Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Extreme flexibility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
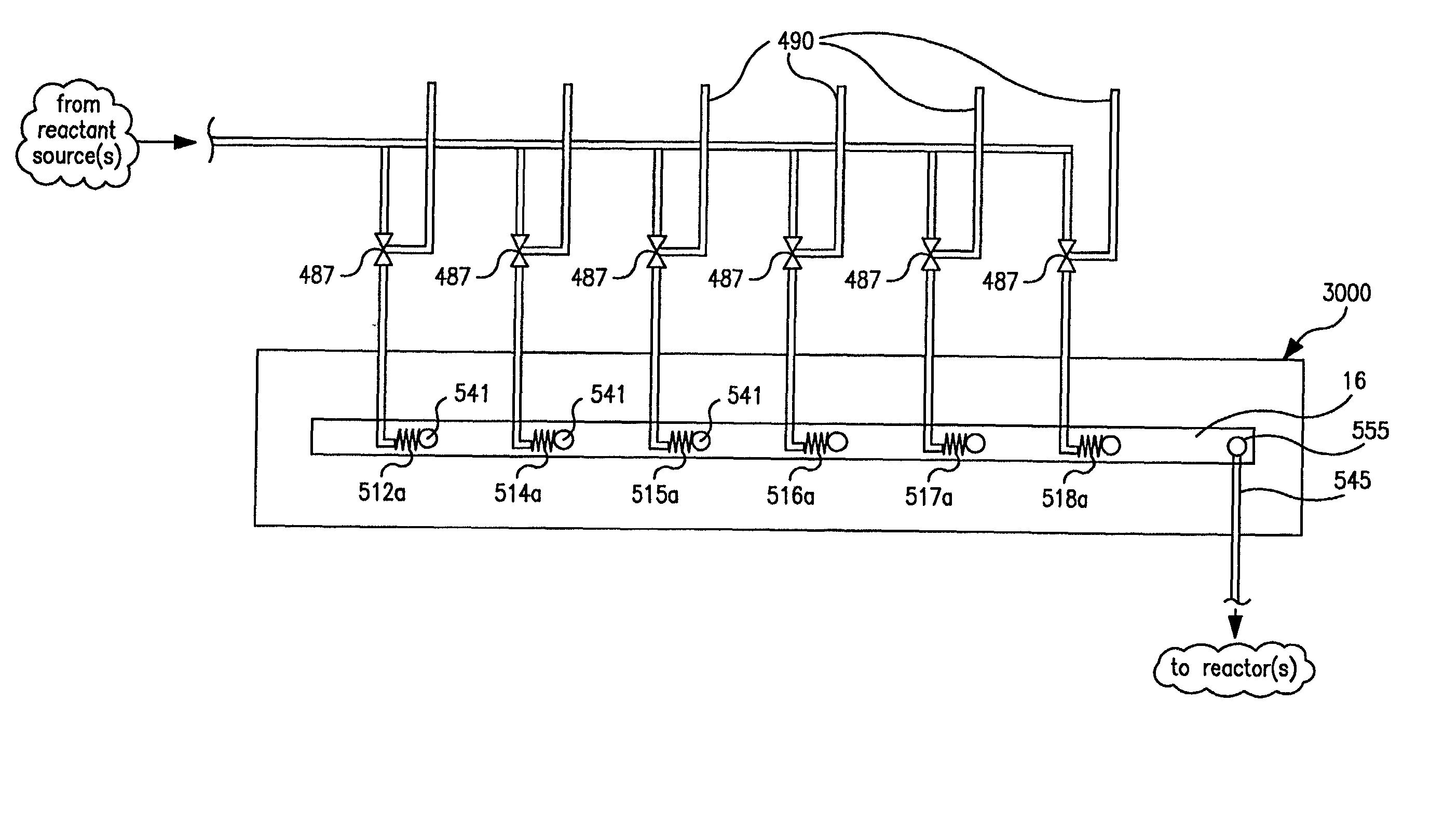
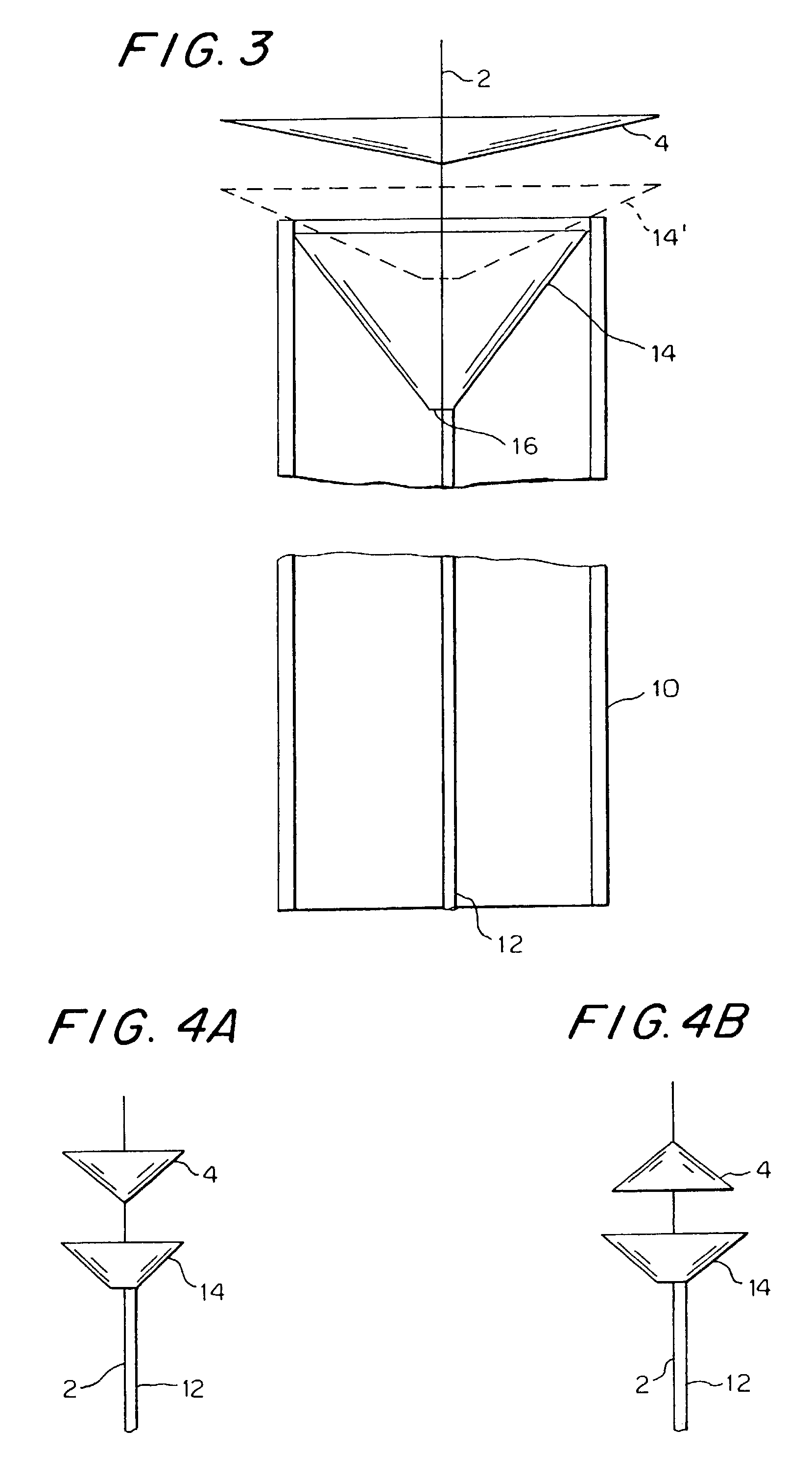
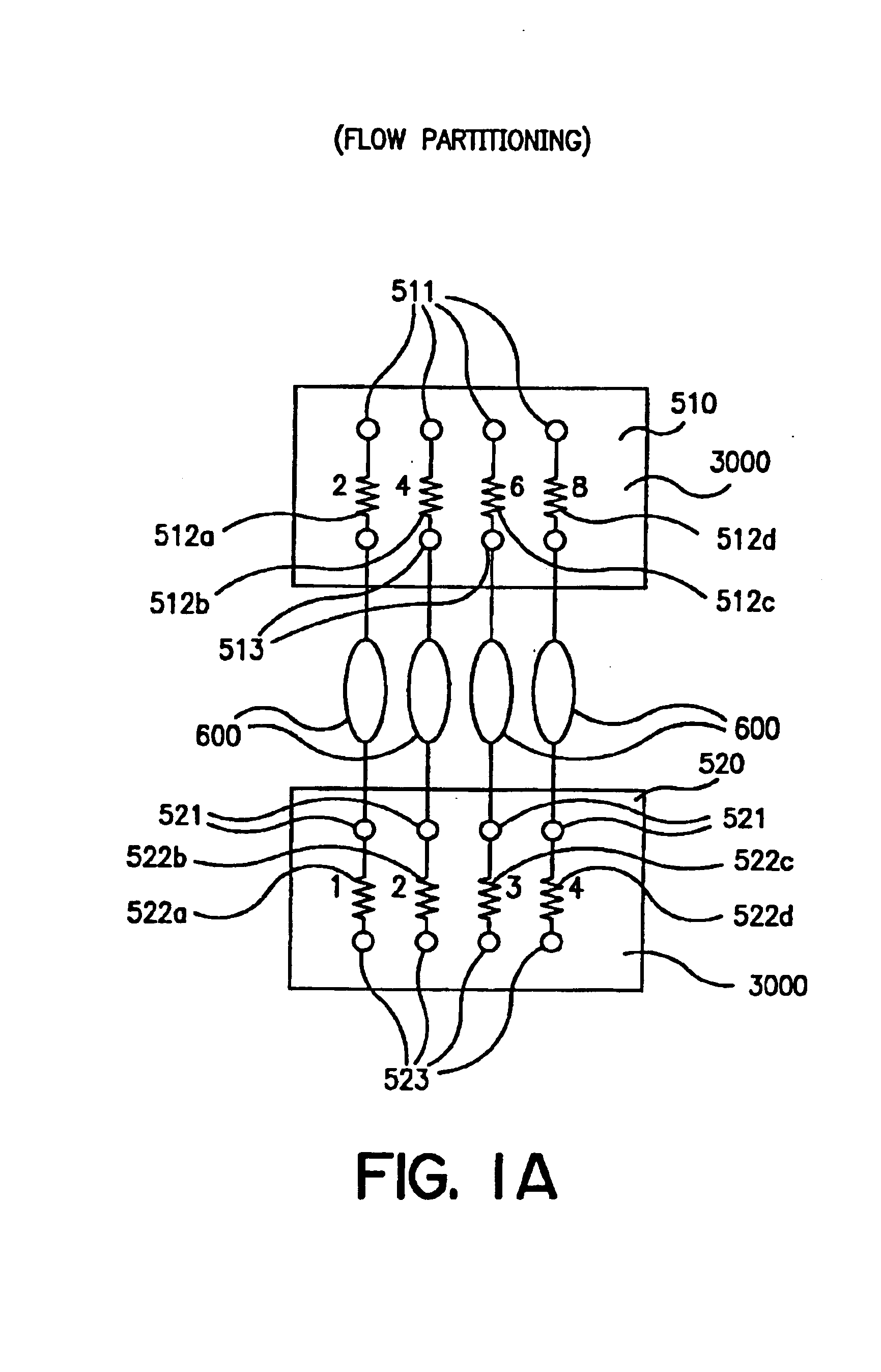
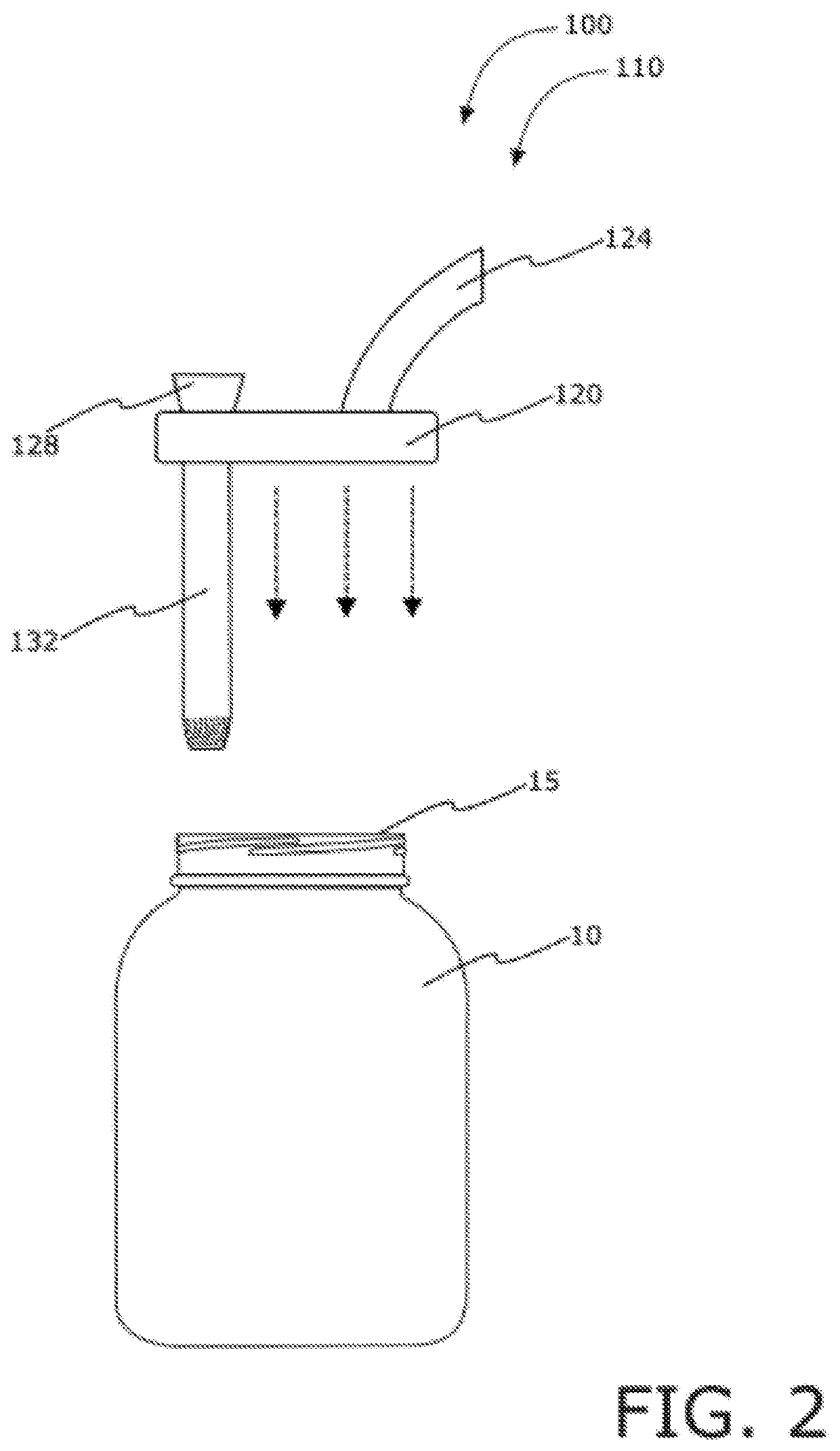
Parallel flow process optimization reactors
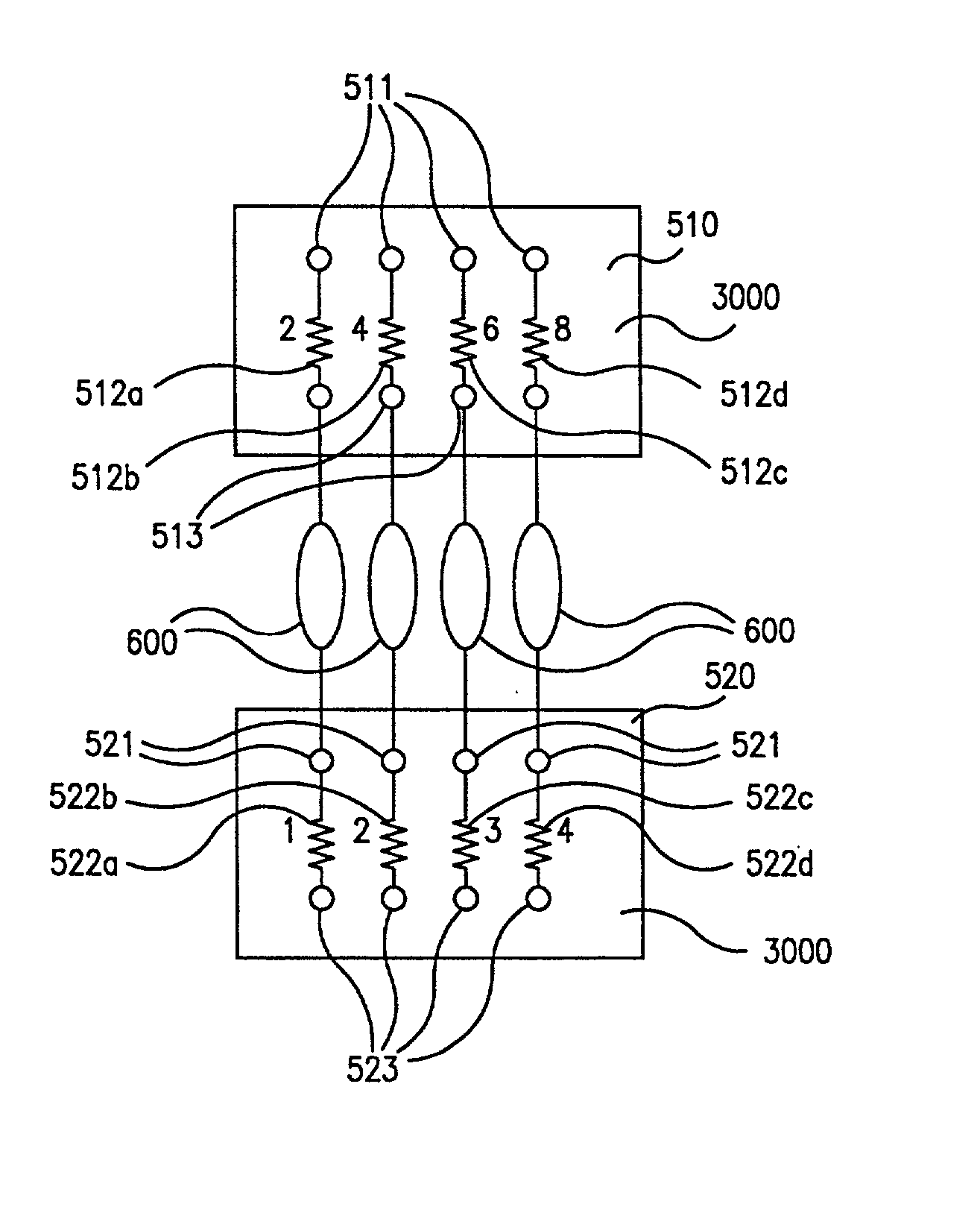
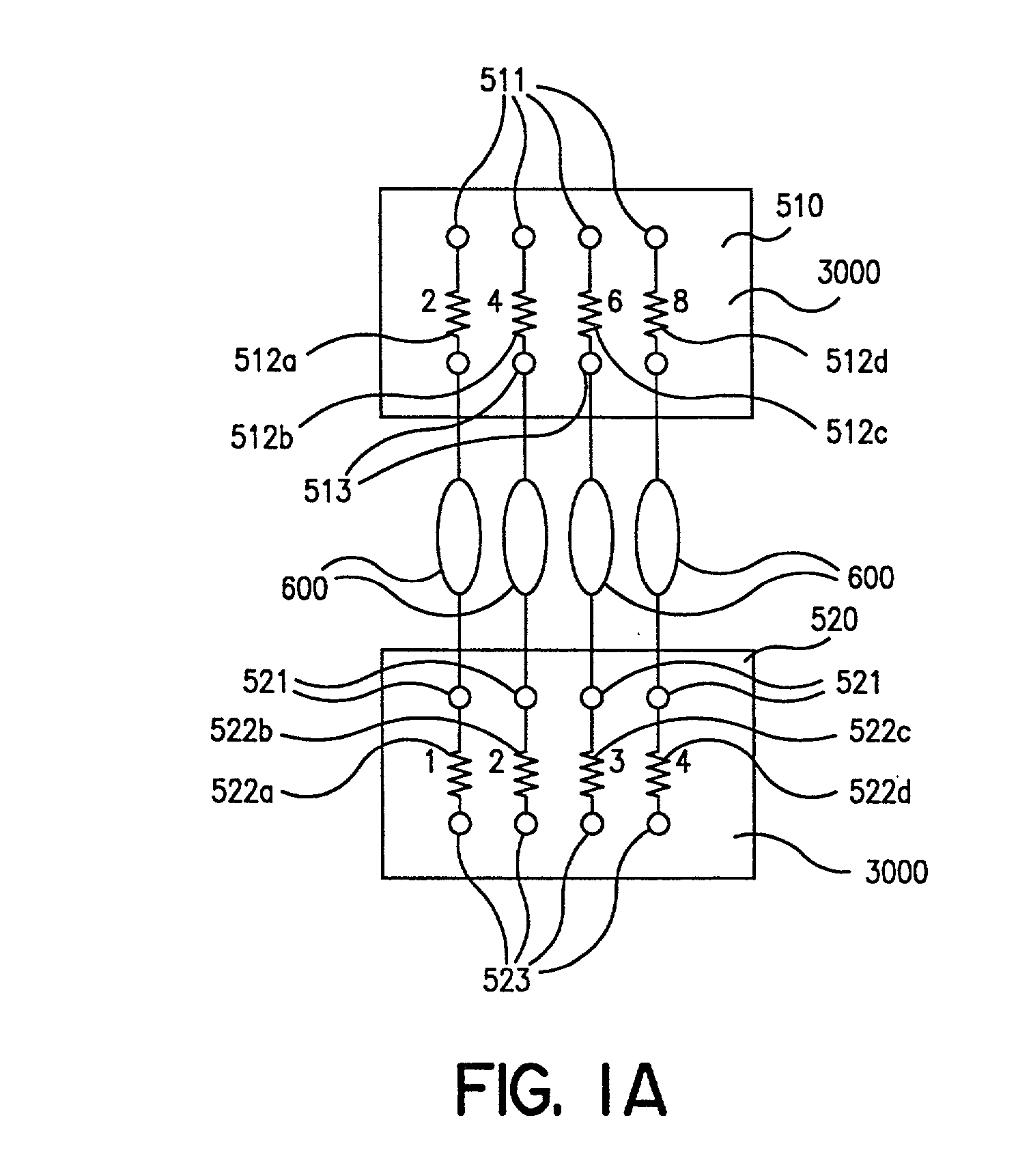
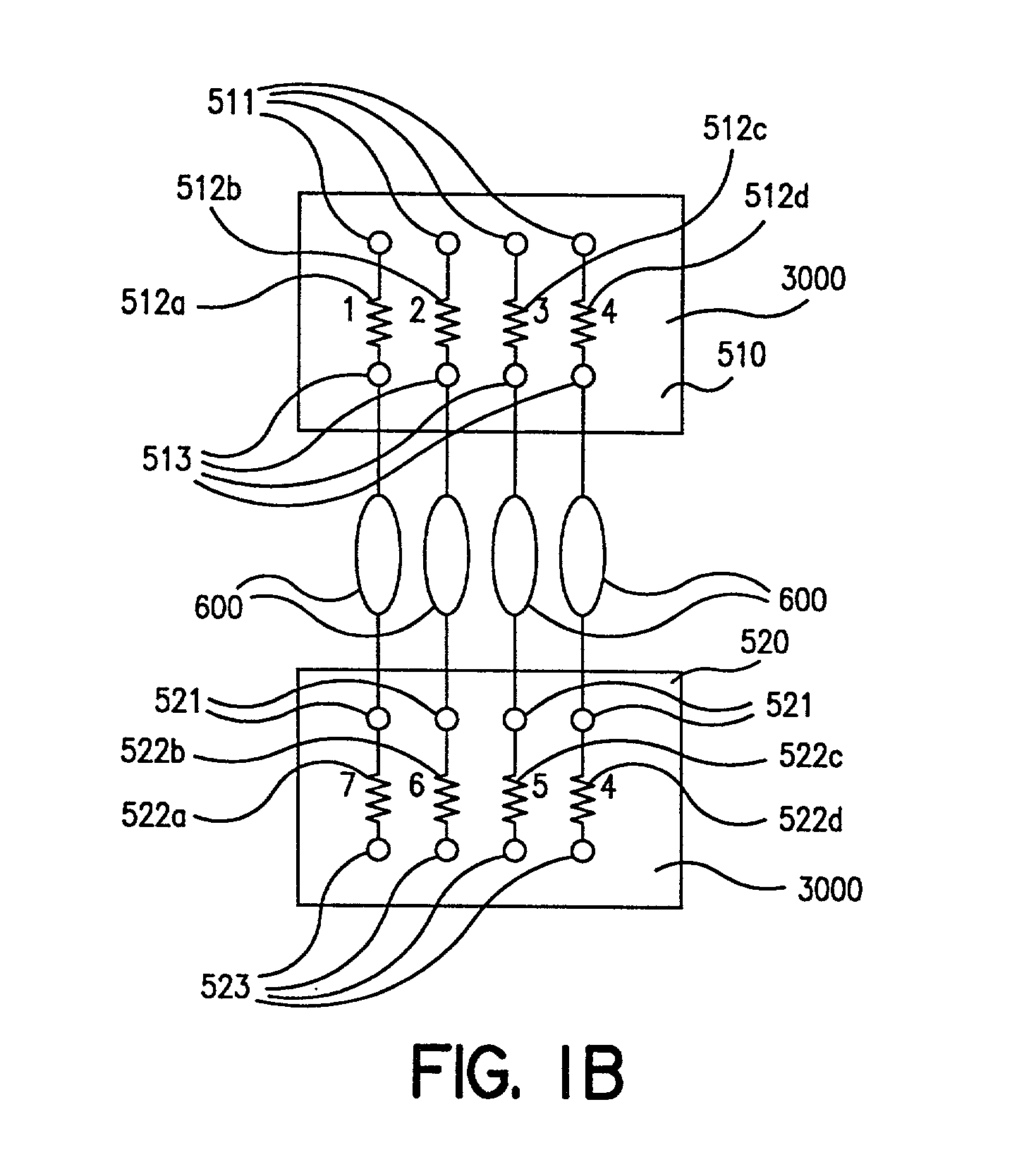
InactiveUS20020048536A1Extreme flexibilityAdvantageously and flexibly employedProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsProcess optimizationDistribution system
Owner:FREESLATE
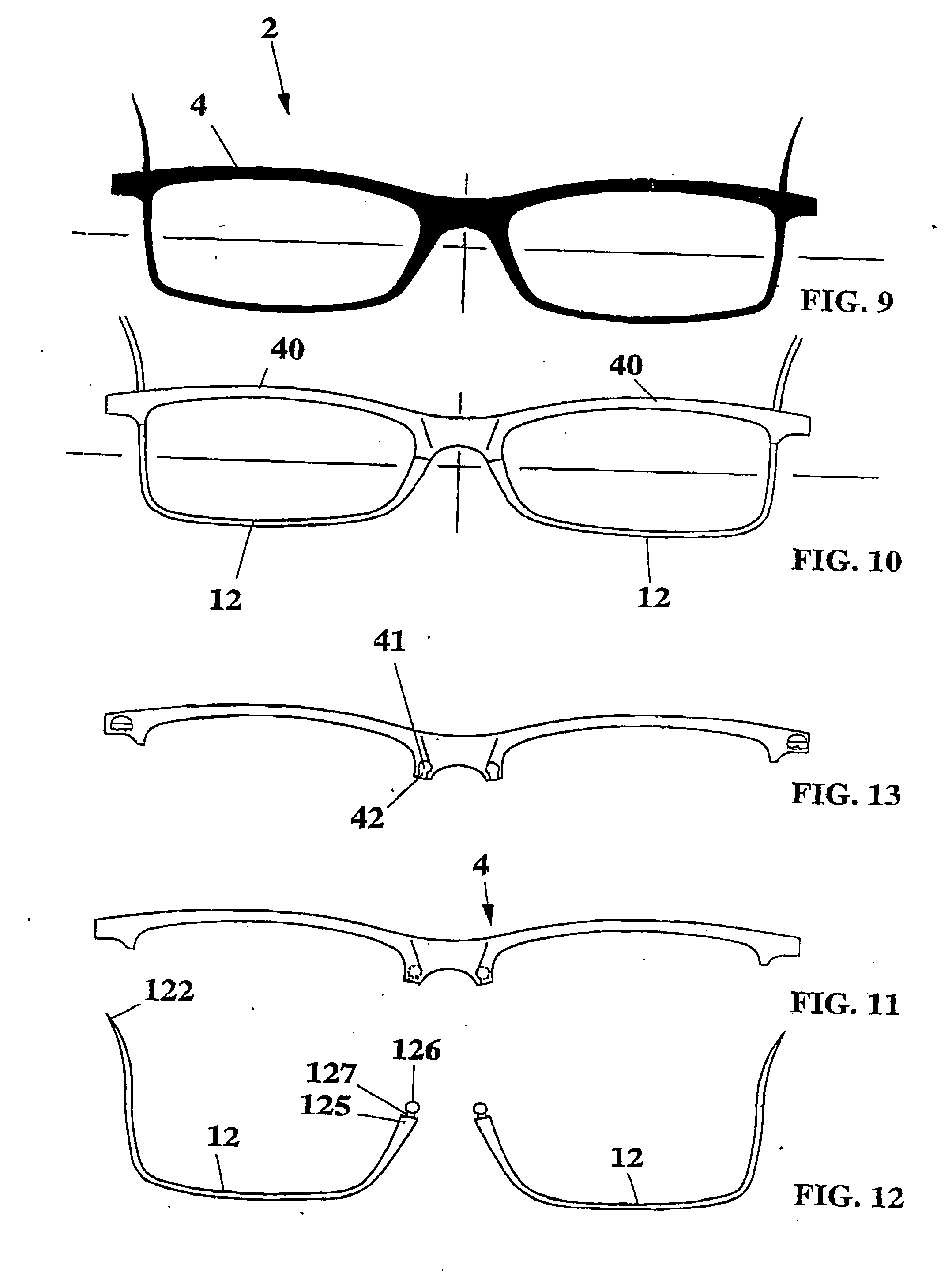
Front for full-rim glasses frame with holding band device and rapid fixing of the lenses to the frame
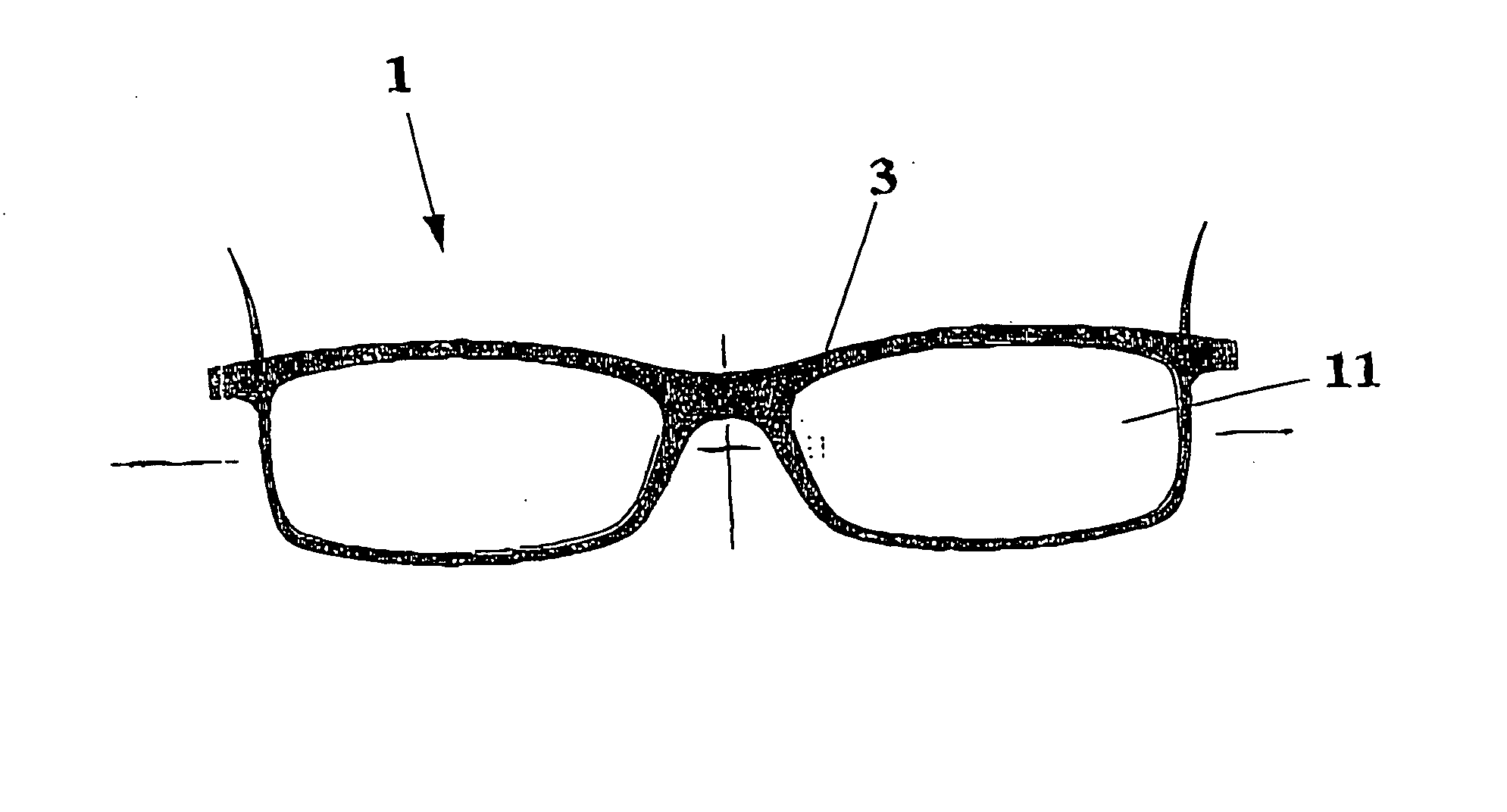
InactiveUS20060268218A1Minimal effortExtreme aesthetic flexibilityNon-optical partsLens assembliesTemporal RegionsEngineering
Front for full-rim glasses frames with a holding device and rapid fixing of the lenses to the frame. The front being of the type with a monopiece arch transversely projected with respect to the face of the user, which includes, at the temporal ends, two shaped and curved cross-pieces joined by a connecting intermediate nose bridge. Each cross-piece provides hinging of the related side, and each cross-piece near to the intermediate connecting nose bridge provides a curved projection, which provides a first of the two ends of flexible holders that partially enclose the peripheral edge of the lens to be joined to the front, the other side being provided with a second end, introduced by a through-hole obtained in correspondence to the temporal region of the front, that is equipped with a tooth that engages unidirectionally the portion of the second end of the flexible holders.
Owner:MEDANA GUIDO
Parallel flow reactor having variable composition
InactiveUS20020045265A1Extreme flexibilityAdvantageously and flexibly employedProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsDistribution systemEngineering
Owner:FREESLATE
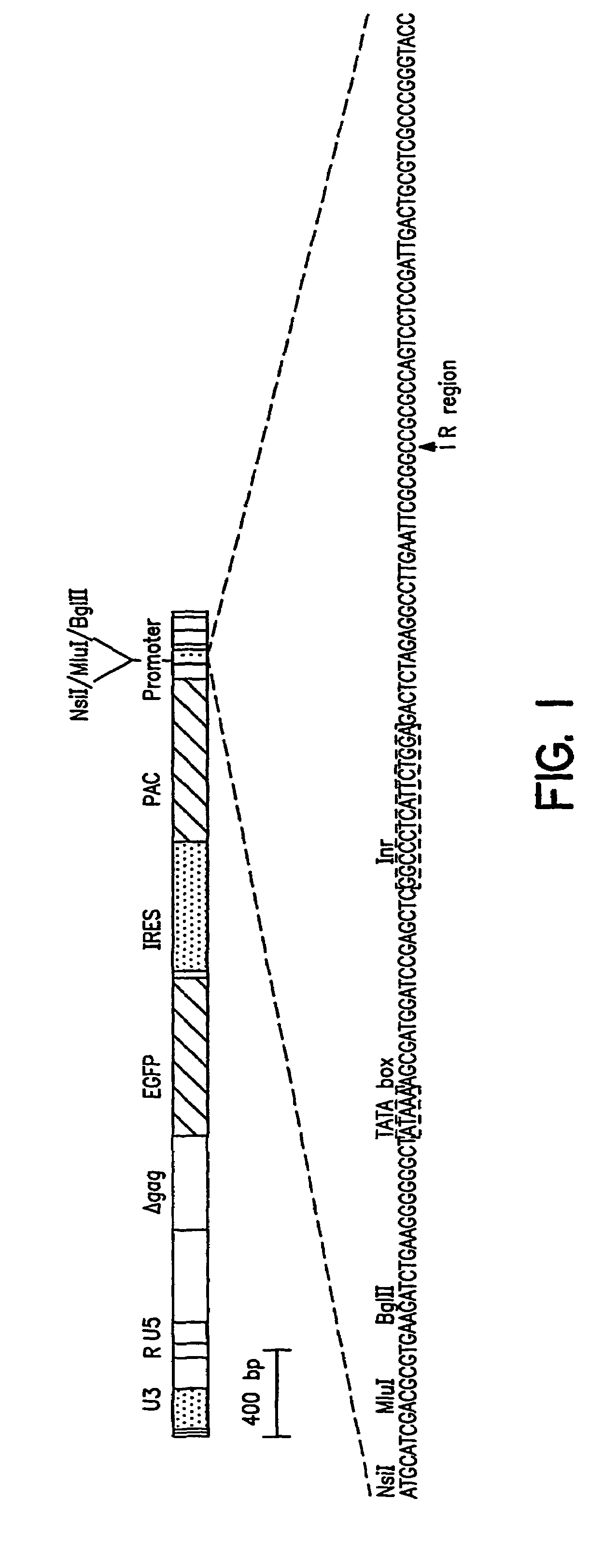
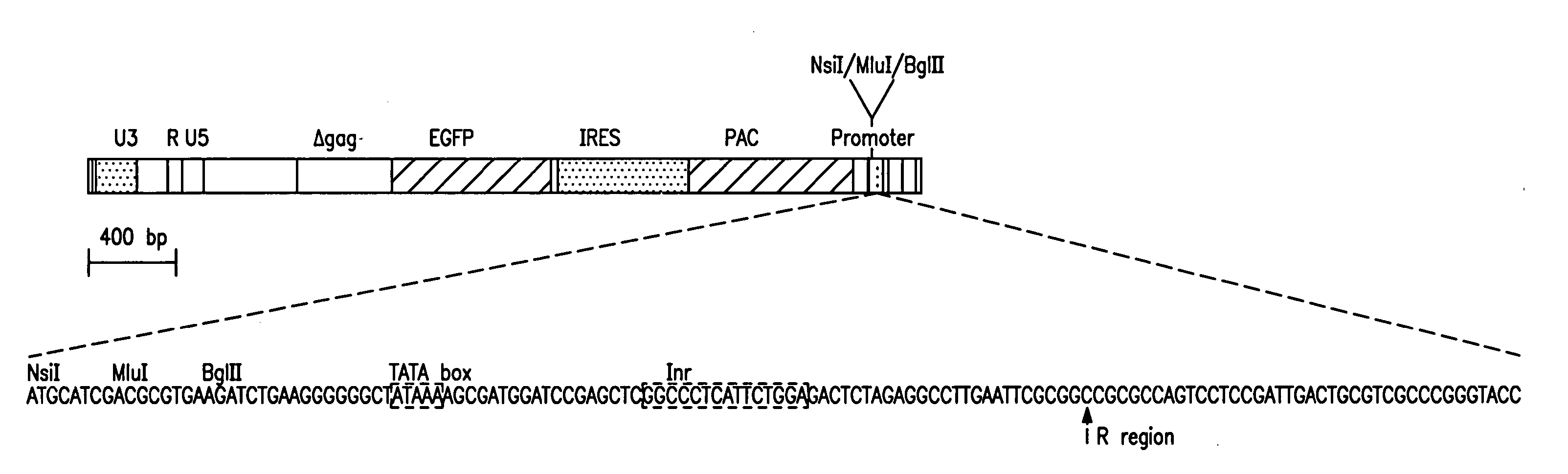
Methods of identifying synthetic transcriptional and translational regulatory elements, and compositions relating to same
InactiveUS7183395B2Facilitate identification and isolationIncrease transcriptionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideEukaryotic cell
Provided are methods of identifying oligonucleotides having transcriptional or translational activity by integrating the oligonucleotide into a eukaryotic cell genome such that the oligonucleotide is operatively linked to an expressible polynucleotide, and detecting a change in expression of the expressible polynucleotide due to the operatively linked oligonucleotide. Also provided are vectors useful for identifying an oligonucleotide having transcriptional or translational regulatory activity according to a method of the invention. In addition, isolated synthetic transcriptional or translational regulatory elements identified according to a method of the invention are provided, as are kits, which contain a vector useful for identifying a transcriptional or translational regulatory element, or an isolated synthetic transcriptional or translational regulatory element or plurality of such elements. Also provided are isolated transcriptional regulatory elements.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
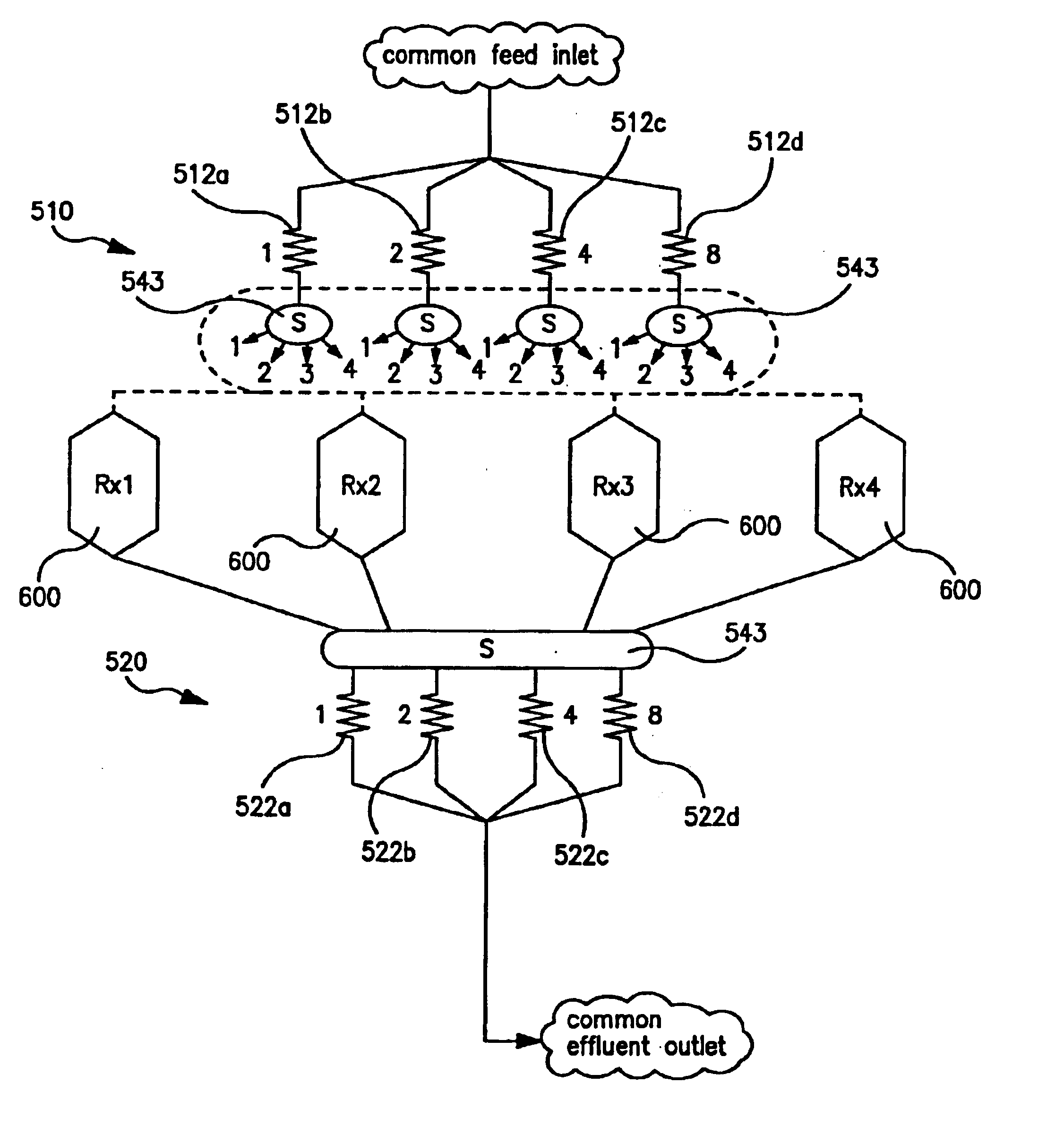
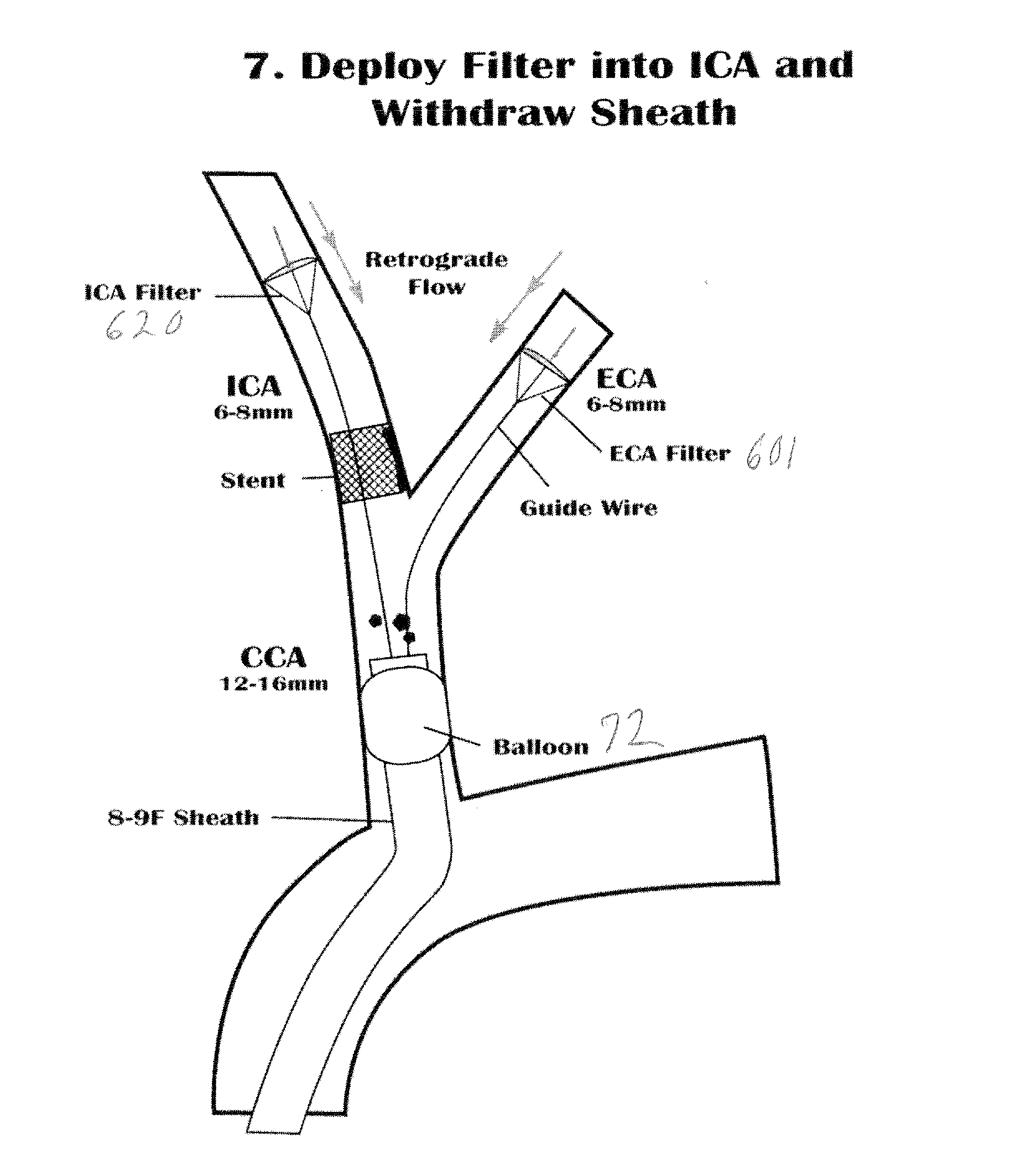
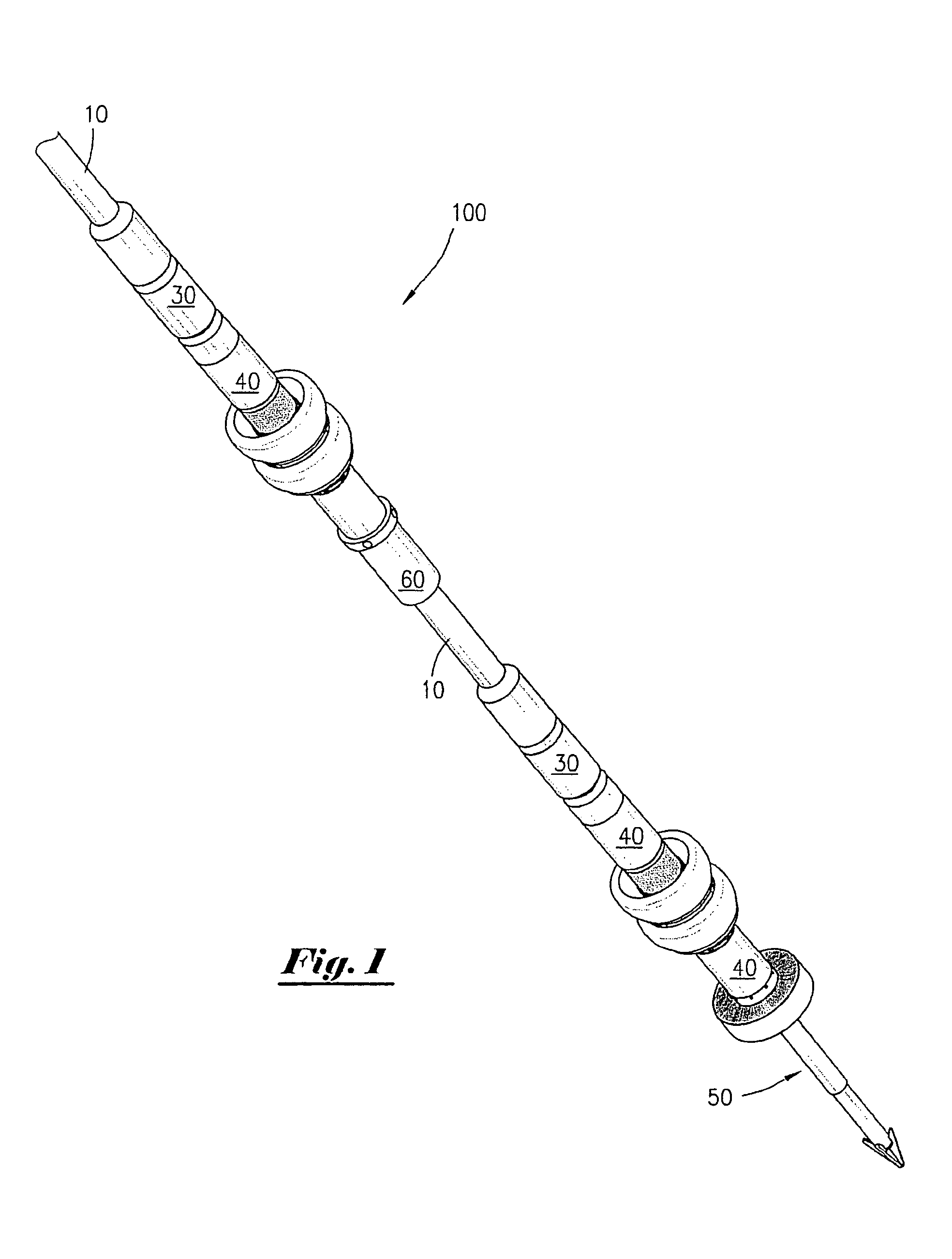
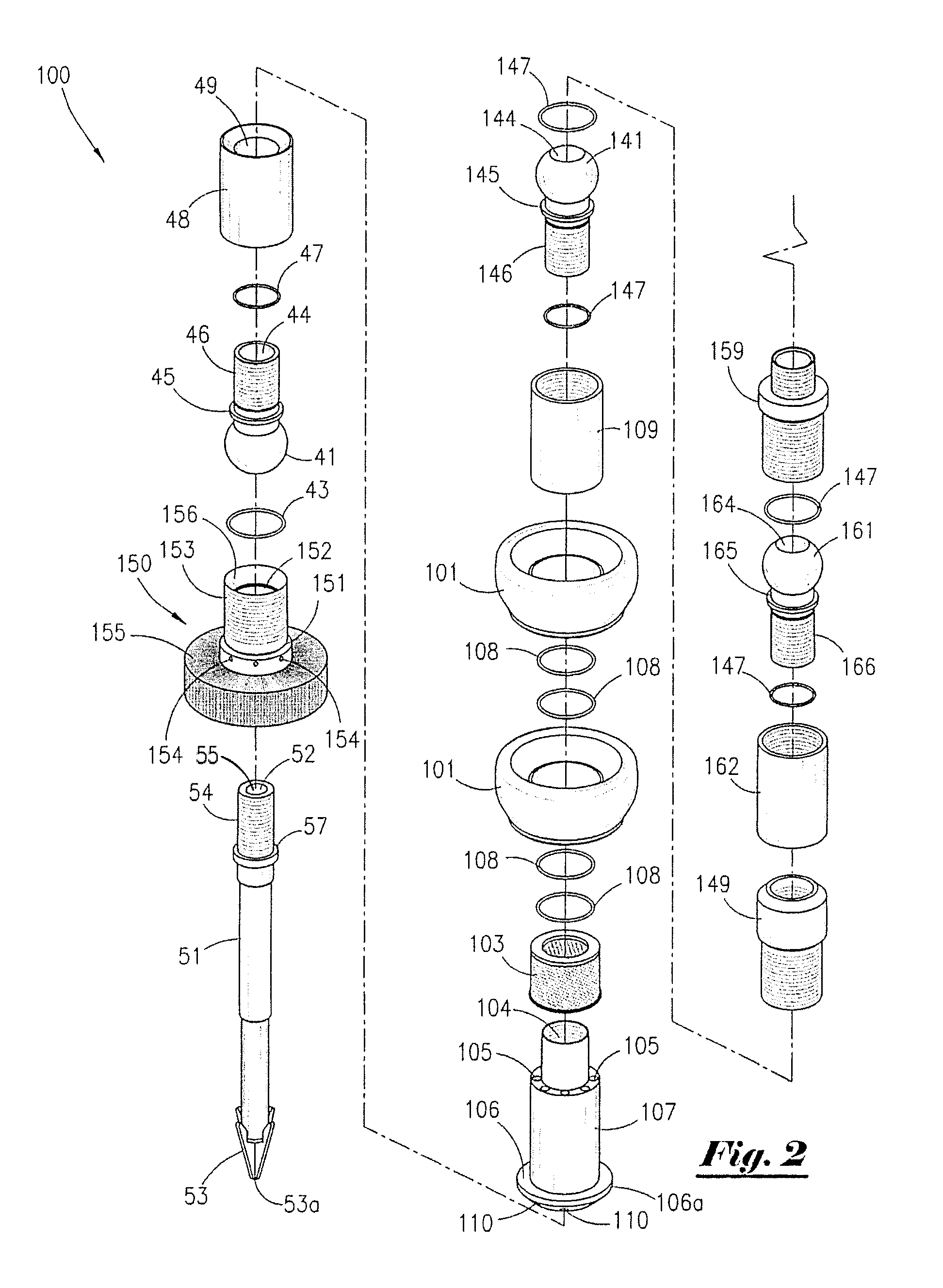
Vascular filter with improved strength and flexibility
A medical device, such as a vascular filter, composed of: a reinforced membrane unit composed of: a thin filter membrane; and fibers of reinforcement material embedded in the membrane to strengthen the filter and securely attach the fibers to the membrane.A method of fabricating the filter by the steps of: providing a mold that can be melted, dissolved, or deformed without damaging membrane material; covering the mold with an intermediate material that is easily separated from the membrane material; covering the intermediate material with the membrane material; placing the fibers in contact with the membrane material that covers the intermediate material; covering the fibers with additional membrane material to form the membrane with embedded fibers; removing the mold by melting, dissolving, or deforming the mold; and removing the intermediate material from the membrane.
Owner:DON MICHAEL INT
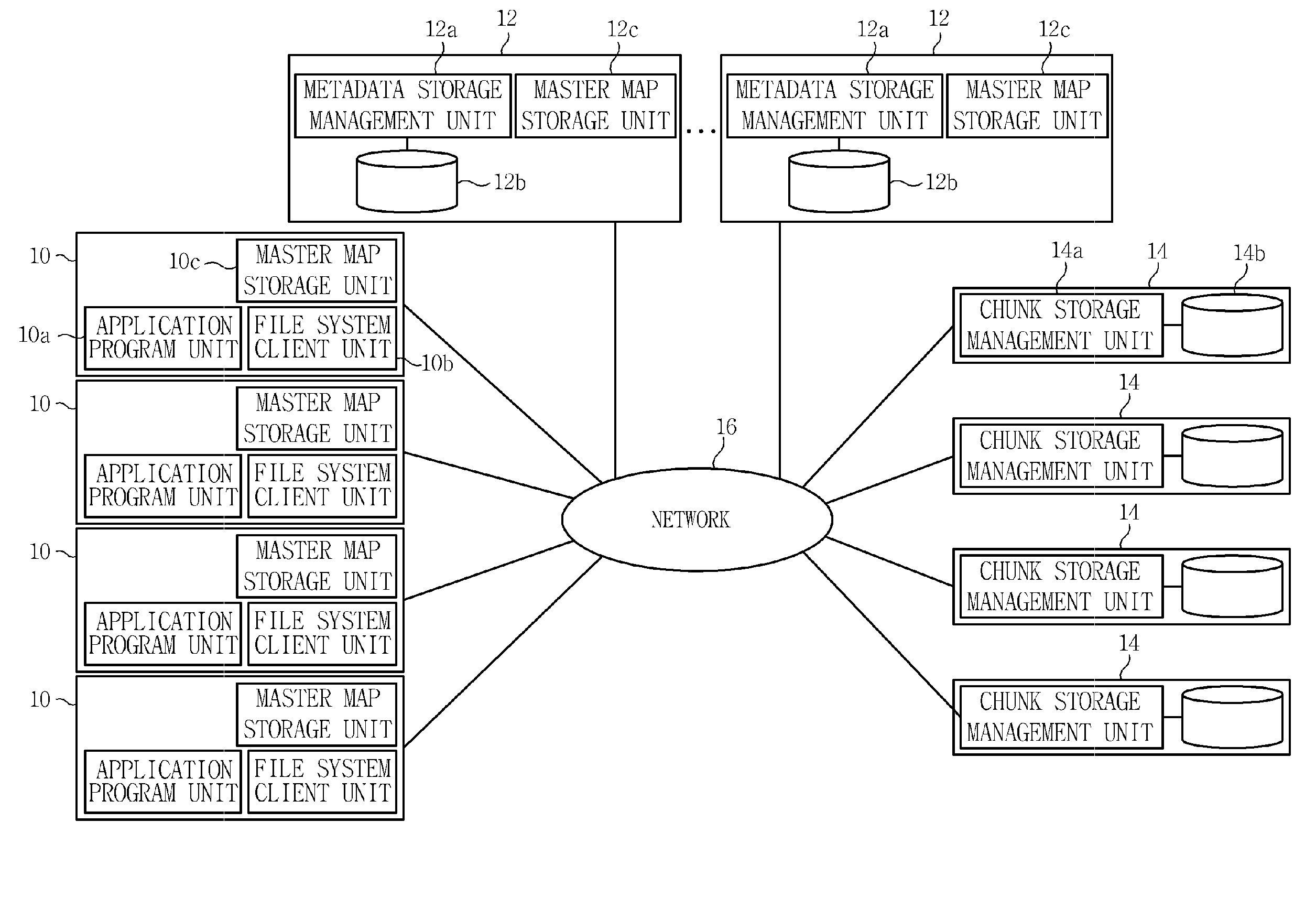
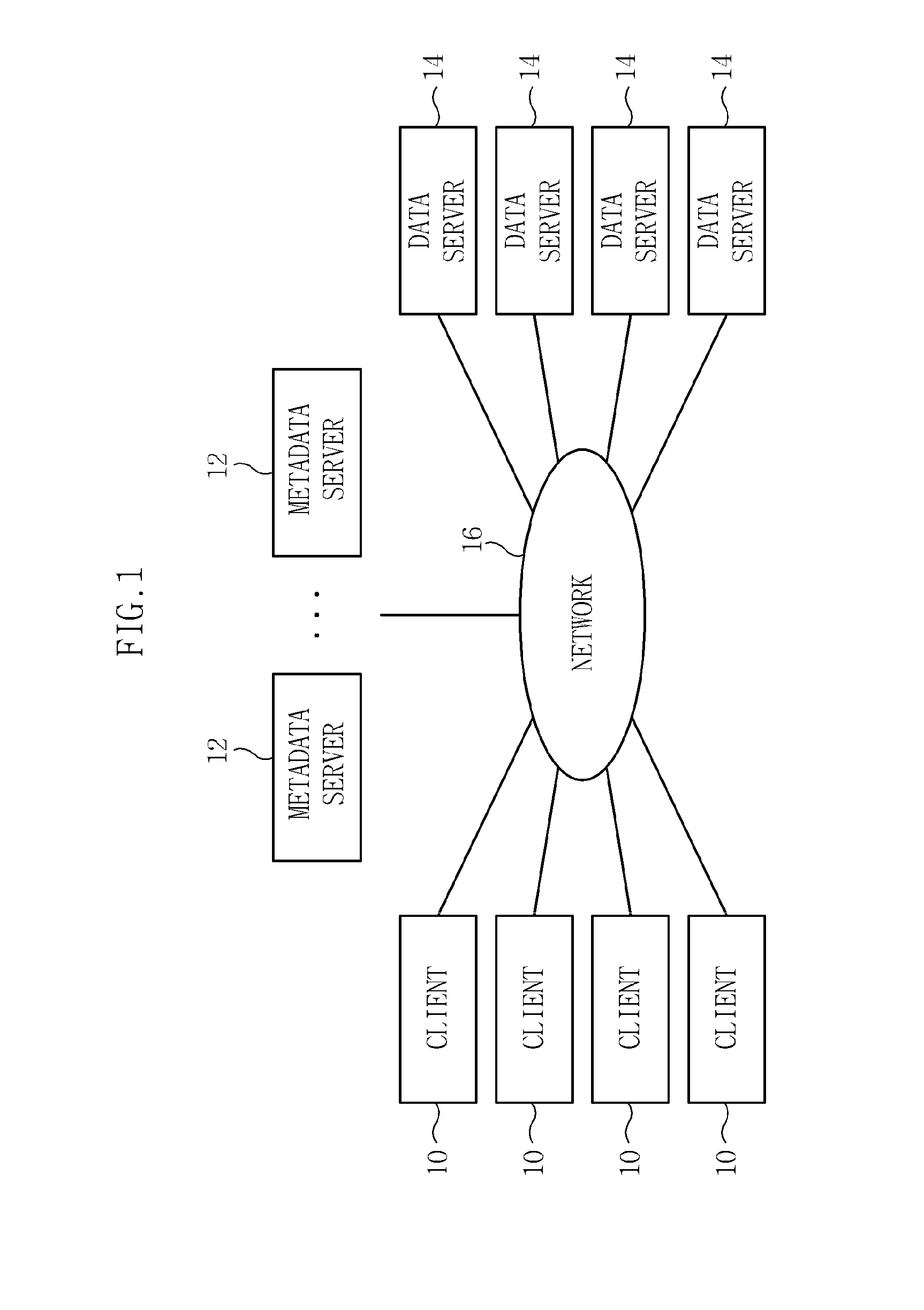
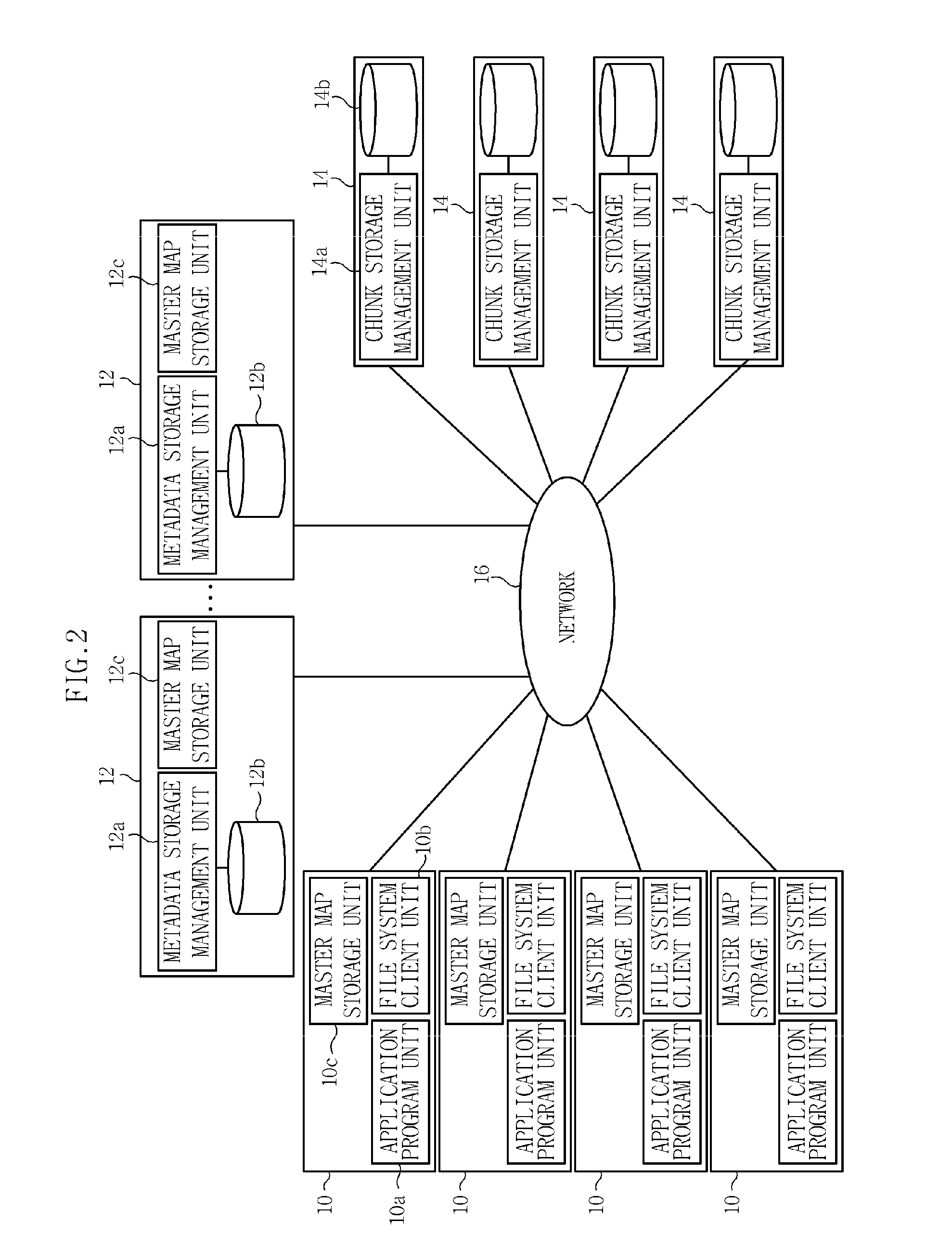
Apparatus and method of managing metadata in asymmetric distributed file system
InactiveUS20110153606A1Avoid loadImprove distributionDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsManagement unitDistributed File System
Provided are an apparatus and a method which can be easily implemented with flexibility enabling distributing all metadata of trees and files in an asymmetric distributed file system. The apparatus includes: a metadata storage unit storing metadata corresponding to a part of partitions of a virtual metadata address space storing metadata for directories and / or files for each of the partitions; and a metadata storage management unit controlling the metadata so that the metadata are stored in the metadata storage unit and manages a master map including information on the part of the partitions. Since all directories and files can be distributed to a plurality of metadata servers without a limitation, it is possible to prevent a load from being concentrated on a predetermined metadata server. Metadata roles of the metadata servers are very simply readjusted and as a result, the load can be easily distributed in a partition level.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
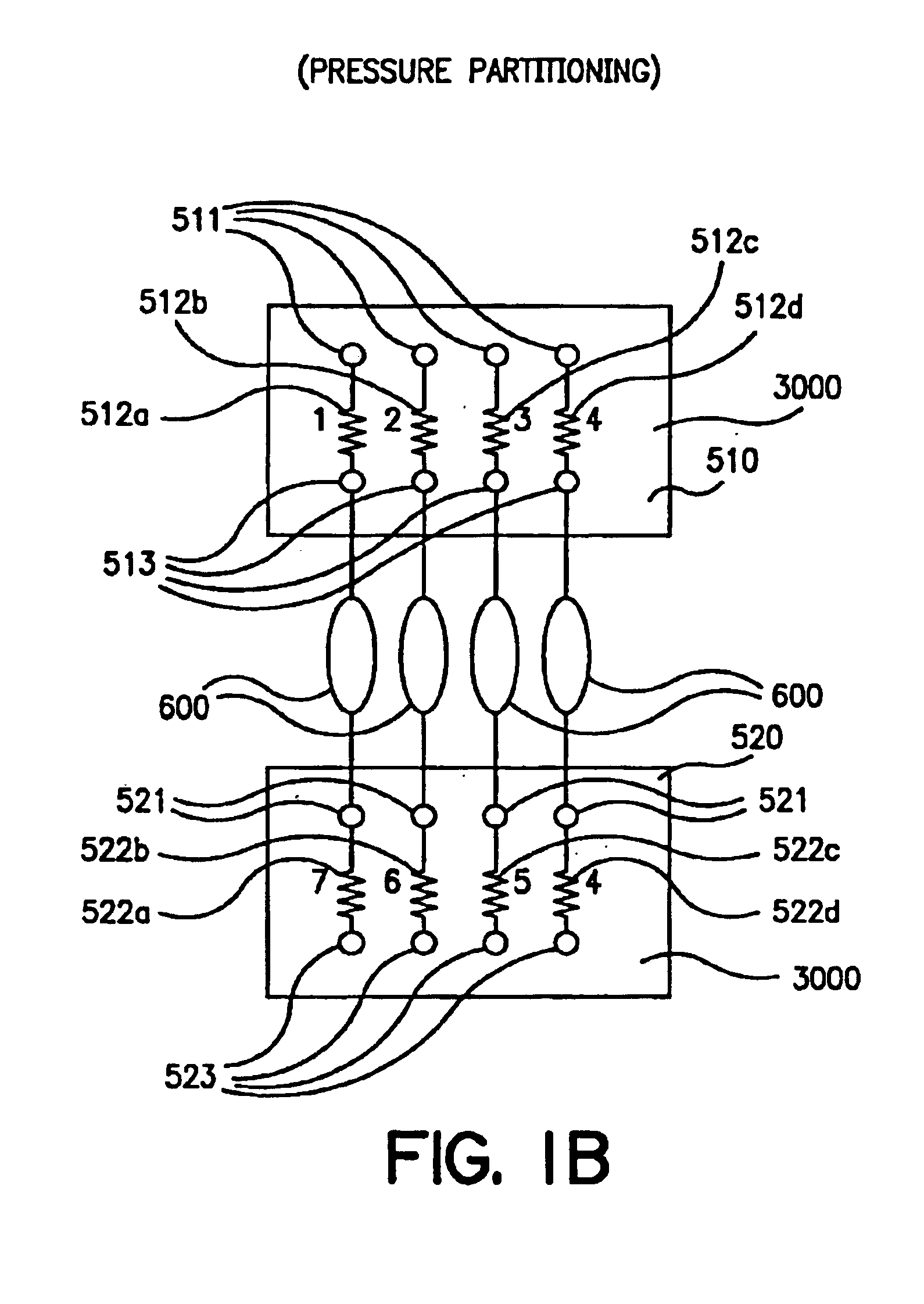
Parallel flow reactor having variable composition
InactiveUS7122156B2Efficient identification and optimizationExtreme flexibilityProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsDistribution systemProcess engineering
Owner:FREESLATE
Flexible luminescent paints
InactiveUS20100283007A1Easy to optimizeIncrease flexibilityLuminescent paintsLuminescent compositionsPolymer sciencePhotoluminescence
Flexible luminescent paints are prepared from physical blends of hybrid epoxy acrylic resins, cementicious acrylic resins and optionally pure acrylic coating resins together with monopropylene glycol, suspension additives, rheological additives and photoluminescent pigments. The luminescent paints exhibit bright, even and long-lasting photoluminescent afterglow, excellent flexibility in both thin and thick layers, and are suitable for spraying, brushing, rolling and screen printing. Optional fluorescent pigments may be utilized to give daylight coloration and up-convert the photoluminescent emissions to the fluorescent emissions color.
Owner:ROBINSON JOHN RUSSELL
Vascular filter with improved strength and flexibilty
InactiveUS20090024153A1High strengthIncrease flexibilityCannulasDilatorsVascular filterUltimate tensile strength
Owner:DON MICHAEL INT
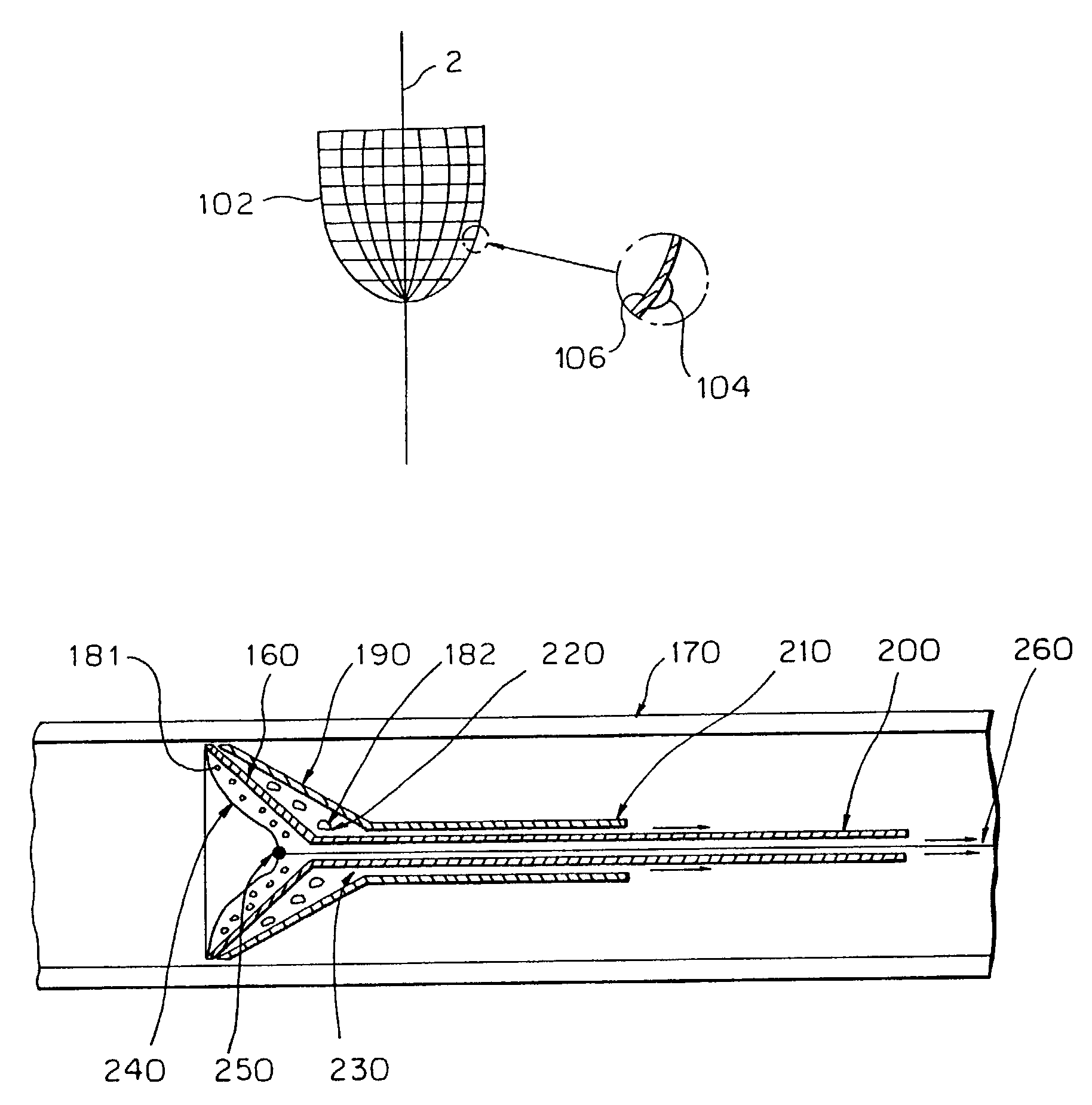
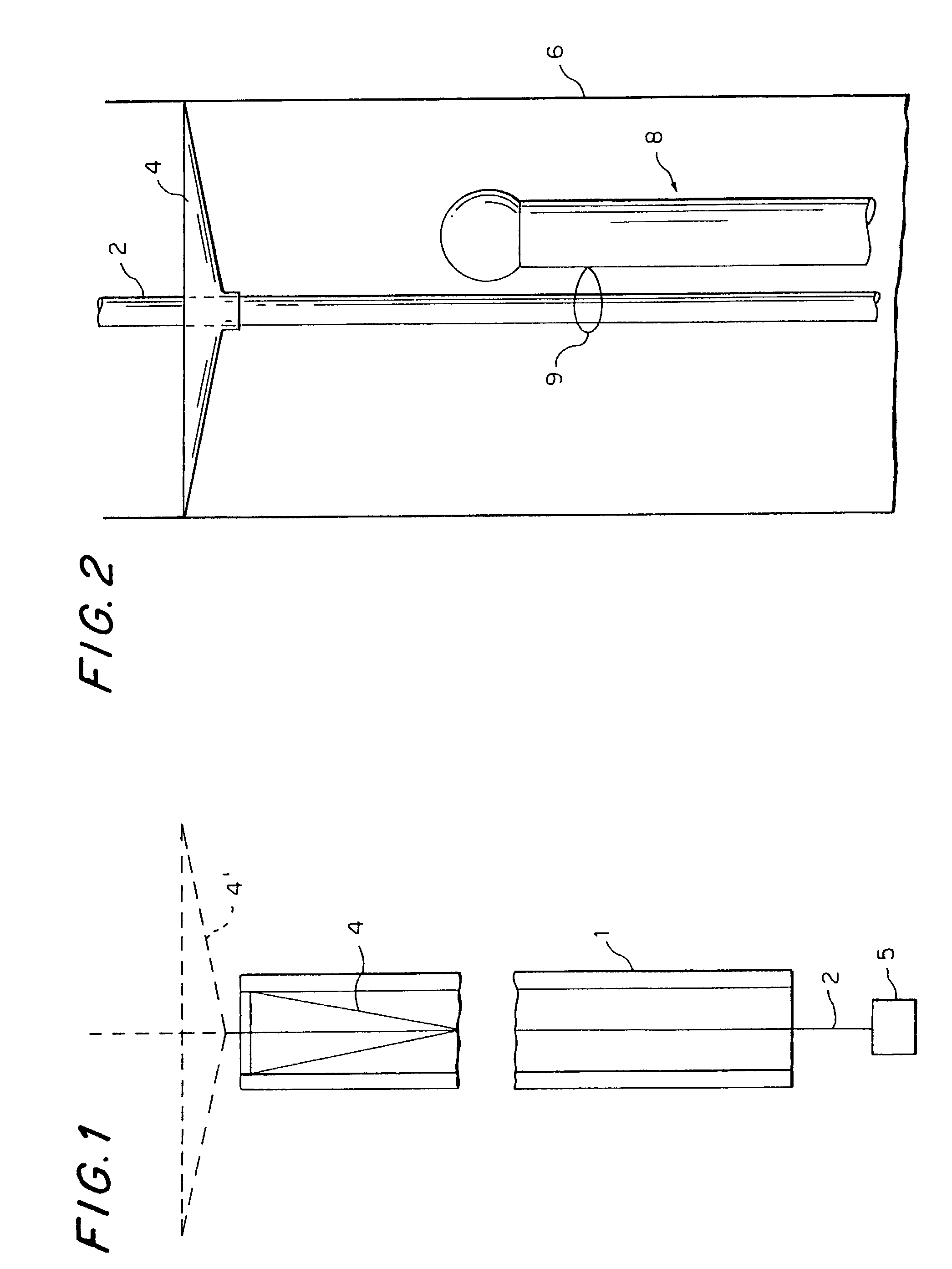
Apparatus and method for checking the attitude of a vehicle
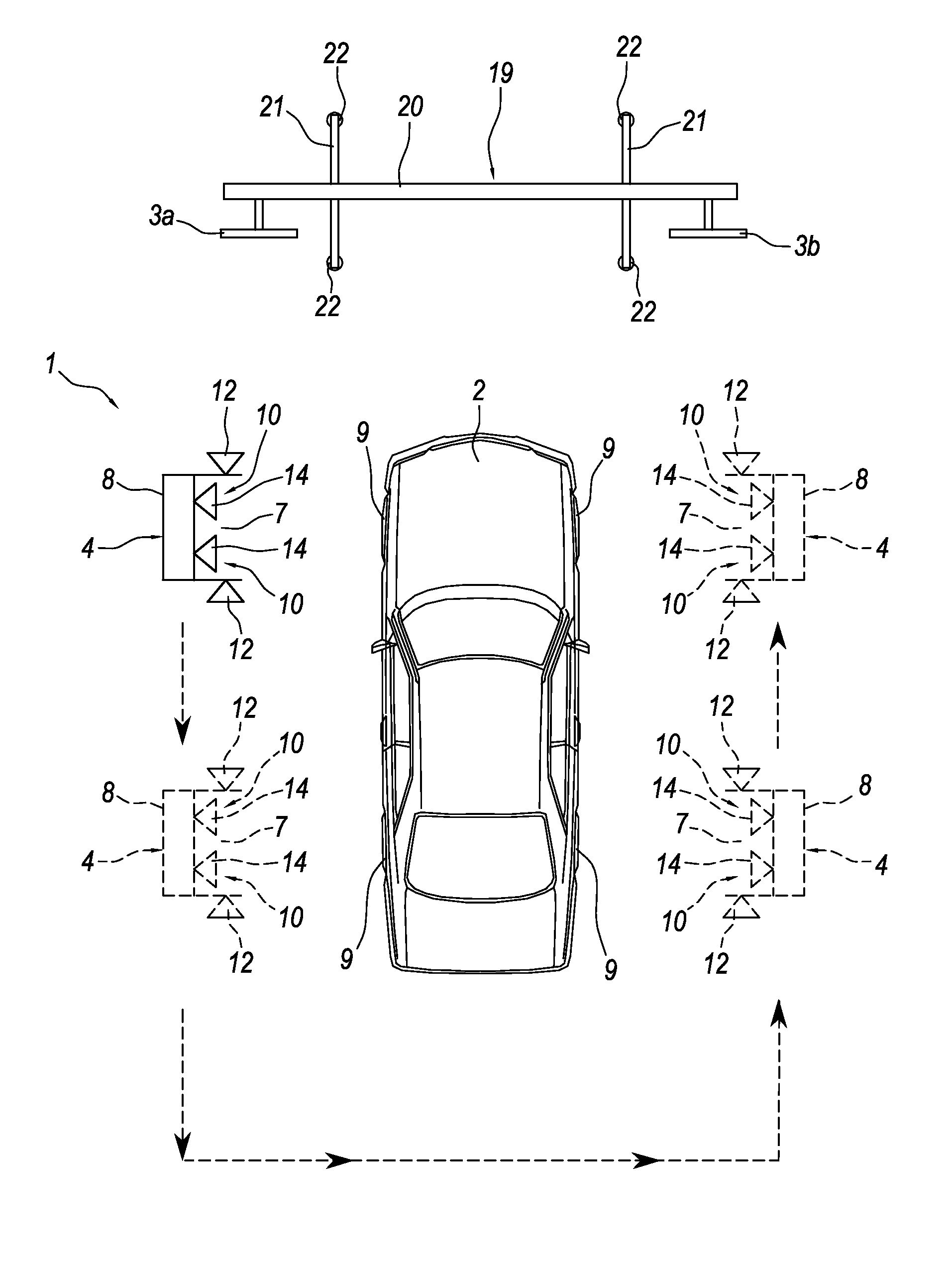
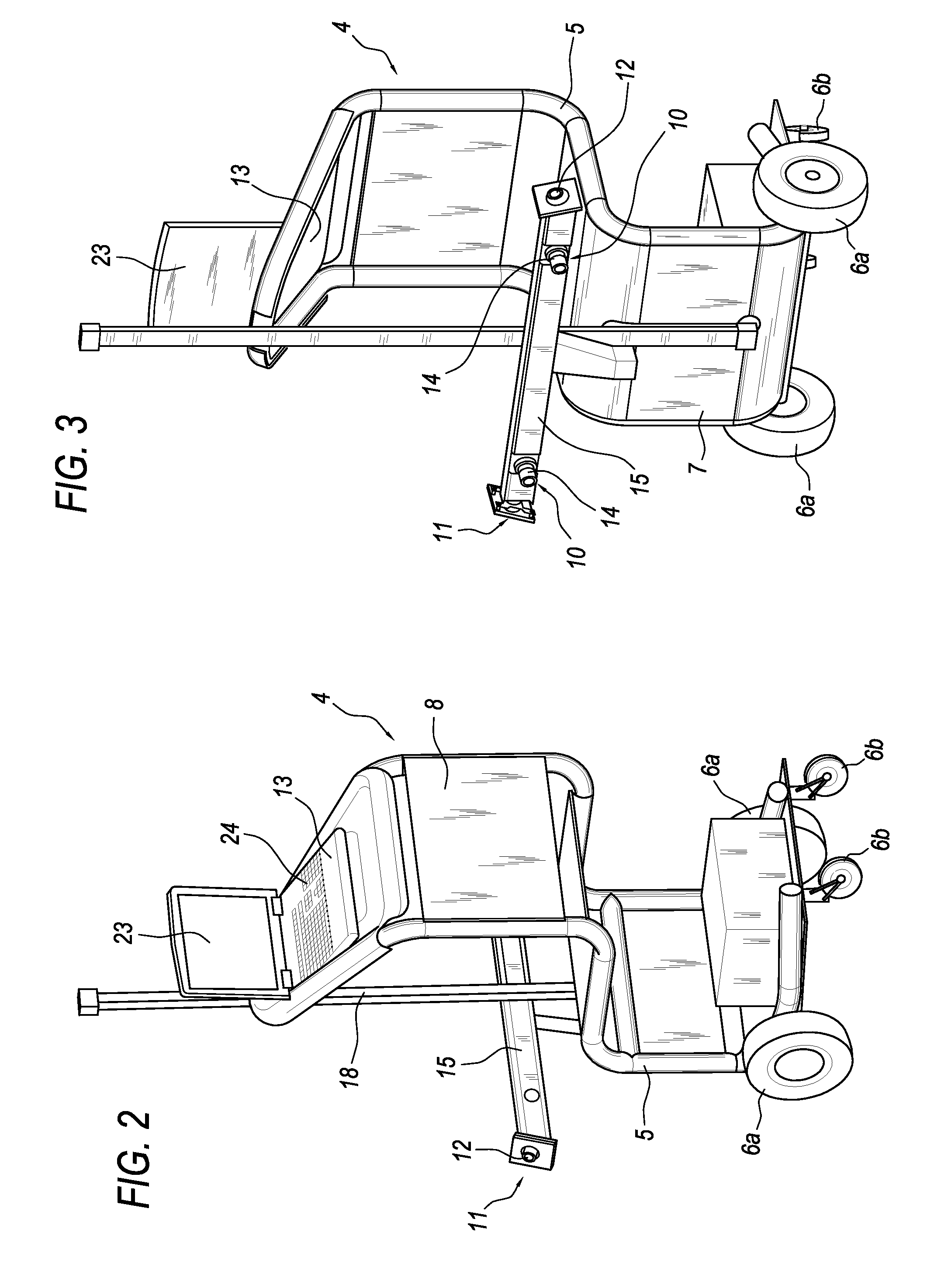
ActiveUS20110077900A1Extreme flexibilityReducing battery weightAngle measurementDigital computer detailsSpatial reference systemEngineering
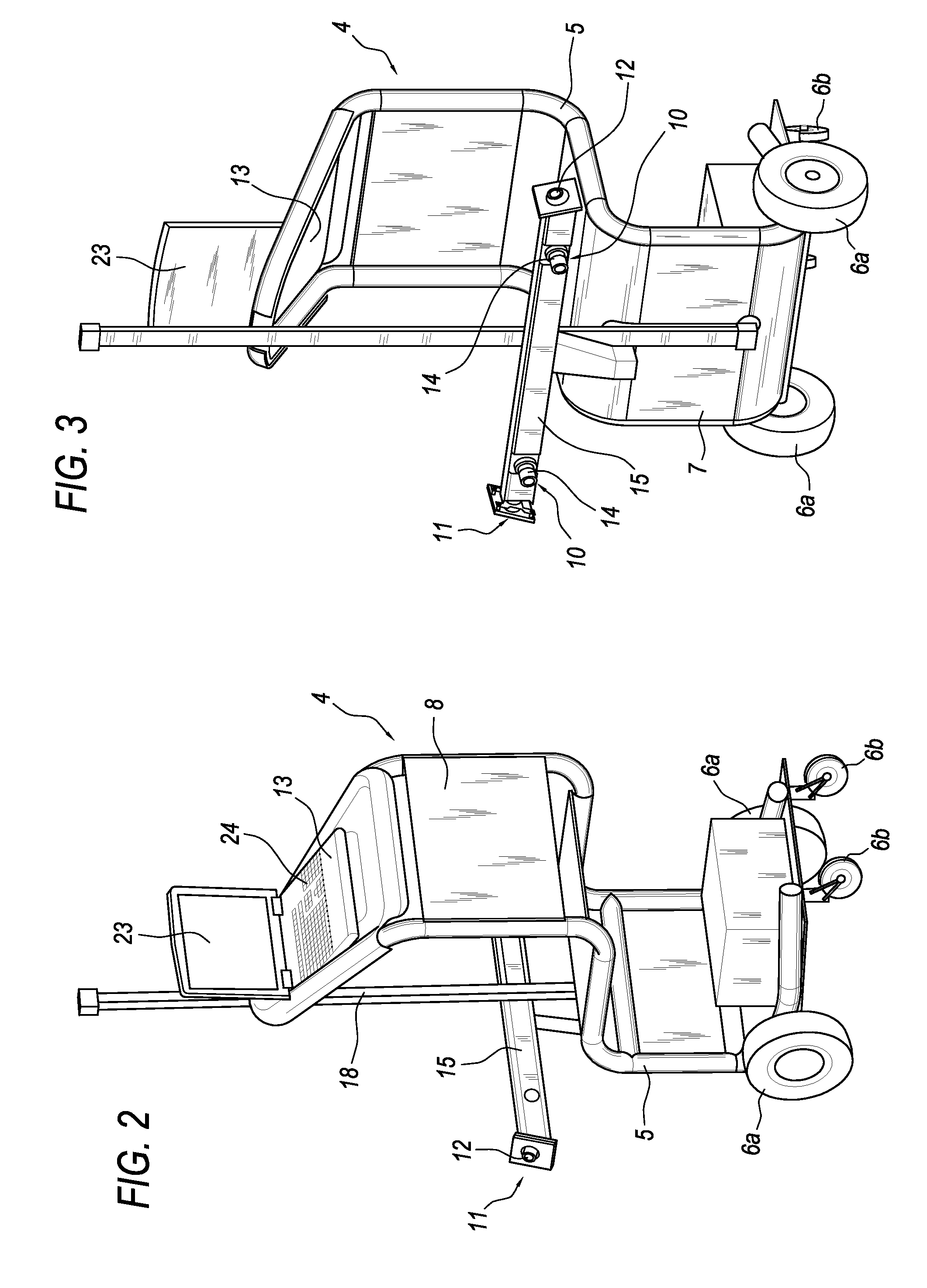
An apparatus (1) for checking the attitude of a vehicle (2) comprises: at least one target (3) defining a spatial reference system; a mobile unit (4) equipped with measuring means (10) for measuring the value of parameters representing the geometric characteristics of a wheel (9) of the vehicle (2) and its position relative to the mobile unit (4), and with means (11) for viewing the at least one target (3); a processor (13) connected to the measuring means (10) and to the viewing means (11) for calculating the position and orientation of the wheel (9) relative to the reference system and to obtain characteristic parameter values for the attitude of the vehicle (2); an interface (23) designed to make available in real time to the user driving the mobile unit (4) information relating to the position of the measuring means (10) relative to the wheel (9), the mobile unit (4) being able to be driven manually by one user to position it in proximity of (facing) the wheel (9).
Owner:NEXION SPA
Parallel flow process optimization reactor
InactiveUS7150994B2Efficient identification and optimizationExtreme flexibilityProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsProcess optimizationDistribution system
Owner:FREESLATE
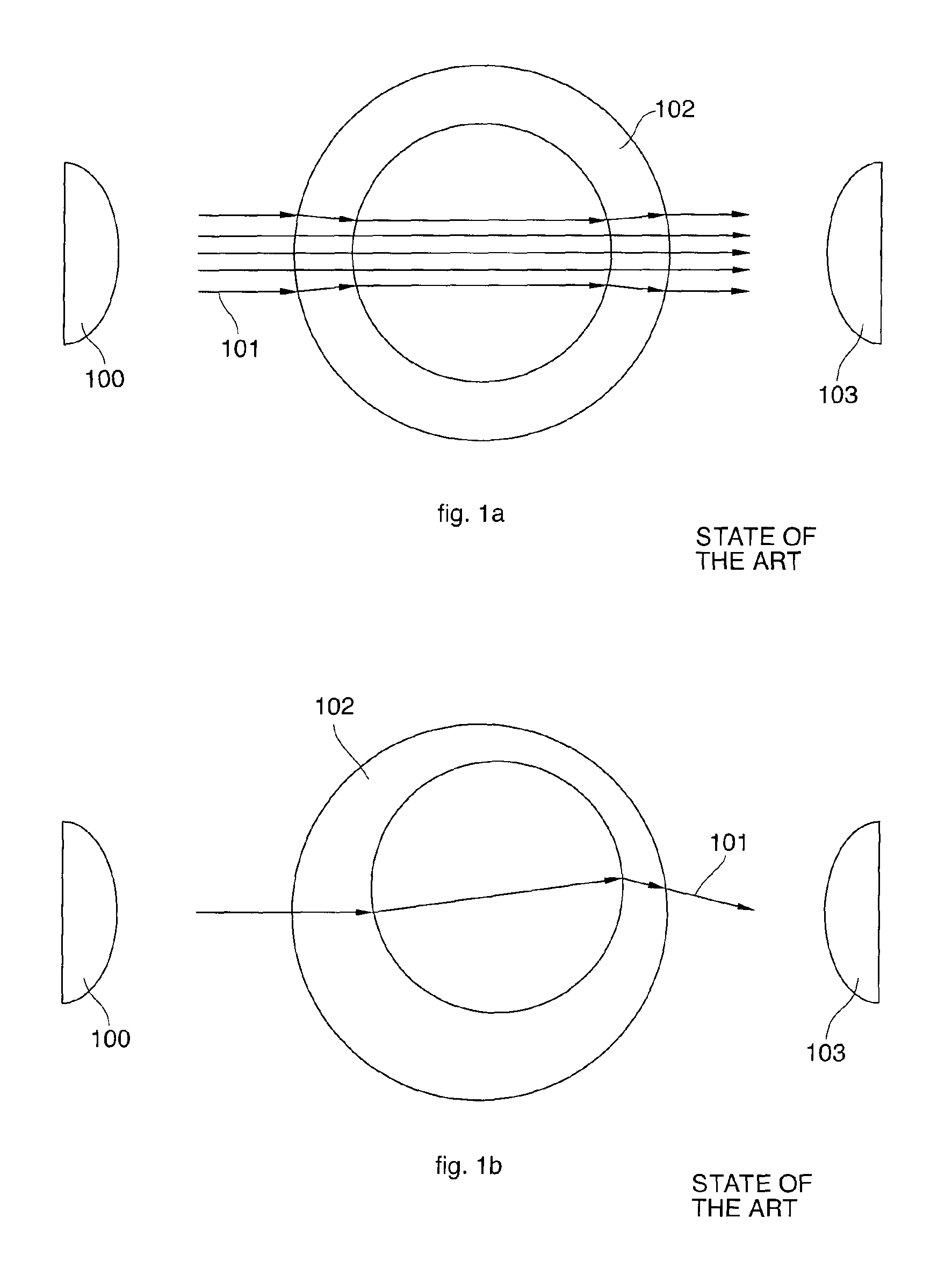
Optoelectronic probe
InactiveUS20060175192A1Powerful tool to assembleEasy to adjustElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor materialsImpedance analyzer
The present invention, referred to as optoelectronic probe, concerns a novel apparatus and method for characterization and micromanipulation of particles or biomolecules in an electrolyte solution. Electric fields, which include both time constant and time-varying components, are applied to a thin insulating layer covered, lightly doped semiconductor material. Illumination injects carriers into the insulator / semiconductor interface to compensate the leaking minority carrier current and maintain an inversion layer, which works as an electrode to control the particle movements. A particle array, or even a single cell, can be assembled in, or moved along with the inversion layer electrode, which is induced by illumination. Furthermore, an impedance analyzer is utilized to characterize the trapped particles, or single cell. The present invention has numerous uses, such as bio-chemical analysis systems, and nanosize structures assembly for electronic or optical devices.
Owner:LIN HAIAN
Delivery System for Remote Treatment of an Animal
ActiveUS20100203122A1Easy accessPromote transdermal absorptionAmmunition projectilesBiocideActive agentBiomedical engineering
A remote treatment delivery system comprising a substantially non-skin piercing dosage projectile containing a biologically active agent and a transdermal carrier.
Owner:SMARTVET
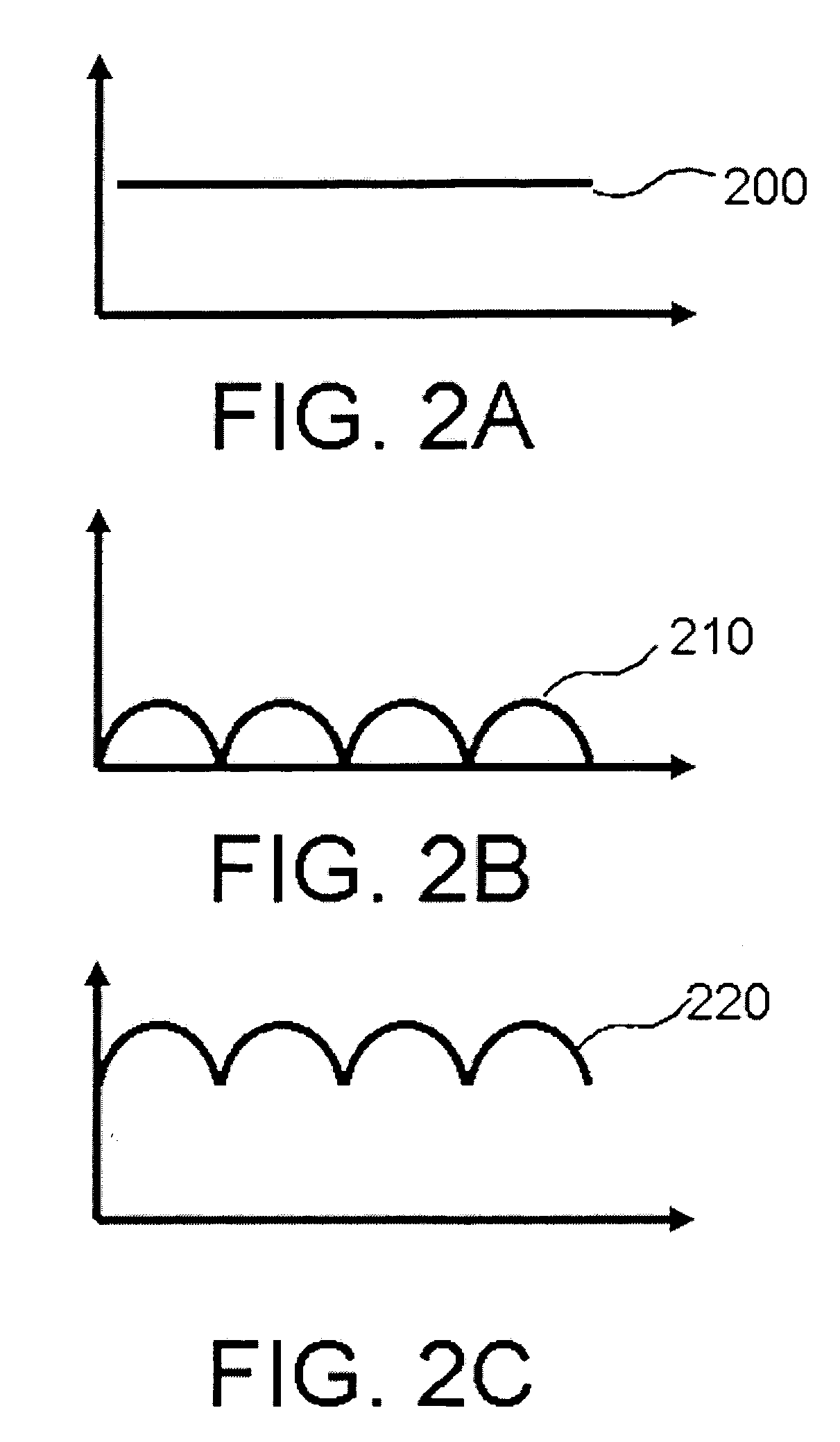
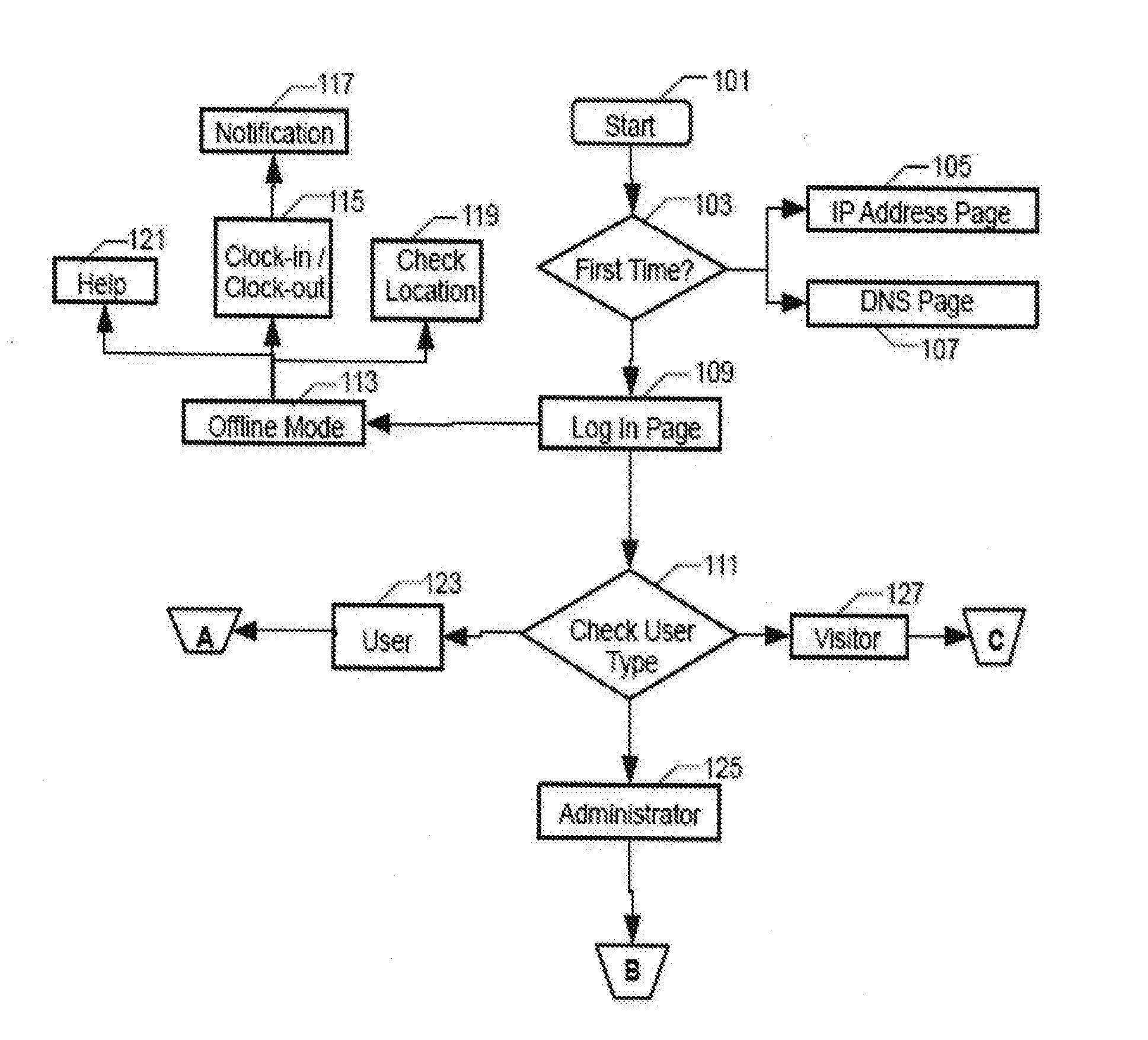
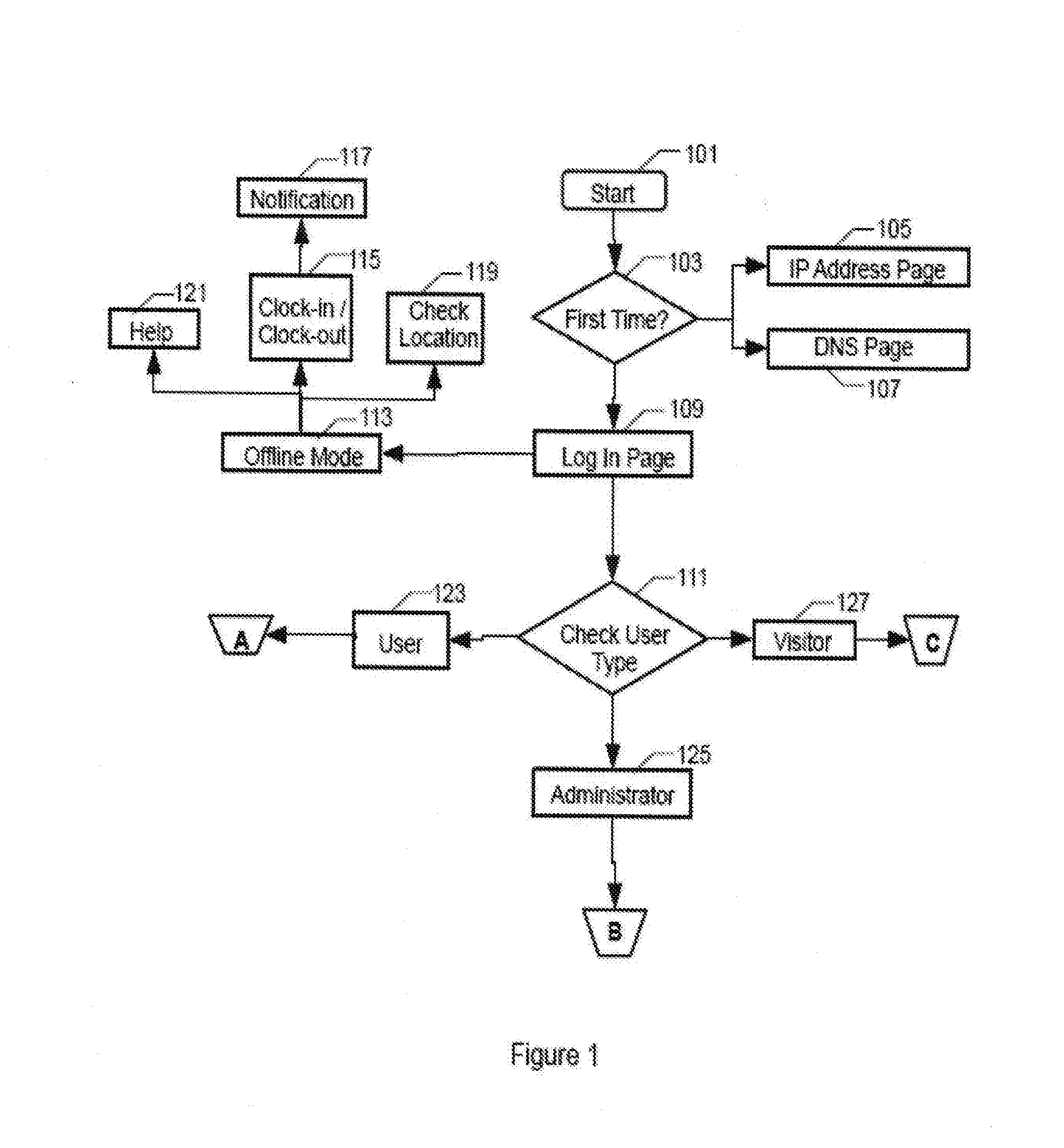
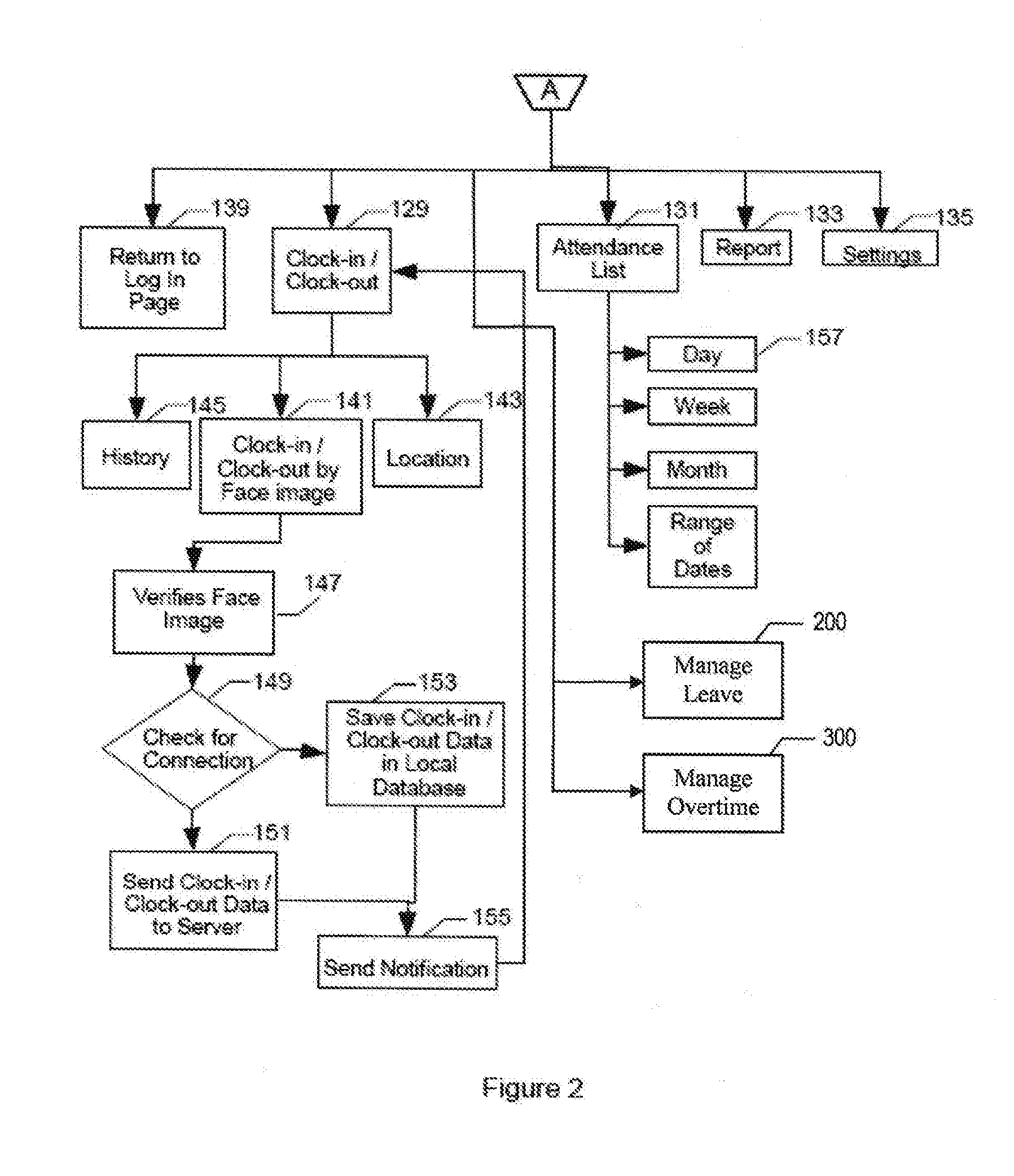
Time attendance tracking method and system
ActiveUS20160132971A1Extreme flexibilityGood motivationRegistering/indicating time of eventsFinanceHand held devicesReal-time computing
A time attendance tracking method is provided by which a hand-held device is set as a primary device and / or a secondary device based on inherent mobile identity of the hand-held device and operable in either a first mode and / or a second mode. The first mode permits the user to clock-in and / or clock-out for attendance recording for the user tied account while the second mode restricts the user to clock-in and / or clock-out for attendance recording for the user tied account.
Owner:INFORSTANDARD SDN BHD
Methods of identifying synthetic transcriptional and translational regulatory elements, and compositions relating to same
InactiveUS20070270580A1Increase transcriptionReplicate more efficientlySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideTranscriptional Regulatory Elements
Provided are methods of identifying oligonucleotides having transcriptional or translational activity by integrating ilie oligonucleotide into a eukaryotic cell genome such that the oligonucleotide is operatively linked to an expressible polynucleotide, and detecting a change in expression of the expressible polynucleotide due to the operatively linked oligonucleotide. Also provided are vectors useful for identifying an oligonucleotide having transcriptional or translational regulatory activity according to a method of the invention. In addition, isolated synthetic transcriptional or translational regulatory elements identified according to a method of the invention are provided, as are kits, which contain a vector useful for identifying a transcriptional or translational regulatory element, or an isolated synthetic transcriptional or translational regulatory element or plurality of such elements. Also provided are isolated transcriptional regulatory elements.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
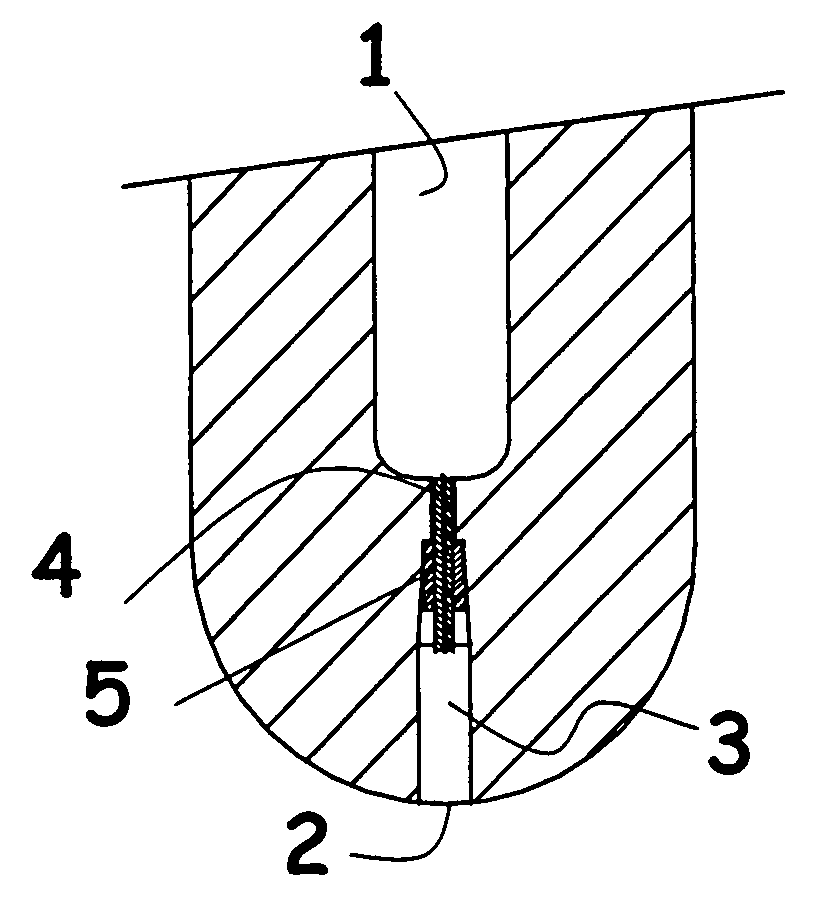
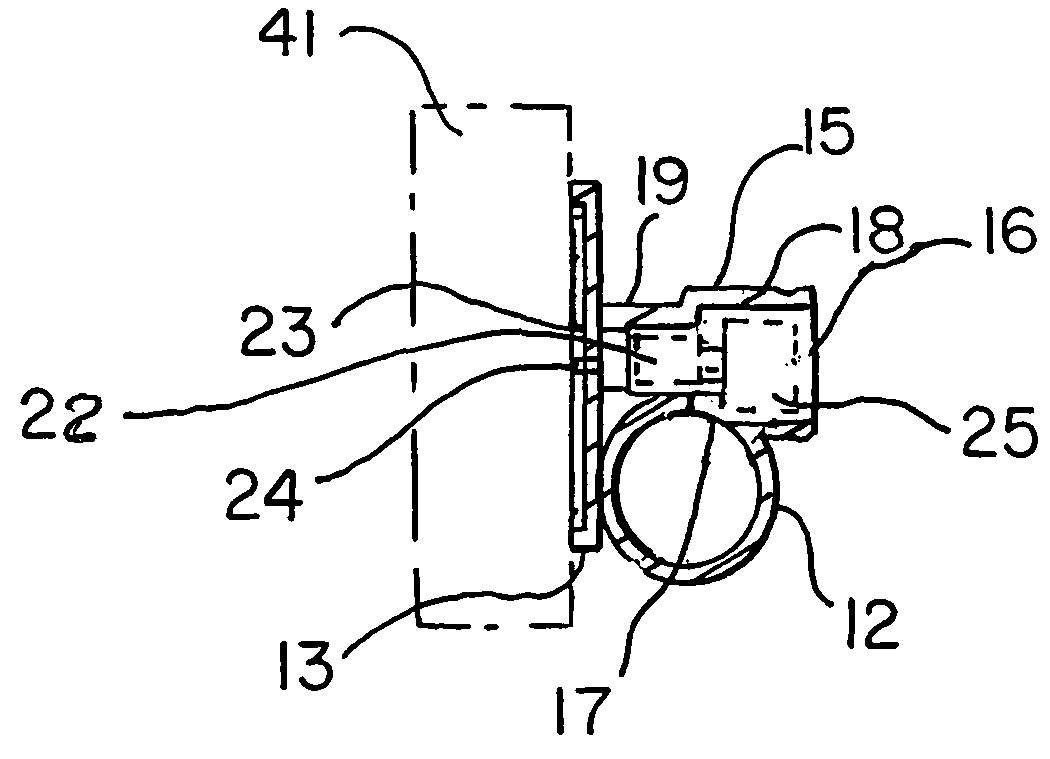
Stopper for reliable gas injection
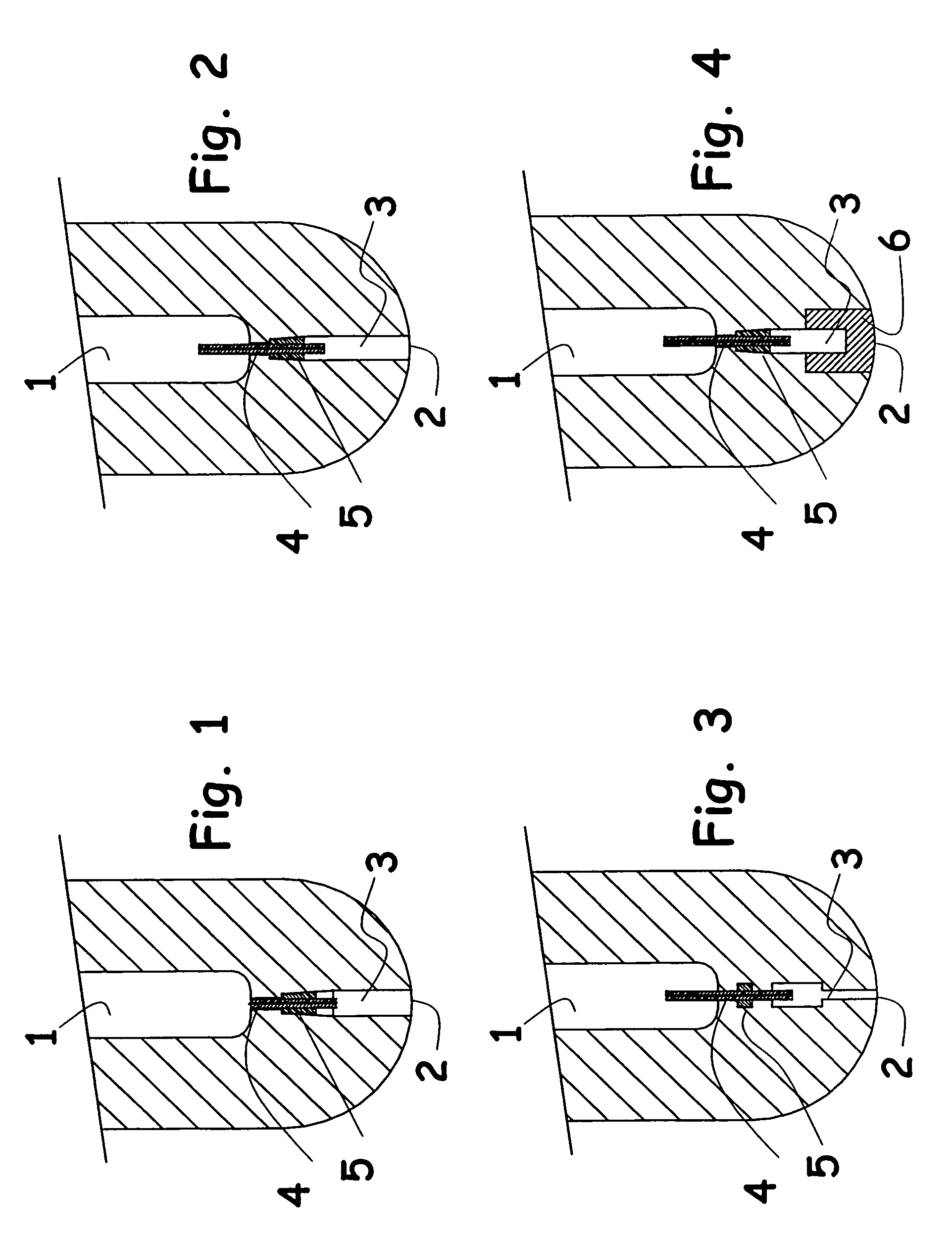
InactiveUS7198181B2Reliable and precise controlExtreme flexibilityMelt-holding vesselsLiquid flow controllersEngineeringMolten metal
The present invention concerns a mono-block stopper adapted to deliver gas during pouring of molten metal comprising a stopper body having an internal chamber (1) and a gas discharge port (2), a bore (3) connecting the internal chamber (1) to the gas discharge port (2), calibrating means (4) being provided in the bore (3) to provide a restricted path. This stopper is characterised by the fact that the calibrating means comprise a rod (4) having at least one axially-extending gas passages therealong, the gas passage(s) having a section such as to offer a predetermined resistance to flow. The stopper of the invention is far more reliable and can be easily adapted to various operational parameters.
Owner:VESUVIUS USA CORP
Apparatus and method for checking the attitude of a vehicle
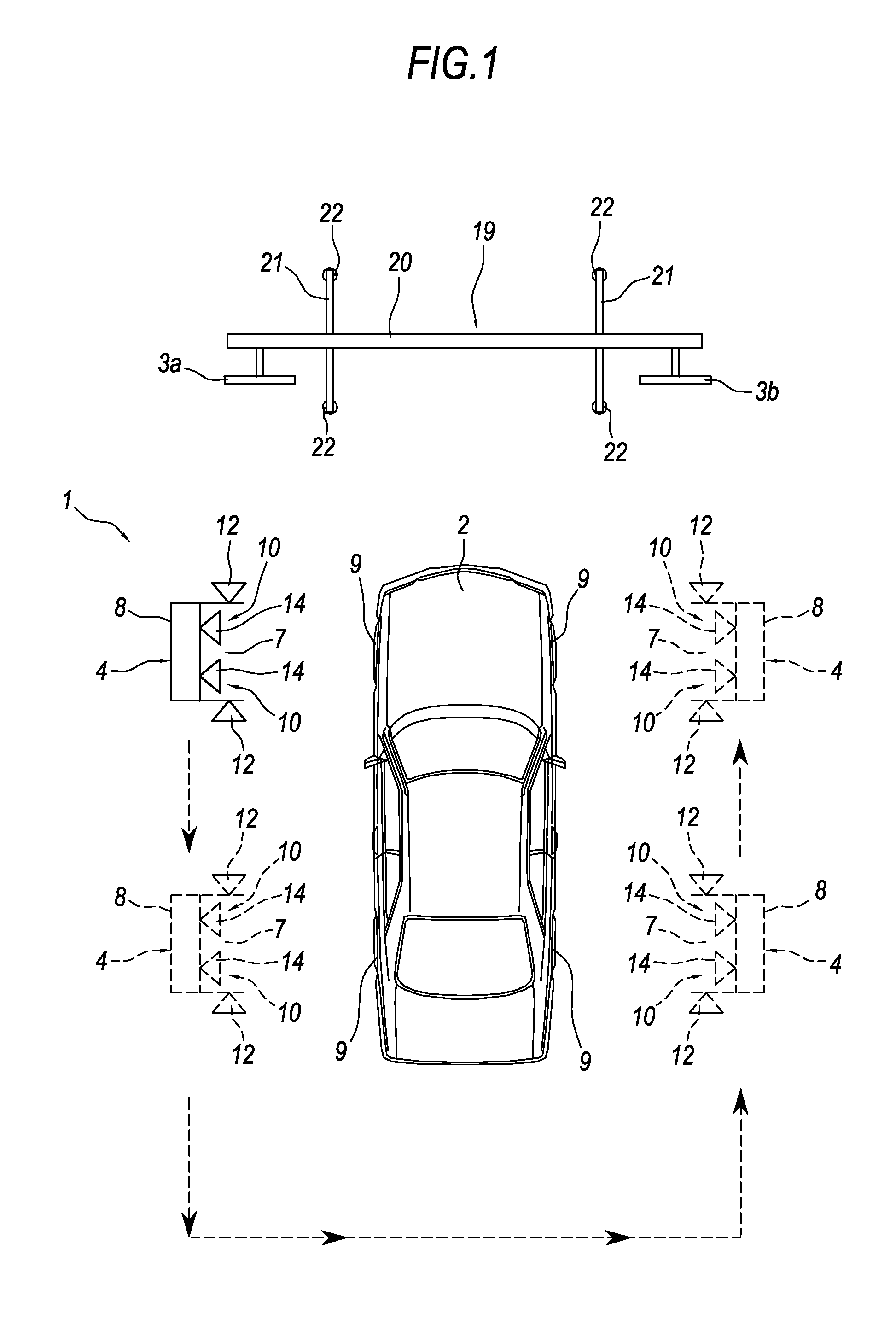
ActiveUS8538724B2Extreme flexibilityReduce weightAngle measurementDigital computer detailsSpatial reference systemUser driven
An apparatus (1) for checking the attitude of a vehicle (2) includes: at least one target (3) defining a spatial reference system; a mobile unit (4) adapted for measuring the value of parameters representing the geometric characteristics of the wheels of the vehicle (2), and for viewing the target (3); a processor (13) is connected to a camera (14) mounted on the mobile unit, for calculating the position of the wheel (9) relative to the reference system to calculate the attitude of the vehicle (2); an interface (23) is provided, designed to make available in real time to the user driving the mobile unit (4) information relating to the position of the camera (14) relative to the wheel (9), wherein the mobile unit (4) can be driven manually by a user to be positioned in proximity of the wheel (9).
Owner:NEXION SPA
Method and apparatus for removal of pigs, deposits and other debris from pipelines and wellbores
ActiveUS8479821B2Extreme flexibilityExtreme serviceHollow article cleaningCleaning apparatusWellboreNozzle
A carrier assembly having at least one sealing cup, a fluid bypass and adjustable wash nozzles, as well as a spear assembly having a central through bore, are attached to the distal end of a length of continuous tubing and inserted in to the flow bore of a pipeline. Fluid is pumped through the annular space between the carrier assembly and the pipeline, providing motive force for advancing the carrier assembly within the pipeline. Fluid can bypass the carrier assembly, enter the central bore of the spear assembly, and return to the surface through the central bore of the continuous tubing. A stuck pig or other obstruction is speared, and thereafter retrieved from the pipeline on the continuous tubing.
Owner:GIBSON IP LLC
Apparatus and Method to Determine the Blood Sedimentation Rate and Other Parameters Connected Thereto
ActiveUS20150300937A1Maximum sensitivityExtreme flexibilityMaterial analysis by optical meansSedimentation analysisPlastic materialsLight beam
An apparatus to determine the blood sedimentation rate and other parameters connected thereto, carried out by emitting, by means of emitter means, a beam of radiations which passes through a sample being examined, and by detecting, by means of receiver means, the beam of radiations after they have passed through said sample, comprising a reading chamber associated to at least a tube connected to a feed of the sample to be analyzed. Said reading chamber is at least partly transparent to radiations in a certain range of wavelengths, and has at least a substantially rectilinear segment of reduced size into which the sample to be analyzed is introduced. The reading chamber consists of a tube made of plastic material, or glass, defining a capillary channel coupled to said tube in fluidic continuity.
Owner:ALIFAX
Delivery system for remote treatment of an animal
ActiveUS8425932B2Easy accessPromote absorptionAmmunition projectilesBiocideTreatment deliveryMedicine
A remote treatment delivery system comprising a substantially non-skin piercing dosage projectile containing a biologically active agent and a transdermal carrier.
Owner:SMARTVET
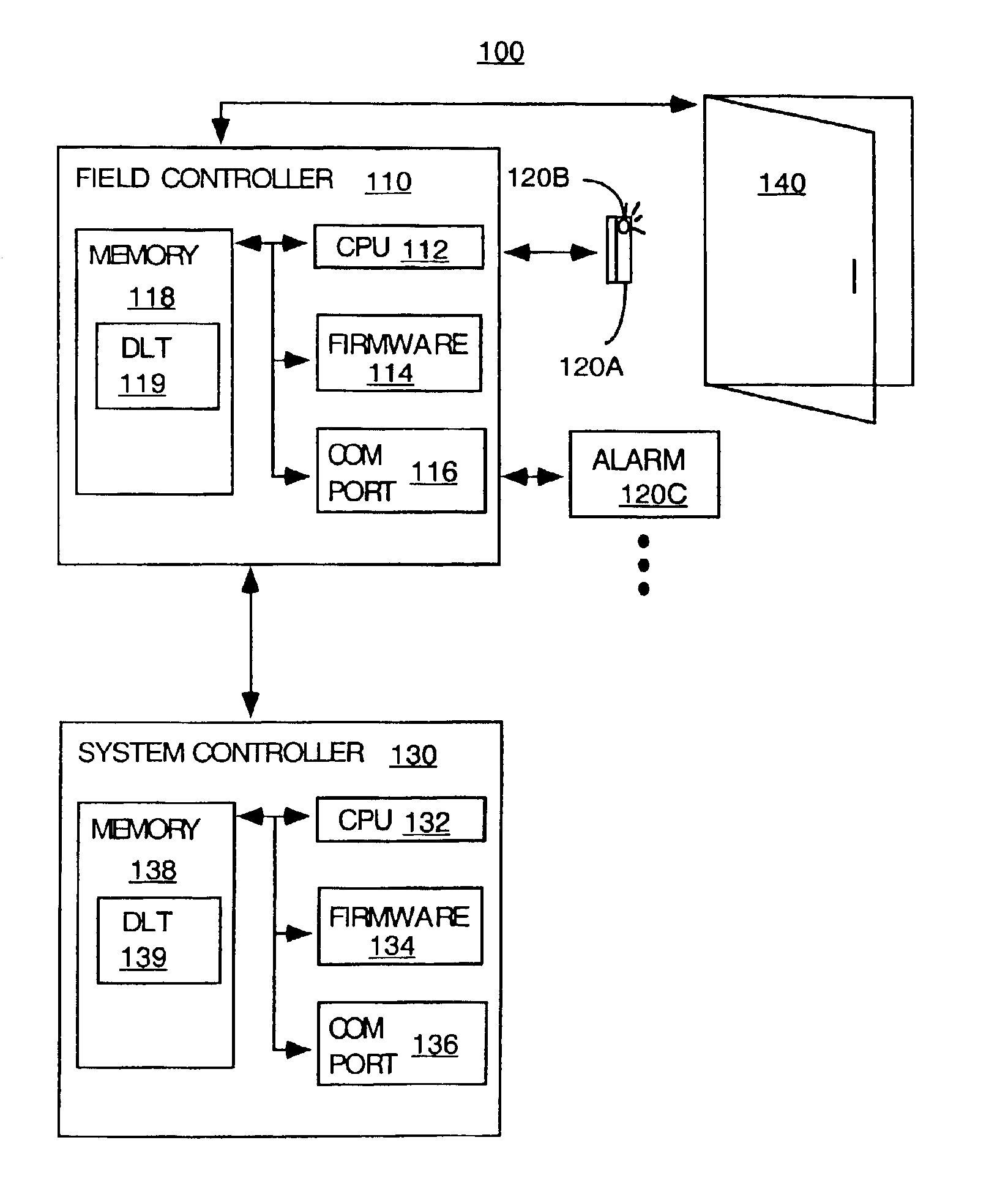
Method and apparatus for providing a dynamically programmable field controller
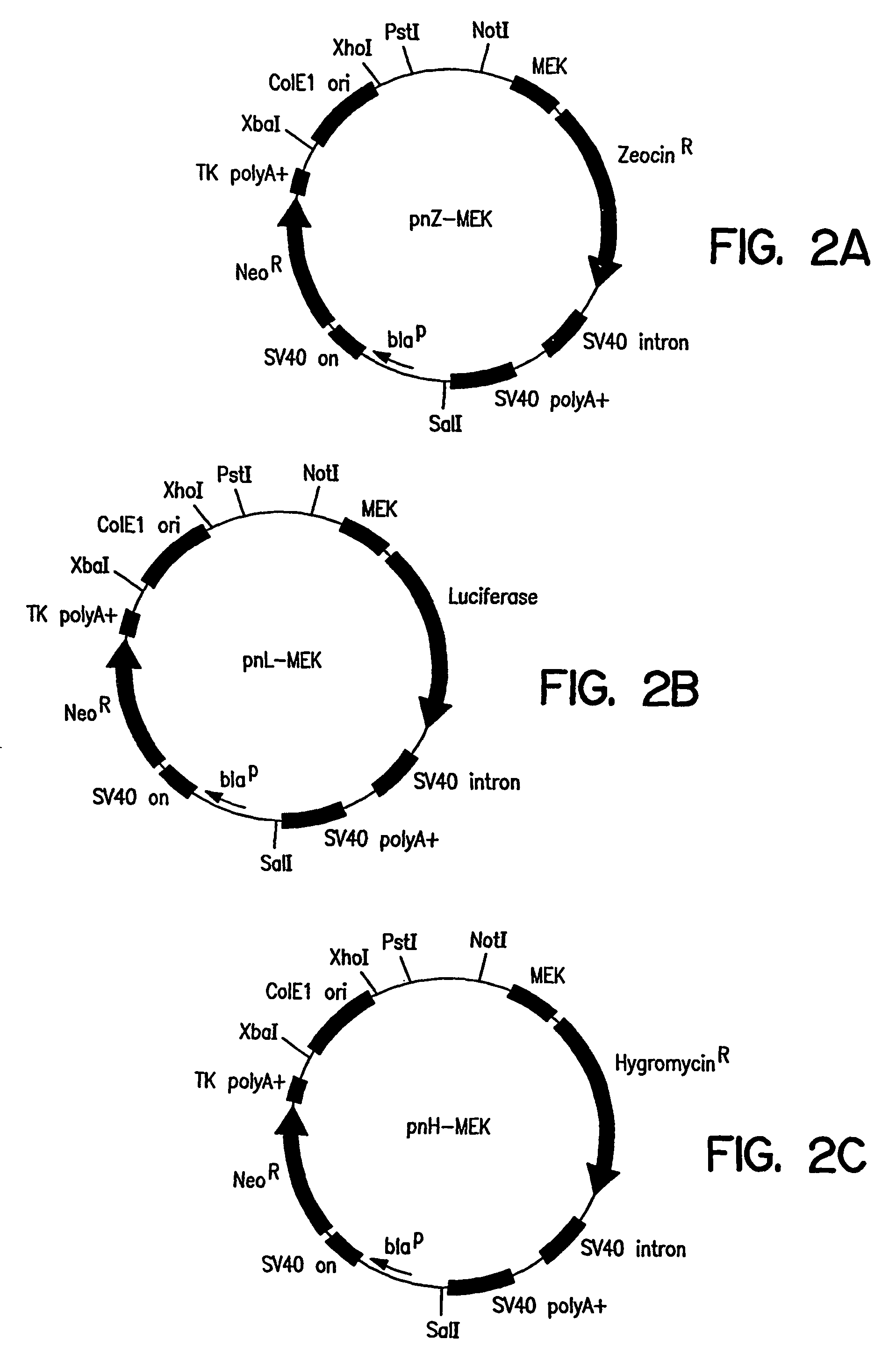
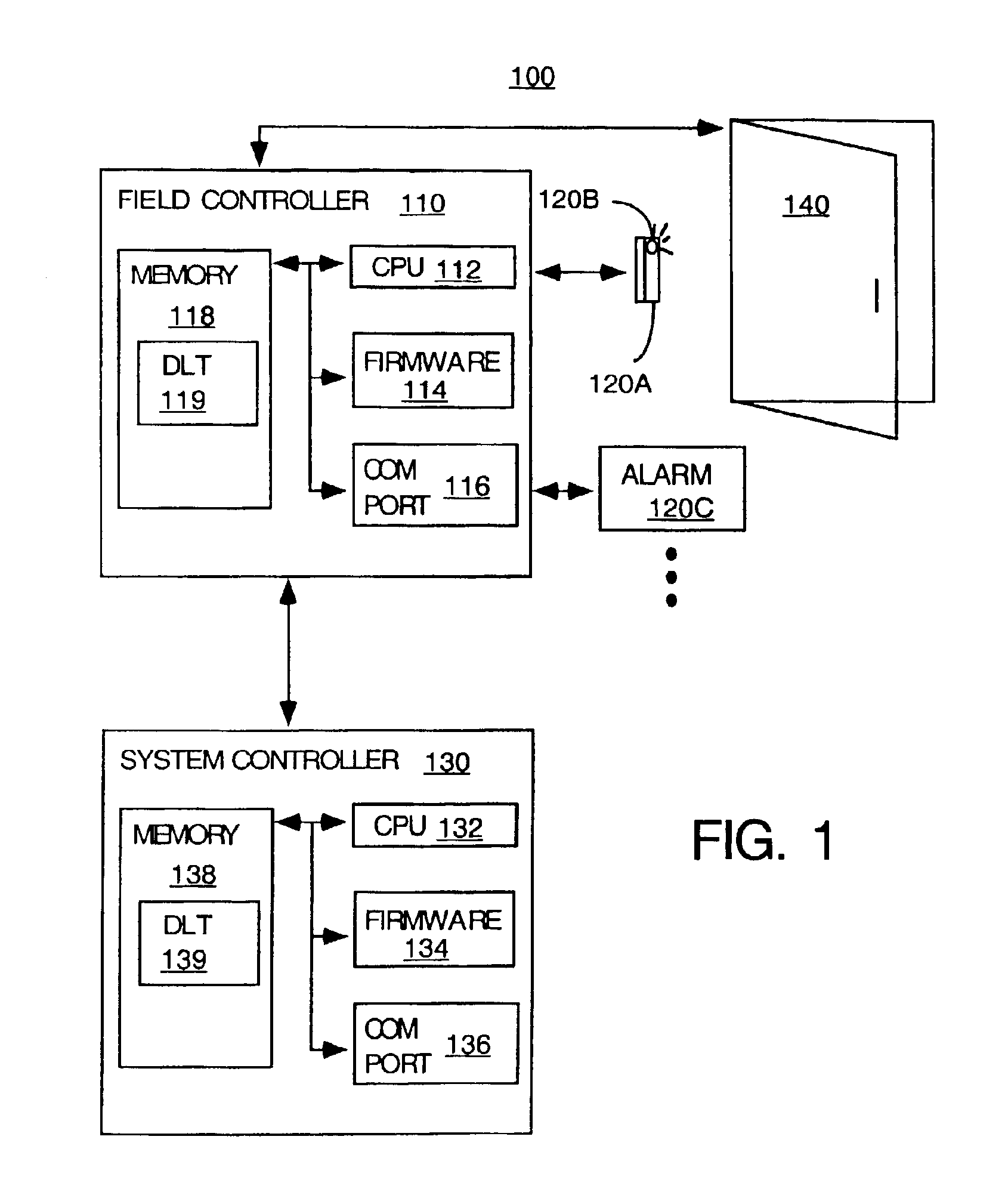
InactiveUS6925337B2Extreme flexibilityComputer controlSimulator controlProgrammable logic controllerField device
A method and apparatus is disclosed that provides a process whereby the parameters and / or functions of a hardware field device, e.g., field controller, can be altered dynamically by the use of a downloadable data table. This programming method is being called “Full Dynamic Linking” (abbreviated as FDL), and provides a mechanism by which software and firmware is written in such a way as to provide extreme flexibility in the application of control processing.
Owner:OLTIS SECURITY SYST INT
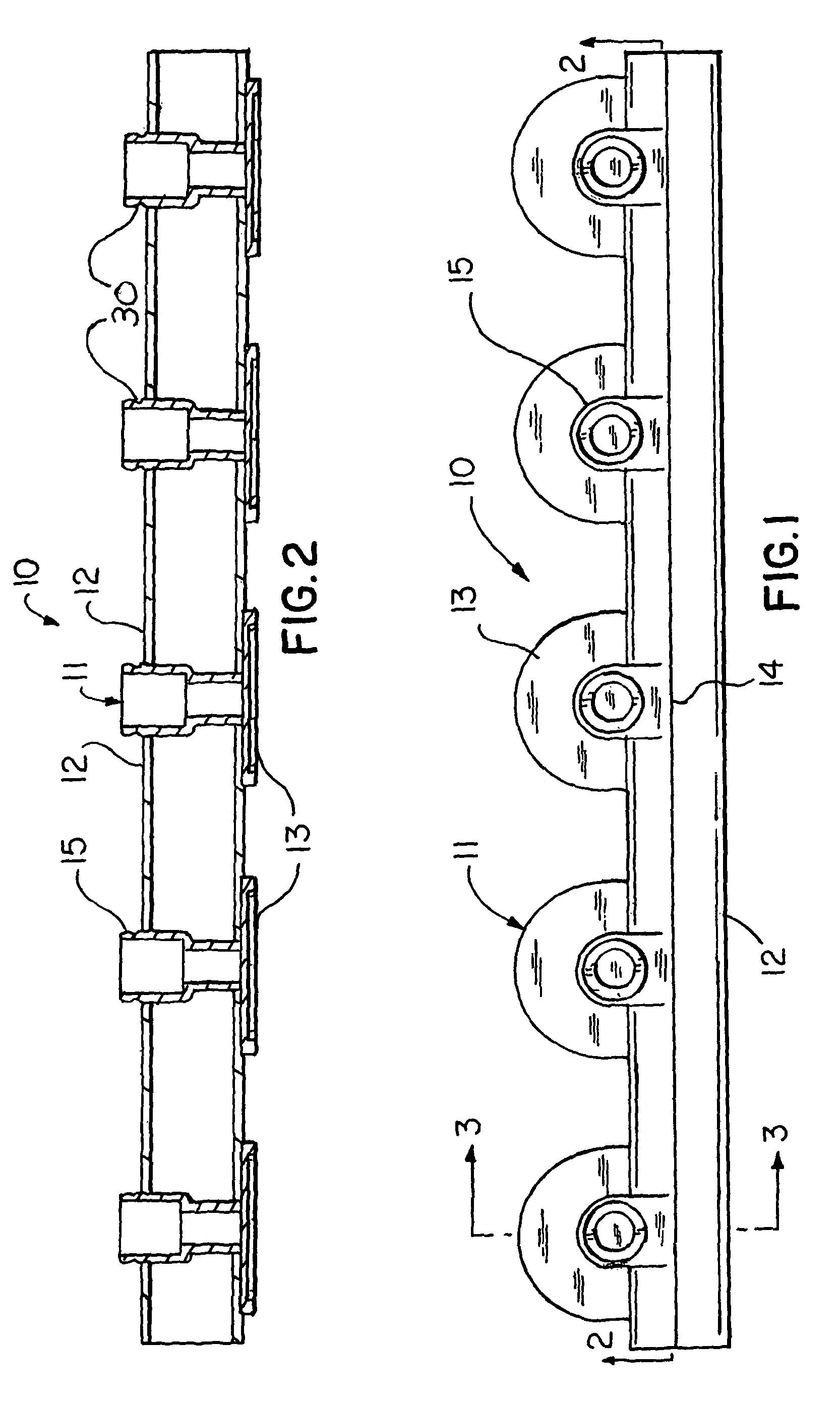
Air injector system apparatus and methods for a tub or spa
Apparatus and methods include an array of a plurality of individual air injector nozzles are integrally connected to a common air flow tube. The individual nozzles include an integral attaching plate and an integral air injector tube in addition to the common air flow tube with the individual nozzles spaced along the common air flow tube. A plurality of arrays can be joined together to form an entire arrangement of any desired configuration of individual air injector nozzles that can be applied as a complete unit to a tub or spa. One or more of the arrays can be cut across the common air flow tube to achieve the exact number of individual nozzles required in accordance with the desired arrangement of air injector nozzles. The arrays, including the cut arrays can be joined together at a location other than at the tub or spa and then transferred as a complete unit to be attached to the tub or spa. The plurality of arrays can be joined by a straight or angled connector fitting that can comprise a separate connector fitting or an individual air injector nozzle having air flow tubes arranged in the straight or angled configuration.
Owner:BEDARD PAUL R
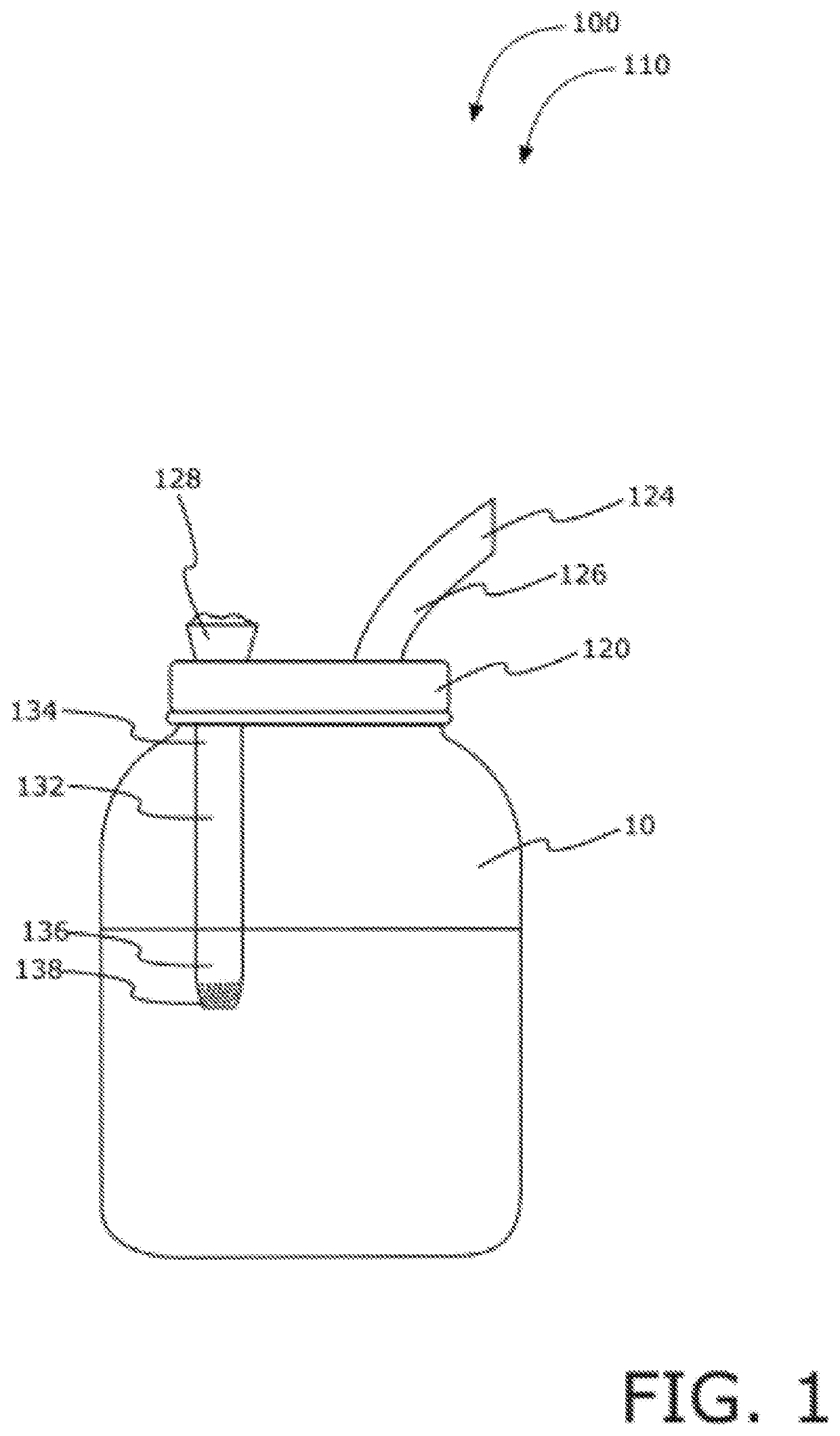
Universal bong lid adaptor system
A universal bong lid adaptor system including an adaptor assembly having a flexible body, a mouthpiece, an opening, and a tubular member having a first-end and a second-end. The adaptor assembly includes the flexible body configured to engage a top lip of a container with the tubular member extending downwardly into the container and the mouthpiece extending upwardly from the container. The device allows a user to transform a container into a smoking device for smoking smokable material.
Owner:LIU I JUEI +1
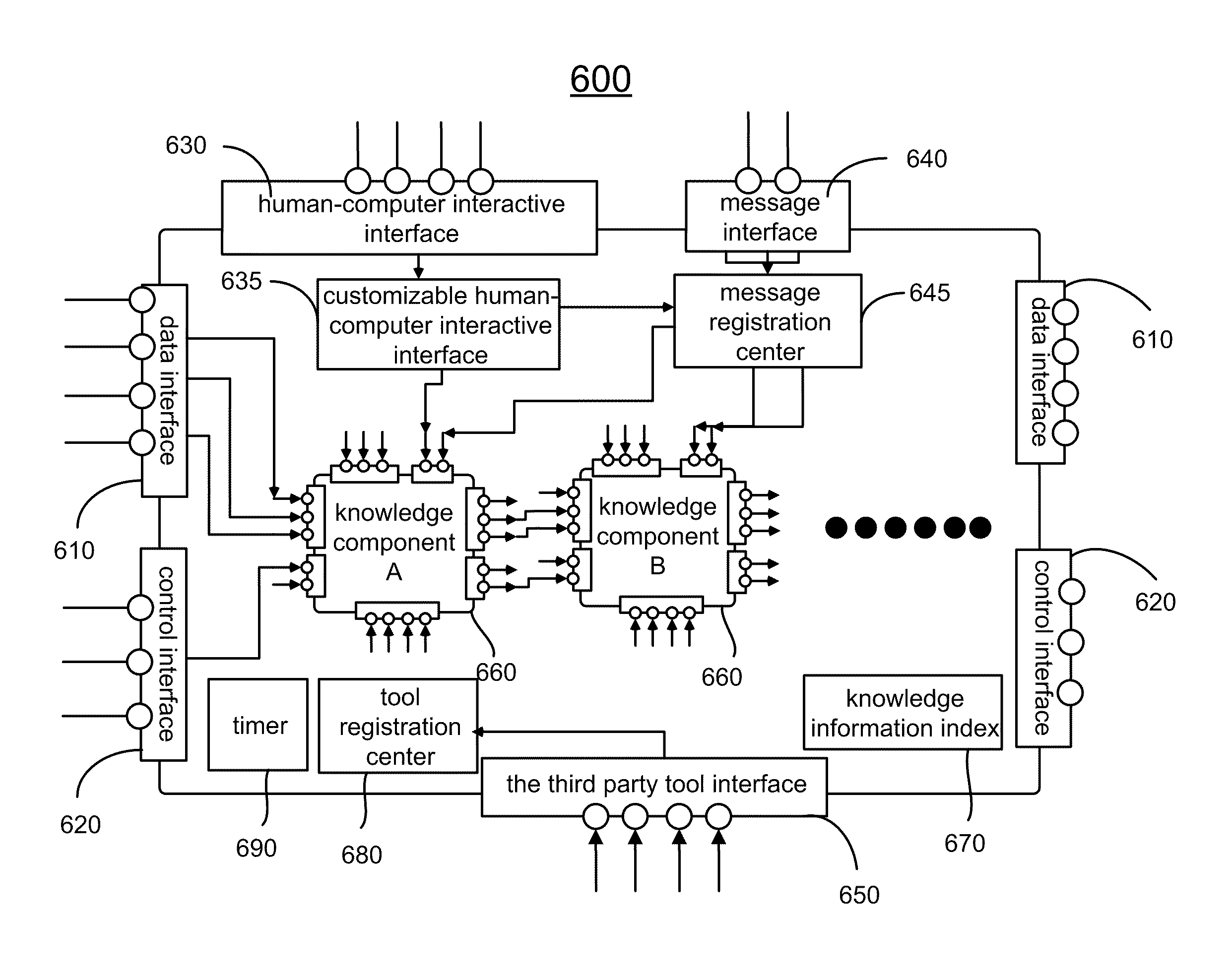
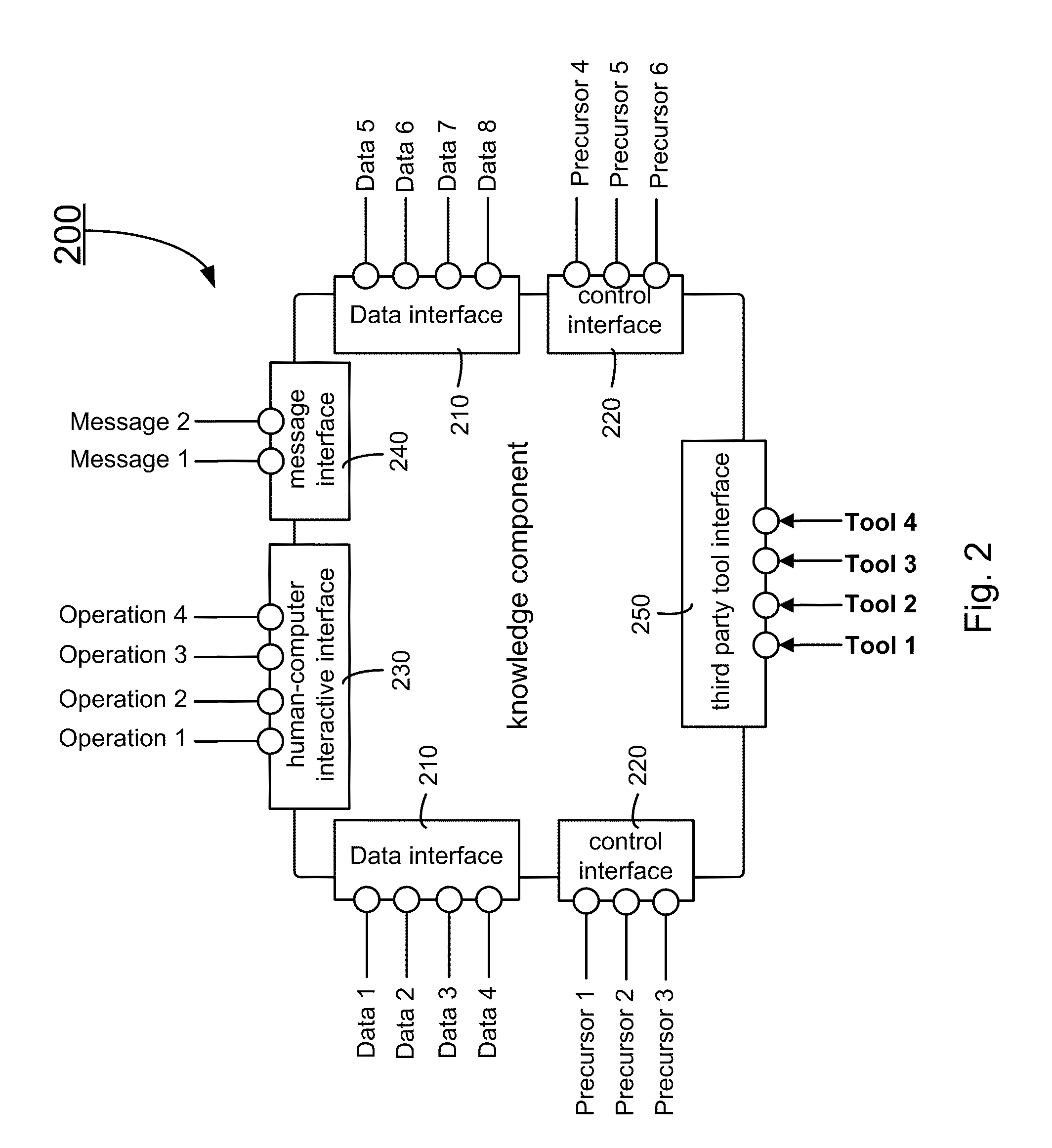
Method and system of knowledge component based engineering design
ActiveUS8060458B2Reduce workloadImprove work efficiencyConfiguration CADKnowledge representationEngineering design processStandard form
The present invention relates to an engineering design method and a system of implementing same. In one embodiment, the method includes a construction process of knowledge components and a design process based on the knowledge components. The knowledge components pack universal modules in the standard forms. Accordingly, the knowledge components are independent from design layouts or design processes of products, and reusable in different projects and platforms. The design process integrates a variety of software platforms via a uniform environment and calls the knowledge components to complete the engineering designs. Further, the design process defines a data relation and an execution relation of the knowledge components and establishes a relationship between the knowledge components without programming. The universal module comprises at least operations, methods, rules and / or flows of an engineering design process and engineering analysis process.
Owner:SYSWARE TECH CO LTD
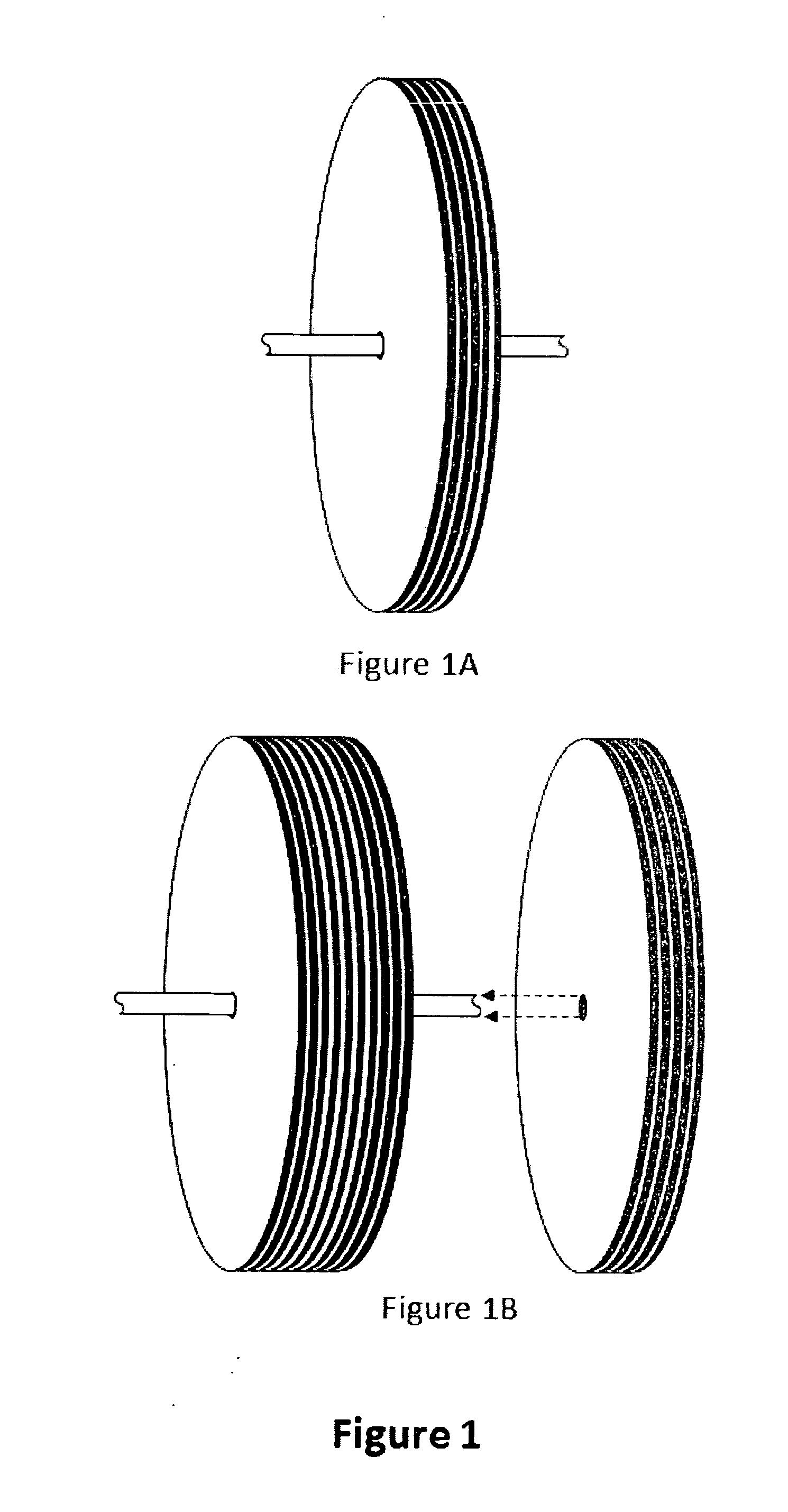
Hybrid metal fiber flywheel
InactiveUS20140260780A1Improve functionalityImprove structural performanceFlywheelsMechanical energy handlingHigh densityMetal fibers
An energy storage flywheel whose energy storage capacity has been enhanced by the use of circumferentially applied composite fibers. The use of high density metal wafers being laminated with isolating low density laminations ensures maximum energy storage for a given mass and safely limits instant total energy release or the ejection of failed objects upon the event of a mechanical failure.
Owner:SIMONS GERALD FR
Apparatus and method to determine the blood sedimentation rate and other parameters connected thereto
ActiveUS9494507B2Maximum sensitivityExtreme flexibilitySedimentation analysisBiological testingPlastic materialsReduced size
Owner:ALIFAX
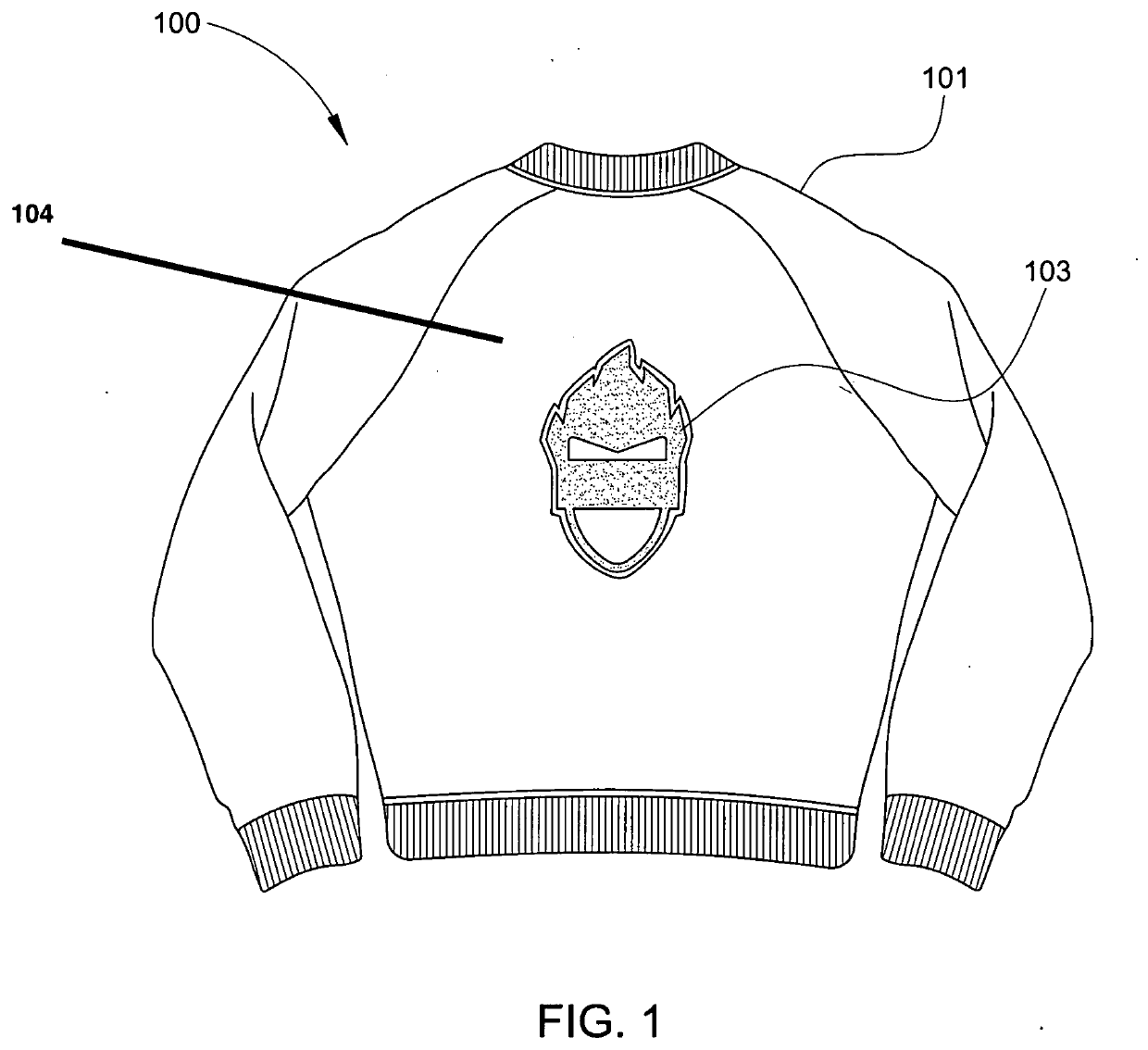
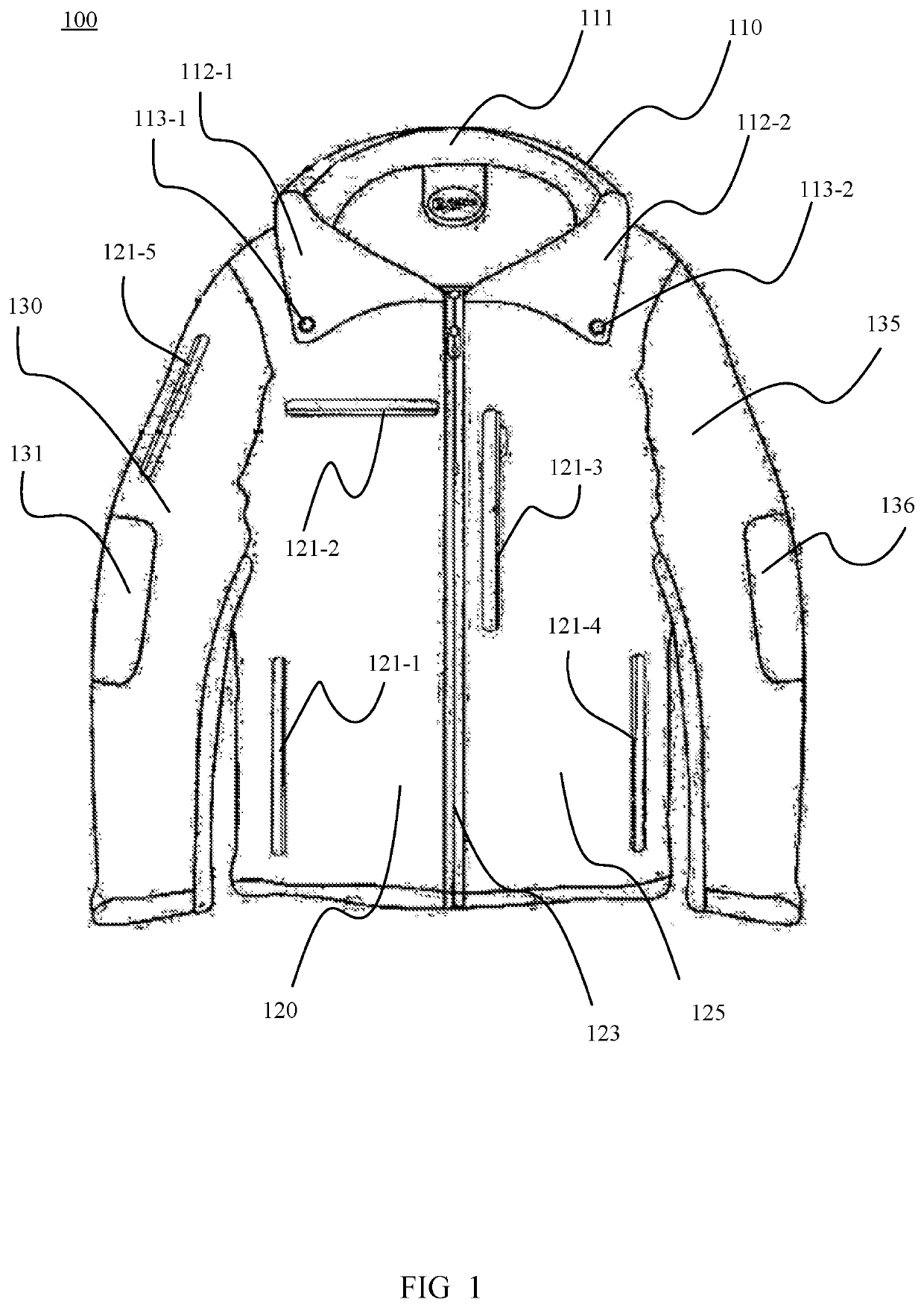
Illuminated Glow Jacket
InactiveUS20200046049A1Long cutMore attentionElectric circuit arrangementsLighting elementsPhysicsPower unit
The invention relates to a jacket assembly consisting of EL PANEL light embedded on the front and back panel of the jacket where jacket has 3 functions while glowing, including solid, strobe and flashing mode which is powered by a small power unit that requires 2 AA batteries. The power pack is located inside of jacket lining in a small pocket
Owner:J BENZ MICHAEL
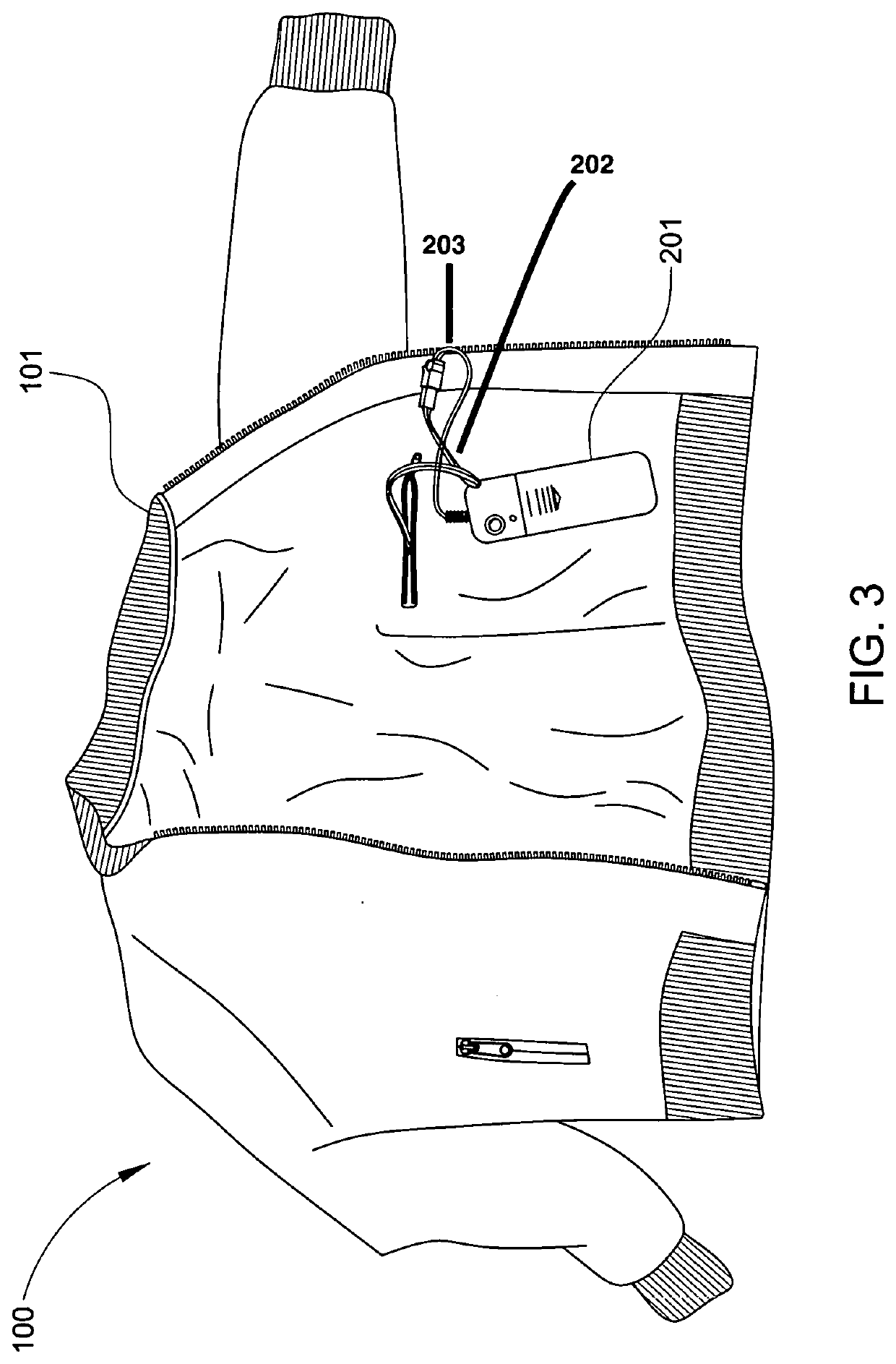
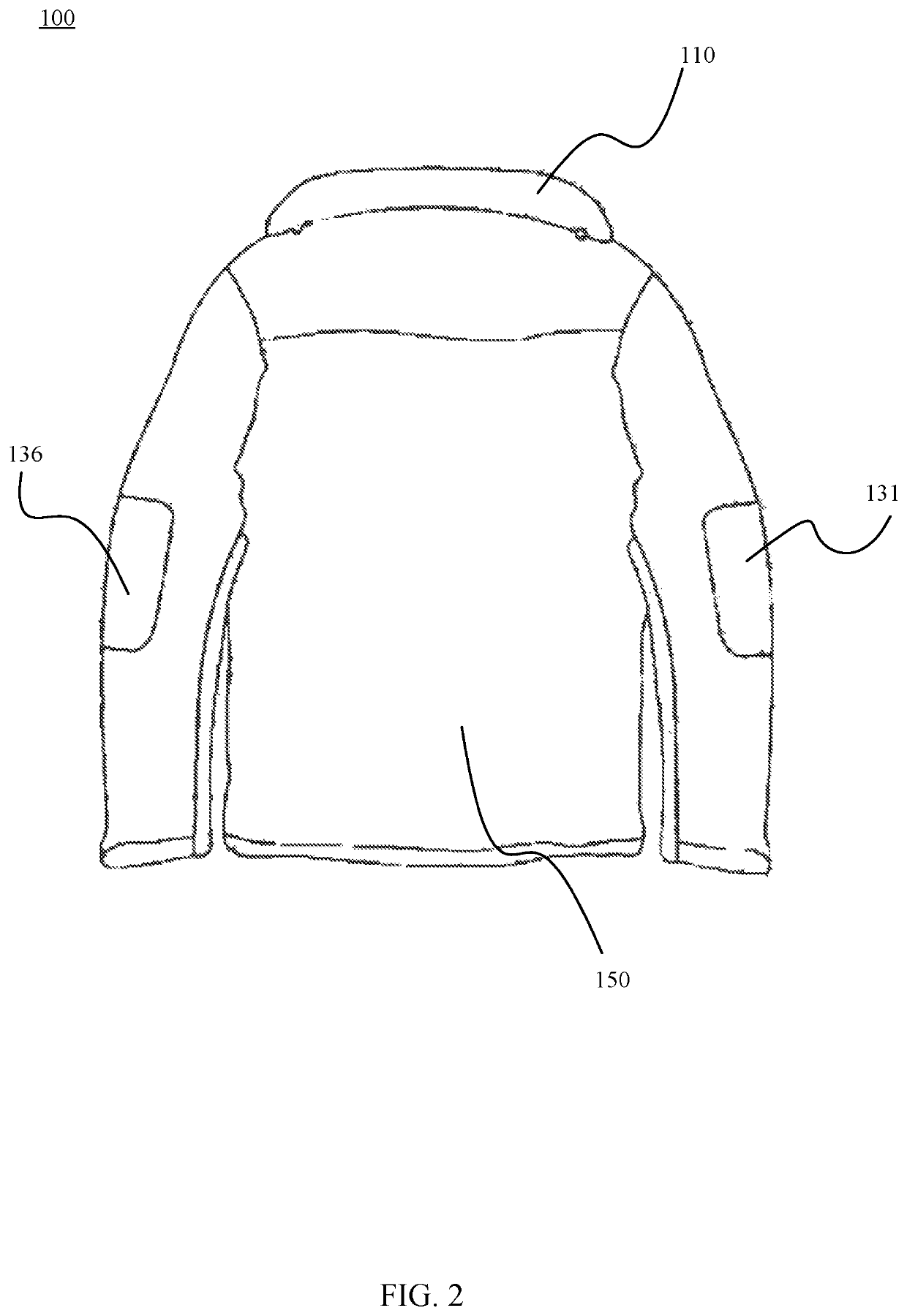
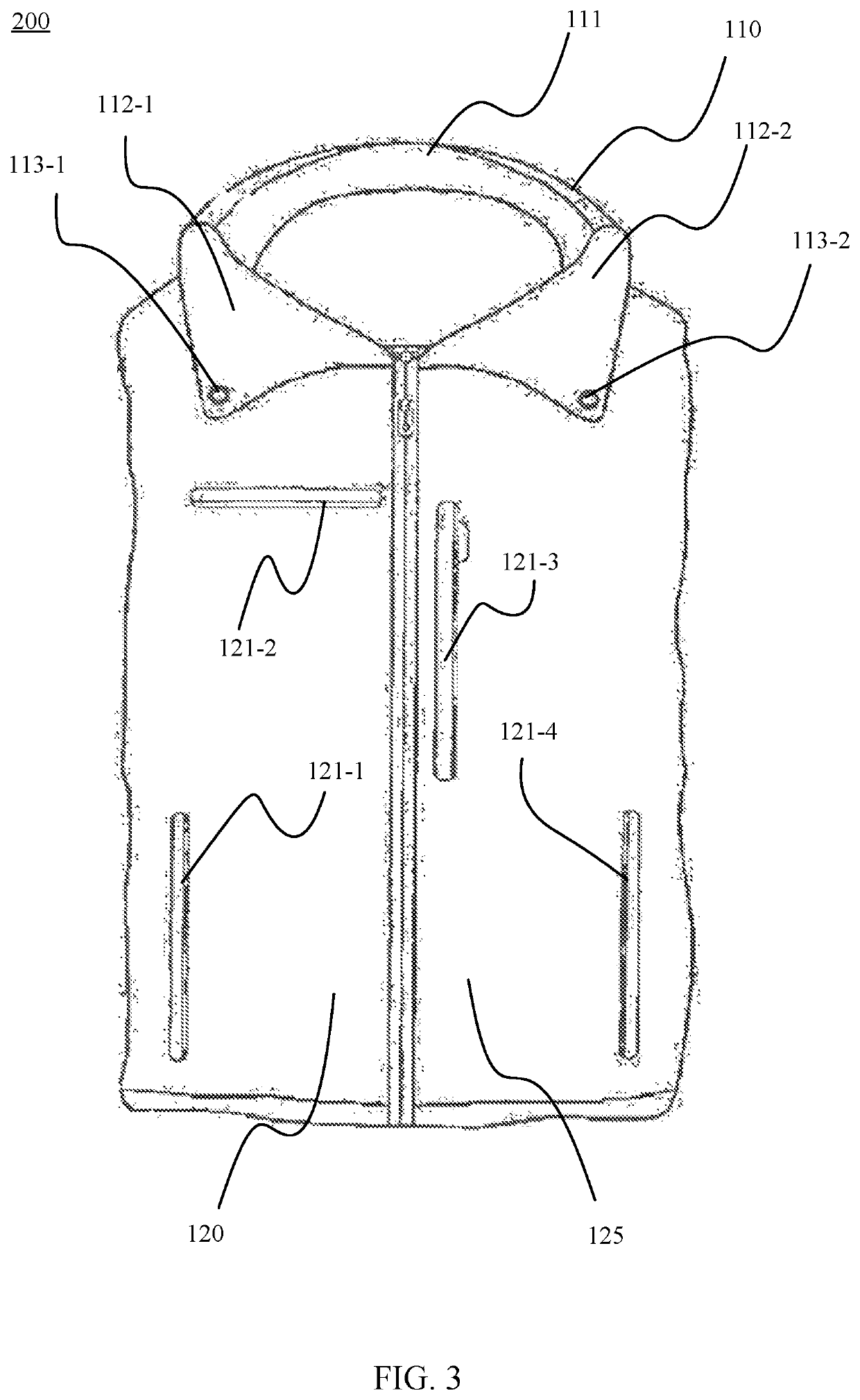
BLC down utility jacket and vest
ActiveUS10694790B2Extreme flexibilityExtreme adaptabilityJacketsOvergarmentsPolymer scienceEngineering
The invention relates to composite memory foam and its uses in the manufacture of jacket for exclusive body supports. The invention also relates to a method of adding or removing composite memory foam when dry cleaning is required. The composite memory foam includes a polyurethane foam and granules of a polyurethane polymer embedded in the polyurethane foam where the memory foam is exclusively added in collar, elbow, and back panel of jacket to improve the support and comfort level.
Owner:BLACKWOOD MATTHEW
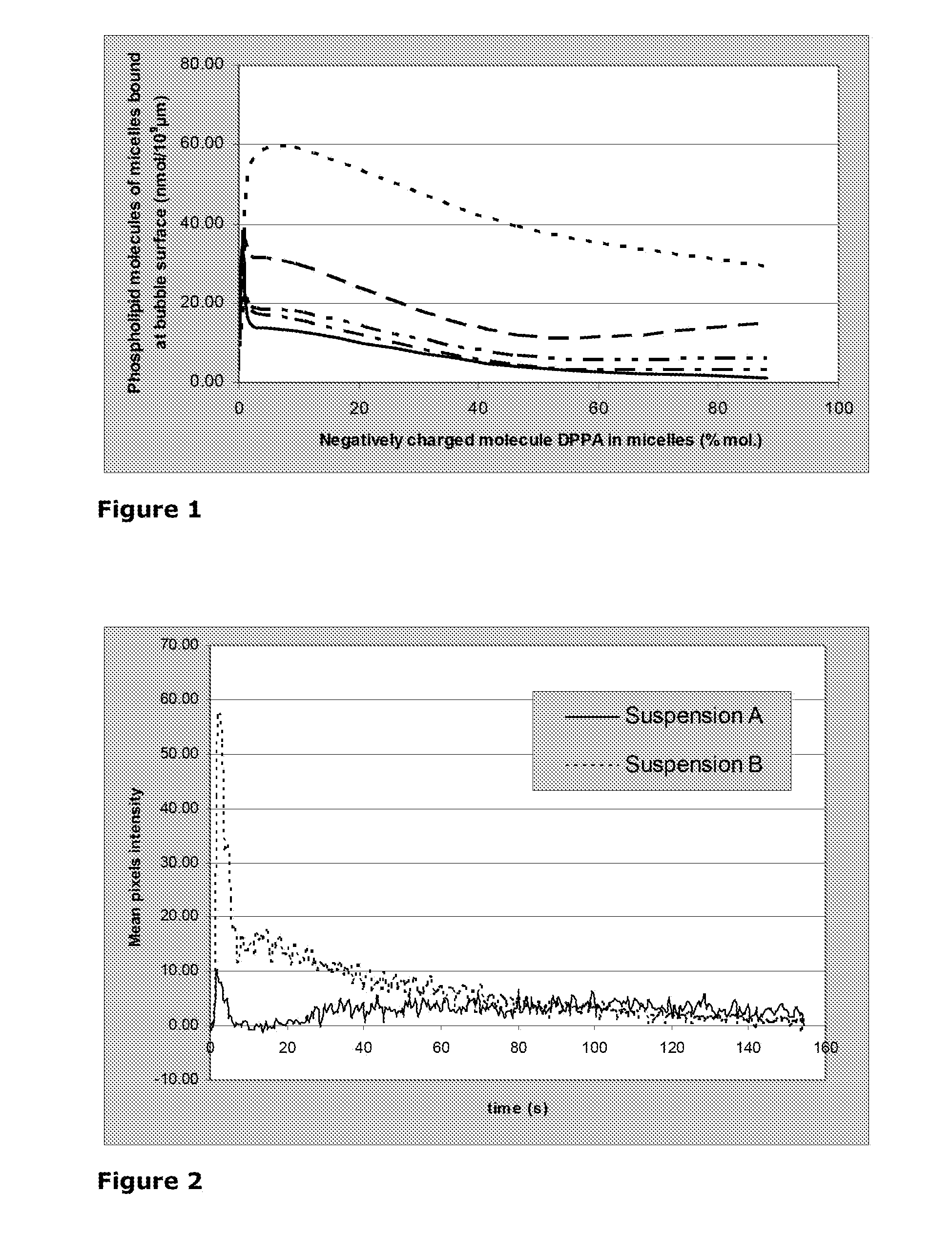
Assembly of Gas-Filled Microvesicle With Active Component For Contrast Imaging
InactiveUS20110150778A1Extreme flexibilityEnhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideActive agentDrug biological activity
Assembly comprising a gas-filled microvesicle and a structural entity which is capable to associate through an electrostatic interaction to the outer surface of said microvesicle (microvesicle associated component—MAC), thereby modifying the physico-chemical properties thereof. Said MAC comprises a targeting ligand a diagnostic agent or any combination thereof. Optionally a bioactive agent can further be associated to the MAC. The assembly of the invention can be formed from gas-filled microbubbles or microballoons and a MAC having preferably nanometric dimensions, e.g. a micelle, and is used as an active component in diagnostically and / or therapeutically active formulations, in particular for enhancing the imaging in the field of ultrasound contrast imaging, including targeted ultrasound imaging, ultrasound-mediated drug delivery and other imaging techniques such as molecular resonance imaging (MRI) or nuclear imaging.
Owner:BRACCO RES USA
Air injector system apparatus and methods for a tub or spa
Apparatus and methods include an array of a plurality of individual air injector nozzles are integrally connected to a common air flow tube. The individual nozzles include an integral attaching plate and an integral air injector tube in addition to the common air flow tube with the individual nozzles spaced along the common air flow tube. A plurality of arrays can be joined together to form an entire arrangement of any desired configuration of individual air injector nozzles that can be applied as a complete unit to a tub or spa. One or more of the arrays can be cut across the common air flow tube to achieve the exact number of individual nozzles required in accordance with the desired arrangement of air injector nozzles. The arrays, including the cut arrays can be joined together at a location other than at the tub or spa and then transferred as a complete unit to be attached to the tub or spa. The plurality of arrays can be joined by a straight or angled connector fitting that can comprise a separate connector fitting or an individual air injector nozzle having air flow tubes arranged in the straight or angled configuration.
Owner:BEDARD PAUL R
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com