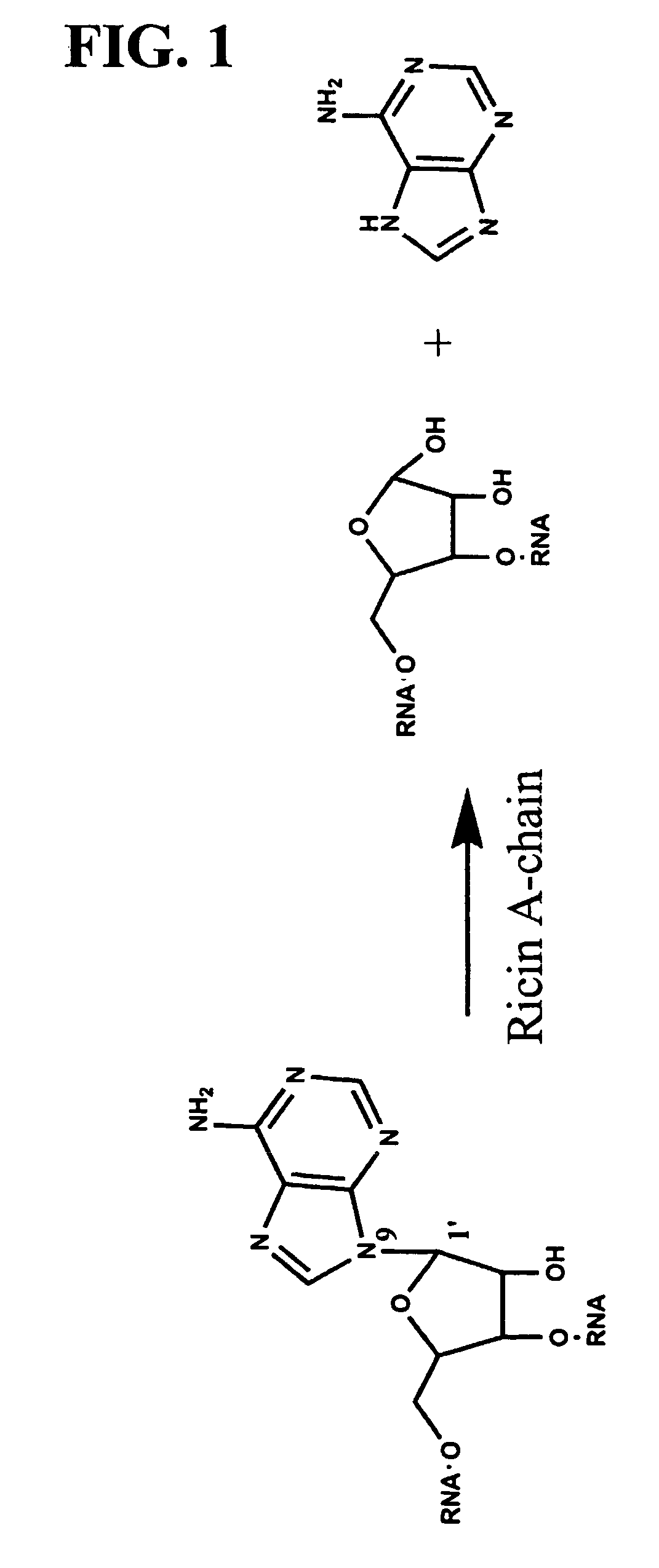
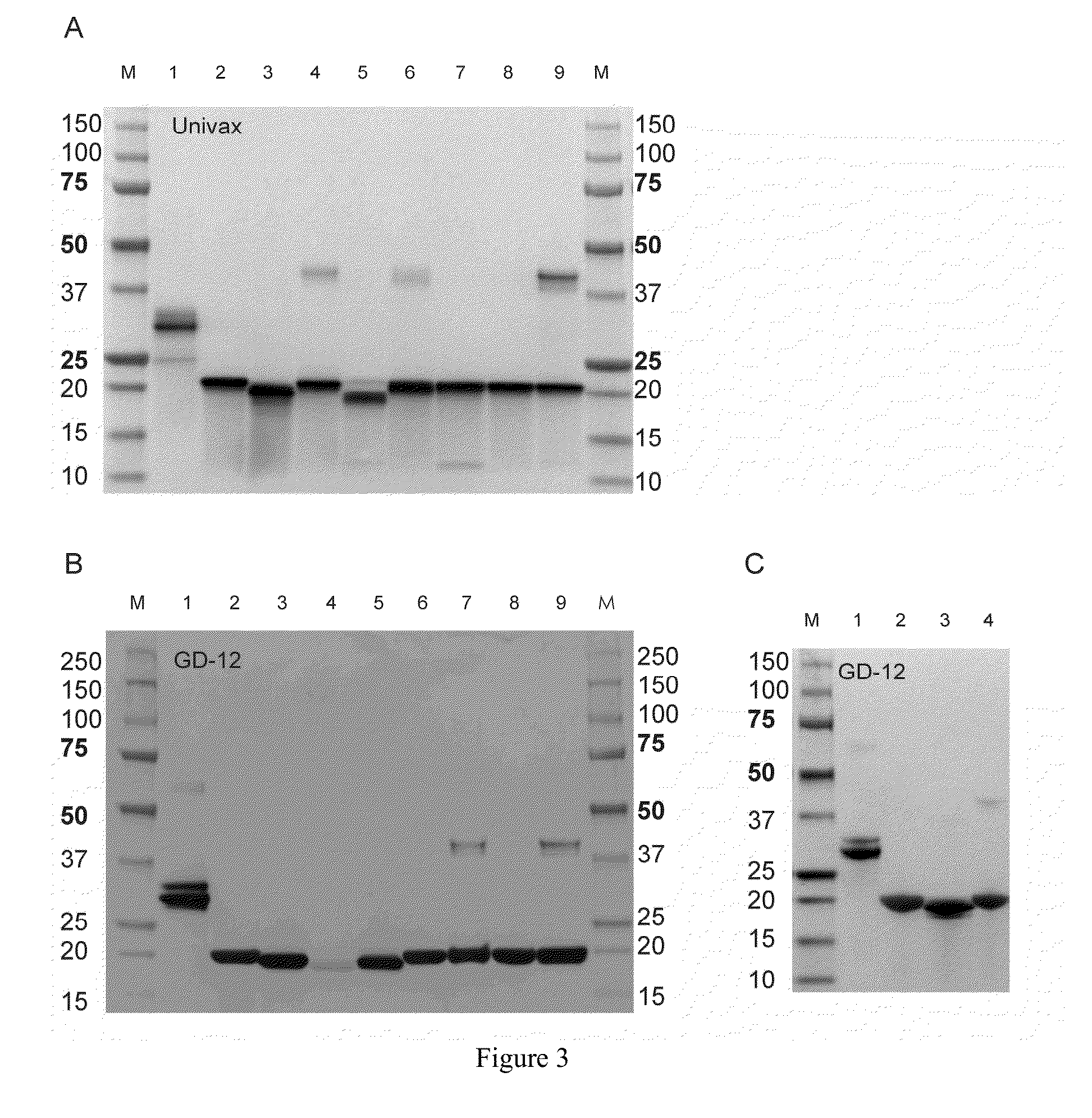
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
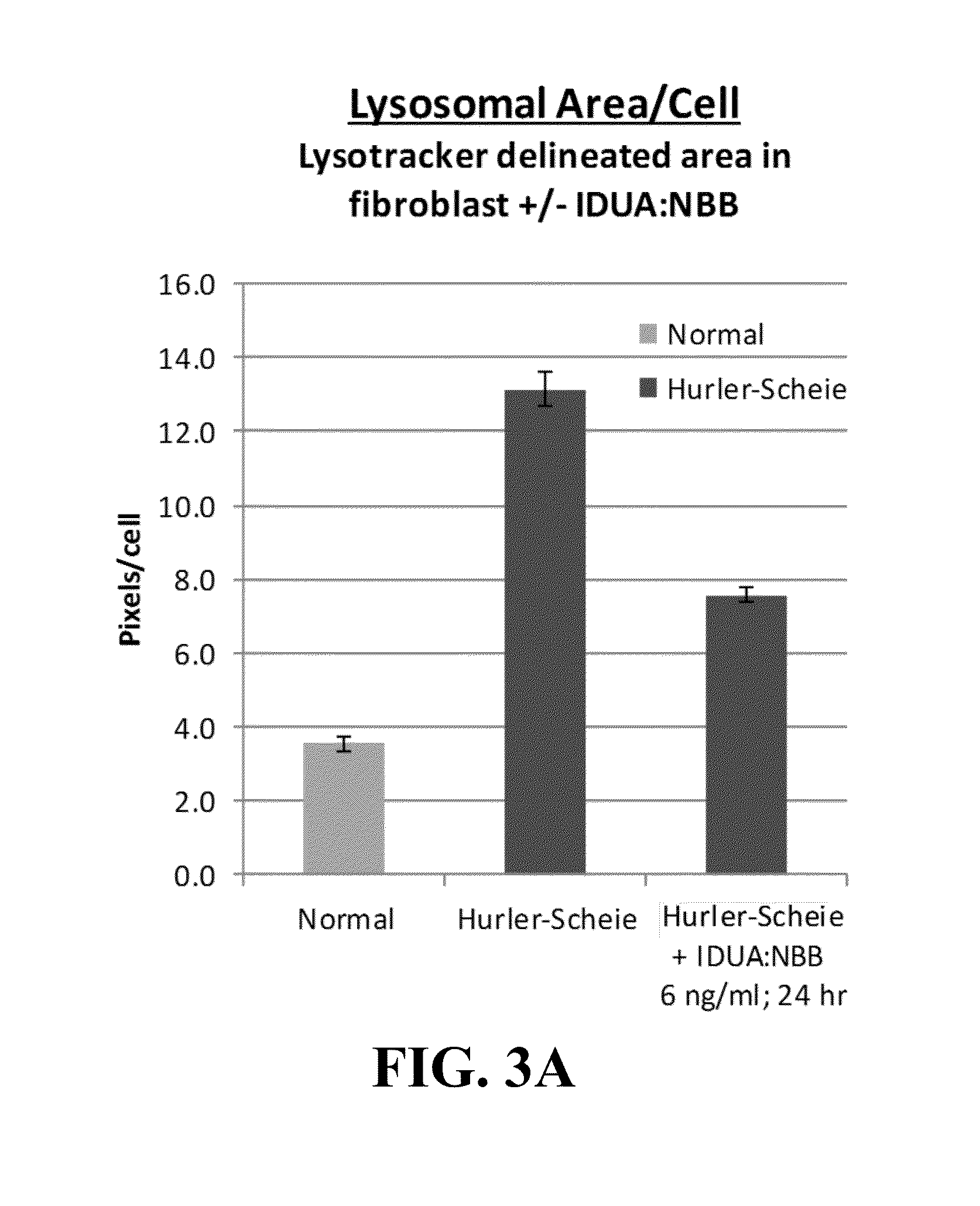
58 results about "Ricin toxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery and methods of using same
ActiveUS20140079774A1Promoting death of cancer cellEfficient packagingBiocideSpecial deliveryLipid formationBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
InactiveUS20150272885A1Large specific surface areaAmenable to high capacity loadingOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancers diagnosisBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Pesticidal fusions
Disclosed are polynucleotides encoding a pesticidal fusion polypeptide comprising (i) a toxin domain; and (ii) a heterologous binding domain capable of binding non-specifically to a cell membrane without disrupting that membrane. Preferably the toxin domain is derived from a Bacillus thuringiensis cry toxin (e.g. CryIA (b) or (c)) and the binding domain is derived from a lectin (e.g. ricin toxin B chain). The use of such fusions may help to inhibit the acquisition of resistance in a pest population treated with the polypeptide. A further aspect of the invention is a method of assessing the toxicity of a polypeptide to a pest species by expressing a nucleic acid encoding said polypeptide in a host cell from that species, observing the viability of the cell and correlating the results of the observation with the toxicity of the polypeptide, wherein the viability is determined by assessing esterase activity or membrane.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery and methods of using same
InactiveUS20160106671A1Inhibit growthBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsLipid formationBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Transition state analog inhibitors of ricin A-chain
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH +1
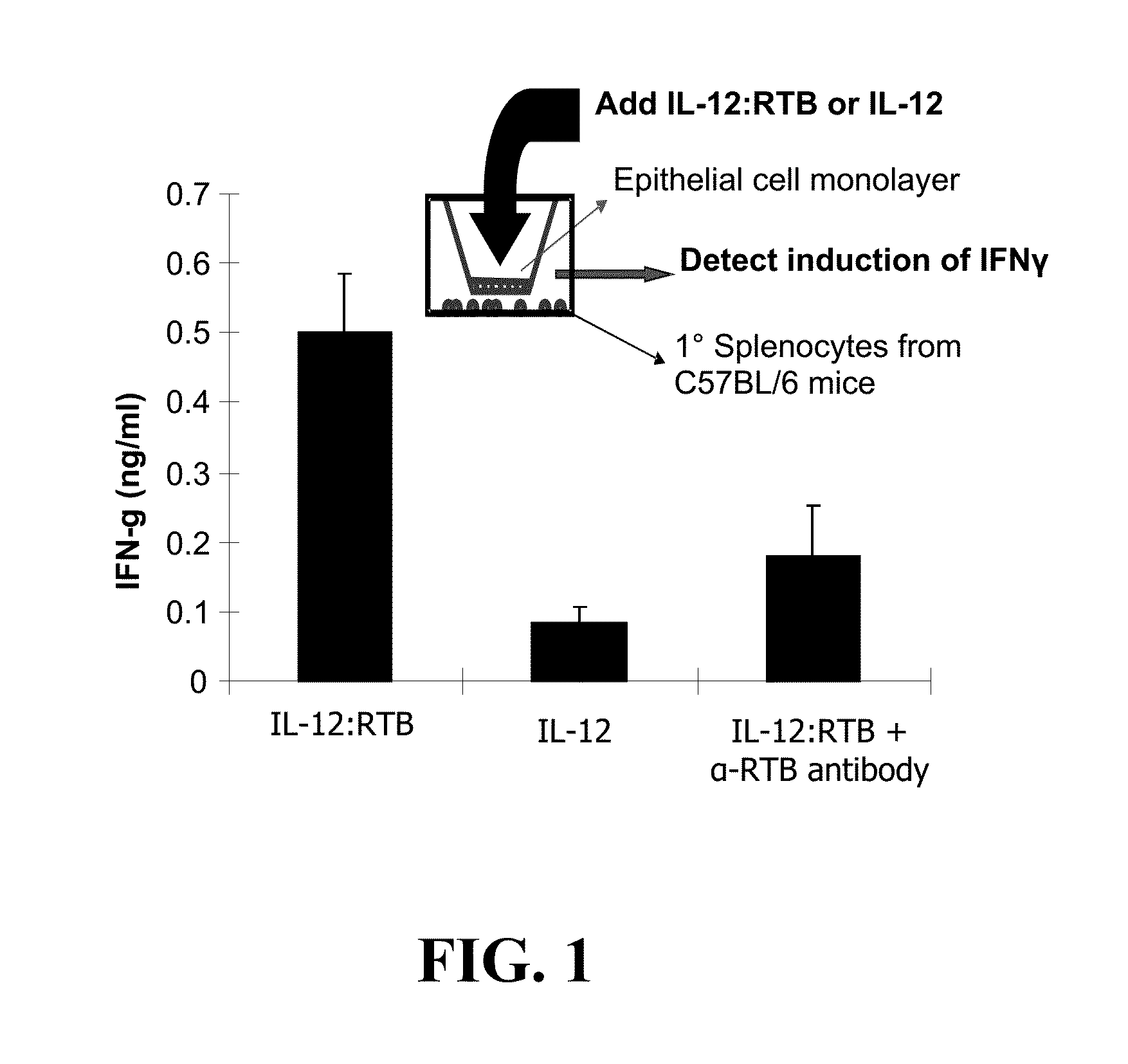
Ricin ribosome binding protein compositions and methods of use thereof
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
InactiveUS20170232115A1Amenable to high capacity loadingPorosity adjustableOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancer cellApoptosis
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
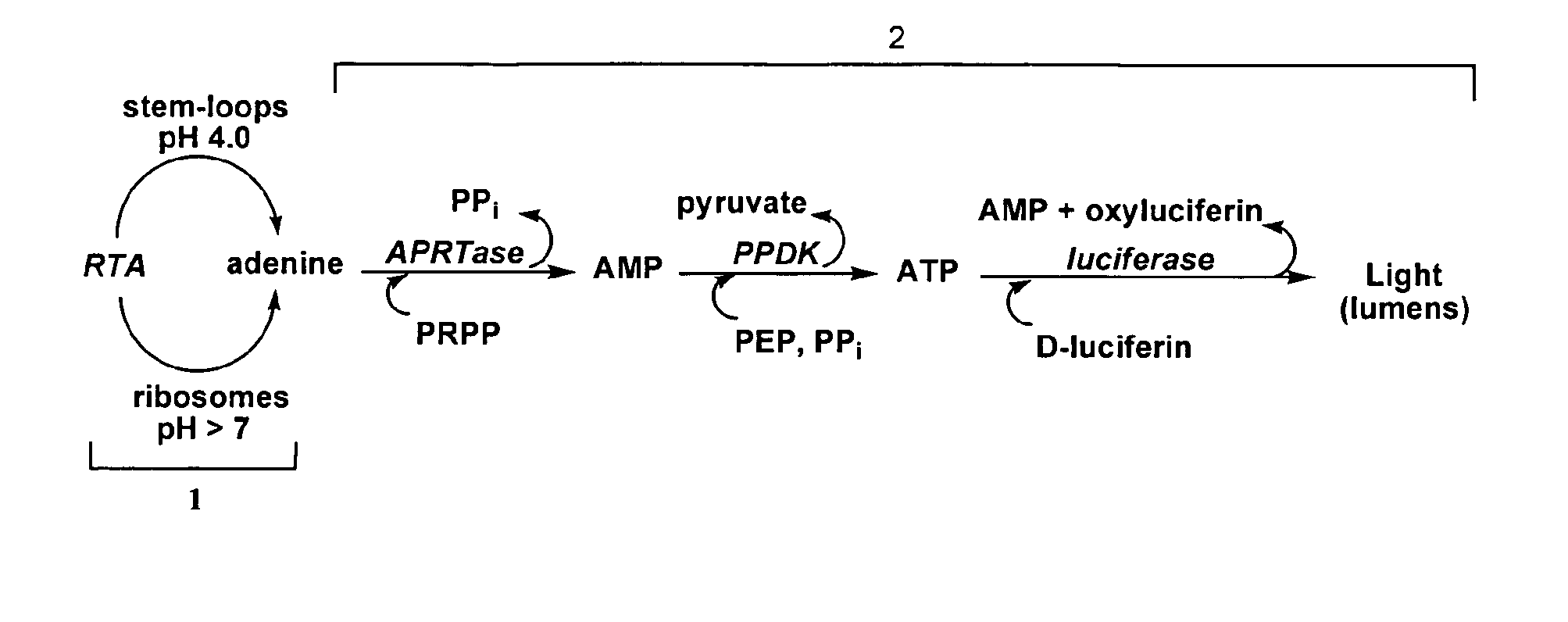
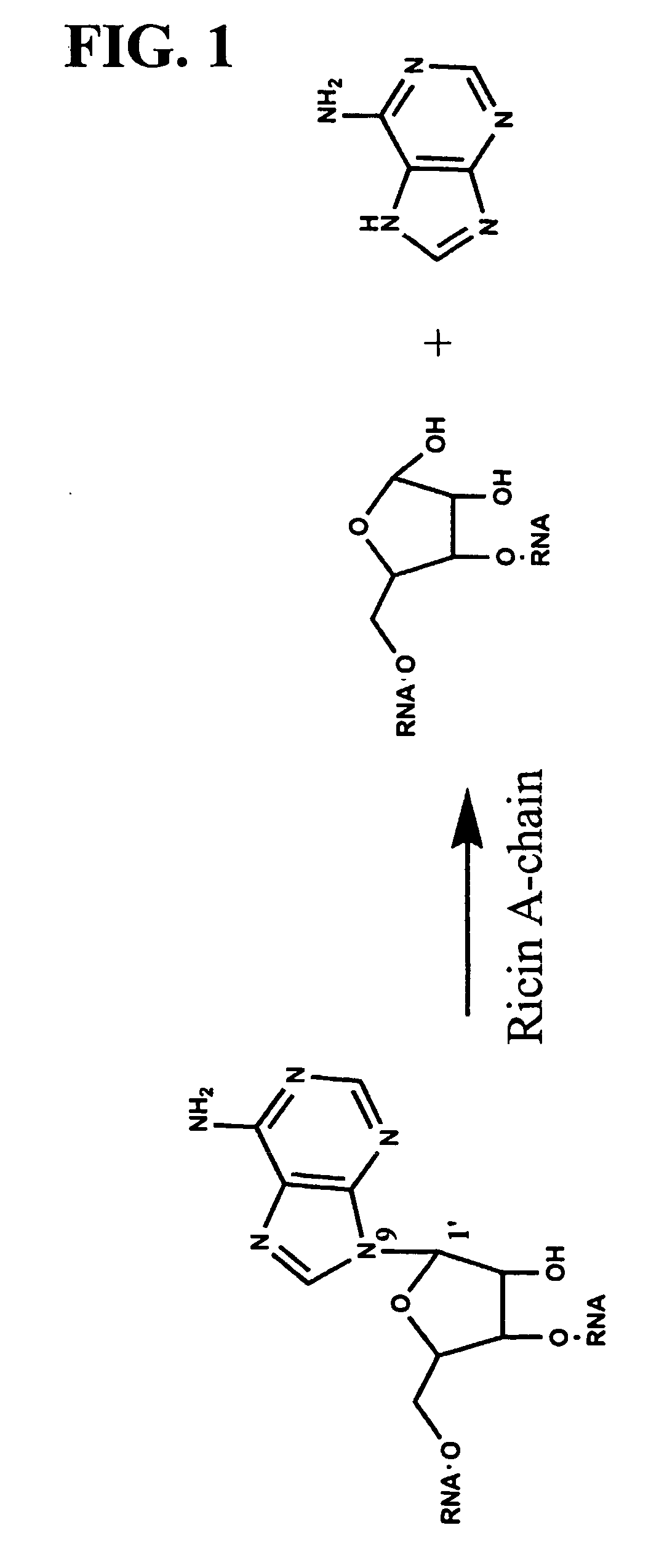
Methods for detecting ricin and related compounds and uses thereof
The present invention is directed to methods for detecting the presence of ricin and compounds that catalyze the release of adenine from nucleic acids or other biological materials and for screening for inhibitors of such compounds.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Transition State Analog Inhibitors Of Ricin A-Chain
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH +1
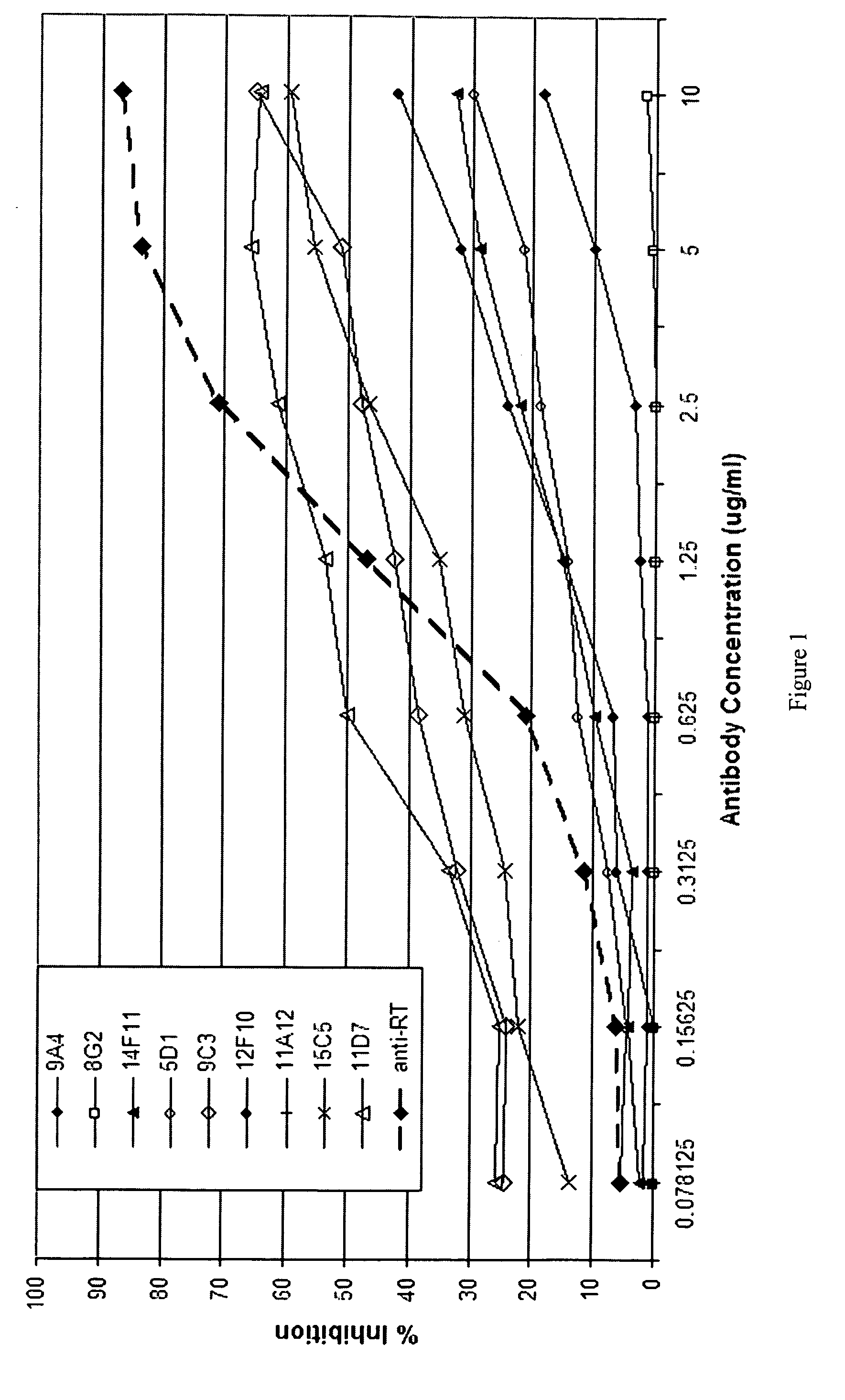
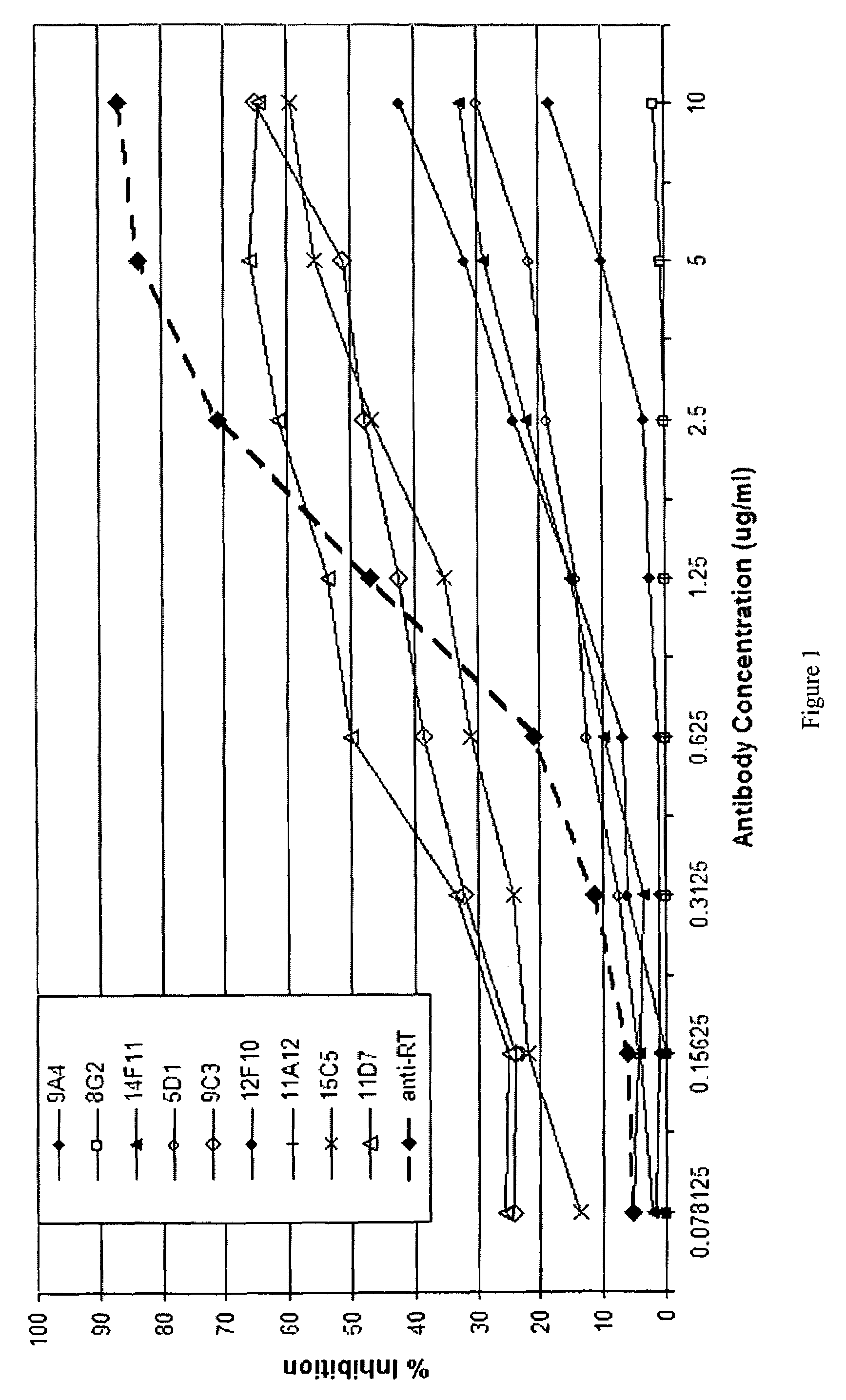
Monoclonal antibodies against ricin toxin and methods of making and using thereof
Disclosed herein are monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) against ricin toxin and its subunits. The Mabs were initially selected based upon their ability to bind to ricin and its individual subunits in a solid-phase enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA). Several candidates were selected for further evaluation, including their ability to inhibit ricin intoxication in vitro and for their utility as immunodiagnostic reagents. As disclosed herein, the Mabs may be used in immunoassays. Also disclosed, are use of the Mabs to inhibit ricin-mediated eukaryotic cell cytotoxicity in vitro, thereby indicating that these Mabs may be used to prevent and treat ricin intoxication in vivo. Kits comprising the Mabs are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
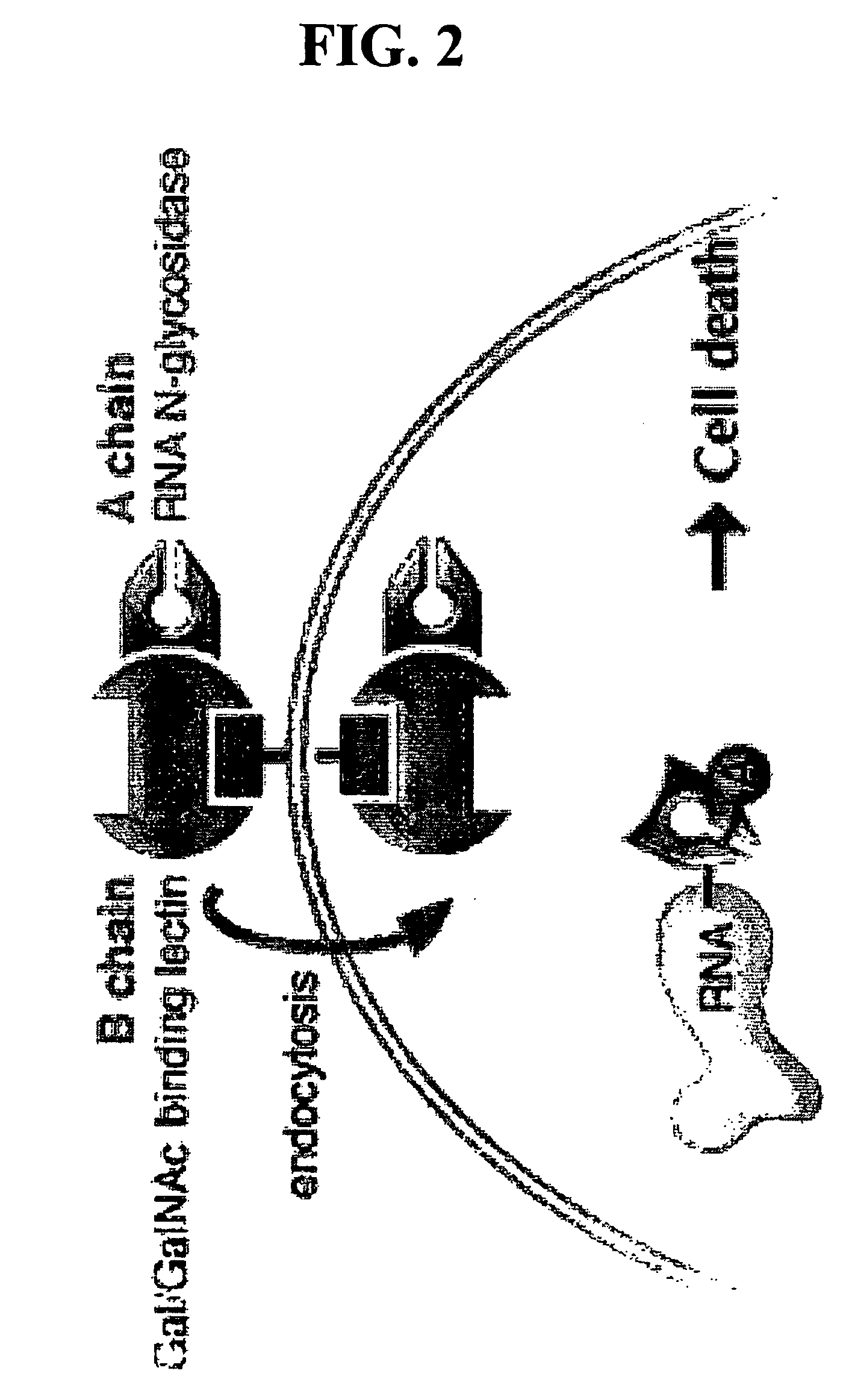
Ricin-like toxins for treatment of cancer
The present invention provides a protein having chain of a ricin-like toxin, a B chain of a ricin-like toxin and a novel heterologous linker amino acid sequence, linking the A and B chains. The linker sequence contains a cleavage recognition site for a specific protease such as those found in inflammatory cells and cancer cells. The invention also relates to a nucleic acid molecule encoding the protein and to expression vectors incorporating the nucleic acid molecule. Also provided is a method of inhibiting or destroying cells having a specific protease, such as cancer cells or inflammatory cells utilizing the nucleic acid molecules and proteins of the invention and pharmaceutical compositions for treating human inflammation and cancer.
Owner:TWINSTRAND HLDG
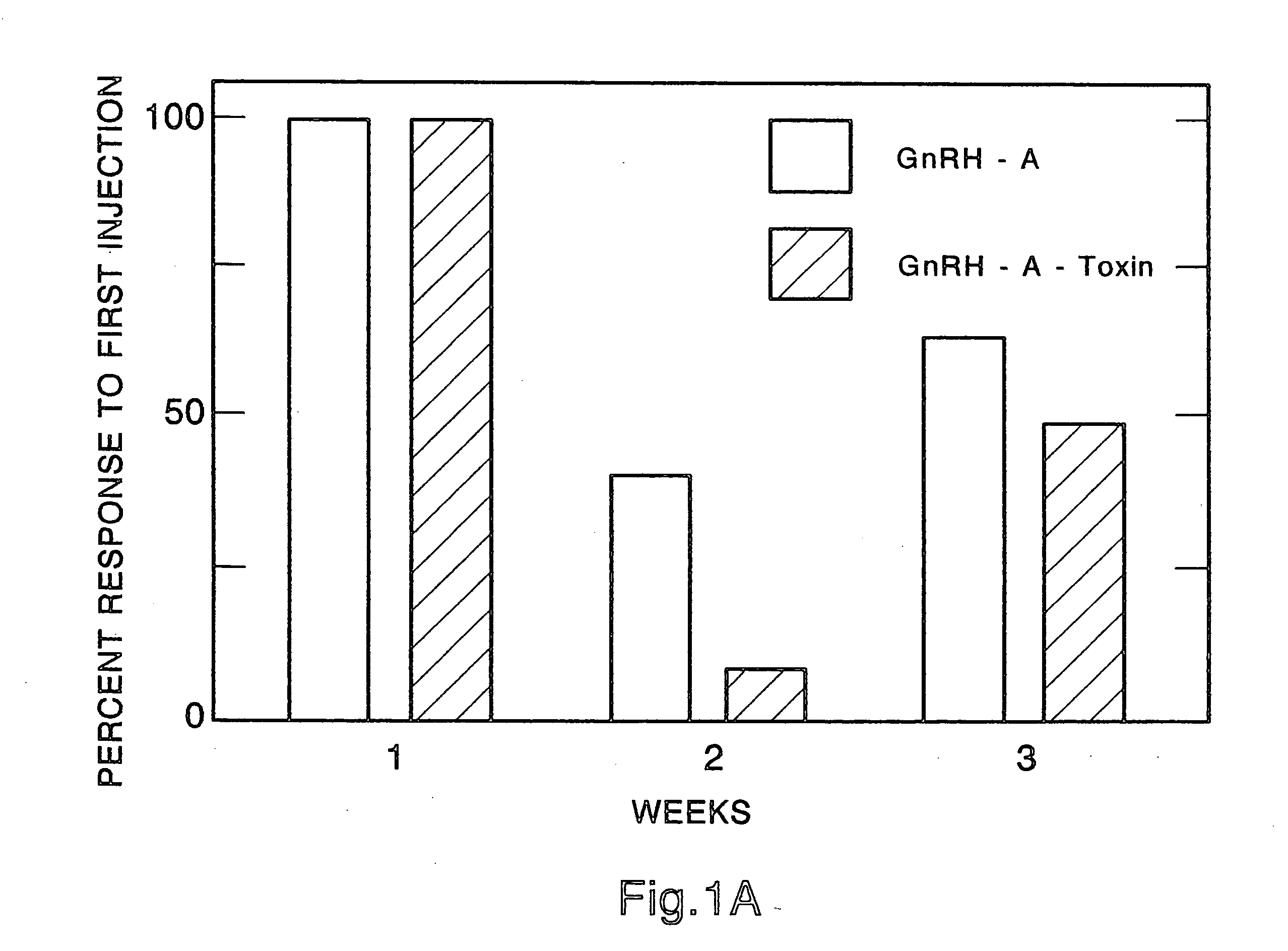
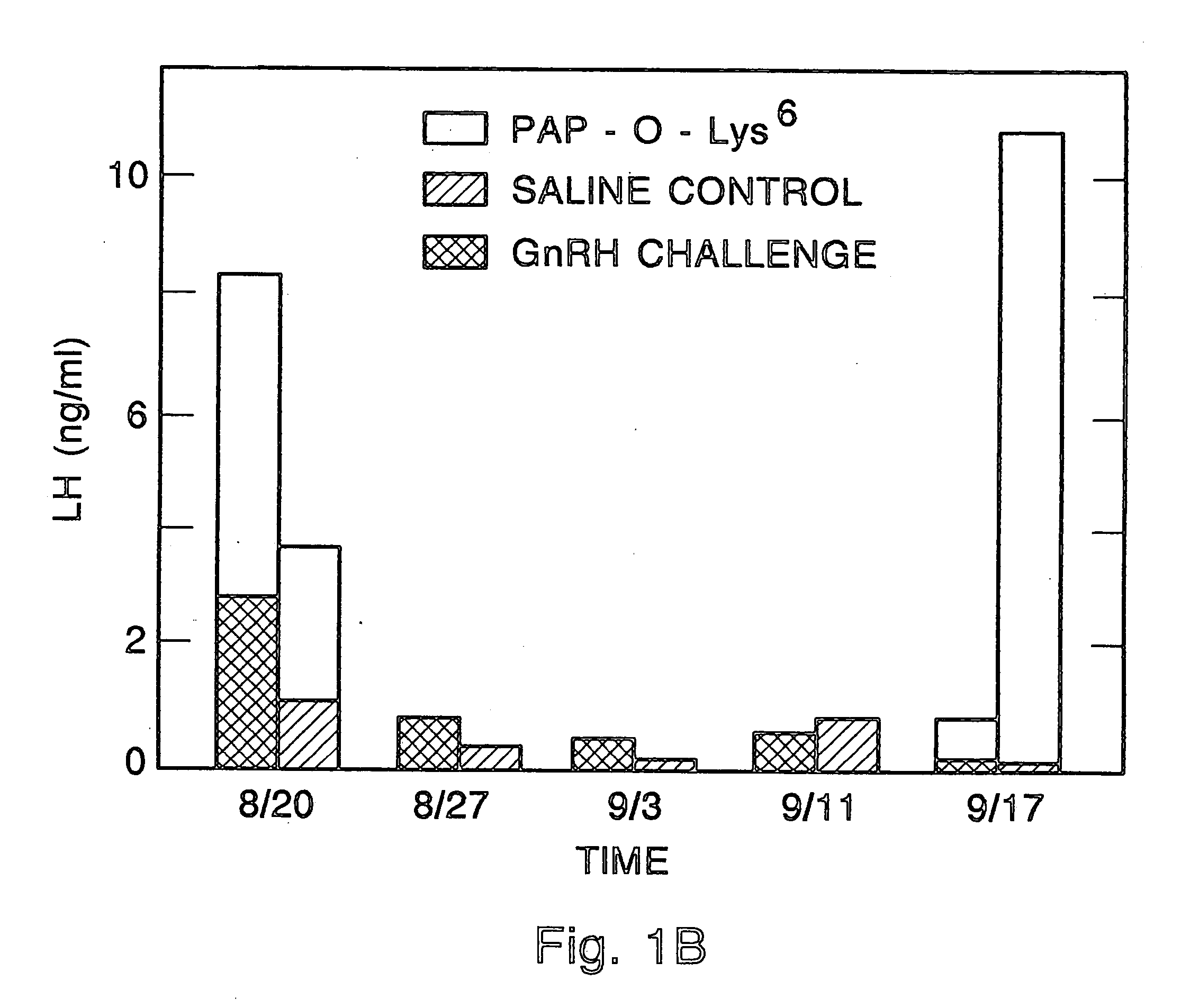
Method for inactivating gonadotrophs
InactiveUS20050277582A1Easy to transportImprove solubilityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesGeloninPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A
Certain toxic compounds (T) such as, for example, compounds based upon diphtheria toxin, ricin toxin, pseudomonas exotoxin, .alpha.-amanitin, pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP), ribosome inhibiting proteins, especially the ribosome inhibiting proteins of barley, wheat, corn, rye, gelonin and abrin, as well as certain cytotoxic chemicals such as, for example, melphalan and daunomycin can be conjugated to certain analogs of gonadotropin-releasing hormone to form a class of compounds which, when injected into an animal, destroy the gonadotrophs of the animal's anterior pituitary gland. Hence such compounds may be used to sterilize such animals and / or to treat certain sex hormone related diseases.
Owner:NETT TORRANCE +3
Haploid cells
InactiveCN104024404AAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementRicinus sanguineusToxin resistance
The present invention relates to the generation of stable haploid cell cultures, uses of said cells in forward and reverse genetics, especially the identification of target genes associated with a modified phenotype and in particular identifying genetic targets associated with toxin resistance, especially ricin toxicity resistance, and therapeutic uses of target compounds.
Owner:IMBA INSTITUT FUR MOLEKULARE BIOTECH
Interferon recombinant fusion protein and application thereof
The invention discloses an interferon recombinant fusion protein and application thereof. The fusion protein is formed by connecting canine interferon alpha and ricin B chain by (G4S)3 flexible linker. Compared with the common dog interferon alpha, the dog interferon fusion protein has the advantages that the anti-virus activity is improved; the broad-spectrum anti-virus function is realized, andthe self immune response of the dog body is improved.
Owner:ACAD OF MILITARY SCI PLA CHINA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI INST OF MILITARY VETERINARY MEDICINE
Monoclonal antibodies against ricin toxin and methods of making and using thereof
Disclosed herein are monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) against ricin toxin and its subunits. The Mabs were initially selected based upon their ability to bind to ricin and its individual subunits in a solid-phase enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA). Several candidates were selected for further evaluation, including their ability to inhibit ricin intoxication in vitro and for their utility as immunodiagnostic reagents. As disclosed herein, the Mabs may be used in immunoassays. Also disclosed, are use of the Mabs to inhibit ricin-mediated eukaryotic cell cytotoxicity in vitro, thereby indicating that these Mabs may be used to prevent and treat ricin intoxication in vivo. Kits comprising the Mabs are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
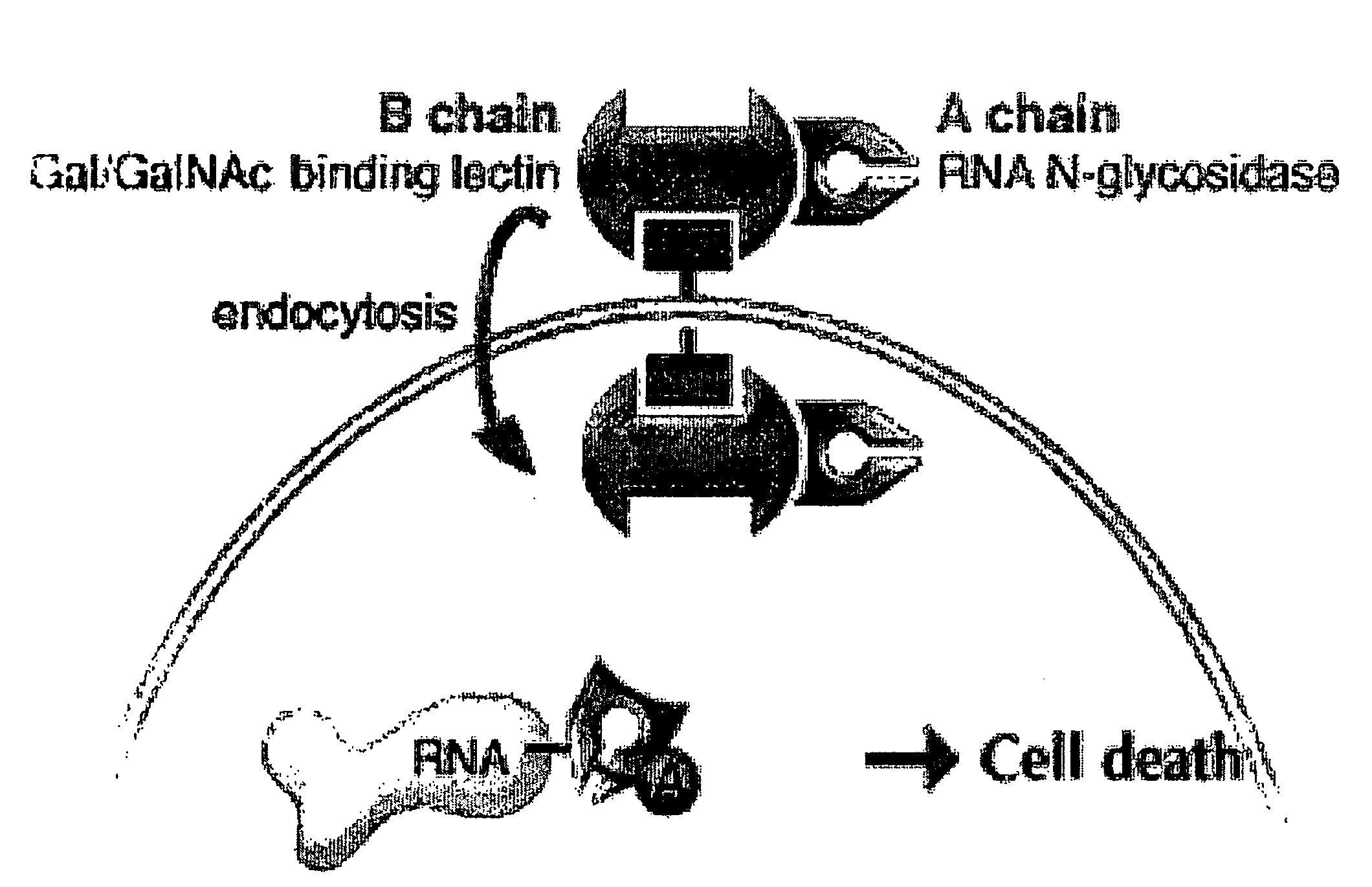
Plant lectins as carriers of associated drug substances into animal and human cells
InactiveUS20130323221A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderPlant LectinsDelivery vehicle
The current invention involves the use of protein lectins produced by plants including the non-toxic carbohydrate binding subunits (B subunits) of plant “AB toxins” (PTB lectins) as delivery vehicles for mobilizing associated drug substances for delivery to animal and human cells. The resulting protein fusions or conjugates retain lectin carbohydrate specificity for binding to cells and cellular trafficking activity so as to deliver an associated drug compound to the site of disease manifestation. One embodiment of this invention concerns the ability of ricin toxin B subunit, as a model PTB lectin, to deliver enzyme replacement therapeutic drugs to cells of several organs of the body including the brain and central nervous system, eyes, ears, lungs, bone, heart, kidney, liver, and spleen for treating lysosomal diseases.
Owner:BIOSTRATEGIES LC
Selective destruction of cells infected with human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS7018633B2Avoid problemsInhibition of replicationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWAS PROTEINViral protease
Compositions and methods for selectively killing a cell containing a viral protease are disclosed. The composition is a varient of a protein synthesis inactivating toxin wherein a viral protease cleavage site is interposed between the A and B chains. The variant of the type II ribosome-inactivating protein is activated by digestion of the viral protease cleavage site by the specific viral protease. The activated ribosome-inactivating protein then kills the cell by inactivating cellular ribosomes. A preferred embodiment of the invention is specific for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and uses ricin as the ribosome-inactivating protein. In another preferred embodiment of the invention, the variant of the ribosome-inactivating protein is modified by attachment of one or more hydrophobic agents. The hydrophobic agent facilitates entry of the variant of the ribosome-inactivating protein into cells and can lead to incorporation of the ribosome-inactivating protein into viral particles. Still another preferred embodiment of the invention includes a targeting moiety attached to the variants of the ribosome-inactivating protein to target the agent to HIV infectable cells.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Chimeric anti-ricin antibody
InactiveUS8535668B2Conserving property of resistanceSure easyBiocideImmunoglobulins against plantsBiochemistryChimeric antibody
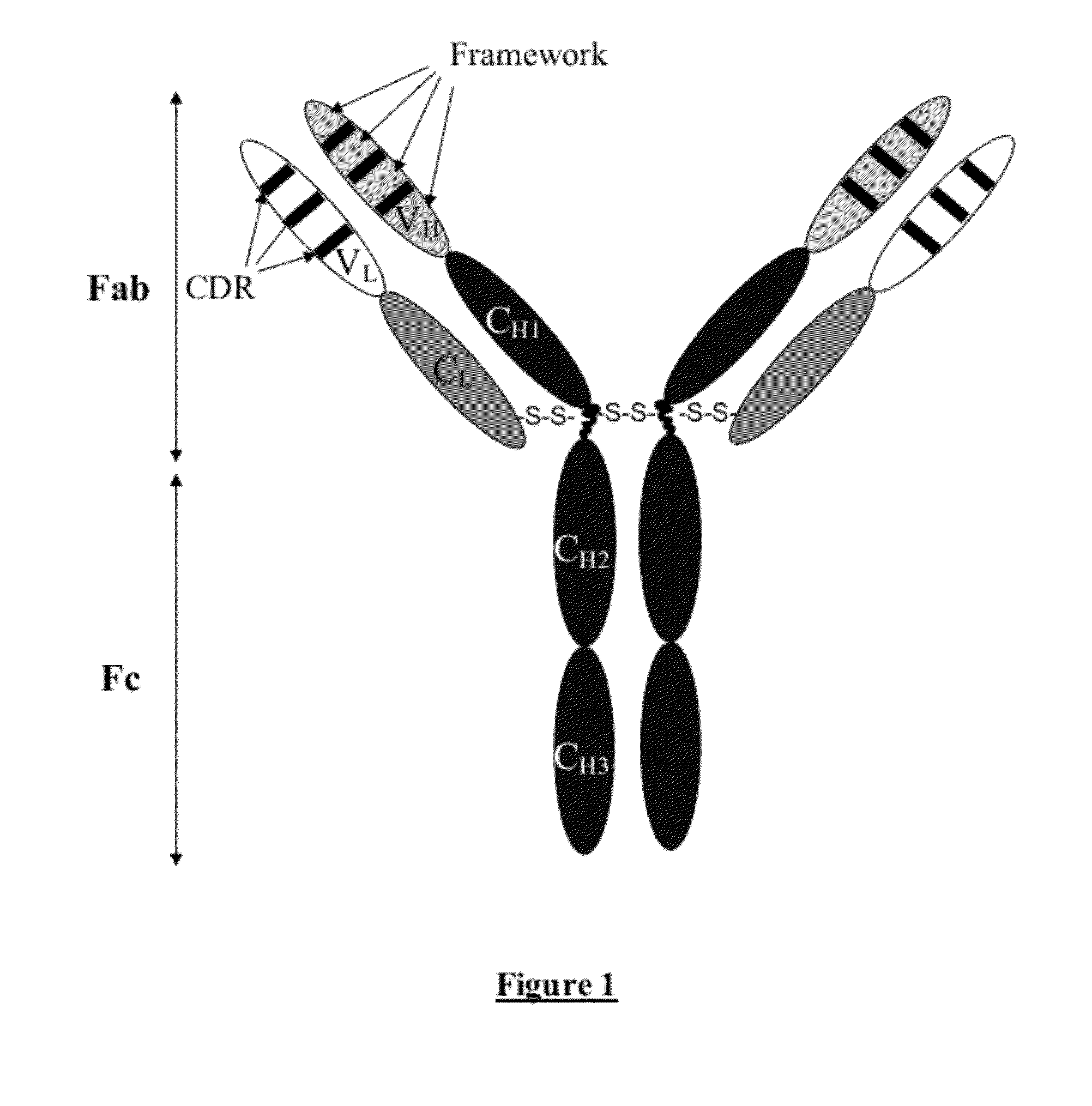
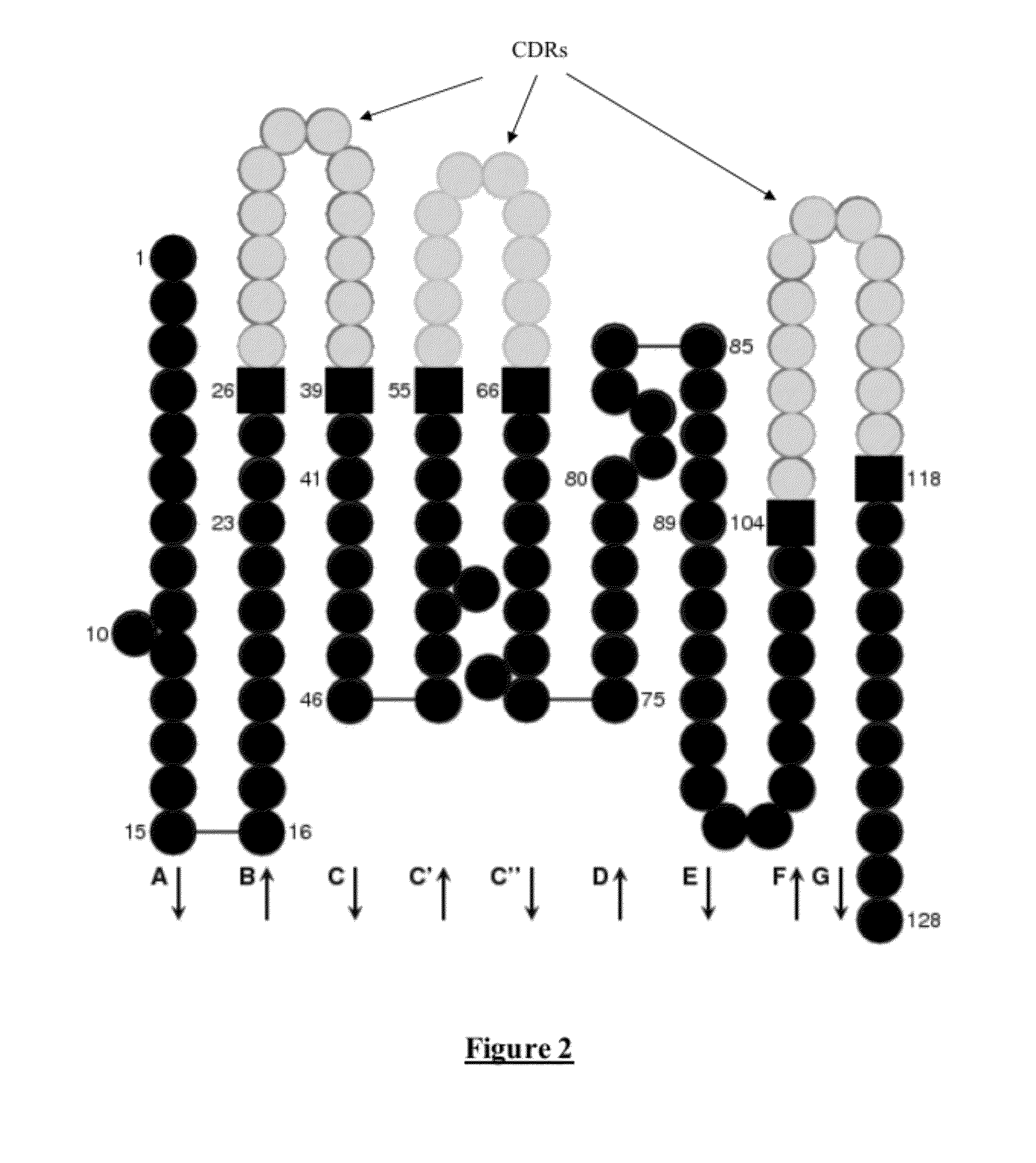
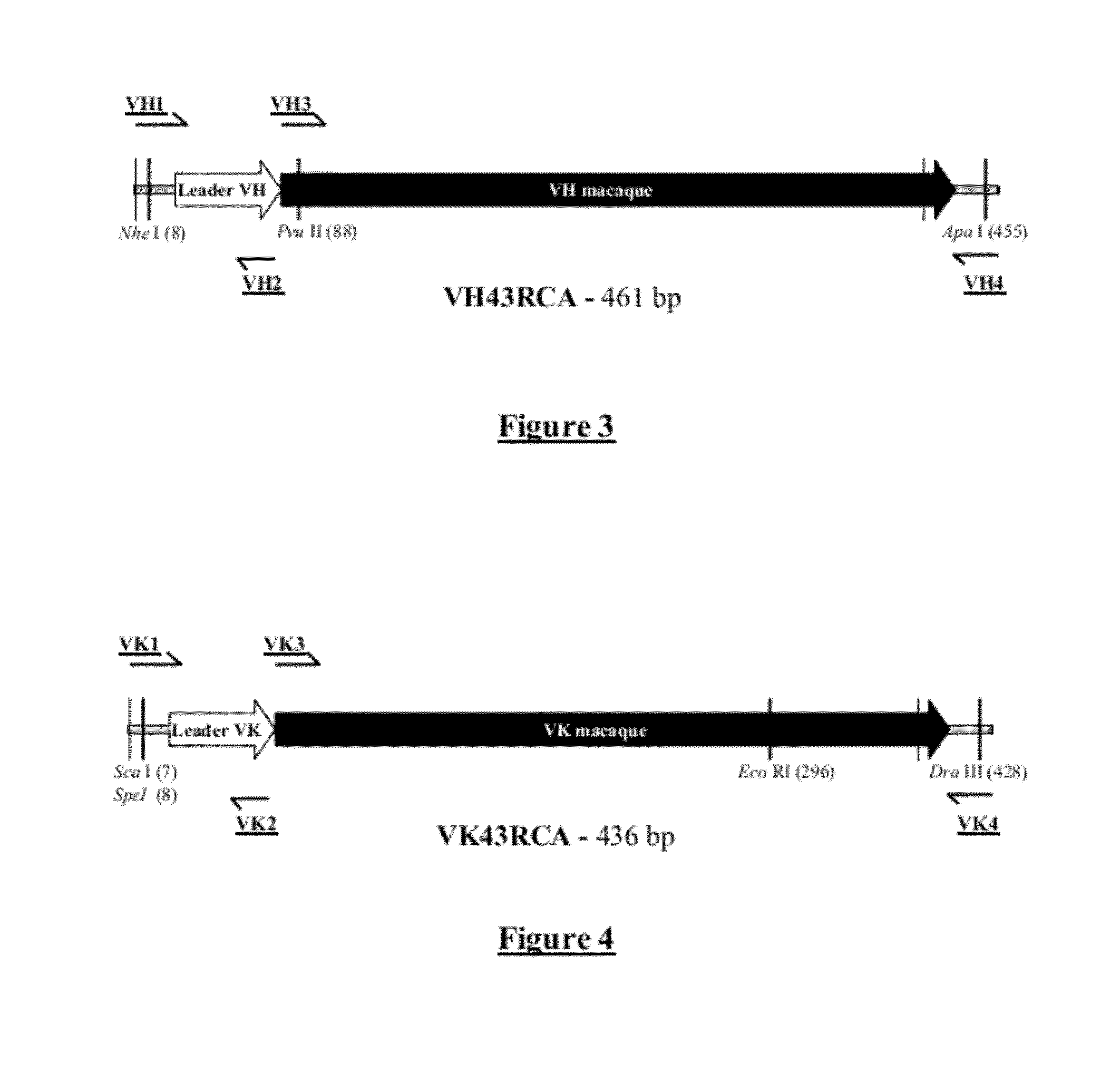
A chimeric monoclonal antibody targeted at ricin, in which the light chain and heavy chain are such that:the constant region of the light chain and the constant region of the heavy chain are essentially made up respectively of the constant region of the light chain and the constant region of the heavy chain of human immunoglobulin,the variable region of the light chain and the variable region of the heavy chain include respectively the variable region of the light chain and the variable region of the heavy chain of macaque immunoglobulin,the monoclonal antibody not substantially inducing an immune response against chimeric antibodies.
Owner:ETAT FR REPRESENTE PAR LE DELEGUE GENERAL POUR LARMEMENT +1
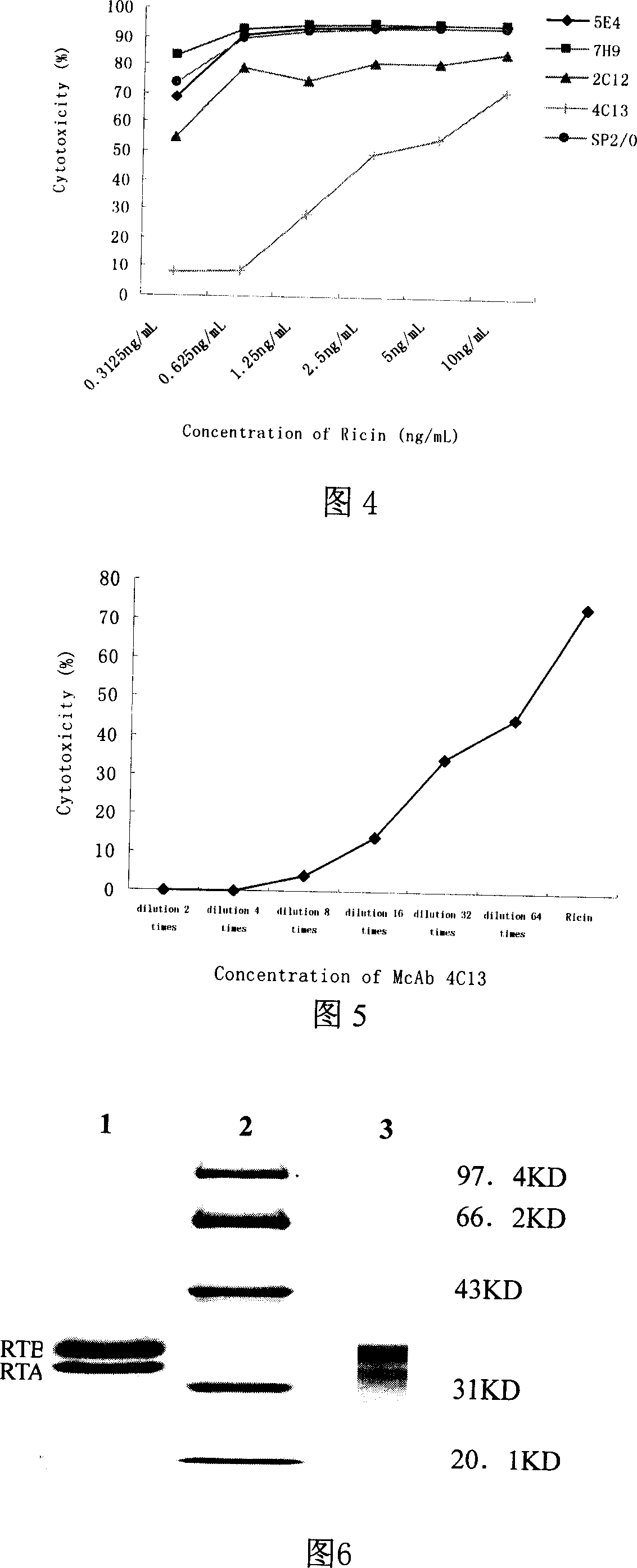
Neutralized monoclone antibody 4C13 of antiricin, its production and use
An anti-recin neutralizing monoclonal antibody 4C13, its production and use are disclosed. The process is carried out by cloning gene of antibody light and heavy chain variable region from 4C13 hybrid tumor cell, encoding mouse antibody variable region, constructing and expressing multiple small-molecular gene engineering antibody based on light and heavy chain variable region gene and cross-linking multiple biological active molecules based on encoded polypeptide or protein. It can be used to inspect recin, diagnose recin and immunotoxin poisoning and prepare related medicines.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Cat granulocyte colony stimulating factor mutant recombinant fusion protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113527520AHigh biological activityImprove protein stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliWhite blood cell
The invention discloses a cat granulocyte colony stimulating factor mutant recombinant fusion protein as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the field of biological genetic engineering. The recombinant fusion protein is formed by connecting a cat granulocyte colony stimulating factor mutant and a ricin B chain truncated peptide through a flexible linker. The preparation method comprises the following steps: constructing a cat granulocyte colony stimulating factor mutation expression vector; constructing an escherichia coli recombinant expression vector; carrying out the expression of the recombinant FeG-CSF-Mut / RTBD1 fusion protein; and carrying out purification and renaturation on the recombinant FeG-CSF-Mut / RTBD1 fusion protein. The long-acting granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is obtained by connecting the cat G-CSF mutant and the ricin B chain truncated peptide, so that the biological activity of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor can be enhanced, the protein stability of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in in-vivo blood is improved, and the half-life period of a drug in an organism is further prolonged. The recombinant fusion protein has the function of treating leucopenia.
Owner:长春萤火虫生物科技有限公司
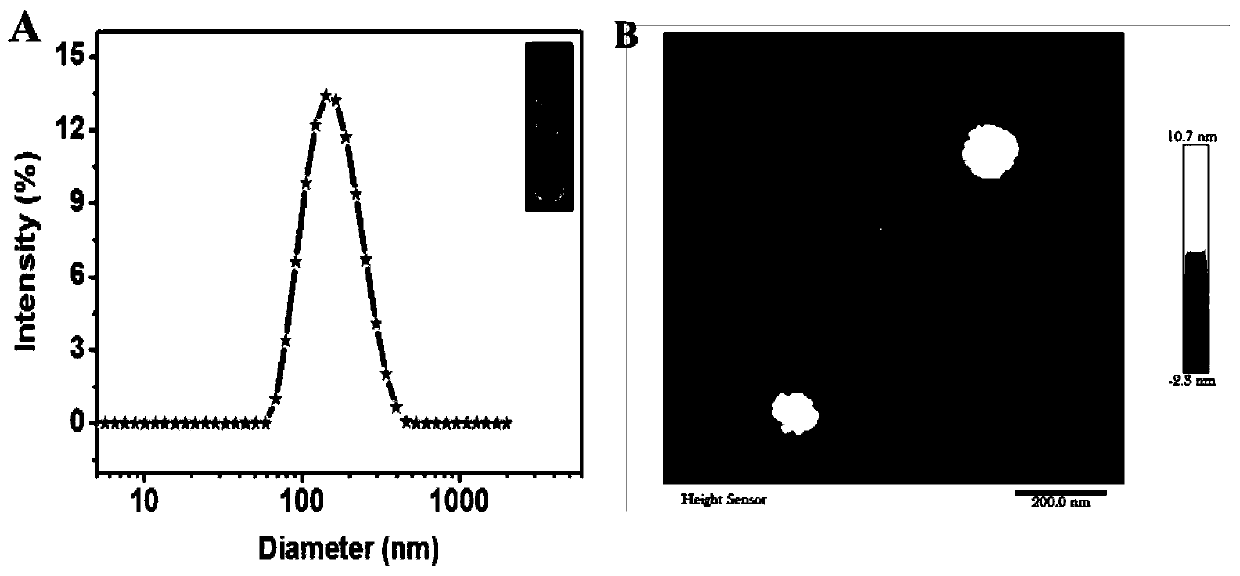
Method for detecting chain B of ricin in real time by using dual amplification strategy of catalytic hairpin assembly mediated lipidosome encoding magnetic beads
ActiveCN111394428AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeLiposome membrane
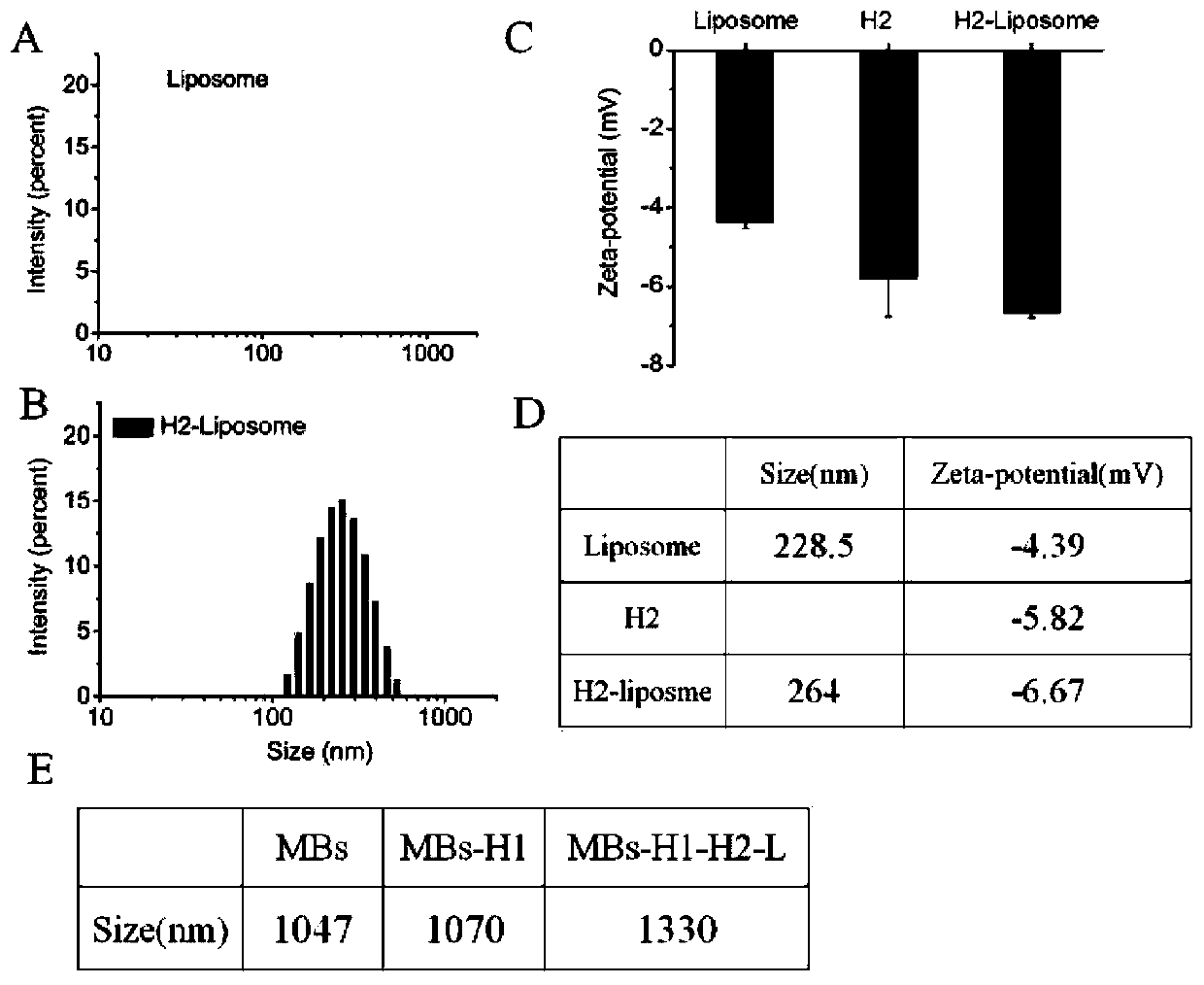
The invention relates to a method for detecting chain B of ricin in real time by using a dual amplification strategy of catalytic hairpin assembly mediated lipidosome encoding magnetic beads. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, releasing a blocker through incubation of a magnetic bead-nucleic acid aptamer-blocker hybrid probe and chain B of ricin, secondly, enabling H1 modified magnetic beads, H2 functionalized lipidosome and the blocker so as to obtain MBs-H1-H2-LGOD, performing magnetic separation, adding a glucose solution into MBs-H1-H2-LGOD, breaking a lipidosome membrane through the reaction to release coated GOD (glucose oxidase) for catalytic oxidation on glucose to generate H2O2, developing the blue color (qualitative) of H2O2 by using PTS (peroxide test), and reading values (quantitative) by using a handheld H2O2 detector, so as to achieve simultaneous naked-eye qualitative and quantitive detection on the chain B of the ricin. The method provided by the invention has super high sensitivity and selectivity, and is simple and convenient and low in cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Anti-ricin immunoglobulin F(ab')2 and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108484760AEffective therapeuticEffective preventionSerum immunoglobulinsAntinoxious agentsSerum igeRicin
The invention discloses an anti-ricin immunoglobulin F(ab')2 and a preparation method thereof. The method for preparing the anti-ricin immunoglobulin F(ab')2 comprises the following steps that an animal is immunized by an immunogen, a ricin IgG antibody is prepared, and an Fc segment is removed from the ricin IgG antibody to obtain the anti-ricin immunoglobulin F(ab')2; antigens of the immunogen are a low-toxic or attenuated ricin mutant or recombinant protein thereof, a DNA molecule encoding the low-toxic or attenuated ricin mutant or the recombinant protein thereof or a carrier or an expression cassette or a recombinant bacterium or a recombinant virus expressing the DNA molecule and detoxified natural ricin. According to the method, the healthy animal is immunized by the non-toxic or low-toxic ricin antigen, a high-titer antiserum for neutralizing the ricin is generated, and the specific protective effect on the treatment and prevention of the ricin is achieved.
Owner:THE FIFTH MEDICAL CENT OF CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL +1
Ricin vaccine and methods of making thereof
Disclosed herein ricin toxin A chain polypeptides having an engineered disulfide bond ((SS)RTA) and compositions thereof. The disclosed (SS)RTA polypeptides retain the immunological epitope of wild type RTA, lack detectable N-glycosidase activity or exhibit reduced N-glycosidase activity as compared to controls, and exhibit increased solubility, thermal stability and a lower tendency to self-aggregate as compared to RTA 198 and / or RTA 1-33 / 44-198. Also disclosed are immunogenic compositions that may be used to immunize a subject against ricin intoxication. Methods of immunizing against, treating, inhibiting, reducing and / and preventing ricin intoxication are disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Plant lectins as carriers of associated drug substances into animal and human cells
ActiveUS20160083707A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderPlant LectinsLysosome
The current invention involves the use of protein lectins produced by plants including the non-toxic carbohydrate binding subunits (B subunits) of plant “AB toxins” (PTB lectins) as delivery vehicles for mobilizing associated drug substances for delivery to animal and human cells. The resulting protein fusions or conjugates retain lectin carbohydrate specificity for binding to cells and cellular trafficking activity so as to deliver an associated drug compound to the site of disease manifestation. One embodiment of this invention concerns the ability of ricin toxin B subunit, as a model PTB lectin, to deliver enzyme replacement therapeutic drugs to cells of several organs of the body including the brain and central nervous system, eyes, ears, lungs, bone, heart, kidney, liver, and spleen for treating lysosomal diseases.
Owner:BIOSTRATEGIES LC
Methods and Systems for the Detection of Ricin and Other Ribosome Inactivating Proteins
ActiveUS20140065623A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceLyase
A device, method, and system for the detection of ribosome inactivating protein activity, including the ricin toxin, in a sample. According to one embodiment, the ribosome inactivating protein in the sample removes an adenine from a labeled DNA substrate to create an abasic site. An AP lyase can then cleave the DNA substrate at the abasic site, allowing the fluorophore located at or near one end of the DNA substrate and the quencher at or near the other end of the DNA substrate to spatially separate. Once the fluorophore and the quencher are sufficiently separated, the fluorophore will emit a fluorescence signal. Increasing fluorescence, indicating ribosome inactivating protein activity, will be monitored in real time using a detection system.
Owner:ACUMEN DETECTION INC
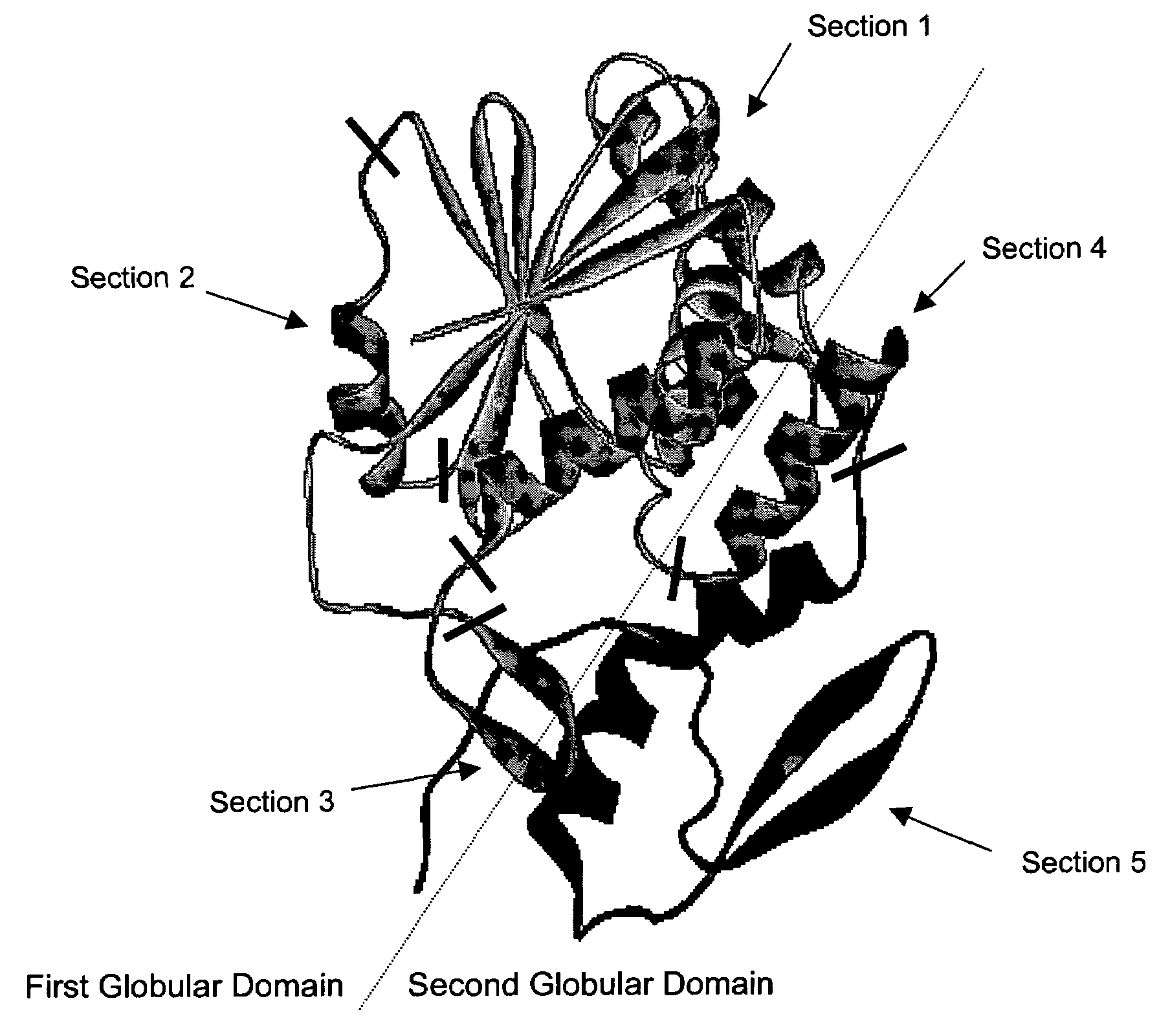
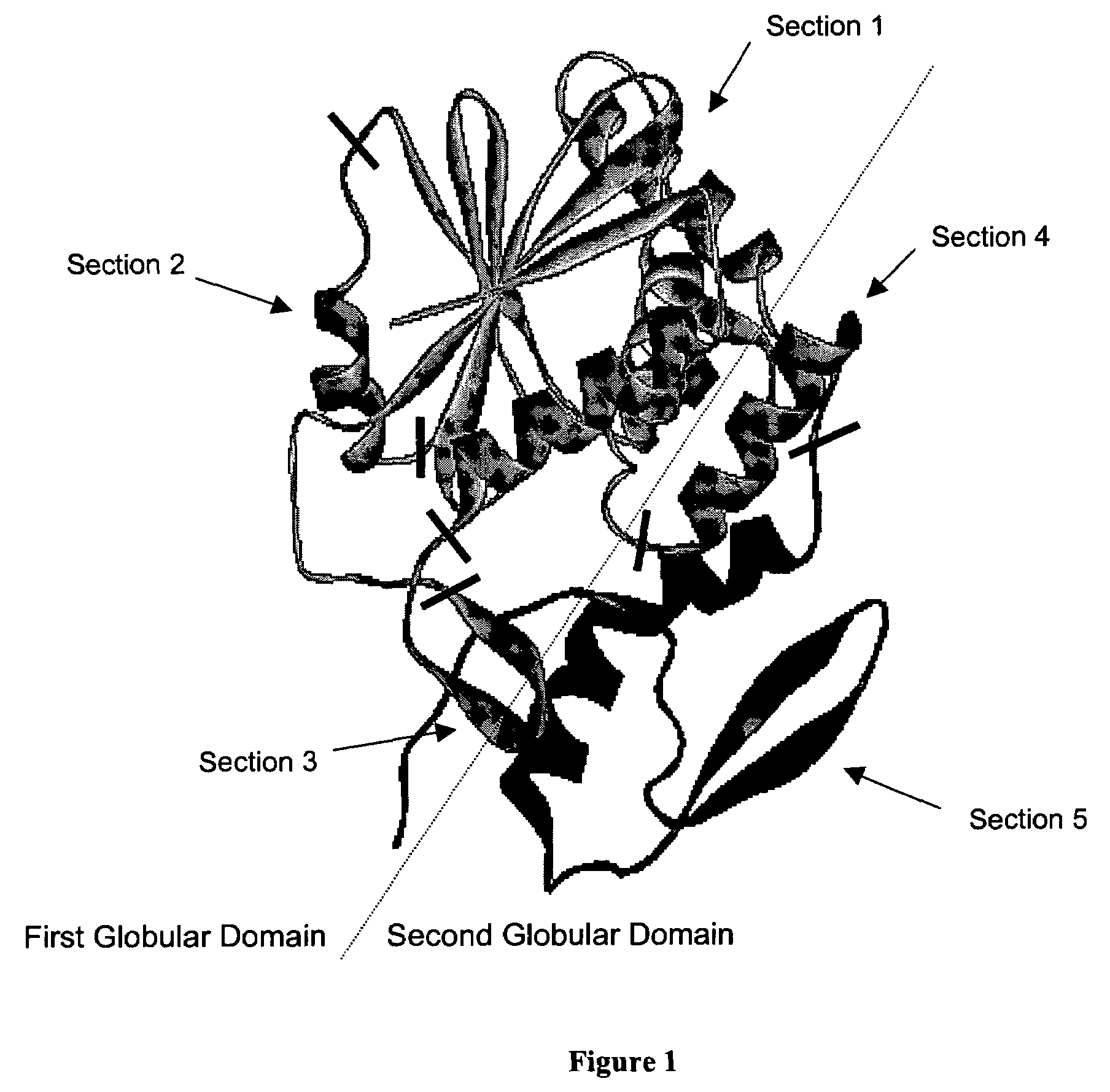
Ricin toxin A-chain fragment for use as a vaccine
InactiveUS7407935B2Lacks detectable N-glycosidase-rRNA activityReduced activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityEpitope
Disclosed herein are polypeptides and variants thereof comprising a polypeptide sequence having substantial identity to ricin A chain (RTA) that lack detectable N-glycosidase-rRNA activity or exhibit reduced N-glycosidase-rRNA activity as compared to controls and methods of making and using thereof. The polypeptides and variants have a greater solubility in aqueous solutions of physiological pH and ionic strength than RTA and also retain the integrity of the neutralizing immunological epitope of wild type RTA. Also disclosed are immunogenic compositions that may be used to immunize a subject against ricin intoxication. Methods of immunizing against, treating, and preventing ricin intoxication are disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Ricin-like toxin variants for treatment of cancer, viral or parasitic infections
InactiveUS20050272048A1Enhance transcytosisImprove securityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousFungal Viruses
The present invention provides a protein having an A chain of a ricin-like toxin, a B chain of a ricin-like toxin and a heterologous linker amino acid sequence, linking the A and B chains. The linker sequence contains a cleavage recognition site for a disease specific protease such as a cancer, inflammatory, fungal, viral or parasitic protease. The invention also relates to a nucleic acid molecule encoding the protein and to expression vectors incorporating the nucleic acid molecule. In addition, the invention relates to a method for producing the recombinant protein in yeast, to nucleic acid molecules for use in yeast and to yeast transformed with such nucleic acid molecules. Also provided is a method of inhibiting or destroying mammalian cancer cells, inflammatory cells, cells infected with a virus, a fugus, or parasite, or parasites utilizing the nucleic acid molecules and proteins of the invention and pharmaceutical compositions for treating human cancer, inflammatory disease, viral infection, fugal infection, or parasitic infection.
Owner:TWINSTRAND HLDG
Capillary gel electrophoresis detection kit containing reducing agent
PendingCN113189183AReduce pollutionReduce harmMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesTumor necrosis factor receptor
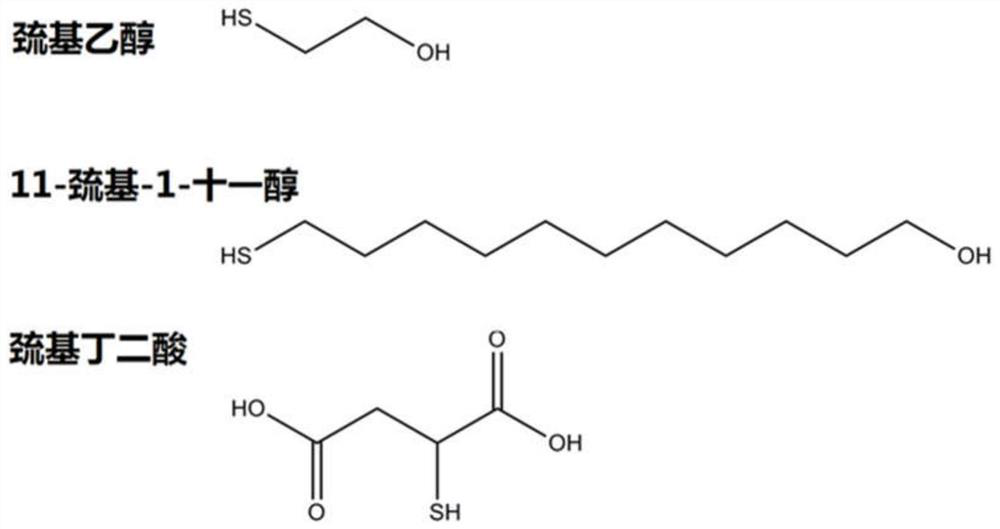
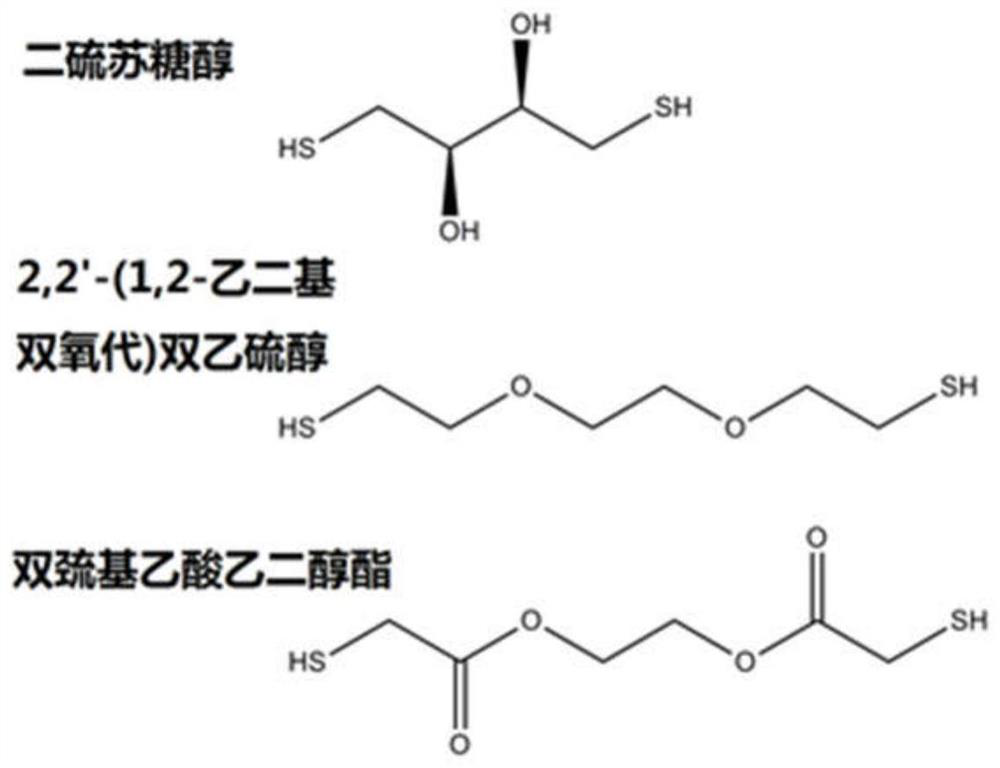
The invention relates to a capillary gel electrophoresis detection kit containing a reducing agent. The reducing agent is selected from a monothiol compound and a dithiol compound, the monothiol compound is selected from 11-mercapto-1-undecanol, and the dithiol compound is selected from 2, 2'-(1, 2-ethanedioxy) bis-ethanethiol and ethylene glycol dithioglycolate. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for reducing environmental pollution and harm to a human body in the process of analyzing biopharmacy such as monoclonal antibodies through reduced capillary gel electrophoresis, and ensuring accuracy of purity under a reduction condition at the same time; the biological drugs comprise a recombinant anti-ricin humanized monoclonal antibody, a recombinant anti-HER2 humanized monoclonal antibody, T-DM1 and a recombinant human type II tumor necrosis factor receptor-antibody fusion protein for injection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and kit for detecting ricin based on relative DNA walker initiation index amplification of gold nanoprobe constructed by freezing
ActiveCN113151414AEasy to operateOperation time savingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRicinus sanguineusToxin detection
The invention belongs to the field of protein toxin detection, and relates to a method and a kit for detecting ricin based on relative DNA walker initiation index amplification of a gold nanoprobe constructed by freezing. The method mainly comprises the following four processes: performing freezing to construct the gold nanoprobe, competitively combining the ricin and the gold nanoprobe with an aptamer, and carrying out a relative DNA walker and index amplification reaction. The method and the kit can be used for detecting the ricin with relatively high sensitivity, good specificity and excellent stability in practical application.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE & OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com