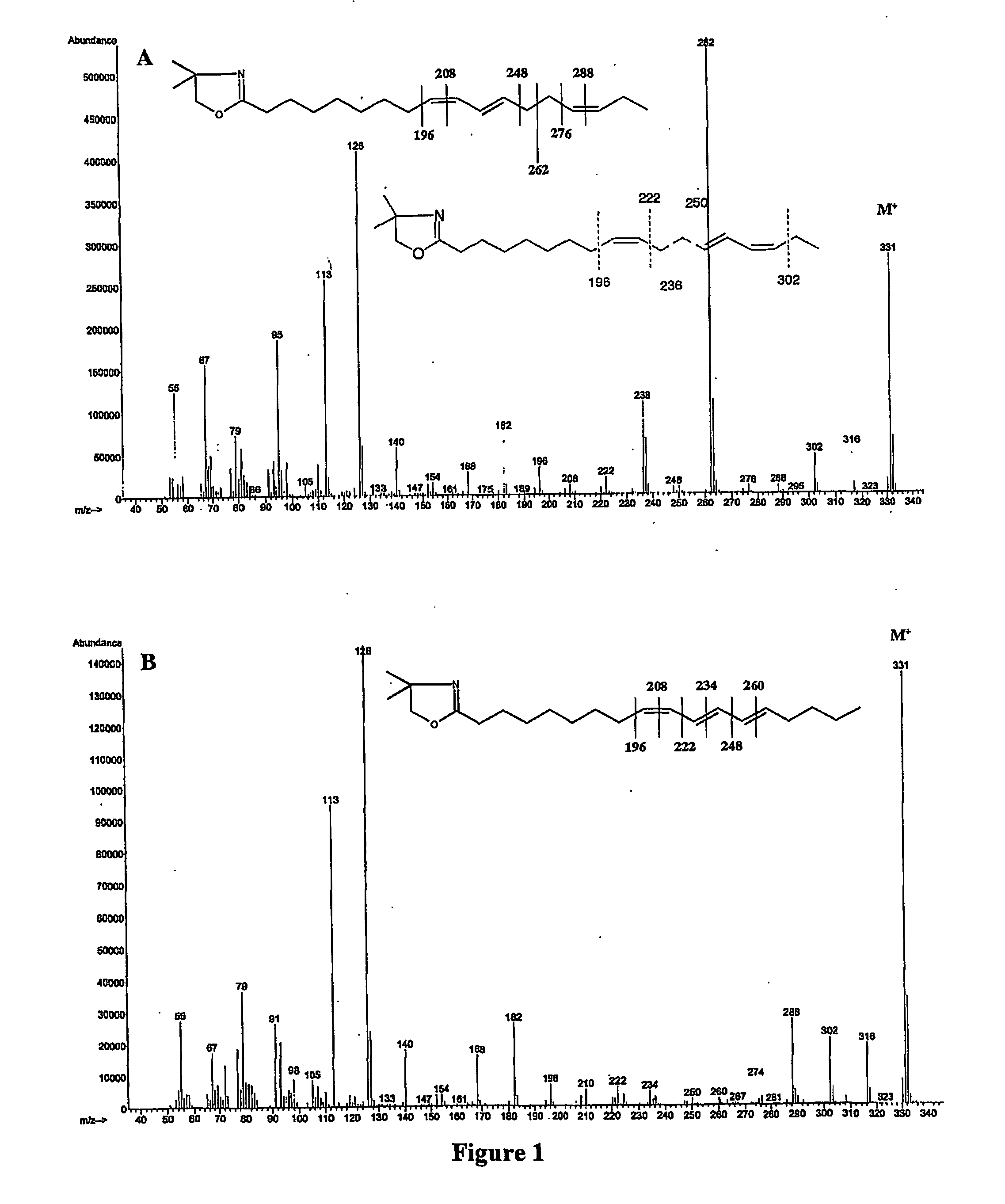
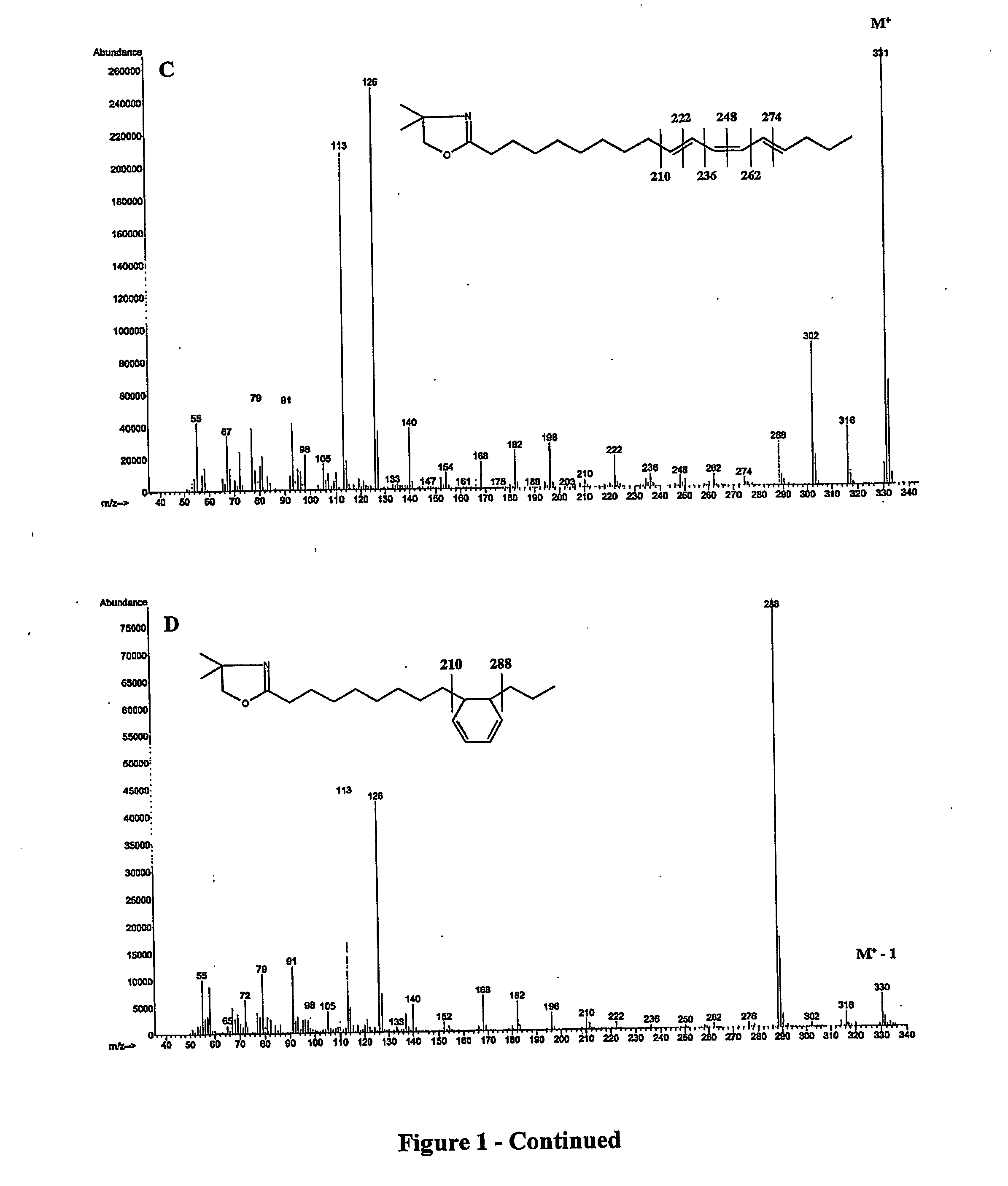
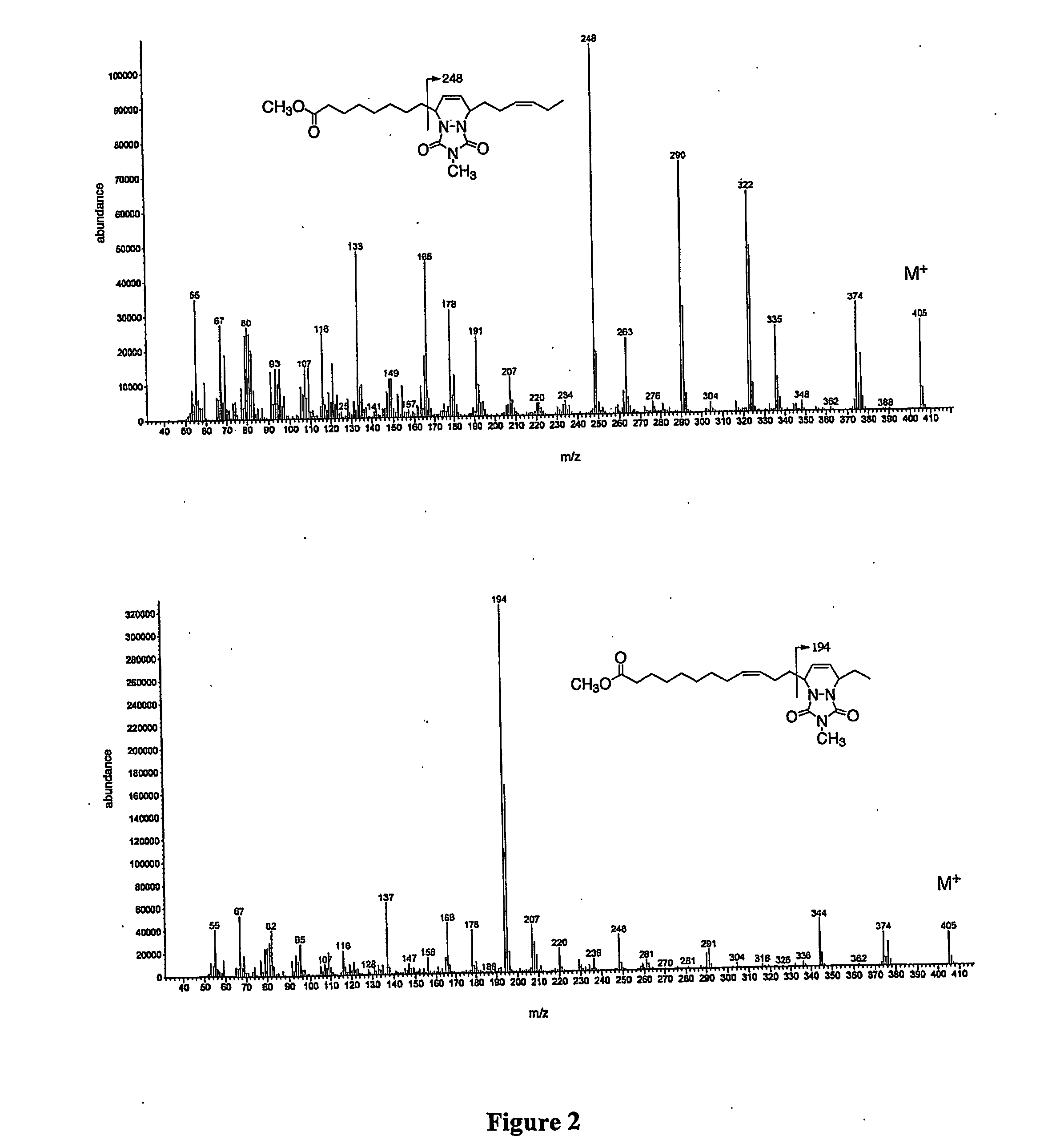
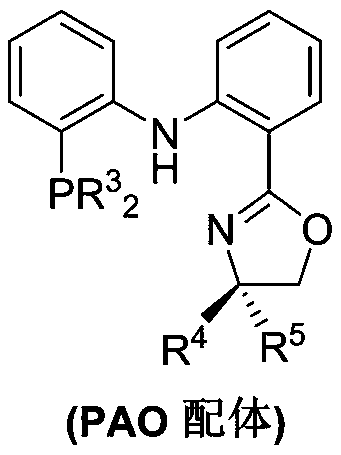
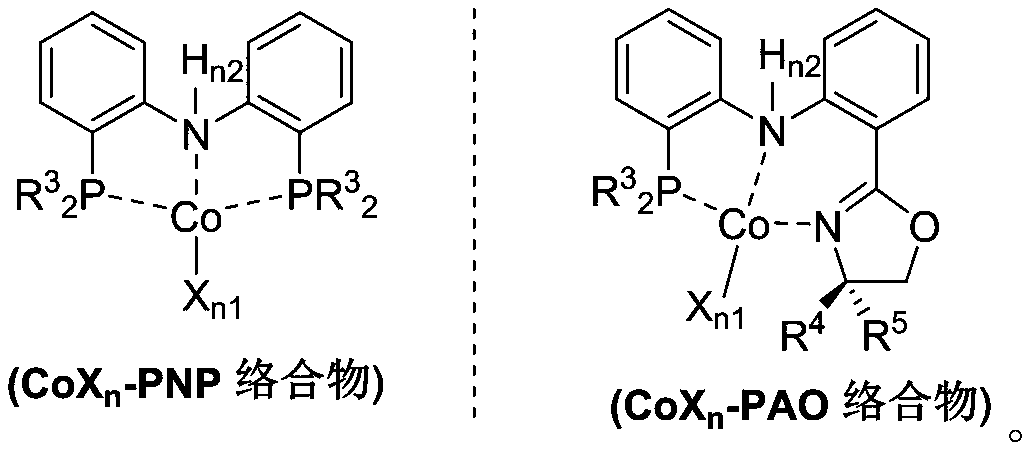
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal catalytic synthesis, and discloses a method for isomerizing and converting (Z)-olefins into (E)-olefins. The (E)-olefins are prepared through a reaction at -30-80 DEG C for 0.5-48 h by using a combination of CoX2 and a PNP or PAO ligand as a catalyst in the presence of an activating reagent; and a molar ratio of the (Z)-olefins to the CoX2 to the PNP or PAO ligand to the activating reagent is 1:(0.00001-0.10):(0.00001-0.10):(0.00003-0.30). The catalyst used in the invention is the combination of the cheap metal cobalt salt and the simple and easily available ligand, no other toxic transition metal (such as ruthenium, rhodium and palladium) salt is added in the reaction, and the method also has the advantages of cheap and easily available raw material, good functional group tolerance, mild reaction conditions, simplicity in operation, and e atom economy of 100%.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Production and purification of esters of conjugated linoleic acids
InactiveUS20070191619A1Reduce pressureImprove stabilityFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid isomerisationIsomerizationTransesterification
A process to refine esters of conjugated linoleic acids via distillation in a single or multi-pass distillation operation is provided. Thermal rearrangement of conjugated linoleic acid components during distillation is prevented or reduced by the use of a low residence time and / or reduced pressure distillation apparatus. A process to produce refined esters of conjugated linoleic acids is also provided. The process transesterifies a linoleic acid-containing oil to generate an alkyl ester composition which further undergoes isomerization at a temperatures typically between about 90-140° C. to form an ester stream containing conjugated linoleic acid esters, which is then distilled to obtain the refined esters of conjugated linoleic acids. The transesterification and isomerization steps can be performed in one reaction vessel without an intervening distillation step. The transesterification and isomerization steps can occur concurrently in a continuous reaction system using a dual reaction zone apparatus. Refined ester compositions produced by the processes and enriched in desirable conjugated linoleic acid isomers are also contemplated.
Owner:STEPAN COMPANY
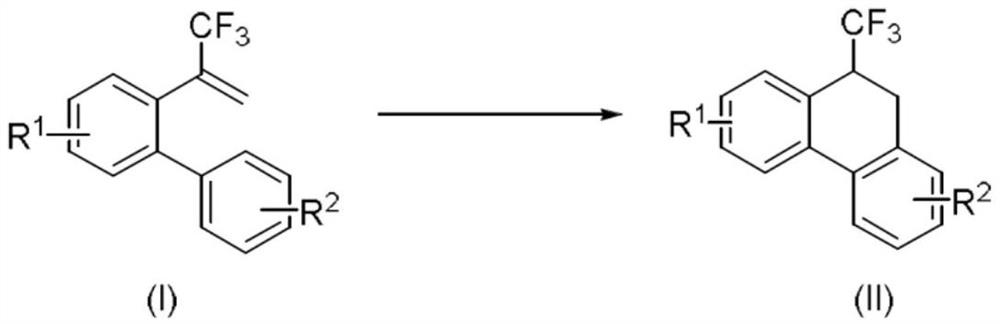
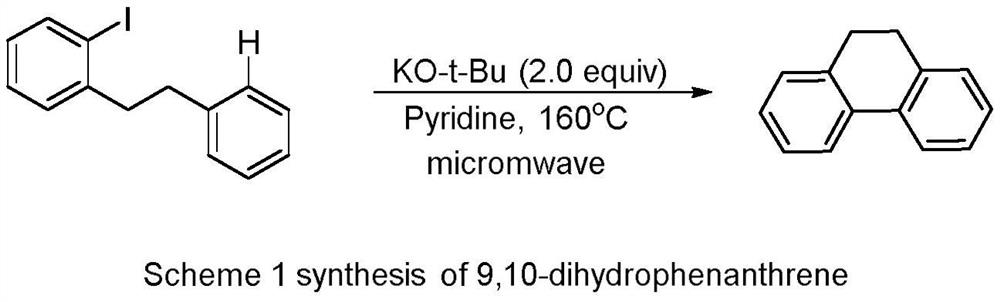
Method for synthesizing 9-trifluoromethyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene compound through copper photocatalysis
ActiveCN112441875AReduce operational riskCircularizationOrganic compound preparationOrganic isomerisationMeth-Photosens
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a 9-trifluoromethyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene compound by copper photocatalysis. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a substrate (I), a photosensitizer, an alkaline substance and a solvent, performing reacting for 20-36 hours under the conditions of blue LED illumination, temperature of 15-40 DEG C and inert gas protection, and carrying out aftertreatment on a reaction solution to obtain a 9-trifluoromethyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene compound (II). The method is safe, environmentally friendly, free of waste gas and low in operation risk; the substrate adaptability is good, and cyclization of various substituent groups can be realized; reaction conditions are mild; and meanwhile, the reaction has certain innovativeness and high atom economy, a traditional heating mode is replaced with a photocatalysis mode, energy consumption is reduced, and the concept of modern green chemistry is better met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
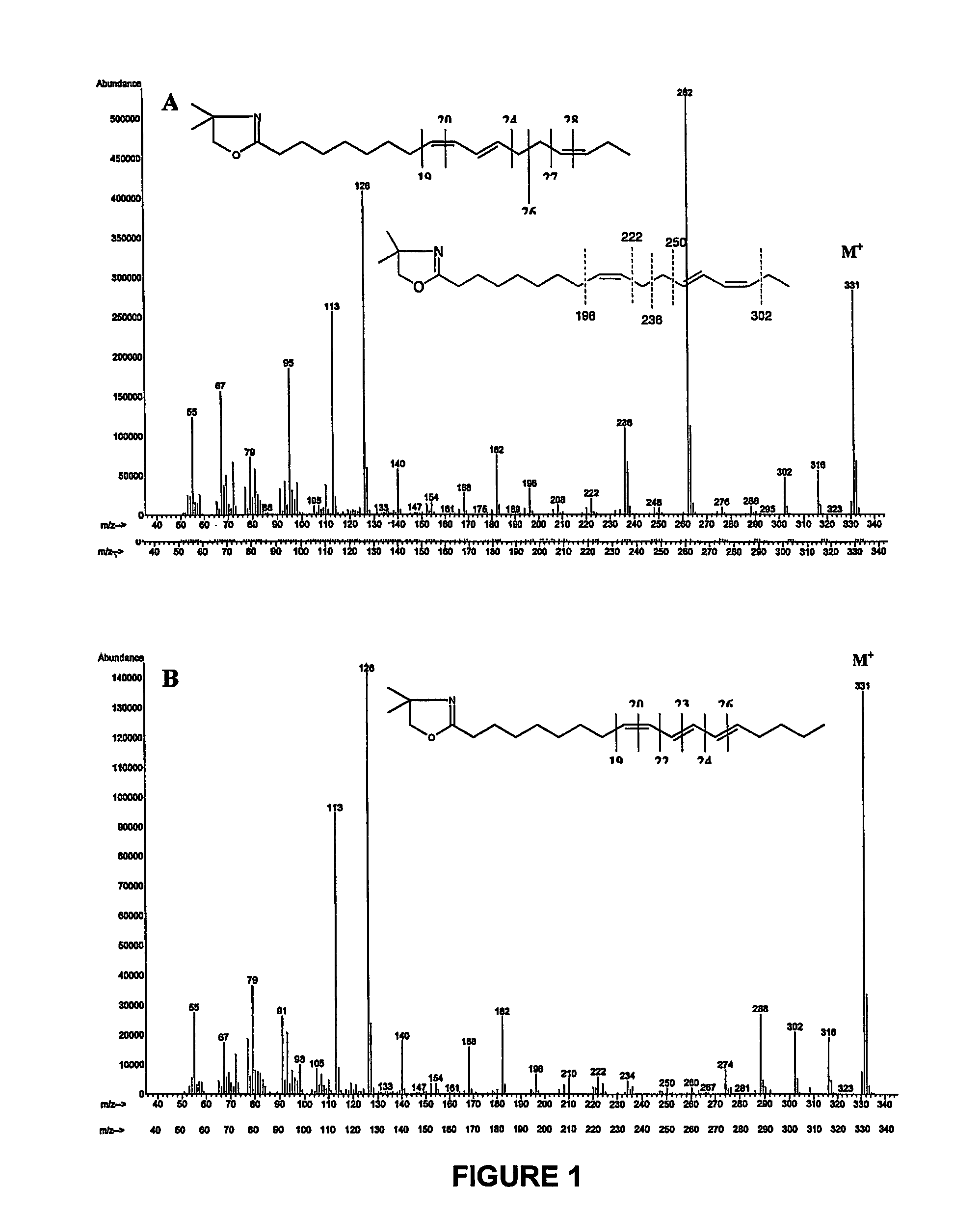
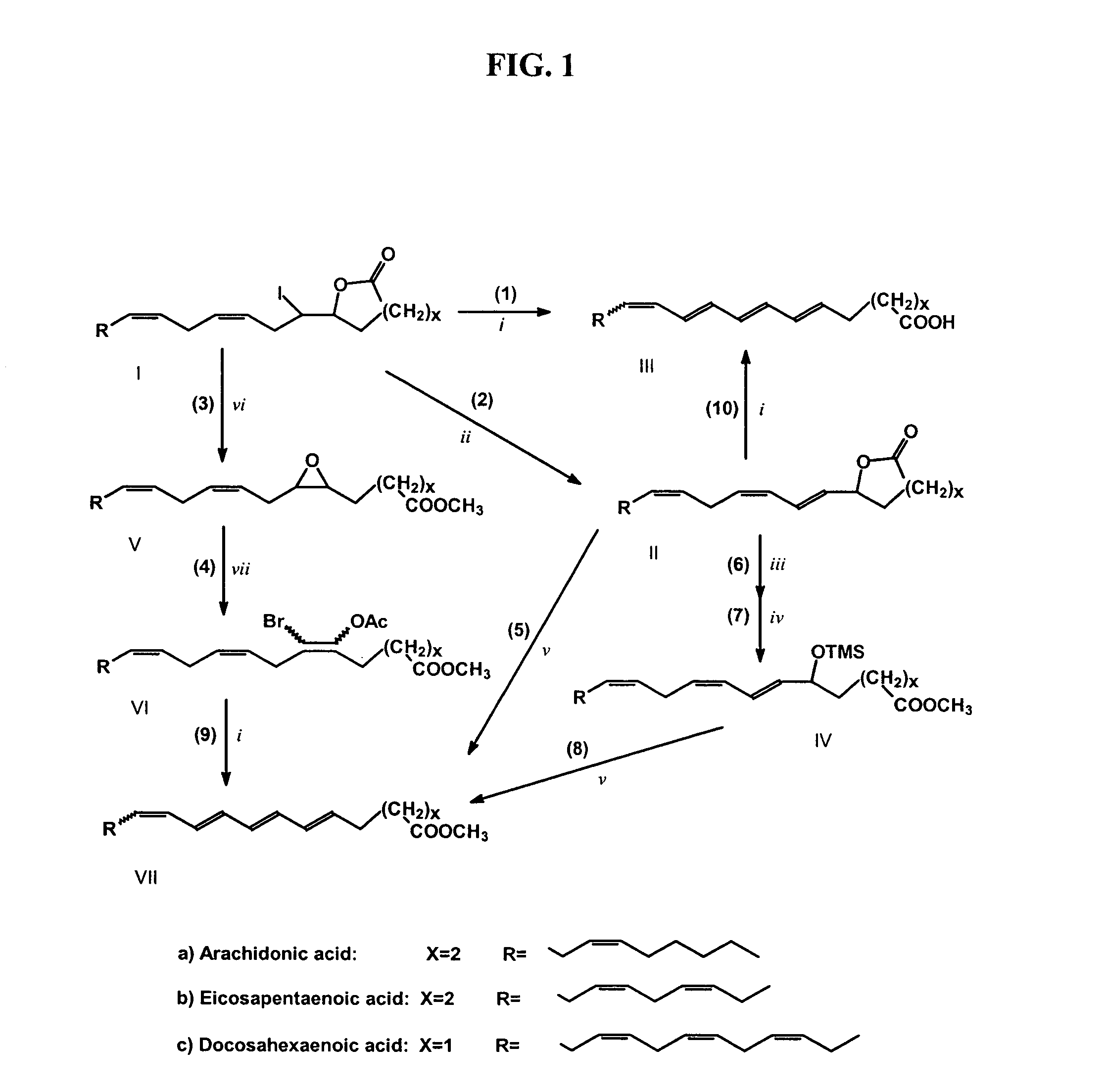
Synthesis of polyconjugated fatty acids
InactiveUS7091369B2High yieldBiocideFatty acid chemical modificationIodo fatty acidCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATUE UNIV THE
Synthesis of polyconjugated fatty acids
InactiveUS20050014826A1High yieldBiocideFatty acid chemical modificationCombinatorial chemistryFatty acid
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATUE UNIV THE
High temperature isomerization of (E)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene
The invention relates to high temperature isomerization of (E)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene. Disclosed are processes for a high temperature isomerization reaction converting (E)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene to (Z)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene. In certain aspects of the invention, such a process includes bringing a feed stream into contact with a heated surface, wherein the feed stream includes (E)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene or a mixture of (E)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene with (Z)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene. The resulting product stream includes (Z)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene and (E)-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene, wherein the ratio of (Z) isomer to (E) isomer in the product stream is higher than the ratio of the feed stream. The (E) and (Z) isomers in the product stream may be separated from one another.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Conjugated linolenic acids and methods of preparation and purification and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060281815A1High selectivityShort timeFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteBiocidePurification methodsConjugated linoleic acid
This invention relates to a new conjugated linoleic acids, a process for preparation thereof and method of use. Thus this invention is concerned with the preparation and purification of conjugated linoleic acids from materials rich in alpha or gamma linoleic acids. The reaction produces a mixture containing a 1:1 ratio of 9Z, 11E, 15Z-octadecatrienoic acid and 9Z, 13E, 15Z-octadecatrieonic acid. The mixture can be purified up to 90% by liquid chromatography, crystallization or urea crystallization. The mixture of 1:1 9Z, 11E, 15Z-octadecatrienoic acid and 9Z, 13E, 15E, 15Z-octadecatrienoic acid have anticancerous activities.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com