Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
272 results about "Water heat recycling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Water heat recycling (also known as drain water heat recovery, waste water heat recovery, greywater heat recovery, or sometimes shower water heat recovery) is the use of a heat exchanger to recover energy and reuse heat from drain water from various activities such as dish-washing, clothes washing and especially showers. The technology is used to reduce primary energy consumption for water heating.
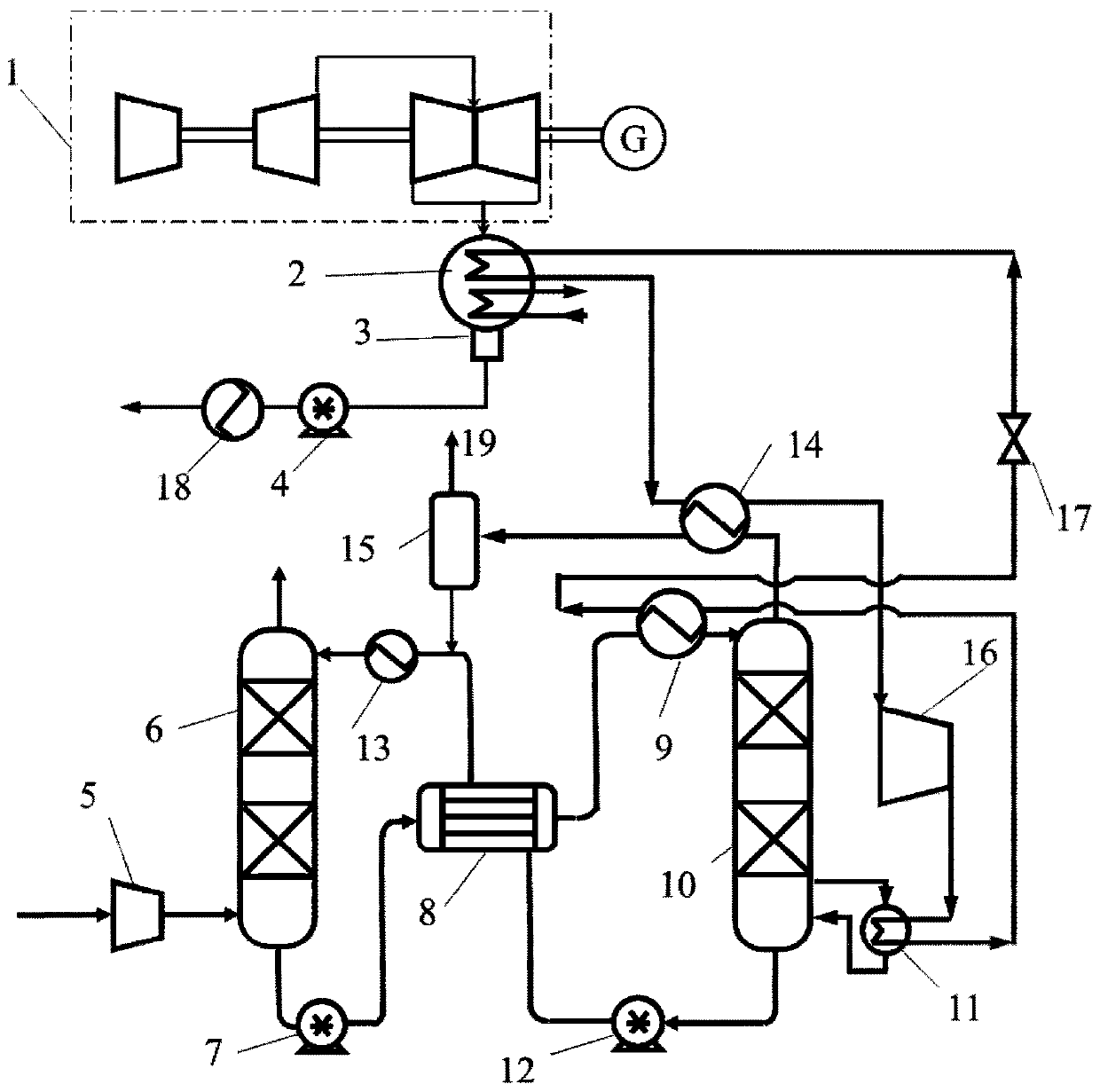
Waste heat recycling system of annealing furnace
The invention provides a waste heat recycling system of an annealing furnace. The waste heat recycling system comprises the annealing furnace, an air heat exchanger, a steam boiler, a hot water boiler, an exhaust fan, a combustion fan and a combustion air pipe. The annealing furnace comprises a heating section and a preheating section, the air heat exchanger is connected with the preheating section, the steam boiler is connected with the air heat exchanger, the hot water boiler is connected with the steam boiler, the exhaust fan is connected with the hot water boiler, the steam boiler is connected with a steam pipeline, the hot water boiler is connected with a hot water pipeline, the combustion fan is connected with the air heat exchanger, the combustion air pipe comprises a main pipe and a plurality of branch pipes communicated with the main pipe, one end of the main pipe is connected with the air heat exchanger, the branch pipes are connected with the heating section, and the main pipe is provided with an exhaust pipe and a pipe explosion prevention device. According to the waste heat recycling system of the annealing furnace, waste heat produced in the annealing process can be made full use of, and safety performance of the waste heat recycling system can be fully guaranteed.
Owner:湖南宏旺新材料科技有限公司
Phase change energy storage device
ActiveCN103344147ALarge latent heat of phase changeHigh latent heat of phase changeHeat storage plantsEnergy storageParaffin waxWarm water
The invention relates to a phase change energy storage device which is characterized by being composed of an outer shell, a paraffin cavity, a plastic cap, paraffin, metal particles and low-melting-point metal. The outer shell is used as a peripheral frame of the phase change energy storage device to be tightly attached to a heat source. A paraffin phase change unit is composed of the paraffin cavity, the plastic cap and the paraffin and evenly filled into the outer shell. The paraffin phase change unit is a heat absorption portion of the phase change energy storage device. The metal particles are filled into the gap between the paraffin phase change unit and the outer shell. The low-melting-point metal is filled into the gap among the outer shell, the metal particles and the paraffin phase change unit so as to enable heat energy to be rapidly transmitted to the paraffin. The paraffin cavity is made of metal so as to be beneficial to heat transfer. The plastic cap is made of flexible plastics so as to compensate a volume expansion effect generated by the paraffin phase exchange. According to the phase change energy storage device, the high latent heat properties of the paraffin are utilized, and the energy storage performance is excellent. Meanwhile, the high heat conductivity properties of the metal particles and the low-melting-point metal are utilized, and the heat conductive performance is excellent. Finally, due to the design of a plurality of paraffin energy storage units, the normal operation of the system can be still ensured when a single energy storage unit in the system loses efficacy. The phase change energy storage device is simple in structure, easy to machine, small in low-melting-point metal charging amount, low in cost and capable of being widely used for heat energy utilization fields such as solar thermal power generation, hot water waste heat recovery, warm water bottles and warmers.
Owner:北京依米康散热技术有限公司
Optimizing control method for sintering waste heat power generation system
ActiveCN102385356AEasy to controlIncreasing energy efficiencySteam engine plantsOptimal controlEngineering
The invention relates to an optimizing control method for a sintering waste heat power generation system; the optimizing control method is characterized in that when parameters of a waste heat boiler and a steam turbine and the smoke flow and the inlet / outlet temperature of the waste heat boiler are constant, the power generation capacity of the steam turbine is only related to the pressure of middle pressure steam and low pressure steam which are output by the waste heat boiler, and the power generation capacity of the steam turbine is maximized by controlling the pressure of middle pressure steam and low pressure steam which are output by the waste heat boiler. Compared with the prior art, the optimizing control method has the beneficial effects: (1). the optimum control on a waste heat recycling system can be realized; and when external conditions change, the real-time automatic tracking is carried out and the optimal pressure value is adjusted; (2). the optimizing control method not only can be used for carrying out optimum control on the sintering waste heat power generation system put into operation, but also can be used for checking the design of the sintering waste heat power generation system and optimizing the design, thereby obtaining parameters such as the optimal outlet temperature of a preheater of the waste heat boiler, the optimal temperature of an evaporator, the optimal outlet temperature of a superheater, the optimal flow of the middle pressure steam and the low pressure steam, and the like and selecting the appropriate steam turbine.
Owner:SINOSTEEL ANSHAN RES INST OF THERMO ENERGY CO LTD
Recovery method of blast furnace slag water residual heat and method thereof
ActiveCN101550461AEnsure safetyGuaranteed lifeIncreasing energy efficiencyWaste heat treatmentRecovery methodSlag
The invention discloses a recovery method of blast furnace slag water residual heat and method thereof. The recovery system of resudual heat includes a blast furnace slag system, a sedimentation tank, a hydrocyclone separator, a water pump, a heat exchanger, a steam turbine, a refrigerant condenser, a refrigerant pump. The recovery method is that applying bicirculating low temperature hot water generation system to recovery residual heat and penerating power. The specific process is: guiding the blast furnace slag water into the heat exchanger after preprocessing of impurity precipitation and transmitting heat to low boiling refrigerant; the low boiling refrigerant absorbing heat in the heat exchanger and entering the steam turbine for expansion of doing work; the refrigerant after doing wirk changing into low-pressure superheated steam, the low-pressure superheated steam entering the concenser to releast heat and changing into liquid refrigerant of low-temperature and low-pressure, then being sent to the heat exchanger by the refrigerant pump for absorbing heat, becoming the superheated steam again to push the steam turbine to do work. The invention can recovery residual heat of the blast furnace slag water and generate power, and reduce energy consumption in steel production; and reduce temperature of blast furnace slag water which is benefit to improve quality of blast furnace water slag and reduce discharge of sulphide in slag washing process.
Owner:HANGZHOU BOILER GRP CO LTD
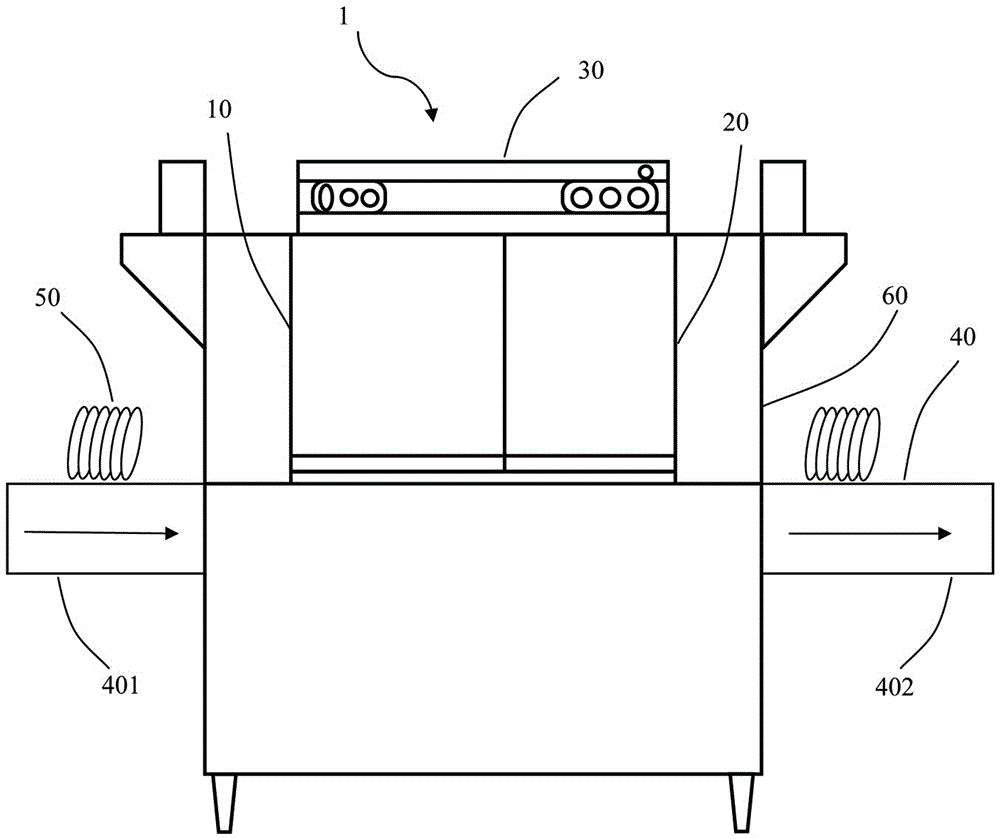
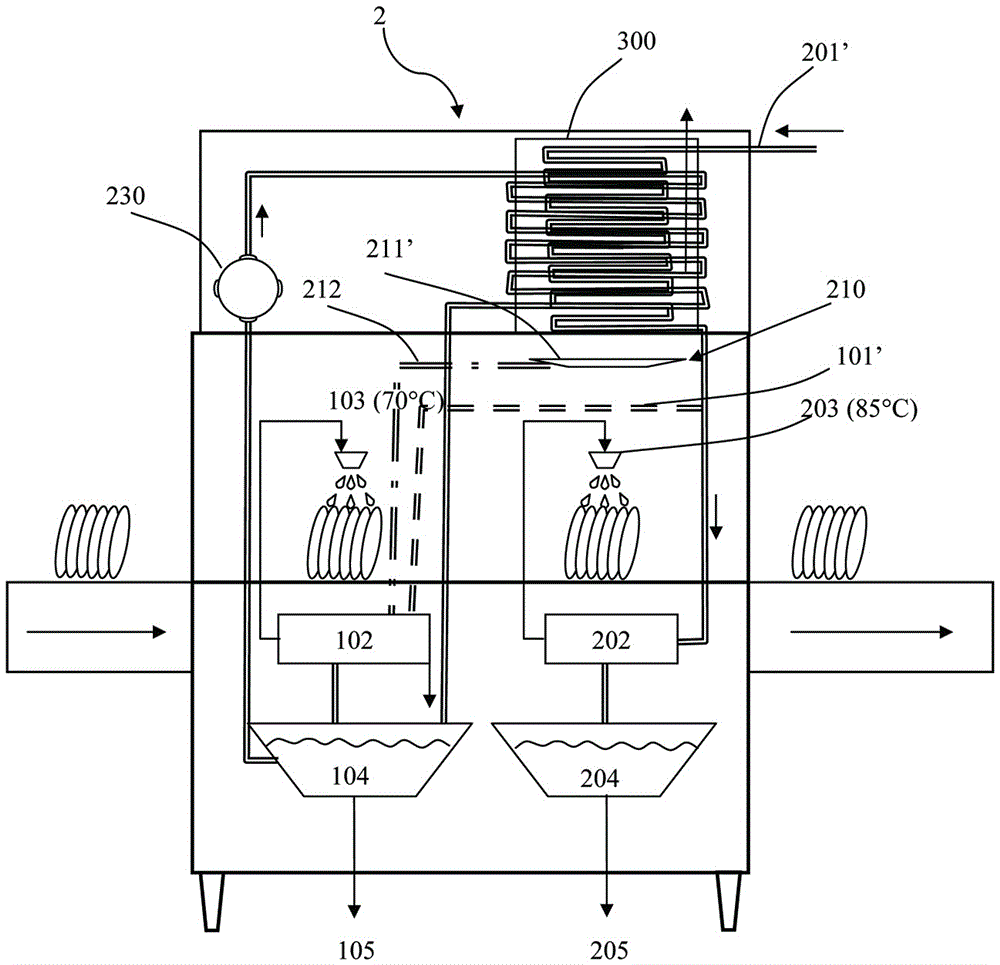
Cleaning device and heat recovery system thereof
ActiveCN105615809ATableware washing/rinsing machine detailsHome appliance efficiency improvementEngineeringProcess engineering
A cleaning device used for cleaning tableware and provided with a waste heat recycling device comprises a water input unit used for inputting water at a first temperature, a heating unit used for heating water from the water input unit into hot water at a third temperature, a water output unit used for outputting the hot water for cleaning work, and the heat recycling device which is communicated with the hot water and / or steam fluid generated from the hot water so as to receive, store, transfer and / or adjust waste heat of the hot water and / or the steam. At least part of the water input unit is connected with the heat recycling device so as to receive the waste heat from the heat recycling device and / or the hot water and / or the steam, and the water in the water input unit is adjusted to a second temperature before being heated by the heating unit. According to the technical scheme, the cleaning device is simple in structure and capable of saving energy, energy consumption is greatly reduced, the heating waiting time is greatly shortened, a heater with low power can be selected and used, and thus the use cost is reduced.
Owner:卓汇集团国际有限公司
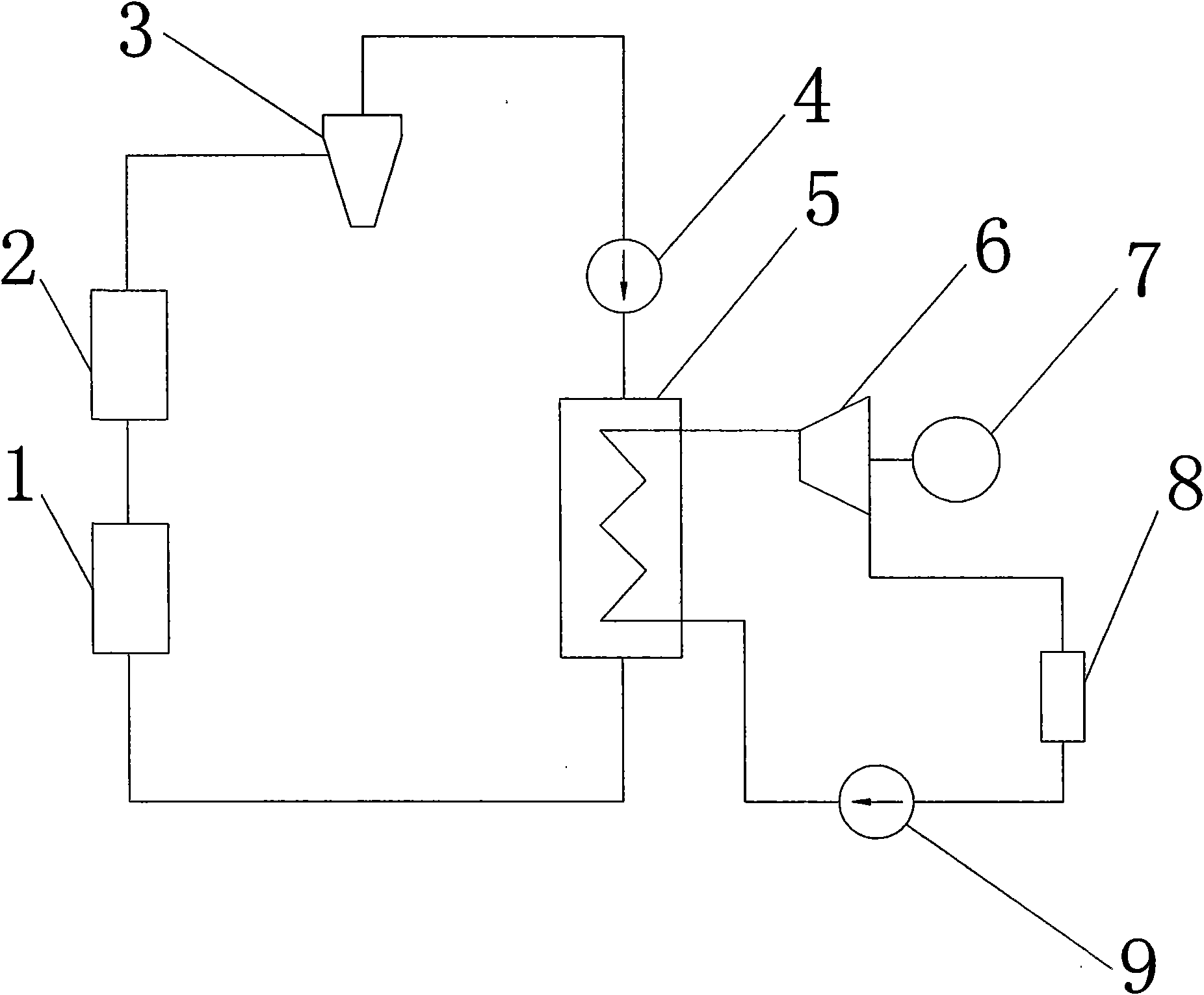
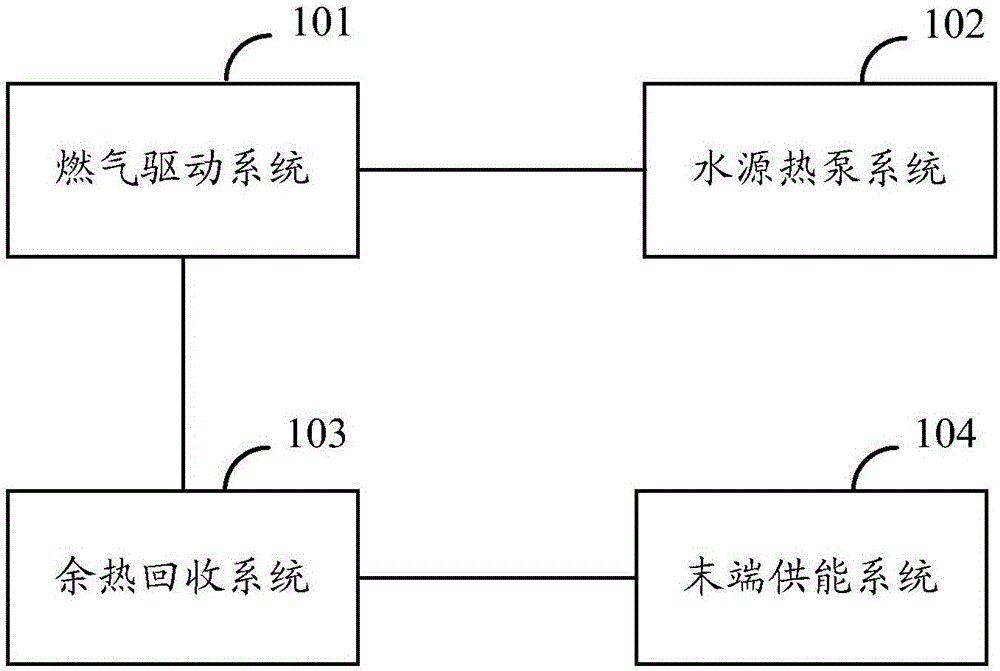
Heat pump smoke waste heat recycling system of gas engine
InactiveCN106369873AHeat recovery systemsClimate change adaptationWater source heat pumpWater source
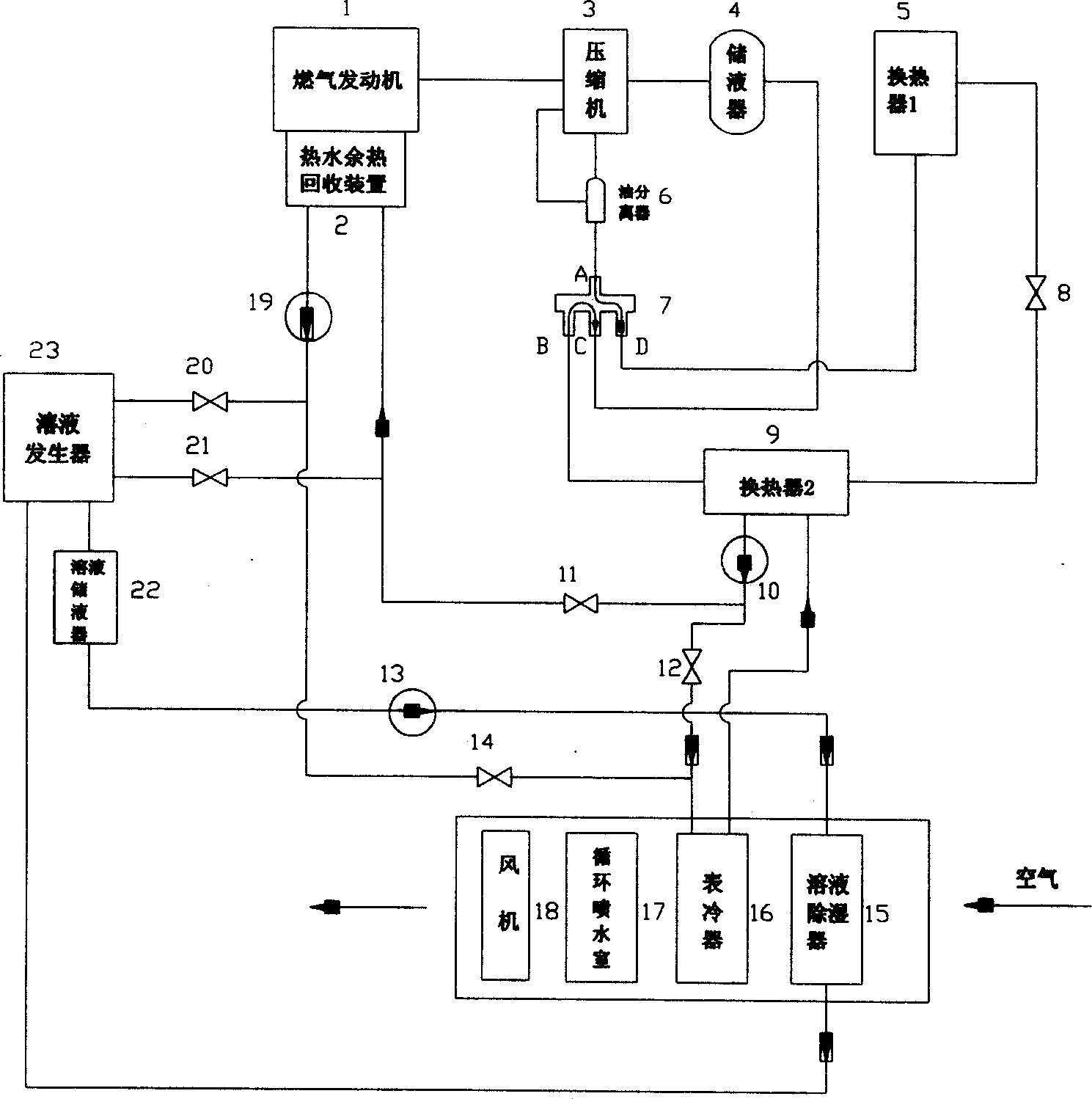
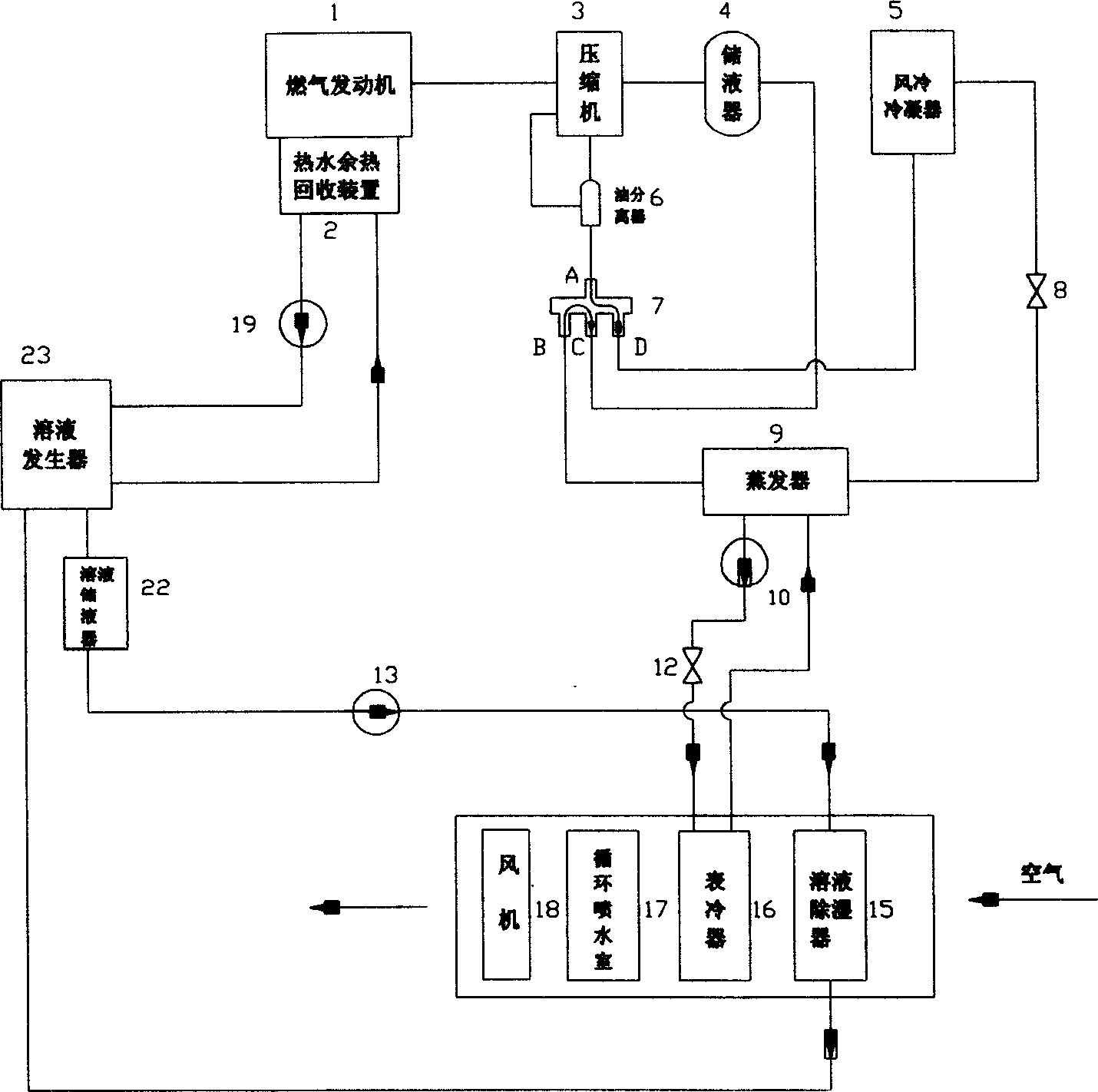
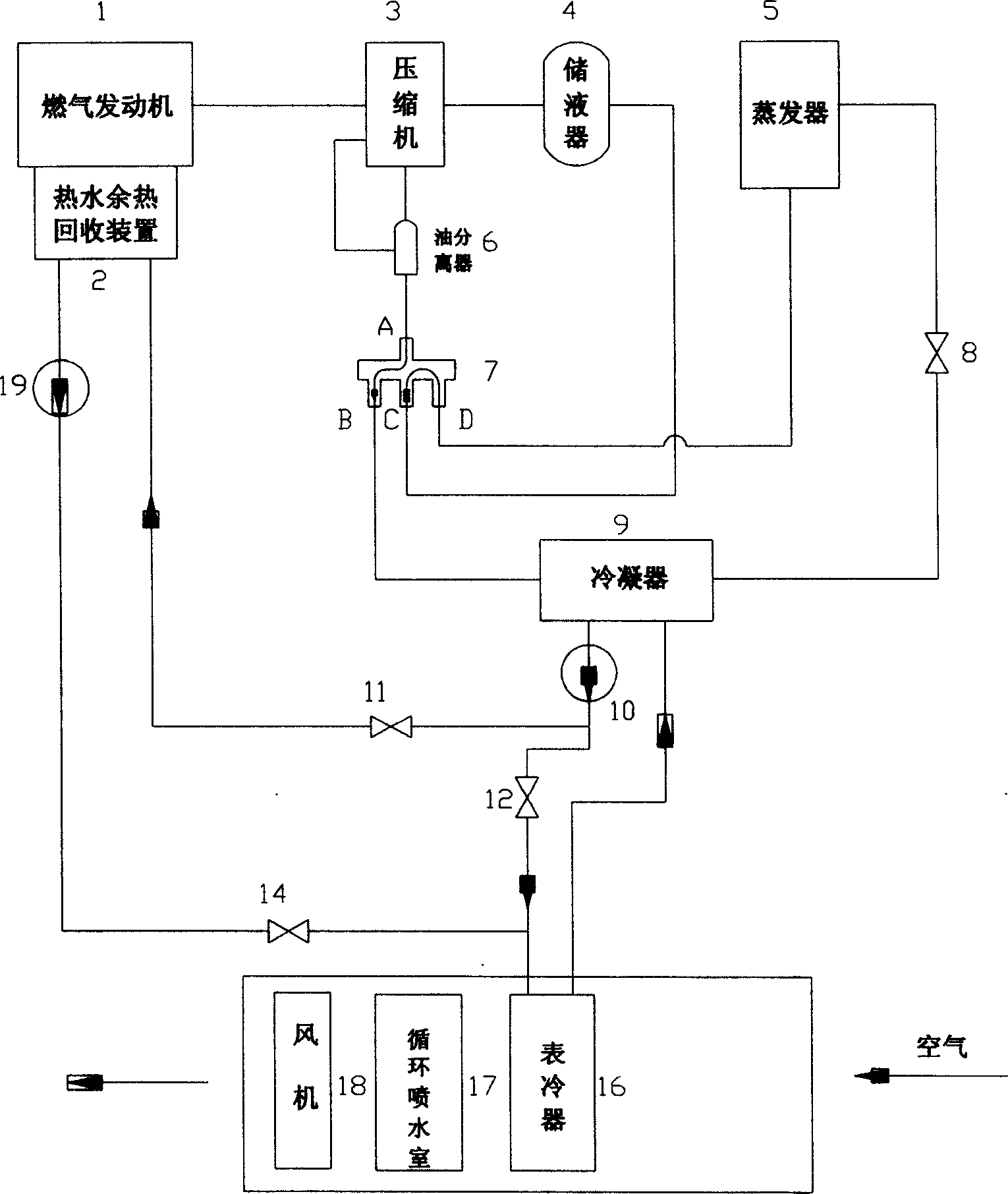
The invention discloses a heat pump smoke waste heat recycling system of a gas engine. The heat pump smoke waste heat recycling system comprises a gas drive system, a water source heat pump system, a waste heat recycling system and a tail end energy supply system. The gas drive system is used for driving the water source heat pump system to work. The water source heat pump system is used for extracting heat on the water source side for supplying heat to users at the tail end. The waste heat recycling system is used for recycling heat of smoke discharged by the gas drive system. The tail end energy supply system is used for utilizing the heat recycled by the waste heat recycling system for supplying cold to the users at the tail end. Thus, by utilization of the scheme, the energy on the gas side and the water source side can be utilized for supplying heat and cold to the users at the tail end at the same time.
Owner:ENN ENERGY SERVICE
Water heat recycling heat pump air-conditioning system for electric automobile
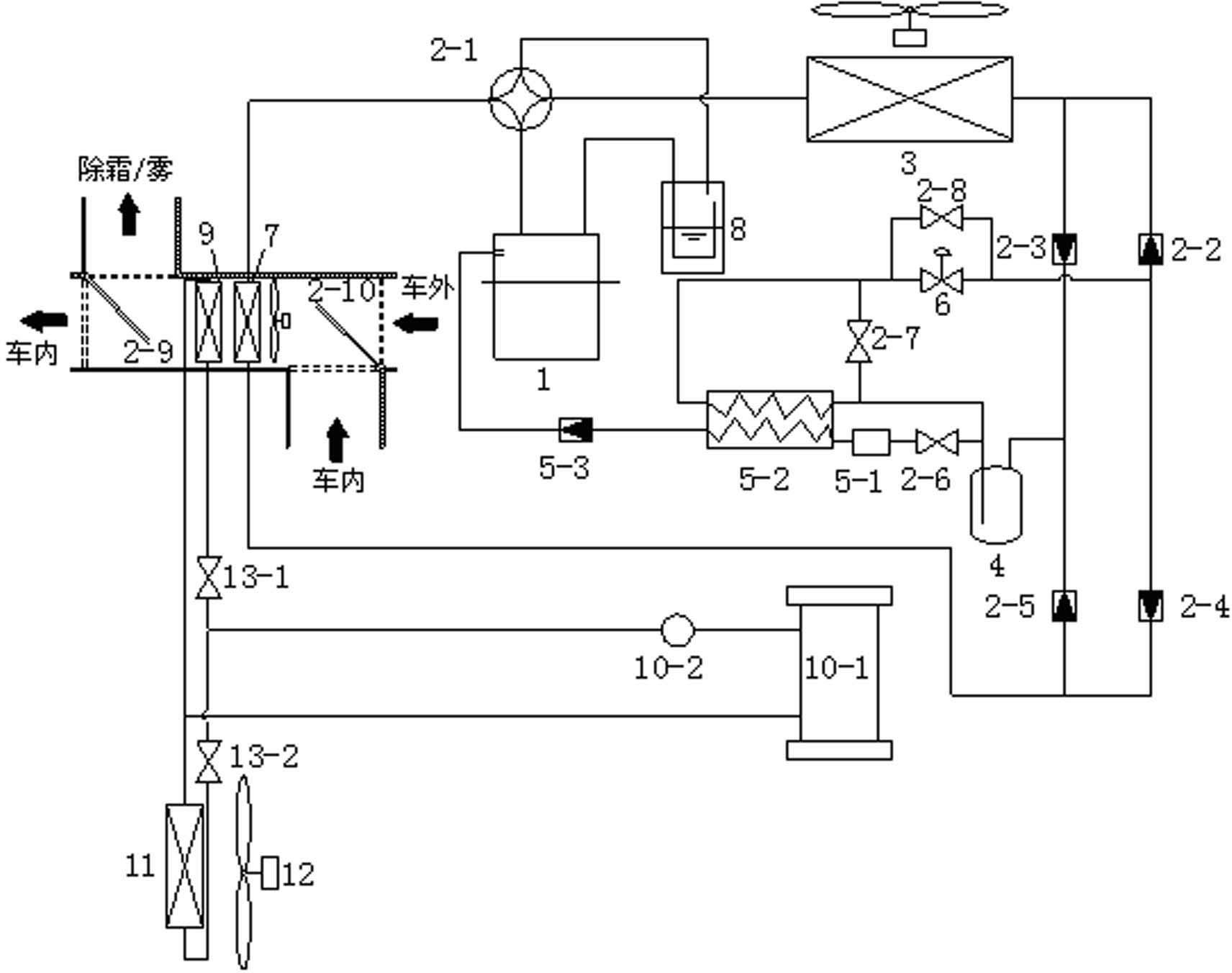
ActiveCN102331045AHigh popularityBroaden applicationSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsHeat recovery systemsVapor–liquid separatorRecuperator
The invention provides a water heat recycling heat pump air-conditioning system for an electric automobile. The system comprises an automobile totally enclosed variable-frequency air-conditioning compressor, an external air heat exchanger, an internal air heat exchanger, a liquid storing drier, a gas-liquid separator, a low-pressure throttling valve, a compressor cooling synergistic air mixing system, a driving motor water heat recycling system, a system mode switching device and the like, wherein the automobile totally enclosed variable-frequency air-conditioning compressor is driven by using a direct-current motor; and the driving motor water heat recycling system consists of a water-air bilateral cooling motor waste heat cooling device, an internal waste heat radiator, an external waste heat radiator, an external waste heat radiator fan, a waste heat recycling control device and a connecting pipeline. Due to the adoption of the water heat recycling heat pump air-conditioning system, five working modes, i.e., refrigerating, ordinary heating, low-temperature heating, vehicle window defrosting / defogging and external low-temperature heat source heat exchanger surface defrosting of the electric automobile can be realized, and the system can be used for stably and efficiently heating circularly at outdoor ultralow environmental temperature through the compressor cooling synergistic air mixing system and the automobile motor water heat recycling system.
Owner:HENAN BEIDI NEW ENERGY REFRIGERATION IND +1
Waste heat recycling system of data room
ActiveCN105258332AAvoid wastingLow costFluid heatersCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsPlate heat exchangerLiquid medium
The invention provides a waste heat recycling system of a data room. The waste heat recycling system comprises a controller, a heat exchange mechanism, a compressor and a waste heat recycling mechanism, wherein the heat exchange mechanism, the compressor and the waste heat recycling mechanism are provided with a conducting refrigerant loop; the heat exchange mechanism comprises a liquid-cooling heat exchanger and an air-cooling heat exchanger which are in parallel connection; the waste heat recycling mechanism comprises liquid medium heating equipment and gaseous medium heating equipment which are in parallel connection; the liquid medium heating equipment of the waste heat recycling mechanism is connected with a hot water output device; the gaseous medium heating equipment is connected with a hot air output device; the controller is respectively connected with the liquid-cooling heat exchanger and the air-cooling heat exchanger for controlling the liquid-cooling heat exchanger or the air-cooling heat exchanger to work so as to cool hot air in the data room by utilizing a refrigerant of the compressor; and the controller is further respectively connected with the liquid medium heating equipment and the gaseous medium heating equipment for controlling the liquid medium heating equipment or the gaseous medium heating equipment to work so as to output hot water or hot air.
Owner:中建环能建筑工程有限公司
Heat recycling backflow welding machine
InactiveCN102485399ARealize the purpose of energy savingReduce consumptionPrinted circuit assemblingHeating appliancesThermal energyElectricity
The invention discloses a heat recycling backflow welding machine comprising a pre-heating zone, a welding zone and a cooling zone which are sequentially distributed from left to right, and a printed circuit board (PCB) conveying system which is used for driving a PCB to sequentially pass through the pre-heating zone, the welding zone and the cooling zone; the heat recycling backflow welding machine also comprises a heat recycling system which is arranged above the pre-heating zone and the welding zone; the heat recycling system comprises a pre-heating zone air inlet channel I, a pre-heating zone air inlet channel II, a heat recovery channel, a pipeline fan, a filter, a welding zone air outlet channel I, a welding zone air outlet channel II and a cold and heat integrated air outlet channel; the left end of the heat recovery channel is communicated with the pre-heating zone air inlet channel I and the pre-heating zone air inlet channel II, and the right end of the heat recovery channel is communicated with the cold and heat integrated air outlet channel; the pipeline fan and the filter are arranged in the middle part of the heat recovery channel; and the welding zone air outlet channel I and the welding zone air outlet channel II are arranged on the heat recovery channel. The heat recycling backflow welding machine can greatly reduce the electricity consumption when the backflow welding machine is used.
Owner:XIAN ZHONGKEMAITE ELECTRONICS TECH EQUIP
Oilfield sewage waste heat recycle and reclaimed water reuse method and device
InactiveCN103277780AReliable principleSimple processFeed water supplyWater/sewage treatment by heatingThermal energyReclaimed water
The invention discloses an oilfield sewage waste heat recycle and reclaimed water reuse method. The method comprises the steps: a. high pressure steam passes through a Venturi tube and generates negative pressure energy which is needed in flash evaporation in a flash tank; b. atomized oilfield sewage which enters the flash tank is vaporized; c. vaporized gas enters a negative pressure cavity of the Venturi tube and enters a heat exchanger with the high pressure steam; d. energy of the vaporized oilfield sewage is transmitted to crude oil which needs to be heated or to water which supplies heat; e. condensate water in the heat exchanger in pumped into a boiler through a water pump and is used as supplemental water for the boiler, and thus boiler water is saved.
Owner:SINOPEC PETROLEUM ENG DESIGN +2
Combined cooling heating and power supply composite energy supply system based on waste heat deep recycling
ActiveCN105841396AReduce the burden onIncrease the thermoelectric ratio adjustment rangeFluid heatersClimate change adaptationRecuperatorAbsorption heat pump
The invention belongs to the correlated technical field of energy utilization and discloses a combined cooling heating and power supply composite energy supply system based on waste heat deep recycling. The combined cooling heating and power supply composite energy supply system comprises a gas turbine, a generator set, a potassium bromide absorption heat pump unit, a magnetic suspension heat pump unit, a high-temperature flue gas heat exchanger, a flue gas condensing heat exchanger and the like. A flue gas outlet of the gas turbine is divided into two pipelines, the first pipeline is connected with the flue gas type potassium bromide absorption heat pump and drives the flue gas type potassium bromide absorption heat pump to achieve refrigerating and heating, and the second pipeline is connected with the high-temperature flue gas heat exchanger and used for heating tap water preheated through the flue gas condensing heat exchanger to a required temperature. An outlet of the high-temperature flue gas heat exchanger is connected with a flue gas inlet of the flue gas condensing heat exchanger. In addition, one part of electricity generated through the gas turbine is supplied to users, and the other part of the electricity generated through the gas turbine is used for driving the magnetic suspension heat pump unit to conduct refrigerating and heating. According to the combined cooling heating and power supply composite energy supply system based on waste heat deep recycling, flexible composite energy supplying can be carried out, and meanwhile waste heat deep recycling can be achieved; and the combined cooling heating and power supply composite energy supply system has the characteristics of being compact in structure, convenient to control, high in adaptability and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Energy accumulation type combustion gas and heat pump composite air-conditioning
InactiveCN1721787ARaise the evaporation temperatureImprove cooling effectHeat pumpsClimate change adaptationFour-way valveProcess engineering
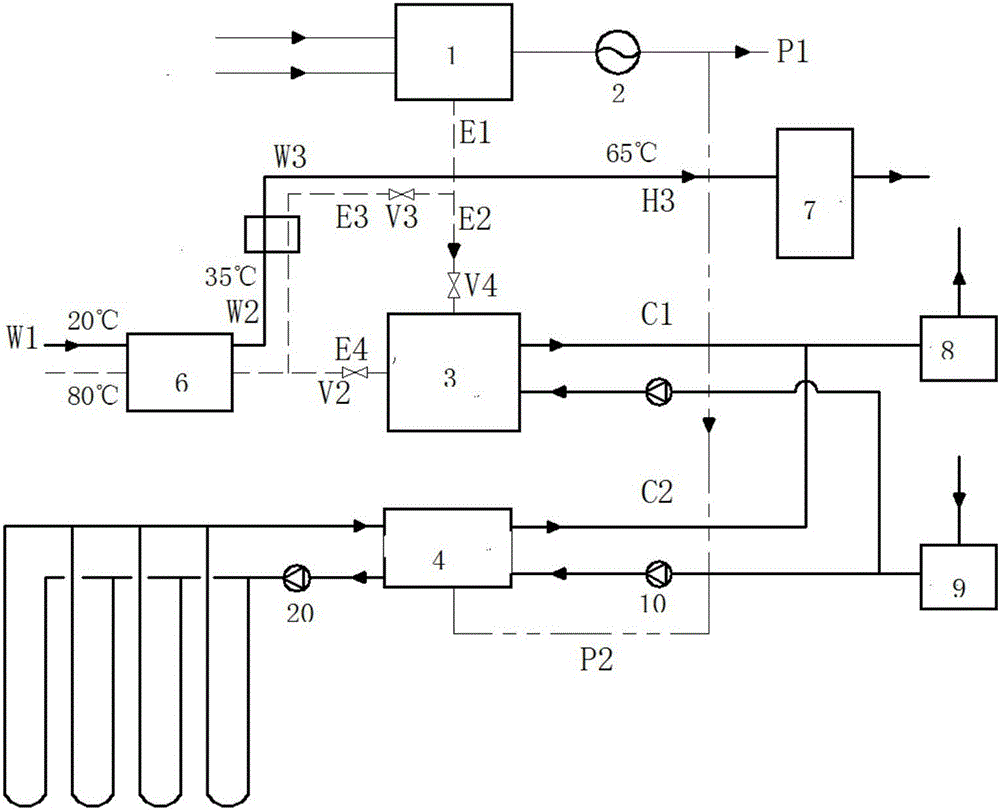
This invention relates to a storage gas pump compound air conditioning, which is the new air conditioning system with integration and comprises the following parts: gas motor, gas motor hot water remainder recycle device, compressor, oil isolation, liquid storage; four-way valve; flow saving device; heat exchanger; liquid humidity remover; solution generation device; solution storage ware; meter cooling device; recycling spraying chamber and fan motor. The summer system adopts air conditioning heat potential charge independent process and uses gas motor to generate heat to process charge into cooling set working situation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Carbon dioxide capturing system and method based on waste heat recycling of turbine exhaust steam
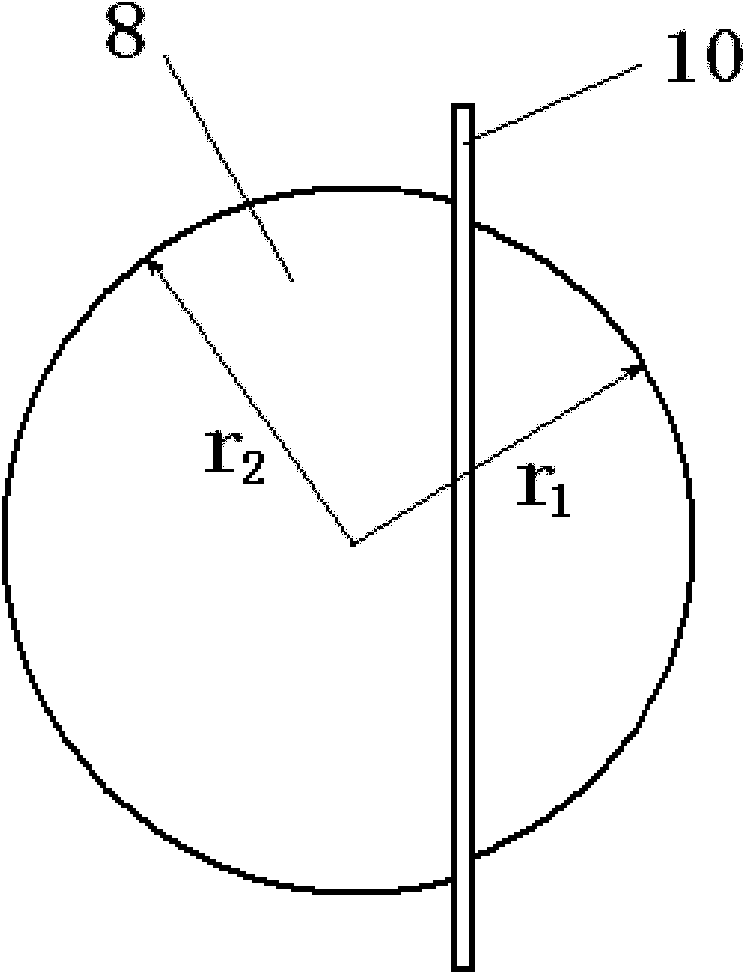
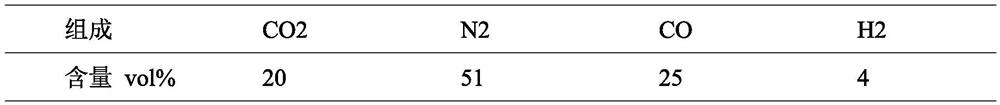
ActiveCN110152489AIncrease profitImprove power generation efficiencyGas treatmentDispersed particle separationVapor–liquid separatorPlate heat exchanger
The invention discloses a carbon dioxide capturing system and method based on waste heat recycling of turbine exhaust steam. The carbon dioxide capturing system based on waste heat recycling of turbine exhaust steam comprises a carbon dioxide collecting sub-system and a waste heat recycling heat pump sub-system based on turbine exhaust steam, wherein the carbon dioxide collecting sub-system comprises an induced draft fan, an absorption tower, a rich liquid pump, a barren / rich liquid heat exchanger, a rich liquid heat exchanger, a desorption tower, a reboiler, a barren liquid pump, a barren liquid cooler, a tower top gas heat exchanger and a gas-liquid separator; the waste heat recycling heat pump subsystem based on turbine exhaust steam comprises a condenser, a tower top gas heat exchanger, a compressor, a reboiler, a barren / rich heat exchanger and a throttling valve; and in the carbon dioxide collecting sub-system, the absorption tower is provided with a bottom gas inlet used for enabling CO2-containing flue gas introduced by the induced draft fan to enter the adsorption tower, and a bottom liquid outlet is connected with an inlet of the rich liquid pump. The system and method provided by the invention are suitable for trapping low-concentration CO2 in flue gas generated by coal-fired power plants and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Excess heat recovery device for shower waste water
InactiveCN101545732ASimple structurePractical structureStationary tubular conduit assembliesElectricityWastewater
The invention relates to an excess heat recovery device for shower waste water, comprising a waste water collecting plastic tray and a circular heat change metal coil pipe fixed in the waste water collecting plastic tray. When a user takes a shower standing on the excess heat recovery device for waste water, flowing waste water has a certain residual temperature. After collected by the waste water tray, the residual temperature and cold water in the cavity of the heat change metal pipe exchange heat. The cold water rises to a certain temperature to heat a heater which can rapidly reach a required temperature so that the energy source is saved. The invention has simple structure, high recovery rate, practicality and convenience, and can be matched with various heaters heated by electricity, coal gas, solar energy, and the like.
Owner:赵铭
Floor drain for recycling heat of bathing waste water
InactiveCN102121264ASimple structureReduce preparation energy consumptionSewerage structuresOther heat production devicesThermal energySocial benefits
The invention discloses a floor drain for recycling heat of bathing waste water, which belongs to the field of energy-saving products. The floor drain for recycling heat of bathing waste water consists of a floor drain main body, a floor drain core, a filter screen, a deodorization and insect prevention device and a waste water heat recycling device, wherein a crimped rim edge at the upper end of the floor drain core is sleeved on a circular step of the floor drain main body; the deodorization and insect prevention device is arranged at the lower end of the floor drain core; a floor drain cover plate of the waste water heat recycling device is arranged in a rectangular step of the floor drain main body; a heat exchange tube is arranged in the floor drain core; the filter screen is arranged on the circular step of the floor drain core; during bathing, tap water exchanges heat with waste water through the floor drain cover plate and the heat exchange tube to recycle heat of bathing waste water; and when the waste water reaches a certain liquid level in the floor drain core, the deodorization and insect prevention device is opened under the action of gravity force to drain the waste water through a sewer. The floor drain has the advantages of simple structure, capabilities of fully recycling heat of bathing waste water, saving energy sources and preventing sewer odor from polluting indoor air, good economic and social benefits and suitability for household bathrooms.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method and system suitable for recovering waste heat of blast furnace slag flushing water
InactiveCN103060496AFix seasonalityImprove waste heat recovery rateIncreasing energy efficiencyRecycling and recovery technologiesCooling towerSlag
The invention relates to a method and a system suitable for recovering waste heat of blast furnace slag flushing water. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, filtering the high-temperature blast furnace slag flushing water and then storing in a hot water tank; S2, performing pressure delivery on the hot water; S3, delivering the hot water to an absorption refrigerating unit or a heating device or a cooling tower; and S4, delivering the water flowing out of the absorption refrigerating unit or the heating device or the cooling tower to a blast furnace slag treatment system to flush slag. The system comprises the blast furnace slag treatment system, the hot water tank and a circulating pump which are connected sequentially, and the cooling tower, the absorption refrigerating unit and the heating device which are connected in parallel. By adopting the method and the system, the low-temperature waste heat in the blast furnace slag flushing water can be fully utilized, so that the aims of energy conservation and environmental friendliness are fulfilled, the seasonal problem of the slag flushing water waste heat recovery is solved, and the recovery rate of the waste heat of the high-temperature slag flushing water is improved.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
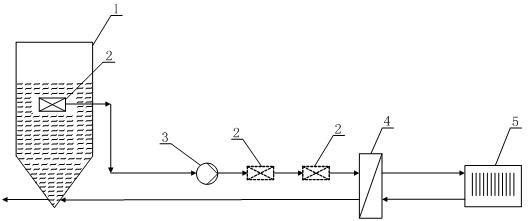
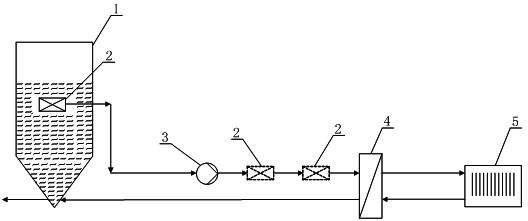
Carbon dioxide trapping system and method based on blast furnace slag flushing water waste heat recycling
PendingCN112126477ADoes not affect normal operationImprove the capture effectProductsGas treatmentCo2 removalReboiler
The invention discloses a carbon dioxide trapping system and method based on blast furnace slag flushing water waste heat recycling. The carbon dioxide trapping system comprises a carbon dioxide trapping and separating system and a heat pump system. The carbon dioxide capture and separation system comprises an absorption tower, a desorption tower, a barren liquor pump, a rich liquor pump, a barrenand rich liquor heat exchanger and a barren liquor condenser; the carbon dioxide capturing and separating system is connected with the heat pump system through a reboiler / condenser, the reboiler / condenser comprises a reboiler and a condenser, the reboiler is communicated with the carbon dioxide capturing and separating system, and the condenser is communicated with the heat pump system; the blastfurnace gas is treated by adopting a chemical absorption method with the advantages of good trapping effect, strong treatment air volume, mature process and the like, so that the carbon emission coefficient of the blast furnace gas can be reduced under the condition that the CO2 removal rate of the blast furnace gas is 90 percent, and the heat value of the blast furnace gas can be increased fromabout 3500kJ / Nm < 3 > to about 4400kJ / Nm < 3 >.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and system for recovering waste heat from INBA slag washing water of blast furnace
InactiveCN102676711AGuarantee the effect of flushing slag againReduce wearProcess efficiency improvementWater useSlag
The invention discloses a method and a system for recovering waste heat from IBNA slag washing water of a blast furnace. The system is formed by the connection of a filter, a water pump, a heat exchanger and a matched electric power meter, and the recovering method is that the high temperature slag washing water in a hot water tank is subjected to filtering and pressurizing and then flows into the heat exchanger for heat exchanging with water used by heat consumers. The method and the system have the advantages that short-process INBA slag washing water is high in temperature, and recovering and utilizing effects are good; water qualities of the filtered slag washing water are good, pipelines are protected from being abraded, and the heat exchanger is protected; and the water used by the heat consumers is clean water and is subjected to heat exchanging with the slag washing water by means of the heat exchanger, and the safety and stability of facilities of the heat consumers are guaranteed.
Owner:涉县亿玮坤节能科技有限公司
Gas heat pump device based on heat source tower
ActiveCN110319617AImprove utilization factorSolve frostingHeat recovery systemsClimate change adaptationWaste heat recovery unitFlue gas
The invention relates to a gas heat pump device based on a heat source tower. The gas heat pump device comprises a solution circulation unit, a gas heat pump unit and a waste heat recycling unit, a solution outlet of the heat source tower in the solution circulation unit is connected with a solution inlet of a solution-refrigerant heat exchanger through a solution pump and a first solution valve,a solution outlet of the solution-refrigerant heat exchanger is connected with a solution inlet of the heat source tower, a cooling water circulating water tank, a cylinder sleeve water circulating water pump and a cylinder sleeve heat exchanger in the waste heat recycling unit are connected through a pipeline to form a cylinder sleeve water waste heat recovery loop, the cooling water circulatingwater tank, a second water pump, a flue gas heat exchanger, a first water valve and the cooling water circulating water tank are sequentially connected through a pipeline to form a flue gas waste heatrecovery loop, and a waste heat utilization loop is formed by sequentially connecting the cooling water circulating water tank, the second water pump, the flue gas heat exchanger, a second water valve, a regeneration heater and the cooling water circulating water tank through a pipeline and sequentially connecting the cooling water circulating water tank, the first water pump, a domestic hot water tank and the cooling water circulating water tank through a pipeline.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Marine absorption refrigeration air conditioning system and working method thereof
PendingCN107152812AEfficient use ofImprove utilization efficiencyMechanical apparatusAuxillariesEngineeringAir conditioning
The invention discloses a marine absorption refrigeration air conditioning system and a working method thereof. The system comprises an absorption refrigeration unit, a waste heat recycling loop and a seawater loop. The method comprises the steps that when cold supplying is conducted in summer, ship main and auxiliary engine cylinder sleeve cooling water is taken as a heat source for a generation cavity of the absorption refrigeration unit, and seawater is taken as a cold source for an absorption cavity and a condensation cavity in the loop; when heat supplying is conducted in winter, heat supplying is achieved by directly taking the cylinder sleeve cooling water as a heat source. According to the marine absorption refrigeration system, a traditional marine compression type refrigeration system is replaced, therefore, consumption of a marine air conditioning system on marine power is effectively reduced, marine waste heat and exhaust heat are fully utilized, the heat efficiency is increased by about 20%, and the overall marine energy source utilization efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
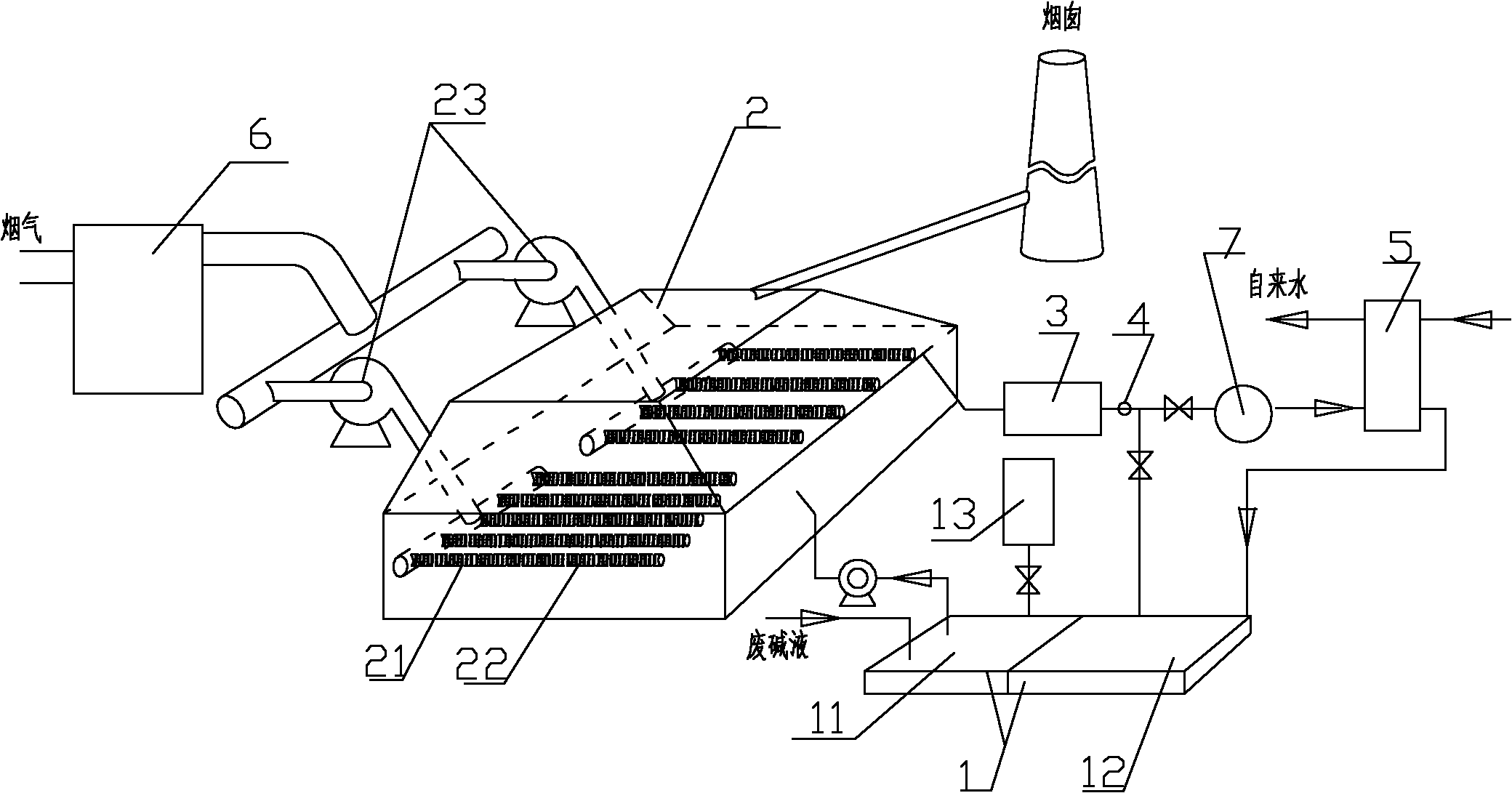
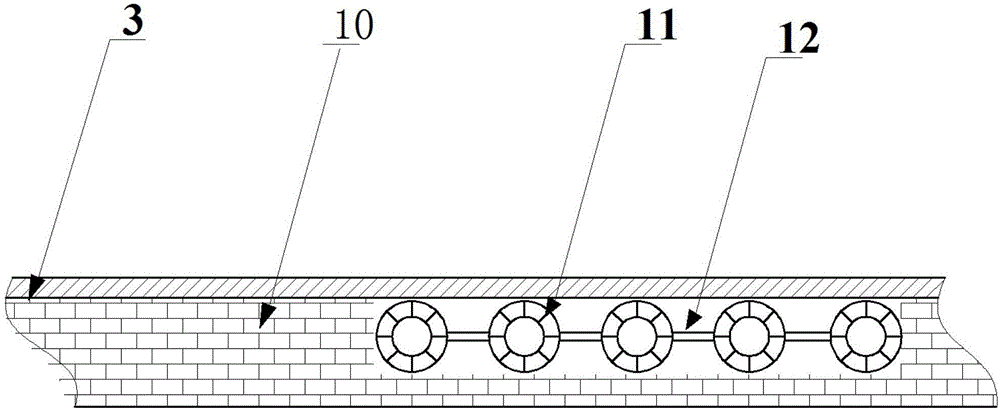
Method and system for combined treatment of boiler smoke and alkaline waste water and waste heat utilization
ActiveCN102172467AGuaranteed coverageHigh desulfurization and dust removal efficiencyUsing liquid separation agentExhaust gasFlue-gas desulfurization
The invention discloses a method and system for combined treatment of boiler smoke and alkaline waste water and waste heat utilization. The method belongs to a waste water and exhaust gas processing method. Firstly, alkaline waste water is sent into an alkali liquor pool so as to evenly stir water quality and water amount; then, the obtained mixture is sent into an integral desulfuration dust collector; the waste water discharged from the desulfuration dust collector is sent to a water-water heat exchanger or is directly sent to an effluent pool after being detected by a temperature sensor; meanwhile, boiler smoke is sent to the integral desulfuration dust collector for desulfuration and dust collection after being subjected to waste heat recovery. Different from the traditional smoke desulfuration and dust collection method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that an aeration mode is adopted to cause the smoke and the waste water to intensively contact, thereby overcoming the problems of big capital construction investment and high operation cost or low desulfuration efficiency of the traditional method; meanwhile, smoke desulfuration, dust collection, smoke waste heat recovery and waste water waste heat recovery are cooperatively controlled; and low-grade waste heat is effectively recovered while the high-efficiency desulfuration and dust collection effect is guaranteed.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Waste heat recycling device and system filled with heat conduction materials and used for grate cooler
InactiveCN105115311AReduce energy consumptionImprove utilizationHeat storage plantsIncreasing energy efficiencyEngineeringEnergy consumption
The invention provides a waste heat recycling device and system filled with heat conduction materials and used for a grate cooler. The waste heat recycling device comprises a barrel body in which a heat exchange pipe is arranged, the barrel body and the heat exchange pipe are coaxially arranged, and the space between the barrel body and the heat exchange pipe is filled with the heat conduction materials. The waste heat recycling device can fully absorb sensible heat released when clinker is cooled at a top speed in a cooling machine, energy consumption of the clinker is reduced, and the waste heat utilizing amount can also be effectively increased.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Waste heat recycling system device for intaglio printing waste gas and method for applying waste heat recycling system device
ActiveCN103818112AResidue reductionReduce energy consumptionPrinting press partsSteam condensationFresh air
The invention discloses a waste heat recycling system device for intaglio printing waste gas. The waste heat recycling system device comprises a waste gas recycling system and a fresh air heating system. The waste gas recycling system comprises a waste gas heat exchange pipeline, an exhaust fan and an exhaust pipeline which are sequentially connected with one another, and a purification heat exchange assembly is mounted on the waste gas heat exchange pipeline; the fresh air heating system comprises a fresh air heat exchange pipeline with two fresh air inlets, and heat-pipe heat exchangers and oven air inlet and suction devices are mounted on the fresh air heat exchange pipeline. The waste heat recycling system device has the advantages that heat of waste gas and steam condensation water is collected in intaglio printing manufacturing procedures, fresh air which is fed into the system device is preheated via heat exchange structures, then preheated fresh air is fed into air inlets of steam heat exchangers of various units of an intaglio printing machine and is used for drying printing ink after being heated by the steam heat exchangers, accordingly, energy consumption can be reduced, and the waste heat recycling system device has excellent economic value.
Owner:JIANGSU LEATER GREEN PACKAGING CORP LTD
Smoke waste heat recycling system based on film absorption
ActiveCN107631290ALower dew point temperatureSolve the problem of waste heat recovery requiring anti-corrosionFeed water supplyCombustion processFiberAir preheater
The invention belongs to the technical field of gas boiler smoke waste heat recycling and film absorption, and relates to a smoke waste heat recycling system based on film absorption. The system comprises a gas boiler, a vacuum film water recoverer, a film bundle heat exchanger, an indirect heat exchanger, an air preheater, a heat supply pipe net, a chimney and the like. Smoke passes through a vacuum hollow fiber film bundle in the vacuum film water recoverer, water steam in wet smoke is separated from dry smoke, the dry smoke obtained after separation sequentially passes through the indirectheat exchanger and the air preheater, return water and air are heated through waste heat, meanwhile, the separated water steam enters the film bundle heat exchanger, primary heated return water in thewater tightness hollow fiber film bundle is further heated and is sent into the boiler or nearby secondary pipe net users, the water steam obtained after heat exchange is condensed, and water can bedirectly supplemented for the boiler. The system can achieve smoke dry and wet separation, heat energy in the water steam and the dry smoke obtained after separation can be efficiently utilized, waterresources are saved, and the phenomenon of chimney white smoke discharging is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CIVIL ENG & ARCHITECTURE
Waste heat recycling system of oil injection screw air compressor
InactiveCN103398011ASafe and stable operationImprove reliabilityRotary/oscillating piston pump componentsLiquid fuel engine componentsCooling towerGas compressor
The invention discloses a waste heat recycling system of an oil injection screw air compressor. The waste heat recycling system comprises an oil cooling system and a heat recycling system, wherein the oil cooling system comprises a cooling tower and a first plate type heat exchanger which is connected with the cooling tower through a pipeline, and the heat recycling system comprises a heat storage water tank and a second plate type heat exchanger which is connected with the heat storage water tank through a pipeline. The waste heat recycling system provided by the invention solves the problems of the existing waste heat recycling system of an air compressor, such as high pressure loss and high leakage possibility.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Cooling water waste heat recycling system
InactiveCN102914085AReduce the temperatureStable temperatureHeat pumpsEnergy industryWaste heat recovery unitCooling tower
The invention discloses a cooling water waste heat recycling system, which comprises a cold water tank, a circulating pump A, a heat production device, a hot water tank, a circulating pump B, a variable frequency pump, a plate type heat exchanger A, a circulating pump C, a small water tank, a heat pump unit, a circulating pump D, a hot water tank, a water supply pump, a plate type heat exchanger B and a cooling tower. The cooling water waste heat recycling system transfers the energy of cooling water to the heat pump by using the plate type heat exchanger A, and then converts the low temperature heat transferred by the plate type heat exchanger into high temperature heat energy by using the heat pump, the water in the hot water tank is used as a carrier of the high temperature heat energy, and the temperature is up to 60 DEG C, so that the use occasions are increased. According to the cooling water waste heat recycling system, the heat supplied to the heat pump is indirectly adjusted by using the plate type heat exchanger A and the variable-frequency pump, so that the temperature of water entering the heat pump of a third internal circulation is stable and is less than 32 DEG C, and the service life of the heat pump as well as the reliability and stability of the waste heat recovery are ensured. The normal temperature water injected in the hot water tank firstly passes through the plate type heat exchanger B, so that the energy consumption in the waste heat recovery process is reduced.
Owner:交大奇莱捷尔高科(大连)有限公司
Pneumatic drier with tail gas waste heat recycling function
InactiveCN103344100AReduce weightGood low temperatureDrying gas arrangementsHeating arrangementEconomic benefitsProcess engineering
A pneumatic drier with a tail gas waste heat recycling function comprises an air heat exchanger, a feeding system, a drying pipeline, a cyclone separator, a discharging screw conveyer and a tail gas pipeline, wherein the tail gas pipeline is in pipe connection with a waste heat recycling device through a fan, the waste heat recycling device comprises a shell body and a heat exchanger arranged in the shell body, a tail gas inlet, a tail gas outlet, an air inlet and an air outlet are formed in the shell body, and the air outlet is in pipe connection with the air heat exchanger. According to the pneumatic drier with the tail gas waste heat recycling function, waste is reduced due to the recycling of waste heat, the waste heat recycling device is additionally arranged on the tail gas pipeline of the pneumatic drier so as to use the heat of tail gas to heat air entering the drier, dry air is then pre-heated, and therefore steam consumption is reduced, the purpose of saving energy and reducing emission is achieved, and good economic benefit and environmental benefit are obtained.
Owner:江苏格兰特干燥浓缩设备有限公司
Condensation type gas heating stove
ActiveCN108344180AImprove condensation efficiencyIncrease profitAir heatersSustainable buildingsCombustorProcess engineering
The invention discloses a condensation type gas heating stove. The condensation type gas heating stove comprises a main heat exchanger, a combustor, a combustion cavity, a smoke collection cover and acircular water pump and further comprises direct-current draught fan subject to directional control through a magnetic field, a waste heat recycling device communicated with the direct-current draught fan and a condensate collecting device; the direct-current draught fan is communicated with the main heat exchanger through the smoke collection cover, the waste heat recycling device and the condensate collecting device are sequentially connected to form a first condensate recycling system. According to the condensation type gas heating stove, the first condensate recycling system formed through sequential connection of the waste heat recycling device and the condensate collecting device is used, the wind amount of the direct-current draught fan is controlled to increase the condensation effect of the stainless steel fin pipe waste heat recycling device on the condensate under the low power, the separated-out condensate water is drained into the condensate collection device, and the condensation efficiency and the waste heat utilization rate of the heating stove can be improved.
Owner:QINGDAO ECONOMIC & TECHN DEV ZONE HAIER WATER HEATER
Waste heat recovery system of blast furnace slag quenching water
InactiveCN101798607AAvoid emissionsReduce pollutionLighting and heating apparatusAir conditioning systemsSprayerSlag
The invention relates to a waste heat recovery system of blast furnace slag quenching water, comprising a generation tower and a dehumidification tower. A sprayer for spraying dilute salt solution, filler and a water pipe communicated with a slag quenching water circulating system are arranged in the regeneration tower; a sprayer for spraying concentrated salt solution, filler and a water pipe in which cold water is introduced are arranged in the dehumidification tower; and dry and cold air from the dehumidification tower is introduced to a ventilating chamber. The blast furnace slag quenching water is used as a drive heat source for dehumidifying liquid and the recovered waste heat of the slag quenching water is used for producing dry air for ventilation, thereby preventing a large quantity of heat from being exhausted to the outside, reducing the pollution on the environment, changing wastes into valuables, and saving energy sources.
Owner:无锡市东方环境工程设计研究所
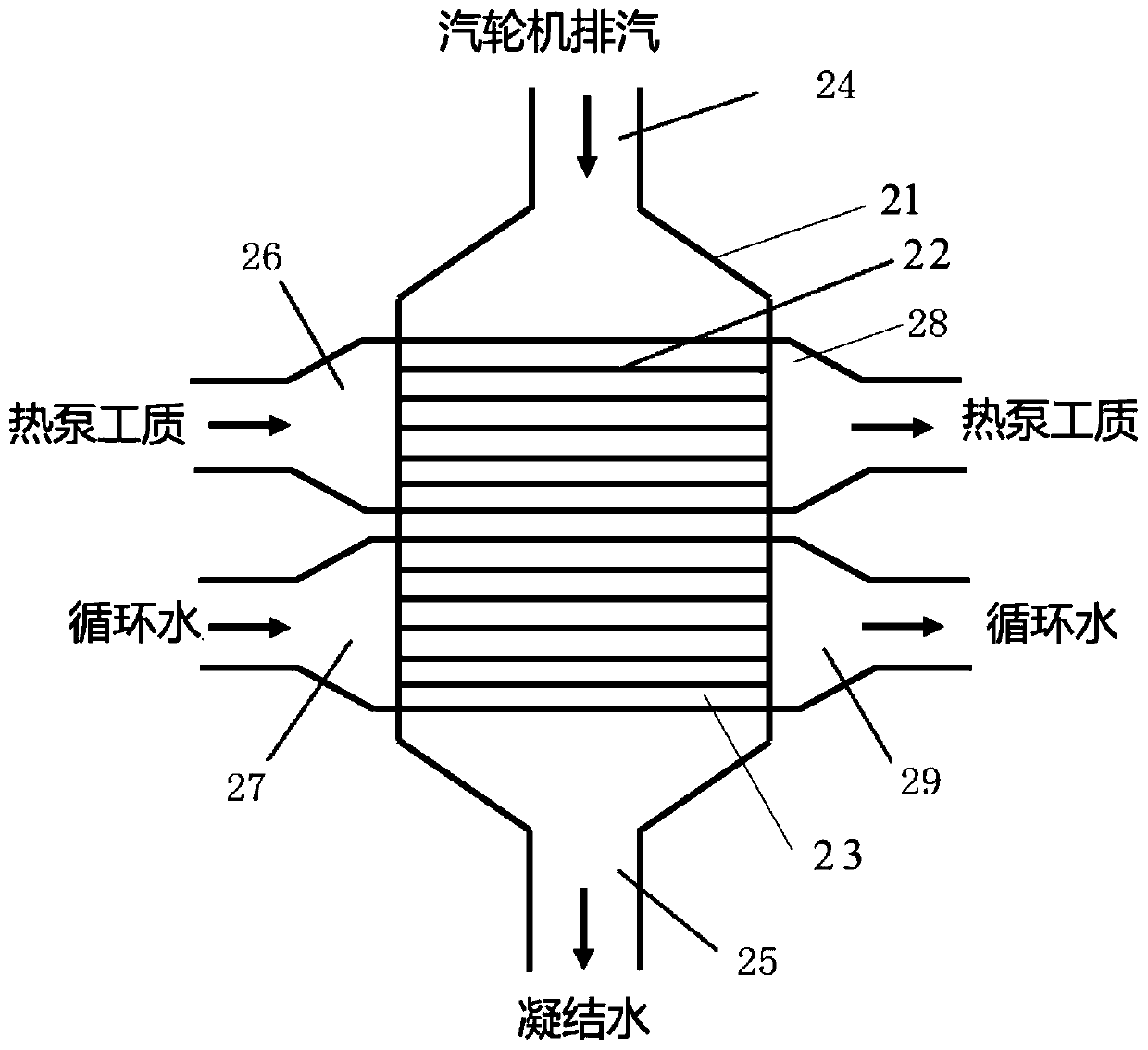
Heat supplying method of cooling water residual heat recycling energy-saving system of thermal power plant
InactiveCN102486317AEfficient use ofReduce lossLighting and heating apparatusHot-water central heatingCooling towerHeat losses
The invention provides a heat supplying method of a cooling water residual heat recycling energy-saving system of a thermal power plant. In the method, steam produced by action of the thermal power plant flows into a condenser through a steam pipeline, and is subjected to heat release and liquefaction; cooling water absorbs heat released when the steam is liquefied in the condenser, and is delivered to a heat exchange station E through a water outlet pipeline A to serve as a low-temperature heat source; water in a heat supply network is heated by utilizing the heat of the low-temperature heat source under the action of a heat pump, and flows into a cooling tower through a return pipeline B; and the water in the heat supply network is heated in the heat exchange station E and delivered to a client end so as to be utilized as a heat supply source, and returns to the heat exchange station E after supplying heat. The temperature of cooling water delivered to the heat exchange station E in urban areas is 35-45 DEG C, so that low-temperature delivery is realized, and the heat loss is small.
Owner:张宏伟
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com