Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97results about How to "Raise the gate voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
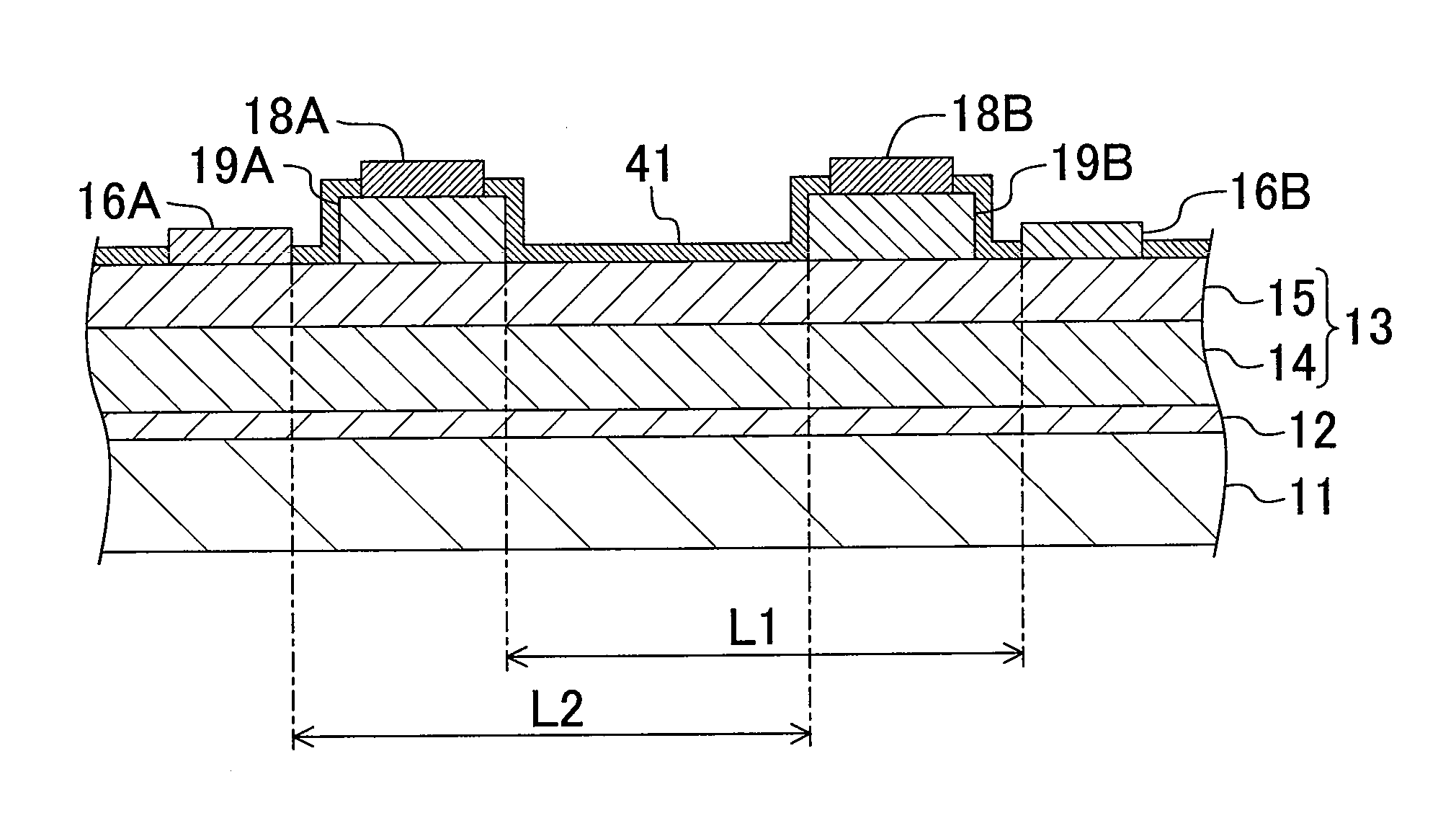
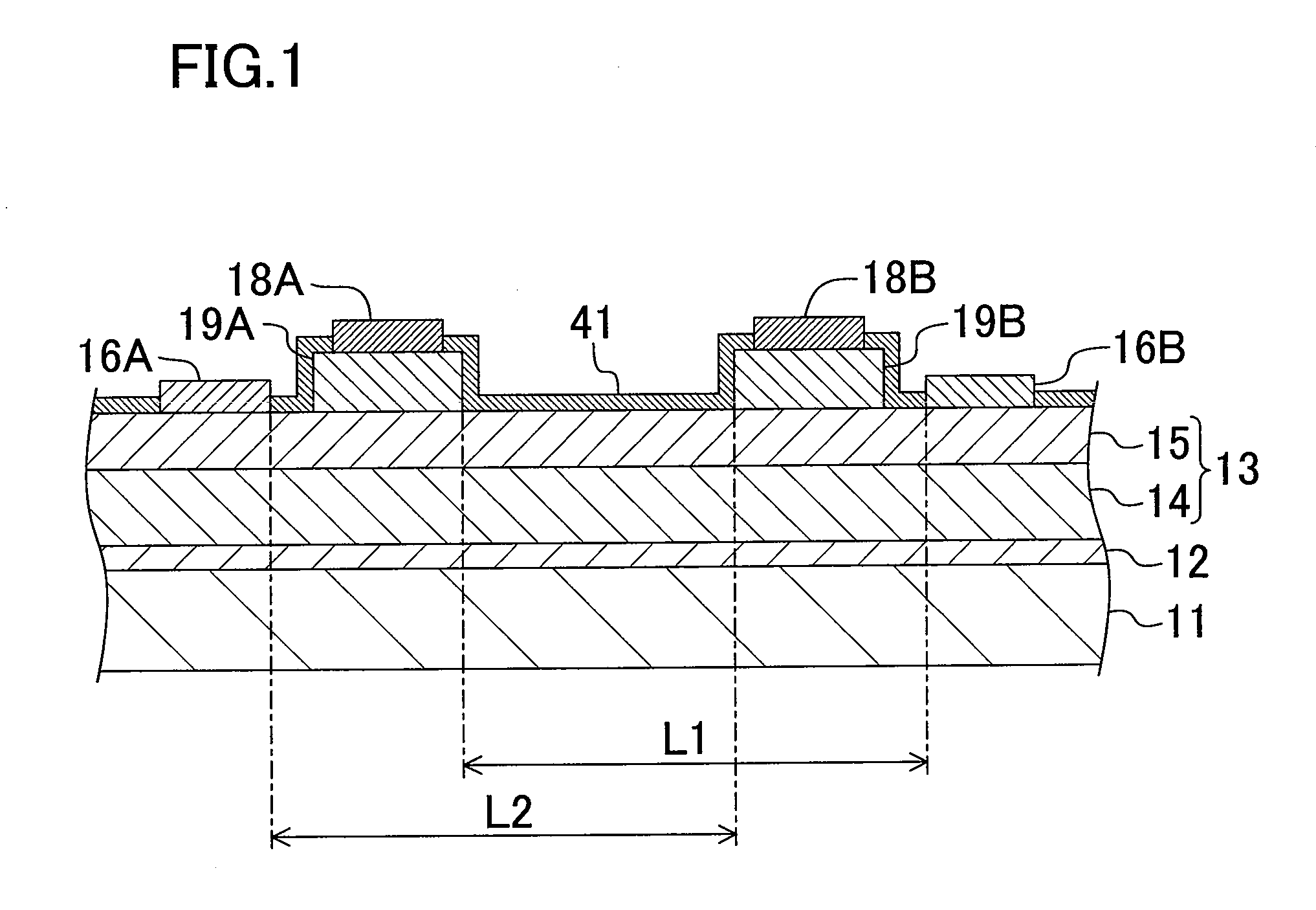
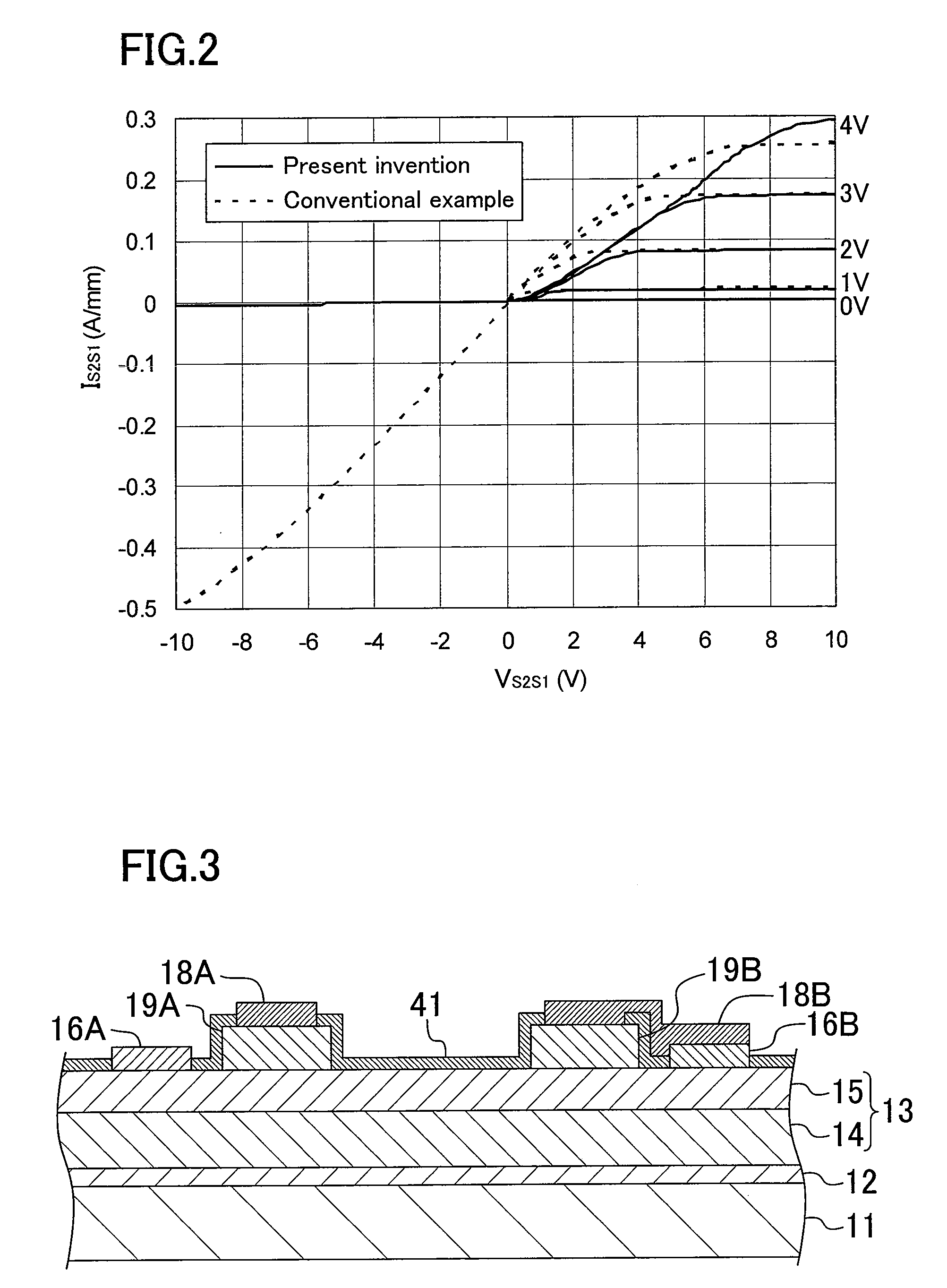
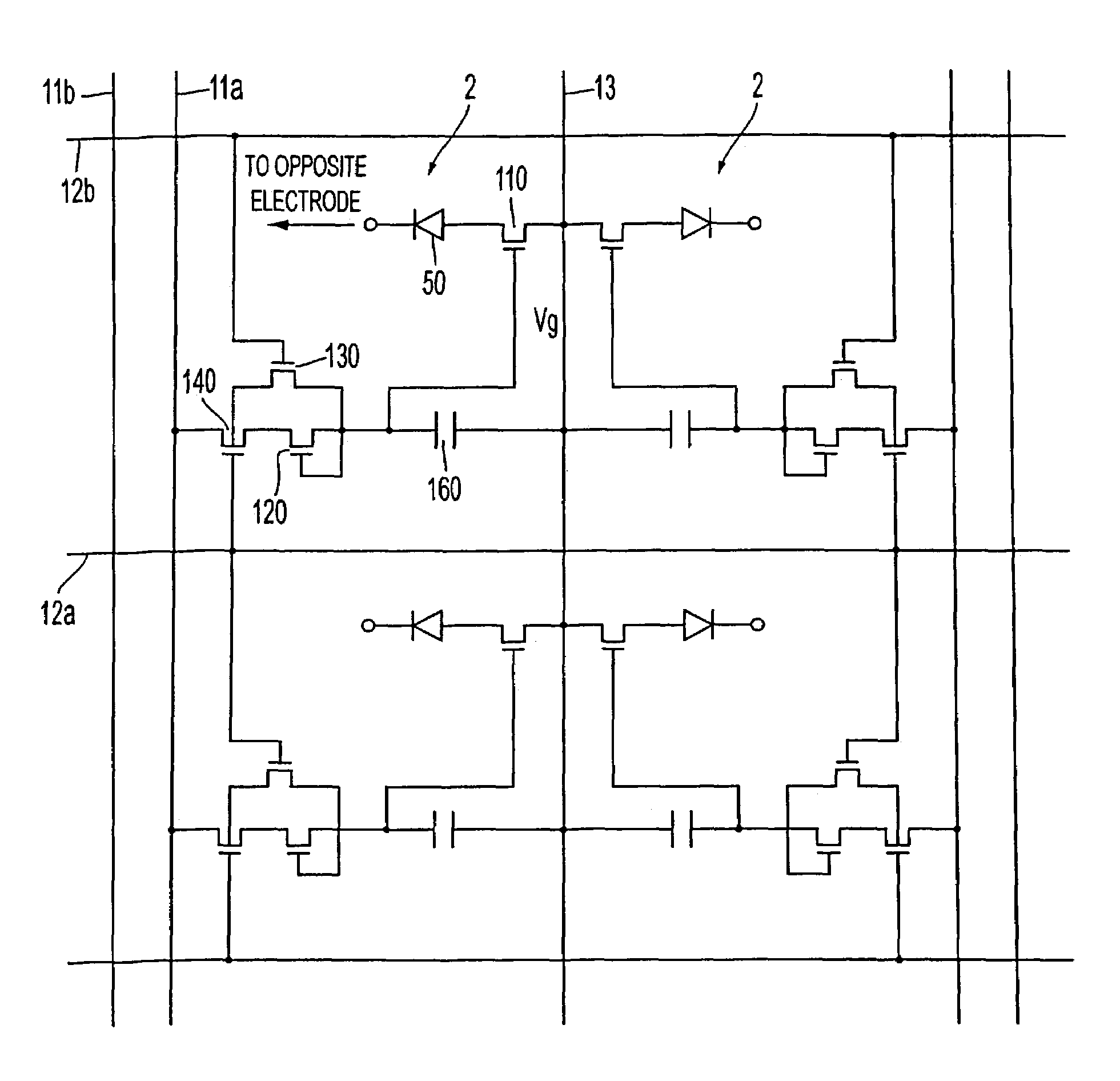
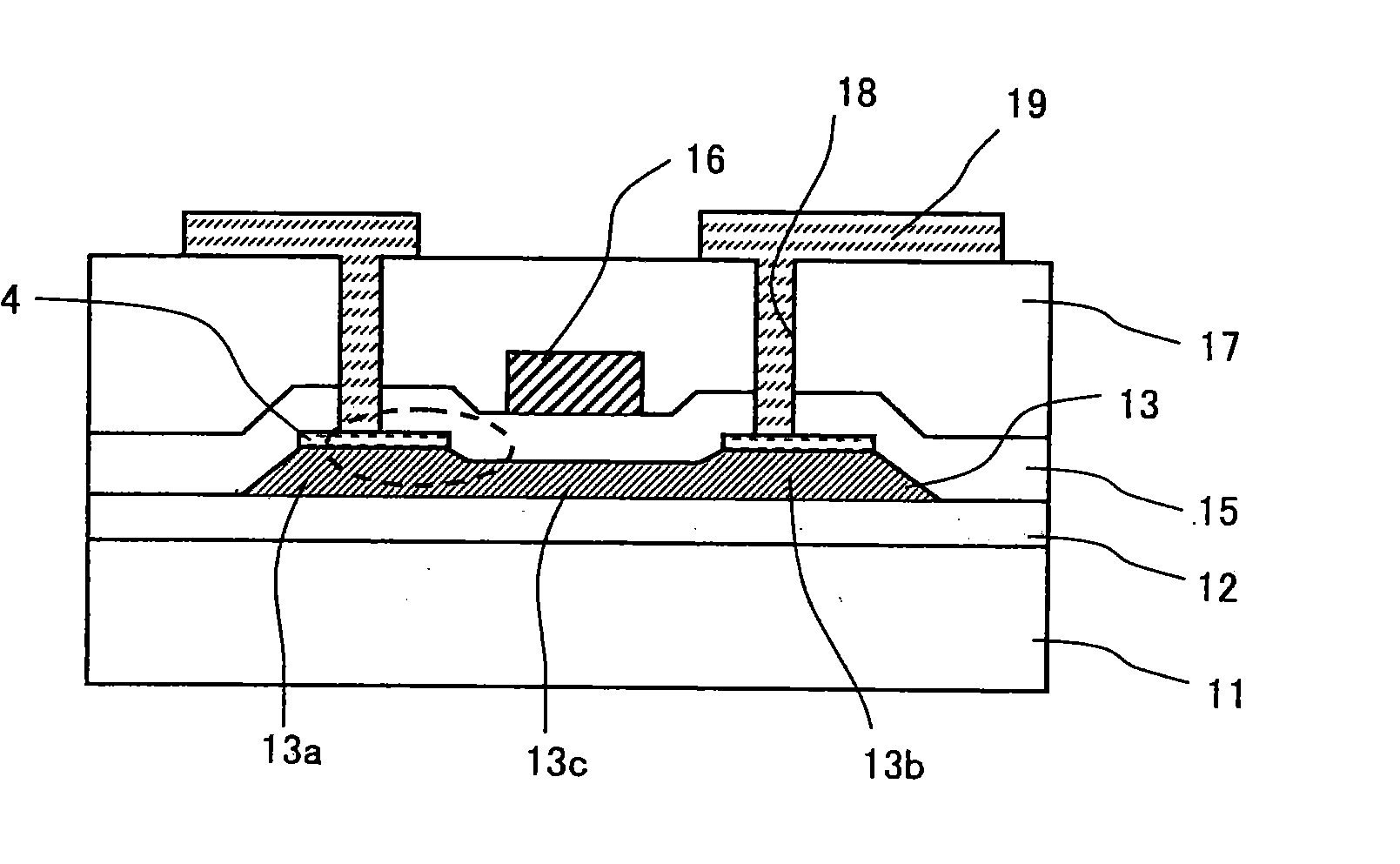
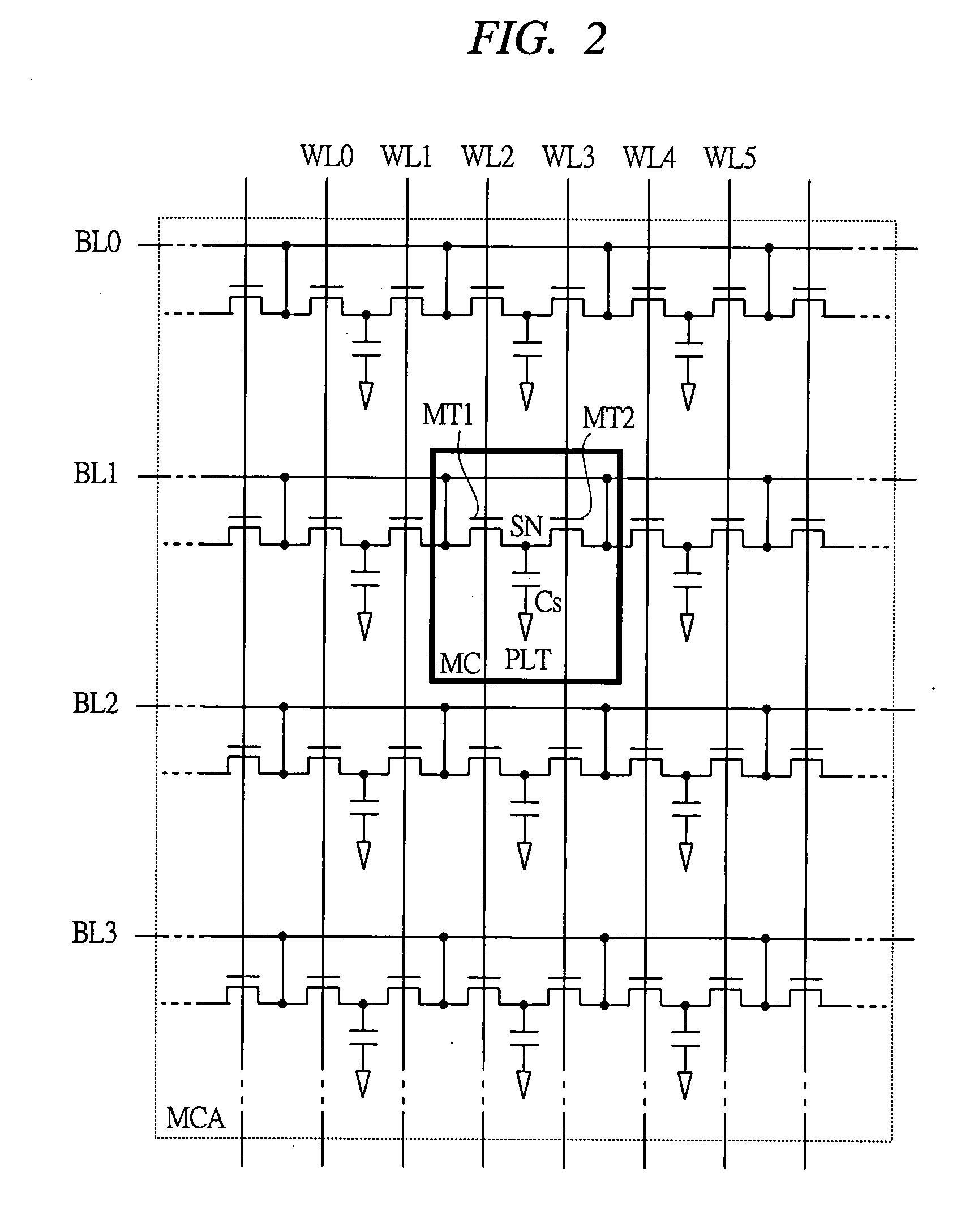
Semiconductor device and method for driving the same
ActiveUS20100097105A1Excellent reverse voltage characteristicRaise the gate voltageSolid-state devicesElectronic switchingControl layerEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor layer stack 13 formed on a substrate 11 and having a channel region, a first electrode 16A and a second electrode 16B formed spaced apart from each other on the semiconductor layer stack 13, a first gate electrode 18A formed between the first electrode 16A and the second electrode 16B, and a second gate electrode 18B formed between the first gate electrode 18A and the second electrode 16B. A first control layer 19A having a p-type conductivity is formed between the semiconductor layer stack 13 and the first gate electrode 18A.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
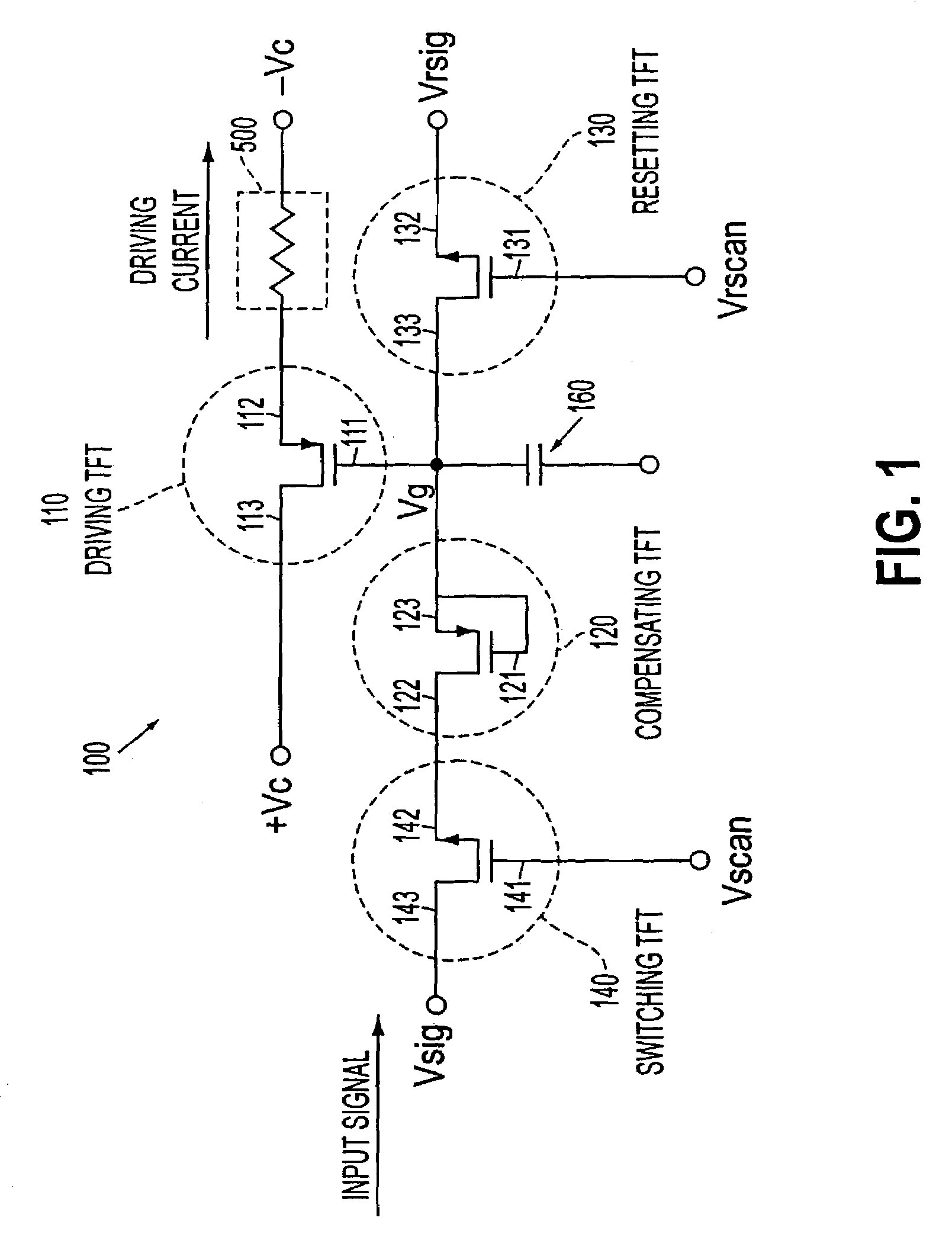
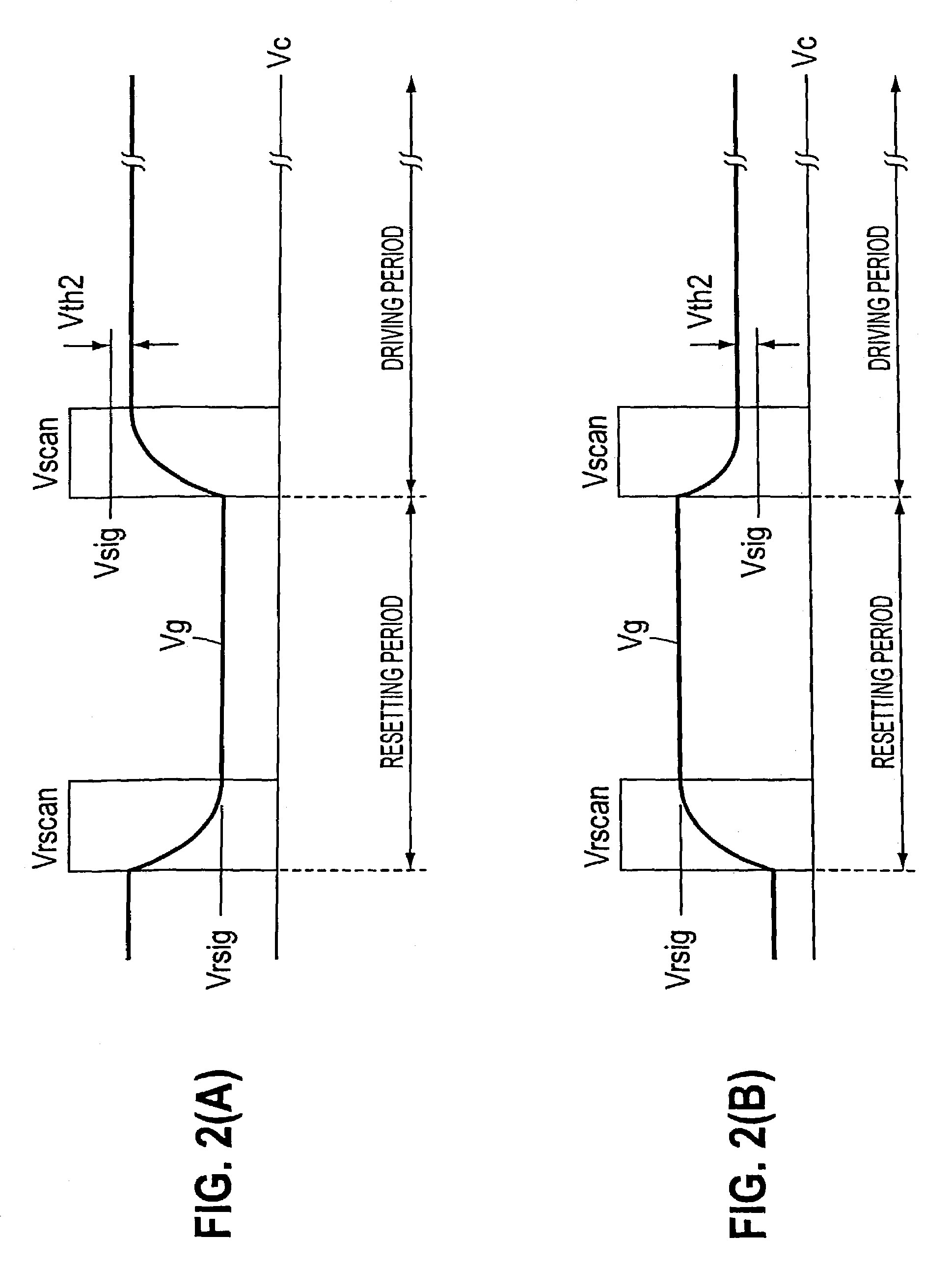
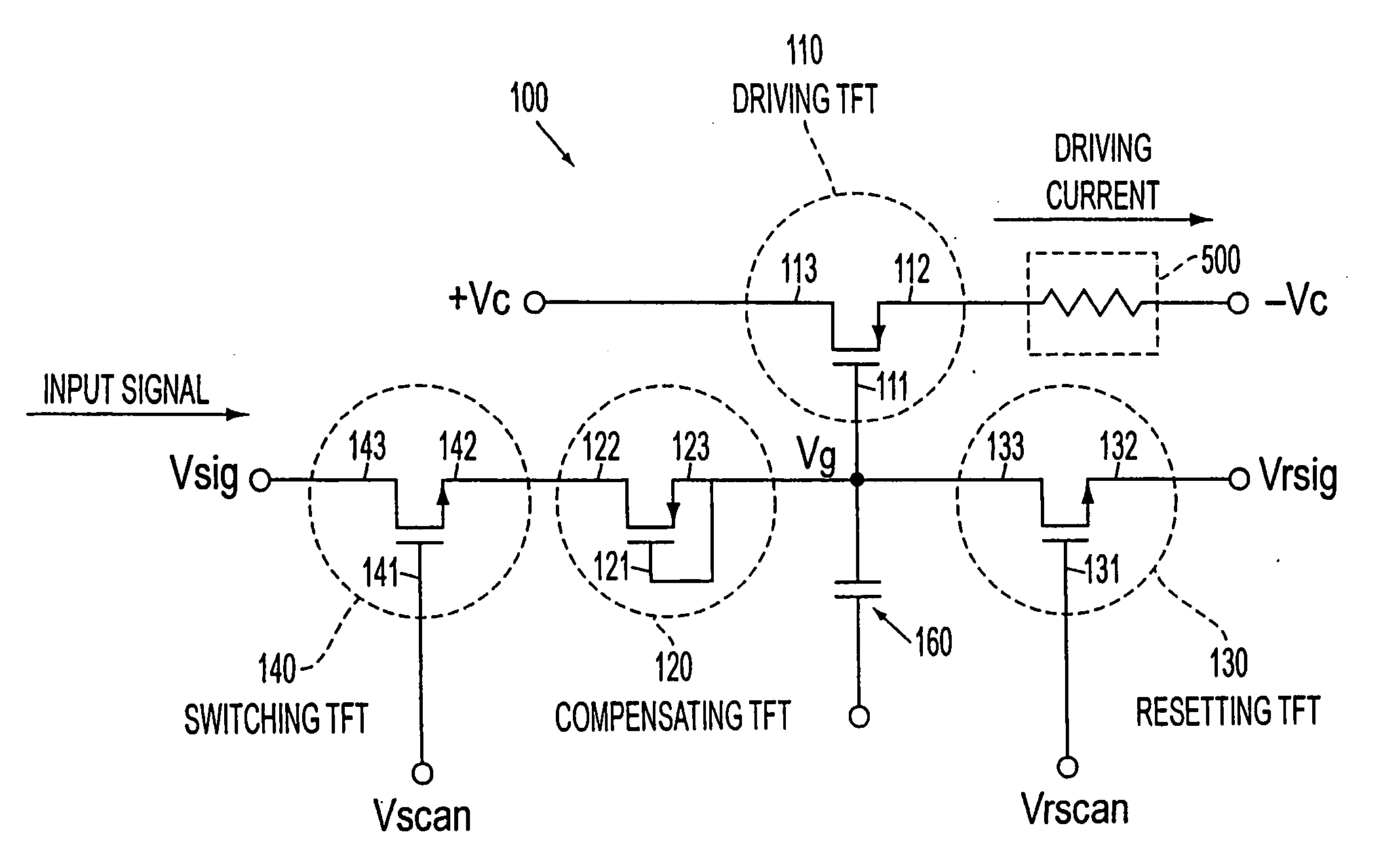
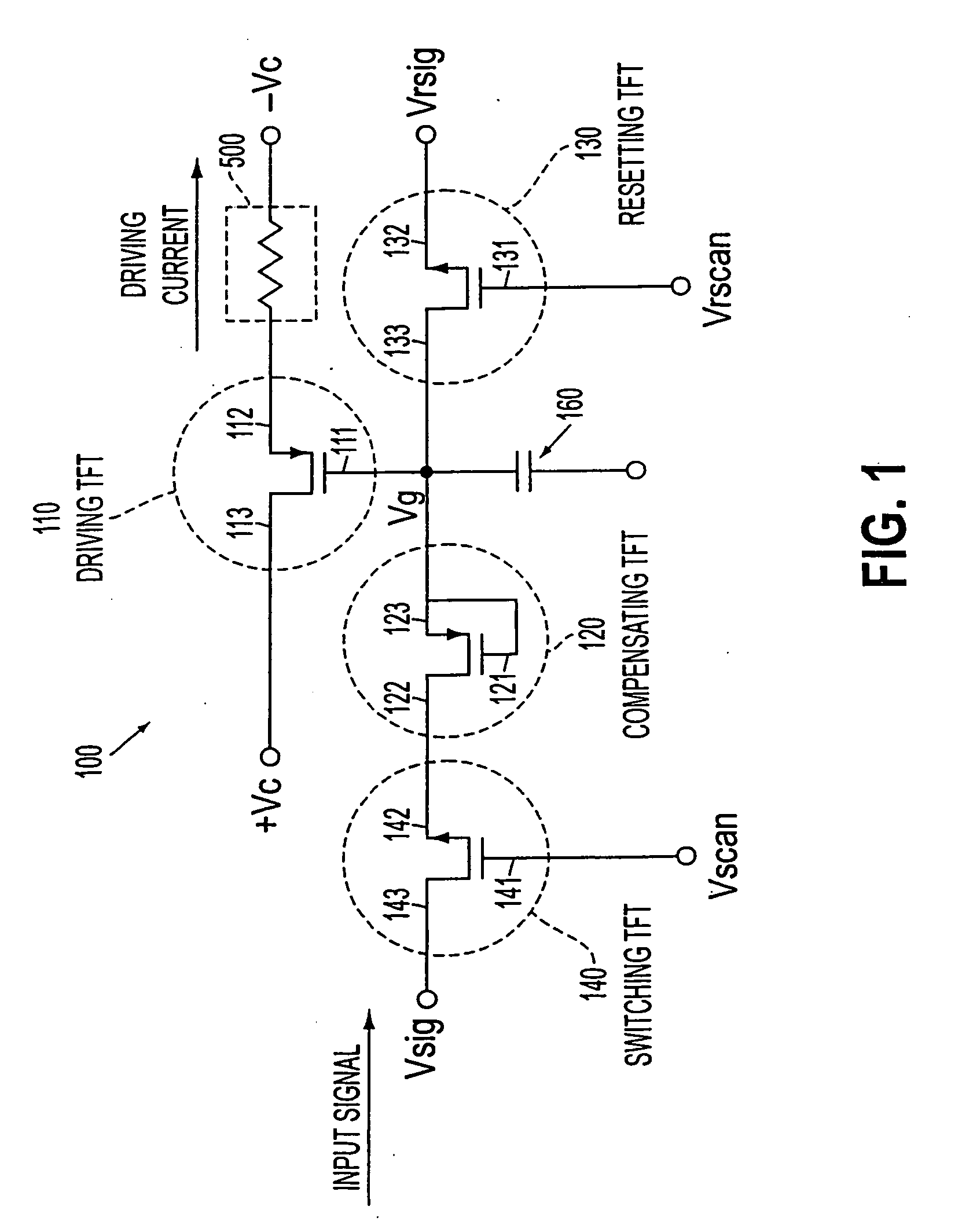
Transistor circuit, display panel and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7173584B2Good precisionReduce brightness unevennessTransistorStatic indicating devicesLow voltageTransistor circuits
A transistor circuit is provided including a driving transistor where conductance between the source and the drain is controlled in response to a supplied voltage, and a compensating transistor where the gate is connected to one of the source and the drain, the compensating transistor being connected so as to supply input signals to the gate of the driving transistor through the source and drain. In a transistor circuit where conductance control in a driving transistor is carried out in response to the voltage of input signals, it is possible to control the conductance by using input signals of a relatively low voltage and a variance in threshold characteristics of driving transistors is compensated. With this transistor circuit, a display panel that can display picture images with reduced uneven brightness is achieved.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Transistor circuit, display panel and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20060256047A1Good precisionReduce brightness unevennessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTransistor circuits
A transistor circuit is provided including a driving transistor where conductance between the source and the drain is controlled in response to a supplied voltage, and a compensating transistor where the gate is connected to one of the source and the drain, the compensating transistor being connected so as to supply input signals to the gate of the driving transistor through the source and drain. In a transistor circuit where conductance control in a driving transistor is carried out in response to the voltage of input signals, it is possible to control the conductance by using input signals of a relatively low voltage and a variance in threshold characteristics of driving transistors is compensated. With this transistor circuit, a display panel that can display picture images with reduced uneven brightness is achieved.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Charge pump circuit using active feedback controlled current sources
ActiveUS20050195003A1Reduce noise contributionRaise the gate voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalPulse automatic controlActive feedbackDriving current
A charge pump circuit utilizes active feedback control circuits to control the currents produced by sinking and sourcing current sources. The feedback control circuits may regulate the drain voltages of sinking and sourcing current source transistors to make them approximately equal to respective reference voltages received by the feedback control circuits. The charge pump circuit may utilize multiple supply voltages, with a higher supply voltage such as a 3.3 V supply voltage being used to drive current source transistors, and a lower supply voltage such as a 1.8 V supply voltage being used to drive switches in a switching section.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
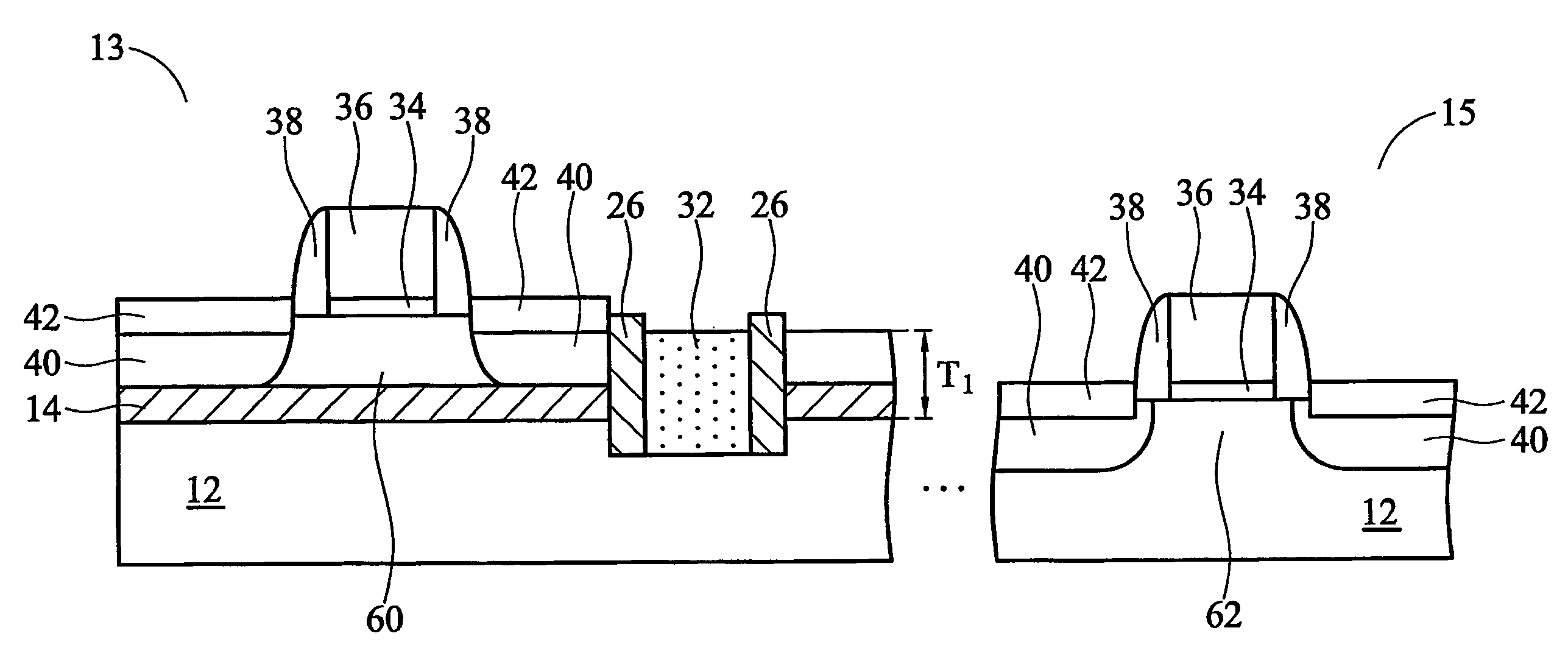
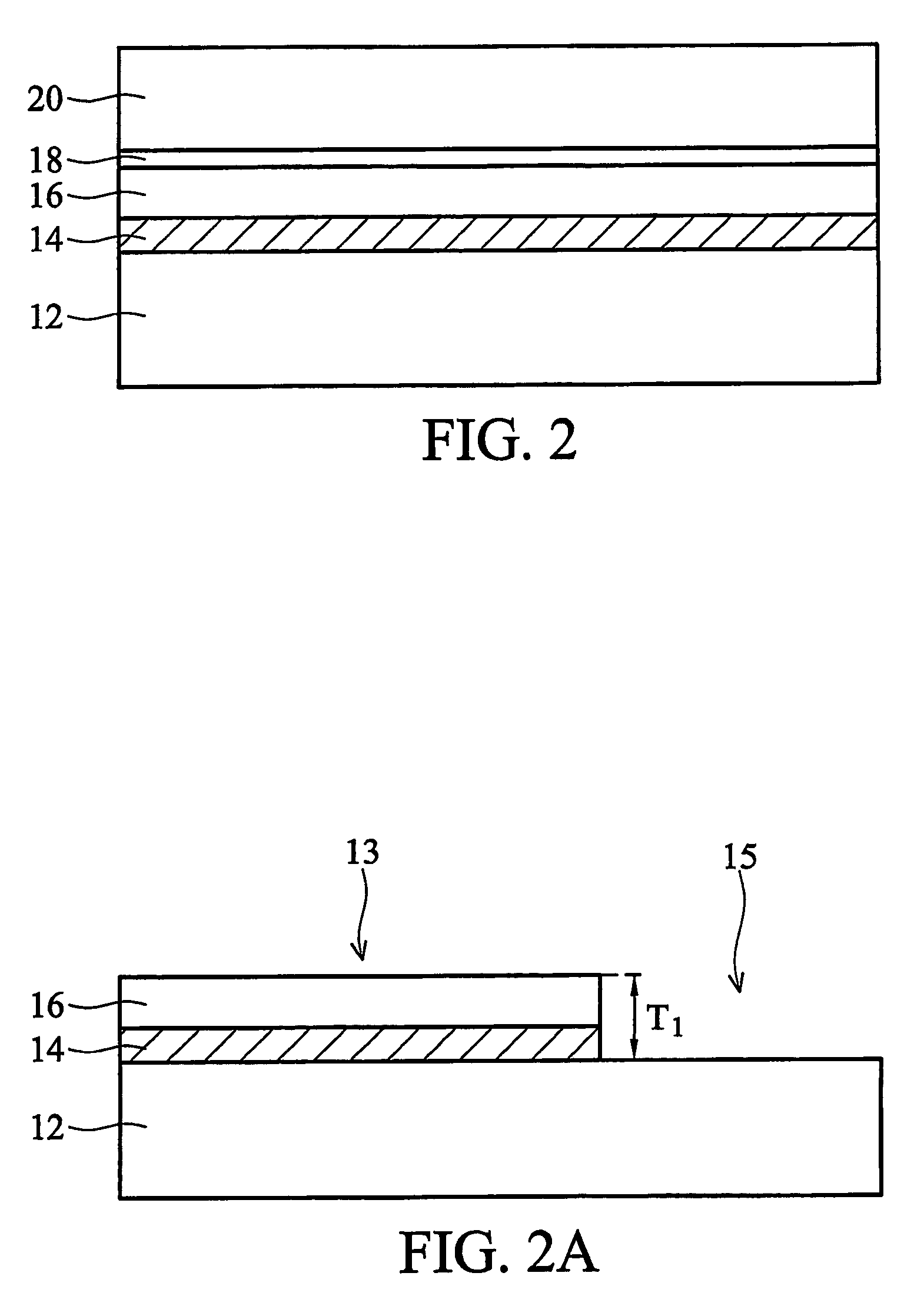
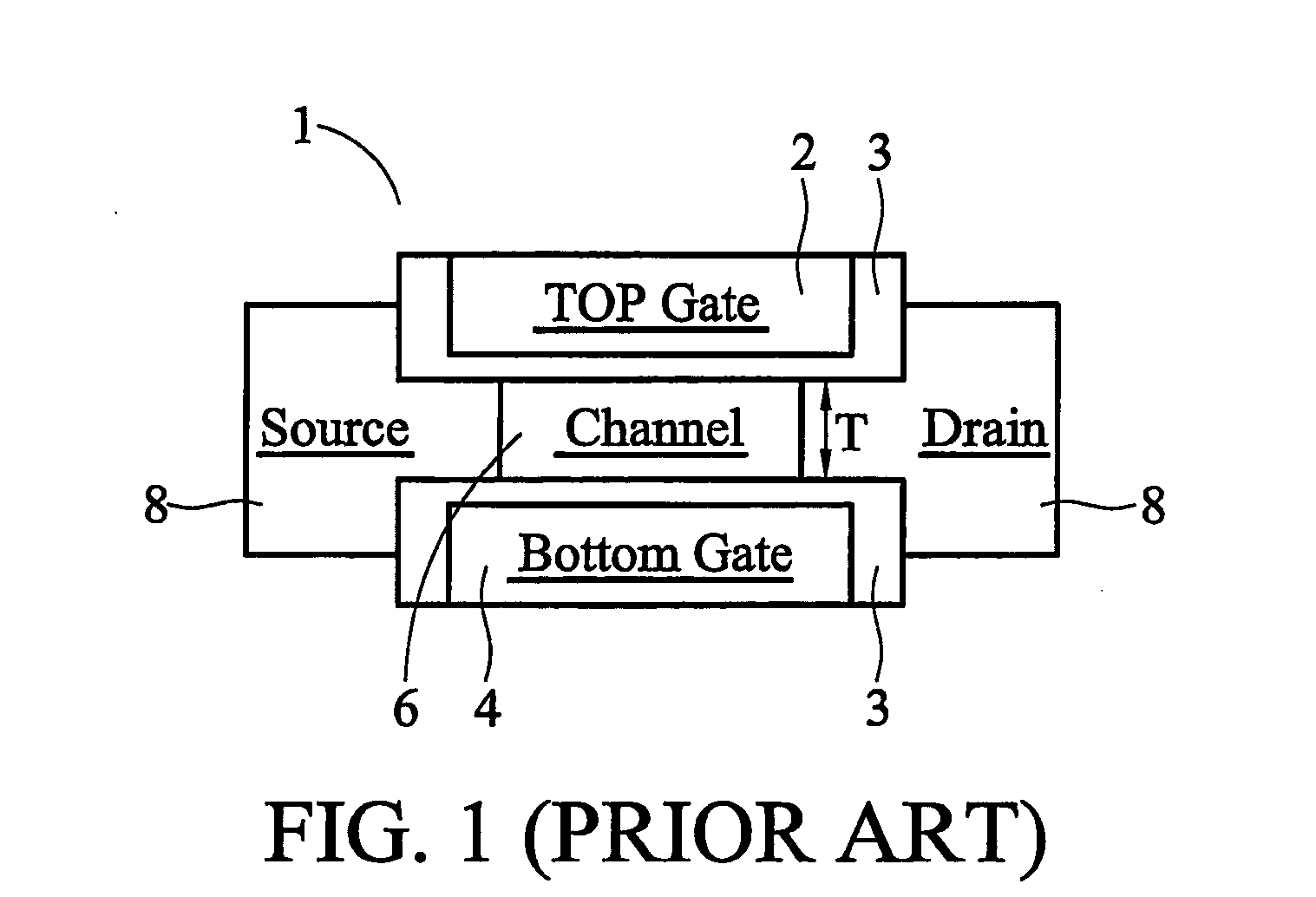
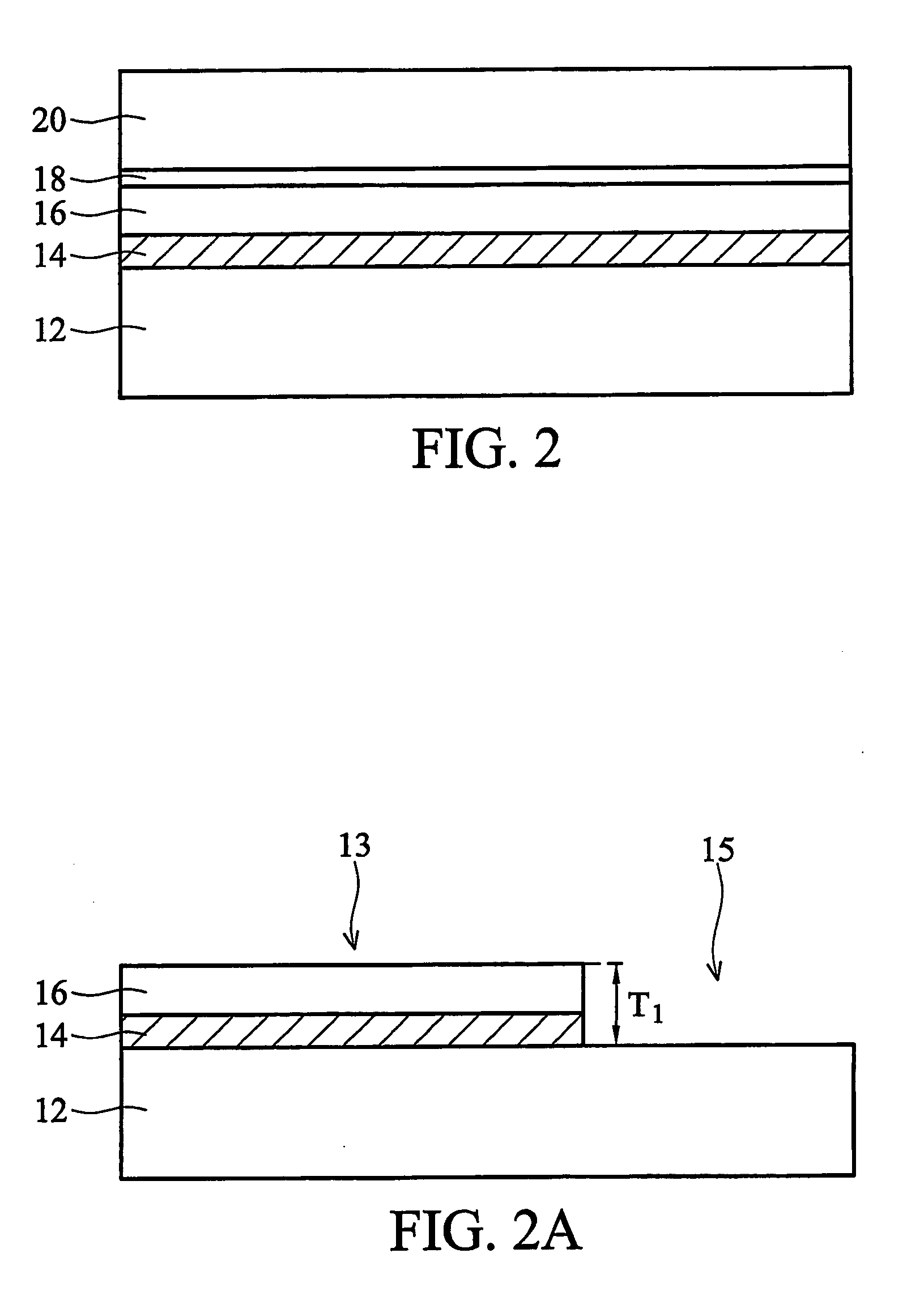
Self-aligned double gate device and method for forming same
InactiveUS7230270B2Improve device performanceSimple manufacturing processTransistorSolid-state devicesBottom gateConductive materials
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Connection device
ActiveUS20130088278A1Low drain to source resistancePerform less-wellTransistorElectronic switchingElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Charge pump circuit
ActiveUS20080186081A1Increase charging voltageBreakdown voltage is limitedAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEngineeringCapacitor
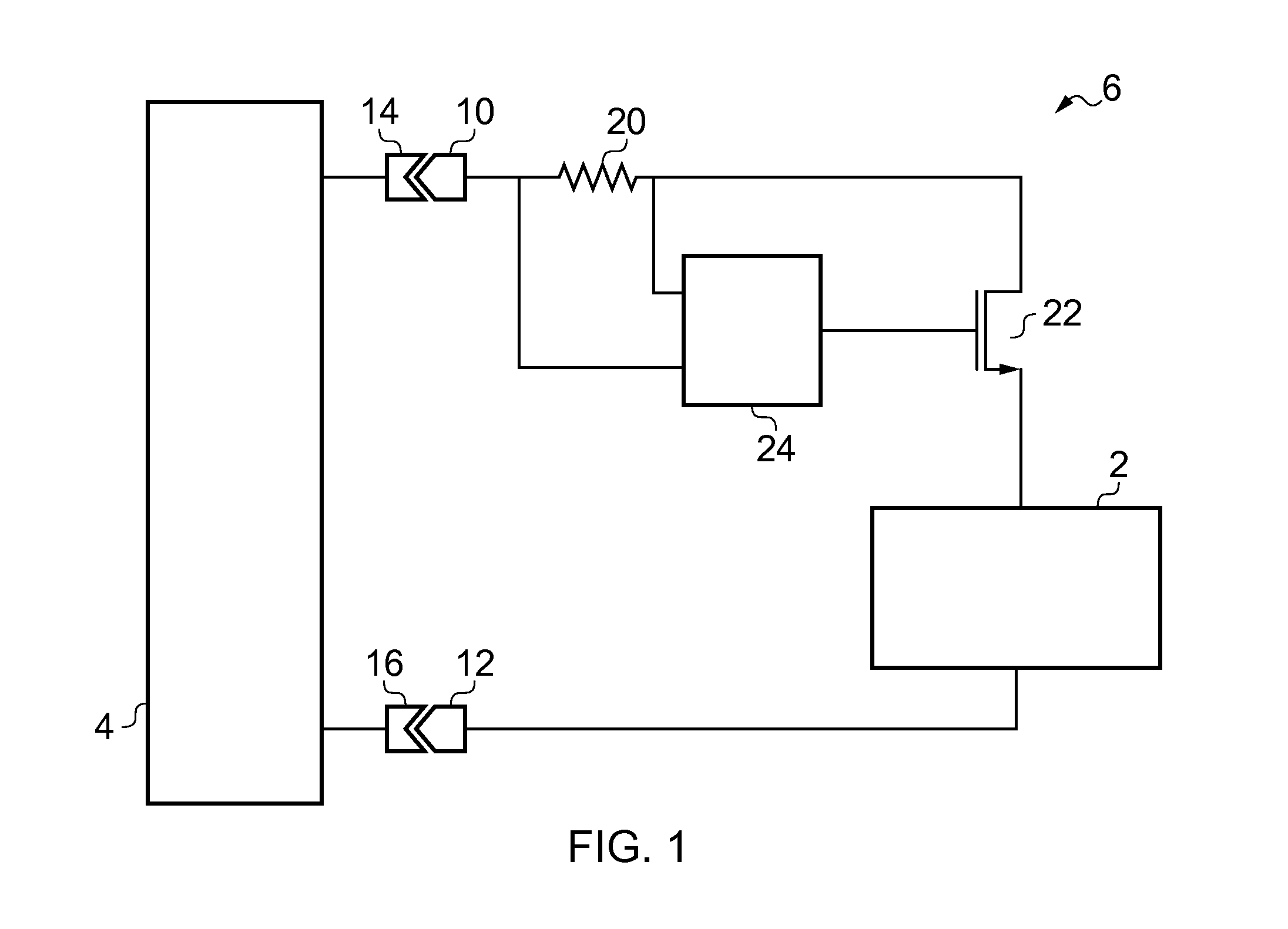
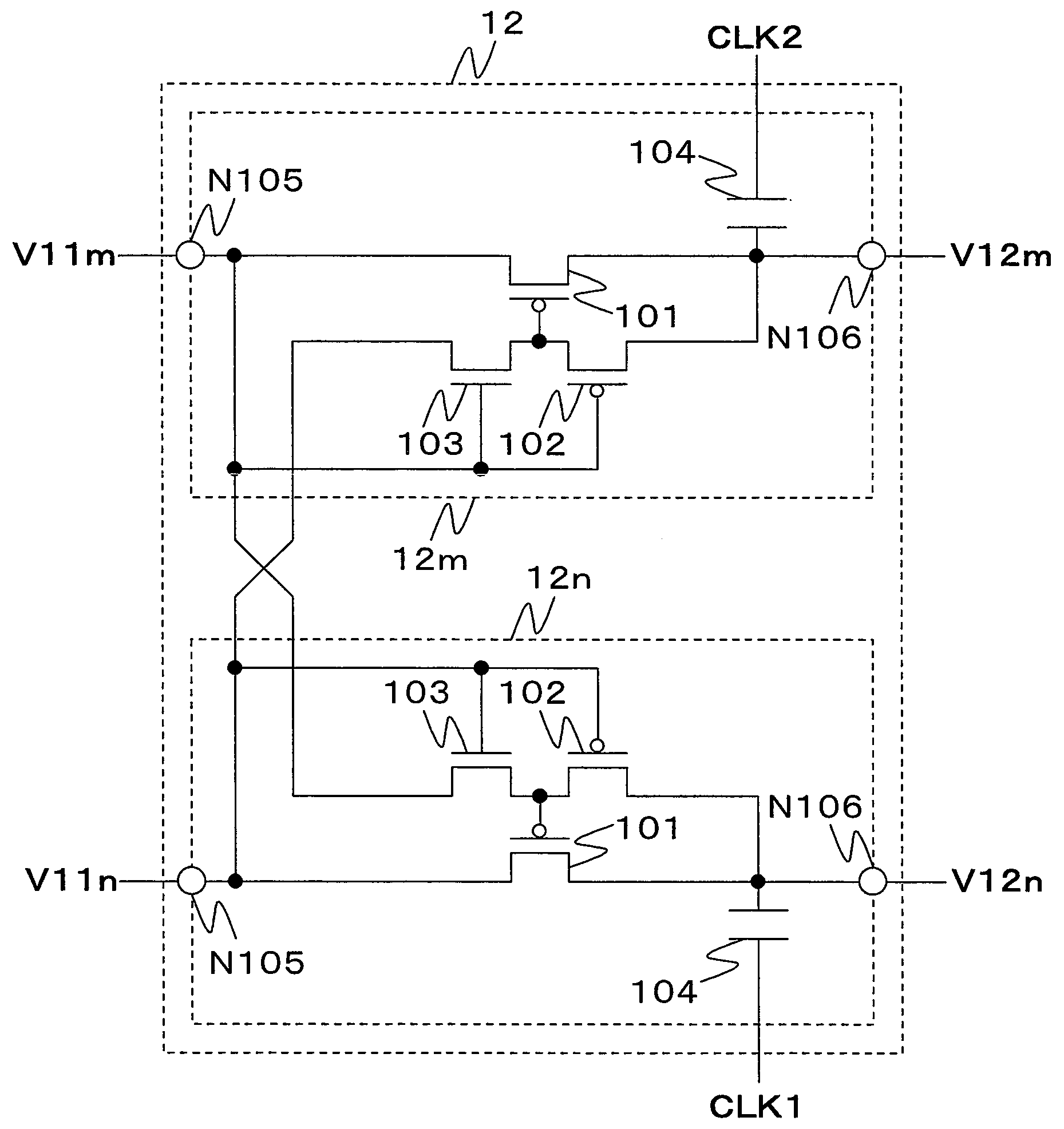
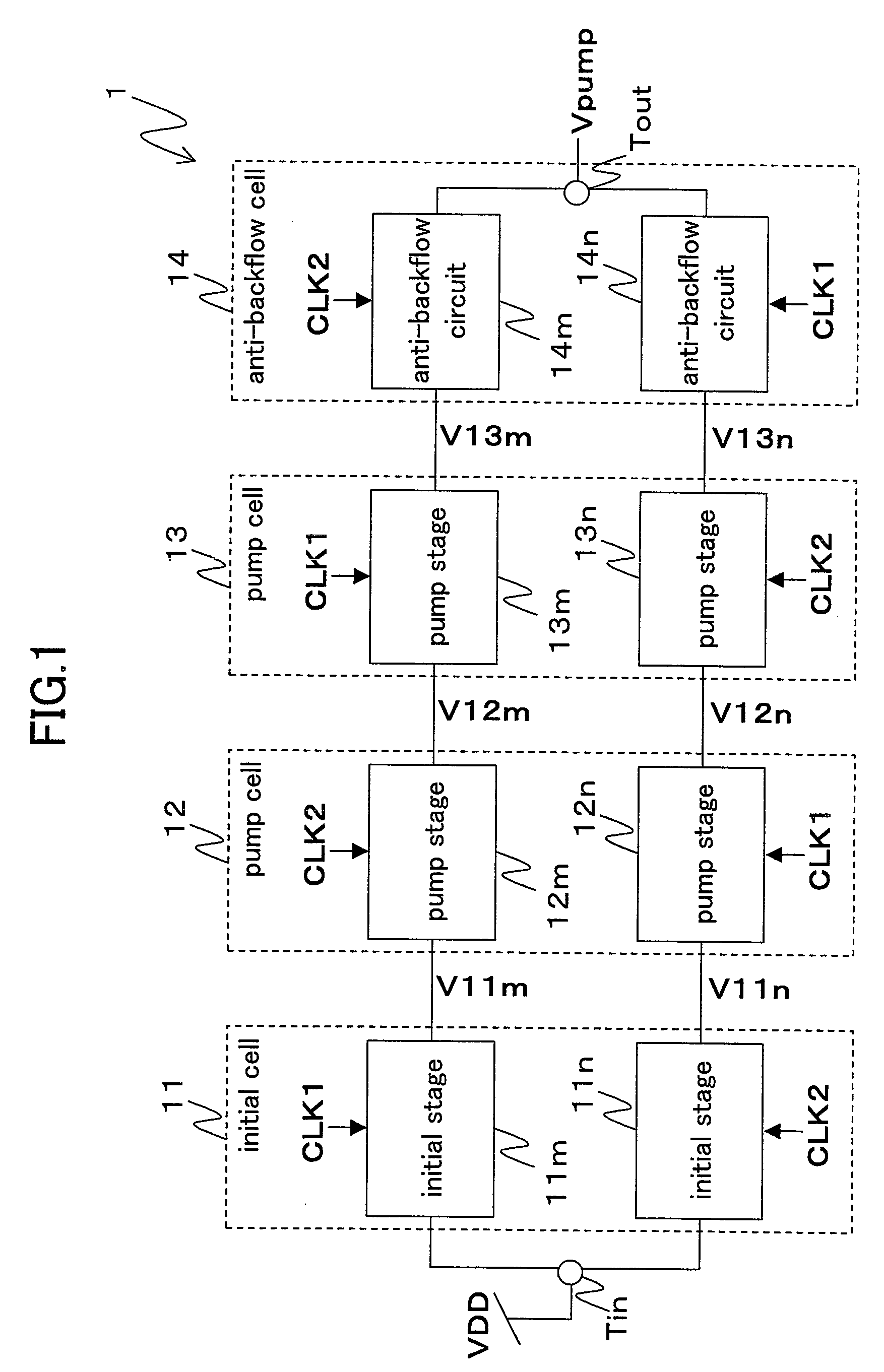
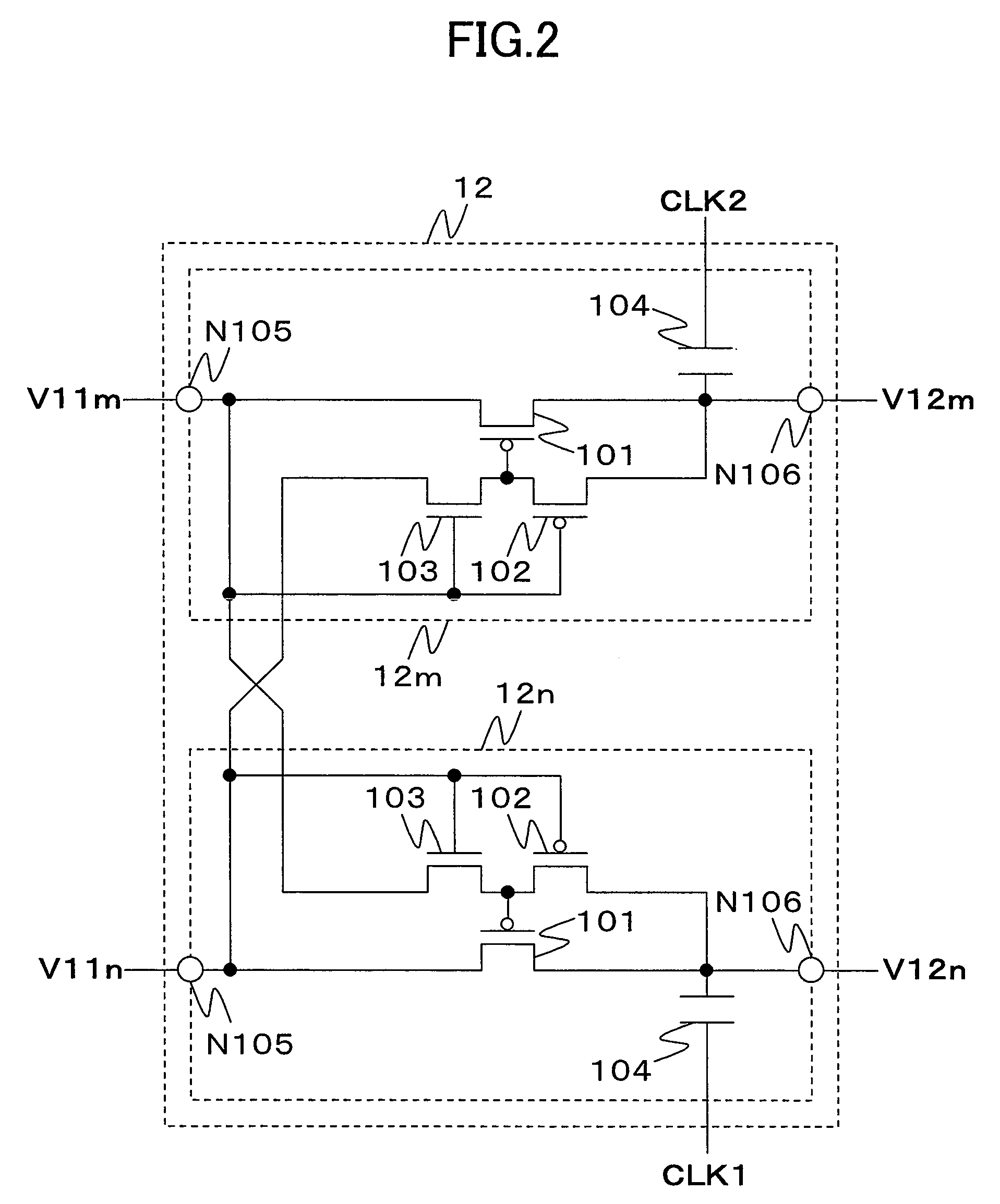
Each of a plurality of pump stages has an input node and an output node and performs a charge pump operation in response to any one of the first and second clock signals. The plurality of pump stages include a first pump stage, in which a charge transfer transistor is connected between the input node and the output node. One end of a pump capacitor is connected to the output node, and the other end is supplied with one of the first and second clock signals corresponding to the first pump stage. A connection switcher connects to the gate of the charge transfer transistor any one of the output node of a pump stage which is supplied with one of the clock signals corresponding to the first pump stage and the input node of a pump stage which is supplied with the other clock signal not corresponding to the first pump stage and which is included in a pump stage row not including the first pump stage.
Owner:CETUS TECH INC
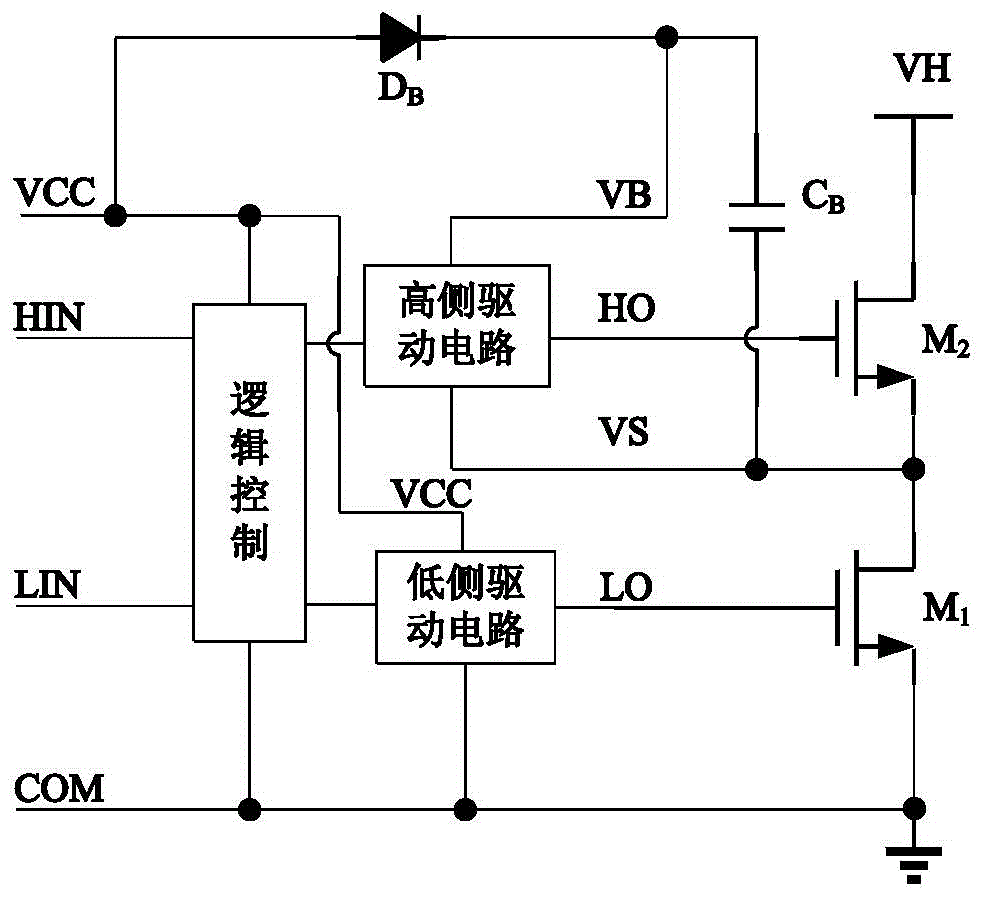
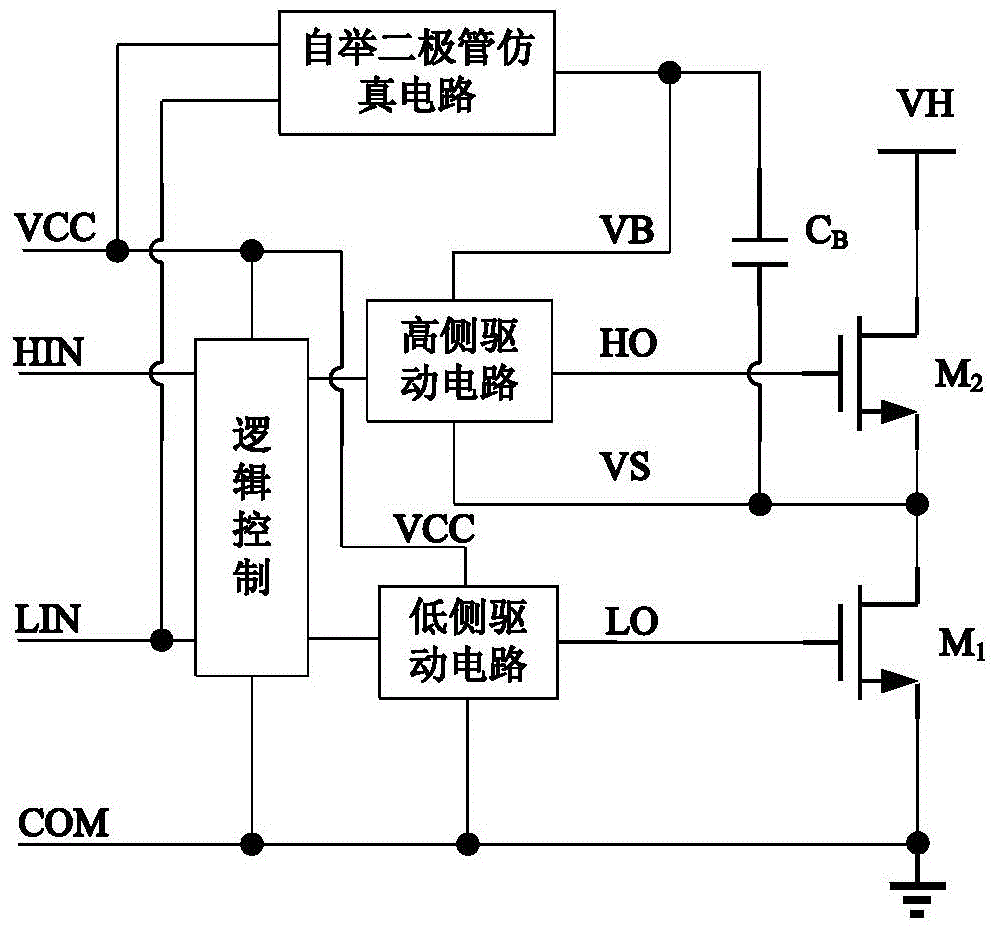
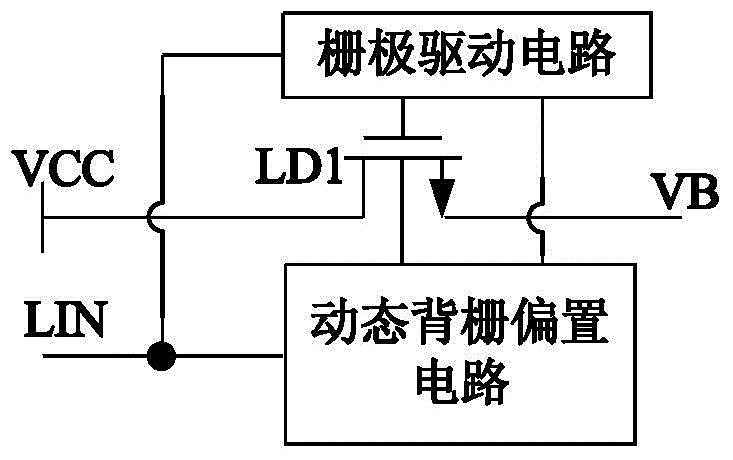
Bootstrapping diode artificial circuit in half-bridge driving circuit
ActiveCN104022776ARaise the gate voltageIncrease charging currentLogic circuits using semiconductor devicesCapacitanceEngineering
The invention provides a bootstrapping diode artificial circuit in a half-bridge driving circuit. An electrical level displacement and a simple charge pump are added into a grid driving circuit structure in an existing bootstrapping diode artificial circuit; when a grid driving input signal is a low electrical level, grid voltage output to an N-channel LDMOS (Lateral Diffusion Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistor LD1 by a grid driving circuit is a low electrical level; the N-channel LDMOS transistor LD1 is turned off. When the grid driving input signal is a high electrical level, the grid voltage output to the N-channel LDMOS transistor LD1 by the grid driving circuit is a high electrical level so that the grid voltage of the N-channel LDMOS transistor LD1 is improved, the conduction resistance of the LD1 is reduced and the charging current to a bootstrapping capacitor is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Thin film transistor device, method of manufacturing the same, and display apparatus
InactiveUS20080191207A1Stable capacitanceRaise the gate voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsSemiconductor
A thin film transistor device includes a semiconductor layer including a source region, a drain region and a channel region formed above a substrate, a metal film formed in a prescribed area on the semiconductor layer, a gate insulating film formed on the metal film and the semiconductor layer, a gate electrode, an interlayer insulating film, and a line electrode. The metal film is formed on the source region and the drain region of the semiconductor layer, the area being at least a bottom of the contact hole. The thickness of the semiconductor layer in a region on which the metal film is not formed is smaller than the thickness of the semiconductor layer in a region on which the metal film is formed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Charge pump circuit using active feedback controlled current sources
ActiveUS6980046B2Reduce noise contributionRaise the gate voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalPulse automatic controlDriving currentActive feedback
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
Thin film transistor, active matrix substrate, display device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20050036080A1Suppress deterioration of the retention characteristicTotal current dropTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationActive matrix
To provide a thin film transistor with off current reduced to a very low level and excellent reliability, which can be applied to a pixel driving element or a peripheral circuit of an ultra high-precision display device, an active matrix substrate including the thin film transistor, and a display device including the active matrix substrate, a thin film transistor according includes a semiconductor layer provided on a substrate body, a gate electrode, a drain electrode, and a source electrode, wherein the semiconductor layer including a high-concentration drain region which is connected to the drain electrode and which is highly doped with an impurity; a low-concentration drain region which is provided at the gate electrode side of the high-concentration drain region and which is lightly doped with an impurity; and an offset region which is a region slightly doped with an impurity, or an intrinsic semiconductor region, the offset region being provided at the gate electrode side of the low-concentration drain region.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Input/output circuit and integrated circuit apparatus including the same
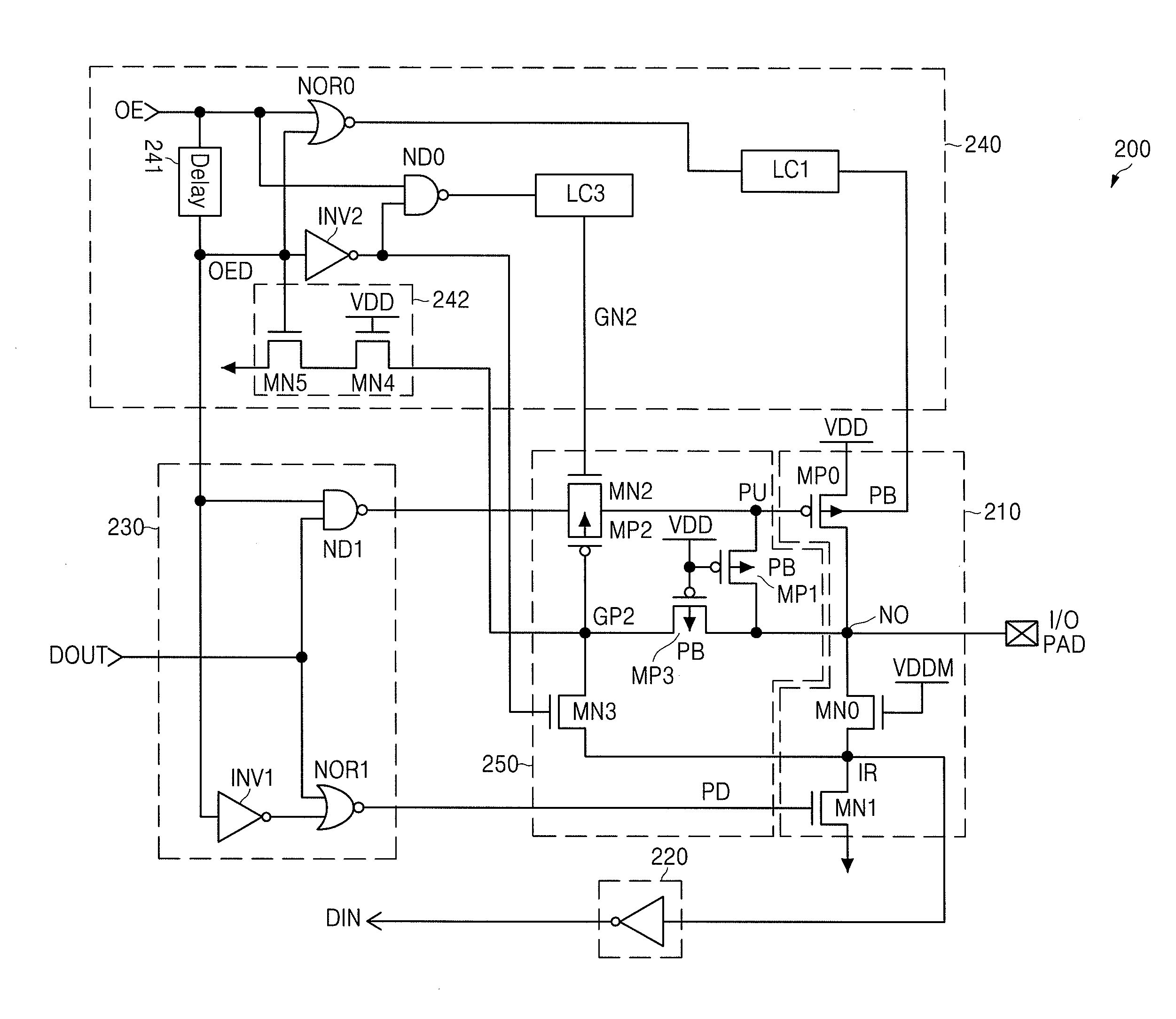
ActiveUS20100271069A1Preventing and reducing leakage currentLow reliabilityDigital storageBaseband systemsEngineeringControl circuit
An input / output circuit includes an I / O node connected to a pull up and pull down circuit having a pull up and pull down transistors. Data is sent and received at through the I / O node. A level shifter provides voltages including a supply voltage and a high voltage higher than the supply voltage. A signal control circuit controls the voltage level applied to the pull up and pull down circuit. During a data input mode, data is received at the I / O node and the pull up transistor is biased at the high voltage to cut off the pull up transistor. During a data output mode, data is output at the I / O node and the pull down transistor pulls down the I / O node to ground when the output data is low, and the pull up transistor is activated when the output data is high.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
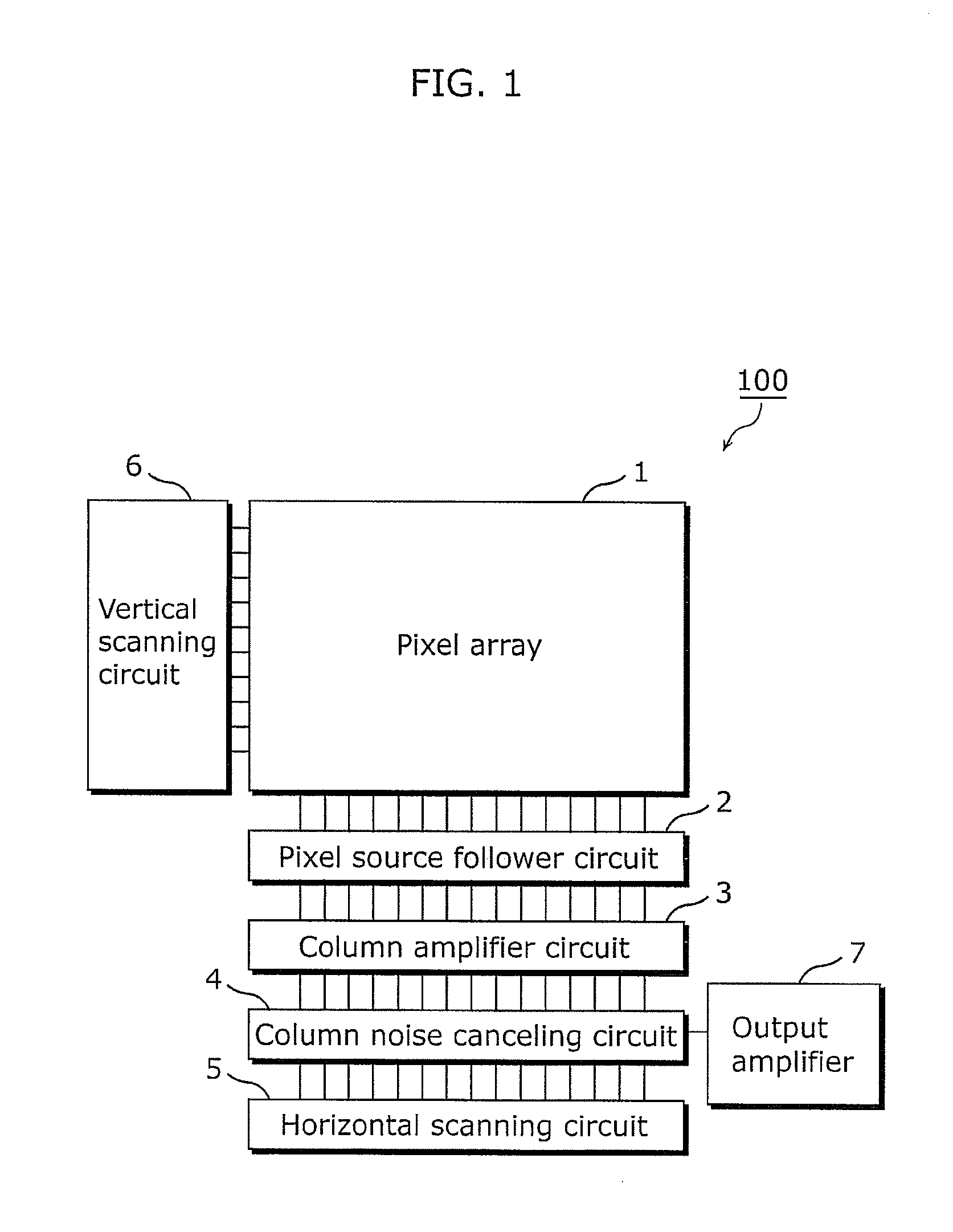
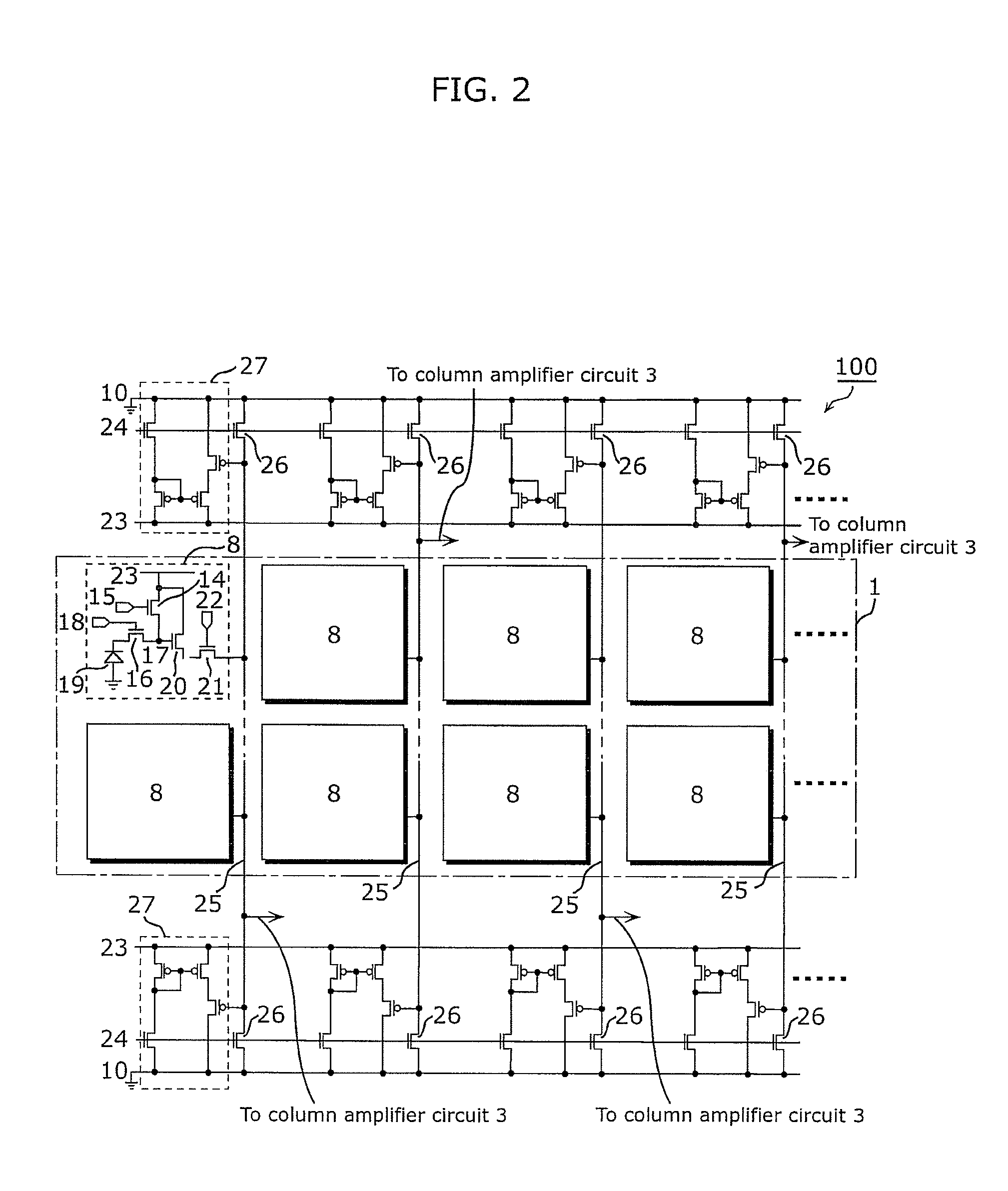
Solid-state imaging device and camera
InactiveUS20110279720A1Suppress power consumptionReduce volatilityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPhotodiode
The solid-state imaging device includes a plurality of pixel units arranged in rows and columns. Each of the pixel units includes: a photodiode that generates a signal voltage corresponding to an intensity of light received; and an amplifier transistor which amplifies the signal voltage in response to a flow of an operating current, and outputs the amplified signal voltage to a column signal line that is provided for each of pixel columns. The solid-state imaging device includes current correction circuits each of which is provided for a corresponding one of the pixel columns and causes a correction current to flow between a power supply line and a grounding line. The correction current fluctuates in an opposite direction to a fluctuation of the operating current flowing into the grounding line from the power supply line via the amplifier element.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
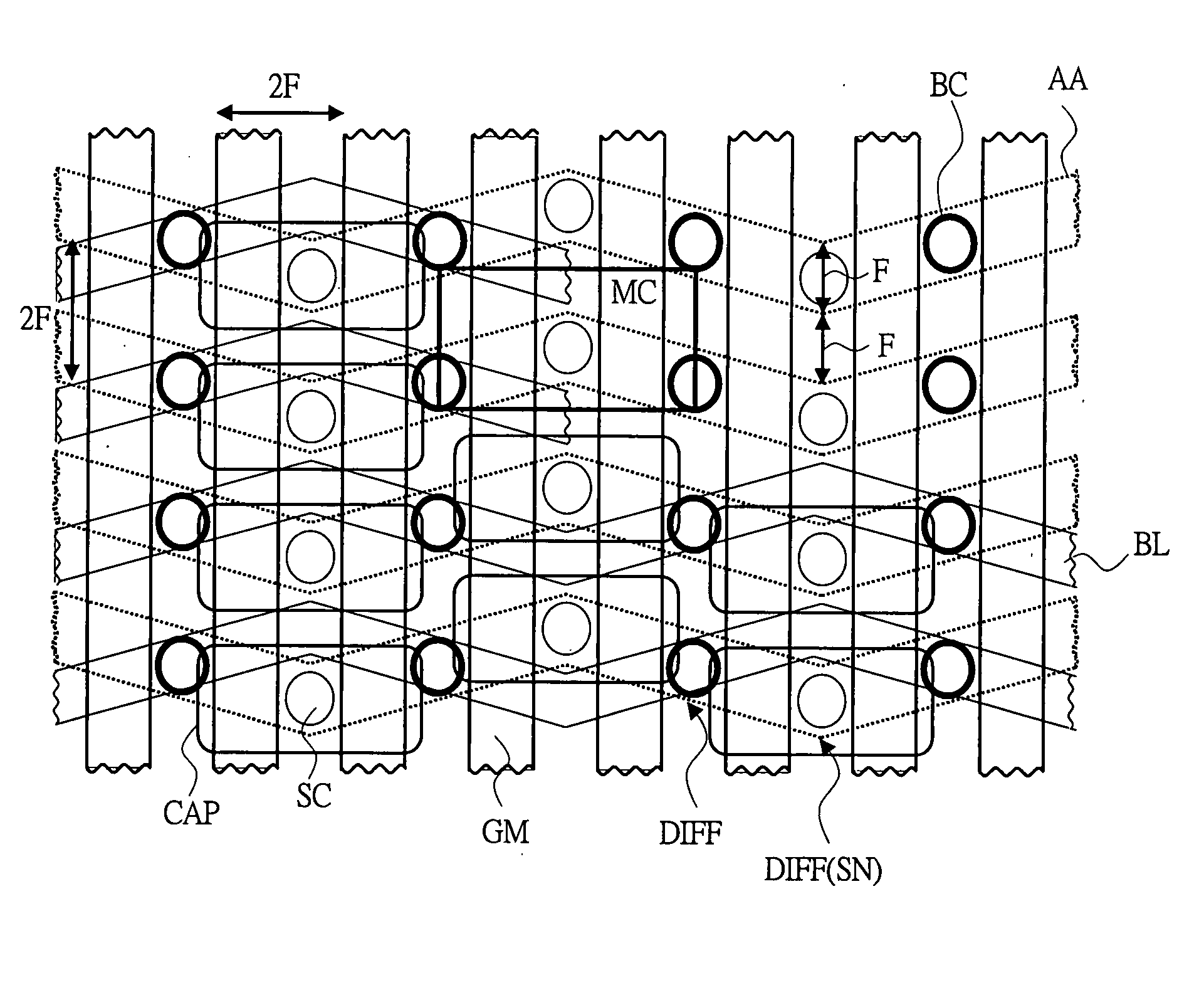
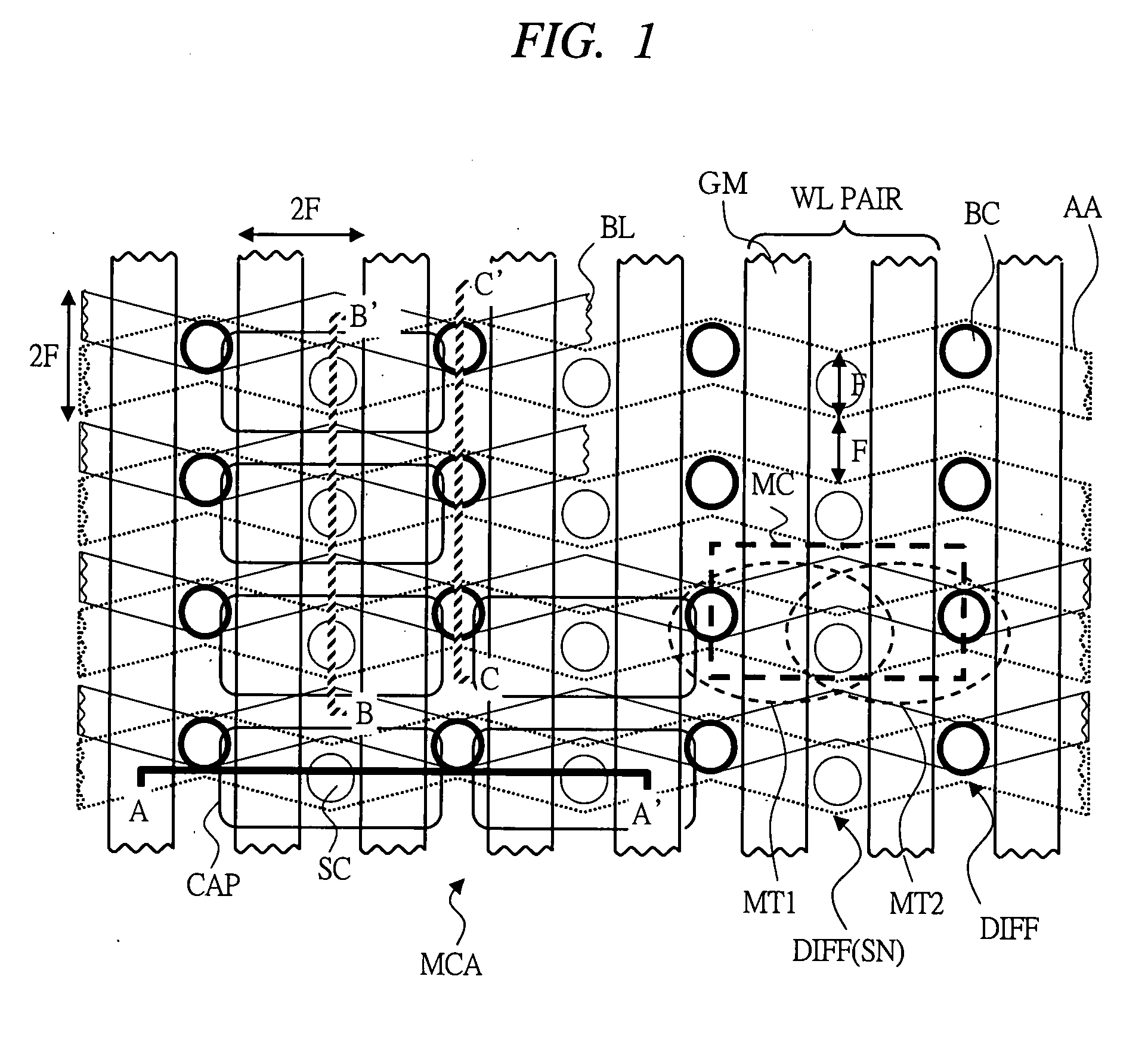
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20080055958A1Degraded drivabilityExtension of timeTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorCapacitor
A semiconductor memory device that can achieve high-speed operation or that is highly integrated and simultaneously can achieve high-speed operation is provided. Transistors are disposed on both sides of diffusion layer regions to which capacitor for storing information is connected and other diffusion layer region of each transistor is connected to the same bit line. When access to a memory cell is made, two transistors are activated and the information is read. When writing operation to the memory cell is carried out, two transistors are used and electric charges are written to the capacitor.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
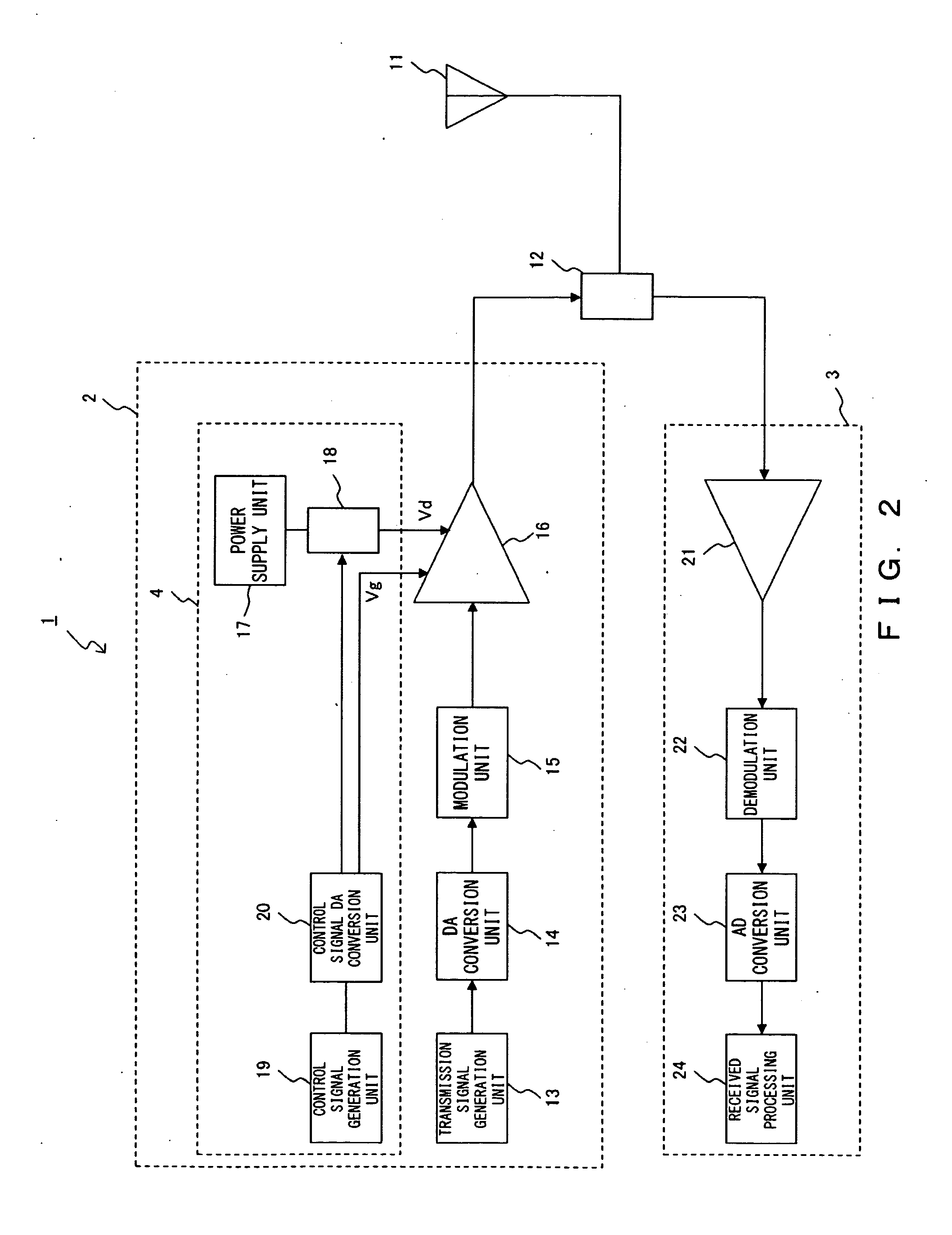
Wireless communication apparatus, power amplifier control method, and power amplifier control apparatus
ActiveUS20090137218A1Inhibit currentPrevent leakageEnergy efficient ICTResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierControl signal
In a wireless communication apparatus in a time division duplex system, a transmission signal generation unit generates a transmission signal. A power amplifying device amplifies the generated transmission signal. A control signal generation device generates a drain voltage control signal for control of the drain voltage of the power amplifying device, and a gate voltage control signal for control of the gate voltage of the power amplifying device. The switch unit switches off the drain power supply of the power amplifying device during reception in the time division duplex system according to the drain voltage control signal. In addition, the power amplifying device sets a higher gate voltage during reception in the time division duplex system higher than during transmission according to the gate voltage control signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
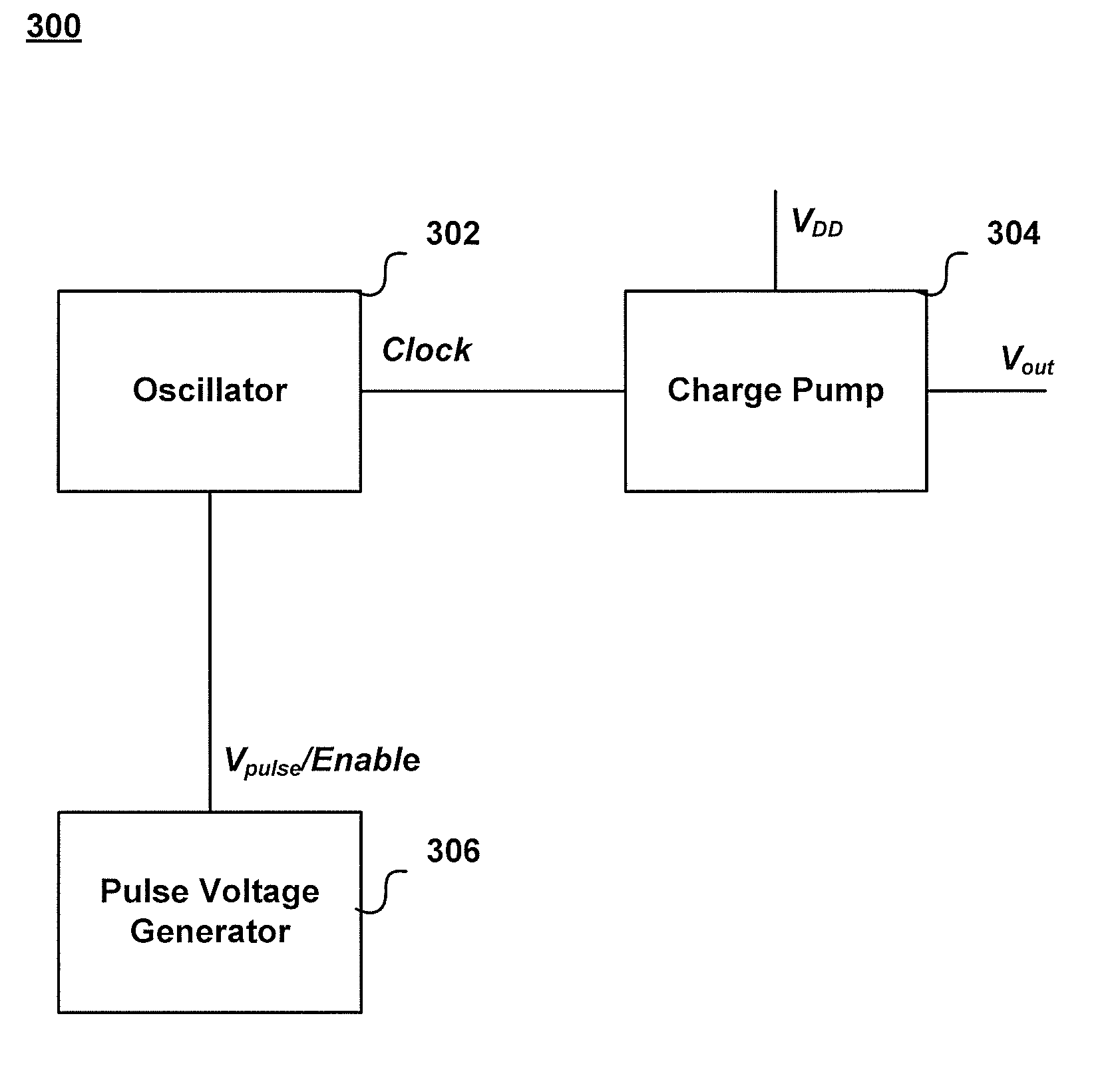
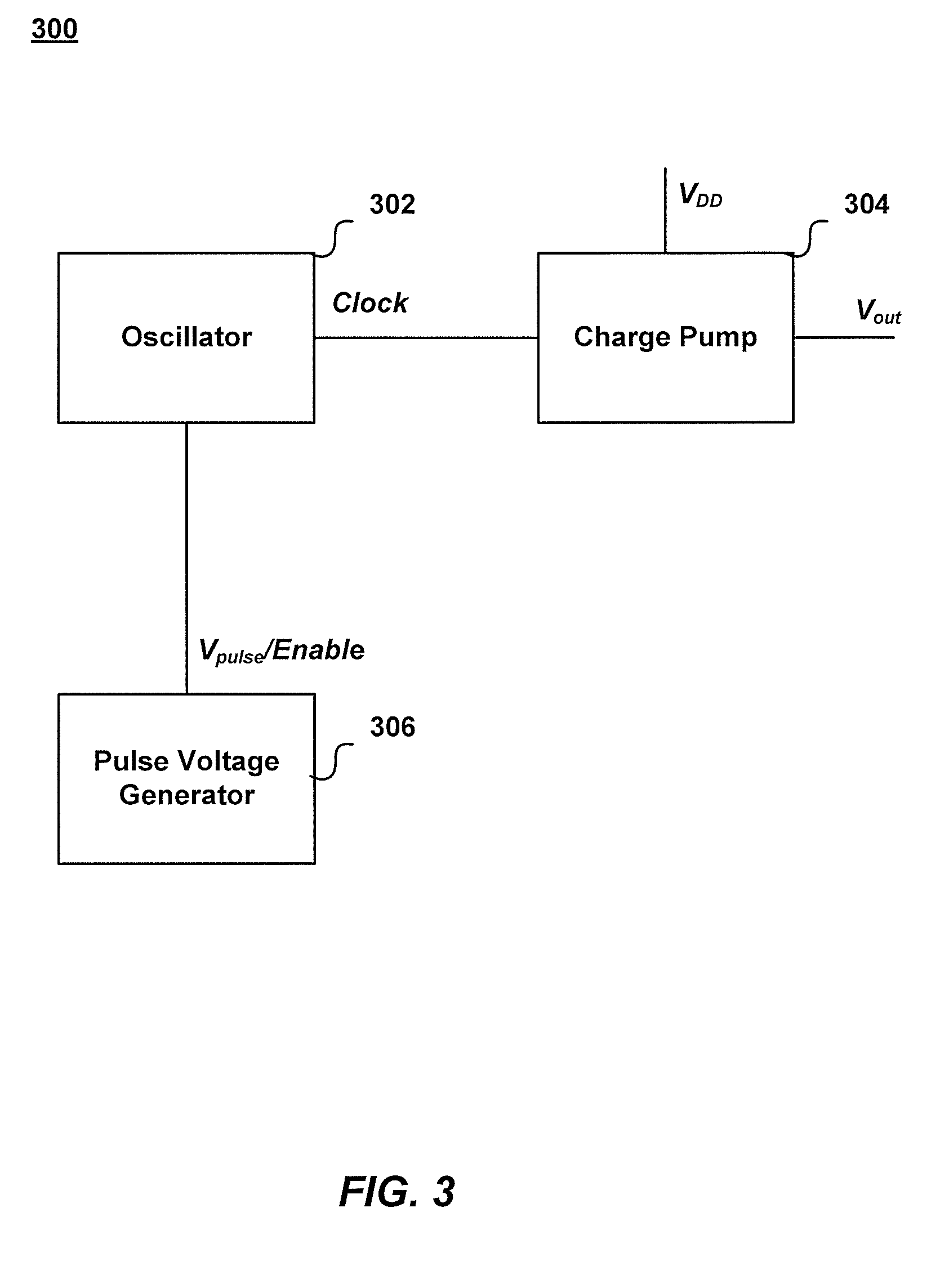
Pulse modulated charge pump circuit
InactiveUS20100148840A1Raise the gate voltageHigh voltageDc-dc conversionElectric pulse generatorTransmission gateComparators circuits
A circuit for increasing a gate voltage of a transmission gate in a high-speed switch to a level higher than a level of a supply voltage is provided. The circuit includes an oscillator generating a clock signal and a charge pump circuit operatively coupled to the oscillator. The charge pump circuit receives the supply voltage and the clock signal as inputs, and outputs the gate voltage. The circuit also includes a comparator circuit coupled to the oscillator circuit and the charge pump circuit and a pulse signal generator circuit operatively coupled to the oscillator, the pulse signal generator circuit generating a pulse signal which enables the oscillator.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
ESD protective device
ActiveCN102025135AImprove protectionFacilitate conductionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesParasitic capacitanceEngineering
The present invention relates to an ESD protective device, wherein, the device is a multi-finger MOS protective device, comprising: a plurality of enhanced MOS tubes arranged in matrix. Source electrodes and grid electrodes of the MOS tubes are grounded; the base electrode of the parasitic triode of each MOS tube is grounded through a base electrode resistor; a multi-finger-type metal layer is formed like that the drain electrode of the MOS pipe of each column is covered by the metal layer which is overlapped with two columns of grid electrodes adjacent to the drain electrode, and the metal layer is not only connected with a PAD but also connected with the drain electrode; the parasitic capacitance is produced as the metal layer is overlapped with the grid electrode. For the ESD protective device of the invention, when ESD pulse appears, the parasitic capacitance couples the grid voltage to a nonzero potential so as to produce enough leakage current, so that parasitic triodes of the ESD protective device are simultaneously conducted and discharged. Thus, the conducted voltage is reduced. Besides, the uniformity of conduction is high and ESD protected capability is highly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Semiconductor device, light emission control circuit, and electronic appliance
ActiveUS20180267395A1Increasing consumptionIncreasing noiseElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalEngineering
A semiconductor device of the invention is a semiconductor device that controls a transistor that controls an electric current that flows through a light emitting element, the transistor including a gate that is connected to one end of a capacitor. The semiconductor device includes: a first terminal that is connected to the gate of the transistor and the one end of the capacitor; a second terminal that is connected to the other end of the capacitor; a first driving circuit that outputs a first control signal to the first terminal; and a second driving circuit that, in order to control the transistor in an on-state or an off-state, activates or deactivates a second control signal, and outputs the second control signal to the second terminal, the second control signal having a potential lower than a potential of the first control signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
GOA circuit and display panel
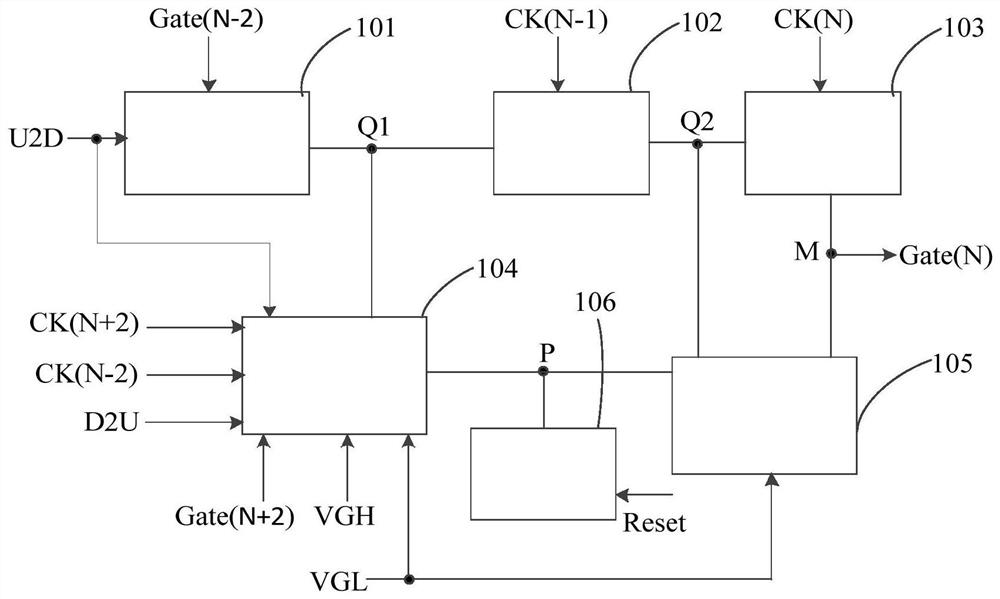
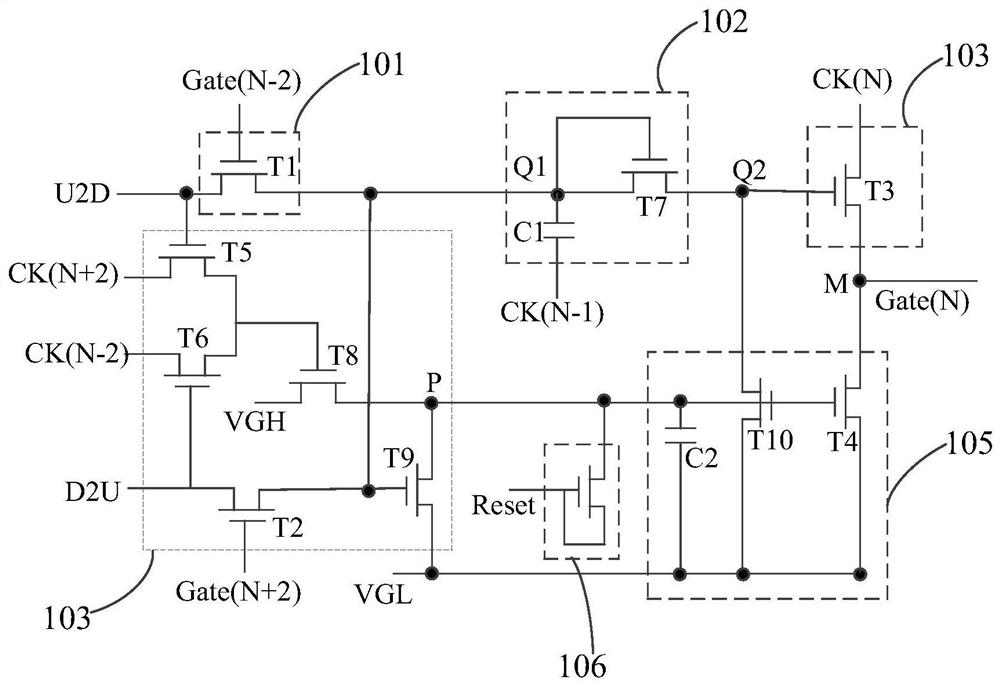
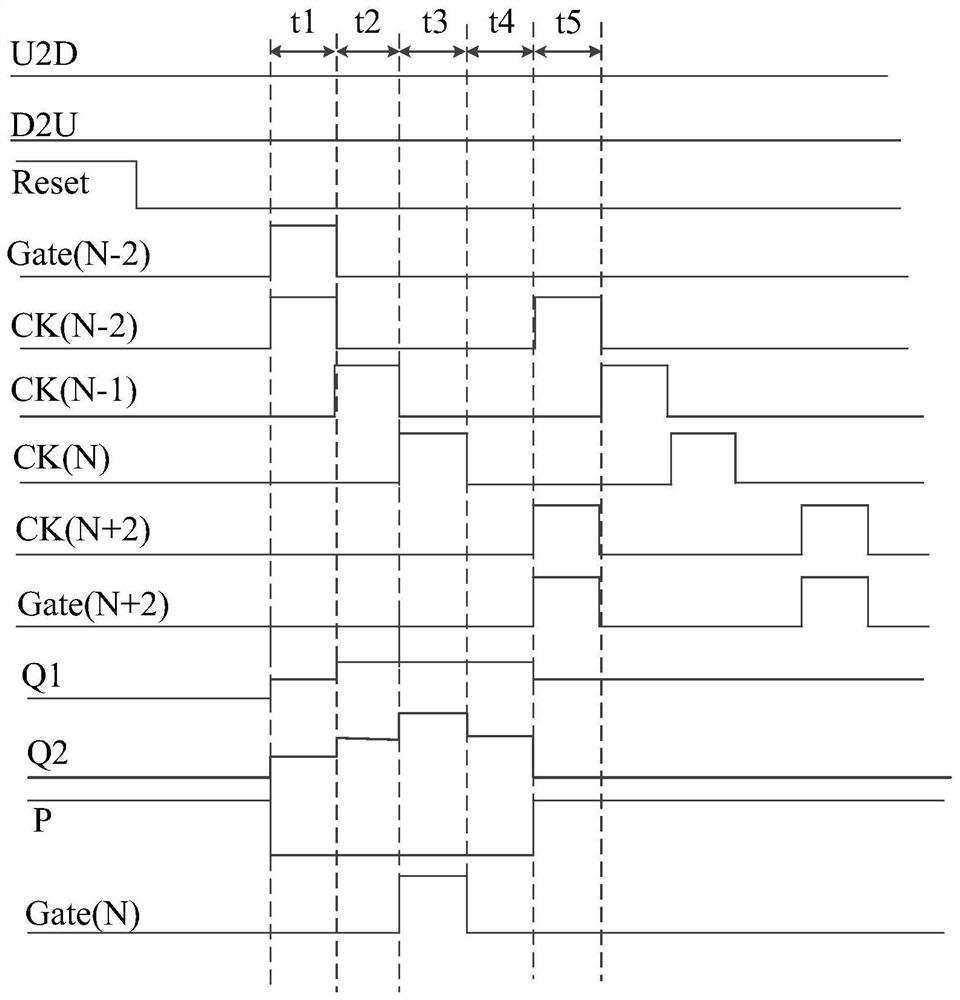
ActiveCN111754923AImprove charging effectRaise the gate voltageStatic indicating devicesHemt circuitsControl theory
The invention provides a GOA circuit and a display panel. The GOA circuit comprises GOA units which are arranged in a multi-stage cascade mode. Each GOA unit comprises a bootstrap module; the bootstrap effect of the bootstrap module is utilized, so the grid voltage of the output transistor is improved, the rising time and the falling time of scanning signals output by each GOA unit can be effectively shortened, and therefore the charging capacity of the display panel is improved.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Array substrate, driving method thereof, electroluminescent display panel and display device
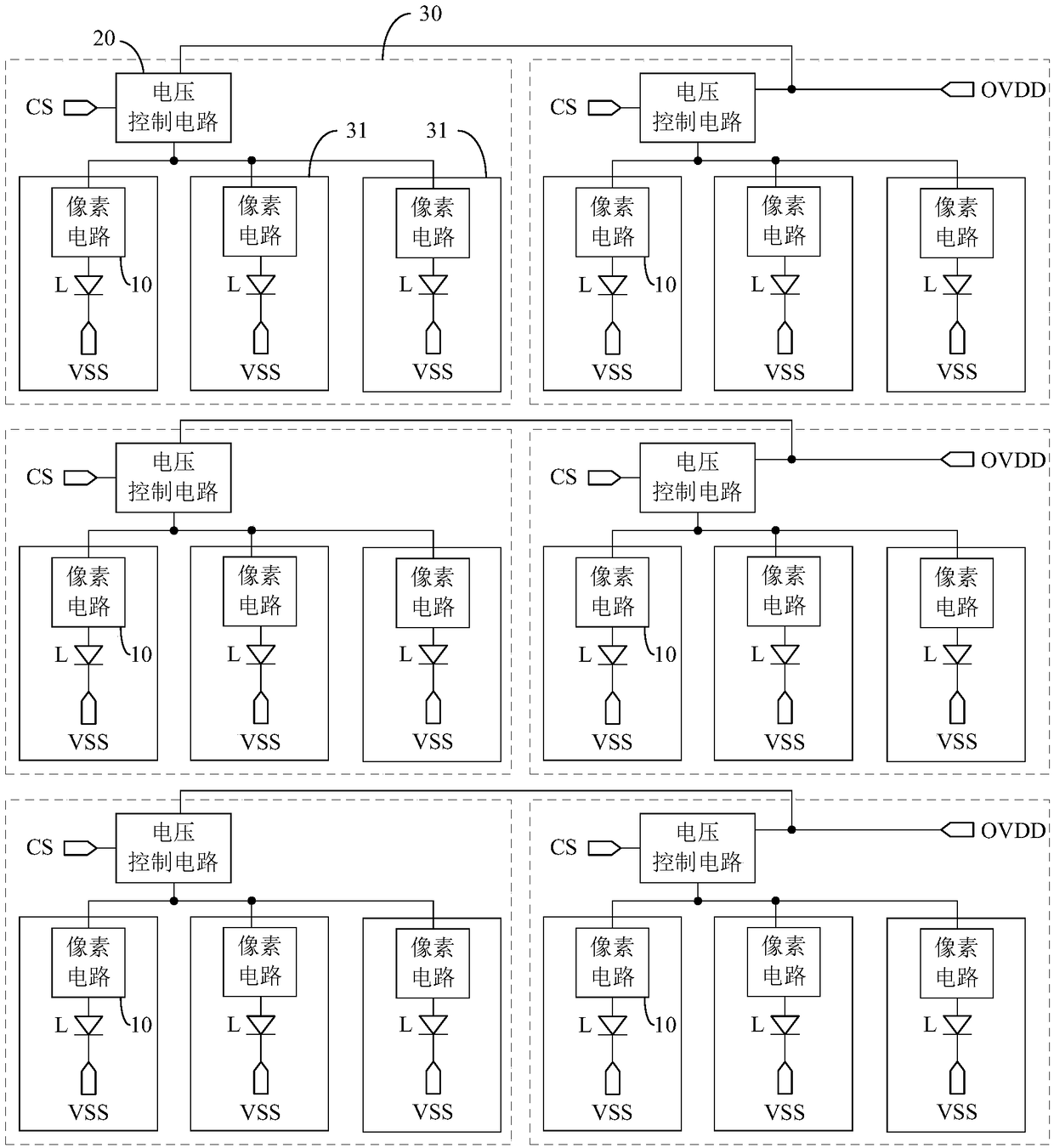
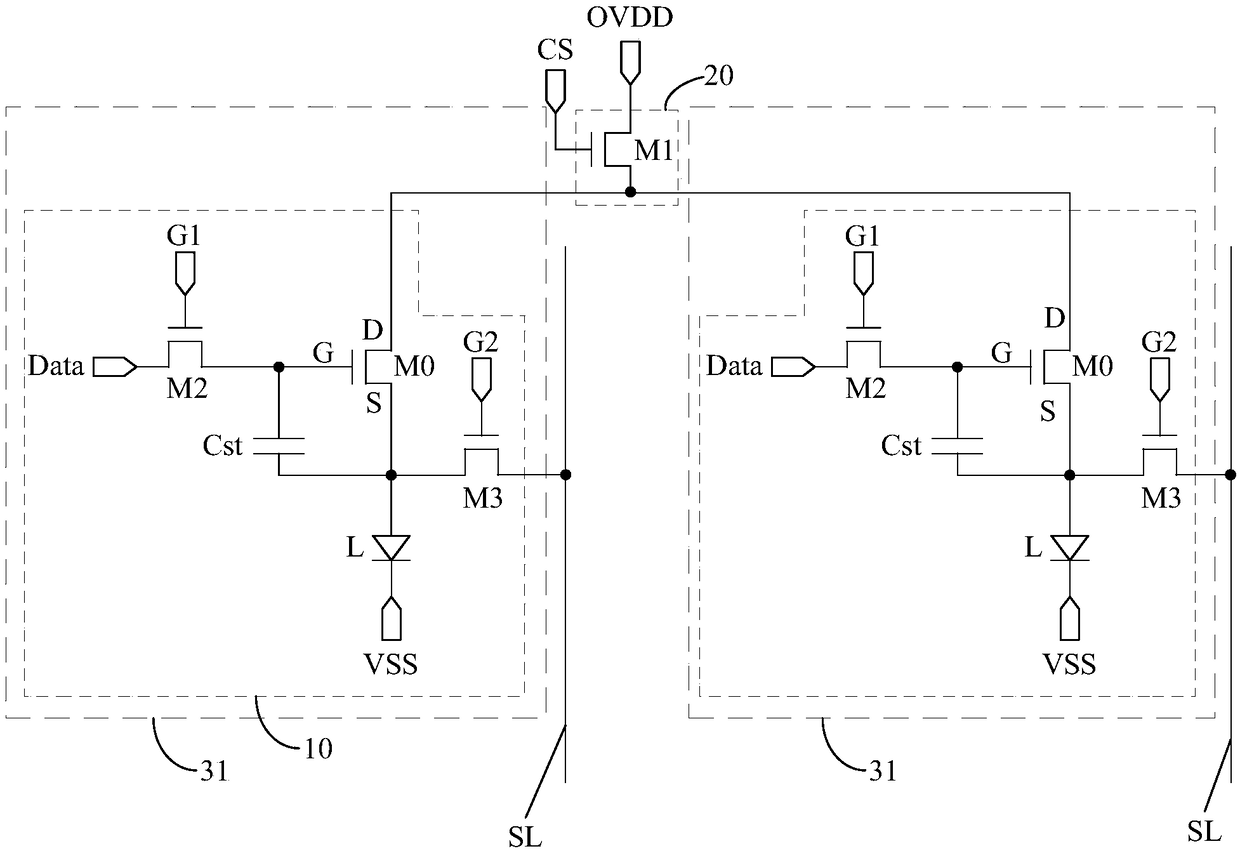
The invention discloses an array substrate, a driving method thereof, an electroluminescent display panel and a display device. The array substrate comprises luminescent devices, pixel circuits coupled to the luminescent devices and voltage control circuits. At least two pixel circuits in the same row share one voltage control circuit, under control of a control signal input end, the voltage control circuit provides a signal of a high-level power supply end for the first pole of each coupled driving transistor, the structure of each pixel circuit is simplified, the occupation area of the pixelcircuit is reduced, and the electroluminescent display panel can realize a high resolution. In addition, the grid voltage is written into the driving transistors and the voltage is written into the second poles of the driving transistors more accurately.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
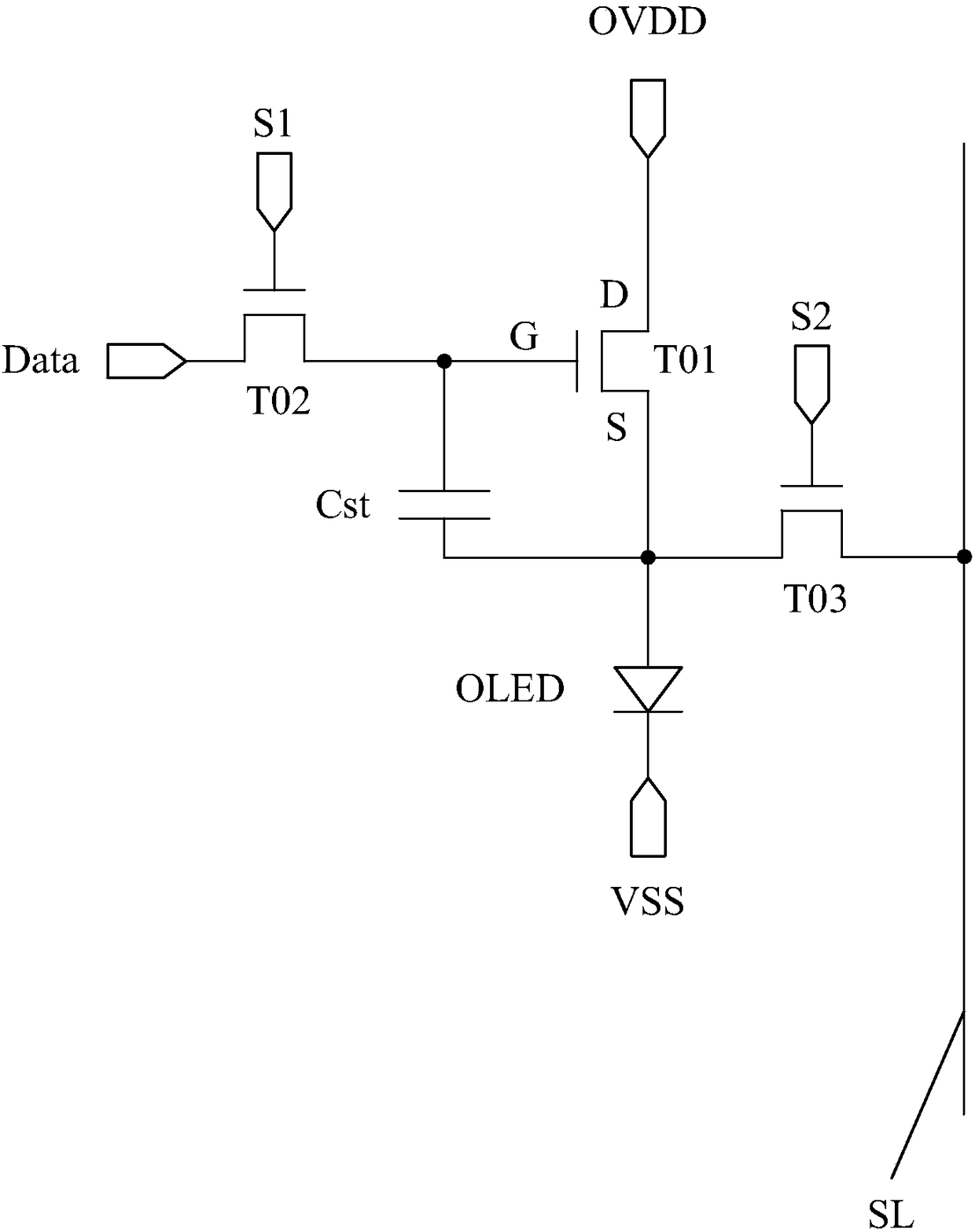
Pixel circuit, driving method thereof, OLED display panel and display device
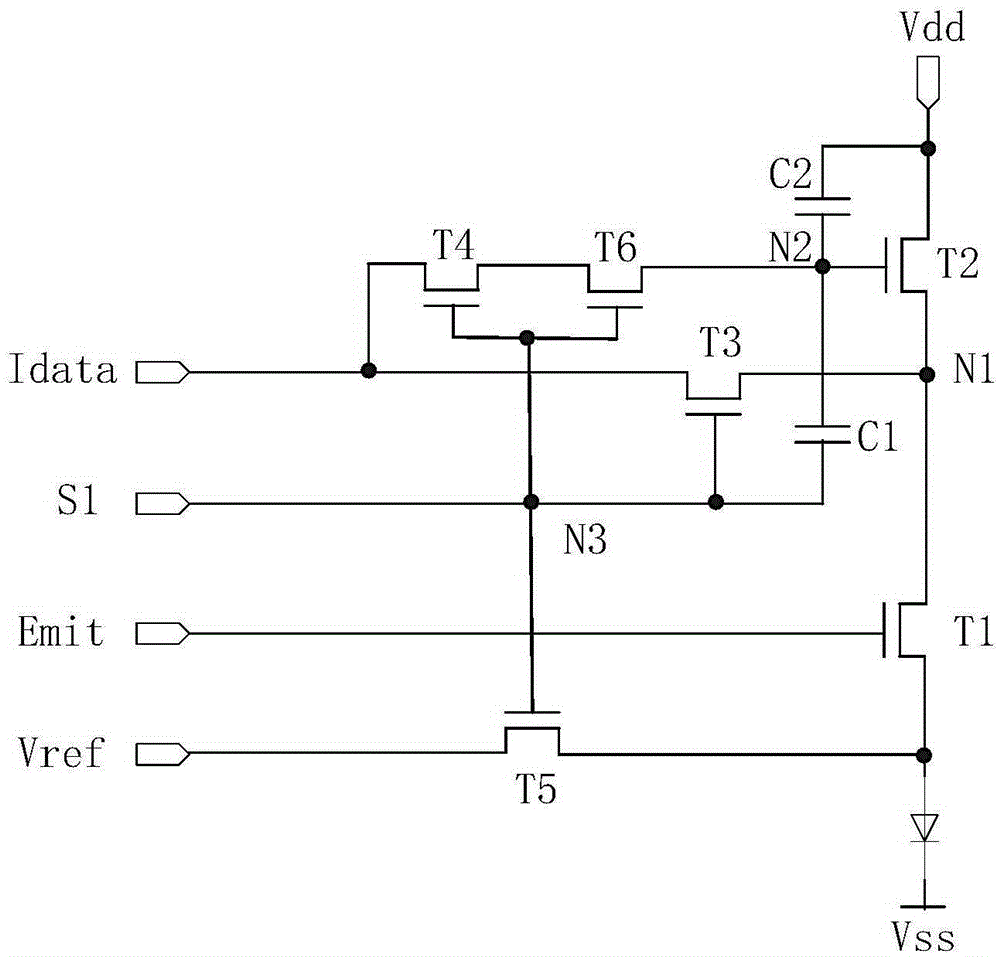
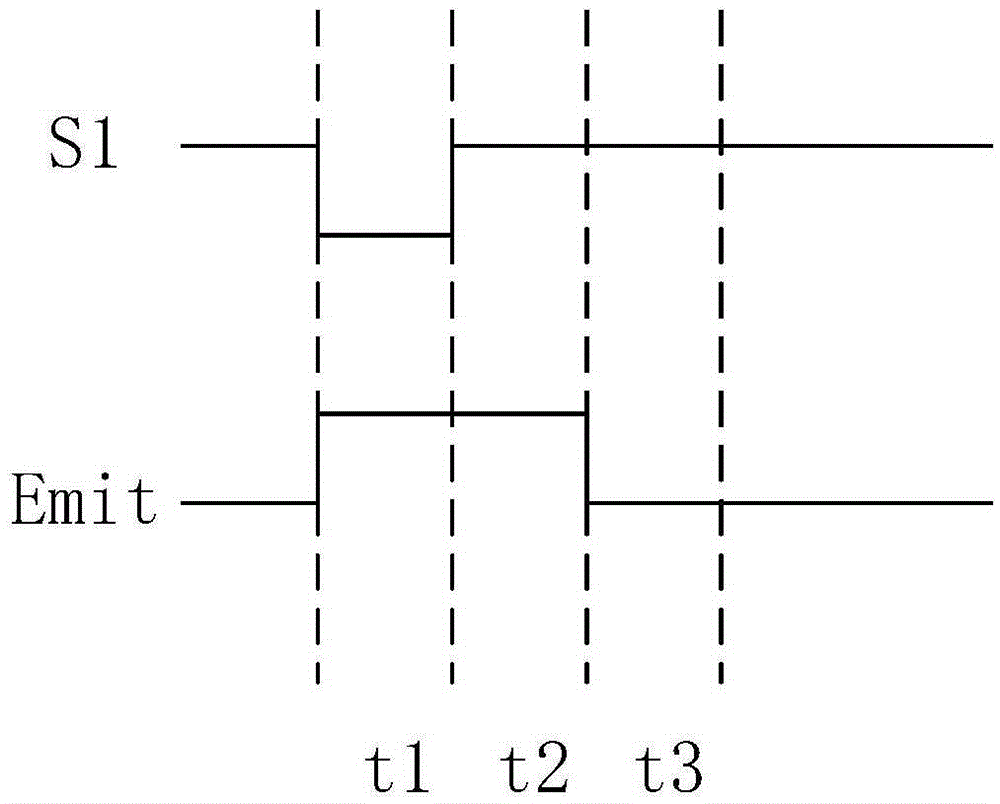
ActiveCN105405404AImprove the display effectAvoid charging for too longStatic indicating devicesCapacitancePower flow
The invention provides a pixel circuit, a driving method thereof, an OLED display panel and a display device. The pixel circuit includes transistors from the first transistor to the fourth transistor, a first capacitor, a second capacitor and a light emitting diode; a data current signal is inputted into the first electrode of the third transistor and the first electrode of the fourth transistor; a first voltage signal is inputted into the gates of the third transistor and the fourth transistor as well as one end of the first capacitor; and a second voltage signal is inputted into the gate of the first transistor. By means of the data current signal and the voltage signals provided by the pixel circuit, a voltage driving and current driving hybrid compensation mode is adopted to compensate the threshold voltage and migration rate of the driving transistors, and therefore, the problem of uneven display can be solved, and the display effect of a whole picture can be improved.
Owner:CHENGDU VISTAR OPTEOLECTRONICS CO LTD
Self-aligned double gate device and method for forming same
InactiveUS20060108644A1Improve device performanceSimple manufacturing processTransistorSolid-state devicesBottom gateEngineering
In a method of forming a double gate device, a buried insulating layer having a thickness of less than about 30 nm is formed on a first substrate. A second substrate is formed on the buried insulating layer. A pad layer is formed over the second substrate. A mask layer is formed over the pad layer. A first trench is formed extending through the pad layer, second substrate, buried insulating layer and into the first substrate. The first trench is filled with a first isolation. A second trench is formed in the first isolation and filled with a conductive material. An MOS transistor is formed on the second substrate. A bottom gate is formed under the buried insulating layer and self-aligned to the top gate formed on the second substrate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
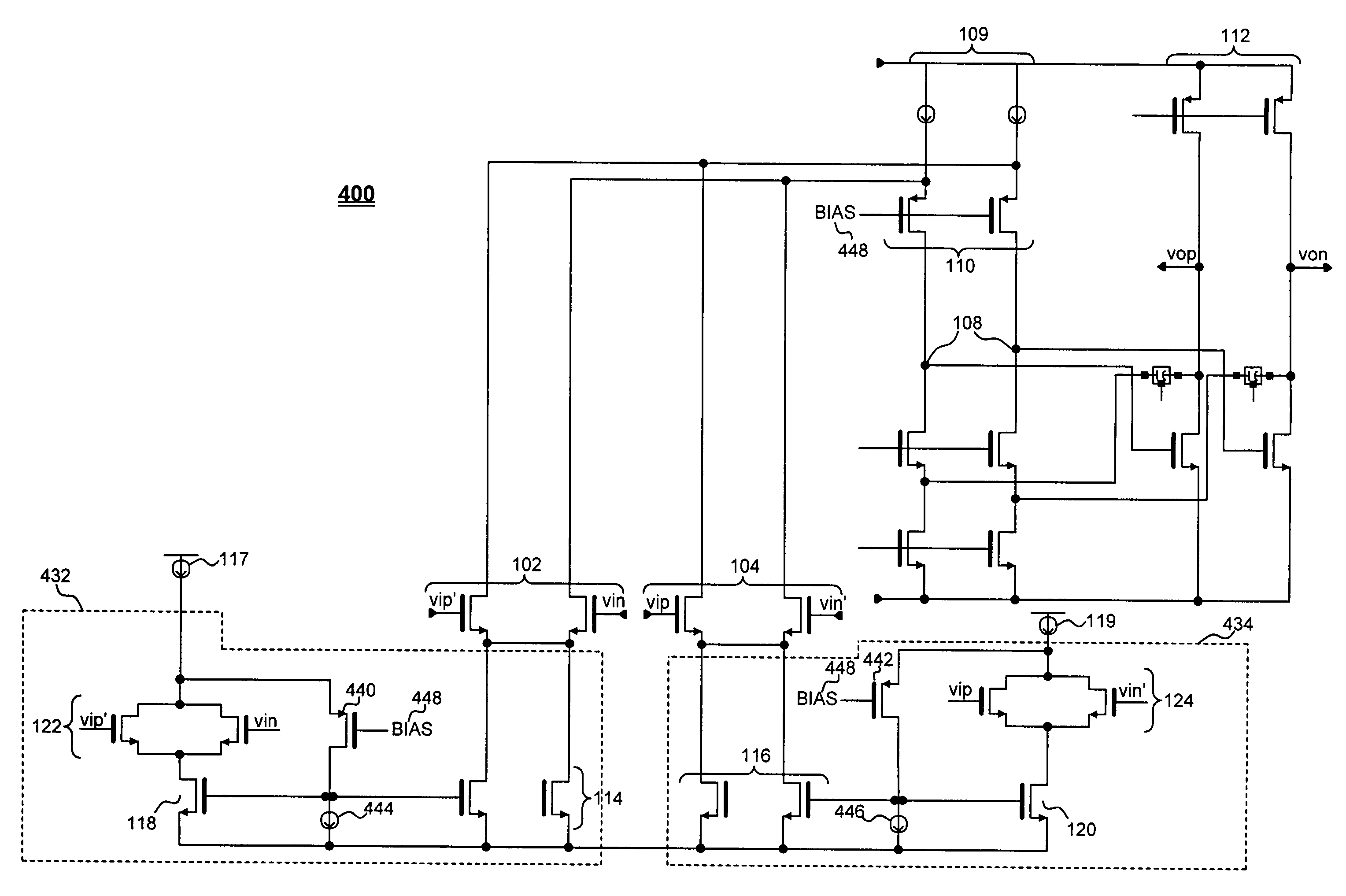
Fully differential input buffer with wide signal swing range
InactiveUS6977526B2Avoid distortionImprove linearityModulated-carrier systemsDifferential amplifiersTransistor arrayEngineering
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Internal power supply voltage generation circuit
InactiveUS20100237931A1Raise the gate voltageApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringClock signal
An internal power supply voltage generation circuit 100 has a first charge pump circuit which steps up the external power supply voltage in response to the first clock signal and outputs a first stepped up voltage from the first voltage stepup output terminal; a second charge pump circuit which steps up the first stepup voltage in response to the second clock signal and outputs a second stepped up voltage from the second voltage stepup output terminal, the second stepped up voltage being higher than the first stepped up voltage; a first voltage stepdown circuit which steps down the first stepped up voltage and outputs a first stepped down voltage; and a second voltage stepdown circuit which steps down the second stepped up voltage and outputs a second stepped down voltage, the second stepped down voltage being higher than the first stepped up voltage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS7310256B2Degraded drivabilityExtension of timeTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringCapacitor
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Static discharging circuit
InactiveCN102611093AExcellent ESD performanceIncreased maximum withstand voltageEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention relates to a static discharging circuit, which comprises a voltage division circuit, a first N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tube and a second NMOS tube, wherein a positive electrode input end of the voltage division circuit is connected with a high-voltage input end, a negative electrode input end of the voltage division circuit is coupled with the ground, and an output end is connected with a grid electrode of the first NMOS tube and is used for outputting bias voltage conducting the first NMOS tube; a drain electrode of the first NMOS tube is connected with the high-voltage input end, and a source electrode is connected with a drain electrode of the second NMOS tube; and a source electrode of the second NMOS tube is grounded, and a grid electrode of the second NMOS tube is coupled with the ground. The static discharging circuit has the advantages that the circuit voltage resistant value is improved, and meanwhile, the static discharging performance of the static discharging circuit is also improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AWINIC TECH CO LTD
Nvsram cells with voltage flash charger
The present invention discloses two preferred embodiments of a 12 T NVSRAM cell with a flash-based Charger and a pseudo 10 T NVSRAM cell with one shared Flash-based Charger. The Flash-based Charger can be made of a 2-poly floating-gate type or a 1-poly charge-trapping SONOS / MONOS flash type, regardless of PMOS type or NMOS type. In an alternative embodiment, the Store operation of above two preferred NVSRAM cell use a DRAM-like charge-sensing scheme with Flash cell configured into a voltage follower associated with Flash Charger and 2-step SRAM amplification technique to amplify the threshold level difference ΔVt stored in the paired Flash transistors. The ΔVt can be detected as low as 1V when the coupled charges through the Flash charger are sufficient by ramping a gate control of the Flash Charger as high as VPP or by increasing the channel length for the Flash Charger.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Semiconductor device
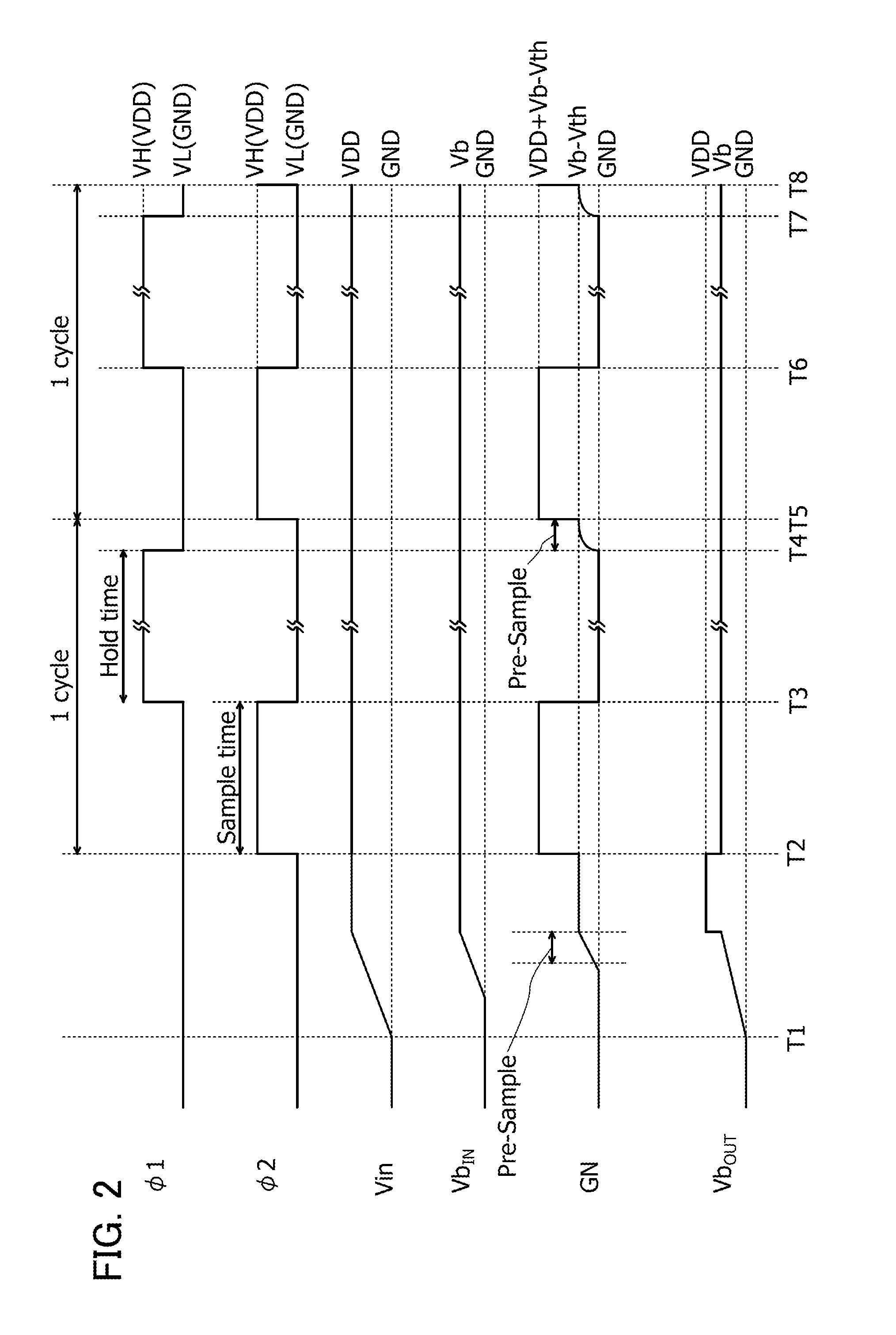
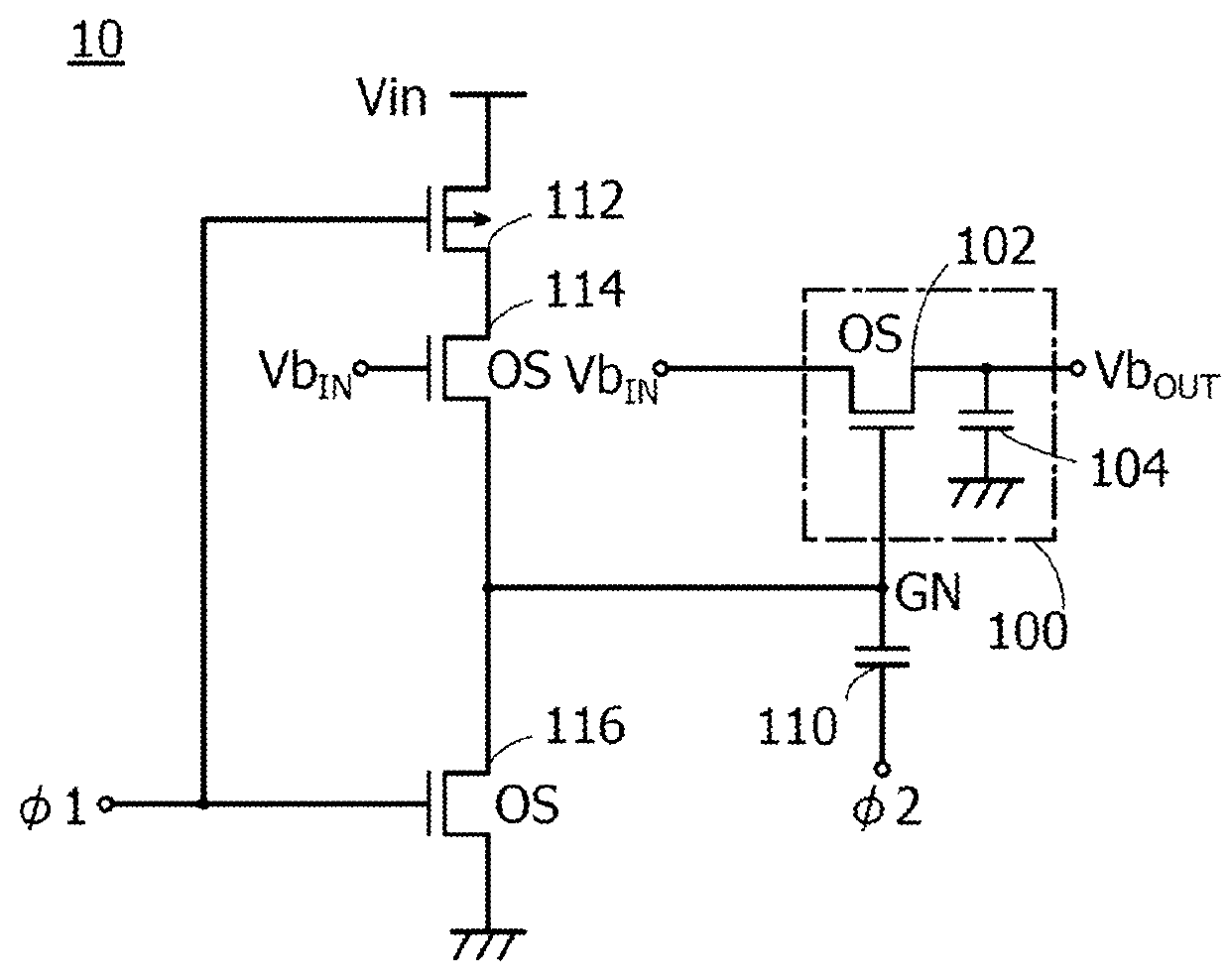
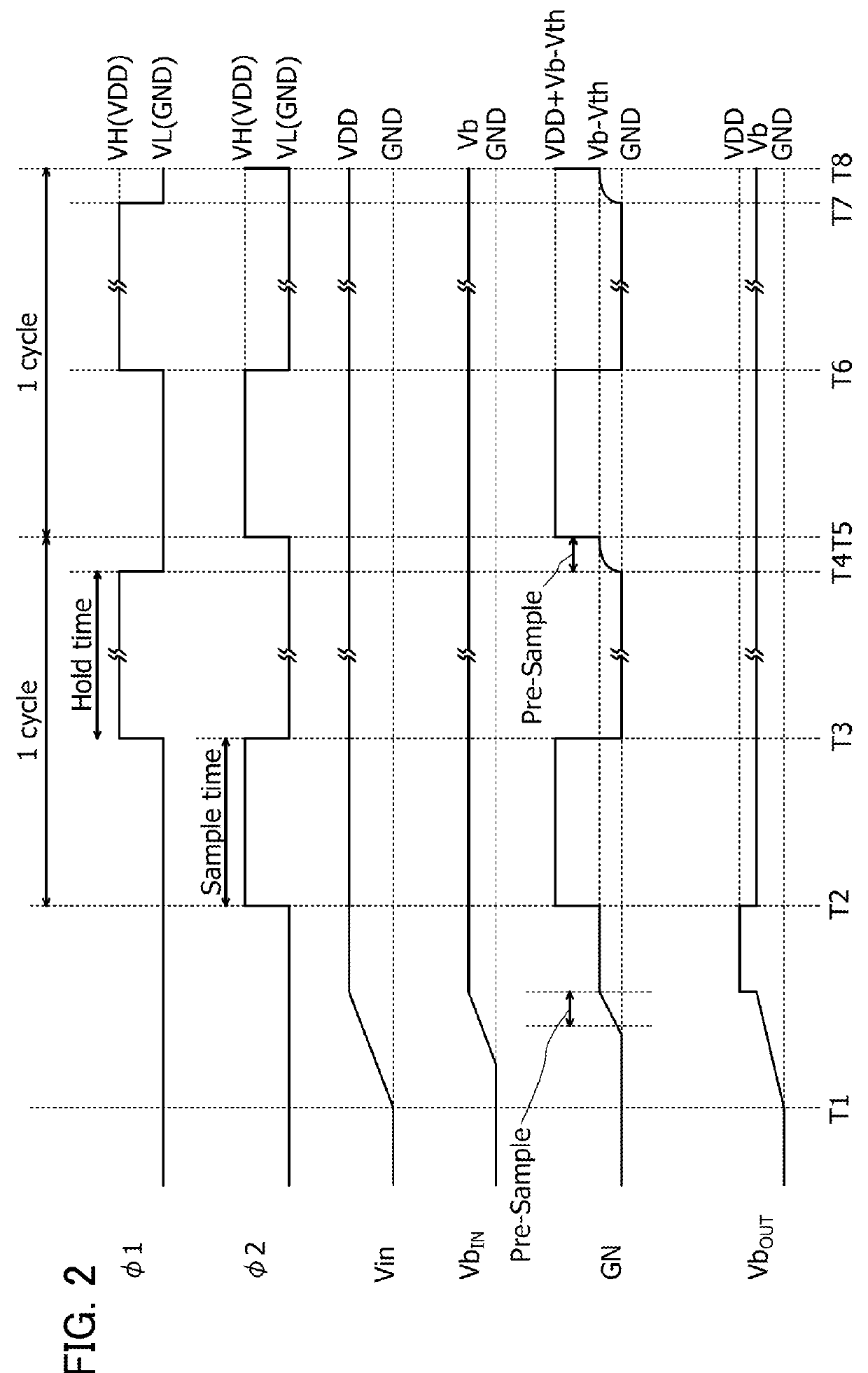
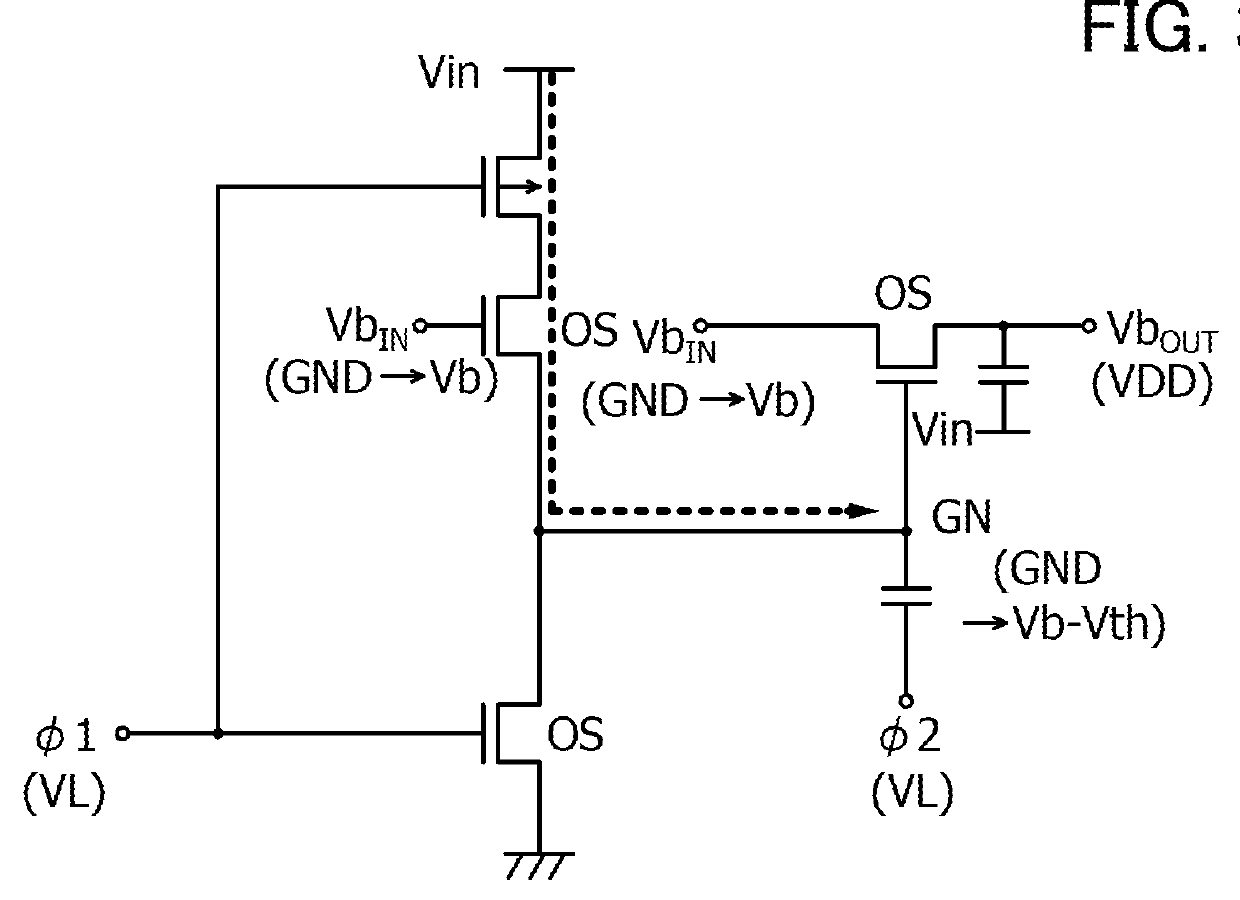
ActiveUS20150034948A1Extended maintenance periodRaise the gate voltageTransistorPulse generatorCapacitanceDevice material
Electric charge is stored, in accordance with a bias voltage, in a gate of a transistor performing switching operation between an input terminal and an output terminal, and the gate is brought into an electrically floating state at the time of completing the storage of electric charge in the gate. One electrode of a capacitor is connected to the gate in an electrically floating state, and the potential of the other electrode of the capacitor is increased, so that the voltage of the gate is increased using capacitive coupling. The potential of the gate of the transistor is increased, and the bias voltage is sampled without being decreased. Each of the transistor performing switching operation and a transistor connected to the gate of the transistor is a transistor with an extremely low off-state current.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device including transistor whose gate is electrically connected to capacitor
ActiveUS9378844B2Extended maintenance periodRaise the gate voltagePulse generatorElectric analogue storesCapacitancePower semiconductor device
Electric charge is stored, in accordance with a bias voltage, in a gate of a transistor performing switching operation between an input terminal and an output terminal, and the gate is brought into an electrically floating state at the time of completing the storage of electric charge in the gate. One electrode of a capacitor is connected to the gate in an electrically floating state, and the potential of the other electrode of the capacitor is increased, so that the voltage of the gate is increased using capacitive coupling. The potential of the gate of the transistor is increased, and the bias voltage is sampled without being decreased. Each of the transistor performing switching operation and a transistor connected to the gate of the transistor is a transistor with an extremely low off-state current.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electro-static discharge (ESD) protection circuit
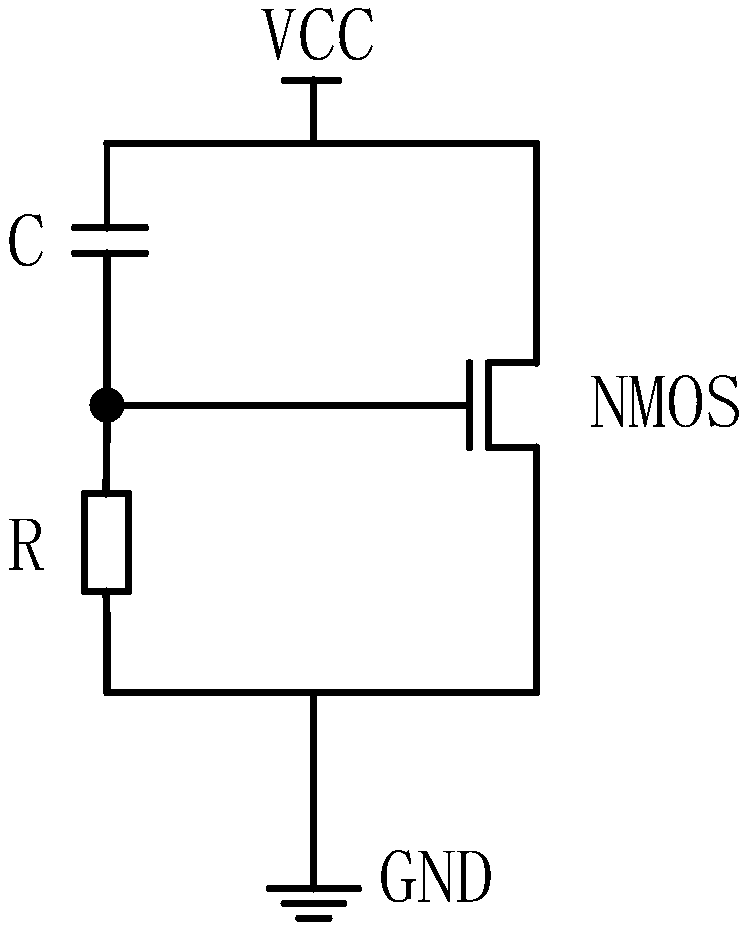
InactiveCN108878416ARaise the gate voltageImprove anti-static performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses an electro-static discharge (ESD) protection circuit. The electro-static discharge protection circuit comprises an NMOS pipe, a capacitor and a resistor; a grid electrode of the NMOS pipe is connected to the power supply end through the capacitor and connected to the grounding end through the resistor; a source electrode of the NMOS pipe is connected with the power supply end; and the drain electrode of the NMOS pipe is connected with the grounding end. According to the electro-static discharge protection circuit, a trigging circuit of the capacitor and the resistor isadditionally arranged on the grid electrode of the NMOS pipe equivalently, the grid electrode voltage can be increased advantageously, the triggering voltage of the ESD protection circuit during the working state can be decreased advantageously, the response speed of the ESD protection circuit is increased, and thus the anti-static performance of the ESD protection circuit is improved greatly.
Owner:WUHAN XINXIN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com