Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7716results about "Heat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
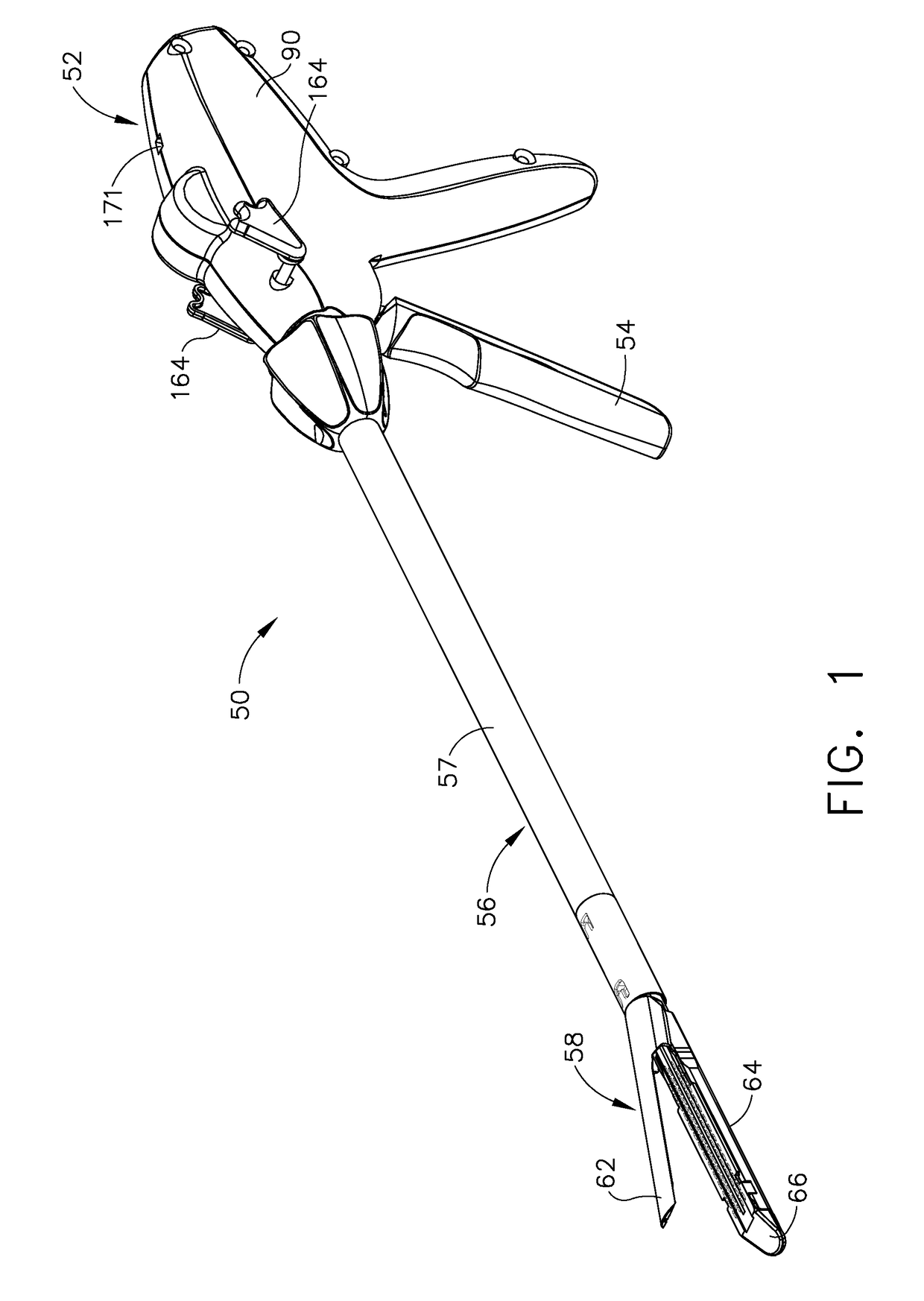
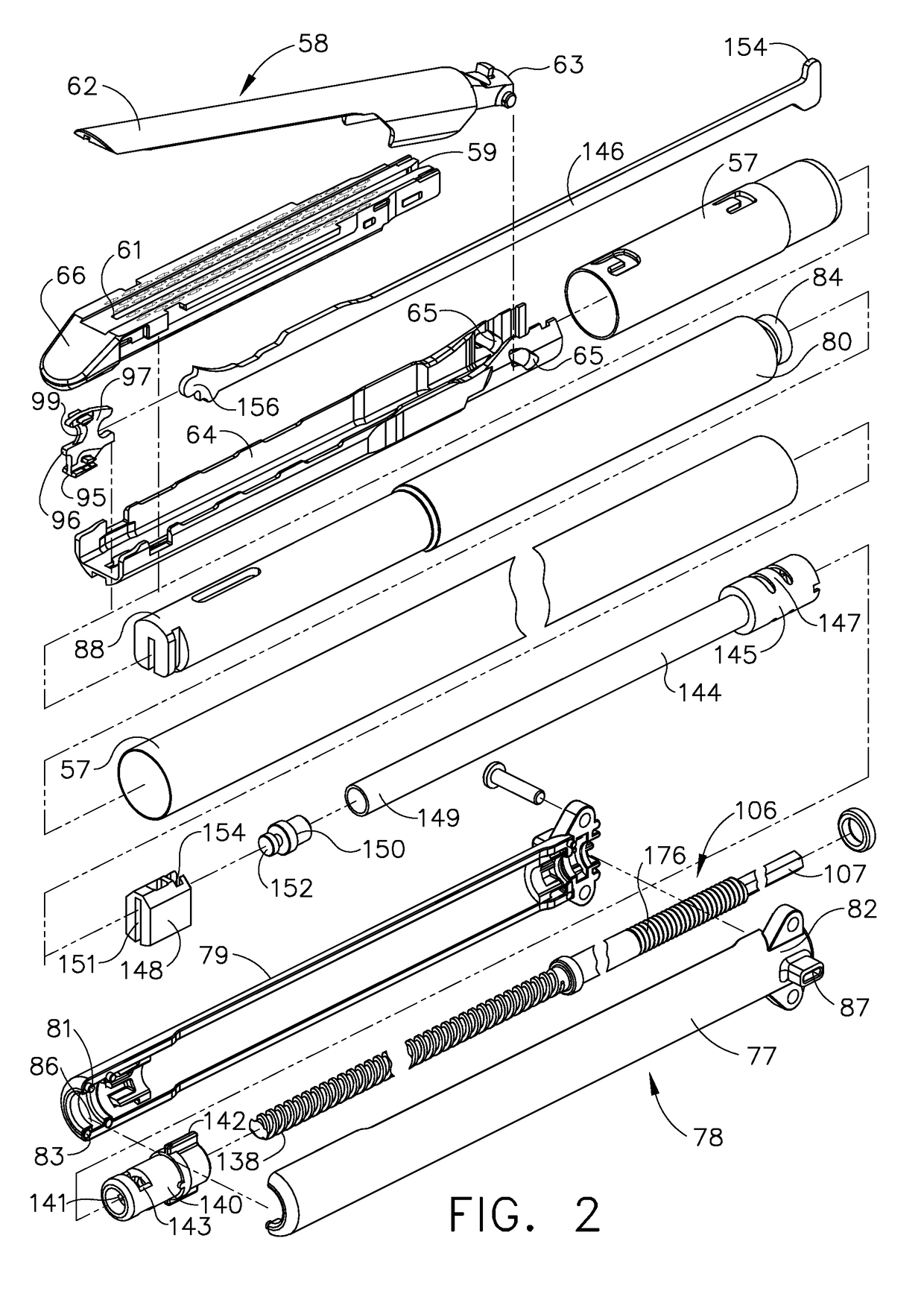
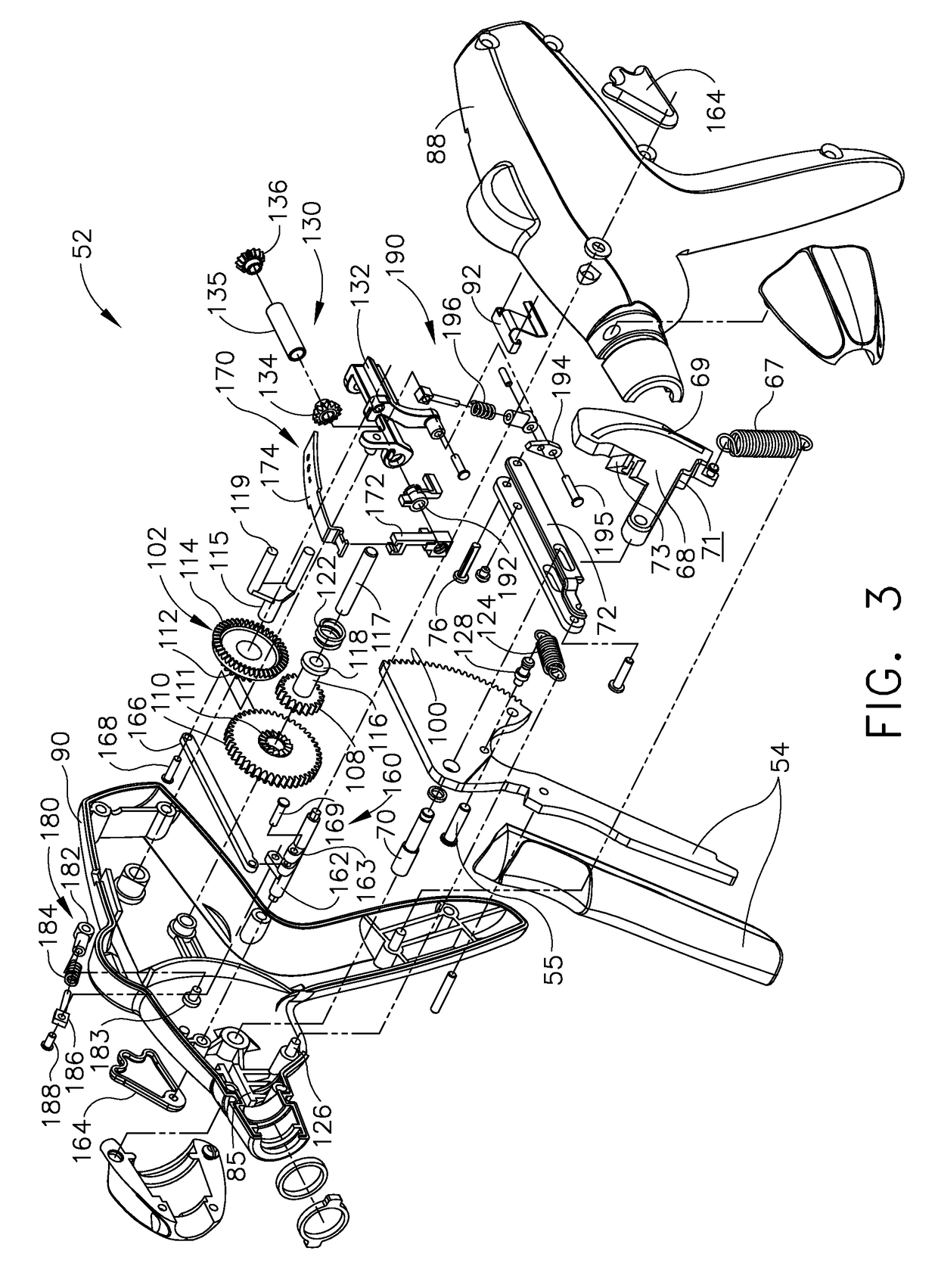
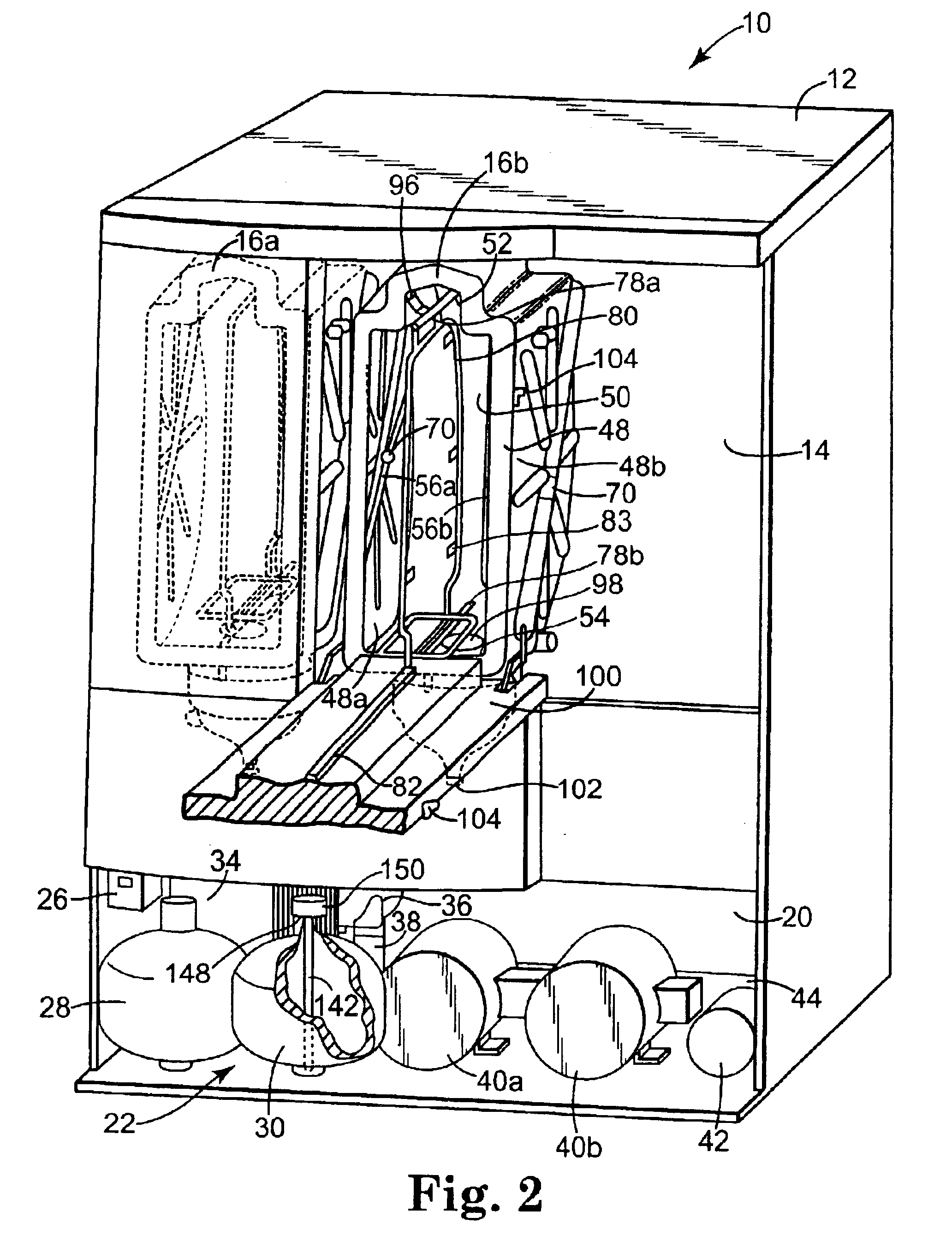
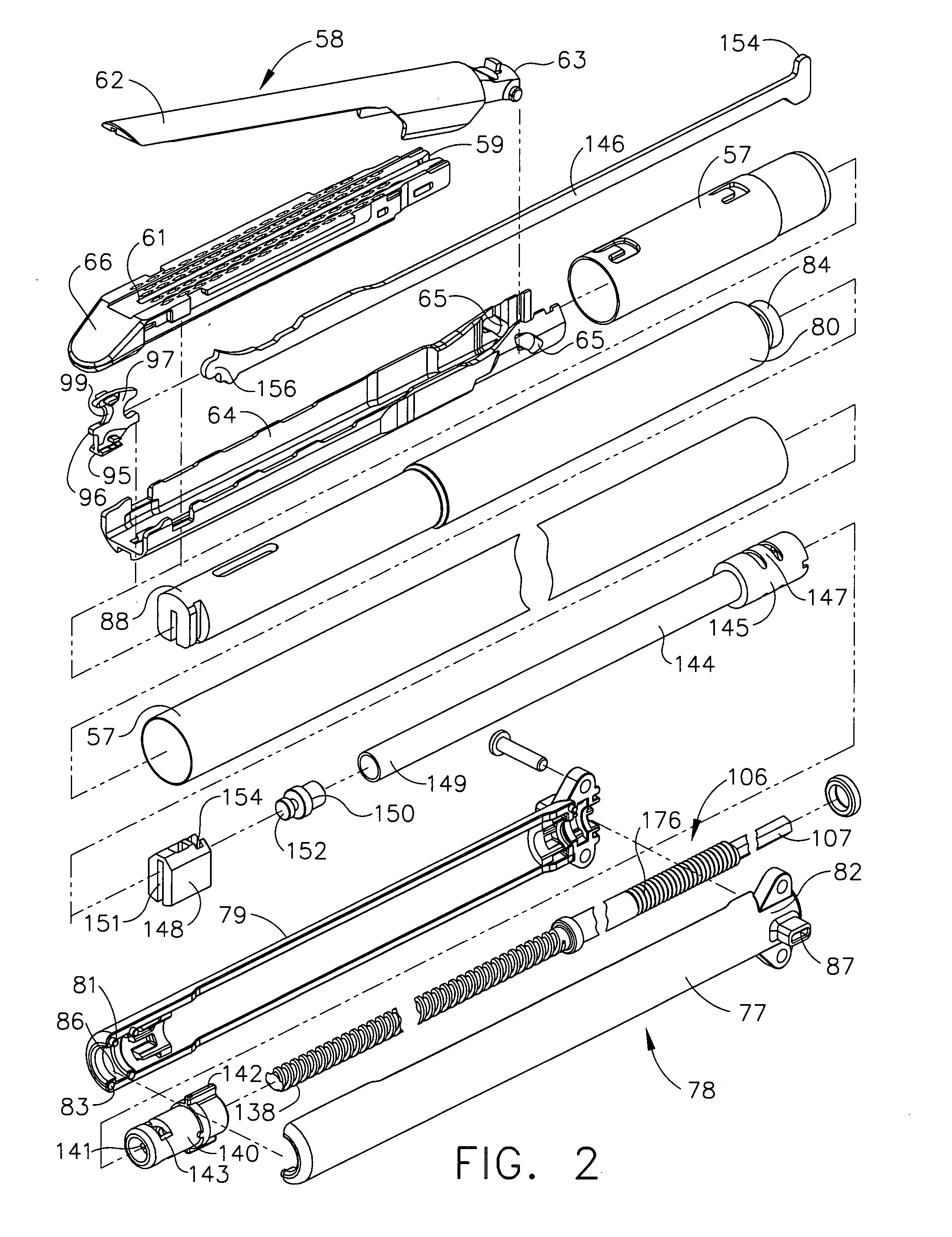
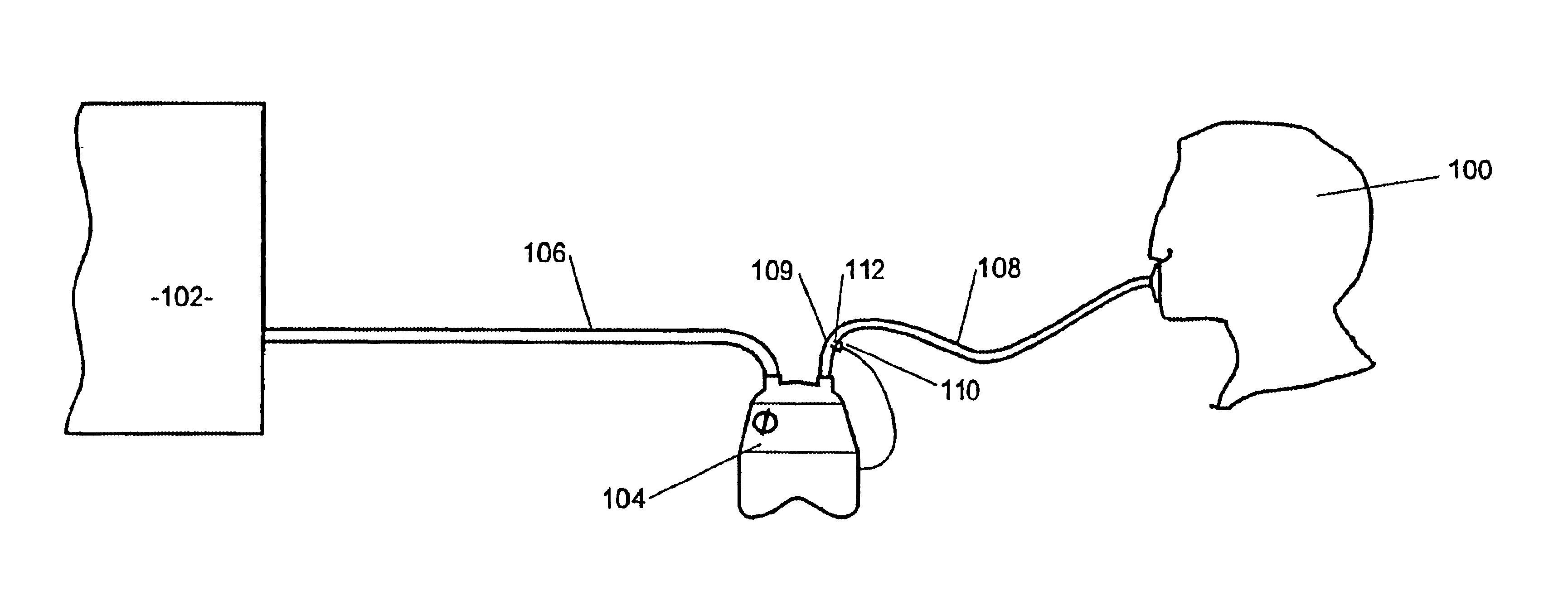
Surgical instrument having a multiple rate directional switching mechanism
ActiveUS7905380B2Quickly and conveniently selectSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringSTAPLE DRIVER
A surgical instrument including a drive mechanism configured to advance a staple driver and / or cutting member at a first rate and retract the staple driver and / or cutting member at a different rate. In at least one embodiment, the rate at which the driver and cutting member is advanced and / or retracted is the distance that the driver and / or cutting member is translated per actuation of a trigger, for example. In various embodiments, the cutting member can be retracted at a faster rate as compared to the rate in which it is advanced. In such embodiments, the surgical instrument can, owing to the slower advancing rate, provide a greater torque or advancing force to the cutting member while, owing to the faster retracting rate, reduce the time required for the surgeon to retract the cutting member.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
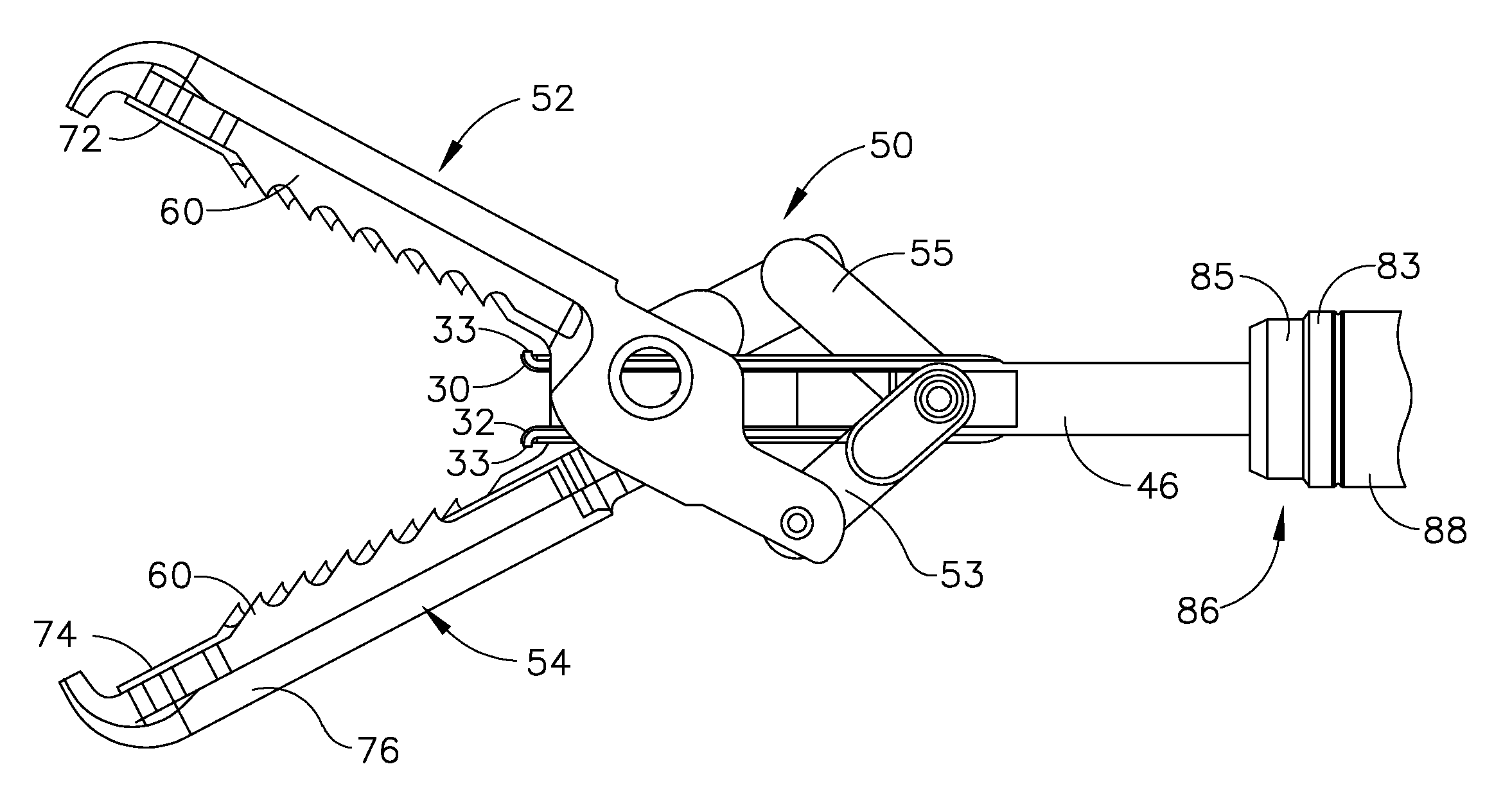
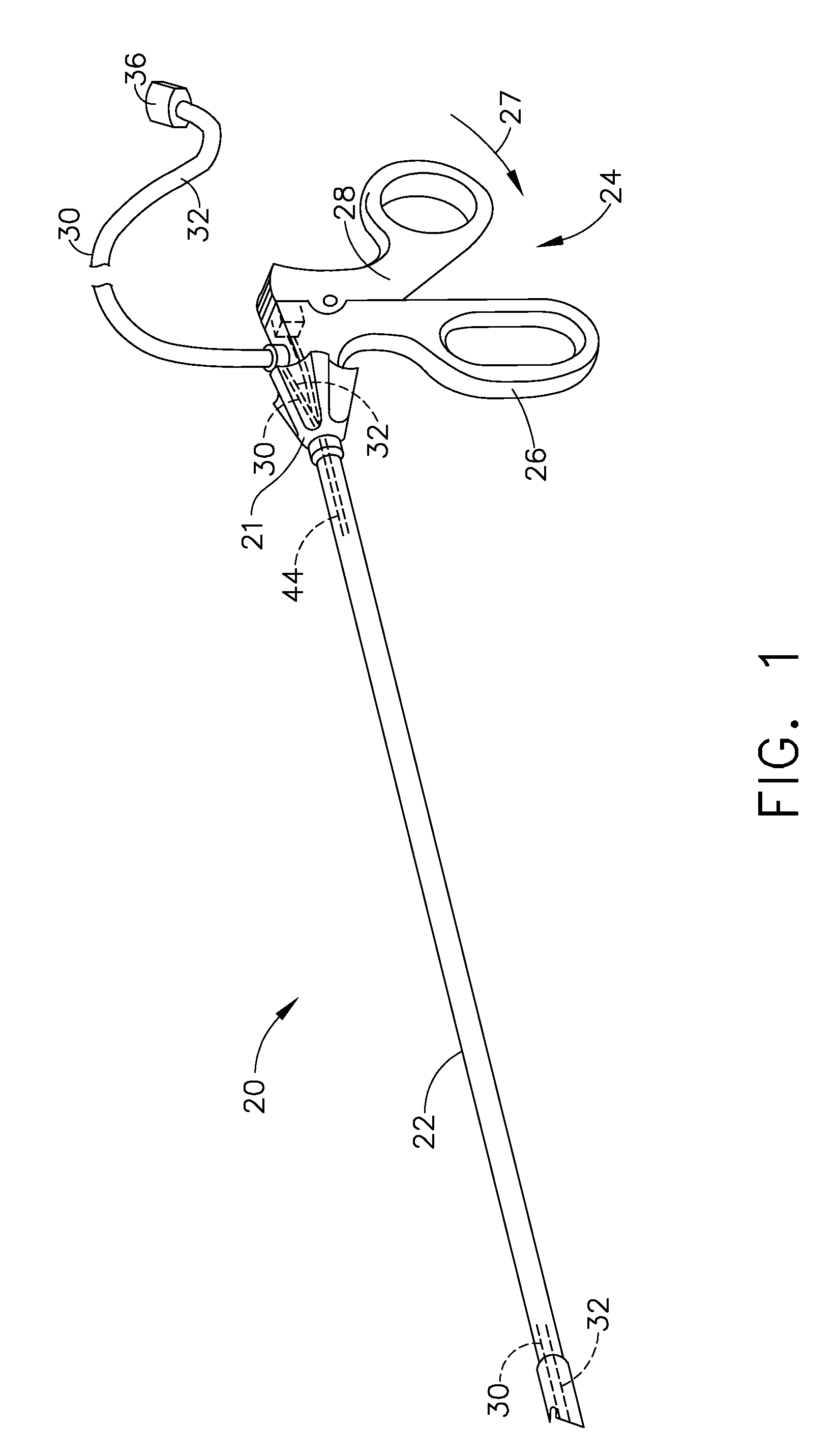
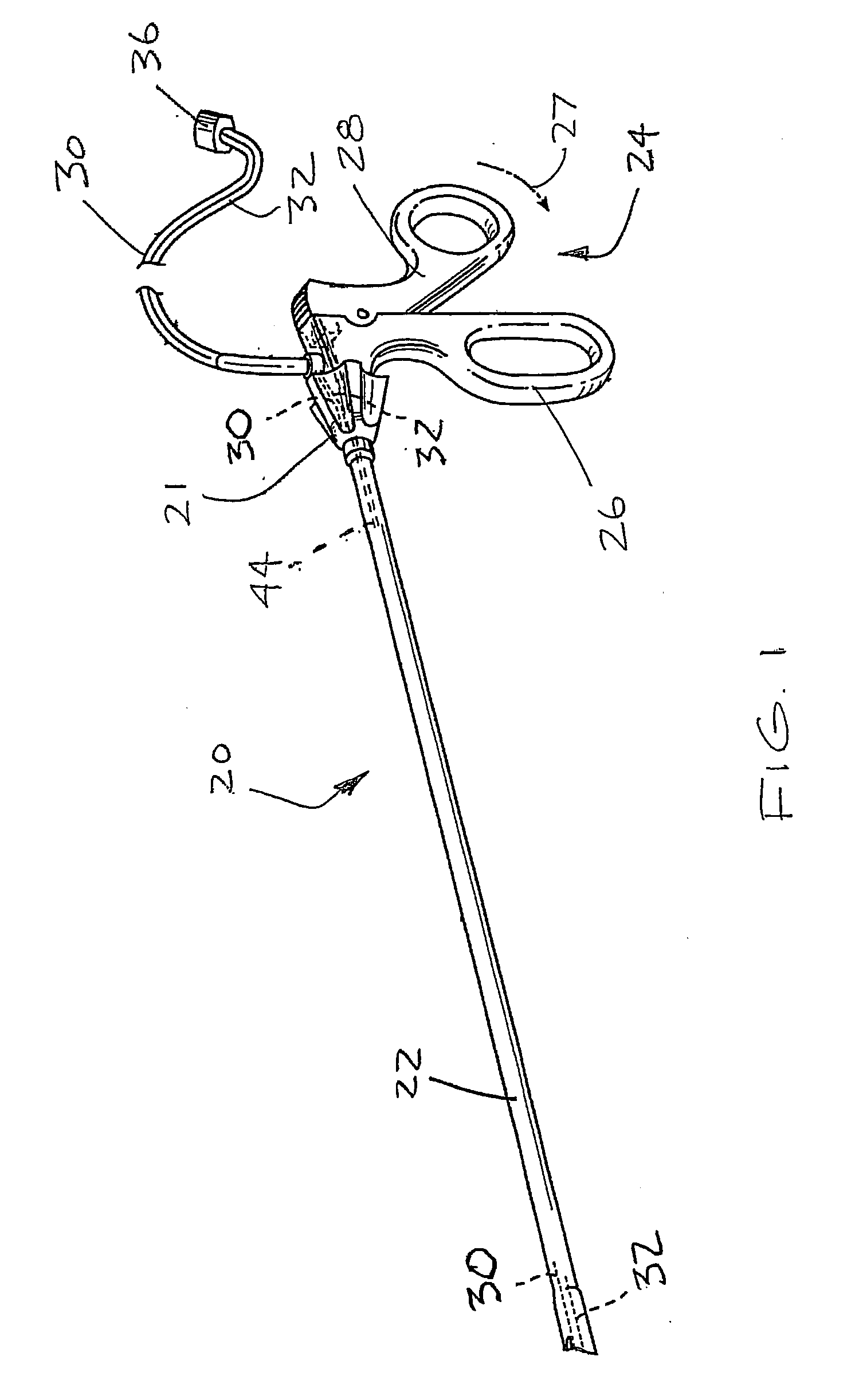
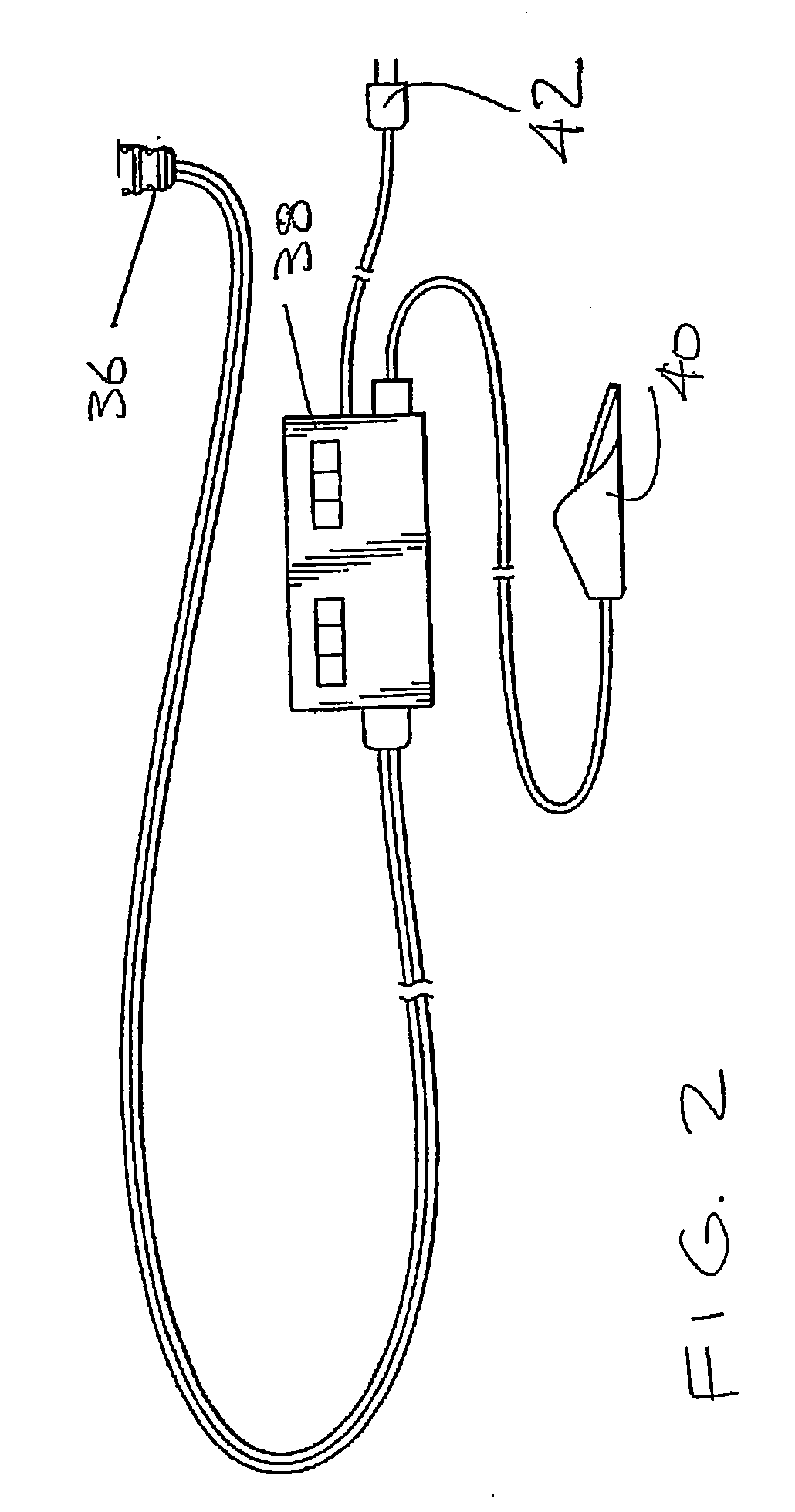
Bipolar forceps
ActiveUS8579897B2Likelihood that the wire may become damaged or broken can be reducedReduce the possibilityLavatory sanitorySurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringSurgical technical
In various surgical techniques, a bipolar forceps can be used to seal a vessel in two locations such that the vessel can be incised at a location positioned intermediate the two seal locations. The bipolar forceps can include a cutting element which can be configured to incise the vessel. In various embodiments, the cutting element can include a sharp edge which can be moved relative to the vessel. In at least one embodiment, the cutting element can be electrically connected to a source of energy. The bipolar forceps can include first and second electrodes positioned within first and second jaw members, respectively, wherein at least one of the jaw members can include a substantially tapered profile and can be configured to pull the vessel away from the surrounding soft tissue. Such jaw members can include ridges, teeth, and / or a textured outer surface configured to grip the soft tissue and / or vessel.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Apparatus and method for steam reprocessing flexible endoscopes
A system for reprocessing flexible endoscopes having lumen therein. The reprocessing system deploys steam to disinfect and / or sterilize the endoscopes, and designs, components, and methods for reducing or balancing the reprocessing cycle time and the effects of thermal expansion and contraction on the endoscopes.
Owner:MEDIVATORS INC
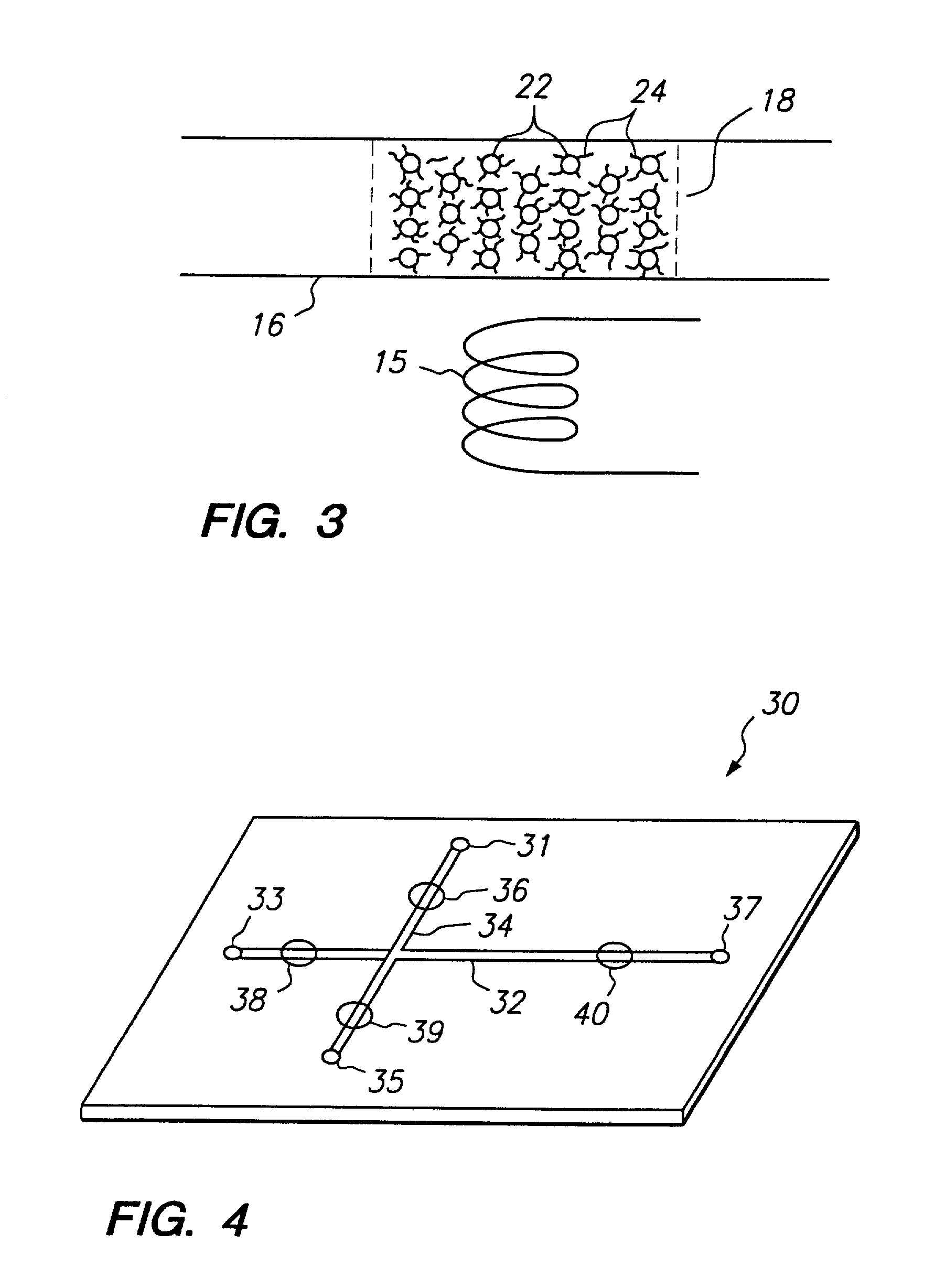
Microfluidic devices and methods of use
InactiveUS20020127736A1Lessening oscillation in velocityReduce oscillation amplitudeSludge treatmentFixed microstructural devicesElastomerThin membrane
A microfluidic device comprises pumps, valves, and fluid oscillation dampers. In a device employed for sorting, an entity is flowed by the pump along a flow channel through a detection region to a junction. Based upon an identity of the entity determined in the detection region, a waste or collection valve located on opposite branches of the flow channel at the junction are actuated, thereby routing the entity to either a waste pool or a collection pool. A damper structure may be located between the pump and the junction. The damper reduces the amplitude of oscillation pressure in the flow channel due to operation of the pump, thereby lessening oscillation in velocity of the entity during sorting process. The microfluidic device may be formed in a block of elastomer material, with thin membranes of the elastomer material deflectable into the flow channel to provide pump or valve functionality.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
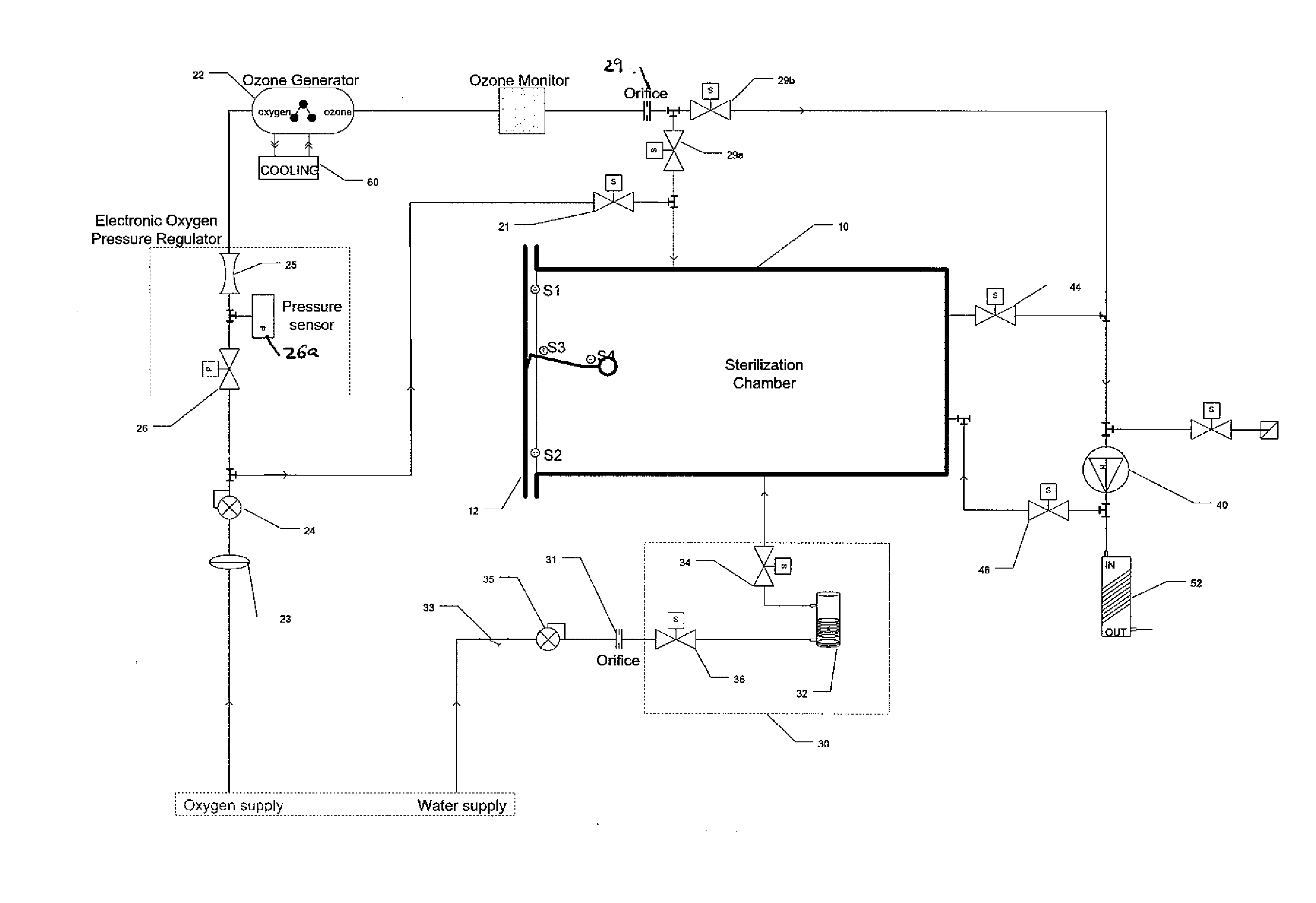
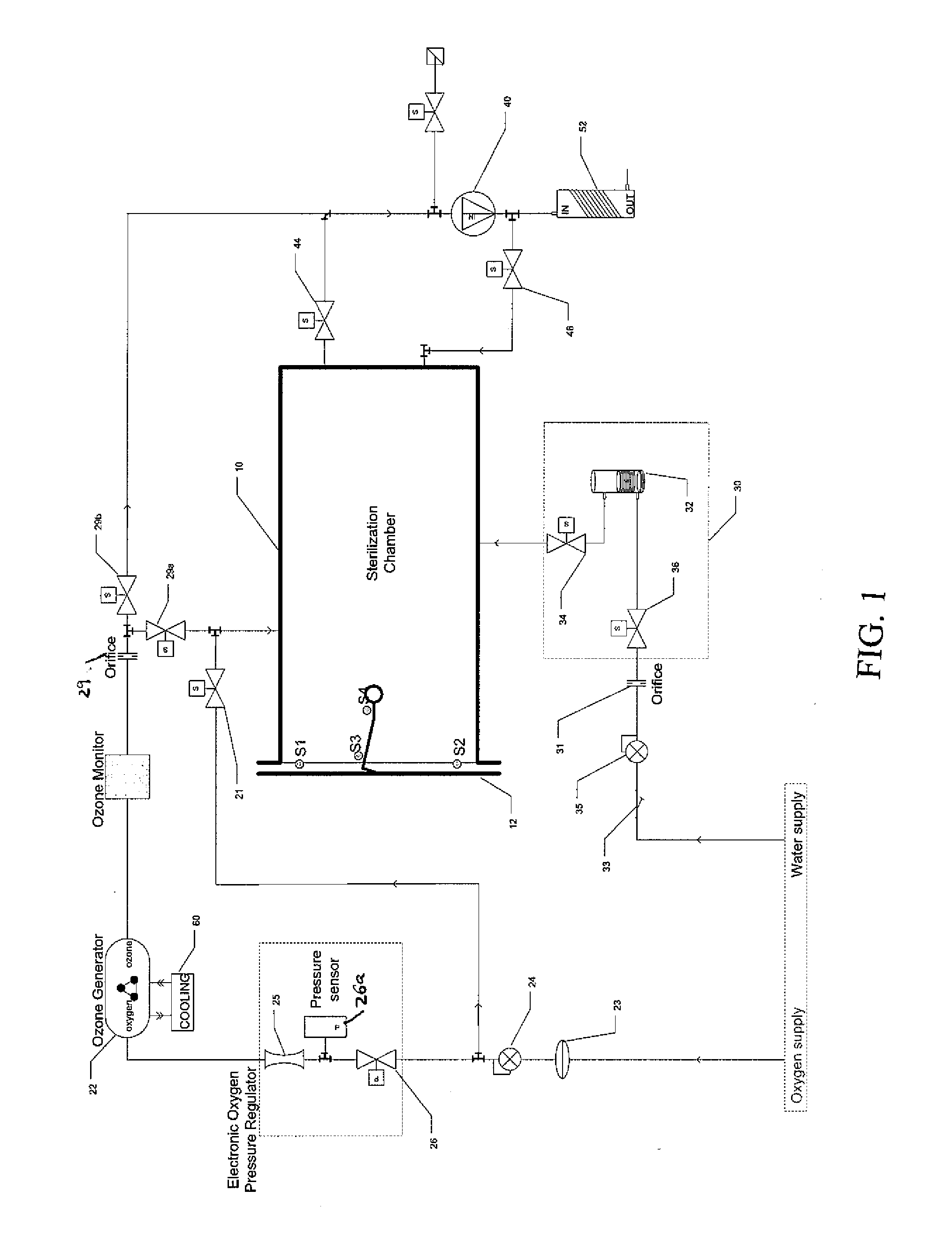
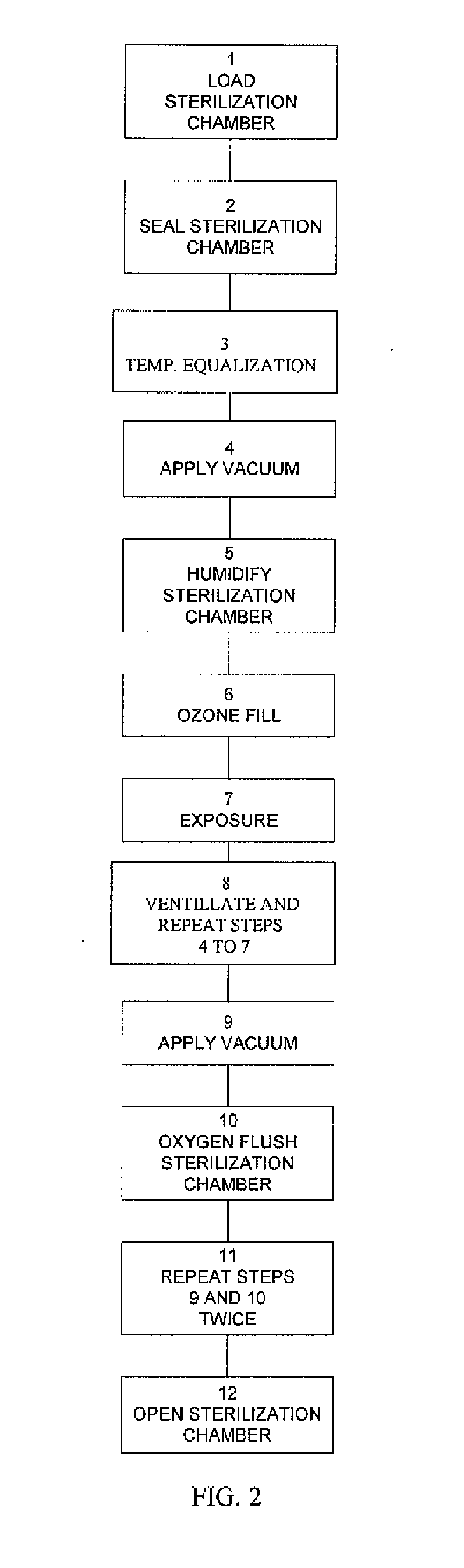
Method and apparatus for ozone sterilization
InactiveUS20070258855A1Avoid condensationPrevent water condensationElectrolysis componentsExhaust apparatusVacuum pressureWater vapor
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for sterilizing articles using an ozone-containing gas, where condensation of water from the sterilization atmosphere during the sterilization process is substantially prevented. The inventive sterilization method includes providing a sterilization chamber and placing an article into the sterilization chamber. The sterilization chamber is sealed prior to equalizing the temperature of the article and the atmosphere in the sterilization chamber. A vacuum is applied to achieve a preselected vacuum pressure in the sterilization chamber. Once the vacuum pressure is set, water vapour is supplied to the sterilization chamber. Ozone-containing gas is then supplied to the sterilization chamber and the sterilization chamber remains sealed for a preselected treatment period, where the sterilization chamber remains sealed throughout the whole process. Finally, vacuum in the sterilization chamber is released.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
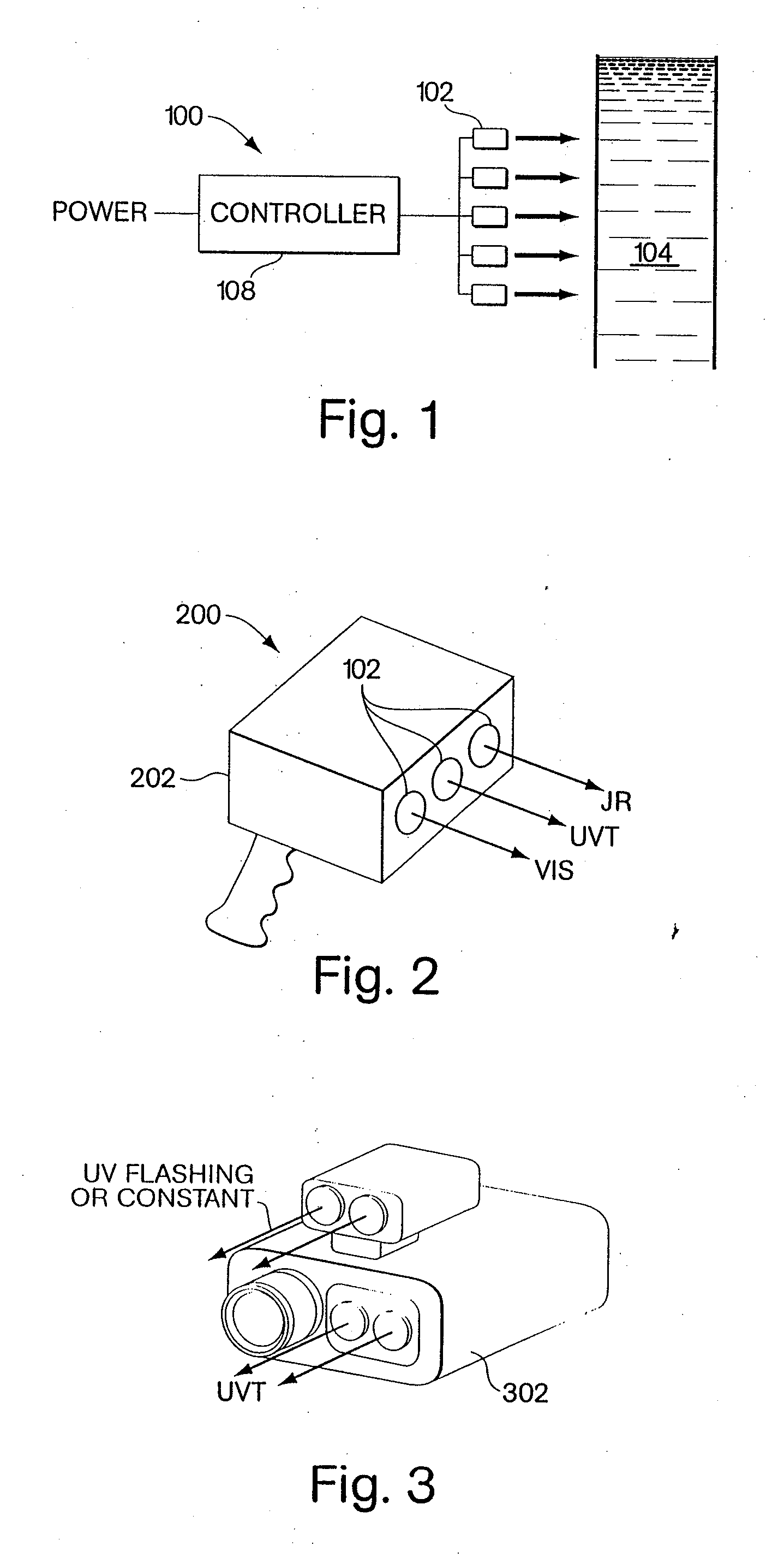
Ultraviolet light emitting diode systems and methods
InactiveUS20070086912A1Impact their growthLavatory sanitoryEnergy based wastewater treatmentUltraviolet lightsUltraviolet light emitting diodes
Methods and apparatus in which ultraviolet radiation is generated from at least one first LED, an object is irradiated with the ultraviolet radiation, and the ultraviolet radiation is controlled so as to generate at least one perceivable visual effect based on an interaction between the ultraviolet radiation and the object.
Owner:PHILIPS SOLID STATE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS
Chemico-mechanical microvalve and devices comprising the same
InactiveUS20020054835A1Valve arrangementsFixed microstructural devicesBiomedical engineeringMicro valve
Owner:ROBOTTI KARLA M +2
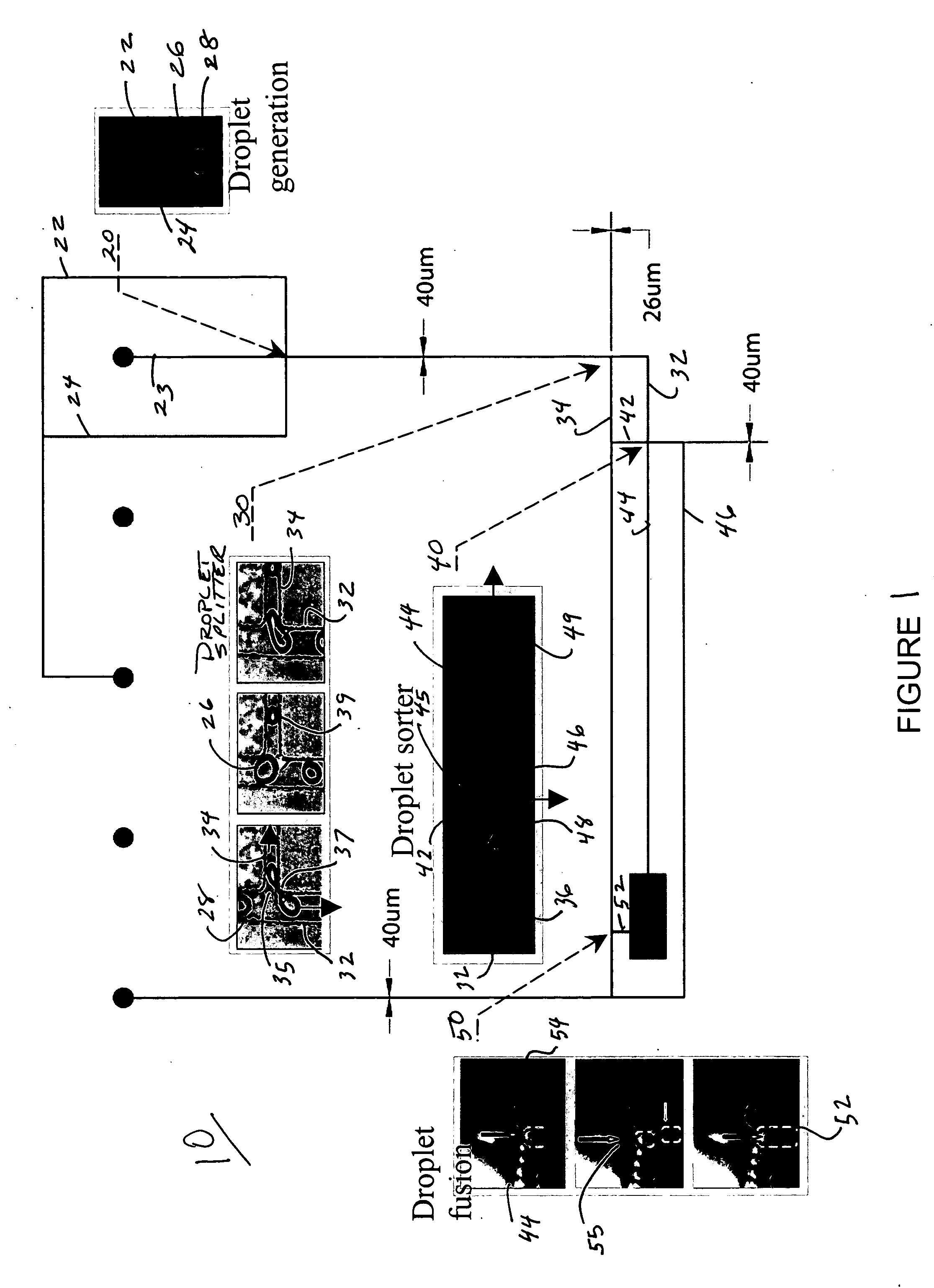
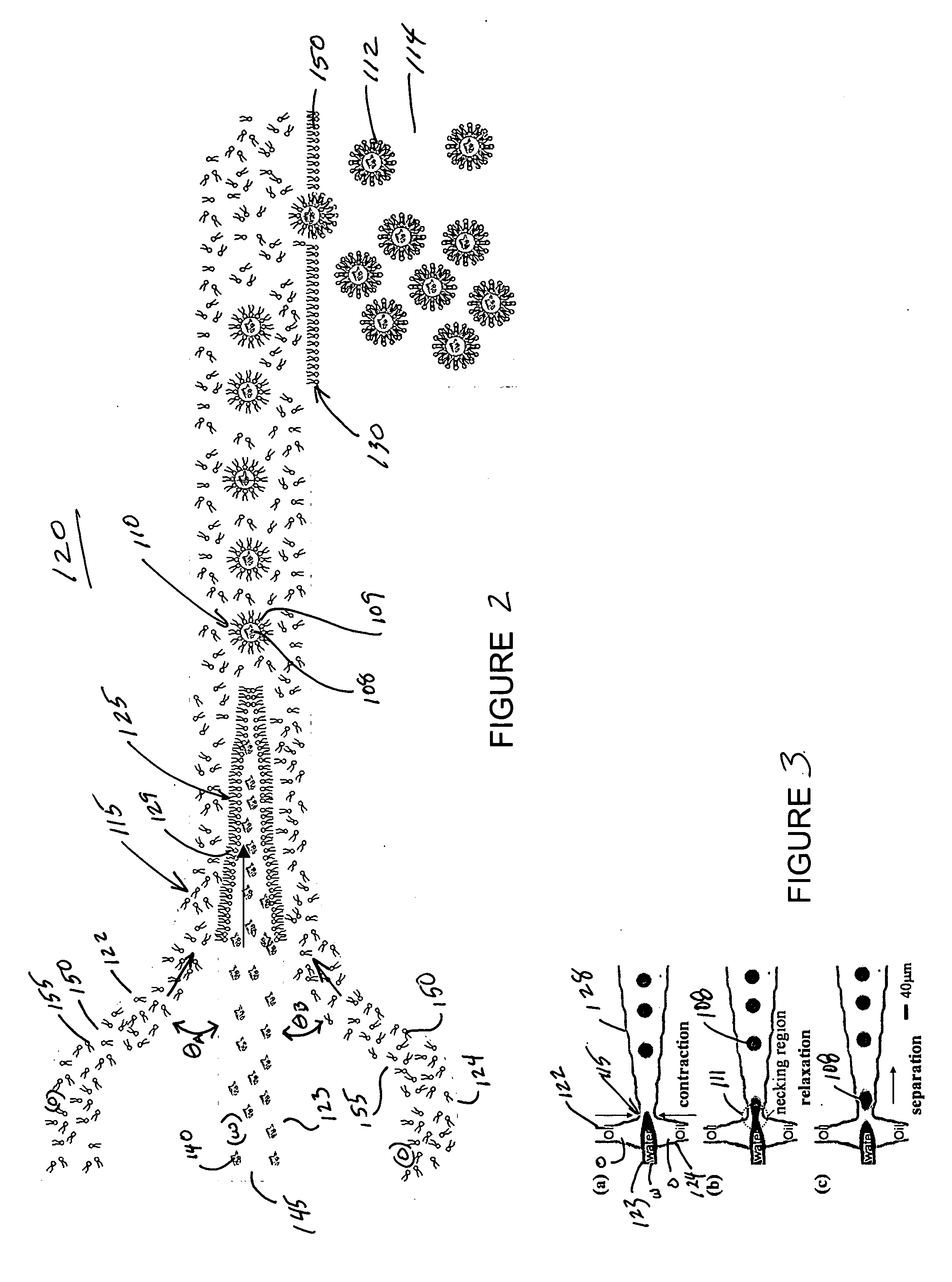
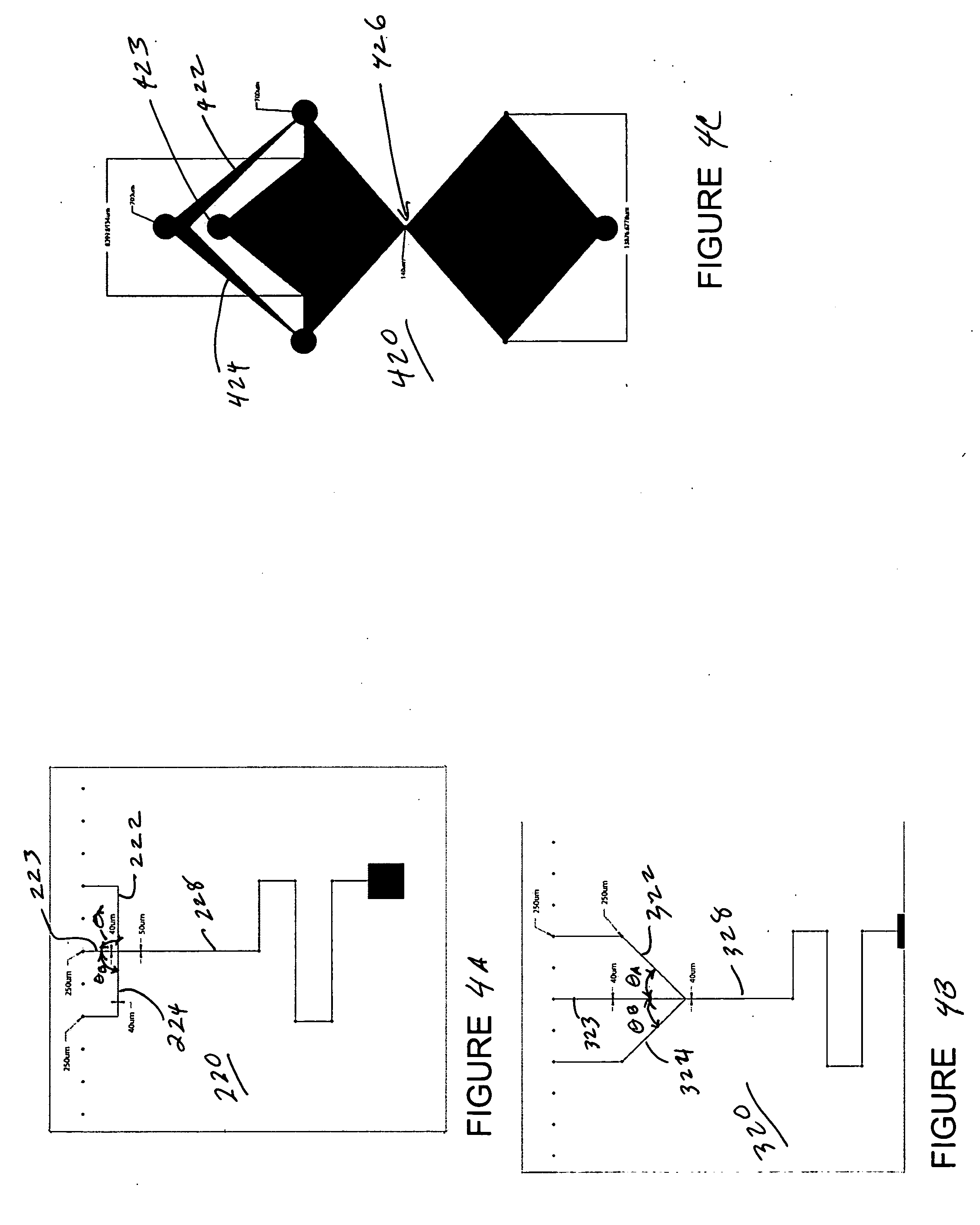
Microfluidic devices for controlled viscous shearing and formation of amphiphilic vesicles
ActiveUS20050032240A1Facilitates programmable control of sizeIncrease shear forceMixing methodsTransportation and packagingViscous shearEngineering
Systems and methods that control the size and composition of emulsified droplets, multi-lamellar and asymmetric vesicles, encapsulation of reagents, membrane proteins, and sorting of vesicles / droplets. More particularly, microfluidic devices for controlled viscous shearing of oil-water emulsions of micro- and nano-scale droplets, the subsequent formation of amphiphilic vesicles such as liposomes, polymer vesicles, micelles, and the like, the post-assembly and post-processing of the droplets including splitting, fusing, sorting and the like, polymer emulsions, and the integration of amphiphilic vesicle production-line on a single microfluidic chip. Preferably, the microfluidic device enables oil-water co-flows with tunable viscous shear forces higher than the immiscible interfacial tension forces that generate favorable conditions for droplet formation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for Anti-biofouling of a protected surface in liquid environments
ActiveUS20130048877A1Avoid biological contaminationReduce and eliminate needWater/sewage treatment by substance additionDeodrantsBiofoulingOptoelectronics
A system includes a UV light source and an optical medium coupled to receive UV light from the UV light source. The optical medium is configured to emit UV light proximate to a surface to be protected from biofouling. A method corresponds to the system.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Color changing steam sterilization indicator
InactiveUS20030211618A1Lavatory sanitoryAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionEngineeringColor changes
Owner:JP LAB INC
Surgical instrument having a multiple rate directional switching mechanism
ActiveUS20080300613A1Quickly and conveniently selectSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringSTAPLE DRIVER
A surgical instrument including a drive mechanism configured to advance a staple driver and / or cutting member at a first rate and retract the staple driver and / or cutting member at a different rate. In at least one embodiment, the rate at which the driver and cutting member is advanced and / or retracted is the distance that the driver and / or cutting member is translated per actuation of a trigger, for example. In various embodiments, the cutting member can be retracted at a faster rate as compared to the rate in which it is advanced. In such embodiments, the surgical instrument can, owing to the slower advancing rate, provide a greater torque or advancing force to the cutting member while, owing to the faster retracting rate, reduce the time required for the surgeon to retract the cutting member.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Parallel flow reactor having variable composition
InactiveUS20020045265A1Extreme flexibilityAdvantageously and flexibly employedProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsDistribution systemEngineering
Owner:FREESLATE
Methods for sterilizing biological materials
InactiveUS6946098B2Lowered residual solventReduce the temperatureOther blood circulation devicesFood preservationBiochemistryBiological materials
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing biological materials to reduce the level therein of one or more biological contaminants or pathogens, such as prions, responsible for the disease states known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) in mammals. These methods involve sterilizing biological materials with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
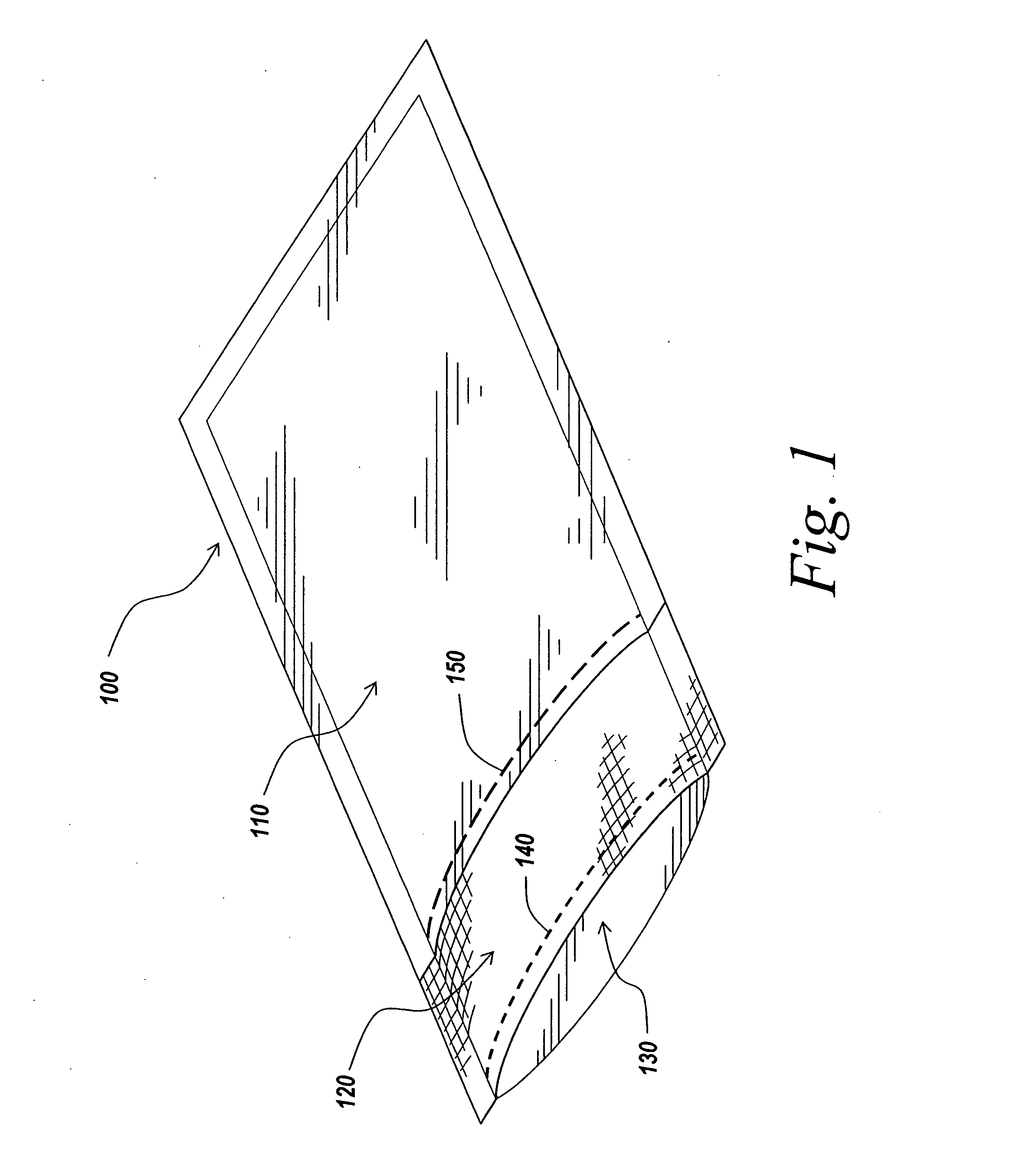
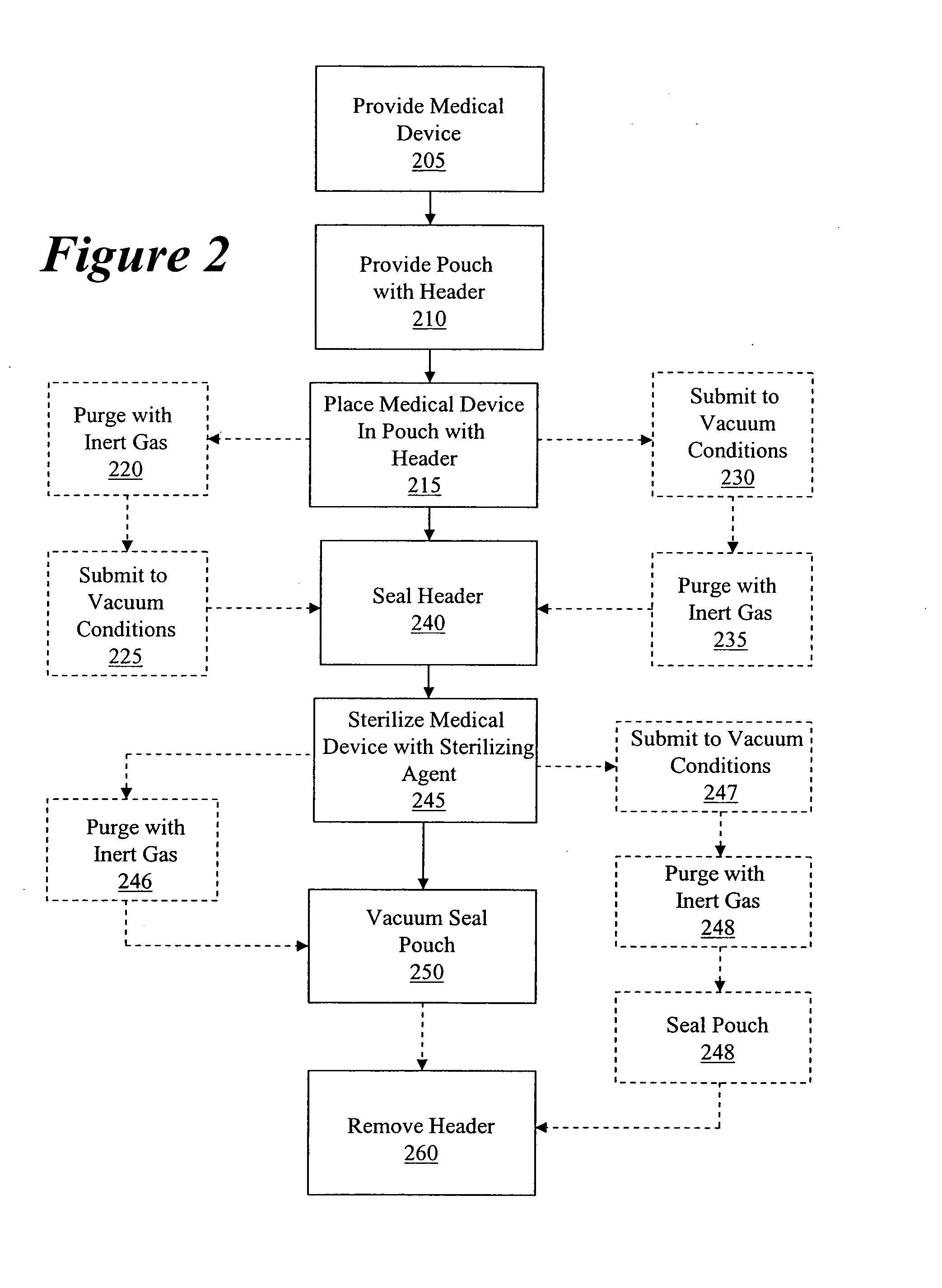
Packaging and sterilization of medical devices
InactiveUS20070084144A1Minimize timeExtended shelf lifeStentsSurgical furnitureCompound (substance)Fish oil
A method for the sterilization and packaging of a chemically sensitive medical device is provided. The chemically sensitive medical device has a coating derived from fish oil, a vitamin E compound or a combination thereof. The packaging pouch for the chemically sensitive medical device comprises a non-permeable chamber and a gas-permeable header. The sterilizing agent is administered to the packaged chemically sensitive medical device at a temperature of between about 20° C. and 40° C.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
Combination of antimicrobial agents and bacterial interference to coat medical devices
This invention relates to a method for coating a medical device comprising the steps of applying to at least a portion of the surface of said medical device, an antimicrobial coating layer and a non-pathogenic bacterial coating layer, wherein the antimicrobial and non-pathogenic bacterial coating layers inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacterial and fungal organisms. The non-pathogenic bacterium used in the bacterial coating layer is resistant to the antimicrobial agent. Furthermore, the non-pathogenic bacterium layer includes at least one of the following: viable whole cells, non-viable whole cells, or cellular structures or extracts. The antimicrobial agent and non-pathogenic bacterium are used to develop a kit comprising these compositions in one container or in separate containers. The kit is used to coat a catheter prior to implantation in a mammal.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Ultraviolet area sterilizer and method of area sterilization using ultraviolet radiation
An ultraviolet area sterilizer (UVAS) is mobile or stationary. The UVAS is positioned in a room, such an operating room or intensive care unit. Motion detectors sense movement, to assure that personnel have evacuated the space to be sterilized. Subsequently, UV-C generators, such mercury bulbs, generate UV-C from multiple locations within the room or other enclosed space. Multiple UV-C sensors scan the room, and determine the area reflecting the lowest level of UV-C back to the sensors. The device calculates the time required to obtain a bactericidal dose of UV-C reflected back to the sensors. Once an effective bactericidal dose has been reflected to all the sensors, the unit notifies the operator and shuts down.
Owner:UVAS
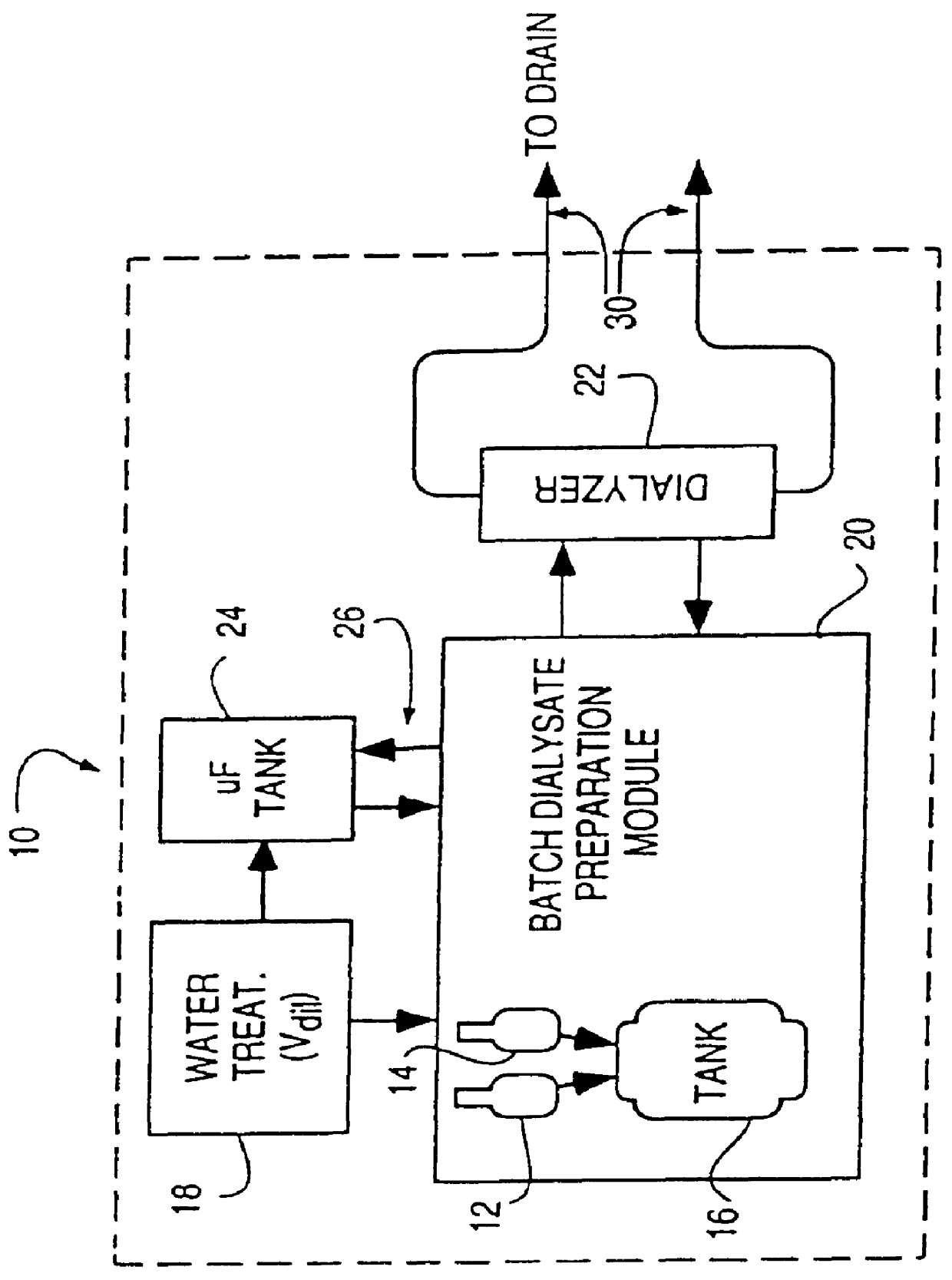
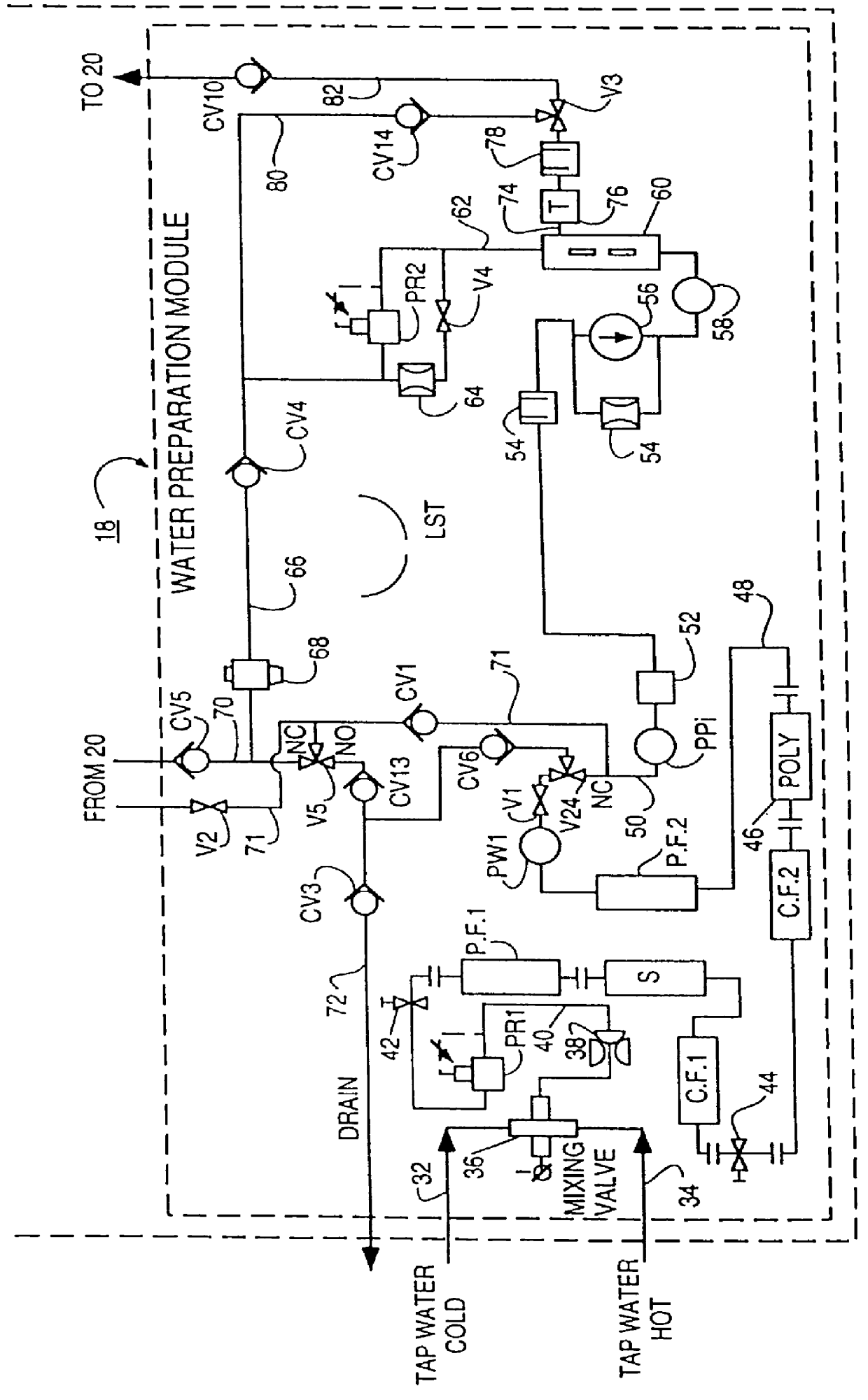
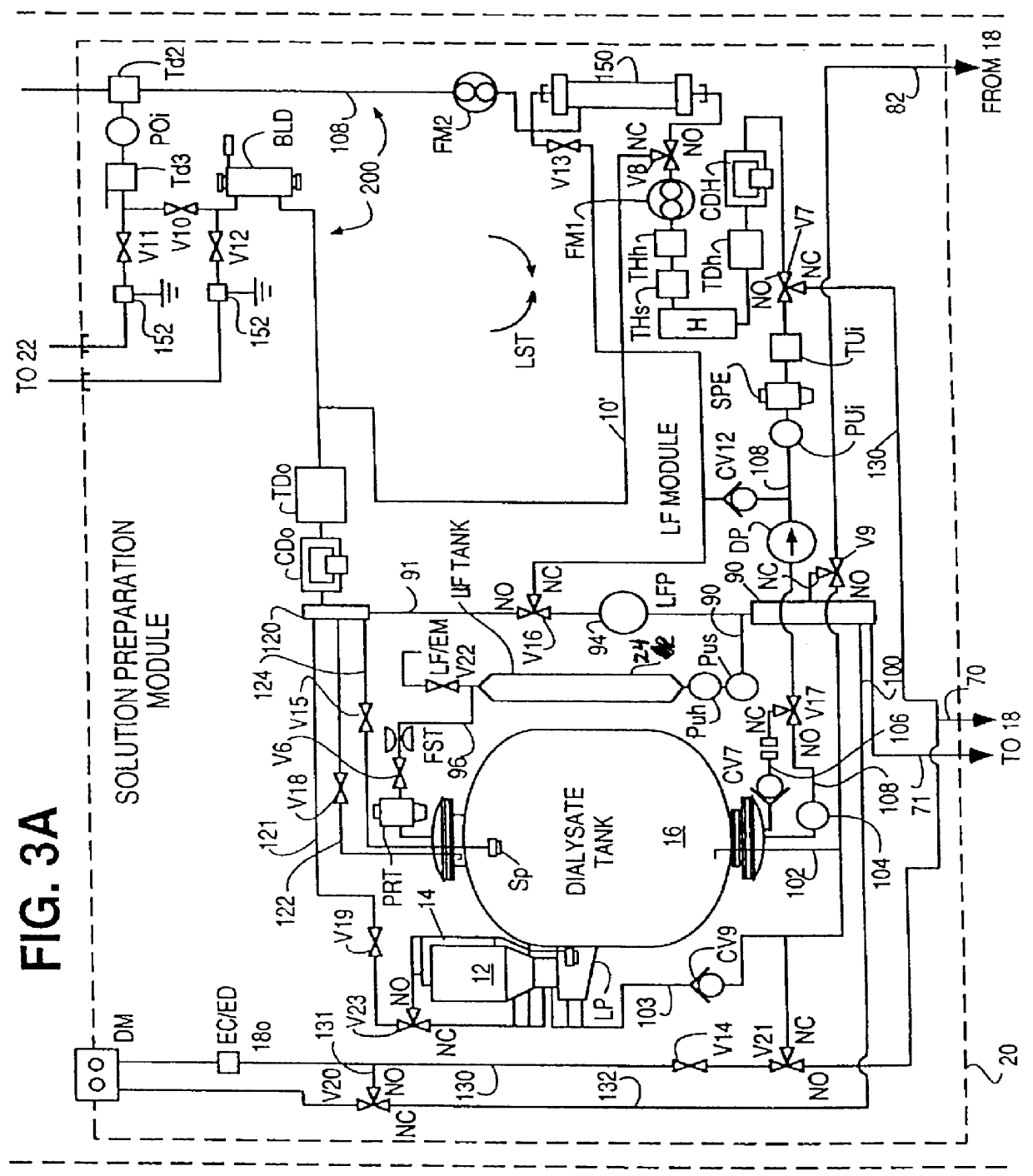
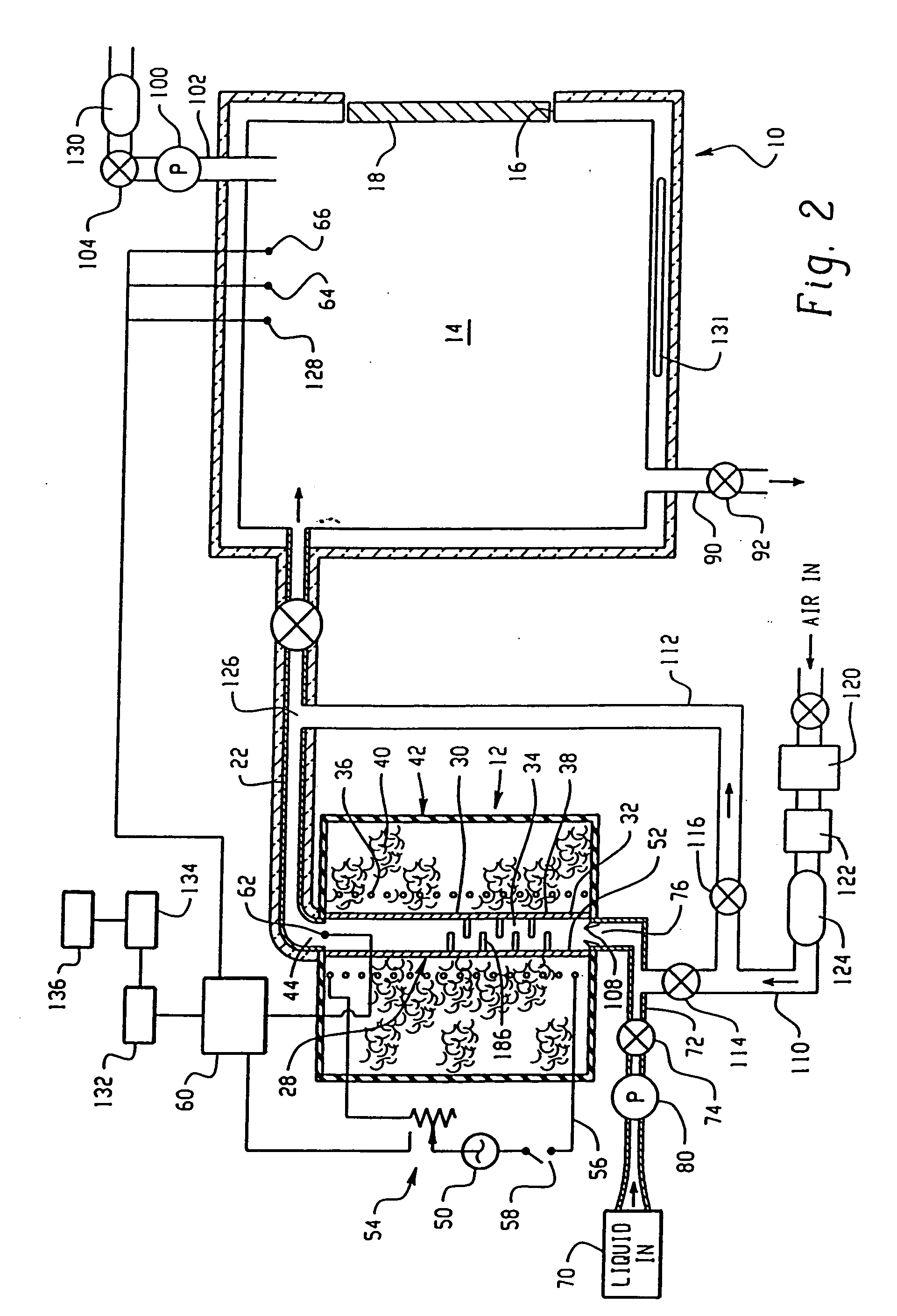
Method of preparation of batch of physiologic solution
A batch of dialysate solution is made from a mixture of bicarbonate formulation and a liquid acid formulation. The liquid acid formulation is introduced into a dialysate tank and then removed from the tank and stored elsewhere, such as in an ultrafiltration tank, where it is diluted with a few litres of water. The dialysate tank is then filled with water and the bicarbonate formulation is added to the dialysate tank. The bicarbonate formulation is mixed and dissolved by circulation in a closed loop, with the liquid acid formulation kept separate. When the bicarbonate solution has been prepared, the liquid acid solution and the bicarbonate solution are mixed together and stored in the dialysate preparation tank. An additional quantity of dilution water is introduced into the dialysate system to bring the final conductivity down to the desired range. The excess dialysate solution can be used for several purposes, such as an endotoxin flush of the blood tubing set or a dialyzer clearance test.
Owner:HHD LLC A DELAWARE LLC +2
Apparatus for purifying nucleic acids and proteins
InactiveUS20030006193A1Facilitating resuspensionReduce the precipitation rateAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionWater/sewage treatment by substance additionHigh rateBiology
The present invention provides an apparatus for purifying nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA or proteins such as enzymes and antibodies from microorganisms such as viruses and bacteria or animal and plant tissues, the apparatus being capable of fast processing of a plurality of samples. More specifically, the present invention provides an apparatus for purifying nucleic acids or proteins using magnetically attractable particles, the apparatus comprising a plurality of piston pumps; a plurality of nozzles capable of having a plurality of disposable tips which are automatically attachable / detachable; and a mechanism which is capable of dispensing a desired amount of a reagent to be used subsequently in the next step into the same number of sections as that of the samples with high accuracy and at a high rate, while a mixture of a sample and a reagent are being mixed (stirred) by the pumps and nozzles, the apparatus being capable of rapidly processing a plurality of samples, wherein a series of steps from mixing (stirring) of the magnetically attractable particles and concentration of the sample to purification is automated with reduced wastes.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Low extractable, thermoplastic syringe and tip cap
InactiveUS20050075611A1Low extractable levelWithout loss of flexible and resilient propertyAmpoule syringesLavatory sanitoryThermoplastic elastomerPrefilled Syringe
A prefilled syringe and syringe assembly having a syringe and a tip cap are produced from materials that do not interfere with the substance contained in the syringe and enable long term storage. The tip cap is made from a blend of a cyclic olefin polymer or copolymer and a thermoplastic elastomer. The thermoplastic elastomer is blended with the cyclic olefin copolymer in an amount so that the normally stiff and hard cyclic olefin copolymer is flexible and resilient to effectively seal and couple to the tip of a prefilled syringe.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
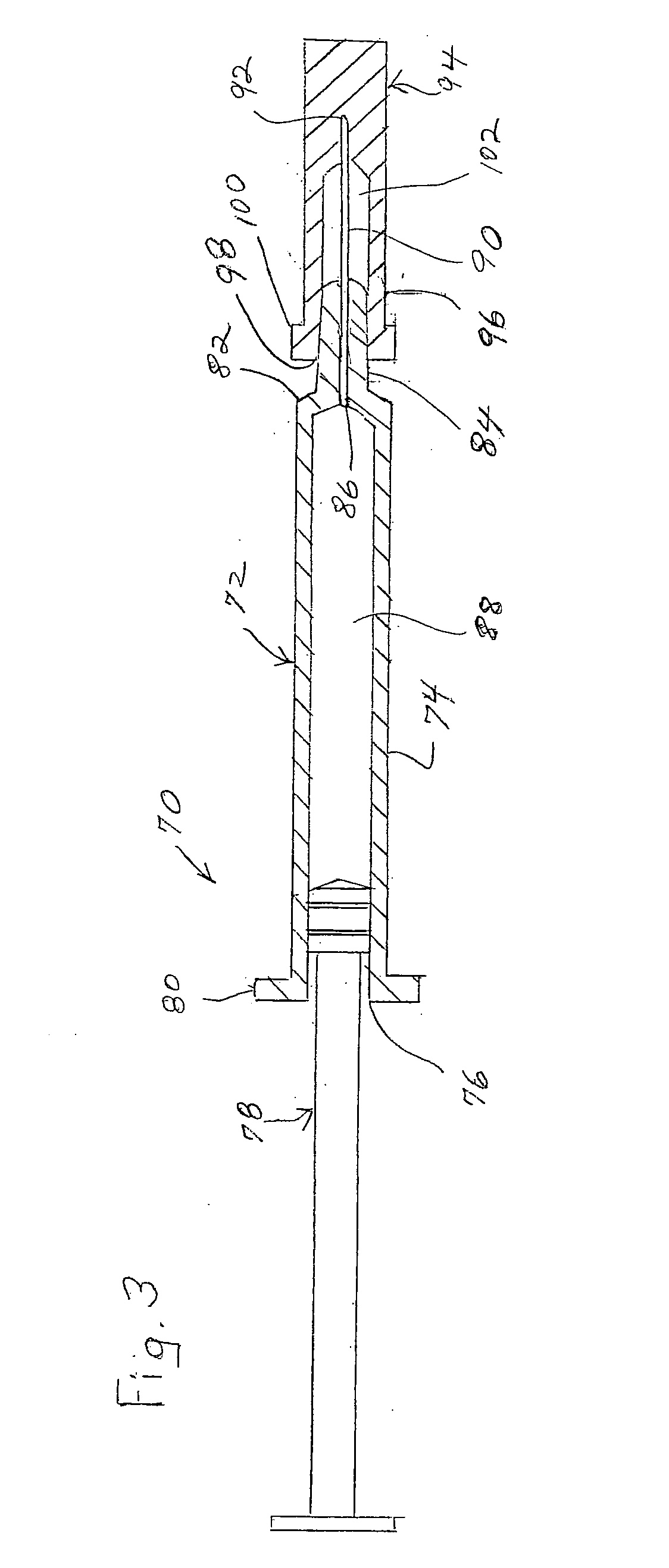
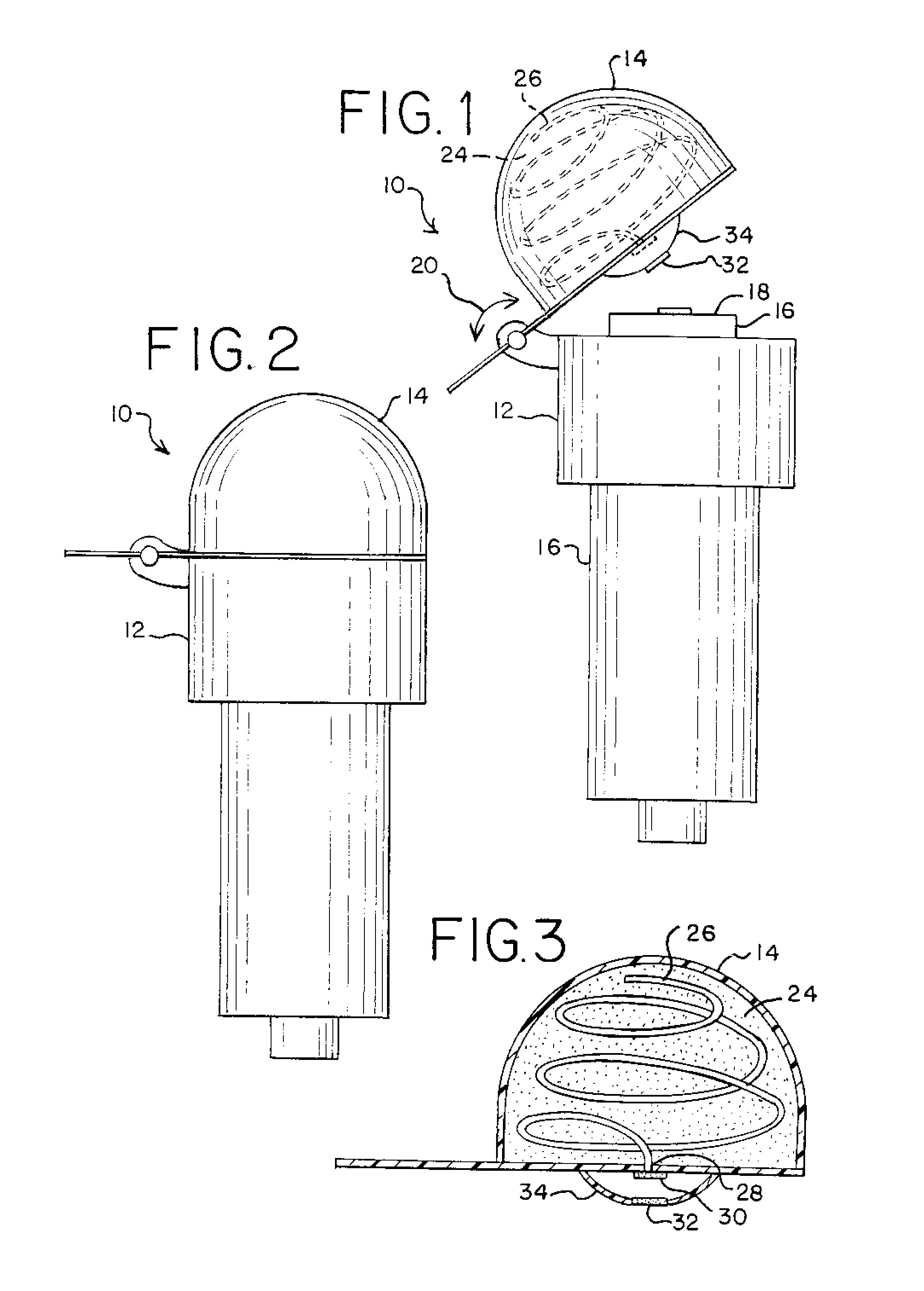
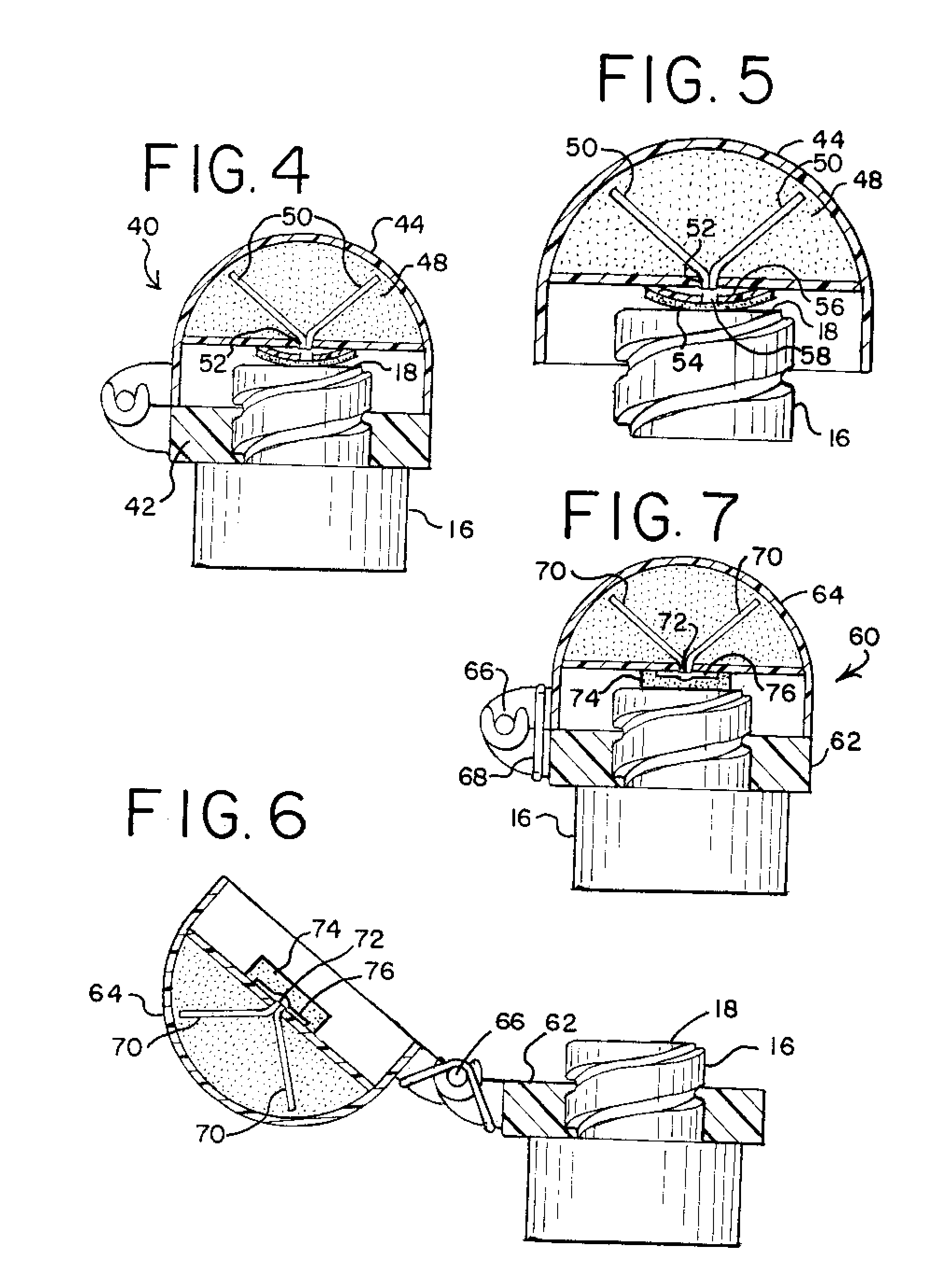
Needleless Hub Disinfection Device
A device for disinfecting a portion of an implement such as a needleless hub or injection port. The device includes a body shaped to engage the implement with the portion to be disinfected exposed. A disinfectant area is located on the body so as to permit pivotal displacement of the area relative to the body such that in a first orientation the portion to be disinfected is exposed and in a second orientation the portion to be disinfected is covered and the disinfectant area engages the portion to be disinfected.
Owner:SAGE PRODS
Area sterilizer and method of disinfection
An ultraviolet area sterilizer or disinfector is incorporated into a building structure where concern exists regarding the presence of pathogenic bacteria on environmental surfaces. Ultraviolet C (UV-C) generators generate UV-C that is directed to architectural partitions of an enclosed area. The architectural partitions reflect UV-C to kill pathogens in the enclosed area. The device transmits a calculated dose of UV-C from a fixture mounted to an architectural partition in the enclosed area. Once an effective cumulative dose of UV-C has been reflected to radiation sensors, as measured by the sensors, the device shuts down.
Owner:UVAS
Bipolar forceps having a cutting element
ActiveUS20090131932A1Reduce the possibilityLikelihood that the wire may become damaged or broken can be reducedLavatory sanitorySurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringSurgical department
In various surgical techniques, a bipolar forceps can be used to seal a vessel in two locations such that the vessel can be incised at a location positioned intermediate the two seal locations. The bipolar forceps can include a cutting element which can be configured to incise the vessel. In various embodiments, the cutting element can include a sharp edge which can be moved relative to the vessel. In at least one embodiment, the cutting element can be electrically connected to a source of energy. The bipolar forceps can include first and second electrodes positioned within first and second jaw members, respectively, wherein at least one of the jaw members can include a substantially tapered profile and can be configured to pull the vessel away from the surrounding soft tissue. Such jaw members can include ridges, teeth, and / or a textured outer surface configured to grip the soft tissue and / or vessel.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
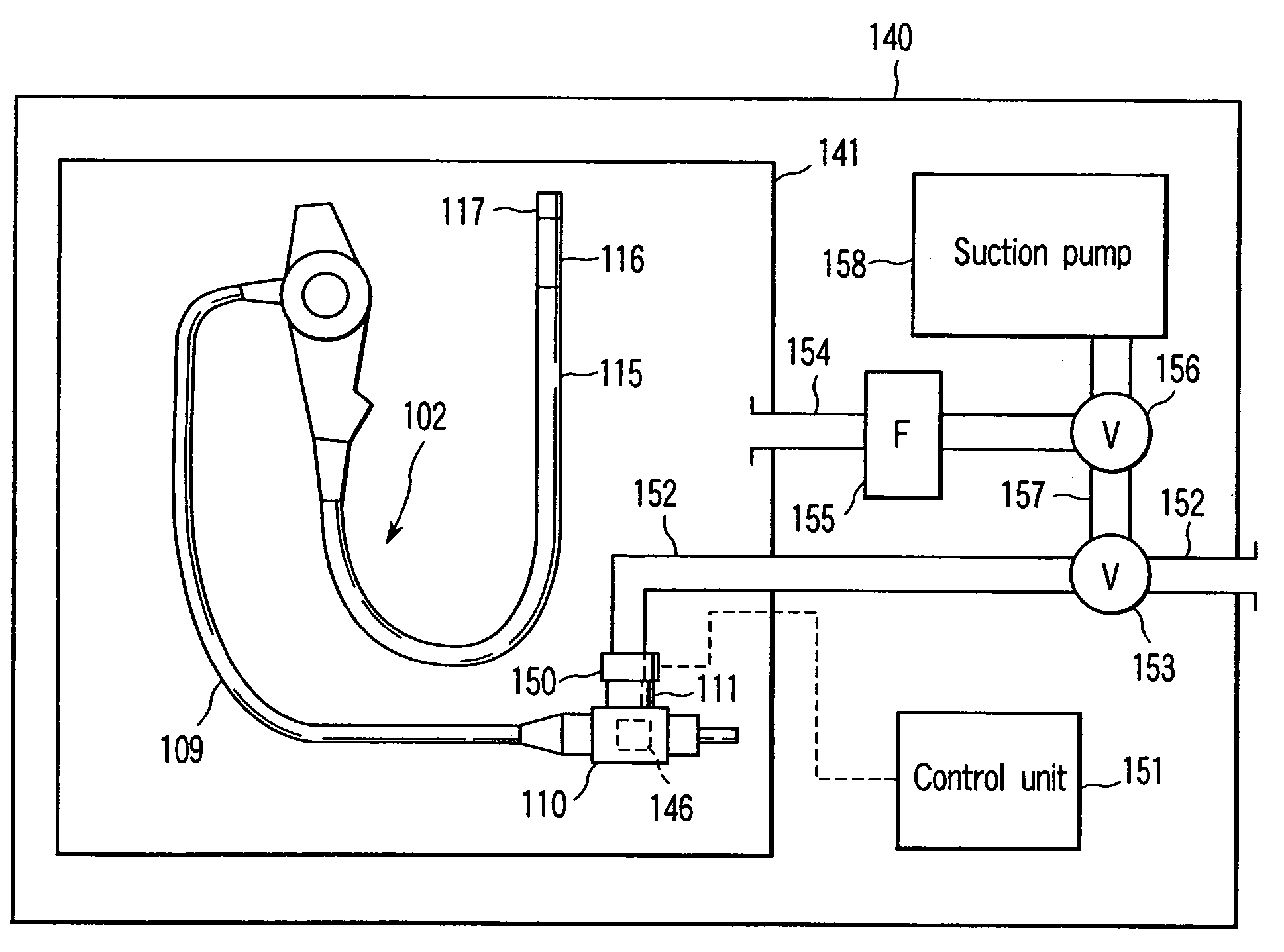
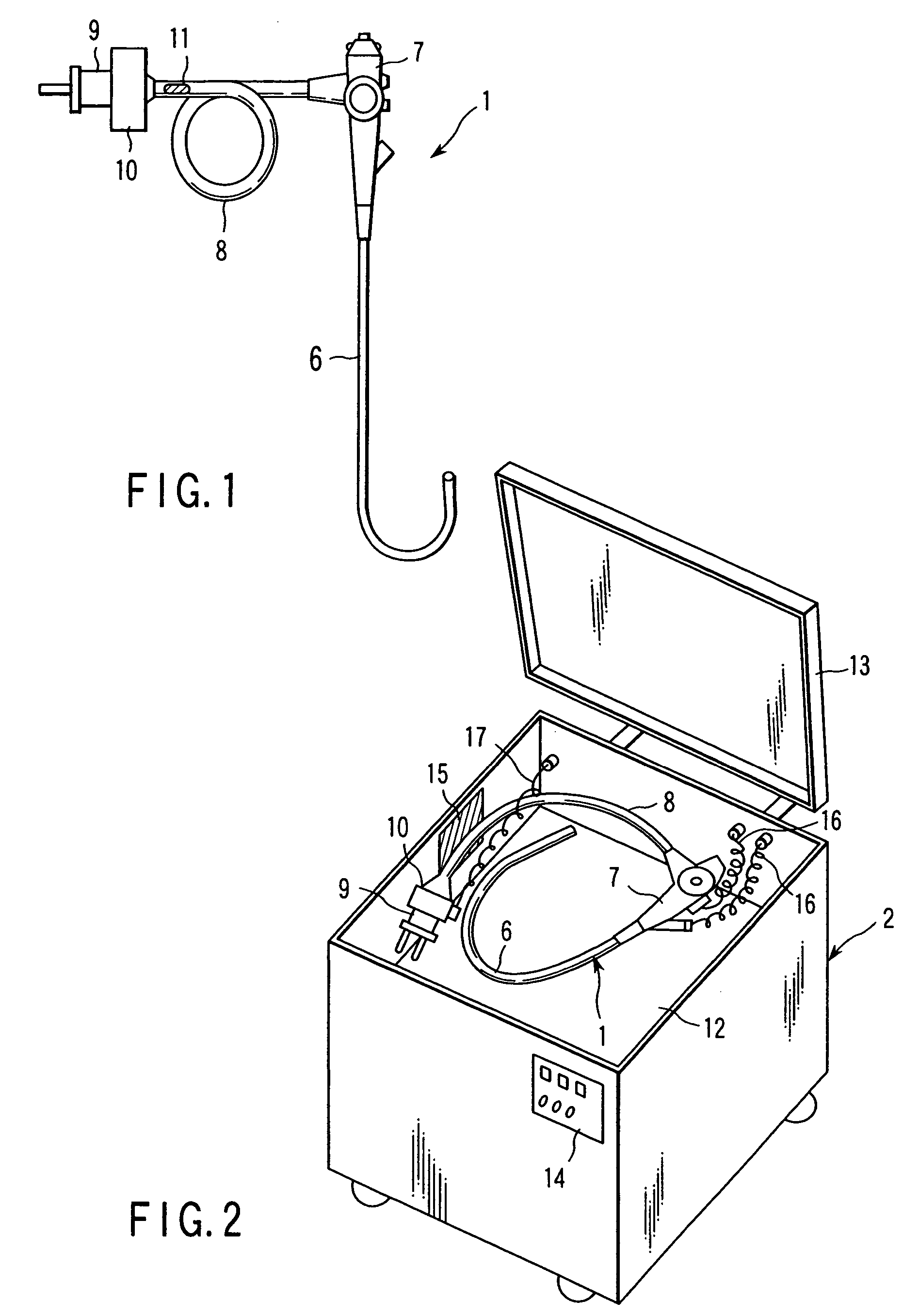
Sterilizing apparatus and sterilizing method
The invention is a sterilizing apparatus that reads information from an information recording section provided in an endoscope, sets a sterilizing process condition for sterilizing the endoscope on the basis of the read information, and controls a sterilizing process in accordance with the sterilizing process condition that is set.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
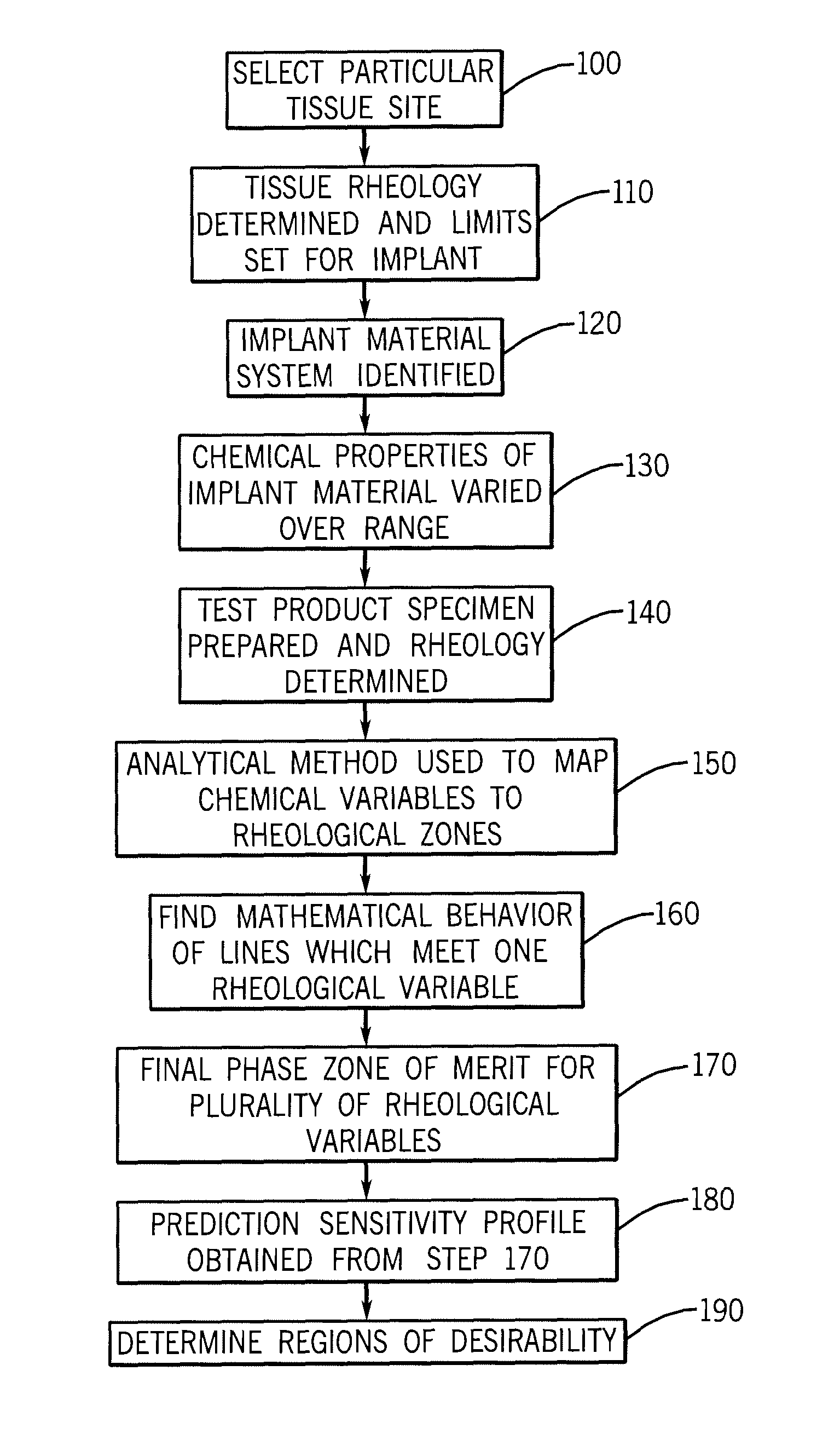
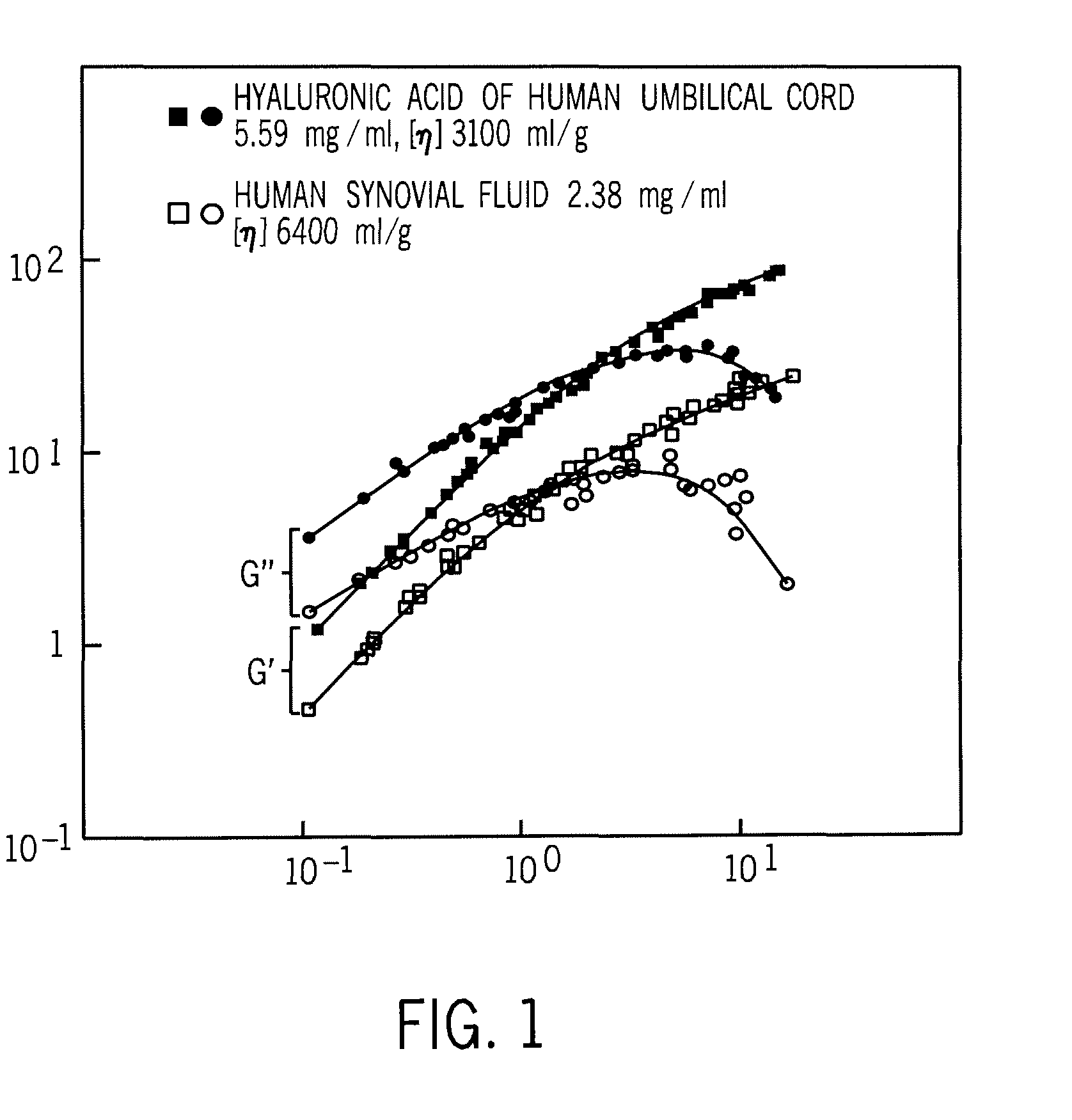
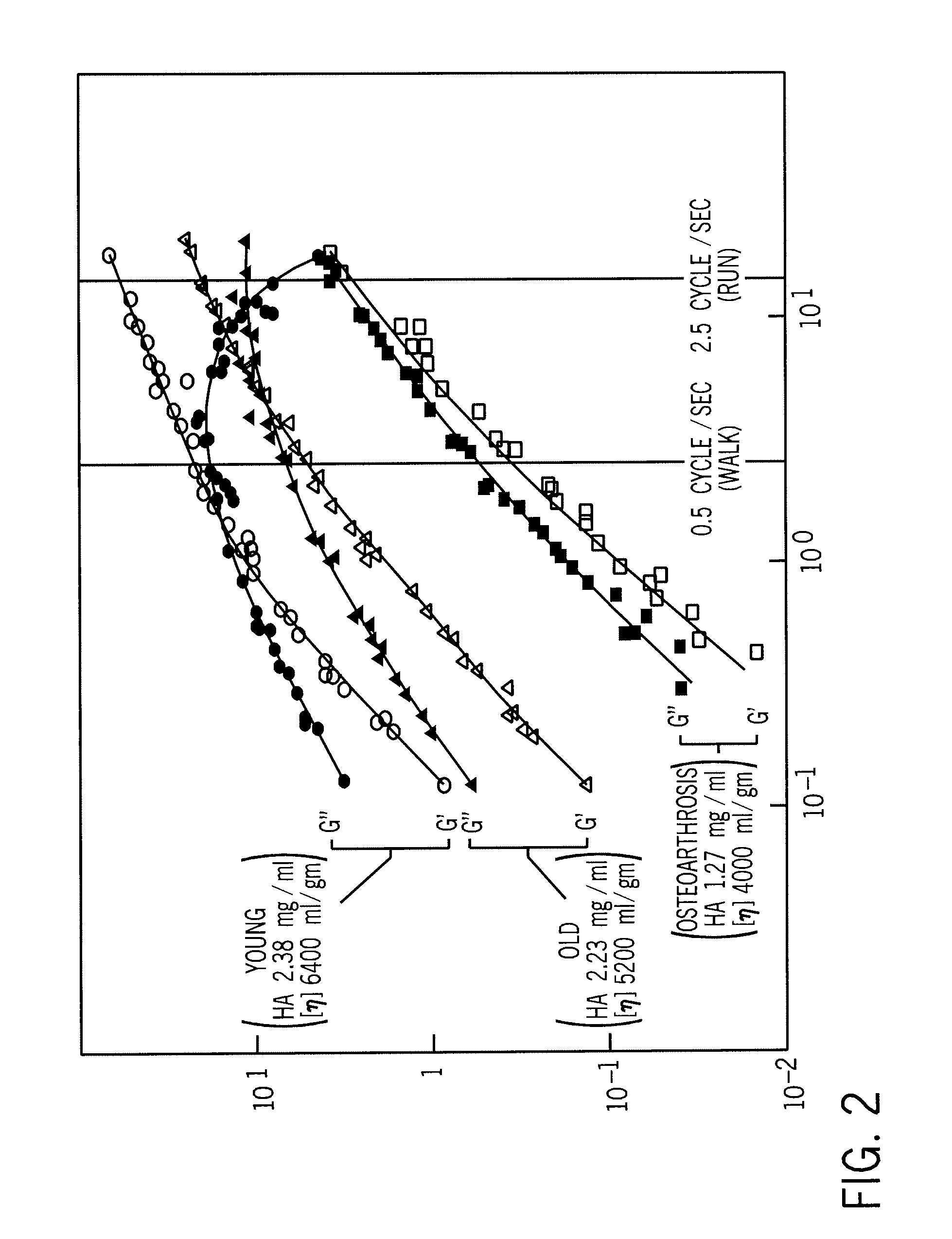
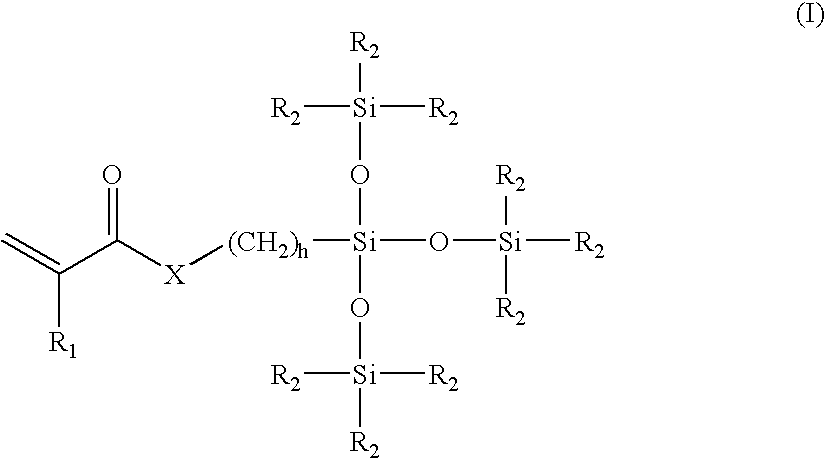
Implantation Compositions for Use in Tissue Augmentation
InactiveUS20100041788A1Good compatibilityMinimized immuno-histo tissue responseOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesPolymer solutionPolysaccharide
A composition of matter and method for preparation of a tissue augmentation material. A polysaccharide gel composition is prepared with rheological properties selected for a particular selected application. The method includes preparing a polymeric polysaccharide in a buffer to create a polymer solution or gel suspending properties in the gel and selecting a rheology profile for the desired tissue region.
Owner:MERZ AESTHETICS
Method of Packaging a Lens
InactiveUS20070149428A1Avoid changeChange physical propertiesLavatory sanitoryOther accessoriesLens plateCopolymer
A contact lens package includes a sealed receptacle containing a contact lens immersed in a sterile solution. The contact lens is made of a silicone hydrogel copolymer, and the solution includes a stabilizing agent in an amount effective to inhibit changes in physical properties of the silicone hydrogel copolymer.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Method for vaporizing a fluid using an electromagnetically responsive heating apparatus
InactiveUS20050095168A1Increase productionReduced resistive electrical power loadSteam generation heating methodsGrinding feed controlElectromagnetic responseEngineering
A vaporizer heating apparatus is comprised of electromagnetically responsive material and electrically non-conductive material. A antimicrobial fluid to be vaporized, such as water or hydrogen peroxide solution, is supplied to the heating apparatus where it is converted to a vapor. In one embodiment of the present invention, electromagnetically responsive material particulate is embedded into the electrically non-conductive material. In another embodiment of the present invention, a microwave generator is used to produce heat.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
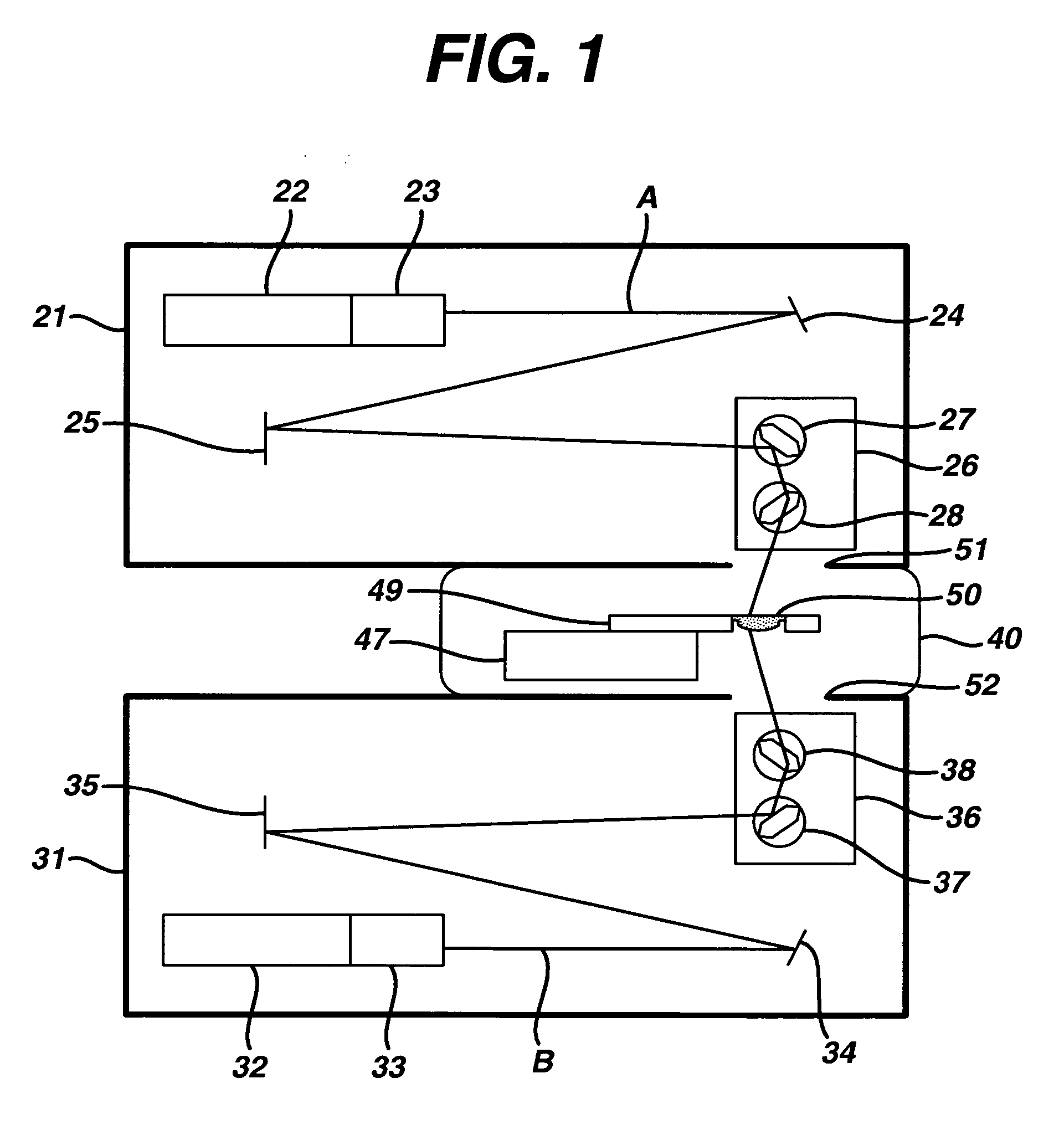
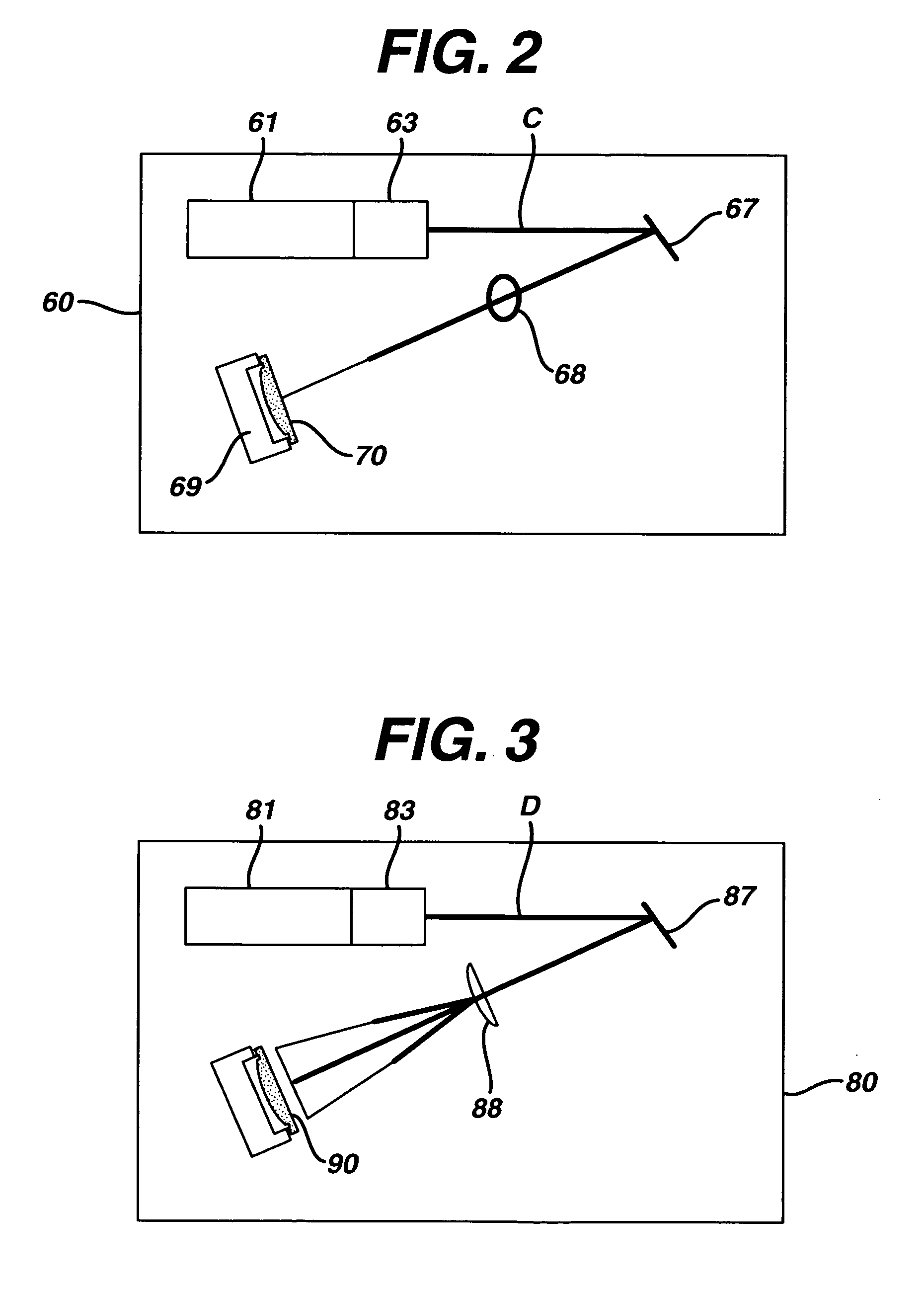
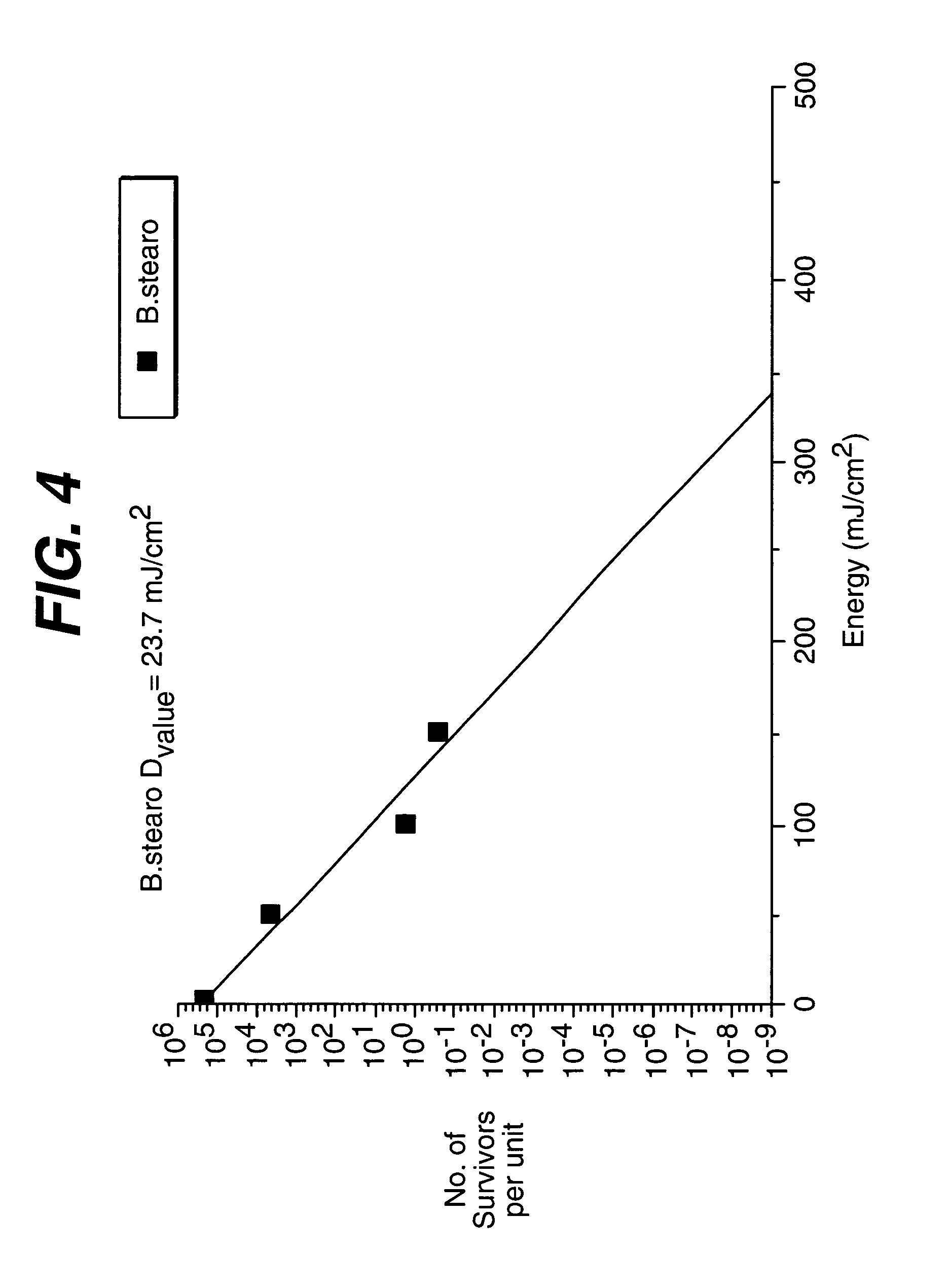
Method and apparatus of sterilization using monochromatic UV radiation source
This invention provides a process of sterilizing a medical device, and preferably the contents of a sealed container which comprises said medical device, comprising the step of exposing said medical device to monochromatic ultraviolet radiation whereby the Dvalue of Bacillus stearothermophilus (ATCC 7953) is at least 23.7 mJ / cm2 monochromatic ultraviolet radiation at 257 nm to the spore. Further, this invention provides a process of sterilizing a medical device comprising the step of subjecting said medical device to monochromatic ultraviolet radiation wherein the minimum total energy density of said monochromatic ultraviolet radiation at 257 nm which reaches the microorganisms present on said medical device is at least 284 mJ / cm2. This invention further provides an apparatus for delivering UV radiation to a medical device for sterilization comprising a laser and a scanner for the laser such that at least 284 mJ / cm2 at 257 nm is applied to a treatment area for said medical device. This invention provides a process and apparatus in which sterilization can be achieved in less than 20 seconds, preferably less than 15 seconds, more preferably in less than 5 seconds. The process and apparatus are efficient and continuous.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
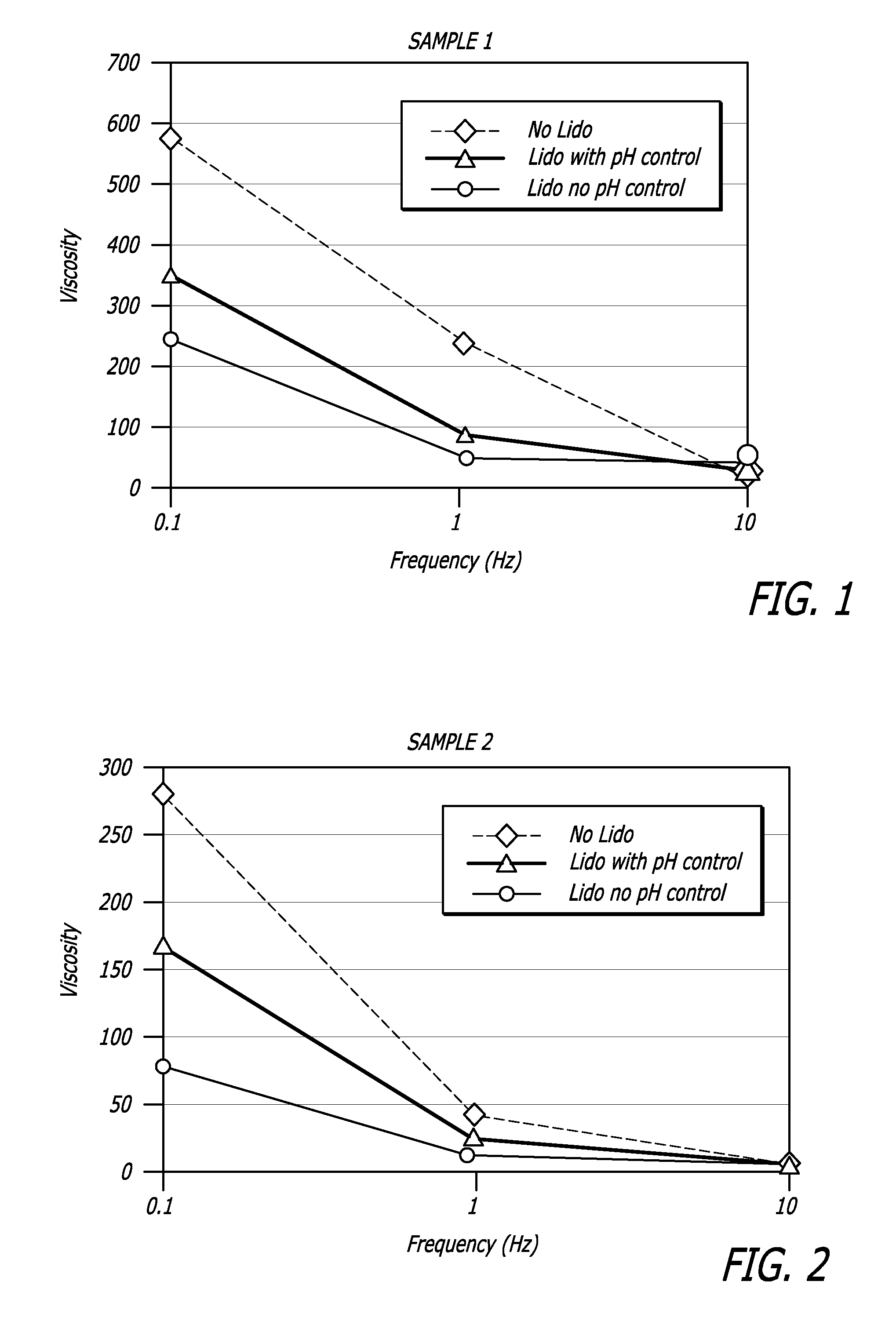
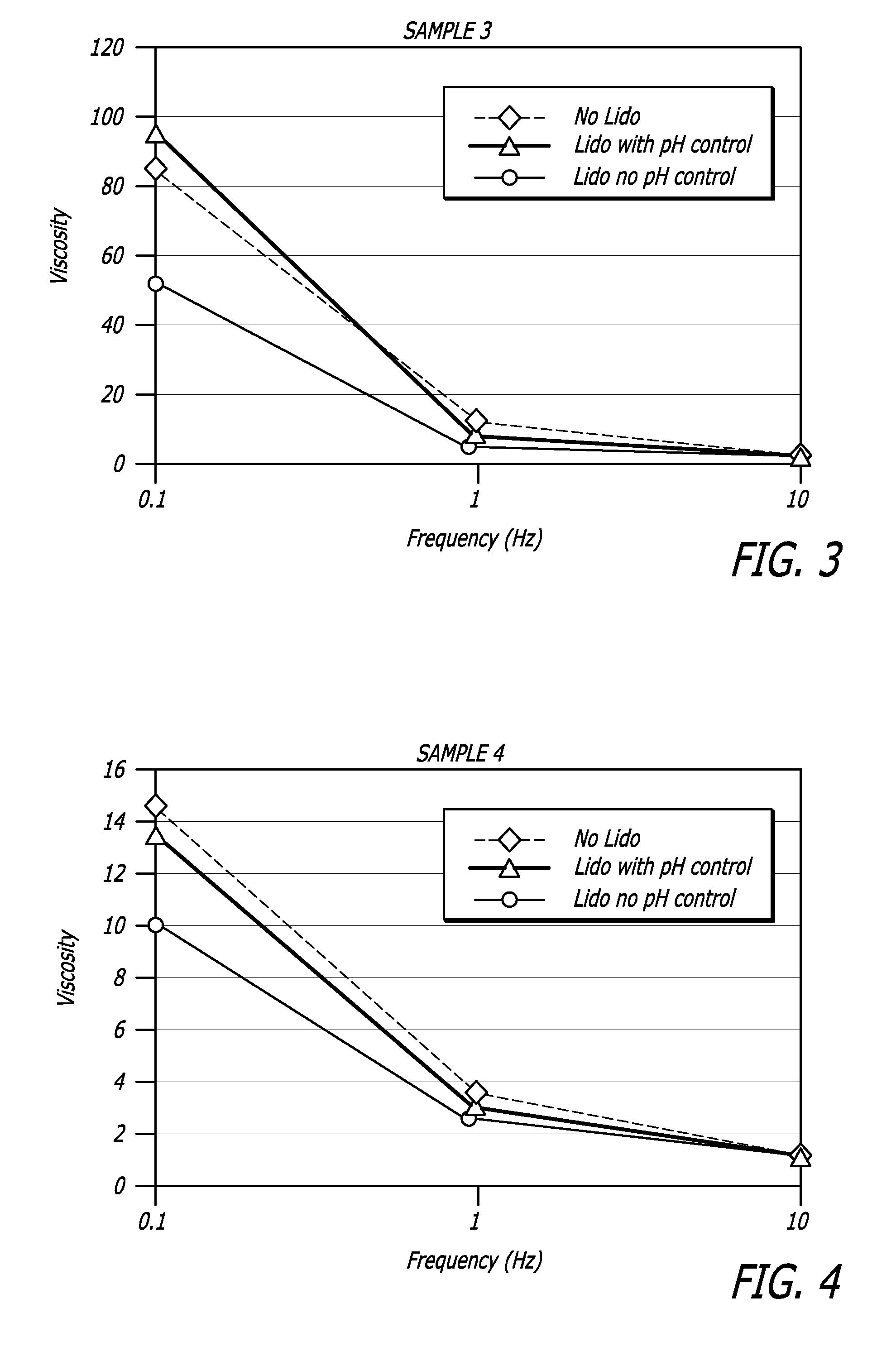
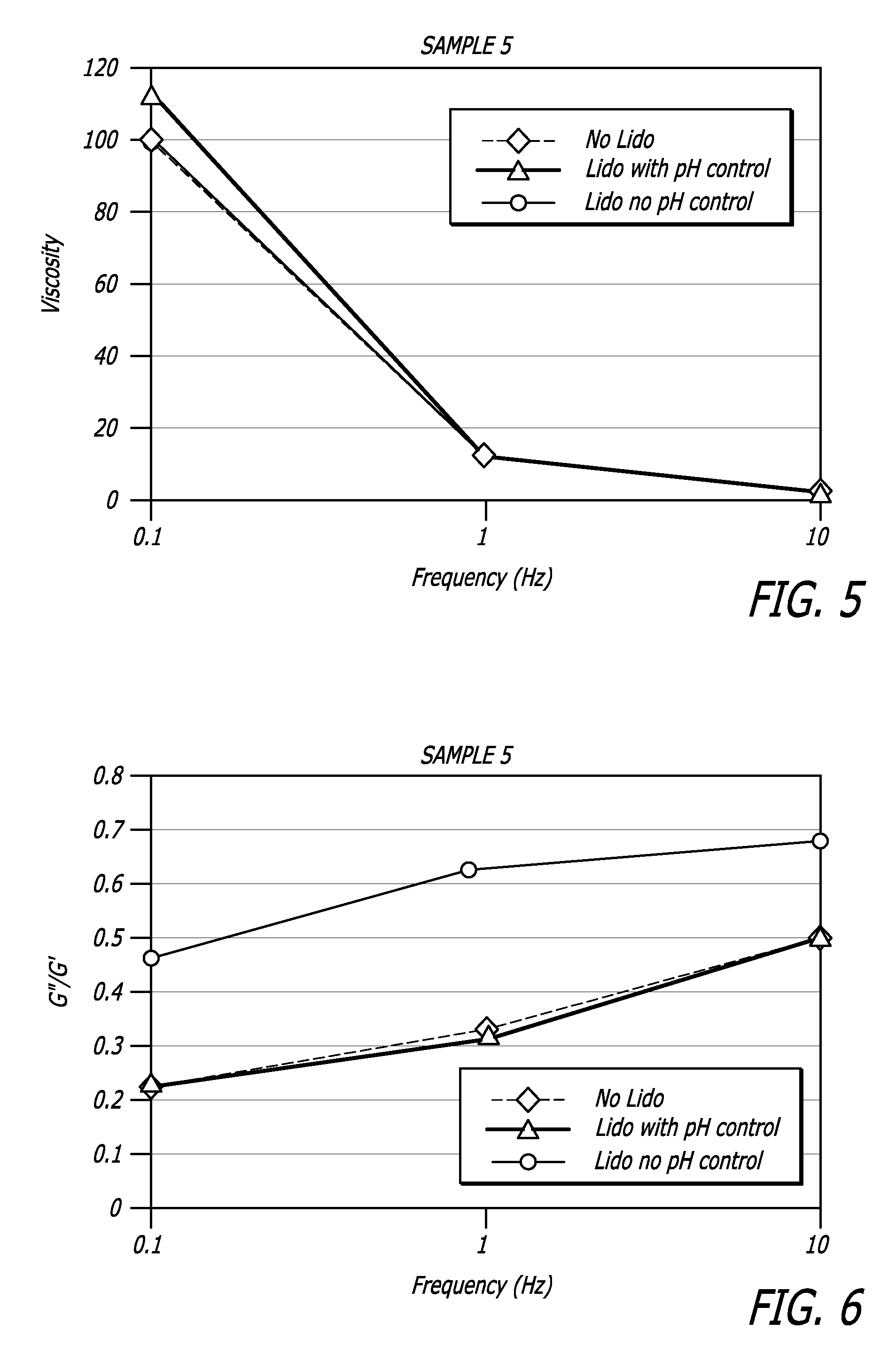
Hyaluronic acid-based gels including lidocaine
Disclosed herein are cohesive soft tissue fillers, for example, dermal and subdermal fillers, based on hyaluronic acids and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. In one aspect, hyaluronic acid-based compositions described herein include a therapeutically effective amount of at least one anesthetic agent, for example, lidocaine. The present hyaluronic acid-based compositions including lidocaine have an enhanced stability and cohesivity, relative to conventional compositions including lidocaine, for example when subjected to sterilization techniques or when stored for long periods of time. Methods and processes of preparing such hyaluronic acid-based compositions are also provided.
Owner:ALLERGAN IND
Humidity sensor
InactiveUS6895803B2RespiratorsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerMoisture sensor
A method and apparatus are described for sensing the absolute humidity of gases where the relative humidity of gases are measured, the humidity transducer is heated, the resulting temperature measured and the absolute humidity calculated (based on the power to heat said transducer, the temperature of said transducer and the relative humidity).In further embodiments the humidity transducer may be heated to a pasteurisation temperature, to substantially kill any common pathogens present on the humidity transducer. The flow rate may be determined to estimate a more instantaneous valve of humidity. The operation of the sensor may be continually monitored for correct operation and various constructions disclosed for improving the efficiency of operation.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
Apparatus and method for continuous depyrogenation and production of sterile water for injection
InactiveUS7122149B2Simple yet dependableReduce contact timeDialysis systemsTreatment involving filtrationDepyrogenationIon exchange
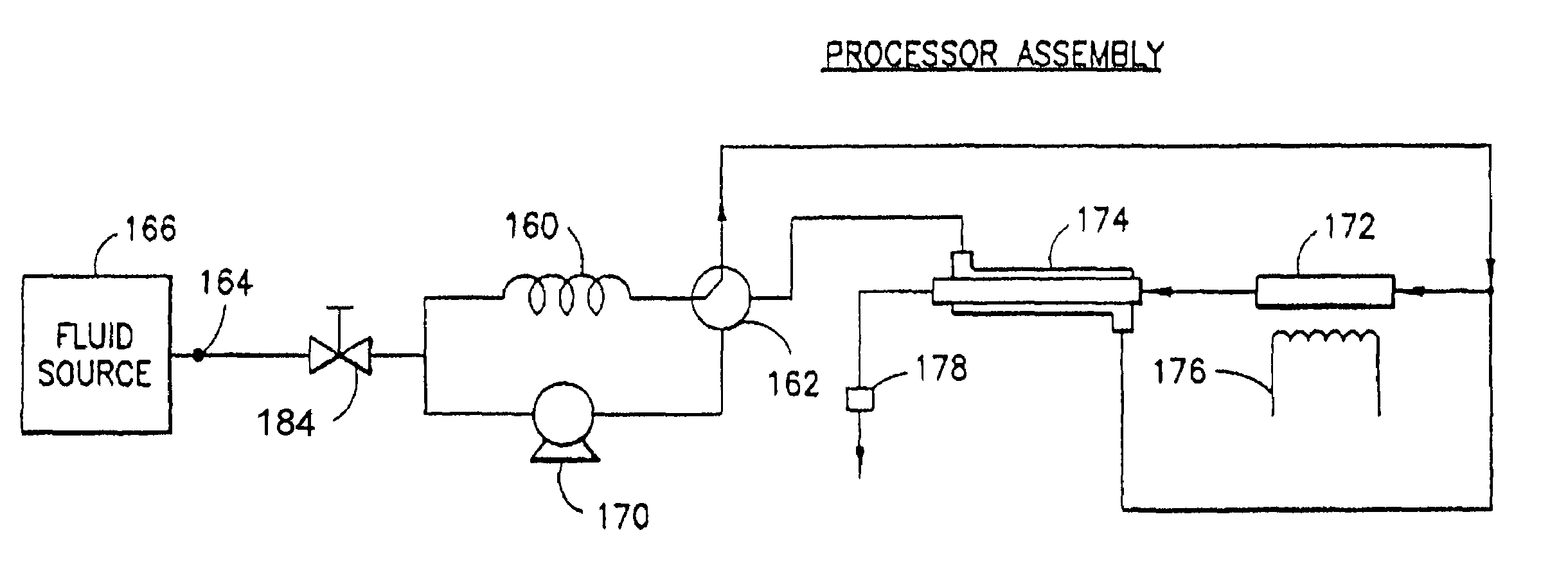
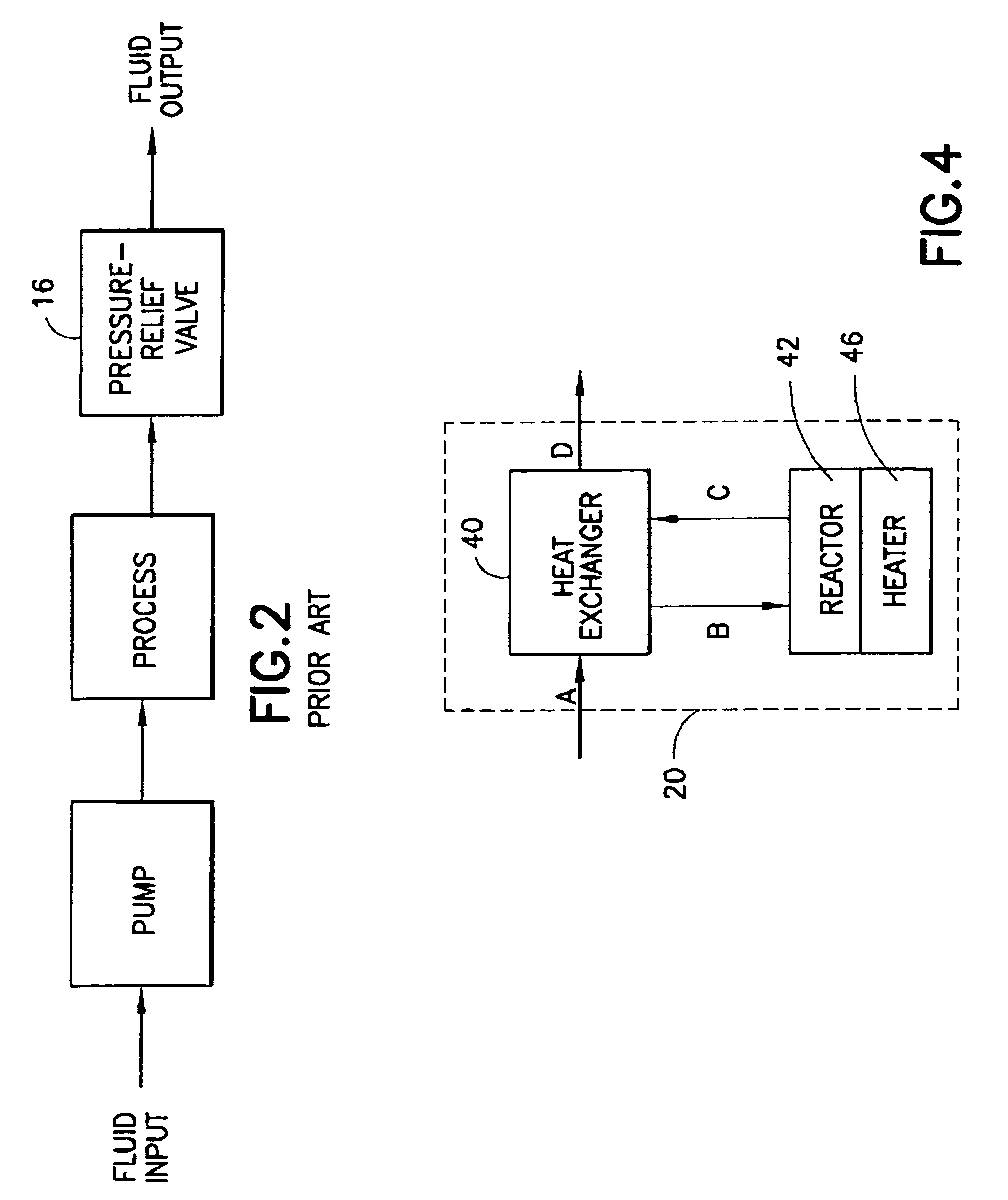
A fluid processor, suitable for the production of sterile water for injection, having a processor assembly and a process control system comprising a pump, a flow splitter, flow restrictors and a pressure relief valve. In a preferred embodiment, the processor assembly comprises a heat exchanger, a reactor and a heater arranged in a nested configuration. The preferred embodiment of the present invention also include a treatment assembly having a combination of filter, reverse osmosis and ion exchange devices and further incorporates an assembly and method allowing for the in situ sanitization of the fluid processor during cold start and shutdown to prevent bacteria growth during storage of the fluid processor. The fluid processor may include an electronic control system comprising a touch screen operator interface, a programmable logic controller and sensors for measuring temperature, pressure, flow rate, conductivity and endotoxin level.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com