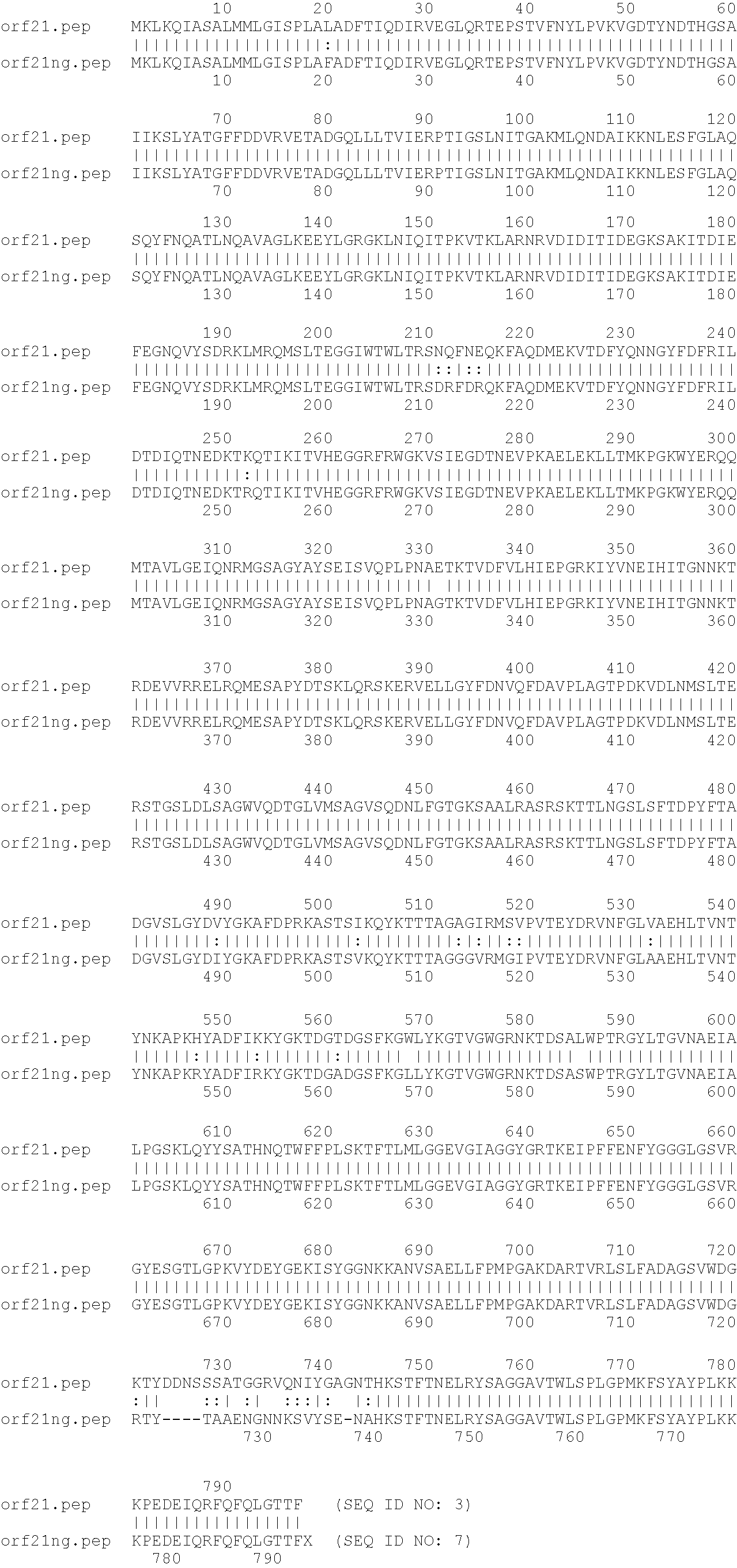Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
205 results about "Neisseria meningitidis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neisseria meningitidis, often referred to as meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. It has also been reported to be transmitted through oral sex and cause urethritis in men. The bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round, and more specifically, diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs. About 10% of adults are carriers of the bacteria in their nasopharynx. As an exclusively human pathogen it is the main cause of bacterial meningitis in children and young adults, causing developmental impairment and death in about 10% of cases. It causes the only form of bacterial meningitis known to occur epidemically, mainly Africa and Asia. It occurs worldwide in both epidemic and endemic form. N. meningitidis is spread through saliva and respiratory secretions during coughing, sneezing, kissing, chewing on toys and even through sharing a source of fresh water. It infects its host cells by sticking to them with long thin extensions called pili and the surface-exposed proteins Opa and Opc and has several virulence factors.
Conjugate vaccine for Neisseria meningitidis
InactiveUS6531131B1Bacterial antigen ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsConjugate vaccineLacto-N-tetraose
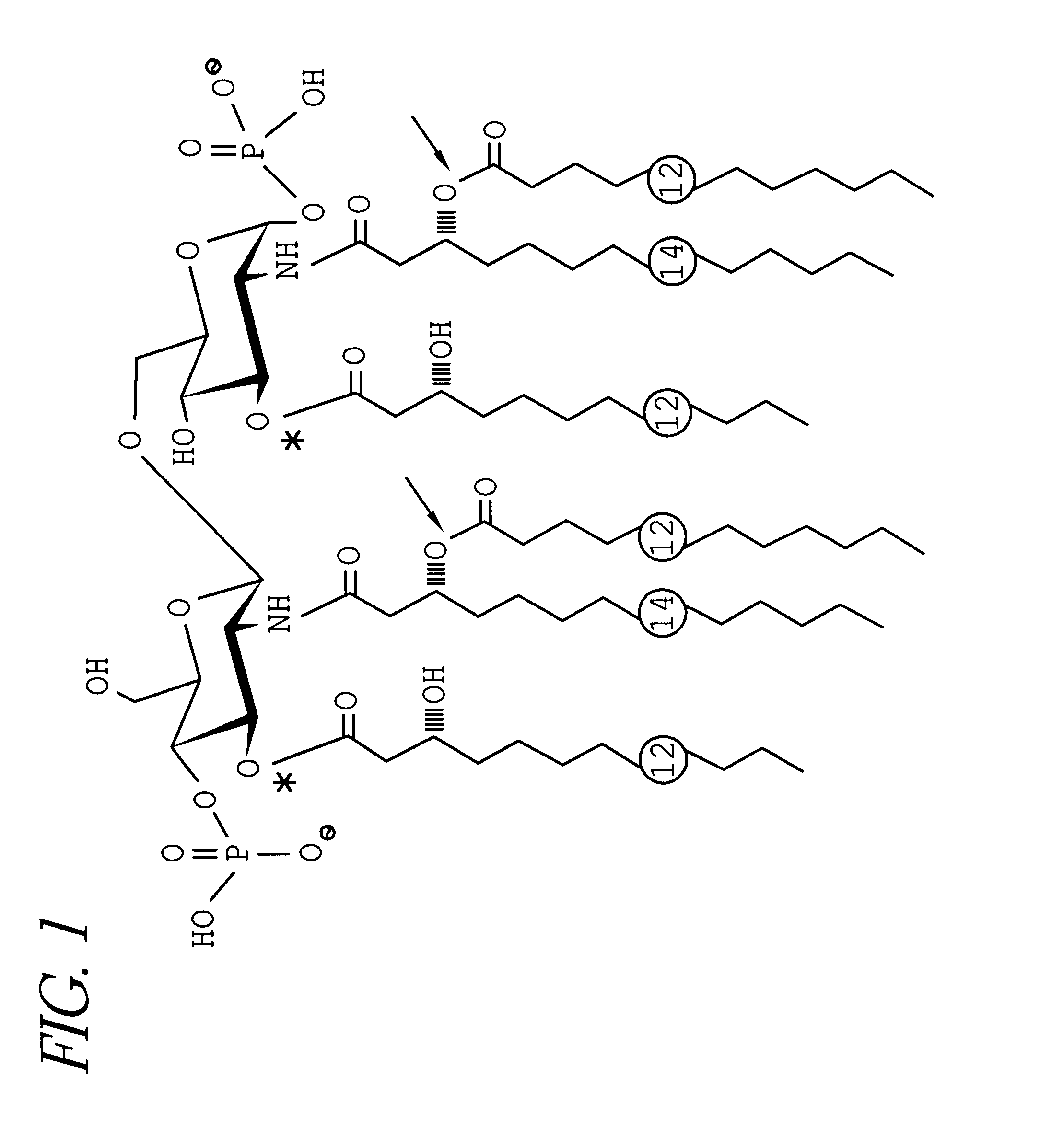
A conjugate vaccine for Neisseria meningitidis comprising lipooligosaccharide which does not contain a lacto-N-tetraose antigen from which at least one primary O-linked fatty acid has been removed conjugated to an immunogenic carrier. The vaccine is useful for prevention of meningitis and septic shock in mammals.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES REPRESENTED BY SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Novel multi-oligosaccharide glycoconjugate bacterial meningitis vaccines
InactiveUS20010048929A1Inhibition effectWeight increaseAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSerotypeTumor antigen
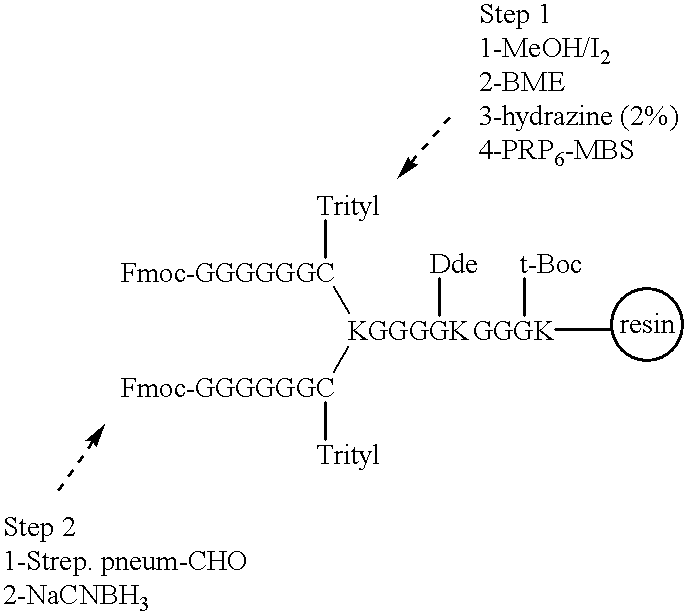
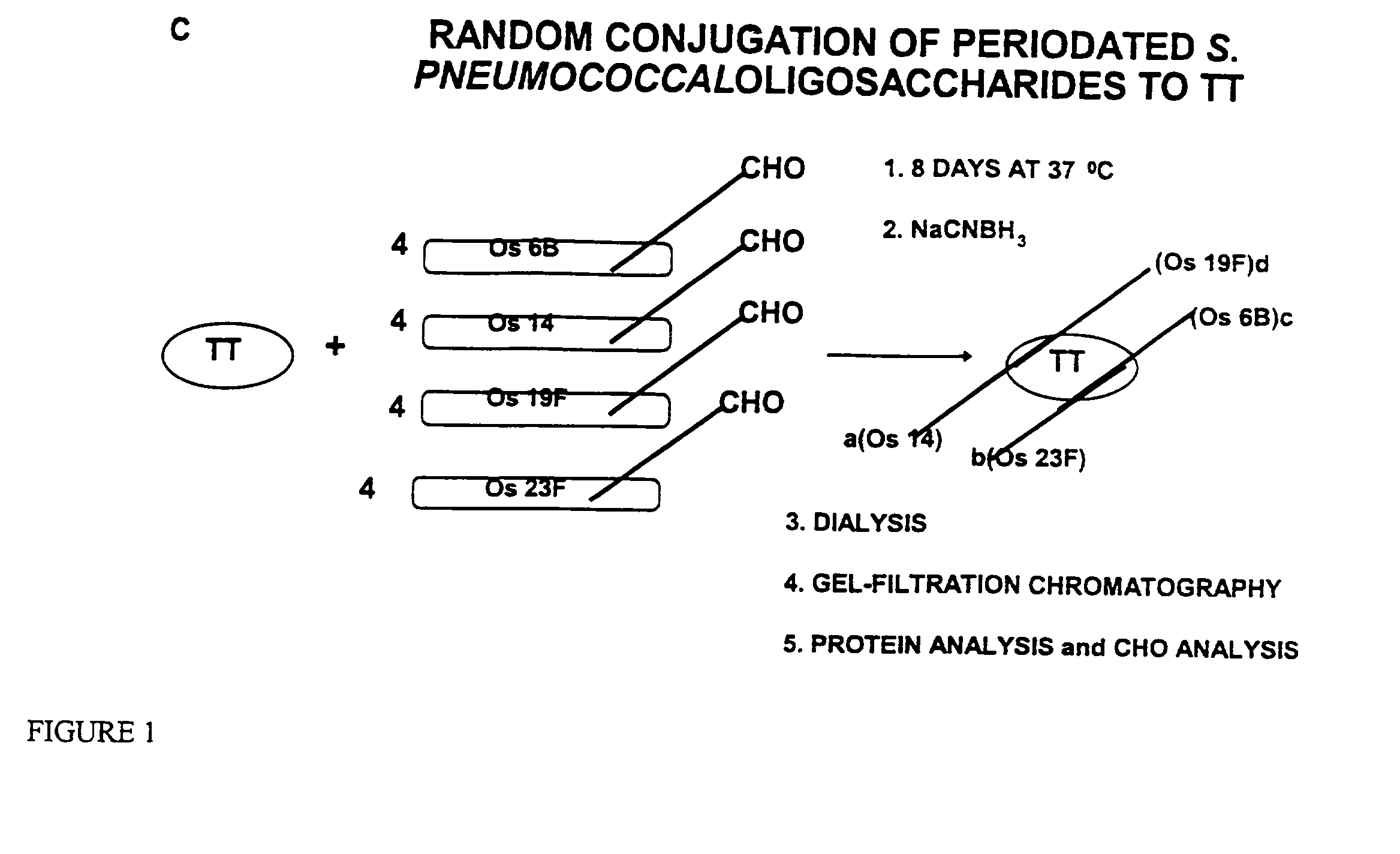
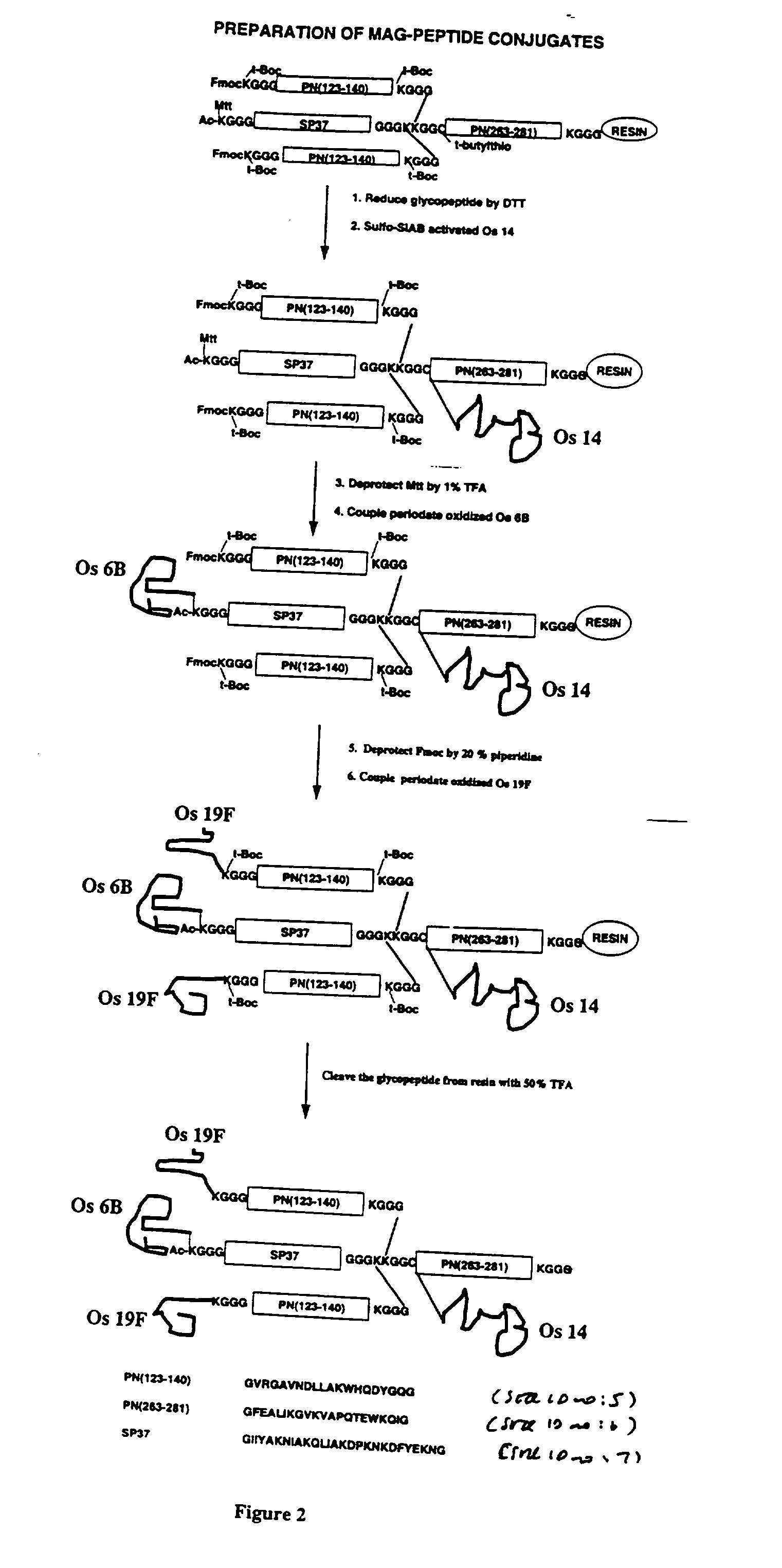
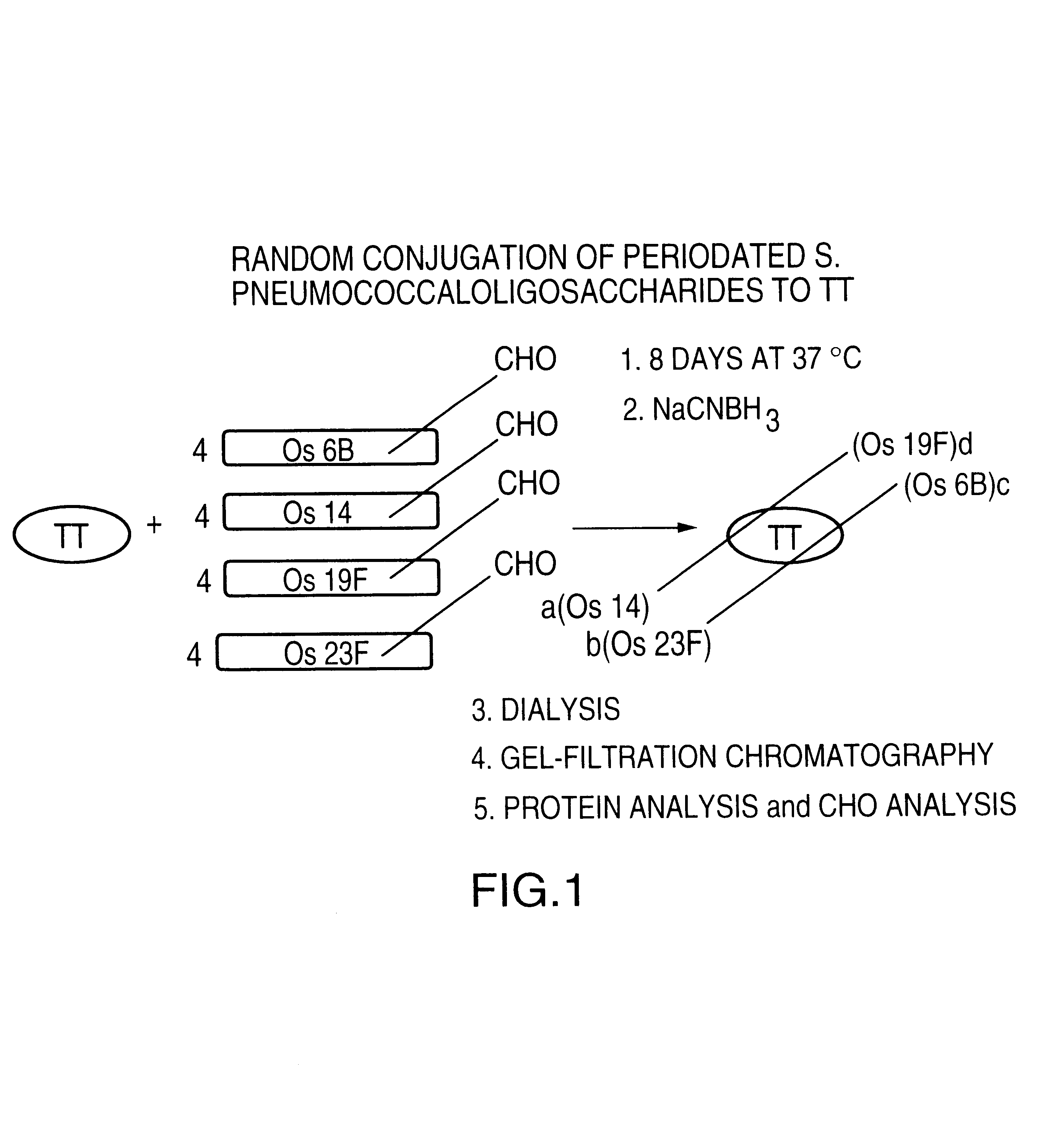
Multivalent immunogenic molecules comprise a carrier molecule containing at least one functional T-cell epitope and multiple different carbohydrate fragments each linker to the carrier molecule and each containing at least one functional B-cell epitope. The carrier molecule inputs enhanced immunogenicity to the multiple carbohydrate fragments. The carbohydrate fragments may be capsular oligosaccharide fragments from Streptococcus pneumoniae, which may be serotypes 1, 4, 5, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F or 23F, or Neisseria meningitidis, which may be serotype A, B, C, W-135 or Y. Such oligosaccharide fragments may be sized from 2 to 5 kDa. Alternatively, the carbohydrate fragments may be fragments of carbohydrate-based tumor antigens, such as Globo H, LeY or STn. The multivalent molecules may be produced by random conjugation or site-directed conjugation of the carbohydrate fragments to the carrier molecule. The multivalent molecules may be employed in vaccines or in the generation of antibodies for diagnostic application.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Injectable vaccines against multiple meningococcal serogroups
ActiveUS20070082014A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismDepsipeptidesStreptococcus pneumoniaeSalmonella serotype typhi
An injectable immunogenic composition comprising capsular saccharides from at least two of serogroups A, C, W135 and Y of Neisseria meningitidis, wherein said capsular saccharides are conjugated to carrier protein(s) and / or are oligosaccharides, and wherein (i) the composition comprises <50 mug meningococcal saccharide per dose, and / or (ii) the composition further comprises an antigen from one or more of: (a) serogroup B N. meningitidis; (b) Haemophilus influenzae type B; and / or (c) Streptococcus pneumoniae. Saccharide antigens in the compositions are generally conjugated to a carrier.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Outer membrane vesicle (OMV) vaccine comprising N. meningitidis serogroup B outer membrane proteins
ActiveUS8273360B2Broadens their efficacyAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderProtective antigenNeisseria weaveri
A composition comprising (a) Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B outer membrane vesicles (OMVs), and (b) an immunogenic component selected from other Neisseria proteins, or immunogenic fragments thereof. Component (b) preferably includes a protein from a different NmB strain from that from which the OMV of component (a) is derived. The OMVs are preferably obtained by deoxycholate extraction. Optionally, the composition may also comprise a protective antigen against other pathogens.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Non-lipidated variants of neisseria meningitidis orf2086 antigens
ActiveUS20120093852A1Raise immunogenic responseImprove responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSalmonella serotype typhiNeisseria meningitidis
The present invention relates to compositions including an isolated non-pyruvylated non-lipidated ORF2086 polypeptide, and methods thereof. In an exemplary embodiment, the compositions described herein are immunogenic. The present invention further relates to compositions that elicit a bactericidal immune response in a mammal against an ORF2086 subfamily B polypeptide from serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis, and methods related thereto.
Owner:WYETH LLC
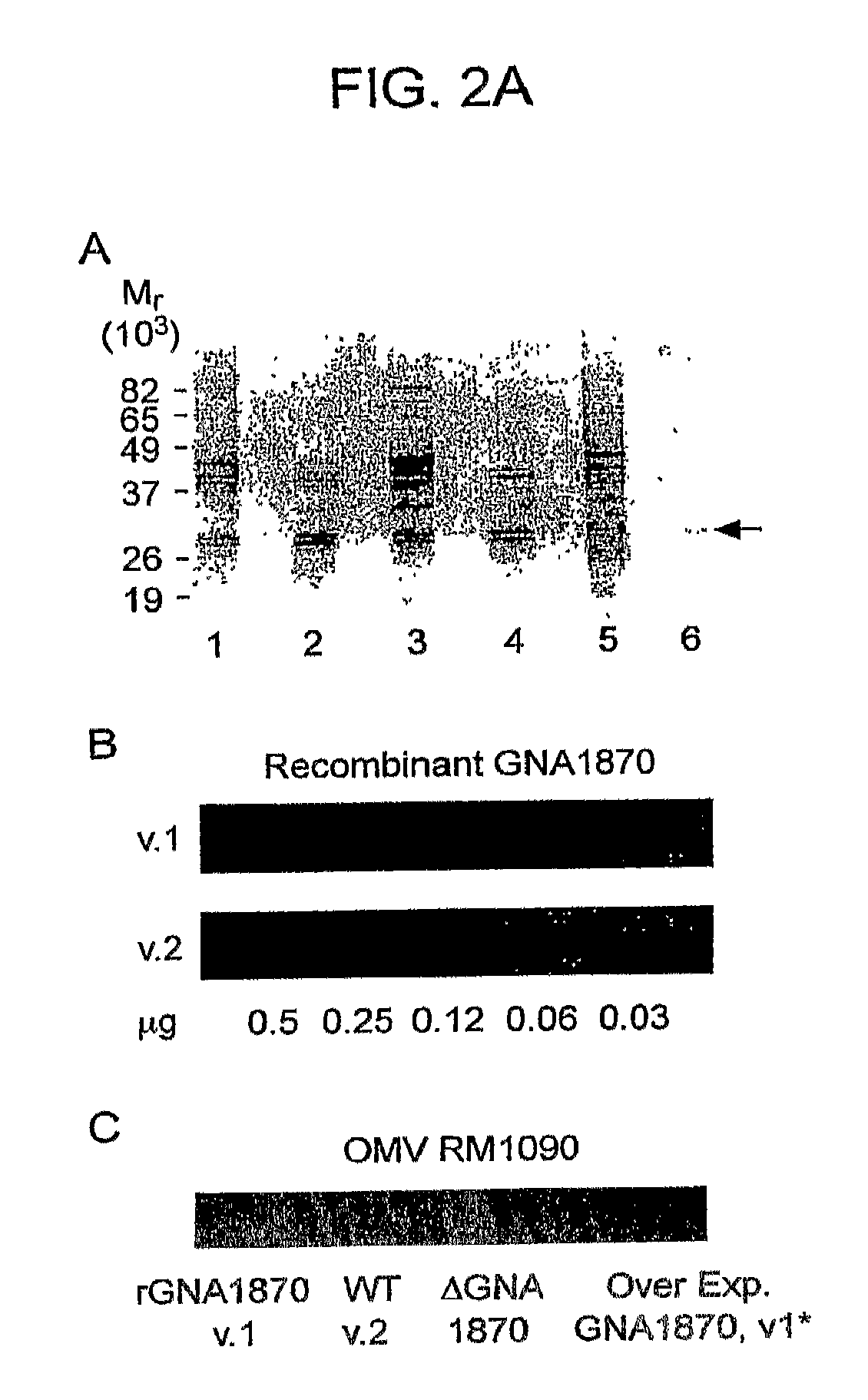
Gna1870-Based Vesicle Vaccines for Broad Spectrum Protection Against Diseases Caused by Neisseria Meningitidis
ActiveUS20080248065A1Broad protectionDecrease of emergenceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesDisease
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Polypeptides from Neisseria meningitidis
InactiveUS8039007B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Various specific meningococcal proteins are disclosed. The invention provides related polypeptides, nucleic acids, antibodies and methods. These can all be used in medicine for treating or preventing disease and / or infection caused by meningococcus, such as bacterial meningitis.
Owner:J CRAIG VENTER INST +1
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20040185478A1Reduce usageDetermine rapidly the bacterial resistance to antibioticsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteroidesNeisseria meningitidis
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6'-lla, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6')-aph(2''), aad(6'), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
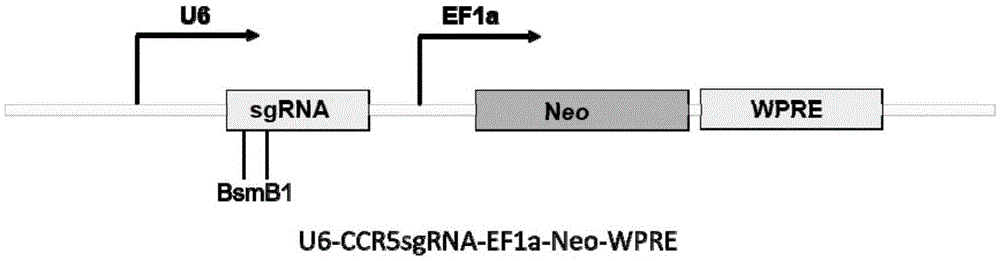
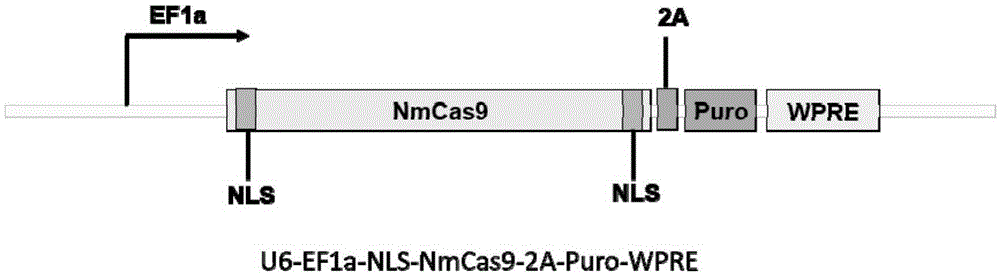
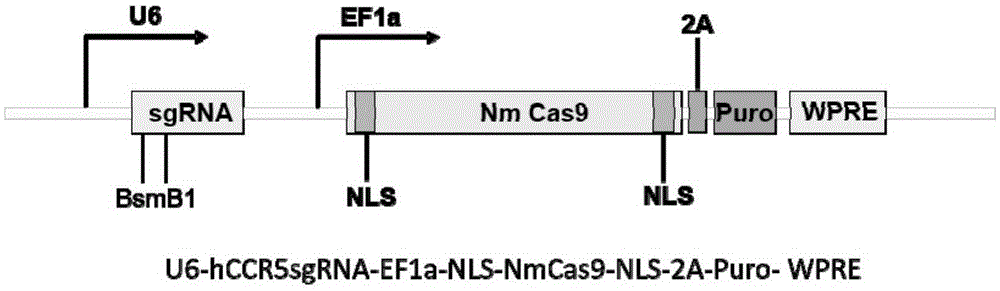
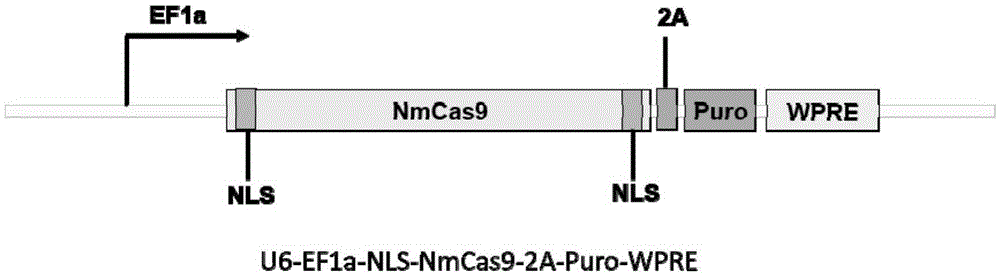
Human CCR5 gene target sequence identified by neisseria meningitidis CRISPR-Cas9 system, sgRNA and application of target sequence and sgRNA
InactiveCN105331609AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGene targetsHIV receptor
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and discloses a target sequence identified by a CRISPR-Cas9 system from neisseria meningitidis. The target sequence is as shown in the nth-24th sites of optional one of SEQ ID No. 1-20, and n=1-9. The invention further discloses sgRNA and coding DNA molecules thereof, the sequence of the sgRNA is 5'-identificiation sequence-sequence recruiting Cas9 protein-3', and the DNA sequence corresponding to the identification sequence is identical with the target sequence. The invention also discloses the CRISPR-Cas9 system which comprises the Cas9 protein, the sgRNA and / or a coding sequence carrying the Cas9 protein and a vector of the coding sequence of the sgRNA. The invention also discloses application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system to editing of CCR5 genes and preparation of medicine for HIV infection. By the CRISPR-Cas9 system, the CCR5 genes can be edited, and cells cannot be infected by HIV.
Owner:张竞方
Neisseria meningitidis compositions and methods thereof
ActiveUS20130243807A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSalmonella serotype typhiMeningococcal carriage
In one aspect, the invention relates to an isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence that is at least 95% identical to SEQ ID NO: 71. In another aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition including an isolated non-lipidated, non-pyruvylated ORF2086 polypeptide from Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B, and at least one conjugated capsular saccharide from a meningococcal serogroup.
Owner:PFIZER INC
GNA1870-based vesicle vaccines for broad spectrum protection against diseases caused by Neisseria meningitidis
ActiveUS8968748B2Broad protectionReduce expressionAntibacterial agentsBiocideTGE VACCINENeisseria meningitidis
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20060263810A1Reduce usageDetermine rapidly the bacterial resistance to antibioticsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNeisseria meningitidisListeria monocytogenes
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6′-IIa, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6′)-aph(2″), aad(6), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
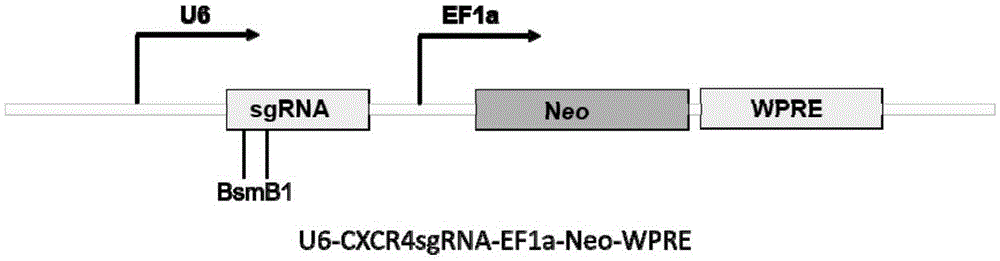
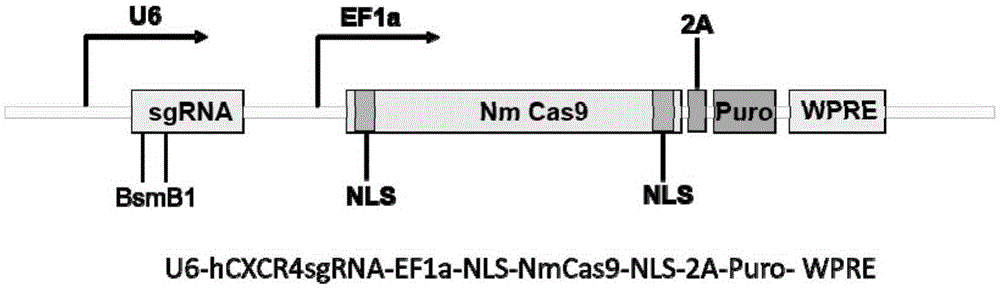
Human CXCR4 gene target sequence identified by neisseria meningitidis CRISPR-Cas9 system, sgRNA and application of target sequence and sgRNA
InactiveCN105331608AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGene targetsRecognition sequence
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and discloses a target sequence identified by a CRISPR-Cas9 system from neisseria meningitidis. The target sequence is as shown in the nth-24th sites of optional one of SEQ ID No. 1-15, and n=1-9. The invention further discloses sgRNA and coding DNA molecules thereof, the sequence of the sgRNA is 5'-identificiation sequence-sequence recruiting Cas9 protein-3', and the DNA sequence corresponding to the identification sequence is identical with the target sequence. The invention also discloses the CRISPR-Cas9 system which comprises the Cas9 protein, the sgRNA and / or a coding sequence carrying the Cas9 protein and a vector of the coding sequence of the sgRNA. The invention also discloses application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system to editing of CXCR4 genes and preparation of medicine for HIV infection. By the CRISPR-Cas9 system, the CXCR4 genes can be edited, and cells cannot be infected by HIV.
Owner:张竞方
Methods for increasing neisseria protein expression and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20070148729A1Improve expression levelBacteriaSugar derivativesNeisseria weaveriNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention broadly relates to polynucleotide sequences encoding porin polypeptides of Neisseria. More particularly, the invention relates to newly identified nucleic acid sequence mutations in polynucleotides encoding PorA polypeptides of Neisseria meningitidis, wherein these sequence mutations result in increased expression levels of PorA polypeptides.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP
Vaccines for broad spectrum protection against diseases caused by Neisseria meningitidis
InactiveUS20060029621A1Wide applicabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSalmonella serotype typhiSerotype
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20030049636A1Low costRapid positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteroidesNeisseria meningitidis
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6'-lla, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6')-aph(2''), aad(6'), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:BERGERON MICHEL G +3
Multi oligosaccharide glycoconjugate bacterial meningitis vaccines
InactiveUS6656472B1Inhibition effectWeight increaseAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticSerotypeTumor antigen
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Chimeric, hybrid and tandem polypeptides of meningococcal NMB1870
InactiveUS8226960B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsNeisseria meningitidis
NMB1870 is a protein in Neisseria meningitidis. Three families of NMB1870 are known. To increase the ability of a NMB1870 protein to elicit antibodies that are cross-reactive between the families, NMB1870 is engineered. Sequences can be substituted from one NMB1870 family into the corresponding position in another family. Proteins of NMB1870 sequences from different families can be joined to each other.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Modified surface antigen
Novel proteins that constitute modified forms of a Neisseria meningitidis surface antigen and encoding nucleic acids are provided. The modified surface proteins are characterized by having deletions of non-conserved amino acids, and thereby being capable of eliciting cross-protective immune responses against Neisseria meningitidis. The invention extends to the use of the modified surface antigens in diagnostics, in therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines and in the design and / or screening of medicaments. The modified surface antigens are particularly useful in vaccines which effectively immunize against a broader spectrum of N. meningitidis strains than would be expected from a corresponding wild-type surface antigen.
Owner:QUEENSLAND THE UNIV OF
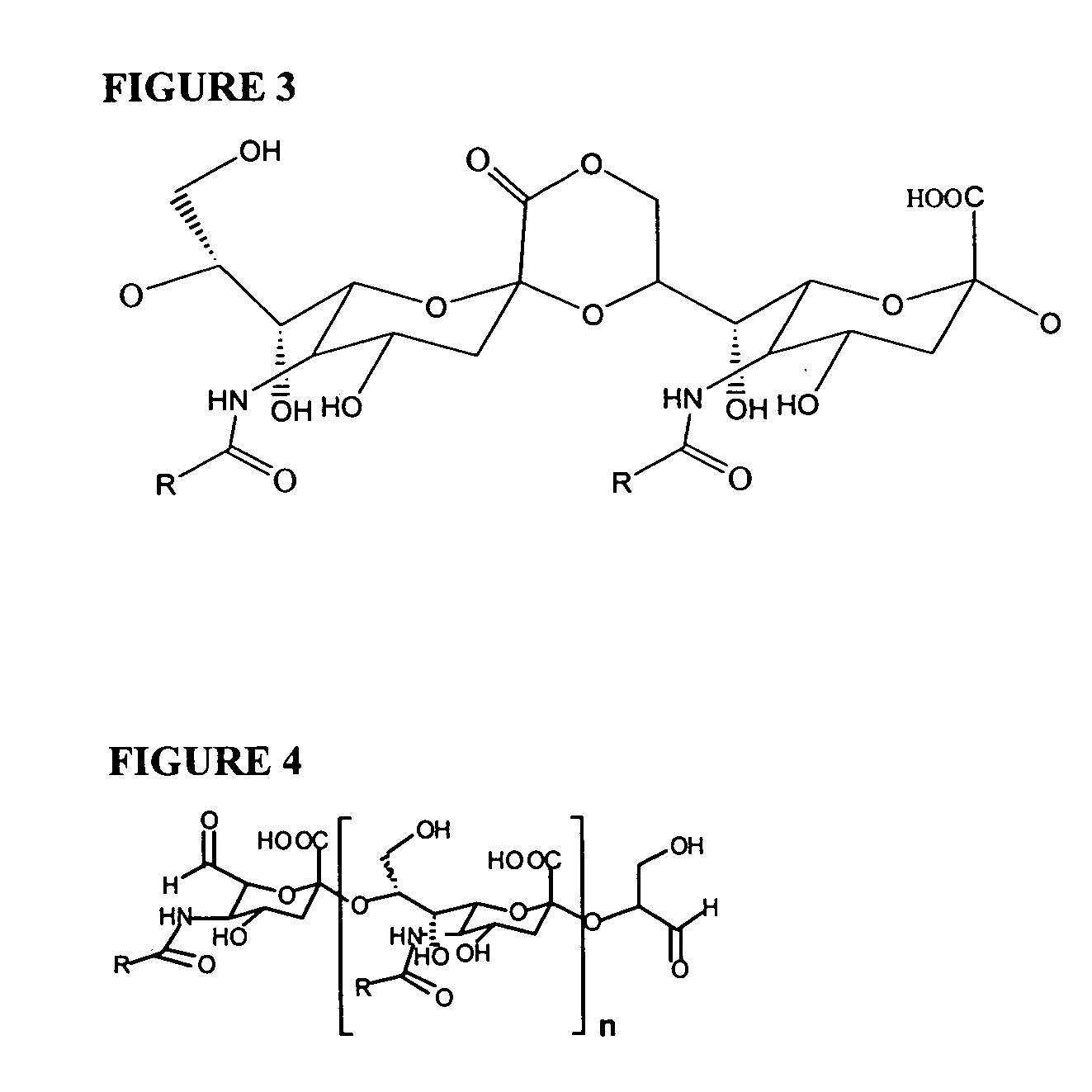
Multivalent meningococcal derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and vaccine
The present invention describes derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates, a composition comprising one or more of such derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and methods of immunizing human patients with the same. The derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates are purified capsular polysaccharides from Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, W-135, and Y, derivatized chemically activated and selectively attached to a carrier protein by means of a covalent chemical bond, forming polysaccharide-protein conjugates capable of eliciting long-lasting immunity to a variety of N. meningitidis strains.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR INC
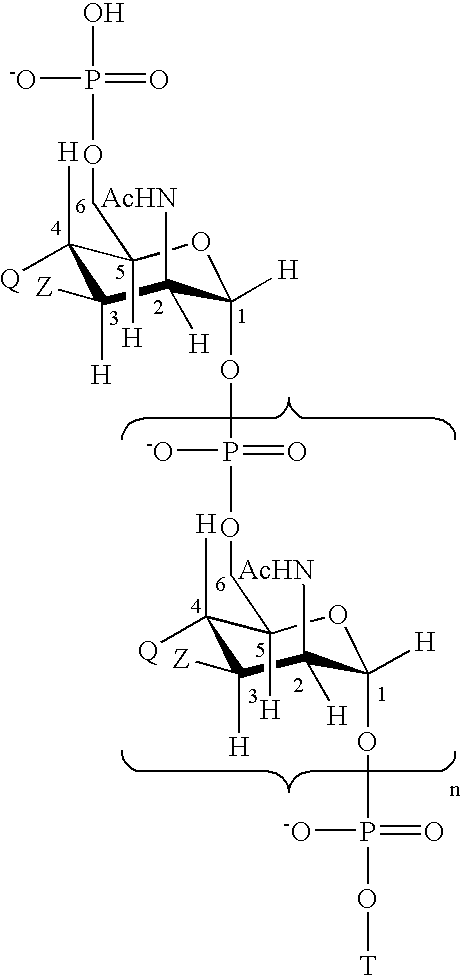
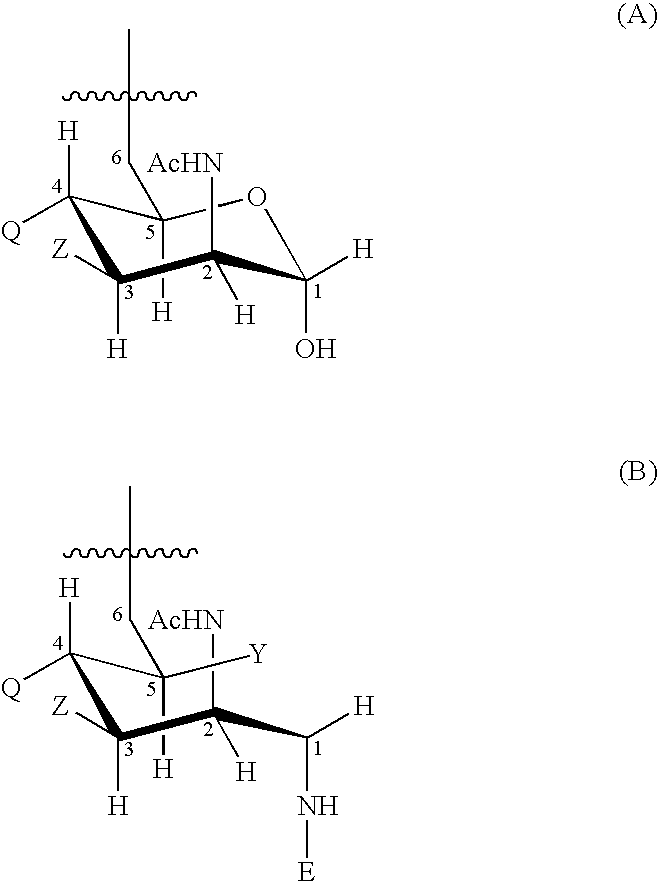
Neisseria meningitdis inner core lipo-oligosaccharide epitopes, multivalent conjugates thereof and immunogenic compositions thereof
The present invention is directed to novel Neisseria meningitidis lipo-oligosaccharide inner core molecules, conjugates thereof and immunogenic compositions thereof. In particular embodiments, the invention relates to multivalent immunogenic compositions comprising five distinct Neisseria meningitidis inner core lipo-oligosaccharide epitope groups, wherein the multivalent compositions induce cross-reactive immune responses against Neisseria meningitidis lipo-oligosaccharide immunotypes.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Neisseria meningitidis compositions and methods thereof
ActiveUS8986710B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMeningococcal carriageImmunogenicity
In one aspect, the invention relates to an isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence that is at least 95% identical to SEQ ID NO: 71. In another aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition including an isolated non-lipidated, non-pyruvylated ORF2086 polypeptide from Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B, and at least one conjugated capsular saccharide from a meningococcal serogroup.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Methods for isolating molecular mimetics of unique Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B epitopes
InactiveUS20060035284A1Determine autoreactivityLeast riskAntibacterial agentsAnimal cellsEscherichia coliSalmonella serotype typhi
Novel bactericidal antibodies against Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B (“MenB”) are disclosed. The antibodies either do not cross-react or minimally cross-react with host tissue polysialic acid and hence pose minimal risk of autoimmune activity. The antibodies are used to identify molecular mimetics of unique epitopes found on MenB or E. coli K1. Examples of such peptide mimetics are described that elicit serum antibody capable of activating complement-mediated bacteriolysis of MenB. Vaccine compositions containing such mimetics can be used to prevent MenB or E. coli K1 disease without the risk of evoking autoantibody.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Neisseria mutants, lipooligosaccharides and immunogenic compositions
Provided herein are mutant strains of Neisseria meningitidis which produce Kdo-free lipid A as well as the Kdo-free lipid A molecules and immunogenic compositions containing such Kdo-free lipid A molecules from a Neisseria strain containing a genetically stable mutation which inactivates a gene selected from the group consisting of genes encoding arabinose-5-phosphate isomerase, CMP-Kdo synthetase and CMP-Kdo transferase. N. meningitidis NMB206 is a specifically exemplified strain which harbors a stable insertion mutation in the gene (ApsF) encoding A5P isomerase; strain NMB-249 is a specifically exemplified strain with a stable insertion mutation in the gene (kdtA) encoding CMP-Kdo synthetase, and strain NMB259 is specifically exemplified strain with a stable insertion mutation in the gene (kdsB) encoding CMP-Kdo transferase. Also provided by the present invention are methods for the production of Lipid A flee of 3-keto-3-deoxyoctanoic acid using these genetically stable N. meningitidis mutants. Also describes is pYT250, a plasmid functional in neisseriae and in enterics such as Escherichia coli.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Multiple vaccination including serogroup C meningococcus
Various improvements to vaccines that include a serogroup C meningococcal conjugate antigen, including: (a) co-administration with acellular B. pertussis antigen; (b) co-administration with an inactivated poliovirus antigen; (c) supply in a kit together with a separate pneumococcal conjugate component, which may be in a liquid form; and (d) use in combination with a pneumococcal conjugate antigen but without an aluminum phosphate adjuvant. A kit may have: (a) a first immunogenic component that comprises an aqueous formulation of a conjugated capsular saccharide from Streptococcus pneumoniae; (b) a second immunogenic component that comprises a conjugated capsular saccharide from Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C.
Owner:GSK VACCINES GMBH
Meningococcal fhbp polypeptides
ActiveUS20110020390A1Stable maintenanceSugar derivativesBacteriaAntiendomysial antibodiesMeningococcal carriage
fHBP is a protein in Neisseria meningitidis. Three families of fHBP are known. To increase the ability of a fHBP protein to elicit antibodies that are cross-reactive between the families, fHBP is selected or engineered to have a sequence which can elicit broad-spectrum bactericidal anti-meningococcal antibodies after administration to a host animal.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
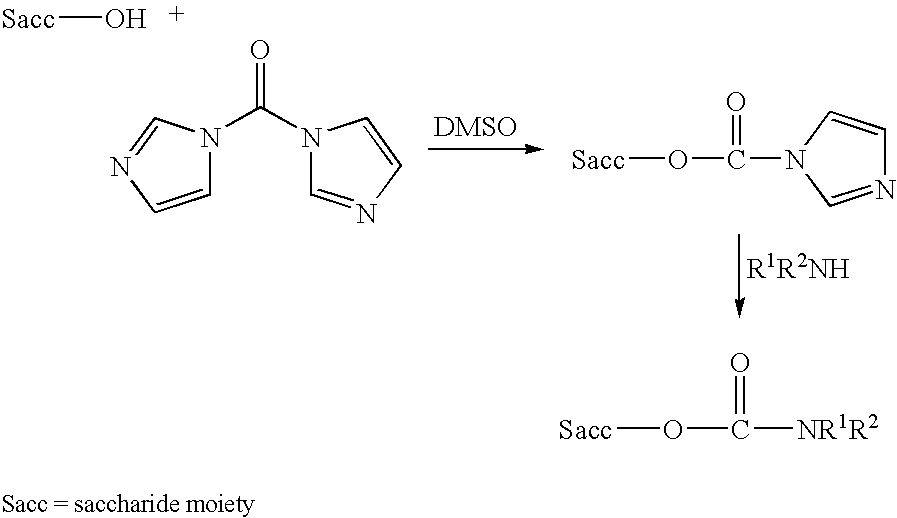
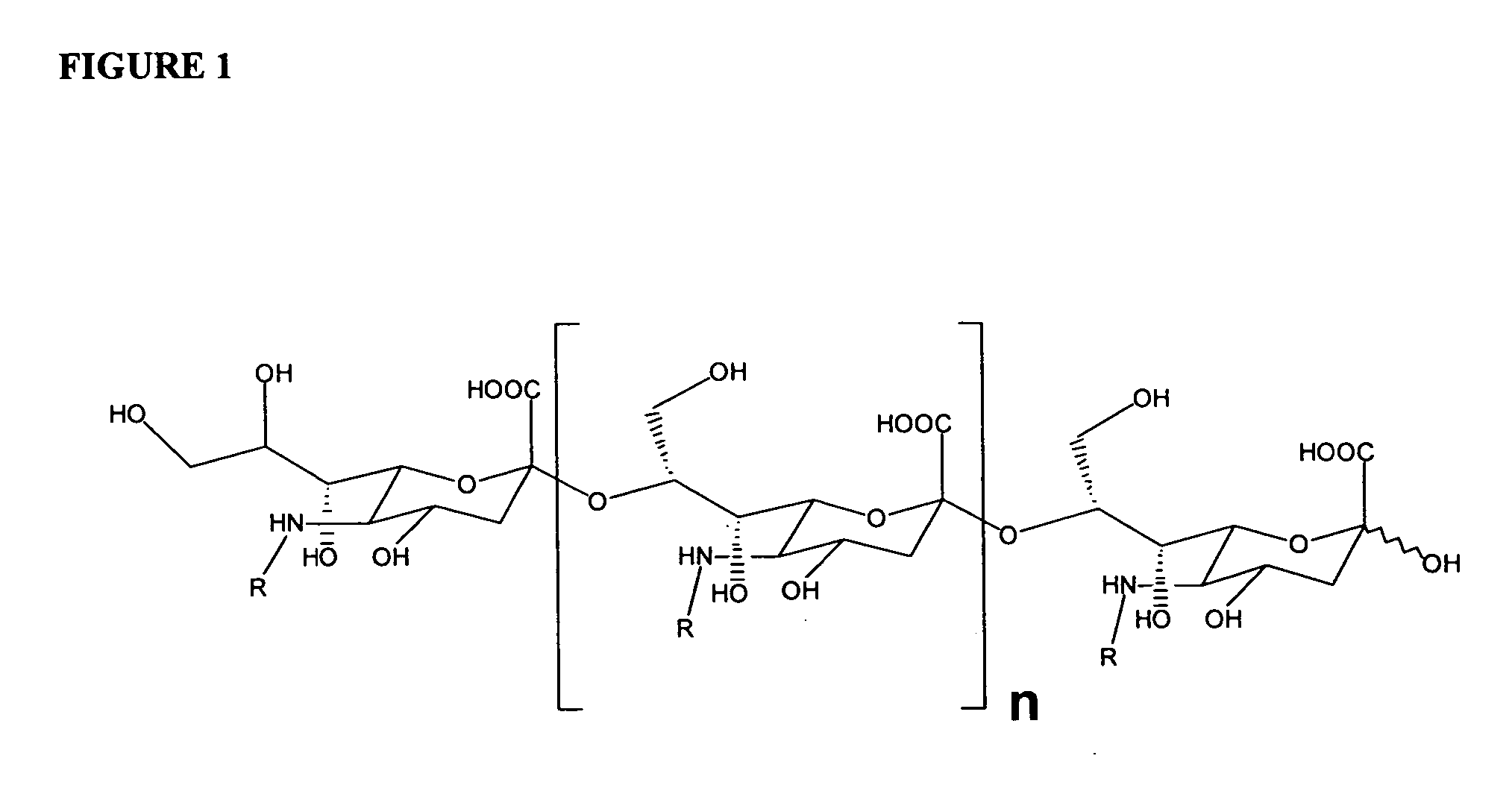
Polysaccharide derivatives and uses in induction of an immune response
The present invention generally provides compositions comprising a polysaccharide derivative, and methods of their preparation and use for the prevention or treatment of diseases caused by Neisseria meningitidis bacteria, particularly group B (NmB) strains, and by E. coli K1. The invention provides a de-N-acetylated PS derivative in which one or more residues of the PS has been modified by de-N-acetylation. The invention also includes derivatives in which one or more of the N-acetyl groups of PS containing de-N-acetylated PS are replaced with other N-acyl groups, usually a lower acyl group of C2-C3. Further, the invention includes de-N-acetylated PS derivatives containing long chain hydrocarbons, as well as conjugates in which the de-N-acetylated PS derivative is linked to a carrier, e.g., a carrier protein.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Proteinase K resistant surface protein of neisseria meningitidis
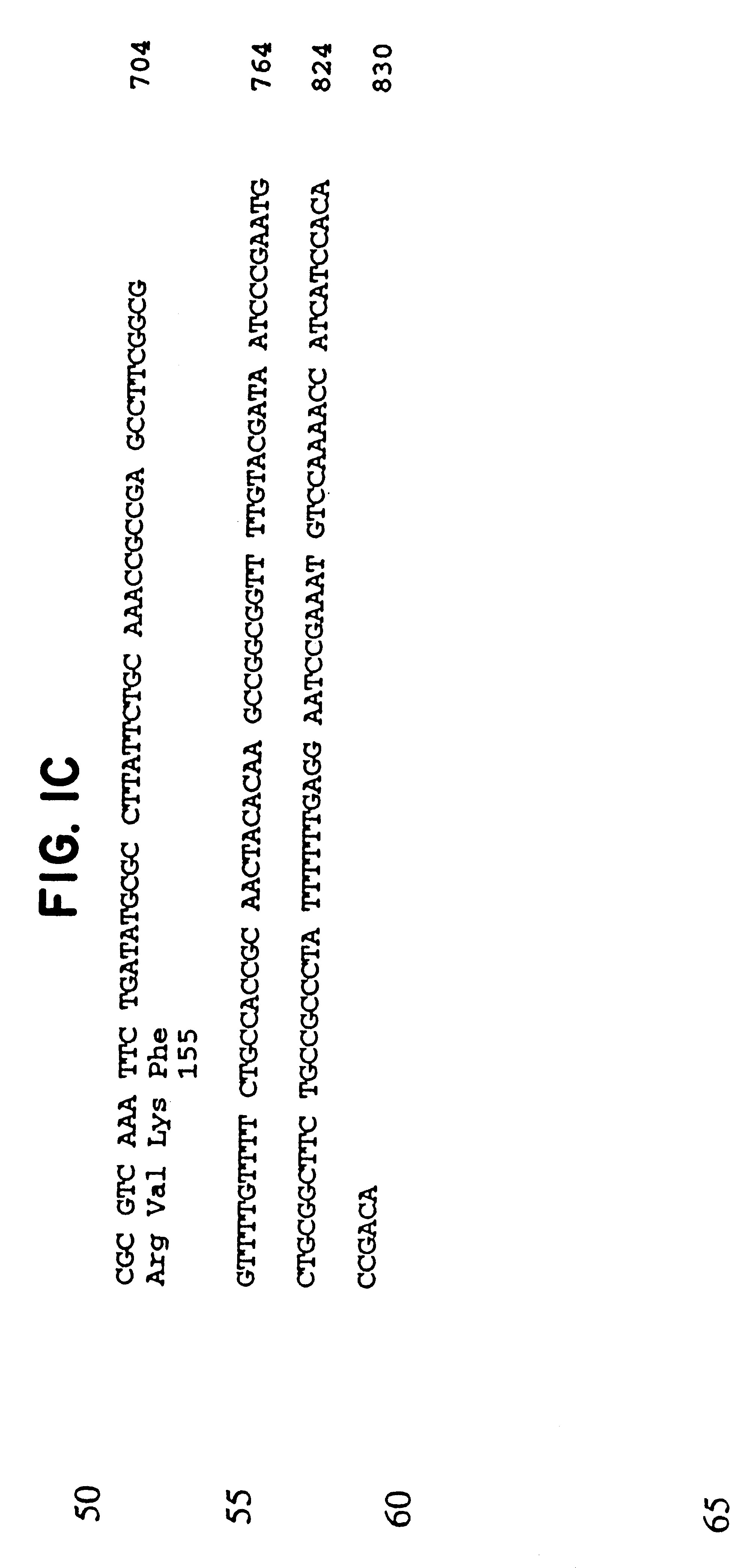
A highly conserved, immunologically accessible antigen at the surface of Neisseria meningitidis organisms. Immunotherapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic compositions and methods useful in the treatment, prevention an diagnosis of Neisseria meningitidis diseases. A proteinase K resistant Neisseria meningitidis surface protein having an apparent molecular weight of 22 kDa, the corresponding nucleotide and derived amino acid sequences (SEQ ID NO: 1, NO:3, NO:5 and NO:7: SEQ ID NO: 2, NO:4, NO:6, and NO:8), recombinant DNA methods for the production of the Neisseria meningitidis 22 kDA surface protein, and antibodies that bind to the Neisseria meningitidis 22 kDA surface protein.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL
Neisseria meningitidis capsular polysacchride conjugates
InactiveUS6080589AEnhance host immune responseImproving immunogenicityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChemical reactionSialic acid
Capsular polysaccharides containing multiple sialic acid residues, particularly the Group B polysaccharide of Neisseria meningitidis, are modified by chemical reaction to randomly introduce pendant reactive residues of heterobifunctional linker molecules to the polysaccharide backbone. The capsular polysaccharide is deacetylated and the heterobifunctional linker molecule is reacted with the deacetylated material and any residual amino groups are blocked by reaction with alkyl acid anhydride. The introduction of the linker molecules to the polysaccharide chain between the termini enables the polysaccharide to be linked to a carrier molecule, such as a protein, to enhance the immunogenicity of the polysaccharide. The conjugate molecule may be formulated as an immunogenic composition for raising antibodies in a host to the polysaccharide.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Immunogenic fusion polypeptides
In one aspect, the invention relates to an isolated polypeptide including the amino acid sequence of a carrier polypeptide and the amino acid sequence of an ORF2086 polypeptide. In another aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic conjugate including ORF2086 polypeptide and a carrier polypeptide. The invention further includes immunogenic compositions and methods for inducing an immune response against Neisseria meningitidis in a mammal.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com