Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48results about How to "Interval becomes small" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS7105365B2Avoid yield lossShort timeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringElectromotive force
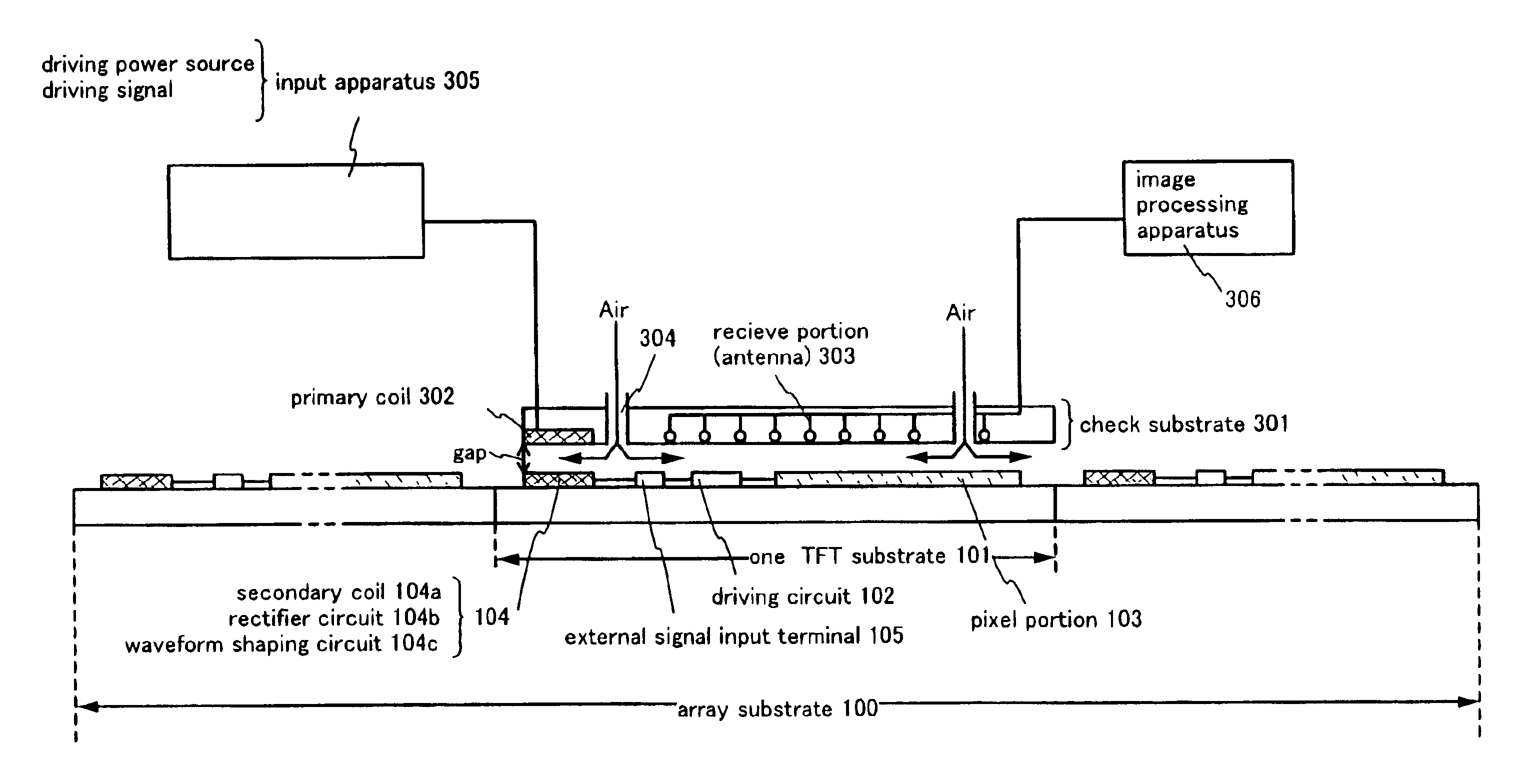
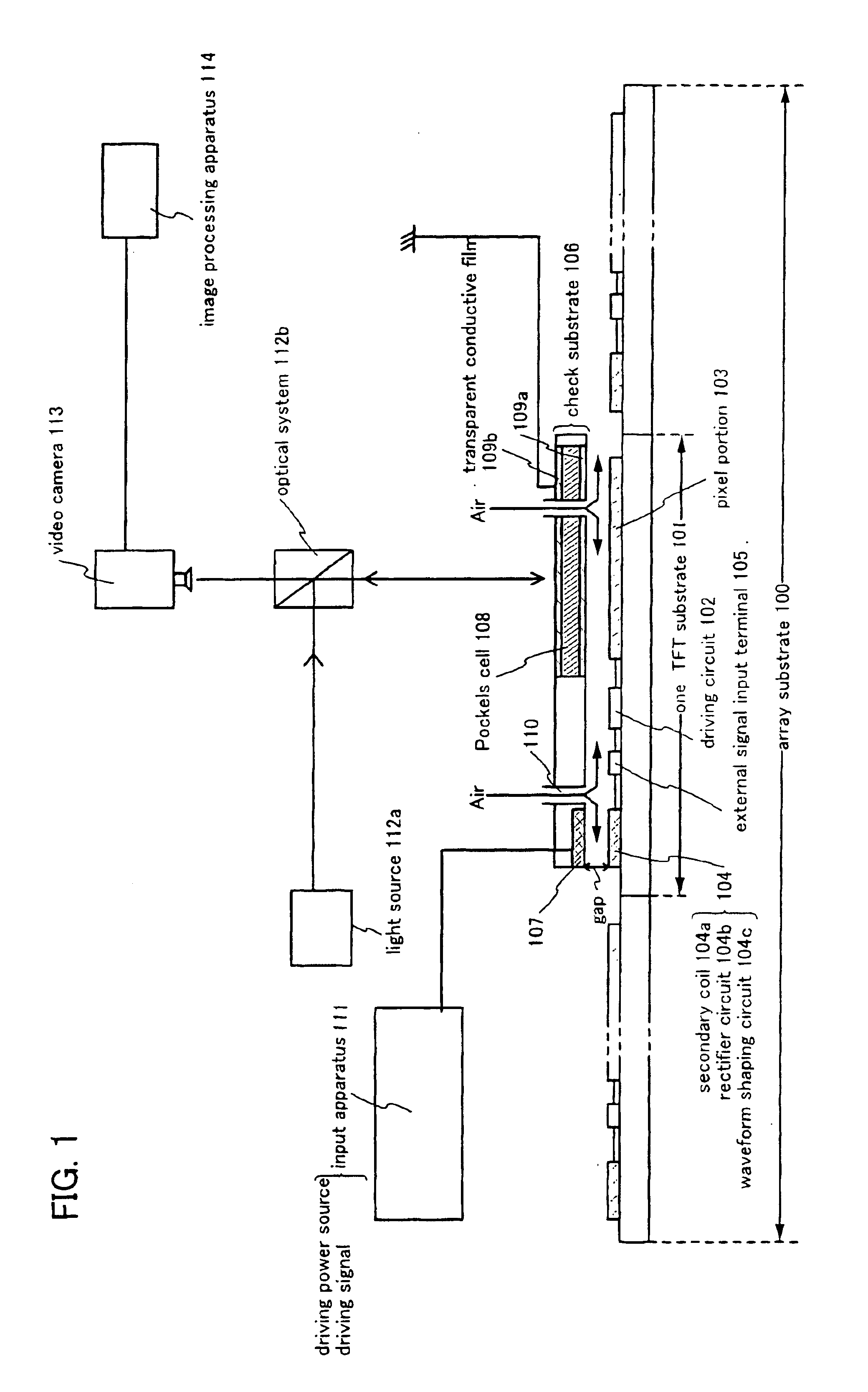
The present invention supplies a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device, which includes a non-contact inspection process capable of confirming if a circuit or circuit element formed on an array substrate is normally performed and can decrease a manufacturing cost by eliminating wastes to keep a defective product forming.An electromotive force generated by electromagnetic induction is rectified and shaped by using primary coils formed on a check substrate and secondary coils formed on an array substrate, whereby a power source voltage and a driving signal are supplied to circuits or circuit elements on a TFT substrate so as to be driven.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
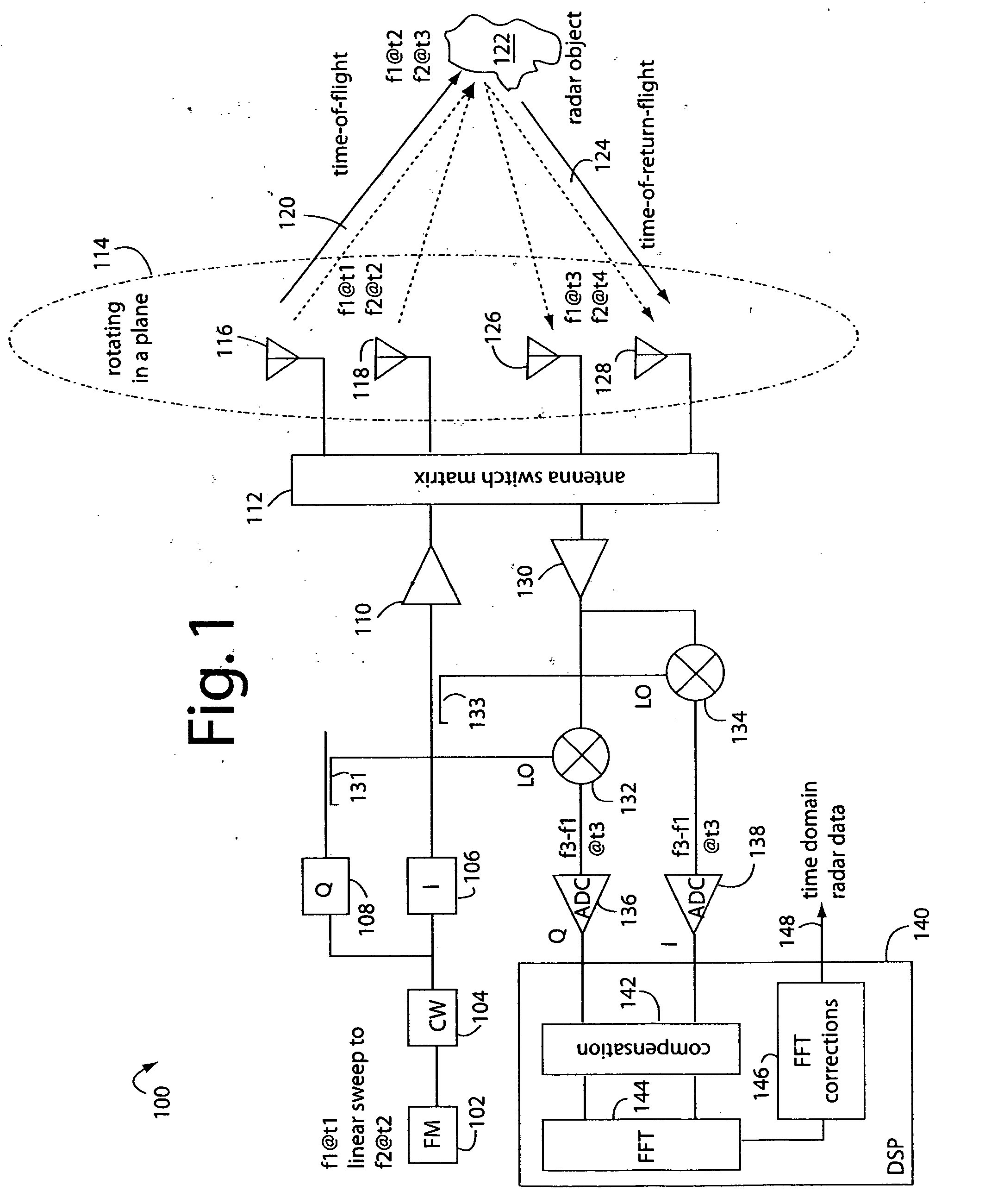
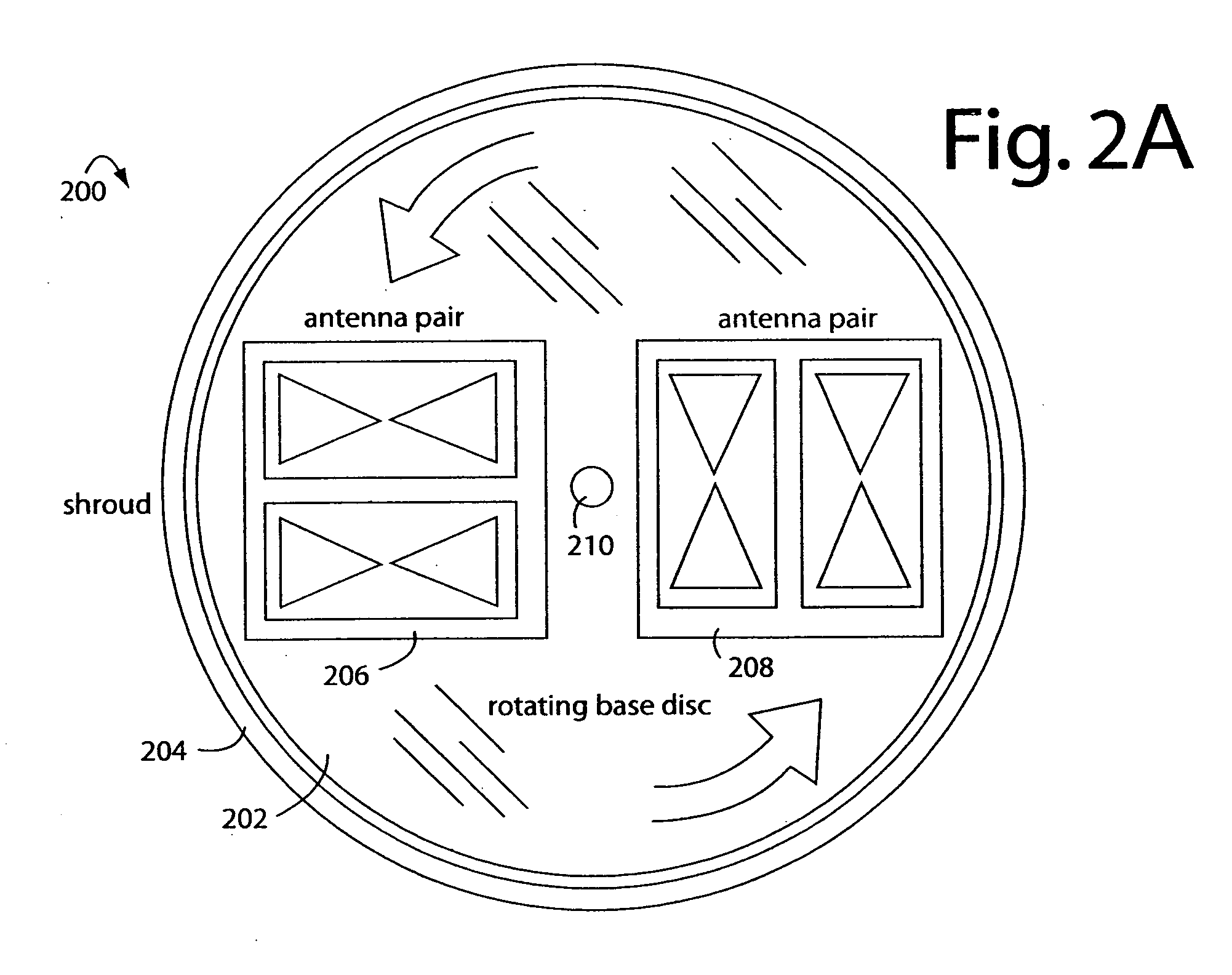
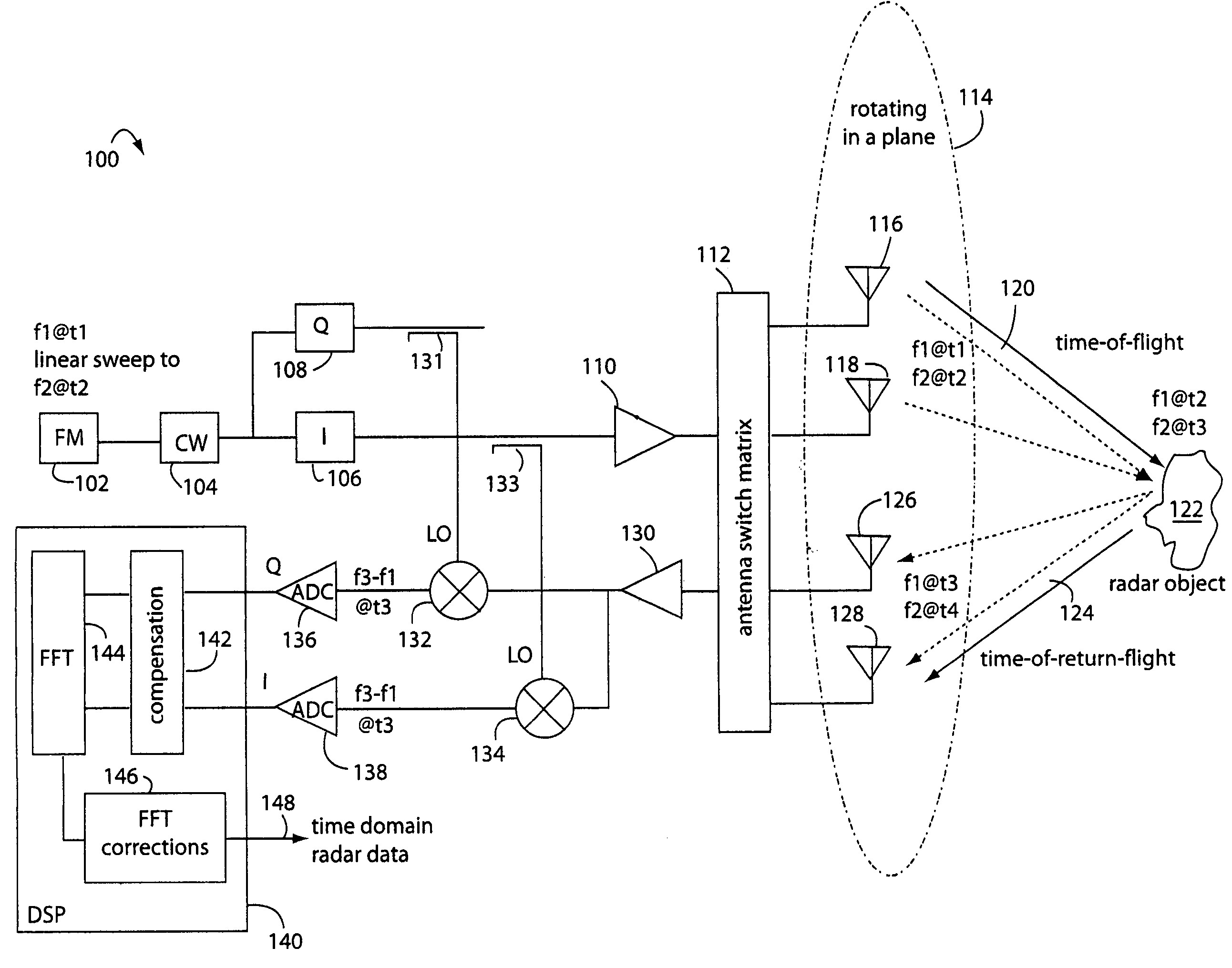
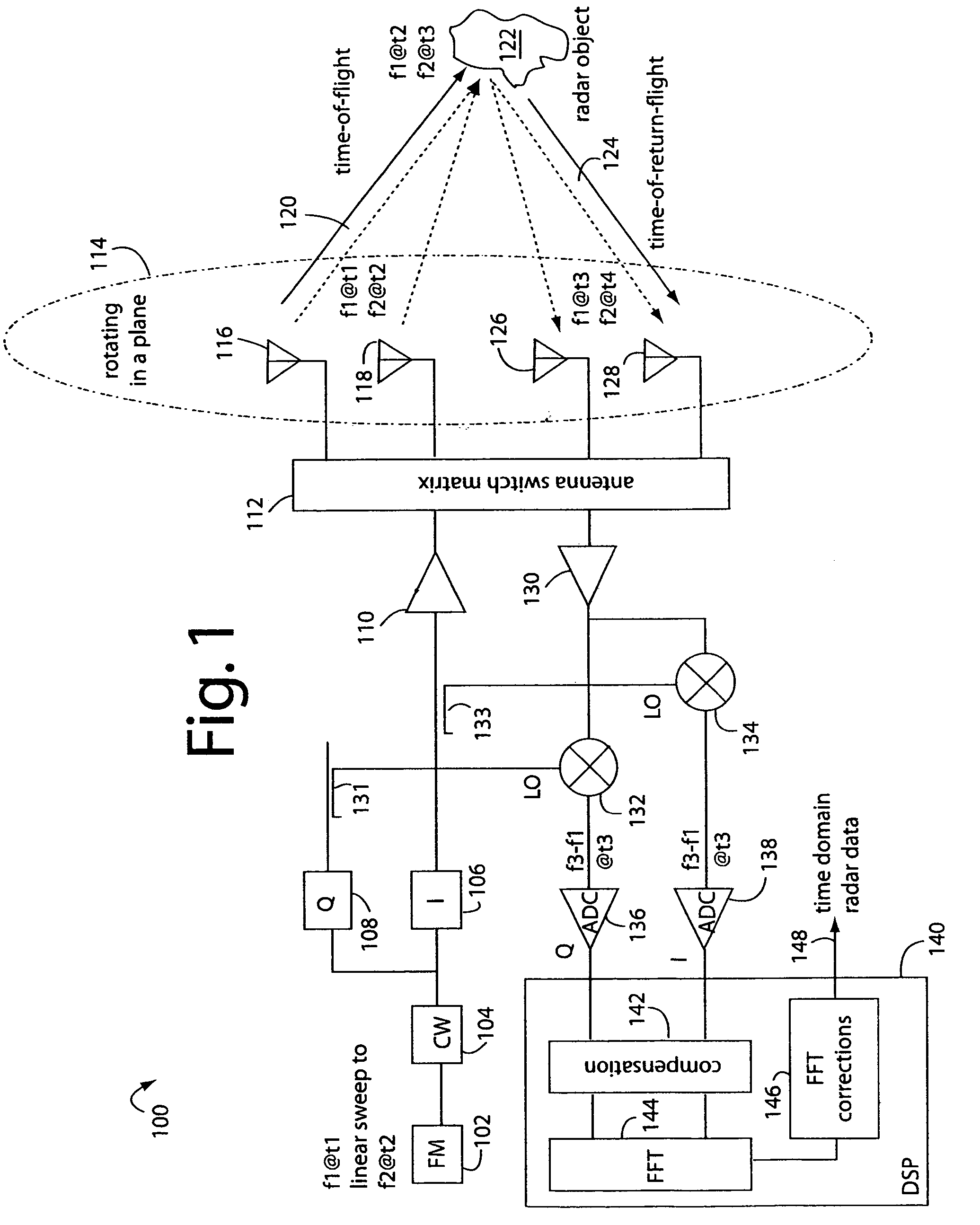
Linear FM radar
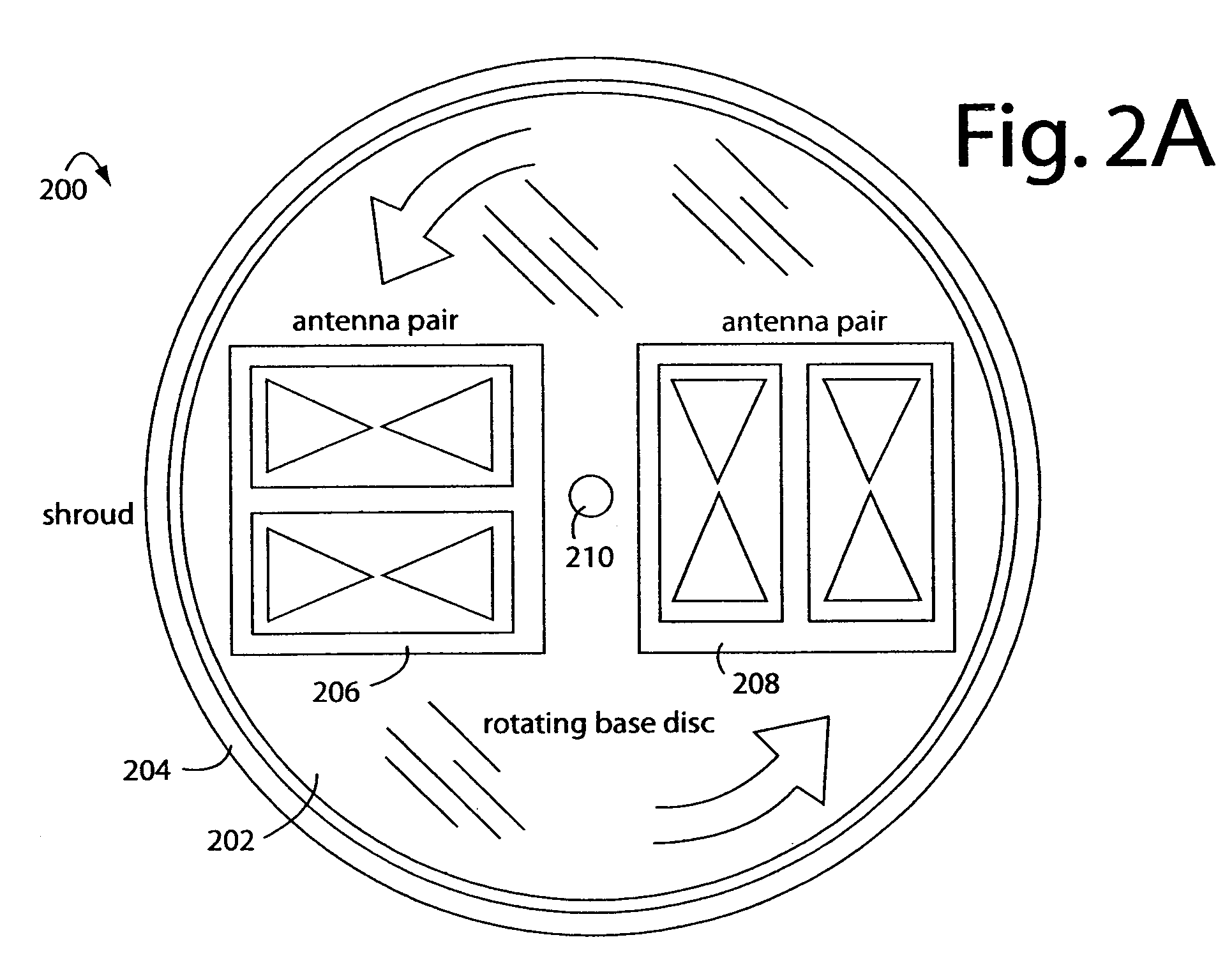
ActiveUS20070132630A1Small volumeEasy to operateAntenna feed intermediatesAntenna detailsRadar systemsDigital down converter
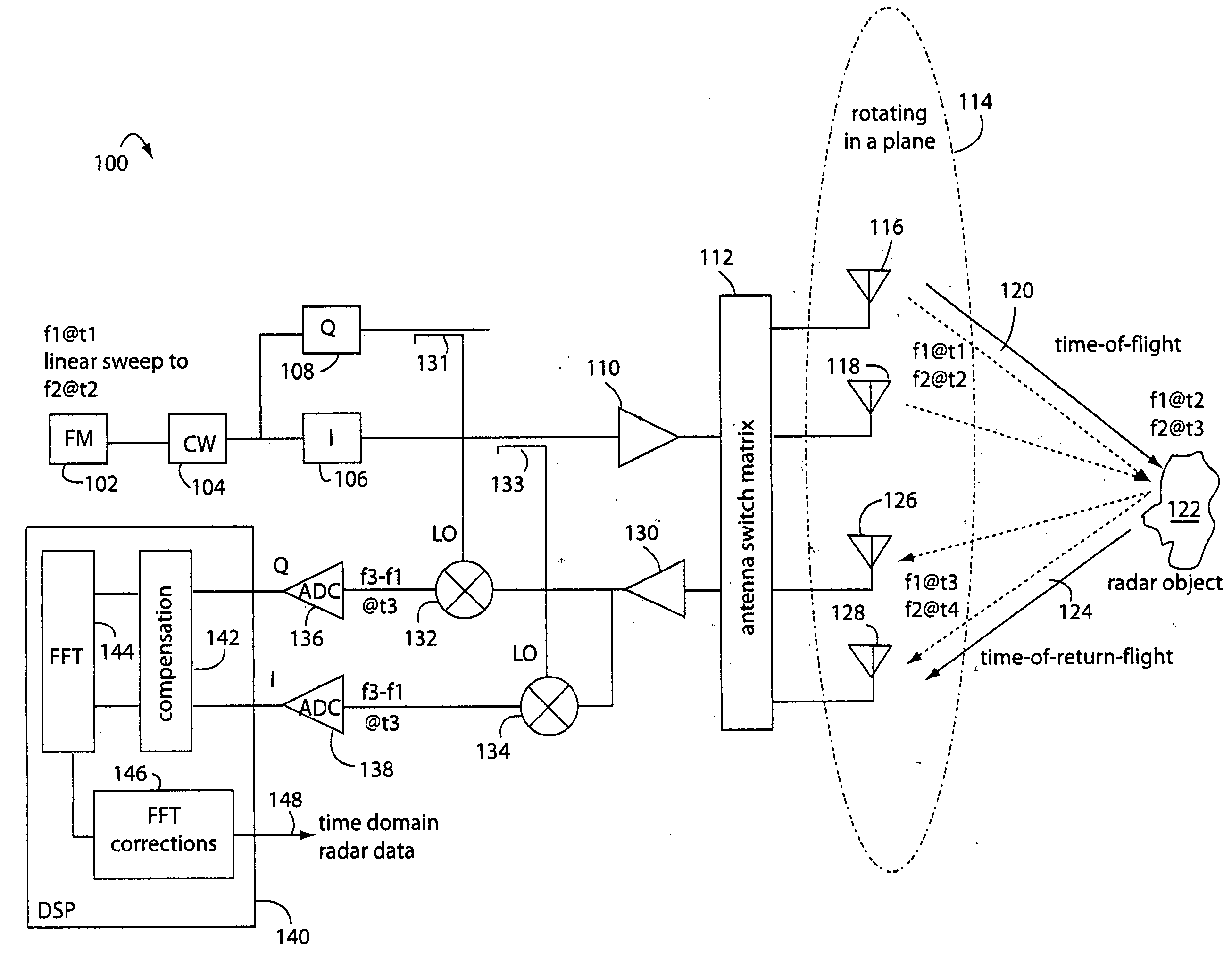
A FM-CW radar system comprises a frequency modulated continuous wave digital generator that produces both in-phase (I) and quadrature-phase (Q) outputs to orthogonally oriented transmitter antennas. A linearly polarized beam is output from a switched antenna array that allows a variety of I-and-Q pairs of bowtie antennas to be alternately connected to the transmitter and receiver. The receiver inputs I-and-Q signals from another bowtie antenna in the array and mixes these with samples from the transmitter. Such synchronous detection produces I-and-Q beat frequency products that are sampled by dual analog-to-digital converters (ADC's). The digital samples receive four kinds of compensation, including frequency-and-phase, wiring delay, and fast Fourier transform (FFT). The compensated samples are then digitally converted by an FFT-unit into time-domain signals. Such can then be processed conventionally for range information to the target that has returned the FM-CW echo signal.
Owner:LANDRAY TECH
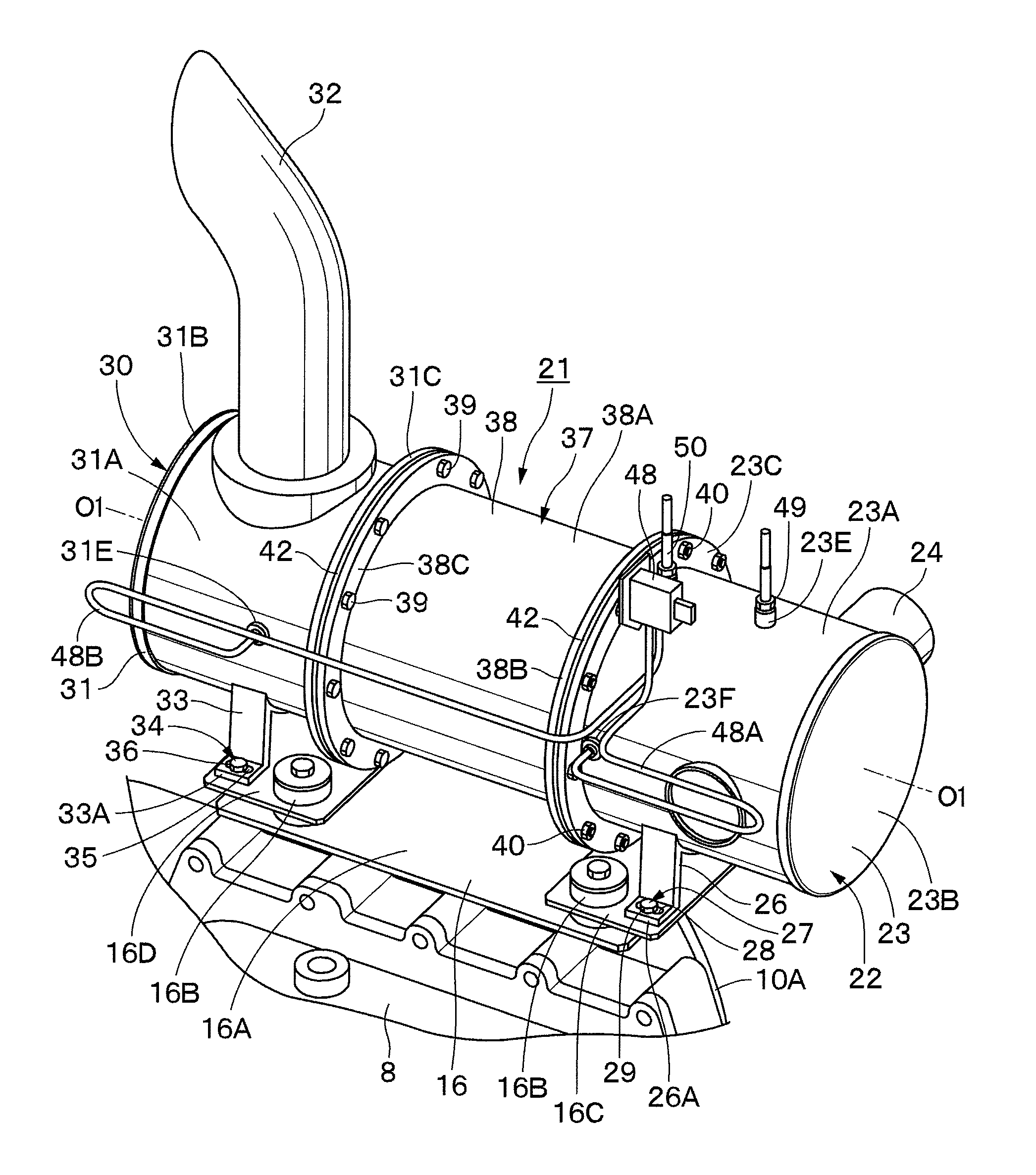
Exhaust gas treatment device
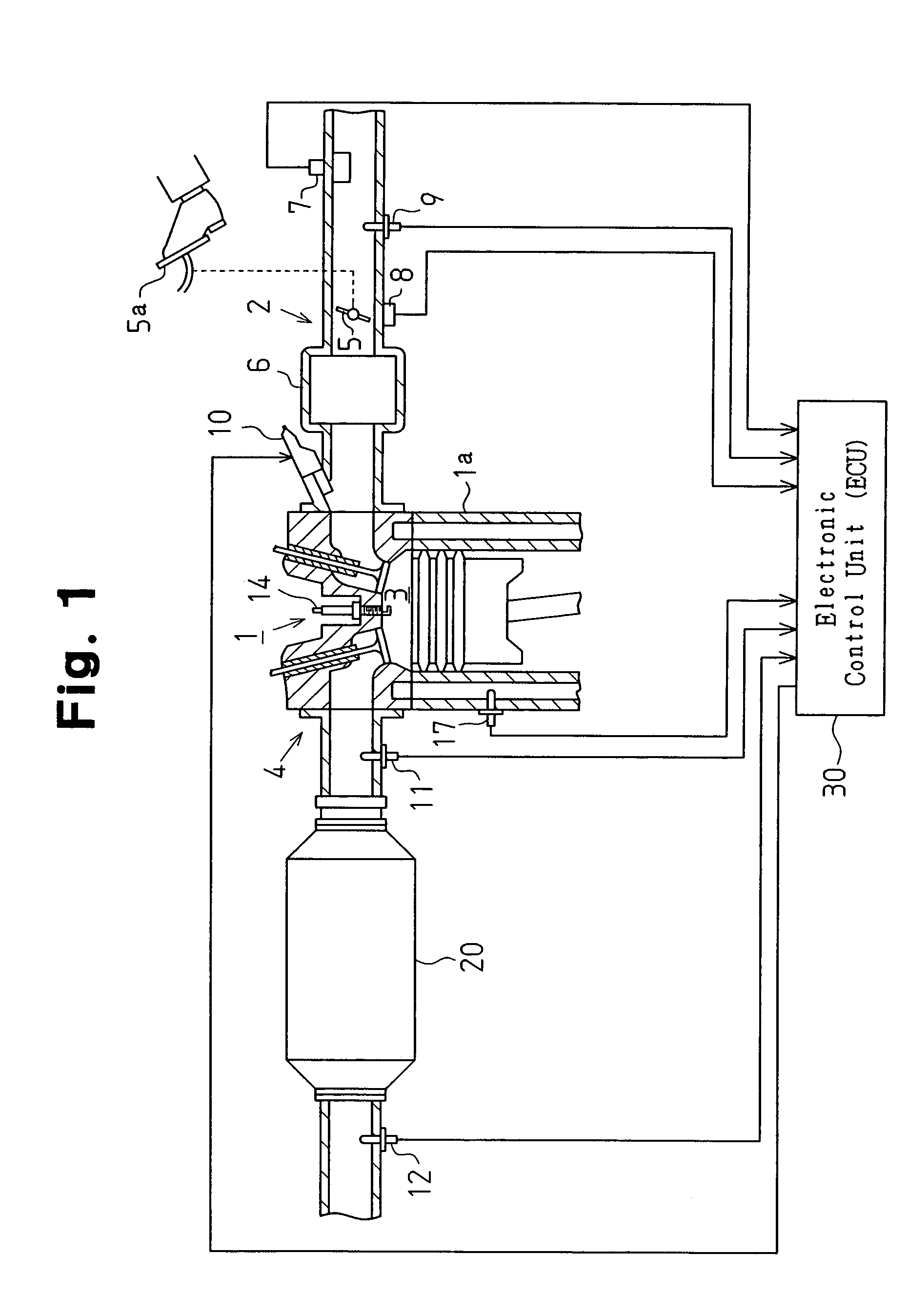
ActiveUS20110120085A1Easy to operateEasy to mountInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusParticulatesEngineering
An engaging groove (47) with which a gasket (42) is engaged is provided in each of a front side projecting portion (44) and a rear side projecting portion (46) formed in a filter accommodating cylinder (37) to be positioned on an outer peripheral surface (44A, 46A) of each projecting portion (44, 46). Therefore, when the gasket (42) latches on each of the projecting portion (44; 46) to be fitted thereon from an outside, the gasket (42) can be engaged with the engaging groove (47) provided in each of the projecting portions (44, 46). In consequence, at the time of mounting and removing the filter accommodating cylinder (37), the falling-off of the gasket (42) can be prevented, and, for example, an inspection operation, a cleaning operation and the like of an accommodated particulate matter removing filter (41) can be easily performed.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
Linear FM radar
ActiveUS7391362B2Small volumeEasy to operateComputerised tomographsTomographyRadar systemsDigital down converter
A FM-CW radar system comprises a frequency modulated continuous wave digital generator that produces both in-phase (I) and quadrature-phase (Q) outputs to orthogonally oriented transmitter antennas. A linearly polarized beam is output from a switched antenna array that allows a variety of I-and-Q pairs of bowtie antennas to be alternately connected to the transmitter and receiver. The receiver inputs I-and-Q signals from another bowtie antenna in the array and mixes these with samples from the transmitter. Such synchronous detection produces I-and-Q beat frequency products that are sampled by dual analog-to-digital converters (ADC's). The digital samples receive four kinds of compensation, including frequency-and-phase, wiring delay, and fast Fourier transform (FFT). The compensated samples are then digitally converted by an FFT-unit into time-domain signals. Such can then be processed conventionally for range information to the target that has returned the FM-CW echo signal.
Owner:LANDRAY TECH
Air/fuel ratio control device for internal combustion engine
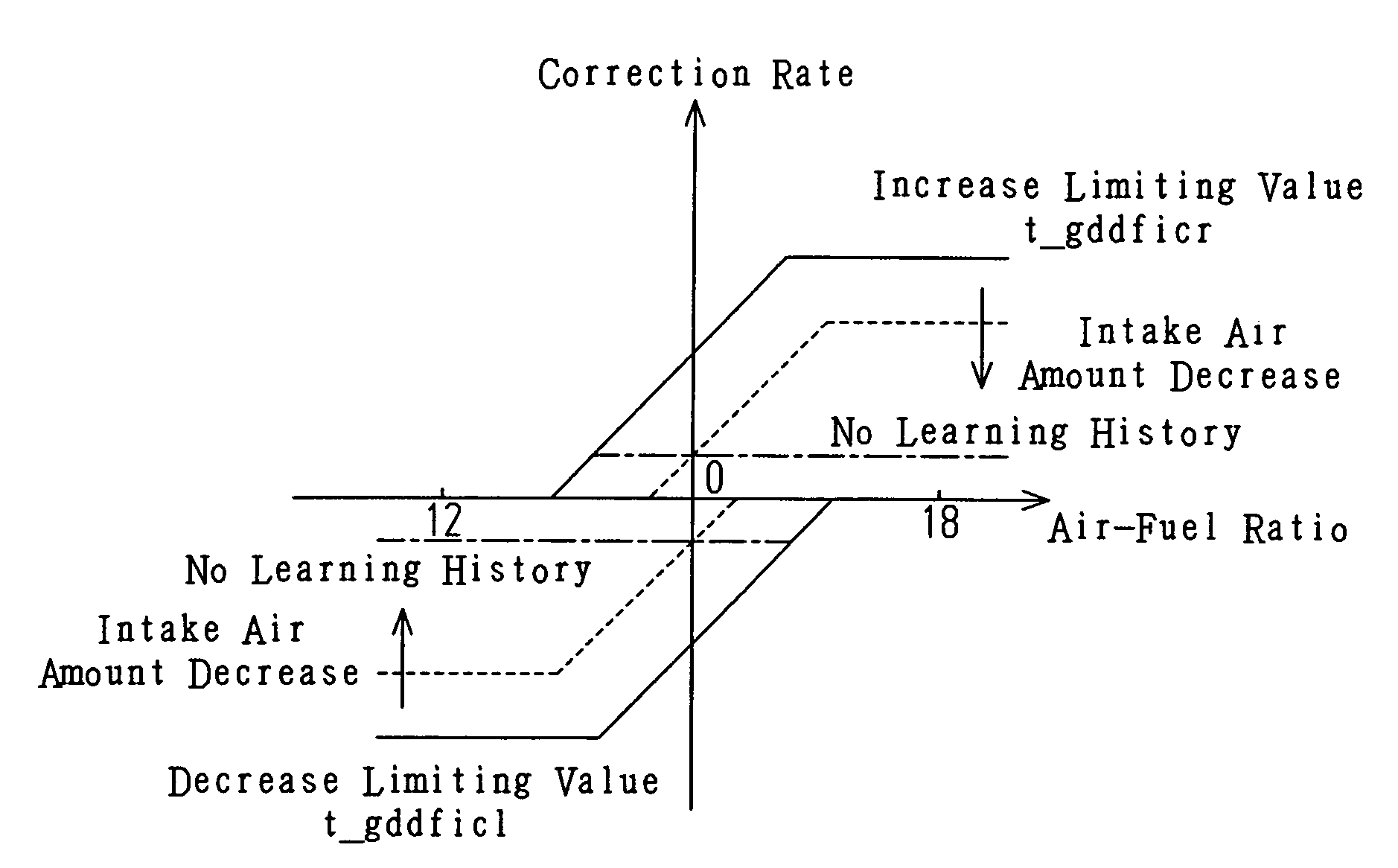
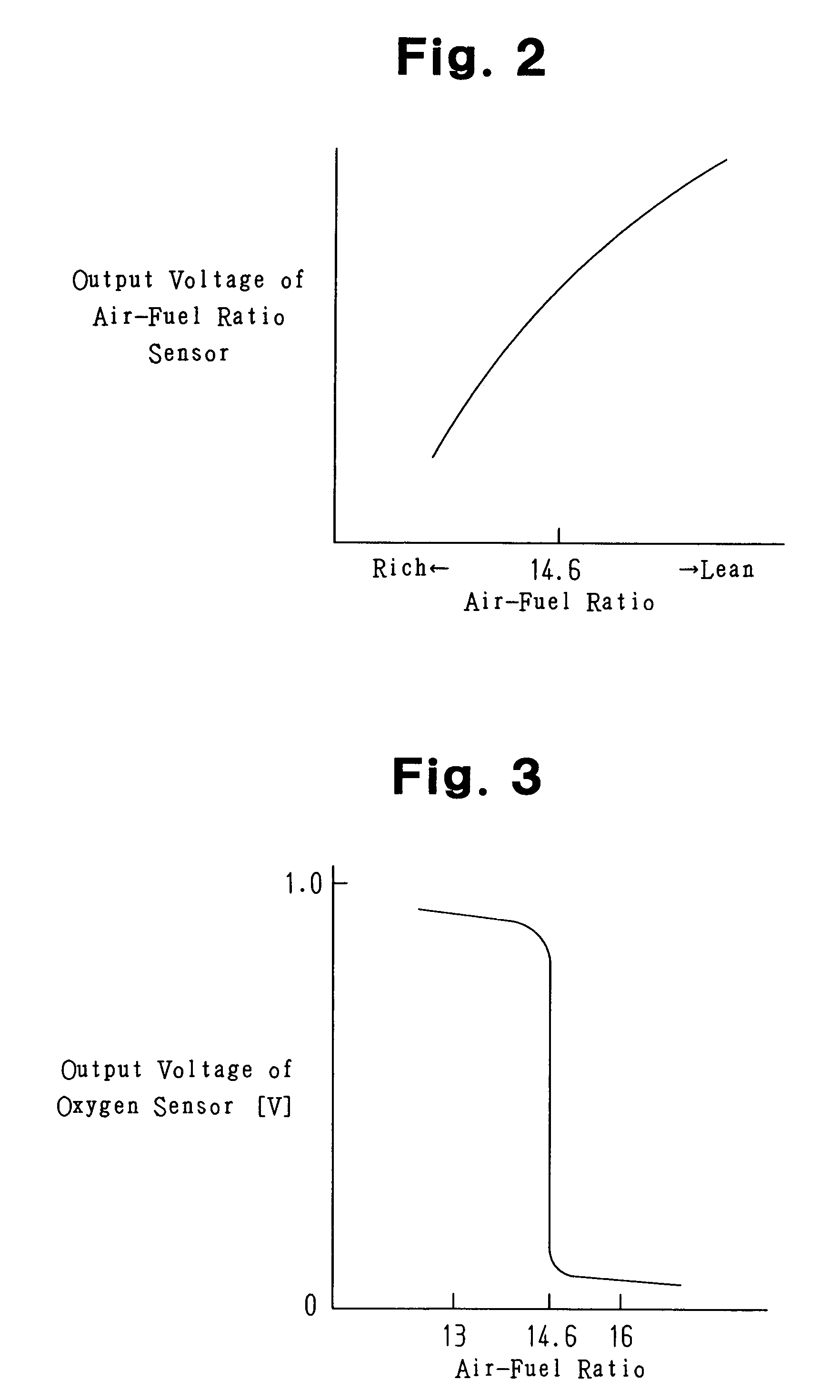
InactiveUS7270119B2Preventing erroneous air-fuel ratio correctionAdequately preventedElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsLower limitEngineering
An air-fuel ratio control apparatus for an internal combustion engine, implementing integral correction of the air-fuel ratio by an integral term edfii obtained by multiplying an integrated difference between a target air fuel ratio and the actual air-fuel ratio by an integral gain, wherein the upper and lower limit values of the integral term are set based on the actual intake air amount and the actual air-fuel ratio. This limits the range of the integral term edfii to prevent it from being set at an excessively high or low level removed from the realities of the intake air amount and the air-fuel ratio, and thereby to prevent erroneous air-fuel ratio correction by the integral term.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
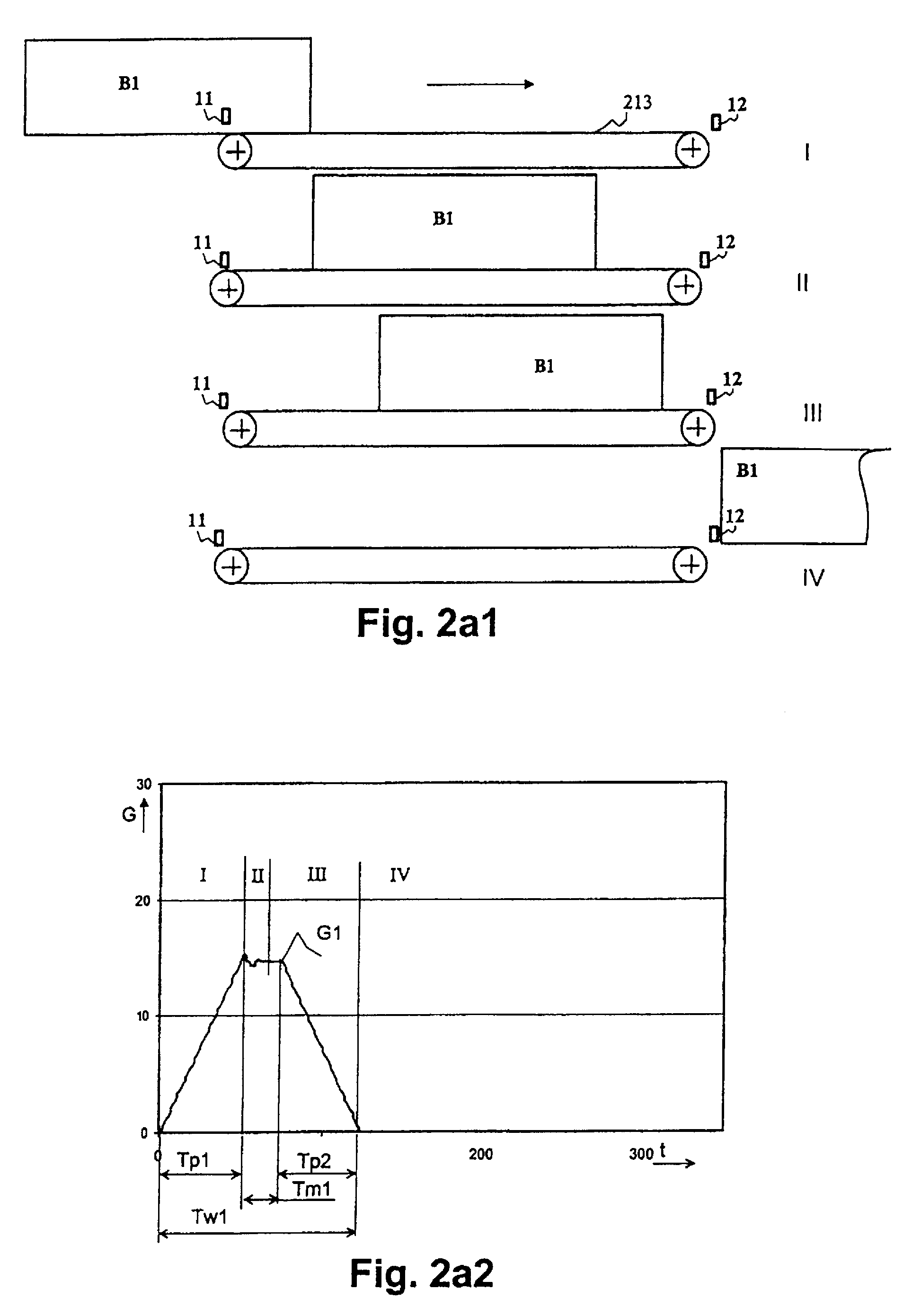
Multilayer printed circuit board and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20080218985A1Lower impedanceInterval becomes smallPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted circuit aspectsPunchingEngineering
A printed circuit board is provided which is capable of shortening intervals among core layer vias and suppressing high impedance. After the core layer vias each having a cylindrical conducting layer are formed so that conducting portions come into contact with one another, a punching process is performed along a symmetric axis of each of four core layer vias so that a through-hole of a specified diameter passes through a core board to form the core layer vias separated from one another and the through-hole is filled with an insulator and a punching process is performed along a central axis of the through-hole filled with the insulator so as to pass through the core board to form the through-hole having a diameter being shorter than that of the through-hole and the conducting layer is formed on an inside wall of the through-hole to form the core layer via.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060263952A1Guaranteed uptimeInterval becomes smallTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementManufacturing cost reductionDevice material
The present invention supplies a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device, which includes a non-contact inspection process capable of confirming if a circuit or circuit element formed on an array substrate is normally performed and can decrease a manufacturing cost by eliminating wastes to keep a defective product forming. An electromotive force generated by electromagnetic induction is rectified and shaped by using primary coils formed on a check substrate and secondary coils formed on an array substrate, whereby a power source voltage and a driving signal are supplied to circuits or circuit elements on a TFT substrate so as to be driven.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Cap members and liquid ejecting devices comprising cap members
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Memory architecture with a current controller and reduced power requirements
ActiveUS20100315858A1Reduce power consumptionInterval becomes smallDigital storageElectricityVoltage reference
Disclosed is a memory architecture comprising at least one memory bit cell and at least one read bit line whose voltage is controlled and changed by a current from a current controller. Each memory bit cell has a storage mechanism, a controlled current source, and a read switch. The controlled current source in each memory bit cell is electrically connected to the read bit line through the read switch. The current from the current controller that controls and changes the read bit line voltage flows through the controlled current source in the memory bit cell. The value of this current is determined by a function of a difference between the voltage on the storage mechanism in the memory bit cell and a reference voltage from a reference voltage input to the current controller. In some versions an indicator is provided for indicating when to stop the current in the controlled current source that controls a voltage change on one of the read bit lines. The indicator has an on and an off condition and a switch is provided for stopping the current in the controlled current source when the indicator is activated in the on condition. The current in the controlled current source is stopped when the voltage change on the read bit line is greater than a predetermined threshold.
Owner:LYNCH JOHN K
Display device and method of manufacturing a display device
ActiveUS20170250377A1Decrease in luminanceInterval becomes smallSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceLuminosity
A display device includes a first substrate provided with a display region including a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix, each of the plurality of pixels having a plurality of sub-pixels, and a second substrate provided with color filters and a light-shielding film, the color filters including transmission regions selectively transmitting lights of specific colors for the respective sub-pixels, the light-shielding film blocking light. The plurality of sub-pixels include a first sub-pixel provided with the transmission region that transmits light of a first color, and a second sub-pixel provided with the transmission region that transmits light of a second color having a luminosity factor lower than that of the light of the first color. A difference in area between a light-emitting region and the transmission region in the second sub-pixel is smaller than a difference in area between a light-emitting region and the transmission region in the first sub-pixel.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
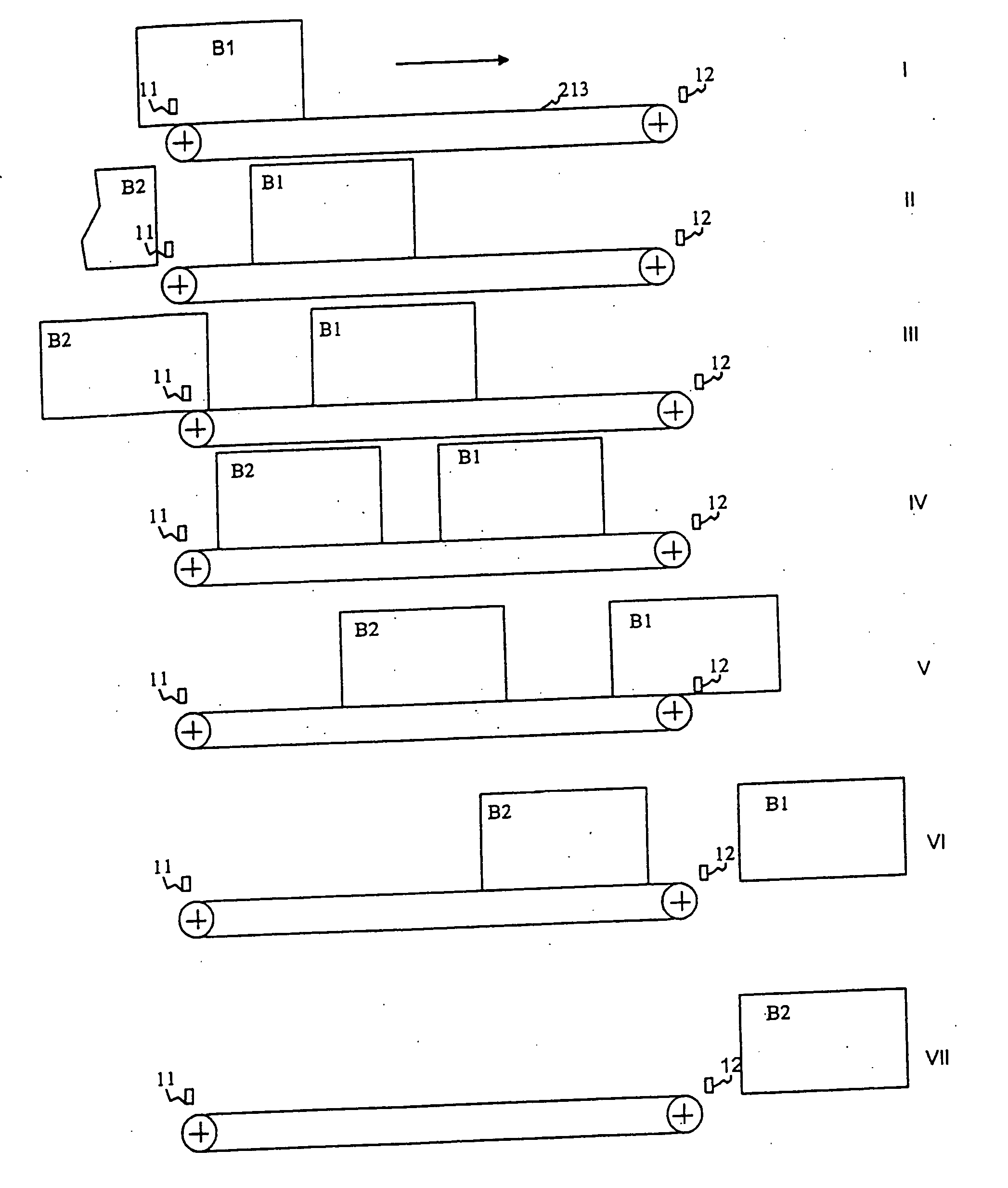
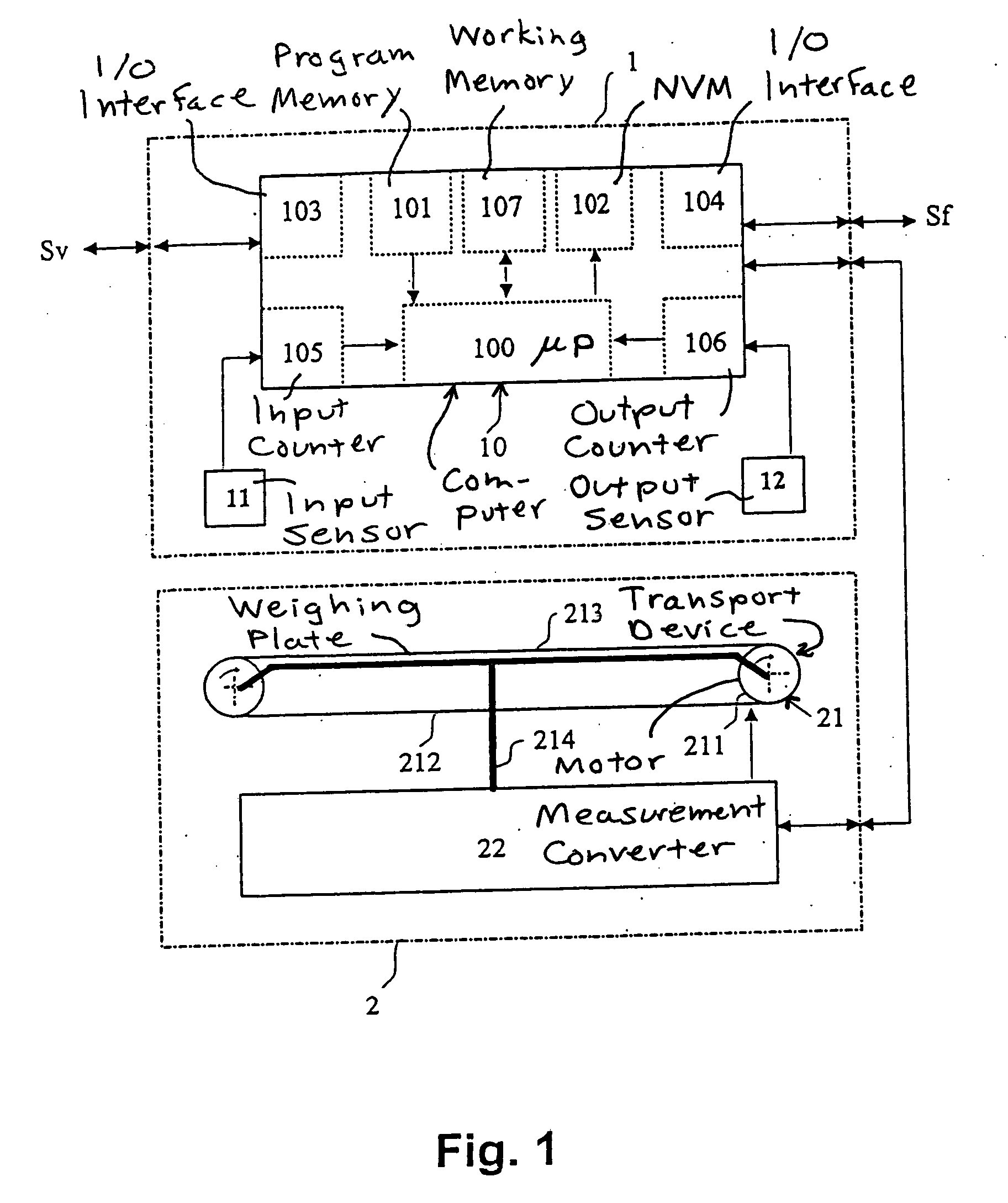
Method for weighing items moving over a weighing plate in succession
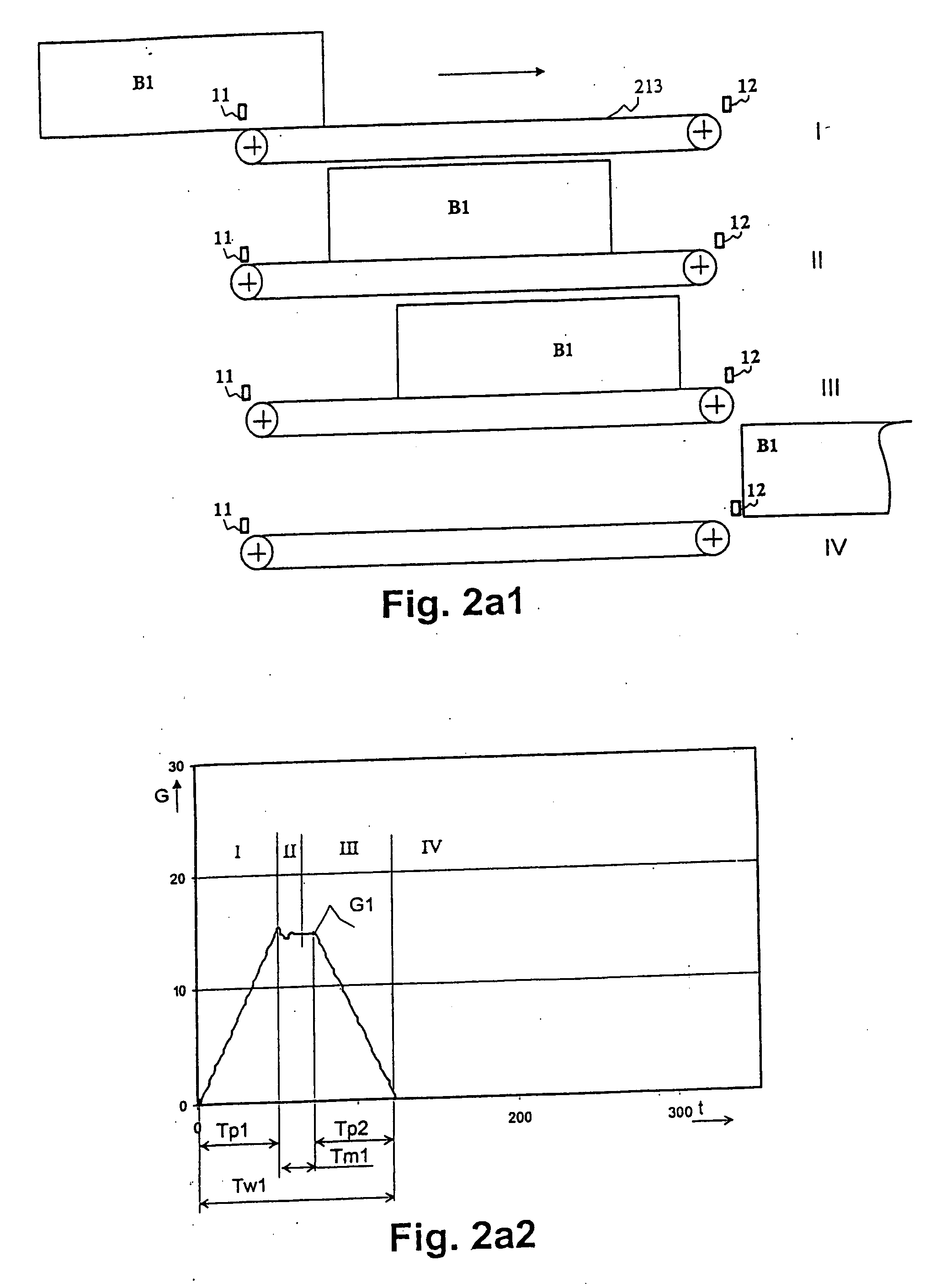
InactiveUS20060122950A1Improve throughputInterval becomes smallFranking apparatusWeighing apparatus for materials with special property/formTime rangeWeight decreasing
In a method for weighing a number of items, such as letters to be franked, on a transport belt that moves over a weighing plate, the base of which is formed by the transport belt, the transport speed of the belt is slowed within a measurement time range, that starts from the beginning of a weighing event on the weighing plate until a stable weight measurement occurs, and is accelerated outside of this measurement time range, after the occurrence of a stable weight value for a current item on the weighing plate, the next-following item is transported onto the weighing plate by the belt, and the weight of the next-following item is determined by the weight increase due to inflow of the next-following item and the weight decrease due to outflow of the current item.
Owner:FRANCOTYP POSTALIA
Lock device of sliding mechanism
InactiveUS7673905B2Reliable lockingInterval becomes smallBelt retractorsBelt anchoring devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Accelerometer
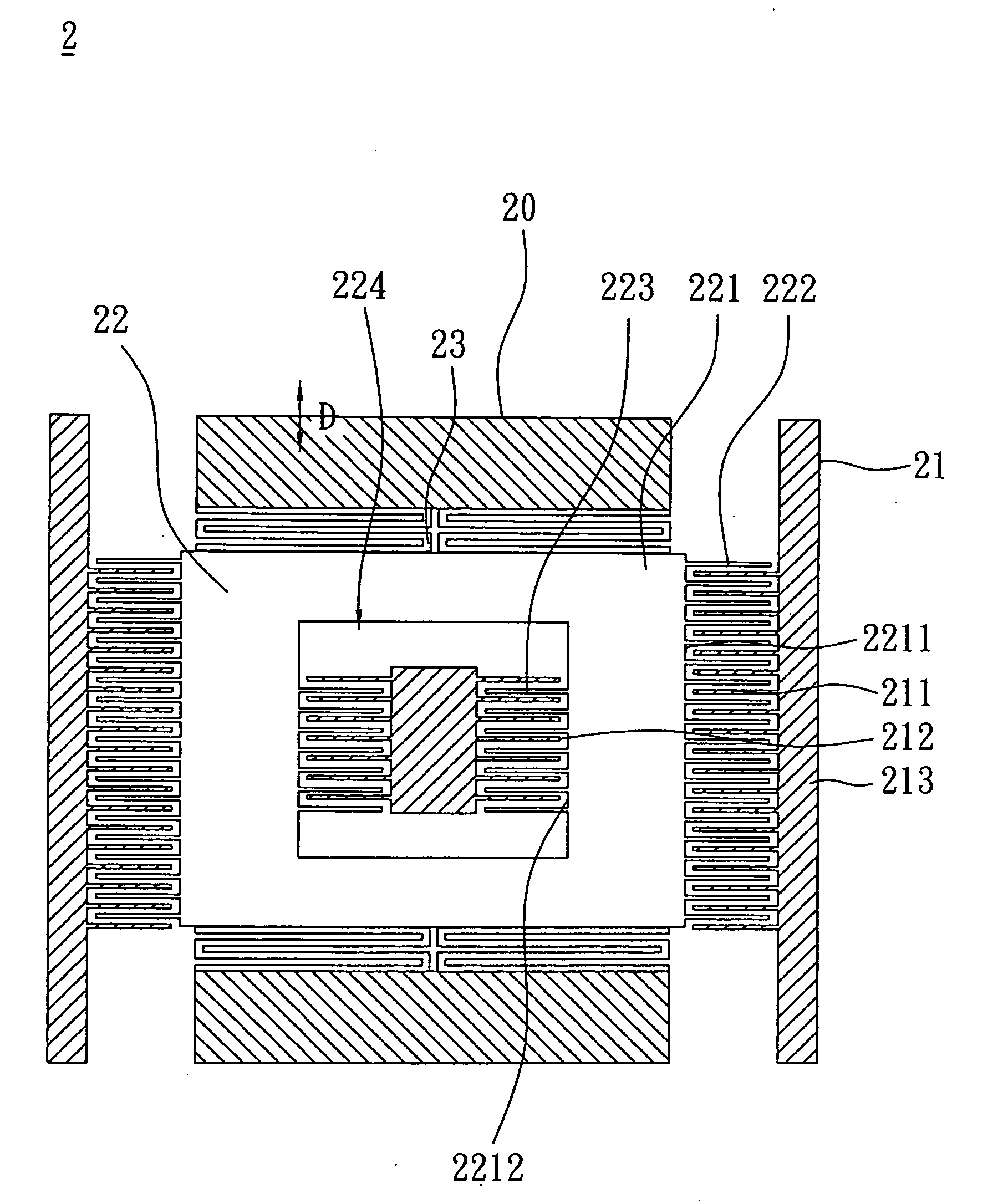
InactiveUS20070144258A1High sensitivityIncrease the number ofAcceleration measurementAccelerometerEngineering
An accelerometer includes a fixing unit and a movable unit. The fixing unit has a plurality of first electrode parts and a plurality of second electrode parts. The movable unit is connected with the fixing unit and includes a body having an opening, a plurality of third electrode parts and a plurality of fourth electrode parts. The third electrode parts are disposed at an outer side of the body with respect to the first electrode parts, respectively. The fourth electrode parts are disposed at the inner side of the body in the opening, and are disposed respectively with respect to the second electrode parts, respectively.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
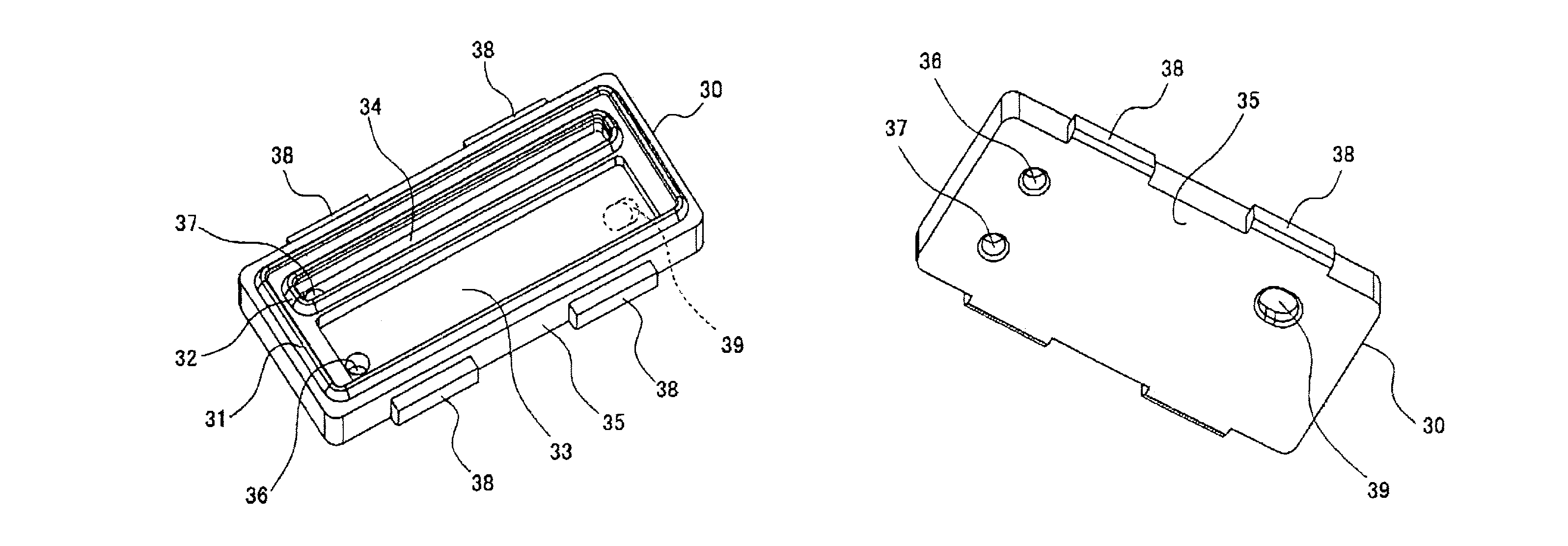
Device package, a printed wiring board, and an electronic apparatus with efficiently spaced bottom electrodes including intervals between bottom electrodes of different lengths
ActiveUS7361997B2Easily made differentIncrease the number ofPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureElectrical and Electronics engineeringElectronic equipment
A device package, such as a BGA, to be mounted on a printed wiring board (PWB) is disclosed. The bottom electrodes of the device package are arranged in an array such that intervals between the edges of the bottom electrodes become different from place to place. The intervals may be set wider at the peripheral positions of the bottom electrodes. The PWB includes pads that are located at positions corresponding to the bottom electrodes.
Owner:RICOH KK
Accelerometer
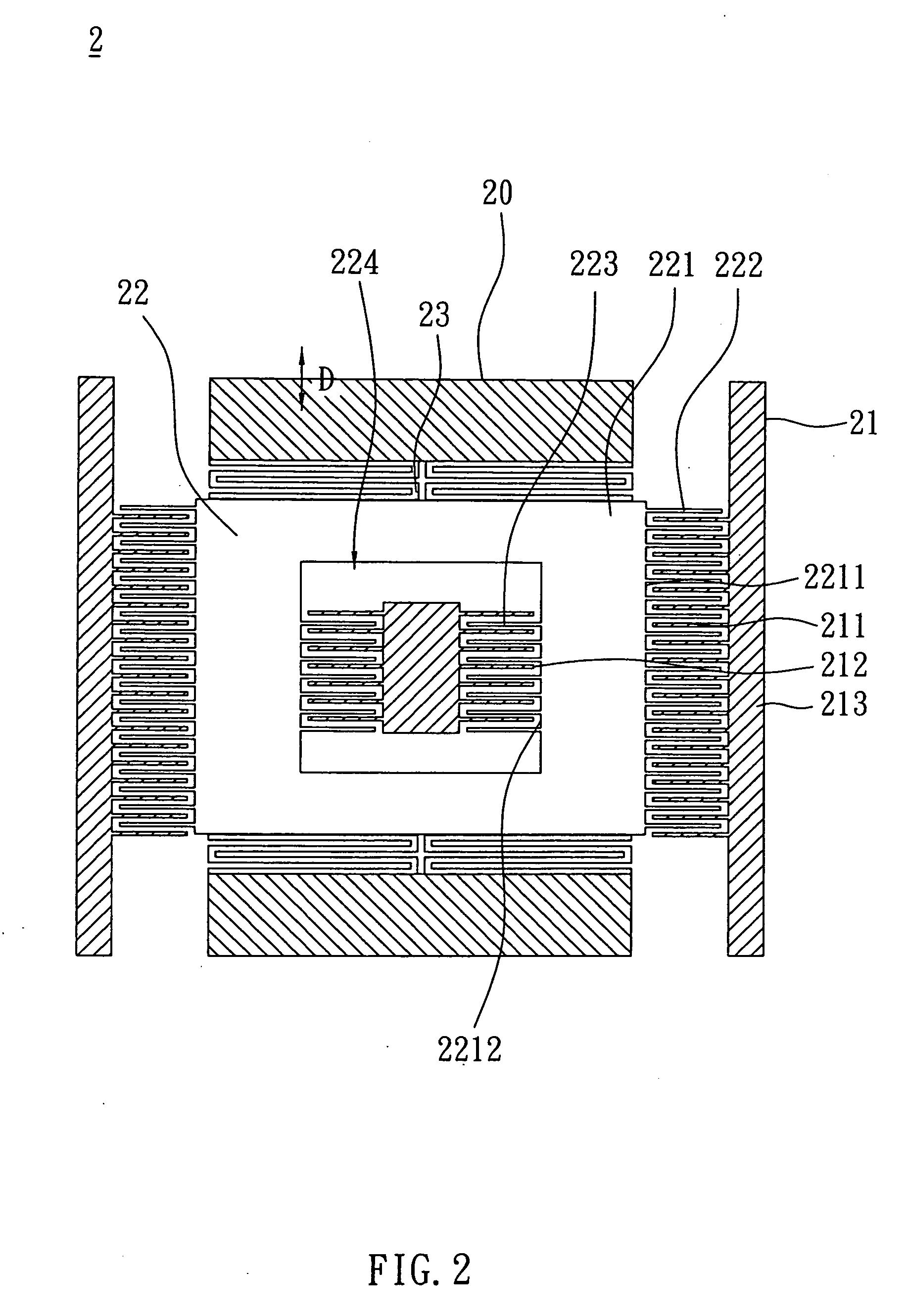
InactiveUS7412888B2High sensitivityIncrease the number ofAcceleration measurementAccelerometerEngineering
An accelerometer includes a fixing unit and a movable unit. The fixing unit has a plurality of first electrode parts and a plurality of second electrode parts. The movable unit is connected with the fixing unit and includes a body having an opening, a plurality of third electrode parts and a plurality of fourth electrode parts. The third electrode parts are disposed at an outer side of the body with respect to the first electrode parts, respectively. The fourth electrode parts are disposed at the inner side of the body in the opening, and are disposed respectively with respect to the second electrode parts, respectively.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Method for weighing items moving over a weighing plate in succession
InactiveUS7358450B2Improve throughputInterval becomes smallFranking apparatusWeighing apparatus with automatic feed/dischargeTime rangeWeight Decrease
In a method for weighing a number of items, such as letters to be franked, on a transport belt that moves over a weighing plate, the base of which is formed by the transport belt, the transport speed of the belt is slowed within a measurement time range, that starts from the beginning of a weighing event on the weighing plate until a stable weight measurement occurs, and is accelerated outside of this measurement time range, after the occurrence of a stable weight value for a current item on the weighing plate, the next-following item is transported onto the weighing plate by the belt, and the weight of the next-following item is determined by the weight increase due to inflow of the next-following item and the weight decrease due to outflow of the current item.
Owner:FRANCOTYP POSTALIA
Semiconductor laser device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070091958A1Increase the number ofManufacturing costOptical wave guidanceSemiconductor laser arrangementsDriving currentLaser light
This invention is to provide a semiconductor laser device with a small interval between light emitting points of laser lights and a method of manufacturing the same. A first light emitting element 1a having a semiconductor substrate 12a and a laser oscillation section 10a, and a second light emitting element 2a having a laser oscillation section 4a, are brought together with a ridged waveguide 8 of the laser oscillation section 10a facing the ridged waveguide 5 of the laser oscillation section 4a, and then bonded together by virtue of SOGs 3a having a small thickness. A conductive wiring layer Qa1 electrically connected with an ohmic electrode layer 9a on the ridged waveguide 8a, and a wiring layer Qa2 electrically connected with an ohmic electrode layer 6a on the ridged waveguide 5a, are arranged to extend until the insulating layer 11a on the semiconductor substrate 12a. Further, the ohmic electrodes Pa1 and Pa2 are formed on the bottom surface of the semiconductor substrate 12a and the top surface of the laser oscillation section 4a, respectively. In this way, when a drive current is supplied between the ohmic electrode Pa1 and the wiring layer Qa1, the laser oscillation section 10a will emit a light. On the other hand, when a drive current is supplied between the ohmic electrode Pa2 and the wiring layer Qa2, the laser oscillation section 4a will emit a light. In this manner, since the laser oscillation sections 4a and 10a are bonded together by virtue of SOGs 3a having a small thickness, it is allowed to form a semiconductor laser device with a small interval between light emitting points.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Branching apparatus
InactiveUS6341982B1Small sizeIncrease the number ofSubstation/switching arrangement detailsCoupling device detailsElectrical conductor
A branching apparatus includes an insulating bottom plate 7, and a plurality of branch connection insulating plates 8 stacked together on the insulating bottom plate 7, and a branch connector portion 11, wires 4 passing through each of the branch connection insulating plates 8 in parallel relation to each other. The branch connector portion 11 includes an insulating housing 9, cooperating with the insulating bottom plate 7 to hold the branch connection insulating plates 8, and a plurality of penetrating connection conductors 10 supported on the insulating housing 9. One end portion of each of the penetrating connection conductors 10 passes through the branch connection insulating plates 8, and is electrically connected to the associated wires 4 to thereby effect the branch connection, and the other end portion of each penetrating connection conductor is exposed to the exterior, and serving as a connector male terminal portion 10a.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Terminal fitting
ActiveUS7670198B2Improve rigiditySufficient locking forceContact member manufacturingIncorrect coupling preventionEngineering
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Exhaust gas treatment device
ActiveUS8701387B2Easy to operateEasy to mountCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesEngineering
An engaging groove (47) with which a gasket (42) is engaged is provided in each of a front side projecting portion (44) and a rear side projecting portion (46) formed in a filter accommodating cylinder (37) to be positioned on an outer peripheral surface (44A, 46A) of each projecting portion (44, 46). Therefore, when the gasket (42) latches on each of the projecting portion (44; 46) to be fitted thereon from an outside, the gasket (42) can be engaged with the engaging groove (47) provided in each of the projecting portions (44, 46). In consequence, at the time of mounting and removing the filter accommodating cylinder (37), the falling-off of the gasket (42) can be prevented, and, for example, an inspection operation, a cleaning operation and the like of an accommodated particulate matter removing filter (41) can be easily performed.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
Illumination apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20200224847A1Small sizeLow costPlanar light sourcesElectric circuit arrangementsMicrocontrollerLed array
An illumination apparatus for vehicle is disclosed, which includes an illumination module and a microcontroller. The illumination module includes a circuit base and an LED array which is disposed on the circuit base and includes a plurality of LED packages. Each of the LED packages includes a driver chip, a light source and a packaging structure, in which the driver chip and the light source are disposed. The driver chip is electrically connected to the light source to drive the light source to emit lights. The microcontroller is electrically connected to the LED packages to control the operation of the LED packages. Therefore, lights emitted from the LED packages can form a dynamic or static image; moreover, the light source (LED chip) and the driver chip are in the same packaging structure, so the circuit layout of the circuit base can be simplified.
Owner:EVERLIGHT ELECTRONICS
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus having the zoom lens
ActiveUS20110254994A1Large rangeInterval becomes smallTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOphthalmologyConditional expression
A zoom lens includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens unit having a positive refractive power, a second lens unit having a negative refractive power, a third lens unit having a positive refractive power, and a rear lens unit including one or more lens units. An interval between respective adjacent lens units varies during zooming such that an interval between the first lens unit and the second lens unit is larger at a telephoto end than at a wide-angle end and an interval between the second lens unit and the third lens unit is smaller at the telephoto end than at the wide-angle end. The third lens unit includes at least one negative lens. An Abbe number (νd3n) and a relative partial dispersion (θgF3n) of a material of the negative lens are appropriately set based on predetermined conditional expressions.
Owner:CANON KK
Terminal fitting
ActiveUS20090117773A1Avoid deformationIncrease productionContact member manufacturingIncorrect coupling preventionMechanical engineeringPhysics
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
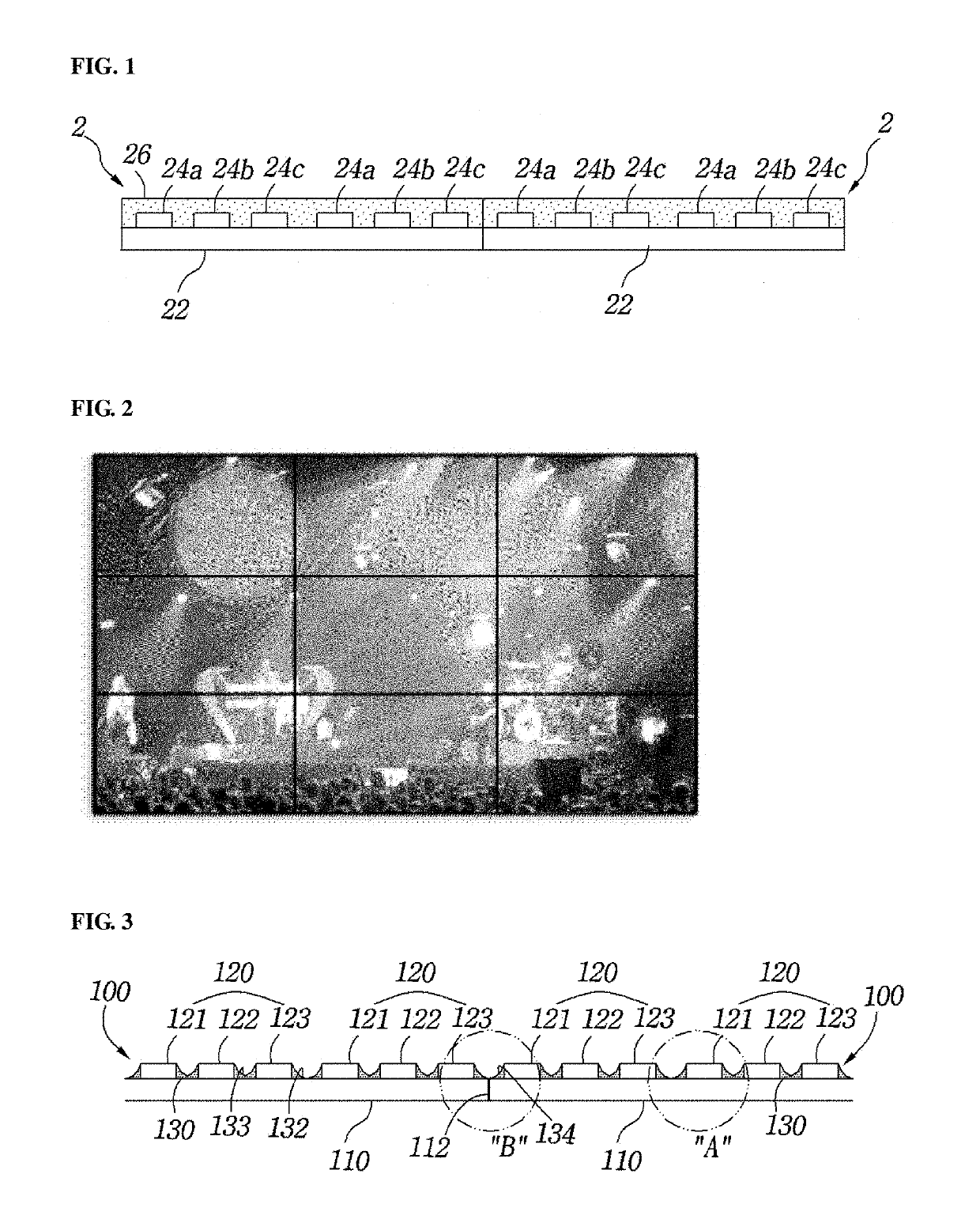
LED module assemblies for displays
ActiveUS10504878B2Interval becomes smallImprove featuresSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Disclosed is an LED module assembly for a display including a first LED module and a second LED module. The first LED module includes a first unit substrate, a plurality of LED chips mounted on the first unit substrate to form a plurality of pixels, and a first light absorbing layer formed on the first unit substrate. The second LED module includes a second unit substrate, a plurality of LED chips mounted on the second unit substrate to form a plurality of pixels, and a second light absorbing layer formed on the second unit substrate. The first unit substrate and the second unit substrate are laterally connected to each other. Each of the first light absorbing layer and the second light absorbing layer includes a plurality of valleys formed between the plurality of pixels. The first light absorbing layer includes a first inclined portion formed obliquely from the upper end edge of the interface between the first unit substrate and the second unit substrate to the upper portion of the side surface of each of the outer LED chips mounted on the first unit substrate. The second light absorbing layer includes a second inclined portion formed obliquely from the upper end edge of the interface between the first unit substrate and the second unit substrate to the upper portion of the side surface of each of the outer LED chips mounted on the second unit substrate. At least one of the plurality of valleys is formed by the first inclined portion and the second inclined portion meeting each other.
Owner:LUMENS
LED module assemblies for displays
ActiveUS20190115329A1Increase the amount of lightEasy maintenanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Disclosed is an LED module assembly for a display including a first LED module and a second LED module. The first LED module includes a first unit substrate, a plurality of LED chips mounted on the first unit substrate to form a plurality of pixels, and a first light absorbing layer formed on the first unit substrate. The second LED module includes a second unit substrate, a plurality of LED chips mounted on the second unit substrate to form a plurality of pixels, and a second light absorbing layer formed on the second unit substrate. The first unit substrate and the second unit substrate are laterally connected to each other. Each of the first light absorbing layer and the second light absorbing layer includes a plurality of valleys formed between the plurality of pixels. The first light absorbing layer includes a first inclined portion formed obliquely from the upper end edge of the interface between the first unit substrate and the second unit substrate to the upper portion of the side surface of each of the outer LED chips mounted on the first unit substrate. The second light absorbing layer includes a second inclined portion formed obliquely from the upper end edge of the interface between the first unit substrate and the second unit substrate to the upper portion of the side surface of each of the outer LED chips mounted on the second unit substrate. At least one of the plurality of valleys is formed by the first inclined portion and the second inclined portion meeting each other.
Owner:LUMENS
Non-Volatile Semiconductor Memory and Manufacturing Process Thereof
InactiveUS20070205458A1Improve capacitanceImprove storage propertyTransistorSolid-state devicesSilicon nitrideCapacitance
A non-volatile semiconductor memory which can suppress a leak current, improve dielectric strength and ensure large capacitance between a control gate and a floating gate and a manufacturing process thereof. A silicon nitride film is formed on the floating gate electrode layer of a memory cell and has a thickness of 5 nm or more. A high dielectric constant thin film is formed on the silicon nitride film. A control gate electrode layer is formed over the high dielectric constant thin film.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Device package, a printed wiring board, and an electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20050127520A1Easily made differentIncrease the number ofPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A device package, such as a BGA, to be mounted on a printed wiring board (PWB) is disclosed. The bottom electrodes of the device package are arranged in an array such that intervals between the edges of the bottom electrodes become different from place to place. The intervals may be set wider at the peripheral positions of the bottom electrodes. The PWB includes pads that are located at positions corresponding to the bottom electrodes.
Owner:RICOH KK
Determining an Optimal Data Transfer Rate Via a Transfer Medium
InactiveUS20080183923A1Accurate measurementEasy transferPower managementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransport mediumChronological time
Sequences that respectively comprise different data are transmitted via a transfer medium, the transfer quality being detected in accordance with the transmitted sequences. Accordingly, the sequences to be transmitted are assigned to several chronologically sequential stages, the sequences that are assigned to one stage having a pre-definable interval in terms of the data transfer rate. The following steps are executed cyclically: a) transmission of at least part of the sequences that are assigned to the first stage and selection of an interval that is situated between two transmitted sequences, in accordance with the determined transfer quality; b) transmission of at least part of the sequences that lie in the selected interval and that are assigned to the subsequent stage. Thus an optimal data transfer rate can be accurately determined for the transmission of information via the transfer medium.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
Multi-beam light source, method for manufacturing the same, light scanning unit using the same, and image forming apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7542652B2Reduce intervalImprove accuracyCoupling light guidesBundled fibre light guideImage formationLight beam
The invention is to provide a multi-beam light source where the interval of core portions is reduced and the core portions are arranged on a straight line. The multi-beam light source includes a first substrate where a plurality of optical fibers each having a core portion and a clad portion surrounding the core portion coaxially are fixed at predetermined intervals, and a second substrate where a plurality of similar optical fibers are fixed at predetermined intervals. The first and second substrates are put and bonded on top of each other so that the core portion of each optical fiber on the second substrate is inserted between core portions of adjacent optical fibers on the first substrate, and the core portions of the optical fibers on the first and second substrate are arranged substantially on a straight line.
Owner:RICOH PRINTING SYST
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050072993A1Avoid damageReduce probabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialSilicon oxide
In a semiconductor device in which a source / drain and a wiring layer are connected to each other through an associated buried conductive layer, a separation width of the buried conductive layer on a upper portion of a gate electrode is made small to manufacture a highly reliable and fine MOS transistor. After a silicon oxide film has been formed on a first polycrystalline silicon film to be aligned with a width of a gate electrode, a second polycrystalline silicon film formed on the whole surface of a substrate is selectively etched away so as to be left only on both side faces of a pattern of the silicon oxide film. Thereafter, the first polycrystalline silicon film is selectively etched away with both the silicon oxide film and the second polycrystalline silicon film as an etching mask so that the first polycrystalline film is separated with a width which is smaller than that of the gate electrode by a width of a pattern of the second polycrystalline silicon film. As a result, the buried conductive layer including the first and second polycrystalline silicon films is formed.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com