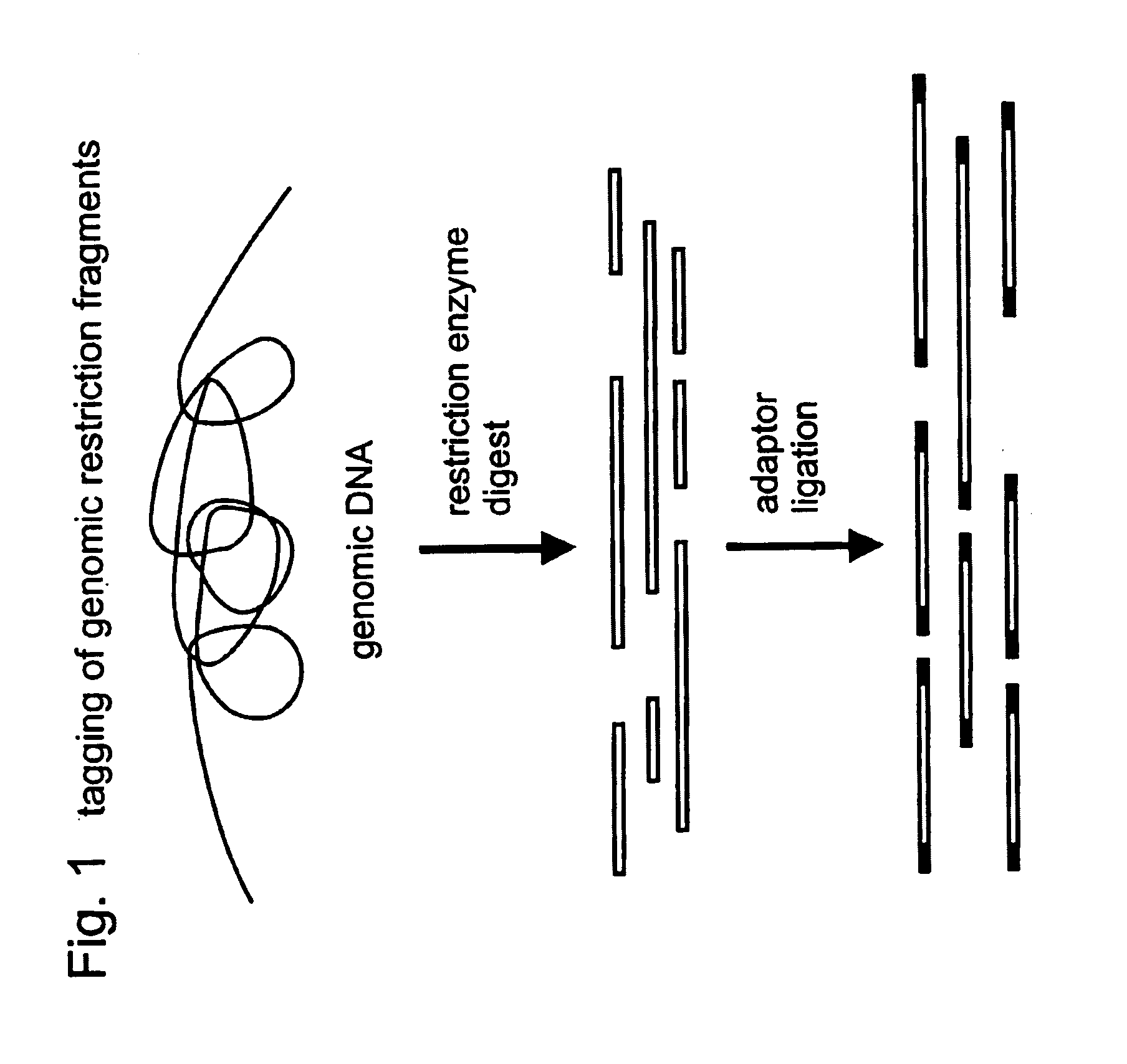
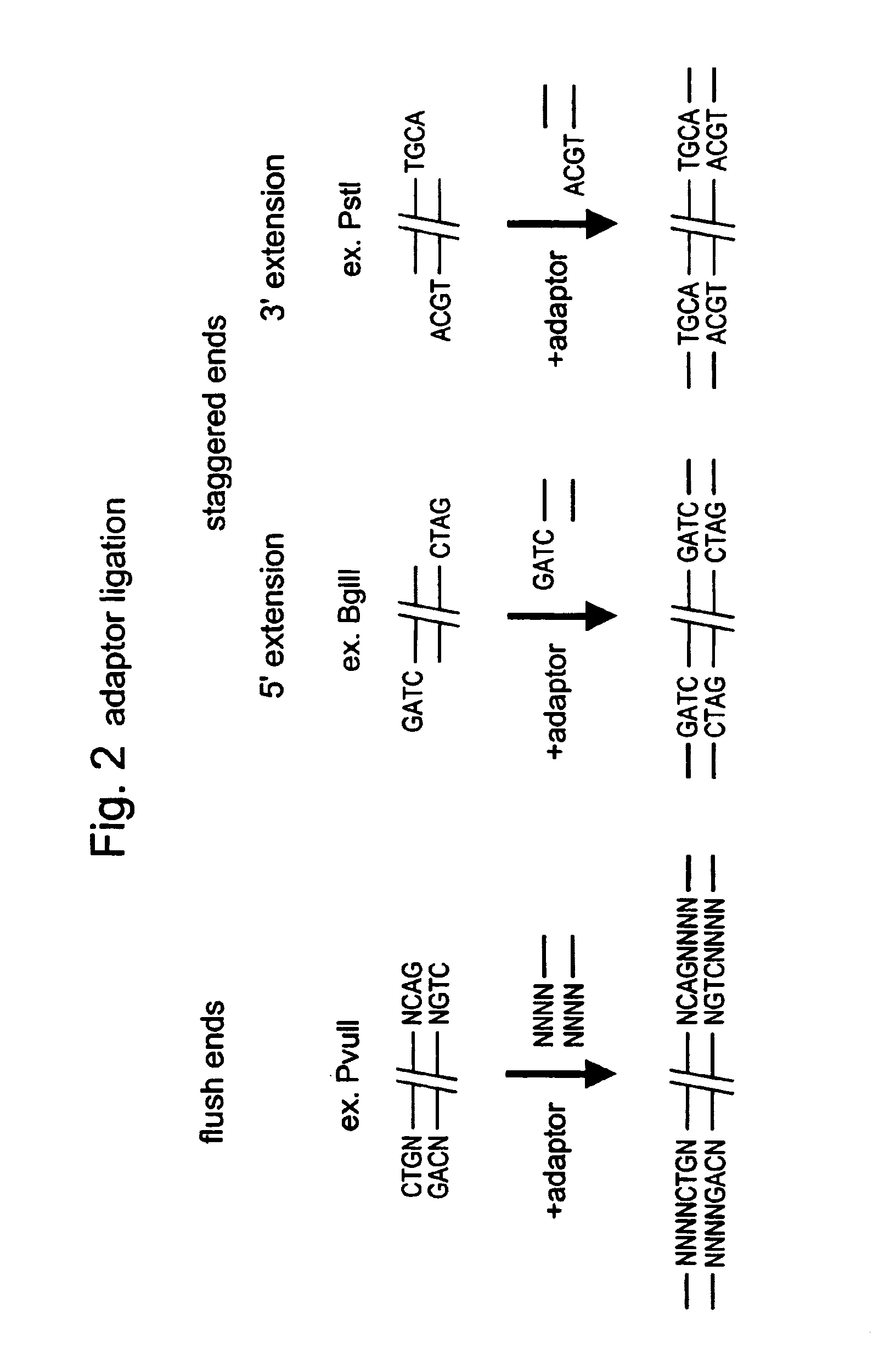
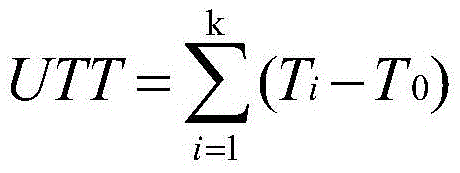Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105 results about "Restriction fragment length polymorphism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
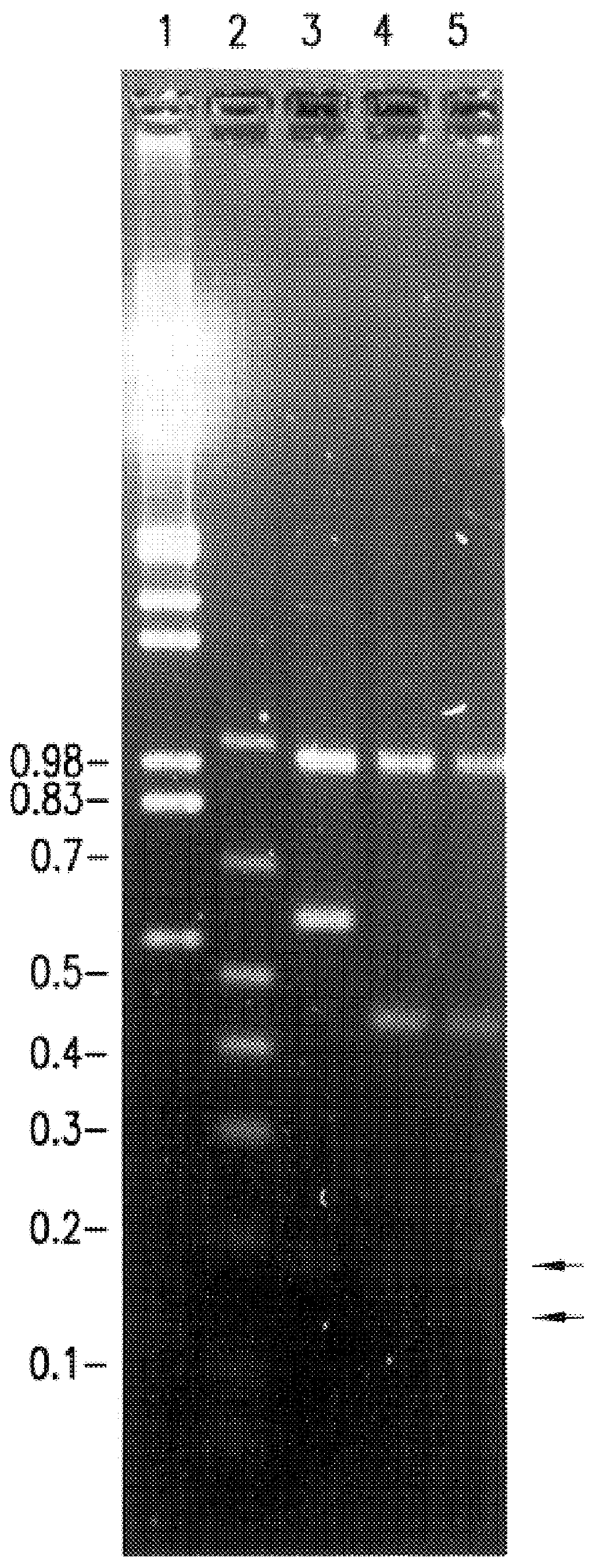
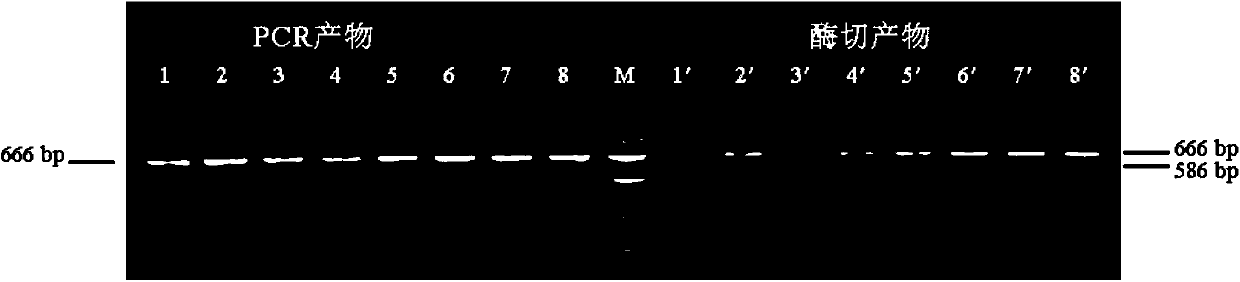
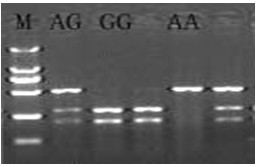
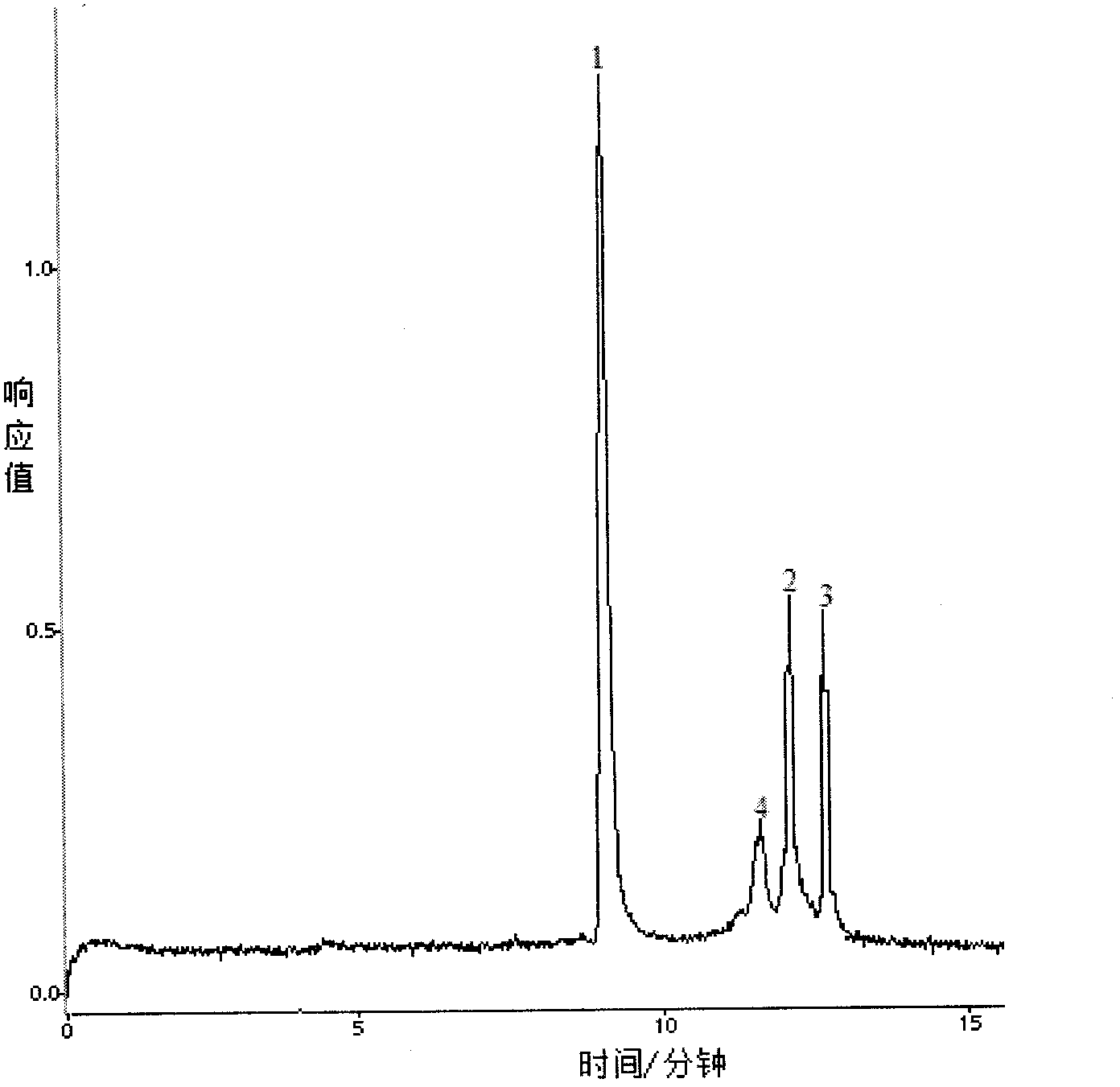
In molecular biology, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a technique that exploits variations in homologous DNA sequences, known as polymorphisms, in order to distinguish individuals, populations, or species or to pinpoint the locations of genes within a sequence. The term may refer to a polymorphism itself, as detected through the differing locations of restriction enzyme sites, or to a related laboratory technique by which such differences can be illustrated. In RFLP analysis, a DNA sample is digested into fragments by one or more restriction enzymes, and the resulting restriction fragments are then separated by gel electrophoresis according to their size.
Methods and systems for molecular fingerprinting
InactiveUS20020034748A1Fast and accurate determinationHigh resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSmall samplePolynucleotide
This invention relates in general to a method for molecular fingerprinting. The method can be used for forensic identification (e.g. DNA fingerprinting, especially by VNTR), bacterial typing, and human / animal pathogen diagnosis. More particularly, molecules such as polynucleotides (e.g. DNA) can be assessed or sorted by size in a microfabricated device that analyzes the polynucleotides according to restriction fragment length polymorphism. In a microfabricated device according to the invention, DNA fragments or other molecules can be rapidly and accurately typed using relatively small samples, by measuring for example the signal of an optically-detectable (e.g., fluorescent) reporter associated with the polynucleotide fragments.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
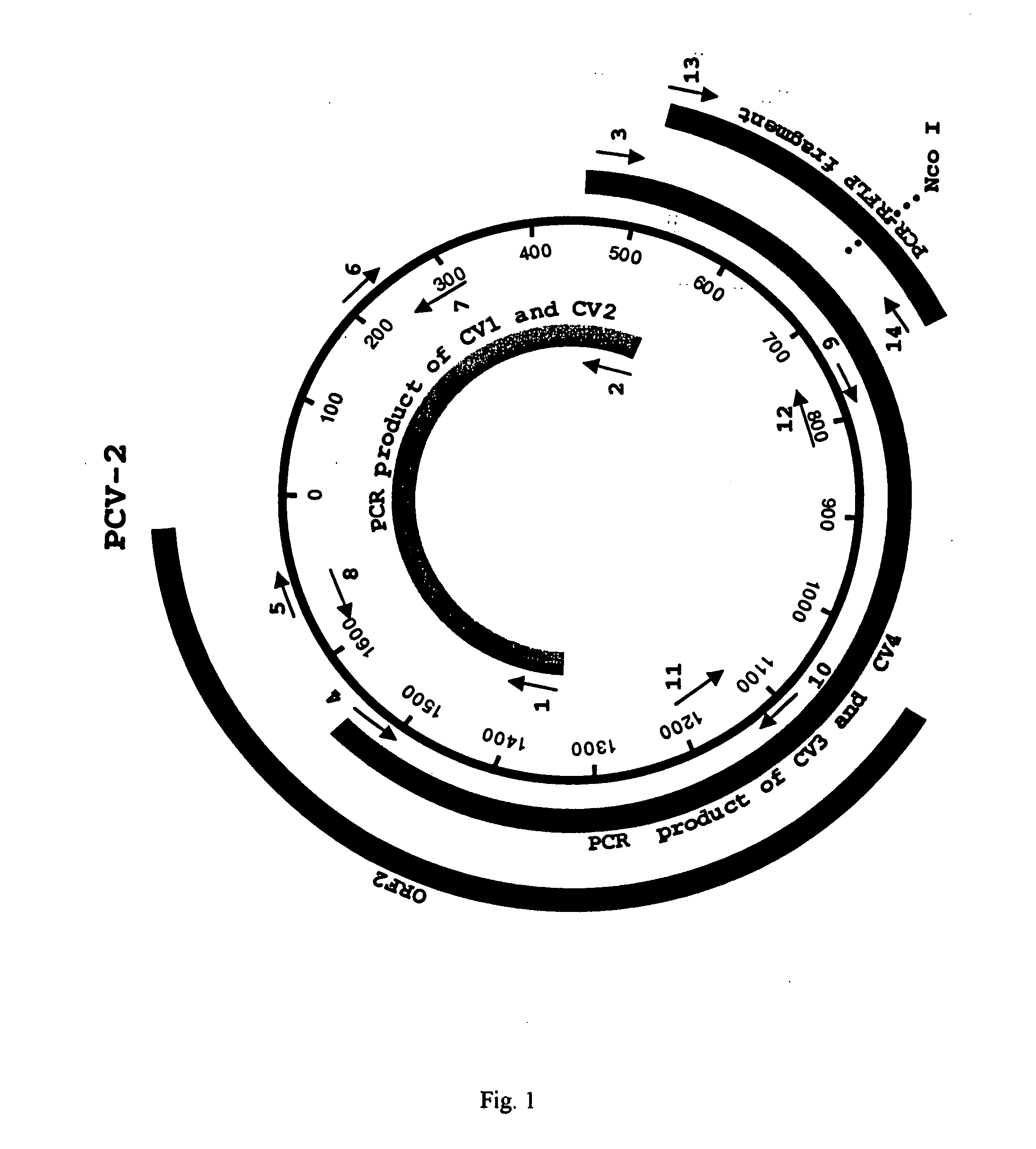
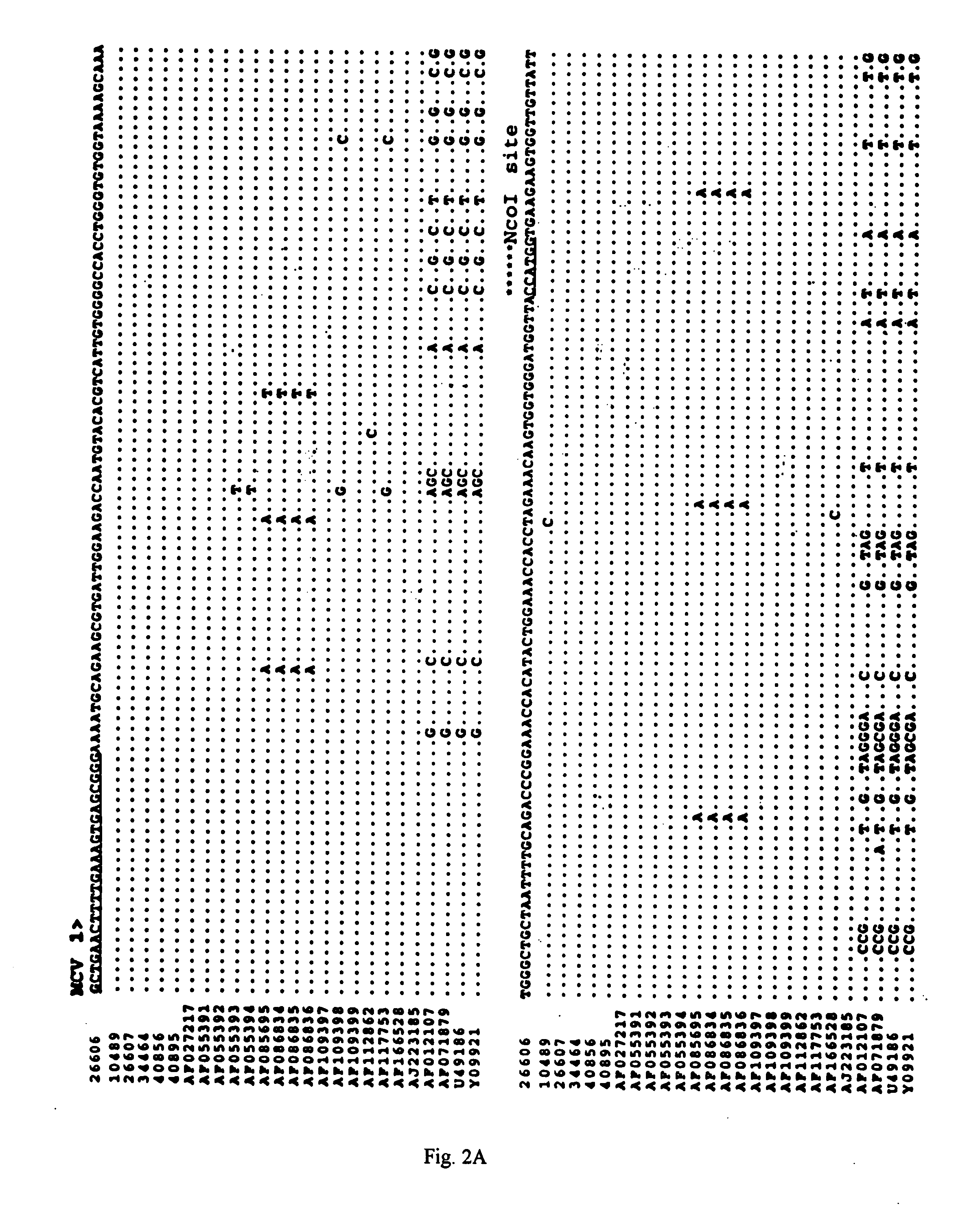
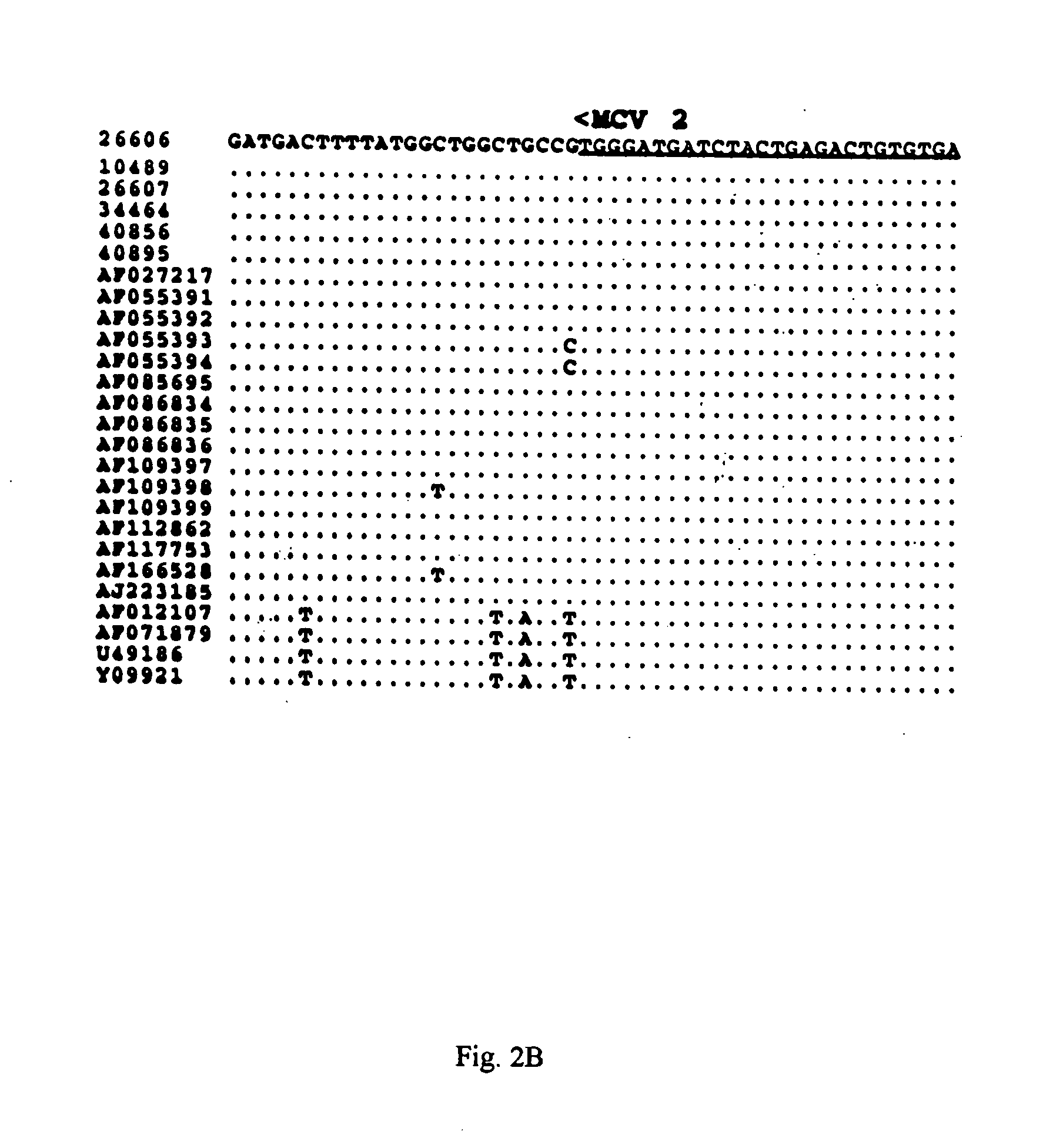
Differential PCR-RFLP assay for detecting and distinguishing between nonpathogenic PCV-1 and pathogenic PCV-2
InactiveUS20050147966A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionNucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for detecting and differentiating PCV infections in a biological sample taken from a pig which involves amplifying a fragment from an extracted nucleic acid; digesting the fragment with a suitable restriction enzyme such as the unique NcoI restriction enzyme; forming a restriction fragment length polymorphism pattern; and then detecting the presence or absence of a PCV isolate. The invention further concerns the new oligonucleotide primers for differentiating PCV infections comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of MCV1 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 and MCV2 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:2. Moreover, this invention provides a novel kit for detecting and distinguishing PCV infections that includes the new oligonucleotide primers and the suitable restriction enzyme.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
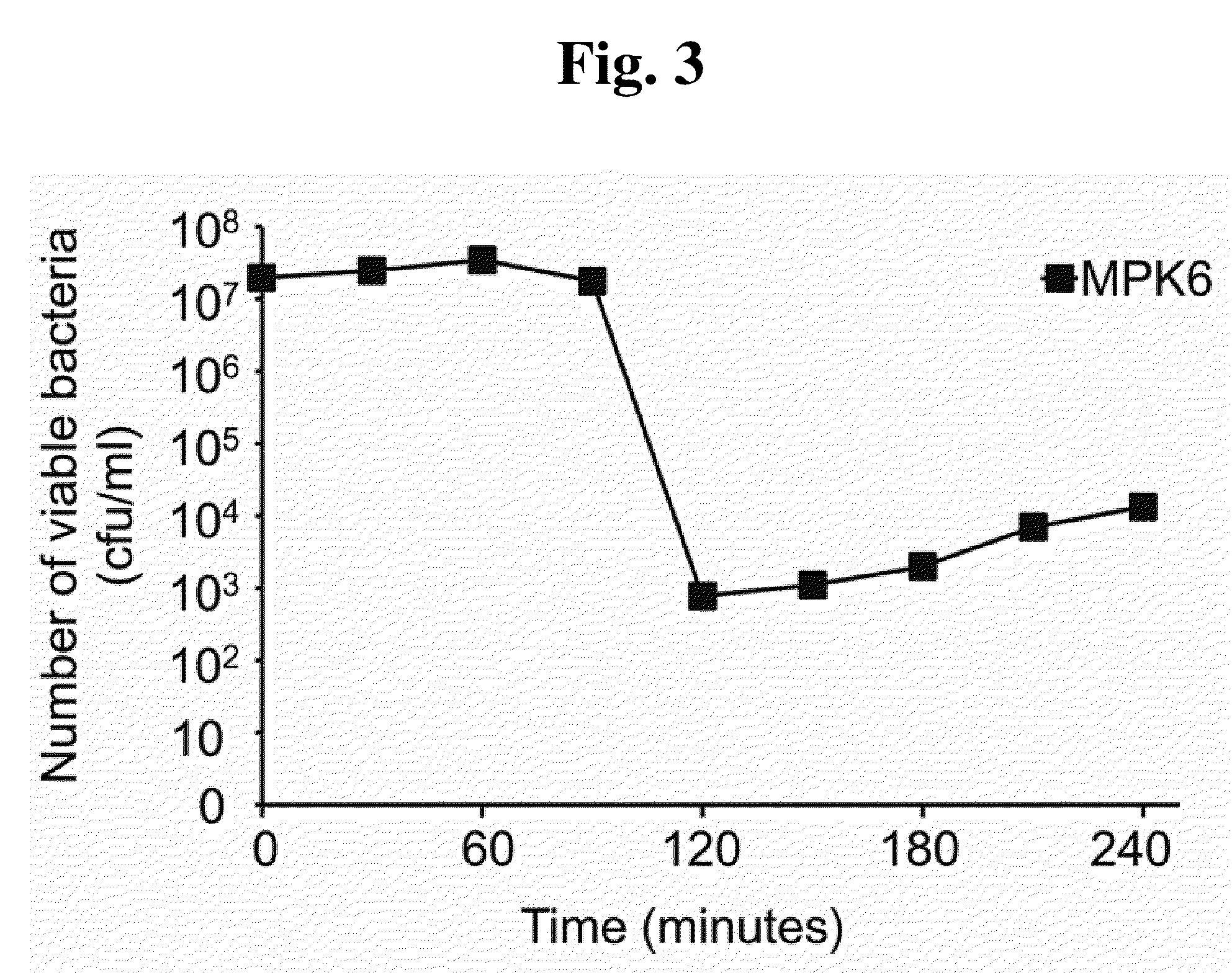
Phage therapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
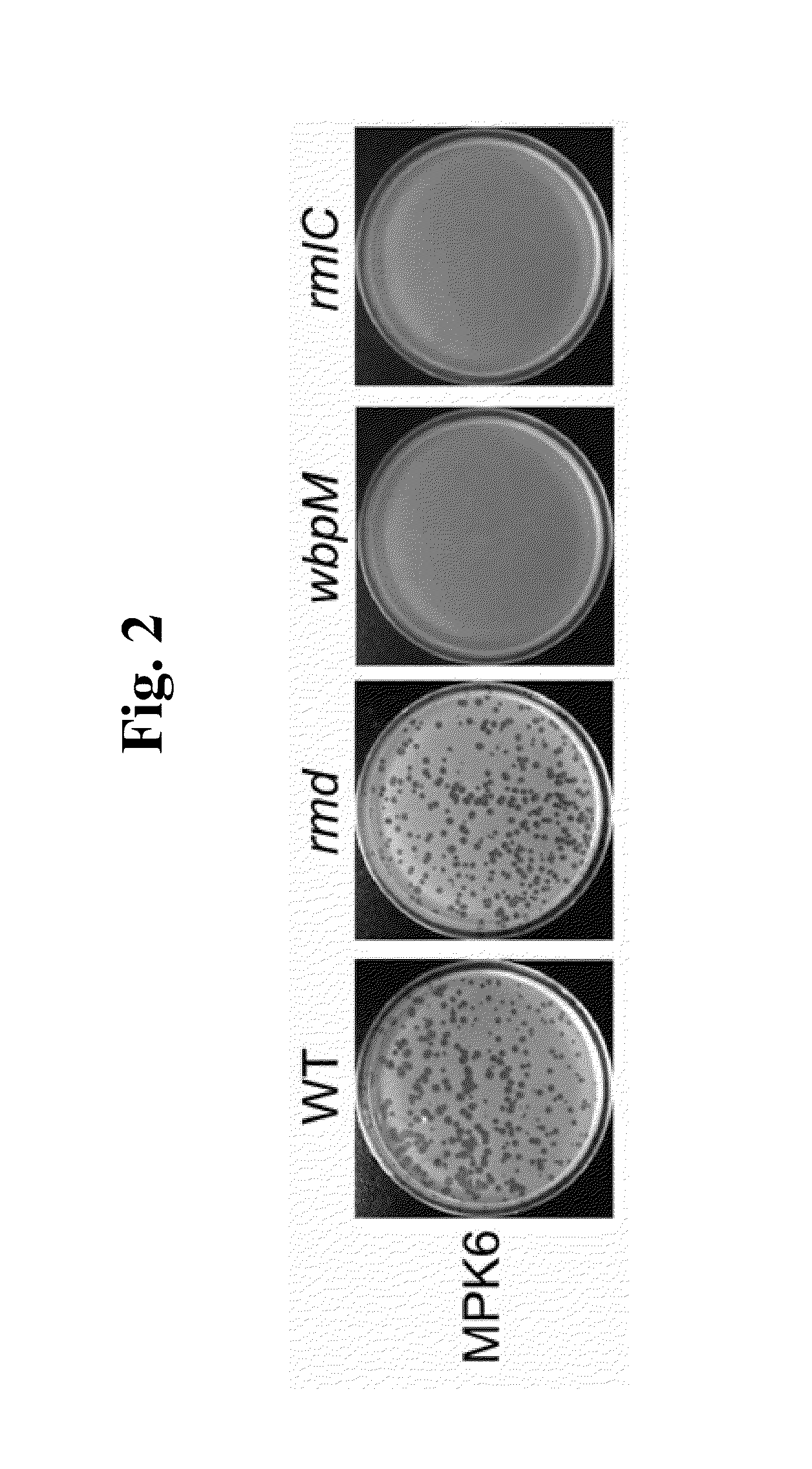
This invention relates to a bacteriophage MPK6 (deposit number: KCCM 11044P) having a lytic activity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or a progeny bacteriophage thereof having a RFLP (Restriction fragment length polymorphism) DNA profile substantially equivalent to the bacteriophage MPK6. The present invention provides a bacteriophage MPK6 or a progeny bacteriophage thereof capable of treating a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection disease, and suggests an anti-bacterial activity of MPK6 and its progeny bacteriophage using a mammalian and non-mammalian infection model. According to the present invention, the present bacteriophage MPK6 or progeny bacteriophage thereof represents very effective efficacy on treatment of P. aeruginosa-induced peritonitis-sepsis.
Owner:IND UNIV COOP FOUND SOGANG UNIV
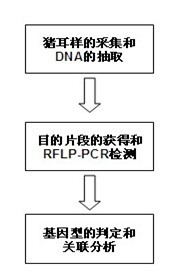
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker related to litter size of sow and application thereof
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker related to the litter size of a sow and application thereof. The SNP molecular marker provided by the invention is positioned on G+701C and T+4578C sites of a GDF2 (Growth Differentiation Factor 2). By designing the primers, the two obtained sequences are respectively positioned on Exons 1 and 2 of the gene GDF2 of the sow, the 701bp of the gene GDF2 (ENSSSCG00000010375) sequence recorded in the Ensemble database has one G701-C701 base mutation and results in the change (Ala-114-Pro) of the amino acid, and the 4578bp has one T4578-4578C base mutation which is a synonymous mutation. An RFLP-PCR (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism-Polymerase Chain Reaction) method is used for researching the polymorphism of the site. The invention provides a new marker for molecular marker-assisted selection of sows.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Differentiation of avian infectious bronchitis virus serotypes
InactiveUS6214538B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSerotypeRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The present invention relates, in general, to the genetics of viruses. In particular, the present invention provides methods of distinguishing between serotypes of avian infectious bronchitis virus based on restriction fragment length polymorphisms derived from the region of the S1 gene of IBV, peptides derived from the restriction fragments, related primers for polymerase chain reaction, and certain restriction length polymorphism patterns.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Primer, kit and method for differentiating fins of different spieces of sharks by polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis (PCR-RFLP)
InactiveCN101984076AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideOligonucleotide primers
The invention relates to oligo nucleotide for differentiating fins of different species of sharks, a method for detecting differentiating fins of different species of sharks by polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis (PCR-RFLP), a detection kit for differentiating fins of different species of sharks by the PCR-RFLP, and application of the oligo nucleotide in identifying fins of different species of sharks. The oligo nucleotide primer, the detection kit and the PCR-RFLP detecting method can simply, quickly, specifically and sensitively detect the fins of different species of sharks.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
PCR-RFLP rapid detection method for common sturgeons
InactiveCN103436610AAccurate identificationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurement3-deoxyriboseSturgeon
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and taxonomy and discloses a PCR-RFLP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) rapid detection method for common sturgeons as well as a primer and a kit for the rapid detection method. The PCR-RFLP rapid detection method for the common sturgeons comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting a genome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a sample to be detected as a template; secondly, carrying out PCR amplification reaction to obtain a PCR product by taking the genome DNA as the template; thirdly, digesting the PCR product by using restriction endonuclease to obtain a digested product; fourthly, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis detection on the PCR product and the digested product and identifying species according to electrophoretogram. According to the PCR-RFLP rapid detection method disclosed by the invention, the simplicity in operation is realized; a small amount of fin rays or muscle is needed to be sheared on the basis of ensuring the survival of fingerling; the identification of fingerlings of the common sturgeons is quickly and accurately carried out; the accuracy and the reliability of the identification result are improved; the working efficiency is greatly increased.
Owner:徐鹏
Chicken heat resistance-associated molecular marker and identification method and use thereof
InactiveCN102154266AGood thermal adaptabilitySimple conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRestriction fragment length polymorphismMolecular marker
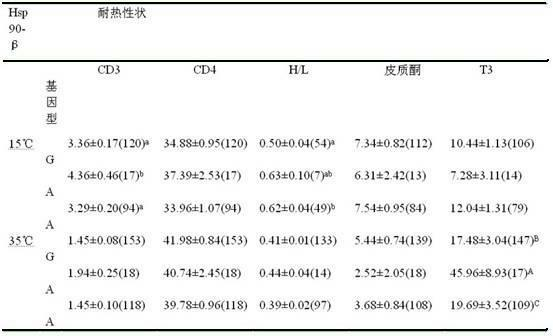
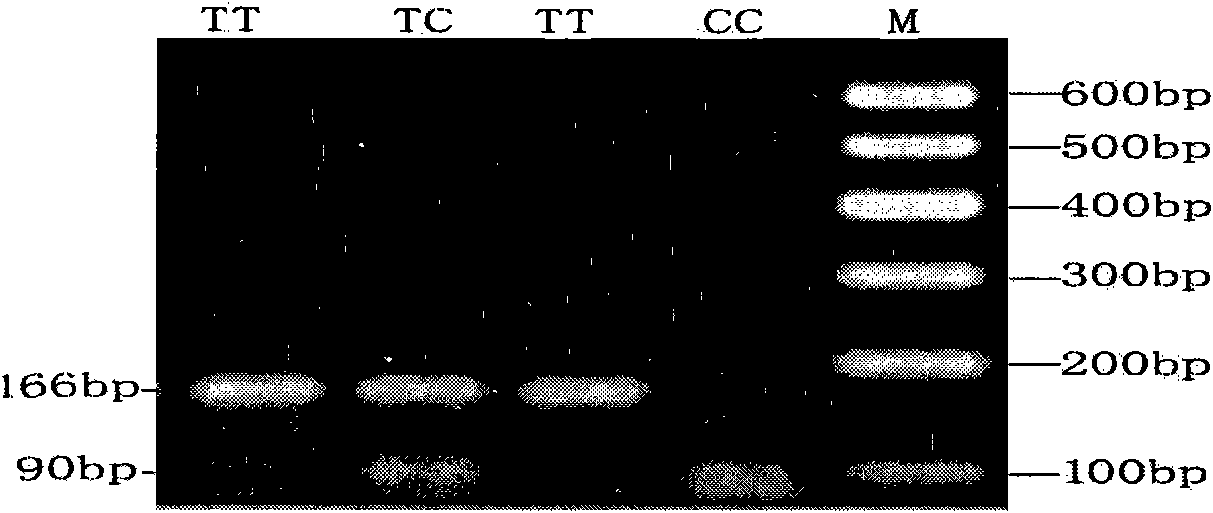
The invention discloses a chicken heat resistance-associated molecular marker and an identification method and use thereof. The molecular marker is G-141A which is positioned in a 5' flanking region in a chicken heat stress protein 90-beta gene. In the invention, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the 5' flanking region in the chicken heat stress protein 90-beta gene, the product of the amplification is subjected to sequencing and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) screening, the screened SNP is subjected to PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism(RFLP) in a large population, the obtained typing result and the heat resistance property index of the population are subjected to association analysis, an SNP locus which is associated obviously is initially determined as heat resistance property auxiliary selection molecular marker, and chicken of a GG genotype has high heat resistance in a high-temperature environment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method for distinguishing goose parvovirus from muscovy duck parvovirus
ActiveCN103409562AIdentification method is simpleImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDistinctinRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method for distinguishing a goose parvovirus from a muscovy duck parvovirus. According to the PCR-RFLP method, NS gene sequence digestion site difference is used for distinguishing the goose parvovirus from the muscovy duck parvovirus. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), carrying out PCR amplification to obtain an NS gene segment, and carrying out RFLP analysis after EcoRI digestion is carried out. The PCR-RFLP method for distinguishing the goose parvovirus from the muscovy duck parvovirus is simple and high in efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-restricted fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method for quickly detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of goat Lhx3 gene
InactiveCN101921853AAvoid instabilitySolve the cost problemMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBiology
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP method for quickly detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of a goat Lhx3 gene. The genetic polymorphism is base polymorphism of T or C at a position-5557 of the goat Lhx3 gene. The method for detecting the SNP of the goat Lhx3 gene comprises the following steps of: performing PRC amplification on the goat Lhx3 gene by using the DNA of a goat genome to be detected which comprises the Lhx3 gene as a template and using a primer pair P as primers; and digesting a PCR amplification product by using a restriction enzyme, performing agarose gel electrophoresis on digested segments, and determining the SNP on the position-5557 of a goat according to the result of the agarose gel electrophoresis. The method is easy to operate, quick, low in cost, high in detection precision and convenient to popularize and use.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method for distinguishing honeysuckle and lonicerae flos
InactiveCN103290127AGood effectIncrease demandMicrobiological testing/measurementLonicerae flosRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention belongs to the technical field of distinguishing traditional Chinese medicinal materials, and in particular relates to a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method for distinguishing honeysuckle and lonicerae flos. The feature DNA base sequence of the honeysuckle is 5'-Y GGCCR-3' and can be identified and cut by restriction enzyme CfrI or EaeI. The distinguishing process comprises the following steps of: extracting medicinal material DNA; performing PCR amplification by a pair of primers; digesting a PCR product by the restriction enzyme CfrI or EaeI; performing agarose gel electrophoresis analysis on the result; and comparing the result with a PCR-RFLP feature result of the lonicerae flos, and judging whether the test piece is the honeysuckle or the lonicerae flos. The quick, convenient and reliable PCR-RFLP method is realized according to the difference between the DNA sequences of the honeysuckle and the lonicerae flos; and the PCR-RFLP method has an important significance for guaranteeing the quality of a honeysuckle medicinal material, cracking down the ill behavior that sellers sell the lonicerae flos as the honeysuckle and protecting the rights and interests of customers.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
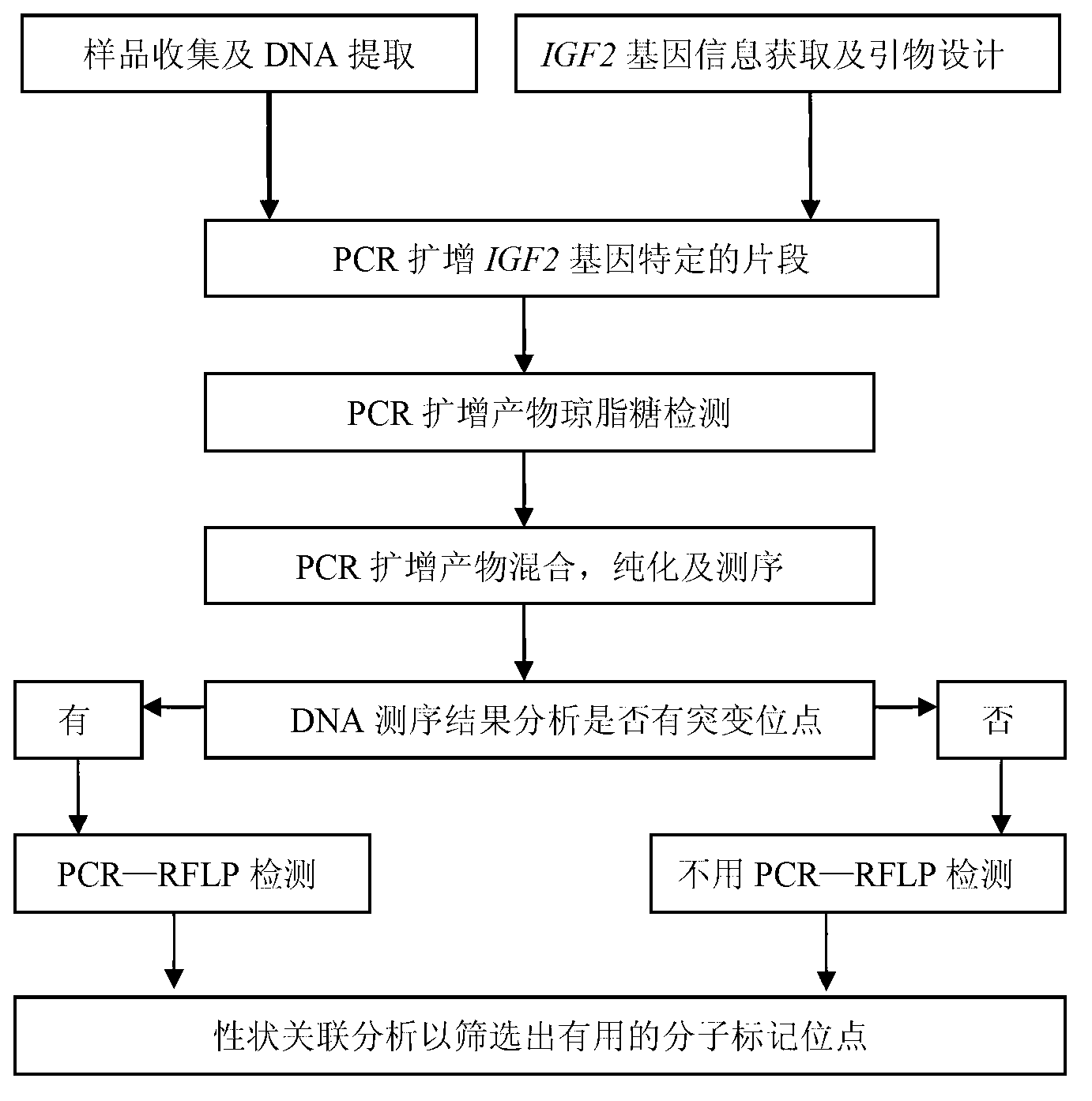
Detecting method and kit of cattle IGF2 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 2) gene mononucleotide polymorphism
InactiveCN103290123AAccurate detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular geneticsRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention discloses a detecting method and a kit of cattle IGF2 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 2) gene mononucleotide polymorphism. The detecting method comprises the following steps of: with IGF2-gene-containing cattle whole genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) to be detected as a template, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the cattle IGF2 gene; and detecting and quickly parting the gene polymorphism through DNA sequencing and polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) technology. The detecting method is used for screening and detecting a molecular genetic marker closely related to cattle growth traits on DNA level. The detecting method disclosed by the invention can be used for molecular marker-assisted selection of cattle growth traits so as to quickly create cattle population with excellent genetic resources. The detecting method disclosed by the invention is simple, low in cost, direct and reliable in detecting result and fit for screening and diagnosing the cattle IGF2 gene mutation sites in large scale.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
PCR-RFLP rapid detection method for common sturgeons
InactiveCN103436611AAccurate identificationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurement3-deoxyriboseSturgeon
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and taxonomy and discloses a PCR-RFLP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) rapid detection method for common sturgeons as well as a primer and a kit for the rapid detection method. The PCR-RFLP rapid detection method for the common sturgeons comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting a genome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a sample to be detected as a template; secondly, carrying out PCR amplification reaction to obtain a PCR product by taking the genome DNA as the template; thirdly, digesting the PCR product by using restriction endonuclease to obtain a digested product; fourthly, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis detection on the PCR product and the digested product and identifying species according to electrophoretogram. According to the PCR-RFLP rapid detection method disclosed by the invention, the simplicity in operation is realized; small amount of fin rays or muscle is needed to be sheared on the basis of ensuring the survival of fingerlings; the identification of fingerlings of the common sturgeons is quickly and accurately carried out; the accuracy and the reliability of the identification result are improved; the working efficiency is greatly increased.
Owner:徐鹏
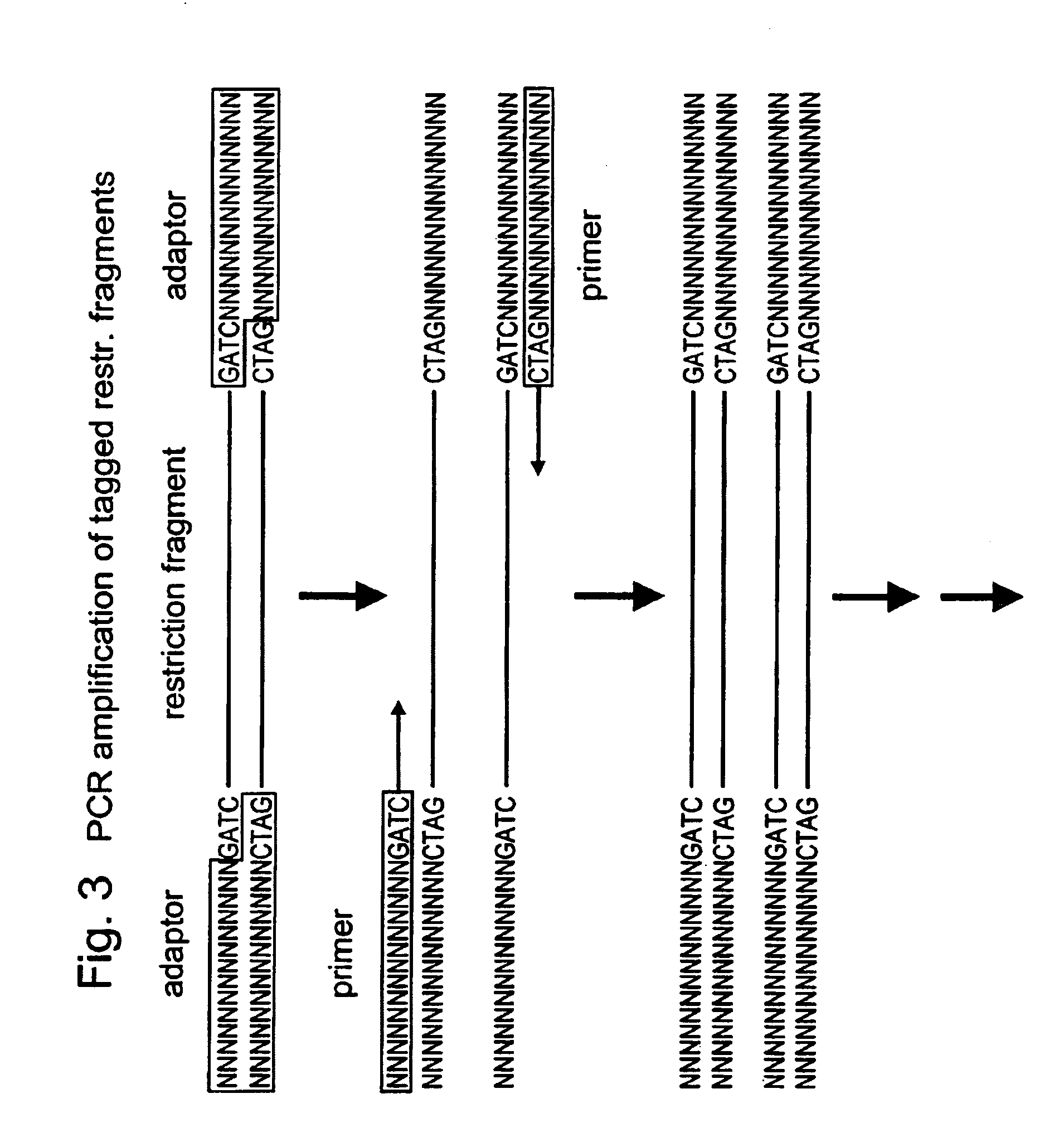
Selective restriction fragment amplification: fingerprinting
InactiveUS7026115B1Enable amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction siteRFLP - Restriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention relates to a process for the controlled amplification of at least one part of a starting DNA containing a plurality of restriction sites for a determined specific restriction endonuclease, and of which at least part or its nucleic acid is unknown.Application of this process to human, animal or plant DNA fingerprinting, to identification of restriction fragment length polymorphisms.Kit for the application of the process.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Method for fast identifying harmful algae
InactiveCN101824481AQuick and easy preliminary identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementRed tideRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention discloses a method for fast identifying harmful algae. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: a, preparation of experimental algae f / 2 and derivative culture media of the experimental algae; b, design and verification of primers; c, obtaining of 18s rDNA fragment of the experimental algae; d, optimization and propagating of (polymerase chain reaction) PCR; e, control experiment of simulated enzyme cutting and practical enzyme cutting; and f, identification of the harmful algae by using restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). As a molecule ecological means for identifying the harmful algae, the method can serve as the supplementary means and auxiliary means of the conventional identification methods. The method establishes a characteristic map based on FELP, standardizes the whole flow, and is favorable for initially identifying the harmful algae fast, easily and conveniently and pre-alarming the outbreak of the red tide of phytoplankton.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Identification of white leghorns red plumage mutagenic mutant genotype and cultivation method for supporting system of red plumage pink shell layer chickens
PendingUS20210007334A1Broad prospect for promotionShorten the generation intervalHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand
The present invention discloses a method for breeding the commercial strains of red feather pink-shell laying hens. It provides a primer pair for identifying the red feather causative mutation homozygous genotype of white leghorn chickens, which is composed of the single-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 2 of the Sequence List and the single-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 3 of the list. After the primer was designed according to the upstream and downstream nucleotide sequences of the 18,288,303rd deoxynucleotide in the positive-sense strand of the 11th chromosome as shown in the sequence information of the chicken reference genome Gallus_gallus-4.0 version published in NCBI, the genotype (SNP) at this site is tested through the restriction fragment length polymorphism, the genotype of the site (SNP) was tested through the restriction fragment length polymorphism; the offspring hens obtained by cross breeding the homogenous female parent (the homogenous female parent was obtained through expanded propagation of the white leghorn chickens with the red feather causative mutation homozygous genotype) and the Rhode Island Red rooster as a male parent are all of red feather phenotype, meeting the market demands and enjoying a broad prospect for promotion.
Owner:BEIJING HUADU YUKOU POULTRY
Method for breeding lean-type Chinese Huai pigs in multi-gene pyramiding manner based on growth traits thereof
InactiveCN101921859AImprove accuracyShorten the generation intervalMicrobiological testing/measurementInsulin-like growth factorCorrelation analysis
The invention relates to a method for breeding lean-type Chinese Huai pigs in a multi-gene pyramiding manner based on growth traits thereof. The method comprises the following operating steps: 1, carrying out DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction on the genome of the pig; 2, designing primers, more particularly, designing the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification primers according to the gene sequences of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), pituitary specific transcription factor-I (PIT-I), liver X receptor alpha (LXR alpha) and melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R); 3, carrying out the PCR; 4, carrying out restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP); and 5, carrying out the correlation analysis on the polymorphism and growth traits of genes. According to the analysis, the method can determine that the single growth rate of the pyramided gene with the gene type thereof being AADDGGFF is the highest one; the method can prevent the genes of other offsprings from being isolated after the selective reservation for breeding, thus achieving the optimal effect of the growth traits of the offsprings on the four gene types; and the method can stabilize the inheritance, particularly lead the genes of the growth traits to become homozygous within one generation, thus accelerating the cultivation of the lean-type Chinese Huai pigs.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Detection method of Chinese simmental cattle carcass and meat quality trait genetic markers
ActiveCN104059963ASolve the cumbersomeFix instabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologySimmental cow
The invention discloses a detection method of Chinese simmental cattle carcass and meat quality trait genetic marker, and the method uses DNA pool sequencing and PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) technology for screening and detection of GPAM (glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, mitochondrial) gene function mutation of Chinese simmental cattle. Through the correlation analysis, Chinese simmental cattle carcass and meat quality trait-related SNPs as a molecular genetic marker is found, and is used in the early selection and molecular pyramiding breeding of beef cattle, and breeding and improving of meat use performance of the Chinese simmental cattle can be further accelerated.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
ESR1 gene polymorphism related to liver cancer and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN101078027AIncreased susceptibilityReduce the risk of liver cancerMicrobiological testing/measurementDirect sequencingHaplotype
This invention proposes a detection method of haplotype comprised of polymophic loci (rs3138774) in (TA)n, rs2077647 in T29C, rs2234693 in Pvu II and (TA)n, T29C, Pvu II and Xba I in susceptibility gene ESR1 relates to liver cancer risk. The methods are PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism), fragment analysis and direct sequencing PCR products. The haplotype is constructed by PHASE program. The invention also relates to the kits detecting susceptibility polymophic locis and using methods. In addition, site(TA)n (rs3138774), T29C(rs2077647) , Pvu II(rs2234693) and the haplotype comprising of (TA)n, T29C, Pvu II and Xba I were related to liver cancer risk. ESR1 is determined as a new susceptibility gene of liver cancer, which provides new genetic consultation content for the liver cancer prevention and control.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Chicken B,D,E-subgroup avian leukaemia genetic resistance related mononucleotide polymorphism molecular marker and application thereof
InactiveCN104152445AAccurate identificationRapid and accurate identification screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryLeucosisNucleotide
The invention discloses a chicken B,D,E-subgroup avian leukaemia genetic resistance related mononucleotide polymorphism molecular marker and application thereof. The molecular marker is TVB gene DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence SNP-3674C / T, or TVB gene coding sequence SNP-298C / T. The molecular marker can be used for identifying chicken B,D,E-subgroup avian leukaemia genetic resistance characteristics; correspondingly, the molecular marker can be distinguished by a PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) process, and can be used for resistance breeding to control the risk of B,D,E-subgroup avian leukaemia from the source; and the molecular marker has the advantages of high purposiveness and the like, is simple to operate and easy to implement, greatly lowers the screening cost, and thus, has important practical meanings.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
SNP marker related to tail type trait of fat tail type sheep, and applications thereof
ActiveCN108384859ASpeed up the breeding processAn Accurate and Reliable Method for Detecting Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of T Gene in Fatty-tailed SheepMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTailRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention relates to a SNP marker related to the tail type trait of fat tail type sheep, and applications thereof, and belongs to the biological field, wherein the SNP marker is located at the 87804589-th base pair of sheep chromosome 8, the sheep with the base of T at the locus has the short tail trait, and the sheep with the base of G has the normal tail length. The invention further provides primers for detecting the SNP marker, a kit containing the primers, and applications of the SNP marker in identification of the tail type trait of lipid tail type sheep and in breeding of Chinese sheep, wherein the SNP marker related to the tail type trait of fat tail type sheep is screened by using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and a sequencing technology, and the genotype of to-be-detectedsheep is detected through a restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method. According to the present invention, with the SNP marker, the breeding of the dominant species with the tail type trait of fat tail type sheep is performed according to the genotype so as to accelerate the breeding process of the fat tail type sheep.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method and kit for detecting polymorphism of ADPRT gene
InactiveCN101570778AIncrease flexibilityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAReverse primer
The invention discloses a method for detecting the polymorphism of an ADPRT gene, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (a) human genomic DNA is used as a template, and a positive primer and a reverse primer of a gene sequence are designed in a region of an ADPRT gene locus; a single basic group is mismatched on the positive primer so as to introduce an enzyme cutting site; and the template genomic DNA is processed by specificity polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification; (b) a restriction enzyme is utilized to carry out enzyme cutting on the genomic DNA; and (c) segment size separation is carried out on the ADPRT gene according to agarose gel electrophoresis so as to determine the gene polymorphism of the ADPRT gene. The invention also discloses a kit for detecting the ADPRT gene polymorphism, which comprises a gene polymorphism primer for amplification, dNTPs, DNA polymerase for the PCR reaction, a buffer solution of the DNA polymerase, a restriction enzyme Bsh1236I for restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and a corresponding buffer solution. The method has simple operation, low cost, intuitional judging result, quick reaction and convenient popularization and application, and the kit is convenient to use.
Owner:夏昭林 +2
PCR-RFLP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) method for differentiating duck circovirus from goose circovirus
ActiveCN103602759AIdentification method is simpleImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDistinctinRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) method for differentiating duck circovirus from goose circovirus. The PCR-RFLP method is used for differentiating by utilizing Rep protein gene sequence enzyme cutting site difference and comprises the following steps of: extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), carrying out PCR amplification to obtain a Rep protein gene segment, and carrying out RFLP analysis after carrying out XhoI digestion. The PCR-RFLP method disclosed by the invention is simple and higher in efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method for identifying seven sea cucumber species
InactiveCN103014175AOvercome accuracyOvercome workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionRestriction enzyme digestion
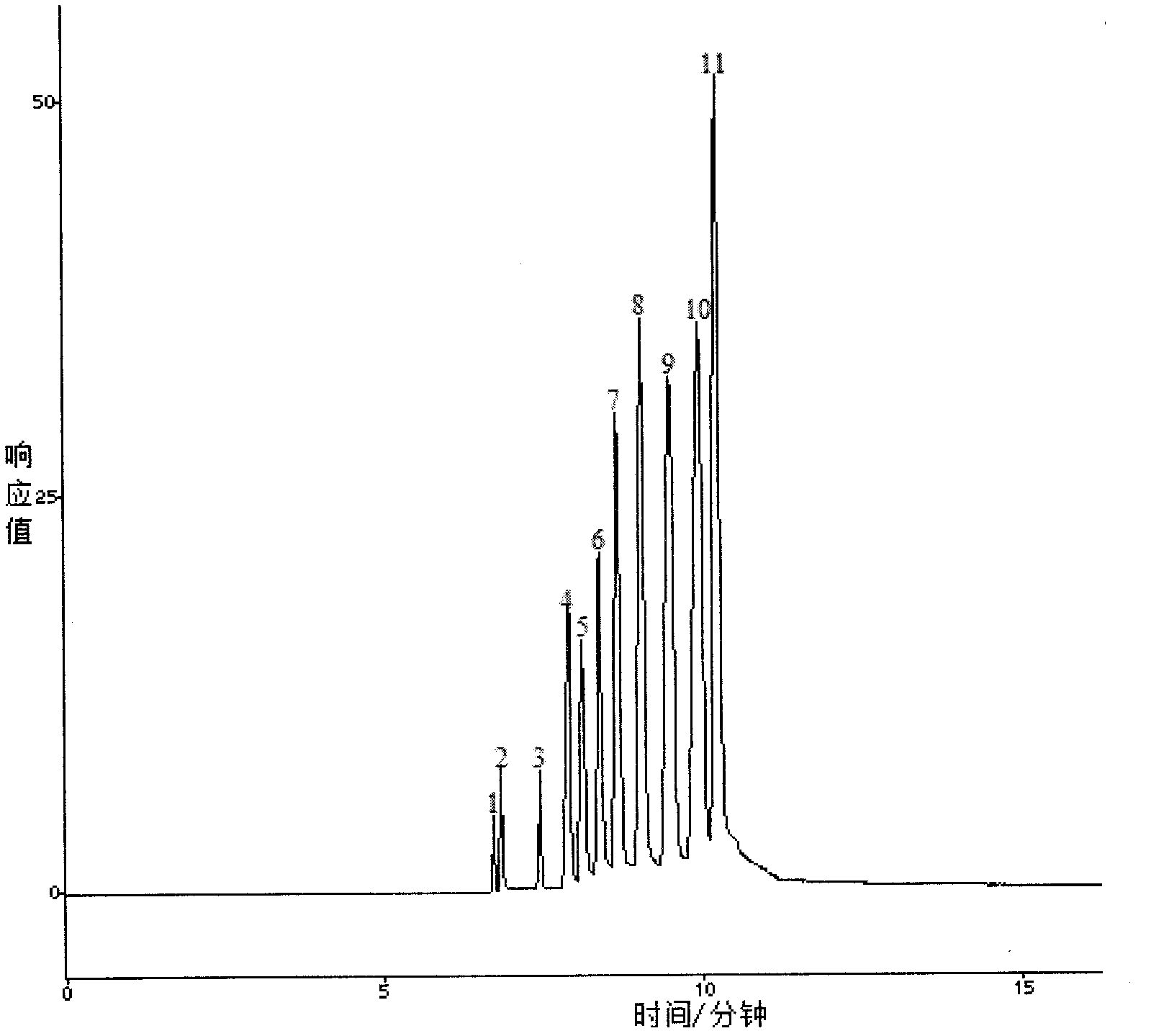
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method for identifying seven sea cucumber species. The PCR-RFLP method includes the steps of firstly extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) modules of sea cucumbers; subjecting specificity fragment of a CO I (coenzyme I) gene to PCR amplification to obtain a fragment about 690bp; secondarily subjecting amplified product to restriction enzyme digestion; and finally subjecting the enzyme-digested product to electrophoresis detection. Different sea cucumbers obtain stripes in different numbers and sizes, and selected specificity incision enzymes respectively include: Californian paracanthurus cucumber: SSP I, North Atlantic Ocean cucumaria: EcoR V, apostichopus japonicas: SSP I, thelenota ananas: EcoR V, acaudina molpadioidea: Sca I, isostichopusbadionotus: Pvu II, and actinopyga mauritiana: EcoR V and SSP I. The PCR-RFLP method overcomes the defects that a conventional morphological identification method is prone to affecting in accuracy, is heavy in workload and long in consumption time and the like. The PCR-RFLP method can be completed by only one-time PCR reaction, one-time enzyme digestion reaction and one-time polypropylene gel electrophoresis, and is simple to operate, short in parting time and good in specificity.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker related to Marsupenaeus japonicus heat resistance and detection method thereof
InactiveCN105567865AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringCorrelation analysisBiology
The invention provides an SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker related to Marsupenaeus japonicus heat resistance and a detection method thereof, relating to detection of shrimp heat-resistant populations in aquiculture. The invention firstly provides an SNP marker related to Marsupenaeus japonicus heat tolerance by using a direct sequencing process. The SNP marker related to Marsupenaeus japonicus heat tolerance is the 3289th site of the HSP60 gene of which the nucleic acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.1, and the base is A or G. The detection method comprises the following steps: carrying out a Marsupenaeus japonicus heat resistance experiment; calculating the heat resistance value; carrying out genotyping by using a PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) technique; and analyzing the heat tolerance of the Marsupenaeus japonicus individuals with different genotypes. The direct sequencing process and the PCR-RFLP process are utilized to give out the polymorphism of the MjHSP60 gene, and the correlation analysis is carried out on the SNP polymorphism and Marsupenaeus japonicus heat tolerance, thereby providing theoretical references for screening high-temperature-resistant SNP molecular markers and developing molecular breeding of Marsupenaeus japonicus heat-resistant lines.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Anther culture method for indica japonica hybrid rice
ActiveCN103782908AImprove flower cultivation efficiencyLarge group sizePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAge limitGenetic engineering
The invention discloses an anther culture method for indica japonica hybrid rice. The method comprises the following steps: sampling, identifying a microspore development period, low-temperature pretreatment, young wheatear sterilization, anther inoculation, still dark cultivation at 25+ / - 2 DEG C until the diameter of embryonic callus is 2-3mm; carrying out a redifferentiation stage to form complete regenerated plants with haploid or double haploids. The double haploids are good breeding materials, and can be directly used for breeding of new varieties or varietal improvement; the breeding age limit is greatly shortened; the selection efficiency is improved; the double haploids also are ideal materials for molecular markers, such as amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP), restricted fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP), randomly amplified polymorphic deoxyribonucleic acid (RAPD) and the like, genetic map drawing, and researches on animal evolution, genetic analysis, plant gene cloning and screening, genetic engineering breeding and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NONGKE SEED IND
Method for detecting tumor mutant gene in blood
InactiveCN102251046AGuaranteed accuracyGood temperature control systemMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAbnormal tissue growthSingle-strand conformation polymorphism
The invention relates to a method for detecting a tumor mutant gene in blood. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a polyethylene oxide sieving medium containing TBE (Tetrabromoethane); (2) extracting a genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) in a blood sample; (3) amplifying a gene target fragment needing to be detected: performing conventional PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by taking the genome DNA as an amplifying template to obtain a p53 gene PCR amplification sample and a k-ras gene PCR amplification sample; (4) treating the samples: performing denaturation or enzyme digestion on the p53 gene PCR amplification sample and the k-ras gene PCR amplification sample to obtain a denatured sample solution and an enzyme digestion solution respectively; and (5) detecting the samples: adding a 10*SYBR Green I fluorescence dye and the genome DNA into the denatured sample solution and the enzyme digestion solution respectively, uniformly mixing, adding deionized water till a system is 30-50 mu l, automatically filling the polyethylene oxide sieving medium by using a capillary electrophoresis apparatus pressure system and performing CE-SSCP (Capillary Electrophoresis-Single Strand Conformation Polymorphism) detection or CE-RFLP (Capillary Electrophoresis-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) detection respectively. The method is easy to operate, and has high repeatability.
Owner:王荣
Phage Therapy Against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
This invention relates to a bacteriophage MPK6 (deposit number: KCCM 11044P) having a lytic activity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or a progeny bacteriophage thereof having a RFLP (Restriction fragment length polymorphism) DNA profile substantially equivalent to the bacteriophage MPK6. The present invention provides a bacteriophage MPK6 or a progeny bacteriophage thereof capable of treating a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection disease, and suggests an anti-bacterial activity of MPK6 and its progeny bacteriophage using a mammalian and non-mammalian infection model. According to the present invention, the present bacteriophage MPK6 or progeny bacteriophage thereof represents very effective efficacy on treatment of P. aeruginosa-induced peritonitis-sepsis.
Owner:IND UNIV COOP FOUND SOGANG UNIV
Method for identifying red feather-induced mutant genotype of white leghorns and breeding method for complete set line of red feather pink shell laying hens
ActiveCN108192981ATo satisfy the market's needsAvoid the tediousness of test cross breedingHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand
Owner:BEIJING HUADU YUKOU POULTRY
Method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of sheep PCNP (PEST-Containing Nuclear Protein) gene by using PCR-RFLP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) and application of method
ActiveCN106755371AAccurately estimate breeding valuesImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular geneticsBiology
The invention discloses a method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of a sheep PCNP (PEST-Containing Nuclear Protein) gene by using PCR-RFLP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out PCR amplification on a sheep PCNP gene segment by taking a sheep whole genome DNA to be measured as a template and taking a primer pair P as a primer; after a PCR amplification product is digested by a restriction enzyme SPhI, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis on the digested amplified segment; authenticating the single nucleotide polymorphism of the 5019th site of the sheep PCNP gene according to an electrophoresis result. As a base mutation site is closely associated with the kidding number of sheep reproduction traits, the method is a method for detecting molecular genetic markers closely associated with the sheep reproduction traits at the DNA level, and can be used for auxiliary selection and molecular breeding of sheep and increasing the improved variety breeding speed of the sheep.
Owner:甘肃润牧生物工程有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com