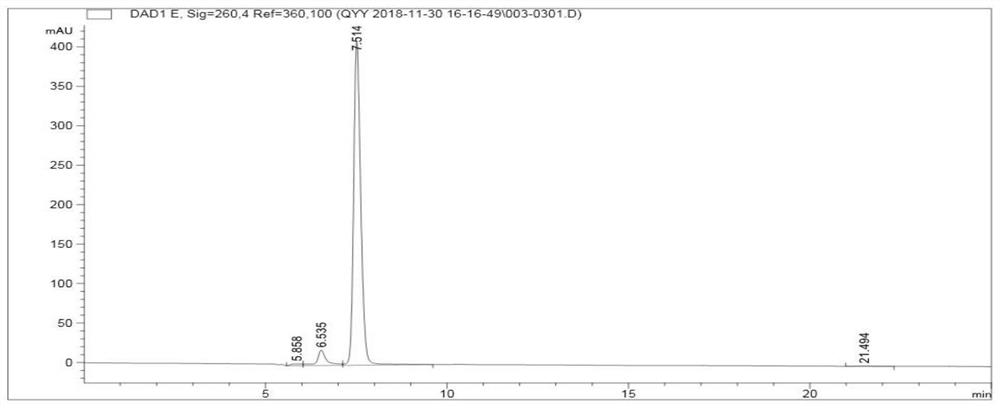
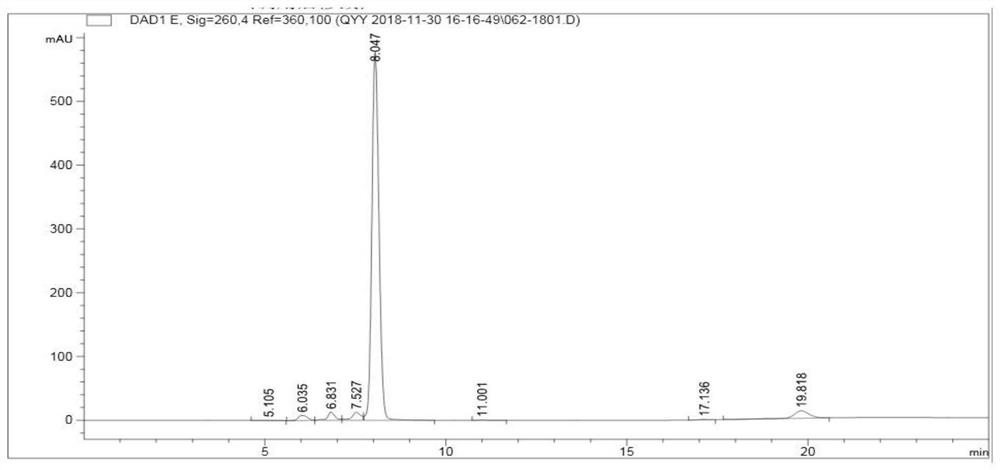
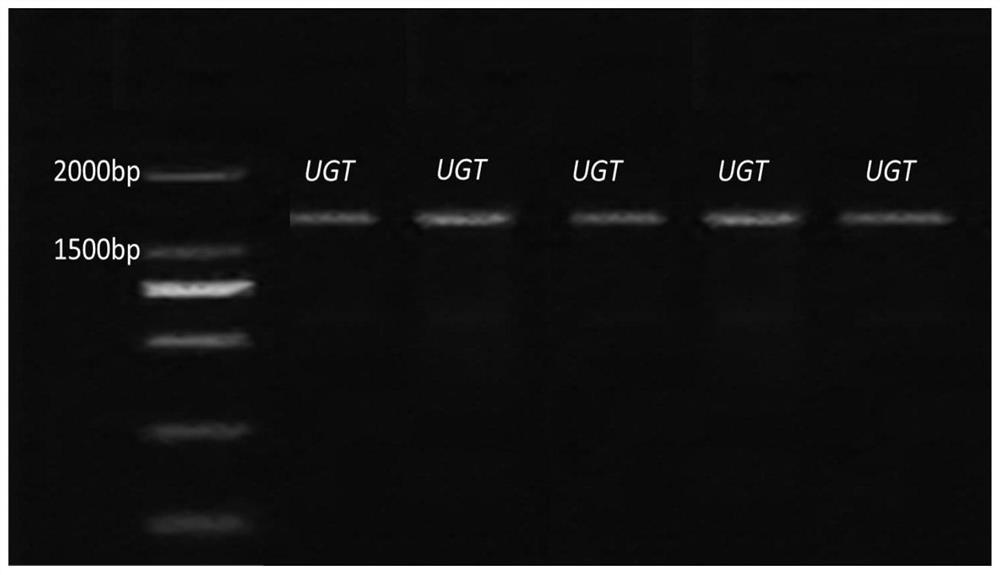
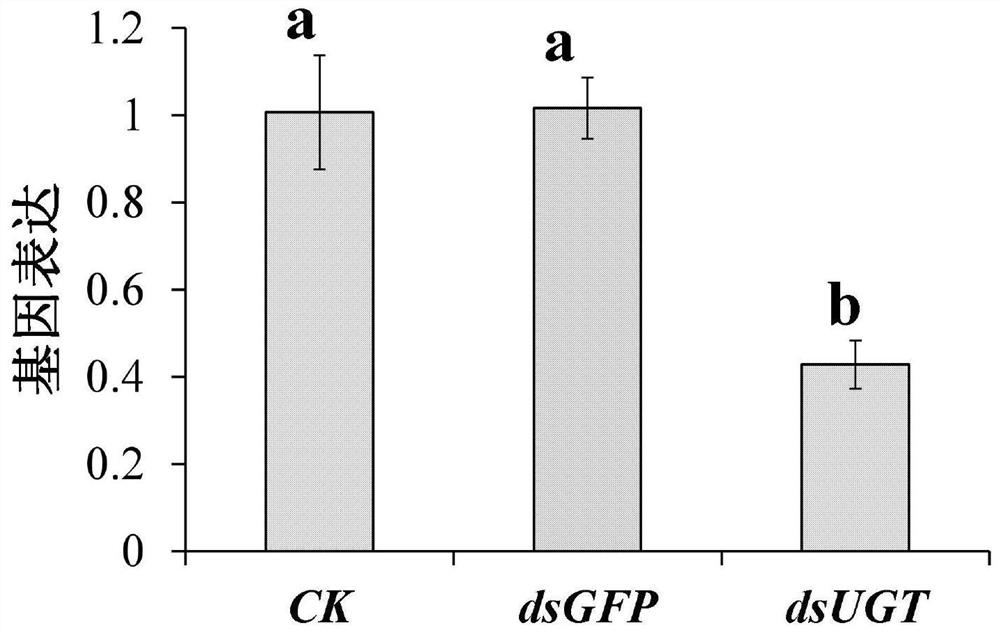
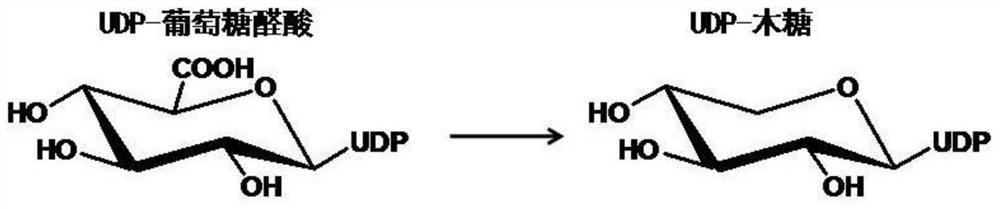
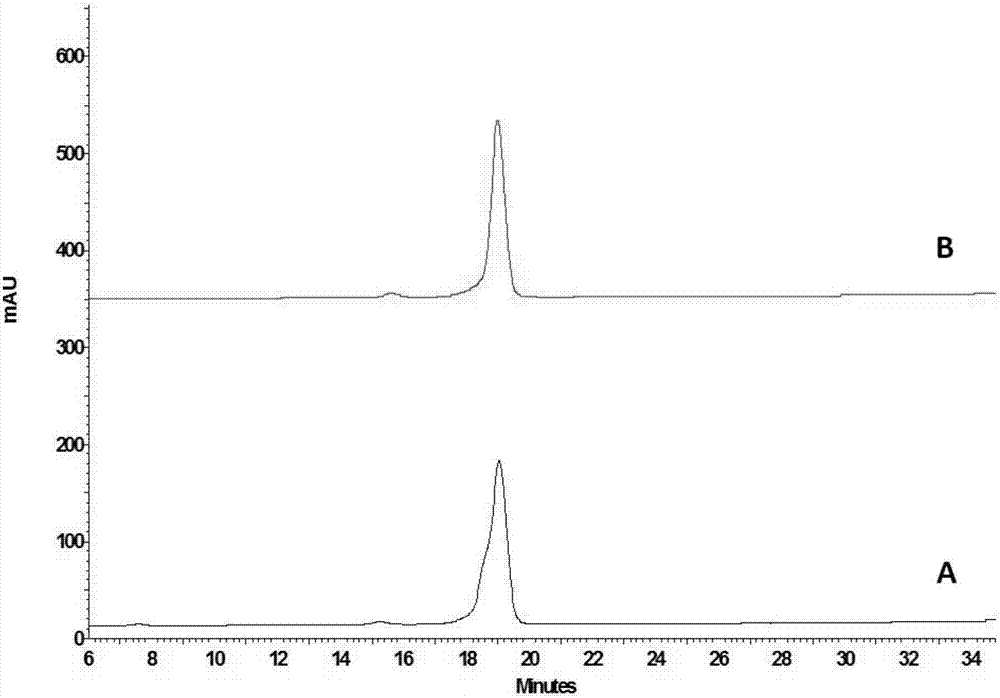
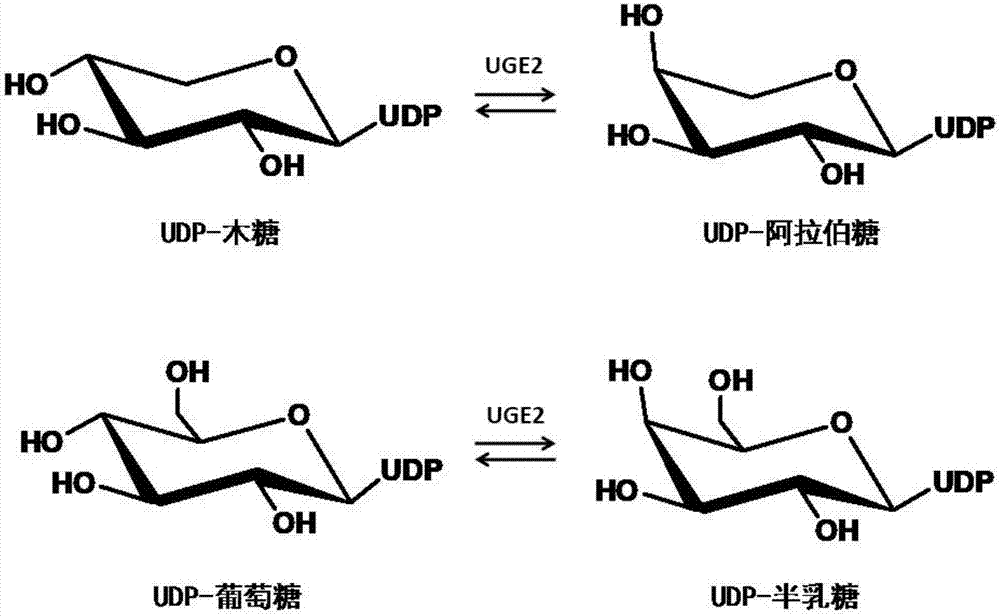
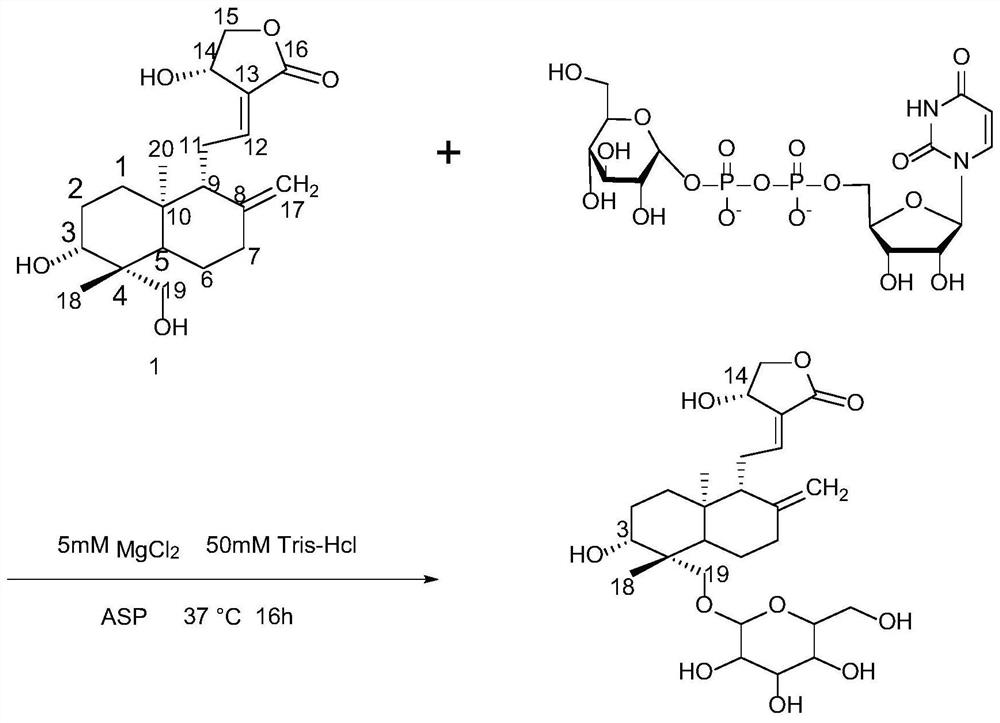
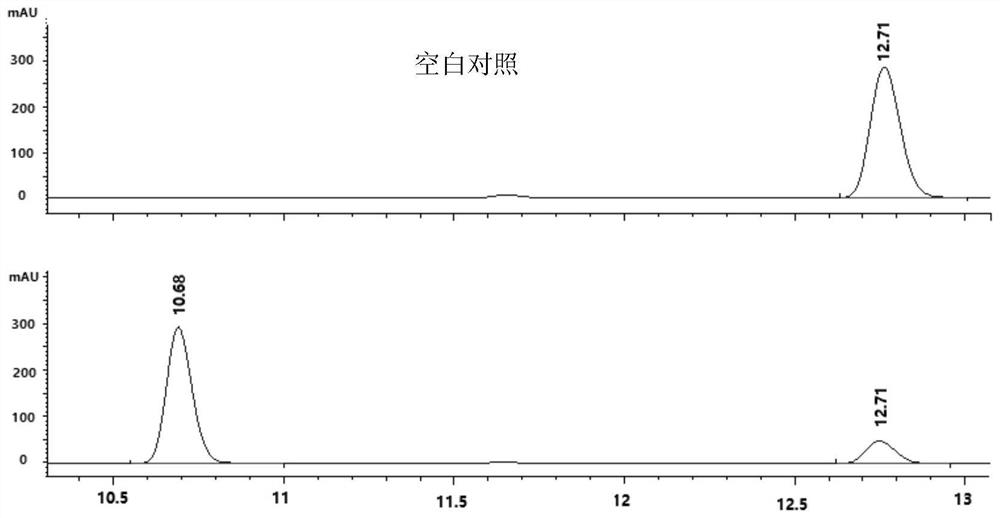
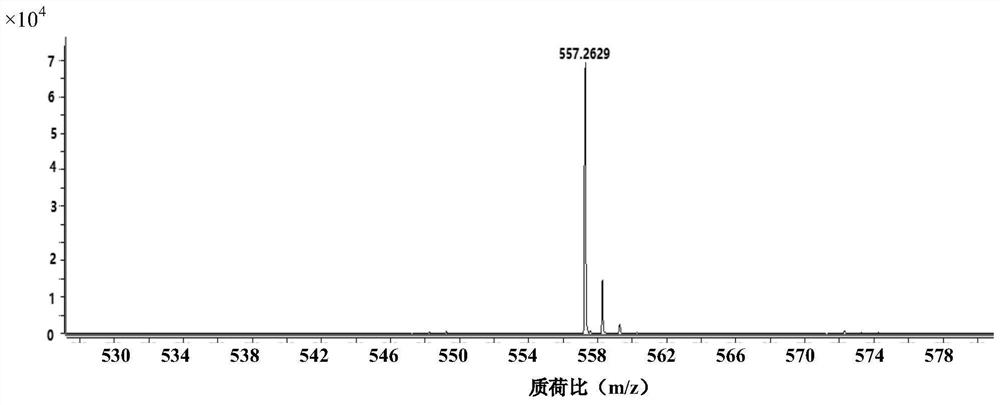
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Uridine Diphosphoglucose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid with enzymic method
ActiveCN107502599AHigh catalytic efficiencyMild reaction conditionsTransferasesGenetic engineeringChemical synthesisEscherichia coli
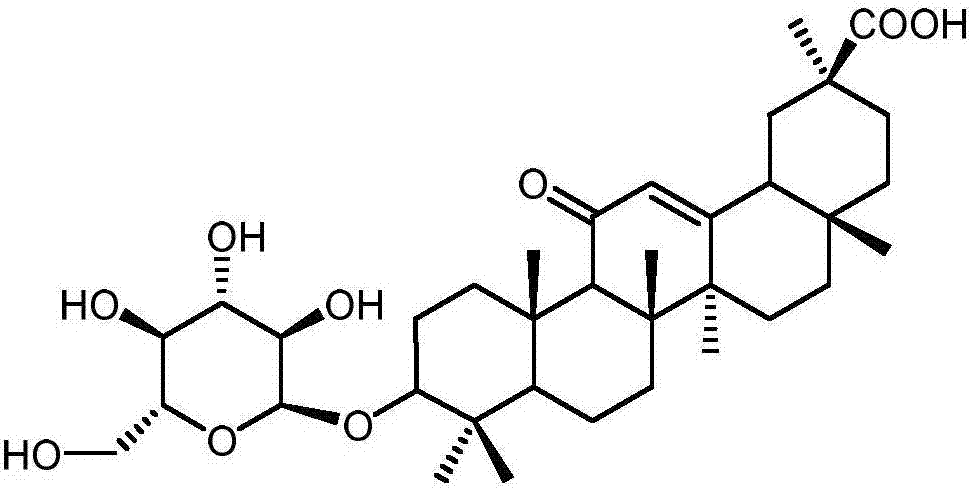
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid with an enzymic method and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. Glycosyltransferase gene Unigene14953, Unigene20323UGT73C11, UGT73C5 and UGT73C6 from plant licorice, barbarea vulgaris or Arabidopsis are cloned or chemically synthesized, escherichia coli is preferably selected as host bacteria, and genetically engineered bacteria containing glycosyl transferase is established; recombinant glycosyl transferase serves as glycyrrhetinic acid substrate and uridine diphosphate glucose, and 3-O-glucose-glycyrrhetinic acid can be synthesized efficiently in pH value of 5.0-11.0 and at the temperature of 25-55DEG C conditions.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
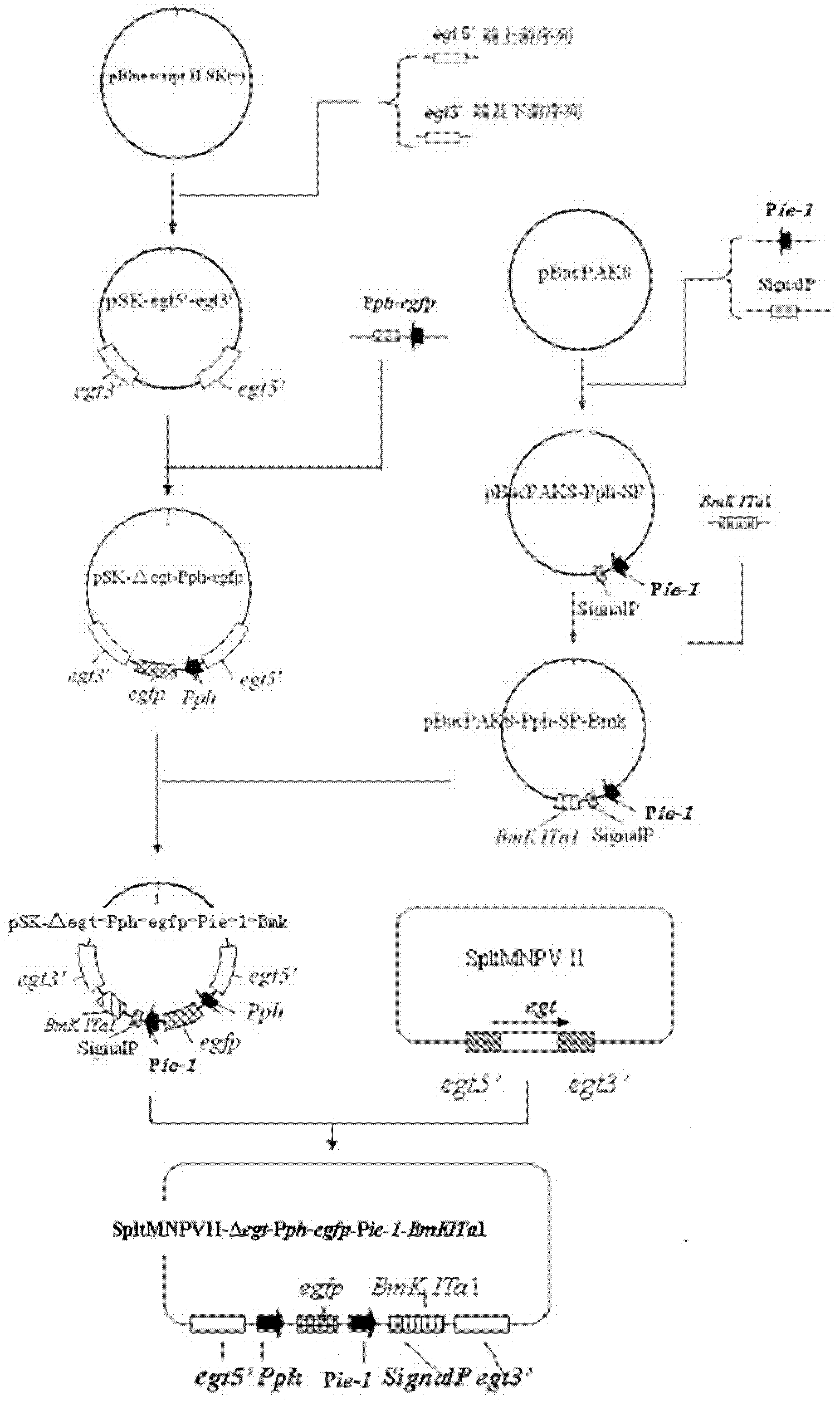
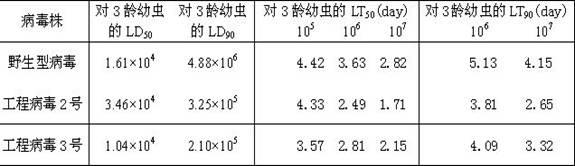
Prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and building method thereof
InactiveCN102329783AFast insecticideLow dose effectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeUridine diphosphate
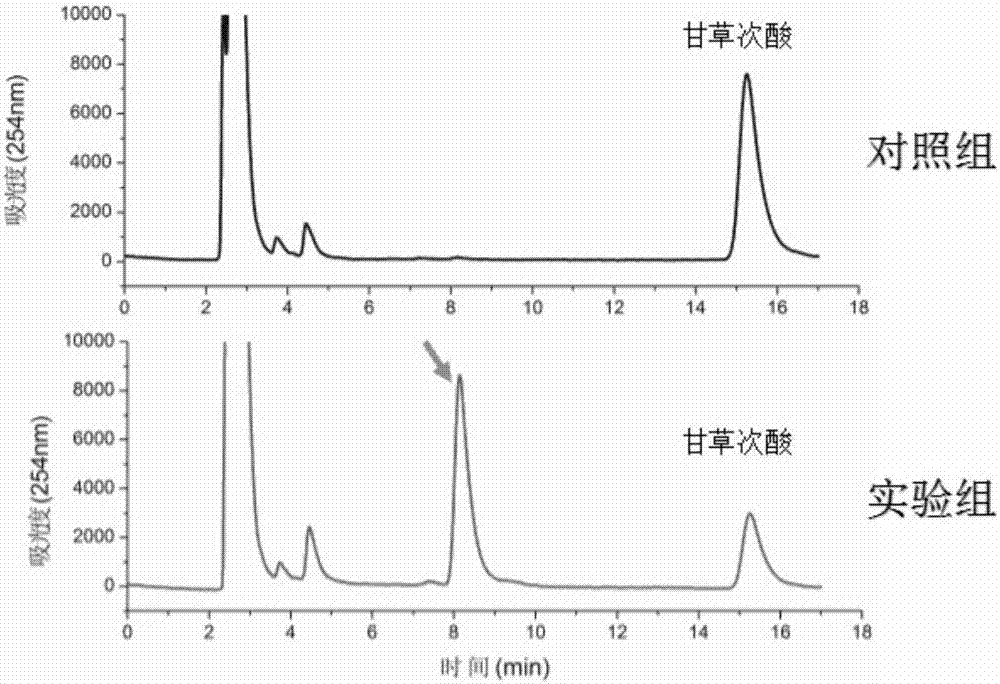
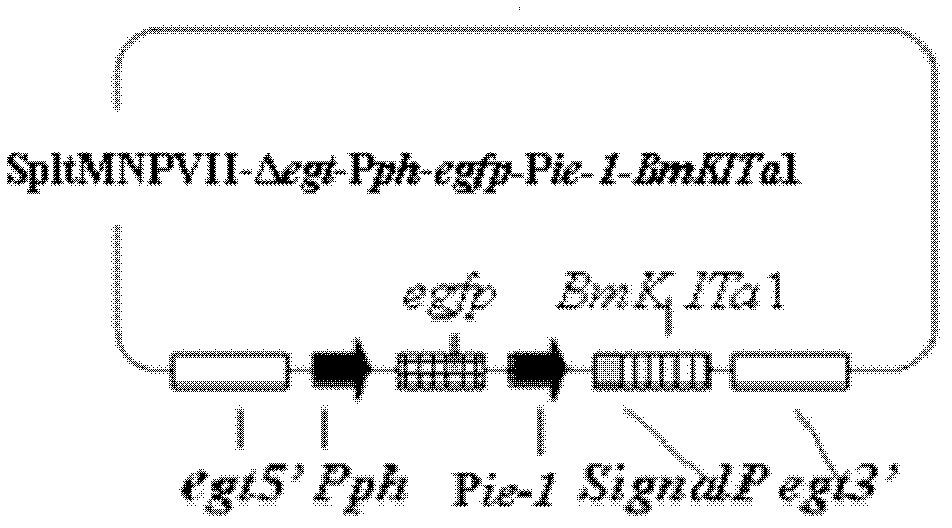
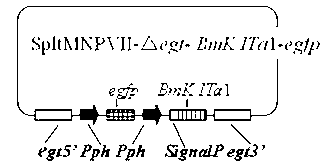
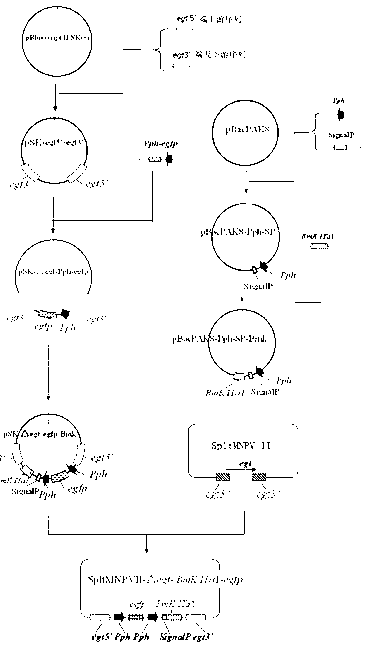
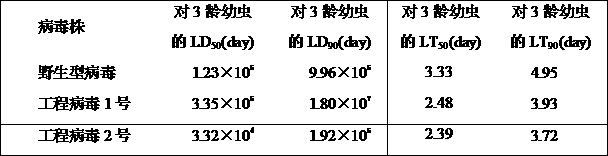
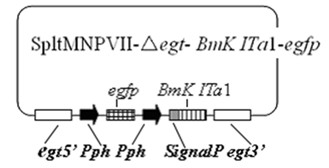
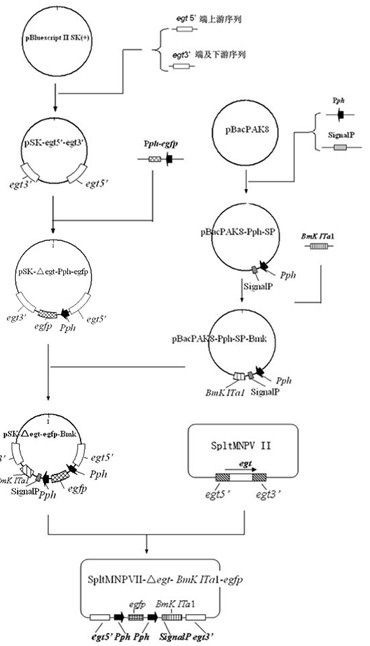
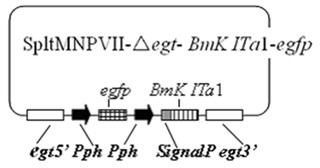
The invention discloses a prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and a building method thereof, in particular relates to a prodenia litura gene engineering virus used for carrying out deficiency and recombination on a wild type virus (SpltMNPV II) by utilizing a gene engineering method. The genome of the virus is deficient in an egt gene, namely an ecdysteroid UDP (uridine diphosphate) glucosyltransferase gene; and at the site of the deficient egt gene, a BmKITa1 gene controlled by a wild type virus, namely an early gene-1(ie-1) starter, and a marker gene, namely an enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene, which is controlled by the wild type virus, namely a polyhedron gene (ph) starterare inserted. The prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of faster insecticidal speed, less dosage effect and better field application effect compared with the wild type virus. Compared with the prior art, the prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 provided by the invention has less dosage effect and lower LT50 at low dose (105 polyhydral bodies / larva).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for improving plant drought hardiness
InactiveCN102409059AImprove drought resistanceImprove drought toleranceVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyUridine Diphosphoglucose
The invention belongs to the field of plant resistance improvement and particularly relates to a method for improving the plant drought hardiness, which aims at solving the technical problem to provide a novel effective method capable of improving the plant drought hardiness. In order to solve the technical problem, the method has the technical scheme that the method for improving the plant drought hardiness is provided, and the drought hardiness is improved through inhibiting the expression of uridine diphosphoglucose glycosyl transferase (UGT) genes in plants. The method provides a novel thought for the field of plant hardiness improvement, belongs to the novel efficient method capable of improving the plant hardiness and has good application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Engineering bacterium with overexpressed uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene and establishment thereof
ActiveCN105624176AIncrease productionHigh flocculation activityWater contaminantsTransferasesEscherichia coliUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
The invention relates to an engineering bacterium with overexpressed uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene and establishment thereof, belonging to the technical fields of gene engineering and microbial fermentation. By cloning the key enzyme uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene in the polysaccharide flocculant synthesis route, an Escherichia coli-Bacillus shuttle plasmid is utilized to establish a recombinant expression vector. The recombinant plasmid is transformed into Bacillus licheniformis by electric transformation to establish recombinant Bacillus licheniformis HN301-2; and compared with the initial strain, the polysaccharide flocculant yield of the recombinant Bacillus licheniformis is enhanced by 15.6%, and the fermentation liquid flocculation activity is enhanced by 70%. The engineering bacterium is hopeful to be used in industrial production of polysaccharide flocculants, and can enhance the yield and lower the cost.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
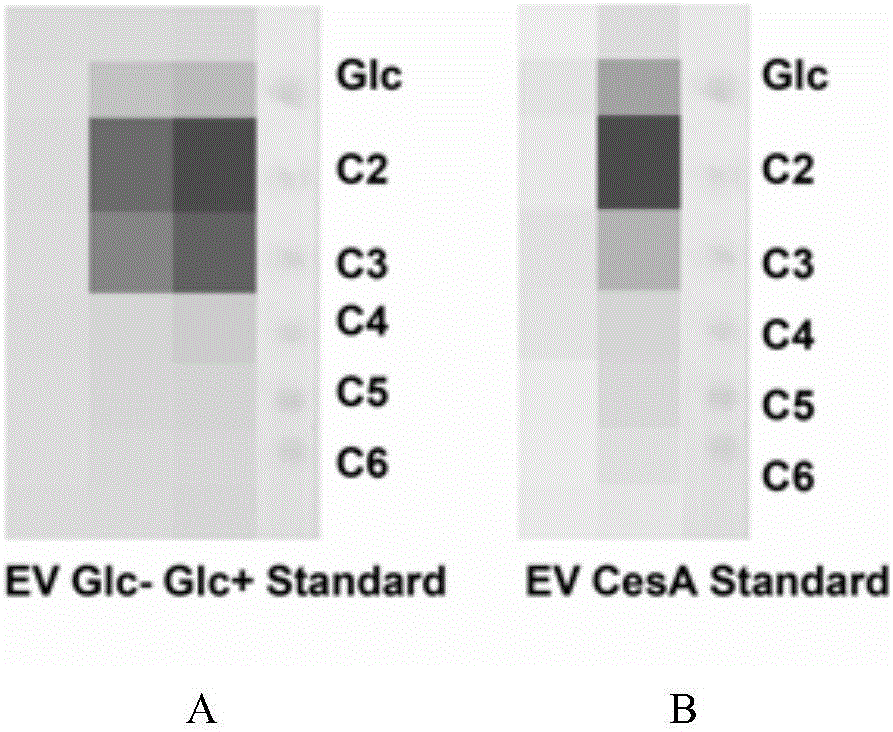
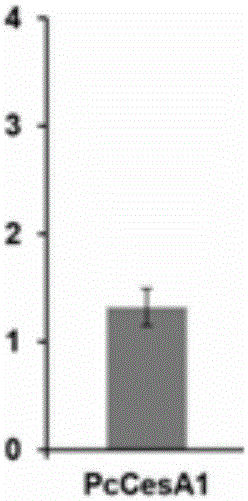
Cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein from phytophthora capsici, and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein from phytophthora capsici, and an encoding gene and application thereof. The PCCESA1 protein provided by the invention is the protein as shown in a sequence 2; the encoding gene of the protein is as shown in a sequence 1. An experiment proves that the protein PCCESA1 provided by the invention can catalyze substrate uridine diphosphate D glucose (UDPG) to generate cellobiose, and has significance on biosynthesis of main component cellulose of a cell wall of the phytophthora capsici; as an oomycetes cell wall plays an important role in maintaining oomycetes vital movement, including maintaining cell shapes, participating in host interaction and the like. Therefore, the cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein provided by the invention provides technical support for the oomycetes cell wall, and provides a new molecular target for future bactericide research and development.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for promoting plant growth and increasing cellulose content and/or yield
InactiveCN102154258AIncrease resistanceImprove energy captureVector-based foreign material introductionCelluloseUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
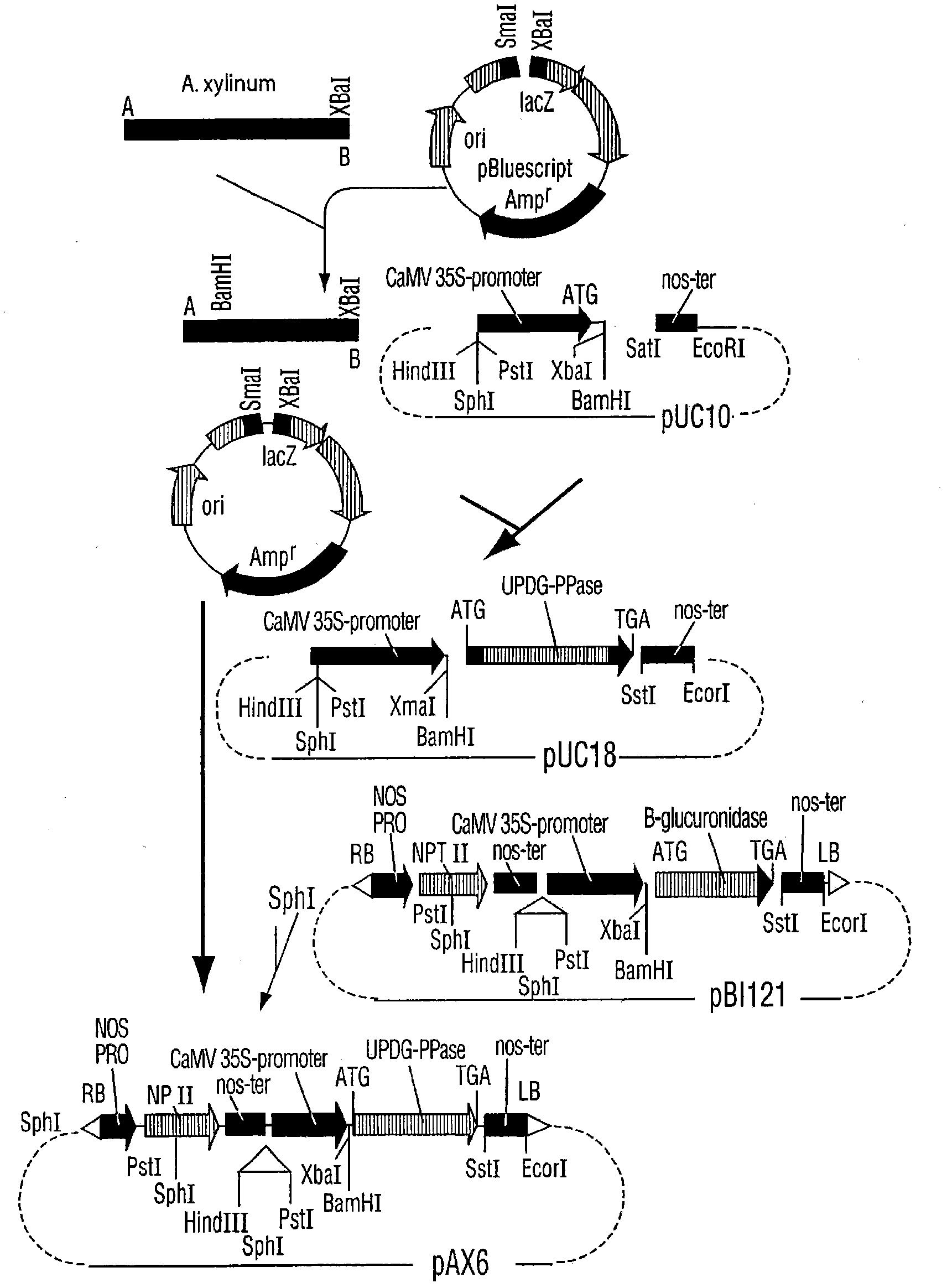
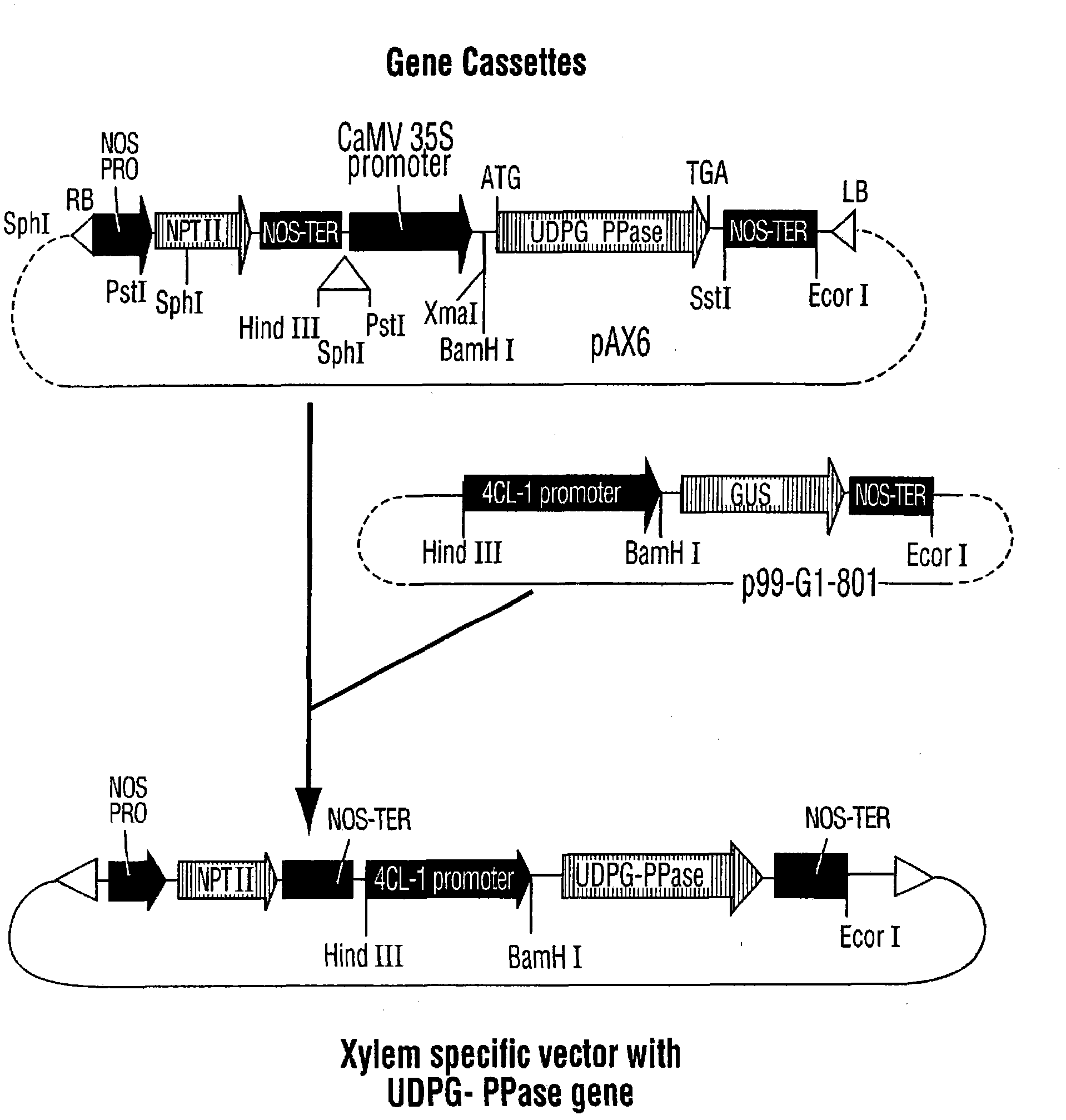
The invention provides a method for promoting the plant growth and increasing the cellulose content and / or yield and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the step of introducing a DNA sequence capable of changing a level of a cellulose precursor into a plant. The cellulose precursor is UPDG (uridine diphosphoglucose). The DNA sequence encodes an enzyme responsible for synthesis of uridine diphosphoglucose, preferably encodes a sequence of UPDG pyrophosphorylase; and is derived from any organisms including plants, bacteria or yeasts, preferably Bacillus xylinus. The expression of the uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene can change the level of the cellulose precursor in plant tissues or cells, so as to promote the growth of plants and increase the cellulose content and / or yield.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cultivation method and application for salidroside-containing plant
The invention provides a cultivation method for a salidroside-containing plant. The method comprises the following steps: spraying hydroxyphenethyl alcohol to growing plant leaves; harvesting the growing plant leaves to obtain the salidroside-containing plant. According to the method provided by the invention, the steps are simple; the synthetic precursor, namely the hydroxyphenethyl alcohol, of the salidroside-containing plant is directly supplied by outside, and the salidroside is synthesized in a plant body by taking uridine diphosphate glucose and glucosyltransferase which are contained in the plant as raw materials. The invention further provides the application of the salidroside-containing plant.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Preparation method and application of tea containing salidroside
InactiveCN104585374AReduce usageReduce lossPre-extraction tea treatmentHorticulture methodsSalidrosideAlcohol
The invention provides a preparation method of tea containing salidroside. The method comprises the following steps: spraying p-hydroxyphenylethyl alcohol to growing camellia sinensis leaves, and picking to obtain the tea containing salidroside. The method provided by the invention is simple in step; a synthetic precursor, namely p-hydroxyphenylethyl alcohol, of the salidroside is directly supplied from the external world; and uridine diphosphate glucose and glucosyltransferase contained in the tea are taken as raw materials, and the salidroside is synthesized in a tea body. The prepared tea containing the salidroside and application of the tea are further protected in the invention.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Cotton ghuxs3 gene, its encoded protein and its application
The invention provides a cotton uridine diphosphate glucuronate decarboxylase (GhUXS3) gene and a protein encoded by the gene. A nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of the gene are shown as SEQID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 respectively. GhUXS3 is a key enzyme for the formation of non-cellulose substances in the developmental process of cotton fibers, and affects the quality of the cotton fibers, so the novel candidate gene is provided for genetic engineering of quality improvement of the cotton fibers; and the GhUXS3 gene can lay a foundation for further transforming cotton so as to improve the quality of the cotton fibers, and has greater economic benefit and application value.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Optically active bicyclol glucoside and preparation method thereof, and application of optically active bicyclol glucoside in prevention and treatment of liver diseases
InactiveCN111285909ANovel preparation methodFew reaction stepsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesUridine DiphosphoglucoseUridine diphosphate glucose
The invention discloses optically active (P)-bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside and (M)-bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside applicable to medicines and a preparation method and application thereof. According tothe invention, bicyclol and uridine diphosphate glucose disodium salt are catalyzed by glycosyltransferase to synthesize optically active (P)-bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside and (M)-bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside in one step. The bicyclol-9-O-beta-D-glucoside prepared according to the invention can be used for preventing and treating liver diseases.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Directed metabolism of compounds by glucuronidation and sulfonation donors to decrease toxicity
InactiveUS20080188439A1Prevention and treatment of toxicityReduce incidenceBiocideDigestive systemGlucuronide metabolismUridine Diphosphoglucose
Disclosed are compositions and methods of treatment with uridine-based and phosphoadenosine-based cofactors for the prevention and treatment of toxicity associated with compounds such as acetaminophen, which undergo Phase II glucuronidation and sulfonation in the liver. Uridine diphosphoglucose, phosphoadenosine-phosphosulfate, and their derivatives can be administered exogenously either to prevent their depletion in the liver during treatment with acetaminophen, or to replace depleted substrates of UDPGA-transferase or PAPS-transferase in order to treat an individual after a toxic dose of acetaminophen has been ingested.
Owner:SALHANICK STEVEN D +1
Drug-loaded vesicle
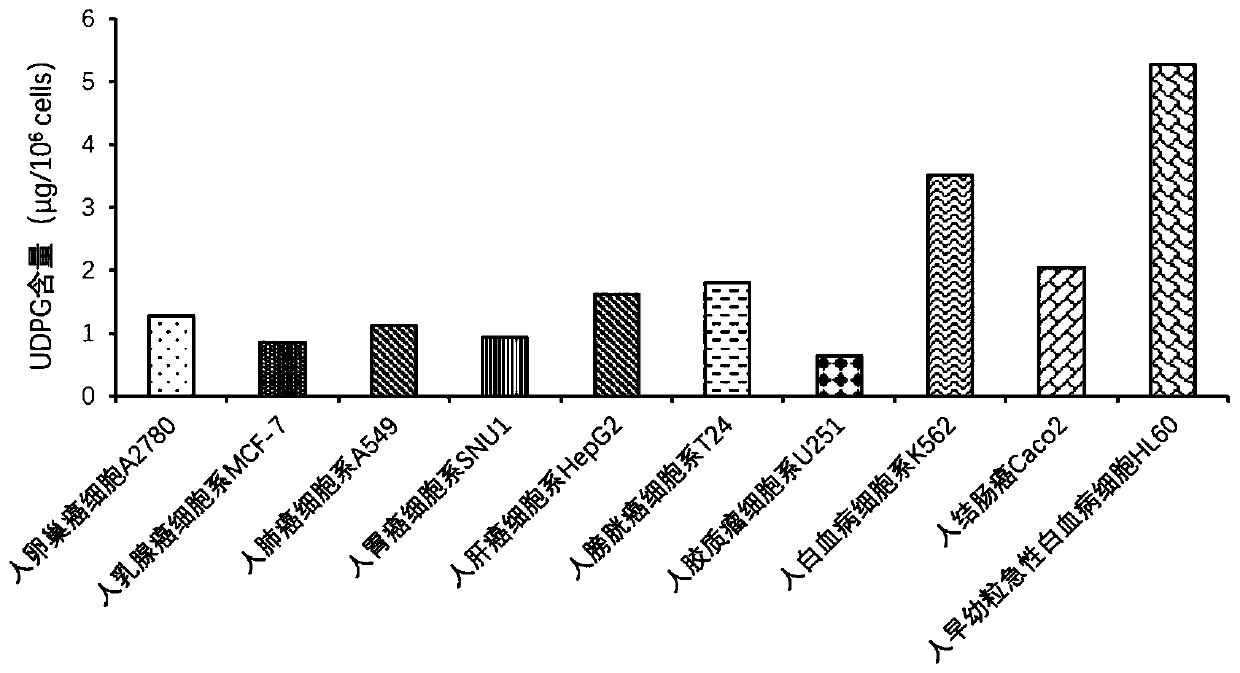
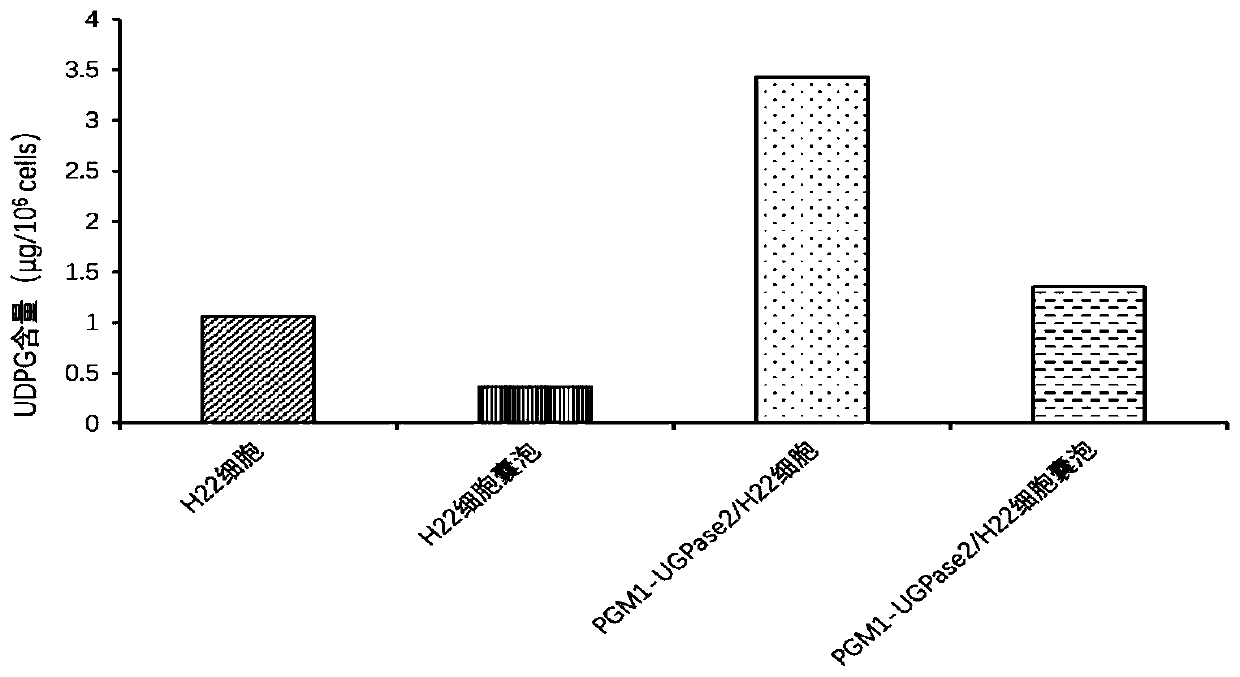
ActiveCN111067868AStable and efficient synthesisStable and efficient tumor killing effectOrganic active ingredientsTransferasesUridine DiphosphoglucoseTumor therapy
The invention relates to a drug-loaded vesicle. The drug-loaded vesicle comprises a vesicle derived from tumor cells and a therapeutic drug wrapped in the vesicle. The tumor cell-derived vesicle is avesicle released by apoptotic tumor cells, a large amount of uridine diphosphate glucose is wrapped in the vesicle, and the therapeutic drug is a tumor therapeutic drug serving as an effective component for treating tumors. The drug-loaded vesicle provided by the invention obtains a more stable and efficient tumor killing effect, and can better treat tumor diseases.
Owner:HUBEI SOUNDNY BIOLOGICAL TECH
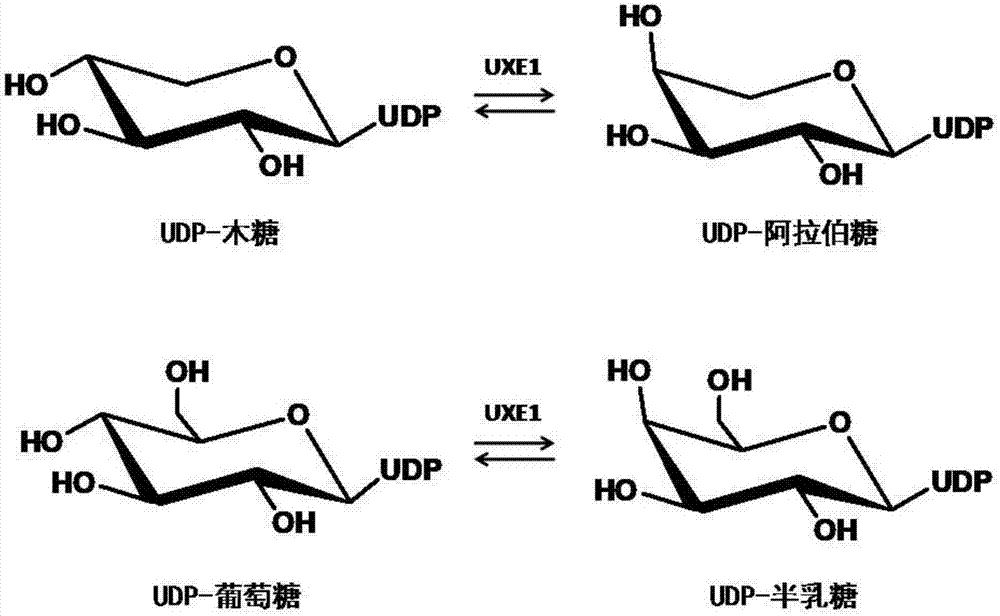
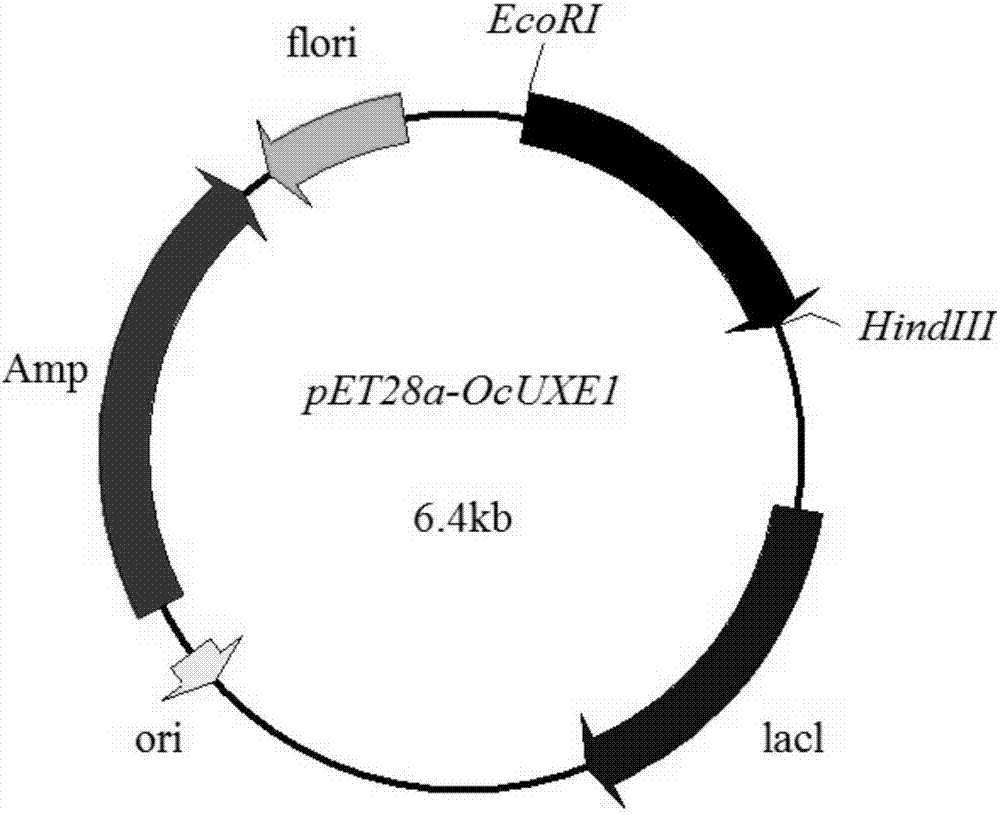
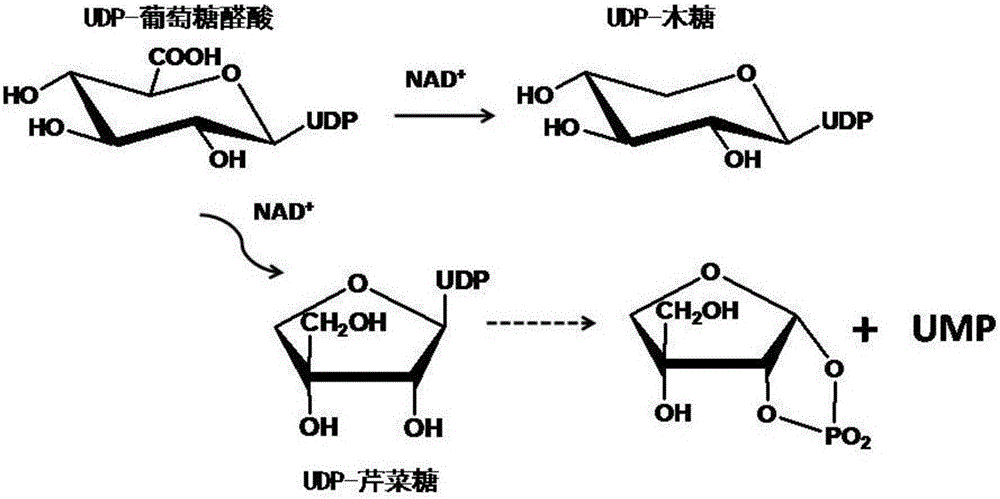
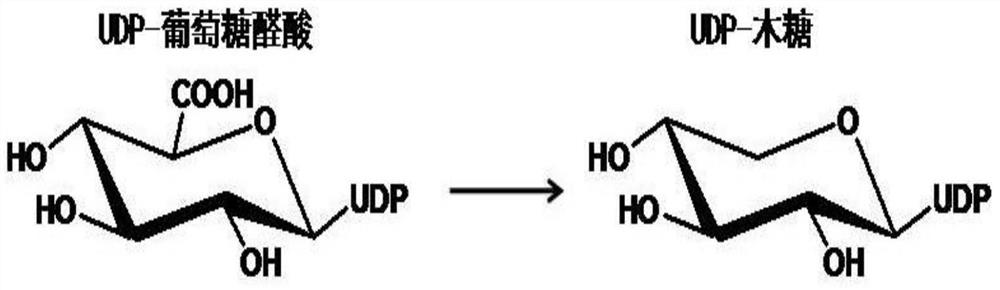
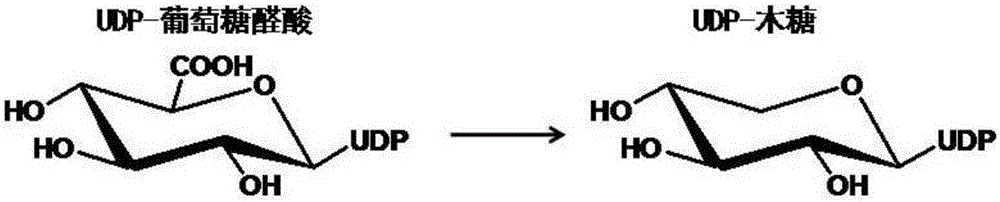
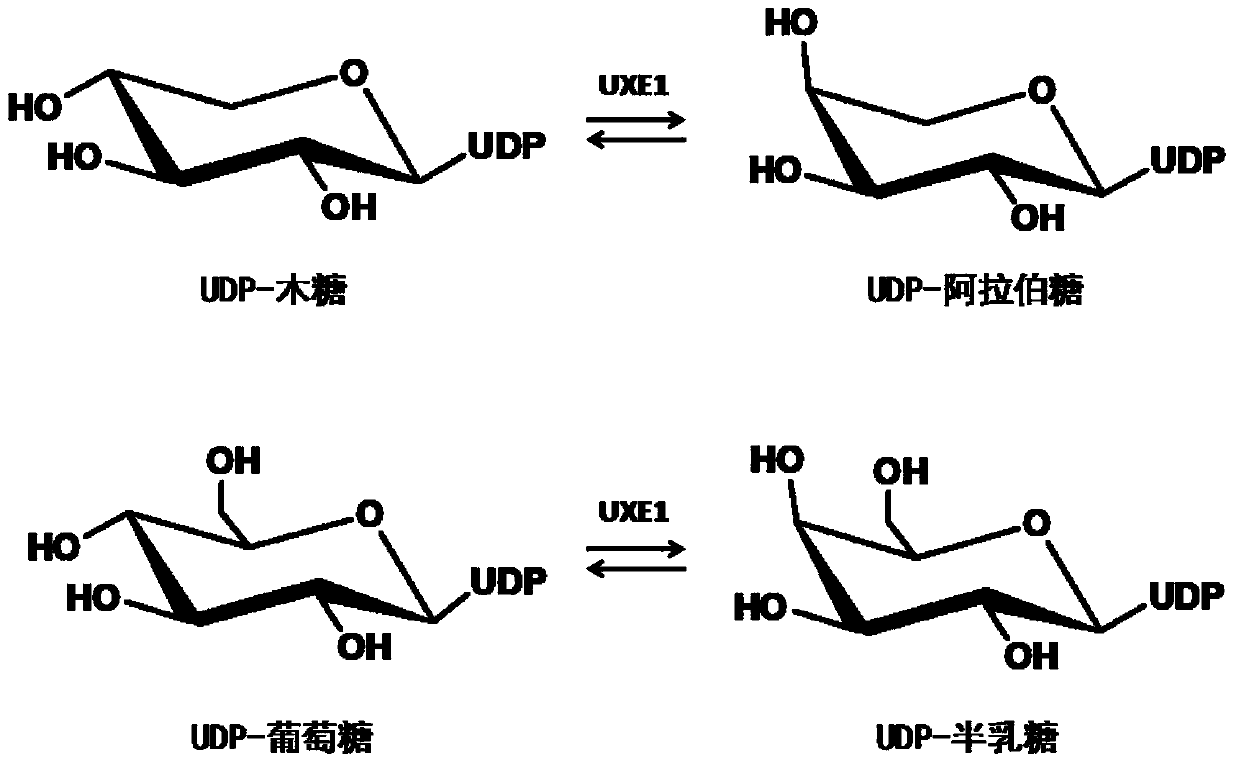
Uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase derived from ornithogalum caudatum, nucleotide sequence of uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase and application
The invention provides uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase derived from ornithogalum caudatum, a nucleotide sequence for encoding uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase genes, a carrier with the encoding nucleotide sequence, a host cell with the encoding nucleotide sequence and an application of the uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase or the cell with the uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase to reaction of catalysis substrates such as uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose, uridine-5'-diphosphate arabinose, uridine-5'-diphosphate glucose and uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose. The amino acid sequence of the uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Preparation method of uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid
PendingCN112608960AAchieve recyclingReduce addNucleic acid vectorOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to a preparation method of uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid. Uridine diphosphate glucose is oxidized by uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase to generate uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid, and lactic dehydrogenase is added for double-enzyme coupling reaction, so that cyclic regeneration of NAD<+> is realized, the addition of NAD<+> is reduced, the cost is saved, and at the same time, the circulation of NAD<+> / NADH reduces the feedback inhibition effect of the byproduct NADH on the product uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid, and the generation amount of the target product can reach 1.01 mg / mL. The nucleotide sequence of lactic dehydrogenase is optimized and modified, so that the target protein can be better expressed in escherichia coli, and efficient synthesis of the target product uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid is facilitated. In-vitro reaction is adopted, a reaction system is more controllable, and compared with intracellular reaction, in-vitro reaction can be more beneficial to reaction under limited conditions.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Engineering bacteria and construction of overexpressing uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene
ActiveCN105624176BIncrease productionHigh flocculation activityWater contaminantsTransferasesBiotechnologyUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
The invention relates to an engineering bacterium with overexpressed uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene and establishment thereof, belonging to the technical fields of gene engineering and microbial fermentation. By cloning the key enzyme uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene in the polysaccharide flocculant synthesis route, an Escherichia coli-Bacillus shuttle plasmid is utilized to establish a recombinant expression vector. The recombinant plasmid is transformed into Bacillus licheniformis by electric transformation to establish recombinant Bacillus licheniformis HN301-2; and compared with the initial strain, the polysaccharide flocculant yield of the recombinant Bacillus licheniformis is enhanced by 15.6%, and the fermentation liquid flocculation activity is enhanced by 70%. The engineering bacterium is hopeful to be used in industrial production of polysaccharide flocculants, and can enhance the yield and lower the cost.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and special engineering bacteria for method
ActiveCN112239771ARaw materials are easy to getLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseUridine Diphosphoglucose
The invention discloses a method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and special engineering bacteria for the method. The method for producing the uridine diphosphate glucose comprises the following steps of by using uridine monophosphate and sucrose as raw materials, producing the uridine diphosphate glucose under the action of the engineering bacteria, wherein the engineering bacteria arerecombinant bacteria for expressing functional protein and are obtained by introducing a gene for encoding the functional protein into starting bacteria, and the functional protein comprises polyphosphokinase, uridine monophosphate kinase and sucrose synthase. The method is of great significance to industrial production of the uridine diphosphate glucose.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of locust uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase gene and its application
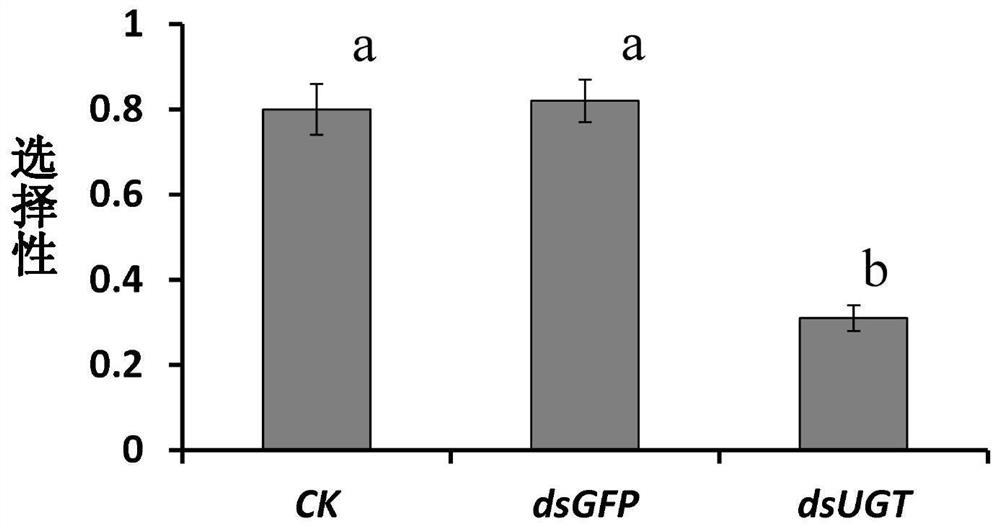
The invention discloses a locust uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase gene, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. According to the gene, primers are designed to synthesize dsRNA for interfering with uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase gene, and dsRNA is introduced into locusts to perform RNA interference on uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase gene, which can significantly reduce the food selectivity of locusts and fitness, thereby providing a new method for green and sustainable pest control, and also providing technical support for the creation of new biopesticides.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
Cultivation method and application of a plant containing salidroside
The invention provides a method for cultivating plants containing salidroside. The method comprises the following steps: spraying p-hydroxyphenylethanol on growing plant leaves, and harvesting to obtain plants containing salidroside. The method provided by the invention has simple steps. The synthetic precursor of salidroside, p-hydroxyphenylethanol, is directly supplied from the outside, and the uridine diphosphate glucose and glucosyltransferase contained in the plant itself are used as raw materials to synthesize the salidroside in the plant. Tianglycoside. The present invention further protects the application of the salidroside-containing plants obtained through cultivation.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
A method for producing uridine diphosphate glucose and its special engineering bacteria
ActiveCN112239771BRaw materials are easy to getLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseGlucose phosphate
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Uridine-5'-diphosphate apiose/xylose synthetic enzyme from ornithogalum caudatum, nucleotide sequence and application thereof
ActiveCN106191017ARelieve pressurePromote sustainable developmentFermentationGenetic engineeringNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides: an uridine-5'-diphosphate apiose / xylose synthetic enzyme from ornithogalum caudatum, of which an amino acid sequence is represented as the SEQ ID No.1; a nucleotide sequence, which is represented as the SEQ ID No.3, for encoding the gene of the uridine-5'-diphosphate apiose / xylose synthetic enzyme; a carrier and a host cell containing the encoding nucleotide sequence; and an application of the uridine-5'-diphosphate apiose / xylose synthetic enzyme or a cell containing same in a reaction of catalyzing a substrate uridine-5'-diphosphate glucuronic acid.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
a drug-loaded vesicle
ActiveCN111067868BStable and efficient synthesisStable and efficient tumor killing effectOrganic active ingredientsTransferasesUridine DiphosphoglucoseTumor therapy
The invention relates to a drug-loaded vesicle, comprising a tumor cell-derived vesicle and a therapeutic drug encapsulated in the vesicle, wherein the tumor cell-derived vesicle is a vesicle released by an apoptotic tumor cell and the vesicle A large amount of uridine diphosphate glucose is encapsulated in the vesicles, and the therapeutic drug is a tumor therapeutic drug as an effective component for treating tumors. The drug-loaded vesicle of the present invention has a more stable and efficient tumor-killing effect, and can better treat tumor diseases.
Owner:HUBEI SOUNDNY BIOLOGICAL TECH
Prodenia litura genetically engineered virus NO.2 and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102174480BFast insecticideLow dose effectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeEngineered genetic
The invention relates to the field of a microorganism technology, in particular relating to a prodenia litura genetically engineered virus which can prevent farming and forestry pests such as prodenia litura. The virus is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: V201028. In the invention, a genetic engineering method is employed to delete and restructure a wild type virus. The egt gene, namely the ecdysone uridine diphosphate glucosyltransferase gene is deleted from the genome of the virus; a BmKTal gene controlled by a wild type virus polyhedron gene (ph) promoter and a marking gene-enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene controlled by the wild type virus polyhedron gene (ph) promoter are inserted into the locus at which the egtgene is deleted. The virus provided by the invention has the advantages of faster pest killing speed than that of the wild type virus, less dosage effect, better field application effect and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
A kind of uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthase derived from Dieffenbachia tiger eye, its nucleotide sequence and application
ActiveCN106191018BReduce contentBig economic interestsFermentationGenetic engineeringEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The present invention provides a uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthase derived from Dieffenbachia tiger's eye, the amino acid sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; The nucleotide sequence of the sugar synthase gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.3, as well as the vector and host cell containing the coding nucleotide sequence. The present invention also provides uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthase or a cell containing uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthase in catalytic substrate uridine-5'-diphosphate glucuronic acid reaction Applications.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
A truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthase, its nucleotide sequence and application
The present invention provides a truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthase derived from Dieffenbachia tiger's eye, the original amino acid sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; it also provides a coded truncated uridine The nucleotide sequence of ‑5'‑diphosphate xylose synthase gene, as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, as well as the vector and host cell containing the coding nucleotide sequence. The present invention also provides truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthase or cells containing truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthase in catalytic substrate uridine-5'-diphosphate Application in phosphoglucuronic acid reaction.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthetase, and nucleotide sequence and application thereof
ActiveCN106191019APromote biosynthesisFermentationGenetic engineeringNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides a truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthetase derived from star-of-bethlehem. The original amino acid sequence of the truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthetase is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention also provides a nucleotide sequence for coding the truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthetase gene disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2, and a vector and host cell containing the coding nucleotide sequence. The invention also provides application of the truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthetase or the cell containing the truncated uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose synthetase in reaction for catalyzing a substrate uridine-5'-diphosphate glucuronic acid.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Recombinant Microorganism for Producing 2,3-Butanediol and a Method of Production of 2,3-Butanediol
A recombinant microorganism for producing 2,3-butanediol consisting of selecting at least three groups from uridine diphosphate glucose phosphate uroglycan transferase gene (galU), acetyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene (acoA), acetyl phosphate transferase gene (pta), adenosine glucosylphosphate transferase gene (glgC), lactose dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), and phosphodiesterase gene (pdeC) which were modified.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION
A uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase derived from Dieffenbachia tiger eye, its nucleotide sequence and application
The invention provides uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase derived from ornithogalum caudatum, a nucleotide sequence for encoding uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase genes, a carrier with the encoding nucleotide sequence, a host cell with the encoding nucleotide sequence and an application of the uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase or the cell with the uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase to reaction of catalysis substrates such as uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose, uridine-5'-diphosphate arabinose, uridine-5'-diphosphate glucose and uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose. The amino acid sequence of the uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose epimerase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Prodenia litura genetically engineered virus NO.2 and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102174480AFast insecticideLow dose effectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeUridine diphosphate
The invention relates to the field of a microorganism technology, in particular relating to a prodenia litura genetically engineered virus which can prevent farming and forestry pests such as prodenia litura. The virus is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: V201028. In the invention, a genetic engineering method is employed to delete and restructure a wild type virus. The egt gene, namely the ecdysone uridine diphosphate glucosyltransferase gene is deleted from the genome of the virus; a BmKTal gene controlled by a wild type virus polyhedron gene (ph) promoter and a marking gene-enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene controlled by the wild type virus polyhedron gene (ph) promoter are inserted into the locus at which the egtgene is deleted. The virus provided by the invention has the advantages of faster pest killing speed than that of the wild type virus, less dosage effect, better field application effect and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose epimerase derived from ornithogalum caudatum, nucleotide sequence of uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose epimerase and application
ActiveCN107164355AIncrease productionBig economic interestsIsomerasesGenetic engineeringGalactose epimeraseAmino acid
The invention provides uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose epimerase derived from ornithogalum caudatum, a nucleotide sequence for encoding uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose epimerase genes, a carrier with the encoding nucleotide sequence, a host cell with the encoding nucleotide sequence and an application of the uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose epimerase or the cell with the uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose epimerase to reaction of catalysis substrates such as uridine-5'-diphosphate xylose, uridine-5'-diphosphate arabinose, uridine-5'-diphosphate glucose and uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose. The amino acid sequence of the uridine-5'-diphosphate galactose epimerase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
A kind of andrographolide-19-o-glucoside and its preparation method and application in the preparation of anti-inflammatory drugs
InactiveCN106868078BHigh yieldGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticAntiinflammatory drugPharmaceutical Substances
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological synthesis of biocatalyst, and discloses andrographolide-19-O-glucoside and a preparation method thereof, as well as application in preparation of an anti-inflammatory drug. The method specifically comprises the following steps: taking uridine-5'-glucose disodium diphosphate as a glycosyl donor in a buffer solution system, and catalyzing andrographolide by applying a mutant A242V / S132F / P67T of glycosyl transferase OleD for glycosylation reaction, thus obtaining the andrographolide-19-O-glucoside. The andrographolide-19-O-glucoside obtained through the method can be applied to preparation of the anti-inflammatory drug; via glycosylation treatment, the andrographolide-19-O-glucoside greatly increases the water solubility of the drug and improves the original anti-inflammatory activity of the drug. According to the preparation method, the glycosyl transferase is adopted to perform glycosylation modification on the andrographolide for the first time; the reaction system has the advantages of mild reaction condition, low energy consumption, high yield, stereoscopic impression, high region selectivity, small quantity of byproducts, easiness for separation of a product and the like.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com