Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
652 results about "Robotic navigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
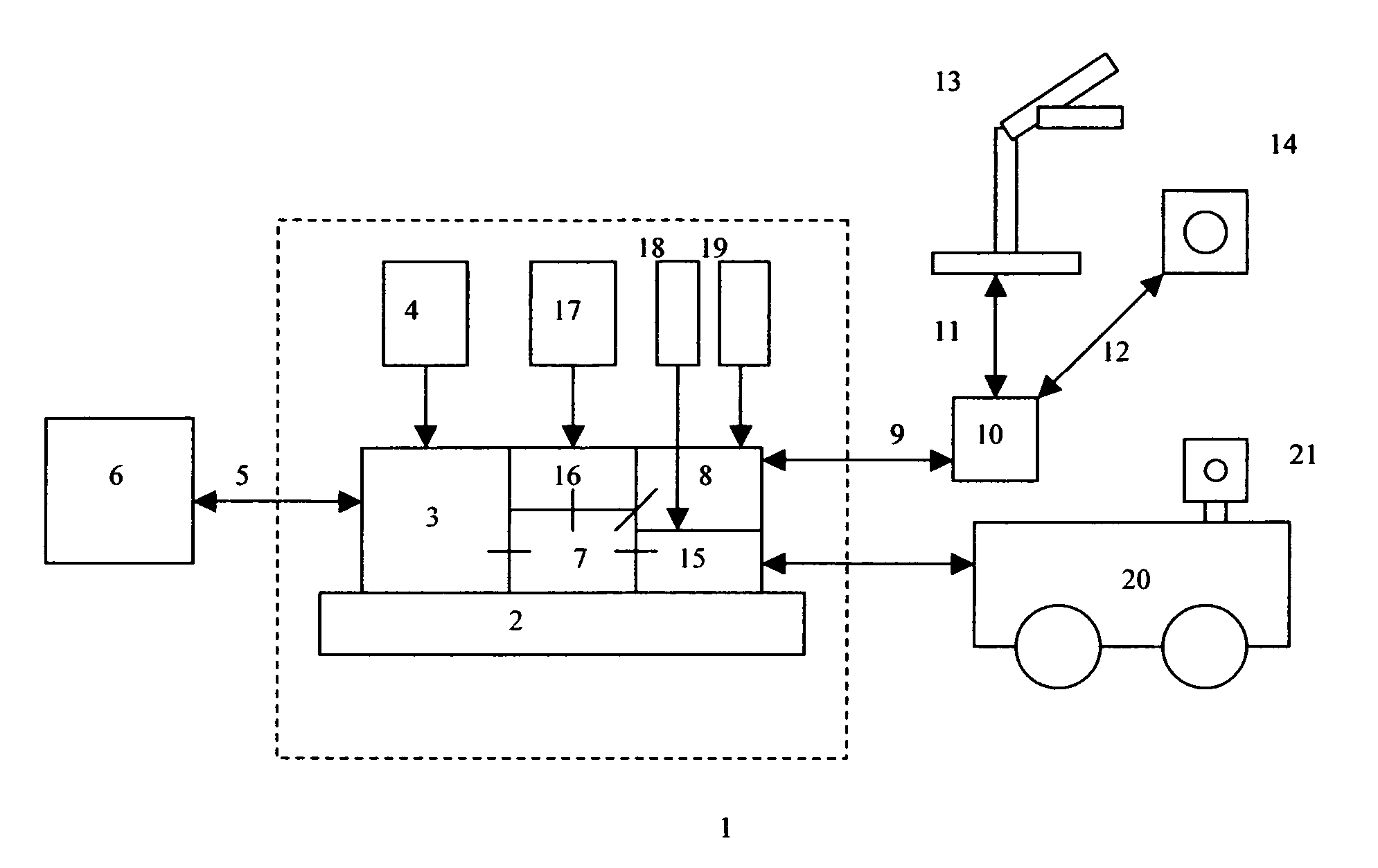
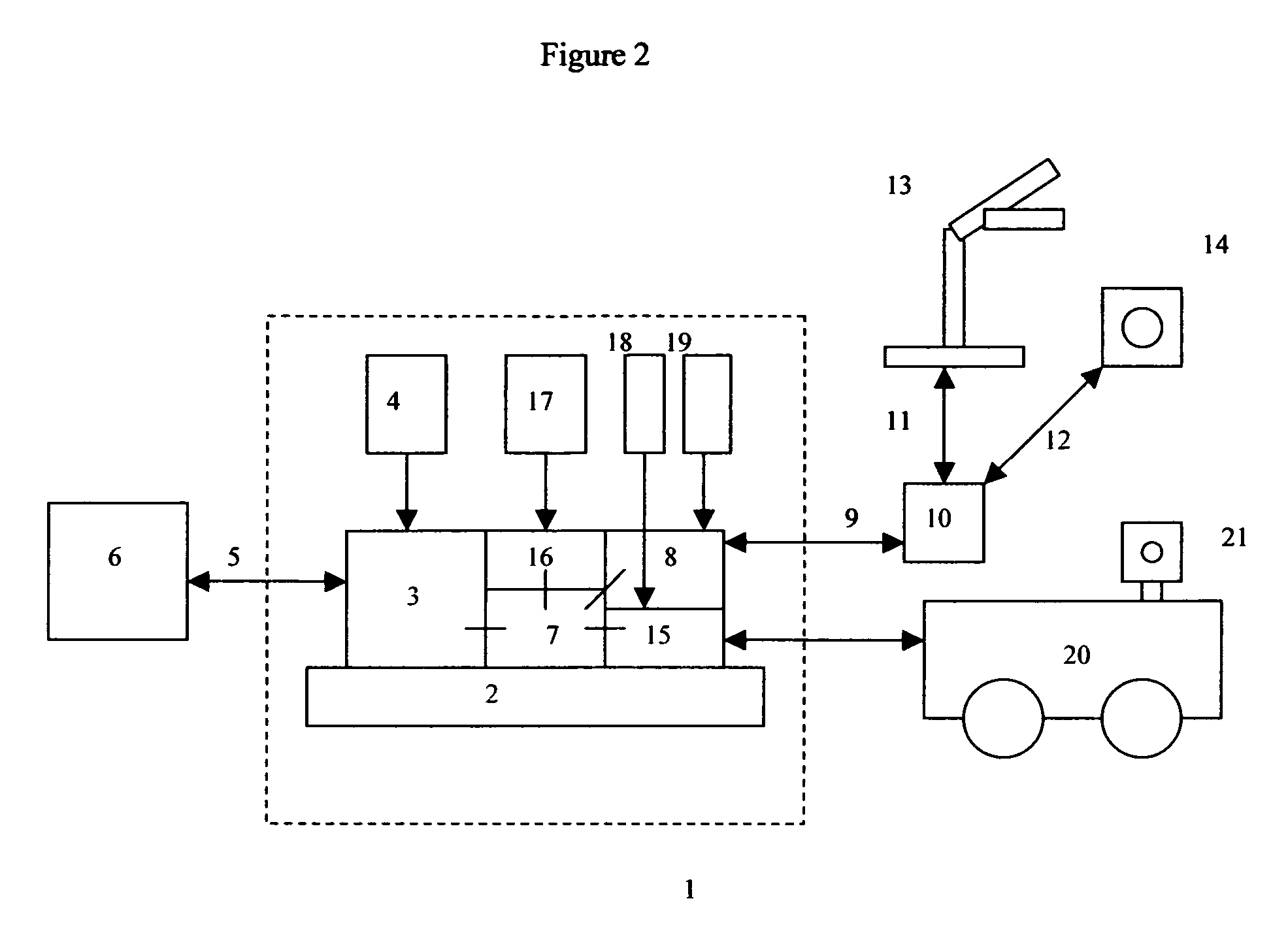
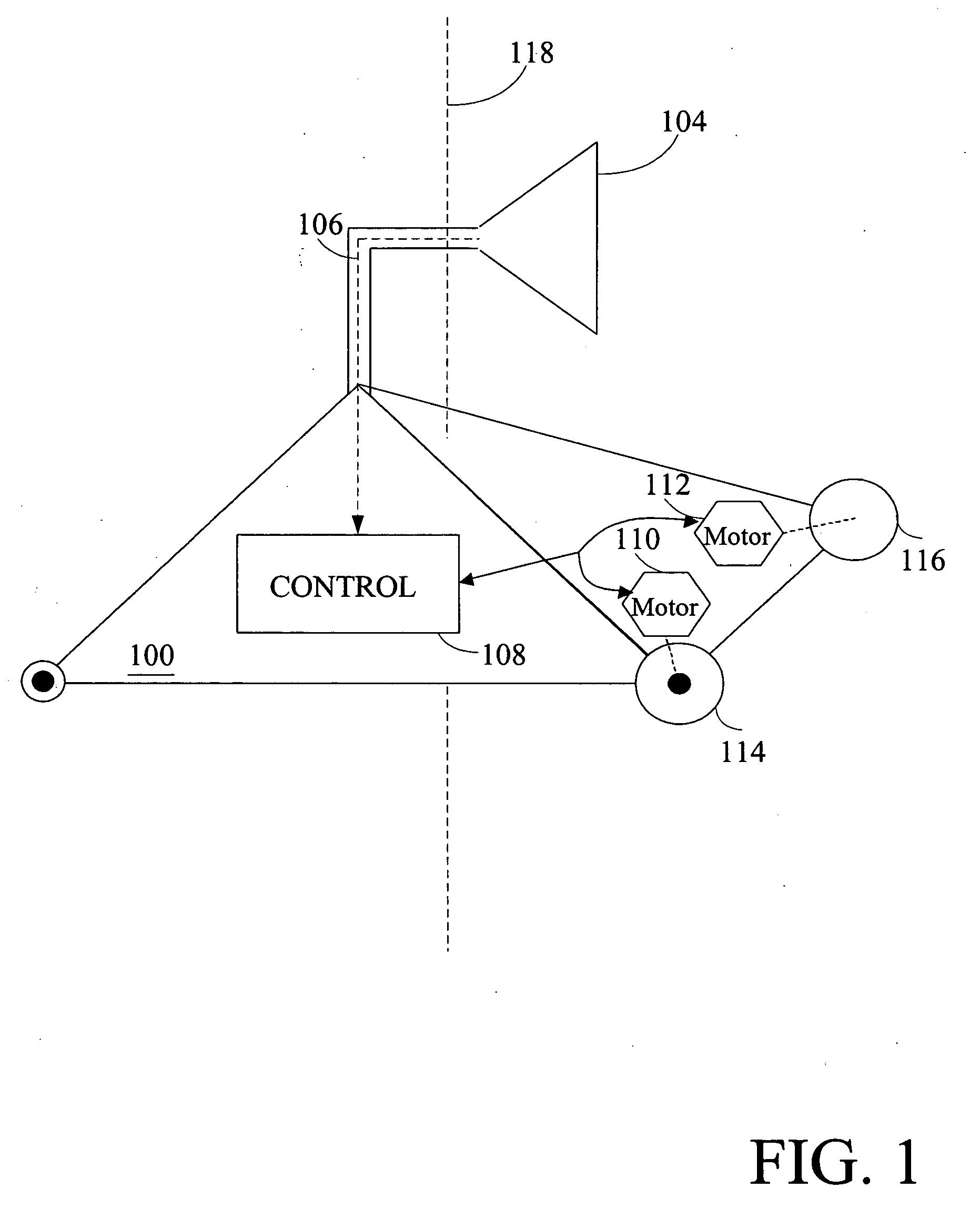
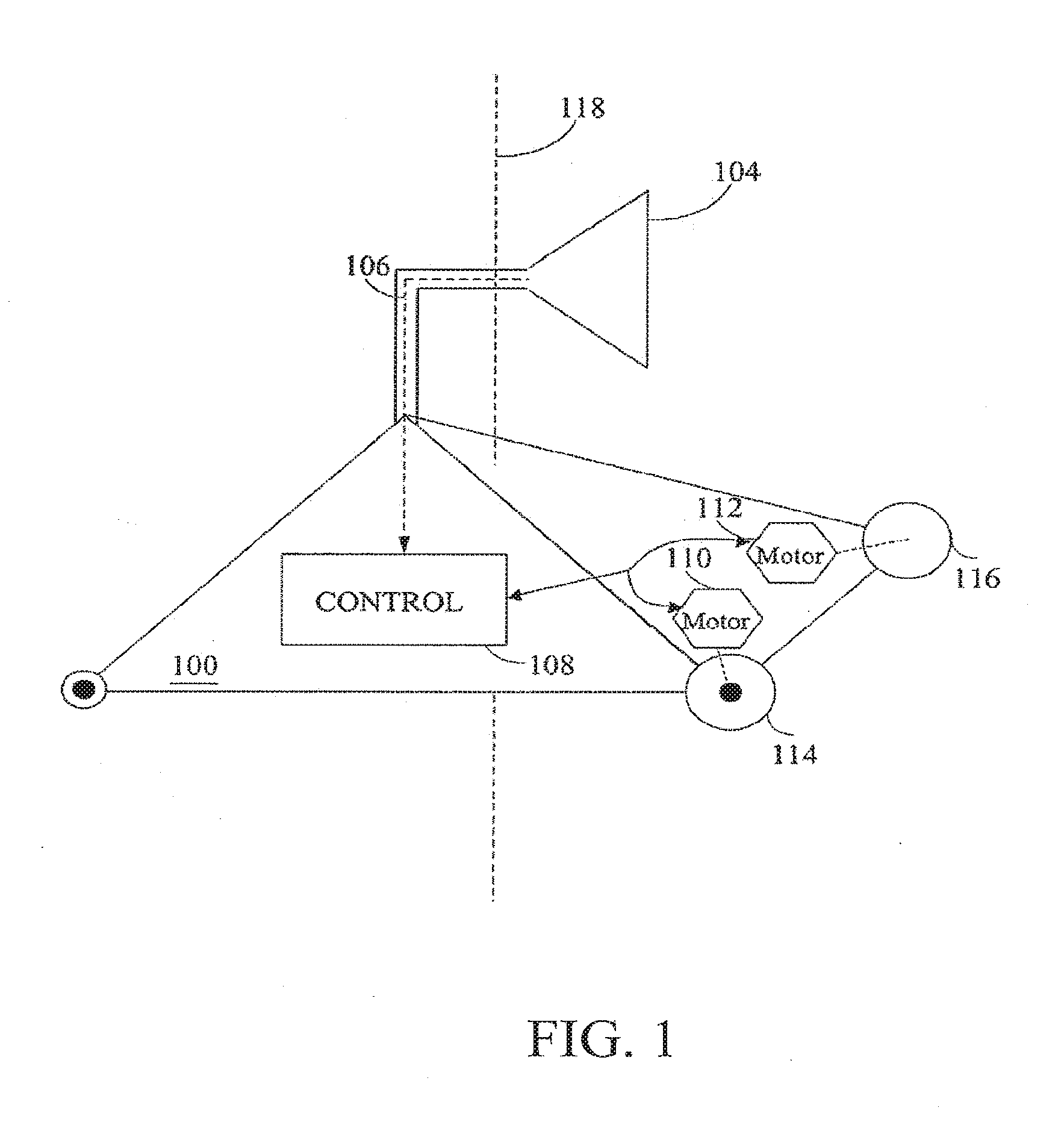
Mobile robot with wireless location sensing apparatus
InactiveUS20070061041A1Simple methodBroaden their knowledgeProgramme controlVehicle position/course/altitude controlWeb browserInternet network
A robotic navigation system for computerized mobile robot. Typically the robot, which may be in an unknown location, will have an onboard internet web server, a capability of establishing a first connection to a remote web browser on the internet for robotic control purposes, and a capability of establishing a second short range bi-directional digital radio connection to one or more nearby computerized digital radio equipped devices external to the robot. Typically at least some of these nearby digital radio equipped devices will have a known location. The robot can exchange short-range bidirectional digital radio signals with nearby devices that have a known location, and obtain location data to determine it's position. This location information can be used to assist in robotic navigation. The robot can also navigate to other objects, which also may have an unknown location, using a similar technique in which the object with an unknown location exchanges short range bidirectional digital radio signals with either the robot itself, or other digital radio linked devices with a known location (which then relay the object's location to the robot).
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
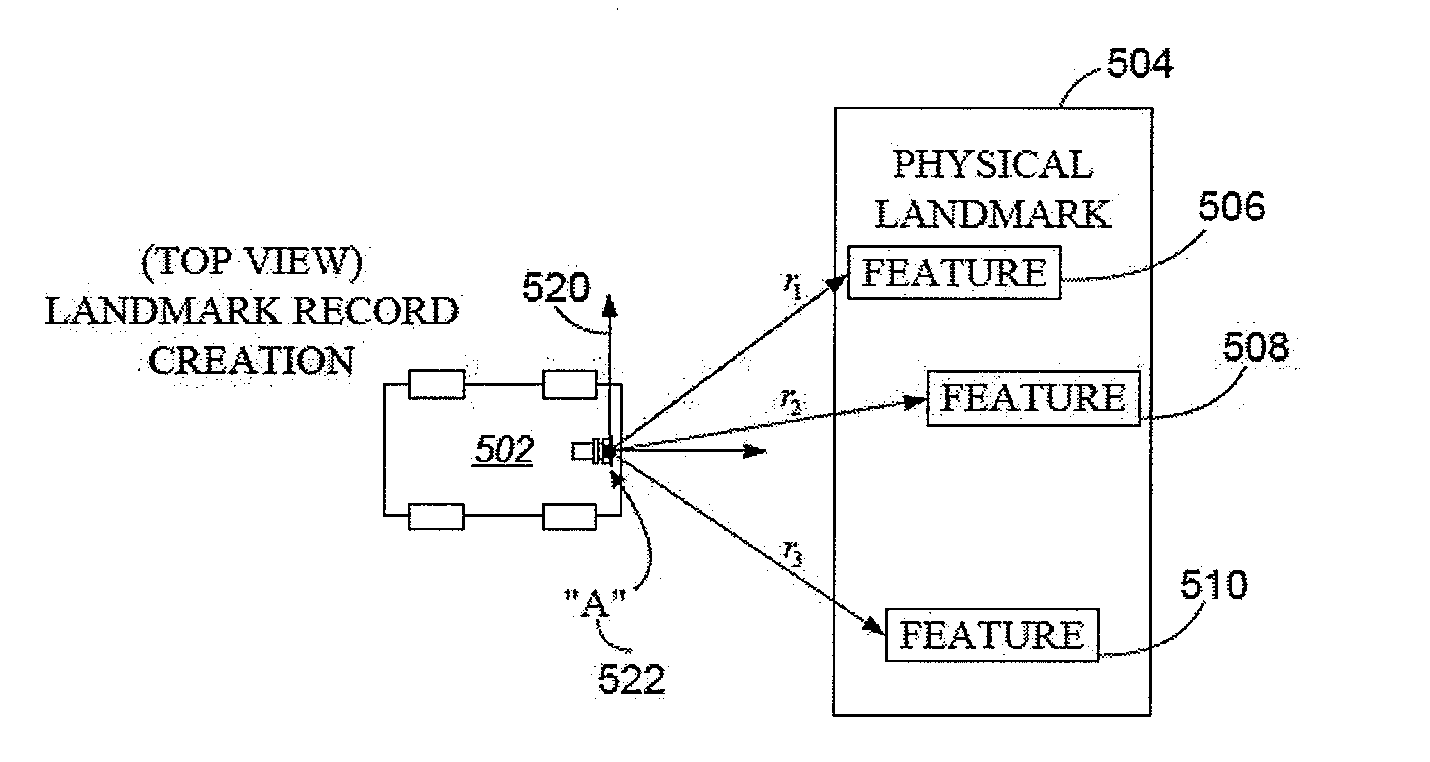
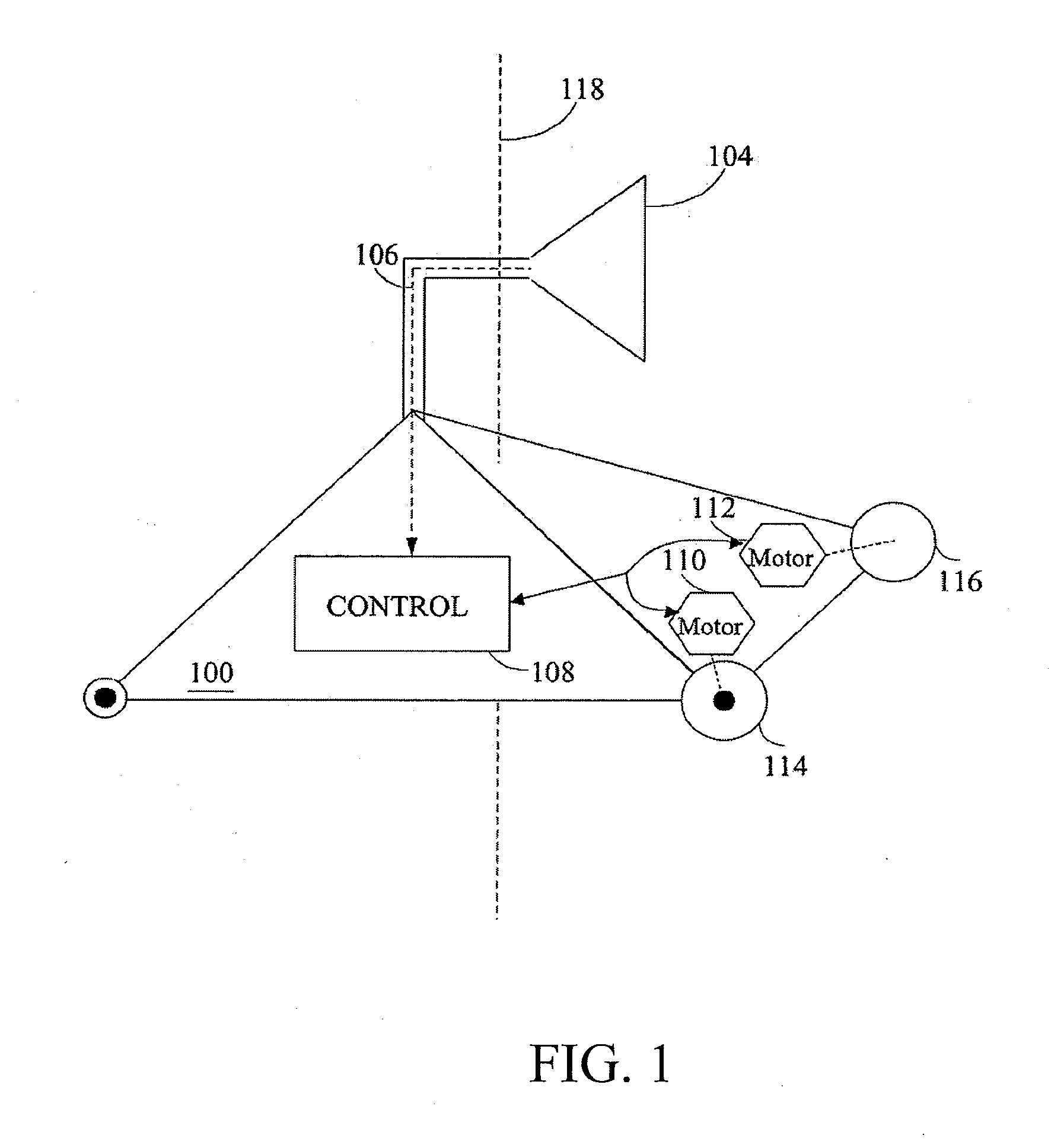
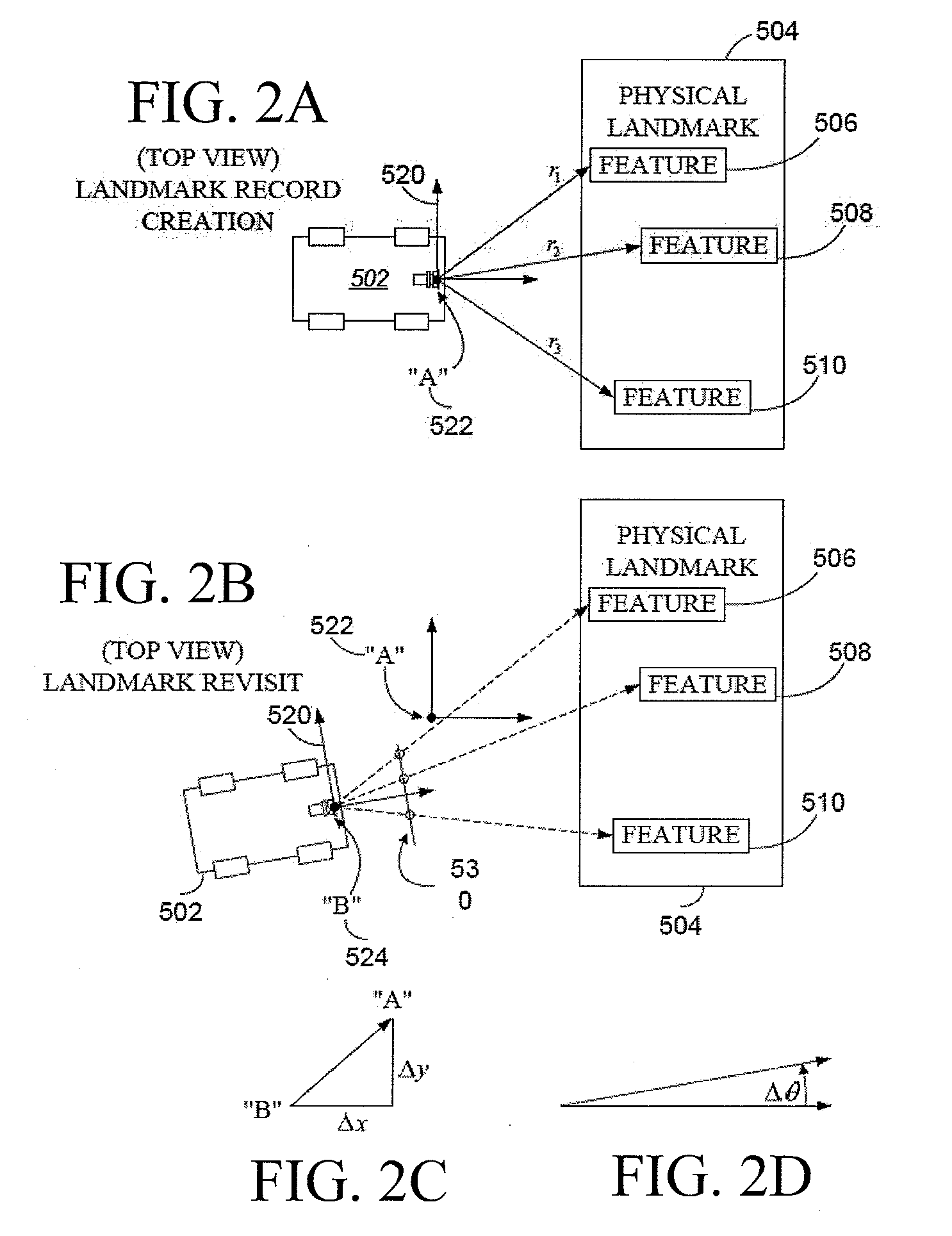
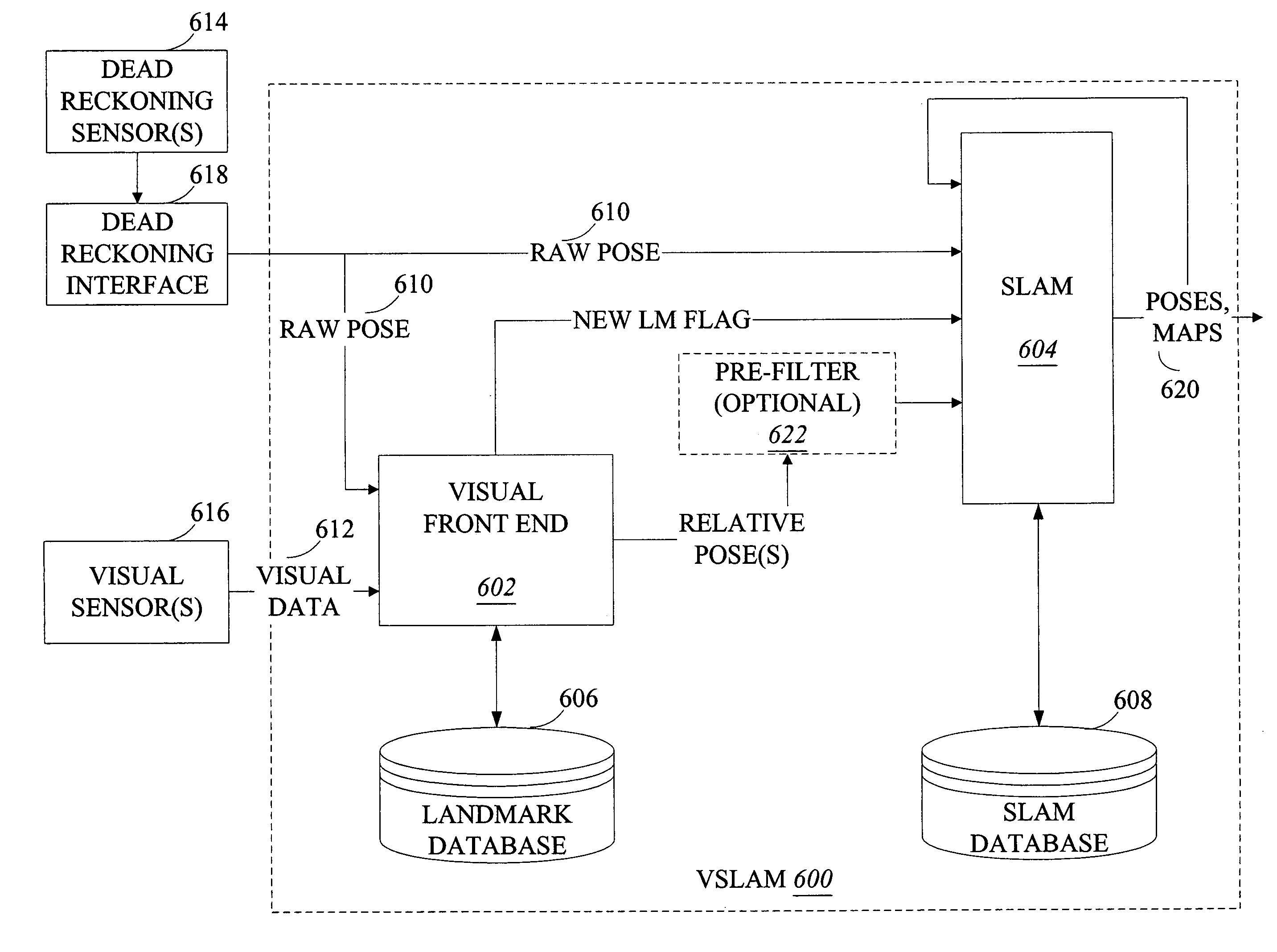
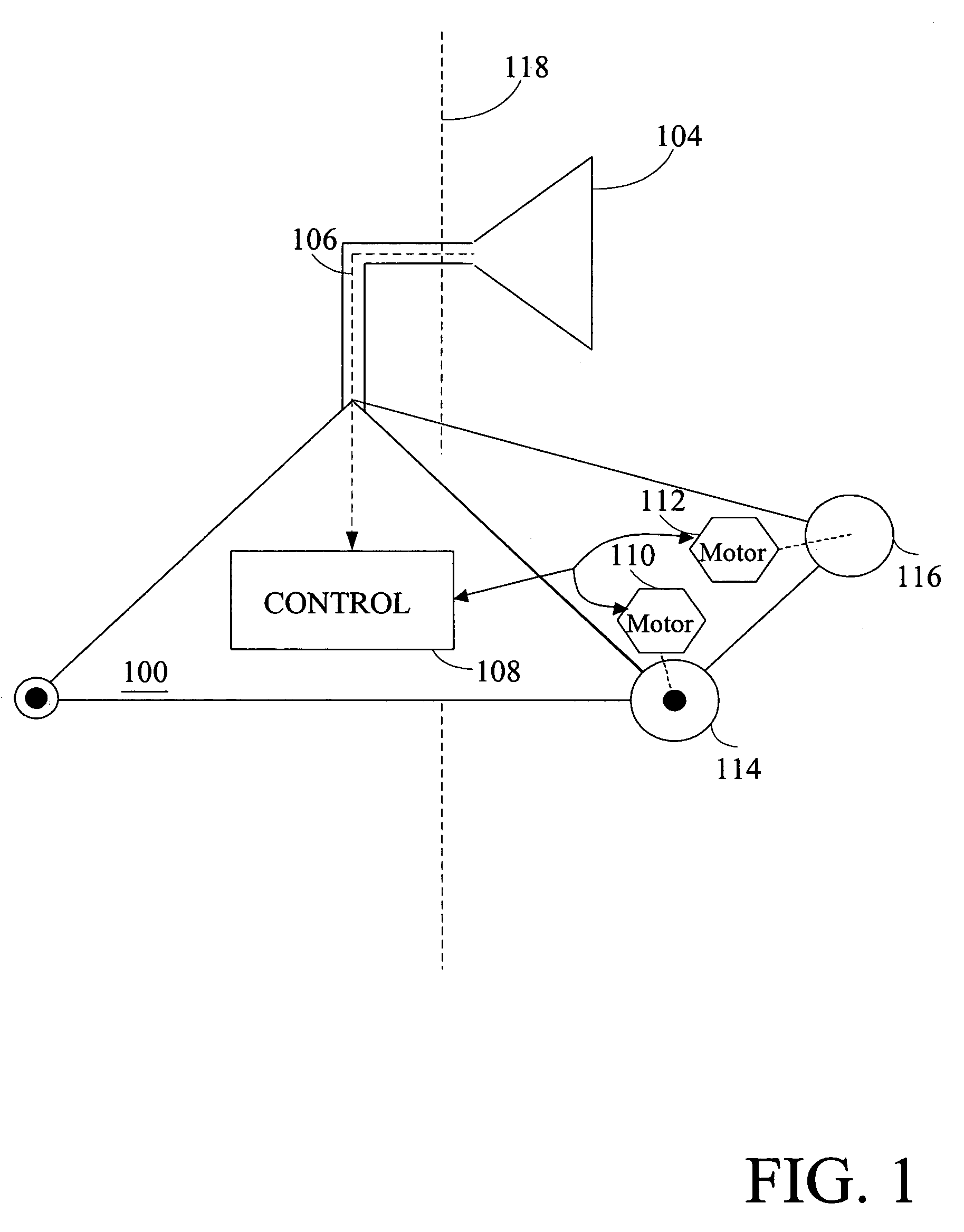
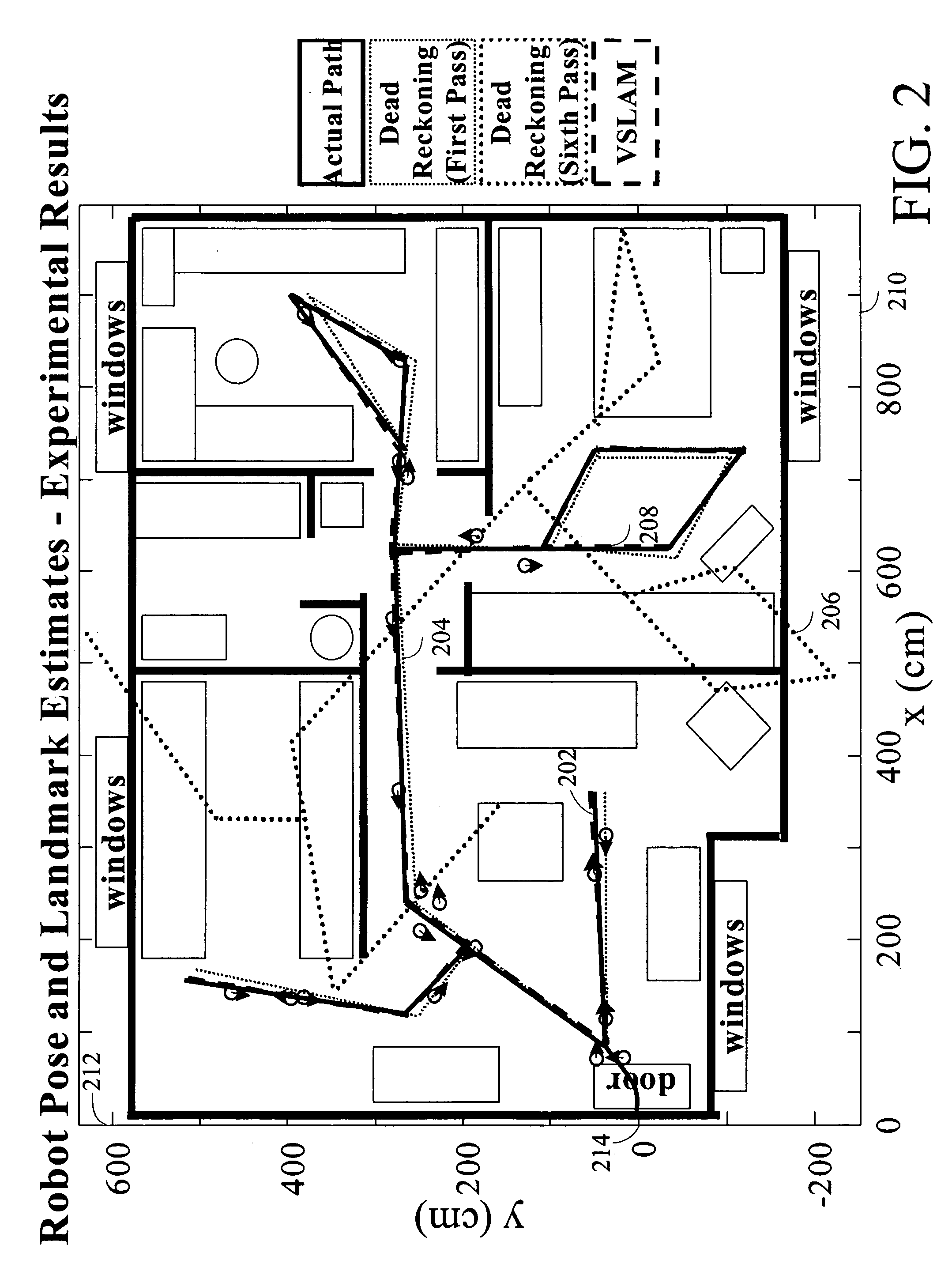
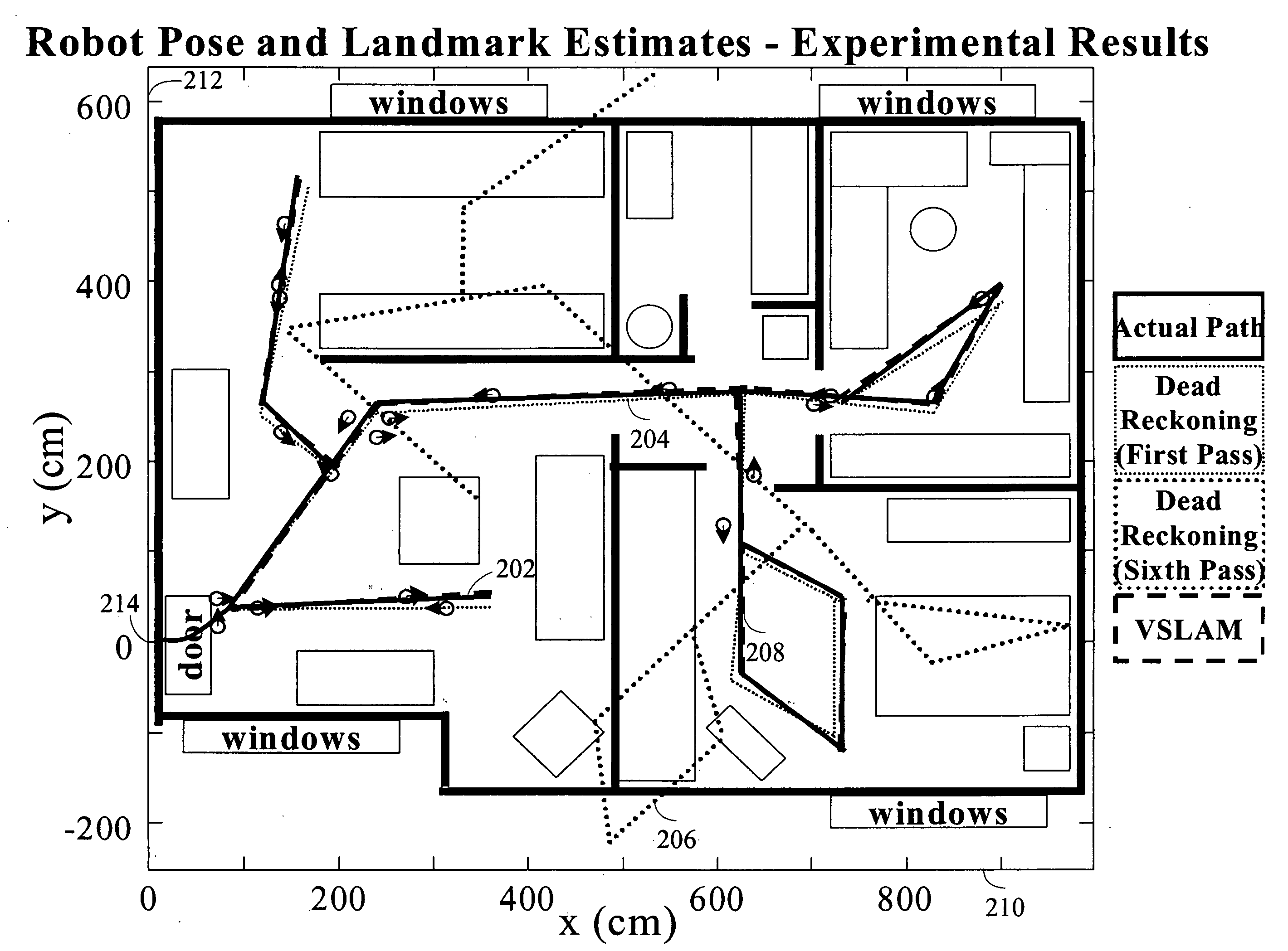
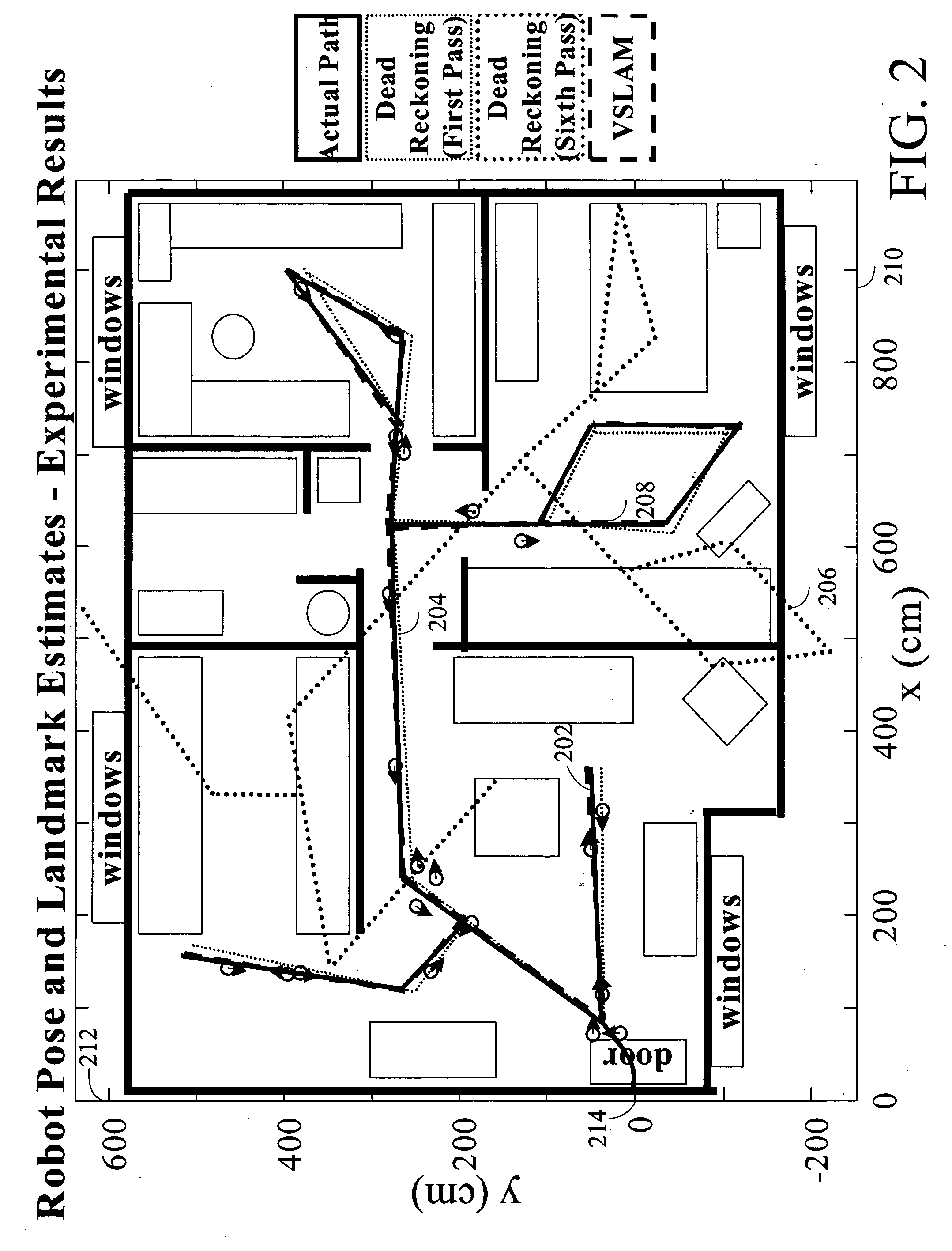
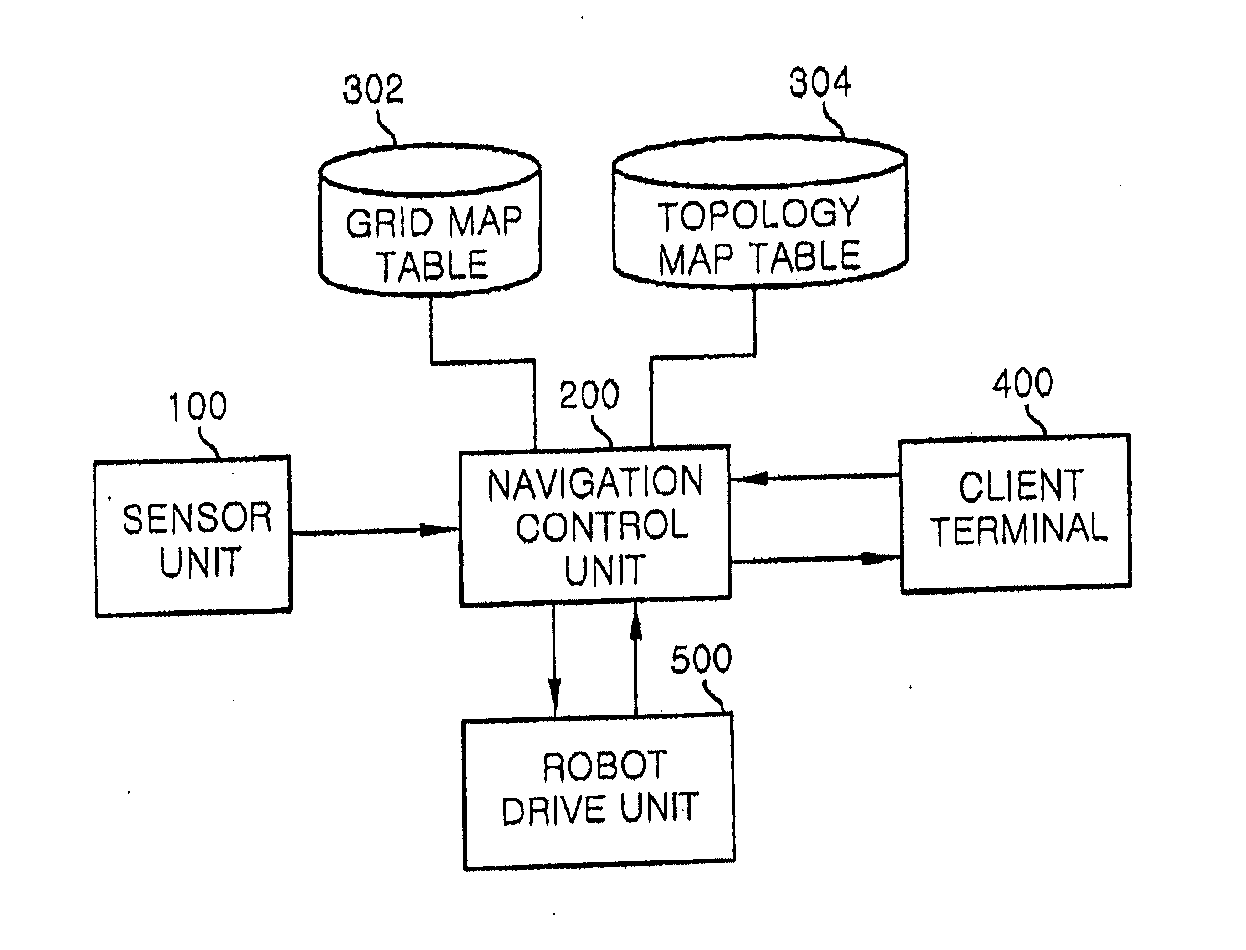
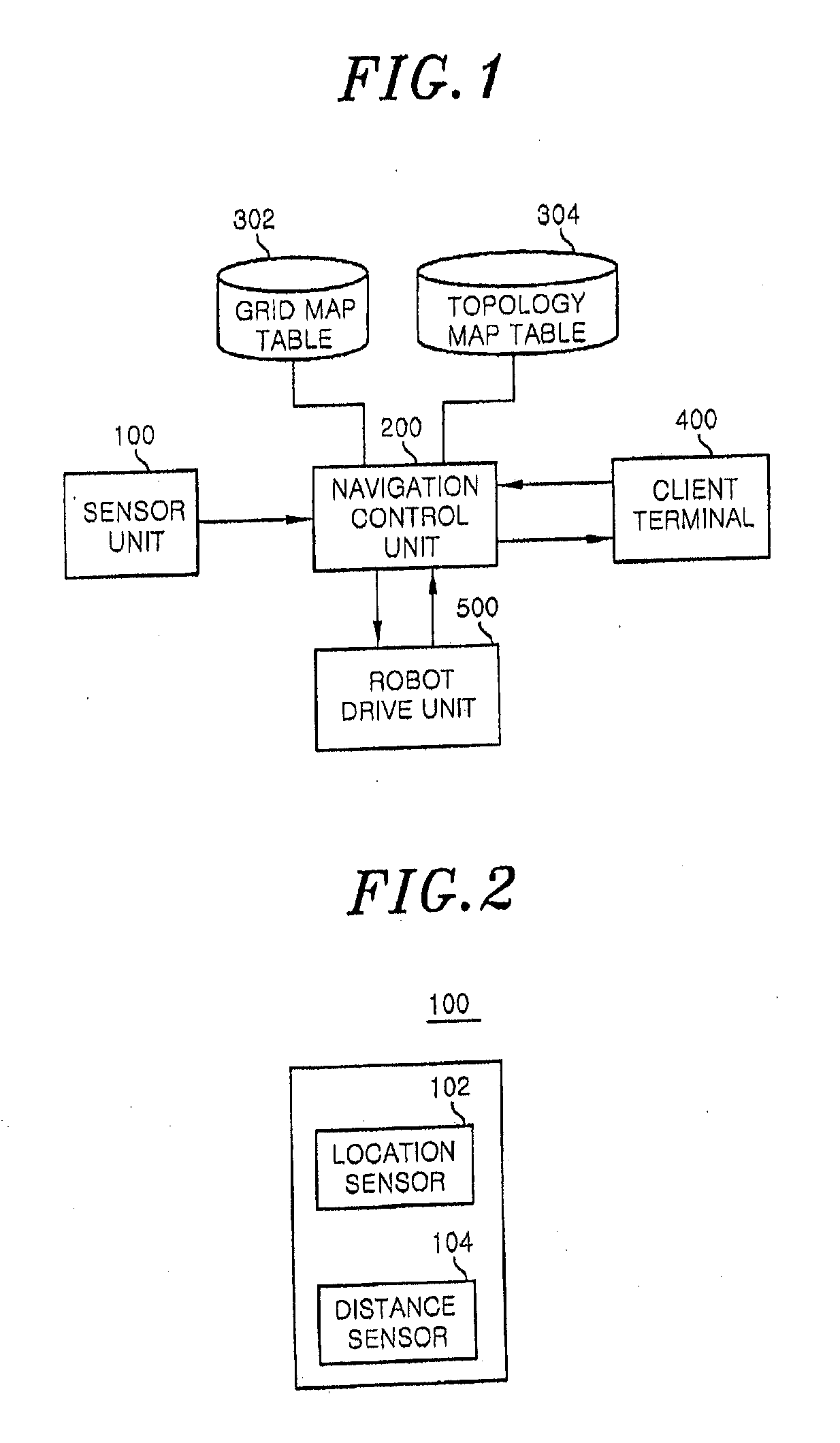
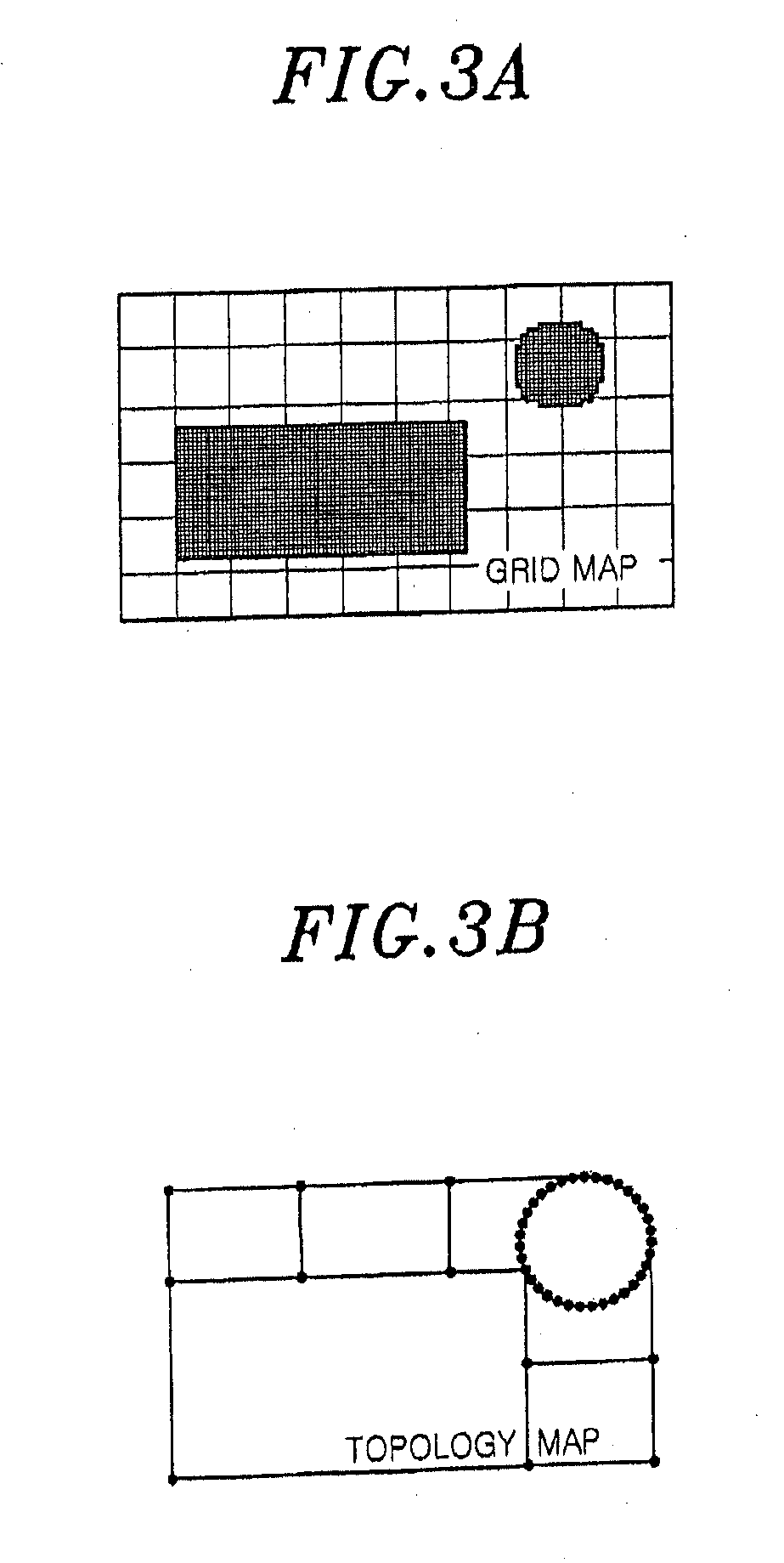
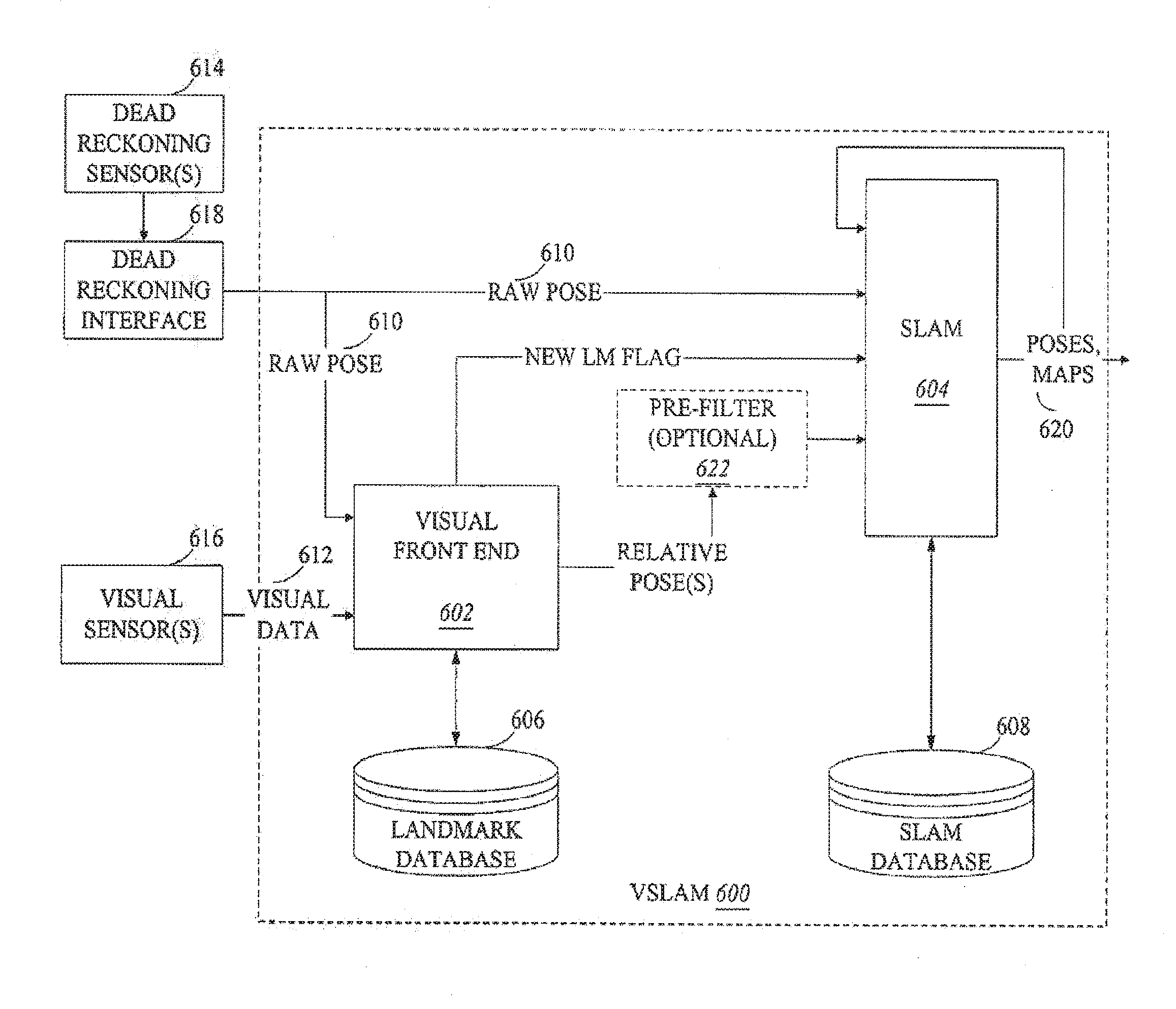
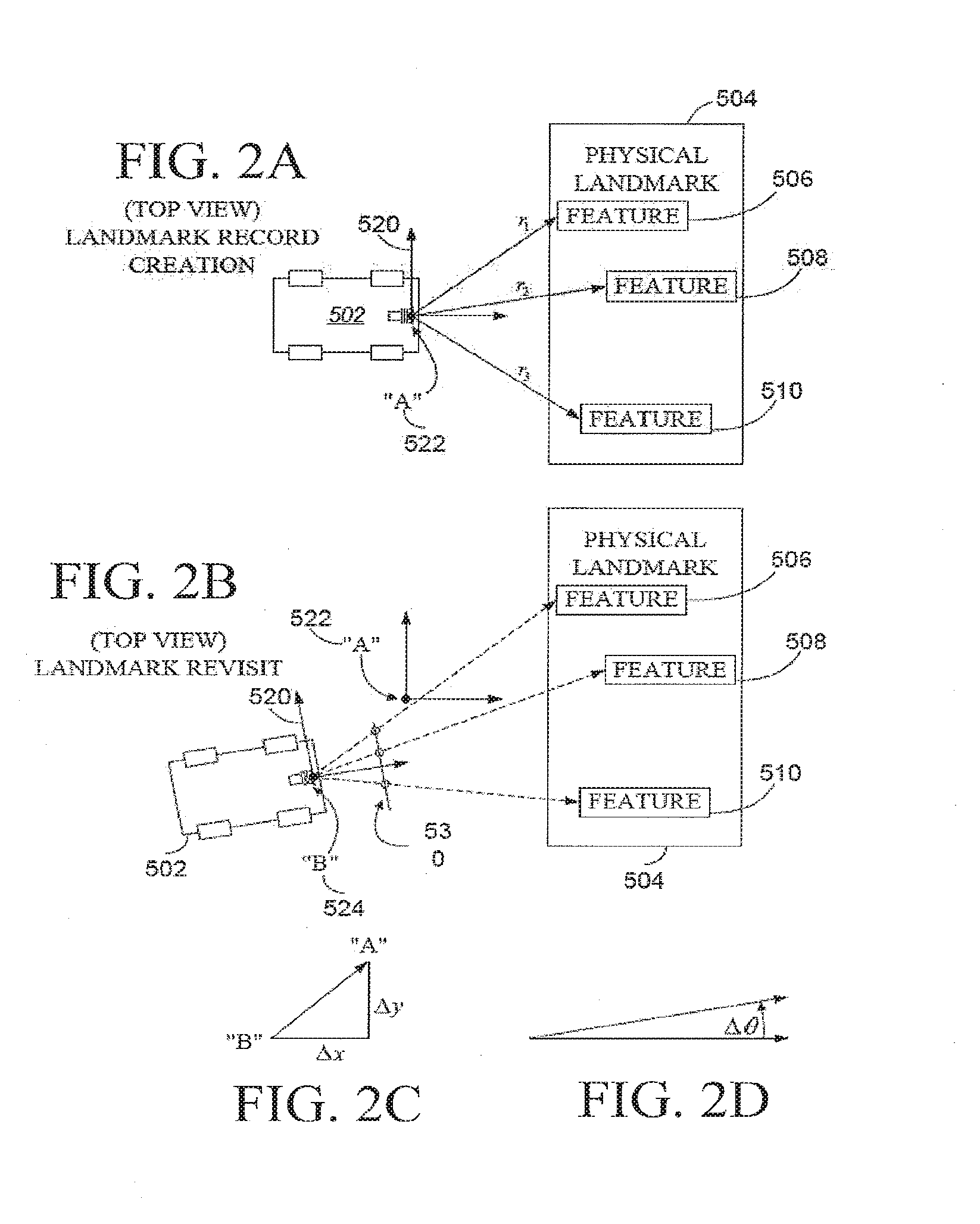
Systems and methods for vslam optimization
ActiveUS20120121161A1Database queryingCharacter and pattern recognitionSimultaneous localization and mappingLandmark matching
The invention is related to methods and apparatus that use a visual sensor and dead reckoning sensors to process Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). These techniques can be used in robot navigation. Advantageously, such visual techniques can be used to autonomously generate and update a map. Unlike with laser rangefinders, the visual techniques are economically practical in a wide range of applications and can be used in relatively dynamic environments, such as environments in which people move. Certain embodiments contemplate improvements to the front-end processing in a SLAM-based system. Particularly, certain of these embodiments contemplate a novel landmark matching process. Certain of these embodiments also contemplate a novel landmark creation process. Certain embodiments contemplate improvements to the back-end processing in a SLAM-based system. Particularly, certain of these embodiments contemplate algorithms for modifying the SLAM graph in real-time to achieve a more efficient structure.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Systems and methods for incrementally updating a pose of a mobile device calculated by visual simultaneous localization and mapping techniques
The invention is related to methods and apparatus that use a visual sensor and dead reckoning sensors to process Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). These techniques can be used in robot navigation. Advantageously, such visual techniques can be used to autonomously generate and update a map. Unlike with laser rangefinders, the visual techniques are economically practical in a wide range of applications and can be used in relatively dynamic environments, such as environments in which people move. One embodiment further advantageously uses multiple particles to maintain multiple hypotheses with respect to localization and mapping. Further advantageously, one embodiment maintains the particles in a relatively computationally-efficient manner, thereby permitting the SLAM processes to be performed in software using relatively inexpensive microprocessor-based computer system.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
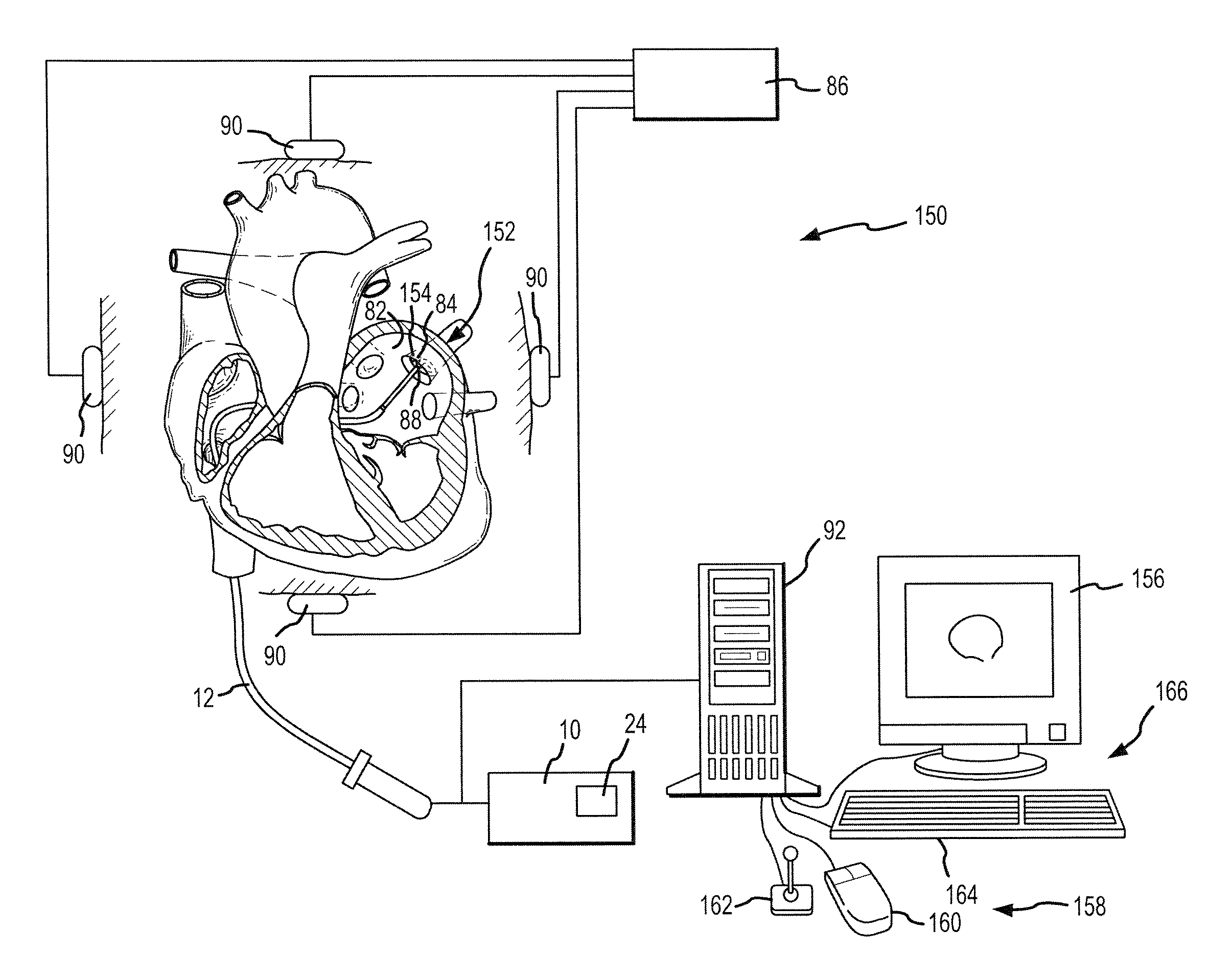
Robotic surgical system and method for automated therapy delivery
ActiveUS20130325035A1Reduce exposureMinimization requirementsSurgical navigation systemsCatheterGraphicsUser input
A method of navigating a medical device through a body of a patient includes providing a topography of at least a portion of the body, accepting user input defining a navigation path, robotically navigating the medical device to a starting point on the path, and robotically navigating the medical device along the navigation path to an endpoint. Waypoints defining the navigation path may be input on a graphical representation of the topography using a user interface such as a pointing device or touchscreen. The navigation path may also be defined by tracing a substantially continuous path on the graphical representation. A therapy may be administered while robotically navigating the medical device along the navigation path, either forward or in reverse, or while navigating the medical device along a return path defined by a plurality of virtual breadcrumbs generated as the medical device traverses the navigation path.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Service robot autonomous navigation method based on raster maps
InactiveCN103914068ASuitable for actual needsBest possible solutionPosition/course control in two dimensionsFeature extractionRadar
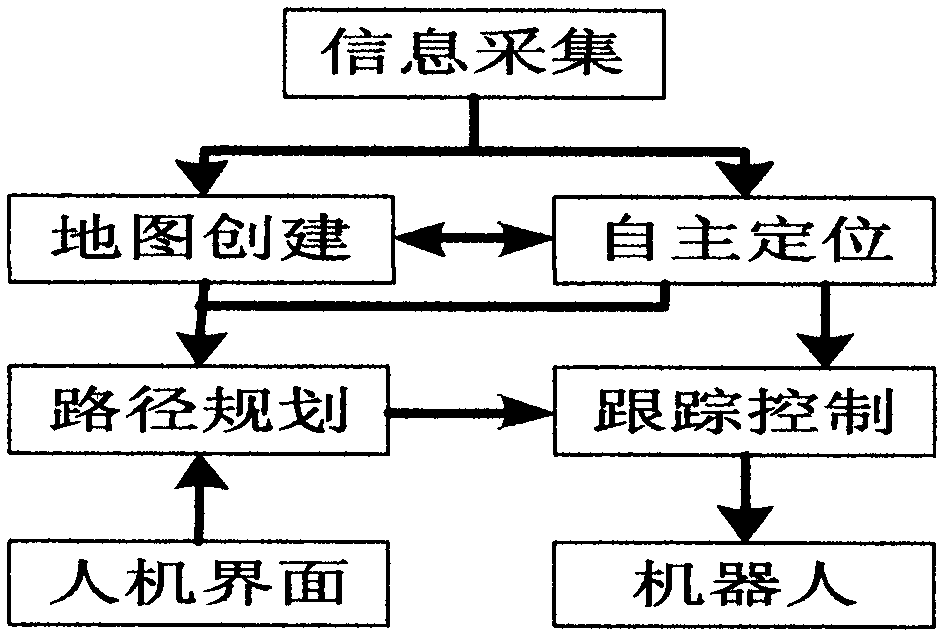
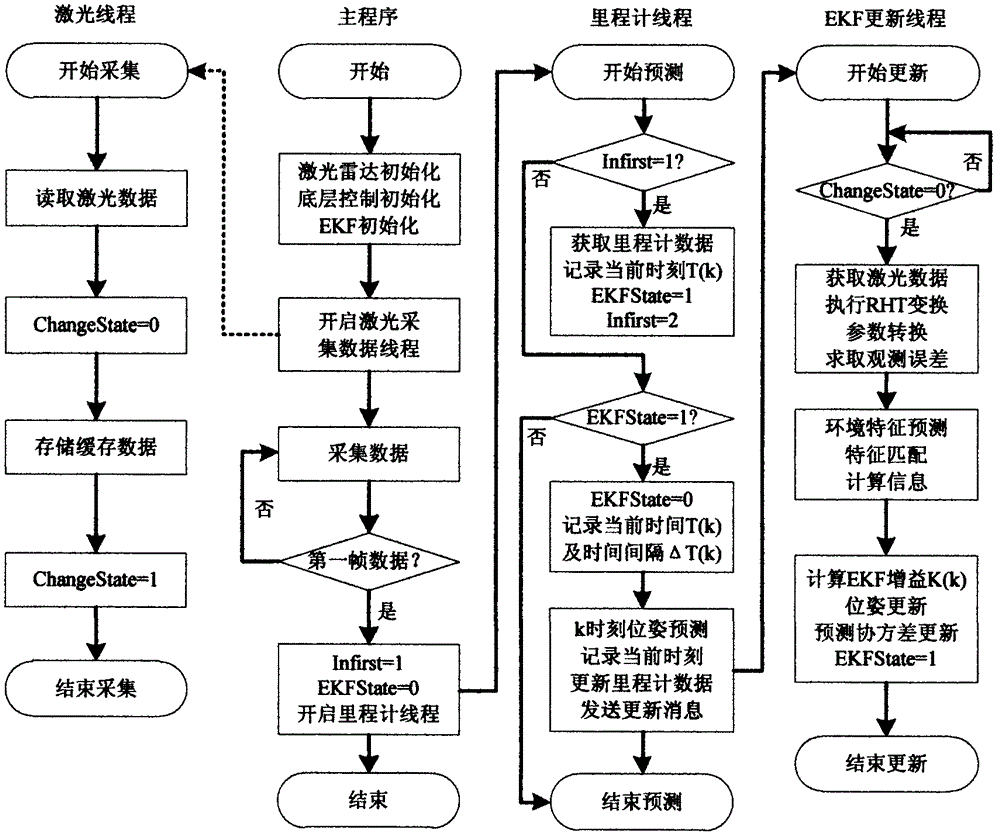
The invention belongs to the technical field of robot navigation and relates to a service robot autonomous navigation method based on raster maps. According to the method, the information of the environment where a robot is located is acquired in real time through 2D laser radar, environment feature extraction is conducted, raster map establishment is conducted according to the acquired information by means of the SLAM technique, autonomous positioning is conducted on the robot in real time at the same time, path planning is conducted on the robot according to navigation task requirements on this basis, and then tracking control is conducted according to the planned path to enable the robot to accomplish the navigation task. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that three key techniques in navigation are improved so that the method can meet actual requirements of service robot navigation better, and then the optimal feasible scheme is obtained; environment information is processed in real time to generate dynamic maps, and then autonomous navigation is achieved effectively, and navigation accuracy and efficiency are improved greatly.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
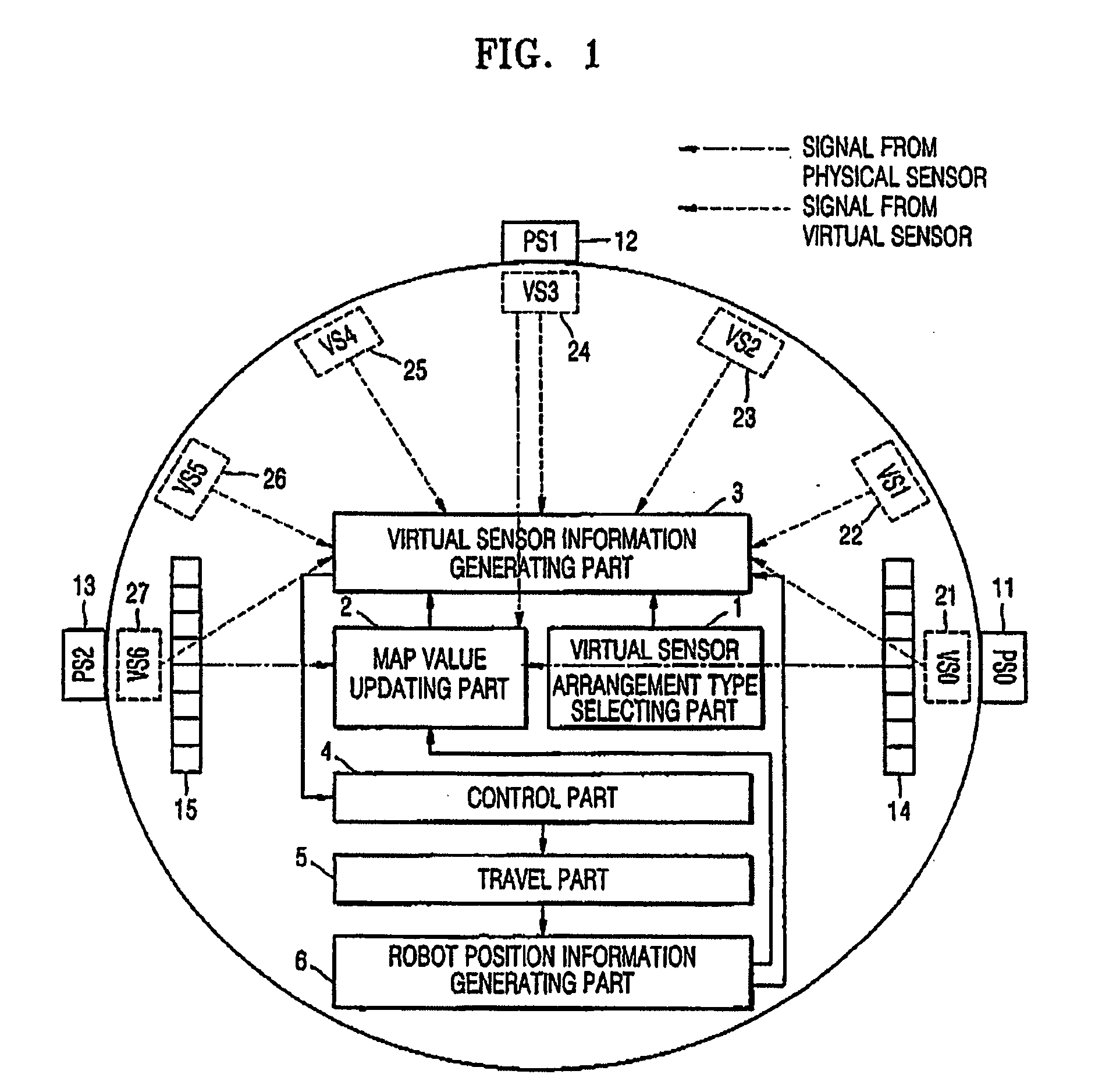
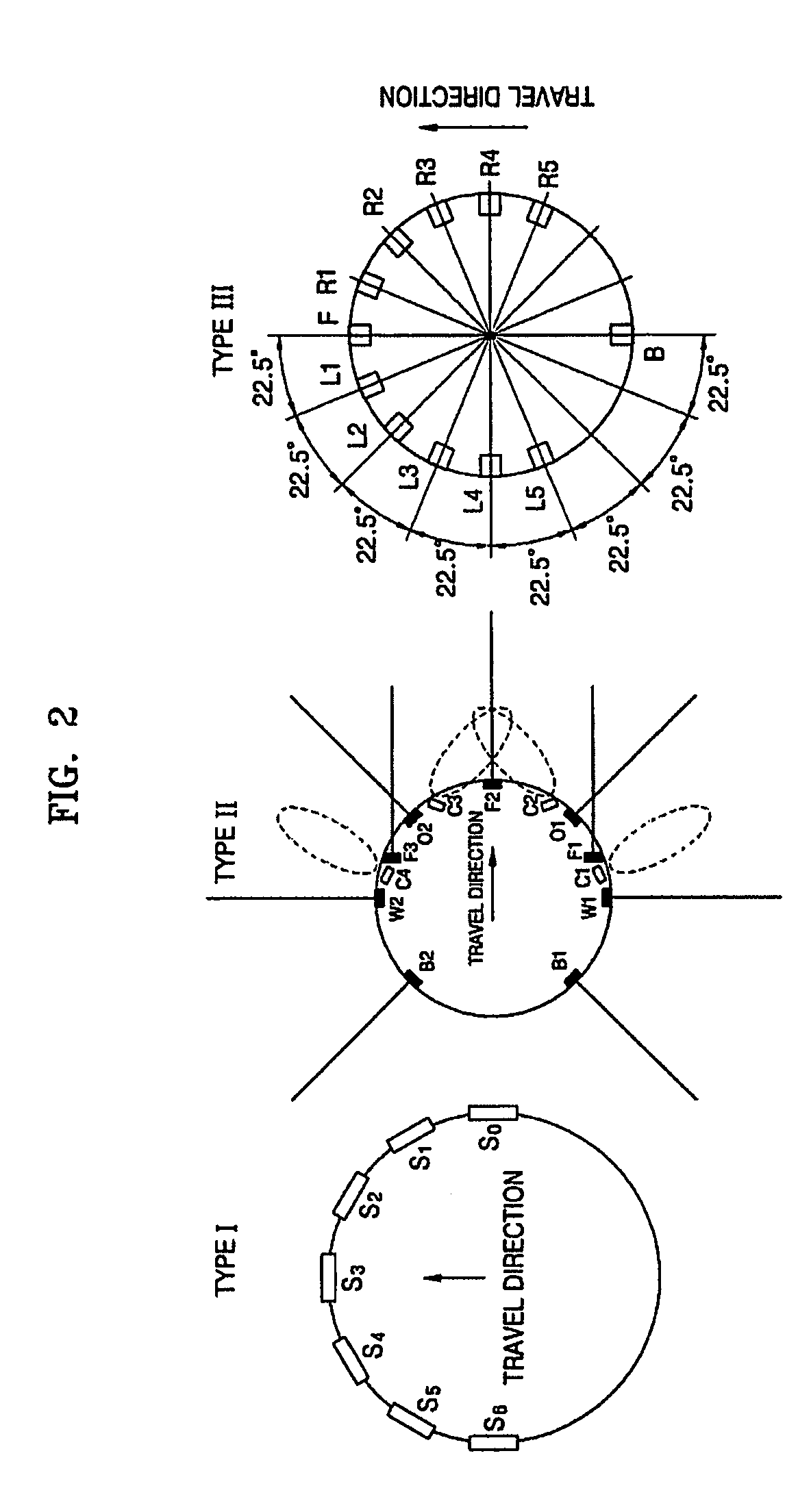
Method and/or apparatus for navigating mobile robot using virtual sensor
InactiveUS20050187678A1Reduce in quantityControllers with particular characteristicsSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationVirtual sensors
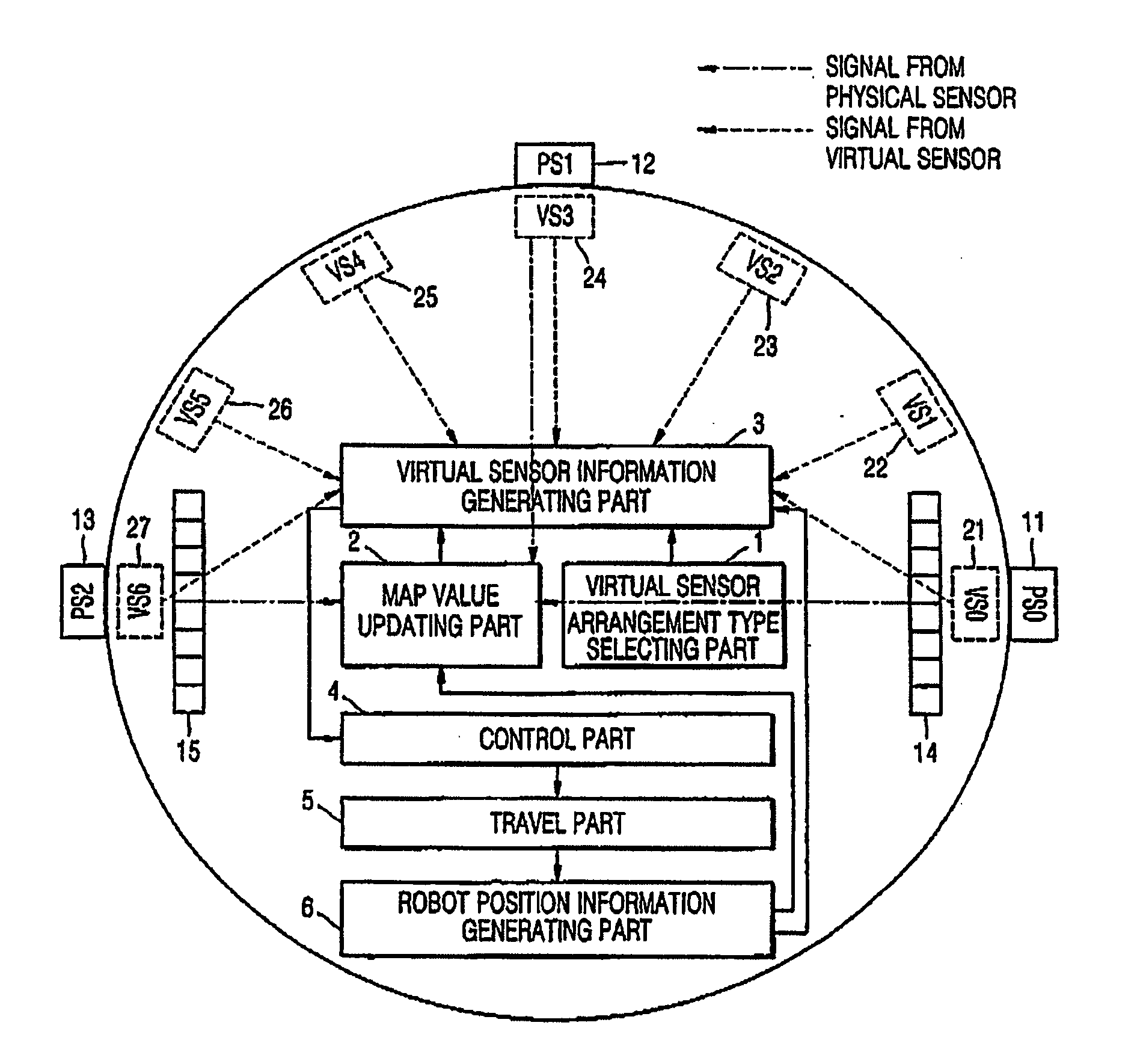
A method and apparatus of improving the navigation performance of robot are provided. The navigation method using a virtual sensor includes: generating information on positions of obstacles, the information which is estimated to be generated by virtual sensors that are virtually present, based on information on positions of the obstacles, which is generated by physical sensors; and controlling a movement of a robot according to the information on the positions of the obstacles. It is possible to overcome limits in the number and arrangement of previously installed physical sensors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
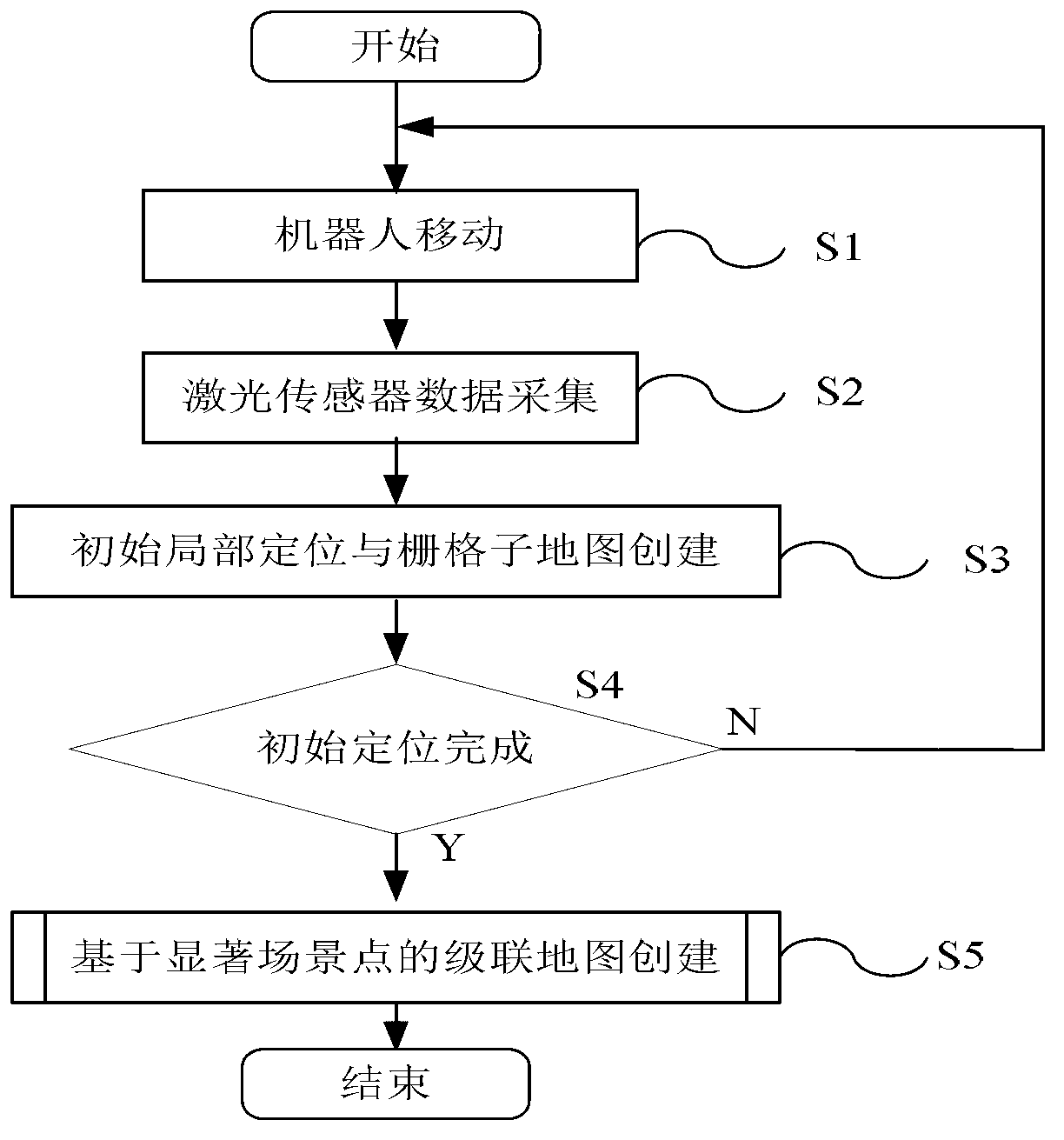
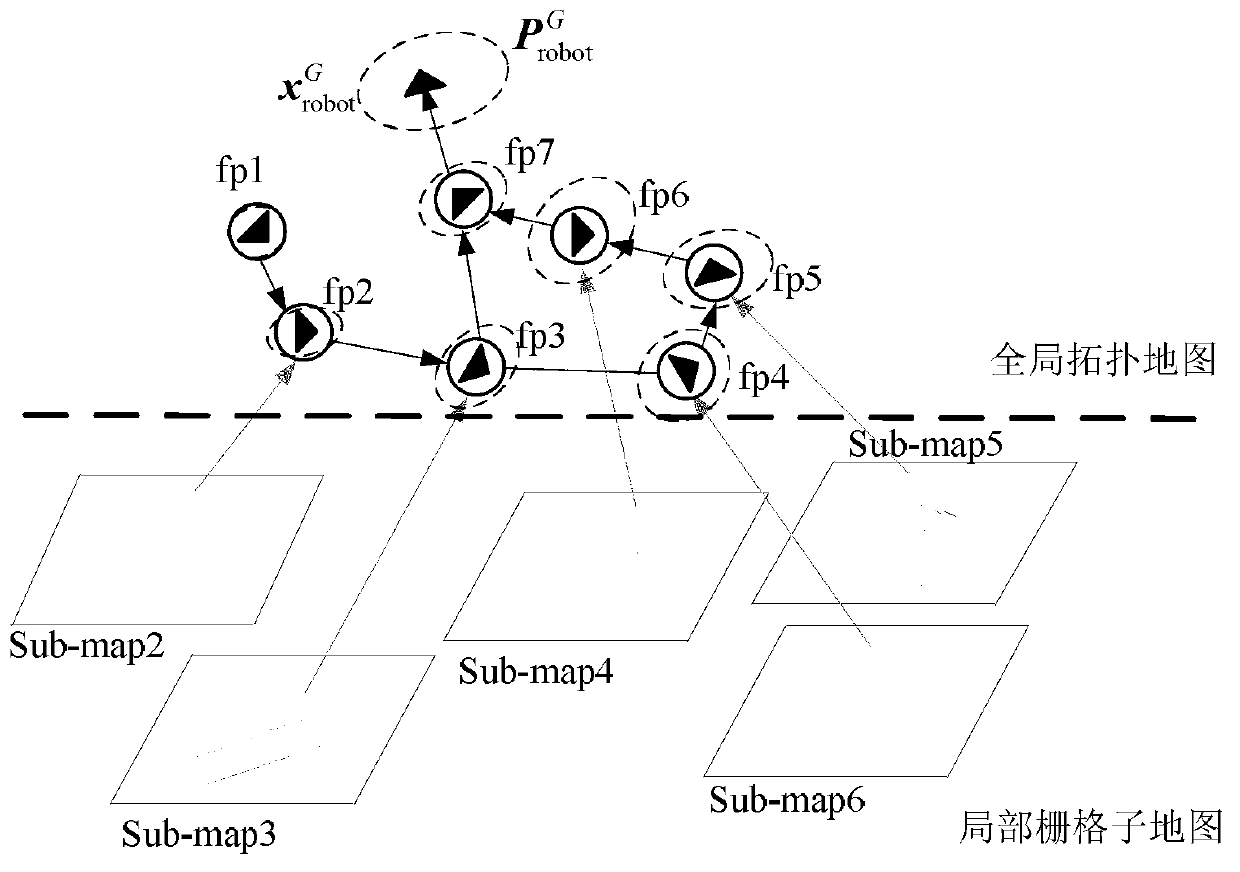
Mobile robot cascading map building method based on remarkable scenic spot detection
InactiveCN103278170ARealize online creationSolve the key problems of automatic segmentationInstruments for road network navigationImage analysisComputer scienceMobile robot navigation
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile robot navigation and discloses a mobile robot cascading map building method based on remarkable scenic spot detection. The mobile robot cascading map building method comprises the steps of: 1) according to image data collected by a mobile robot sensor, carrying out on-line detection on a road sign of a natural scene corresponding to a remarkable scene so as to generate a topological node in a global map; 2) updating the pose of a mobile robot and a local grid map; and 3) building a global topological map structure by taking a remarkable scenic spot as the topological node, and optimizing the topological structure by introducing a weighted scanning and matching method and a relaxation method on the basis of the closed detection of trajectory of the robot to ensure the global consistency of the topological map. The mobile robot cascading map building method is applicable to the autonomous path planning and navigation application for various mobile robots in large indoor environment ranges such as a plurality of rooms and corridors.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Service mobile robot navigation method in dynamic environment
InactiveCN103558856AEnsure predictabilityImprove securityPosition/course control in two dimensionsLocation trackingLaser sensor
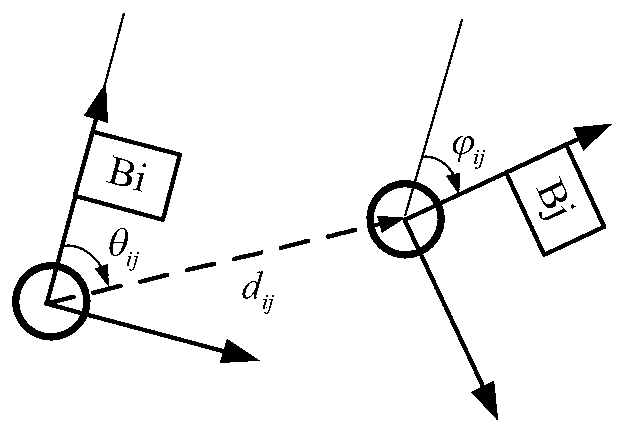
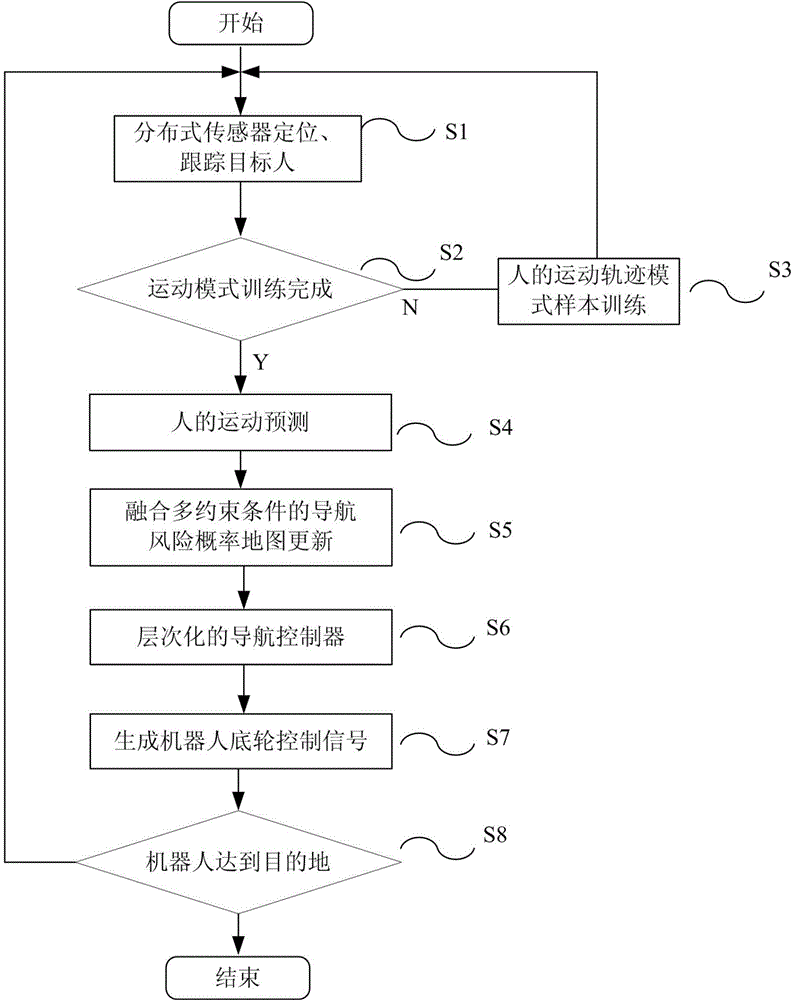
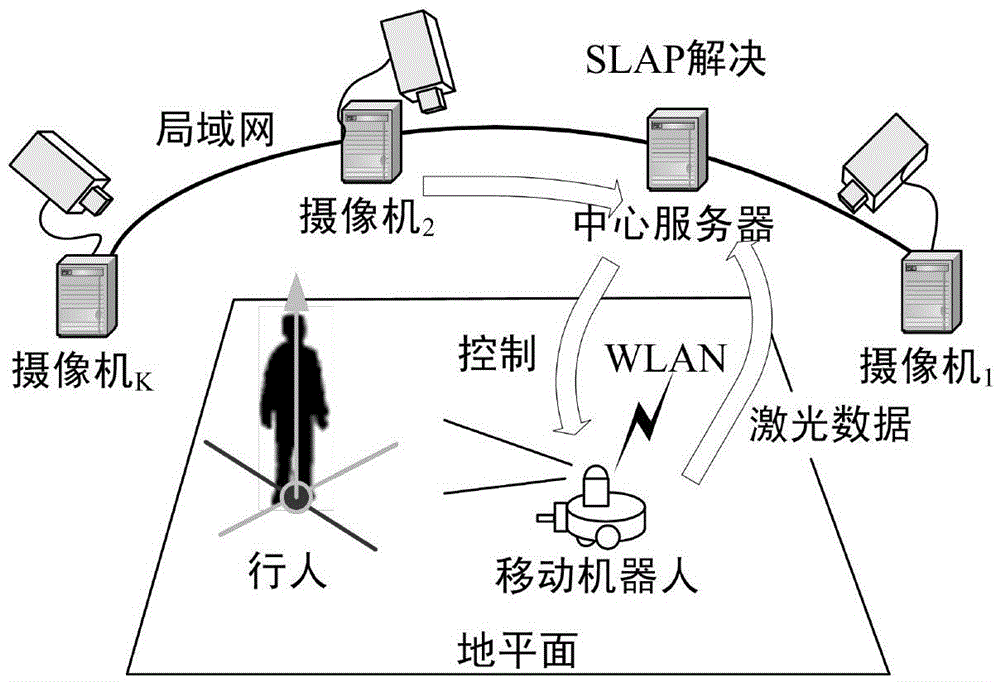
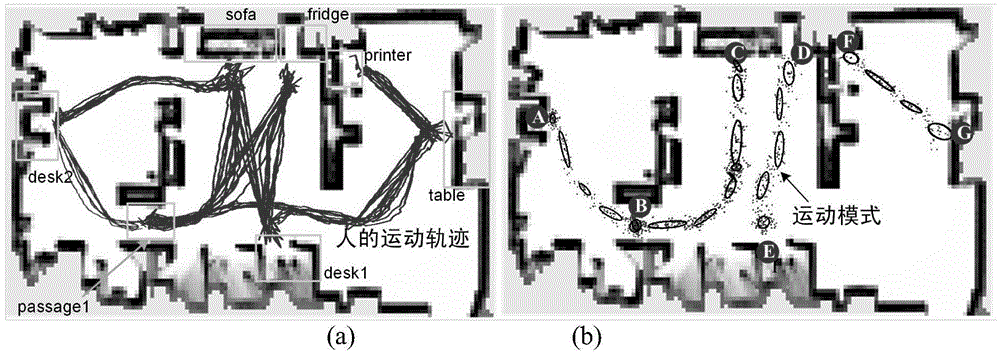
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile robot autonomous navigation and discloses a service mobile robot navigation method in a dynamic environment. The service mobile robot navigation method in the dynamic environment includes the following steps that firstly, position tracking of people can be achieved by utilizing multiple global cameras and robot vehicle-mounted laser sensors in an indoor environment; secondly, the moving mode of people under a specific indoor environment site is trained according to collected samples, and the moving trend of people is predicated; thirdly, a current position and a predicated position of people are merged with an environment static obstacle raster map, and a navigation risk probability map is generated; fourthly, a robot navigation movement controller of a global route planning-local obstacle avoidance control gradational structure is adopted to control robot navigation behavior, and safe and efficient navigation behavior of a robot under a complex dynamic environment where the robot coexists with people is ensured through controlling.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
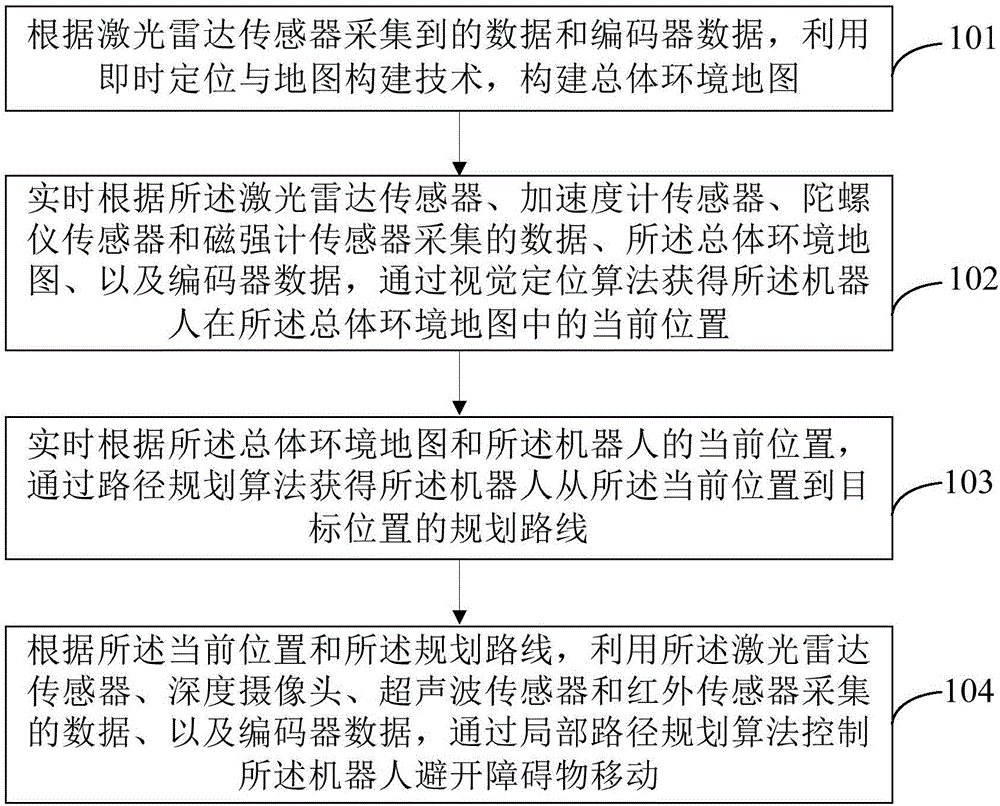
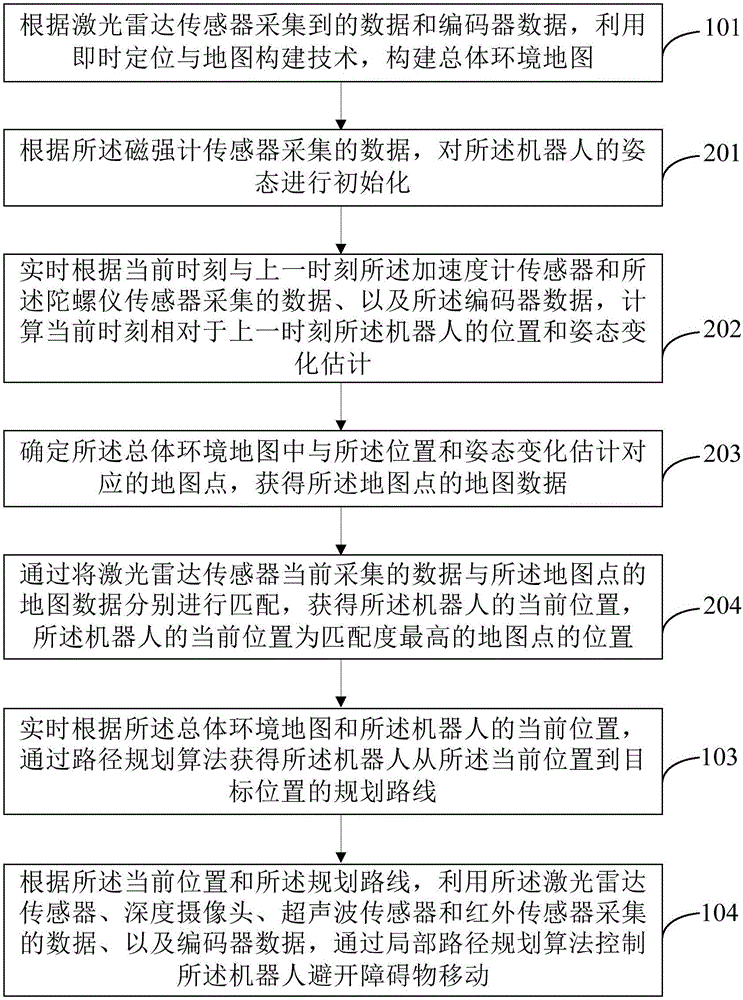
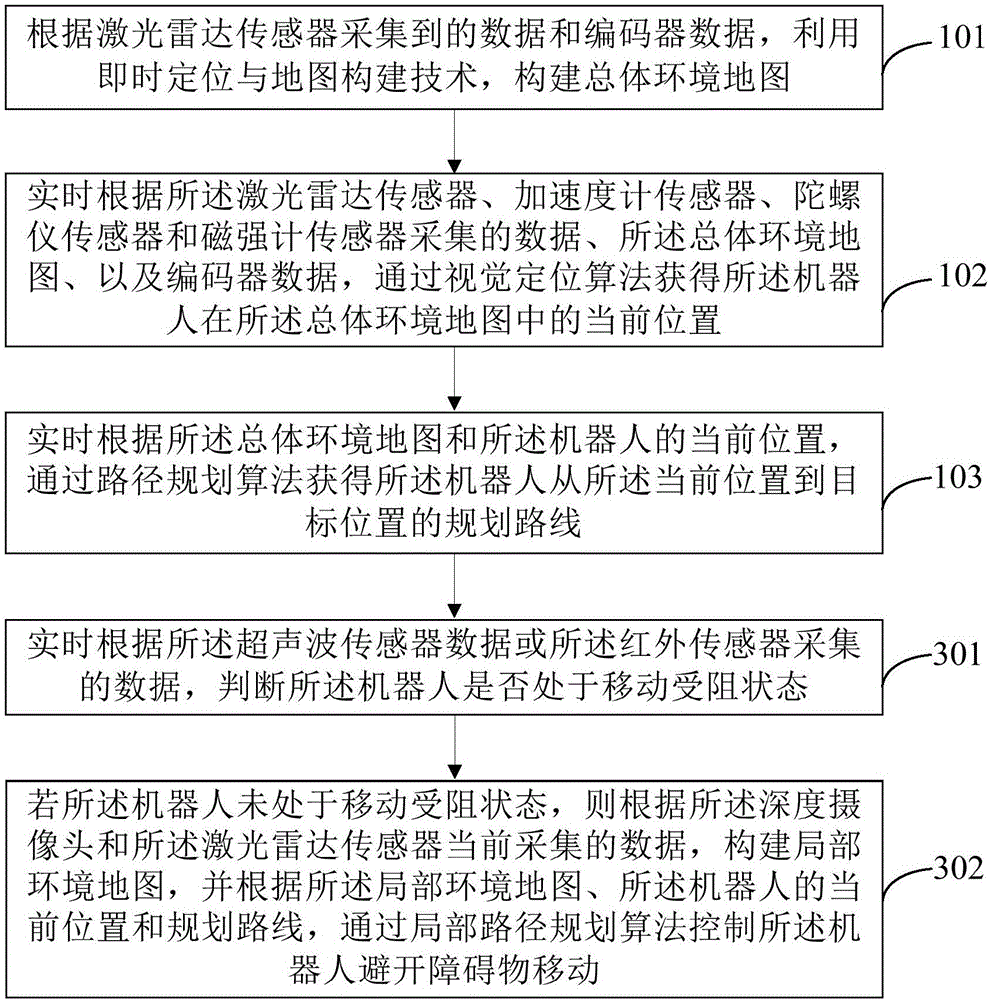
Robot navigation method and device based on multi-sensor data fusion
InactiveCN106681330ARealize autonomous navigationTaking into account the costPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesUltrasonic sensorGyroscope
The invention provides a robot navigation method and device based on multi-sensor data fusion. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a map of a total environment according to data acquired by a laser radar sensor and data of an encoder; acquiring the current position of a robot in the map of the total environment in real time according to data acquired by a laser radar sensor, an accelerometer sensor, a gyroscope sensor and a magnetometer sensor, the map of the total environment and the data of the encoder; acquiring a planned route of the robot from the current position to a targeted position in real time according to the map of the total environment and the current position of the robot; and controlling the robot to keep away from barriers during movement by the data which are acquired by the laser radar sensor, a deep camera, an ultrasonic sensor and an infrared sensor and the data of the encoder. On the basis of reasonable utilization of the sensors to realize navigation of the robot, the method is flexibly applied to various scenes, costs are considered, and the autonomous navigation effect can be achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Systems and methods for incrementally updating a pose of a mobile device calculated by visual simultaneous localization and mapping techniques
ActiveUS20060012493A1Image enhancementInstruments for road network navigationPattern recognitionSimultaneous localization and mapping
The invention is related to methods and apparatus that use a visual sensor and dead reckoning sensors to process Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). These techniques can be used in robot navigation. Advantageously, such visual techniques can be used to autonomously generate and update a map. Unlike with laser rangefinders, the visual techniques are economically practical in a wide range of applications and can be used in relatively dynamic environments such as environments in which people move. One embodiment further advantageously uses multiple particles to maintain multiple hypotheses with respect to localization and mapping. Further advantageously, one embodiment maintains the particles in a relatively computationally-efficient manner, thereby permitting the SLAM processes to be performed in software using relatively inexpensive microprocessor-based computer systems.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
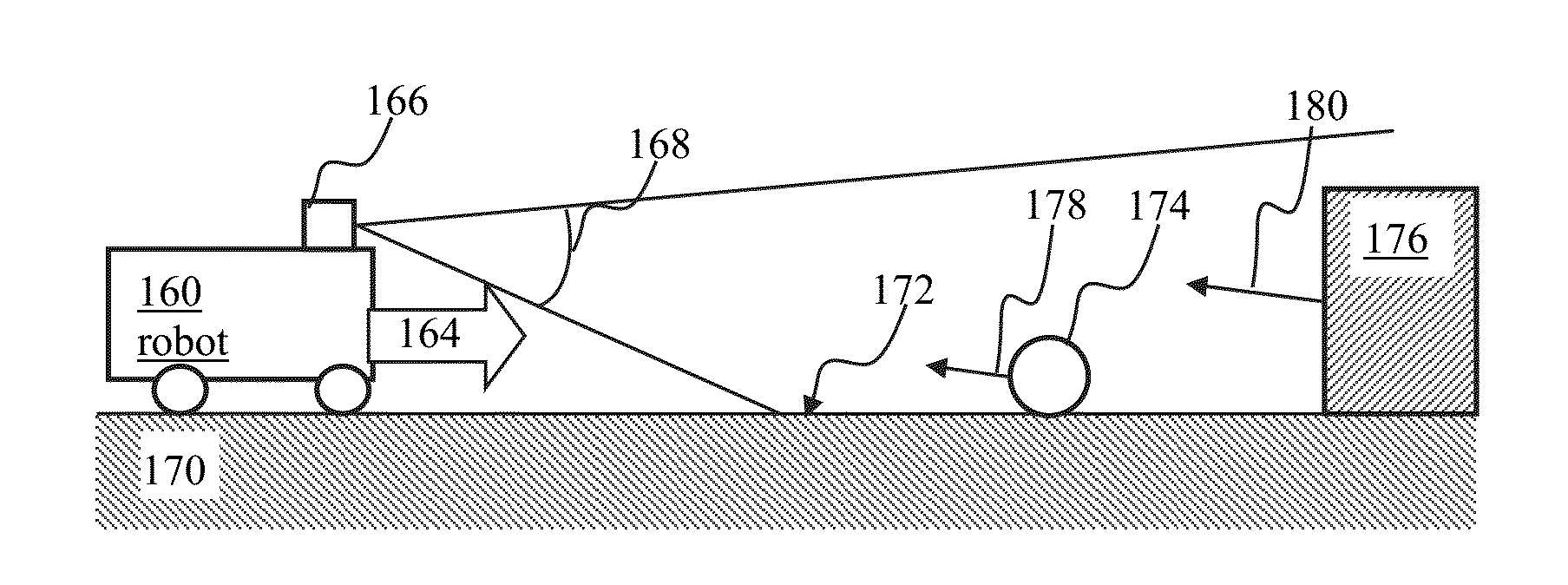
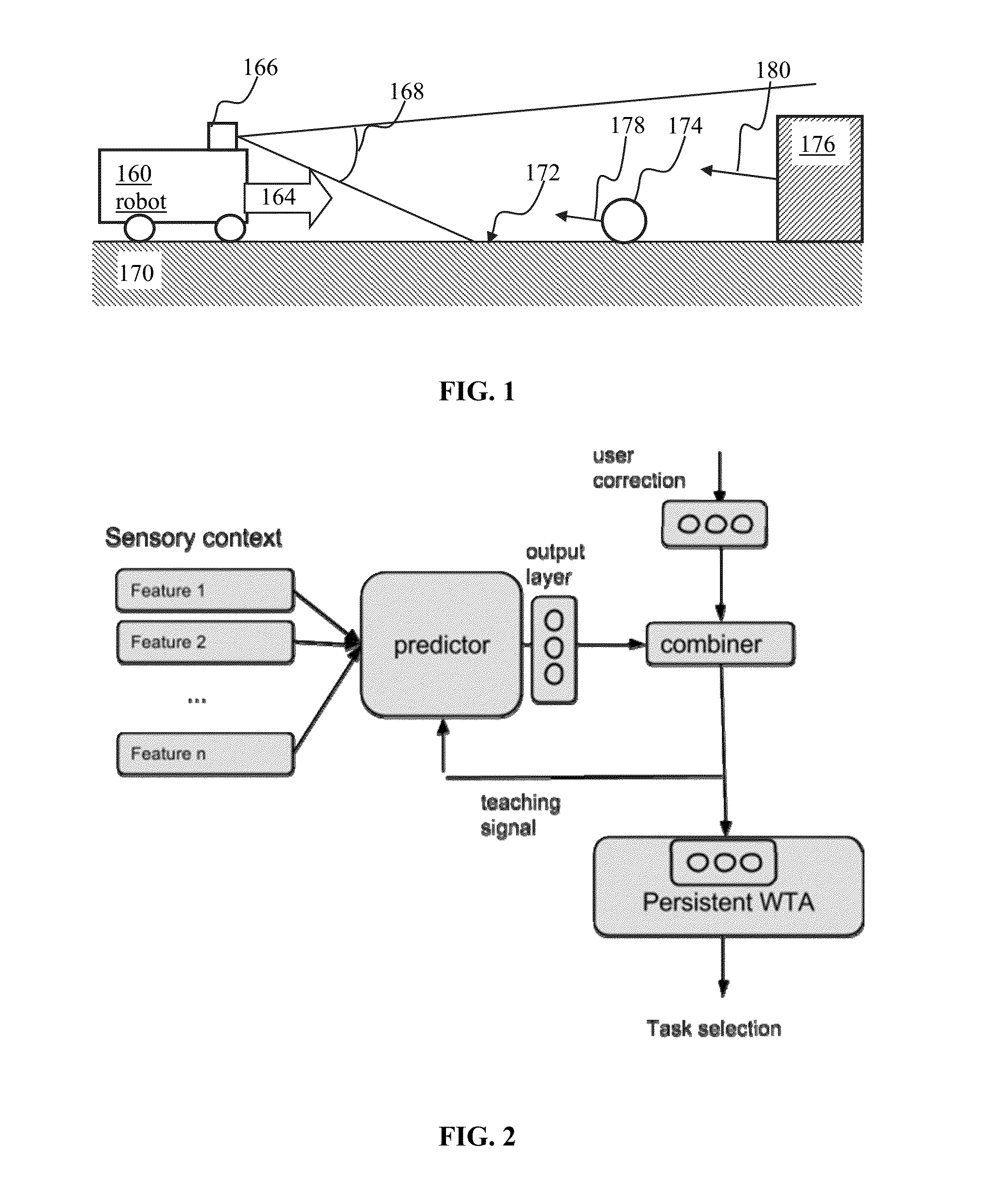
Apparatus and methods for training of robots
ActiveUS20160096272A1Programme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processVision basedCharacteristic space
A random k-nearest neighbors (RKNN) approach may be used for regression / classification model wherein the input includes the k closest training examples in the feature space. The RKNN process may utilize video images as input in order to predict motor command for controlling navigation of a robot. In some implementations of robotic vision based navigation, the input space may be highly dimensional and highly redundant. When visual inputs are augmented with data of another modality that is characterized by fewer dimensions (e.g., audio), the visual data may overwhelm lower-dimension data. The RKNN process may partition available data into subsets comprising a given number of samples from the lower-dimension data. Outputs associated with individual subsets may be combined (e.g., averaged). Selection of number of neighbors, subset size and / or number of subsets may be used to trade-off between speed and accuracy of the prediction.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Indoor map building method for improving robot path planning efficiency
ActiveCN104898660AAvoid planningPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimultaneous localization and mappingTopological order
The invention discloses an indoor map building method for improving robot path planning efficiency. The method combines a topological map and a grid map, the planning problem happens in space represented by topological nodes, and planning of global space is avoided. In addition, laser is used for identifying a door in the indoor environment, a topological relationship between rooms is built, the process is merged in particle filter SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) algorithm, the grid map represented by the environment and the topological map based on the grid map can be obtained finally, and the path planning algorithm in robot navigation is simpler and more efficient.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
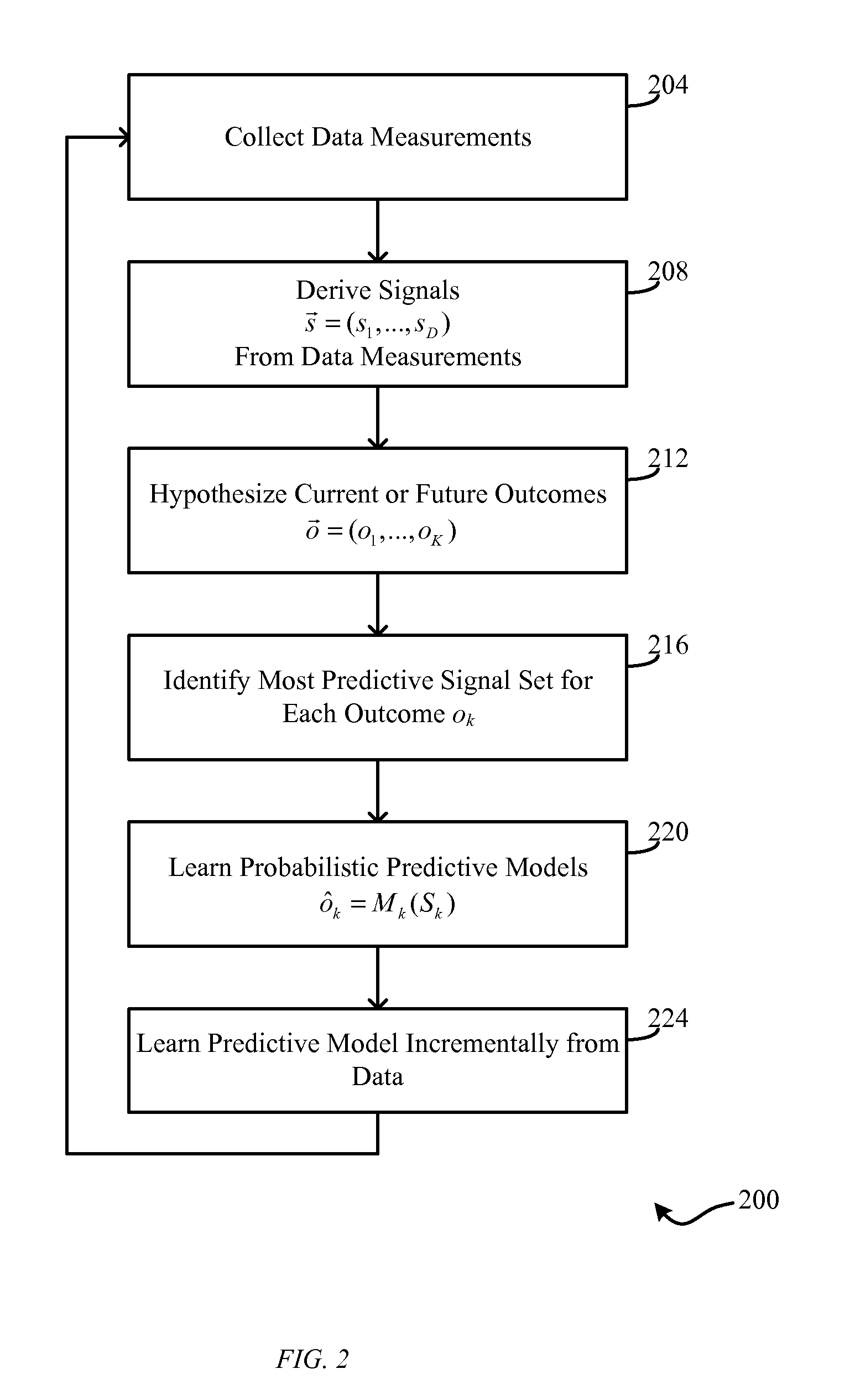
Long Term Active Learning from Large Continually Changing Data Sets
InactiveUS20110282169A1Accurate predictionIncrease speedMedical simulationMathematical modelsData setData mining
Methods and systems are disclosed for autonomously building a predictive model of outcomes. A most-predictive set of signals Sk is identified out of a set of signals s1, s2, . . . , sD for each of one or more outcomes ok. A set of probabilistic predictive models ôk=Mk (Sk) is autonomously learned, where ôk is a prediction of outcome ok derived from the model Mk that uses as inputs values obtained from the set of signals Sk. The step of autonomously learning is repeated incrementally from data that contains examples of values of signals s1, s2, . . . , sD and corresponding outcomes o1, o2, . . . , oK. Various embodiments are also disclosed that apply predictive models to various physiological events and to autonomous robotic navigation.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
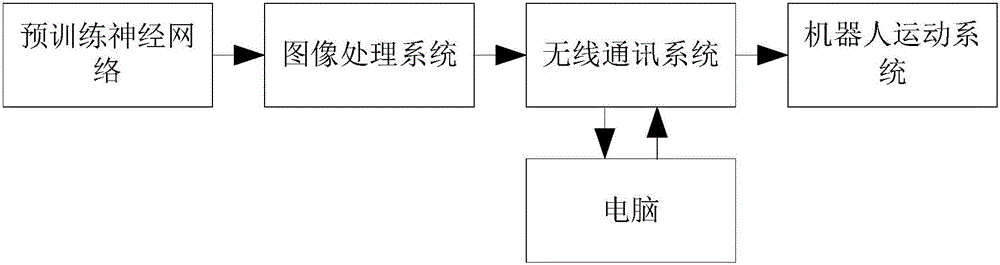
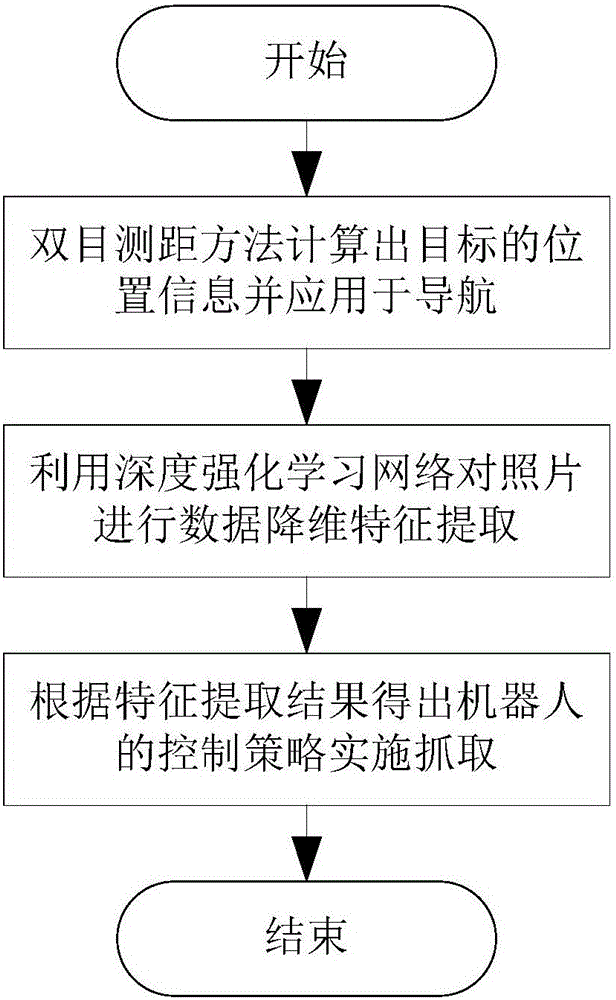
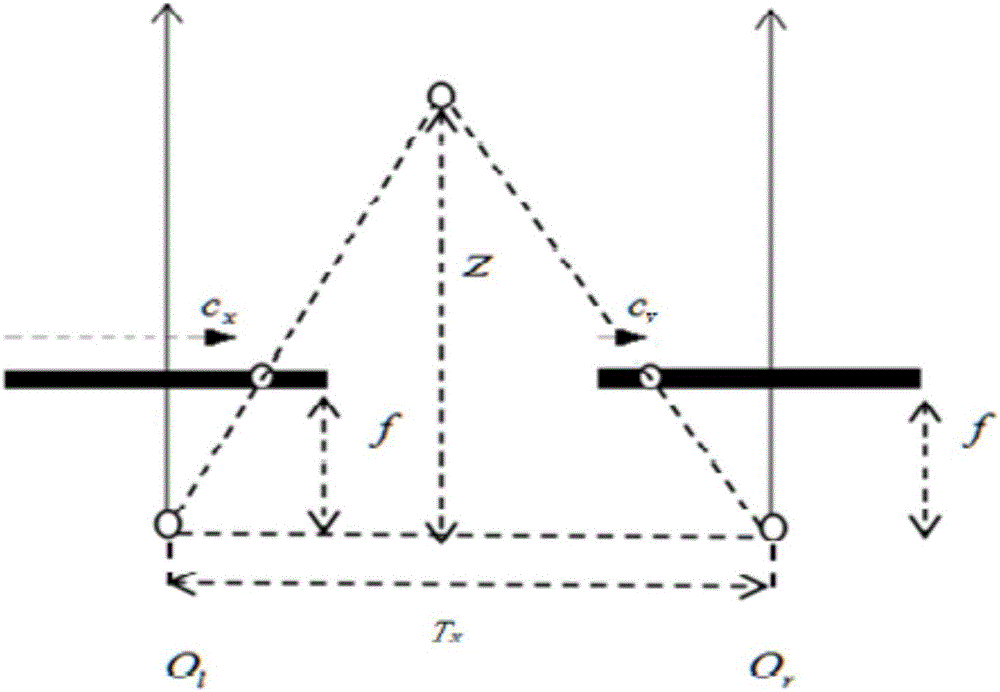
Robot adaptive grabbing method based on deep reinforcement learning
InactiveCN106094516AGuaranteed convergenceSolve problems that require each other independentlyAdaptive controlFeature extractionRobotic arm
The invention provides a robot adaptive grabbing method based on deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises the following steps: when distanced a certain distance away from an object to be grabbed, a robot obtaining a picture of a target through a pick-up head in the front, then according to the picture, calculating position information of the target by use of a binocular distance measurement method, and applying the calculated position information to robot navigation; when the target goes into the grabbing scope of a manipulator, taking a picture of the target through the pick-up head in the front again, and by use of a DDPG-based deep reinforcement learning network trained in advance, performing data dimension reduction feature extraction on the picture; and according to a feature extraction result, obtaining a control strategy of the robot, and the robot controlling a movement path and the posture of the manipulator by use of a control strategy so as to realize adaptive grabbing of the target. The grabbing method can realize adaptive grabbing of objects which are in different sizes and shapes and are not fixedly positioned and has quite good market application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Indoor movable robot real-time navigation method based on visual information correction
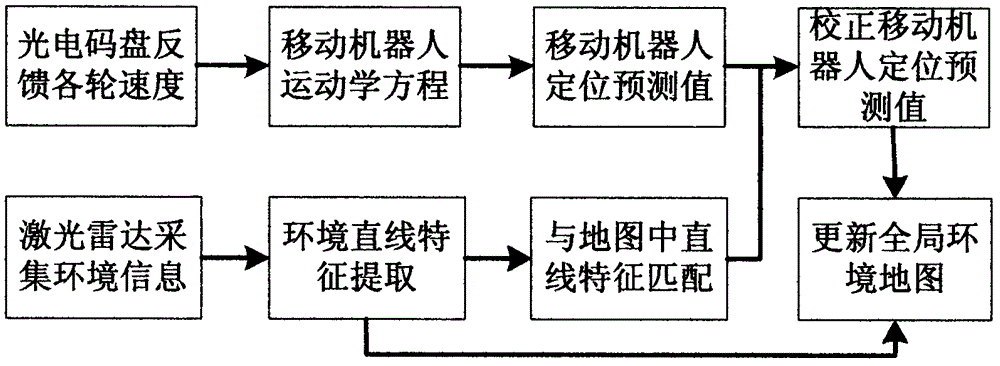
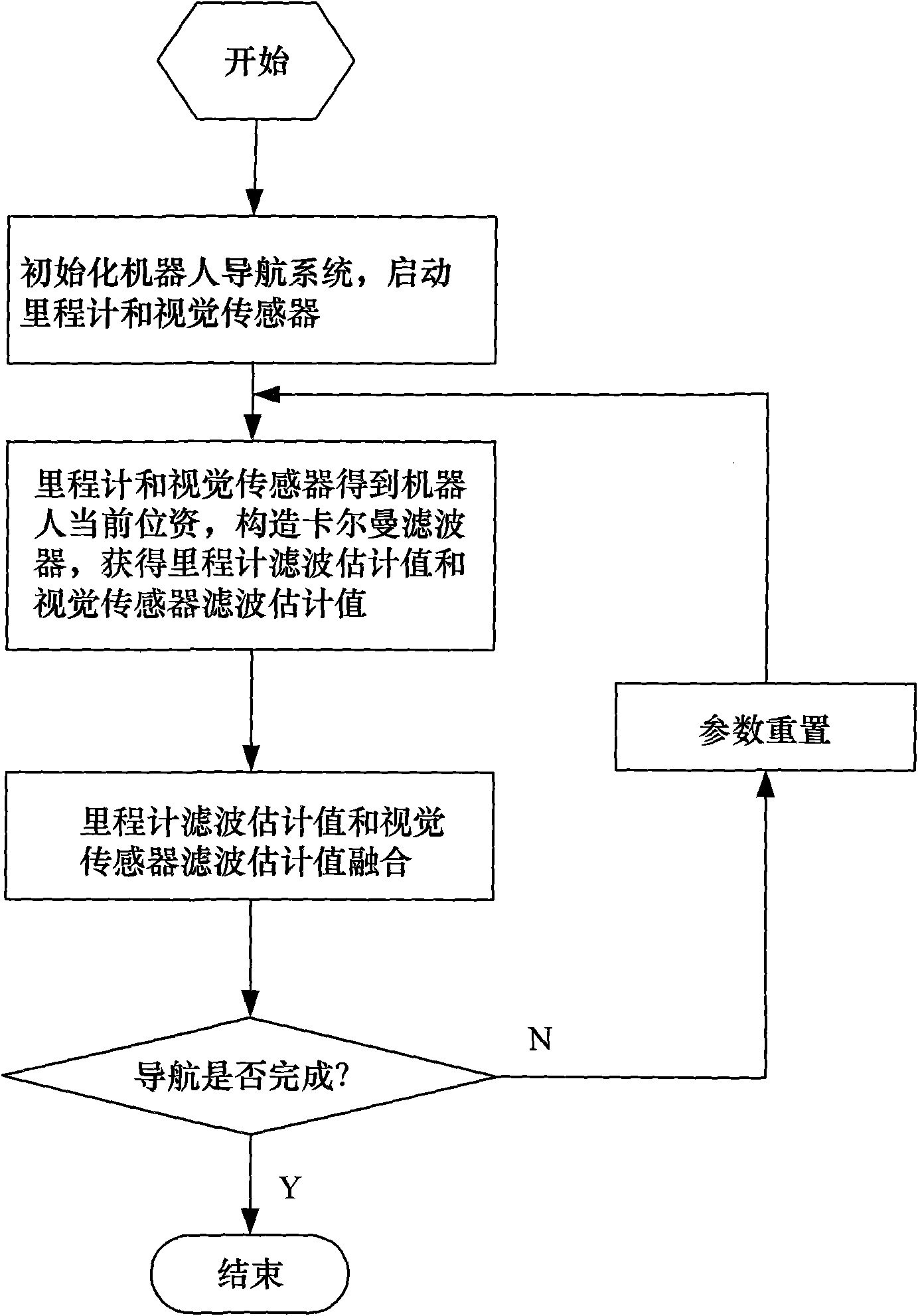
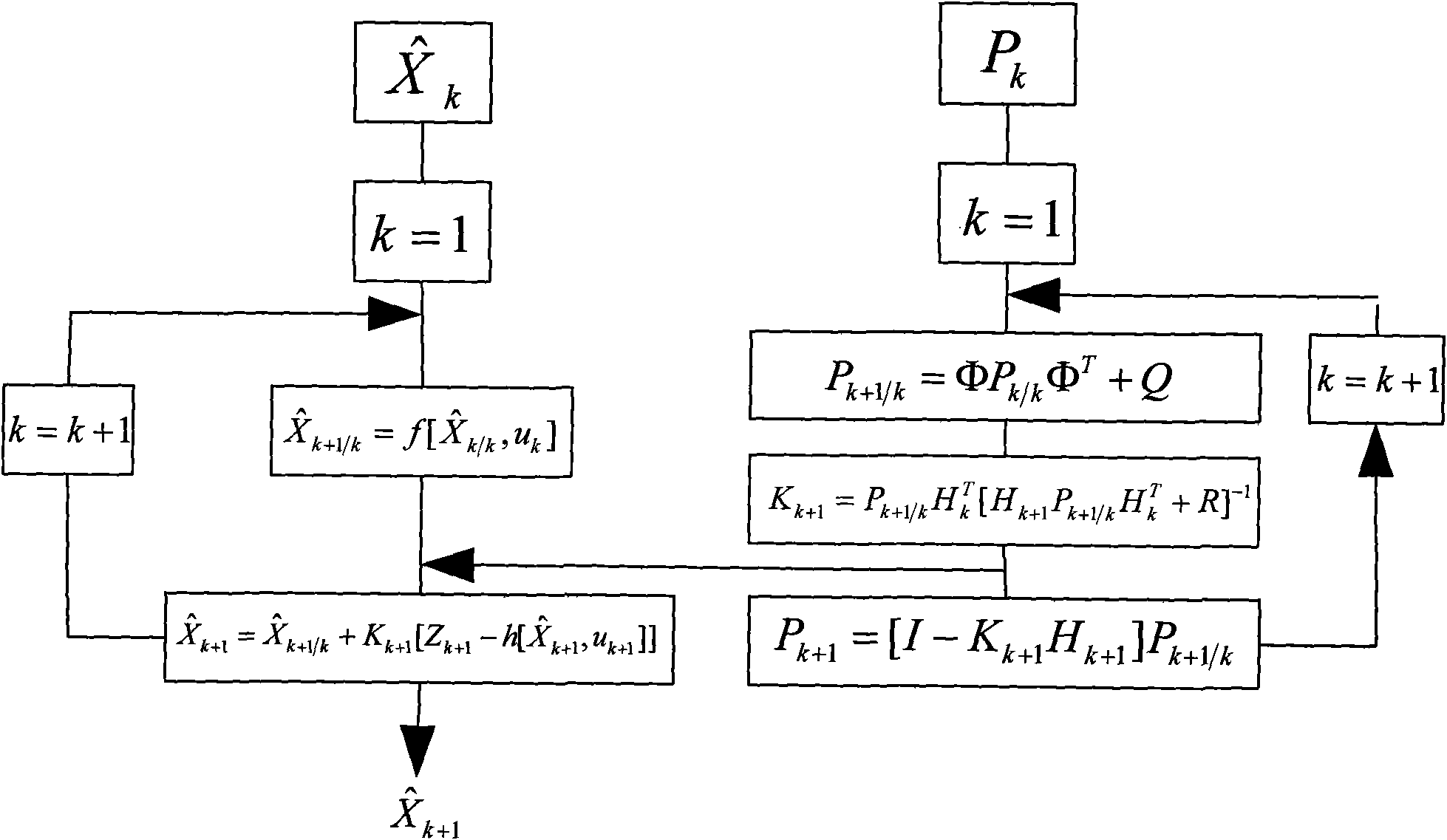
InactiveCN101576384AEnsure real-time requirementsImprove accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFiltrationVision based
The invention discloses an indoor movable robot real-time navigation method based on visual information correction, comprising the following steps of: (1) initializing a robot navigation system, and starting a mile meter and a visual sensor; (2) obtaining the current position of a robot by the mile meter and the visual sensor and forming a kalman filter so as to obtain a mile meter filtration estimation value and a visual sensor filtration estimation value; (3) fusing the mile meter filtration estimation value and the visual sensor filtration estimation value; and (4) resetting parameters. The invention sufficiently utilizes the respective advantages of visual information and mile meter information and combines the precision of the visual information and the real-time property of the mile meter information; the invention utilizes the mile meter self information to carry out the recurrence computation to obtain navigation data at most of the time, thereby ensuring the real-time requirement of the navigation system; in addition, the invention also utilizes the visual information to correct the accumulated errors generated in the dead reckoning of the mile meter, thereby greatly enhancing the accuracy of the navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Service robot autonomous navigation method based on deformable topological map
InactiveCN101619985ARealize autonomous navigationReduce labor intensityInstruments for road network navigationPhysiognomyService robot
The invention relates to a service robot autonomous navigation method based on a deformable topological map in the technical field of robot navigation, which comprises the following steps: collecting the geography and physiognomy condition of an indoor and outdoor environment in which a robot is located in real time by a SLAM technology; extracting environmental characteristics; creating a topological map of collected information and establishing the needed different sizes of a topological point according to the posture change of the service robot in the foundation; taking the sizes as input amount to reconstruct the topological map; and generating a topological point self-adapting topological map conforming to the posture change of the mobile robot.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
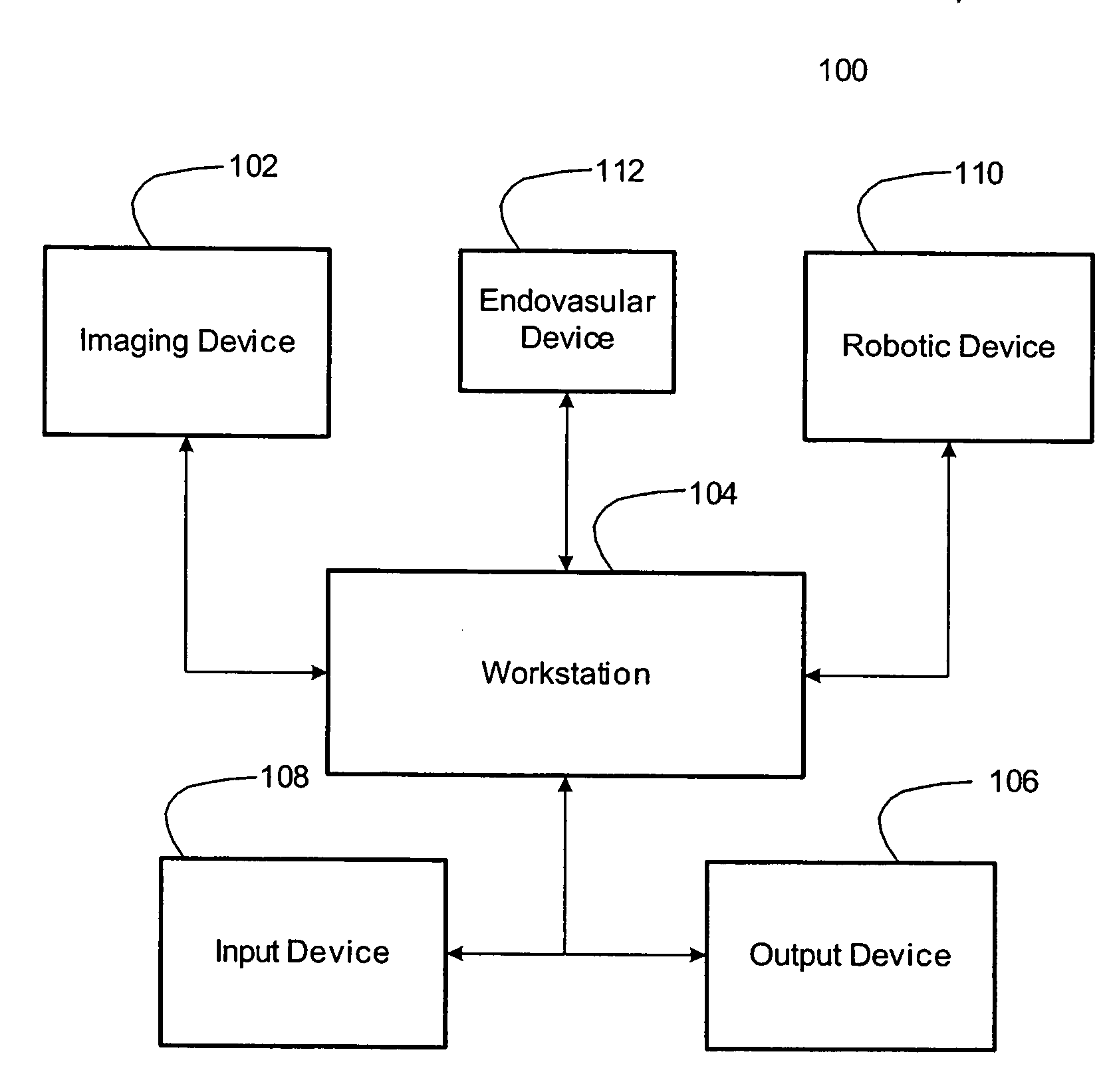
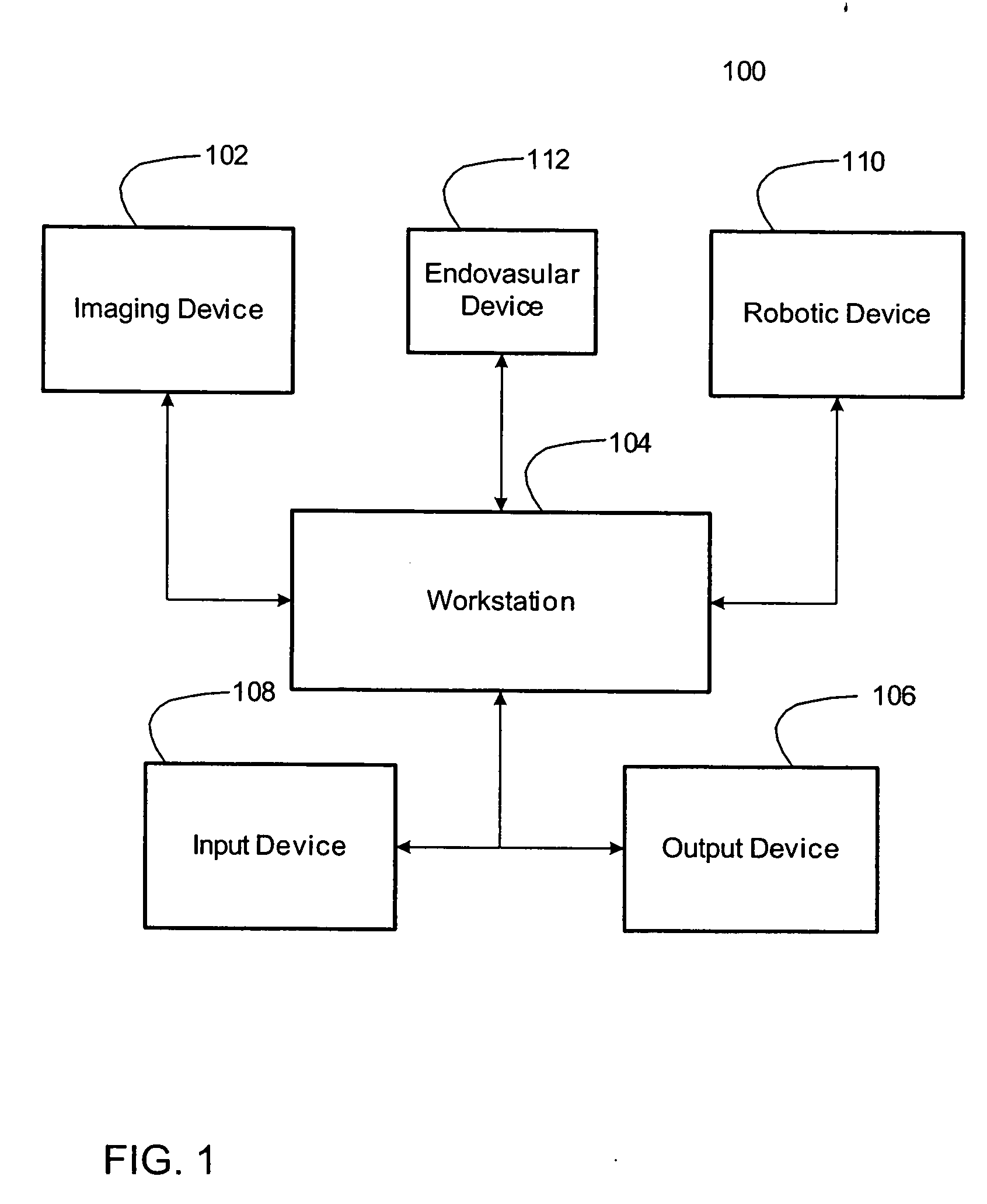
System for autonomous robotic navigation
The present invention provides systems and corresponding methods for autonomous robotic navigation that are capable of obtaining a volumetric image data set of the structure having a lumen, defining a volume of interest between a first point within the structure having a lumen and a second point within the structure having a lumen, creating a virtual navigation pathway for navigating a navigable device with a robotic device between the first and second points, registering the navigable device within the volume of interest, and navigating the navigable device iteratively along the virtual navigation path with the robotic device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
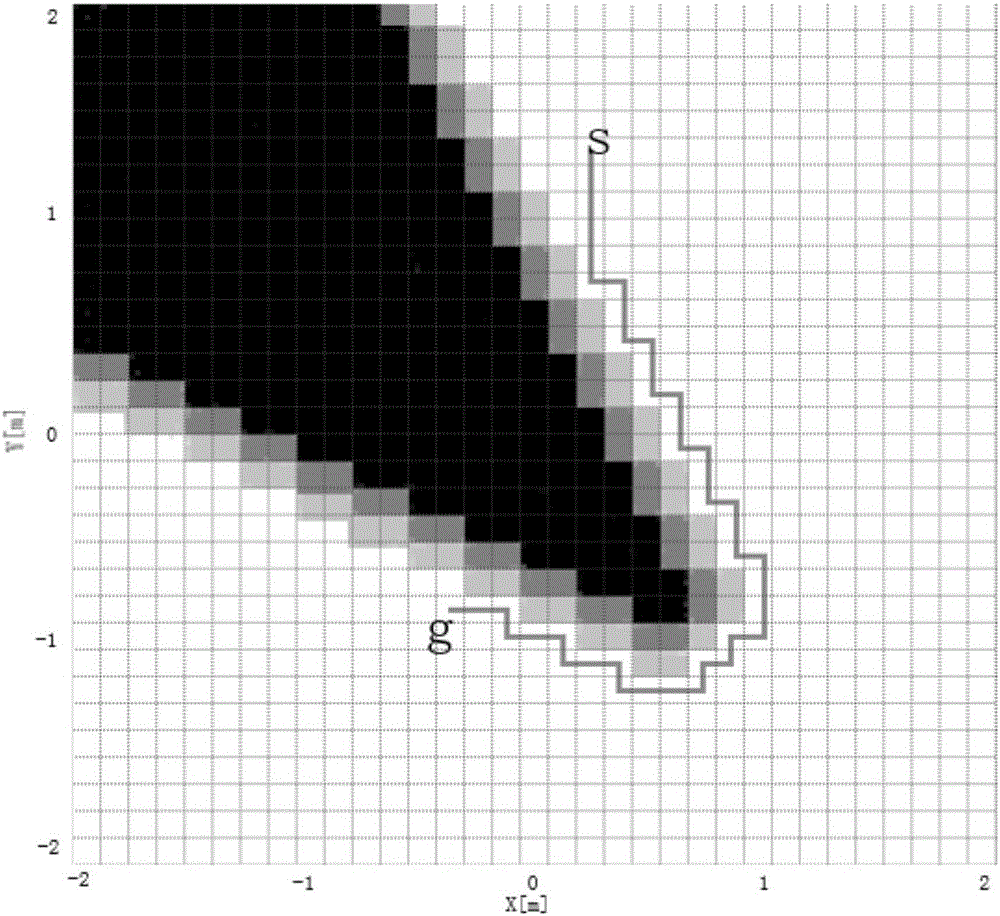
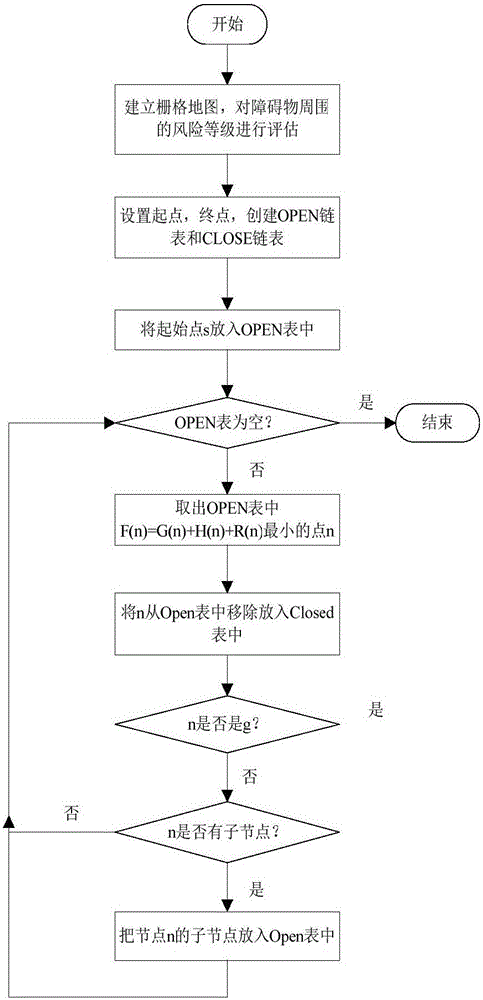
AGV path tracking and obstacle avoiding coordination method based on A* extraction guide point
The invention discloses an AGV path tracking and obstacle avoiding coordination method based on an A* extraction guide point, and relates to the field of mobile robot navigation. The method can achieve the coordination of path tracking and obstacle avoiding. The method comprises the steps: planning a safe global path; building an initial grid map according to the environment information; carrying out the evaluation of the risk level of surrounding nodes of an obstacle avoiding object through a risk evaluation function R(n); obtaining a new safety grid map with a risk region; extracting a key path point from the global path obtained through planning. For the path tracking and obstacle avoiding coordination, the method employs a dynamic window based on a laser sensor for obstacle avoiding, takes the key path point as the guide point, carries out the updating of the guide point, and achieves the coordination of the path tracking and obstacle avoiding.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Warehousing system with simple and convenient positioning function and cargo delivery method
ActiveCN105775544ASolve the problem of not being able to walk arbitrarily on the groundSolve the costStorage devicesSlide plateControl theory
The invention relates to a warehousing system with a simple and convenient positioning function and a cargo delivery method. The system comprises a warehousing cargo shelf, a cargo pallet, a robot forklift and a robot navigation and positioning system, wherein the cargo pallet is mounted on the warehousing cargo shelf; the robot navigation and positioning system comprises a positioning device for the cargo pallet on the cargo shelf and a positioning device for an optional target point on the ground; the robot forklift can optionally walk on the ground in a non-track manner and transversely stores and takes cargoes; the robot forklift comprises a transverse cargo storing and taking device; and one end of the transverse cargo storing and taking device is mounted in a lifting chute in the robot forklift. The warehousing system is reasonable in design, while the robot forklift linearly moves in the front-back direction and the direction is not changed, transverse movement of a sliding plate replaces transverse movement of wheels to longitudinal position the cargo shelf, the problems of transverse deviation rectifying and longitudinal deviation rectifying are solved, and cargo delivery speed is increased effectively.
Owner:普智联科(深圳)有限公司
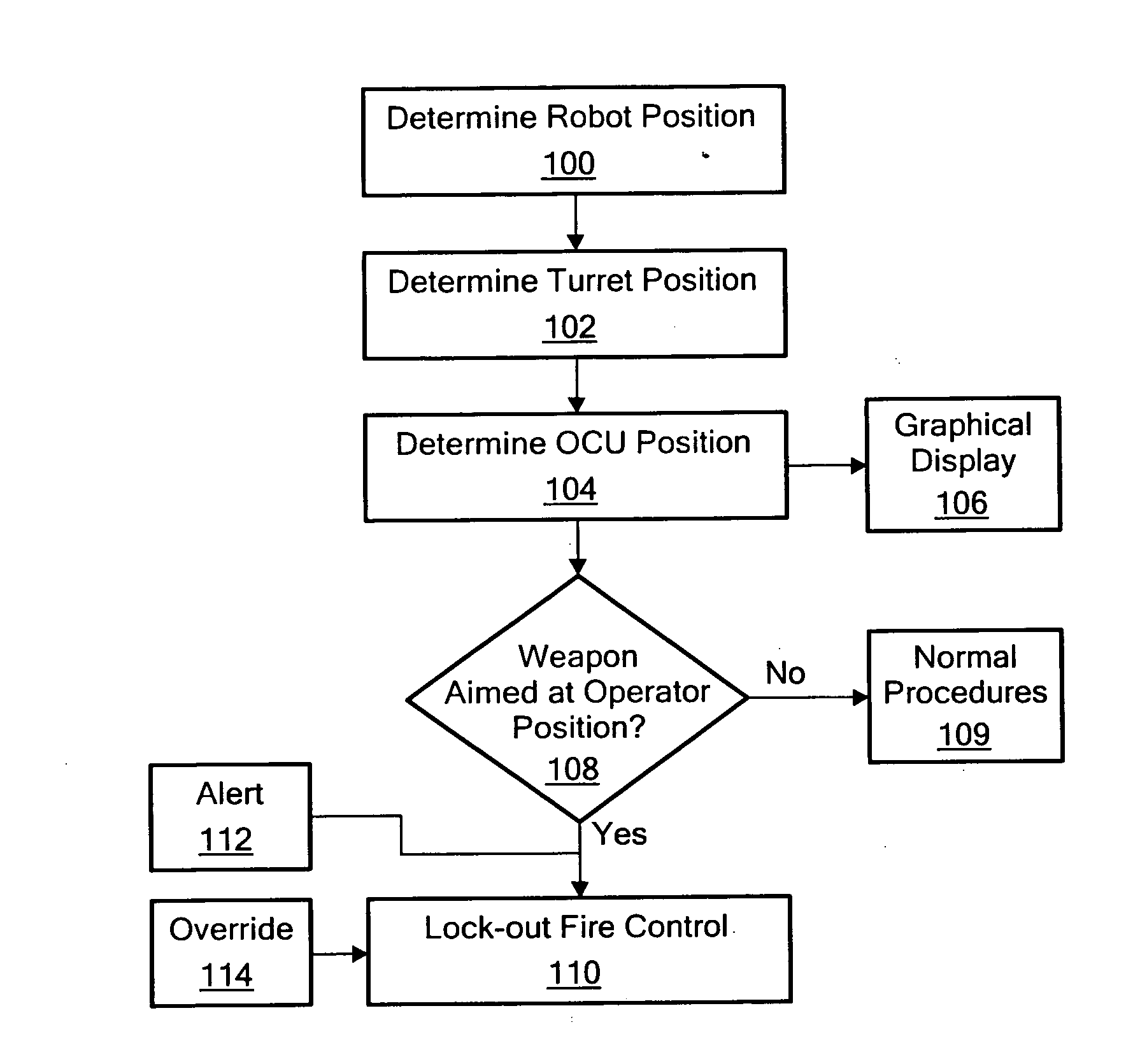
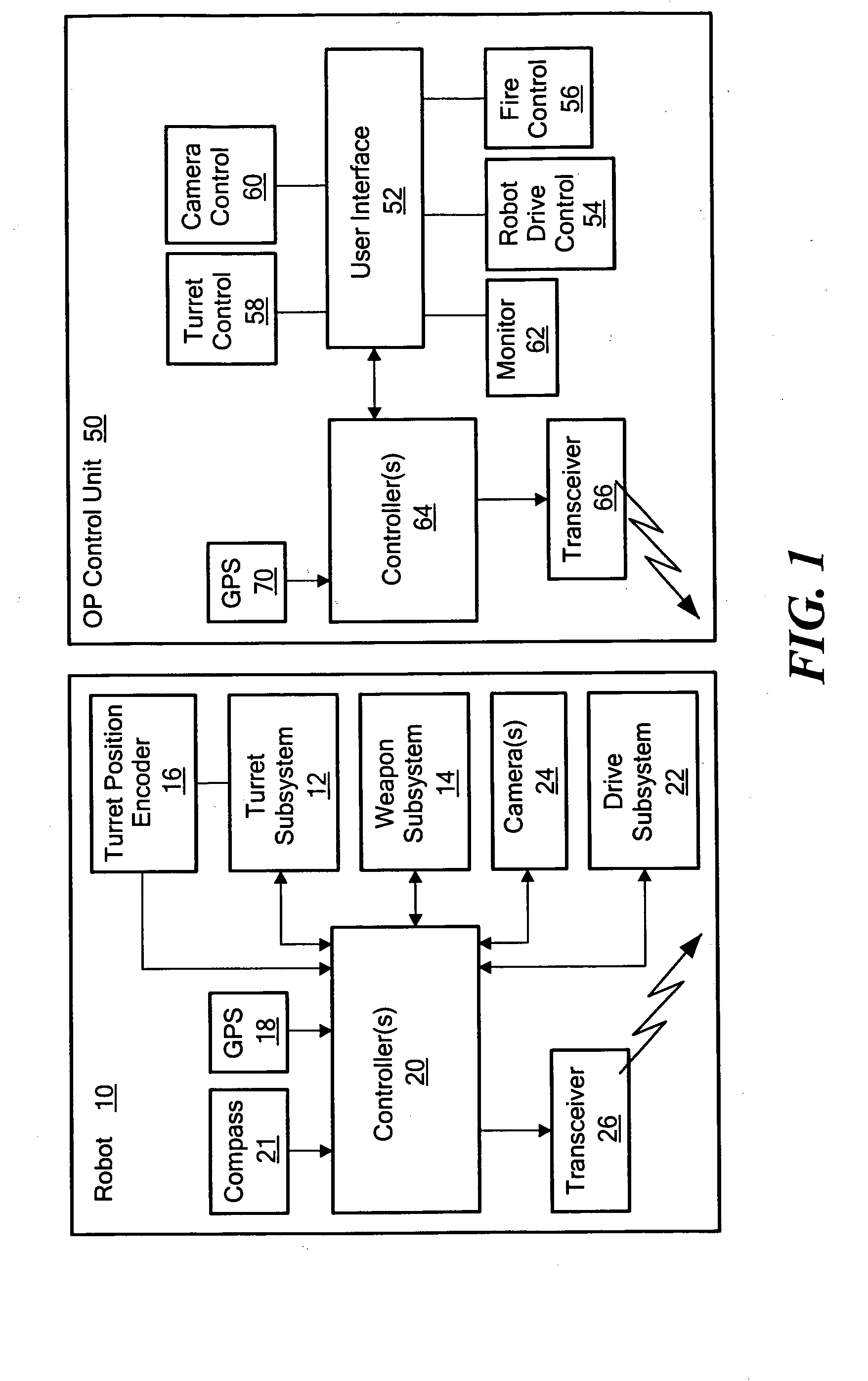
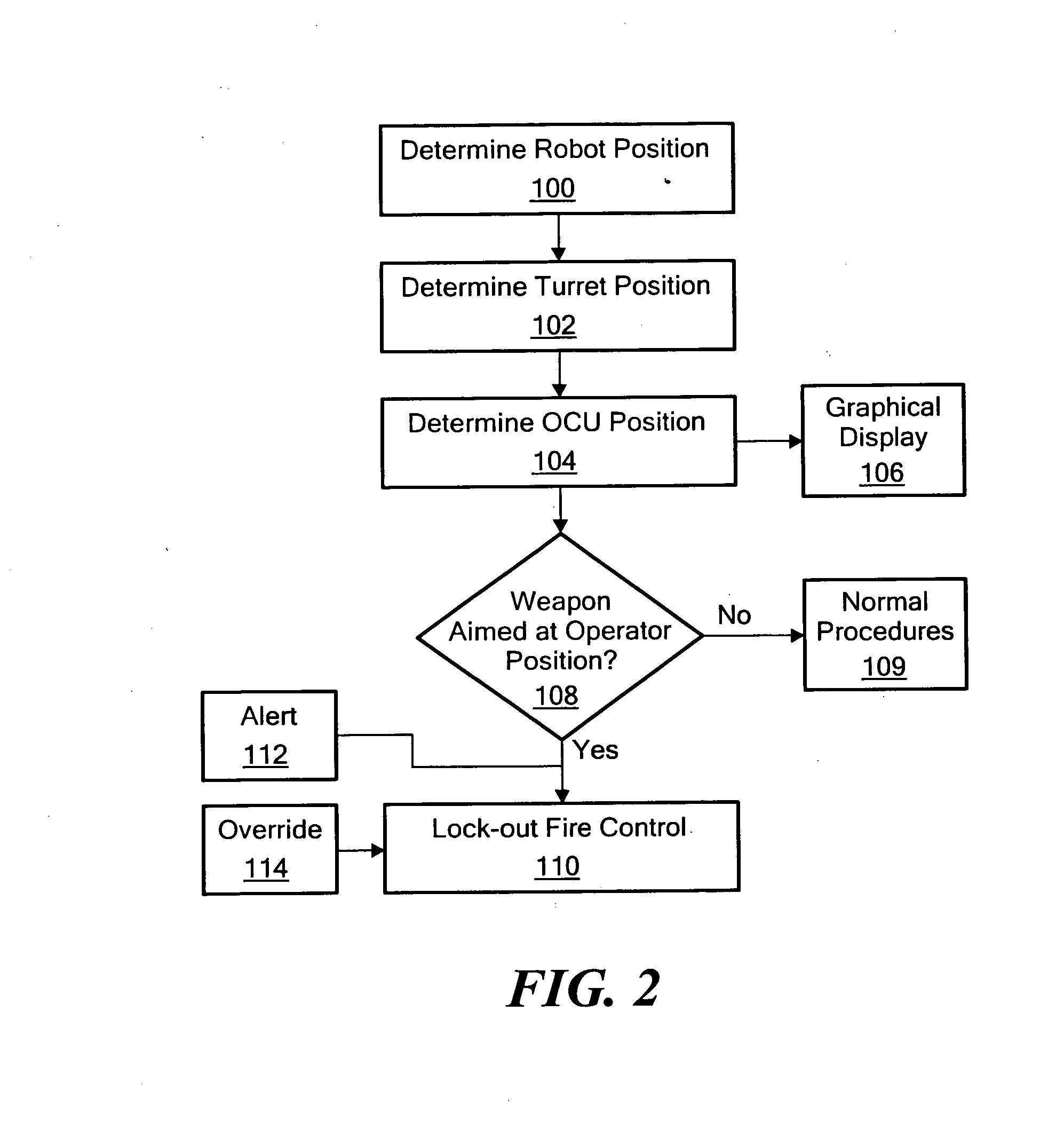
Weapon robot with situational awareness
ActiveUS20090164045A1Provide situational awarenessReduce the possibilityProgramme controlSafety arrangementTeleoperated robotRobot position
A mobile, remotely controlled robot includes a turret subsystem, a robot controller subsystem configured to control the robot, control the turret, and fire the weapon, a robot navigation subsystem configured to determine the position of the robot, a turret orientation determination subsystem, and a robot communications subsystem for receiving commands and for transmitting robot position data and turret orientation data. An operator control unit includes a user interface for commanding the robot, the turret, and the weapon. An operator control unit communications subsystem transmits commands to the robot and receives robot position data and turret orientation data from the robot. An operator control unit navigation subsystem is configured to determine the position of the operator control unit. An operator control unit controller subsystem is responsive to the robot position data, the turret orientation data, and the operator control unit position and is configured to determine if the weapon is aimed at the operator control unit within a predetermined fan angle.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
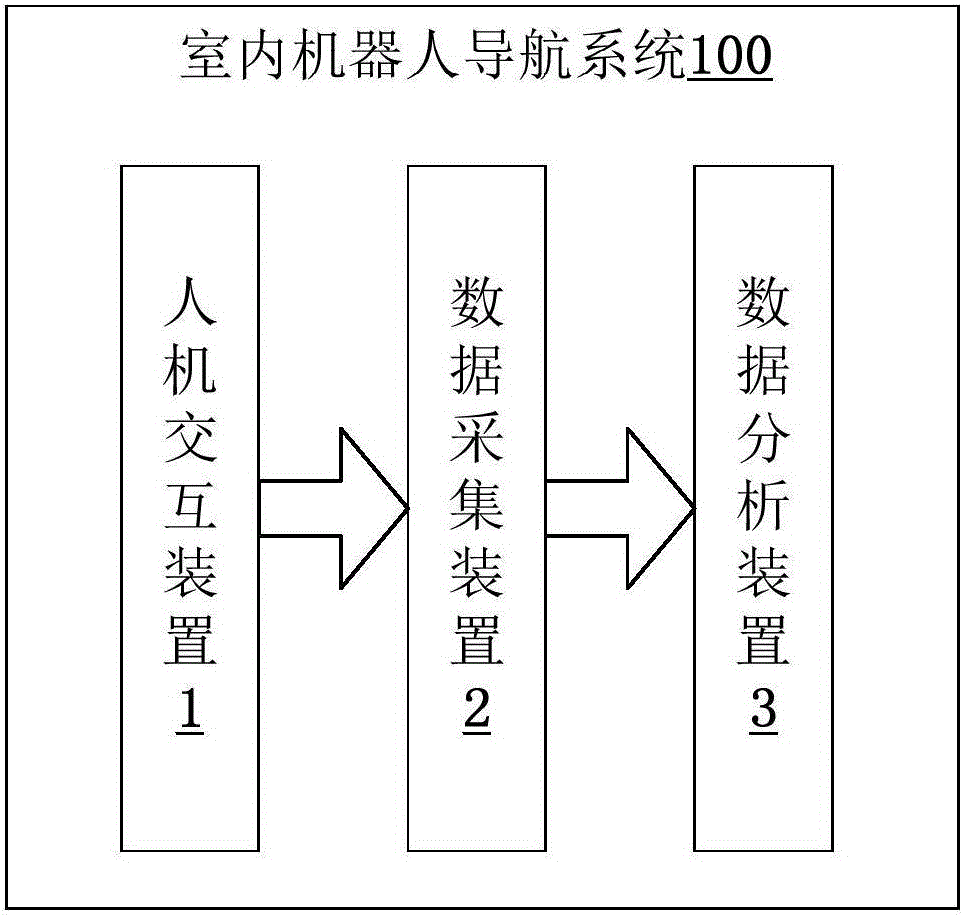
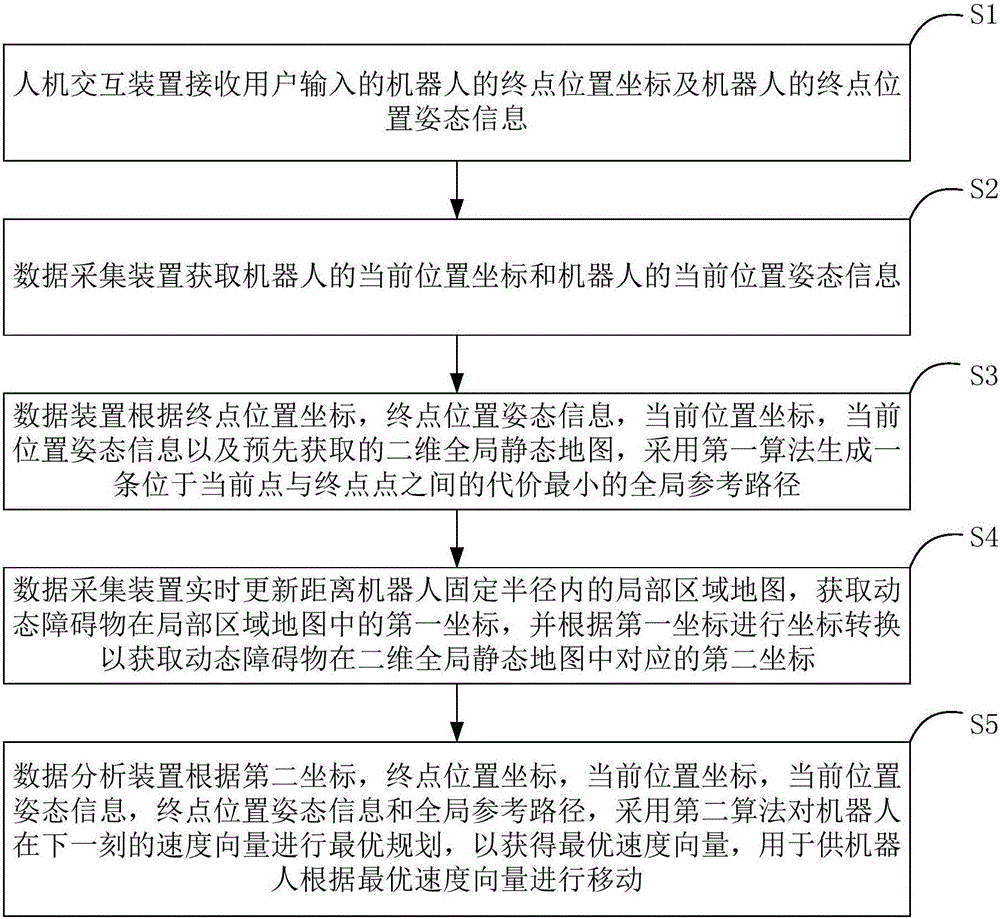
Indoor robot navigation system and method
InactiveCN105955273AImprove practicalityNavigation implementationPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesData acquisitionNavigation system
The invention provides an indoor robot navigation system and method. The system comprises a man-machine interaction device, a data collection device and a data analysis device; the man-machine interaction device receives terminal-point position coordinate and terminal-point position attitude information input by a user; the data collection device obtains preset position coordinate and present position attitude information, updates a local area map in real time, and obtains a corresponding second coordinate of a dynamic barrier in a 2D global static map via coordinate transformation; and the data analysis device generates a global reference path via a first algorithm, and plans an optimal speed vector of a robot in next time by utilizing a second algorithm to obtain the optimal speed vector, and thus, the robot moves according to the optimal speed vector. The indoor robot navigation system and method are higher in practicality.
Owner:SUGAN TECH BEIJING
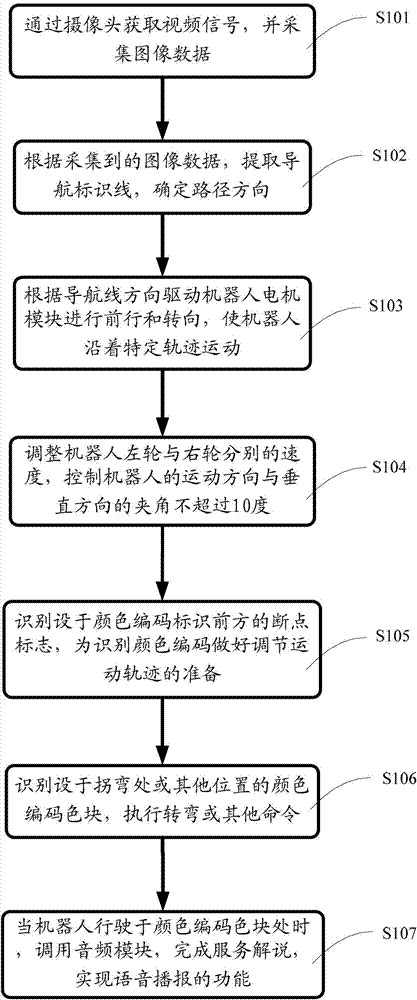
Robot navigation method and robot navigation system based on color coding identifiers
InactiveCN102789234AThe principle is simpleImprove scalabilityInstruments for road network navigationPosition/course control in two dimensionsPattern recognitionOperand
The invention discloses a robot navigation method based on color coding identifiers, which comprises the following steps of: extracting a navigation identification line according to the acquired image data, and determining the path direction; identifying a breakpoint mark in front of the color coding identifier, and preparing to regulate the movement trail for the color coding identifier; and identifying a color coding block around a corner or other positions, and executing turning or other command. The invention further discloses a robot navigation system based on the color coding identifiers. The robot navigation system has a simple principle, strong expandability and good visual perception, and can complete the positioning and navigating tasks of an indoor service robot; the robot navigation system can be combined with other navigation systems, so the stability and practicability of the navigation system are improved; and the problems of weaker applicability to complicated environments, error navigation accumulation, large operand, mutual interfered sensors and the like in the current robot navigation field can be effectively solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG SCI CENT
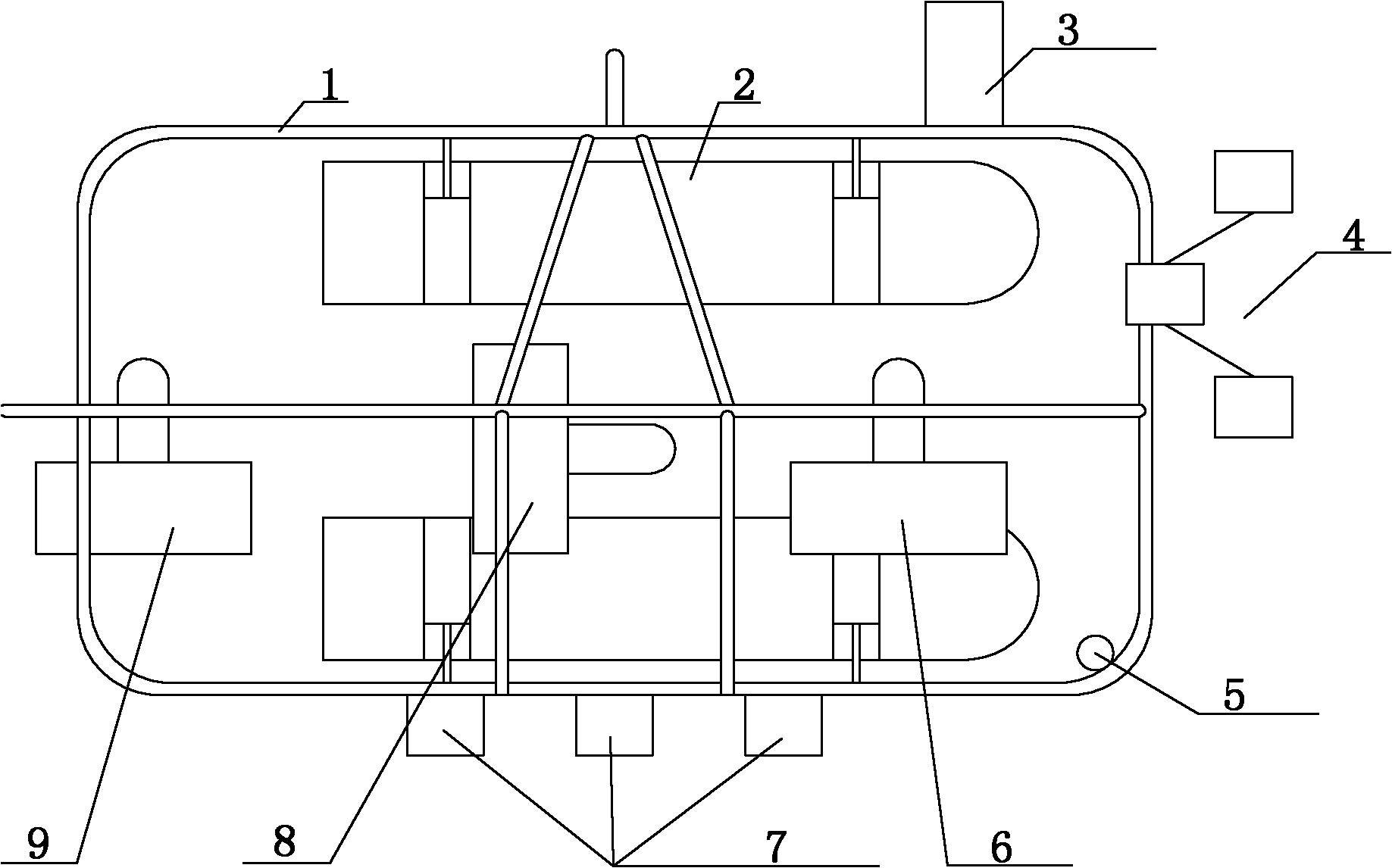
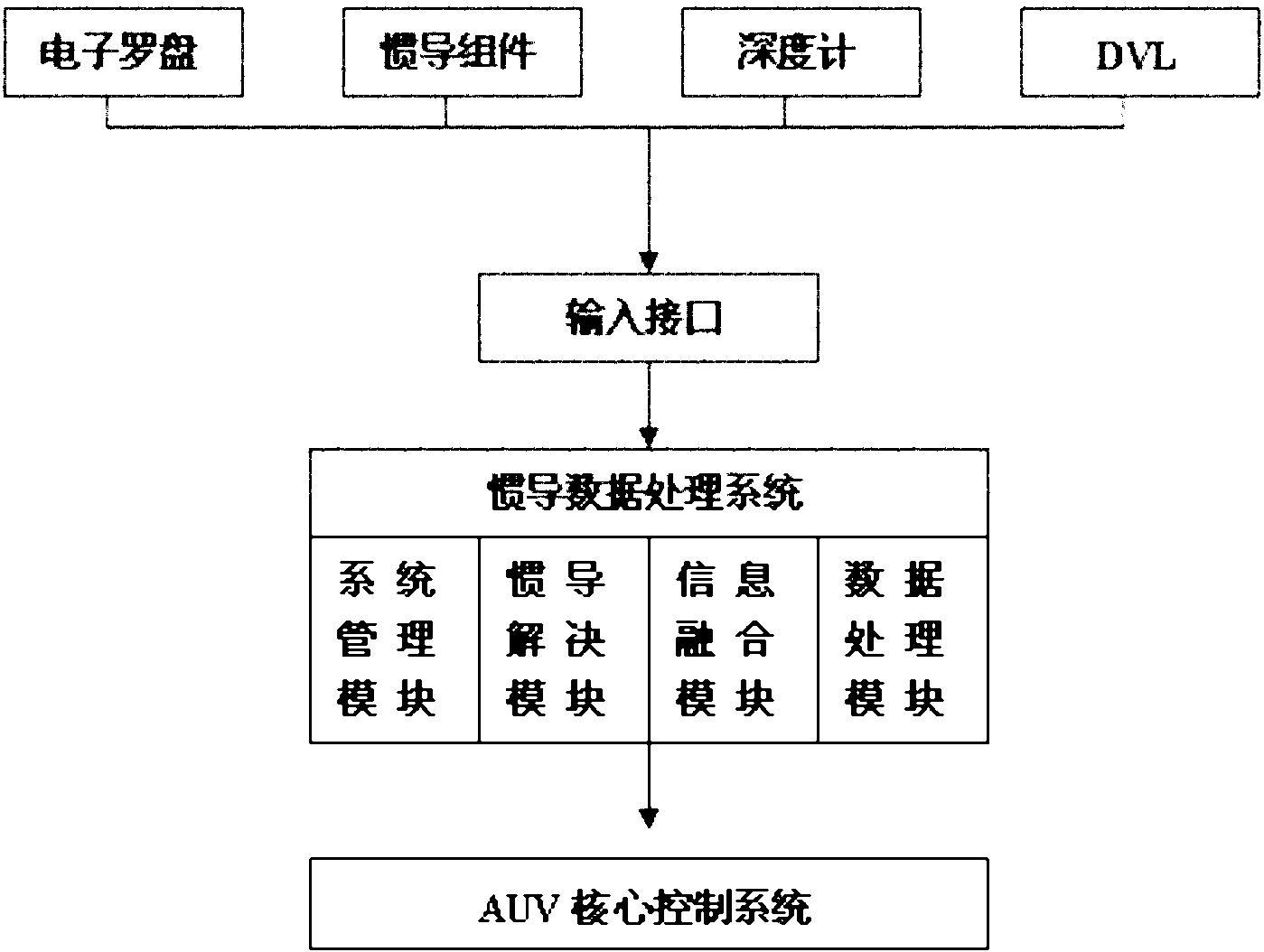
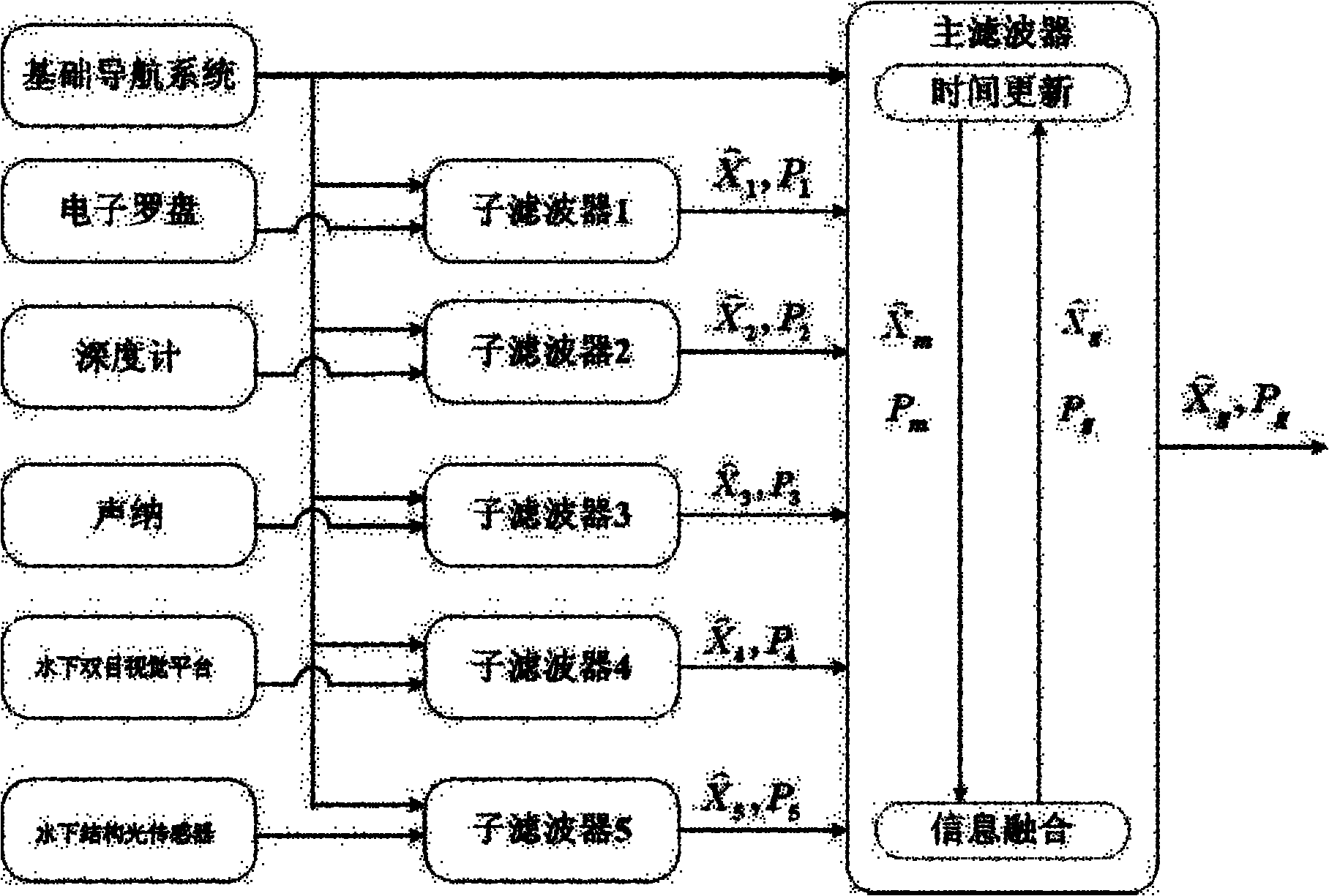
Autonomous underwater vehicle combined navigation system
ActiveCN102042835ARealize autonomous navigationPrecise NavigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation systemVisual perception
The invention relates to an underwater vehicle navigation system, in particular to an autonomous underwater vehicle combined navigation system. The system comprises an inertia basis navigation device and an external sensor navigation device, wherein the inertia basis navigation device comprises a Doppler velocimeter, an optical fiber gyro, a pressure sensor, an electronic compass and a depthometer; and the external sensor navigation device comprises a sonar. The combined navigation system also comprises an underwater structure optical sensor and an underwater binocular vision platform, wherein the underwater structural optical sensor comprises a forward-vision structure optical sensor positioned on the front of an outer frame of an autonomous underwater vehicle, and a downward-vision structure optical sensor positioned at the bottom of the outer frame; the underwater binocular vision platform comprises a forward-vision binocular vision platform positioned on the front of the outer frame, and a downward-vision binocular vision platform positioned at the bottom of the outer frame; the forward-vision structure optical sensor and the forward-vision binocular vision platform form a forward-vision structure optical and visual system module positioned on the front of the outer frame; and the downward-vision structure optical sensor and the downward-vision binocular vision platform form a downward-vision structure optical and visual system module positioned at the bottom of the outer frame.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
A method for semantic segmentation of scene point cloud
ActiveCN109410307AAchieve forecastEfficient extractionNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsVisual technologyPoint cloud
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer vision. A method for semantic segmentation of scene point cloud is provided, a framework of point cloud semantic segmentation model for large-scale dense scene based on depth learning technology is designed, For the input large-scale dense scene point cloud, it can transform the three-dimensional information of point cloud into two-dimensional information which can be processed directly by convolution without losing the information, and complete the task of point cloud semantic segmentation combined with image semantic segmentation technology. In this framework, we can effectively solve the semantic segmentation task of large-scale dense scene point cloud. The semantic segmentation result of the scene point cloud obtained by the method of the invention can be directly used in tasks such as robot navigation, automatic driving and the like. And this method is especially effective in non-synthetic natural scenes.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
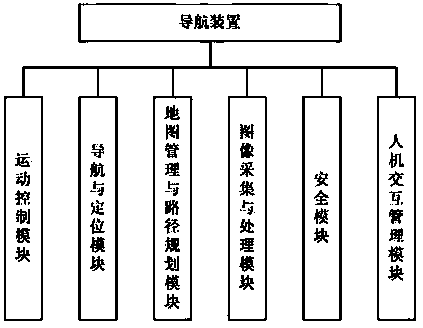
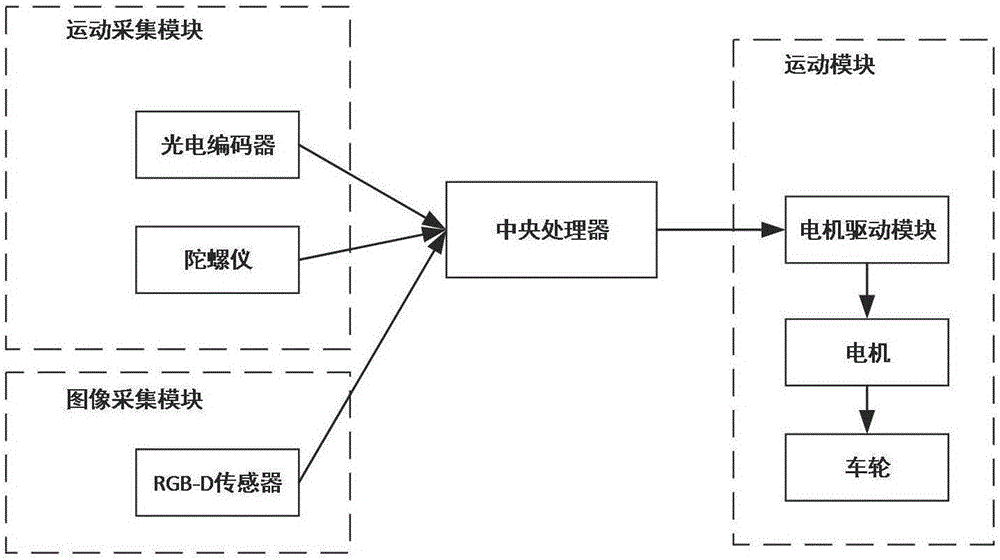
Indoor robot navigation device and navigation technology thereof
ActiveCN103353758AOvercoming the problem of poor positioning accuracyImprove anti-interference abilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsInterference resistanceComputer module
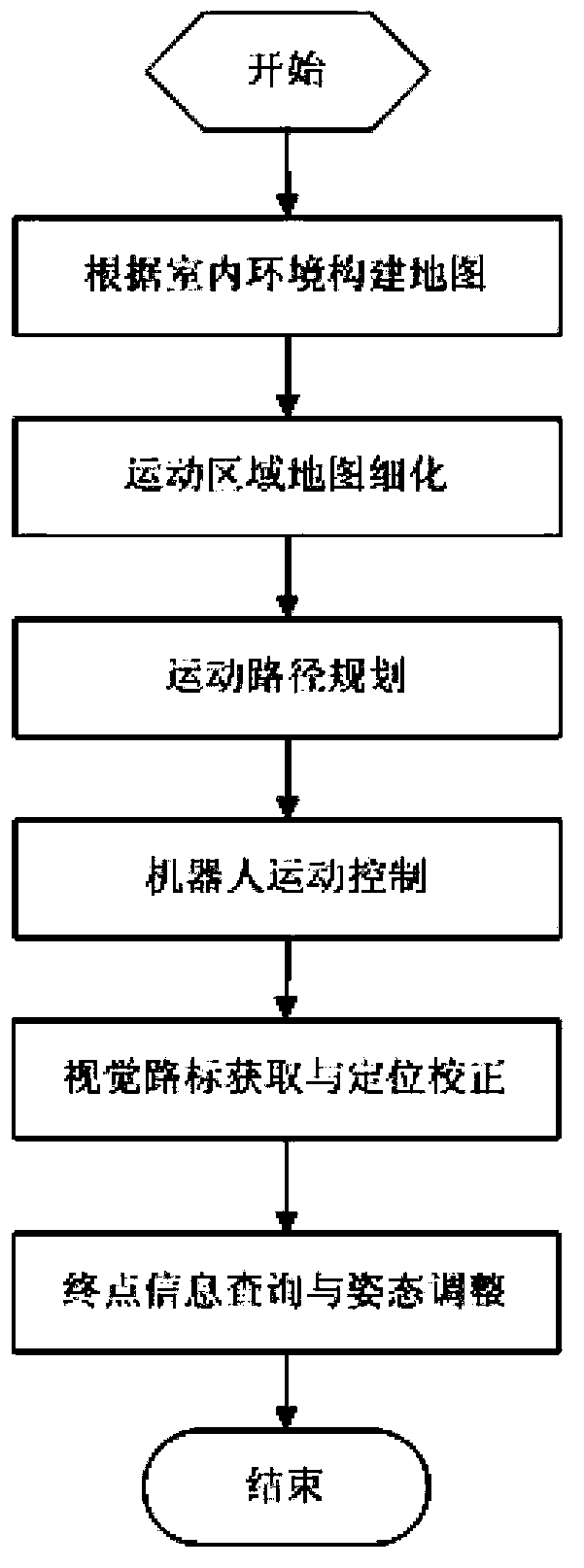
The invention discloses an indoor robot navigation device which is characterized by comprising a circuit board, wherein a motion control module, a navigation and location module, a map management and path planning module, an image acquisition and processing module, a safety module and a man-machine interaction management module. The invention also provides an indoor robot navigation technology. The technology is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (a) establishing a map and planning a motion path of the robot; (b) refining a area and setting a visual signpost; (c) acquiring and processing the visual signpost, and performing motion location and correction; (d) storing and querying area and signpost information. The device has the advantages of autonomous navigation, high interference resistance capacity, zero track movement and the like, and the problem that most of the conventional navigation modes are low in positioning precision is solved through visual positioning correction.
Owner:苏州海通机器人系统有限公司
Robot navigation positioning system and method
InactiveCN109959377AEliminate cumulative errorsAchieve optimizationNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsPath lengthMultiple sensor
The invention discloses a robot navigation positioning system and method, which are used for map construction, positioning and path planning of a robot. The method comprises the following steps: S100,positioning is carried out, in the positioning step, the robot detects surrounding environment information through multiple sensors, and later, based on an adaptive particle filtering SLAM algorithmand in match with different odometers, real-time map construction and positioning are completed; and S200, path planning is carried out, in the path planning step, a two-phase hybrid state A*-based path planning algorithm is adopted, after a path length and the number of extended nodes are obtained when path planning is carried out on a rasterized map, a higher rasterized map is obtained through parsing and extension, and the acquired path length and the acquired number of extended nodes are used as input of fuzzy reasoning, a heuristic weight is obtained through fuzzy reasoning and is used asinput of search of a second stage, and path planning is performed on a higher rasterized map. The system and the method disclosed in the invention can not only adapt to different environments but also can perform dynamic path planning.
Owner:BEIJING ORIENT XINGHUA TECH DEV CO LTD
Method and apparatus for navigating robot
ActiveUS20110098874A1Avoid obstaclesProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMarine navigation
A method of navigating a robot includes creating a robot navigation map using a map database required for navigation of the robot; and creating a path on which no obstacle is located in the map database using the created robot navigation map. Further, the method of navigating the robot includes primarily controlling the robot so that the robot travels along the created path; and secondarily controlling the robot so that the robot avoids an obstacle on the path.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
Systems and methods for vslam optimization
ActiveUS20160154408A1Database queryingCharacter and pattern recognitionLandmark matchingVisual technology
The invention is related to methods and apparatus that use a visual sensor and dead reckoning sensors to process Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). These techniques can be used in robot navigation. Advantageously, such visual techniques can be used to autonomously generate and update a map. Unlike with laser rangefinders, the visual techniques are economically practical in a wide range of applications and can be used in relatively dynamic environments, such as environments in which people move. Certain embodiments contemplate improvements to the front-end processing in a SLAM-based system. Particularly, certain of these embodiments contemplate a novel landmark matching process. Certain of these embodiments also contemplate a novel landmark creation process. Certain embodiments contemplate improvements to the back-end processing in a SLAM-based system. Particularly, certain of these embodiments contemplate algorithms for modifying the SLAM graph in real-time to achieve a more efficient structure.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
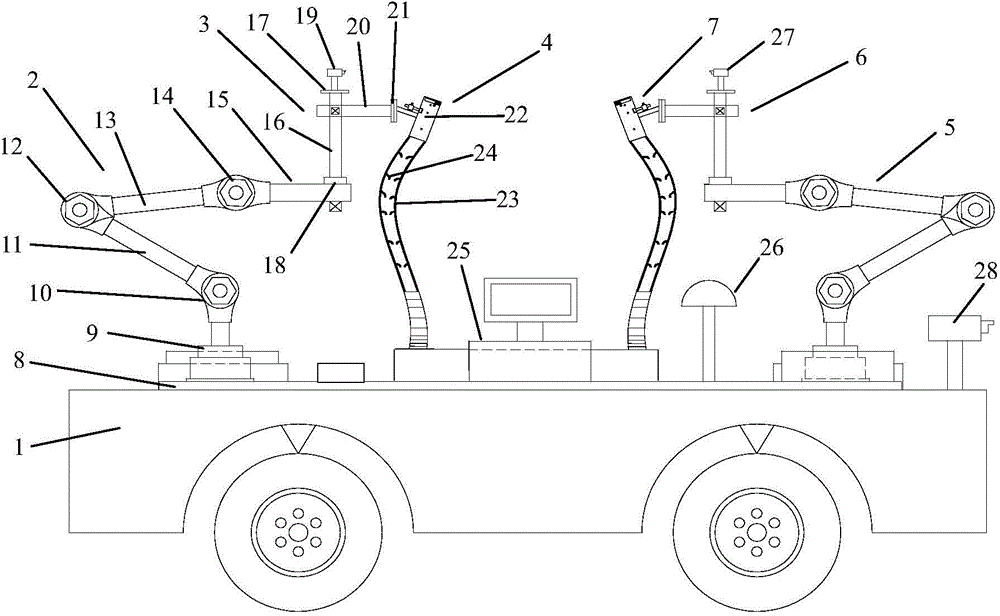
Double-arm fruit picking robot and fruit picking method
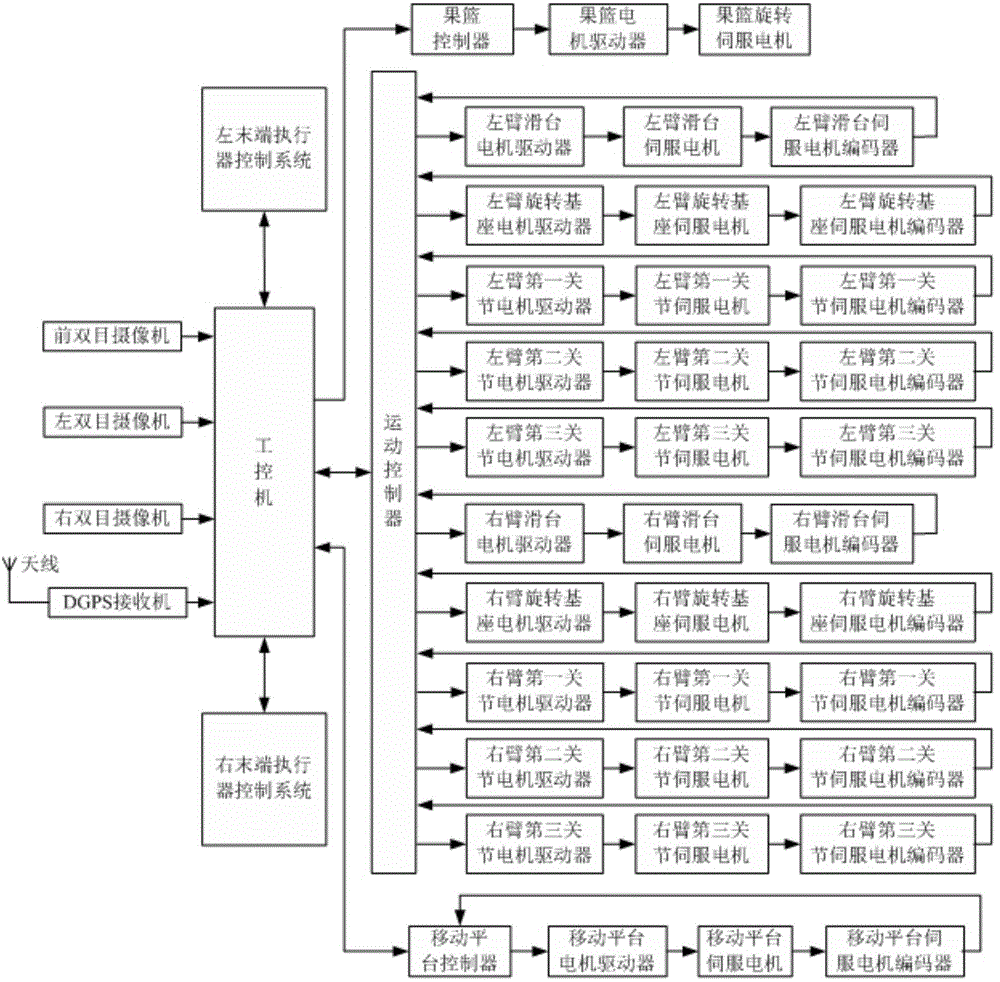
ActiveCN103947380AThe average picking period is shortImprove picking efficiencyPicking devicesFruit treeControl system
The invention discloses a double-arm fruit picking robot and a fruit picking method. The double-arm fruit picking robot comprises a fruit picking mechanical device and a control system, wherein the fruit picking mechanical device comprises a left mechanical arm, a right mechanical arm, a left tail end actuator, a right trail end actuator, a moving platform and a fruit basket, the left mechanical arm and the right left mechanical arm are of the same structures, are respectively arranged at the left side and the right side of the moving platform, and respectively complete the work of conveying the left tail end actuator and the right trail end actuator to specified picking points, the left tail end actuator and the right trail end actuator are of the same structures, are respectively arranged at the front end of the left mechanical arm and the front end of the right mechanical arm, and respectively complete the work of obtaining and recovering fruits of fruit trees at the left side and the right of the advancing direction of the robot, and a control system completes the control tasks of robot navigation, walking and picking. The invention also discloses a fruit picking method of the double-arm fruit picking robot. According to the method, the mechanical arms carry out picking in different picking points, and the continuous and respective picking of a plurality of fruits can be realized in one picking point.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
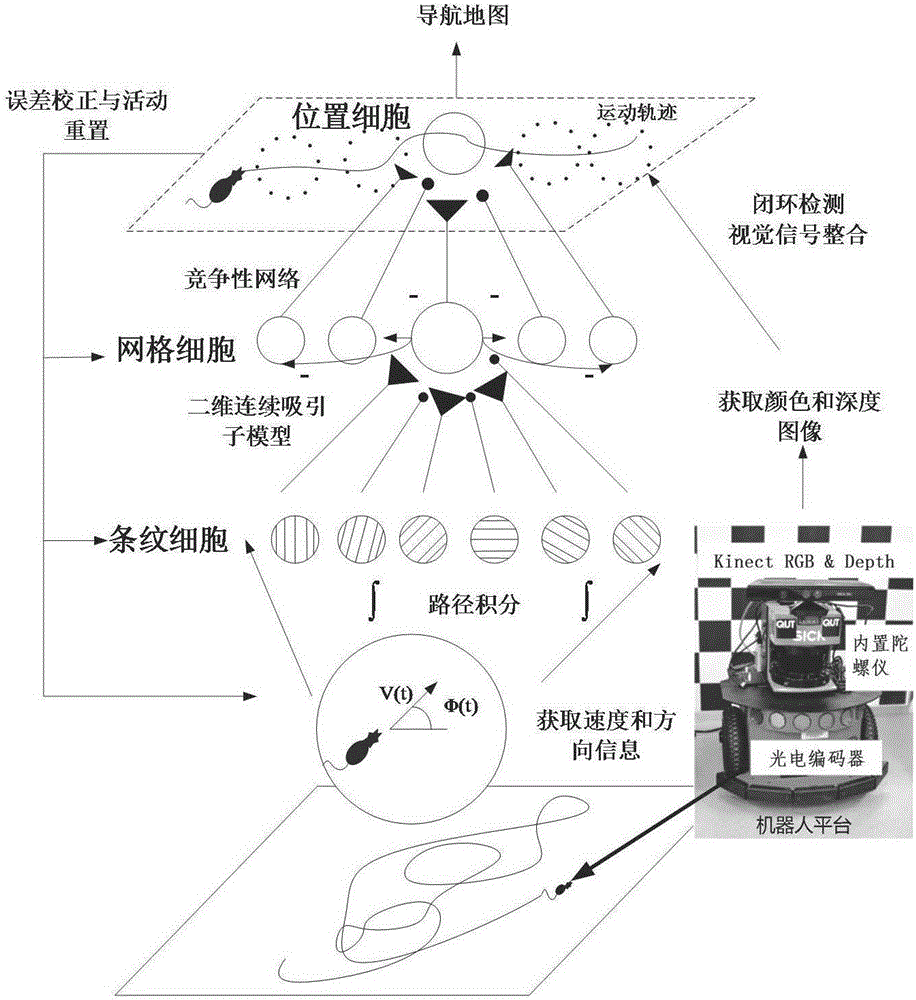
Robot navigation map construction method based on rat brain hippocampus spatial cells
The invention provides a robot navigation map construction method based on rat brain hippocampus spatial cells. According to an information transfer loop of spatial navigation related cells in a hippocampus structure of a mammal, a robot acquires a current autonomic movement clue and color depth image information through environment exploration. The autonomic movement clue progressively forms coding to the spatial environment through path integration and characteristic extraction of the spatial cells in the hippocampus structure. The place field of place cells is gradually formed in an exploration process and furthermore covers the whole spatial environment, thereby forming a cognitive map. Meanwhile, Kinect acquires color depth image information of a view scene right in front of the current position as an absolute reference for performing closed-loop detection on the path and correcting a path integration error. At a closed-loop point, a system resets spatial cell discharging activity and performs correction on the path integration error. Nodes on a final navigation map comprise place cell mass coding information, corresponding visual cues and place topological relationships.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com