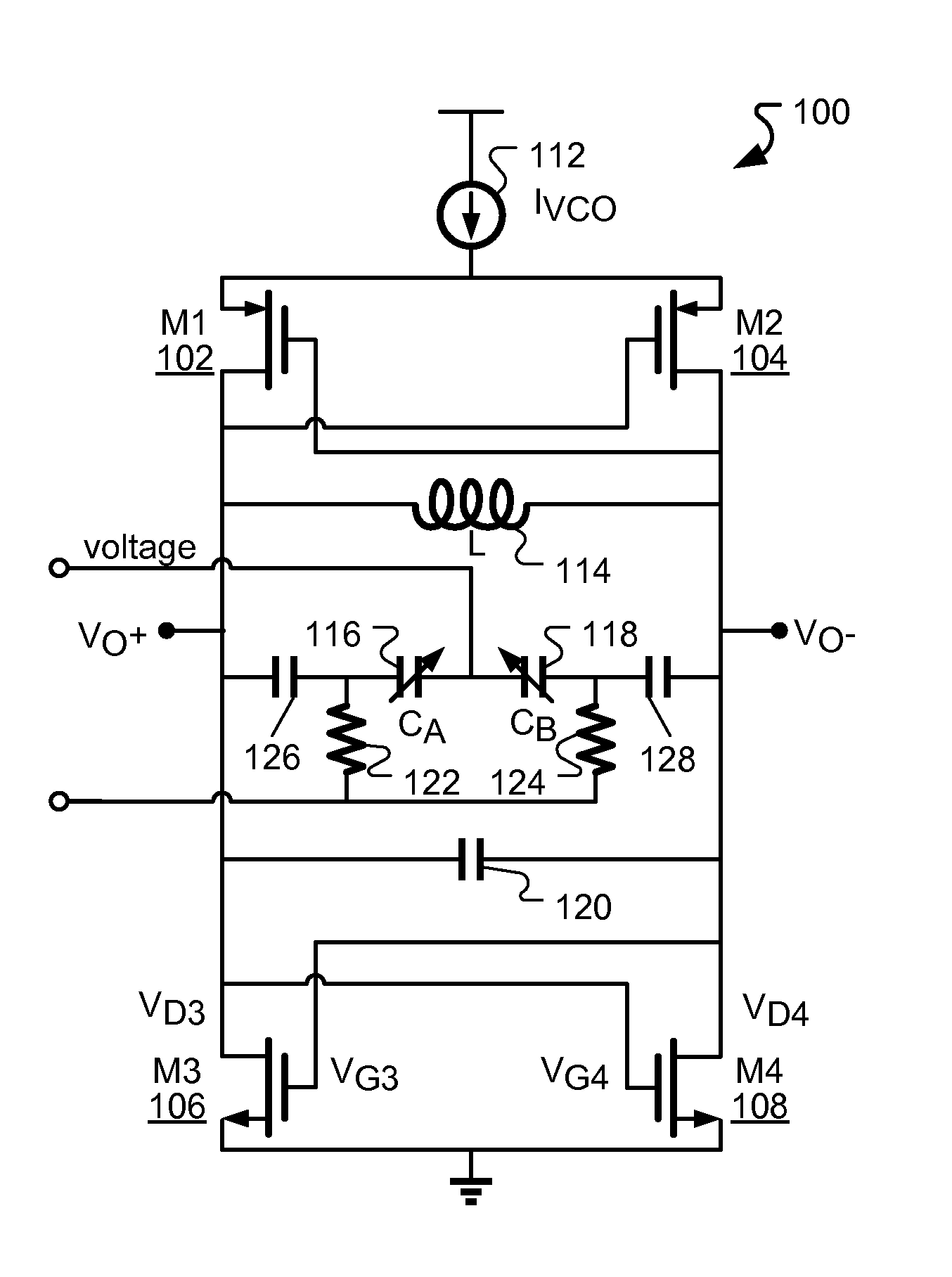
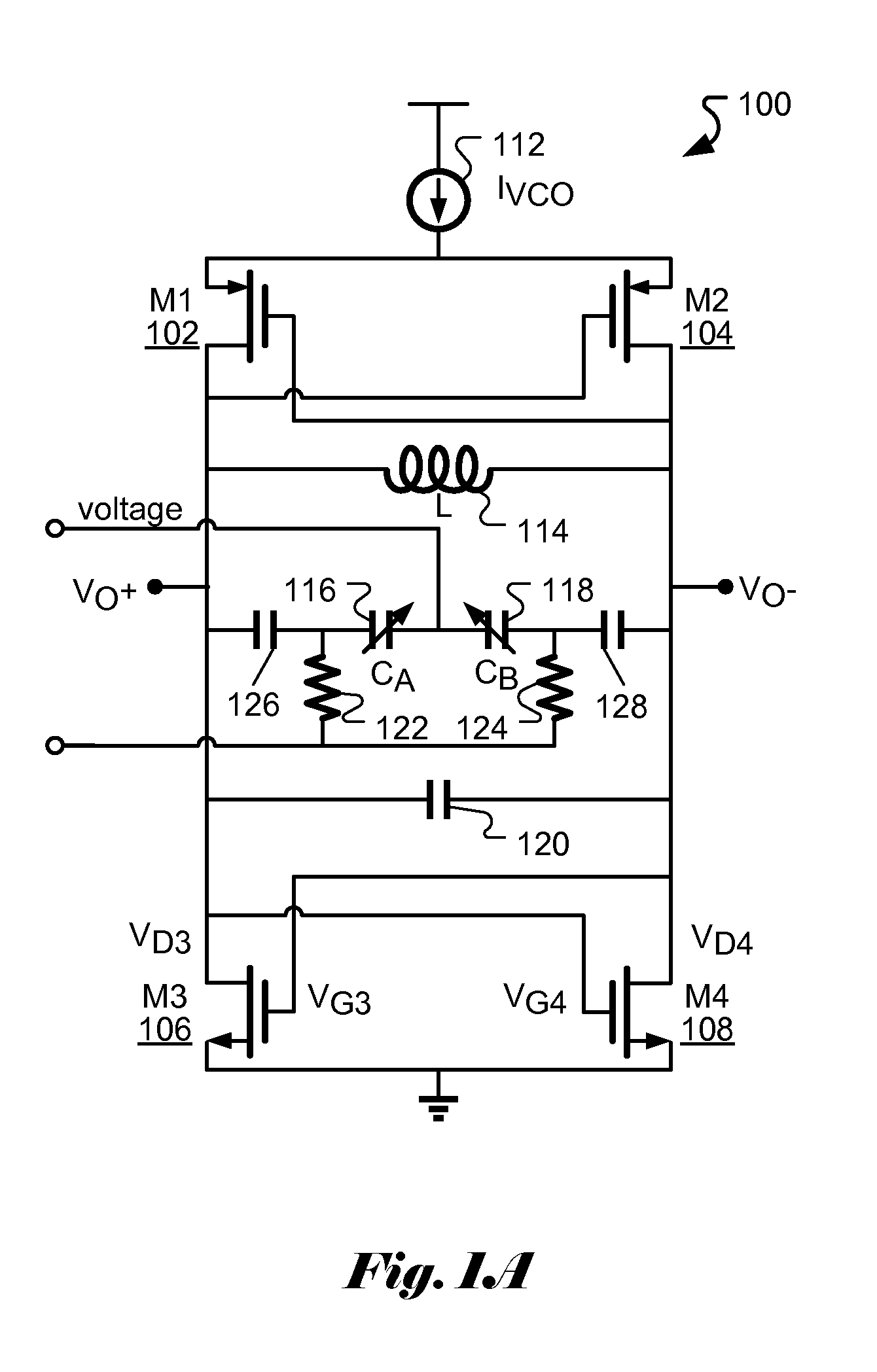
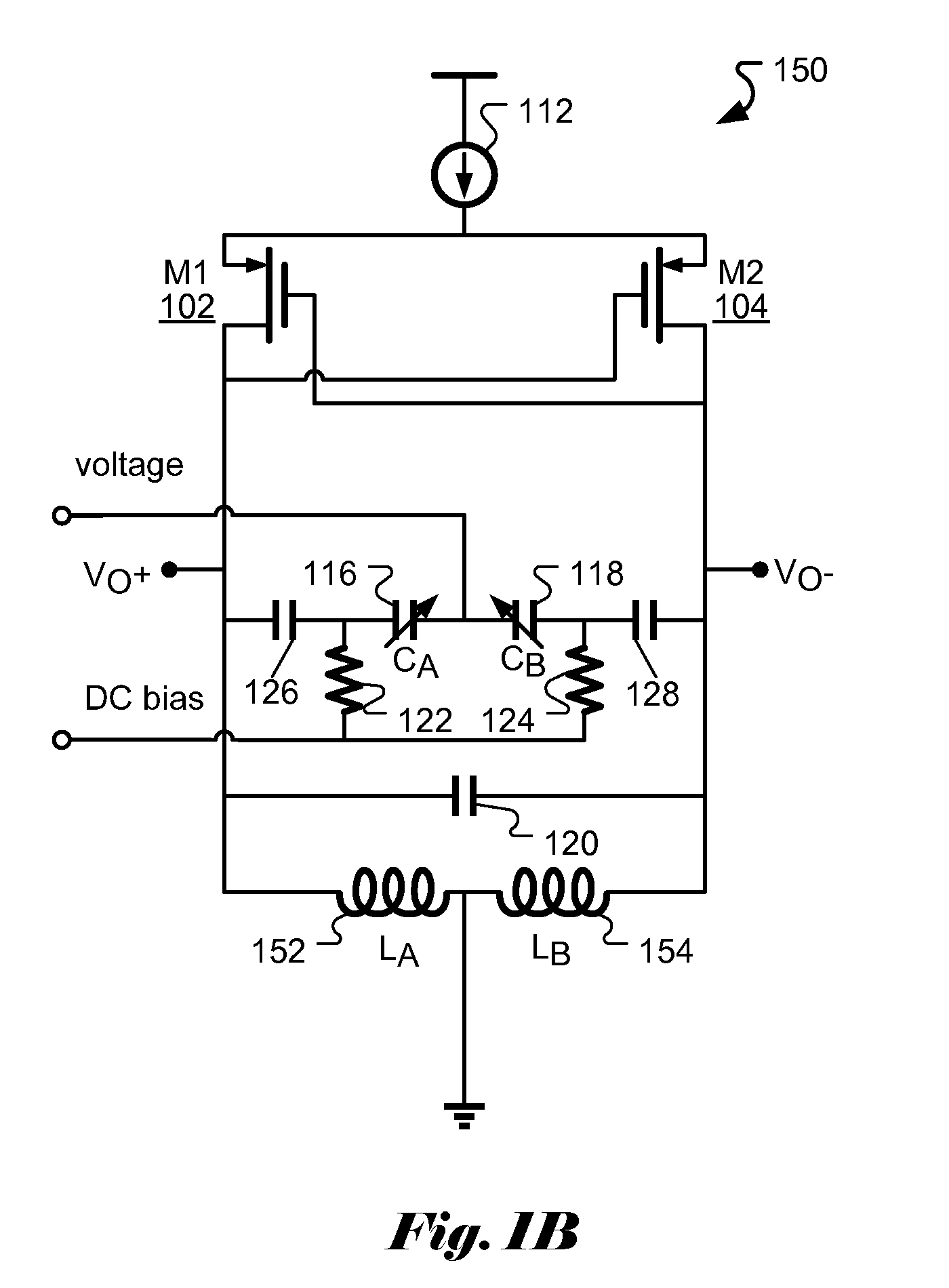
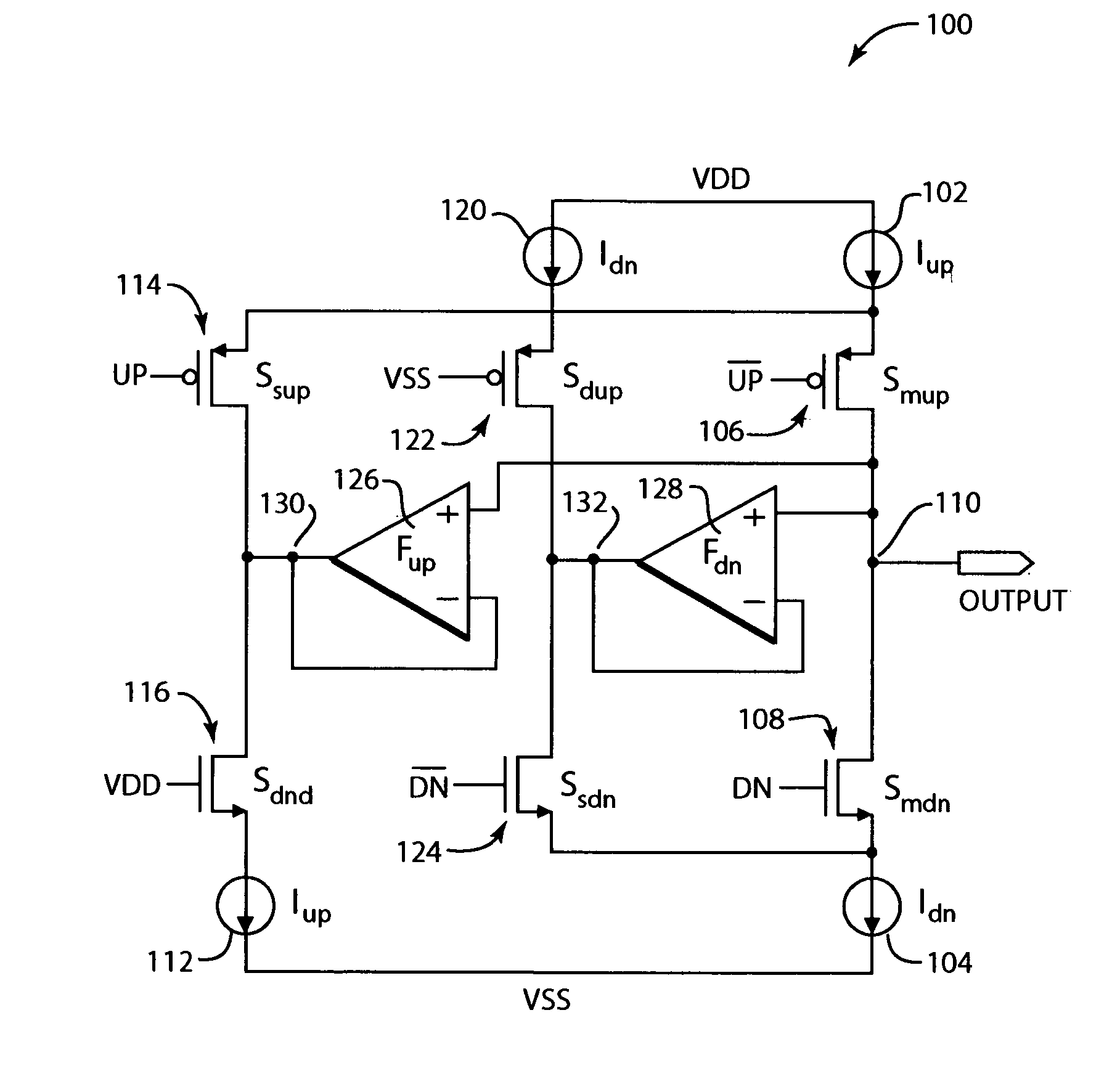
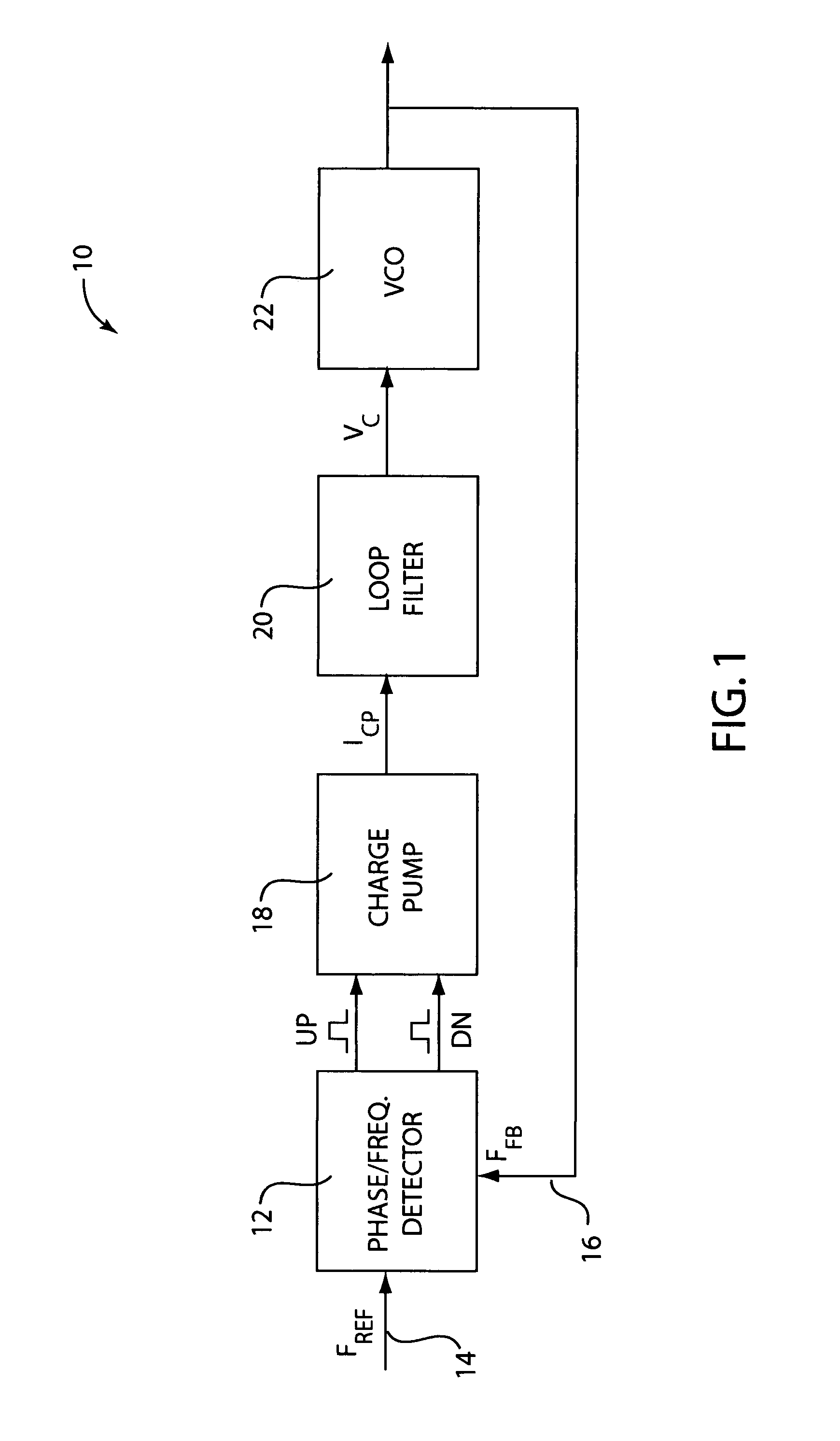
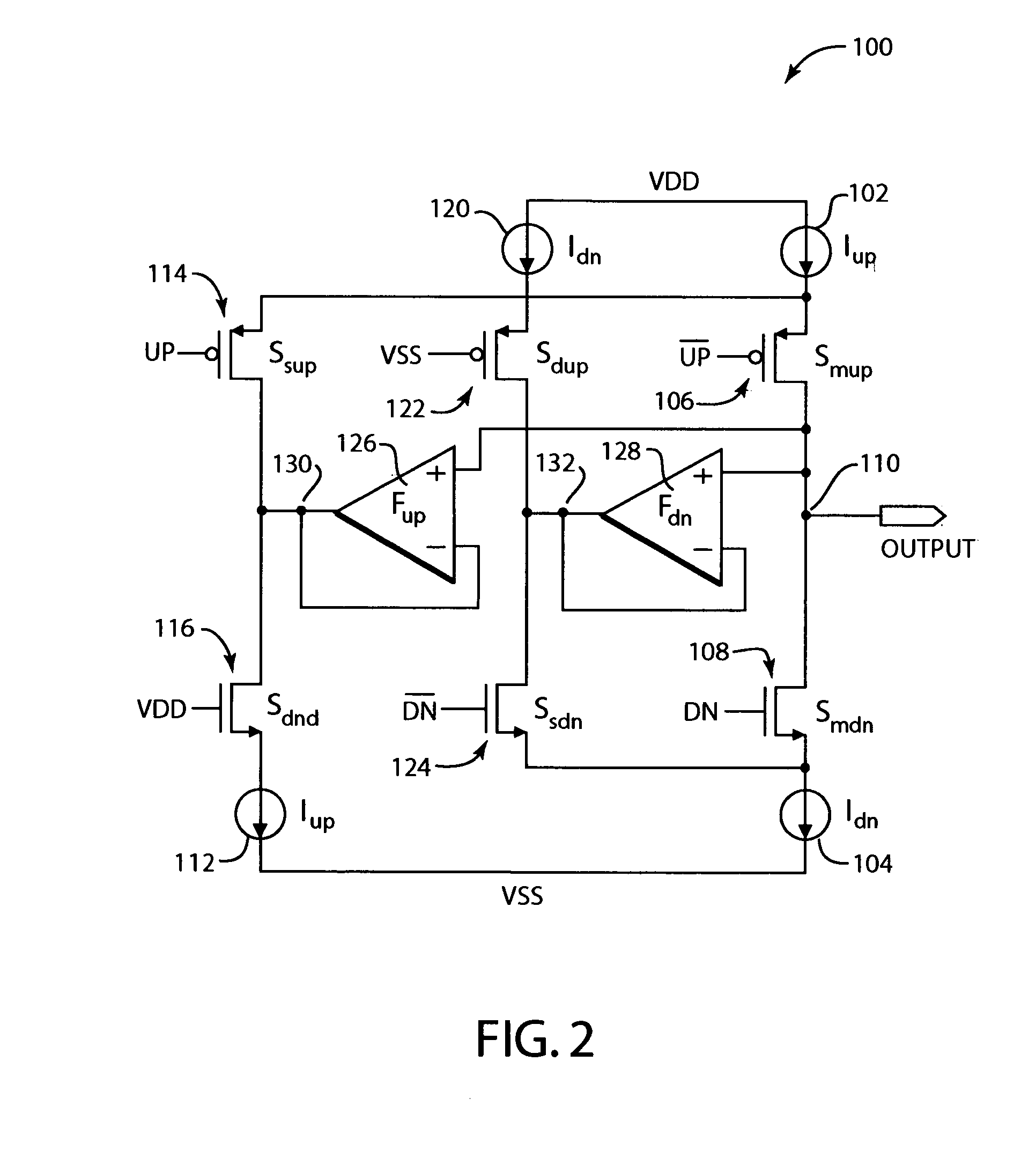
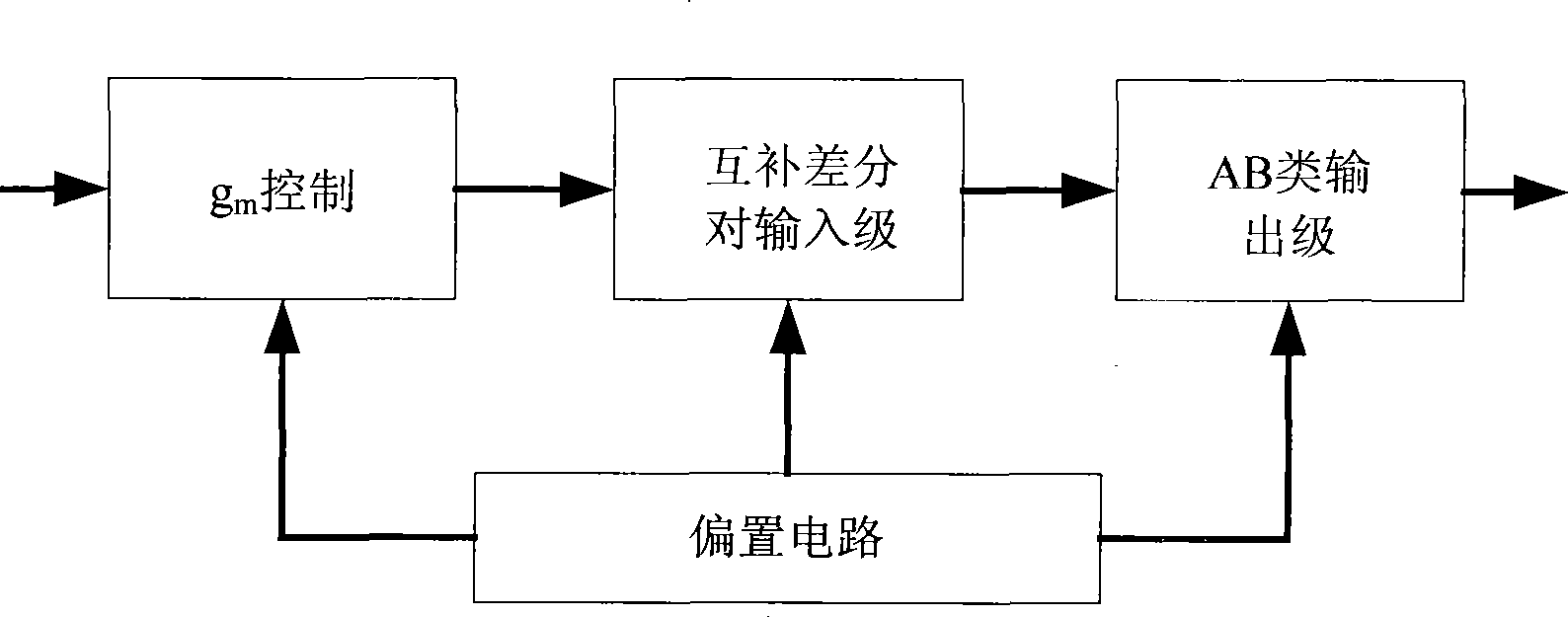
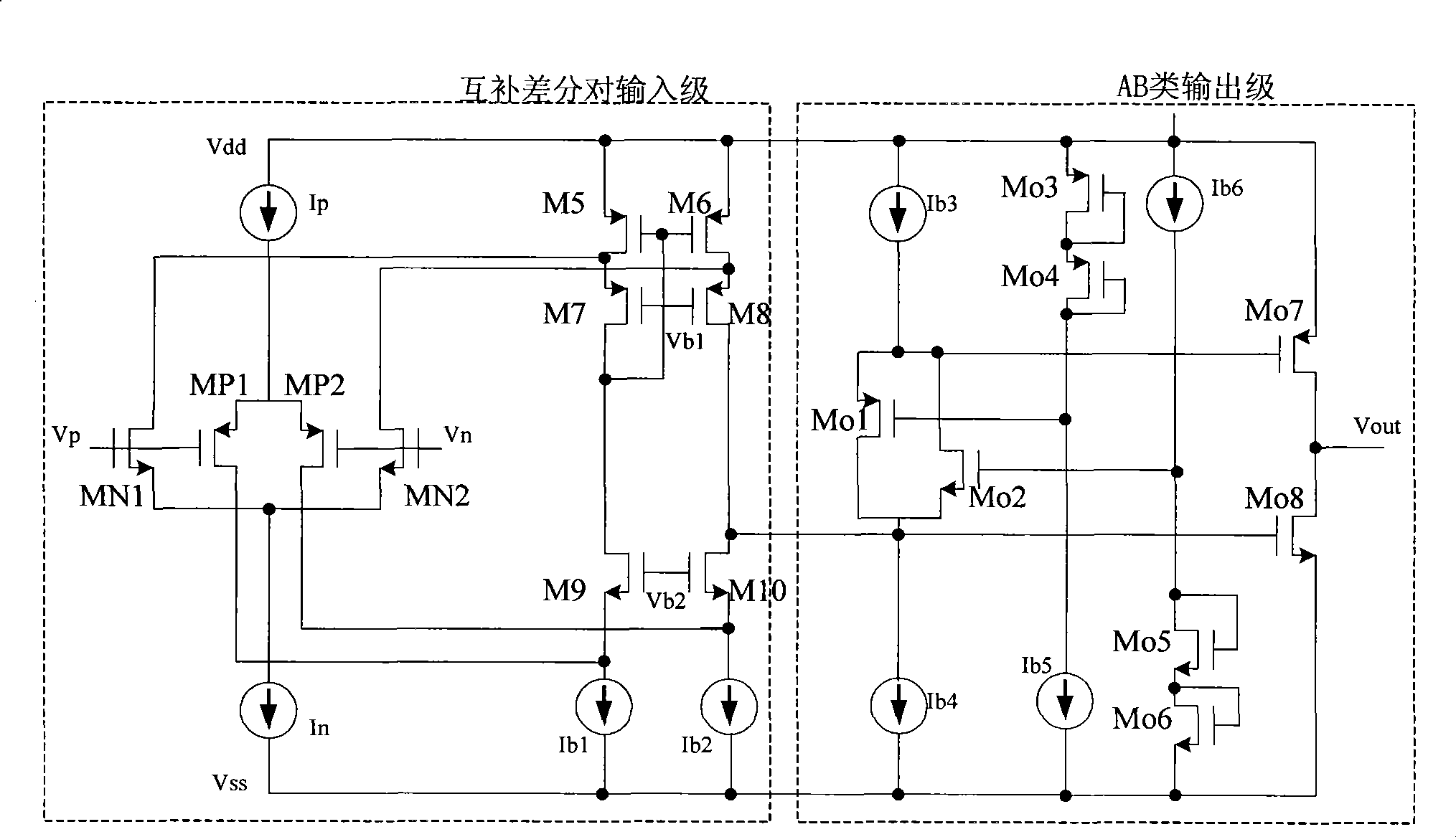
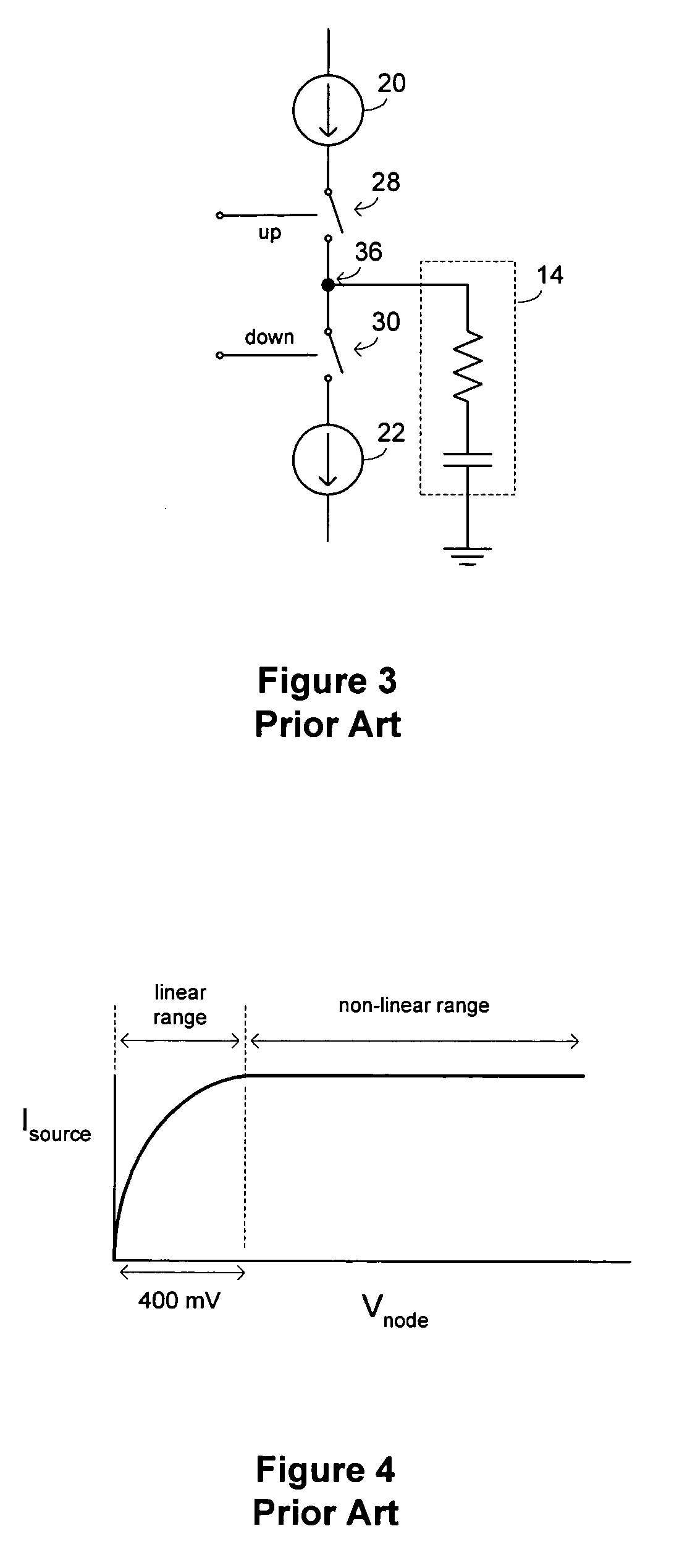
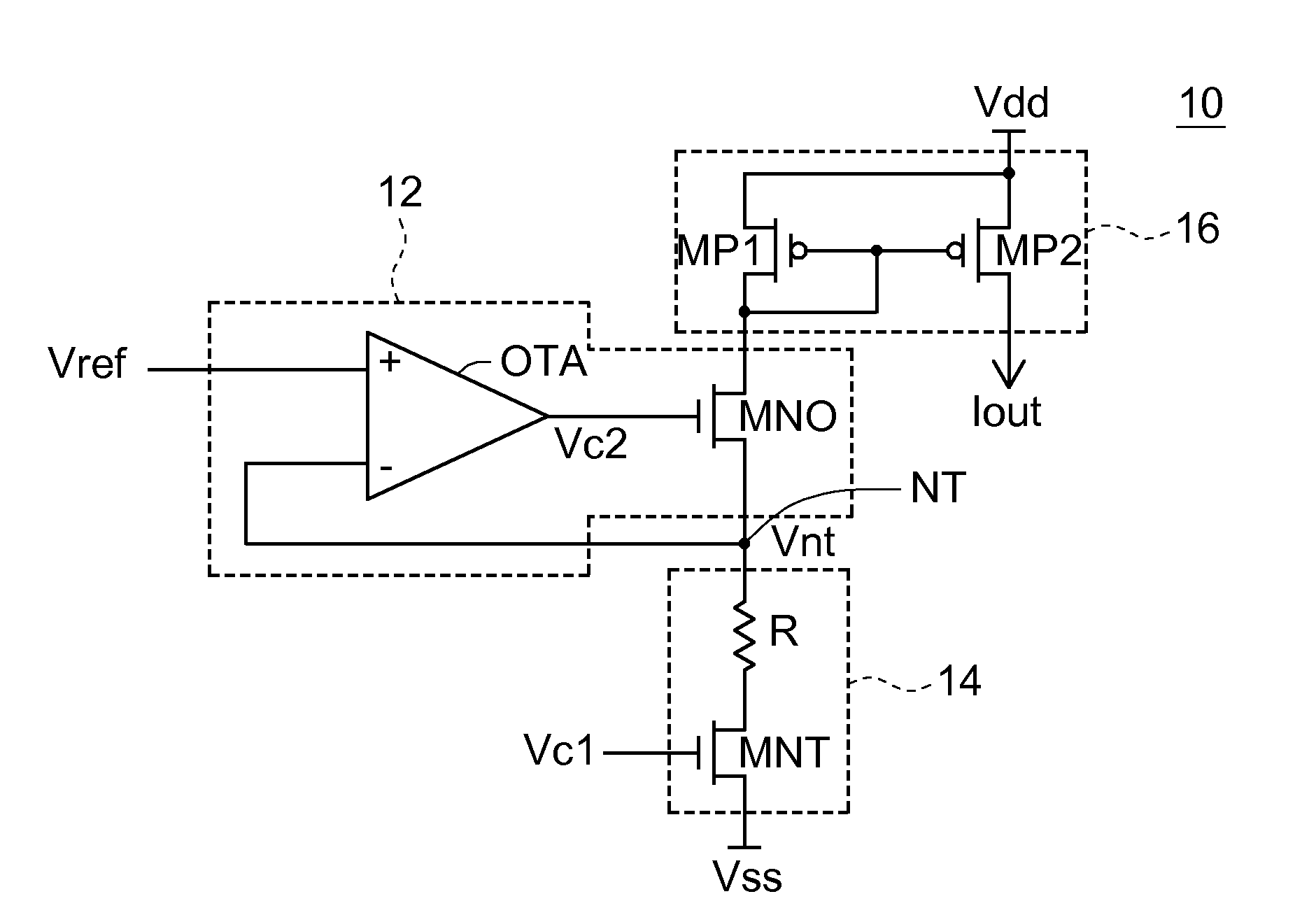
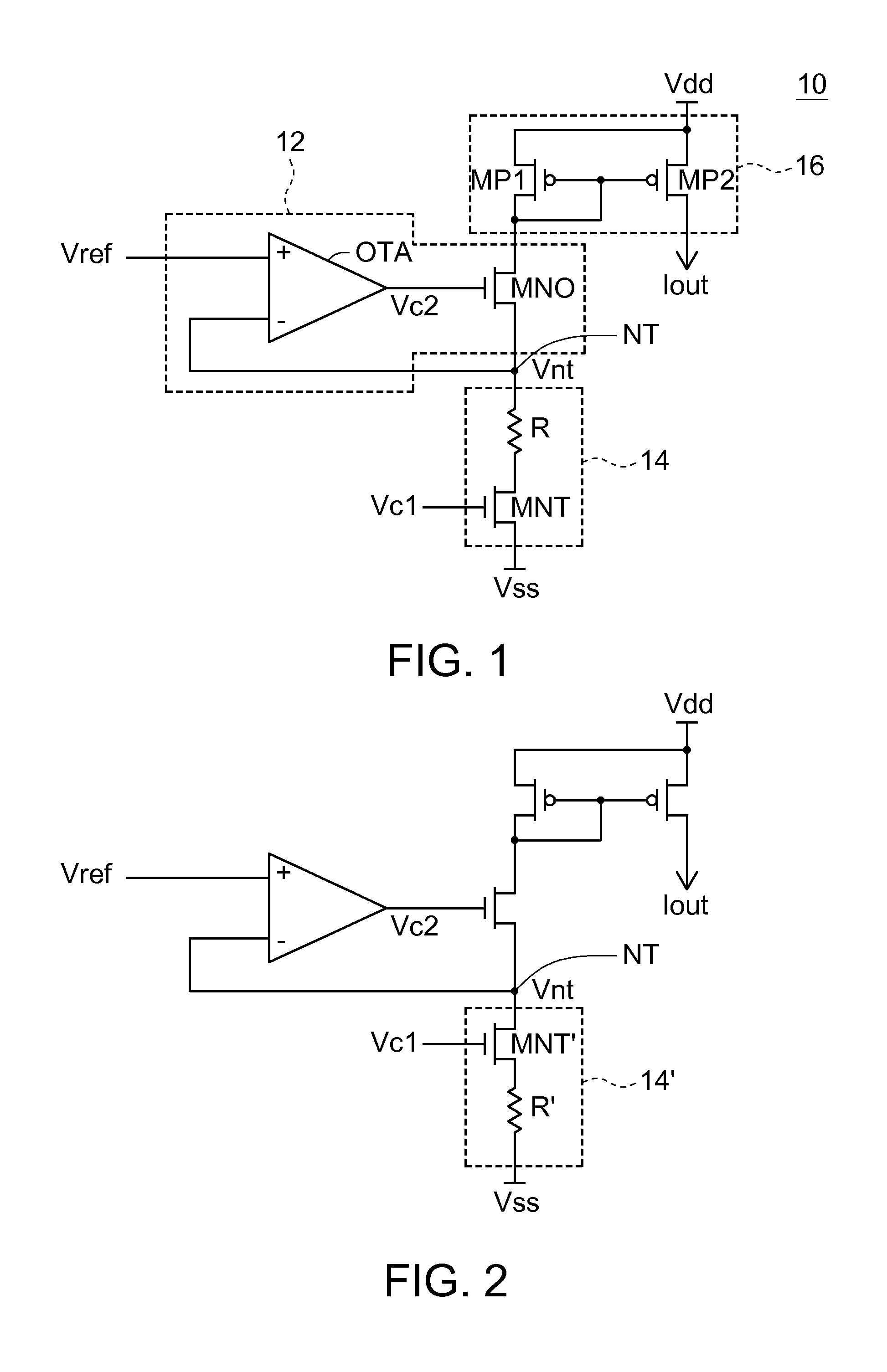
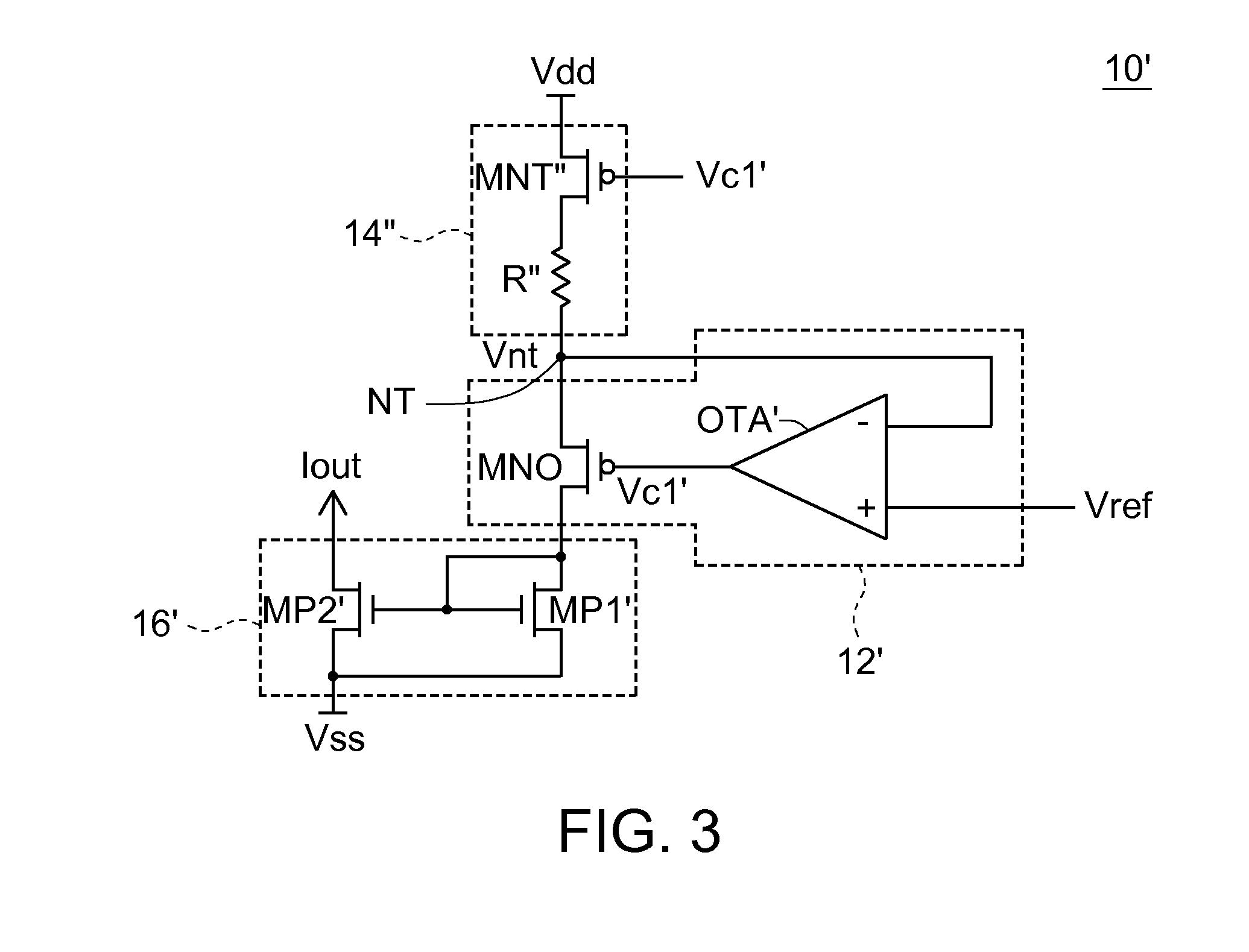
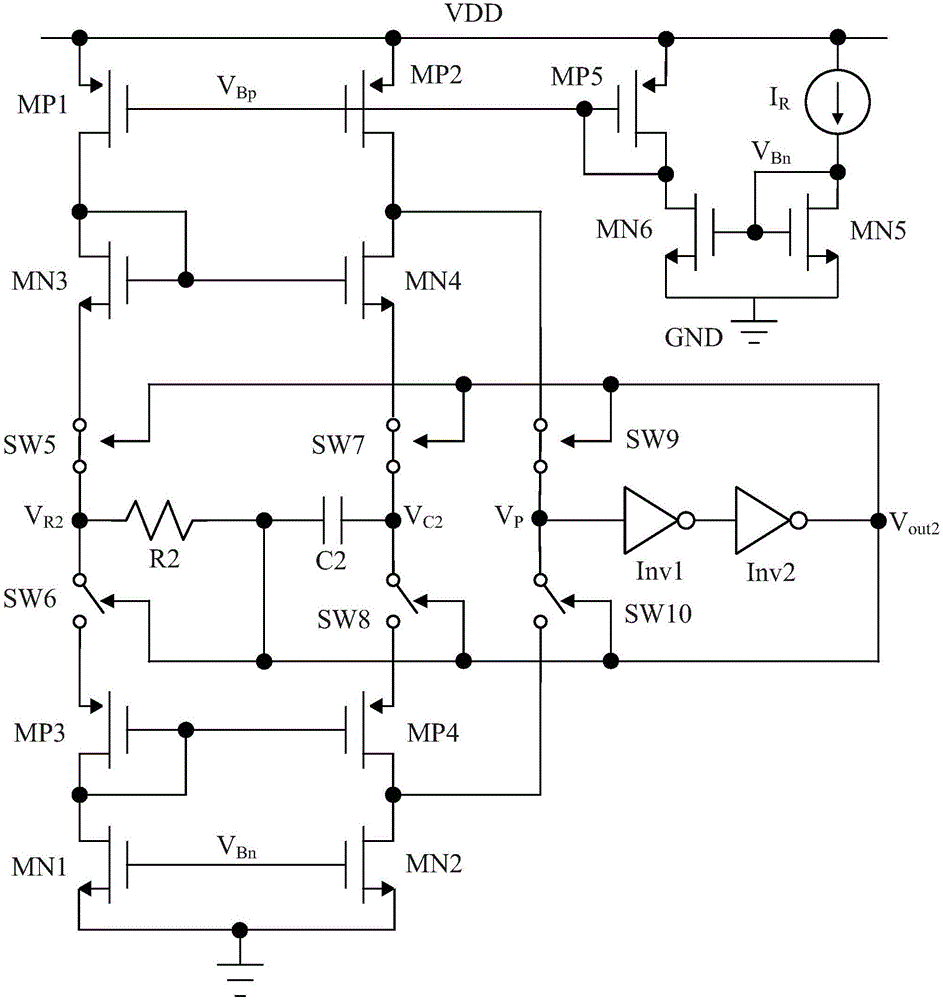
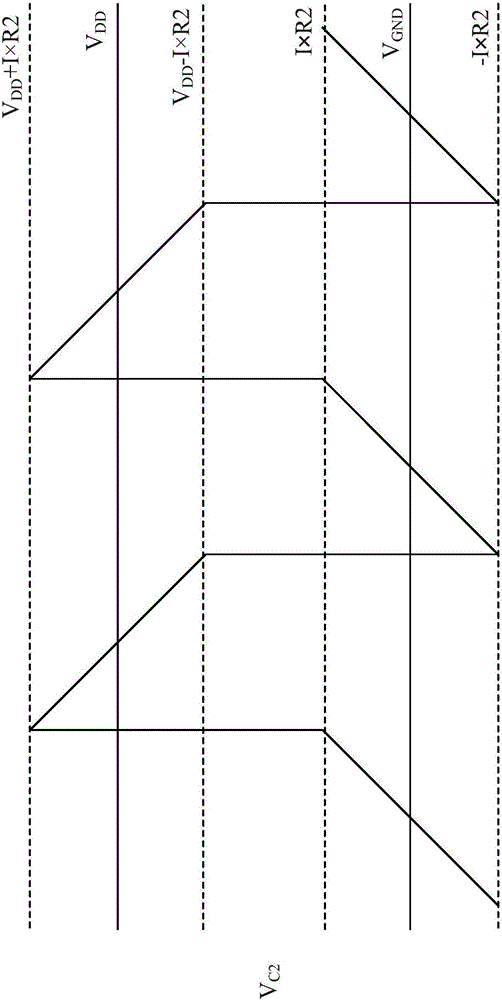
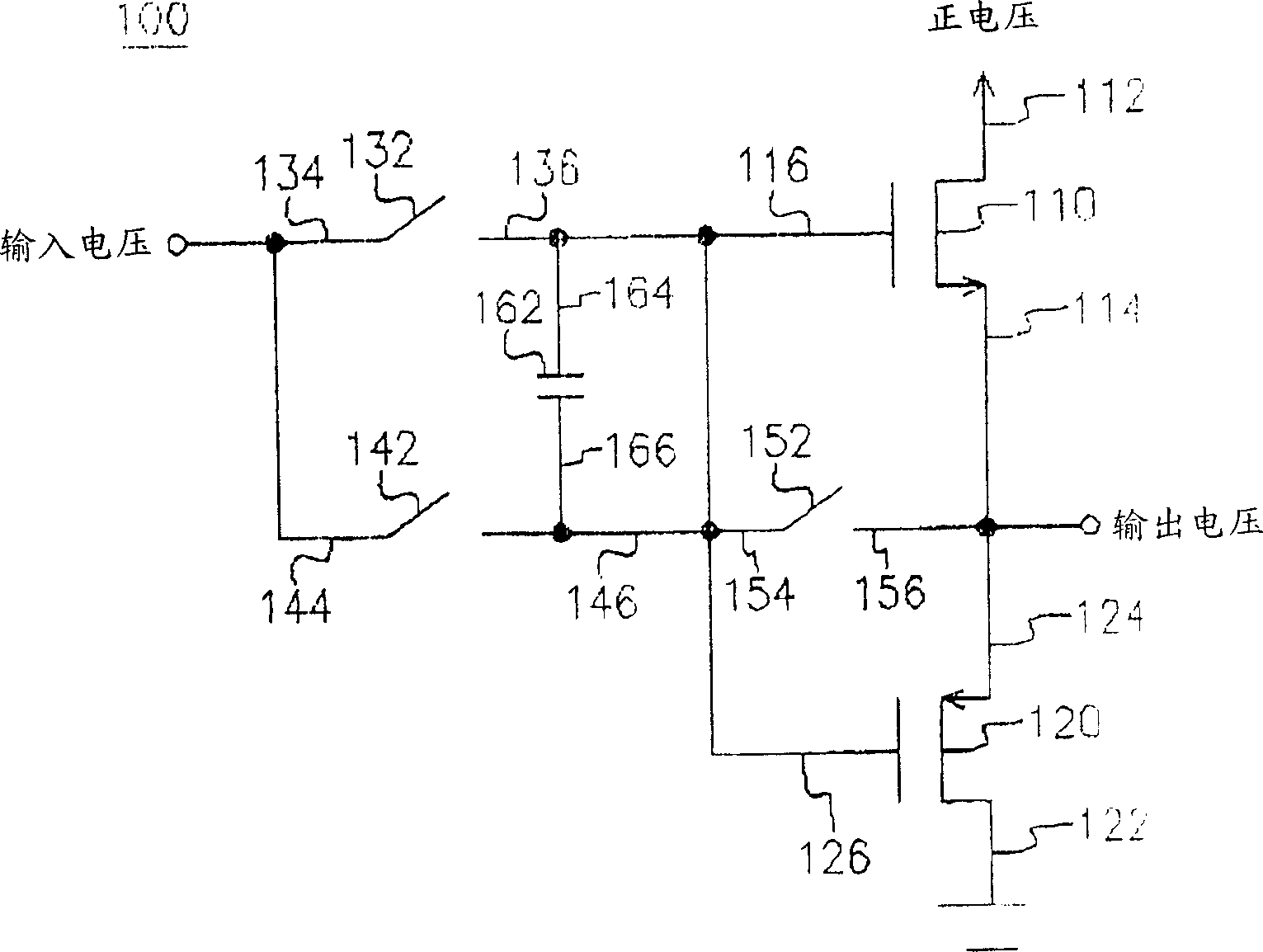
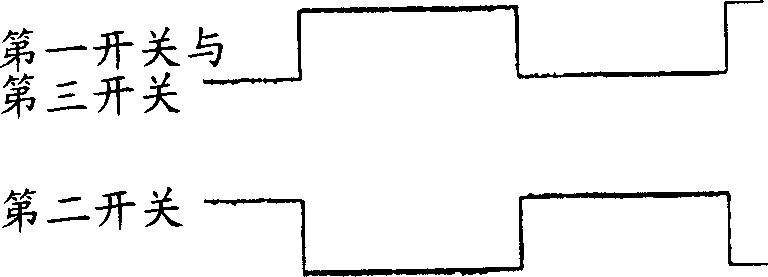
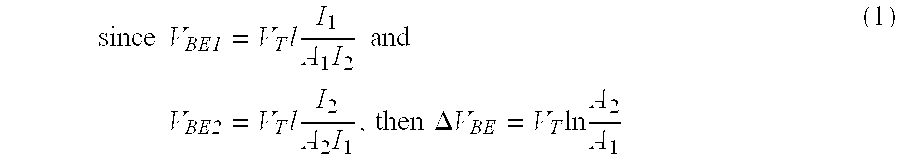Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
155 results about "Widlar current source" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
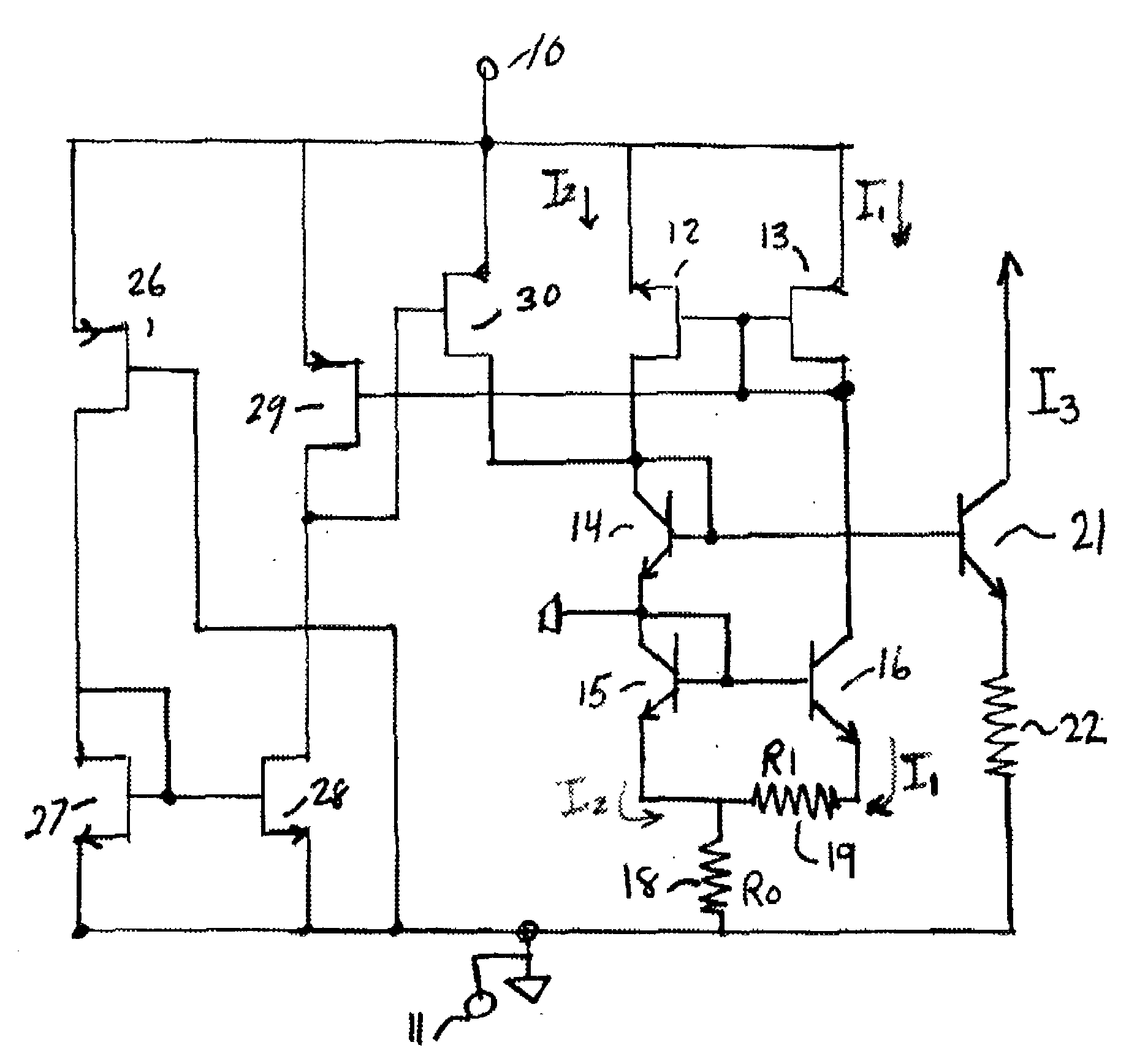
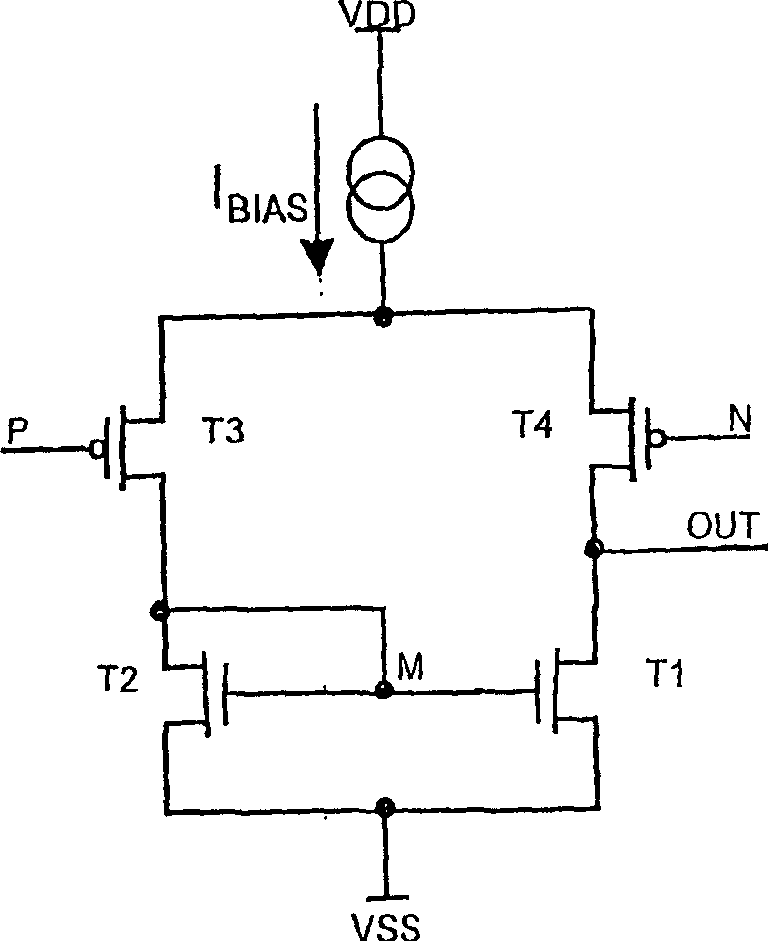
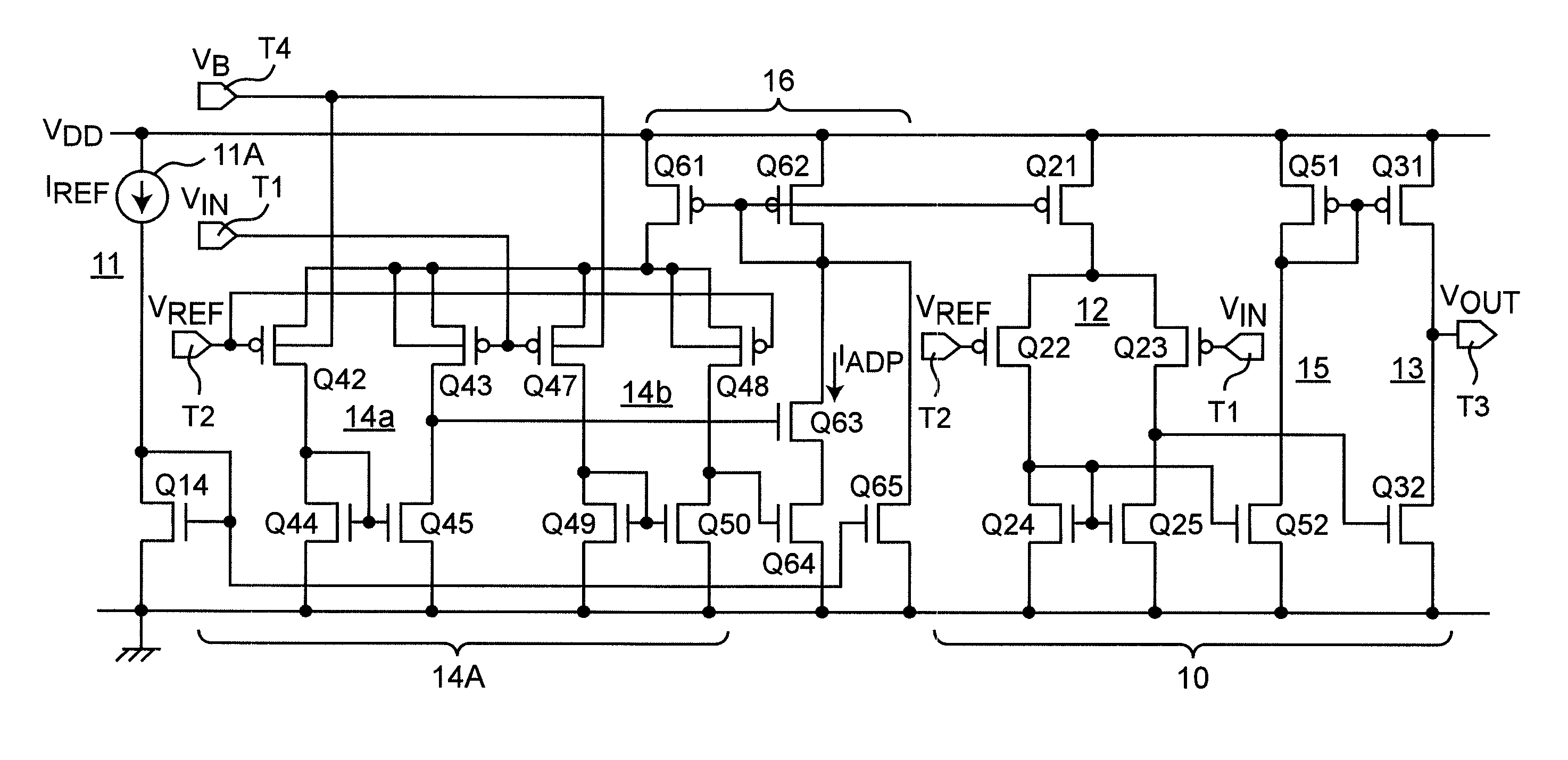
A Widlar current source is a modification of the basic two-transistor current mirror that incorporates an emitter degeneration resistor for only the output transistor, enabling the current source to generate low currents using only moderate resistor values.
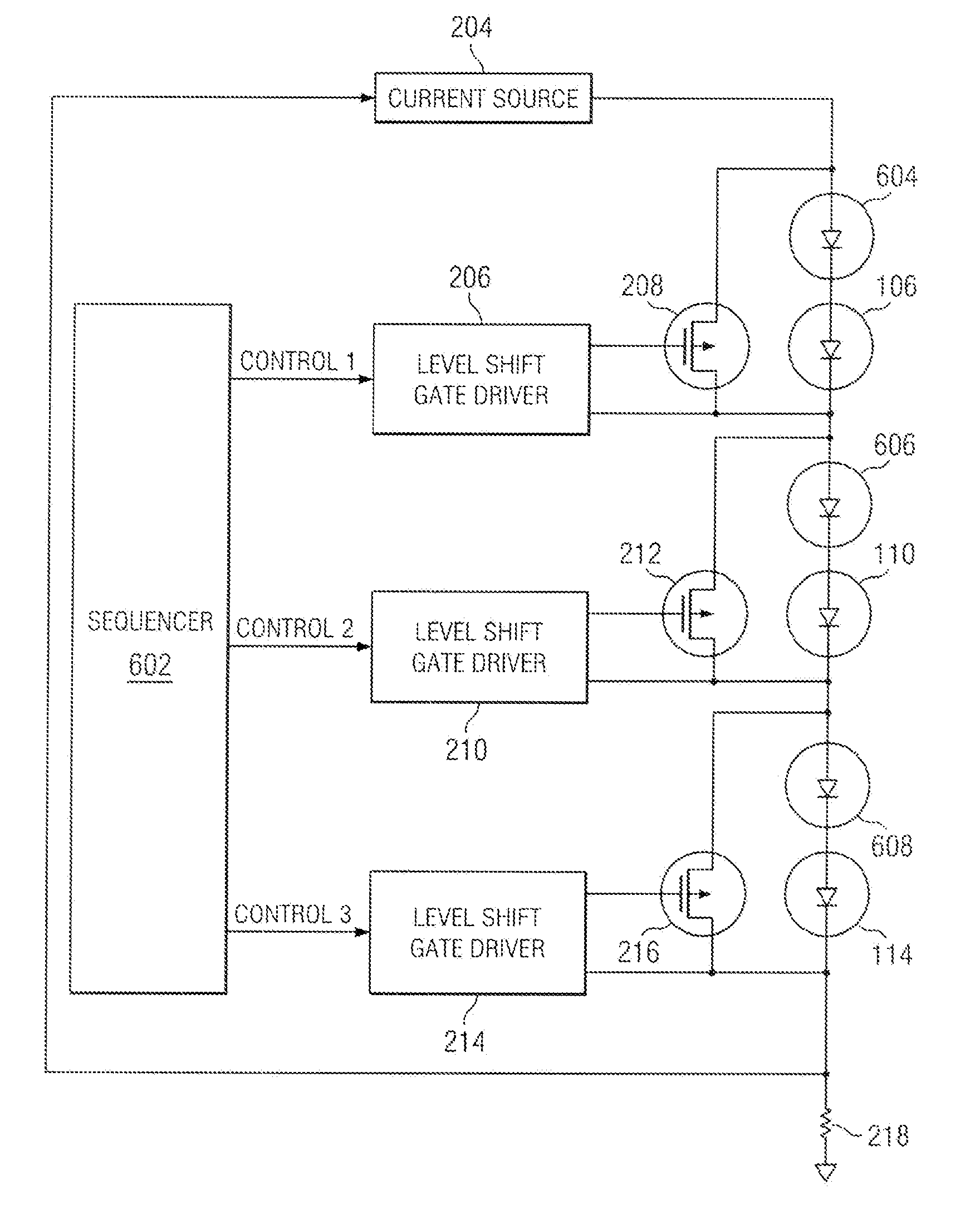
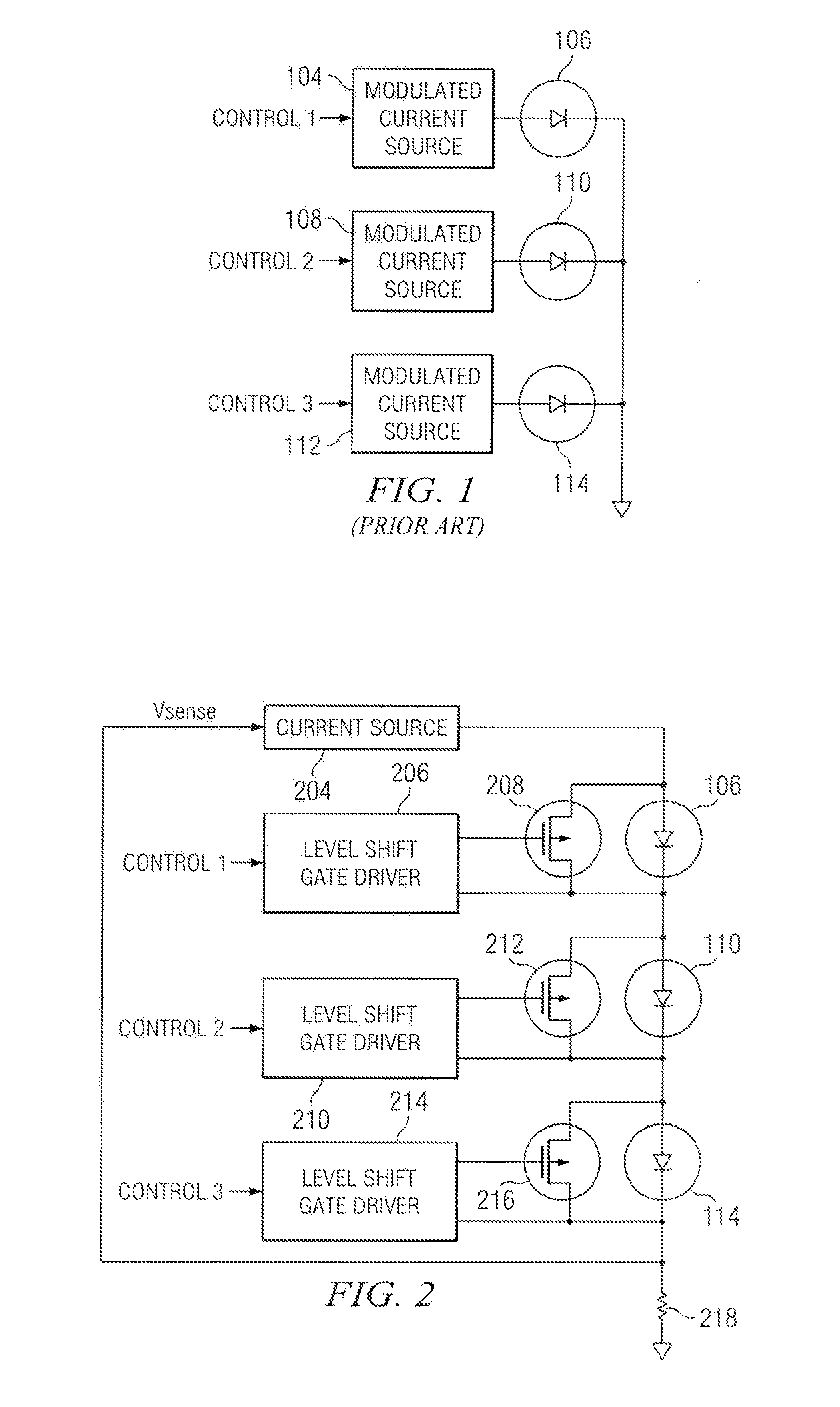
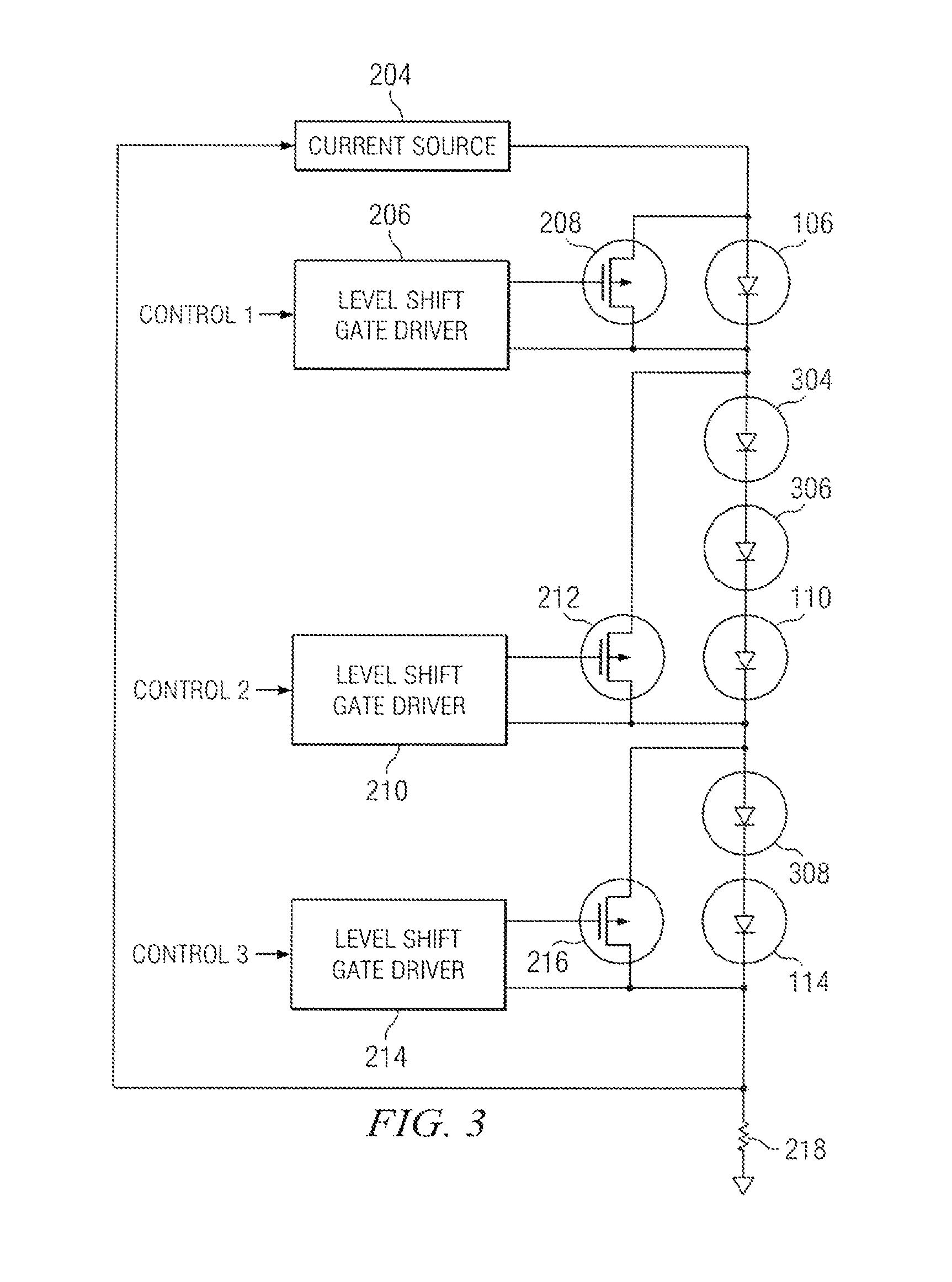
Highly efficient series string LED driver with individual LED control
ActiveUS7649326B2Increase brightnessStable changeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalField-effect transistor
A current source generates, with high efficiency, a current that is substantially constant over a wide range of output voltages. This current is injected into the first end of a series-connected string of LEDs, with the second end of the string connected through a resistor to ground. The voltage developed across this resistor, which is a measure of current flow in the series string, is fed back to the current source, wherein feedback maintains nearly constant current output over a wide range of output voltages. A field effect transistor (FET) is placed in parallel with each LED in the string. A level shift gate driver couples a pulse width modulated control signal to the gate of each FET. With the FET being coupled across a particular LED, the LED can be bypassed when the FET is actuated or receive current when the FET is deactuated. By modulating the duty cycle of each FET, the brightness of each associated LED may be varied smoothly over its full range.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
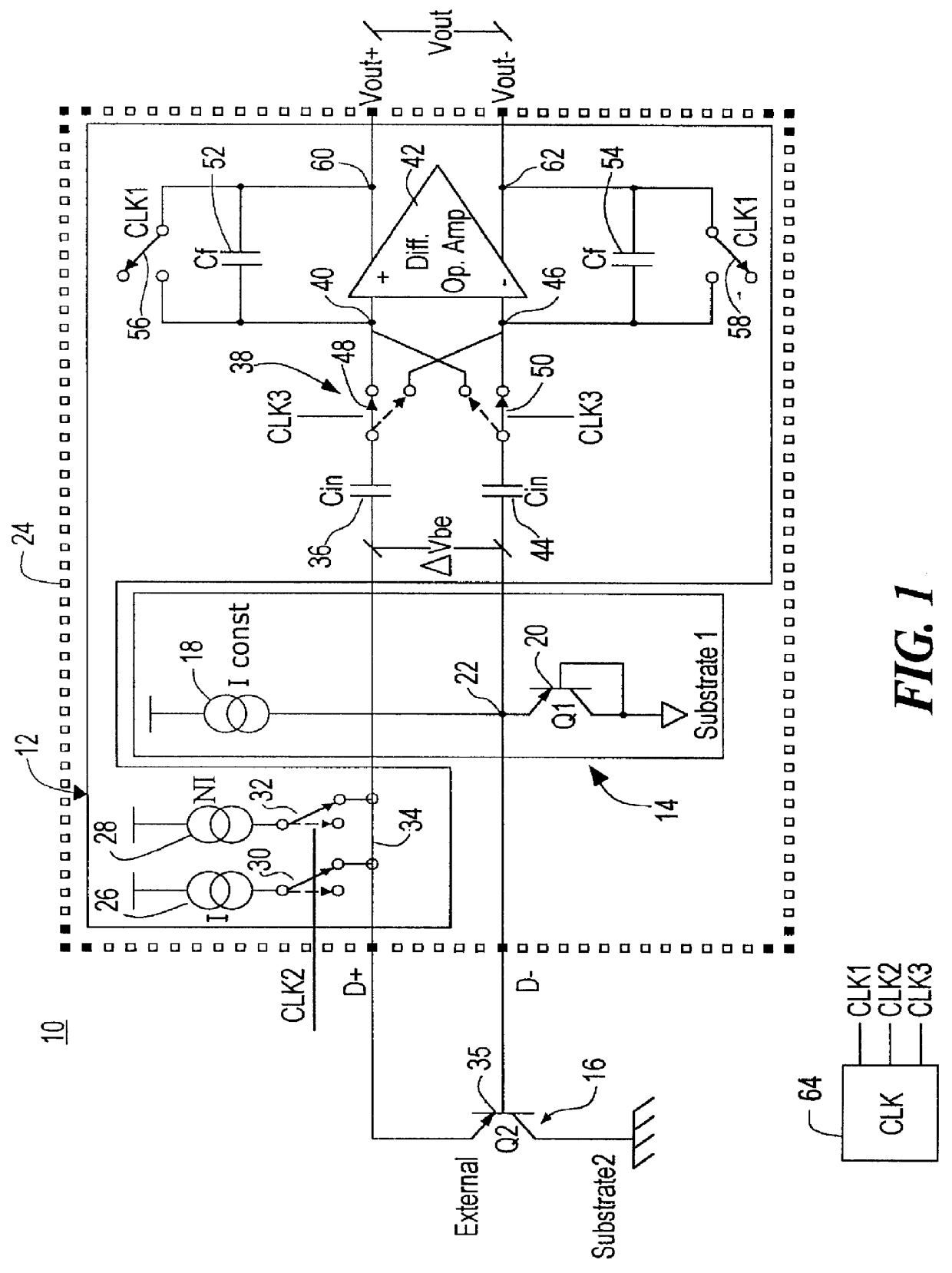
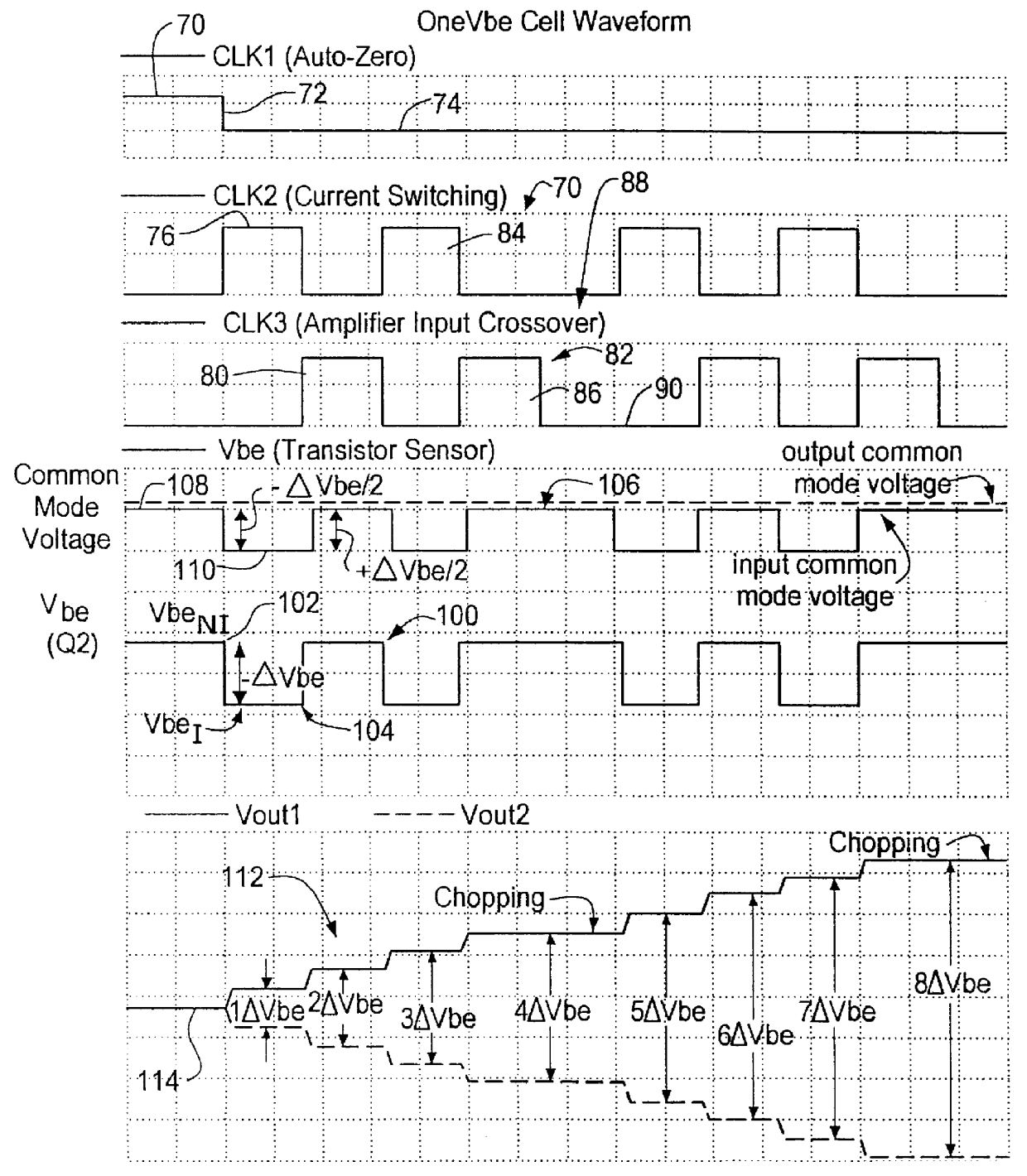
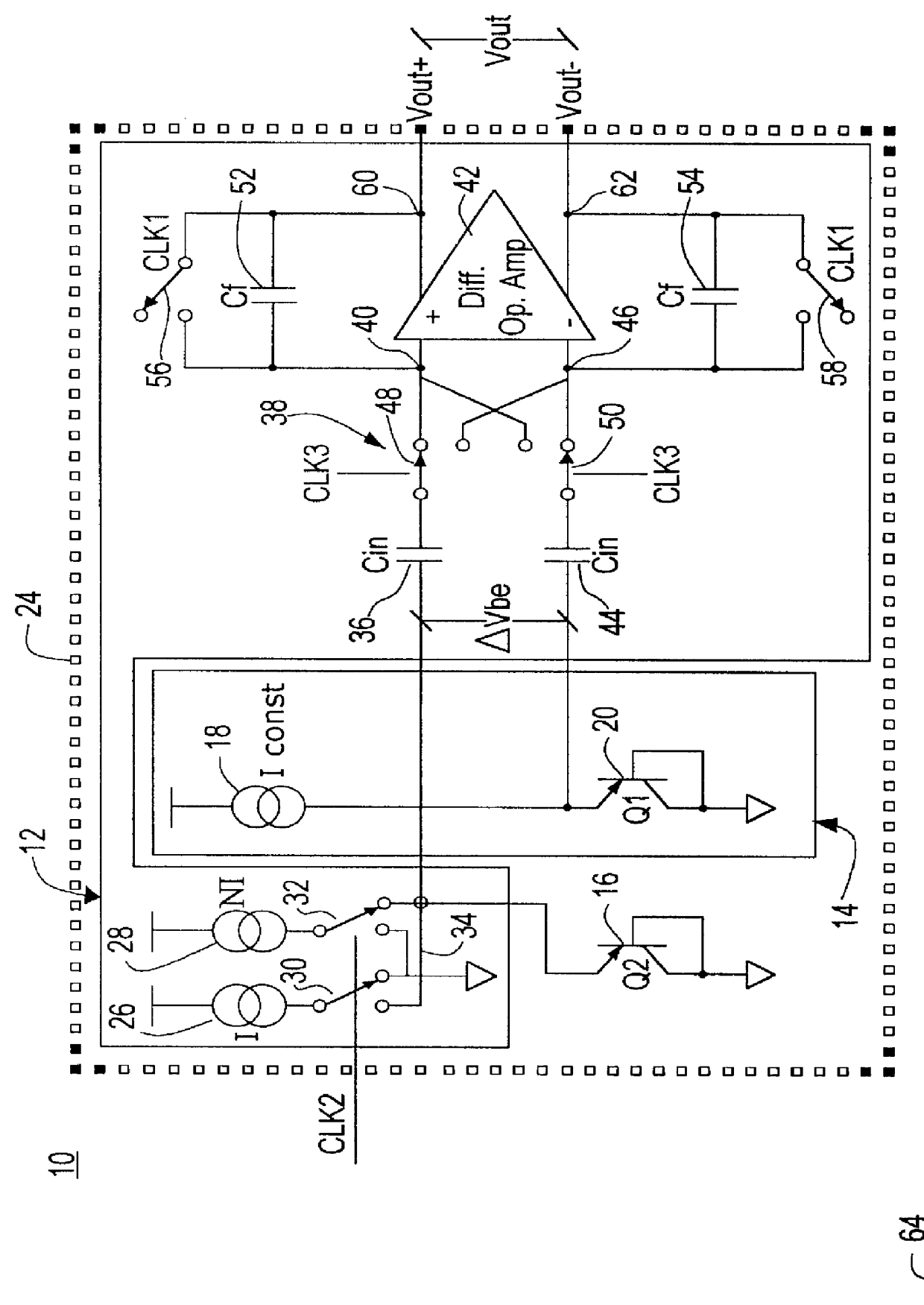
Decoupled switched current temperature circuit with compounded DELTA V be
InactiveUS6097239AThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectronic switchingDelta-vAudio power amplifier
A decoupled switched current temperature circuit with compounded DELTA Vbe includes an amplifier having an inverting input with corresponding non-inverting output and a non-inverting input with a corresponding inverting output; a PN junction connected to the non-inverting input through a first input capacitor and a voltage reference circuit is connected to the inverting input through a second input capacitor; a current supply includes a low current source and a high current source; a switching device applies the high current source to the PN junction and applies the low current source to the PN junction for providing the DELTA Vbe of the PN junction to the first capacitor; a first feedback capacitor is interconnected between the inverting output and the non-inverting input and a second feedback capacitor is interconnected between the non-inverting output and inverting input of the amplifier to define the gain on each of the inputs to produce a differential voltage across the outputs representative of the temperature of the PN junction; first and second reset switching devices discharge the first and second feedback capacitors, respectively, and a multi-phase switched device alternately interchanges the connection of the first and second input capacitors with the amplifier inputs for compounding the single DELTA Vbe .
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
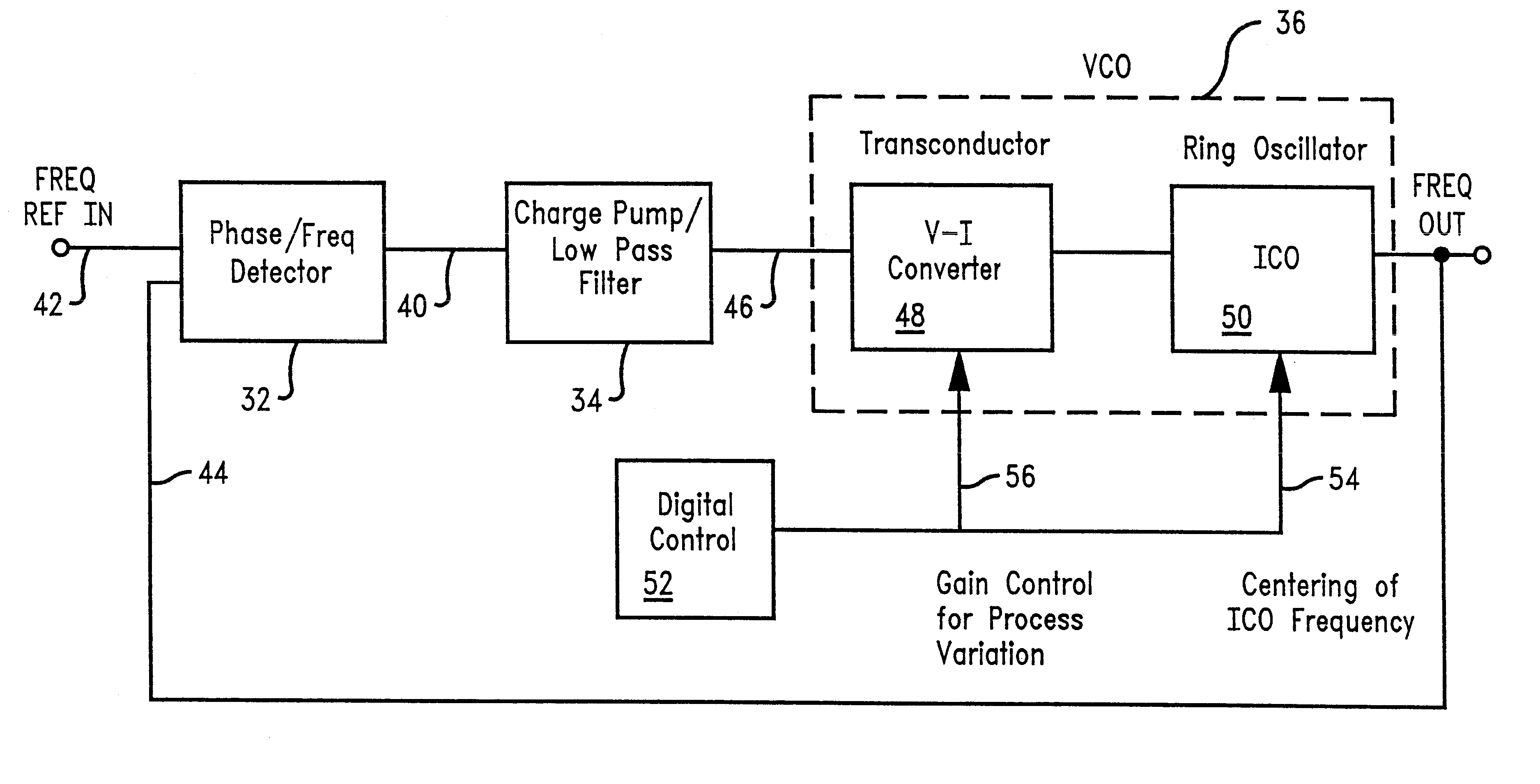
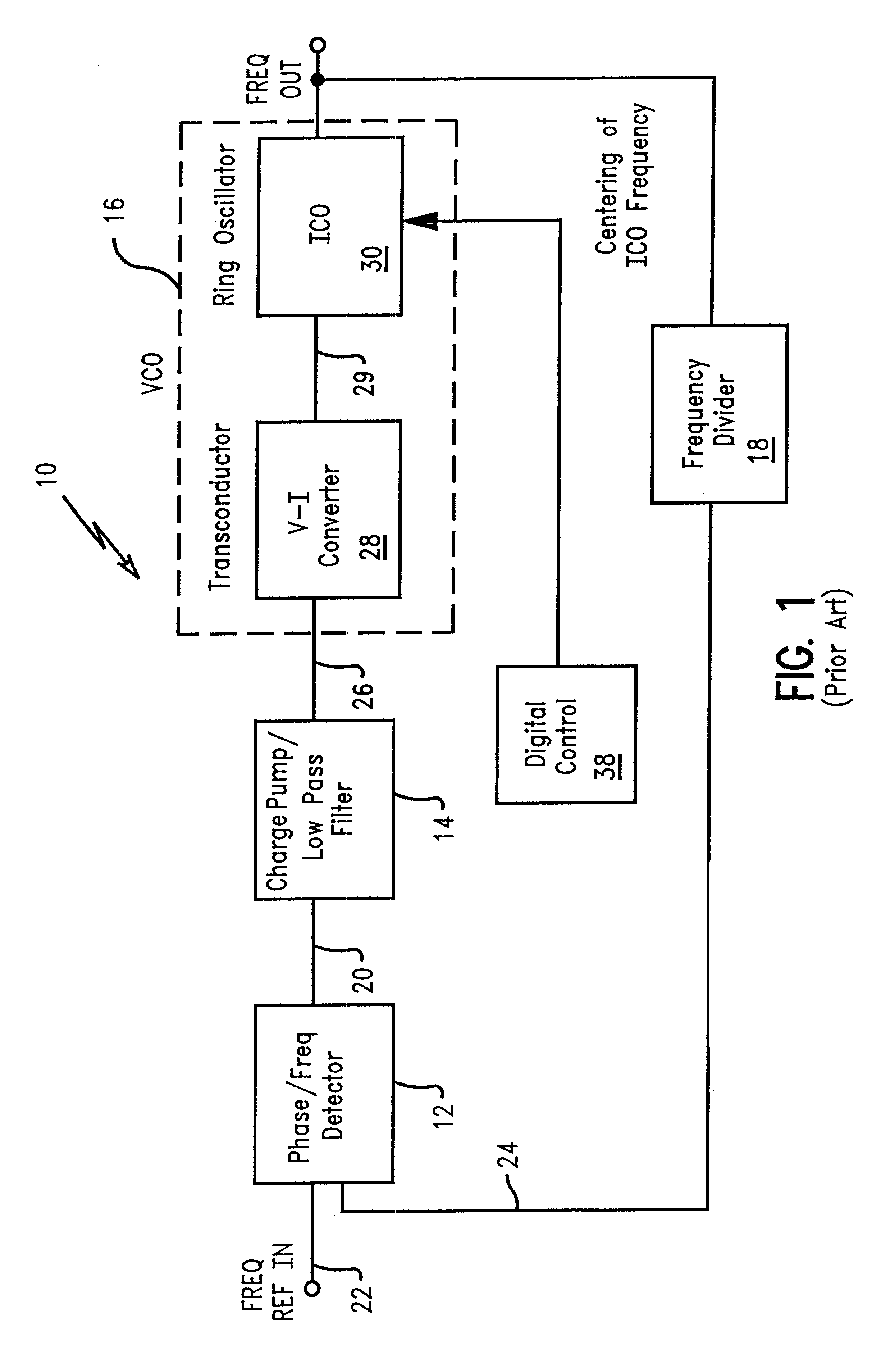
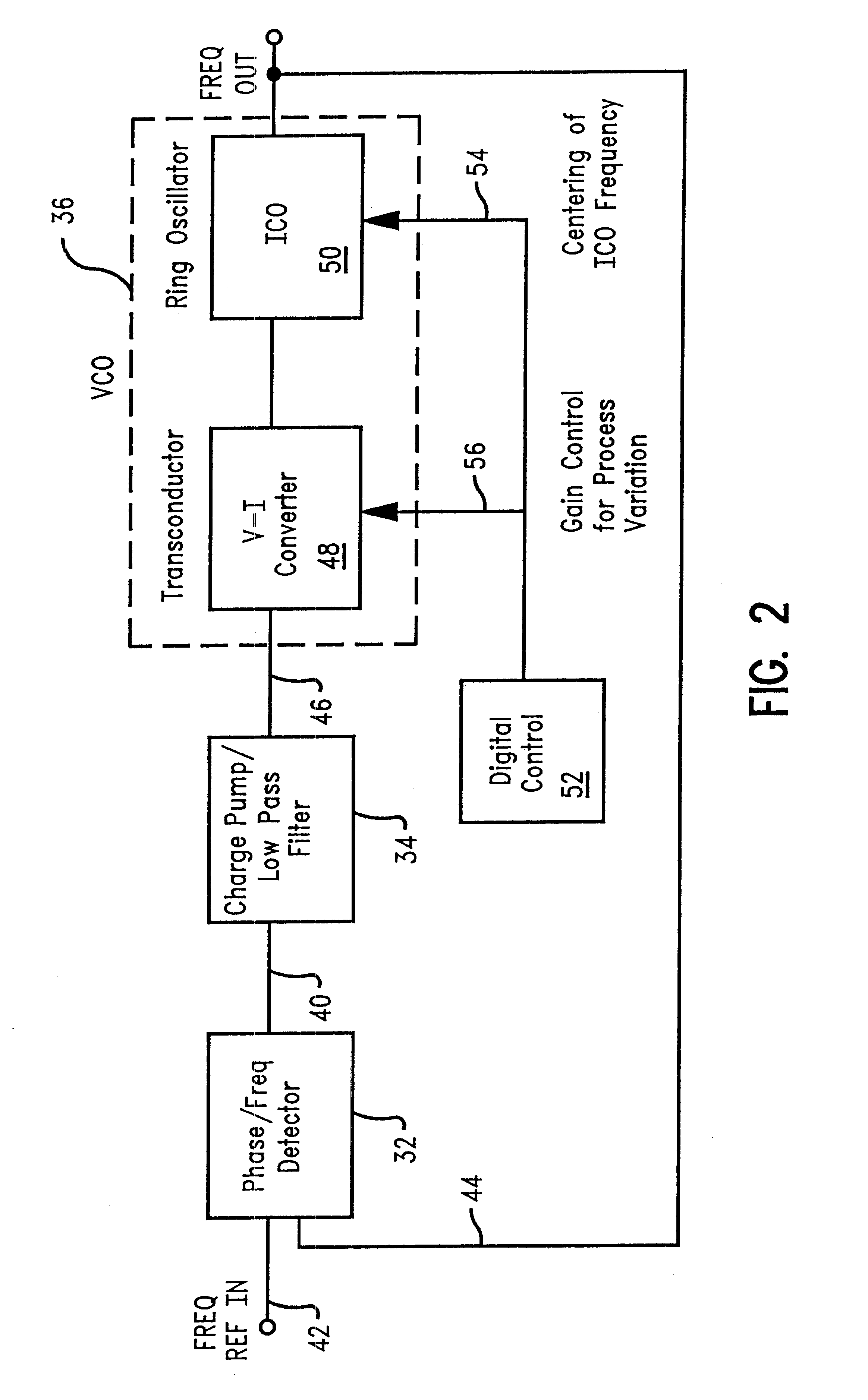
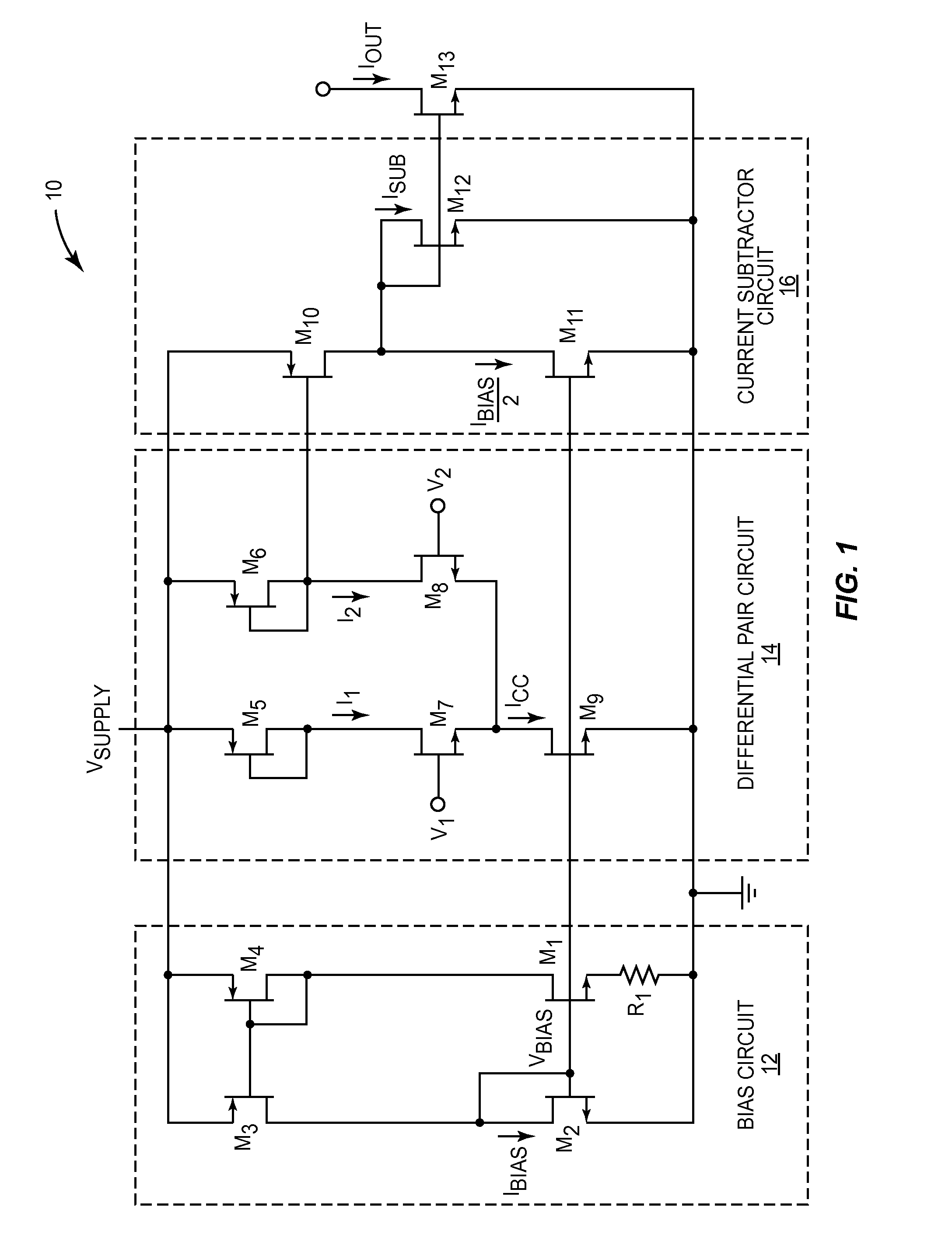
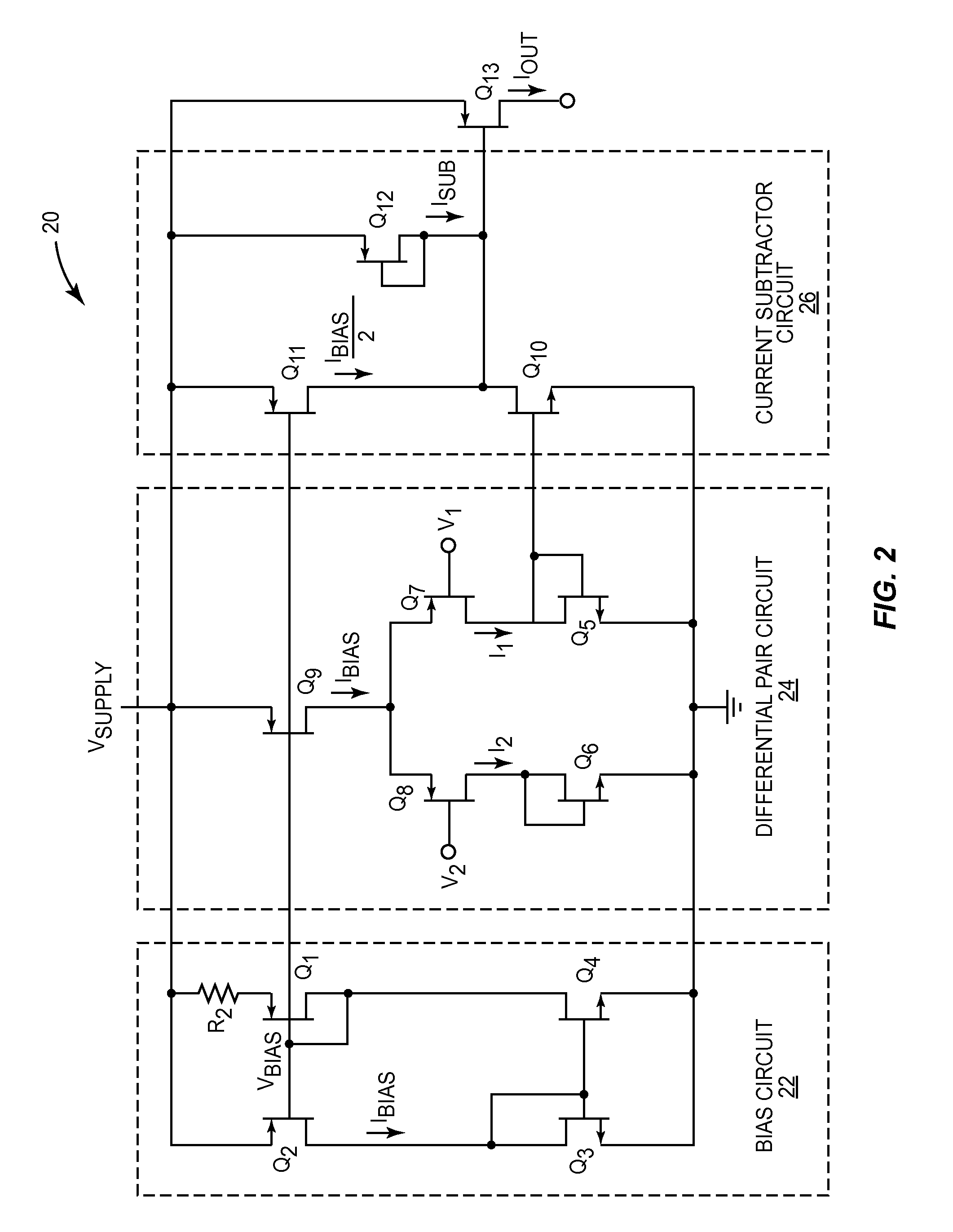
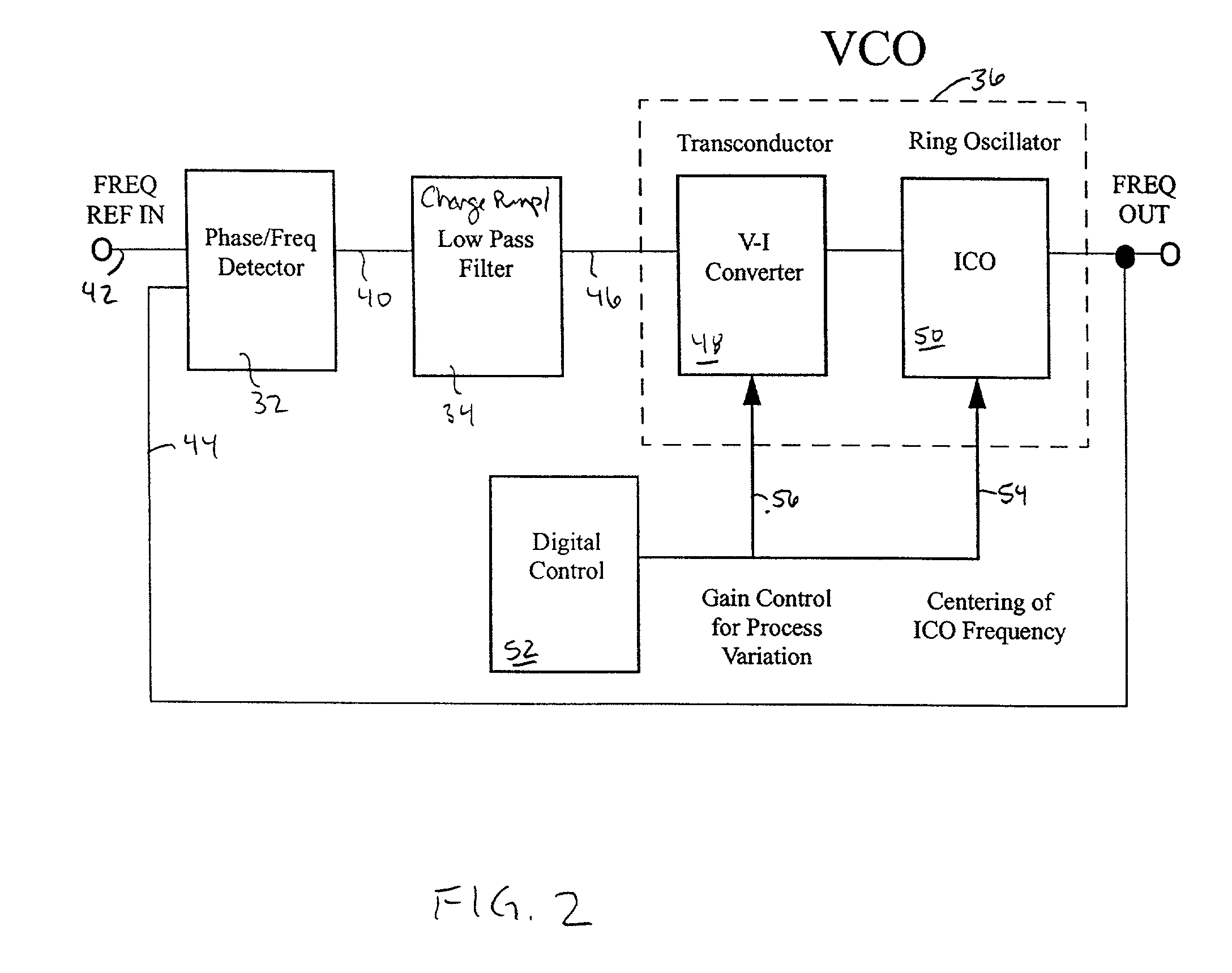
Linear voltage controlled oscillator transconductor with gain compensation
InactiveUS6466100B2More of the gainLess of the gainPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase locked loop circuitLow-pass filter
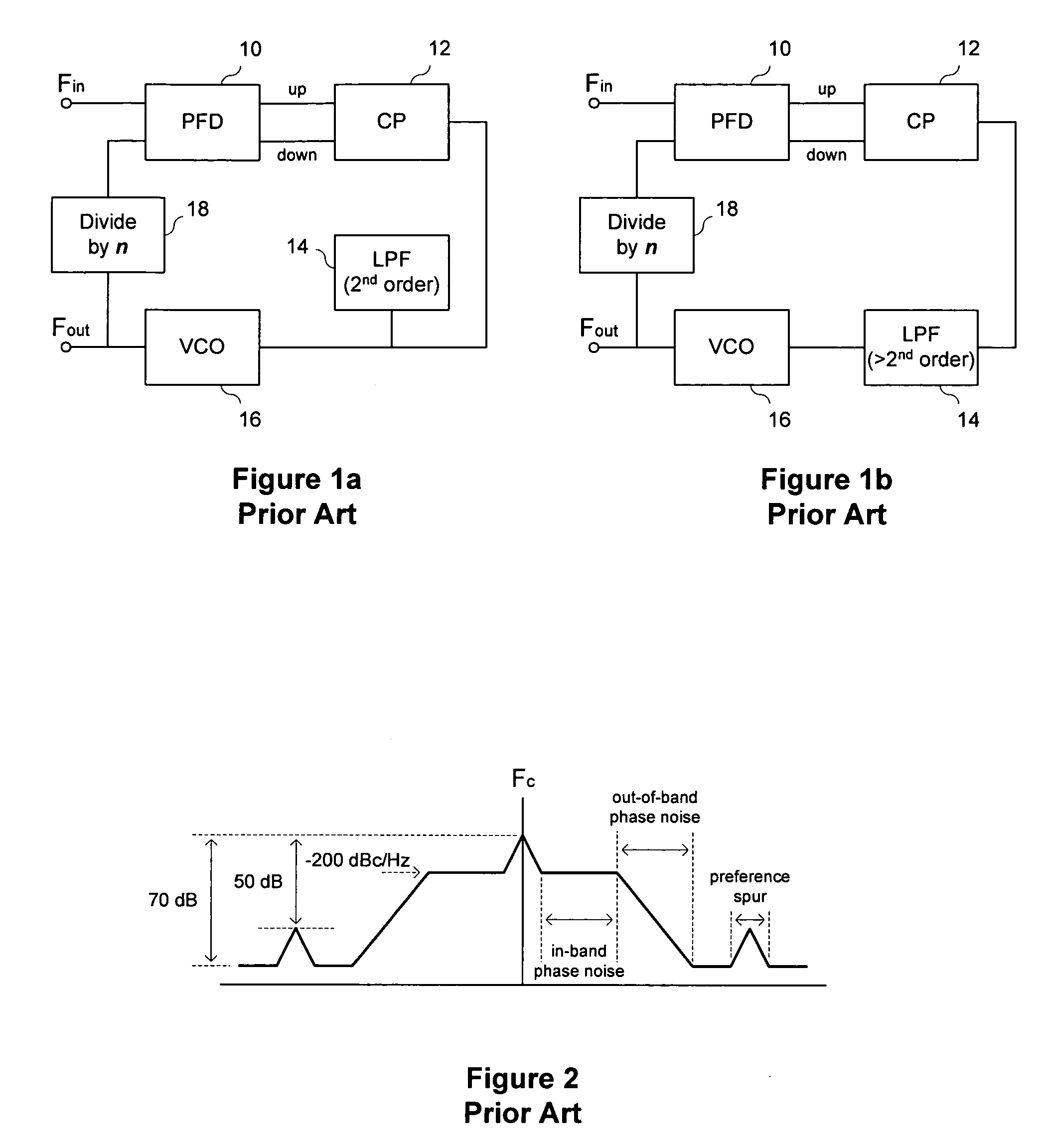
A voltage controlled oscillator of a phase locked loop circuit having digitally controlled gain compensation. The digital control circuitry provides binary logic input to the voltage controlled oscillator for a digitally controlled variable resistance circuit, a digitally controlled variable current transconductor circuit, or differential transistor pairs having mirrored circuitry for adjusting the V-I gain. The latter configuration requires the voltage controlled oscillator to incorporate a source-coupled differential pair which is driven by a low pass filter capacitor output voltage, and connected to load transistors; a current source and a current mirror for generating a tail current; individual banks of transistors to mirror the load transistor currents; a digital-to-analog converter with control lines outputted there from, the digital-to-analog converter used to increase the amount of current allowed to flow to the transconductor output, the current being digitally increased and decreased corresponding to an amount of current pulled from the current source, and mirroring the current through at least one transistor mirror circuit.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Source follower capable of compensating the threshold voltage
A source follower capable of compensating the threshold voltage is provided. The source follower comprises a current source, a switching circuit, and a thin film transistor. The source follower makes the threshold voltage of the thin film transistor constant by using the current source, and makes the input voltage nearly equal to the output voltage by using the storage capacitor and the compensating capacitor. Thus, it can make the error of the output voltage fall in the error range of the gray level voltage.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Low Noise VCO Circuit Having Low Noise Bias
A low noise VCO circuit for an LC VCO circuit comprising MOS varactors is disclosed. The LC VCO circuit usually comprises an LC tuning circuit coupled with a pair of cross-coupled transistors used as a negative impedance element. A pair of varactors is used to provide fine tuning by applying a control voltage to the varactor. Since the varactor is also coupled to the pair of cross-coupled transistor, the process variation and temperature change may affect the bias voltage coupled to the pair of varactors. Therefore, a bias circuit usually is used to alleviate the impact of process variation and temperature change associated with the pair of transistor. Nevertheless, the bias voltage typically is implemented by providing a current flowing through a resistor, wherein the current is generated by a current source. The noise associated with the current source will affect the performance of the VCO circuit. A low noise VCO circuit is disclosed which utilizes a low noise bias circuit. The low noise bias circuit comprises a current source, a load device and a voltage divider wherein the load device is coupled to the voltage divider in parallel. The load device may be implemented using a bipolar transistor or a diode-connected MOS device.
Owner:QUINTIC MICROELECTRONICS WUXI
Current steering charge pump having three parallel current paths preventing the current sources and sinks to turn off and on
InactiveUS7012473B1Mismatch errorCurrent mismatchPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionControl signalElectrical current
A current steering charge pump that receives control signals and sources and sinks current in response to the control signals. One embodiment includes a main current source, secondary current source, main current sink, and secondary current sink, and three different current paths between various of the current sources and current sinks. One embodiment includes buffers operative to maintain the node voltages of central nodes at the same voltage as the output node of the charge pump, where each buffer is coupled between two of the three current paths.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Full scale input-output operational amplifier
ActiveCN101459412AReduce noiseLower Offset VoltageAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention discloses an operational amplifier with full input and output, wherein the current of an input tube is controlled by current sources unsymmetrical up and down on the basis of an existing operational amplifier with full input and output, a source end of an NMOS differential pair is connected with the source electrode of a first switch transistor, the output end of a first current mirror and a first current source, and a source end of a PMOS differential pair is connected with the source electrode of a second switch transistor, the output end of a second current mirror and a second current source, the drain of the first switch transistor is connected with the input end of the second current mirror, the drain of the second switch transistor is connected with the input end of the current mirror, and the grid of a complementary differential pair of PMOS and NMOS is connected with input differential signals, wherein the first current source is equal to the second current source, and the first current source and the second current source are of 1:3 current mirrors. The operational amplifier with full input and output can keep the transconductance constant in the common mode input range.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Current difference divider circuit
A current difference divider circuit with a plurality of current sources is provided. The divider circuit includes a first current source which is operable to generate a first current, a second current source for generation of a second current less in magnitude than the first current, and a third current source for generating a difference current with its magnitude equivalent to a difference between the first and second currents and for generating a third current resulting from the division thereof. The circuit further includes a fourth current source for generating a fourth current obtainable by mirroring of the second current. The third and fourth currents are added together to provide a fifth current, which is then output.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Constant current source having a controlled temperature coefficient
A bandgap circuit for producing a constant current having a controllable temperature coefficient. A current mirror supplies first and second substantially identical currents to first and second bipolar transistors. A first resistor is connected across the emitters of the bipolar transistors. A second resistor connects one to the bipolar emitters to a common terminal where the current source currents are recombined and supplied to a common terminal of a power supply. The band gap voltage produced at the common base connections of the bipolar transistors have a voltage temperature coefficient which is controlled by the values of the resistors. A current source is coupled to receive the bandgap voltage and produces a current having a temperature coefficient corresponding to the voltage temperature coefficient of the bandgap voltage.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Charge pump circuit using active feedback controlled current sources
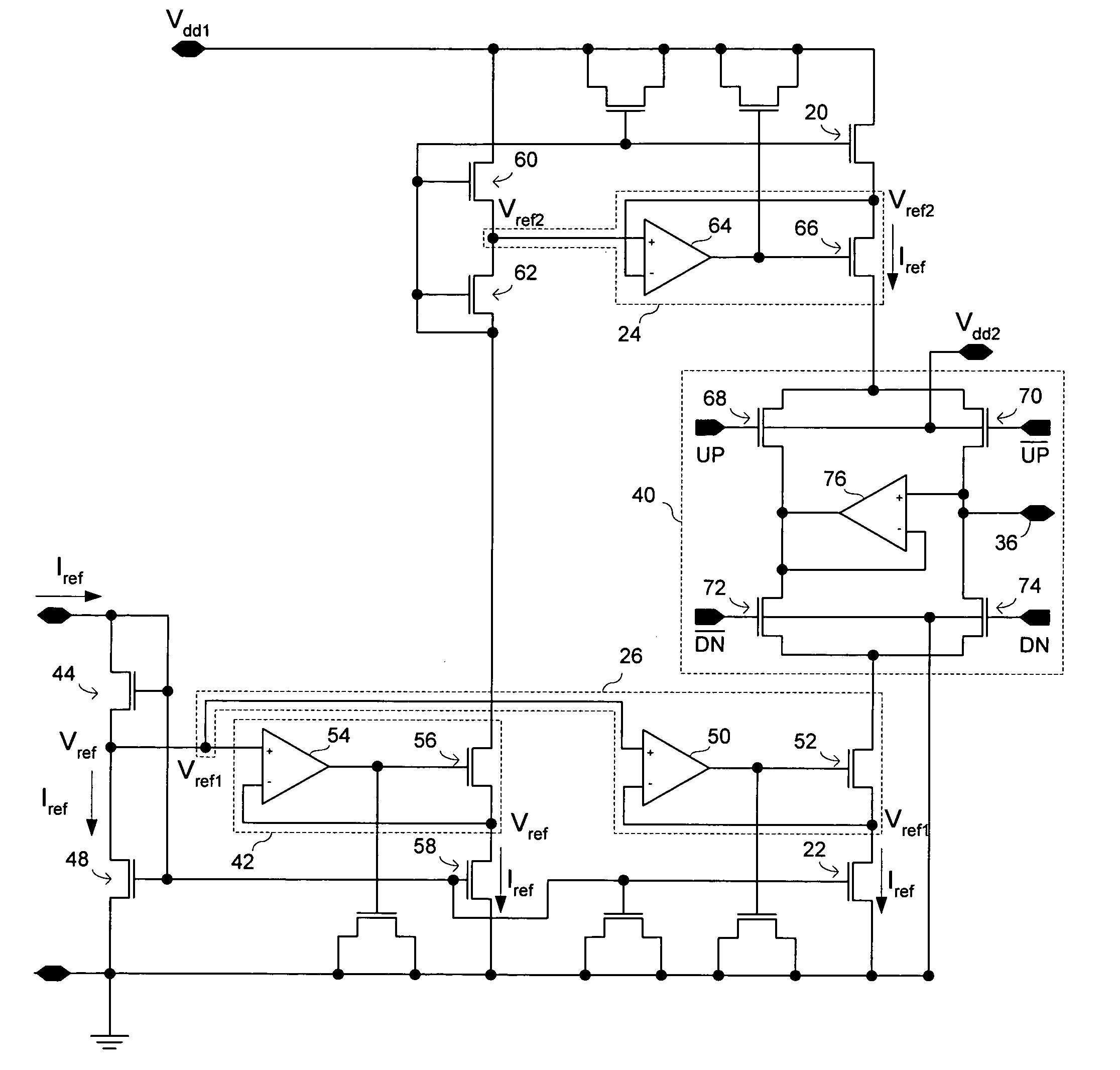
ActiveUS6980046B2Reduce noise contributionRaise the gate voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalPulse automatic controlDriving currentActive feedback
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
Current source
A current source includes a node, a biasing circuit, a loading circuit and a current mirror. The node has a specified voltage. The biasing circuit biases the specified voltage to be a first reference voltage. The loading circuit provides an equivalent resistor across the node and a second reference voltage to generate a reference current. The loading circuit includes a resistor and a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET). The resistor has a first temperature coefficient. The transistor operating in a linear region is controlled by a control voltage to turn on and to form a transistor resistor coupled with the resistor in series. The transistor resistor has a second temperature coefficient, wherein a temperature coefficient of the equivalent resistor is relevant to the first and second temperature coefficients. The current mirror receives the reference current and provides a mirrored current of the reference current as the output current.
Owner:RAYDIUM SEMICON
Autonomous controlled headroom low dropout regulator for single inductor multiple output power supply
A controlled headroom low dropout regulator (CHLDO) having an LDO with an input voltage provided by a capacitor. An incremental voltage is added to an output voltage of the LDO to create a reference voltage. The reference voltage is compared to the input voltage to determine when to couple / de-couple the capacitor with a current source. If the capacitor is coupled to the current source, the capacitor will charge only if the voltage driven by the current source exceeds the input voltage provided by the capacitor. When the input voltage developed on the capacitor exceeds the reference voltage, the capacitor is automatically de-coupled from the current source. Multiple CHLDOs can be charged from a single current source, wherein charging automatically proceeds from the lowest voltage CHLDO to the highest voltage CHLDO.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Method of generating multiple current sources from a single reference resistor
ActiveUS20120218026A1Electronic switchingElectric pulse generator detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A differential voltage controlled current source generating one or more output currents is based upon a single external resistor. The differential voltage controlled current source may generate an output current that is proportional to a received differential voltage and a bias current with the use of a single external resistor. The technique may be used to generate multiple accurate and process independent current sources. The current sources may be a zero temperature coefficient (ZTC) current, a proportional to absolute temperature (PTAT) current, or an inversely proportional to absolute temperature (NTAT) current. The output of the current sources may be inversely proportional to the resistance of the external resistor.
Owner:QORVO US INC
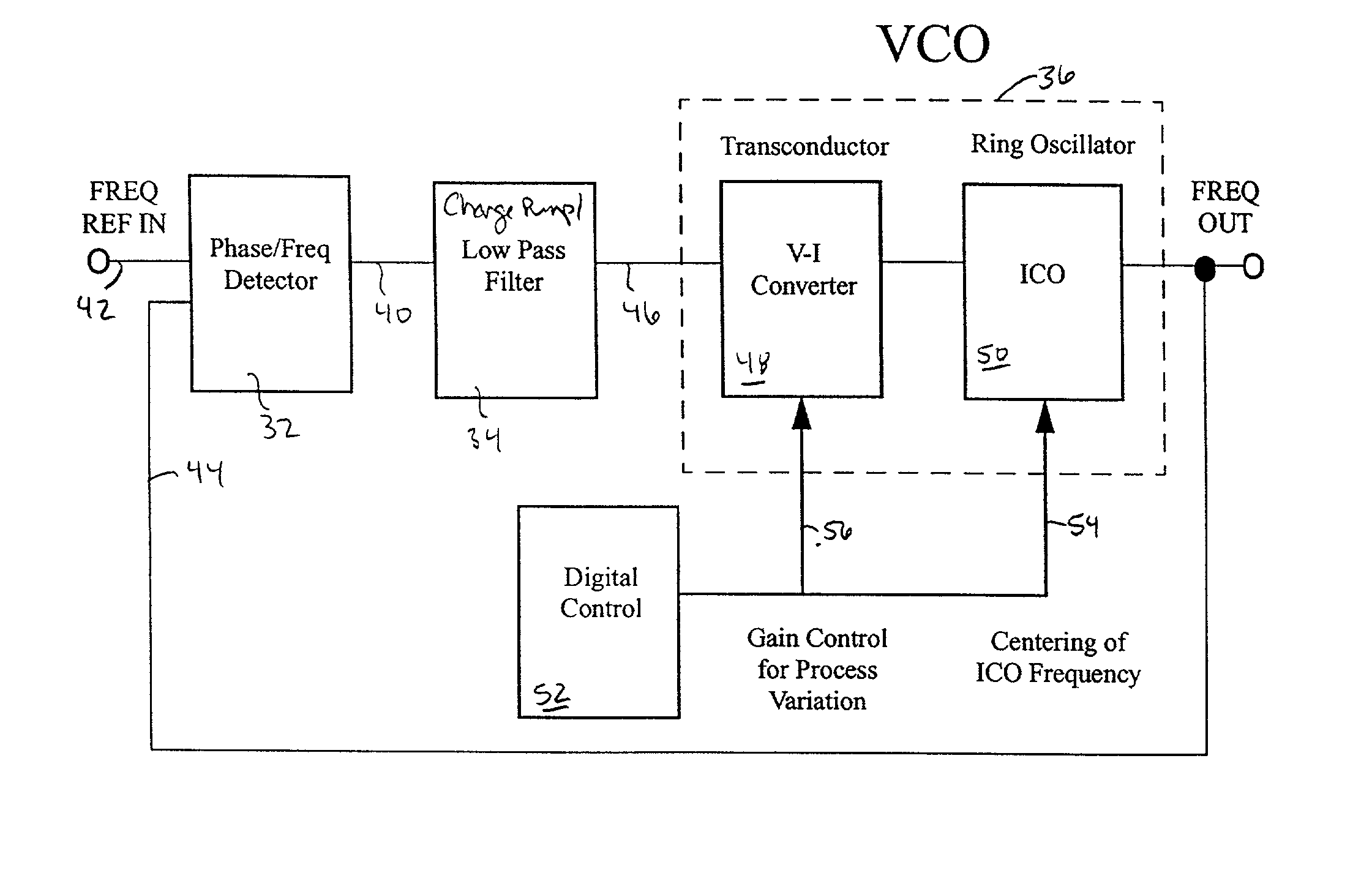
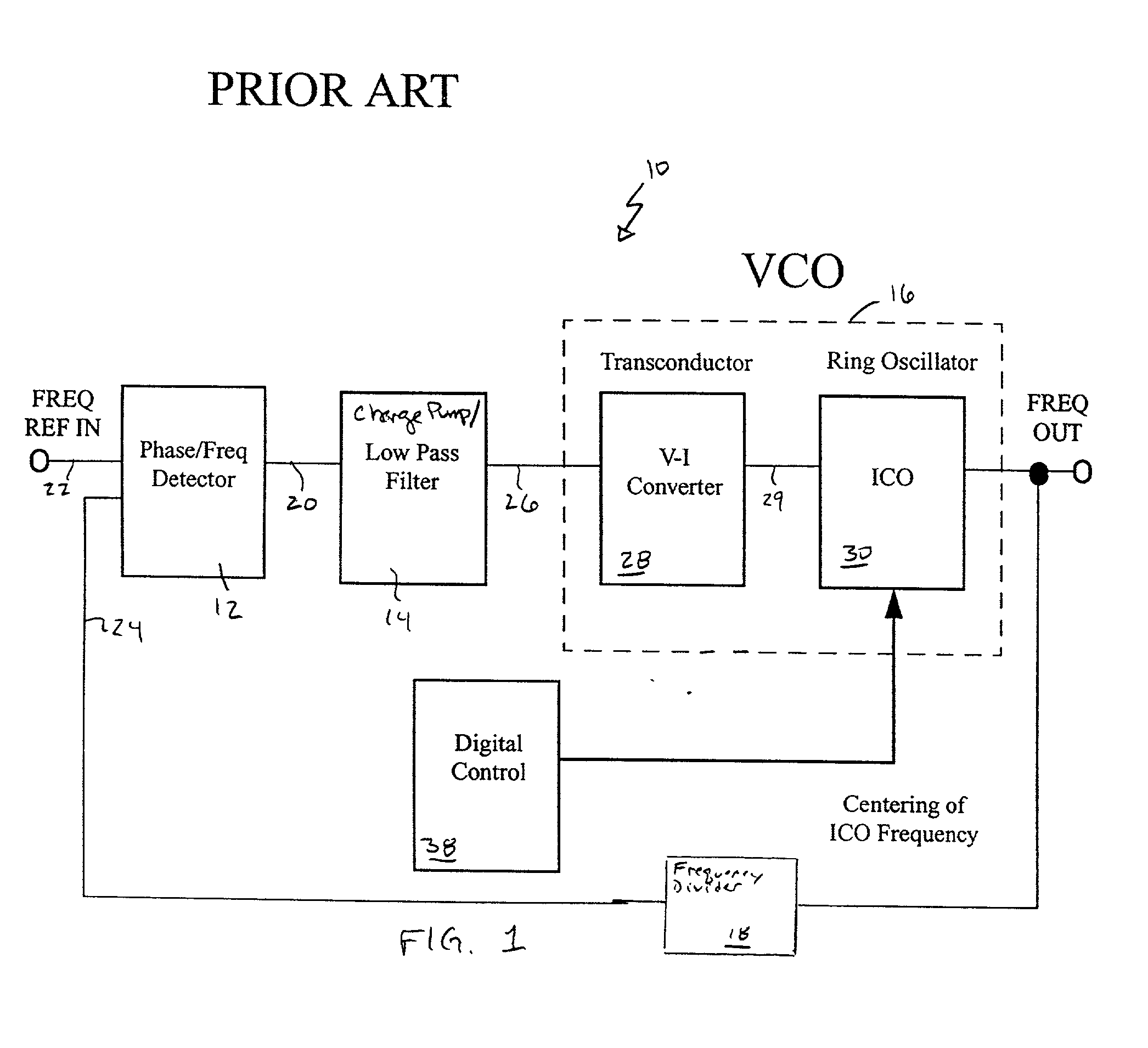
Linear voltage controlled oscillator transconductor with gain compensation
InactiveUS20020089381A1Decrease resistance of variable resistanceMore of the gainPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase locked loop circuitLow-pass filter
A voltage controlled oscillator of a phase locked loop circuit having digitally controlled gain compensation. The digital control circuitry provides binary logic input to the voltage controlled oscillator for a digitally controlled variable resistance circuit, a digitally controlled variable current transconductor circuit, or differential transistor pairs having mirrored circuitry for adjusting the V-I gain. The latter configuration requires the voltage controlled oscillator to incorporate a source-coupled differential pair which is driven by a low pass filter capacitor output voltage, and connected to load transistors; a current source and a current mirror for generating a tail current; individual banks of transistors to mirror the load transistor currents; a digital-to-analog converter with control lines outputted there from, the digital-to-analog converter used to increase the amount of current allowed to flow to the transconductor output, the current being digitally increased and decreased corresponding to an amount of current pulled from the current source, and mirroring the current through at least one transistor mirror circuit.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
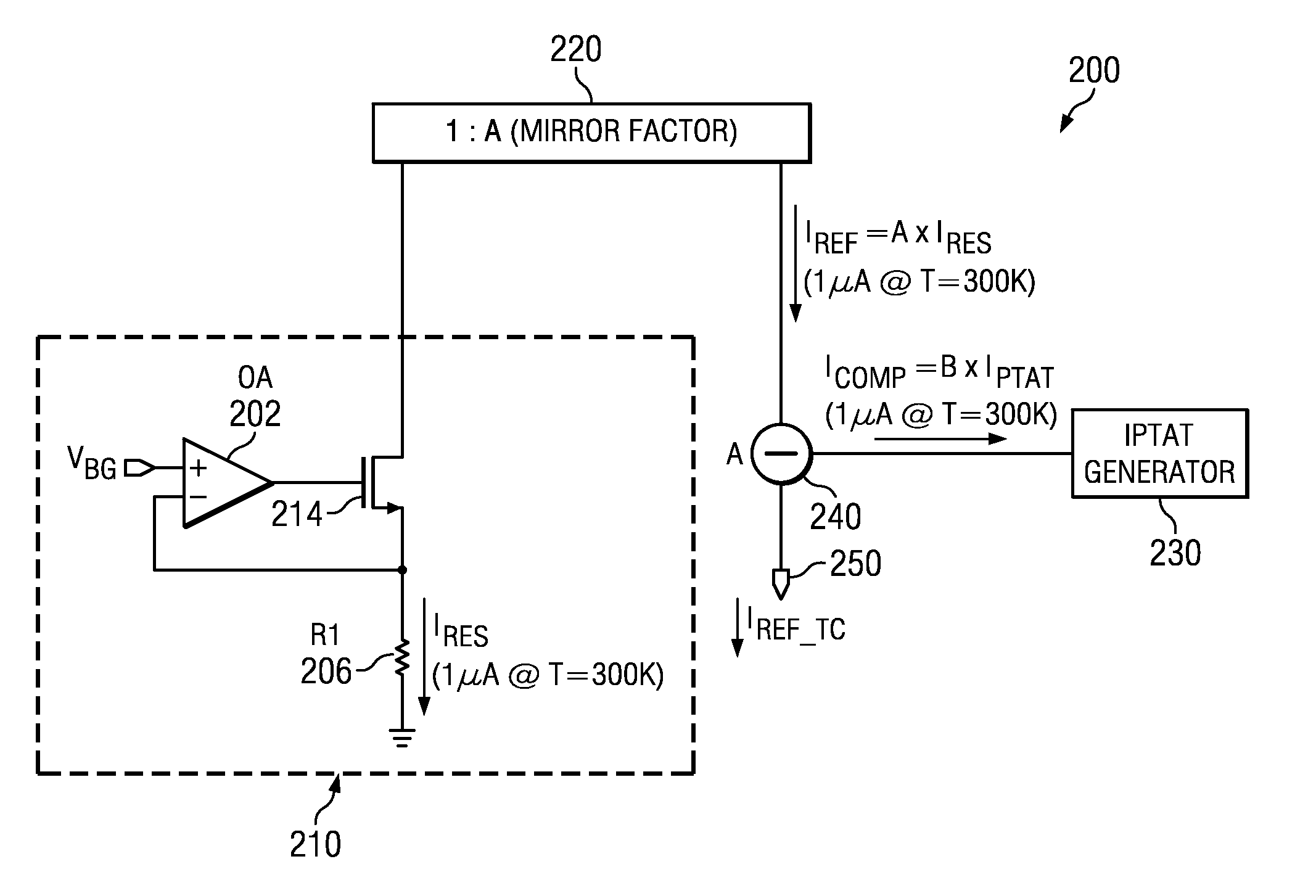
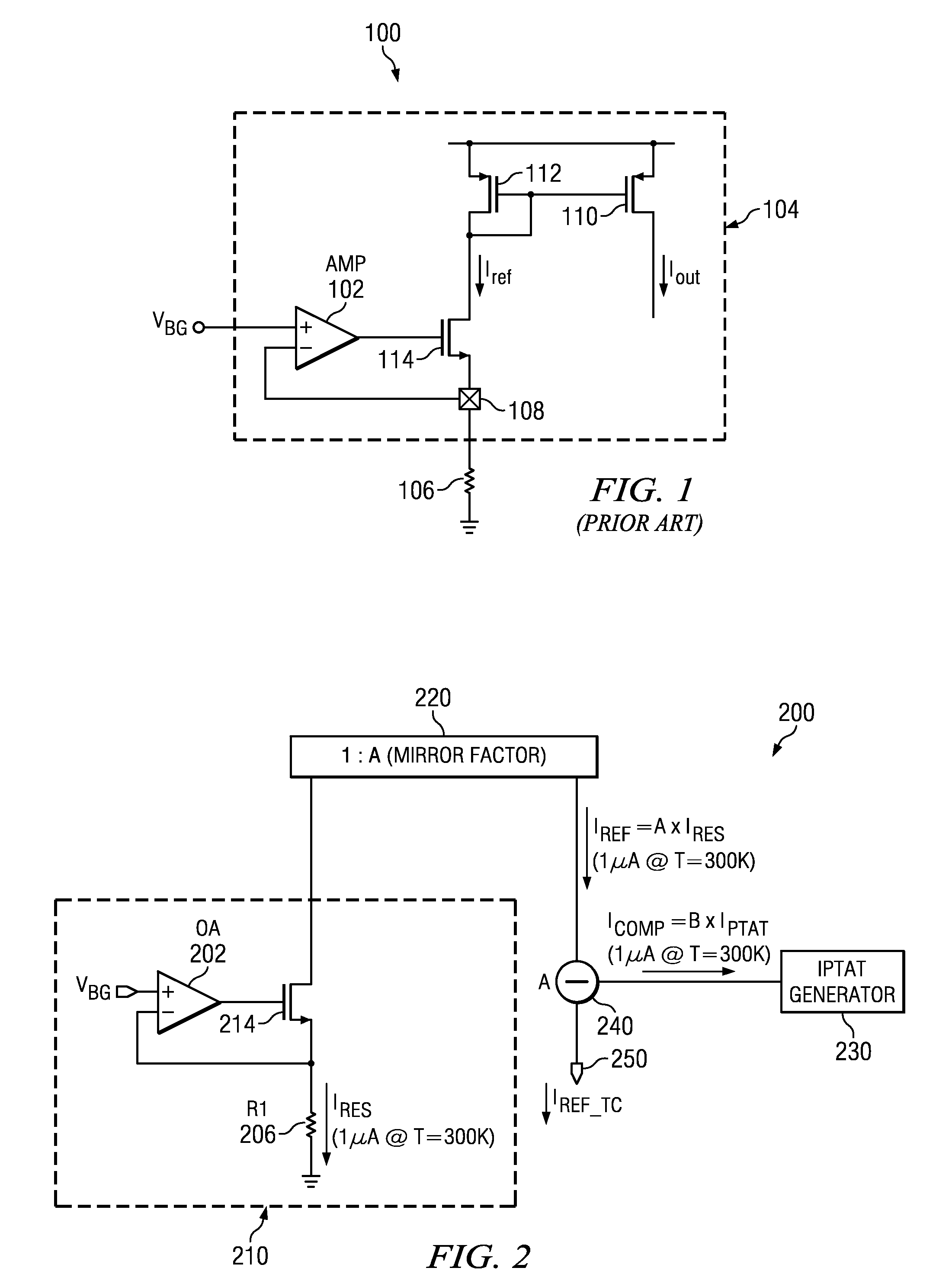
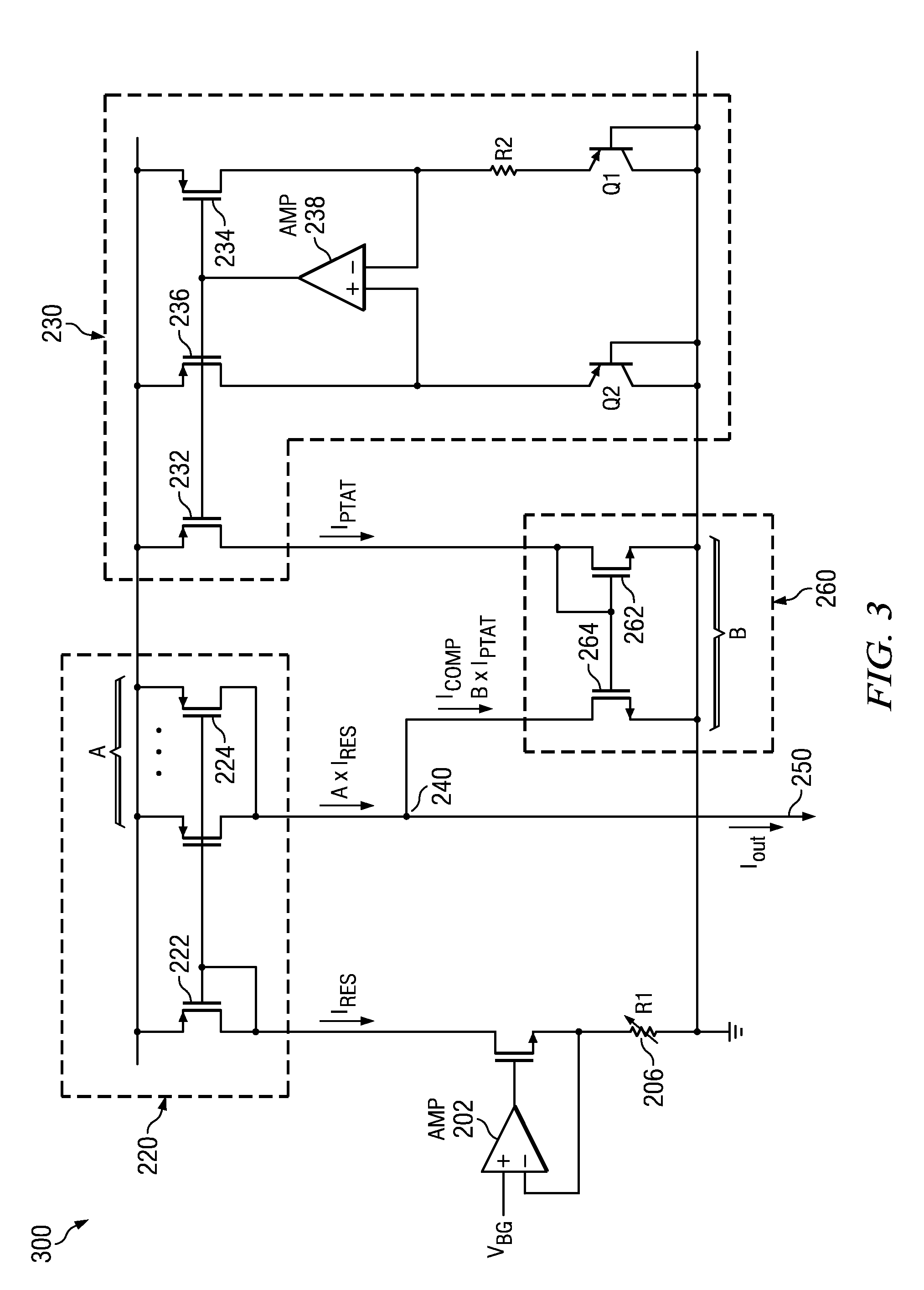
Temperature Compensated Current Source
ActiveUS20120007659A1Electronic switchingPulse generation by opto-electronic devicesVoltage referenceEngineering
A temperature compensated current source forms an uncompensated source current that is proportional to a reference voltage applied to an impedance, wherein the impedance varies with temperature. A temperature compensation current is formed that is proportional to absolute temperature (IPTAT). The uncompensated source current and the temperature compensation current is combined to form a temperature compensated source current and provided as an output of the current source.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Comparator circuit provided with differential amplifier making logical judgment by comparing input voltage with reference voltage
ActiveUS20110210762A1Shorten judgment timeIncrease speedMultiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsAdaptive biasPower flow
In a comparator circuit having a differential amplifier, which makes a logical judgment by comparing an input voltage with a reference voltage, generates and outputs a resulting output voltage thereof, a current source generates and supplies a bias current of a predetermined minute current to the differential amplifier, and a first inverter circuit inverts a differential voltage from the differential amplifier. An adaptive bias current generator circuit detects the bias current of the current source, and a through current of the first inverter circuit. The adaptive bias current generator circuit generates and supplies an adaptive bias current for executing adaptive bias current control to the differential amplifier to allow the differential amplifier to operate with the bias current upon no logical judgment, and to allow the differential amplifier to operate by using the adaptive bias current obtained by increasing the bias current upon logical judgment.
Owner:SONY CORP
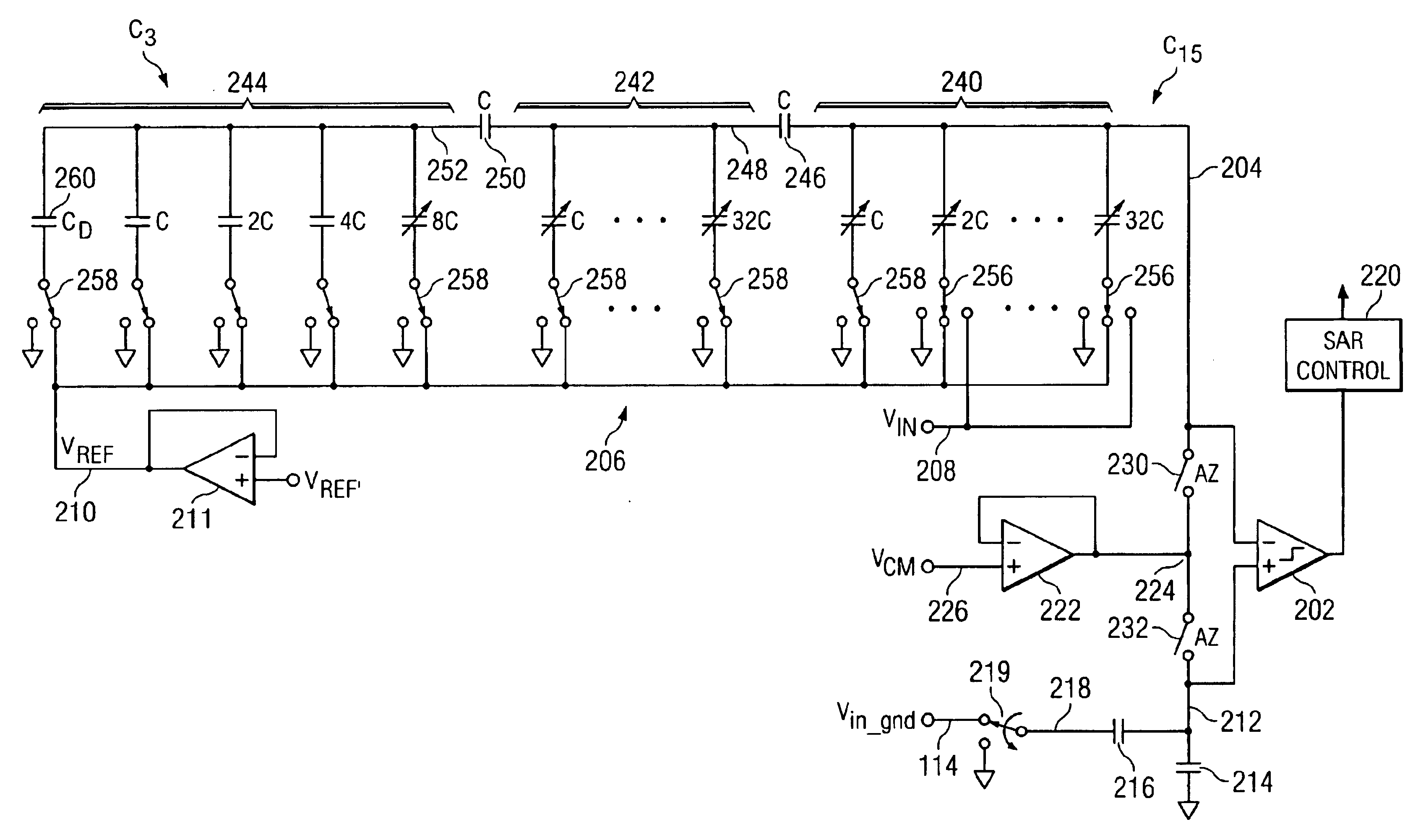
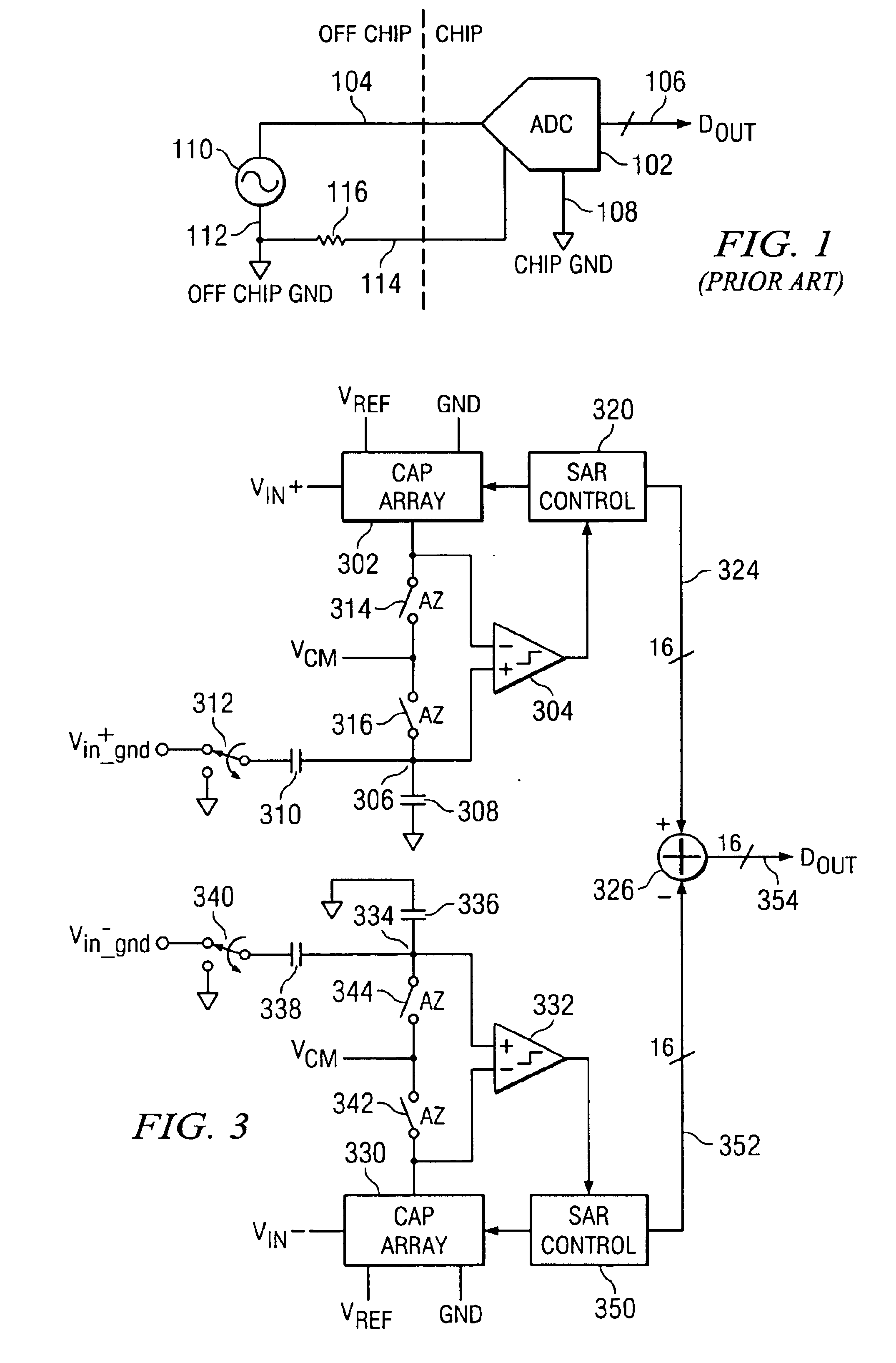
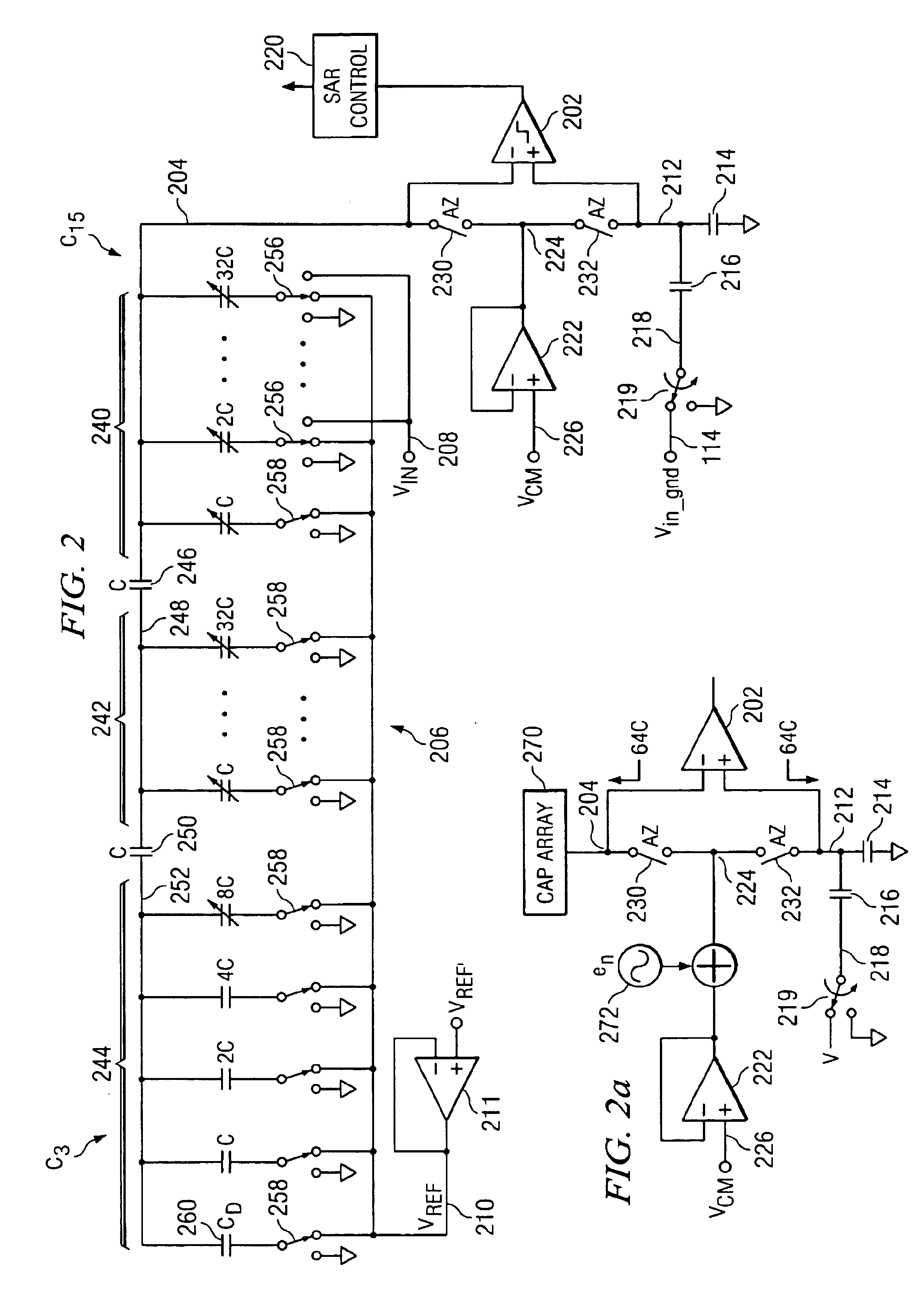
High speed comparator for a SAR converter with resistor loading and resistor bias to control common mode bias
InactiveUS6882295B2Electric signal transmission systemsResistors with plural resistive elementsDriving currentElectrical polarity
High speed comparator for a SAR converter with resistor loading and resistor bias to control common mode bias. A differential comparator having positive and negative inputs and positive and negative outputs is disclosed. The comparator includes a current source for driving current from a supply to a common node. A differential pair of transistors is disposed such that one side of the source / drain paths are tied together and to the common node, with the other side of the source / drain paths thereof for each of the transistors in the differential pair interfaced to the positive and negative outputs, respectively for applying drive thereto. A first resistor load is disposed between the positive output and a supply reference opposite in polarity to the supply. A second resistor is disposed between the negative output and the supply reference. The gate of the one of the transistors in the pair associated with the positive output is connected to the negative input and the gate of the other of the transistors in the pair is connected to the positive input. The current through the current source defines the common mode bias. A ratiometric bias circuit having associated therewith a bias resistor with a current driven there through is provided that controls the current through the current source, such that it is a ratio of the current through the bias resistor.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Voltage controlled current source and frequency sweep device using same
InactiveCN101114177AAccurateGood linear effectTelevision systemsElectric variable regulationElectrical impedanceVoltage control
The invention relates to a voltage-controlled current source and a sweep device using the voltage-controlled current source, wherein, the voltage-controlled current source comprises an impedance circuit, an amplifier, a transistor and a current mirror circuit. The impedance circuit is coupled with a common voltage at one end, the amplifier is coupled with the other end of the impedance circuit at a first end and receives a controlled voltage at a second end, and the transistor is coupled with an output of the amplifier at the gate, and a first source / drain is coupled with the other end of the impedance circuit. The current mirror circuit is coupled with a second source / drain which comprises a current output, wherein, the current which is output from the current output is in proportion to the current passing the transistor.
Owner:BEYOND INNOVATION TECH
Reference voltage regulation method and circuit as well as constant-current source driving circuit utilizing same
ActiveCN102413608AThe output voltage is not smallGuaranteed to workElectroluminescent light sourcesAc-dc conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage regulation
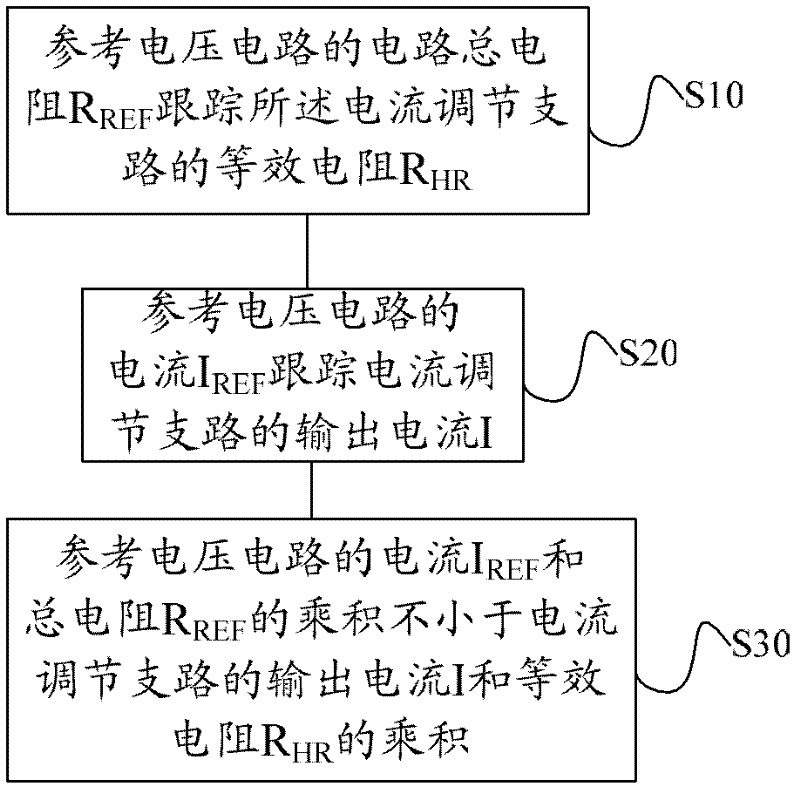
The invention discloses a reference voltage regulation method and circuit as well as a constant-current source driving circuit utilizing the same. The method comprises: the circuit total resistance RREF of a reference voltage circuit tracks the equivalent resistance RHR of a current output branch; the reference voltage circuit receives a current IREF, and the current IREF tracks the output current I of the current output branch, so that the voltage VREF (which is the product of the current IREF and the total resistance RREF) of the reference voltage circuit is not less than the voltage threshold value VHR (which is the product of the output current I and the equivalent resistance RHR) of the current output branch, and the voltage of the reference voltage circuit is used as a reference voltage of the constant-current source driving circuit, thus realizing the self-adaptive regulation of the reference voltage of the constant-current source driving circuit. By virtue of the self-adaptive regulation of the reference voltage of the constant-current source driving circuit, the problem of larger constant-current source loss is solved, and the system efficiency is improved.
Owner:SILERGY SEMICON TECH (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Column current source
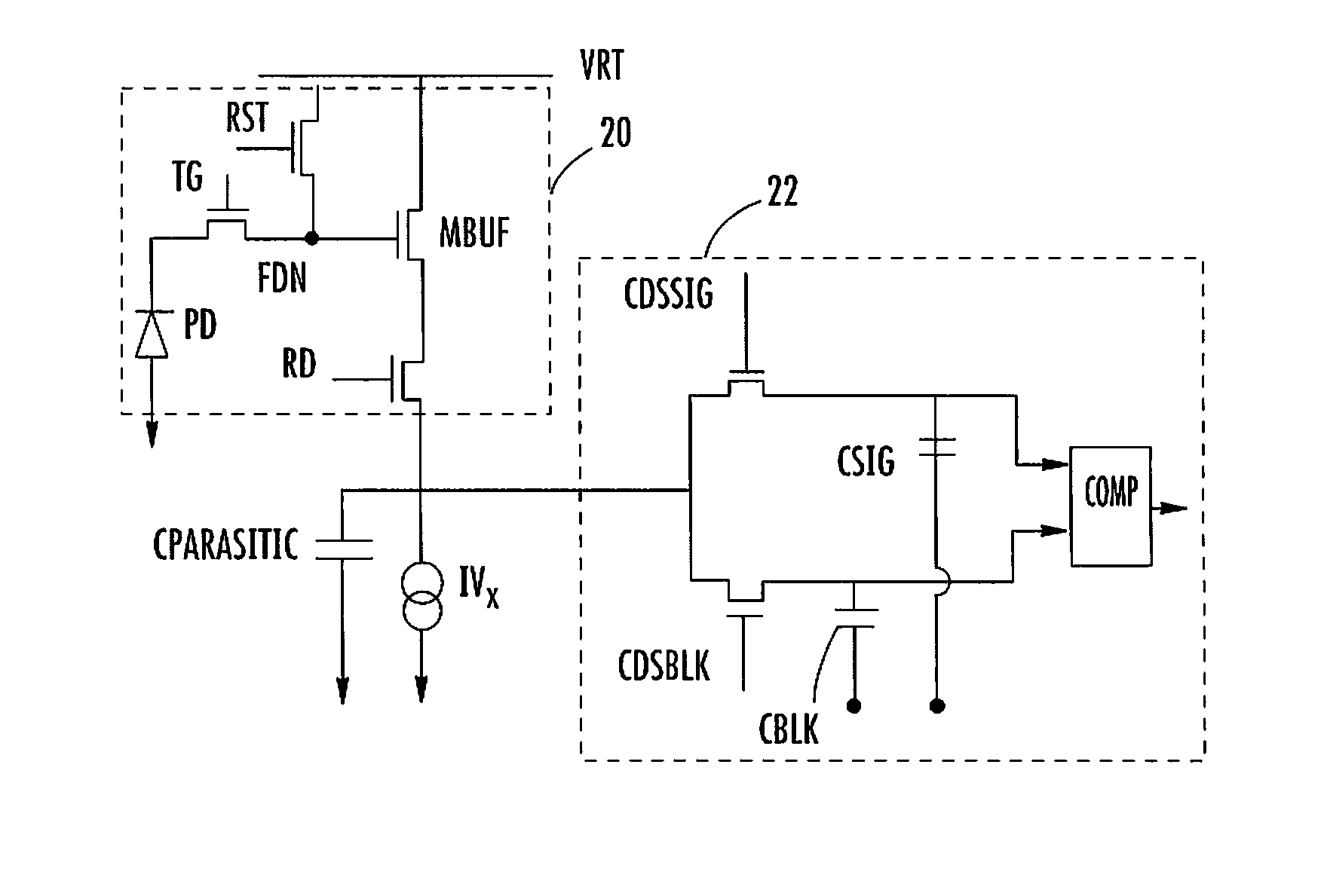
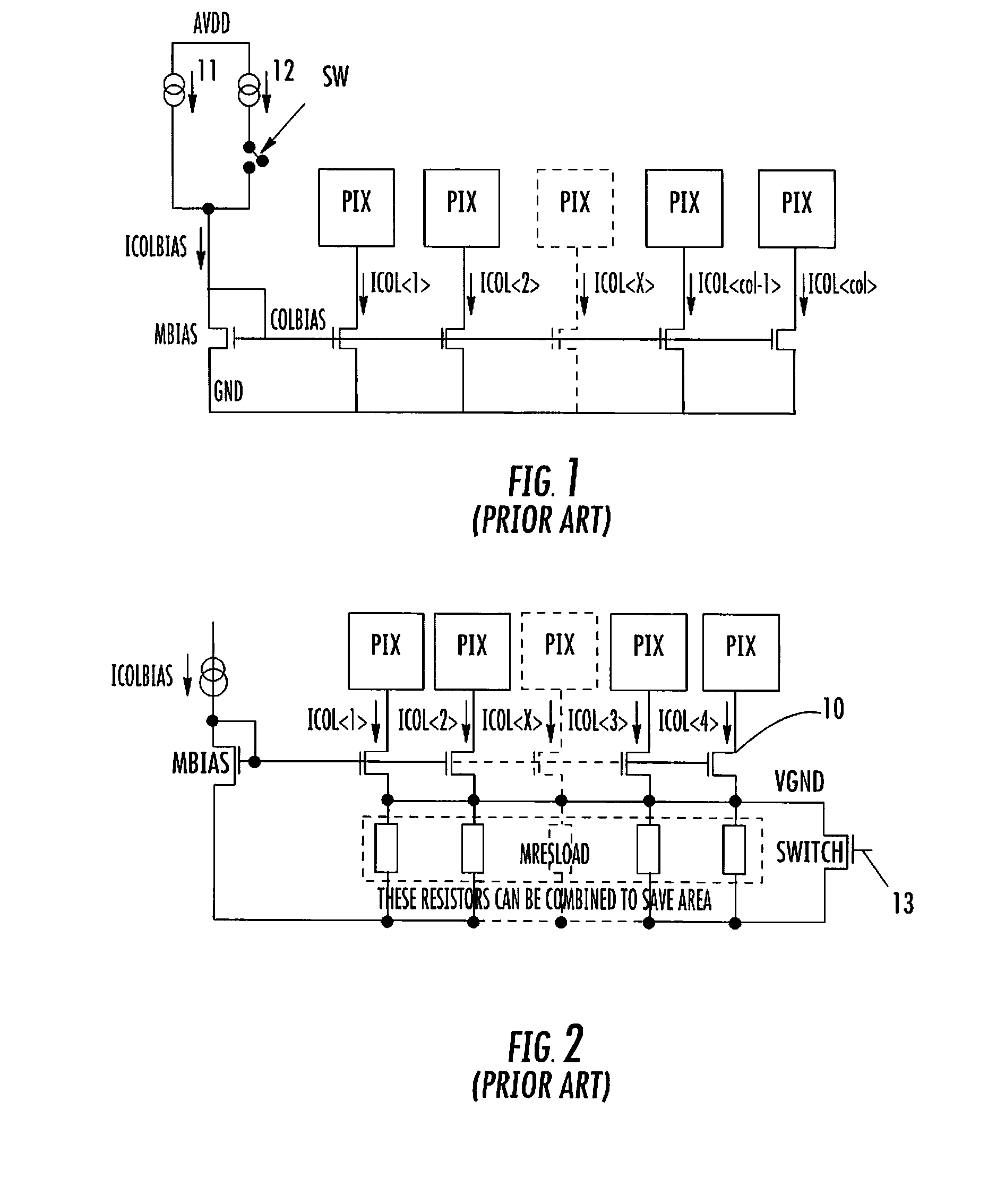
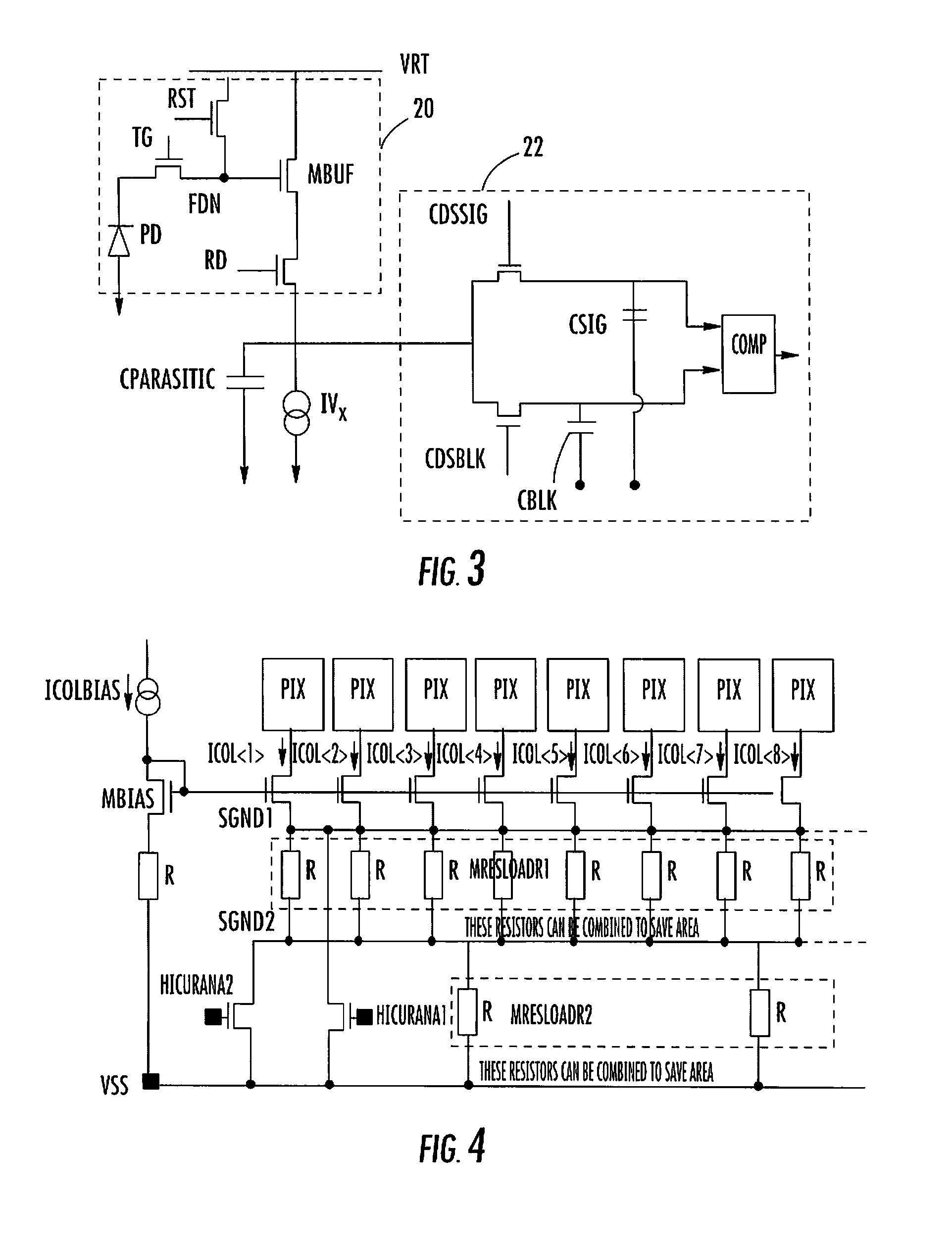
ActiveUS20080210848A1Reduce circuit sizeSmall sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsReference currentCurrent consumption
A column current source for an image sensor includes an array of pixels arranged in rows and columns, a reference current source, a transistor connected as a source follower to the reference current source and forming one half of a current mirror, and a plurality of current sources each connected to a column of pixels and with each current source forming the other half of the current mirror, thereby mirroring the reference current source. The current sources are connected to a first common node. A resistor is connected between the first common node and a second common node. One or more resistors are connected in series between the second common node and the transistor drain, and two or more switches are selectively operable to short circuit the resistors allowing the current sources to provide more than two current levels, thereby optimizing the image sensor current consumption for mobile devices.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS RES & DEV
Offset correction circuit for voltage-controlled current source
InactiveCN101147424AAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationElectroluminescent light sourcesAudio power amplifierEngineering
Novel circuitry and methodology are provided for correcting the offset associated with a voltage-controlled current source. An offset correction circuit is coupled to the current source to prevent the output current produced by the current source from deviating from a desired level. The current source may include a transconductance amplifier or a chopper amplifier, and may be configured to produce a zero or non-zero value of the output current.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Relaxation oscillator and monolithic integrated chip
ActiveCN106209027ASimple structureFew modulesElectric pulse generatorEngineeringRelaxation oscillator
The invention provides a relaxation oscillator and a monolithic integrated chip. The relaxation oscillator comprises a relaxation oscillator circuit, and the relaxation oscillator circuit comprises a threshold voltage generating circuit, a capacitance charging and discharging circuit and a comparator circuit, wherein the threshold voltage generating circuit inputs a threshold voltage signal to an inverting input end of the comparator circuit; the capacitance charging and discharging circuit inputs capacitance voltage signals to an in-phase input end and an inverting input end of the comparator circuit; the threshold voltage generating circuit comprises a first current source, a second current source and a threshold resistance, the first current source supplies current to the threshold resistance through a first inverter switch element, and the second current source extracts the current from the threshold resistance through a first in-phase switch element; and the capacitance charging and discharging circuit comprises a third current source, a fourth current source and a capacitor, the third current source supplies the current to the capacitor through a second inverter switch element, and the fourth current source extracts the current from the capacitor through a second in-phase switch element. The monolithic integrated chip provided by the invention can be applied to the relaxation oscillator.
Owner:ALLWINNER TECH CO LTD
Source follower capable of compensating threshold voltage
The source follower capable of compensating the threshold includes current source, switching circuit and thin film transistor. The source follower has the current source to fix the threshold voltage of the thin film transistor, and storing capacitor and compensating capacitor to make the input voltage and the output voltage almost the equal, so that the output voltage error may be kept within the error voltage of grey scale voltage.
Owner:TPO DISPLAY
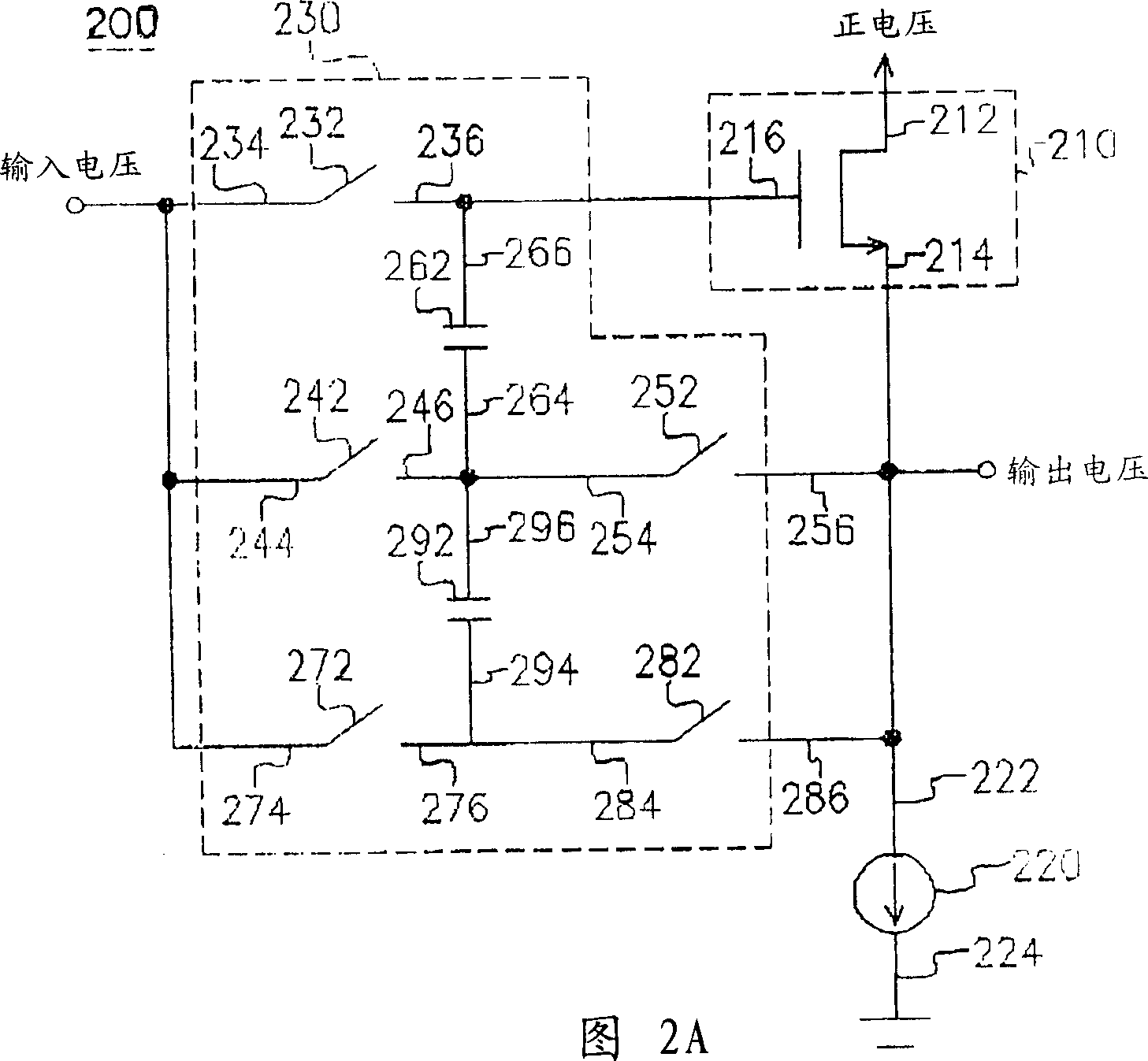
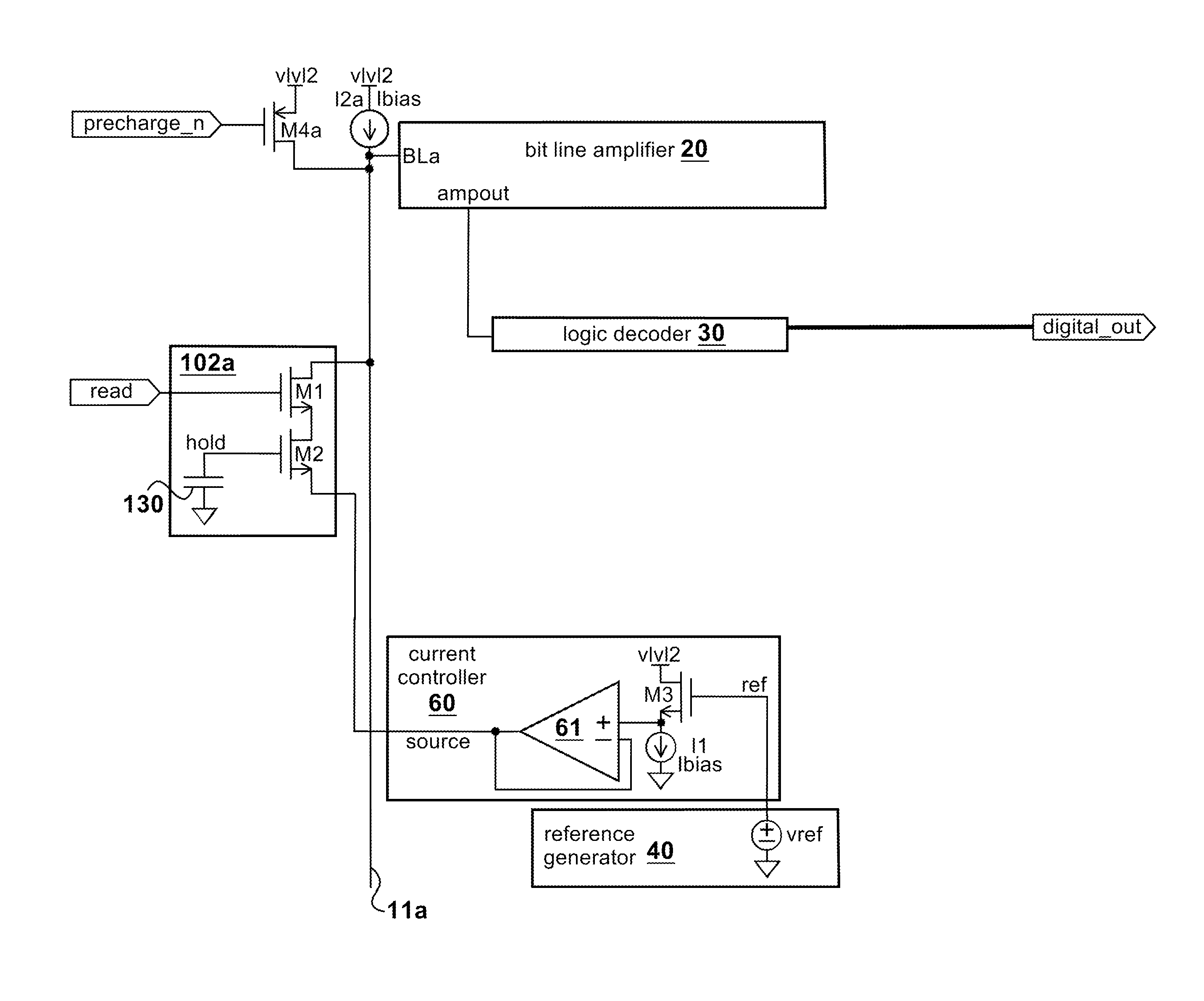
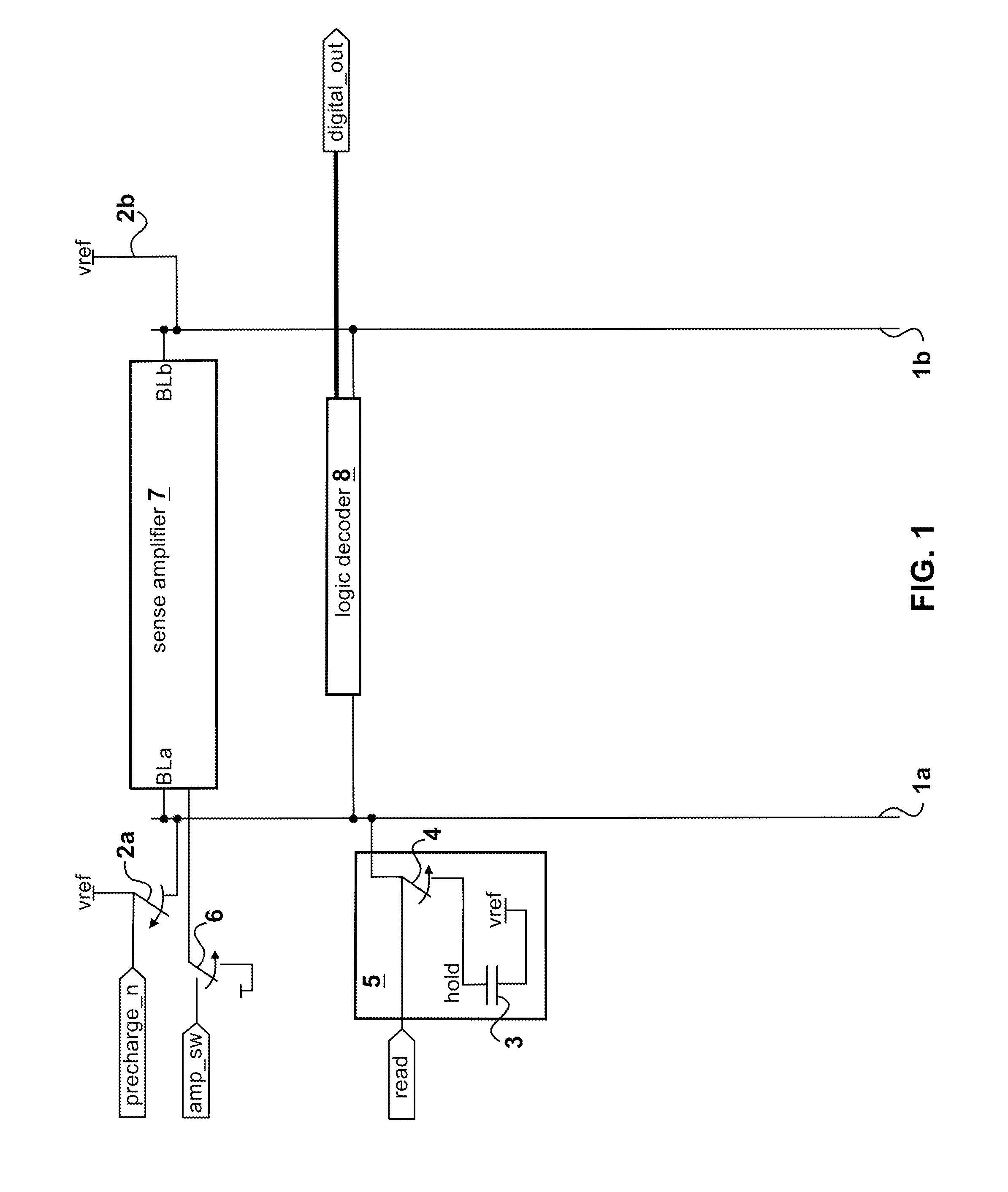
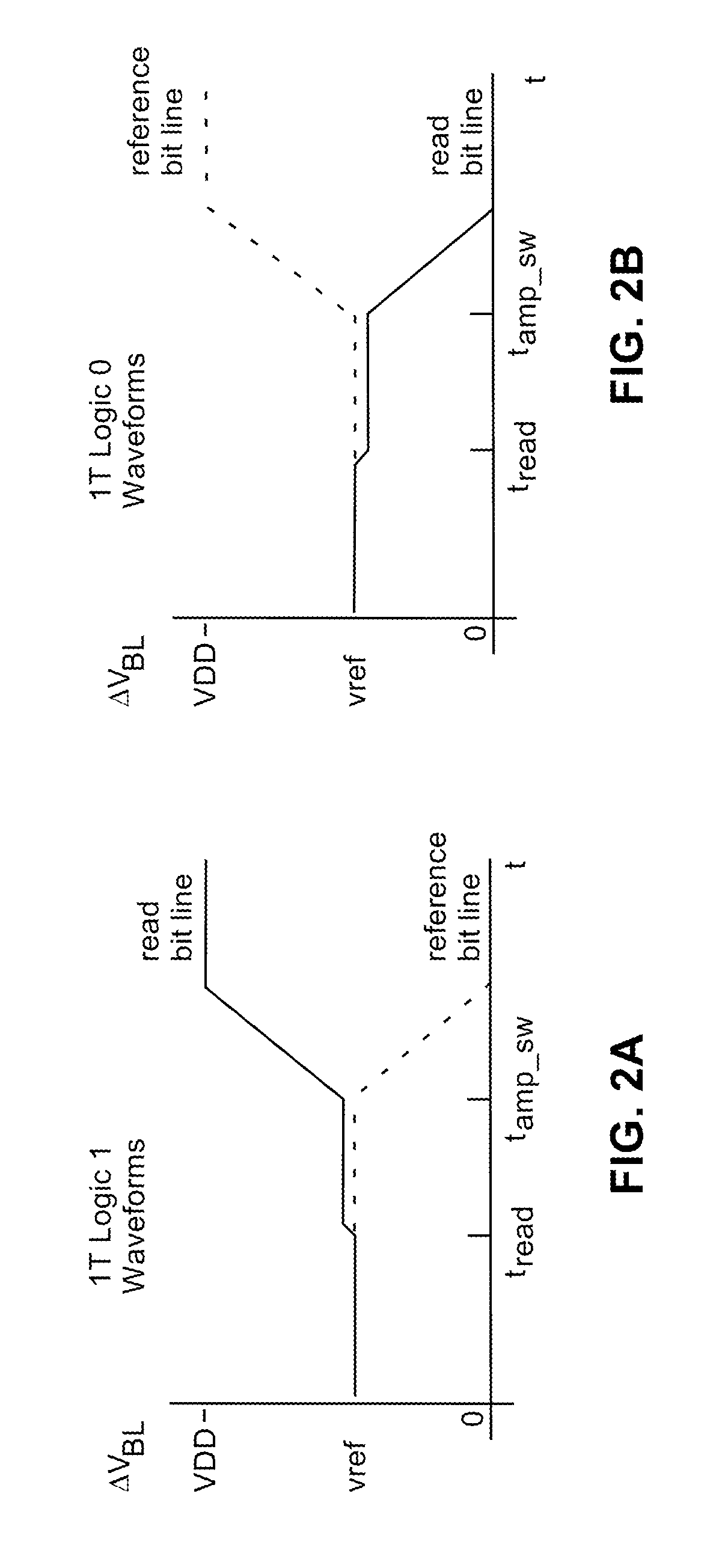
Memory architecture with a current controller and reduced power requirements
Disclosed is a memory architecture comprising at least one memory bit cell and at least one read bit line whose voltage is controlled and changed by a current from a current controller. Each memory bit cell has a storage mechanism, a controlled current source, and a read switch. The controlled current source in each memory bit cell is electrically connected to the read bit line through the read switch. The current from the current controller that controls and changes the read bit line voltage flows through the controlled current source in the memory bit cell. The value of this current is determined by a function of a difference between the voltage on the storage mechanism in the memory bit cell and a reference voltage from a reference voltage input to the current controller. In some versions an indicator is provided for indicating when to stop the current in the controlled current source that controls a voltage change on one of the read bit lines. The indicator has an on and an off condition and a switch is provided for stopping the current in the controlled current source when the indicator is activated in the on condition. The current in the controlled current source is stopped when the voltage change on the read bit line is greater than a predetermined threshold.
Owner:LYNCH JOHN K
Memory architecture with a current controller and reduced power requirements
ActiveUS20100315858A1Reduce power consumptionInterval becomes smallDigital storageElectricityVoltage reference
Disclosed is a memory architecture comprising at least one memory bit cell and at least one read bit line whose voltage is controlled and changed by a current from a current controller. Each memory bit cell has a storage mechanism, a controlled current source, and a read switch. The controlled current source in each memory bit cell is electrically connected to the read bit line through the read switch. The current from the current controller that controls and changes the read bit line voltage flows through the controlled current source in the memory bit cell. The value of this current is determined by a function of a difference between the voltage on the storage mechanism in the memory bit cell and a reference voltage from a reference voltage input to the current controller. In some versions an indicator is provided for indicating when to stop the current in the controlled current source that controls a voltage change on one of the read bit lines. The indicator has an on and an off condition and a switch is provided for stopping the current in the controlled current source when the indicator is activated in the on condition. The current in the controlled current source is stopped when the voltage change on the read bit line is greater than a predetermined threshold.
Owner:LYNCH JOHN K
Linear low noise transconductance cell
InactiveUS7002405B2Improve linearityReduce noiseMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDifferential amplifiersLow noiseEngineering
A low noise transconductance cell includes a resistor and a differential circuit pair having two equivalent half-circuits. Each half-circuit includes a feedback loop coupled to the resistor. The feedback loop includes an input transistor coupled to an inverting gain stage. The inverting gain stage is coupled to an output transistor which in turn is coupled to the input transistor and the resistor. In a low noise transconductance cell, a bias current source is coupled to the center of series connected resistors. In a high swing transconductance cell, a first bias current source is coupled to the left terminal of a resistance stage and a second bias current source is coupled to the right terminal of the resistance stage. The resistance stage can include a single resistor or a plurality of resistors.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
CMOS reference voltage source without Bipolar transistors
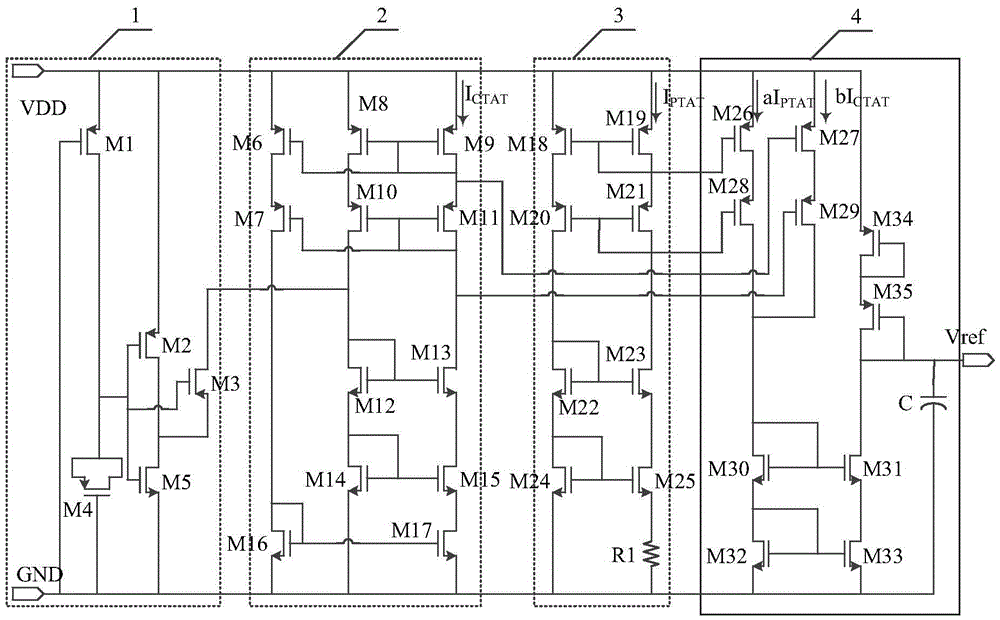
ActiveCN105468085AHigh rejection ratioEliminate the effects of temperature changesElectric variable regulationElectricityHemt circuits
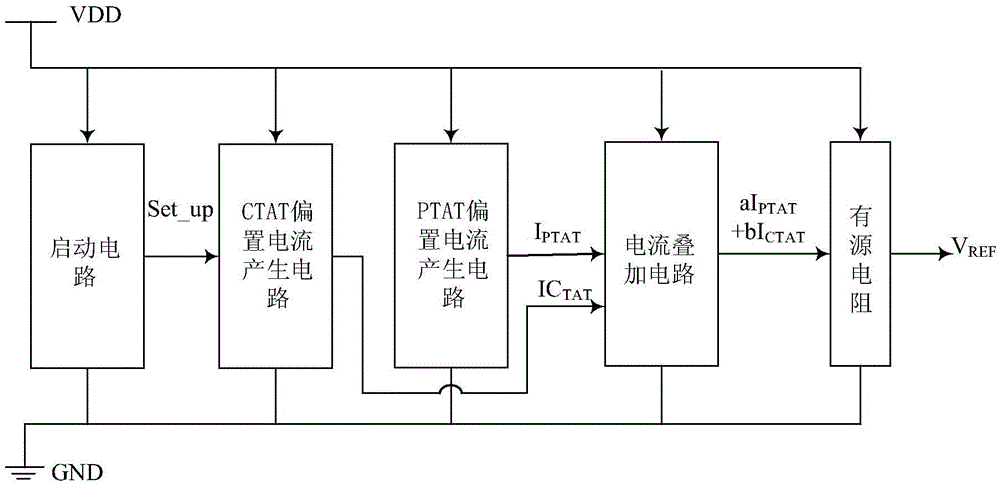
The invention discloses a CMOS reference voltage source without Bipolar transistors. The CMOS reference voltage source comprises a starting circuit which is connected between a power source (VDD) and the ground (GND) in parallel, a CTAT voltage generating circuit, a PTAT voltage generating circuit and a current superposed circuit; the output end of the starting circuit is connected with the CTAT voltage generating circuit and used for making the reference voltage source break away from a degeneracy bias point when a power source powers up; the output end of the CTAT voltage generating circuit is connected with the current superposed circuit; the output end of the PTAT voltage generating circuit is connected with the current superposed circuit; the current superposed circuit is used for superposing a current generated in the CTAT voltage generating circuit and a current generated in the PTAT voltage generating circuit, so that a current source having the zero temperature drift is obtained, and the current source generates the reference voltage (Vref) through an active subcircuit. By the adoption of the CMOS reference voltage source with the mentioned composition, BJT and diodes are not used, influence of temperature variation can be eliminated, complete compatibility with a standard CMOS process is achieved, system cost is effectively lowered, and the CMOS reference voltage source has the advantages of being extremely low in power consumption, high in power supply rejection ratio and good in performance.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Differential circuits
InactiveCN1720661ATelevision system detailsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsAudio power amplifierEngineering
A single-transistor current mirror interfaced with an appropriate load, in combination with an appropriate set of switches, implements the comparator function. Specifically, the differential circuit includes a single-transistor current mirror comprising a capacitor connected to the transistor through a switch and two current sources connected to the current mirror through respective independent switches, one of the current sources being operated with a capacitor switch to charge the capacitor and to operate the switch of the other current source so that the circuit operates as a source follower amplifier with a current source load. Therefore, the spatial distribution of transistor characteristics does not affect the comparator function.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Comparator circuit provided with differential amplifier making logical judgment by comparing input voltage with reference voltage
ActiveUS8330499B2Reducing logical judgment timeReduced operating requirementsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsAdaptive biasComparators circuits
In a comparator circuit having a differential amplifier, which makes a logical judgment by comparing an input voltage with a reference voltage, generates and outputs a resulting output voltage thereof, a current source generates and supplies a bias current of a predetermined minute current to the differential amplifier, and a first inverter circuit inverts a differential voltage from the differential amplifier. An adaptive bias current generator circuit detects the bias current of the current source, and a through current of the first inverter circuit. The adaptive bias current generator circuit generates and supplies an adaptive bias current for executing adaptive bias current control to the differential amplifier to allow the differential amplifier to operate with the bias current upon no logical judgment, and to allow the differential amplifier to operate by using the adaptive bias current obtained by increasing the bias current upon logical judgment.
Owner:SONY CORP
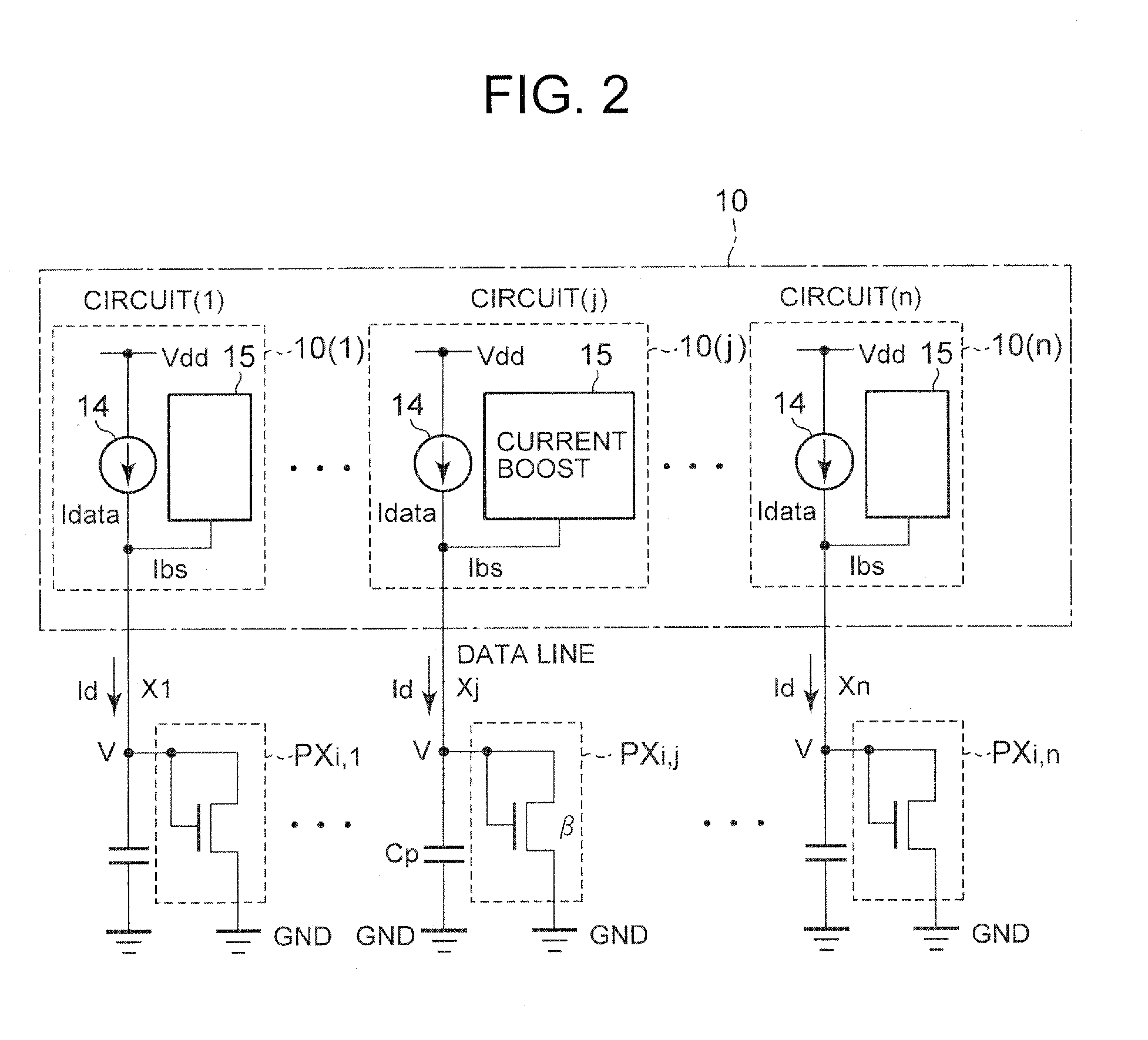
Current driver device
InactiveUS20090135165A1Increase speedHigh-speed chargeSolid-state devicesSpeech analysisPower flowData signal
The present invention provides a current-driven driver device capable of current writing at high speed even when a parasitic capacitance exists in a circuit to be driven. Each of current driver circuits includes a first current source for supplying a data current of a current value corresponding to a data signal, and a second current source including a differentiation circuit generating a differential value of a voltage applied to each data line and for supplying a boost current of a current value corresponding to the differential value to the data line.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com