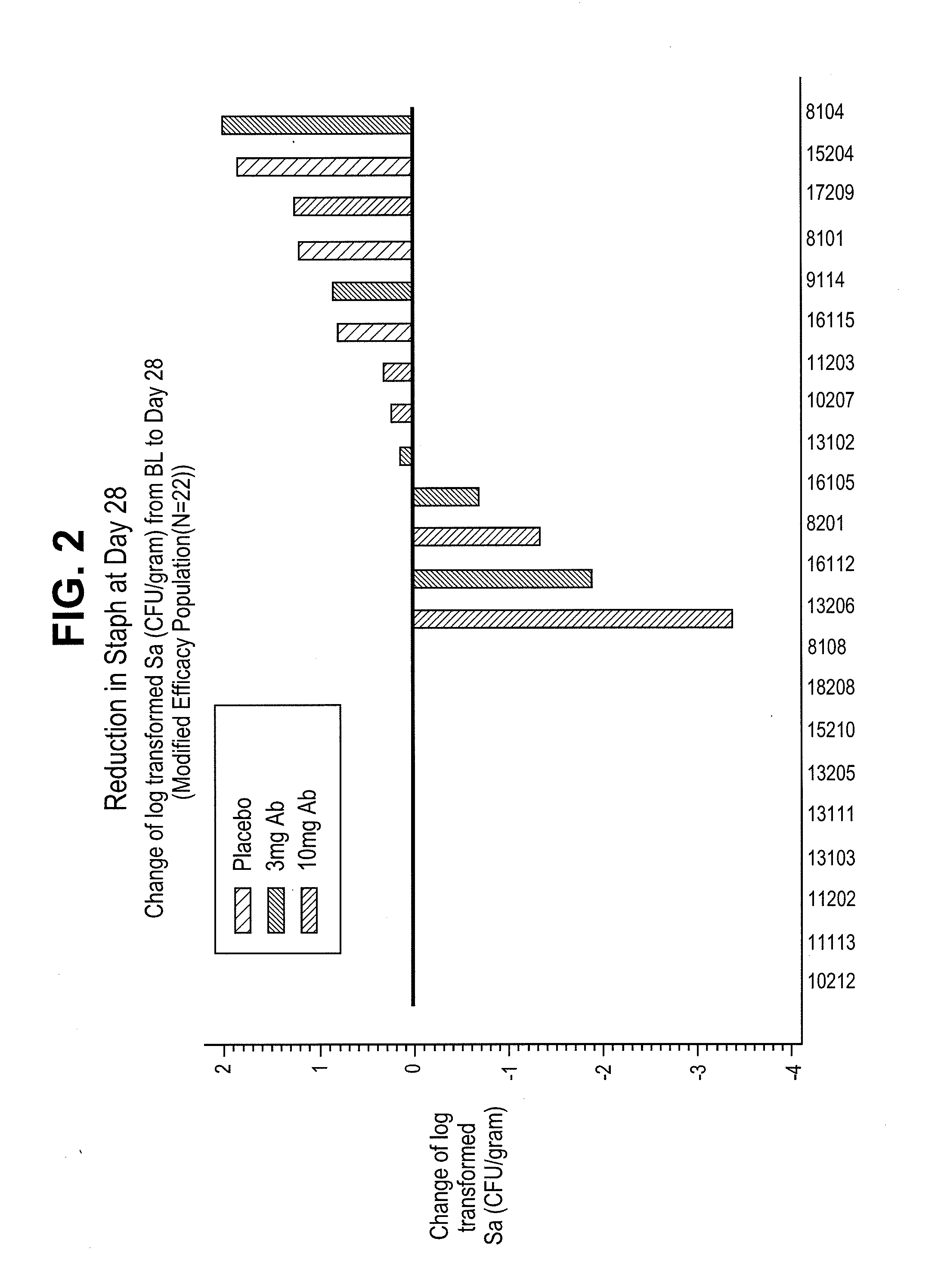
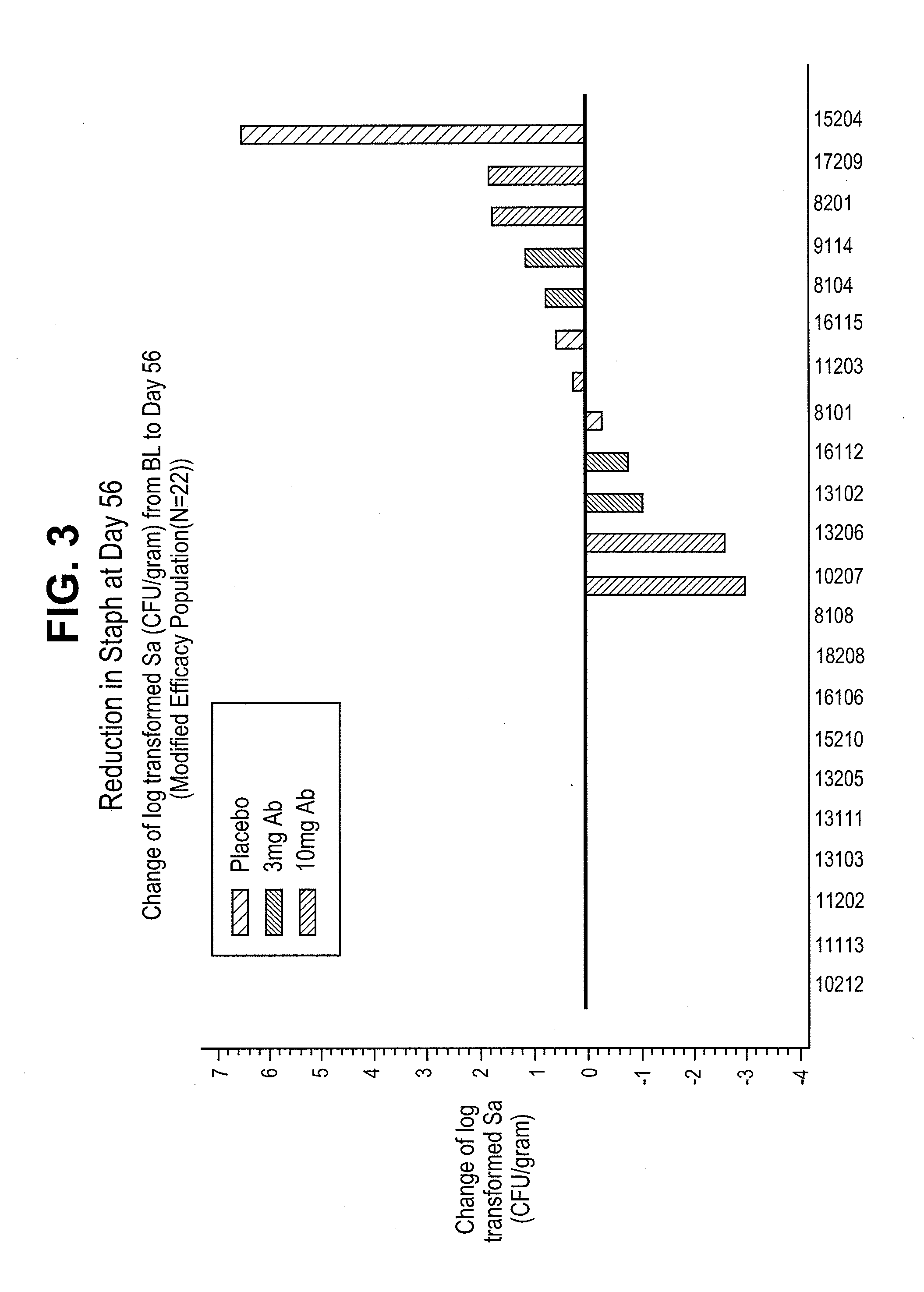
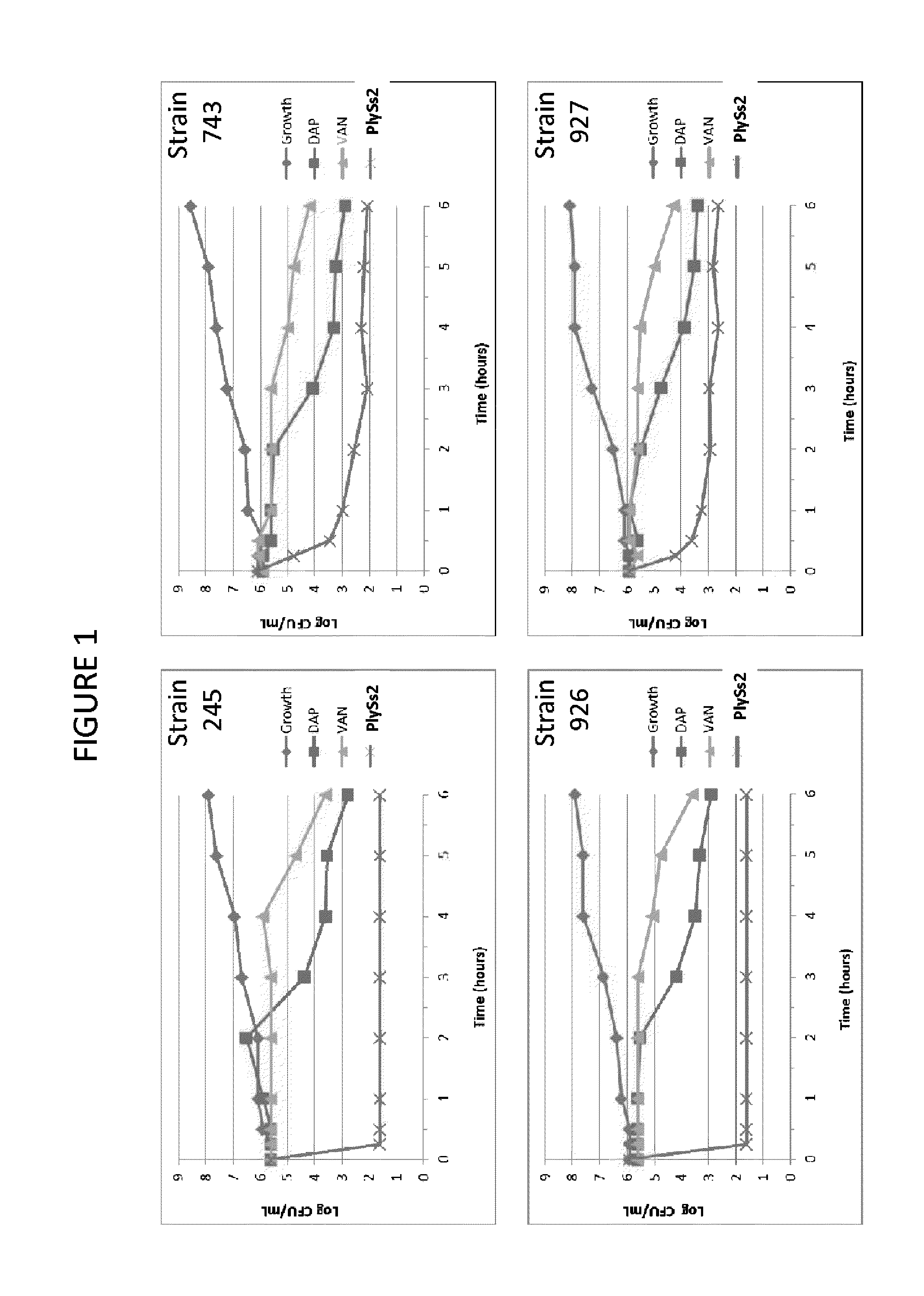
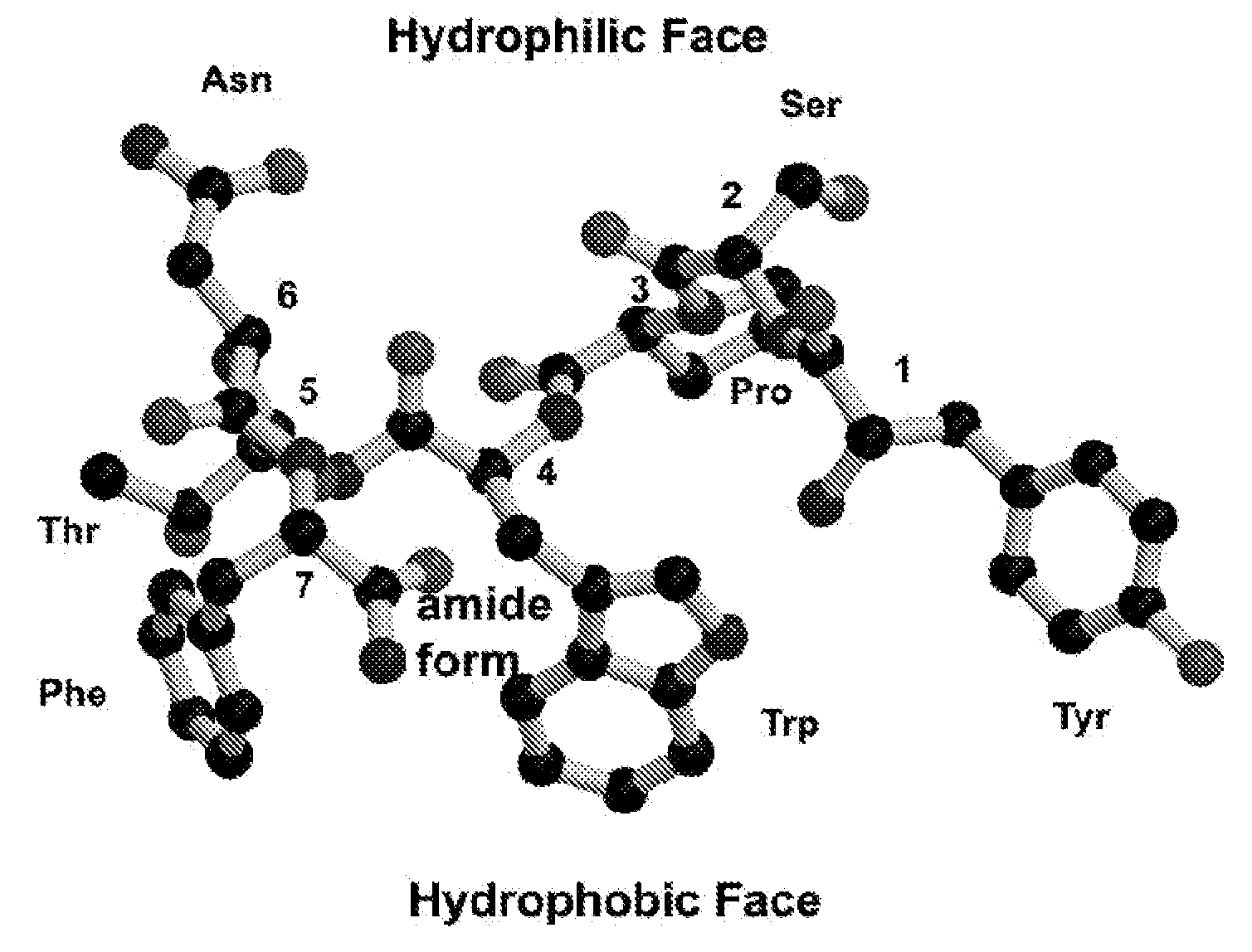
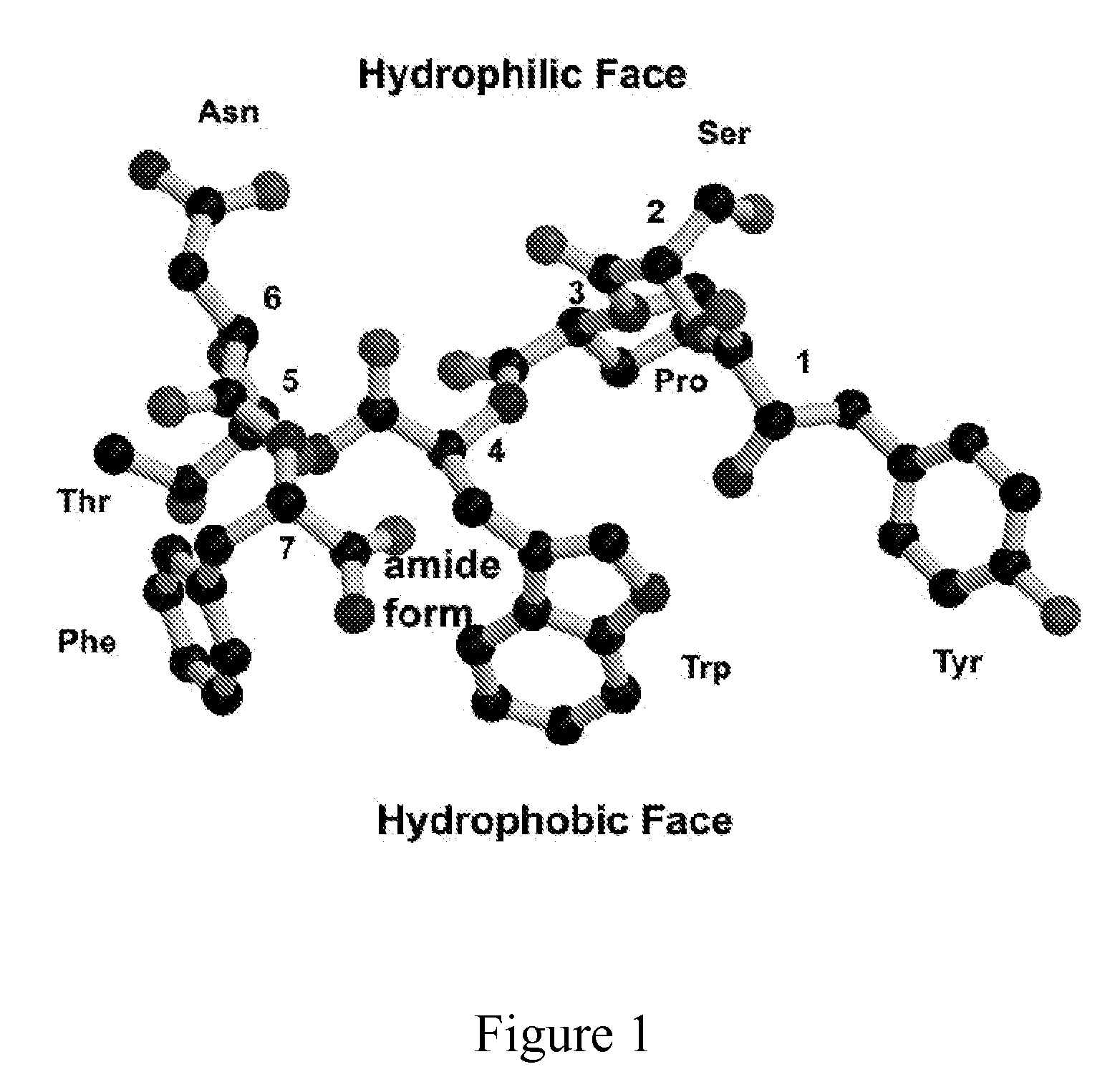
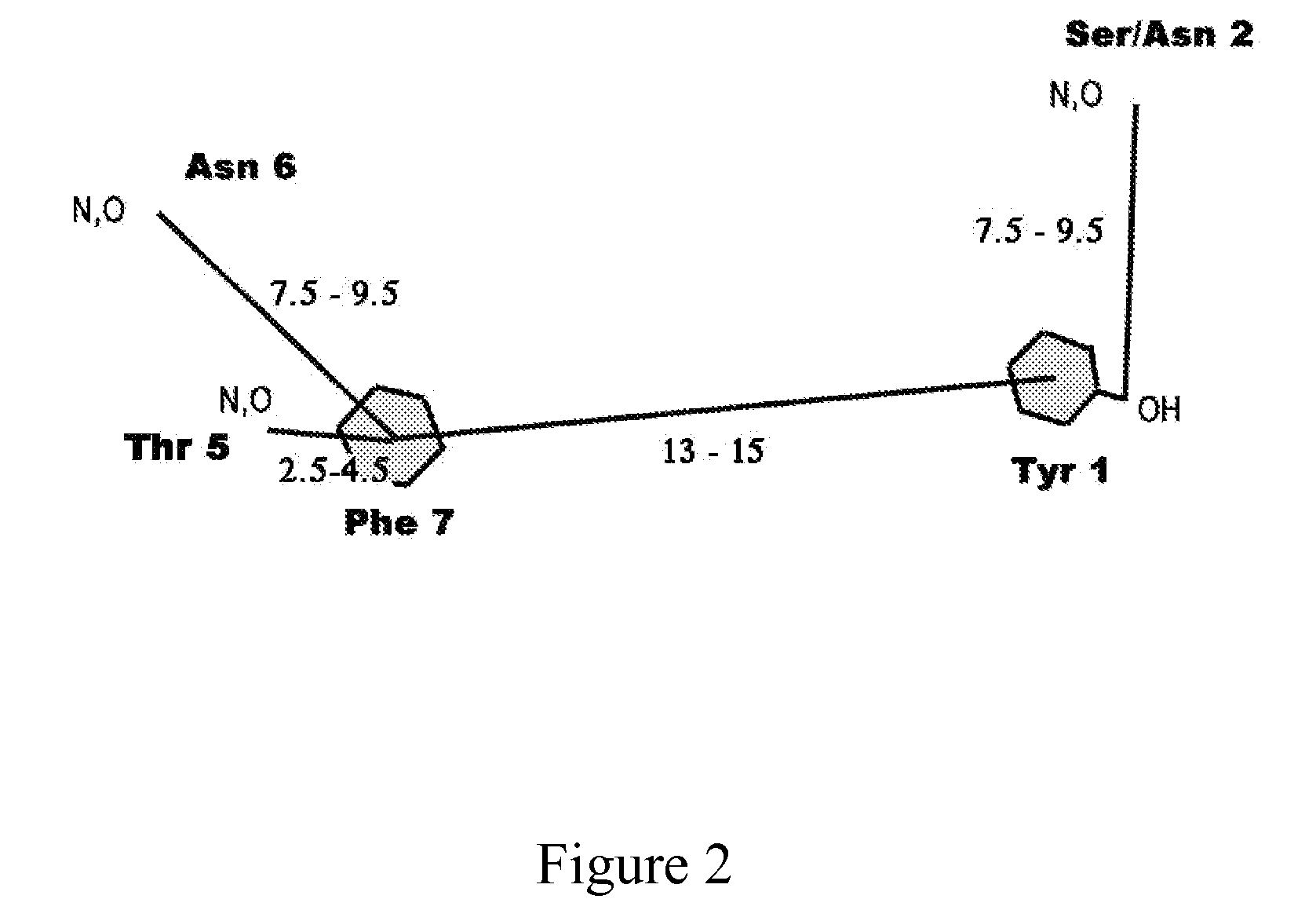
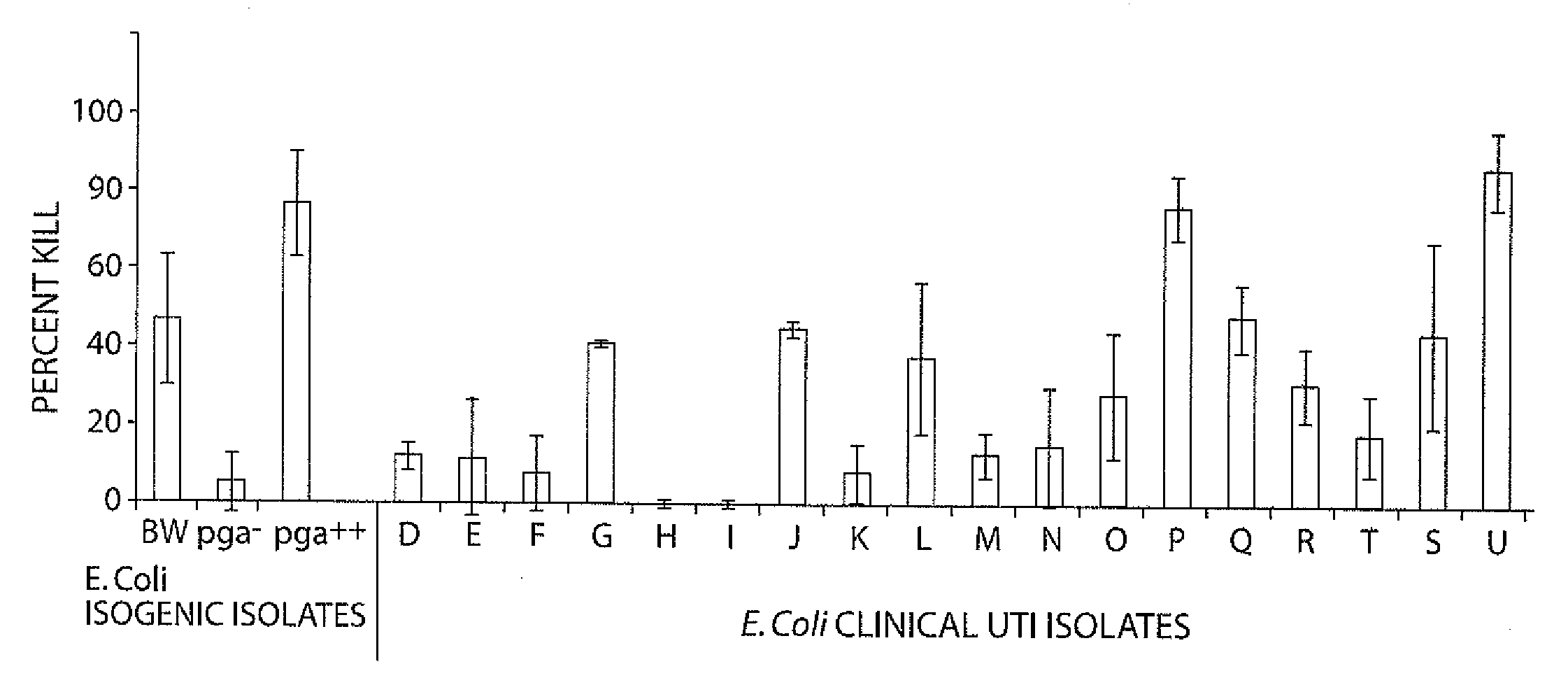
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
129 results about "Staphylococcus saprophyticus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Staphylococcus saprophyticus is a Gram-positive coccus belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. S. saprophyticus is a common cause of community-acquired urinary tract infections.
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20060263810A1Reduce usageDetermine rapidly the bacterial resistance to antibioticsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNeisseria meningitidisListeria monocytogenes
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6′-IIa, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6′)-aph(2″), aad(6), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
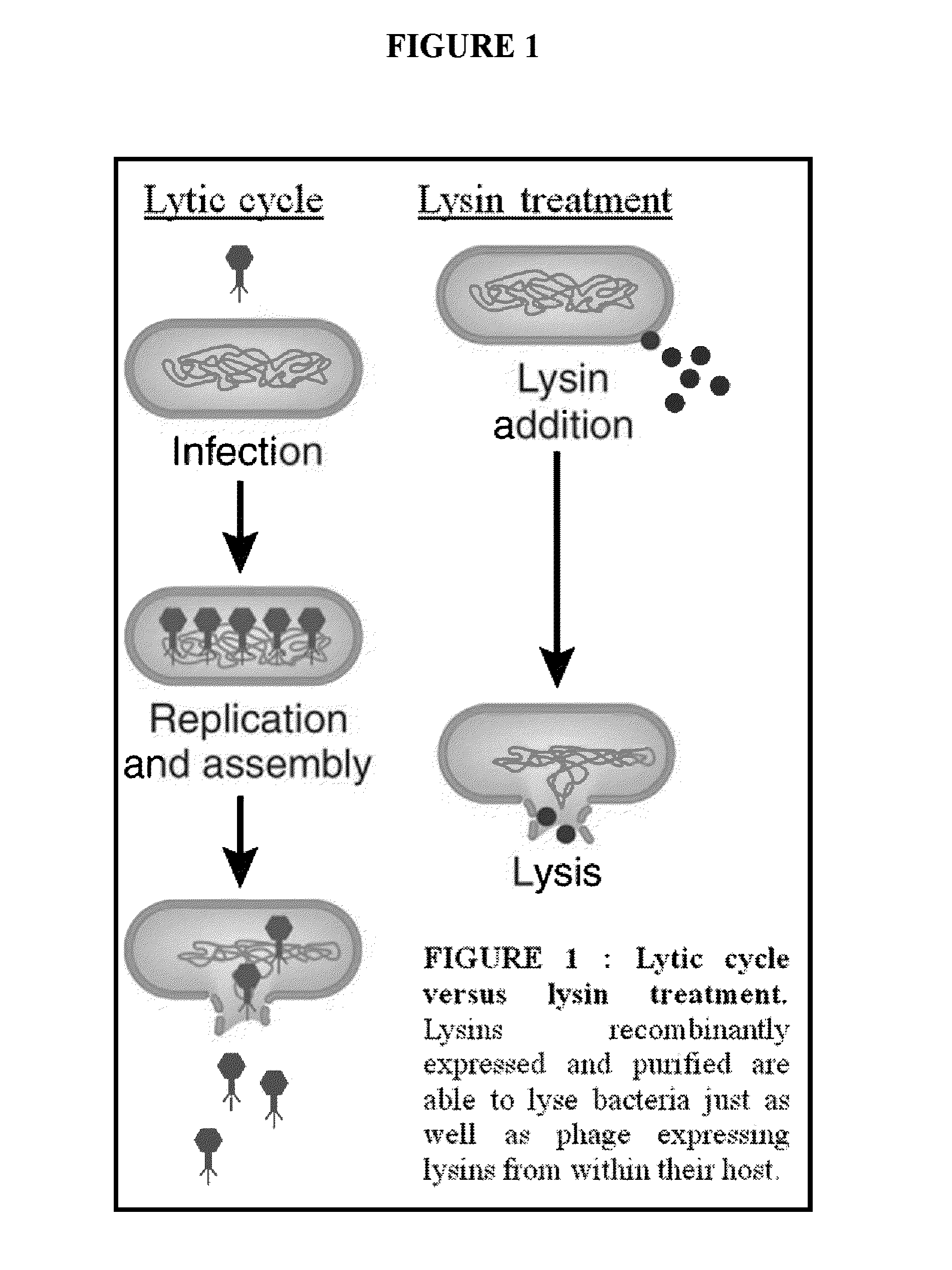
Streptococcus bacteriophage lysins for detection and treatment of gram positive bacteria
ActiveUS9034322B2Efficient killingReduce in quantityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryStreptococcus constellatusStaphylococcus xylosus
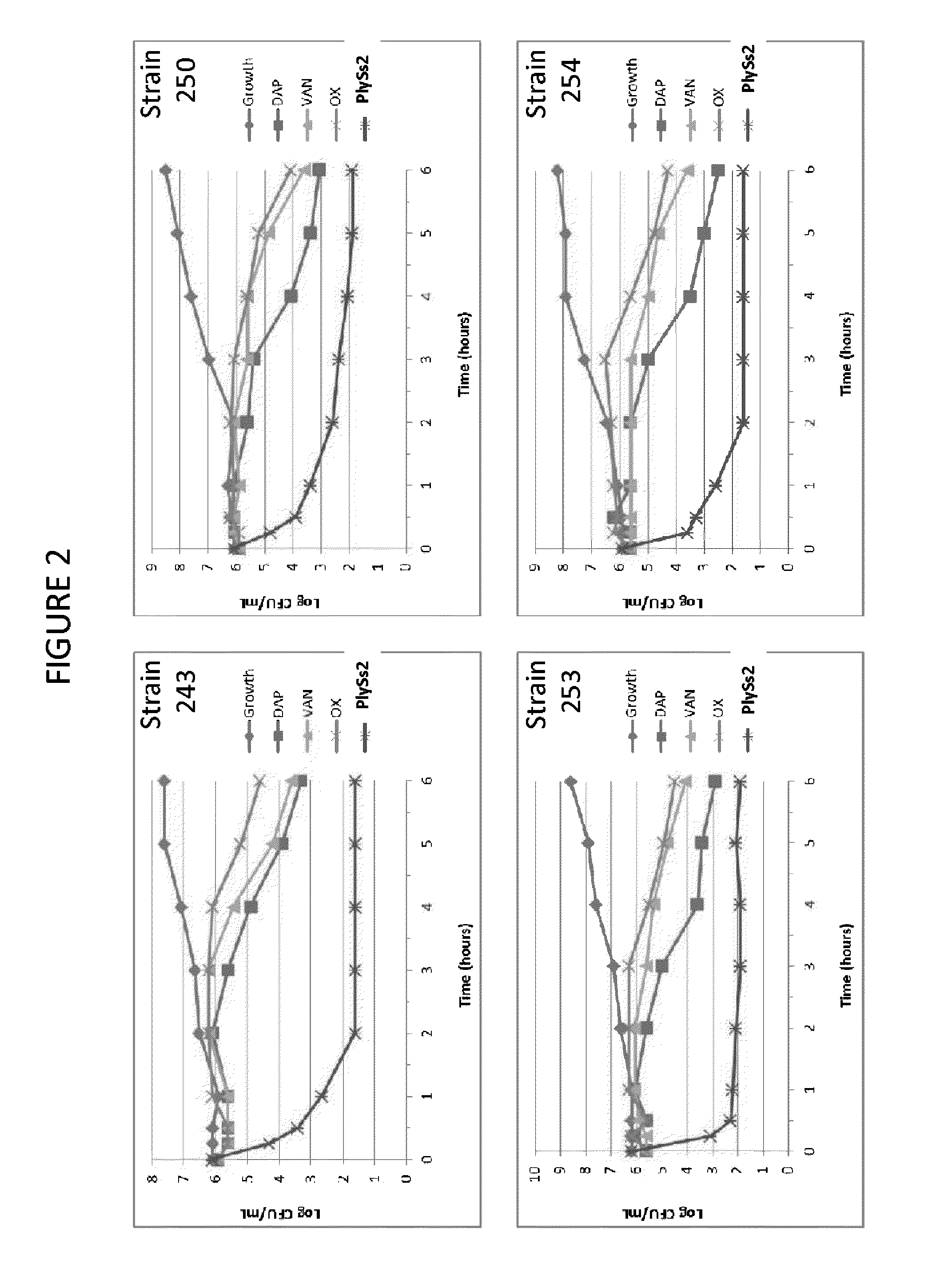
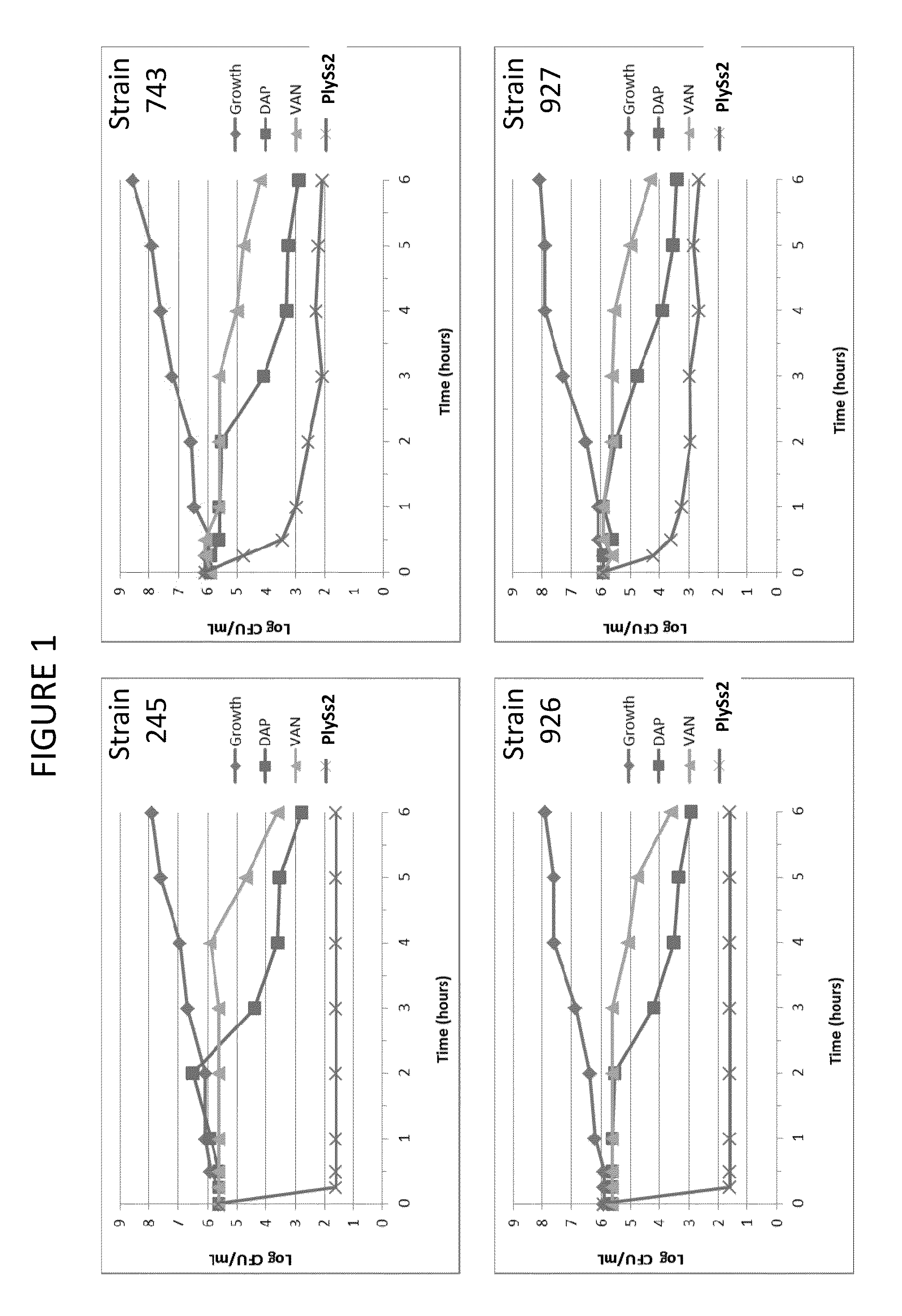
The present invention provides methods, compositions and articles of manufacture useful for the prophylactic and therapeutic amelioration and treatment of gram-positive bacteria, including Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, and related conditions. The invention provides compositions and methods incorporating and utilizing Streptococcus suis derived bacteriophage lysins, particularly PlySs2 and / or PlySs1 lytic enzymes and variants thereof, including truncations thereof. Methods for treatment of humans are provided.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20050042606A9Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesGenomic SegmentMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
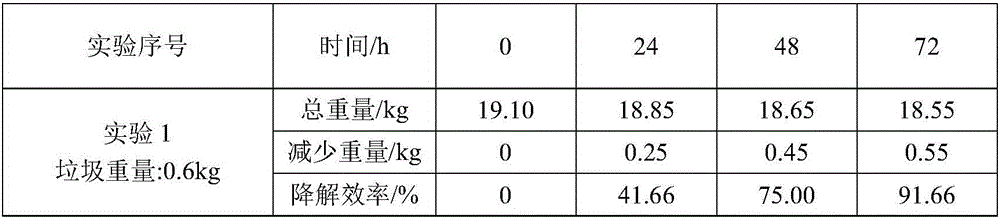
Kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106591178AEfficient degradationFast degradation rateBacteriaSolid waste disposalStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus xylosus
The invention relates to a kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and a preparation method and application thereof. The kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum is prepared by mixing a mixed inoculum of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, radiation-resistant methylobacterium, dispersed pantoea, pseudomonas oryzihabitans, citrobacter freundii and staphylococcus cohnii and a carrier, wherein the mass of the mixed inoculum accounts for 15-25% of the total mass of the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum; the mass ratio of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the radiation-resistant methylobacterium, the dispersed pantoea, the pseudomonas oryzihabitans, the citrobacter freundii and the staphylococcus cohnii is (1.5-3):(1-1.5):(1-1.5): (1-1.5):(1-1.5):(1-1.5); the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum is used for degrading kitchen garbage. Compared with the prior art, the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum has the advantages as follows: the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum can effectively degrade common vegetables, grains, fish, poultry meat and other kitchen garbage, has the degradation rate being above 80%, is high in degradation speed rate and small in odor, does not produce pollutants or poisonous substances, and is low in cost and stable in performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Method of treating a staphylococcus infection in a patient having a low-level pathogenic pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
InactiveUS20110165172A1Lower Level RequirementsLow levelAntibacterial agentsAntibody ingredientsStaphylococcal infectionsPseudomonas
This invention provides methods of treating patients having a Staphylococcus infection where the patient also has a low level of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The methods comprise administering an antagonist of the Pseudomonas Type III Secretion System, e.g., an anti-PcrV antibody antagonist.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20070009947A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090053702A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStreptococcus pyogenes
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Bacteriophage lysin and antibiotic combinations against gram positive bacteria
ActiveUS20130302306A1Quick killBroad killing activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLysinLinezolid
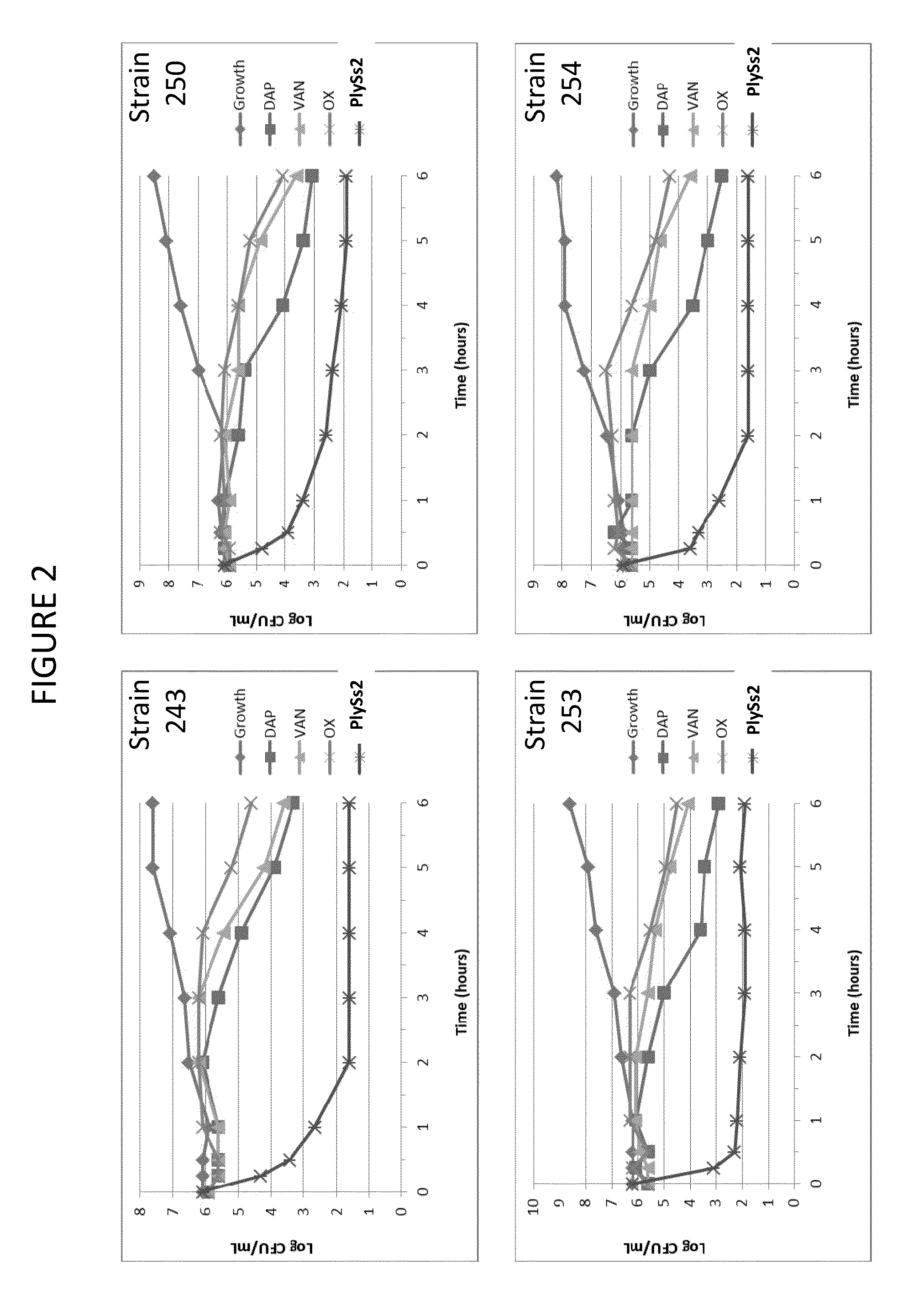
The present invention provides compositions and methods for prevention, amelioration and treatment of gram positive bacteria, particularly Staphylococcal bacteria, with combinations of lysin, particularly Streptococcal lysin, particularly the lysin PlySs2, and one or more antibiotic, including daptomycin, vancomycin, oxacillin, linezolid, or related antibiotic(s).
Owner:CONTRAFECT CORP
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090047671A1Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
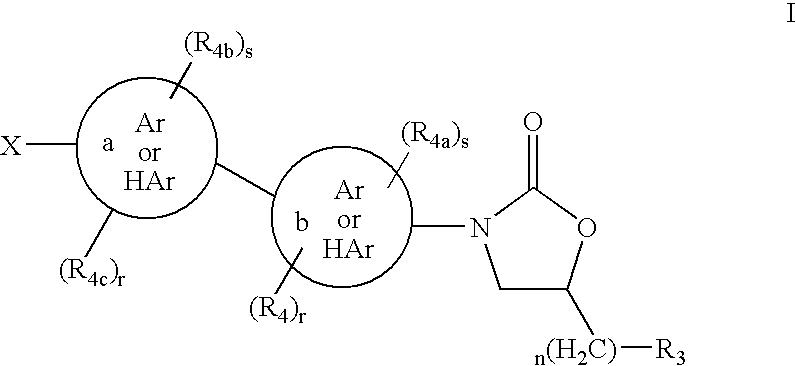
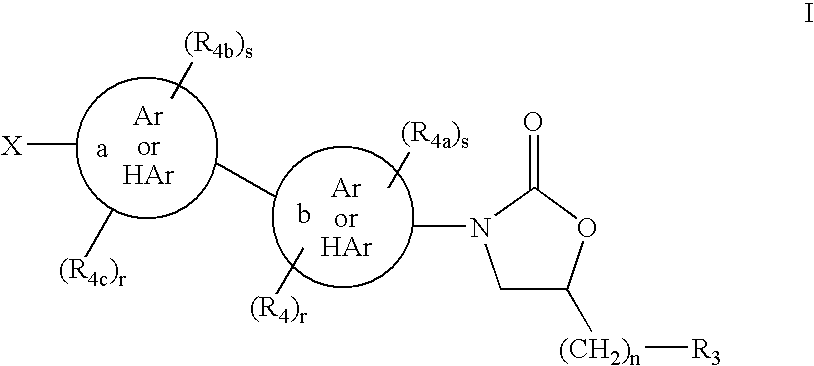
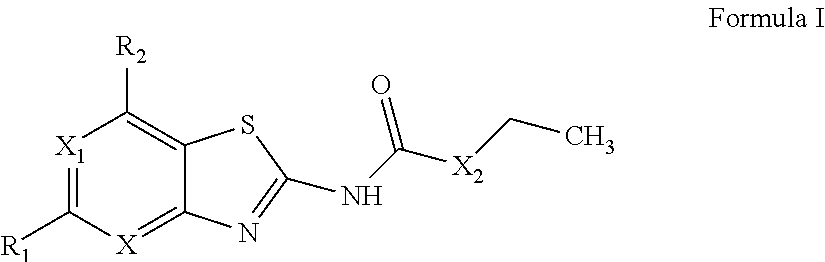
Cyclopropyl group substituted oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof
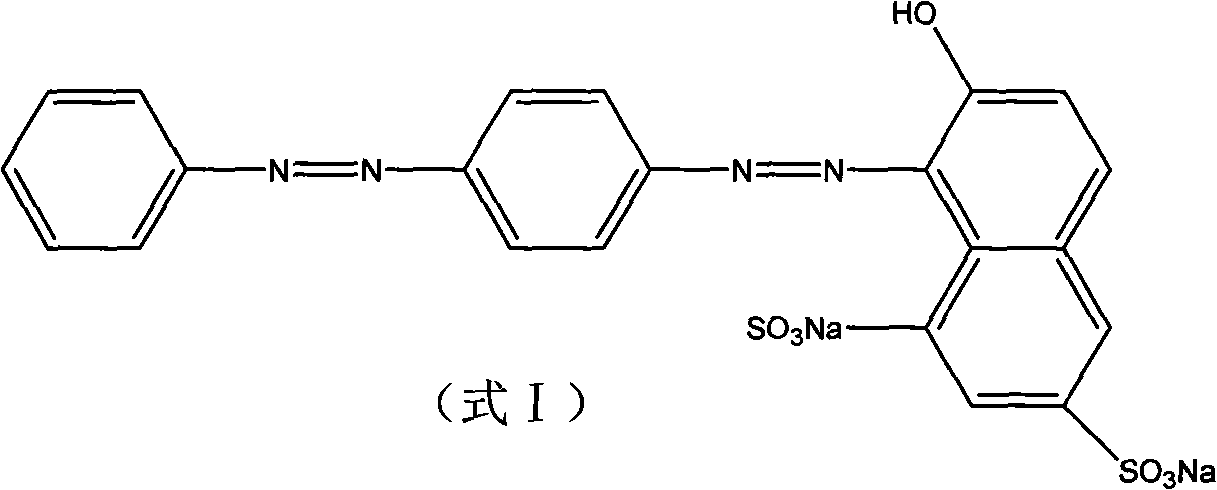
This invention relates to new oxazolidinones having a cyclopropyl moiety, which are effective against aerobic and anerobic pathogens such as multi-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci, Bacteroides spp., Clostridia spp. species, as well as acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species. The compounds are represented by structural formula I: its enantiomer, diastereomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Staphylococcus saprophyticus nucleic acids and polypeptides
Isolated nucleic acid molecules which encode proteins from Staphylococcus saprophyticus are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated proteins, mutated proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the treatment, prevention or detection of an S. saprophyticus-associated disease or disorder. Furthermore, the nucleic acid molecules and polypeptide molecules of the invention may be used for the identification of agents which modulate S. saprophyticus activity, e.g., a small molecules.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
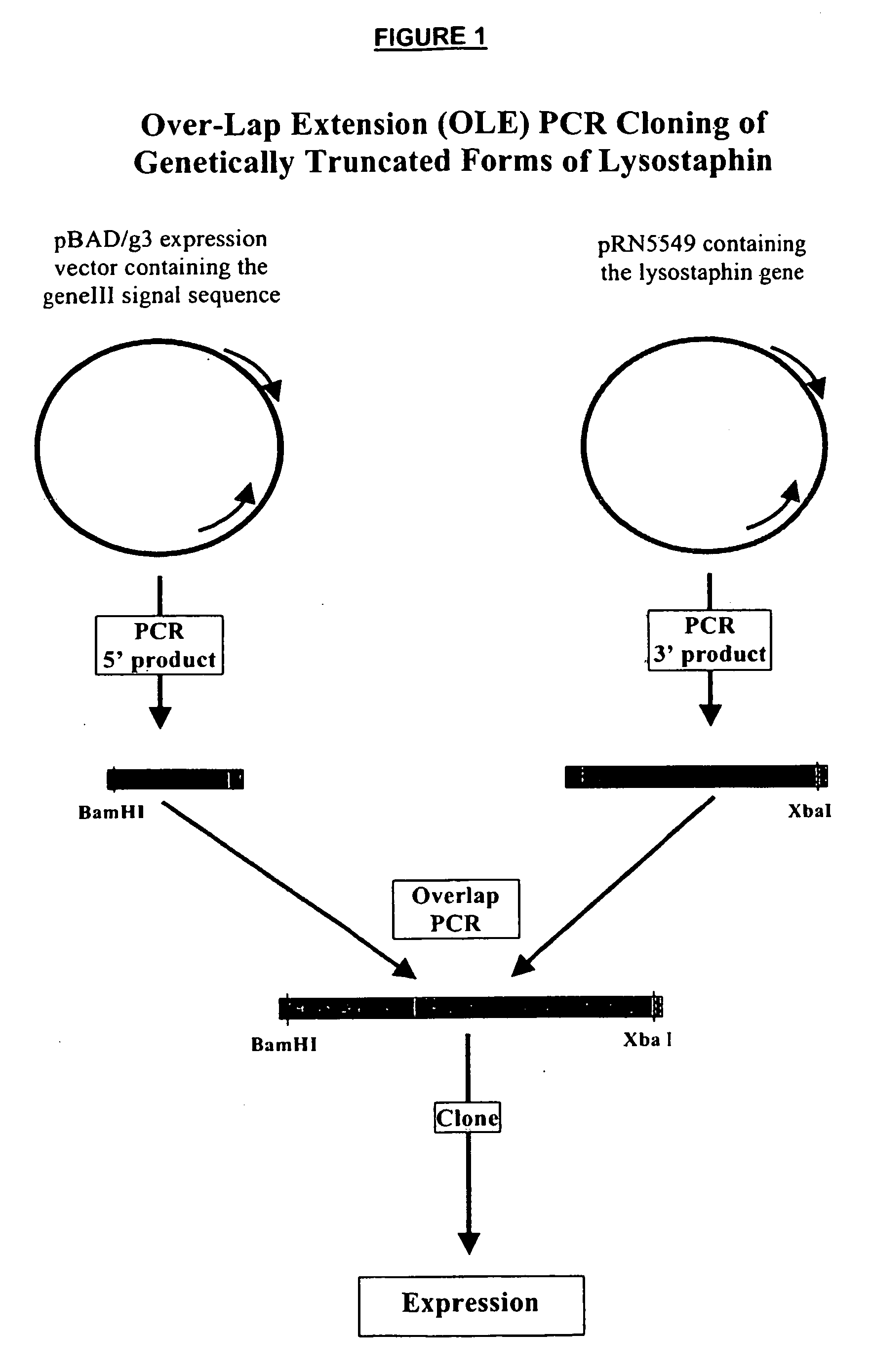
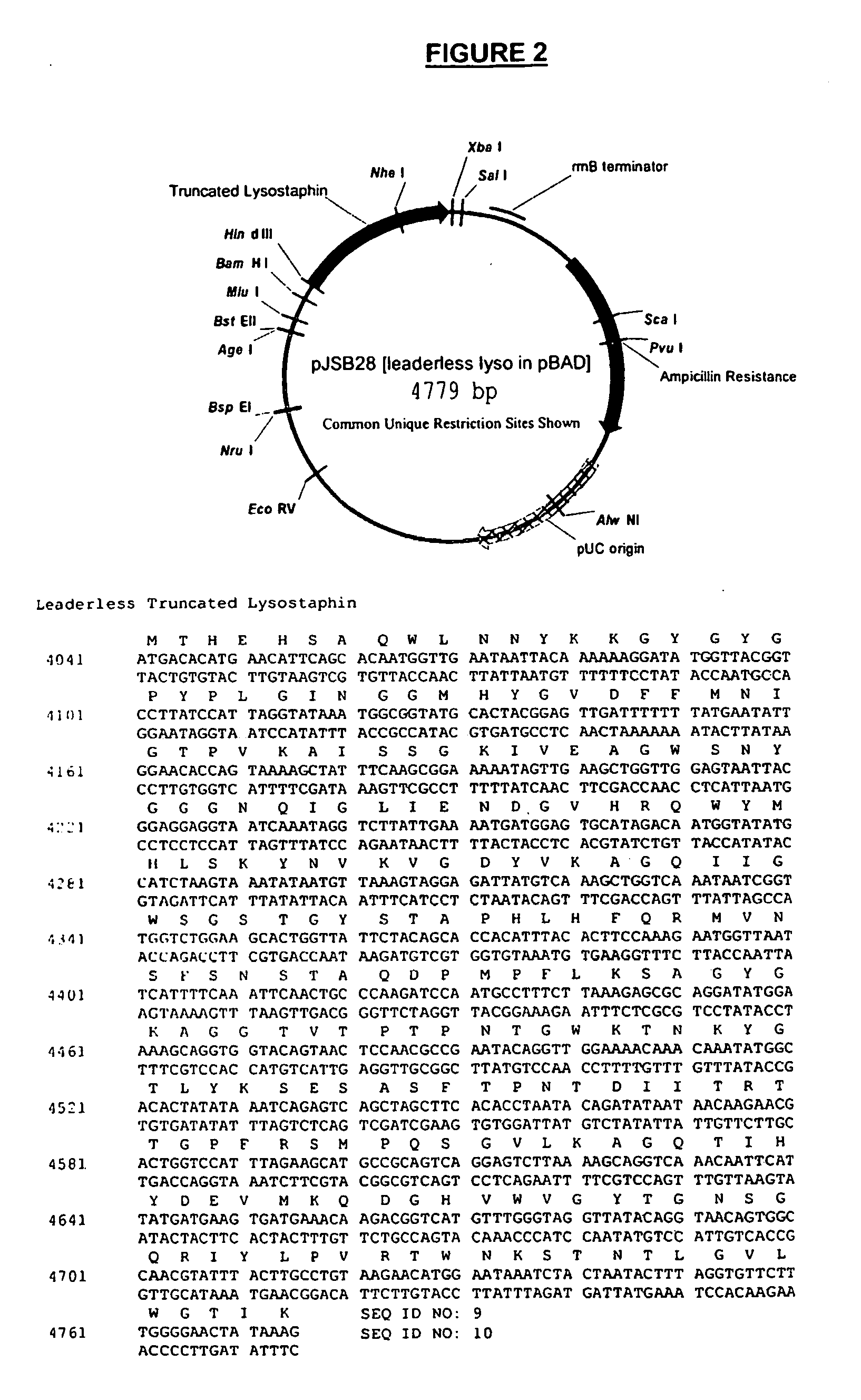
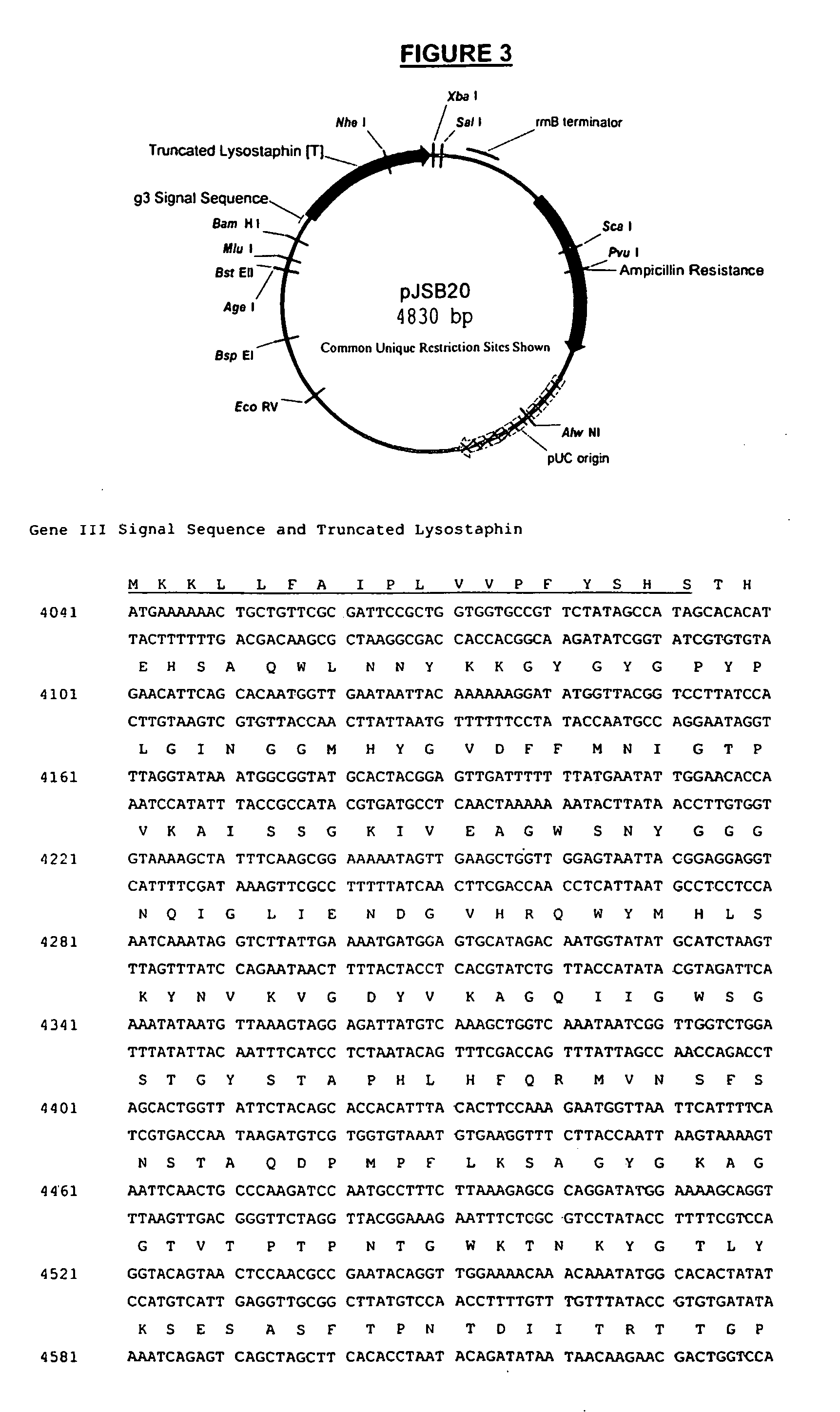
Truncated lysostaphin molecule with enhanced staphylolytic activity
InactiveUS20050118159A1Reduce individual infectionAvoid spreadingAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesStaphylococcal infectionsStaphylococcus saprophyticus
This invention relates to the production of recombinant lysostaphin in a homogenous form through the use of recombinant DNA molecules that express homogenous lysostaphin and host cells transformed with these DNA molecules. This invention also relates to the production of truncated forms of lysostaphin. The resulting lysostaphin preparations can be administered to those at infected or risk for infection by staphylococcal bacteria.
Owner:BIOSYNEXUS INC
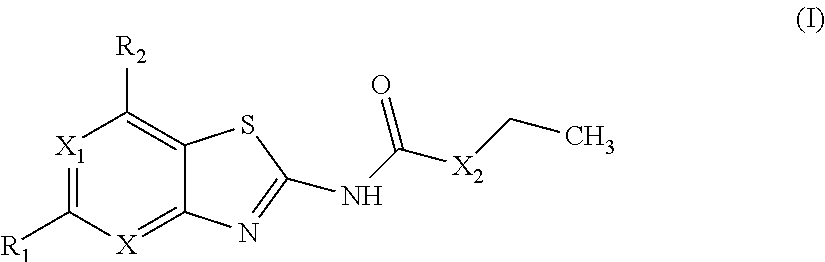
Benzothiazoles and aza-analogues thereof use as antibacterial agents
The present invention provides Gyrase B and / or Topoisomerase IV par E inhibitors, which can be used as antibacterial agents. Compounds disclosed herein can be used for treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed by gram positive, gram negative and anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Pseudomonas spp., Acenetobacter spp., Moraxalla spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasma spp., Legionella spp., Ktycobacterium spp., Helicobacter, Clostridium spp., Bacteroides spp., Corynebacterium, Bacillus spp., Enterobactericeae,’ (E. coli, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., etc.) or any combination thereof. Also provided, are processes for preparing compounds disclosed herein, pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds disclosed herein, and methods of treating bacterial infections. (Formula)
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Method for detecting staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN102645536AImprove stabilityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysisStaphylococcus cohniiFood safety
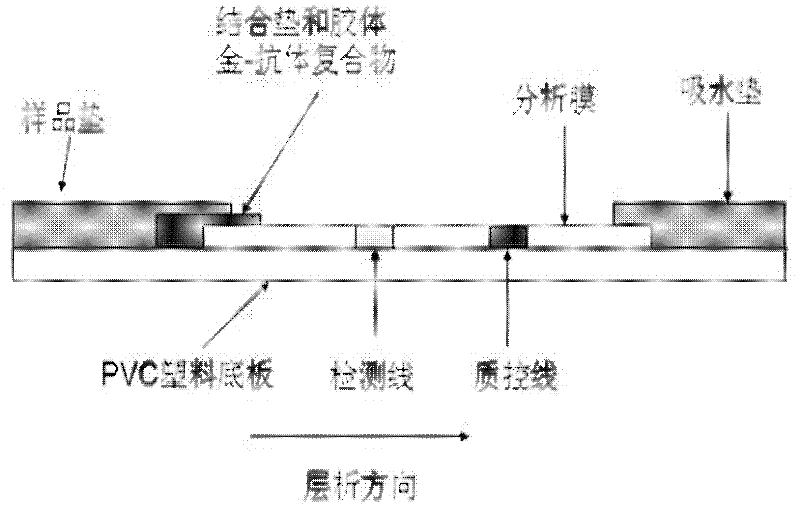
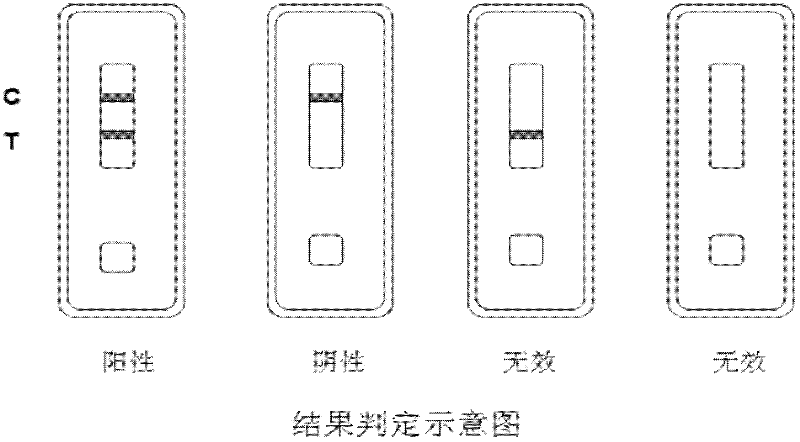
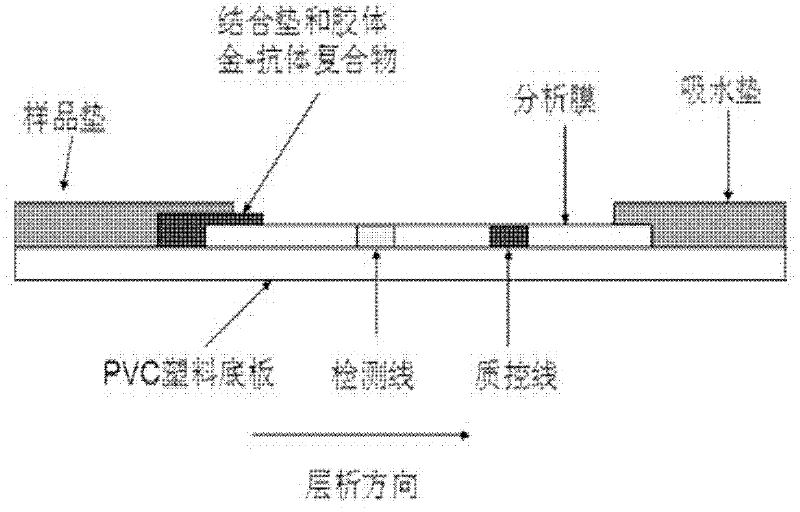
The invention relates to a method for detecting staphylococcus aureus, namely a method for enriching and screening the staphylococcus aureus by a one-step method. The method comprises the following steps of: utilizing a superparamagnetic nano particle covered by a staphylococcus aureus specific antibody to be specially combined with the staphylococcus aureus to form a composite; collecting a superparamagnetic nano particle composite under the attraction effect of an external magnetic field; inoculating the enriched composite into a culture medium to culture for 6-12 hours; and utilizing a staphylococcus aureu colloidal gold colloidal gold test paper to carry out qualitative and quantitative detection. The invention further provides the corresponding colloidal gold colloidal gold test paper for rapidly detecting the staphylococcus aureus, which has the flexibility of 104 cfu / mL of bacteria liquid and can be used for food safe detection, clinical rapid diagnosis, and onsite rapid screening of samples including water quality and the like.
Owner:沈鹤柏
Methods and Compositions Including Diagnostic Kits For The Detection In Samples Of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
InactiveUS20120077684A1Cost-effective management and controlMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSCCmecStaphylococcus saprophyticus
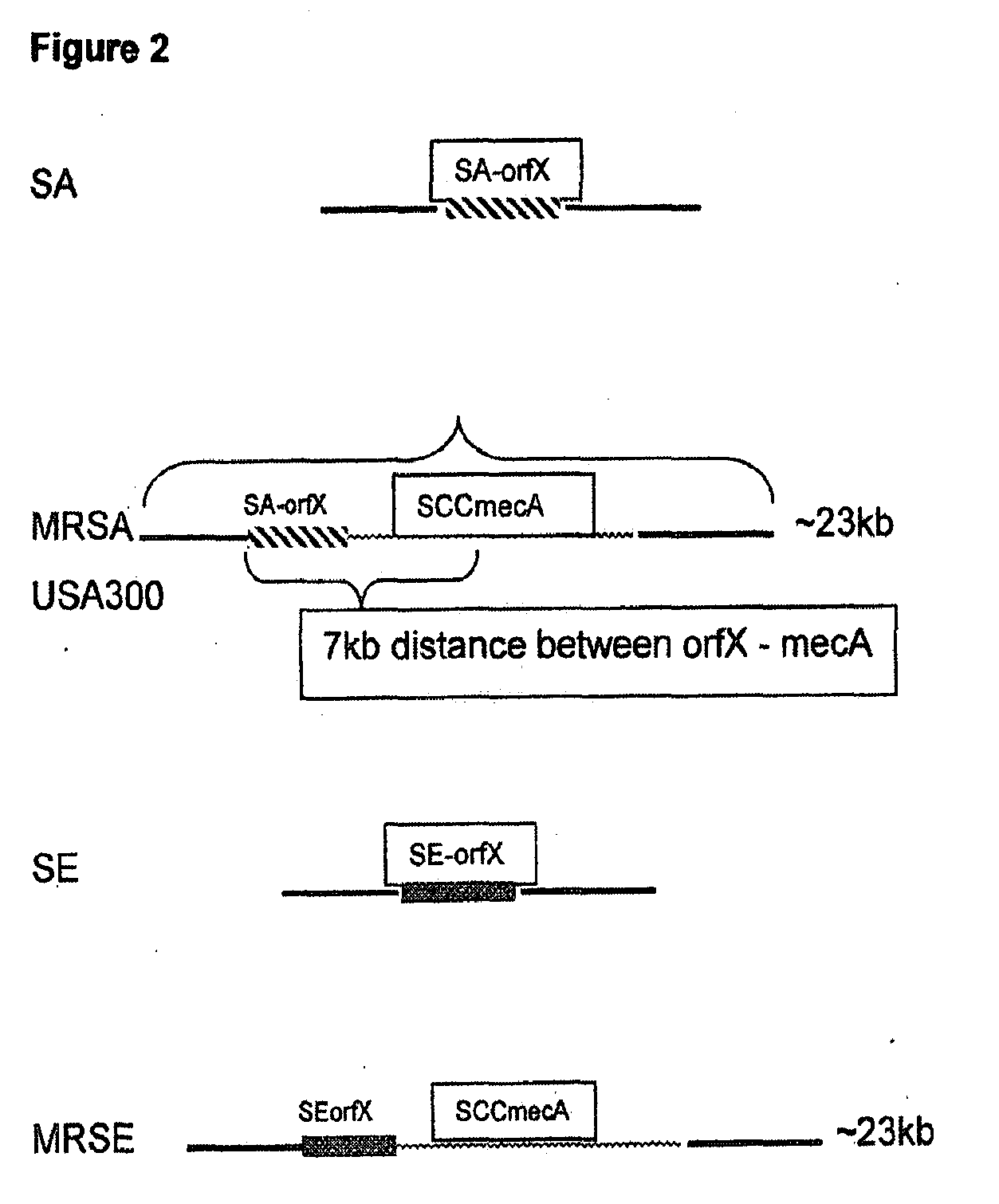
The present invention provides methods, compositions and diagnostic kits for the detection of Staphylococcus Aureus (SA) and antibiotic resistant forms and variants thereof, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA), mupirocin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (mupSA), and the like, in a sample population. The invention preferably involves the improvements of bacterial sampling by means of SA enrichment, followed by SA cell disruption and amplification procedures incorporating the use of multiplex assays for SA specific genes, such as mecA and coagulase negative Staphylococci (CONS) specific genes such as tufA, for SA identification and identification of its known species. This provides means for controlling for the thirty or more known CONS species in assessing SA samples, especially those CONS species that may carry antibiotic resistance genes, such as SCCmec.
Owner:ZEUS SCI
Staphylococcus pasteuri and application thereof in decolorization
InactiveCN101880639AImprove efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus pasteuriWastewater
The invention discloses staphylococcus pasteuri and application thereof in decolorization. The strain is staphylococcus pasteuri CGMCC No.3431. The staphylococcus pasteuri has broad-spectrum azo dye decolorizing capacity, can adapt to extreme environment and can still decolorize azo dye under the alkaline condition. The strain has the advantages of solving the problems existing in the prior art, improving the efficiency of the conventional wastewater treatment method and having industrial application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods and compositions related to immunizing against staphylococcal lung diseases and conditions
Embodiments of the invention include methods and compositions useful in a vaccination strategy capable of neutralizing HIa to provide immunoprotection against S. aureus pneumonia. In certain aspects the invention includes a HIa with reduced toxicity, represented by a recombinant mutant form of HIa (HlaH35L) in which histidine 35 is converted to leucine, which can be used to abrogate the productive assembly of the toxin and protect a subject from staphylococcal pneumonia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
DNA sensor for detecting staphylococcus aureus as well as preparation method and application of DNA sensor
ActiveCN104630869AInhibit aggregationGood dispersionElectrolytic coatingsMaterial electrochemical variablesStaphylococcus aureusA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA sensor for detecting staphylococcus aureus as well as preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of rapid pathogenic bacteria detection. A electrochemical carbon nano tube / gold nano particle composite membrane DNA sensor is prepared by utilizing the biological fixation effect and electrochemical electron transfer rate enhancing function of the gold nano particle, and is capable of effectively improving the detection sensitivity. According to the invention, a detection method, having high universality, high sensitivity and high accuracy, and detection conditions for staphylococcus aureus are preliminarily established through a detection technology in which specific staphylococcus aureus gene sequence is synthesized to be used as probe ssDNA so as to form a hybridization system with a complementation target ssNDA segment and methylene blue is used as a hybridization indicator.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Treatment of microbial infections
InactiveUS20110150918A1Improve the level ofStimulate immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesMicroorganism
The present invention is directed to improved microbial antigen vaccines, pharmaceutical compositions, immunogenic compositions and antibodies and their use in the treatment of microbial infections, particularly those of bacterial origin, including Staphylococcal origin. Ideally, the present invention is directed to a recombinant staphylococcal MSCRAMM or MSCRAMM-like proteins, or fragment thereof, with reduced binding to its host ligand, for use in therapy.
Owner:TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN
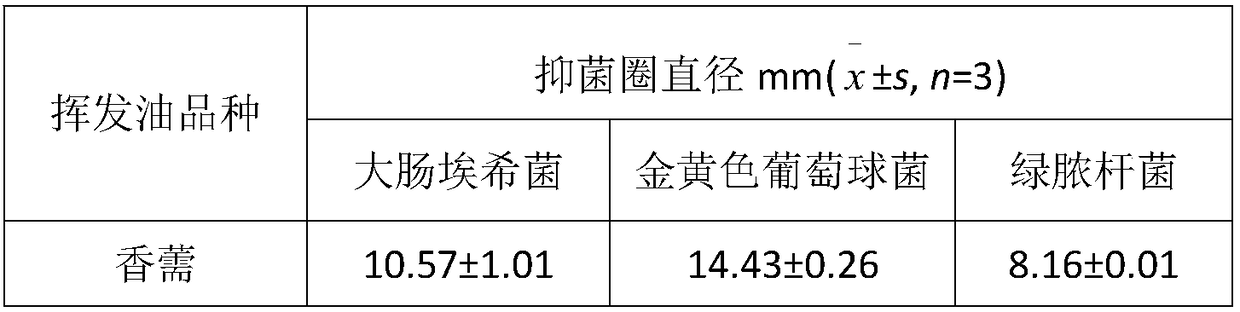
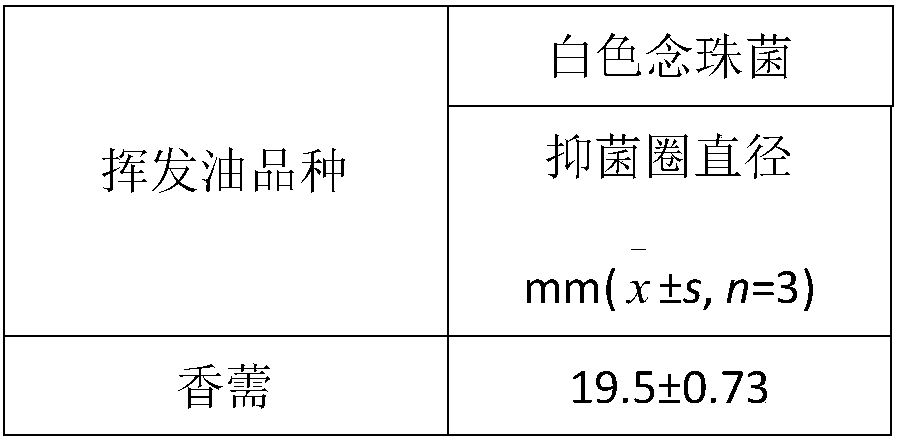
Application of elsholtzia volatile oil in sterilizing and/or anti-bacteria and antibiotic resistant bacteria and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses application of elsholtzia volatile oil in anti-bacteria and antibiotic resistant bacteria. The elsholtzia volatile oil is extracted by steam distillation. The elsholtzia volatile oil has certain functions of killing and / or inhibiting growth on bacteria of staphylococcus, escherichia coli, candida, pseudomonas, enterobacter, streptococcus and the like and fungi. The elsholtzia volatile oil has certain functions of killing and / or inhibiting growth on bacteria of drug-resistant staphylococcus, drug-resistant escherichia coli, drug-resistant enterobacter, drug-resistant klebsiella, drug-resistant pseudomonas, drug-resistant acinetobacter, drug-resistant streptococcus, and drug-resistant enterococcus and the like. The elsholtzia volatile oil can be used in industries offood, medicine, health care products, cosmetics and the like and can be used for preparing various forms of products with antibacterial and antibiotic resistant bacteria functions, and belongs to thenew application field of the elsholtzia volatile oil.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
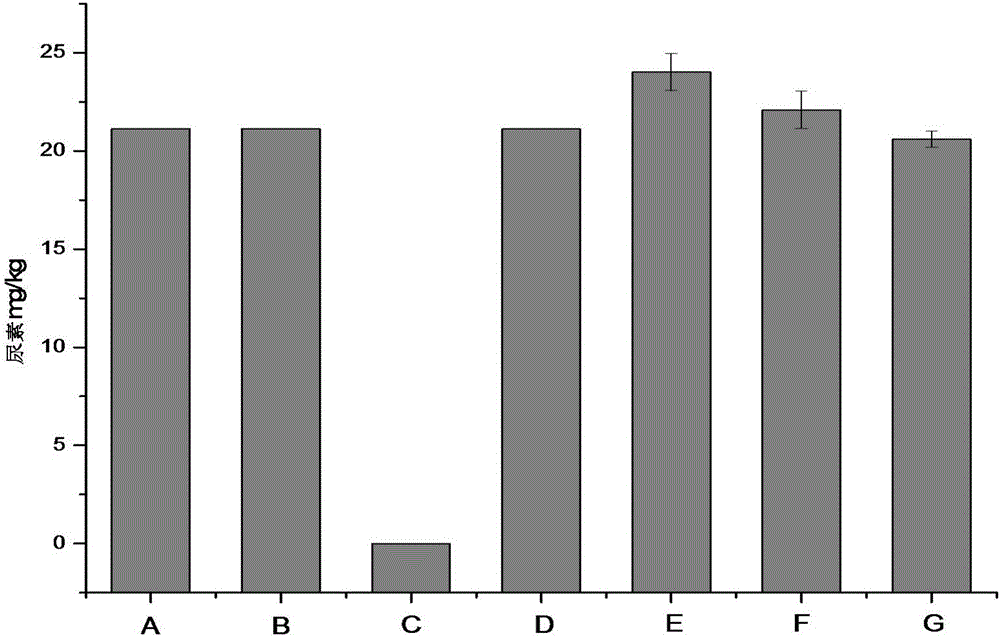
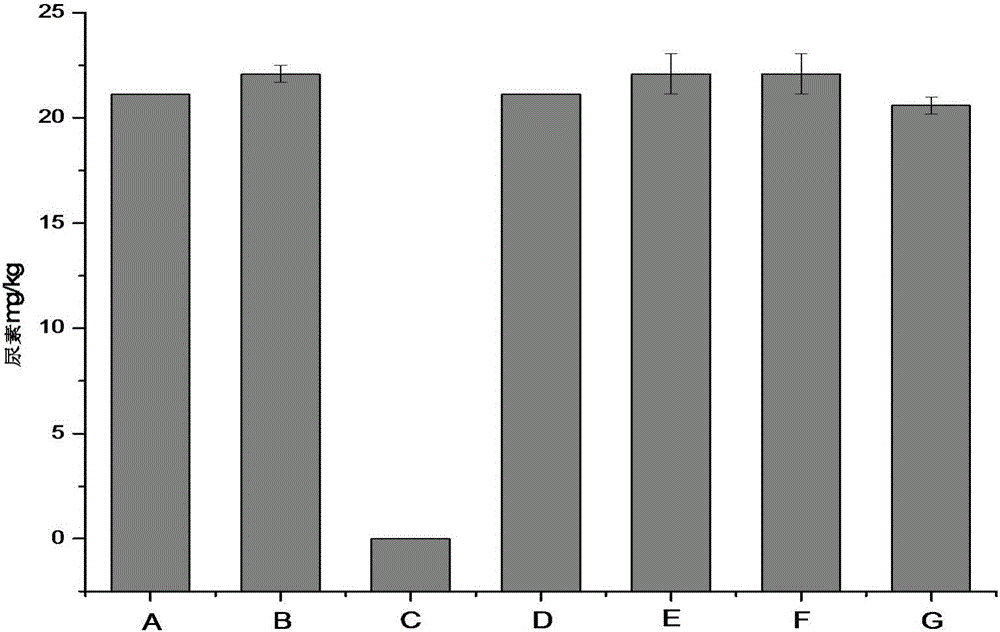
Method for reducing urea in fermented grains of Luzhou-flavor liquor
ActiveCN105861235AReduce contentMicroorganism based processesAlcoholic beverage preparationMicroorganismFood grade
The invention discloses a method for reducing urea in the fermented grains of Luzhou-flavor liquor, belonging to the fields of microorganism production and utilization. In the invention, lactobacillus reuteri or crude enzyme liquid thereof is added before the fermented grains of liquor are added into a pit for fermentation, and the content of important precusor substance urea of EC in the fermented grains is reduced by 100% while basically no effect is realized without adding a bacterial strain or enzyme liquid or by adding staphylococcus saprophyticus or enzyme liquid thereof. In the invention, the adopted lactobacillus reuteri is food-grade safe bacteria, and other harmful substances are not generated after the lactobacillus reuteri is applied to the fermented grains. The method disclosed by the invention has good industrial application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
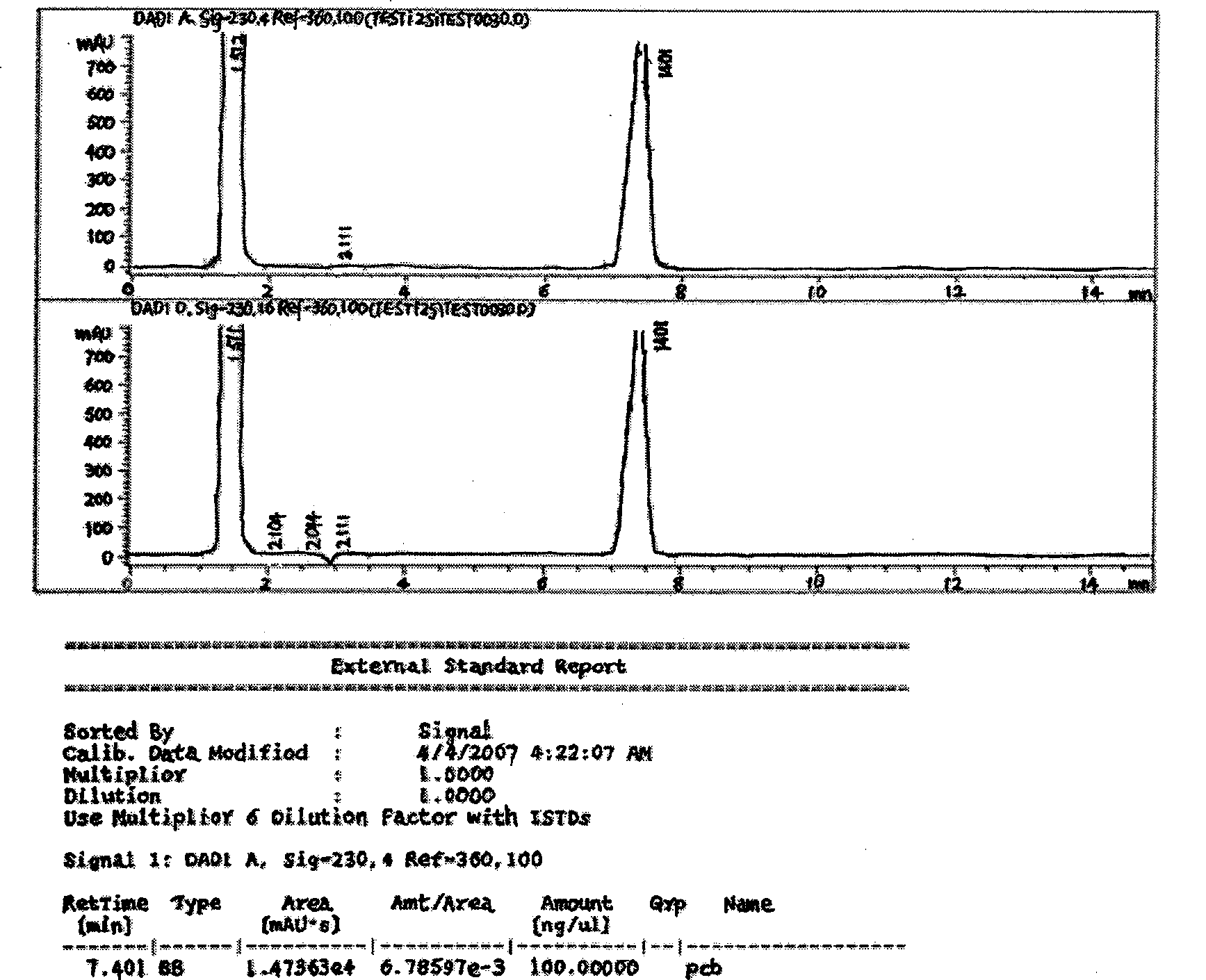
Degradation method for polychlorinated biphenyl with staphylococcus epidermidis
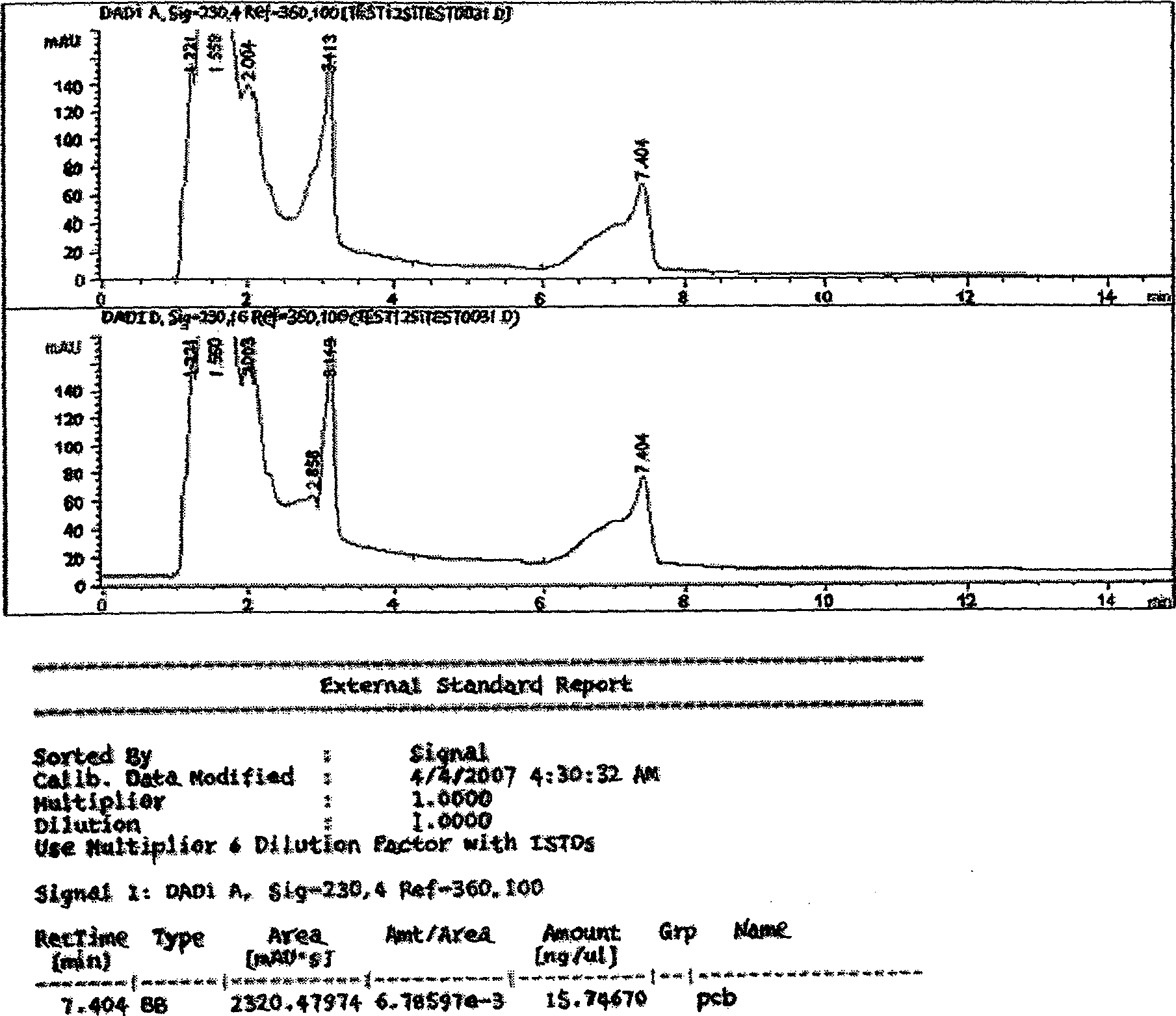
The invention relates to a method for degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by staphylococcus epidermidis. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating staphylococcus epidermidis in a polychlorinated biphenyl degradation culture medium and subjecting the staphylococcus epidermidis to the shaking culture at 28-32 DEG C for 24-120 hours; and analyzing the degradation effect of the bacterial strain on the PCBs after the culture is subjected to high performance liquid chromatograph determination. By the addition of extra carbon source glucose, the method can ensure that the staphylococcus epidermidis is more efficient in degrading the polychlorinated biphenyls, thereby allowing the bacteria to obtain the conditions for degrading the polychlorinated biphenyl.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Compositions and methods for altering human cutaneous microbiome to increase growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis and reduce Staphylococcus aureus proliferation
ActiveUS9370476B2Selectively inhibiting growthImprove scalabilityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsArginineStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
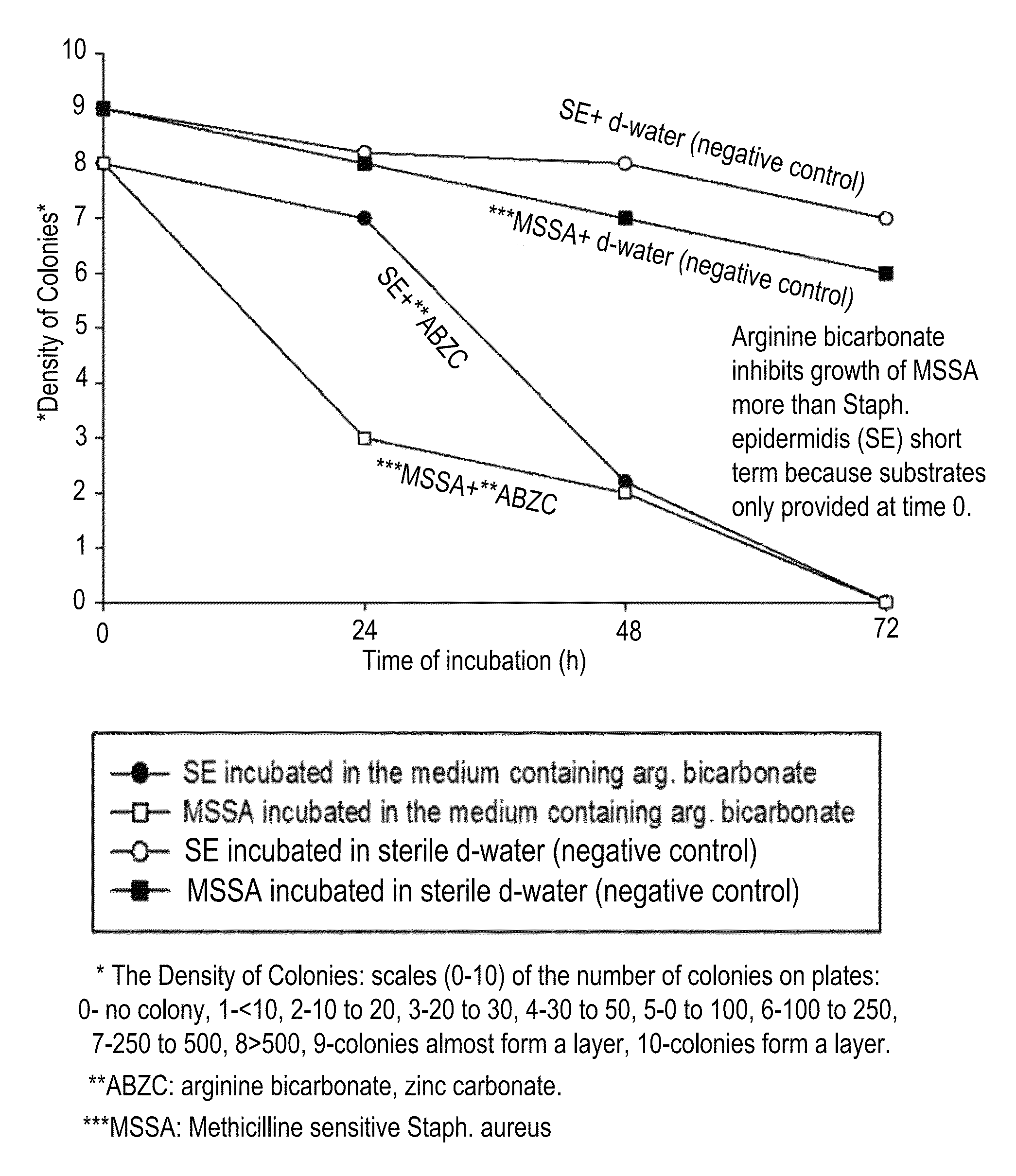
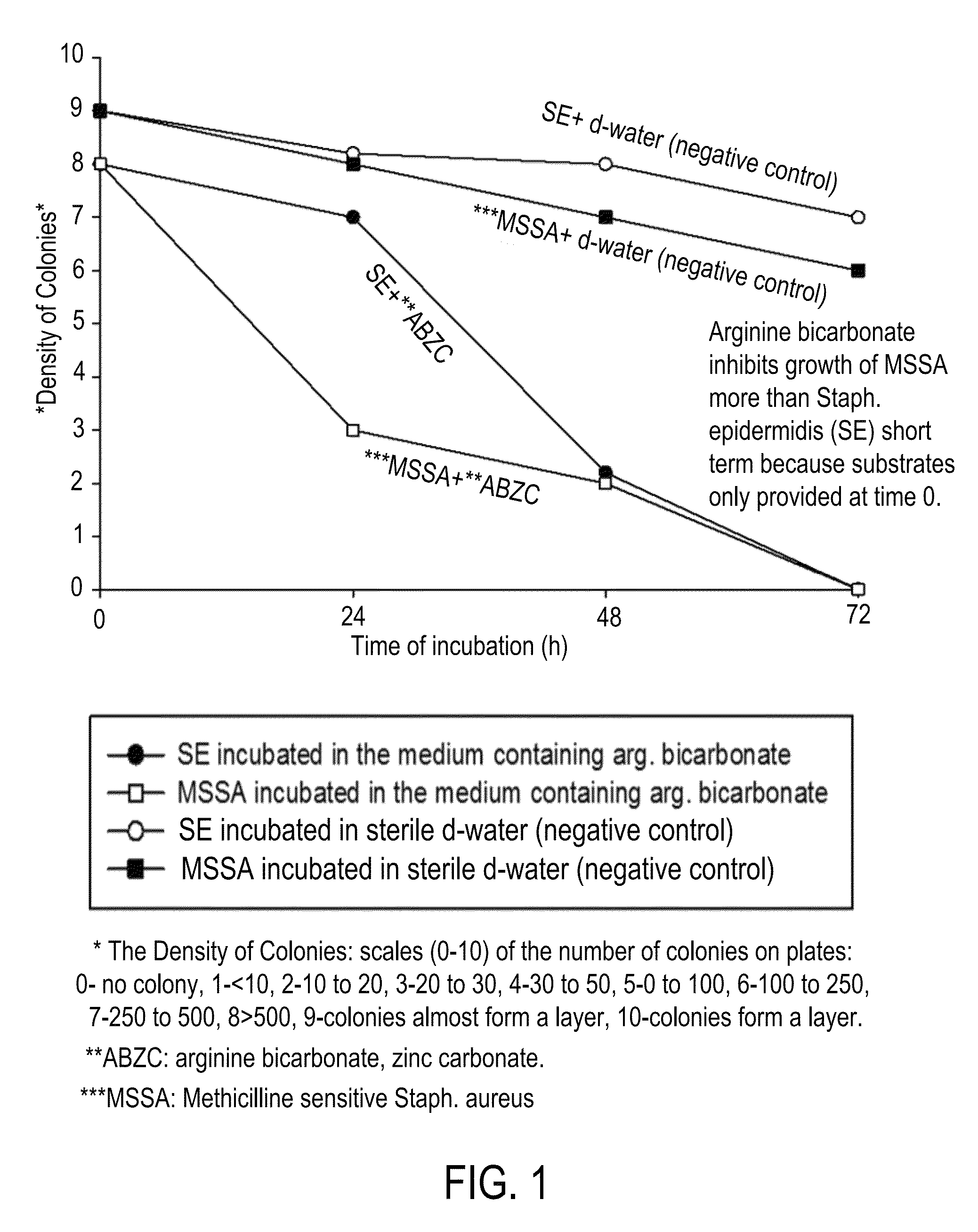
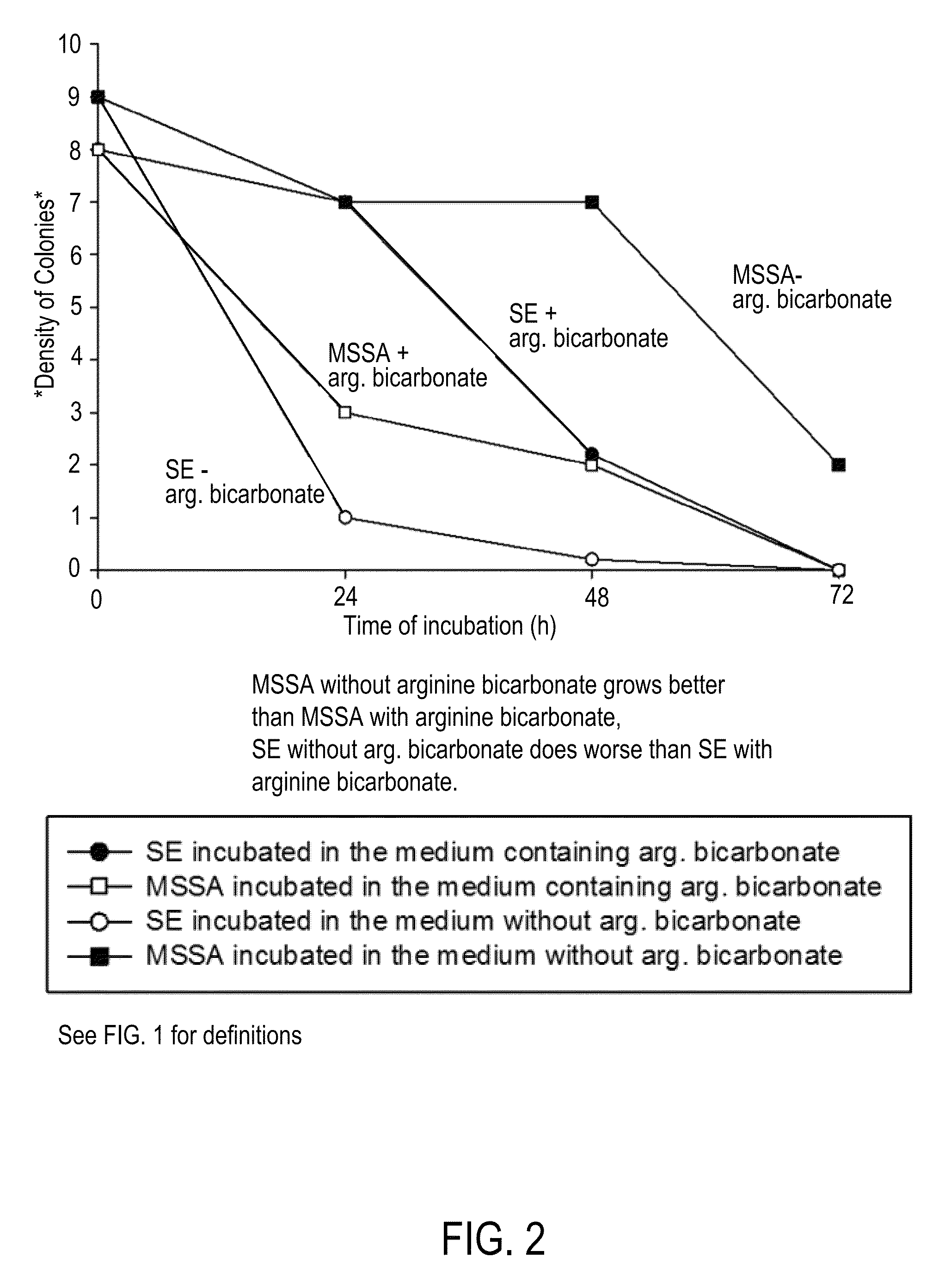
A composition including arginine or a salt thereof, a zinc salt, preferably arginine bicarbonate and zinc carbonate (ABZC), in combination, plus one or more physiologically acceptable excipients, administered for the modification of cutaneous microfloras, generally to inhibit the growth of pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus bacteria and also promote the growth of non-pathogenic Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria, and methods for using such composition.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Bacteriophage lysin and antibiotic combinations against gram positive bacteria
ActiveUS20150290299A1Quick killBroad killing activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLysinLinezolid
The present invention provides compositions and methods for prevention, amelioration and treatment of gram positive bacteria, particularly Staphylococcal bacteria, with combinations of lysin, particularly Streptococcal lysin, particularly the lysin PlySs2, and one or more antibiotic, including daptomycin, vancomycin, oxacillin, linezolid, or related antibiotic(s).
Owner:CONTRAFECT CORP
Method for E, coli to express lysostaphin in high efficiency via external secretion
ActiveCN1900290AReduce pollutionHigh recovery ratePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
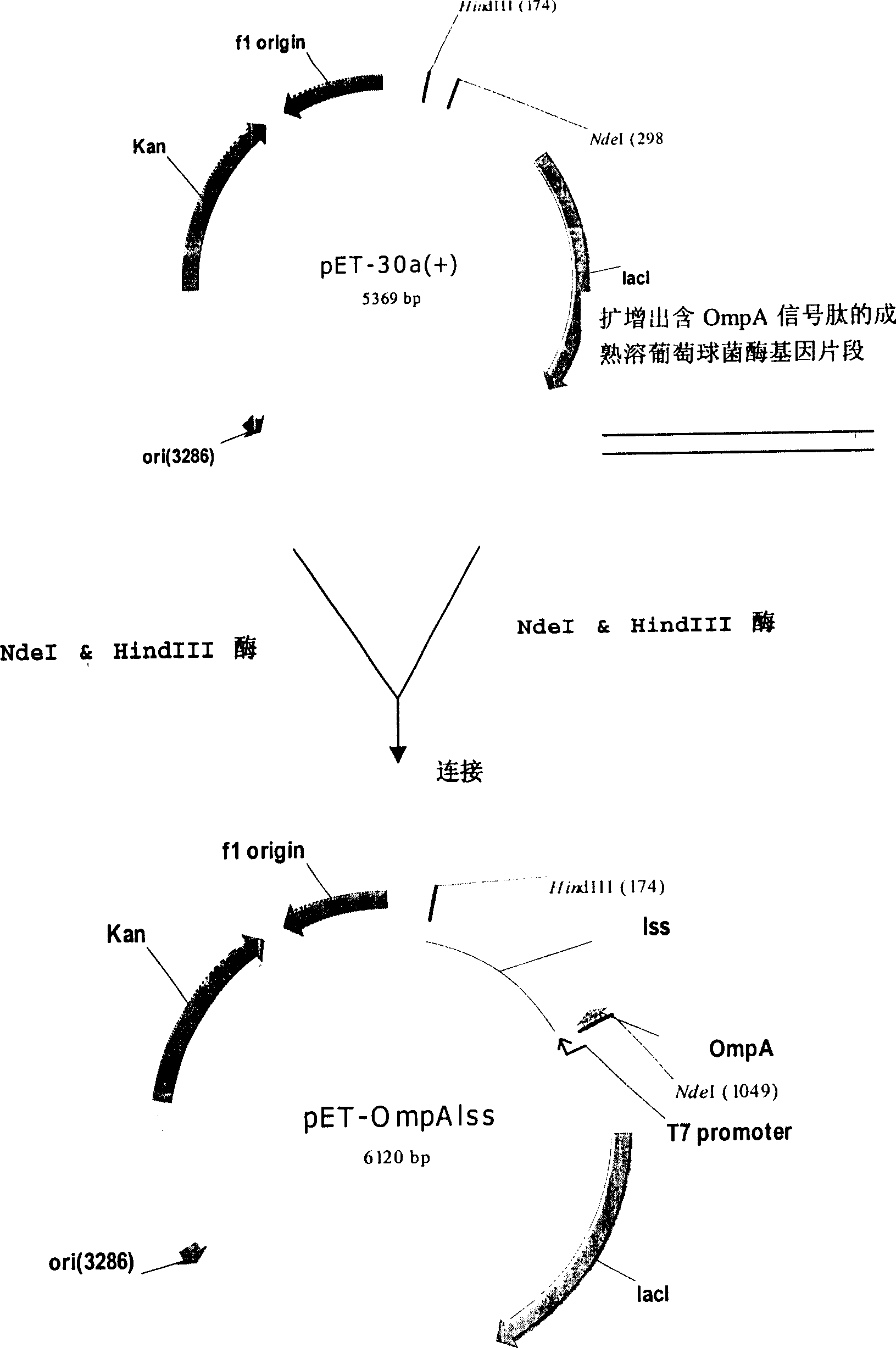
The present invention provides method for E. coli to express lysostaphin in high effect via external secretion. The method includes cloning coding signal peptide suitable for secreting expression in E. coli in front of the gene sequence of partially or completely mature lysostaphin and connecting to promoter to constitute the expression vector; transforming the expression vector to E. coli and culturing fermentation; and separating lysostaphin from the supernatant of the fermented liquid. The external secretion expression has the advantages of the expression product existing in the culture medium in ultimate active form and without need of inclusion body renaturation and other steps; simple purification from culture medium supernatant and high recovering rate; and less host bacteria protein pollution.
Owner:SHANGHAI HI TECH UNITED BIO TECHCAL RES
Method for preparing quick magnetic separation electrochemistry immunosensor and method for detecting staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN105203756ALarge specific surface areaMany surface active sitesMaterial analysisStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus aureus
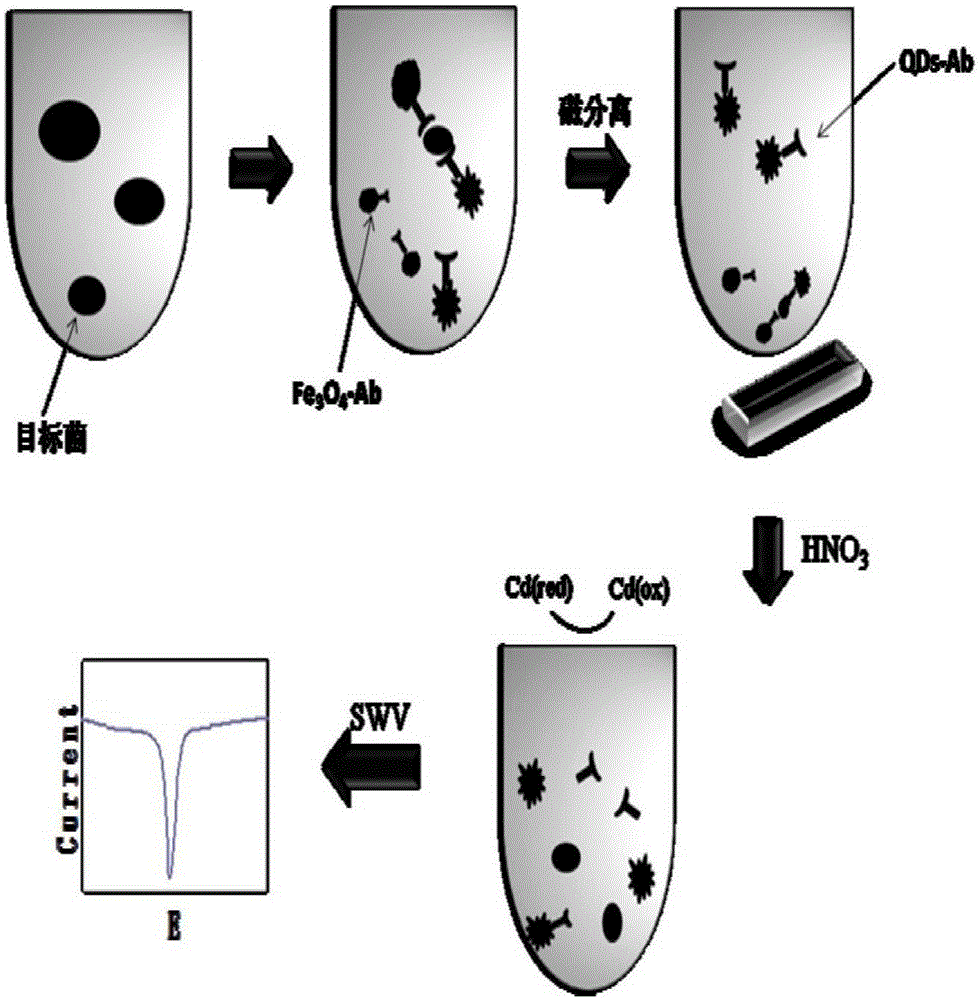
The invention discloses a method for preparing a quick magnetic separation electrochemistry immunosensor and a method for detecting staphylococcus aureus and belongs to the technical field of biosensing. Supernatant liquid is removed through separation and concentration under the effect of a magnetic field, sediment is dissolved through 0.1 M HNO3 and then subjected to ultrasounds, and the dissolved matter is then mixed with HAC / NaAC. A polished and cleaned electrode is steeped into the mixed solution, and staphylococcus aureus is detected through an SWV electrochemical method. Test results show that the concentration range of staphylococcus aureus detected by the sensor is 2.21*10<2>-2.21*10<7> CFU mL-1, and the detection limit is 83 CFU mL-1. In addition, the immunosensor successfully conducts quantitative detection on staphylococcus aureus in milk, compared with a traditional microorganism method, by means of the technology, the analyzing time is greatly shortened, operation is simple, and the requirement for quickly detecting staphylococcus aureus in the fields of food, environments and the like can be better met.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for restoring arsenic-polluted soil by plant-microorganism combination
The invention discloses a method for restoring arsenic-polluted soil by plant-microorganism combination. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, screening plants and microorganisms, so asto obtain plant clinopodium urticifolium with high arsenic resistance and microbial staphylococcus saprophyticus with high arsenic resistance; next, planting the plant clinopodium urticifolium with high arsenic resistance into heavy metal arsenic-polluted soil, and adding the arsenic-resistant microbial staphylococcus saprophyticus into the root soil of arsenic-enriched plant; and carrying out conventional culture, watering and moisturizing, wherein arsenic in the enriched soil is restored by utilizing the absorption effect of the arsenic-enriched plants on the arsenic and the strengthening effect of the arsenic-resistant microorganisms, and the aim of repairing the arsenic-polluted soil in a tail mining area can be achieved by repeating the above process. The soil restoring method is good in effect, low in cost and easy to manage and operate, no secondary pollution is generated, and the method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:HECHI UNIV
Identification and Use of Non-Peptide Analogs of RNAIII-Inhibiting Peptide for the Treatment of Staphylococcal Infections
InactiveUS20070293435A1Reduce and prevent sameAvoid bacterial infectionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPharmacophoreHamamelitannin
RNAIII inhibiting peptide (RIP) has been established as an effective inhibitor of staphylococcal infections. Non-peptide small molecule analogs based on a pharmacophore conforming to the putative atomic structure of RIP, can be identified by computer screening of that pharmacophore against established libraries of known small molecules other than peptides. One such identified structural analog is hamamelitannin. When tested for effective inhibition of staphylococcal infections, hamamelitannin demonstrated inhibition similar to that exhibited by RIP. Other analogs can be identified and similarly used.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV +1
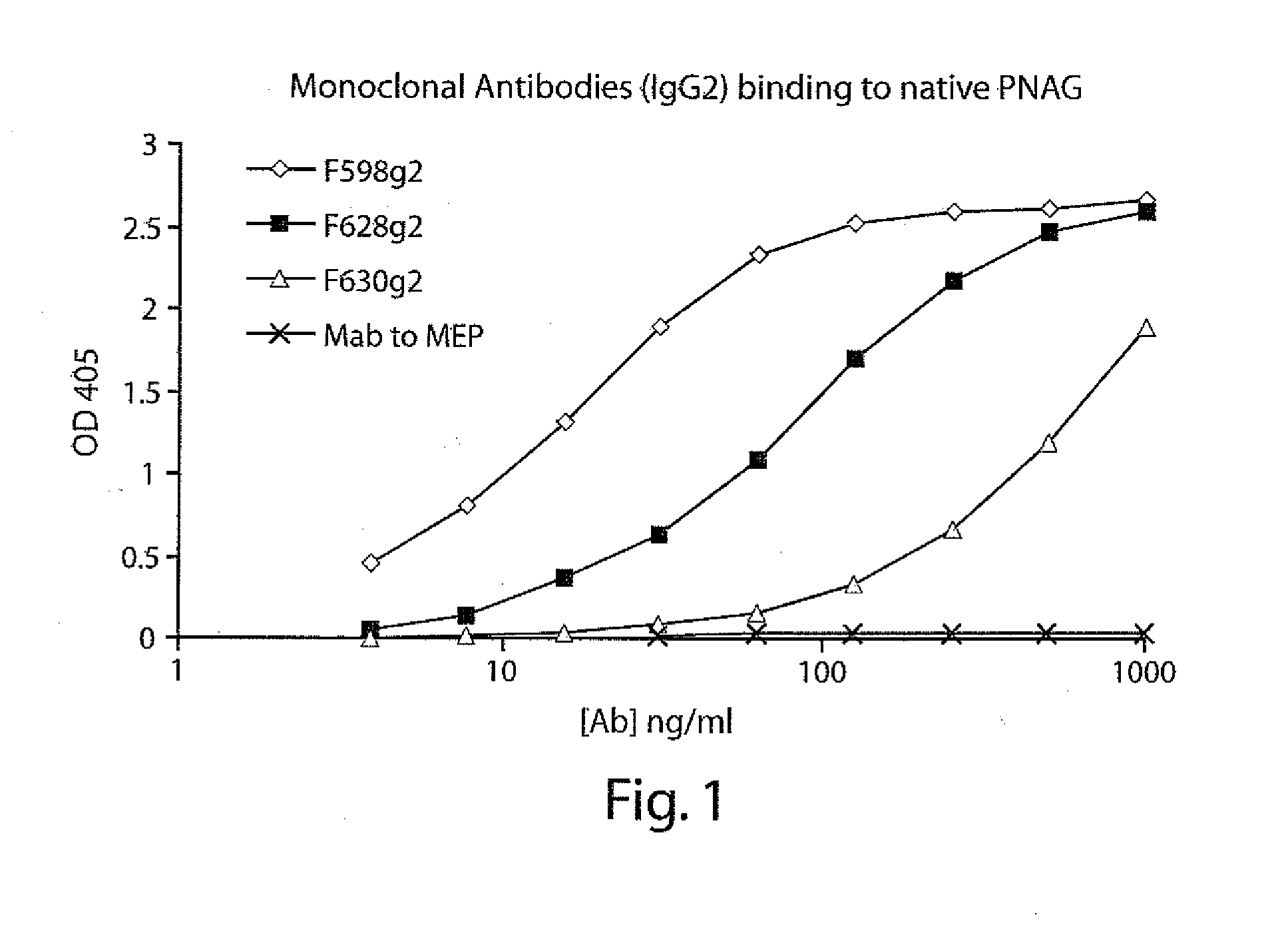
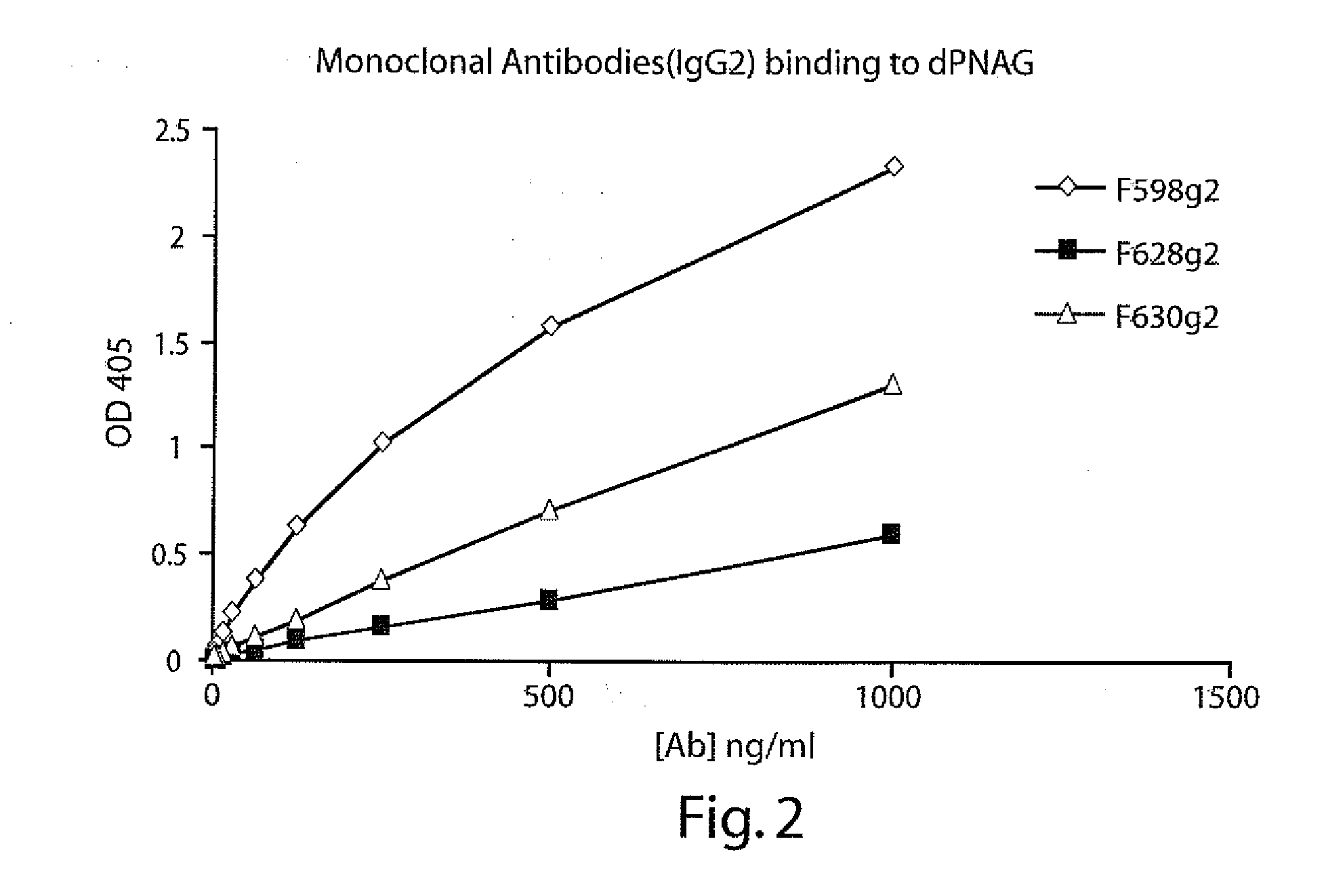
POLY-N-ACETYL GLUCOSAMINE (PNAG/dPNAG)-BINDING PEPTIDES AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF
InactiveUS20110002932A1Bacterial load in subjectReduce bacterial loadAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliBinding peptide
The present invention relates to peptides, particularly human monoclonal antibodies, that bind specifically to poly-N-acetyl glucosamine (PNAG), such as Staphylococcal PNAG, in acetylated, partially acetylated and / or fully deacetylated form. The invention further provides methods for using these peptides in the diagnosis, prophylaxis and therapy of infections by bacteria that express PNAG such as but not limited to Staphylococci and E. coli. Some antibodies of the invention enhance opsonophagocytic killing and in vivo protection against bacteria that express PNAG such as but not limited to Staphylococci and E. coli. Compositions of these peptides, including pharmaceutical compositions, are also provided, as are functionally equivalent variants of such peptides.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Chlorine resistant strain V430 and its screening method
InactiveCN1900272AEfficient degradationBacteriaWater/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The present invention relates to a kind of chlorine tolerant microbe and its screening process. The chlorine tolerant microbe strain is Staphylococcus saprophyticus V430 in the preservation number of CCTCC No. M205145. The Staphylococcus saprophyticus V430 has circular opaque colony shape with lug and smooth edges; spherical single, paired or piled cells of d in 0.6-0.9 micron without flagellum; no motion, no endogeneous spore, gram positive and anaerobic property; and optimal growth pH value of 6.0-7.5 and temperature of 25-45 deg.c. It can survive in high chlorine ion concentration environment and degrade high concentration organic pollutant effectively.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com