Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
169 results about "Residual magnetic field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The residual magnetic field is the field that remains after the main field windings have been secured. This is closely related to magnetic hysteresis. This residual magnetic field is important for machines like DC generators.
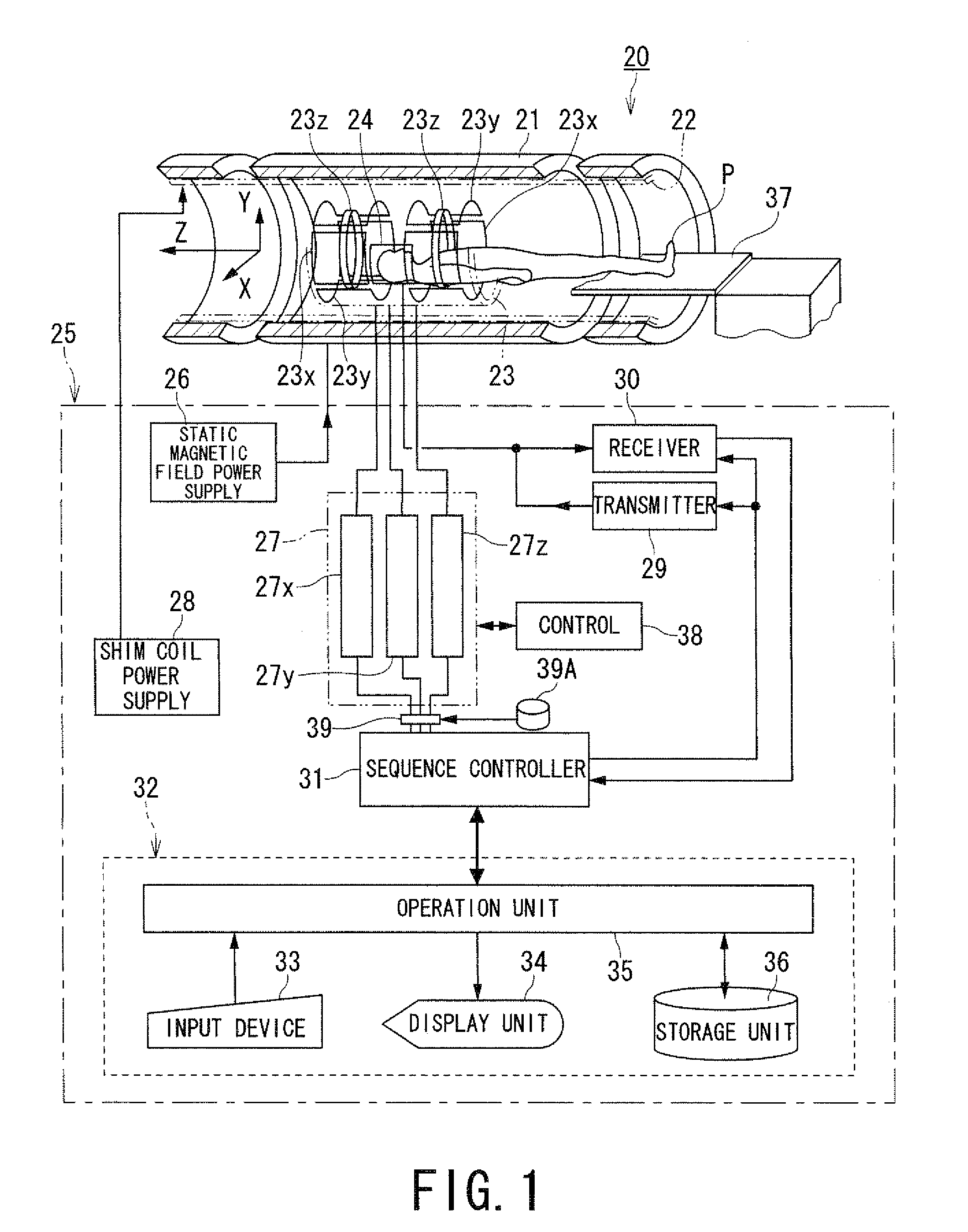
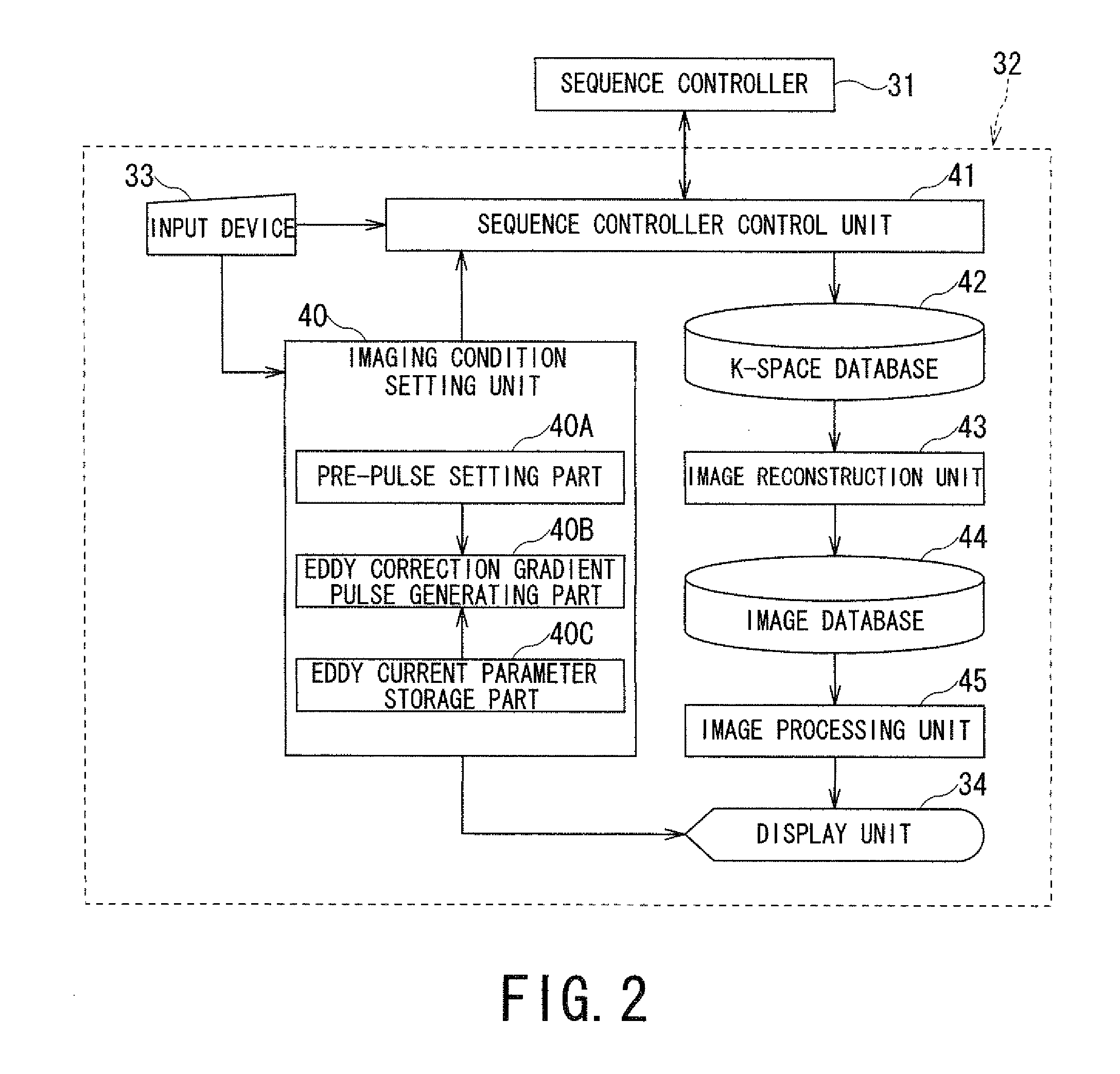
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20100148774A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceResidual magnetic field
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes an imaging unit and a compensation unit. The imaging unit acquires image data by imaging with applying a pre-pulse for controlling a contrast. The compensation unit suppresses a remanent magnetic field having an intensity according to a slice position. The remanent magnetic field is at an application timing of the pre-pulse and due to an eddy current generated by at least one gradient magnetic field applied before applying the pre-pulse.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
System and method for damping vibration in a drill string using a magnetorheological damper
ActiveUS20100224410A1Change viscosityReduce induced remanent magnetic fieldSurveyDrilling rodsAlternatorEngineering
A system for damping vibration in a drill string can include a magnetorheological fluid valve assembly having a supply of a magnetorheological fluid, a first member, and a second member capable of moving in relation to first member in response to vibration of the drill bit. The first and second members define a first and a second chamber for holding the fluid. Fluid can flow between the first and second chambers in response to the movement of the second member in relation to the first member. The valve assembly can also include a coil for inducing a magnetic field that alters the resistance of the magnetorheological fluid to flow between the first and second chambers, thereby increasing the damping provided by the valve. A remanent magnetic field is induced in one or more components of the magnetorheological fluid valve during operation that can be used to provide the magnetic field for operating the valve so as to eliminate the need to energize the coils during operation except temporarily when changing the amount of damping required, thereby eliminating the need for a turbine alternator power the magnetorheological fluid valve. A demagnetization cycle can be used to reduce the remanent magnetic field when necessary.
Owner:APS TECH
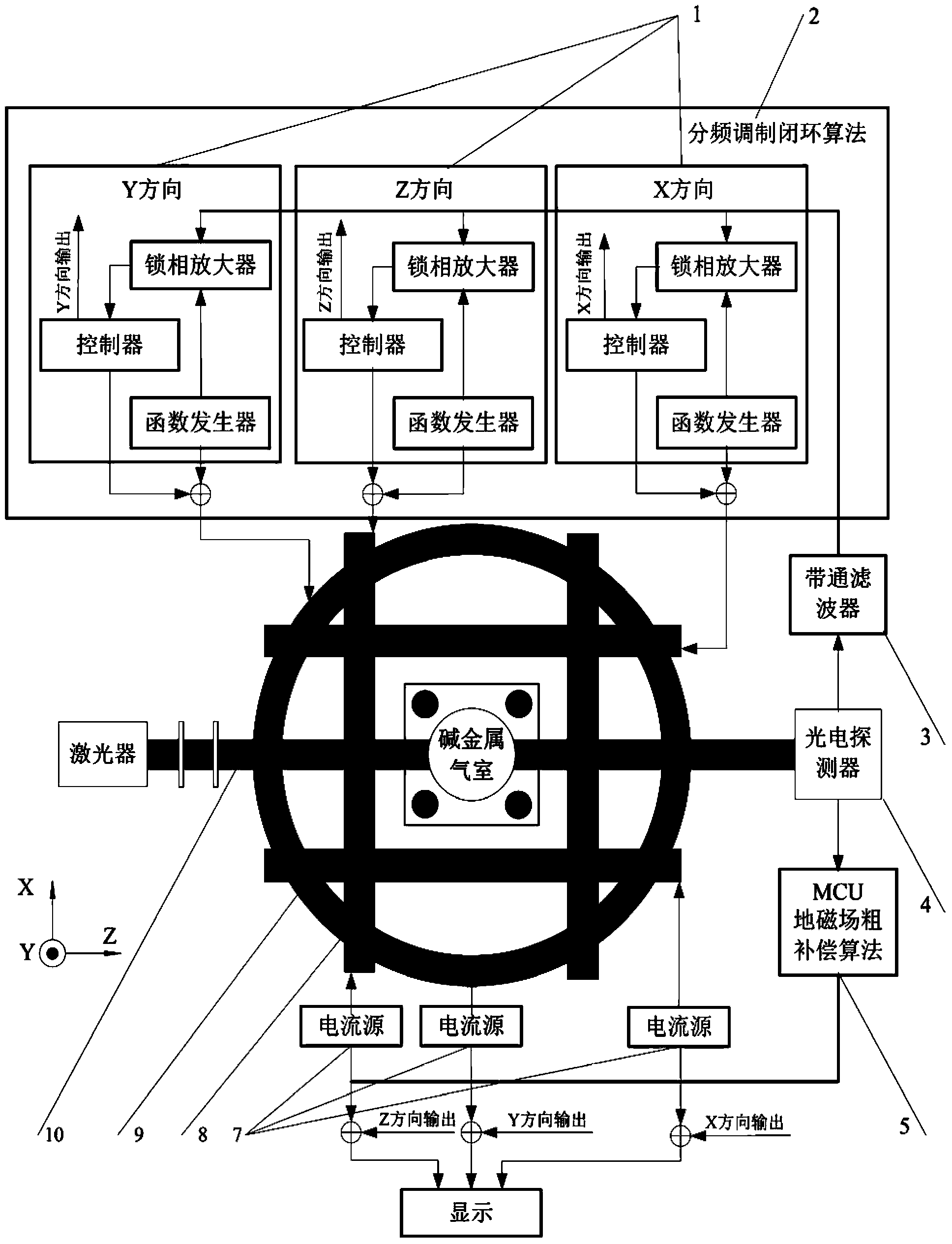
Single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer and detection method thereof
InactiveCN103412268AHigh sensitivitySimple structureMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesClosed loopAlkali metal
The invention discloses a single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer and a detection method of the single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer. The single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer comprises two sets of triaxial orthogonal coils, wherein one set of triaxial orthogonal coils are used for geomagnetic field coarse compensation and the other set of triaxial orthogonal coils are used for closed loop frequency-division modulation. A single beam of pumped laser passes through a heated alkali metal gas chamber and then is received by a photoelectric detector. The detection method of the single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer comprises the following steps that firstly, a geomagnetic field is counteracted by the triaxial orthogonal coils which are controlled in a feedback mode according to a geomagnetic field coarse compensation algorithm of a micro control unit (MCU), and a weak magnetic field environment is created in the gas chamber; secondly, fine compensation for a residual field is completed according to a closed loop frequency-division modulation algorithm; finally, the feedback amount of geomagnetic field coarse compensation and the feedback amount of closed loop frequency-division modulation are added together, so that the size of an external magnetic field is obtained. The single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer and the detection method of the single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer are high in integration level and sensitivity, and capable of obtaining triaxial magnetic field vector information simultaneously, and having wide application prospects in the fields such as deep space exploration and mineral resource exploration.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Thin film perpendicular magnetic recording head, their fabrication process and magnetic disk drive using it
InactiveUS7221538B2Avoid erasureSuppress remanent magnetizationHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageResidual magnetic fieldGigabit
Thin film perpendicular magnetic head with a narrow main pole capable of a high recording density in excess of 100 gigabits per square inch and generating a high magnetic recording field exceeding 10 kOe while suppressing remanent magnetic fields occurring immediately after write operations. The perpendicular magnetic head comprises a main pole, a return path for supplying a magnetic flux to that main pole, and a conductive coil for excitation of the main pole and return path. The main pole has a pole width of 200 nanometers or less, and a magnetic multilayer made up of a high saturation flux density layer and low saturation flux density layer. The low saturation flux density layer has a thickness within 0.5 to 5 nanometers, and The high saturation flux density layer has a thickness from 10 to 50.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Measurement of torsional dynamics of rotating shafts using magnetostrictive sensors
A device and method for the non-contact measurement of dynamic torsion in a rotating shaft using magnetostrictive sensors (MsS). The monitoring and detection system has specially configured magnetostrictive signal detectors that include inductive pick-up coils, in which signals corresponding to localized shaft torques are induced. The basic system sensor utilizes either a permanent DC bias magnet positioned adjacent the rotating shaft or applies a residual magnetic field to the shaft. The techniques described in conjunction with the system are particularly advantageous for on-line monitoring of loaded rotating shafts that are integral parts of power trains, by providing a low-cost and a long-term sensor for acquiring dynamic data of the shaft portion of the machinery system being monitored and / or controlled.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
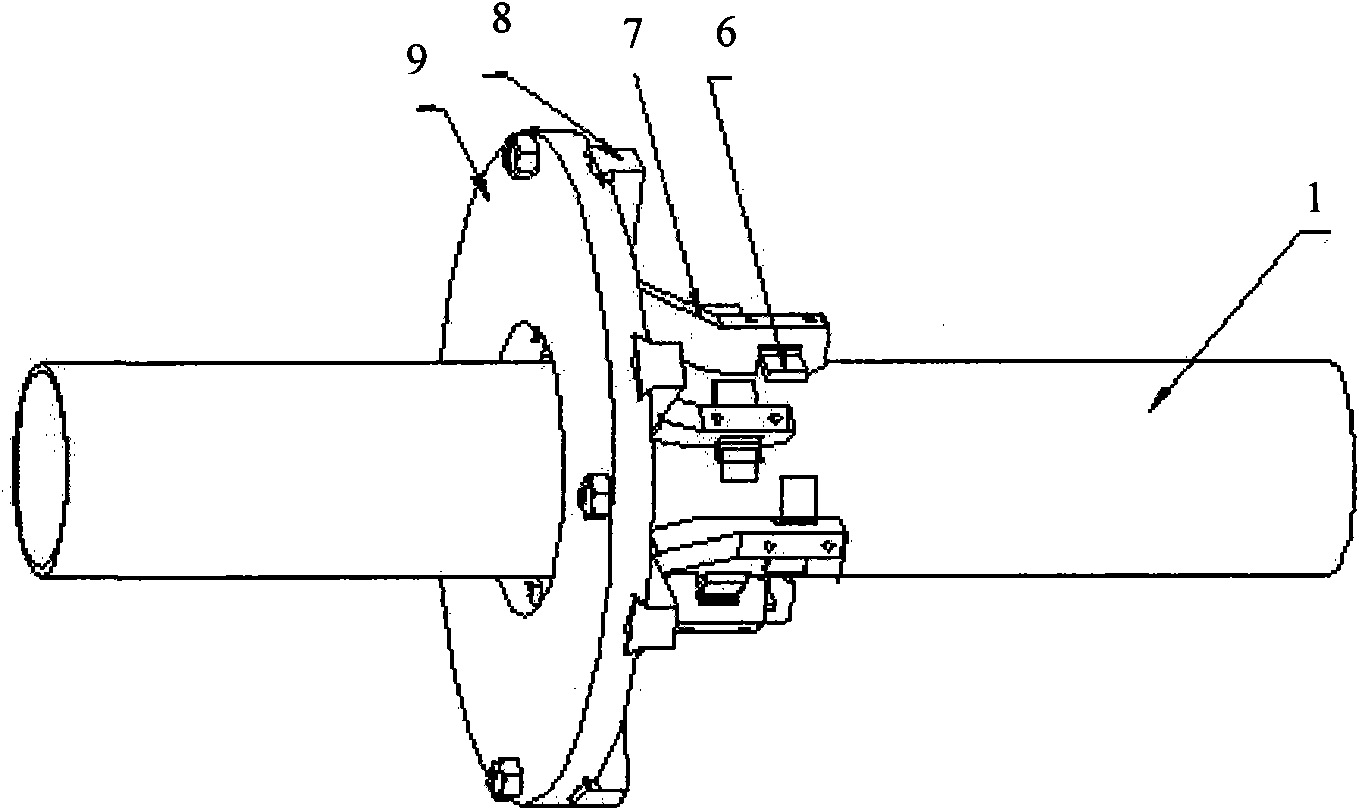
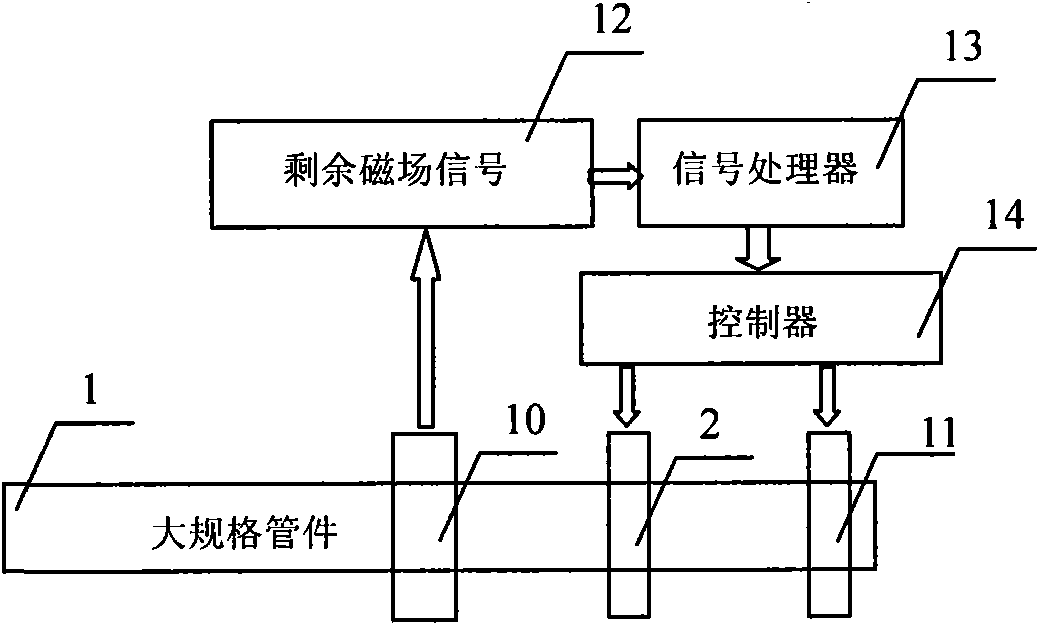
Demagnetization method of large-scale ferromagnetic pipe fitting and magnetic-sensitive sensor
InactiveCN101651006AOvercome the problem of not being able to cover the residual magnetism of pipe fittingsTargeted for degaussingMagnetic bodiesMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsPipe fittingResidual magnetic field
The invention relates to a demagnetization method of a large-scale ferromagnetic pipe fitting and a magnetic-sensitive sensor. The invention is characterized in that: for a remnant magnetic field formed at the end of the large-scale ferromagnetic pipe fitting under the action of an axial DC magnetic field, the pipe fitting is demagnetized by the DC magnetic field, wherein the direction of the DC magnetic field is opposite to that of the remnant magnetic field, the strength of the DC magnetic field is consistent with that of the detected remnant magnetic field, and then the pipe fitting is demagnetized by an alternating magnetic field with the strength gradually damped to zero; for an alternating remnant magnetic field formed in the axial direction of the large-scale ferromagnetic pipe fitting under the action of an axial alternating magnetic field with variable directions, pitches and strength, a section of pipe fitting in each pitch is demagnetized by the DC magnetic field, wherein the direction of the DC magnetic field is opposite to that of the remnant magnetic field, the strength of the DC magnetic field is consistent with that of the detected remnant magnetic field, and the pipe fitting is demagnetized by the alternating magnetic field with the strength gradually damped to zero. By adopting a complex demagnetization method, the invention solves the problem that magnetic hysteresis loops can not cover the remnant magnetic field of the pipe fitting sometimes in the conventional damped AC demagnetization method.
Owner:HEFEI ZHONGDA INSPECTION TECH
Reduction of hysteresis in a magnetoelastic torque sensor
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
System and Method of Measuring Defects in Ferromagnetic Materials
ActiveUS20150330946A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial defectResidual magnetic field
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Non-magnetic heating device for nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscope
ActiveCN104505273AImprove heating efficiencyHeating evenlyContact operating partsOhmic-resistance heatingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceGyroscope
The invention provides a non-magnetic heating device for a nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscope. The device consists of a heating body, a heating wire, a heat insulating framework and magnetic compensation coils, wherein the heating body is made of a non-magnetic high-heat-conductivity material, and is of a hollow structure; an atomic gas chamber is placed into the heating body for being uniformly heated; the four faces of the outer side of the heating body are provided with heating grooves; the nickel-chromium alloy non-magnetic heating wire can be placed into the heating grooves positively or reversely, thereby constructing a spatial symmetrical non-magnetic heating structure under the constraints of the heating grooves; after the heating body and the heating wire are fixedly assembled, the combination is fixed in the polytetrafluoroethylene heat insulating framework; three groups of winding grooves are formed in the heat insulating framework for winding enameled wires, thereby constructing three groups of orthogonal Helmholtz magnetic compensation coils for compensating a residual magnetic field. Compared with the prior art, the non-magnetic heating device has the advantages of compact structure, easiness in assembly, easiness in implementing engineering, high heating uniformity, high heating efficiency and high heating magnetic field counteracting capability.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
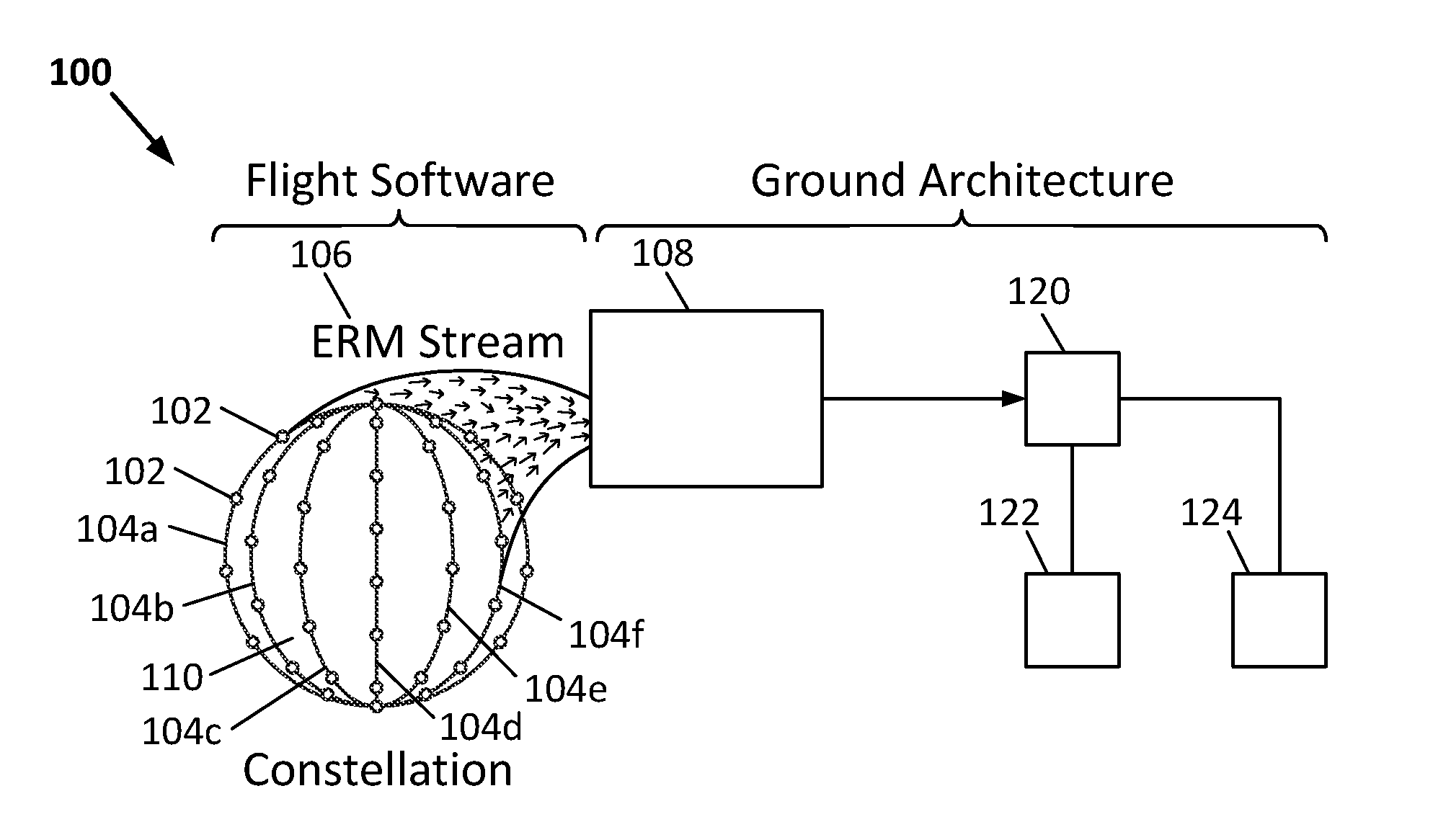
Automated Pre-Processing of Body-Mounted Magnetometer Data from Constellations of Low Earth Orbit Satellites for Derivation of Birkeland Current Signatures
A system, method and computer-readable medium for mapping magnetic activity for a current linking a planet's space environment to an ionosphere of the planet are disclosed. Magnetic field measurements of the current are obtained from a plurality of satellites orbiting the planet. A residual magnetic field is determined from the obtained magnetic field measurements. The determined residual magnetic field is arranged to create a time series for a selected location of a planet-centered coordinate system. The magnetic activity is mapped using the created time series for the selected location.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
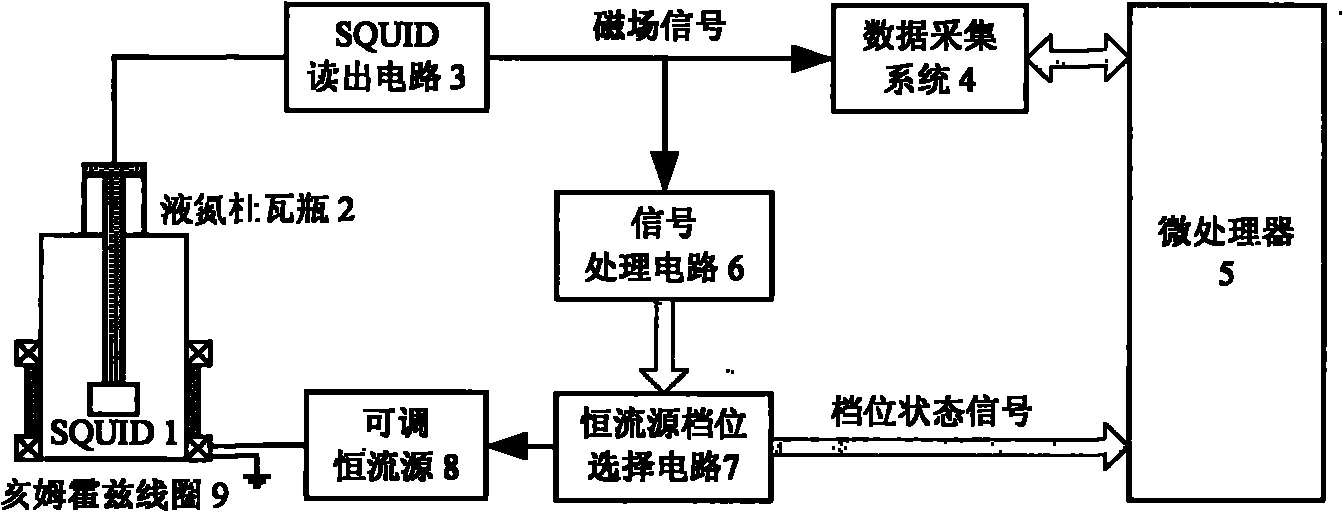
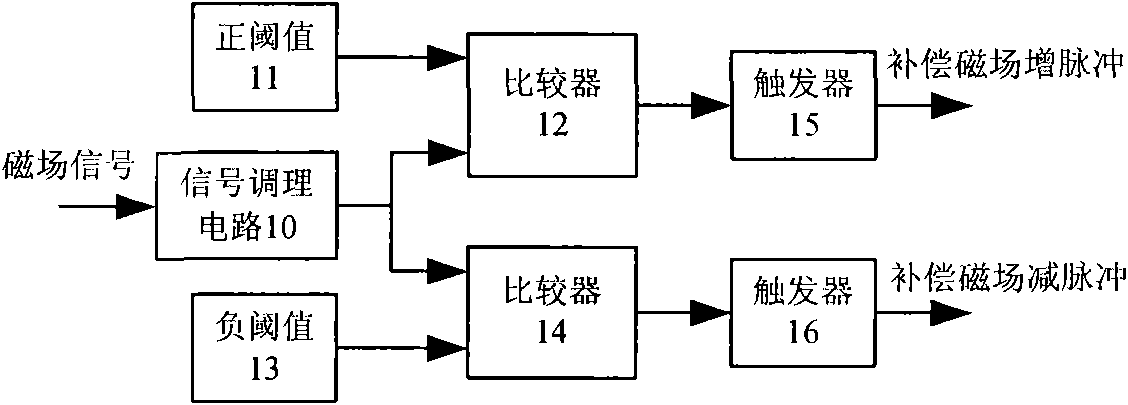
Wide-dynamic-range high-temperature superconducting magnetometer
InactiveCN101893721AImprove dynamic rangeNo loss of sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationSignal processing circuitsHelmholtz coil
The invention relates to a wide-dynamic-range high-temperature superconducting magnetometer comprising a superconducting quantum probe, a liquid nitrogen Dewar flask, a readout circuit, a data collection system and a micro-processor, wherein the superconducting quantum probe is arranged in a Helmholtz coil, more particularly, the superconducting quantum probe is connected with the Helmholtz coil via the liquid nitrogen Dewar flask, the readout circuit, the data collection system, the micro-processor, a constant-current source gear-selecting circuit and an adjustable constant-current source; and the readout circuit is formed by connecting a signal processing circuit with the constant-current source gear-selecting circuit. By using the standard magnetic field generated by the Helmholtz coil, part of the external magnetic field to be measured can be neutralized, and the value of the residual magnetic field to be measured after neutralization can be always within the dynamic range of the high-temperature superconducting magnetometer, the actual value of the magnetic field to be measured can be obtained by adding the value of the neutralized magnetic field to the detection value of the high-temperature superconducting magnetometer, thus preventing the sensitivity and accuracy of the high-temperature superconducting magnetometer from being reduced, widening the dynamic range thereof and meeting the operation requirements thereof within various measurement environments. Above all, the high-temperature superconducting magnetometer is suitable for the geophysical exploration in field sections where the electromagnetic interference is high.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for measuring critical current homogenity of every portion for super conducting strip
InactiveCN1580803AQuick measurementEasy to measureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMagnetic property measurementsResidual magnetic fieldRatio value
The method for measuring critical current uniformity of all the portions of superconducting tape material, is characterized by that energizing back field magnet with direct current to produce stable-constant PC magnetic field used as background magnetic field, making the superconducting tape material be passed through said background magnetic field; when the superconducting tape material is moved to the exterior of the background magnet, utilizing Hall probe to measure residual magnetic field of the superconducting tape material, when the residual magnetic field of superconducting tape material is measured, the space in which the superconducting tape material is placed has no background magnetic field; the ratio value of residual magnetic fields of all the portions of superconducting tape material is equal to the ratio value of critical currents of all the portions of superconducting tape material, i.e. it is uniformity of critical current of superconducting tape material.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for in-situ compensation of residual magnetic field of single-beam SERF atom magnetometer
InactiveCN109738837AQuick and accurate compensationIncreased zero-field resonance widthMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesActive compensationSingle beam
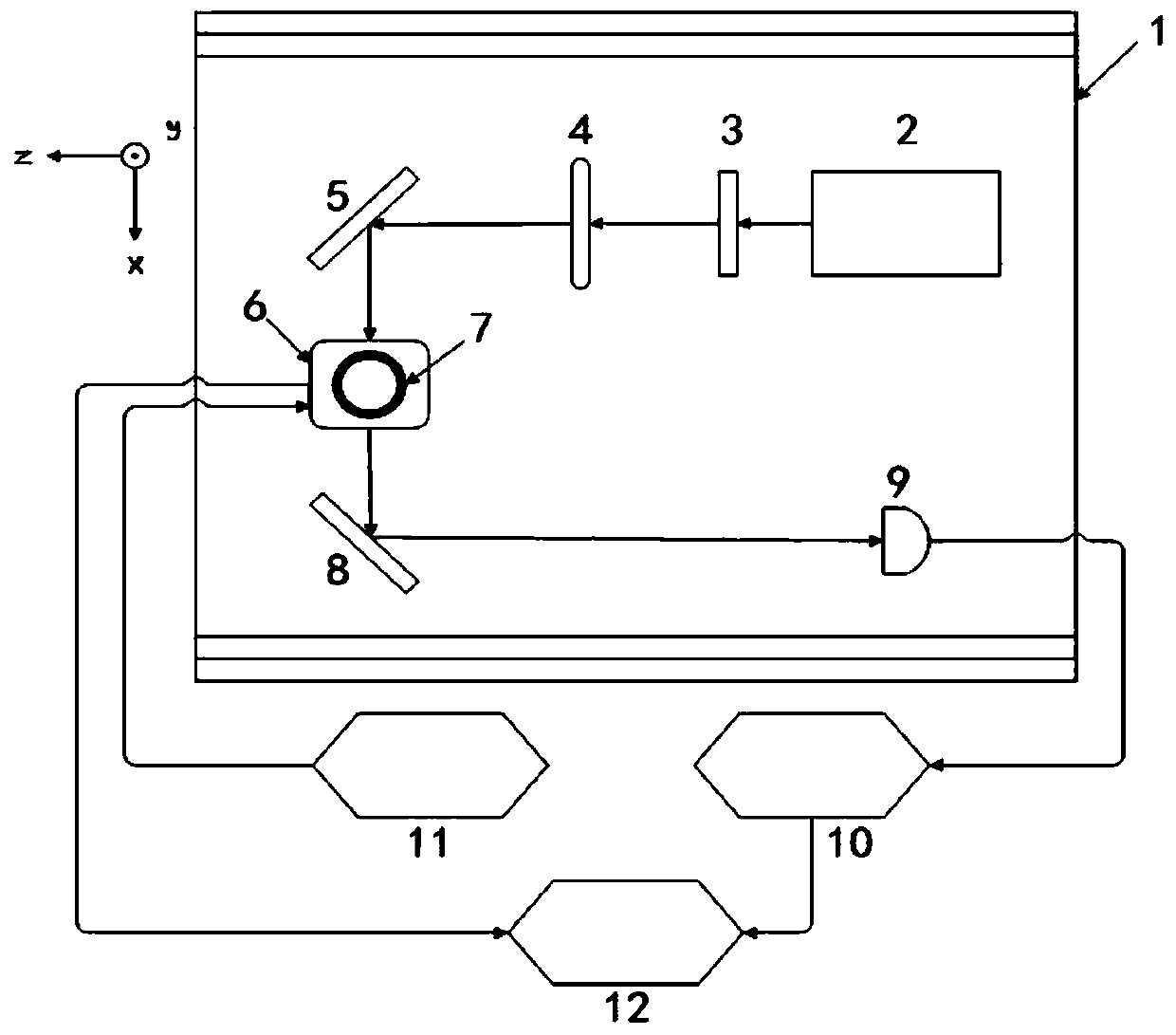
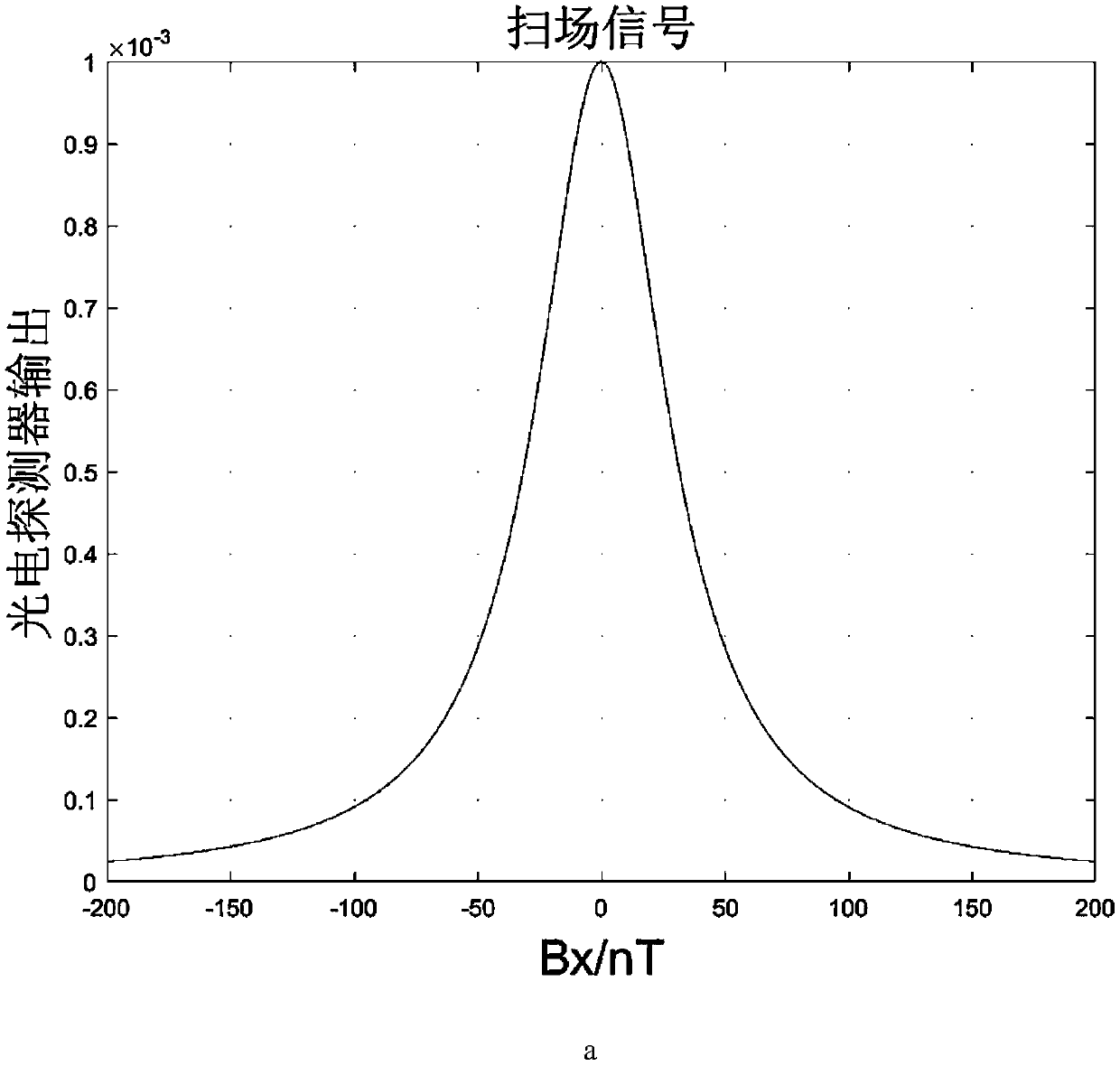
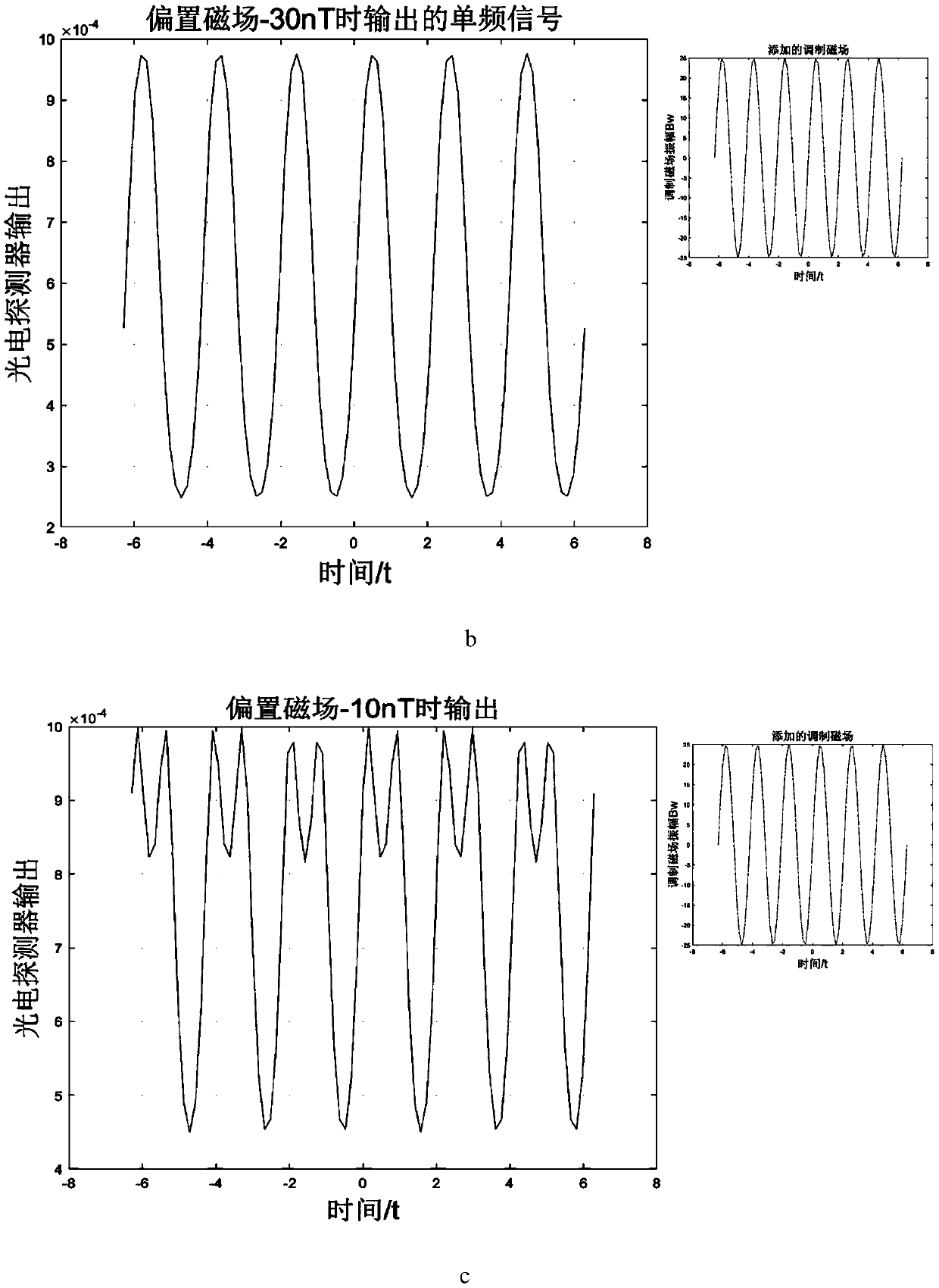
The invention relates to a method for in-situ compensation of a residual magnetic field of a single-beam SERF (Spin-Exchange-Relaxation-Free) atom magnetometer, and belongs to the field of atom magnetometers. Due to the fact that the SERF atom magnetometer is extremely high in precision, an SERF state meeting the working state requirements is more dependent on a high-quality zero-magnetic environment, passive compensation is difficult to achieve, and an active compensation method of locking an extreme point of the output curve is greatly affected by the environment, the noise and the like; anddue to the fact that the single-beam atom magnetometer only has a beam of light, the magnetic field compensation methods for a double-beam atom magnetometer are limited. According to the designed method, an offset is added in a direction of a non-sensitive axis of the single-beam SERF magnetometer in order to increase the resonance width of a zero field, so that the output response is more obvious, and FFT of an output signal is compensated by three-axis modulation, so that the residual magnetic field can be more accurately compensated to the zero point, and the method can be applied to the fields of automation, miniaturization and the like of cardio-cerebral magnetic measurement of the ultra-high-precision SERF atom magnetometer in the future.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Wireless Sensor for Rotating Elements
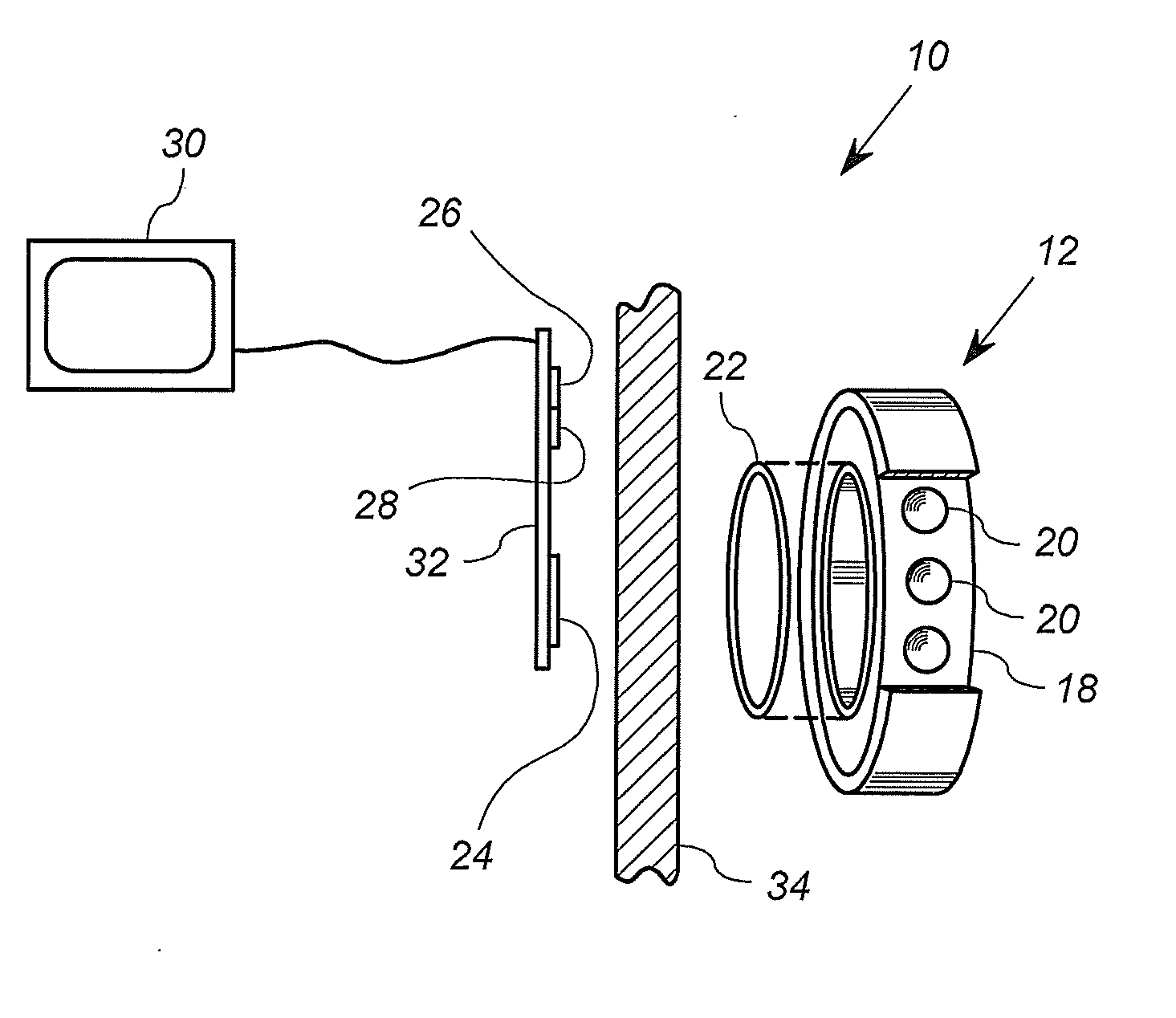
ActiveUS20140355644A1Engine sealsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLine sensorResidual magnetic field
A system for measuring a physical characteristic of a bearing includes a permanent magnet and a magnetic sensor. The permanent magnetic is coupled to at least a portion of a bearing, and has a magnetic field that changes as a function of the physical characteristic. For example, the permanent magnet has a magnetic characteristic that changes as a function of temperature. The magnetic sensor is operably disposed in a magnetic field sensing relationship with the permanent magnet, and is configured to generate a voltage signal and / or current signal corresponding to a sensed magnetic field.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Electric power connection part of electromagnetic clutch field coil assembly
ActiveUS20070017770A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove productivityLine/current collector detailsMechanical actuated clutchesResidual magnetic fieldElectromagnetic clutch
An electric power connection part of an electromagnetic clutch field coil assembly connected with an electric power connector at a side of a vehicle engine includes a housing assembly connected to the field coil assembly with electric wires, which is extracted therefrom, interposed therebetween; a discharge device for absorbing a surge voltage; and a magnetic field elimination device for eliminating a residual magnetic field are injection molded and combonined within the housing assembly. Accordingly, on the electric power connection part has an advantage in that it is not directly influenced by heat radiated from a field coil assembly so that electric / electronic devices can be prevented from being damaged; since an epoxy applying process for attaching electric / electronic devices such as a discharge device and a magnetic field elimination device is omitted, a manufacturing process is greatly simplified; and the number of components are reduced so that manufacturing process thereby decreasing costs.
Owner:HANON SYST
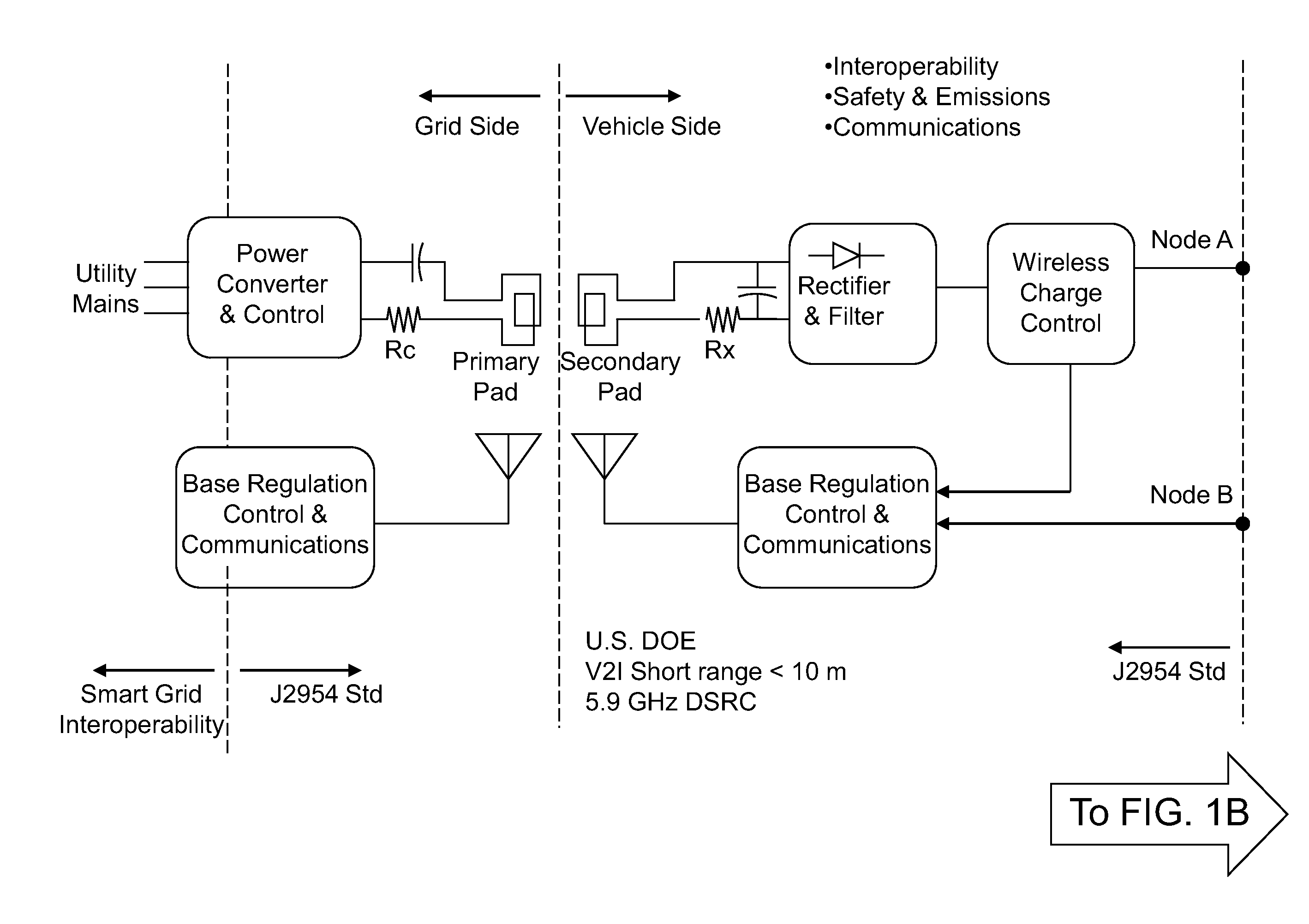
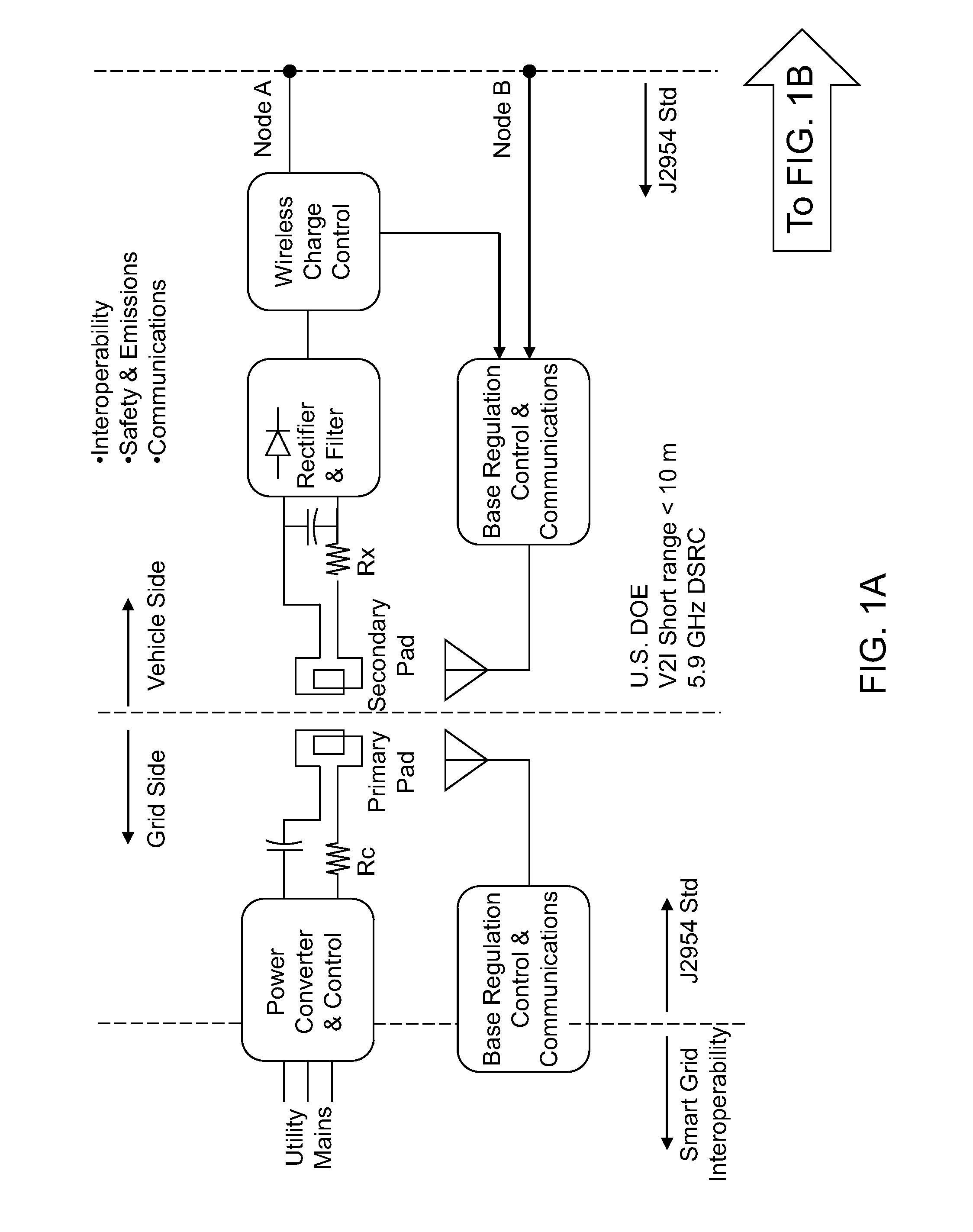
Wireless power transfer electric vehicle supply equipment installation and validation tool
ActiveUS20130021168A1Determine efficiencyElectric signal transmission systemsCharging stationsElectric power transmissionEngineering
A transmit pad inspection device includes a magnetic coupling device, which includes an inductive circuit that is configured to magnetically couple to a primary circuit of a charging device in a transmit pad through an alternating current (AC) magnetic field. The inductive circuit functions as a secondary circuit for a set of magnetically coupled coils. The magnetic coupling device further includes a rectification circuit, and includes a controllable load bank or is configured to be connected to an external controllable load back. The transmit pad inspection device is configured to determine the efficiency of power transfer under various coupling conditions. In addition, the transmit pad inspection device can be configured to measure residual magnetic field and the frequency of the input current, and to determine whether the charging device has been installed properly.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
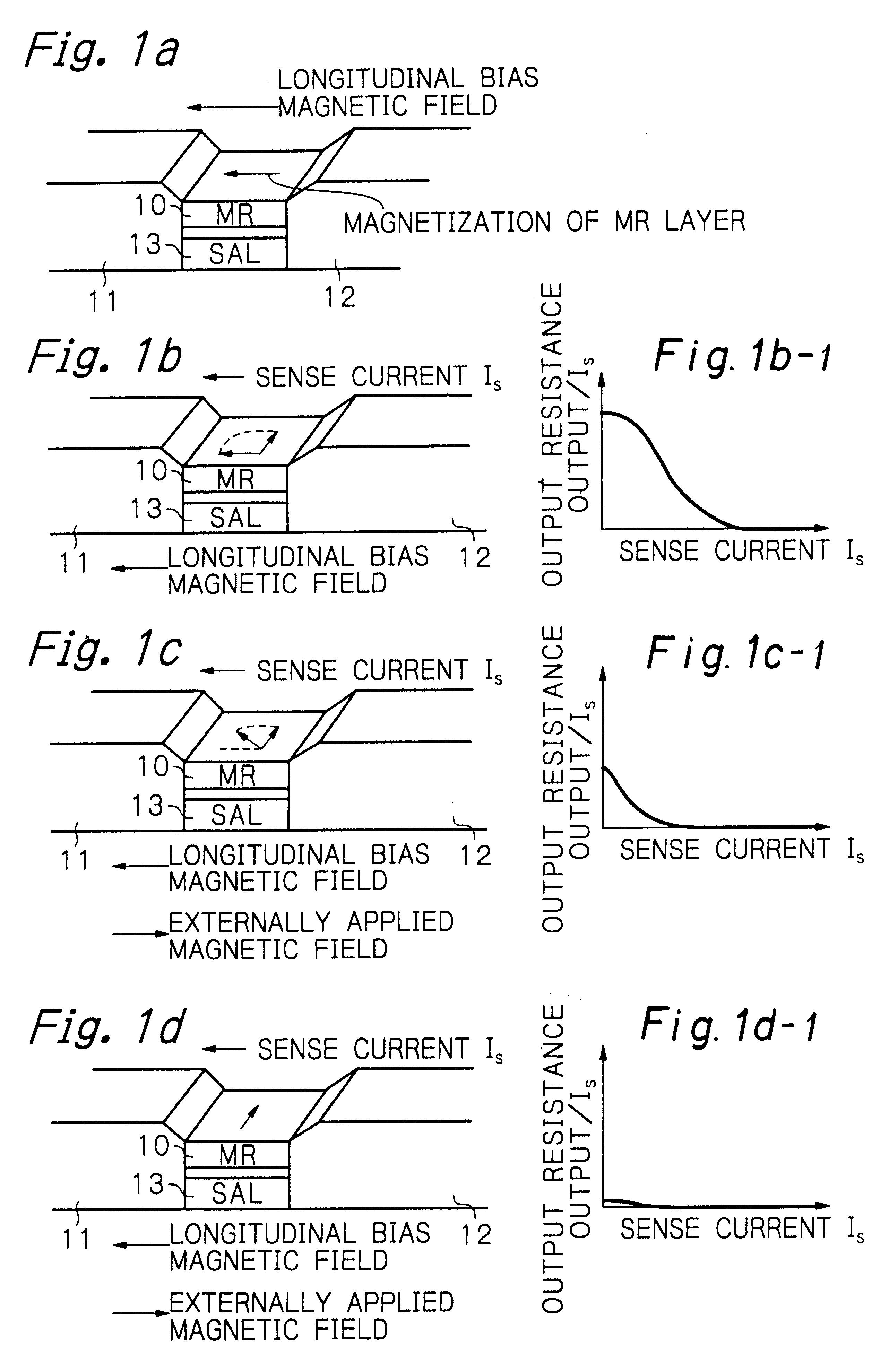
Method and apparatus for measuring bias magnetic field for controlling magnetic domain of magnetoresistive effect element
A method for measuring bias magnetic field for controlling magnetic domain (longitudinal bias magnetic field) of a MR element has the step of applying an external measurement magnetic field onto the MR element which is biased with the magnetic field for controlling the magnetic domain (longitudinal bias magnetic field) in parallel to the direction of the bias magnetic field, the step of measuring rho-H loop of the MR element (output resistance of MR element versus magnetic field strength loop) under the application of the external measurement magnetic field, and the step of determining a shifted amount of the measured rho-H loop.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
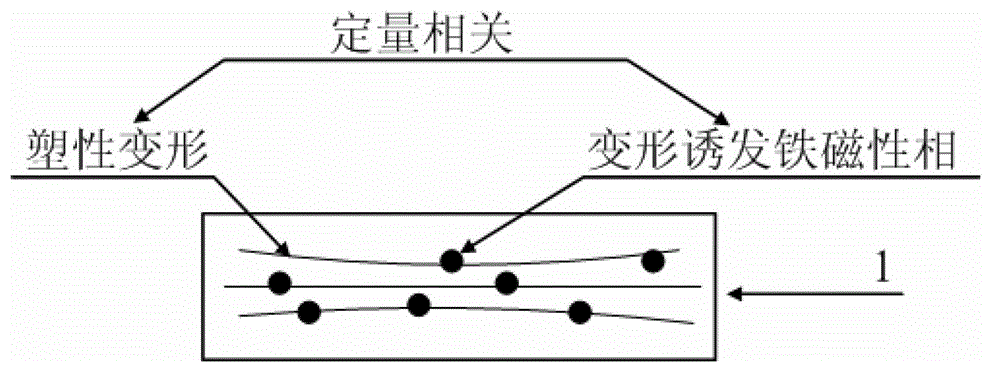
Detection method of austenite stainless steel plastic deformation
InactiveCN103063124AEasy to operateImprove detection efficiencyElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementMeasurement deviceResidual magnetic field
The invention relates to a detection method of austenite stainless steel plastic deformation. The detection method of the austenite stainless steel plastic deformation is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) series of specimens are manufactured for different austenite stainless steel materials; (2) the series of specimens are damaged in different degrees of plastic deformation, and meanwhile the plastic deformation is detected; (3) the damaged specimens are direct current magnetized; (4) a magnetic field measurement device is adopted to determine intensity of residual magnetic field of different specimens; (5) the austenite stainless steel plastic deformation and standardization relation curve (5) of the residual magnetic field are got; (6) the austenite stainless steel detected object is direct current magnetized; (7) the standardization relation curve (5) is compared according to the detected intensity of residual magnetic field to get actual plastic deformation of the corresponding detected object. The nondestructive detection method can nondestructively and quantitatively detect the plastic deformation degree of low-magnetic austenite stainless steel materials before macroscopic defects are produced, and fill a vacancy of the detection method of the field.
Owner:BEIFANG UNIV OF NATITIES
Magnetic heads disk drives and methods with floating pole tip or shunted pole tip for reduced pole tip erasure
InactiveUS7688544B1Minimize impactAvoid magnetizationManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageResidual magnetic fieldMagnetic poles
A write head includes a write return yoke, a write yoke connected to the write return yoke, conductive coils surrounding the write yoke, a write pole tip, and a non-magnetic spacer connecting the write pole tip to the write yoke. The non-magnetic spacer allows for reducing a magnetization of the write pole tip due to a remnant magnetic field in the write yoke. In another embodiment, the write head comprises a write shield, a write return yoke, a write yoke, conductive coils, a write pole tip, and a saturable yoke shunt connecting the write pole tip and the write shield. The saturable yoke shunt directs a limited amount of magnetic flux from the write pole tip to the write shield, such that when there is a remnant magnetic field in the write pole tip, the magnetic flux is directed to the write shield rather than to a disk.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic sensor device
InactiveCN102194273ANot affectedPrevent adhesionPaper-money testing devicesFault location by increasing destruction at faultResidual magnetic fieldDevice form
The invention relates to the following magnetic sensor device, which can prevent the magnetic powder adsorbed by a magnet for applying a magnetic field from being adsorbed to a magnetic flux detecting part and can reduce the influence caused by the magnetic field of the magnet for applying a magnetic field to the magnetic flux detecting part. In a magnetic pattern detecting device, the magnetic sensor device comprises a magnetic field applying magnet for applying a magnetic field to a medium, and a magnetic sensor element, wherein the magnetic sensor device forms a magnetic flux detecting part for detecting the magnetic flux at a state of applying a bias magnetic field to the medium which is applied with a magnetic field. The magnets for applying the magnetic field are arranged on the two sides of the movement direction of the medium relative to the magnetic sensor element so as to act as a first magnet and a second magnet for applying magnetic fields, and the first magnet and the second magnet for applying magnetic fields, which are opposite to each other in the movement direction of the medium, are opposite to each other by different poles in a manner of clamping the magnetic sensor element.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Measuring method for quantity of driven rubidium atom frequency standard residual magnetic field
InactiveCN101839965AImprove frequency stabilityKnow the sizeMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsHeterodyning/beat-frequency comparisonFrequency stabilizationResidual magnetic field
The invention discloses a measuring method for the quantity of a driven rubidium atom frequency standard residual magnetic field. The measuring method comprises the following steps of: applying a positive direction C field to an atom frequency standard cavity-cell system and measuring a resonance frequency F1 when an external magnetic field corresponding to the positive direction C field H1 is H1; and applying a reverse direction C field to the atom frequency standard cavity-cell system, measuring a resonance frequency F2 when the external magnetic field corresponding to the reverse directionC field -H1 is -H1 and indirectly acquiring the quantity of a corresponding residual magnetic field by comparing the difference frequency data of the resonance frequency F1 and the resonance frequency F2. By using the method, the quantity of the residual magnetic field in the atom frequency standard system can be better known, and more important, a reference for further improving the stability ofthe atom frequency standard whole frequency is convenient to provide after the influence of the change of the residual magnetic field on whole indexes and the influence quantity of the quantity and the change of the residual magnetic field on the whole indexes are known.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Magnetic compensation coil structural component for miniature nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscope
ActiveCN104819712AUniform longitudinal static magnetic fieldCompact structureTurn-sensitive devicesNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceGyroscope
The invention provides a magnetic compensation coil structural component for a miniature nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscope, wherein a mandrel bracket is in a cylindrical shape, with an atomic gas chamber optical path component being arranged inside, and a wire winding groove as well as a paster groove being arranged on the outer wall thereof for fixing a transverse magnetic compensation coil and a vertical magnetic compensation coil. The vertical magnetic compensation coil is a circular Helmholtz coil structure enwound by a varnished wire; besides compensating a vertical residual magnetic field of the gyroscope, the vertical magnetic compensation coil is also used for providing a uniform static magnetic field for the gyroscope. The transverse magnetic compensation coil employs a saddle-type coil structure; the transverse magnetic compensation coil is used for compensation a transverse residual magnetic field of the gyroscope. The power is supplied to each coil independently; the coils are all printed on one flexible circuit board, sticking inside a mounting groove of the internal mandrel bracket in a bended manner. Comparing with the prior art, the magnetic compensation coil structural component is better in magnetic field evenness, more compact in structure, better in technology, easier to be installed, integrated and maintained.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Particle beam system and pattern data generation method for particle beam system
ActiveUS20140152199A1Reduce in quantityReduction in number of stepMagnetic resonance acceleratorsResidual magnetic fieldParticle beam
To reduce the number of steps of generating control pattern data needed for achieving beam irradiation with desired energy in the beam extraction from a synchrotron accelerator, a data generator 41 divides adjusted control pattern data, defines the divided data intervals as data modules, and reuses each of the data modules to generate new control pattern data. For extraction energy level changes, which are characteristic of multi-energy extraction, energy change control pattern data is generated based on the extraction pattern data before an energy level change and the extraction pattern data after the energy level change by using an interpolation function thereby to allow the control pattern data to be automatically generated. Effects of residual magnetic fields are calculated in advance, and then adjustment values that allow for the effects of the residual magnetic fields are incorporated into the control pattern data and operation is controlled.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus/method counter-actively suppressing remnant eddy current magnetic fields generated from gradients applied before controlling contrast pre-pulses and MRI image data acquisition
InactiveUS8487614B2Reduce impactMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResidual magnetic fieldData acquisition
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes an imaging unit and a compensation unit. The imaging unit acquires image data by imaging that applies a pre-pulse for controlling contrast. The compensation unit suppresses a remnant magnetic field having an intensity according to slice position. The remnant magnetic field is at an application timing of the pre-pulse and due to an eddy current generated by at least one gradient magnetic field applied before applying the pre-pulse.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Current sensor
ActiveUS20150022199A1Consumes less powerHigh Sensitivity FeaturesCurrent measurements onlyMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectricityResidual magnetic field
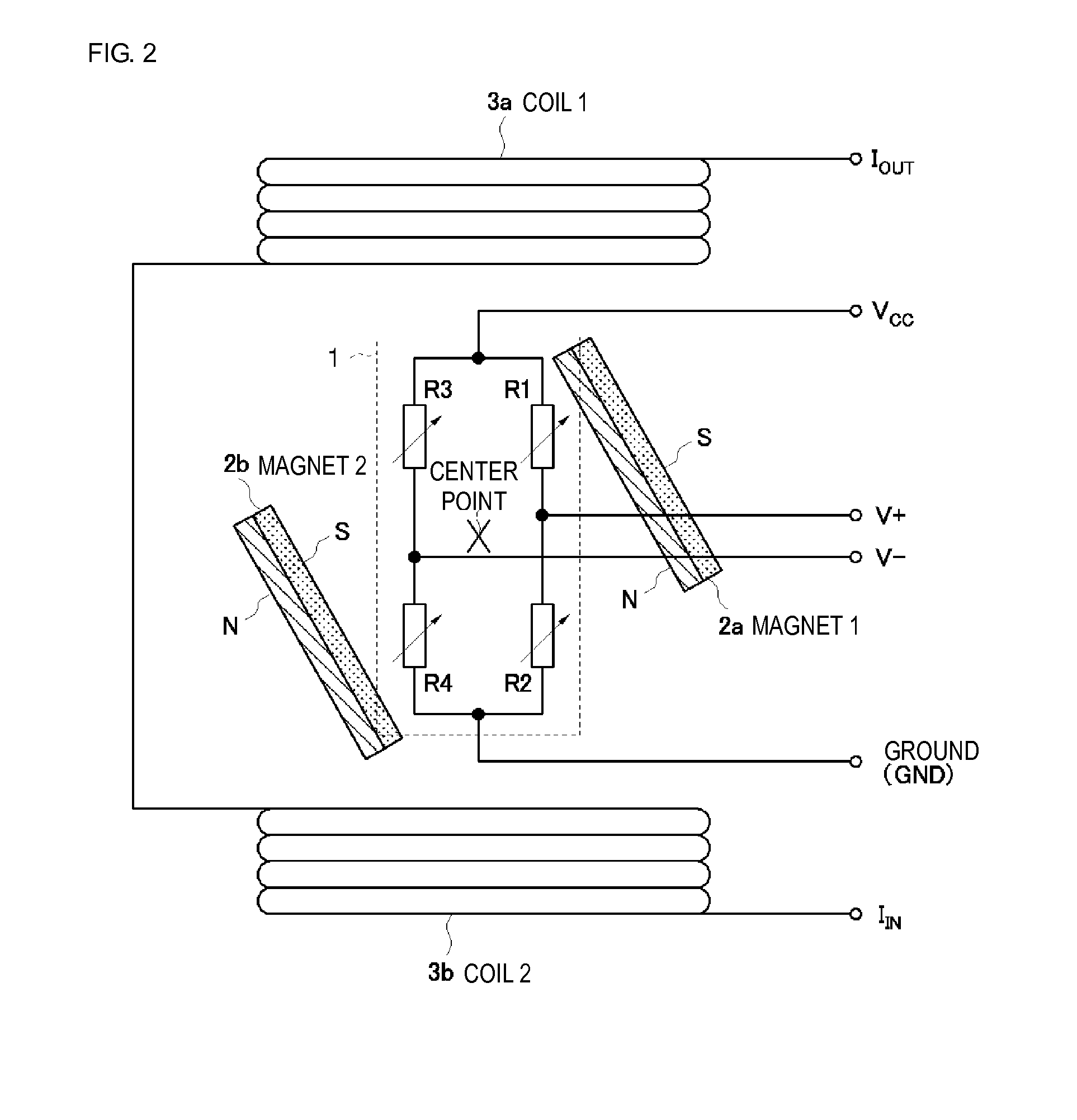
A current sensor includes: four magnetic sensor elements arranged within a plane orthogonal to a measured current, having a symmetrical magnetic characteristics curve, and adapted to convert a magnitude of a magnetic field into an electrical signal and output the electrical signal; a bridge circuit including the four magnetic sensor elements; and a bias magnetic field application member adapted to applying a bias magnetic field to the magnetic sensor elements.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Electric power connection part of electromagnetic clutch field coil assembly
ActiveUS7772946B2Reduce manufacturing costImprove productivityLine/current collector detailsMechanical actuated clutchesElectromagnetic clutchResidual magnetic field
An electric power connection part of an electromagnetic clutch field coil assembly connected with an electric power connector at a side of a vehicle engine, includes a housing assembly connected to the field coil assembly with electric wires, which is extracted therefrom, interposed therebetween; a discharge device for absorbing a surge voltage; and a magnetic field elimination device for eliminating a residual magnetic field are injection molded and combonined within the housing assembly. Accordingly, the electric power connection part has an advantage in that it is not directly influenced by heat radiated from a field coil assembly so that electric / electronic devices can be prevented from being damaged; since an epoxy applying process for attaching electric / electronic devices such as a discharge device and a magnetic field elimination device is omitted, a manufacturing process is greatly simplified; and the number of components are reduced so that manufacturing process thereby decreasing costs.
Owner:HANON SYST
MRAM memory with residual write field reset
A magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM) (900) that is susceptible to a residual magnetic field is compensated during a write operation. A first magnetic field (208) is applied to a memory cell during a first time period, the first magnetic field having a first direction (y) and a first magnitude. A second magnetic field (212) is applied to the memory cell during a second time period and having a second direction (x) and a second magnitude. A third magnetic field (702) is applied to the memory cell during a third time period, wherein the third time period overlaps at least a portion of the second time period, the third magnetic field having a third direction (−y) which is approximately opposite to the first direction of the first magnetic field. Currents are selectively applied through conductors in the memory cell to apply the three magnetic fields.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
Magnetic immunoassay system
InactiveUS20070254375A1Eliminate the effects ofReduce impactMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRemanenceMagnetic marker
A magnetic immunoassay system with a mechanism for compensating the direct current residual magnetic field in the vicinity of the specimen measurement position, in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic marker direction of magnetization for the measurement target. This invention reduces the effects of the magnetic field emitted from the unbound magnetic marker due to the residual magnetic field in the specimen solution and detects with high sensitivity the signal of the bound target magnetic marker. The magnetic field at the measurement position is regulated so as to intersect the direction of magnetization of the magnetic marker for the measurement target, in order to make the magnetization direction of the magnetic marker that is unbound due to residual magnetism or remanence in the sample solution, intersect the magnetization direction of the magnetic marker for the measurement target. The signal of the bound target magnetic marker can be therefore measured with high sensitivity since it is isolated from the unbound magnetic marker signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic current sensor and current measurement method
ActiveUS20160061863A1Increase currentSmall sizeMagnetic measurementsBase element modificationsMagnetic currentResidual magnetic field
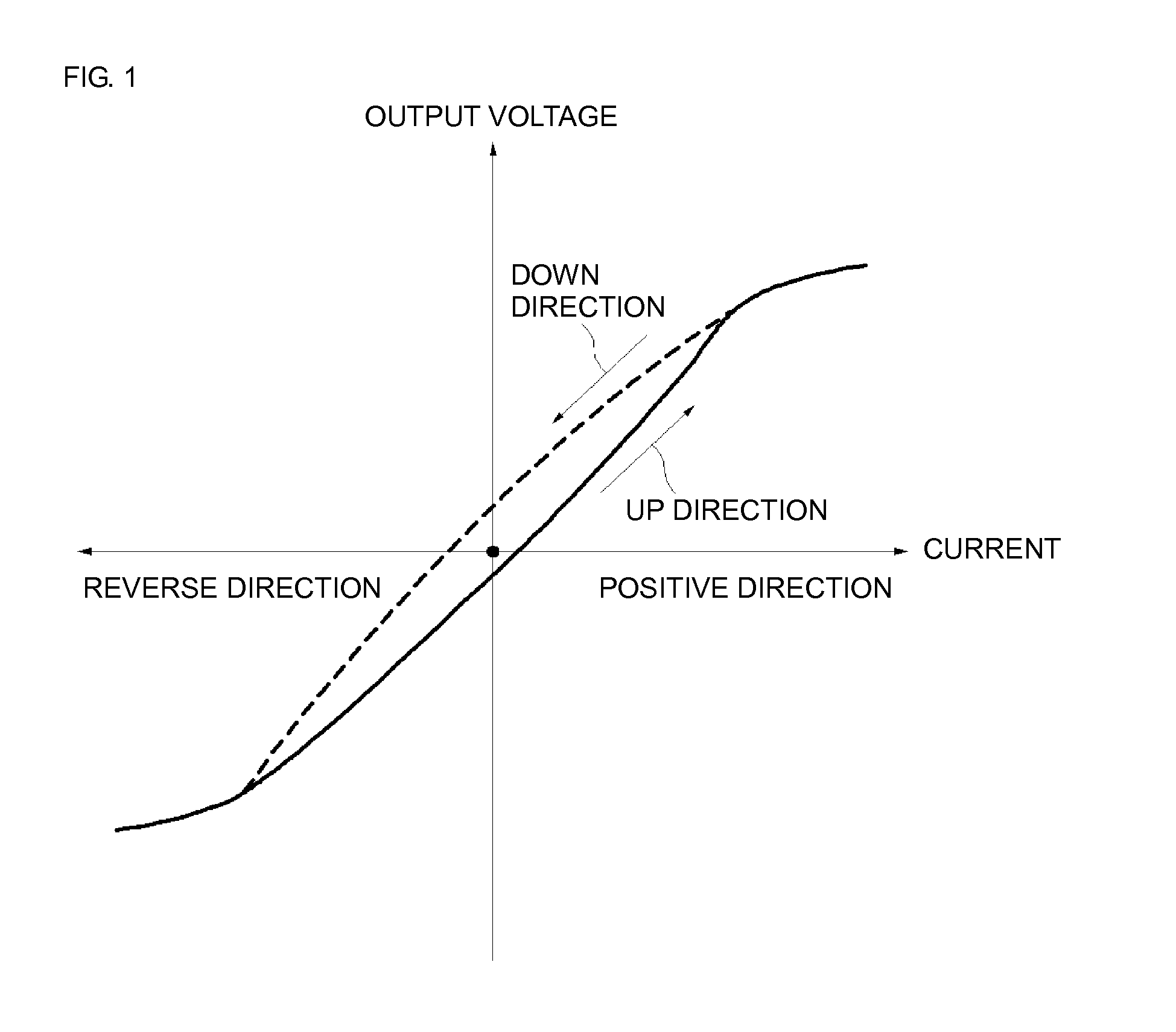
A magnetic current sensor including a Wheatstone bridge circuit formed of four magnetoresistance devices; bias magnetic field application that applies a bias magnetic field to the magnetoresistance devices; and air-core coils provided on both sides of the Wheatstone bridge circuit. The Wheatstone bridge circuit generates a voltage corresponding to an induction magnetic field generated by a current to be measured flowing through the air-core coils. According to the magnetic current sensor and current measurement method, the linearity between a current and an output voltage is near 0 mA as a result of magnetic hysteresis being suppressed, and an increase in current and a reduction in size and cost are realized as a result of insulation between the current circuit side and the MR device side being excellent.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
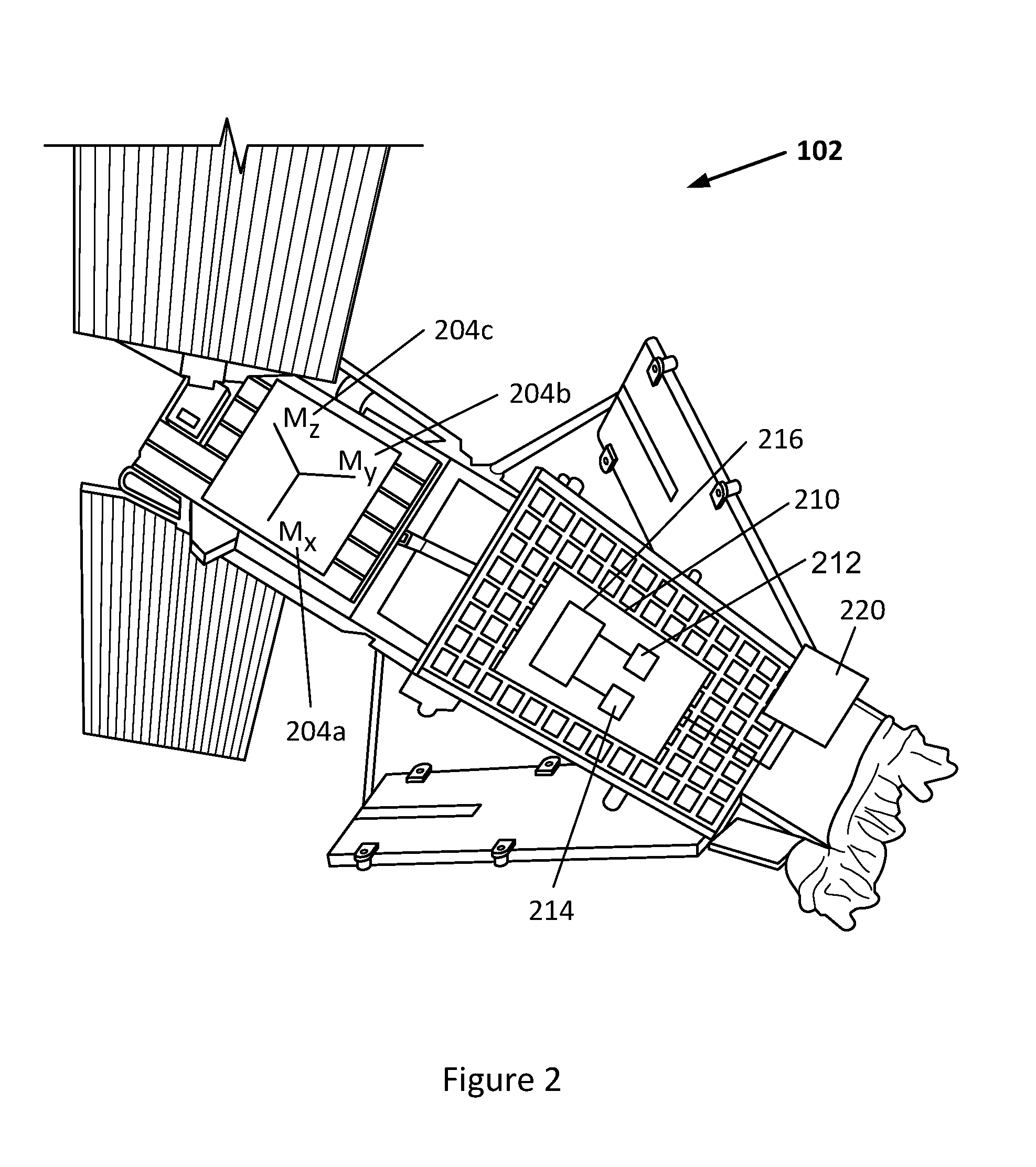
Determining method for compensating factor of magnetometer for magnetic control moonlet
InactiveCN104210677ASolve the problem of magnetic field measurement accuracySolve the problem of magnetic noise interferenceCosmonautic condition simulationsResidual magnetic fieldLaboratory facility
The invention provides a determining method for a compensating factor of a magnetometer for a magnetic control moonlet. The method comprises the following steps that the whole moonlet is placed in a zero-magnetism laboratory, a moonlet body coordinate system is regulated to be consistent with a laboratory magnetic field coordinate system in the pointing direction, and the magnetometer is used for measurement to obtain the whole moonlet residual magnetic field value in a residue magnetic field environment; a real ground magnetic field is simulated in the zero-magnetism laboratory, a controllable magnetic field is generated through adopting a coil galvanization method, simulated ground magnetic intensity values are respectively loaded in the three-axis directions of the moonlet, and in addition, the magnetometer is use for measurement to obtain the whole moonlet magnetic induction intensity in the simulated ground magnetic field environment; the compensating factor of the magnetometer is determined. The determining method has the greatest innovation point that the problem of magnetic field measuring precision of the magnetic control moonlet is solved, the solution to the problem is a necessary premise for successfully completing a space mission by the moonlet of which the posture is determined by the measuring value of the magnetometer, and the method has a very crucial engineering practical significance.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com