Method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and special engineering bacteria for method
A technology of uridine diphosphate glucose and uridine monophosphate, which is applied in the field of production of uridine diphosphate glucose, and can solve the problems of harsh reaction conditions, long reaction time, and low yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Embodiment 1, the construction of recombinant expression vector
[0067] 1. Replace the fragment between the XhoI and SpeI restriction sites of the pBAD-hisB vector with the DNA molecule shown in Sequence 2 to obtain the recombinant expression vector pBAD-GS-AT-EC-1 (sequenced and verified).
[0068] In sequence 2 of the sequence listing, positions 1-1029 from the 5' end encode a polyphosphate kinase derived from Gemmobacter sp.LW-1, positions 1041-3467 encode a sucrose synthase derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, and position 3479 -4204 encodes a uridine monophosphate kinase derived from Escherichia coli.
[0069] The DNA molecule shown in Sequence 2 of the Sequence Listing encodes the protein shown in Sequence 1. In sequence 1 of the sequence listing, positions 1-342 from the N-terminus are polyphosphate kinases derived from Gemmobacter sp.LW-1, positions 343-1150 are sucrose synthases derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, and positions 1151- Position 1391 is uridine mo...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Embodiment 2, the preparation of recombinant engineered bacteria
[0077] 1. The recombinant expression vector pBAD-GS-AT-EC-1 prepared in Example 1 was introduced into Escherichia coli BW25113 to obtain recombinant engineering bacteria TY001.
[0078] 2. The recombinant expression vector pBAD-GS-GM-EC-2 prepared in Example 1 was introduced into Escherichia coli BW25113 to obtain recombinant engineering bacteria TY002.
[0079] 3. The recombinant expression vector pBAD-GS-AC-EC-3 prepared in Example 1 was introduced into Escherichia coli BW25113 to obtain recombinant engineering bacteria TY003.
[0080] 4. Introduce the pBAD-hisB vector into Escherichia coli BW25113 to obtain a control recombinant engineered bacterium.
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3, utilize recombinant engineered bacterium to produce uridine diphosphate glucose
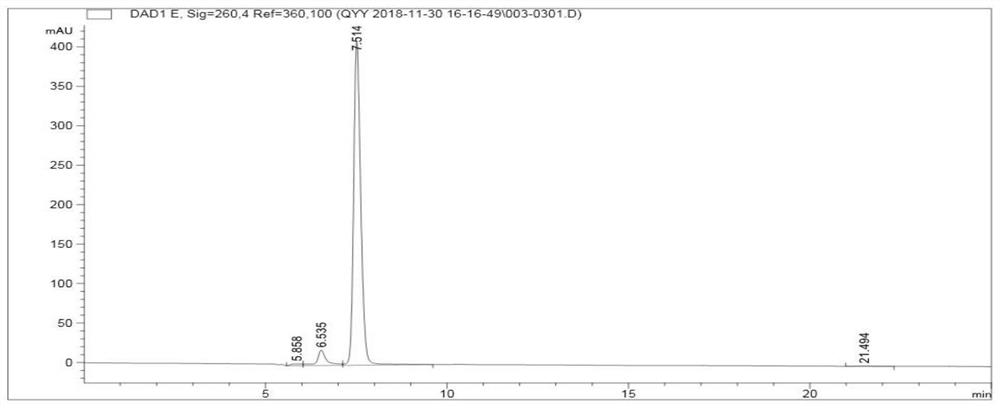
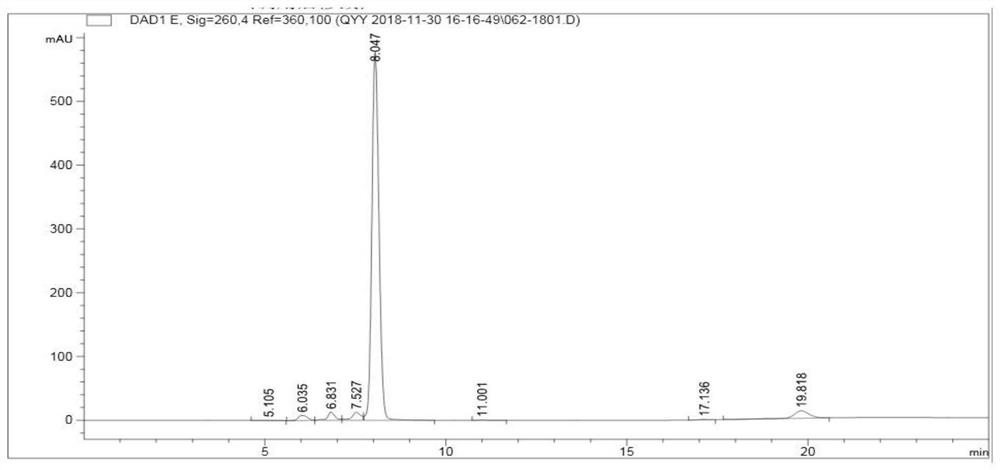
[0082] Synthetic principles such as Figure 4 shown.
[0083] 1. Utilization of recombinant engineering bacteria TY001 to produce uridine diphosphate glucose
[0084] 1. The recombinant engineered bacteria TY001 prepared in Example 2 was inoculated into 2YT liquid medium containing 50 μg / ml streptomycin, cultivated at 37° C. and 220 rpm until the OD was 0.8, and arabinose (Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) was added to the culture system. Co., Ltd., product number: S11032) (the concentration of arabinose in the culture system is 0.2mM), after induction culture at 30°C and 220rpm for 16 hours, the culture system was collected, centrifuged at 4°C and 8000rpm / min for 10min, and the bacterial pellet was collected.
[0085] 2. Use 50mM sodium citrate buffer (pH5.5) to resuspend the bacterial pellet obtained in step 1, ultrasonically (power 195W) for 10min, then add uridin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com