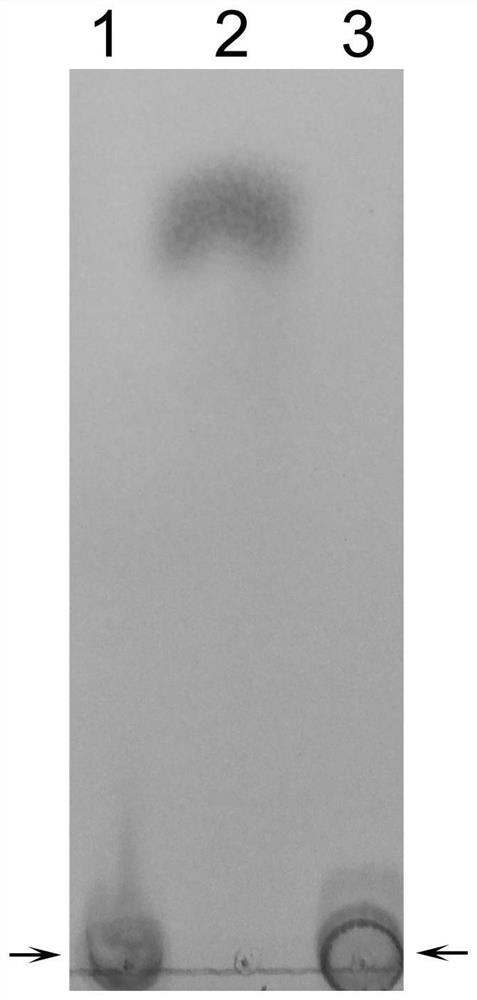
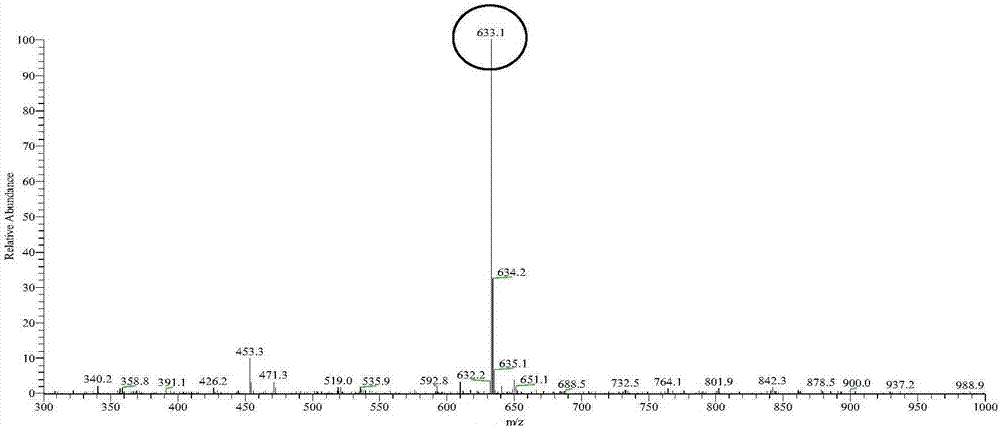
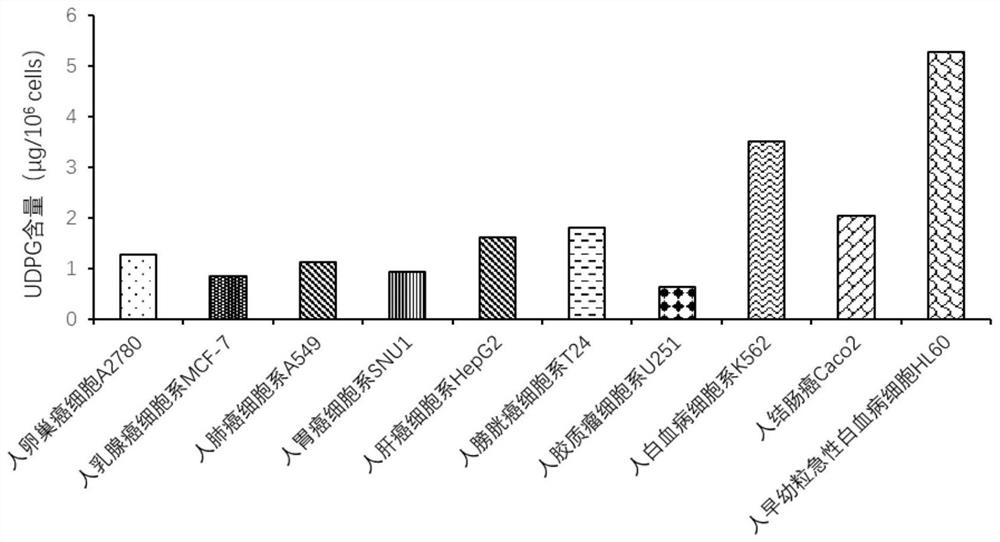
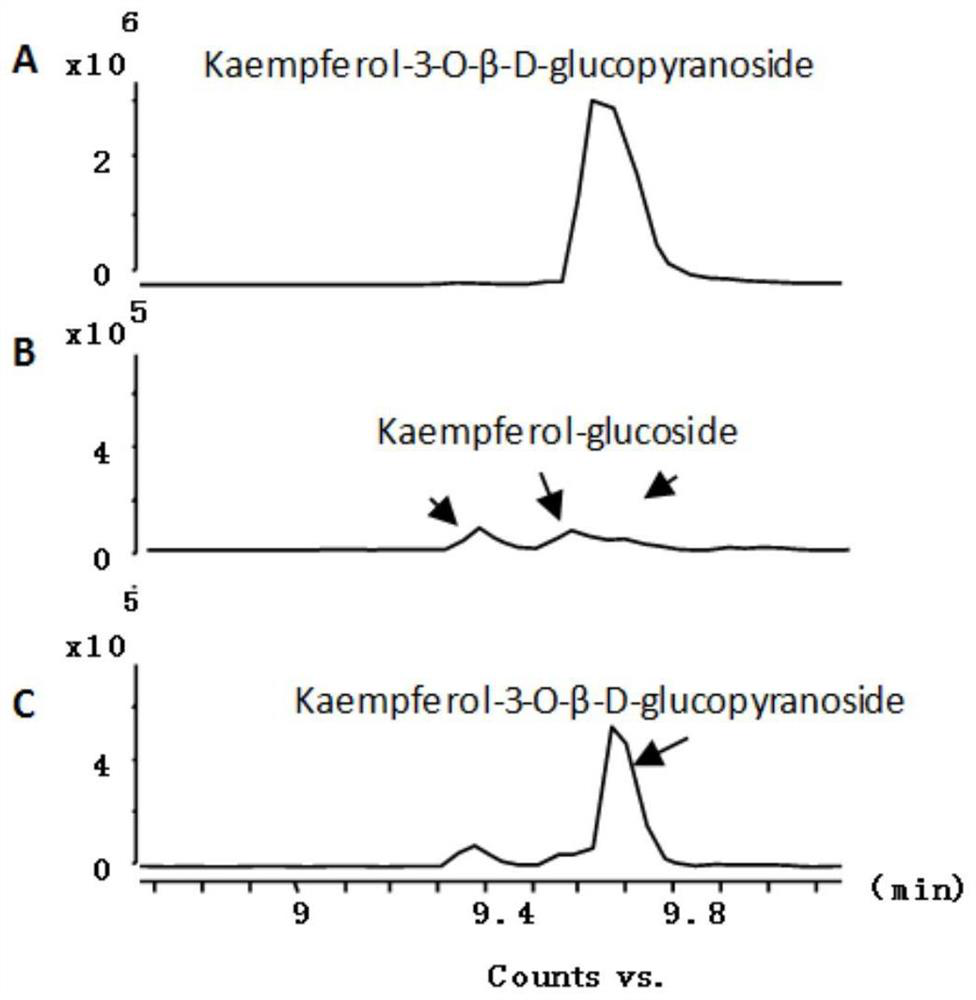
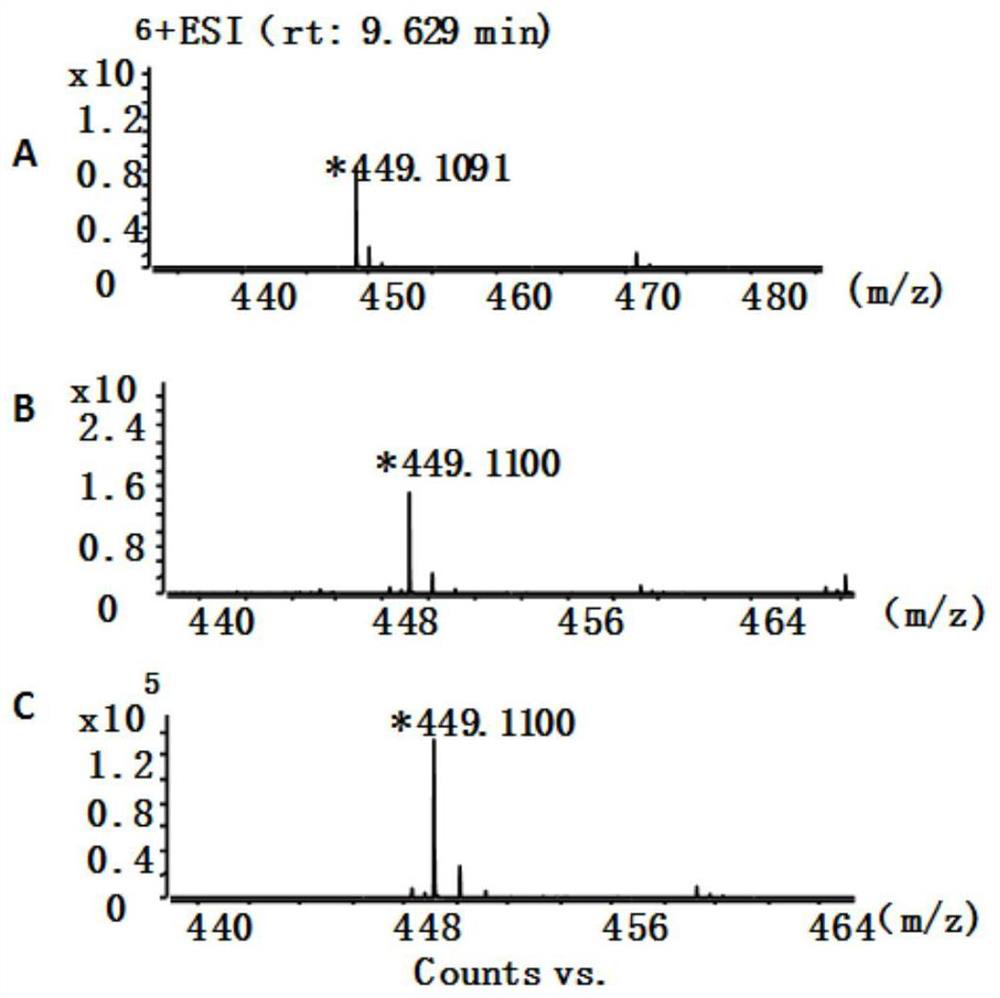
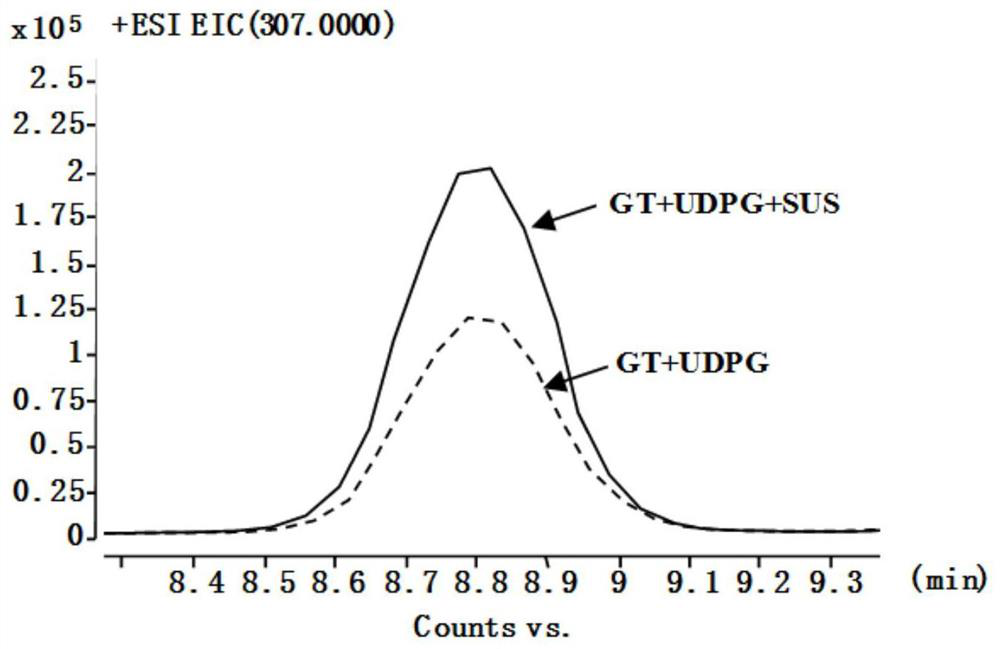
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Uridine diphosphate glucose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
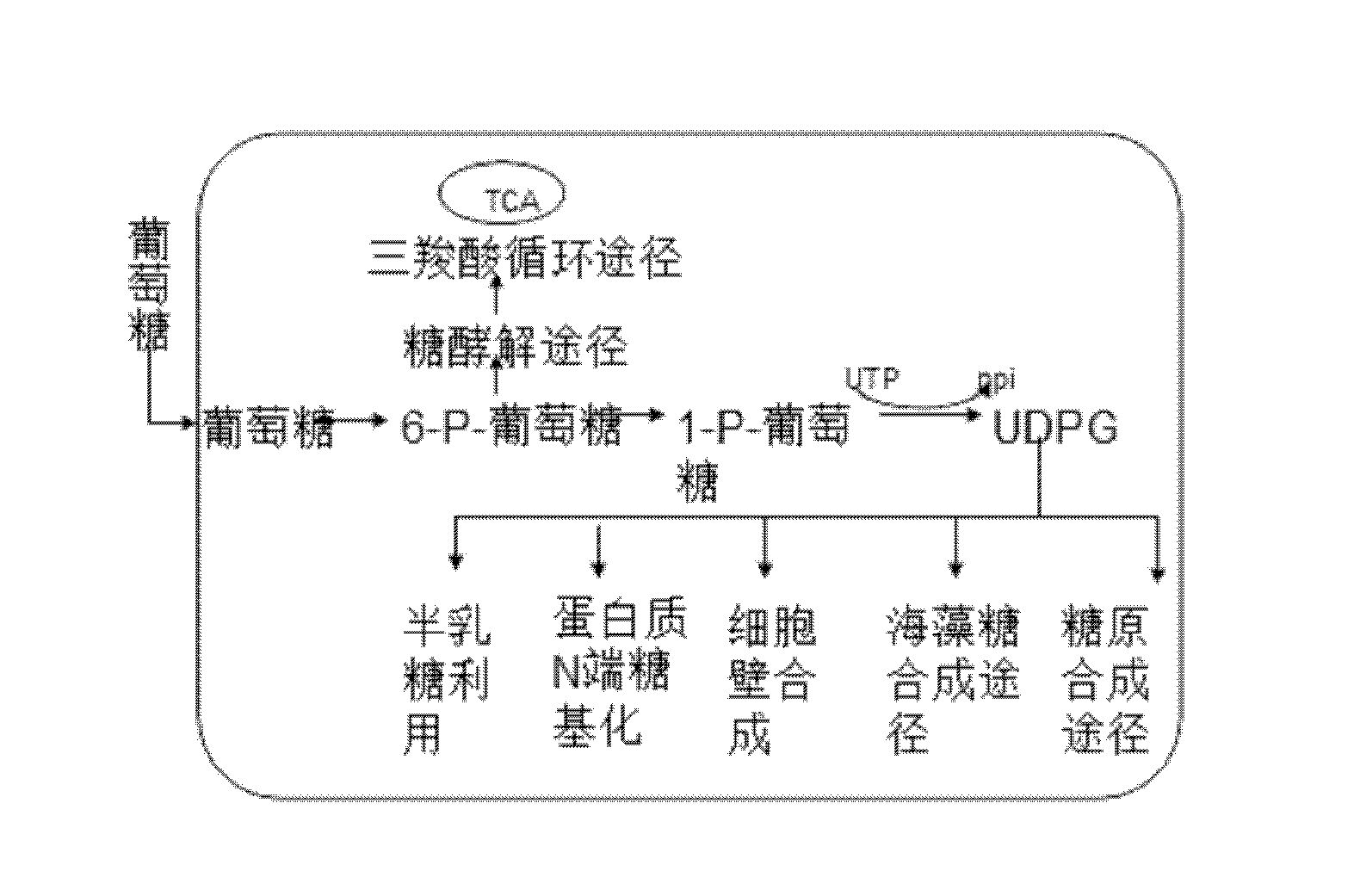
Uridine diphosphate glucose (uracil-diphosphate glucose, UDP-glucose) is a nucleotide sugar. It is involved in glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism.
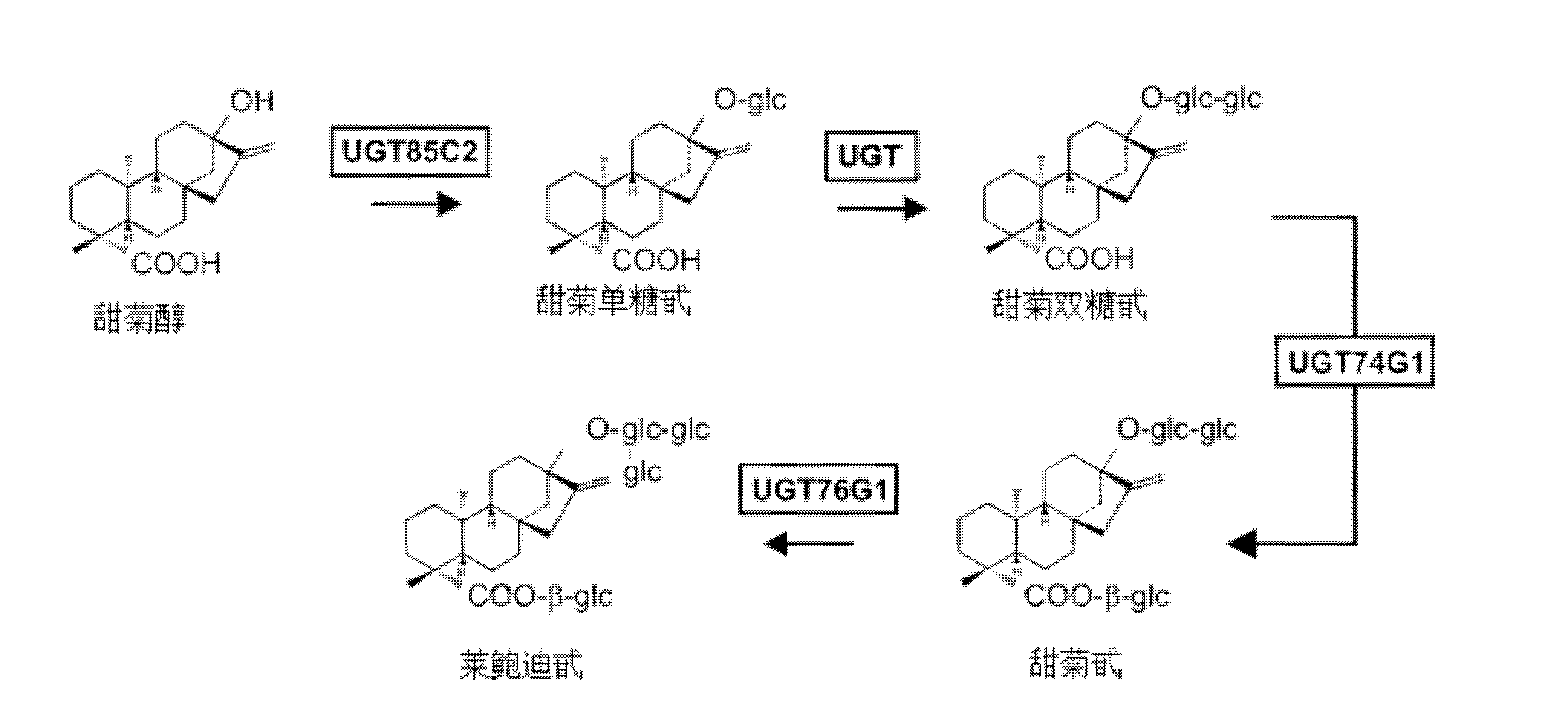
Genetically engineered bacteria used for producing stevia glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacteria used for producing stevia glycosyltransferase UGT76G1; a UGT76G1 coding gene is inserted between the restriction enzyme cutting sites EcoRI and XhoI of a PYes2 carrier, so as to construct a recombinant plasmid, and then the recombinant plasmid is introduced to expression host Saccharomyces cerevisiae YPH499 to obtain the engineered bacteria; and the coding gene of the UGT76G1 is GenBank, No. GenBank: AY345974.1, and the gene sequence of the coding gene is named as UGT (Udp Glucuronyl Transferase). The invention also discloses a construction method of the genetically engineered bacteria and the application of the bacteria to the production of rebaudioside A. According to the invention, under the condition that expensive UDPG (Uridine Diphosphate Glucose) is not added, cheap carbon source glucose is used as a substrate, the metabolic pathway of UDPG in the yeast is regulated, and then the rebaudioside A is produced from St glycosides through whole cell catalysis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
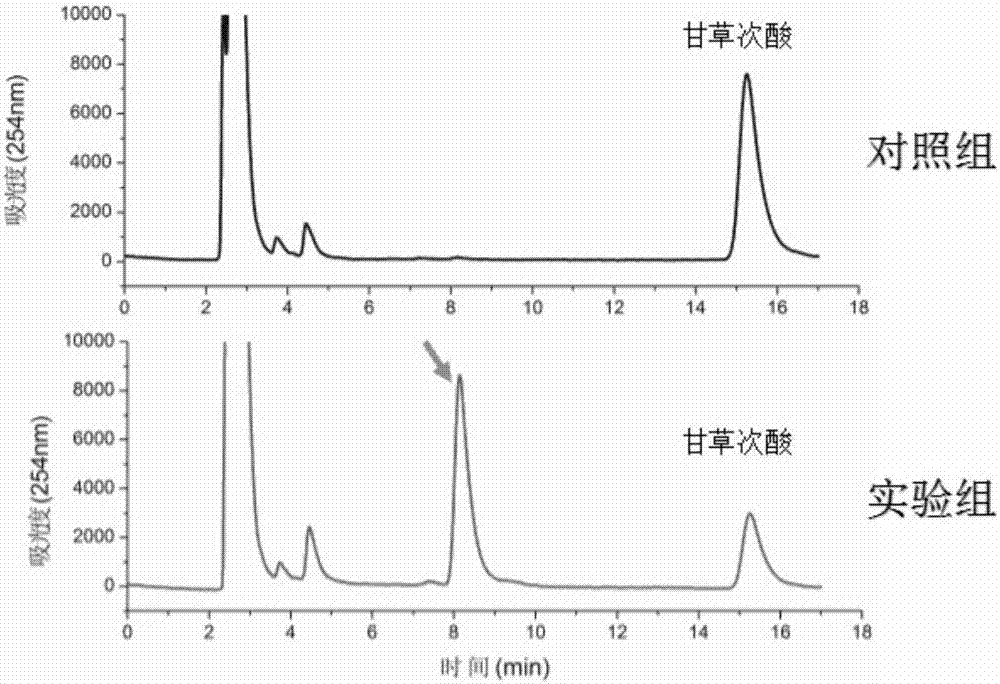
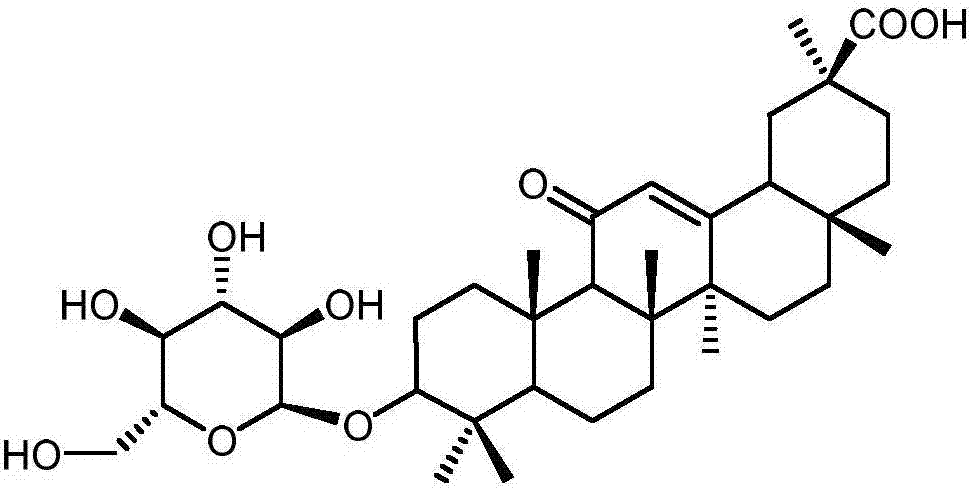
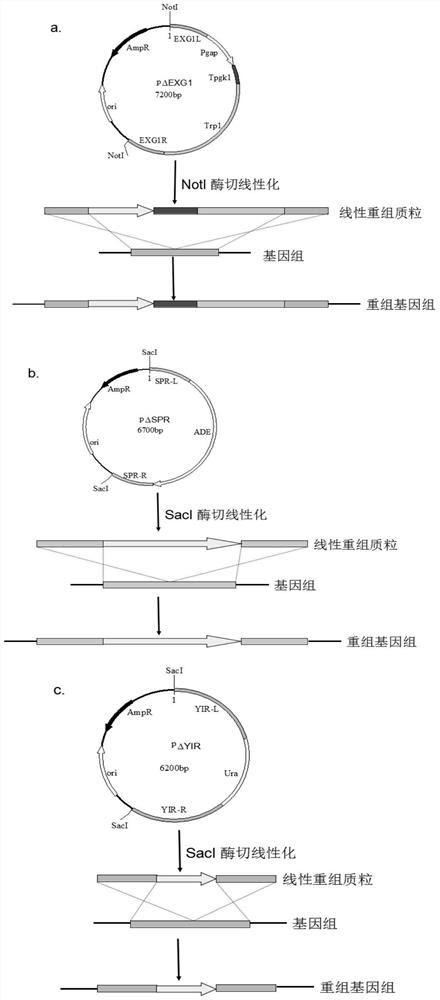
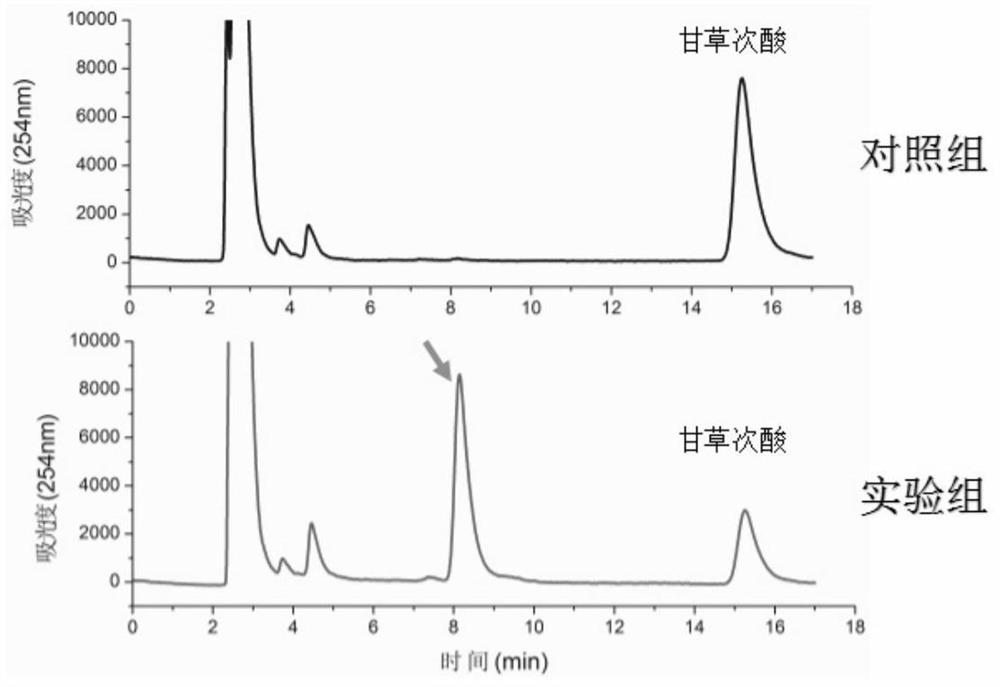
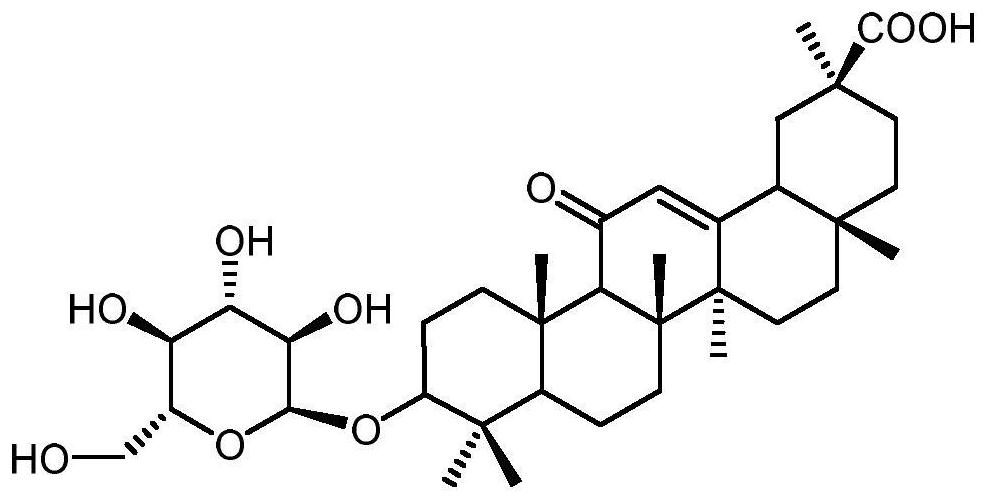
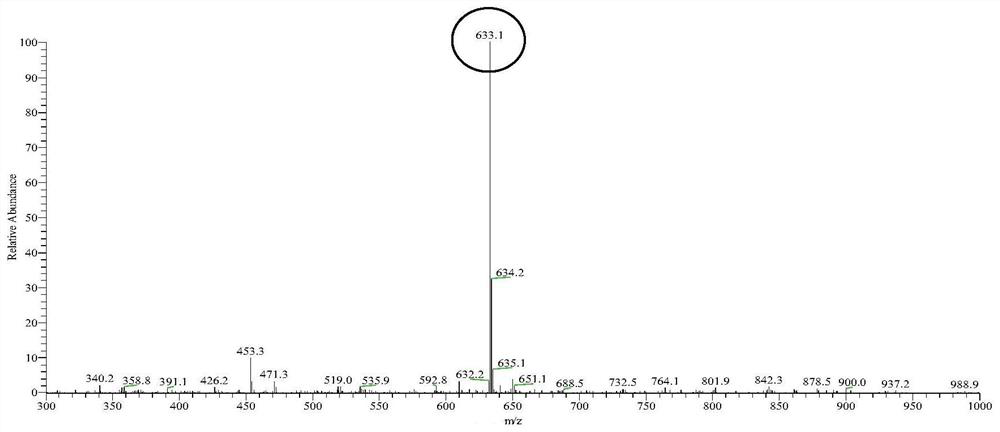
Method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid with enzymic method
ActiveCN107502599AHigh catalytic efficiencyMild reaction conditionsTransferasesGenetic engineeringChemical synthesisEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid with an enzymic method and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. Glycosyltransferase gene Unigene14953, Unigene20323UGT73C11, UGT73C5 and UGT73C6 from plant licorice, barbarea vulgaris or Arabidopsis are cloned or chemically synthesized, escherichia coli is preferably selected as host bacteria, and genetically engineered bacteria containing glycosyl transferase is established; recombinant glycosyl transferase serves as glycyrrhetinic acid substrate and uridine diphosphate glucose, and 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid can be synthesized efficiently in pH value of 5.0-11.0 and at the temperature of 25-55DEG C conditions.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Biomarker compositions for diagnosing cervicitis and cervical cancer
InactiveCN106124763AComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCysteine thiolateCervicitis
The invention discloses biomarker compositions, and provides biomarker compositions for diagnosing cervicitis and a cervical cancer. The biomarker compositions are characterized by at least comprising one or a combination of uridine-5'-monophosphate disodium, histamine, 3'-O-methyl-guanosine and phenyllactic acid. The biomarker composition for diagnosing the cervicitis is characterized by comprising one or a combination of uridine-5'-monophosphate disodium, L-cysteine, isocitric acid, uridine diphosphate glucose, adenosine monophosphate, inosine 5'-monophosphate, L-pipecolic acid, N-acetyl putrescine and saccharose. The biomarker composition for diagnosing the cervical cancer is characterized by comprising one or a combination of histamine, phenyllactic acid, citraconic acid, L-2-aminoadipic acid, 3'-O-methyl-guanosine, beta-D-glucosamine, glycerin and cholesterol sulfate.
Owner:上海阿趣生物科技有限公司
Method for generating rebaudioside M by catalyzing rebaudioside A via immobilized glycosyltransferases
PendingCN110846305AEasy to separateImprove thermal stabilityTransferasesOn/in organic carrierUridine diphosphate glucoseGlucose phosphate
The invention discloses a method for generating rebaudioside M by catalyzing rebaudioside A via immobilized glycosyltransferases, which comprises the steps of: (1) crosslinking glycosyltransferase UGT1 and glycosyltransferase UGT2 on activated chitosan beads to obtain immobilized glycosyltransferases; (2) adding rebaudioside A into a container, adding uridine diphosphate glucose, and adding the immobilized glycosyltransferases, and catalyzing obtain rebaudioside M. The immobilized glycosyltransferases according to the invention are easy to separate, can be repeatedly used, have high thermal stability and high operation stability, and can, when compared with free enzymes, directly yield a higher amount of rebaudioside M by catalyzing rebaudioside A via the immobilized glycosyltransferases;the free enzymes can only be used once, while the immobilized glycosyltransferases can be reused; after the immobilized glycosyltransferases are reused 10 times, the activity of the immobilized glycosyltransferases is still more than 50% of that of the immobilized glycosyltransferase used for the first time. The method is simple and easy to implement. The process steps are reduced, the cost is reduced, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:SINOCHEM HEALTH IND DEV CO LTD +1
Cultivation method and application for salidroside-containing plant
The invention provides a cultivation method for a salidroside-containing plant. The method comprises the following steps: spraying hydroxyphenethyl alcohol to growing plant leaves; harvesting the growing plant leaves to obtain the salidroside-containing plant. According to the method provided by the invention, the steps are simple; the synthetic precursor, namely the hydroxyphenethyl alcohol, of the salidroside-containing plant is directly supplied by outside, and the salidroside is synthesized in a plant body by taking uridine diphosphate glucose and glucosyltransferase which are contained in the plant as raw materials. The invention further provides the application of the salidroside-containing plant.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Preparation method and application of tea containing salidroside
InactiveCN104585374AReduce usageReduce lossPre-extraction tea treatmentHorticulture methodsSalidrosideAlcohol
The invention provides a preparation method of tea containing salidroside. The method comprises the following steps: spraying p-hydroxyphenylethyl alcohol to growing camellia sinensis leaves, and picking to obtain the tea containing salidroside. The method provided by the invention is simple in step; a synthetic precursor, namely p-hydroxyphenylethyl alcohol, of the salidroside is directly supplied from the external world; and uridine diphosphate glucose and glucosyltransferase contained in the tea are taken as raw materials, and the salidroside is synthesized in a tea body. The prepared tea containing the salidroside and application of the tea are further protected in the invention.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Optically active bicyclol glucoside and preparation method thereof, and application of optically active bicyclol glucoside in prevention and treatment of liver diseases
InactiveCN111285909ANovel preparation methodFew reaction stepsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesUridine DiphosphoglucoseUridine diphosphate glucose
The invention discloses optically active (P)-bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside and (M)-bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside applicable to medicines and a preparation method and application thereof. According tothe invention, bicyclol and uridine diphosphate glucose disodium salt are catalyzed by glycosyltransferase to synthesize optically active (P)-bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside and (M)-bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside in one step. The bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside prepared according to the invention can be used for preventing and treating liver diseases.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Use of uridine diphosphate glucose 4-epimerase
The present invention relates to a new use of uridine diphosphate glucose 4-epimerase (also called uridine diphosphate galactose 4-epimerase), and a method of converting uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) to uridine diphosphate N-acetylgalactosamine (UDP-GalNAc) by using the said enzyme. The process for producing UDP-GalNAc by using the uridine diphosphate glucose 4-epimerase and the UDP-GalNAc supply system according to the present invention are practical and efficient, and greatly beneficial to the industries.
Owner:YAMASA SHOYU CO LTD
Method for preparing rebaudioside A by liquid fermentation
PendingCN111621456AControllable fermentation processSimple stepsBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a method for preparing rebaudioside A by liquid fermentation. The method includes: (1) transferring a glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 gene to a pUC18 plasmid vector, transferringto DH5alpha escherichia coli competent cells, inoculating into an LB medium, and culturing for 10-18 hours at 30-37 DEG C and 200-250 rpm; (2) inoculating into a seed tank according to an inoculationamount of 0.1-10% by volume, and culturing for 5-12 hours at 100-400 rpm, a ventilation ratio of 0.2-1 V / V. min and 30-37 DEG C; (3) inoculating into a fermentation tank according to an inoculation amount of 1-15% by volume, and culturing for 20-30 hours at 100-800 rpm, a ventilation ratio of 0.5-2 V / V. min and 30-37 DEG C; (4) adding an inducer when cell concentration OD600 reaches 20-60, whereinthe concentration is 0.05-1 mmol / L; (5) carrying out pressure filtration, resuspension, high-pressure homogenization and crushing, and pressure filtration to obtain a crude enzyme liquid; and (6) mixing stevioside, uridine diphosphate glucose, a phosphate buffer solution and the crude enzyme liquid, and reacting at 25-40 DEG C for 12-48h. The method high enzyme activity, high catalytic substrateconcentration, high conversion rate, easy control of the fermentation process, simple steps and low fermentation cost.
Owner:ANHUI JINGHE IND
Drug-loaded vesicle
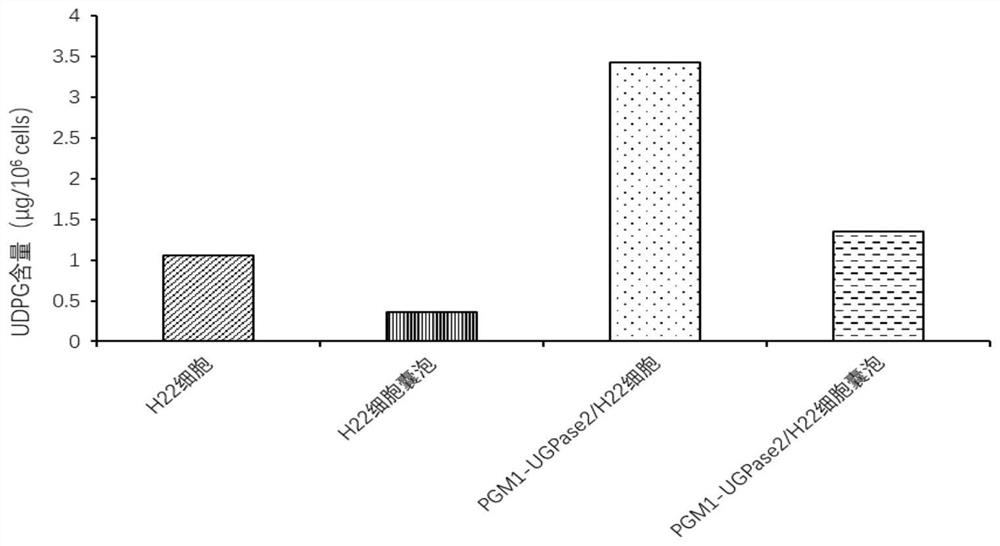
ActiveCN111067868AStable and efficient synthesisStable and efficient tumor killing effectOrganic active ingredientsTransferasesUridine DiphosphoglucoseTumor therapy
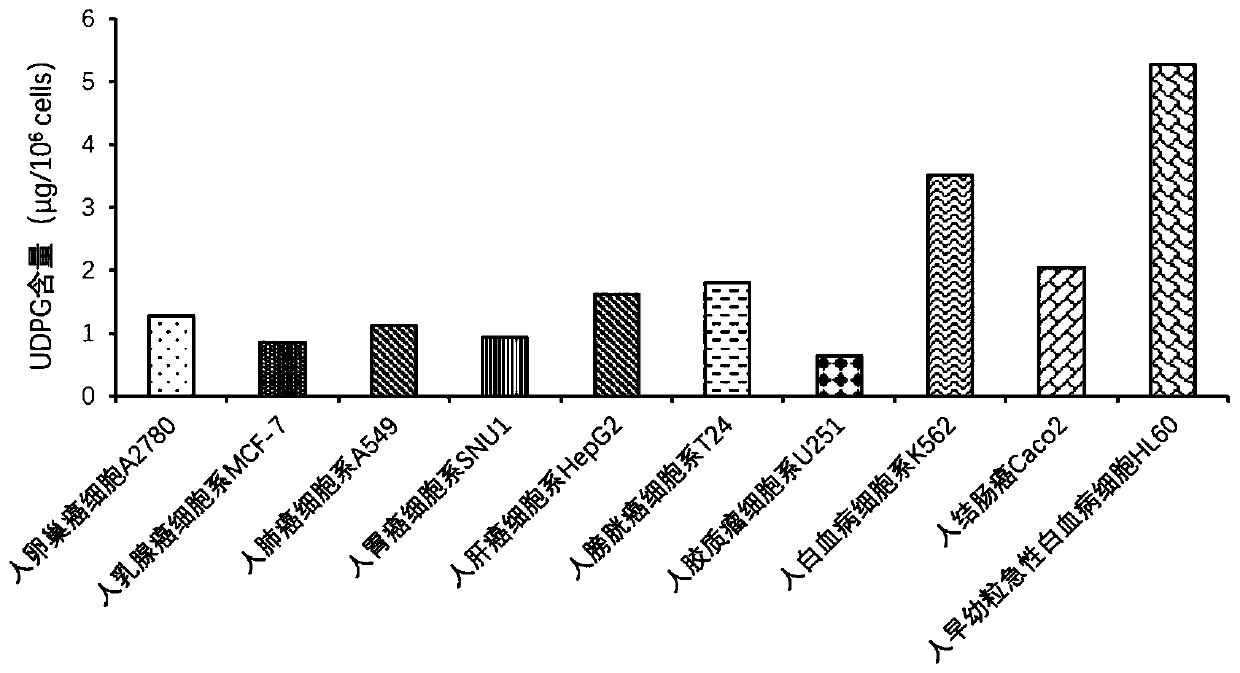
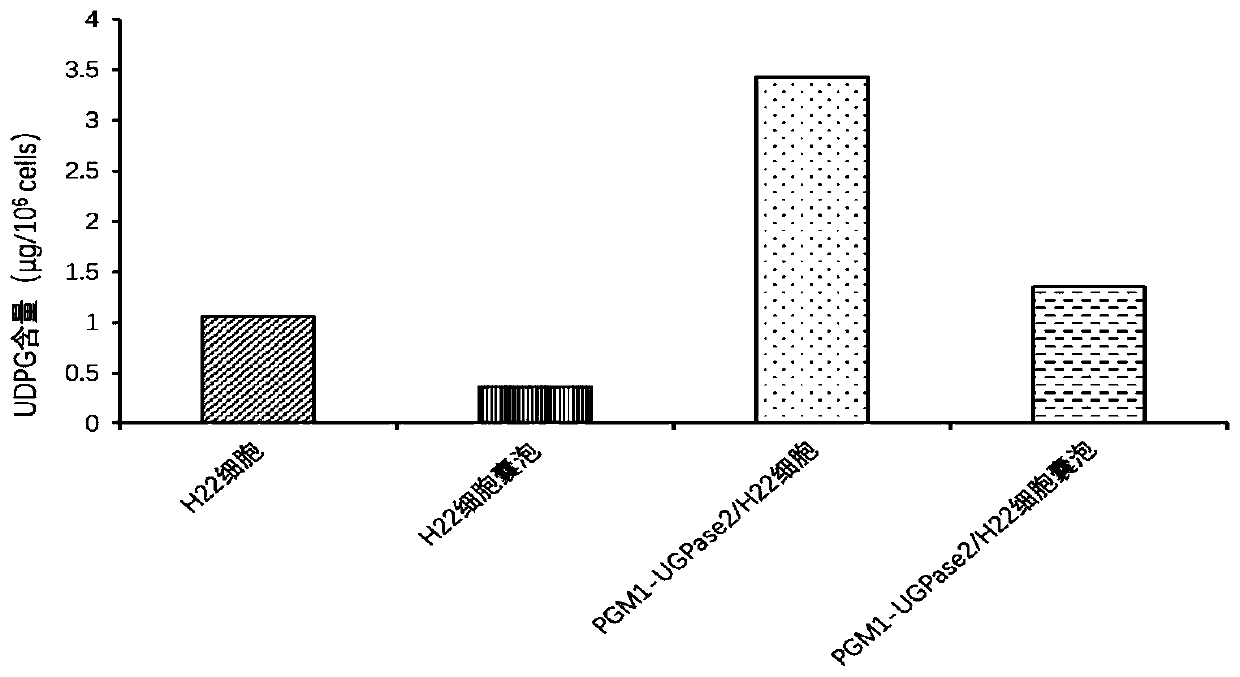
The invention relates to a drug-loaded vesicle. The drug-loaded vesicle comprises a vesicle derived from tumor cells and a therapeutic drug wrapped in the vesicle. The tumor cell-derived vesicle is avesicle released by apoptotic tumor cells, a large amount of uridine diphosphate glucose is wrapped in the vesicle, and the therapeutic drug is a tumor therapeutic drug serving as an effective component for treating tumors. The drug-loaded vesicle provided by the invention obtains a more stable and efficient tumor killing effect, and can better treat tumor diseases.
Owner:HUBEI SOUNDNY BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for preparing rebaudioside M through fermentation catalysis of bacillus subtilis
PendingCN114214378AReduce stepsLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a method for preparing rebaudioside M by fermentation catalysis of bacillus subtilis, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) connecting glycosyl transferase UGT76G1 and UGT11 genes to a PBR322 plasmid vector, guiding into the bacillus subtilis, inoculating into an LB culture medium, and culturing for 20-24 hours at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C and the speed of 100-250 rpm; (2) inoculating into a seed tank according to the inoculum size of 1%-10%, and culturing for 20-24 hours at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C at the speed of 200-400 rpm and the ventilation ratio of 0.1-1 V / V.min; (3) inoculating into a fermentation tank according to the ratio of 1%-10%, and culturing for 48-72 hours at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C and the pH value of 6-8 at the speed of 200-1000 rpm and the ventilation ratio of 0.1-2 V / V.min; (4) carrying out ceramic membrane ultrafiltration on the fermentation liquor, carrying out resuspension and high-pressure homogenization on the thallus, and carrying out ceramic membrane ultrafiltration on the thallus crushing liquor to obtain crude enzyme liquor; and (5) mixing stevioside, uridine diphosphate glucose, a phosphate buffer and the crude enzyme according to a mass ratio of (5-10): (1-5): (40-60): (5-20), and reacting at 25-40 DEG C for 12-48 hours. The method has the advantages that two crude enzyme solutions are obtained through one-time fermentation, the operation is simple, the cost is low, and the conversion rate is 88.4% or above.
Owner:ANHUI JINGHE IND
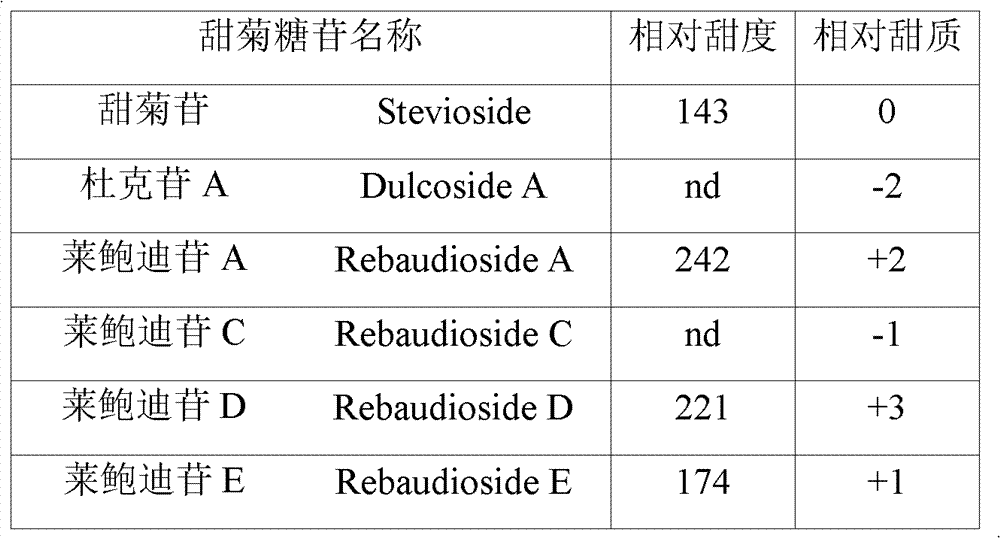
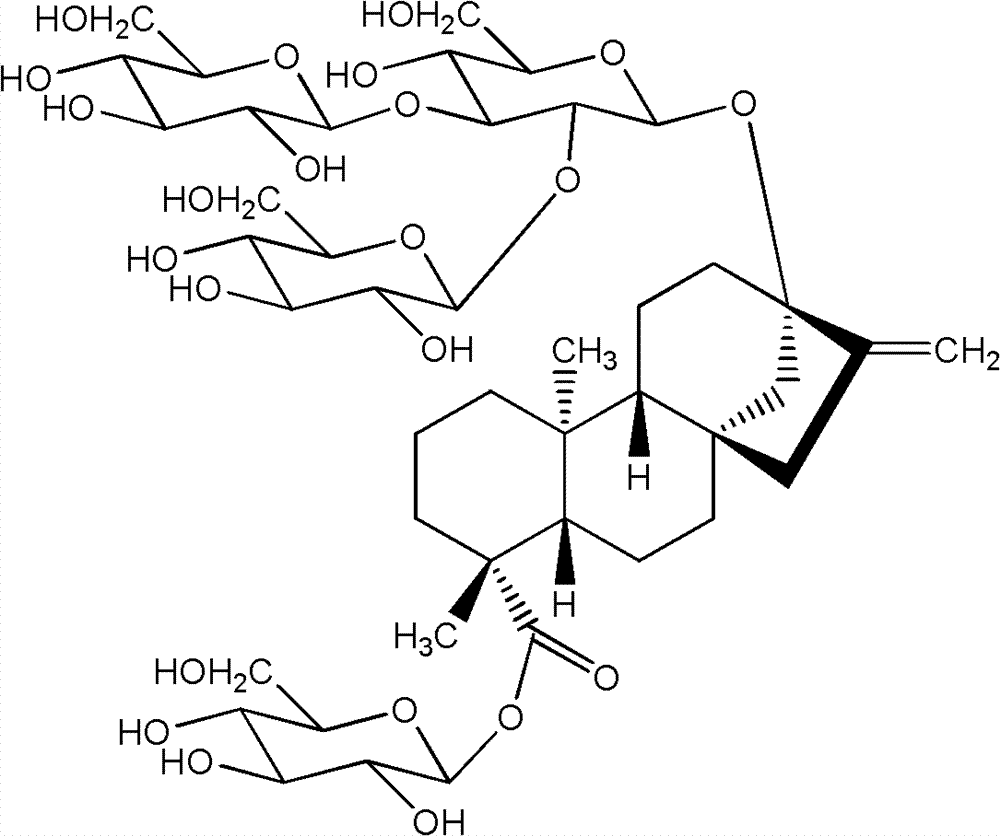
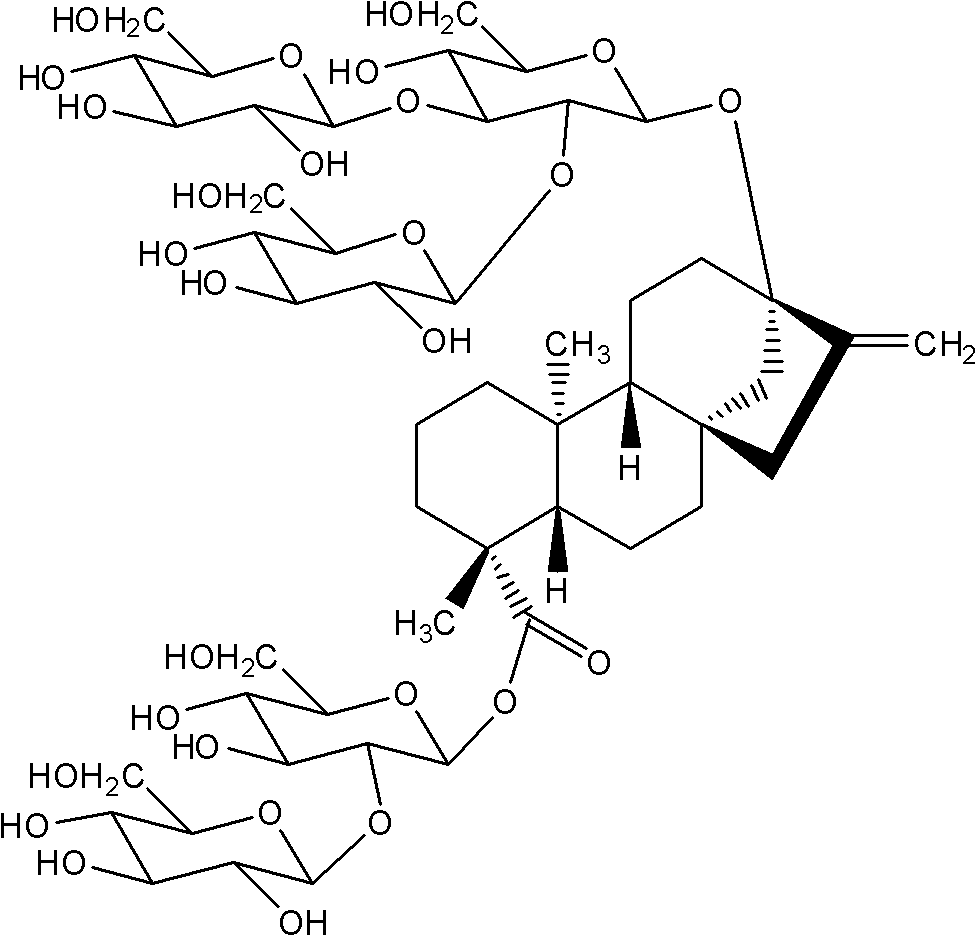
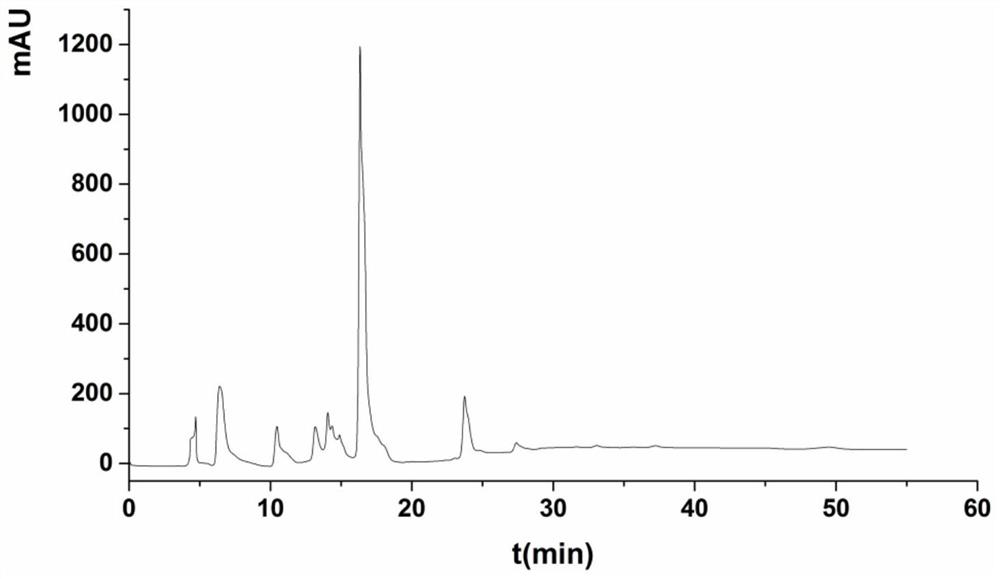
Stevia rebaudiana enzyme VI and method for converting rebaudioside-A into rebaudioside-D
The invention belongs to the field of food chemistry, and particularly relates to a method for converting RA (rebaudioside-A) which is taken as a raw material into RD (rebaudioside-D), and the key is stevia rebaudiana enzyme VI and a preparation method thereof. The converting method comprises the following steps: A, the RA of which the purity is higher than 90% is dissolved with water according to the weight measurement ratio of 1:6-1:10m / v; B, UDP-Glu (Uridine Diphosphate Glucose) is added according to the weight ratio that RA:UDP-Glu=15:5-15:9; C, the stevia rebaudiana enzyme VI is added according to the weight ratio that RA: stevia rebaudiana enzyme VI=(800-1200):1 (preferably 1000:1), and then reaction is carried out for 3-7h at the temperature of 40-60 DEG C and the pH of 6-8; and D, a reaction solution is filtered and dried to obtain RD-containing solid matter. The conversion rate of converting RA into RD is larger than or equal to 70%, and the RD content in the solid matter is 60%-70%, can achieve 80% after further separation and purification, and even can be larger than 90%.
Owner:SICHUAN INGIA BIOSYNTHETIC CO LTD
Preparation method of uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid
PendingCN112608960AAchieve recyclingReduce addNucleic acid vectorOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to a preparation method of uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid. Uridine diphosphate glucose is oxidized by uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase to generate uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid, and lactic dehydrogenase is added for double-enzyme coupling reaction, so that cyclic regeneration of NAD<+> is realized, the addition of NAD<+> is reduced, the cost is saved, and at the same time, the circulation of NAD<+> / NADH reduces the feedback inhibition effect of the byproduct NADH on the product uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid, and the generation amount of the target product can reach 1.01 mg / mL. The nucleotide sequence of lactic dehydrogenase is optimized and modified, so that the target protein can be better expressed in escherichia coli, and efficient synthesis of the target product uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid is facilitated. In-vitro reaction is adopted, a reaction system is more controllable, and compared with intracellular reaction, in-vitro reaction can be more beneficial to reaction under limited conditions.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and special engineering bacteria for method
ActiveCN112239771ARaw materials are easy to getLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseUridine Diphosphoglucose
The invention discloses a method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and special engineering bacteria for the method. The method for producing the uridine diphosphate glucose comprises the following steps of by using uridine monophosphate and sucrose as raw materials, producing the uridine diphosphate glucose under the action of the engineering bacteria, wherein the engineering bacteria arerecombinant bacteria for expressing functional protein and are obtained by introducing a gene for encoding the functional protein into starting bacteria, and the functional protein comprises polyphosphokinase, uridine monophosphate kinase and sucrose synthase. The method is of great significance to industrial production of the uridine diphosphate glucose.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing rebaudioside A by fermentation and catalysis of bacillus subtilis
PendingCN111593062AIncrease productionSolve the problems of low enzyme activity, complicated operation and high production costTransferasesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhosphate
The invention relates to a method for preparing rebaudioside A by fermentation and catalysis of bacillus subtilis. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, connecting a glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 gene onto a PBR322 plasmid vector, transferring the plasmid vector to a competent state of bacillus subtilis, inoculating the bacillus subtilis into an LB culture medium, andculturing at 30-37 DEG C for 20-24 h; 2, inoculating into a seed tank according to an inoculation amount of 1-10% volume ratio, culturing, introducing air, and culturing at 30-37 DEG C for 20-24 h; 3,inoculating into a fermentation tank according to an inoculation amount of 1-10% volume ratio, culturing, introducing air, controlling the pH to be 6-8, and culturing at 30-37 DEG C for 48-72 h; 4, carrying out filter pressing to obtain bacillus subtilis thalli, re-suspending, carrying out high-pressure homogeneous crushing, and carrying out filter pressing to obtain crude enzyme solution; and 5,mixing stevioside, uridine diphosphate glucose, phosphate buffer solution and the crude enzyme solution according to a mass ratio of (5-10): (1-5): (40-60): (5-20), and carrying out a reaction at 25-40 DEG C for 12-48 h. The method in the invention has the advantages that: the yield of the rebaudioside A is increased, and can reach 85.3 g / L; and the method is few in operation step, low in production cost and easy for industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI JINGHE IND
Method for preparing uridine diphosphate glucose by means of immobilized enzyme method
PendingCN110846361AImprove responseReaction is easy to controlOn/in organic carrierFermentationNucleotideEnzyme catalysis
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a method for preparing uridine diphosphate glucose by means of an immobilized enzyme method. The method specifically comprisesthe steps of: (1) preparing UDPG (uridine diphosphate glucose) production enzymes; (2) immobilizing the UDPG production enzymes; and (3) separating a product. According to the invention, two UDPG production enzymes UGP and SPA are adopted, and the UDPG can be synthesized by just two-step enzymatic reaction; compared with a complex process for producing UDPG by chemical and fermentation methods, the method here has a simpler reaction process, with the reaction easier to control, and the product quality being more stable; the UDPG is prepared by means of an immobilized enzyme catalysis method,and the immobilized enzymes can be continuously and repeatedly used many times, so that the production cost is greatly reduced; in addition, a large amount of pigments, other types of nucleotides andother impurities introduced by the use of yeast are avoided, so that purification is easier; the method is suitable for large-scale production of UDPG.
Owner:美亚药业海安有限公司
Cultivation method and application of a plant containing salidroside
The invention provides a method for cultivating plants containing salidroside. The method comprises the following steps: spraying p-hydroxyphenylethanol on growing plant leaves, and harvesting to obtain plants containing salidroside. The method provided by the invention has simple steps. The synthetic precursor of salidroside, p-hydroxyphenylethanol, is directly supplied from the outside, and the uridine diphosphate glucose and glucosyltransferase contained in the plant itself are used as raw materials to synthesize the salidroside in the plant. Tianglycoside. The present invention further protects the application of the salidroside-containing plants obtained through cultivation.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
A method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and its special engineering bacteria
ActiveCN112239771BRaw materials are easy to getLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseGlucose phosphate
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
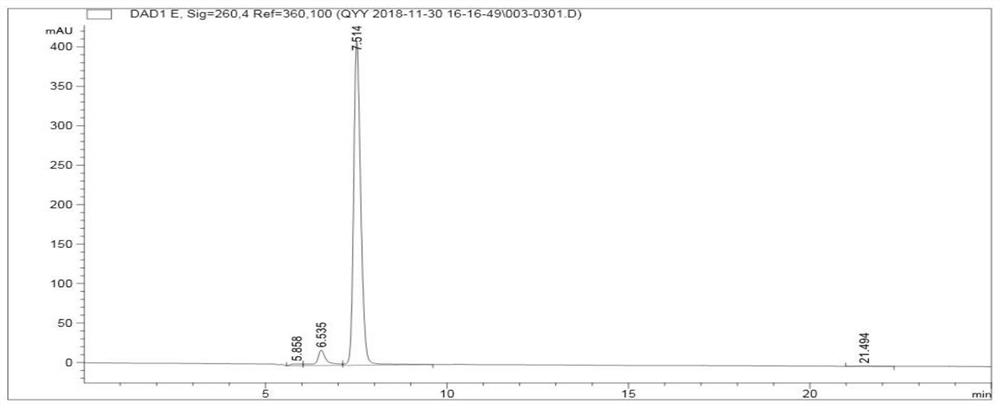
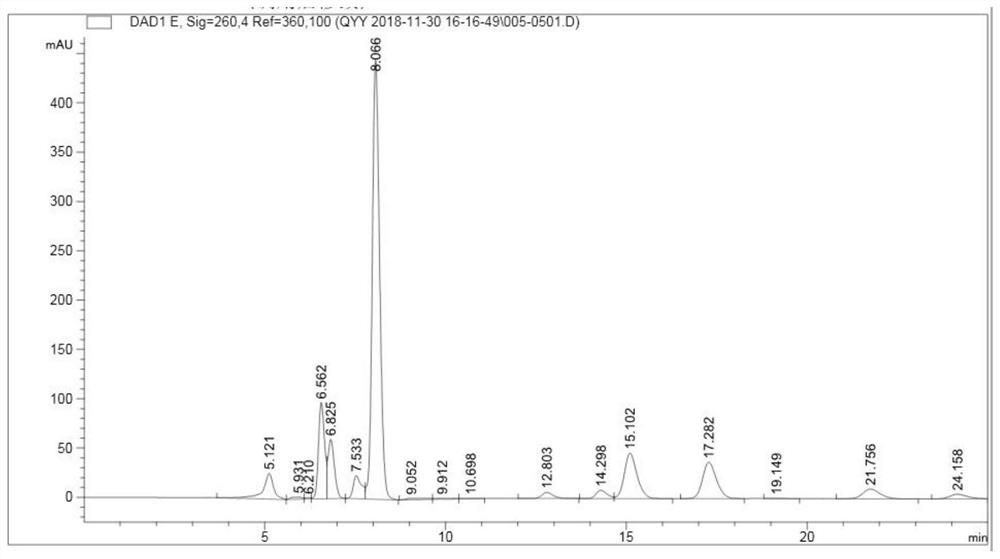
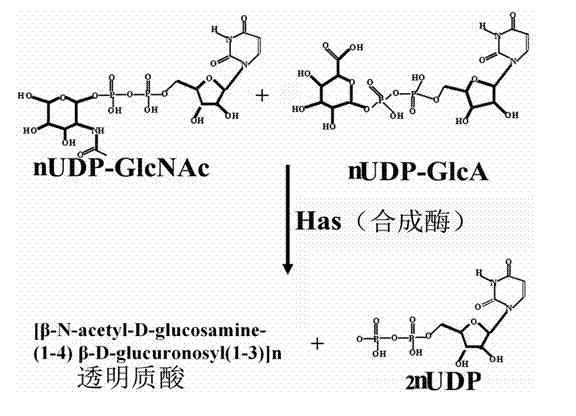
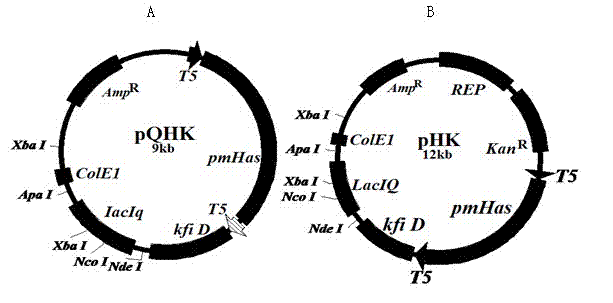
Engineering escherichia coli capable of efficiently producing hyaluronic acid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102154190BIncrease productionHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHyaluronan synthetase
The invention provides an engineering escherichia coli capable of efficiently producing hyaluronic acid (HA) and a preparation method thereof. The engineering escherichia coli is obtained by transferring escherichia coli through constructing recombinant expression vector commonly expressed in escherichia coli by gene Has containing HA synthetase and gene containing uridine diphosphate glucose phosphate dehydrogenate. The engineering escherichia coli capable of efficiently producing HA, provided by the invention, is pHK / JM109 with CGMCC No.3926. The engineering escherichia coli provided by the invention can produce 29-2.5g / L of HA. Compared with the yield in the prior art, the highest yield of HA obtained from gene spHas synthesized by Gram positive strep HA which is expressed in escherichia coli is enhanced by about more than 10 times.
Owner:MICROBIAL FERMENTATION ENG RES CENT CO LTD OF YUNNAN PROVINCE
a drug-loaded vesicle
ActiveCN111067868BStable and efficient synthesisStable and efficient tumor killing effectOrganic active ingredientsTransferasesUridine DiphosphoglucoseTumor therapy
The invention relates to a drug-loaded vesicle, comprising a tumor cell-derived vesicle and a therapeutic drug encapsulated in the vesicle, wherein the tumor cell-derived vesicle is a vesicle released by an apoptotic tumor cell and the vesicle A large amount of uridine diphosphate glucose is encapsulated in the vesicles, and the therapeutic drug is a tumor therapeutic drug as an effective component for treating tumors. The drug-loaded vesicle of the present invention has a more stable and efficient tumor-killing effect, and can better treat tumor diseases.
Owner:HUBEI SOUNDNY BIOLOGICAL TECH
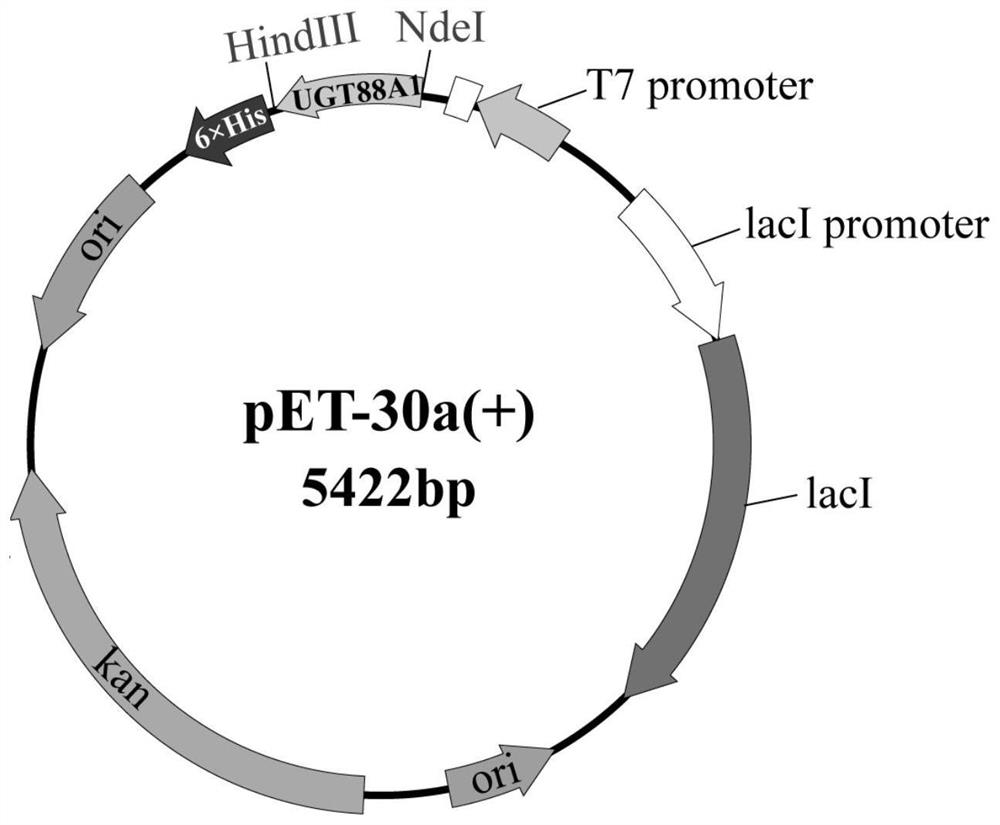
Grifola frondosa UDP glucosyltransferase as well as coding gene and application thereof
PendingCN114214296AIn vitro catalytic synthesis with a high degree of polymerizationHigh degree of polymerizationBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention provides grifola frondosa UDP (User Datagram Protocol) glucosyltransferase as well as a coding gene and application thereof, and belongs to the field of edible mushroom molecular biotechnology and genetic engineering. According to the invention, UDP (User Datagram Protocol) glucosyltransferase UGT88A1 is obtained by cloning from Grifola frondosa and is named as GUFGT88A1, and the amino acid sequence of the UDP glucosyltransferase UGT88A1 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2; the UDP glucosyltransferase is glucosyltransferase on which uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) depends; the UDP glucosyltransferase can be used for catalyzing polysaccharide synthesis.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Recombinant Microorganism for Producing 2,3-Butanediol and a Method of Production of 2,3-Butanediol
A recombinant microorganism for producing 2,3-butanediol consisting of selecting at least three groups from uridine diphosphate glucose phosphate uroglycan transferase gene (galU), acetyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene (acoA), acetyl phosphate transferase gene (pta), adenosine glucosylphosphate transferase gene (glgC), lactose dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), and phosphodiesterase gene (pdeC) which were modified.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION
A method for synthesizing sucrose-6-phosphate by using recombinant high temperature resistant sucrose phosphate synthase
ActiveCN110885804BHigh temperature resistantCatalytic generationMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliO-Phosphoric Acid
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
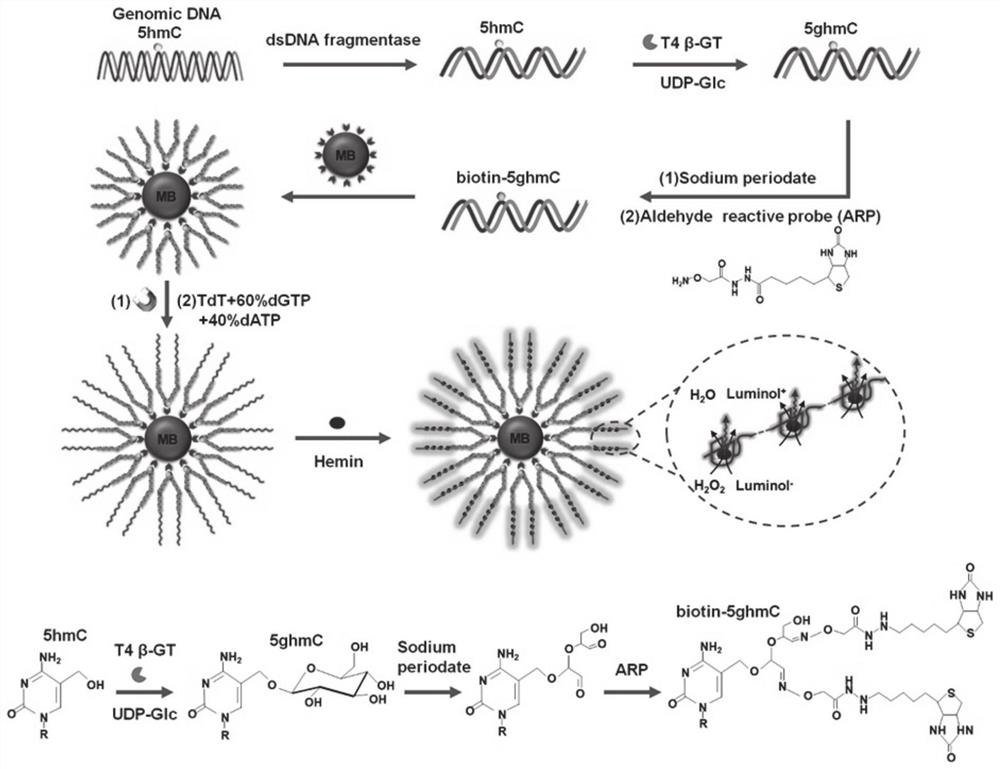
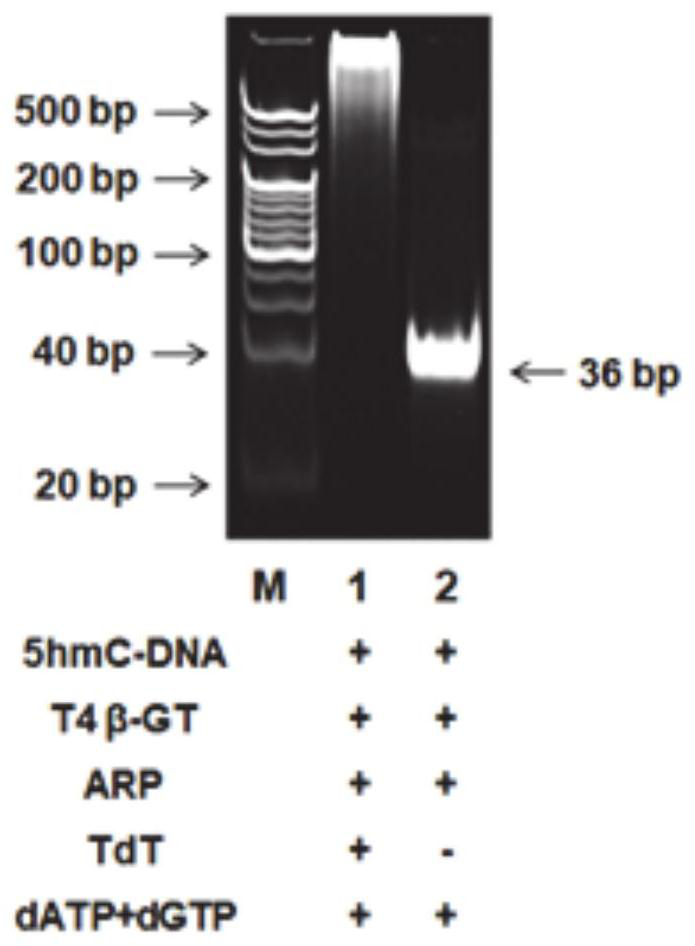
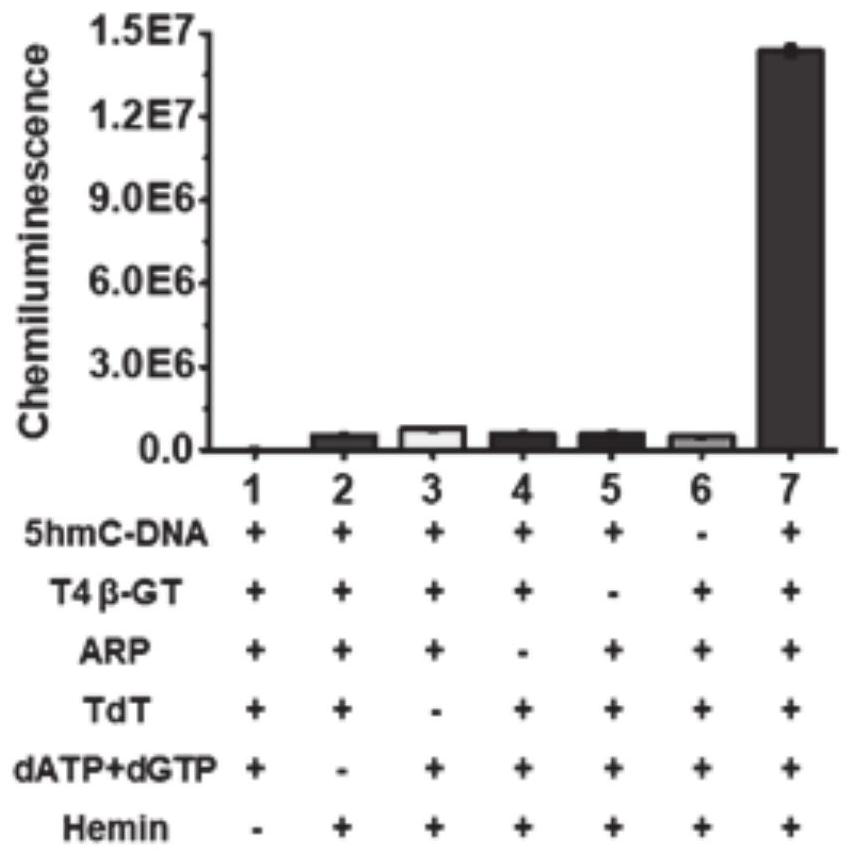
A chemiluminescent biosensor for detecting 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its detection method and application
ActiveCN112326637BIngenious designEasy to operateChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceNucleic Acid ProbesGenome wide analysis
The invention provides a chemiluminescence biosensor for detecting 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, a detection method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular detection. The chemiluminescent biosensor of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine includes T4 bacteriophage β-glucosyltransferase, uridine diphosphate glucose, sodium periodate, aldehyde group reaction probe ARP, terminal transferase, hemoglobin and luminol solution. The hydroxymethylcytosine-glycosylation, periodate oxidation, biotinylation-isothermal signal amplification strategy designed in the present invention does not need to change the reaction temperature, nor does it require a special labeled nucleic acid probe or a specific template for signal amplification , which can detect 5hmC of any sequence in genomic DNA and does not involve isotopic labels or specific antibodies, eliminating radioactive hazards and misinterpretation of genome-wide mapping data in antibody-based experiments. This enables genome-wide analysis of 5hmC in a limited number of biological and clinical samples.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Improvement of Astragaloside content by endogenous gene overexpression technology
InactiveCN1314804CImprove pharmacological activityImprove survival rateOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationAstragalosideUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
The invention discloses an improvement of Astragaloside content by endogenous gene overexpression technology, wherein the two metabolism reaction coupled key enzyme genes of the polysaccharide metabolic pathway, i.e., ugp gene (uridine diphosphate glucose phosphorylase gene) and gbss gene (adenosine diphosphate glucose glycoside transferase gene) are modified in vitro, so as to reinforce the enhanced expression regulation element and construct intermediate carrier, and electrical perforation method is employed to transfer the expression intermediate carrier pBI-UG into Agrobacterium rhizogenes LBA-9402, thus obtaining polysaccharide synthesize double gene Radix Astragali hairyroot.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
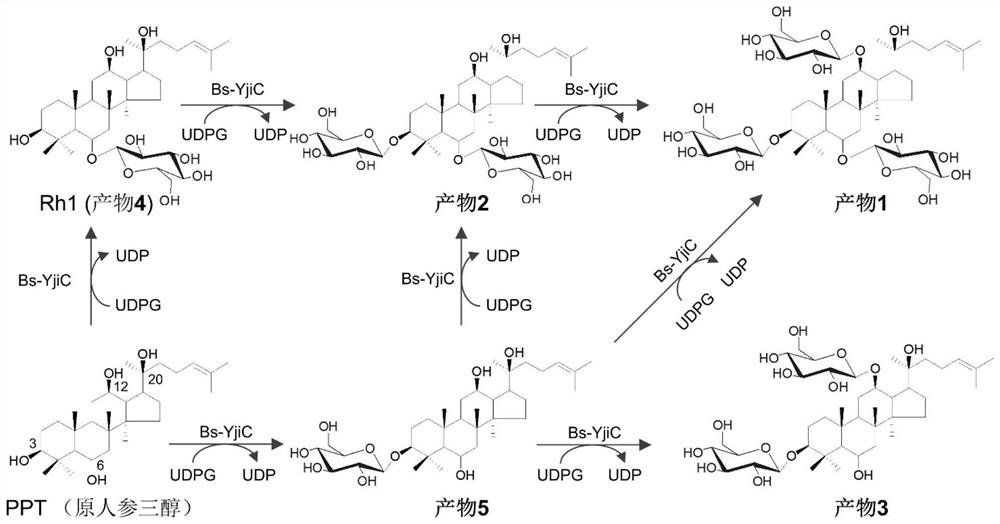
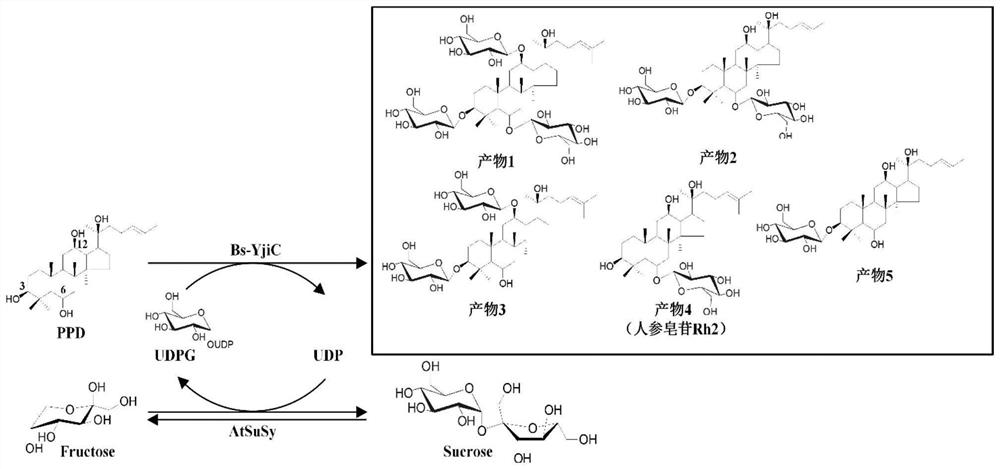
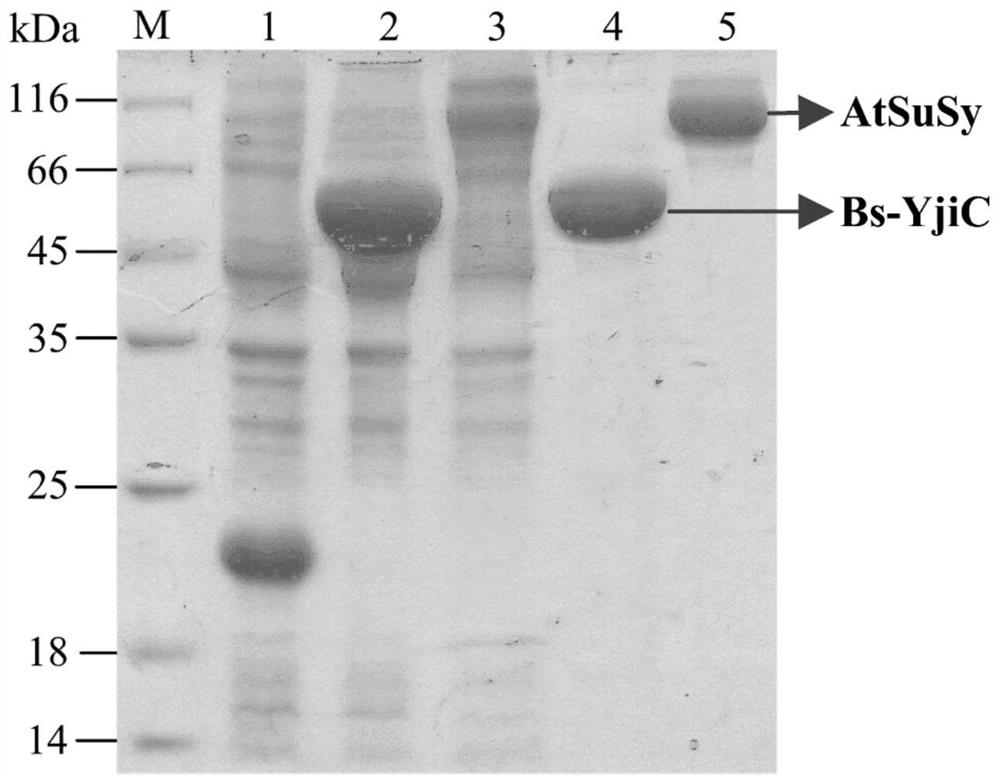
A group of synthetic methods of natural and unnatural protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides
ActiveCN109796516BUnique pharmacological activityIncrease productivityTransferasesSteroidsSucrose synthetasePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for biocatalytically synthesizing natural and non-natural protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides. The invention uses protopanaxatriol (PPT) as a substrate and glycosyltransferase as a catalyst, which can efficiently It catalyzes the glycosylation of the C3, C6 and C12 hydroxyl groups of protopanaxatriol to generate a variety of natural and non-natural protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides. The invention also discloses a method for synthesizing various natural and non-natural protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides by utilizing sucrose synthase and glycosyltransferase coupling reaction to catalyze protopanaxatriol. The method can use cheap sucrose and a small amount of ginsenosides. Using uridine diphosphate as a cofactor for the reaction can realize the recycling and regeneration of expensive uridine diphosphate glucose, thereby catalyzing protopanaxatriol to synthesize various natural and non-natural protopanaxatriol-type ginseng in a more efficient and inexpensive way. saponins.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
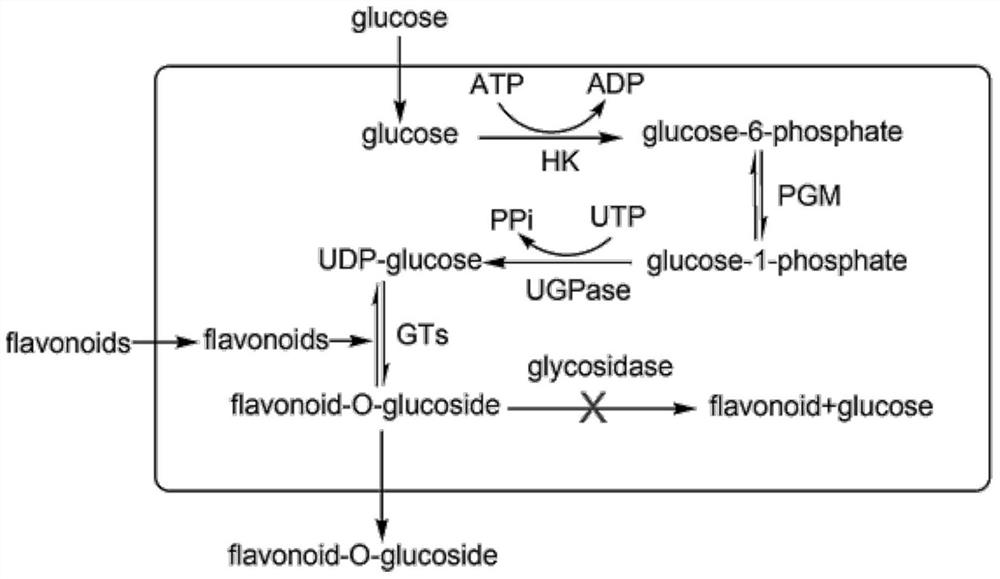
A genetically engineered bacterium that catalyzes the glucosidation of flavonoids and its application
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of a flavonoids compound and an application thereof. Specifically, a Beta-glycoside hydrolases gene of a chassis biological cell is removed according to the genetically engineered bacterium, and endogenous degradation of a glycosylation product is reduced; the high-expression regulation is performed to two key enzymes of glucophosphomutase (PGM) and uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGP1) of the chassis biological cell for participating in the synthesis of glycosylated-donor uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-Glu), and a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene for catalyzing the flavonoid aglycones glucose glycosylation is combined so as to obtain a genetically engineered strain for effectively catalyzing the glucose glycosylation of the flavonoids compound, and finally scutellarein is used as a catalytic substrate for fermenting for 54 h in 10 L of a fermentation tank, wherein the yield of scutellarein-7-O-glucose of the glycosylation product is up to 1200 mg / L. The used strategy provides a technology reference for biologically-catalyzing chemical micromolecular glycosylation by using a microbiological method.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for preparing rebaudioside D through fermentation catalysis of bacillus subtilis
PendingCN114150031ASolve the problems of low enzyme activity, complicated operation and high production costReduce stepsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a method for preparing rebaudioside D by fermentation catalysis of bacillus subtilis, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) inoculating glycosyl transferase UGT76G1 and AtSUSY genes to a PBR322 plasmid vector, guiding into the bacillus subtilis, inoculating into an LB culture medium, and culturing for 20-24 hours at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C and the speed of 100-250 rpm; (2) inoculating into a seed tank according to the inoculation amount of 1%-10%, and culturing for 20-24 hours at the temperature of 30-37 DEG C at the speed of 200-400 rpm and the ventilation ratio of 0.1-1 V / V.min; (3) inoculating into a fermentation tank according to the volume ratio of 1%-10%, and culturing for 48-72 hours under the conditions that the speed is 200-1000 rpm, the ventilation ratio is 0.1-2 V / V.min, the temperature is 30-37 DEG C and the pH value is 6-8; (4) carrying out ultrafiltration on the fermentation liquor by adopting a ceramic membrane, resuspending bacteria, carrying out high-pressure homogeneous crushing, and carrying out ultrafiltration on the crushed liquor by adopting the ceramic membrane to obtain crude enzyme liquor; and (5) mixing stevioside, uridine diphosphate glucose, a Tris-HCl buffer solution and the crude enzyme solution according to a mass ratio of (5-10): (1-5): (40-60): (5-20), and reacting at 25-40 DEG C for 12-48 hours. The method has the advantages that two crude enzymes are obtained through one-time fermentation, the cost is low, and the conversion rate of rebaudioside D reaches 88-90 g / L.
Owner:ANHUI JINGHE IND
A method for enzymatically synthesizing 3-o-glucosylglycyrrhetinic acid
ActiveCN107502599BHigh catalytic efficiencyMild reaction conditionsTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a method for enzymatically synthesizing 3-O-glucosylglycyrrhetinic acid, which belongs to the field of bioengineering and technology. The present invention clones or chemically synthesizes the glycosyltransferase genes Unigene14953, Unigene20323UGT73C11, UGT73C5 and UGT73C6 from plants Glycyrrhiza thaliana, European mountain thaliana or Arabidopsis, preferably Escherichia coli as a host bacterium, and constructs a genetically engineered bacterium containing glycosyltransferase. 3-O-glucosylglycyrrhetinic acid can be efficiently synthesized by using recombinant glycosyltransferase to act on the substrates glycyrrhetinic acid and uridine diphosphate glucose under the conditions of pH 5.0-11.0 and temperature 25-55°C.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A kind of tea tree sucrose synthase cssus587, preparation method and application
ActiveCN109943547BHigh synthesis efficiencyReduce manufacturing costTransferasesFermentationSucrose synthetaseUridine diphosphate
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and in particular relates to a tea tree sucrose synthase CsSUS587, a preparation method and an application, comprising using tea tree cDNA as a template, designing primers, and PCR amplifying a target gene; Transform into competent cells; separation and purification of tea tree sucrose synthase. The sucrose synthase CsSUS587 prepared by the invention has high purity, can promote uridine diphosphate and sucrose to catalyze the generation of uridine diphosphate glucose which can be used for glycoside synthesis, and can be used in combination with glycosyltransferase to improve the synthesis efficiency of corresponding glycosides.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com