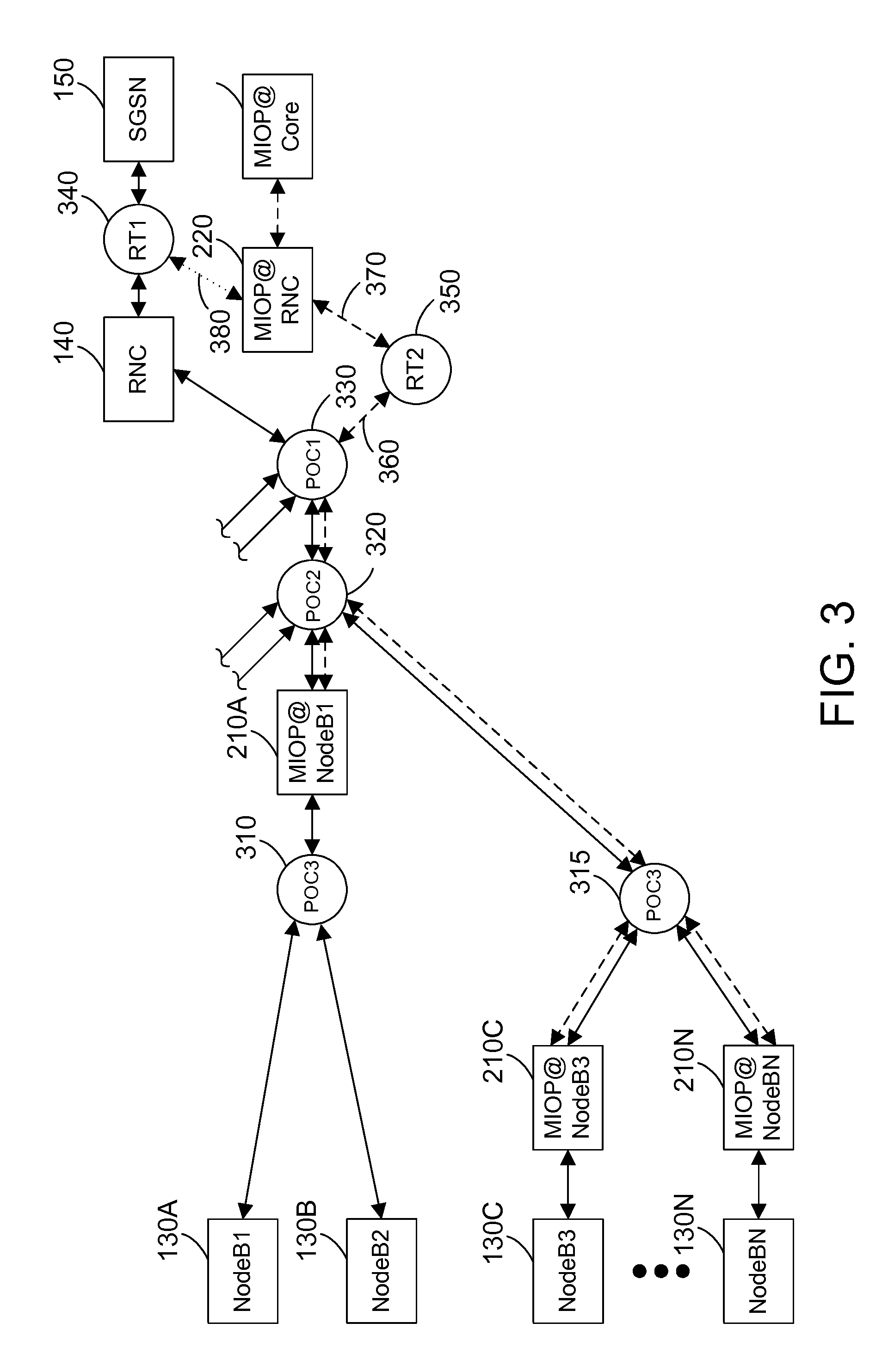
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
146 results about "Recovery - action" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
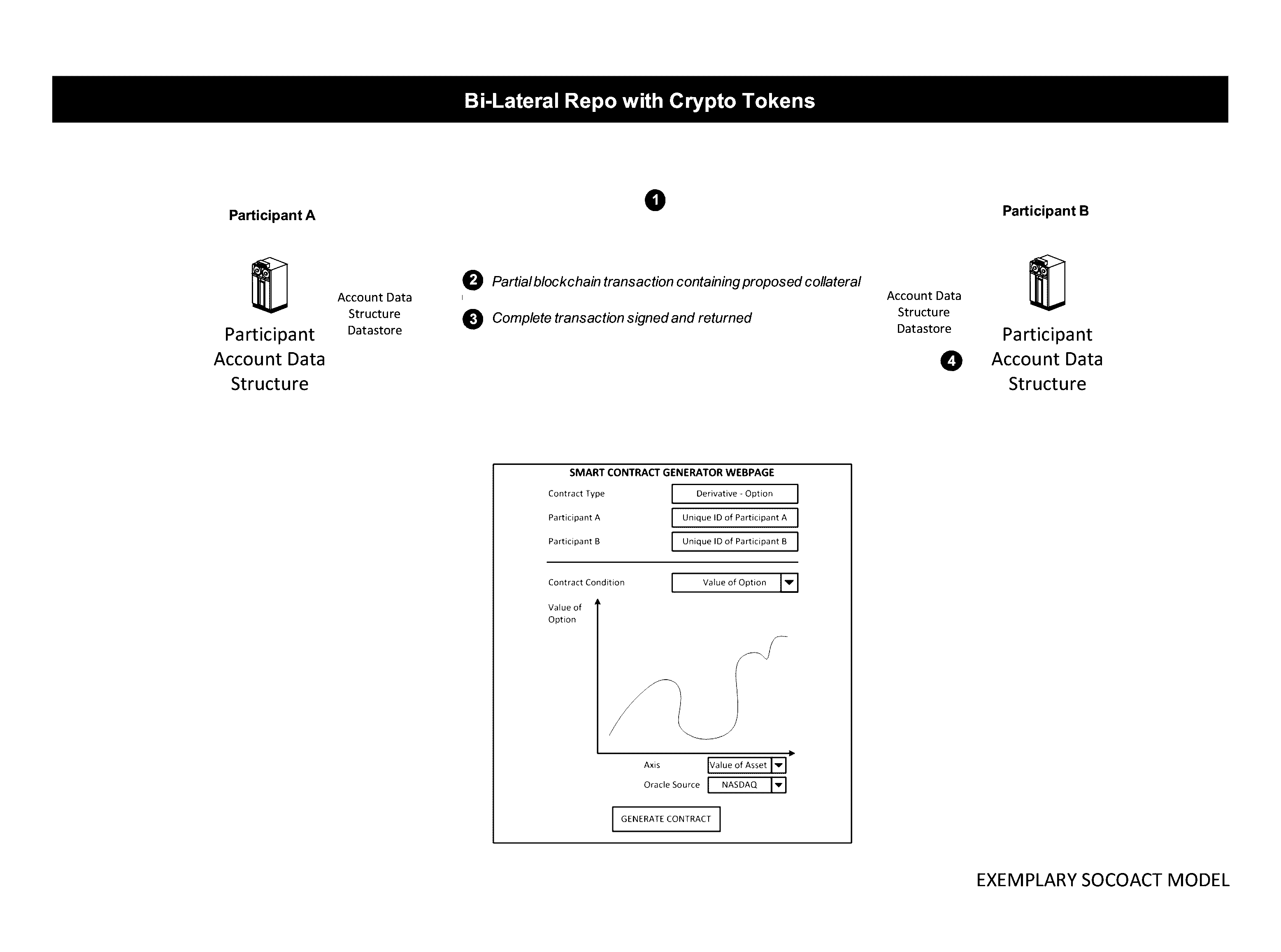
Crypto Key Recovery and Social Aggregating, Fractionally Efficient Transfer Guidance, Conditional Triggered Transaction, Datastructures, Apparatuses, Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20170048209A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageCryptography processingData structureKey recovery
The Crypto Key Recovery and Social Aggregating, Fractionally Efficient Transfer Guidance, Conditional Triggered Transaction, Datastructures, Apparatuses, Methods and Systems (“SOCOACT”) transforms MKADSD generation request, trigger event message inputs via SOCOACT components into transaction confirmation, recovery notification outputs. A multiple key account data structure datastore (MKADSD) generation request may be obtained from a user. A set of crypto public keys for a MKADSD may be determined. The MKADSD may be instantiated in a socially aggregated blockchain datastructure using the determined set of crypto public keys. A crypto recovery private key may be associate with the MKADSD and trigger event recovery settings for the MKADSD may be set. A trigger event message associated with the MKADSD may be obtained and recovery settings associated with a trigger event may be determined. The crypto recovery private key may be retrieved and a recovery action may be facilitated.
Owner:FMR CORP
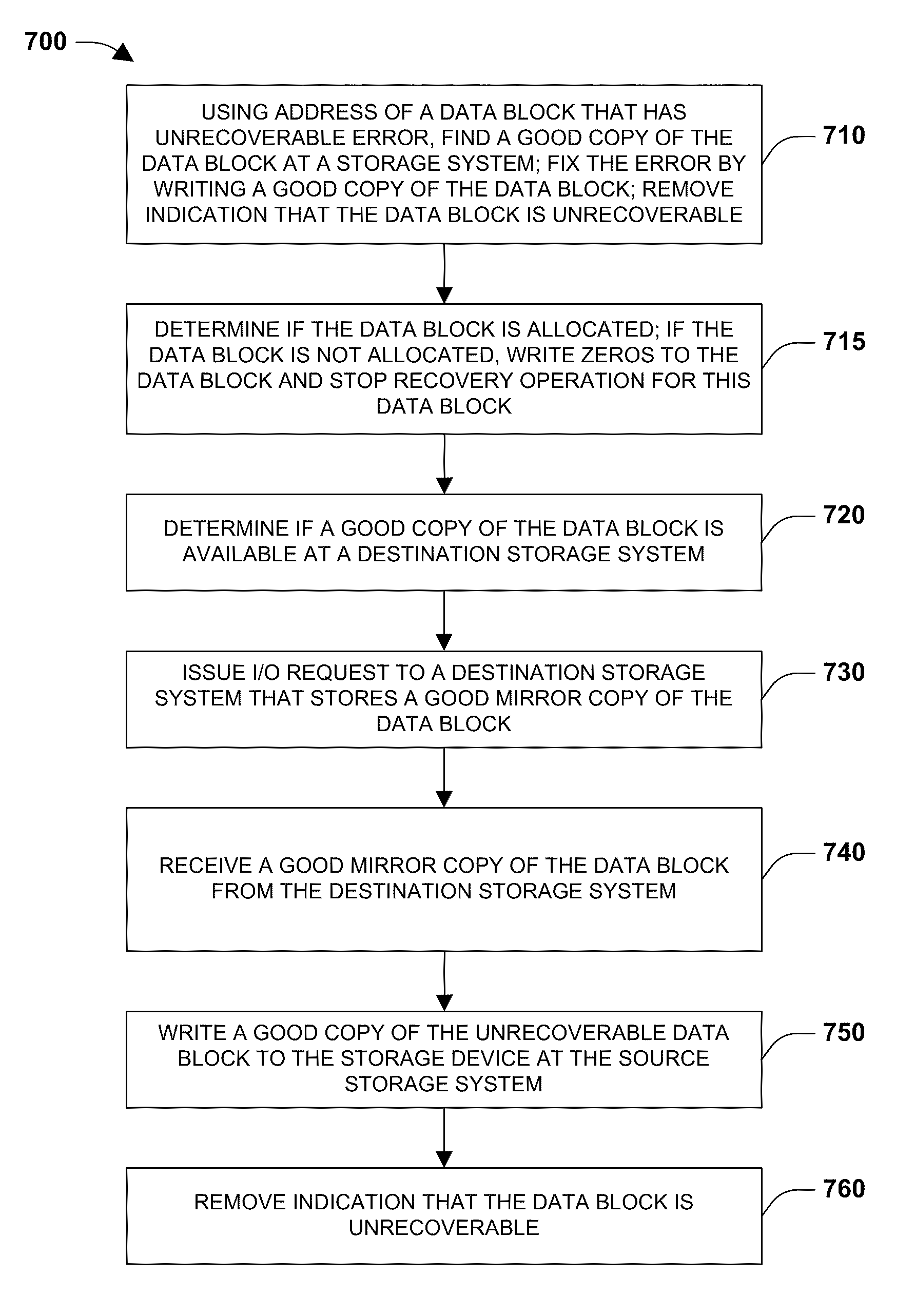
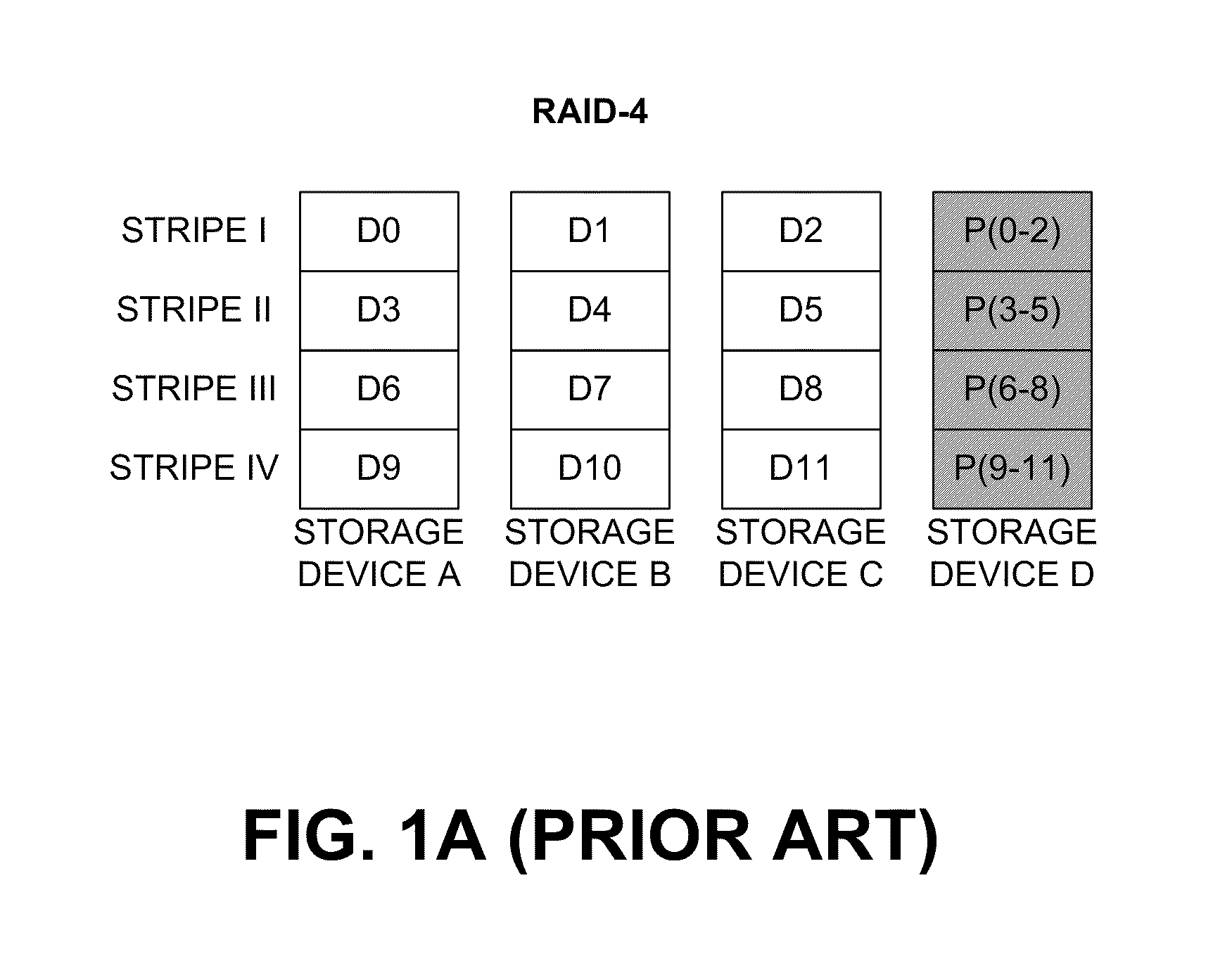
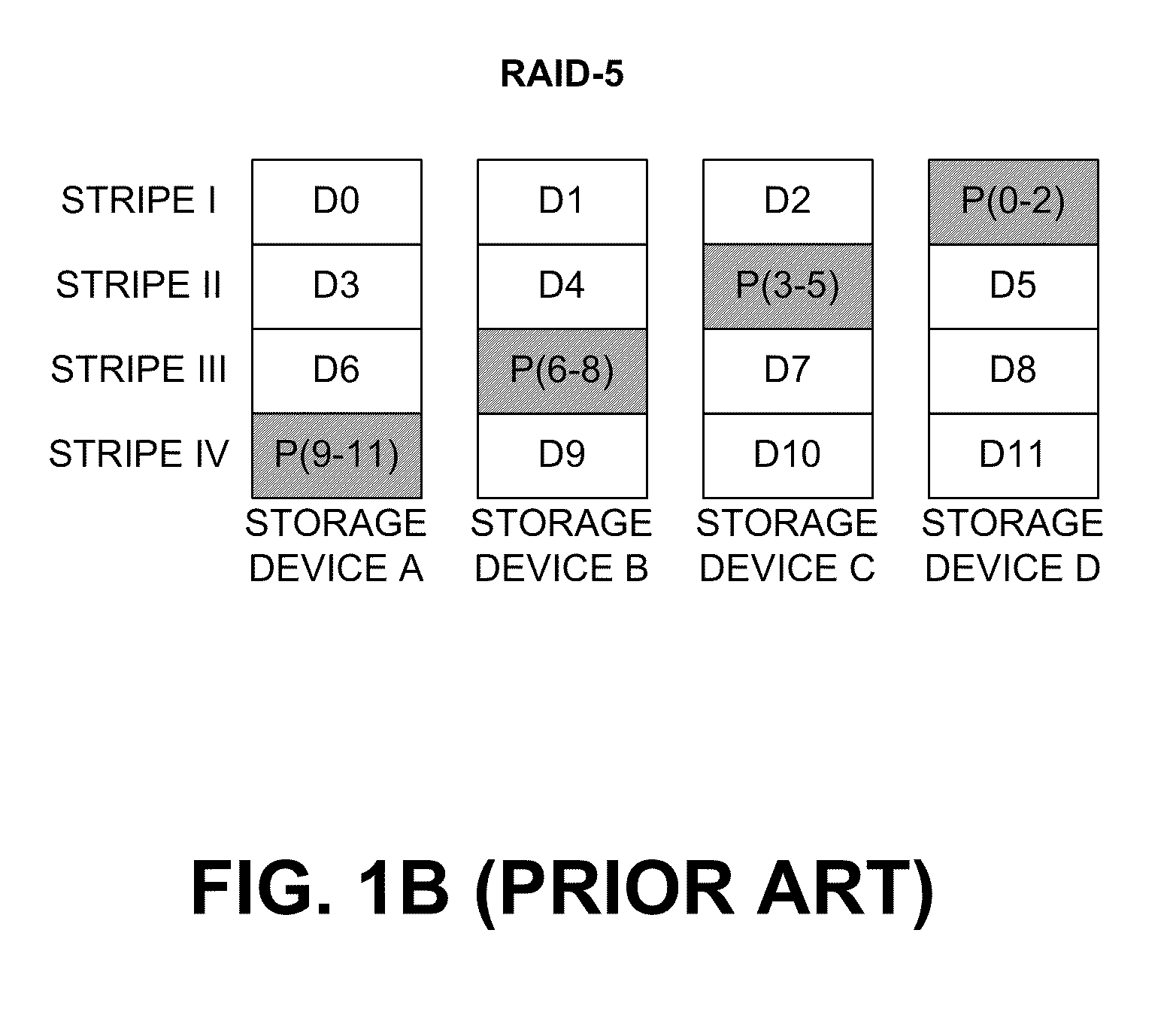
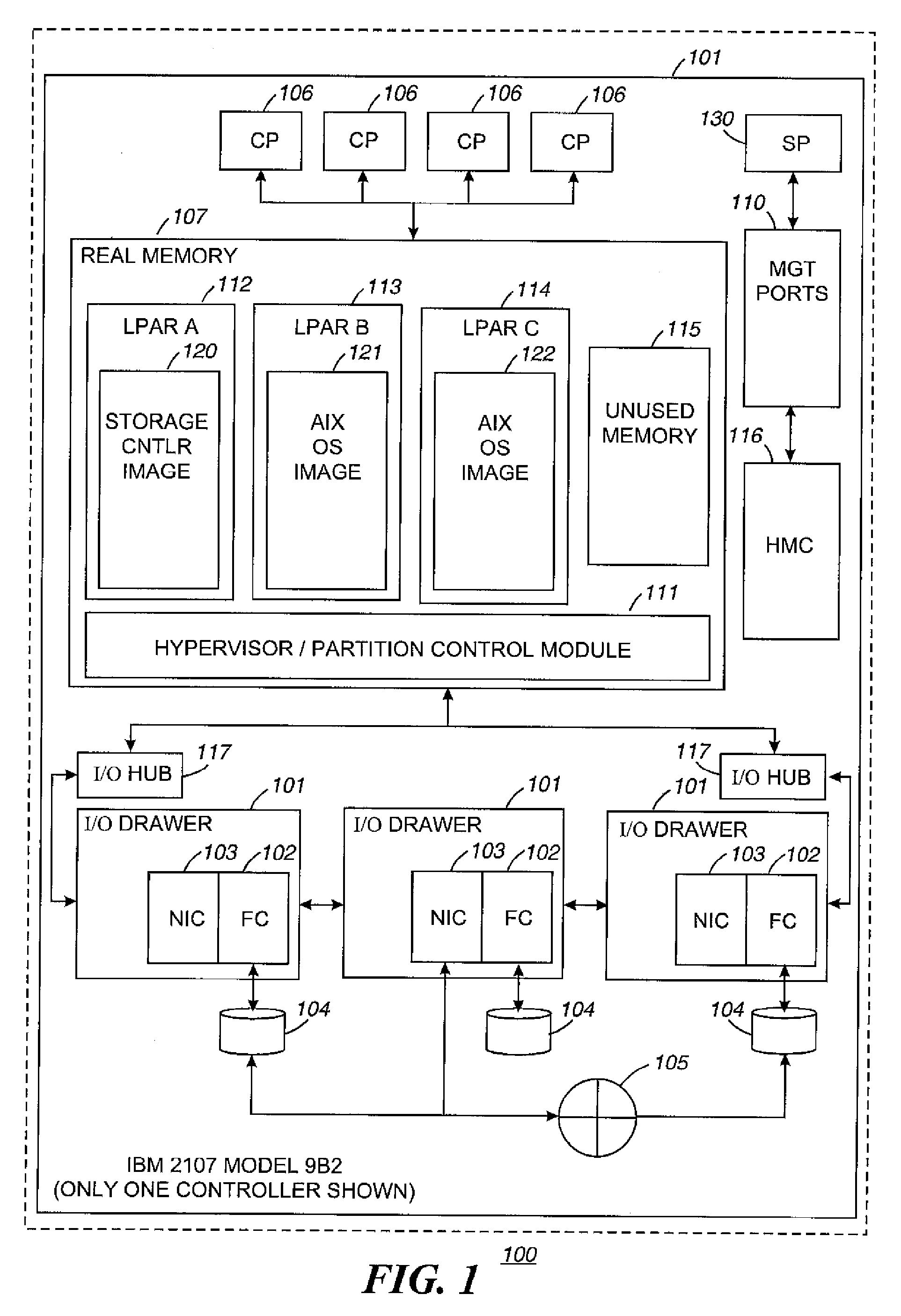
Mechanism for correcting errors beyond the fault tolerant level of a raid array in a storage system
ActiveUS8417987B1Increase resiliencyImprove availabilityRedundant hardware error correctionRAIDFault tolerance
Embodiments of the present invention provide novel, reliable and efficient technique for tracking, tolerating and correcting unrecoverable errors (i.e., errors that cannot be recovered by the existing RAID protection schemes) in a RAID array by reducing the need to perform drastic recovery actions, such as a file system consistency check, which typically disrupts client access to the storage system. Advantageously, ability to tolerate and correct errors in the RAID array beyond the fault tolerance level of the underlying RAID technique increases resiliency and availability of the storage system.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Self-healing network
InactiveUS6088141AShorten the timeRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsSelf-healingProtection ring
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00794 Sec. 371 Date May 27, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 27, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 18, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 01907 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 16, 1997A communication network system having at least three nodes, which are interconnected by transmission links carrying traffic to and from the nodes. The transmission links are divided into a working ring and a protection ring where the working ring and the protection ring can transmit traffic in opposite directions. A node is able to detect when an error occurs in the surrounding transmission links or the node itself. Each node can, by itself, divert traffic from the working ring to the protection ring and / or from the protection ring to the working ring. A recovery action is performed when the error is healed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
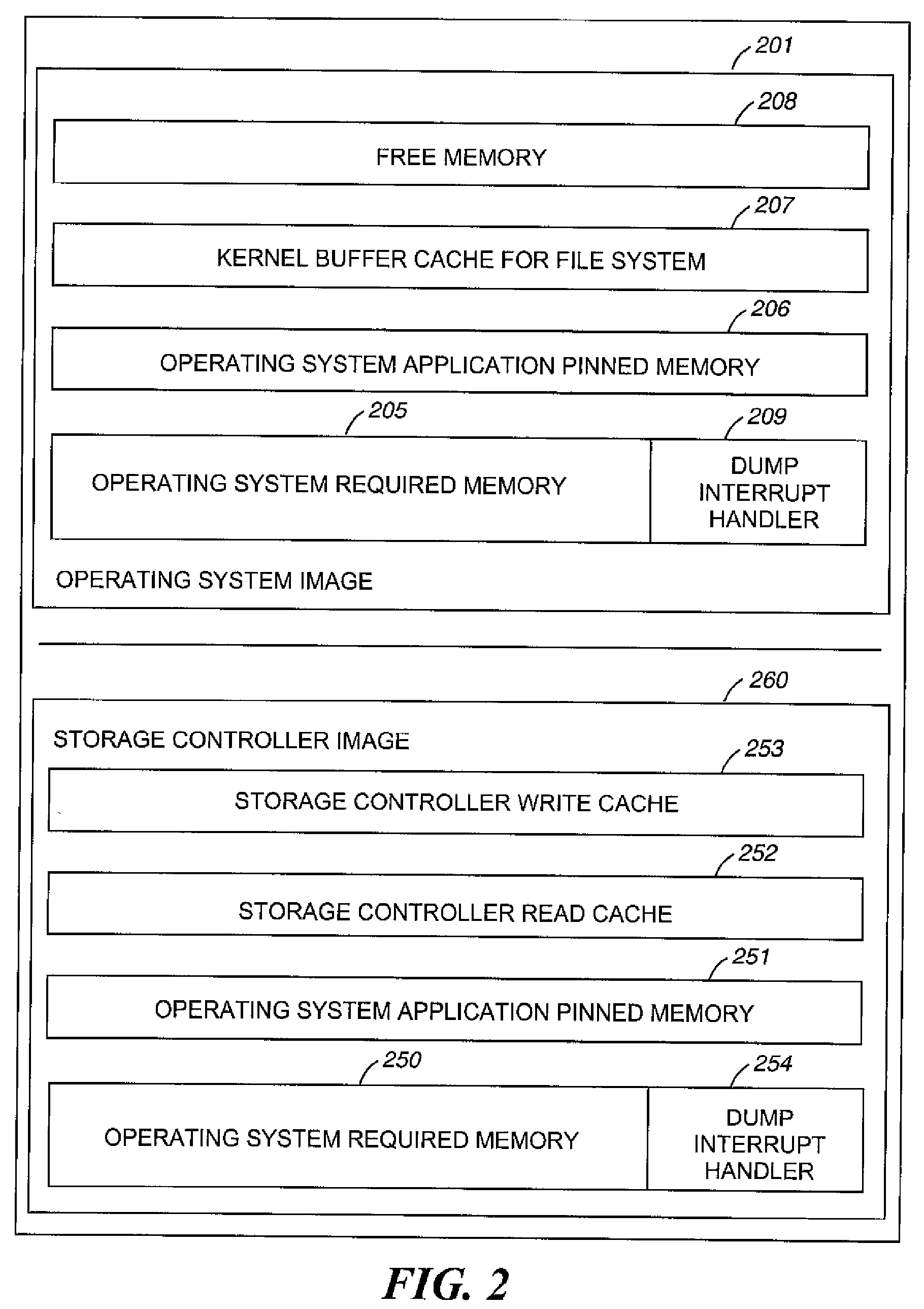
Storage control unit with memory cash protection via recorded log
InactiveUS20090031083A1Performance advantageEasy accessError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl storeDatabase
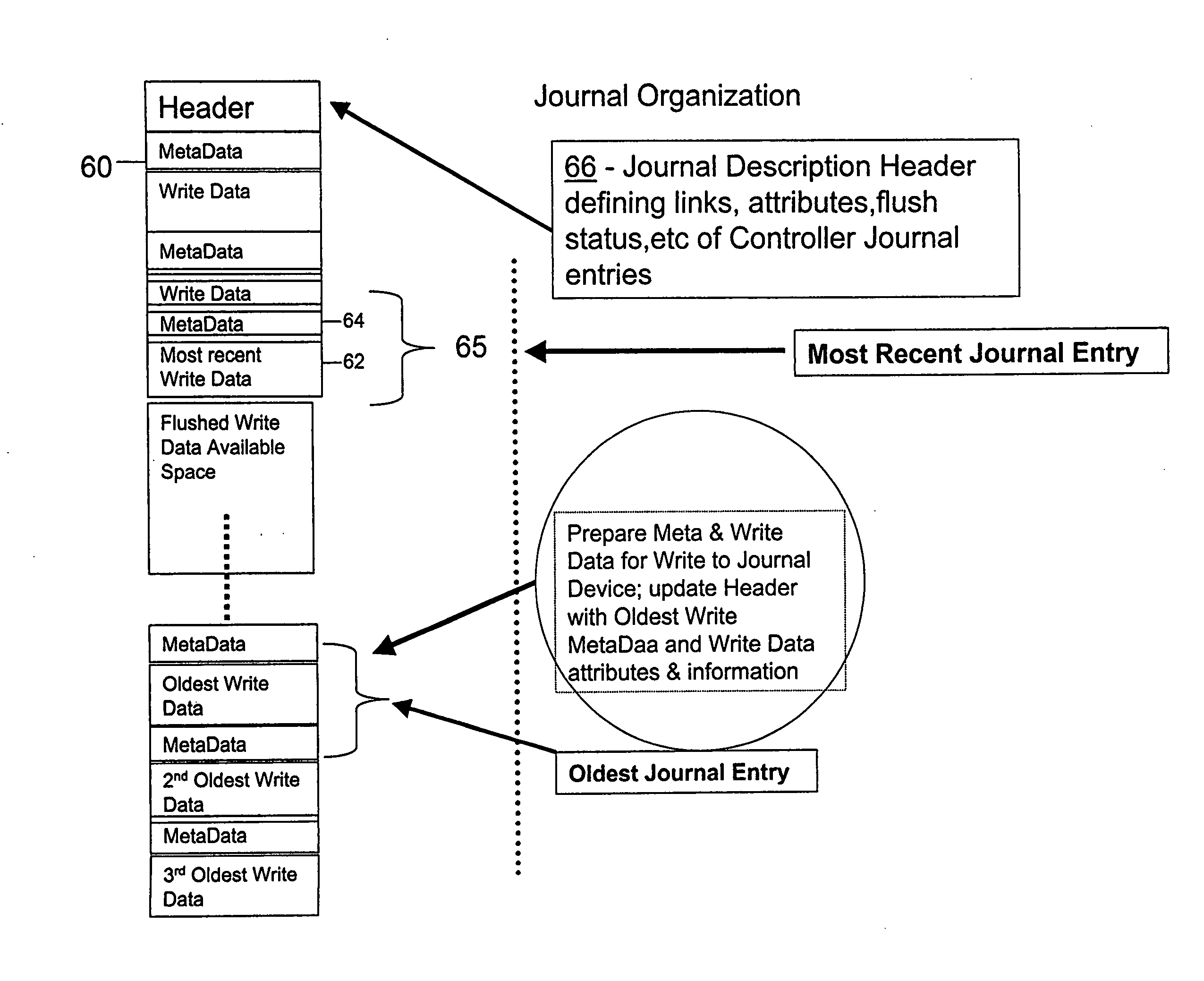
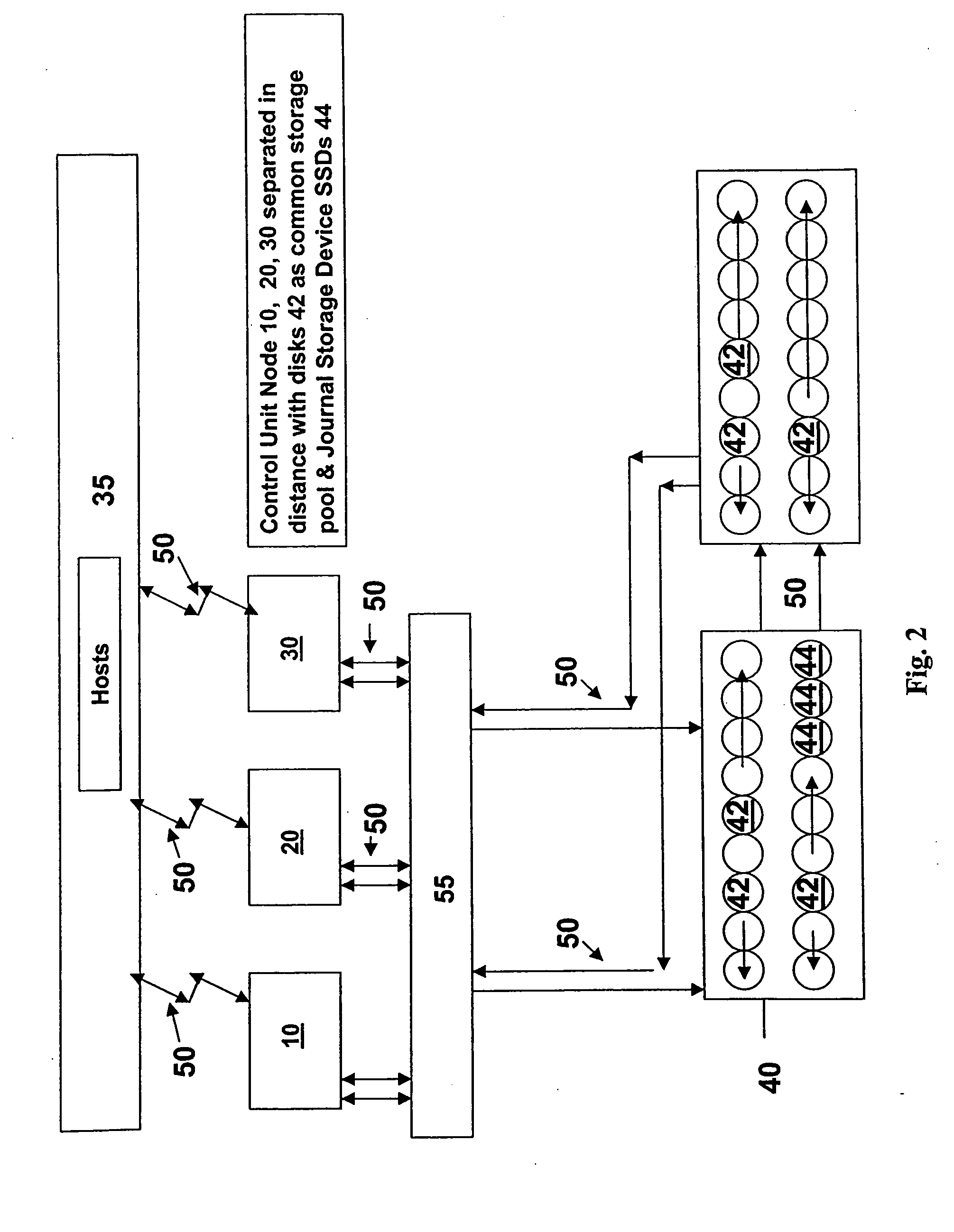
A “Logging” method and apparatus is provided to protect control unit cached data not yet written to backing storage disk drives. This recording mechanism will copy “WRITE DATA” to a log at a target logically or physically external (to the storage controllers) location equally common to all members of the set of distributed storage control units managing a common storage pool. Upon the failure of one the members of the set of control units, the “Log” information is available to insure that pending “write” data is written to the proper location on the disk drives upon a recovery action. One of the surviving members of the set assumes control of the storage managed by the failing unit by utilizing the recorded information to insure that data not written to backing storage (disks) up to the point of failure is then written to the disk backing storage. The surviving member of the set recovering the failing control unit storage (disk set) ownership will thereby “flush” (WRITE) the Journaled WRITE DATA to the backing storage disk drives before allowing normal operations to proceed.
Owner:DIGI DATA CORP
Preventive recovery action in hard disk drives
InactiveUS6401214B1Not easy to failError minimizationRecord information storageHardware monitoringData processing systemHard disc drive
A method in a data processing system for minimizing read / write errors caused by impaired performance of a hard disk drive during runtime operation of the hard disk drive. The runtime operation includes an active mode during which read / write operations are conducted and a standby mode which occurs while no read / write operation is underway. First, at least one performance parameter of a hard disk drive is monitored during a standby mode of operation. Next, in response to detecting a degraded value of the at least one performance parameter, performing preventive recovery action only during the standby mode of operation, such that the performance parameter is restored to an acceptable value without interfering with hard disk drive operation during an active mode.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
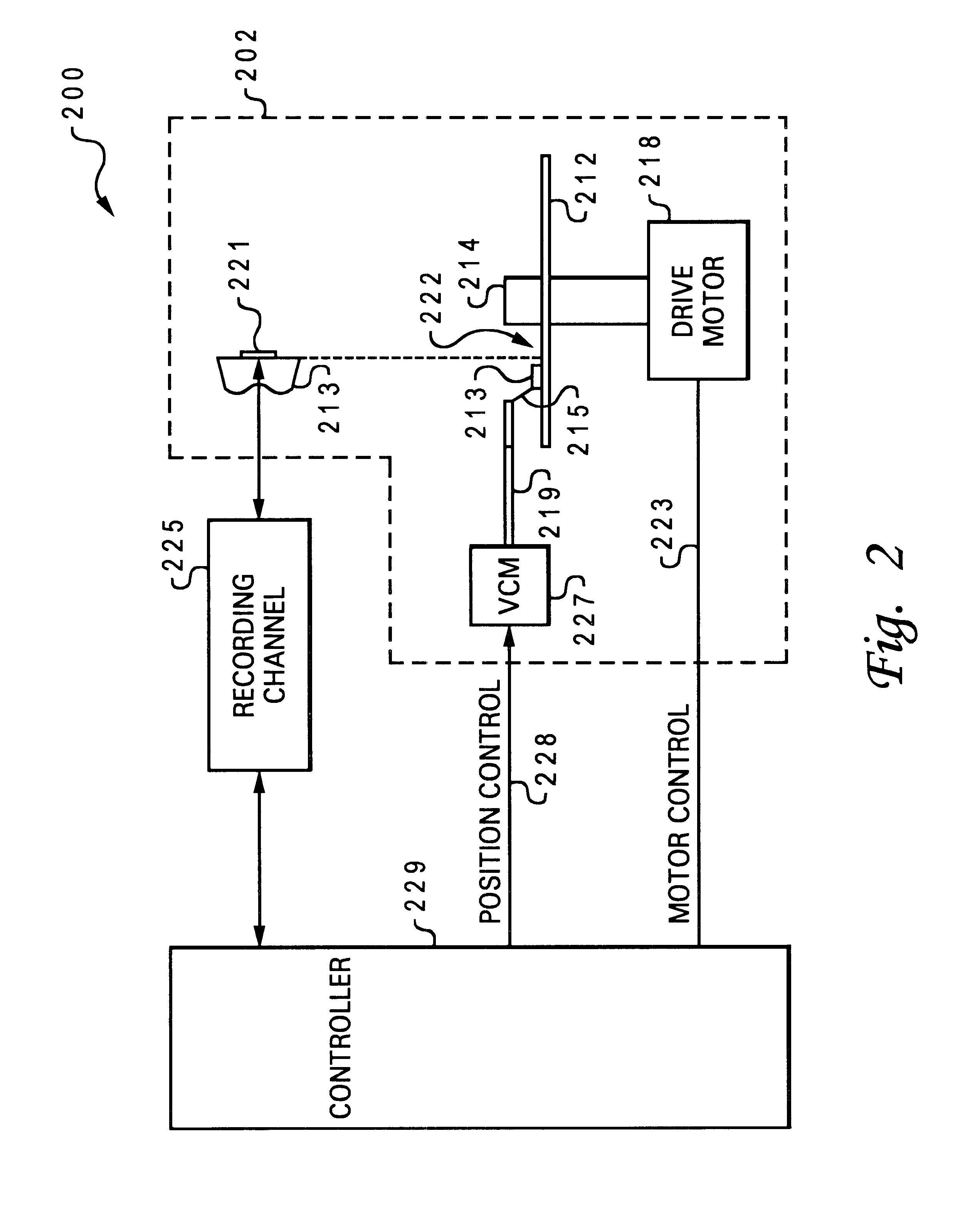
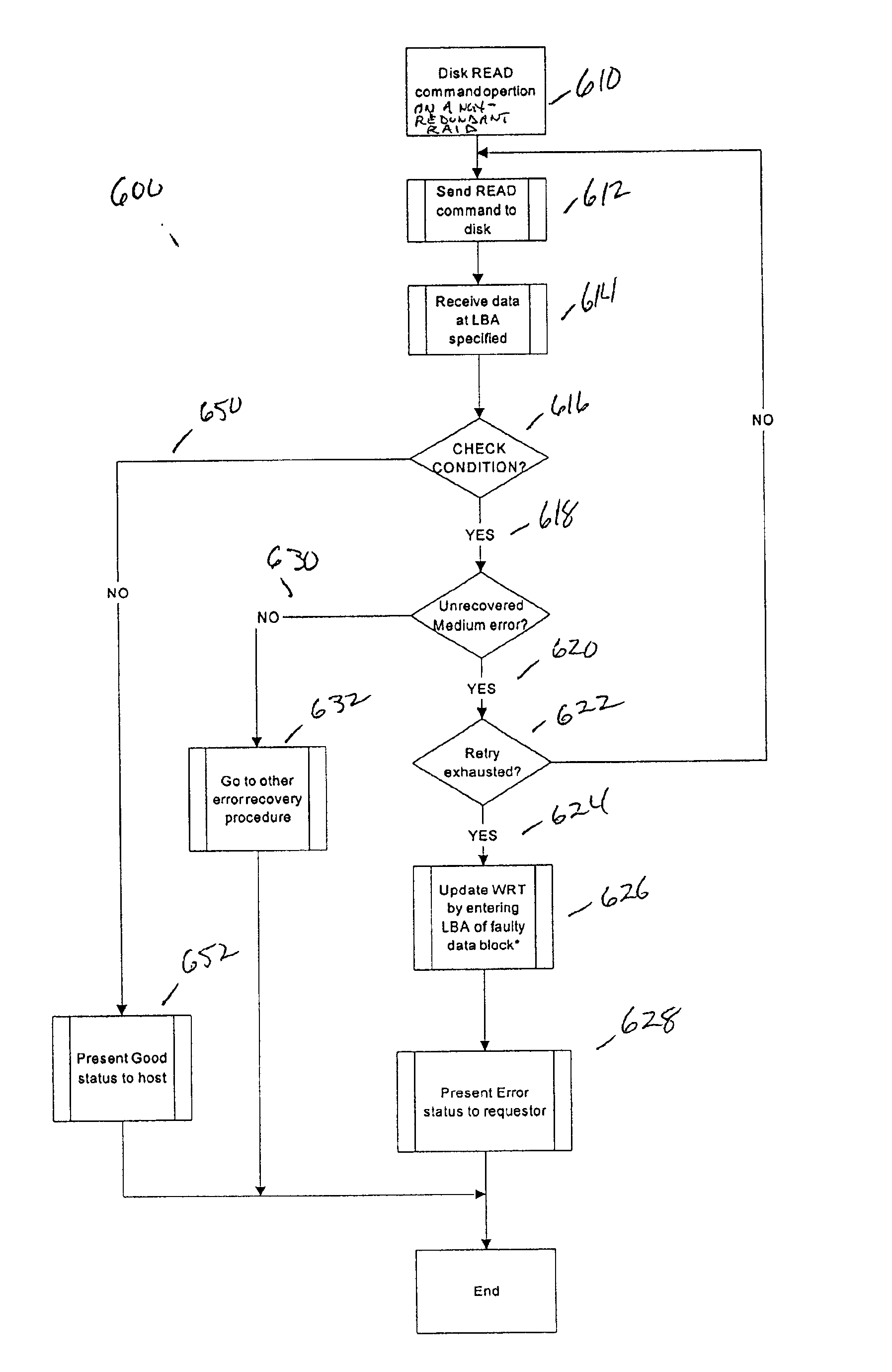
Method and apparatus for providing write recovery of faulty data in a non-redundant raid system
A table for identifying potentially bad location addresses based on prior knowledge and performing specific operations using the table data to ensure write recovery is disclosed. A Write Recovery Table (WRT) is provided, which consists of a list of LBAs requiring such special write recovery action so that a WRITE AND VERIFY command is issued instead of a WRITE command. If the WRITE AND VERIFY command fails, the RAID controller can issue a REASSIGN BLOCKS command for the bad block and re-issue the WRITE AND VERIFY command. If WRITE AND VERIFY commands are not supported, then the system can use a READ command with the “Force Unit Access” flag bit being set to “1” to verify the written data. Further, the WRT may be combined with Bad Data Table (BDT) to reject a Read Request from the host for a matched LBA (that is listed therein) because the data in the addressed block is known incorrect when a write recovery action is not warranted.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Highly available transaction processing
ActiveUS7058853B1Minimize data lossImprove availabilityError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsHandling systemTransaction processing system
A generalized architecture for a highly available transaction processing system that combines commercially available components and software components specifically developed to implement the architecture into an integrated, highly available transaction processing system that minimizes planned and unplanned downtime, minimizes data loss in the event of failures, provides proactive monitoring of both hardware and software components of the highly available transaction processing system, provides automated recovery actions that involve fast failover, either locally to an Inactive Node, or remotely to a Standby Site, and provides an easy-to-use graphical-user-interface-based management interface that provides service-oriented views of the state of the system, with context-directed commands and meta-commands to guide managers in execution of their tasks.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
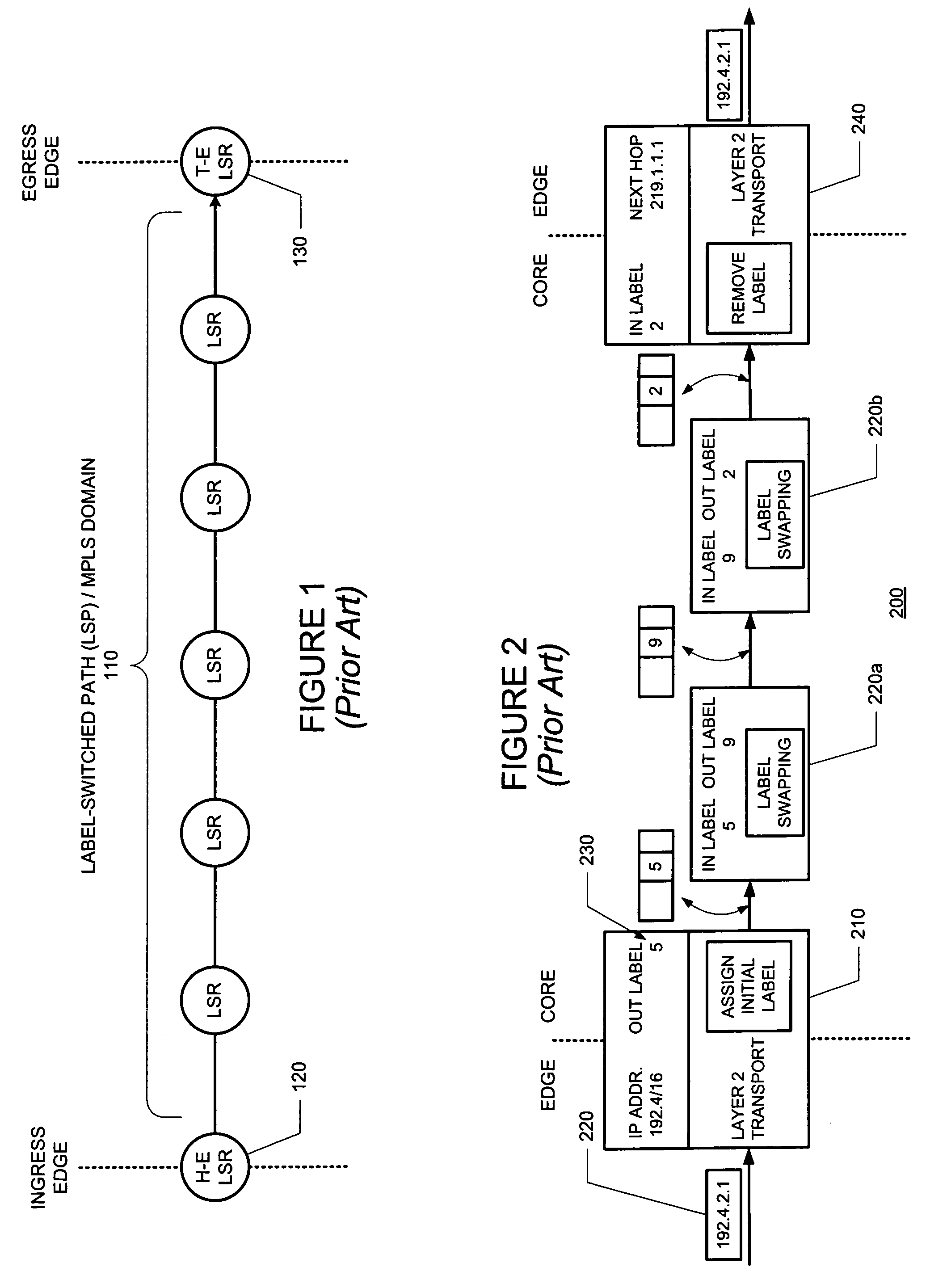
Detecting data plane livelines in connections such as label-switched paths
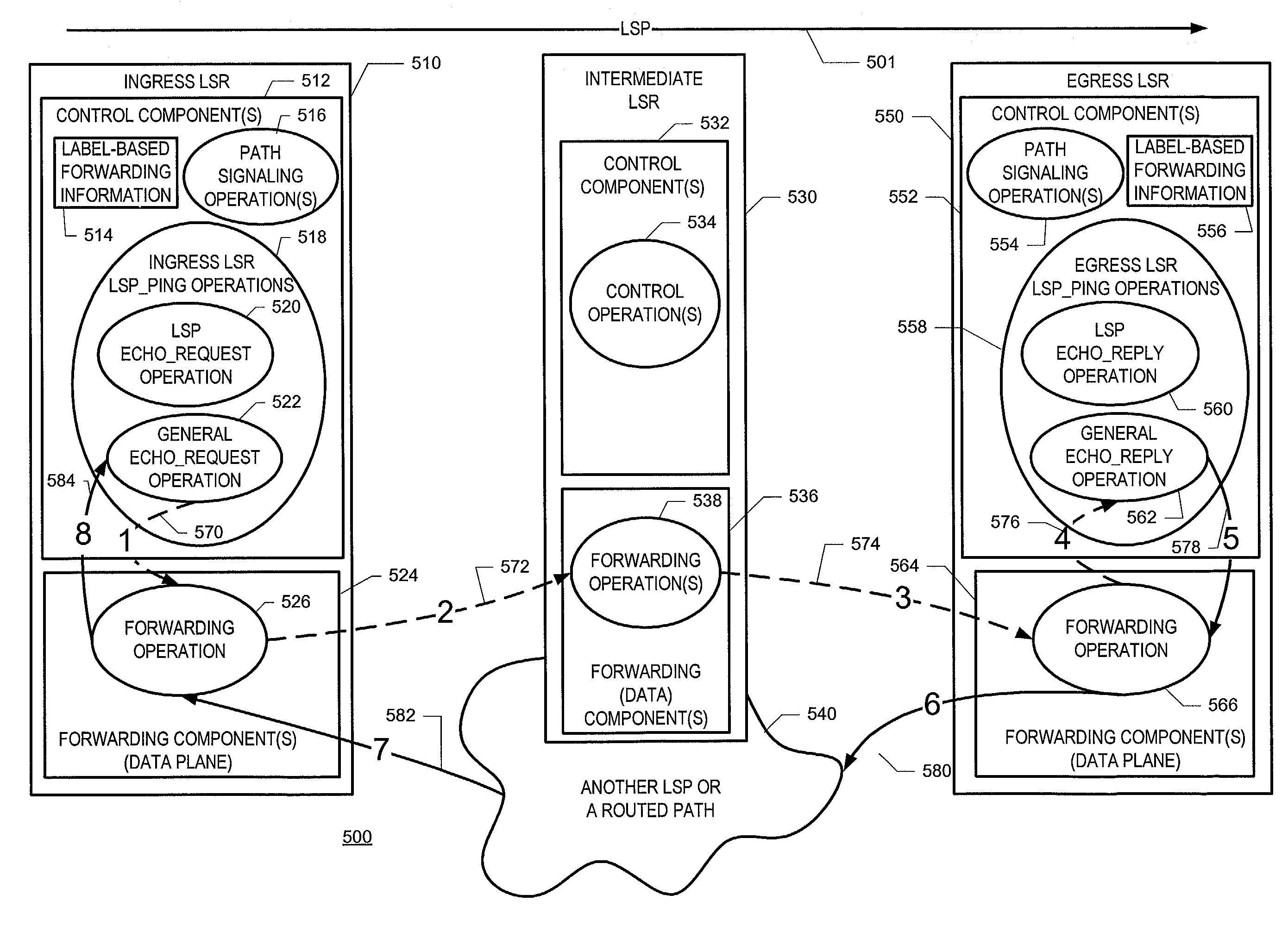
ActiveUS7336615B1Minimizes processing overheadMinimize overheadError preventionTransmission systemsLabel switchingStream control
Testing the liveliness of a data plane of a label switched path (LSP) using a two stage approach. The first stage may use a general echo request operation that may be implemented using hardware. Therefore, the first stage does not heavily burden the control plane of the LSR. If a suspect LSP passes the first stage of the diagnostic operation, nothing more needs to be done. If, however, the suspect LSP fails the first stage, the diagnostic operation proceeds to a second stage. The second stage of the diagnostic operation sends probing massages through the suspect LSP, but uses the control plane to deliver the acknowledging messages. If the suspect LSP fails the second stage of the diagnostic operation, the ingress LSR can infer that the LSP is down, and begin recovery actions. The probing messages may include padding so that MTU limits can be tested. In addition, the probing messages may be encapsulated in a protocol that allows flow control, thereby protecting an LSR that can receive such messages from DoS attacks.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
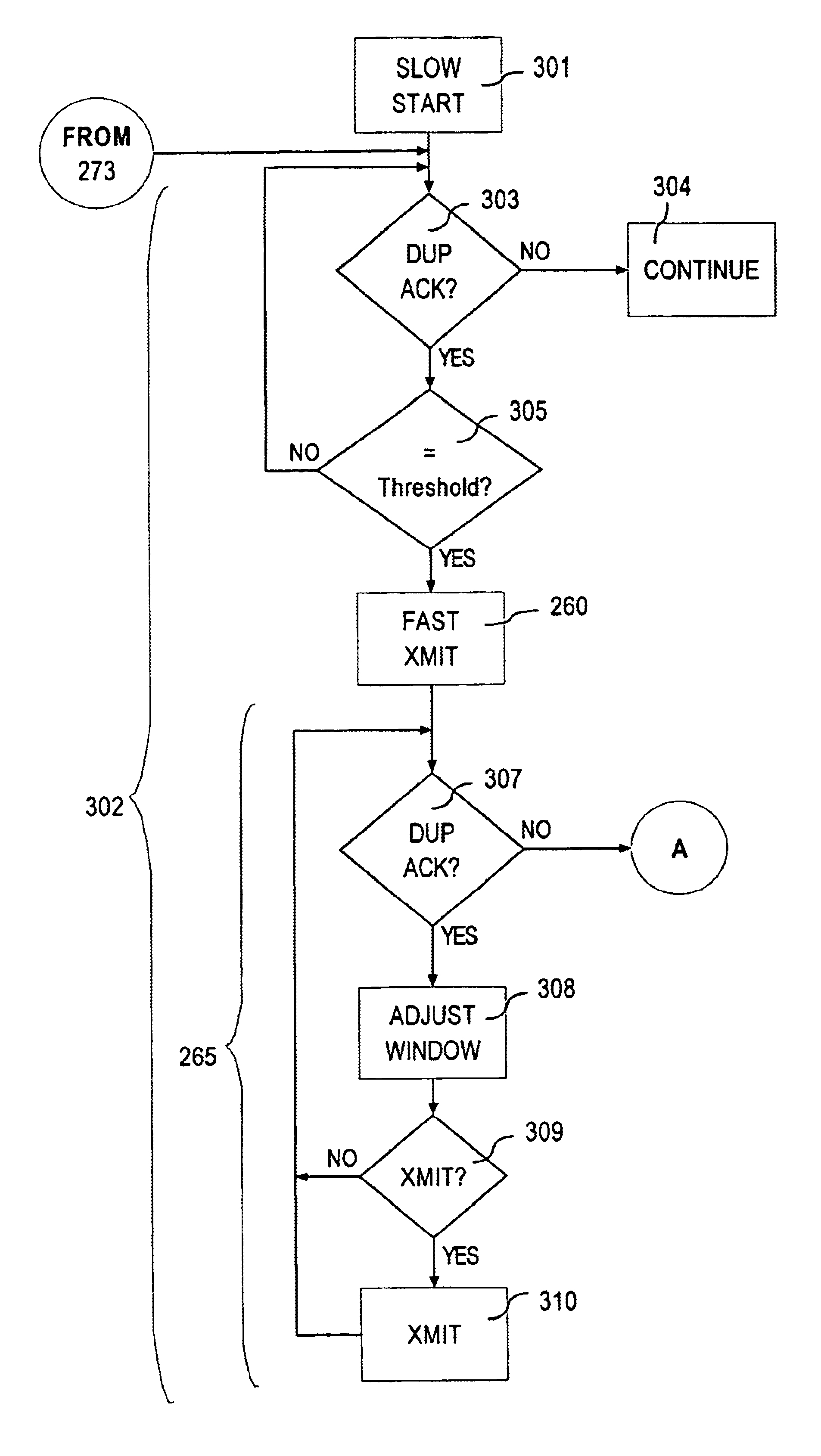
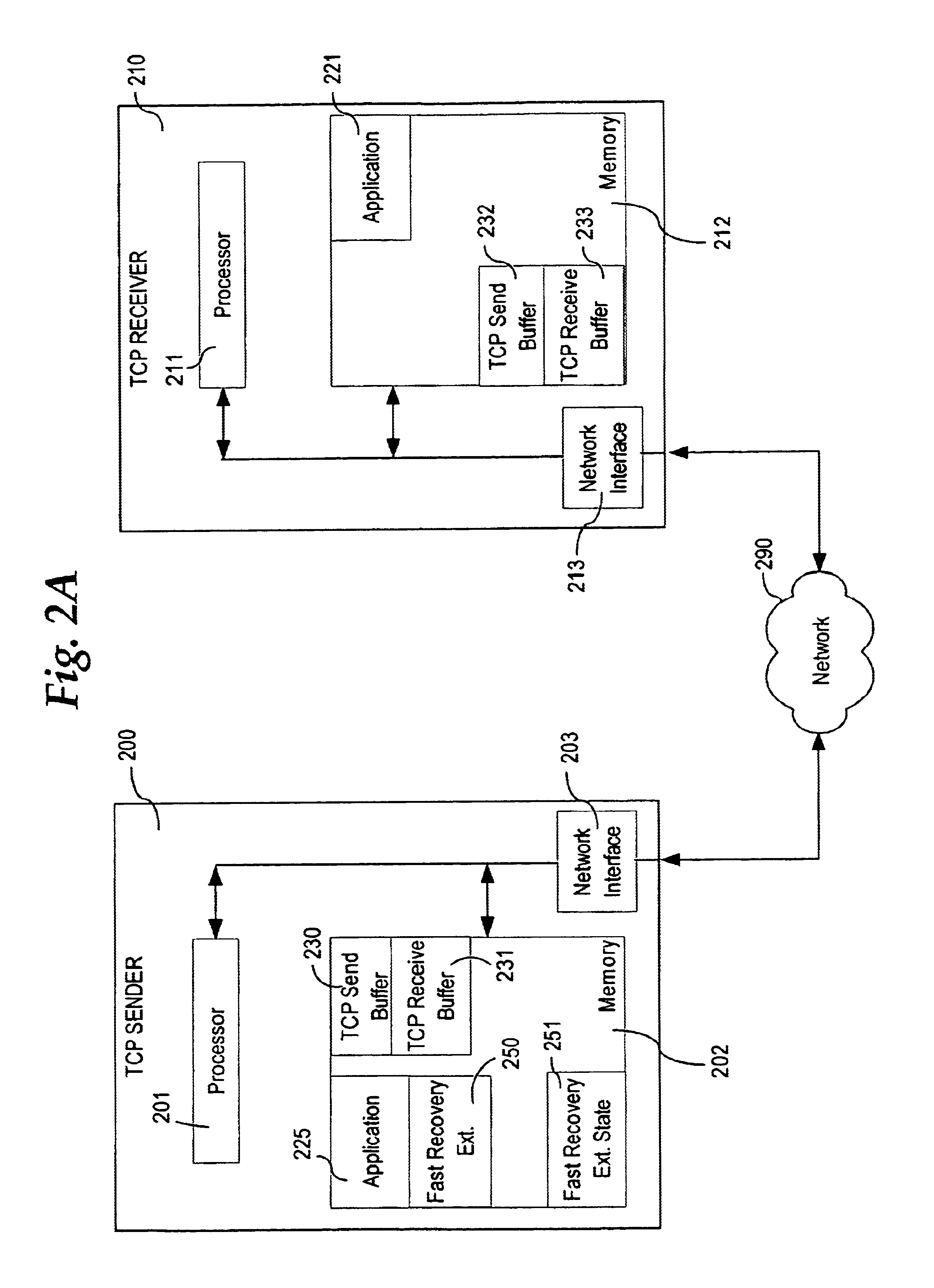
TCP fast recovery extended method and apparatus
InactiveUS6958997B1Smoother and faster recoveryEasy to useError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsNetwork packetRecovery procedure
A fast recovery extended method is used to enhance the performance of TCP fast recovery when multiple segment losses occur within a single round trip time between a TCP sender and a TCP receiver. A TCP fast recovery process is performed by a TCP sender, and then a TCP fast recovery extended process is performed by the TCP sender upon receiving acknowledgement of receipt of new data from a TCP receiver in the TCP fast recovery process. The fast recovery extended process determines, following receipt of the acknowledgement of receipt of new data, an excess number of duplicate acknowledgements based upon a count of consecutive duplicate acknowledgement packets. The fast recovery extended process takes a network packet transmission recovery action based upon the excess number of duplicate acknowledgements, and then stores the excess number of duplicate acknowledgements as a number of duplicate acknowledgements for further use.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
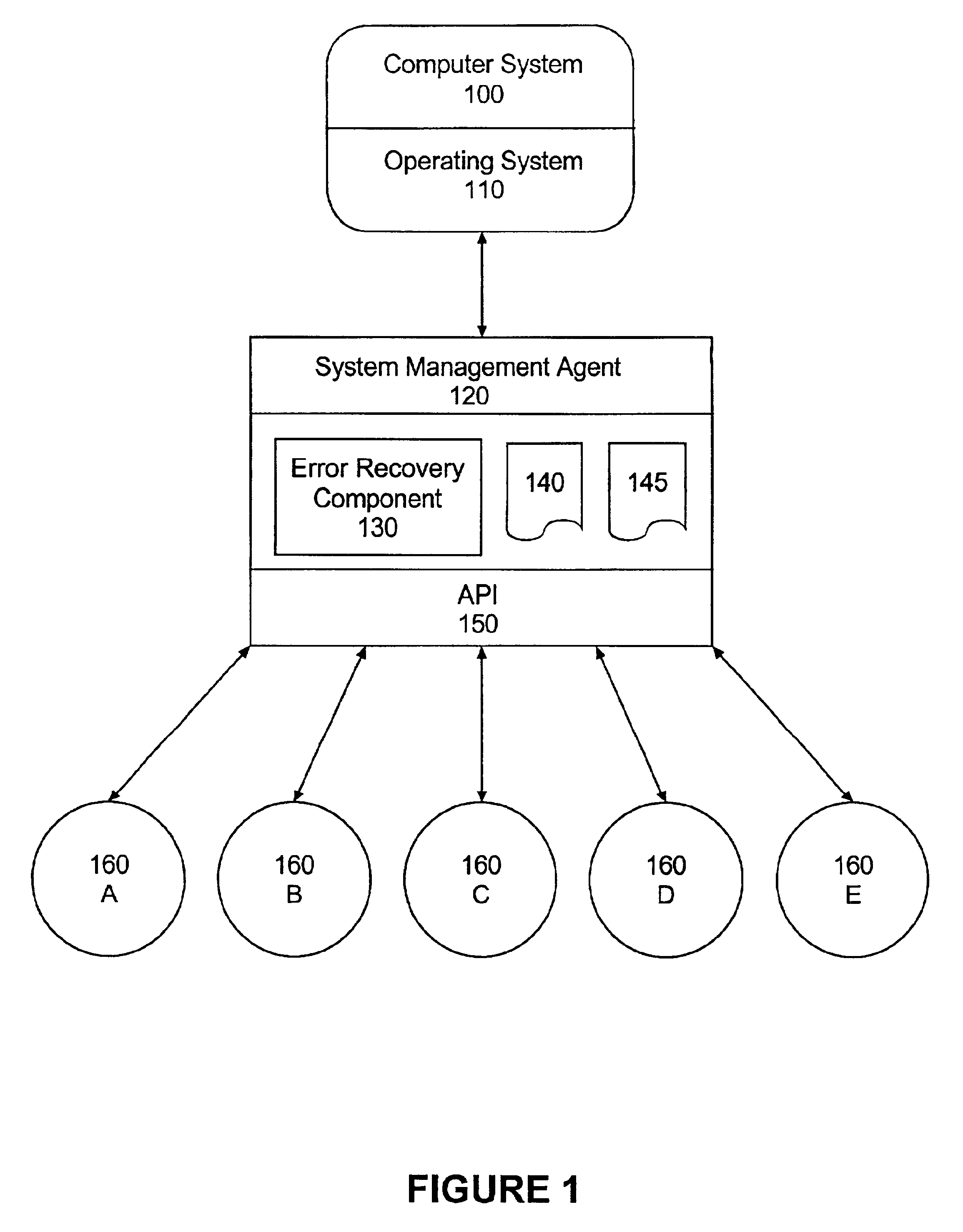
First failure data capture
InactiveUS7080287B2Digital data processing detailsSoftware testing/debuggingTreatment errorProblem solve
An example of a solution provided here comprises: selecting an incident that requires further processing, capturing data associated with said incident, outputting captured data, and outputting a description for said captured data, whereby problem-solving is promoted. Another example comprises: providing runtime features for data capture, selecting an incident that requires further processing, capturing data on a thread that encounters said incident, and outputting captured data. In some cases, such a solution might include comparing a current incident to known incidents, and if a match is found, retrieving information that is relevant to said current incident. In some cases, such a solution might include taking recovery action or corrective action in response to said incident. Methods for handling errors, systems for executing such methods, and instructions on a computer-usable medium, for executing such methods, are provided.
Owner:LINKEDIN
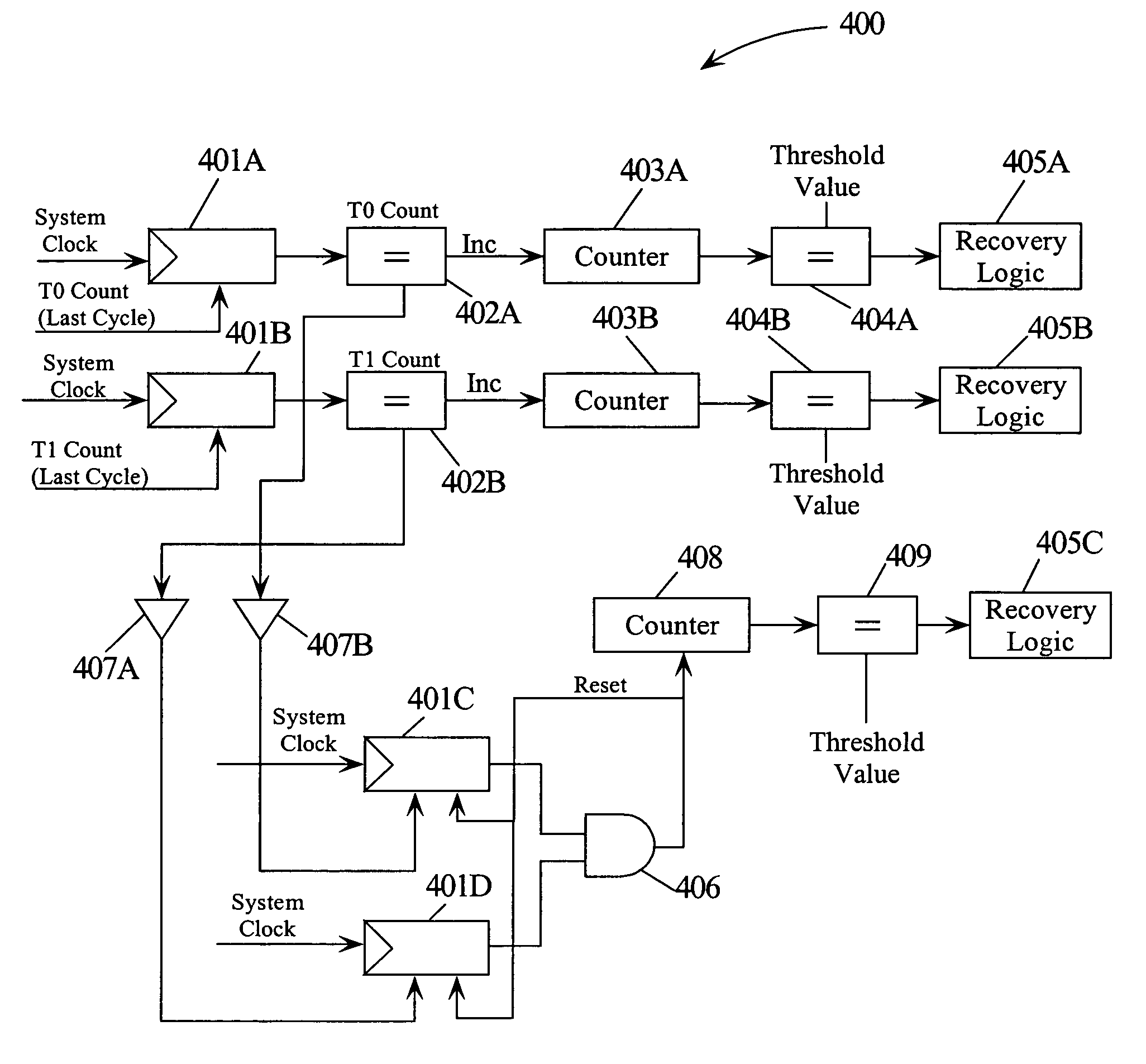
Mechanism for effectively handling livelocks in a simultaneous multithreading processor
InactiveUS7000047B2Preventing executionRuntime instruction translationUnauthorized memory use protectionOperating systemSimultaneous multithreading
A method and multithreaded processor for handling livelocks in a simultaneous multithreaded processor. A number of instructions for a thread in a queue may be counted. A counter in the queue may be incremented if the number of instructions for the thread in the queue in a previous clock cycle is equal to the number of instructions for the thread in the queue in a current clock cycle. If the value of the counter equals a threshold value, then a livelock condition may be detected. Further, if the value of the counter equals a threshold value, a recovery action may be activated to handle the livelock condition detected. The recovery action may include blocking the instructions associated with a thread causing the livelock condition from being executed thereby ensuring that the locked thread makes forward progress.
Owner:IBM CORP
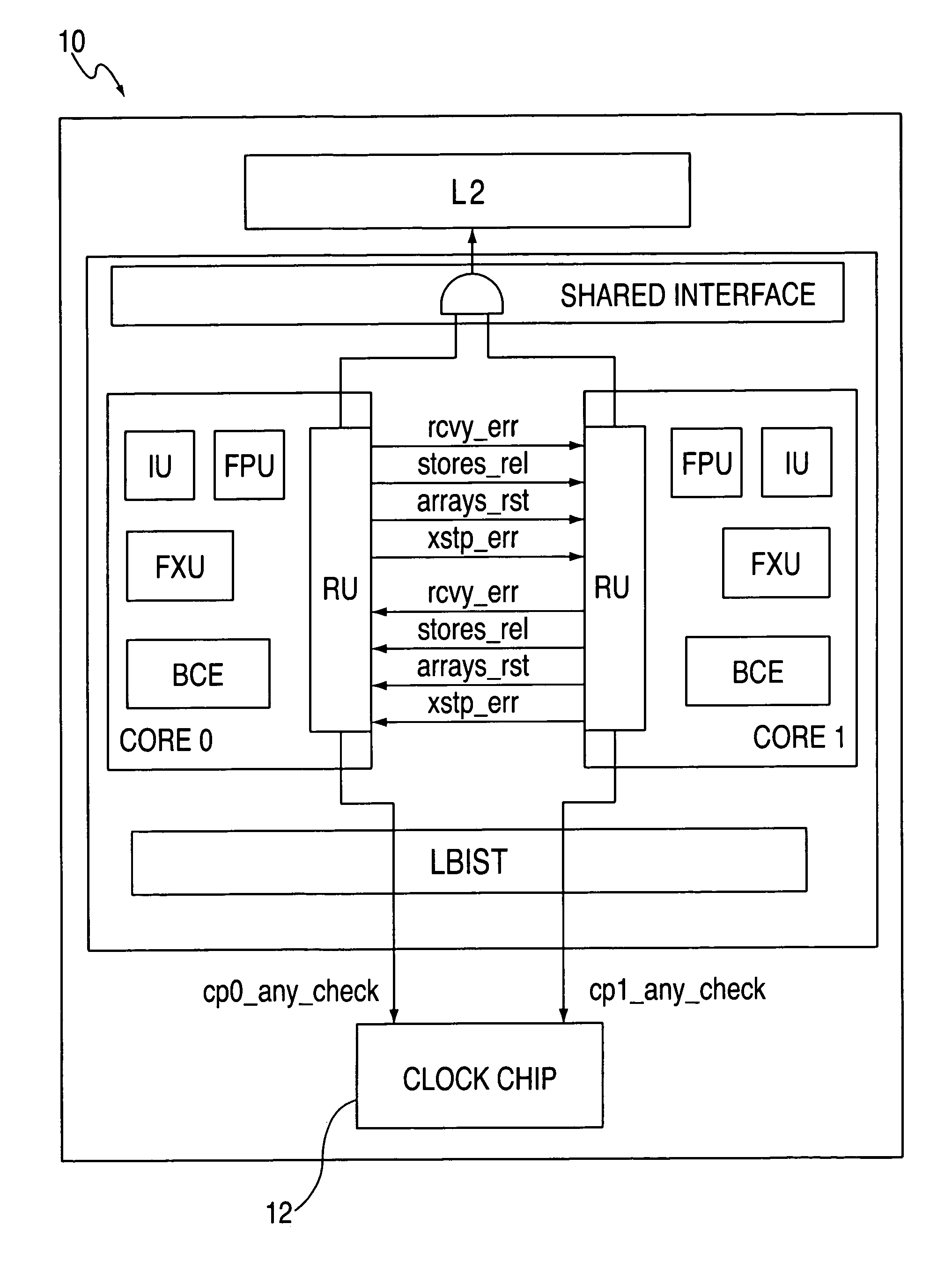
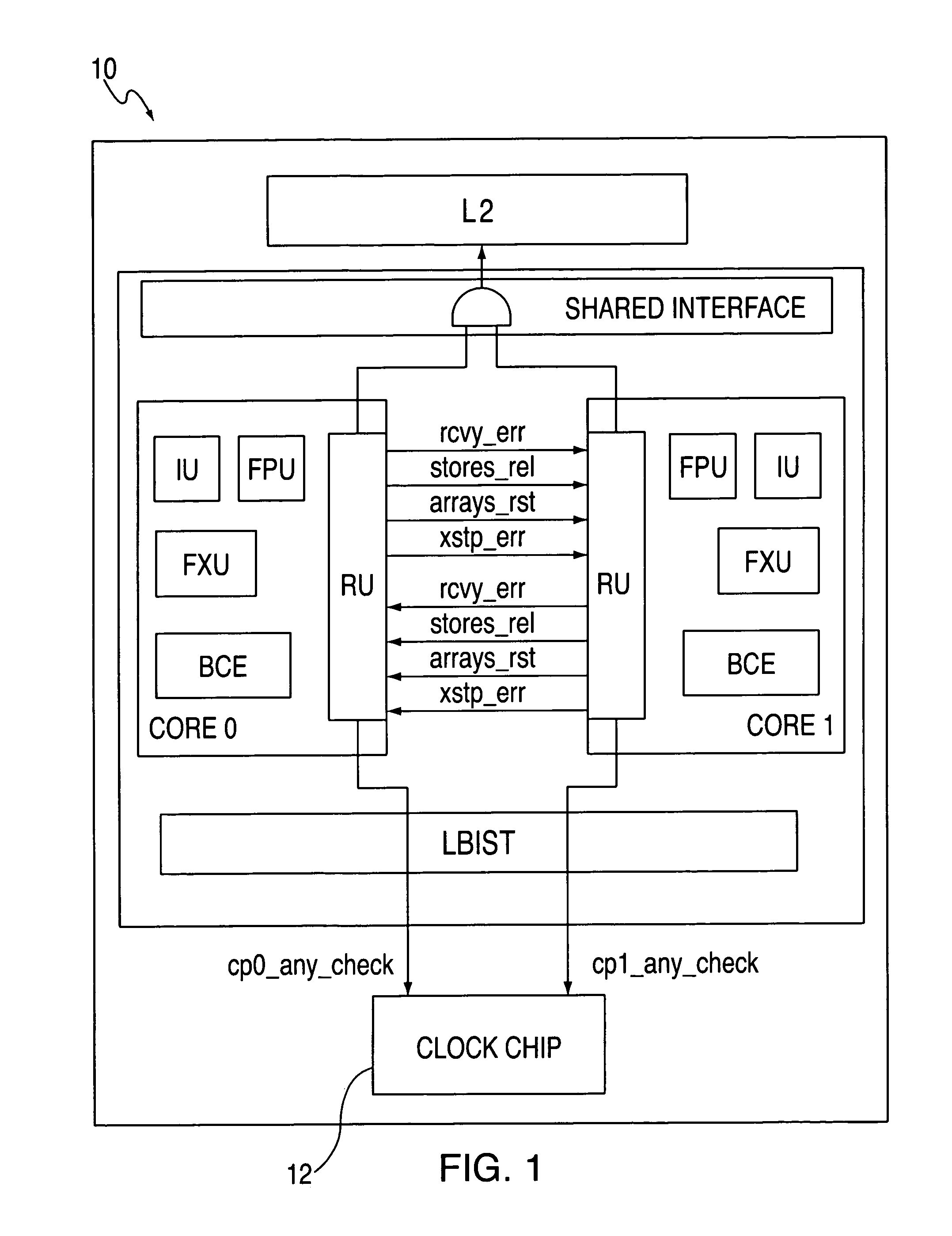
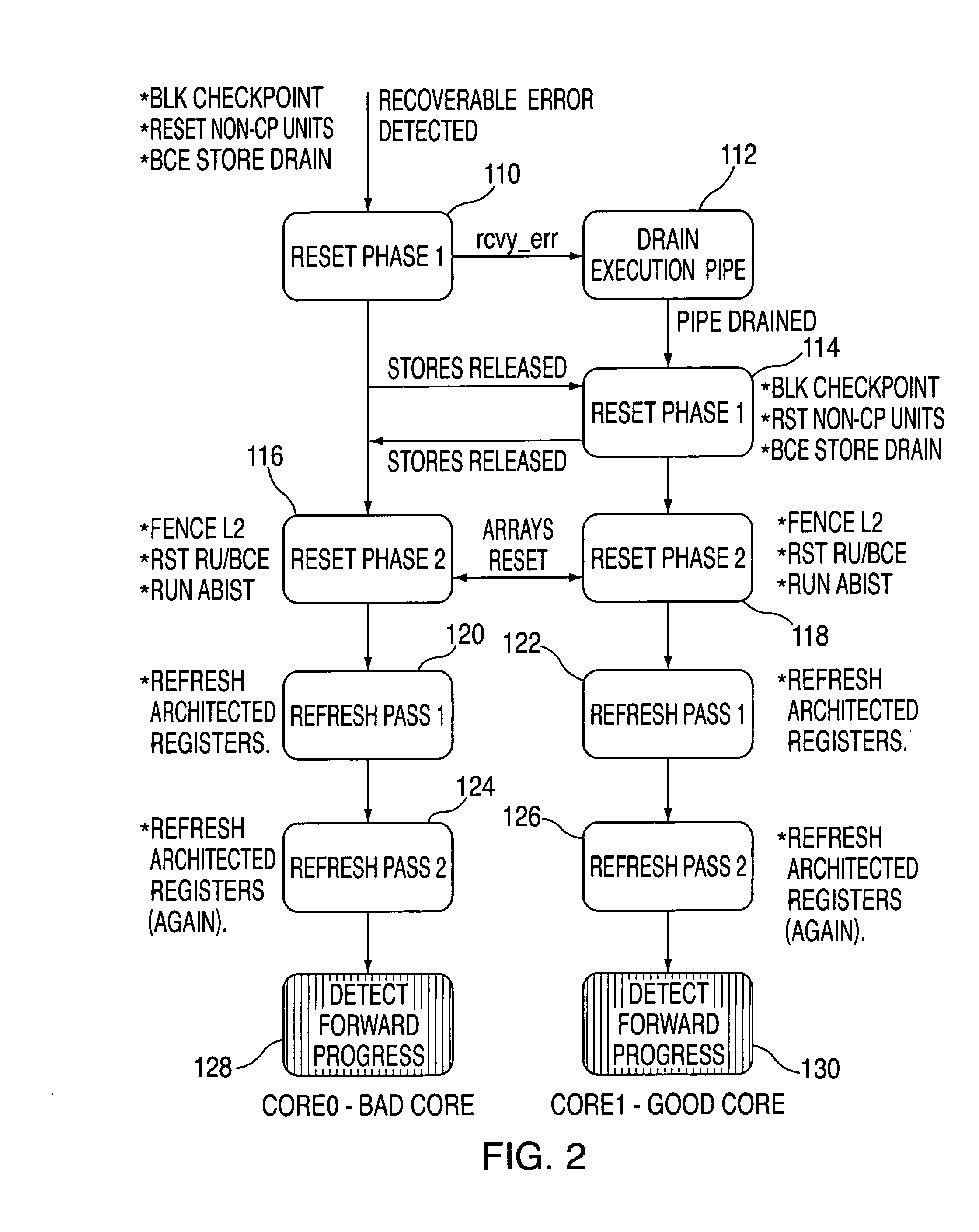
System and method for providing processor recovery in a multi-core system
An embodiment of the invention is a multiprocessor system for detecting and recovering from errors. The multiprocessor system includes a first processor and a second processor. The first processor detects an error and initiates a recovery process. The first processor and said second processor synchronize at least one recovery action during the recovery process.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Recovery action management system
InactiveUS20080155553A1Reduce outage timeImprove the level ofMultiprogramming arrangementsNon-redundant fault processingInformation processingResource recovery
Disclosed are a method, information processing system, and computer readable medium for resource recovery. The method comprises associating at least one bit with at least one block of memory. The bit denotes a borrow status for the block of memory. The bit is set for resource recovery. A resource recovery event is detected and in response to the bit being enabled for resource recovery, the block of memory is borrowed for a given duration of time. The bit is borrowed to temporarily store information associated with the resource recovery there into until the information is written to persistent storage.
Owner:IBM CORP
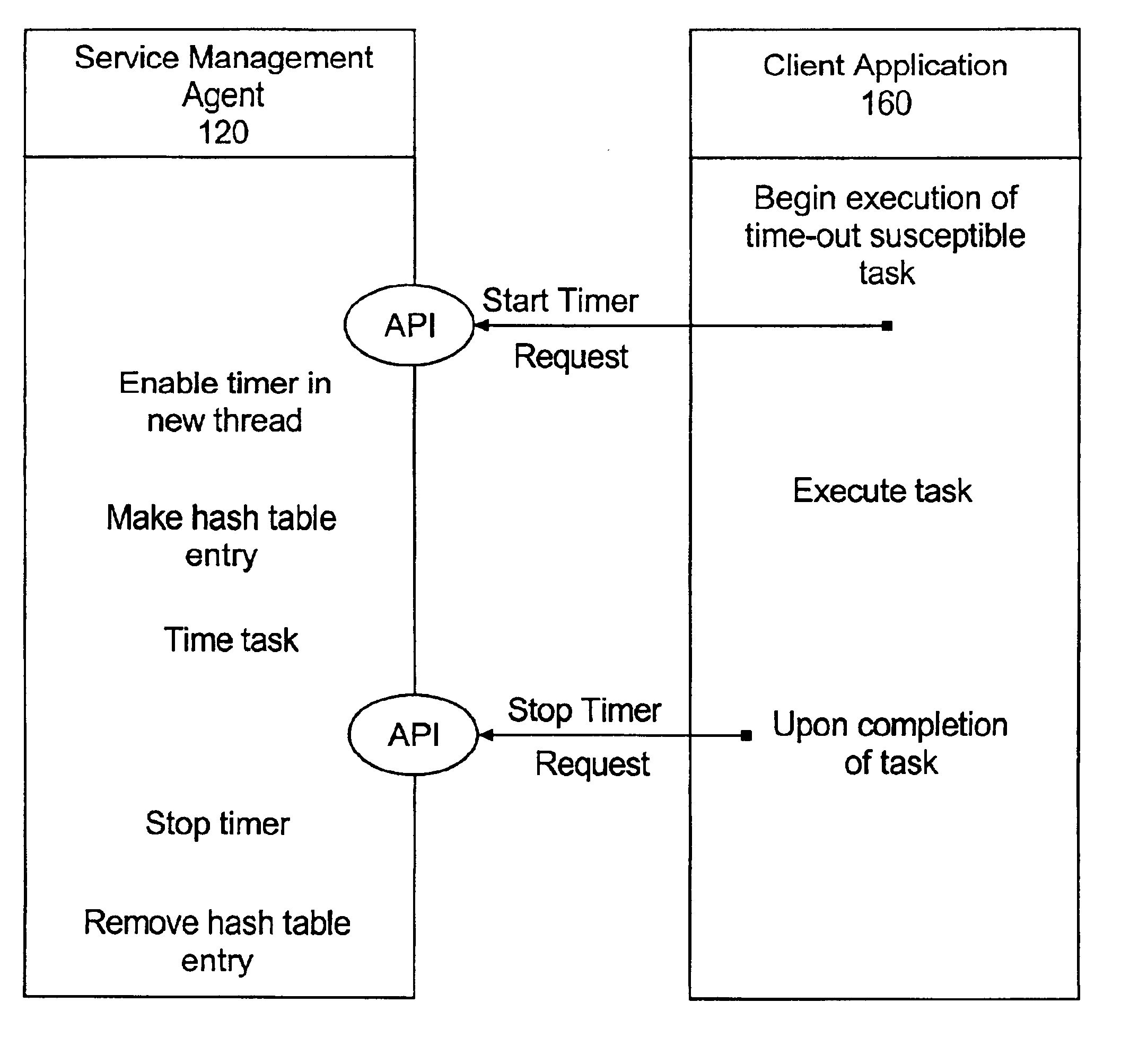
Method and system for error detection in a managed application environment
A method of managing at least one client computer program in a managed application environment can include receiving a request from at least one of a plurality of client computer programs to begin a timer. The timer can correspond to an identified task of the client computer program which has been identified as a time-out susceptible task, and which is executing within a particular thread of execution of the client computer program. The timer corresponding to the request and the time-out susceptible task can be selectively started in a separate thread of execution. The identified task can be timed. If the timer expires, a recovery action can be performed corresponding to the time-out susceptible task.
Owner:IBM CORP
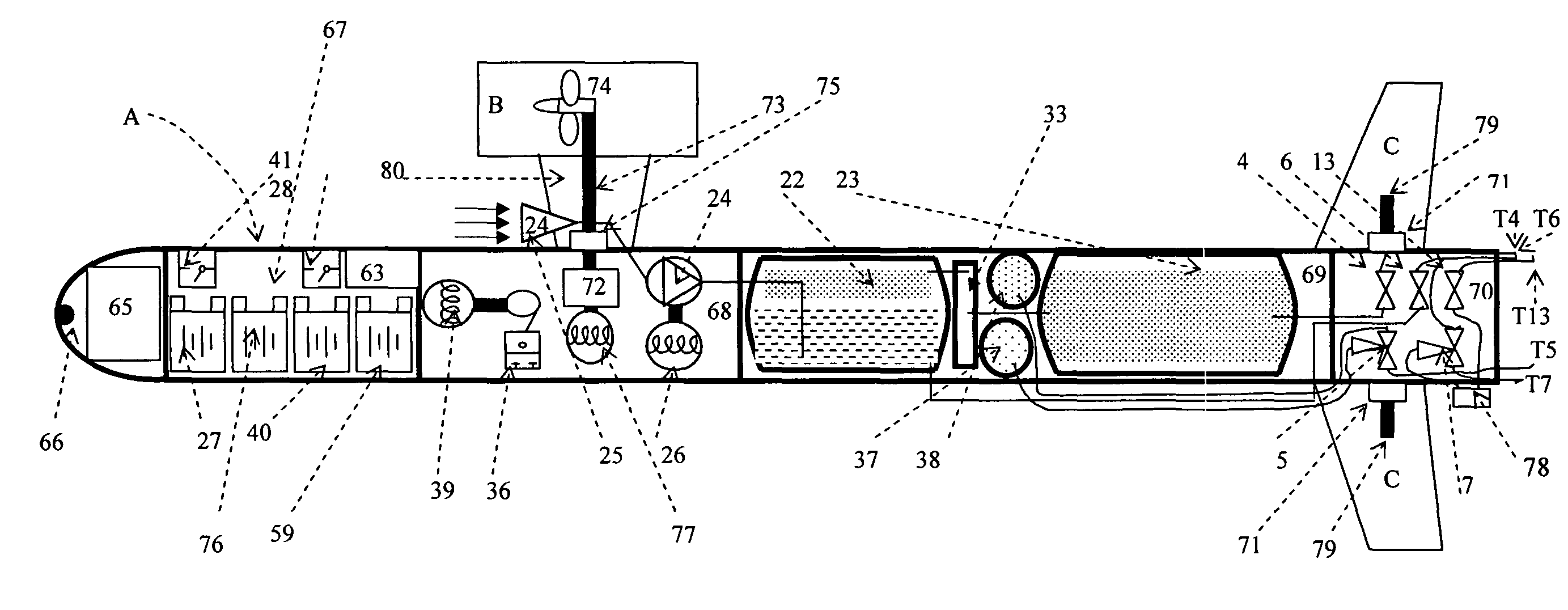
System for generating pressure waves in an underwater environment
ActiveUS20120113756A1High energyMinimizing resonance effectSound producing devicesSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyEngineering
System for generating pressure waves for deep seismic surveys operating in an underwater environment below the surface, suitable for investigating subcrustal objectives for prospecting purposes in the search for hydrocarbons and / or minerals. The system comprises one or more autonomous underwater vehicles organized in swarms, independent and coordinated, each housing one or more autonomous acoustic sea sources with self-propelled striker pistons. This system is served by a system of supporting surface stations, for reprovisioning, recovery actions, checking the well-being of the single vehicles and swarms and maintenance. The system is capable of using both conventional and non-conventional self-charged acoustic sea seismic sources. The system is capable of replicating the effect of a conventional source operated from the surface. The seismic sea source of the non-conventional acoustic type, proposed herein, can release a high-intensity pressure wave produced by a system of two striker pistons, which does not consume air when operating as it does not disperse air or another gas in water and does not produce mass variations of the device during its functioning and allows the amplitude and duration of the sound wave emitted and characteristics of the emission spectrum, to be regulated.
Owner:ENI SPA
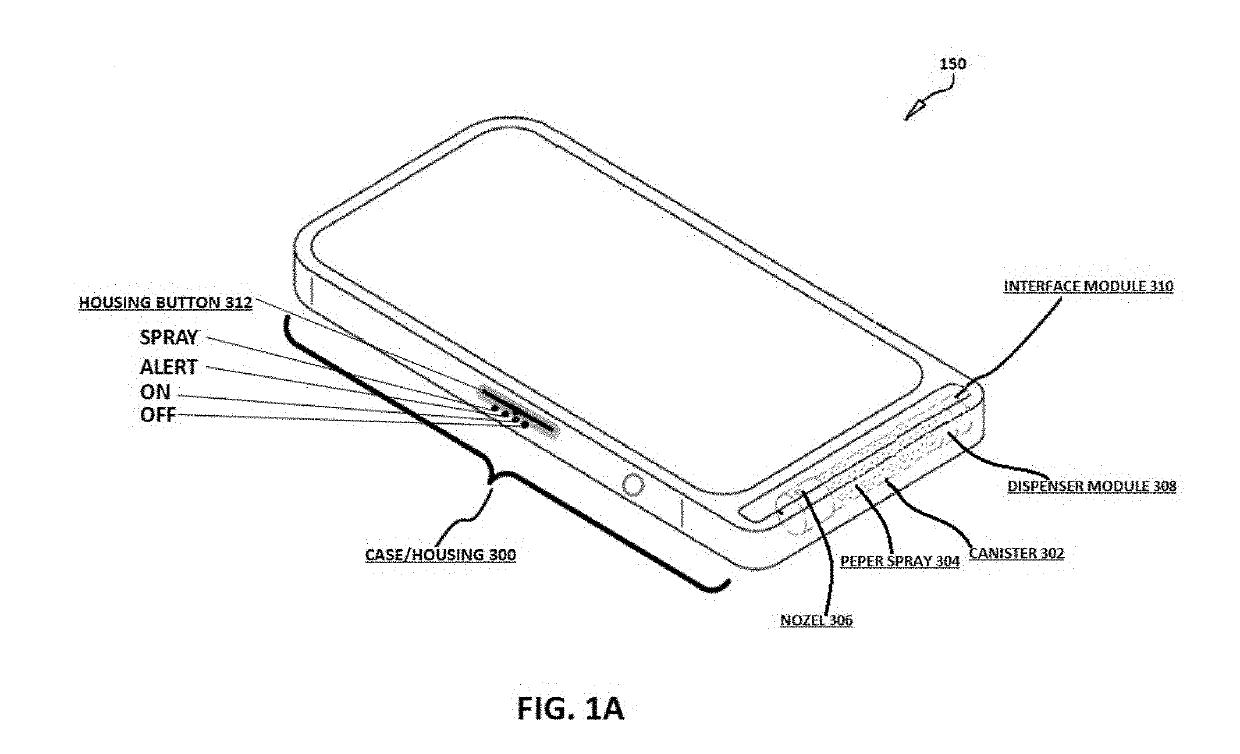
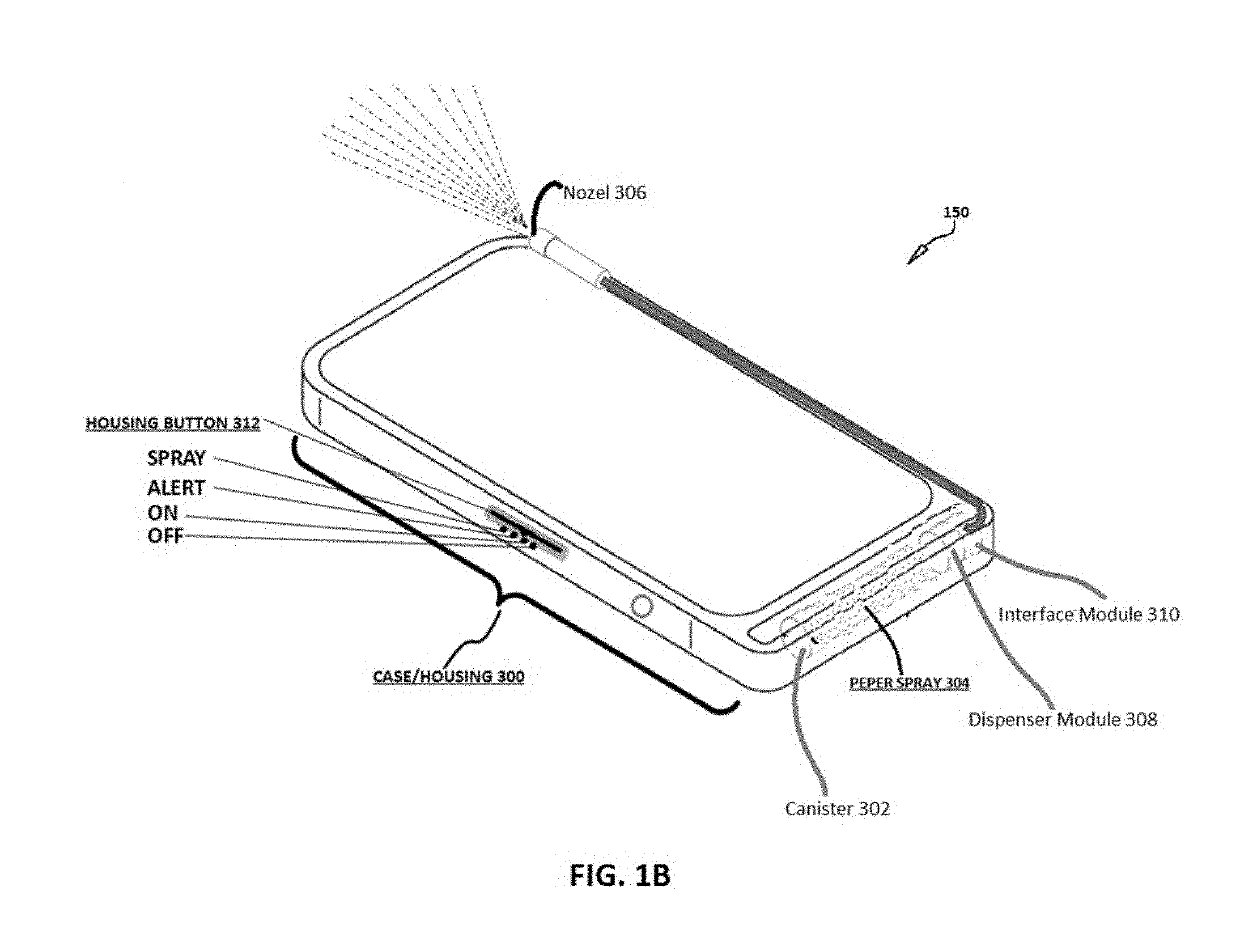
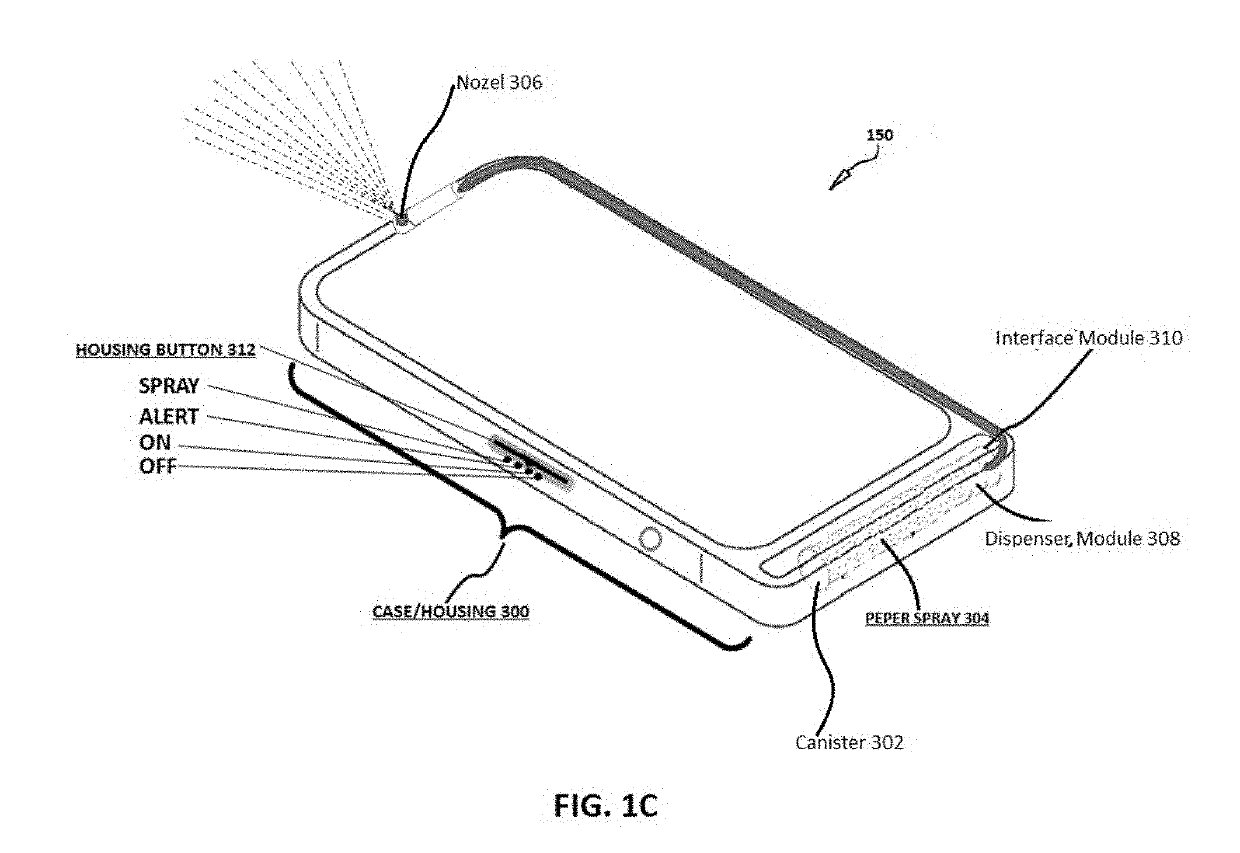
Portable phone with integrated personal protection and emergency notification means
InactiveUS20190109932A1Alarms using portable personal devicesRepellant gas/chemical self-defence devicesTablet computerIn vehicle
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed operable with any mobile communication device such as mobile phone, tablet, electronic watch or any other portable device and providing a self-defense capability to a user by dispensing a liquid or fluid or gas or powder such as but not limited to pepper spray, tear gas, powder or the like at a potential attacker in response to the user depressing one or more pre-configured virtual or physical controls provided on his / her mobile communication device, having a case or enclosure which partially envelopes a canister of pepperspray or any other similar compound for personal protection. The system enables a citizen to seek police / emergency aid while moving in vehicles etc. The system enables keeping of text / audio / video / images record including location of such emergency events and generates a case summary of the emergency situation with recovery actions performed.
Owner:HIGGINS SAMUEL
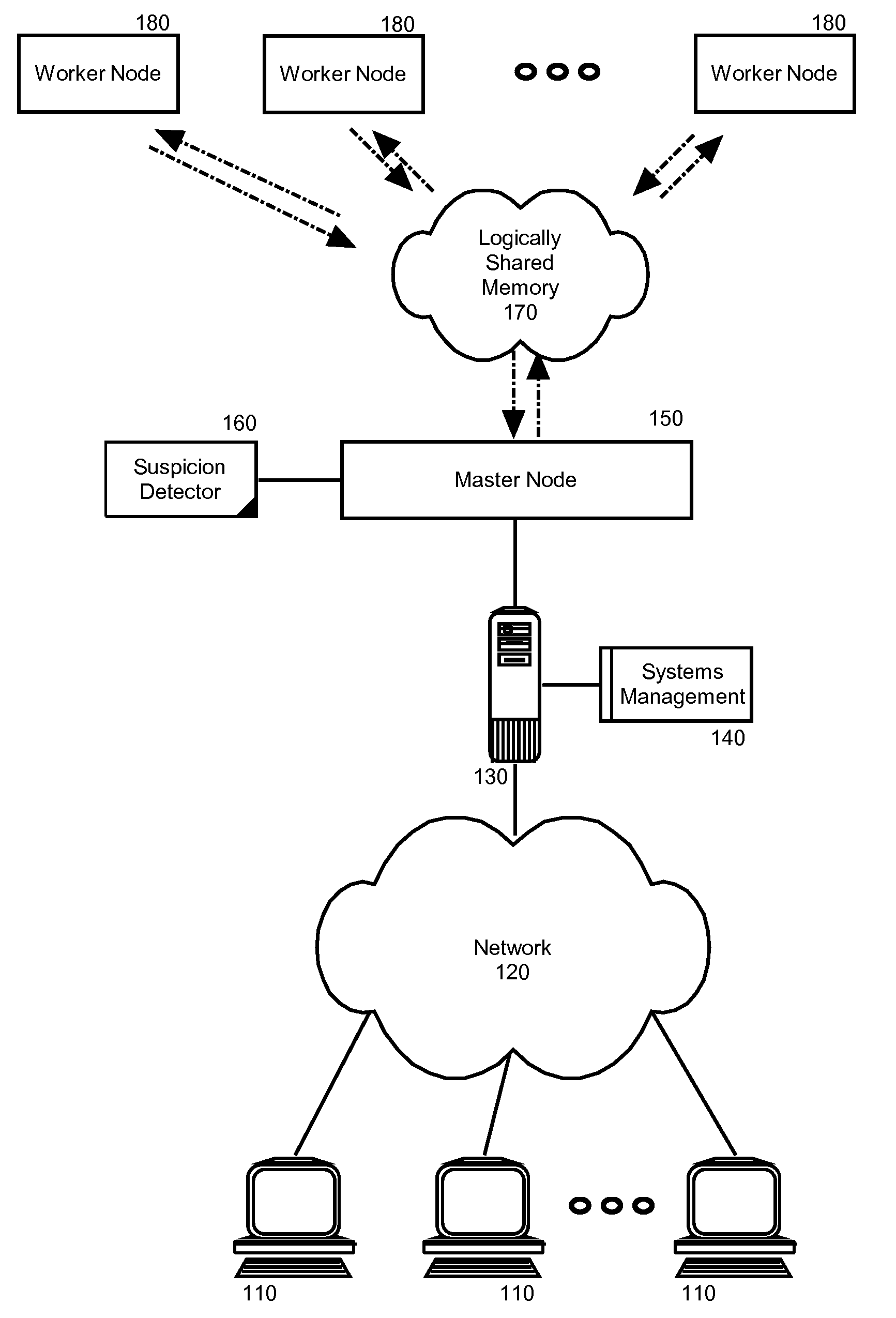
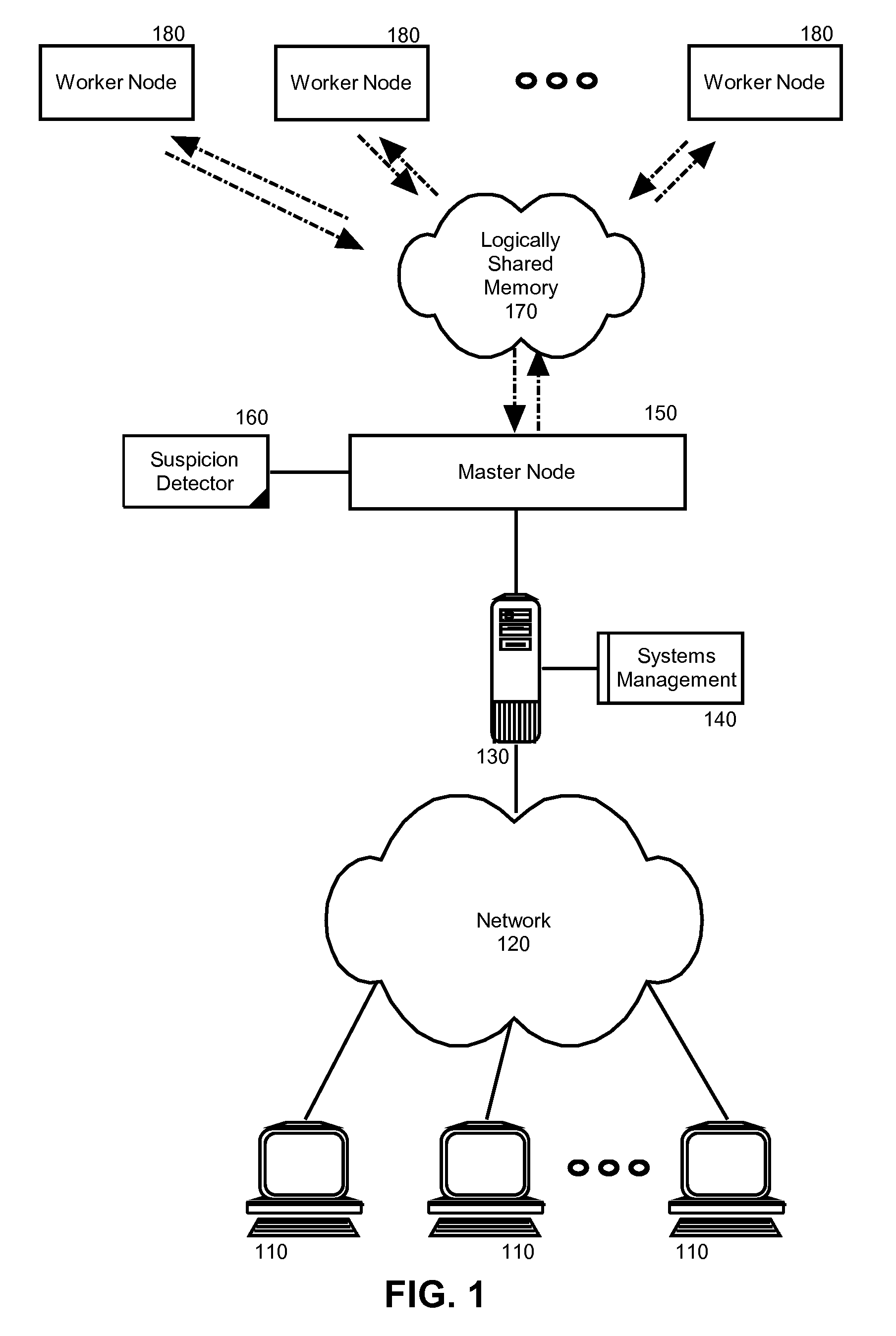
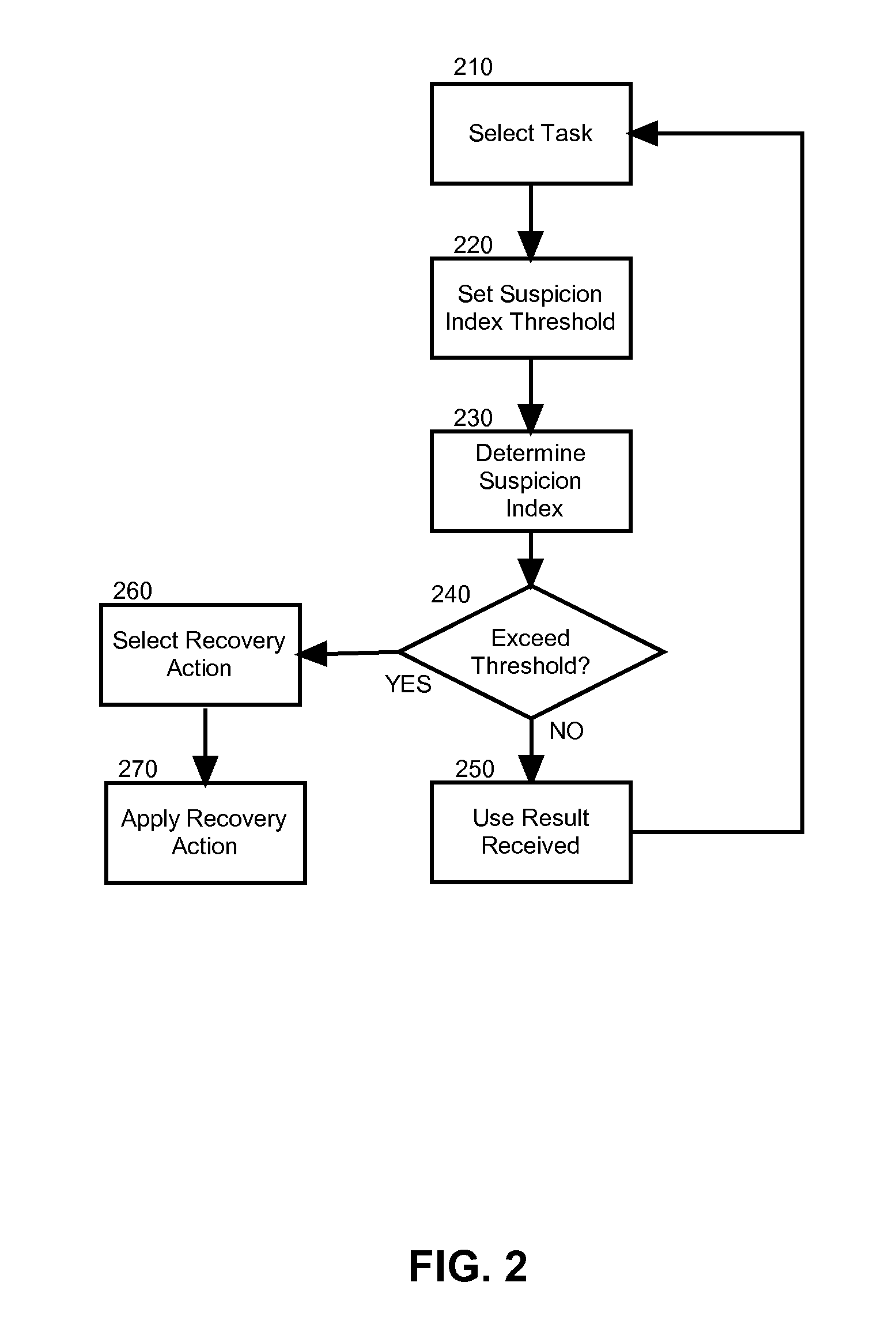
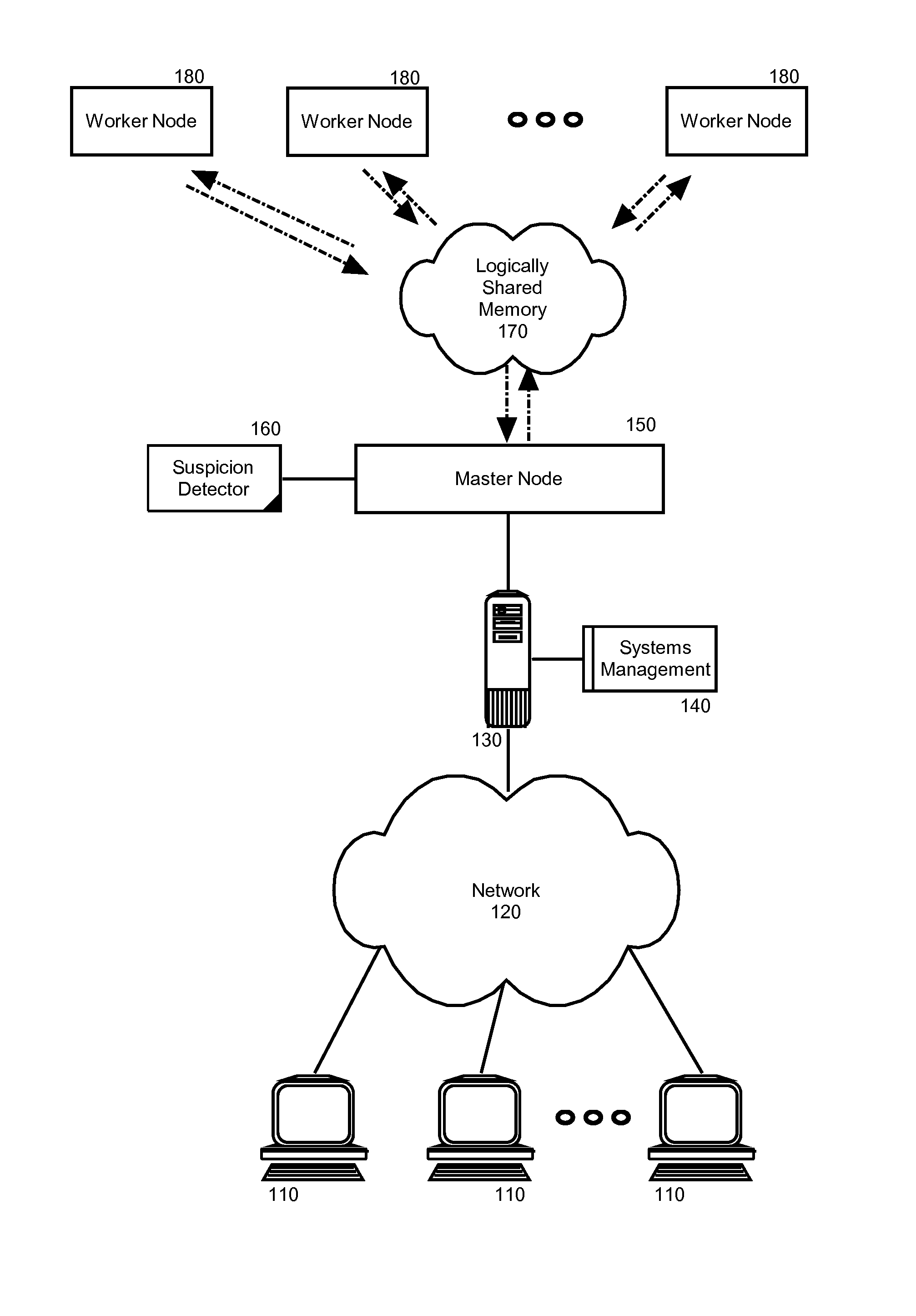
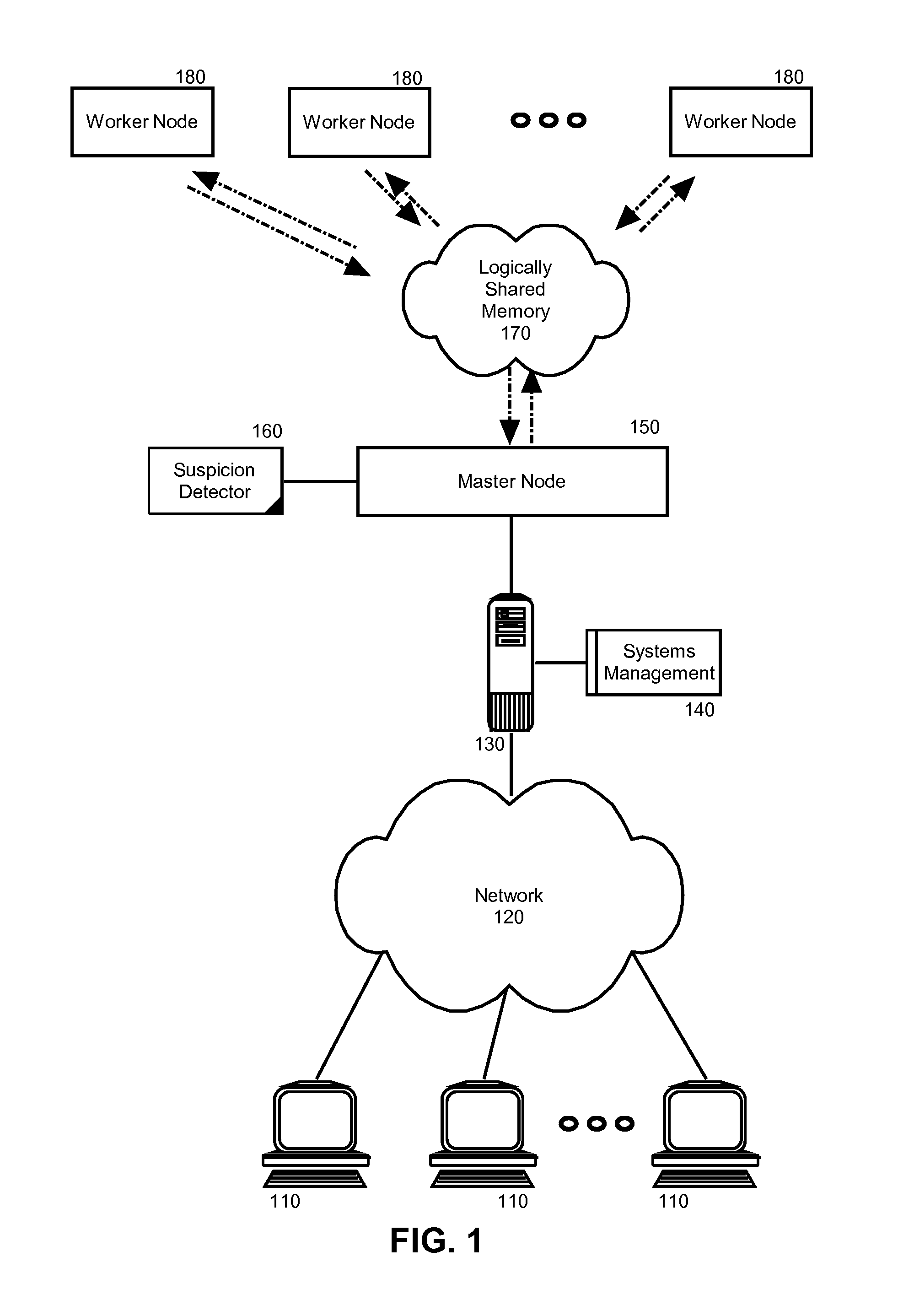
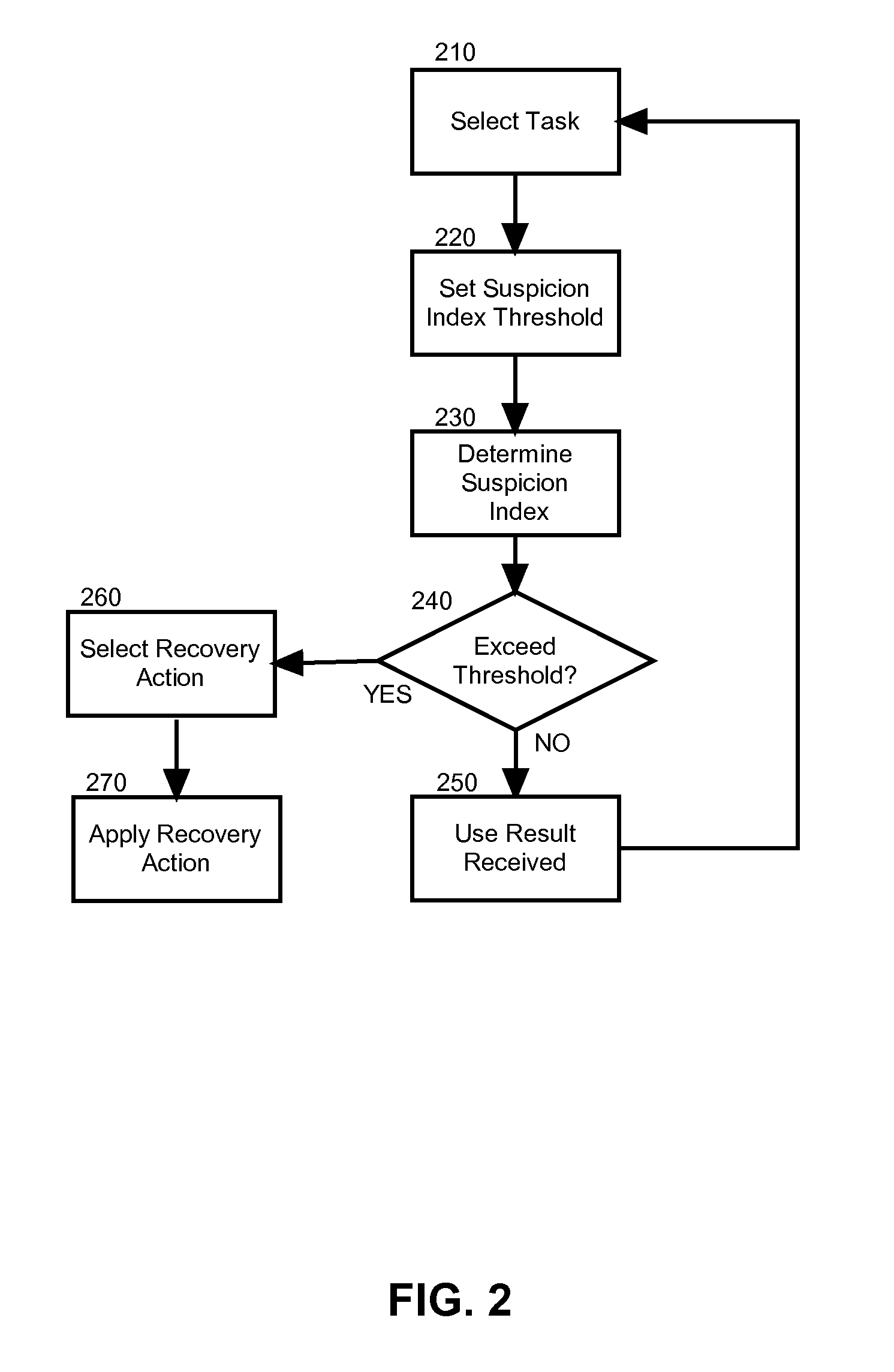
Suspicious node detection and recovery in mapreduce computing
Embodiments of the present invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to distributed computing for large data sets on clusters of computers and provide a novel and non-obvious method, system and computer program product for detecting and correcting malicious nodes in a cloud computing environment (e.g., MapReduce computing). In one embodiment of the invention, a computer-implemented method for detecting and correcting malicious nodes in a cloud computing environment can include selecting a task to dispatch to a first worker node, setting a suspicion index threshold for the selected task, determining a suspicion index for the selected task, comparing the suspicion index to the suspicion index threshold and receiving a result from a first worker node. The method further can include applying a recovery action when the suspicion index exceeds the selected suspicion index threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
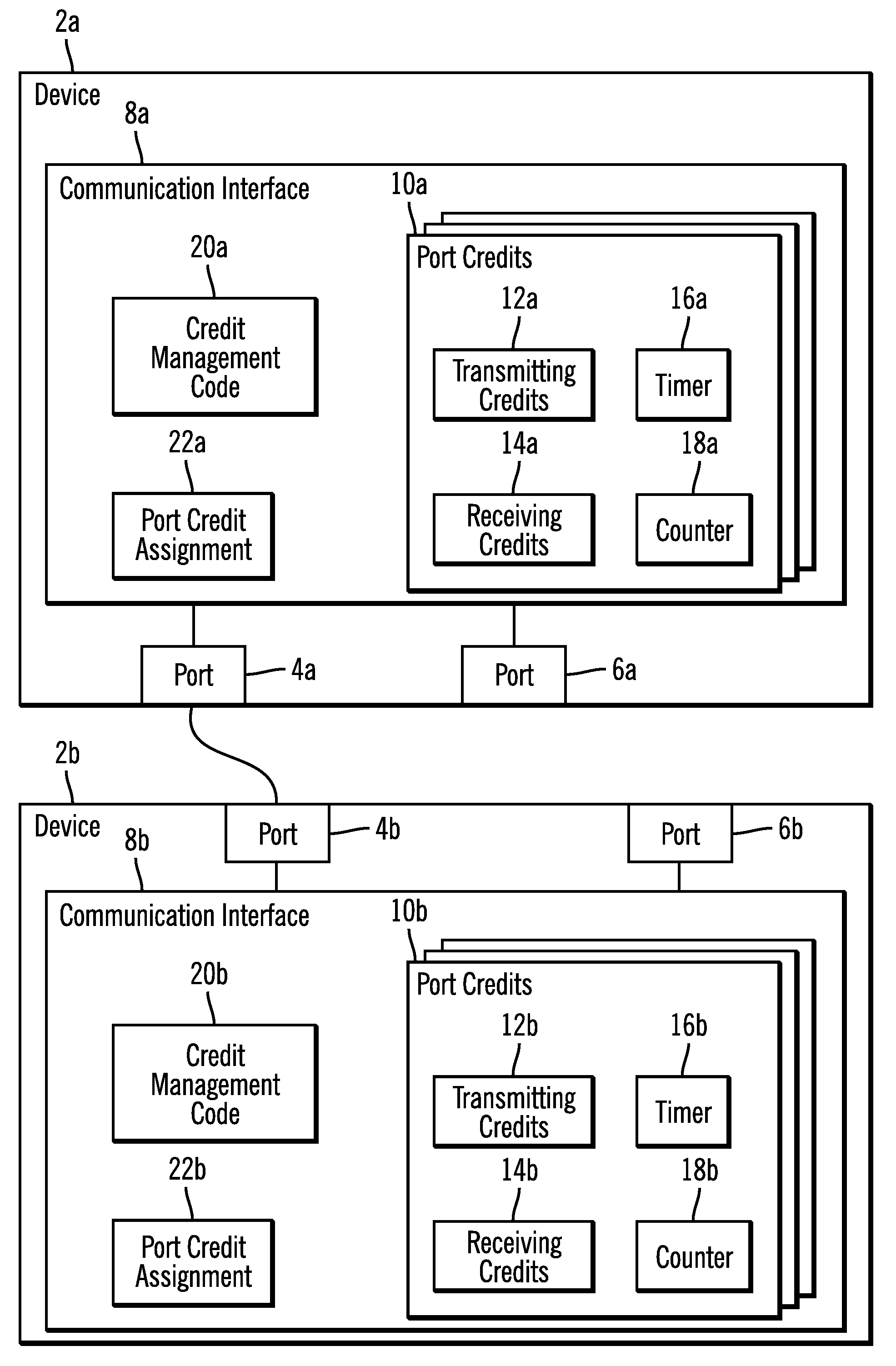
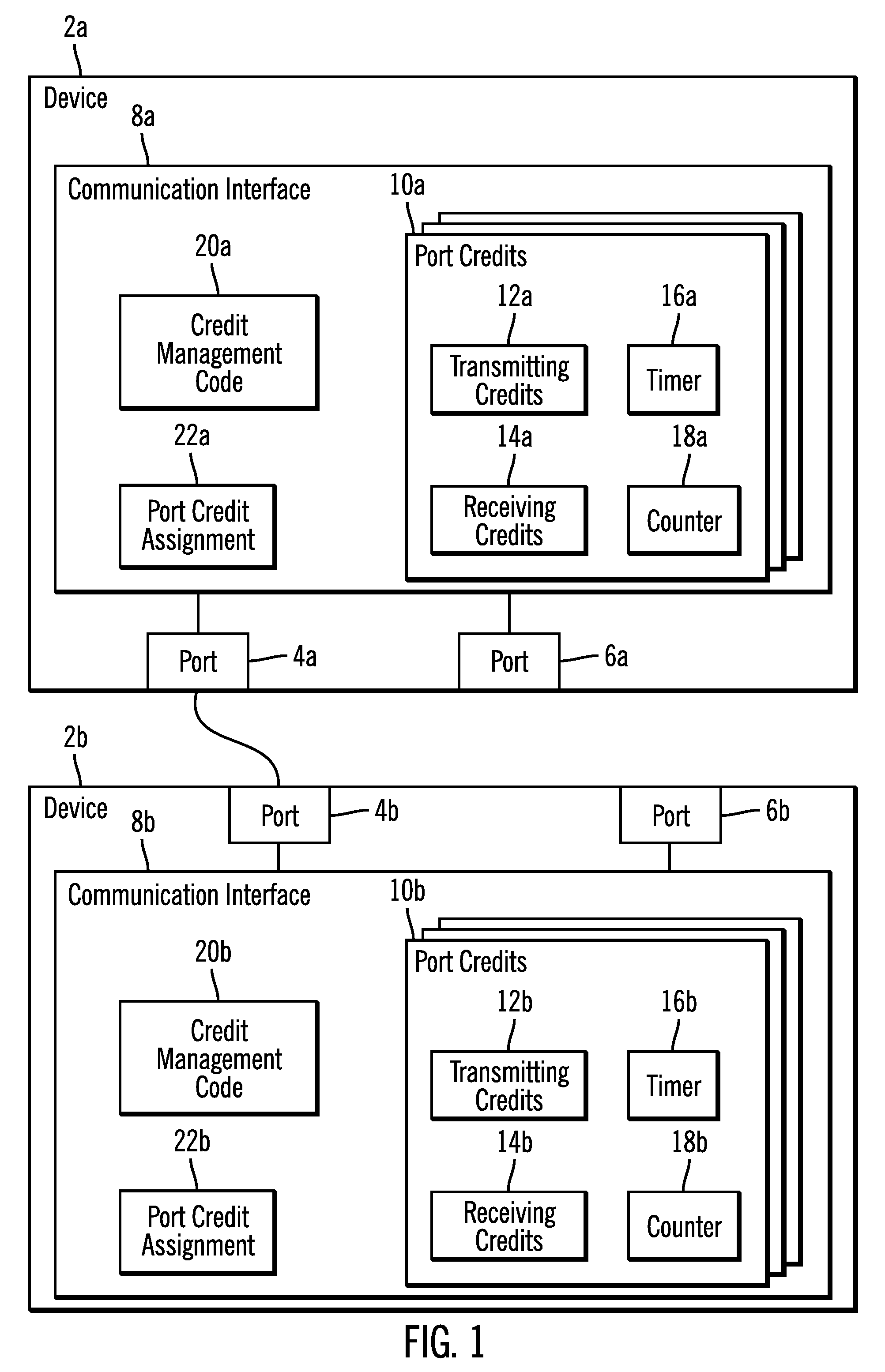
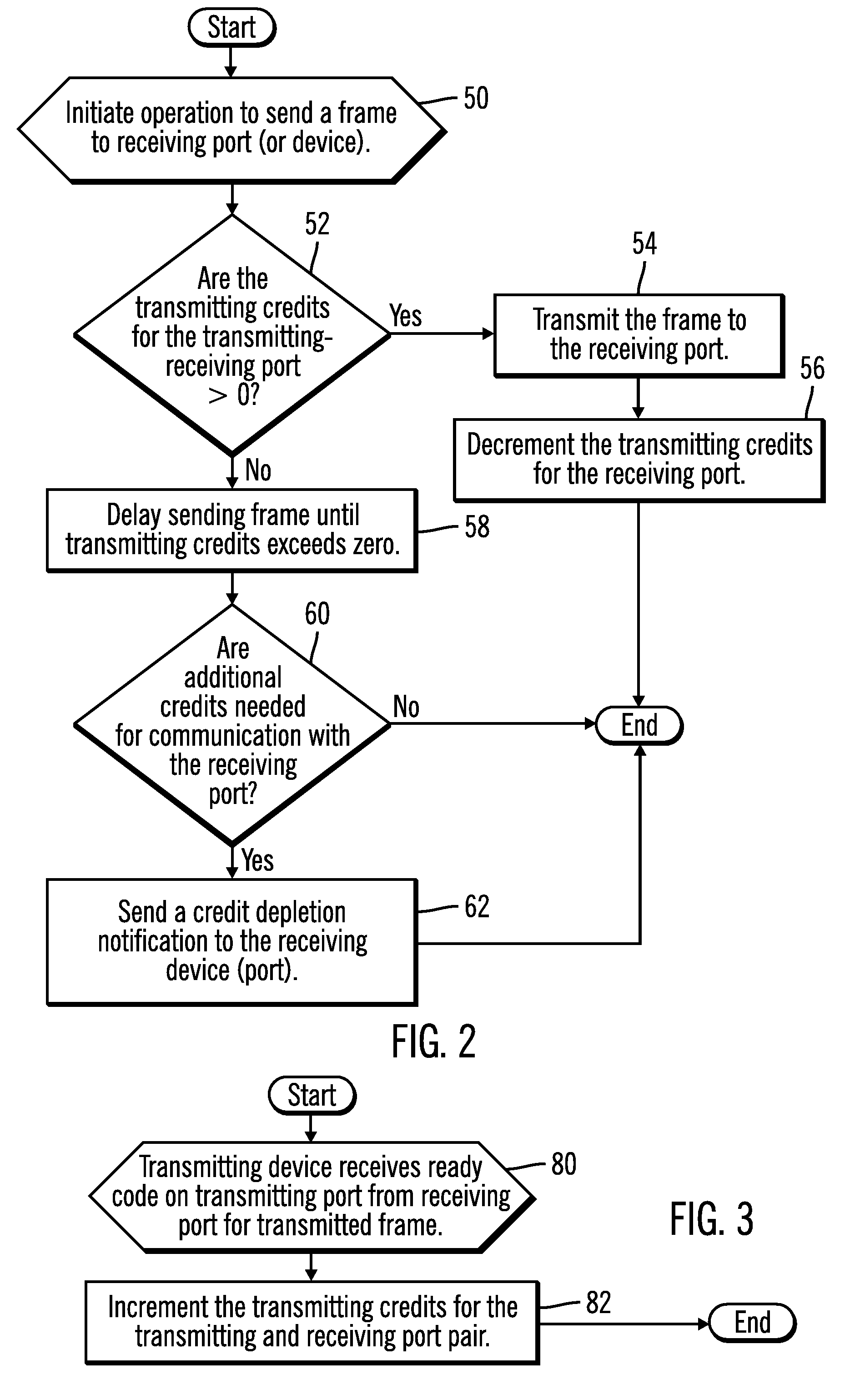
Performing a recovery action in response to a credit depletion notification
Provided are a method, system, and program for managing communication between a first device and a second device and performing a recovery action at the second device in response to a credit depletion notification from the first device. The second device assigns credits indicating a number of outstanding frames the first device may transmit to the second device. The second device receives a first type or second type of credit depletion notification from the first device indicating that the first device needs additional credits to transmit further frames to the second device. The second device performs one of a plurality of recovery actions depending on whether the first type or second type of credit depletion notification was received.
Owner:IBM CORP
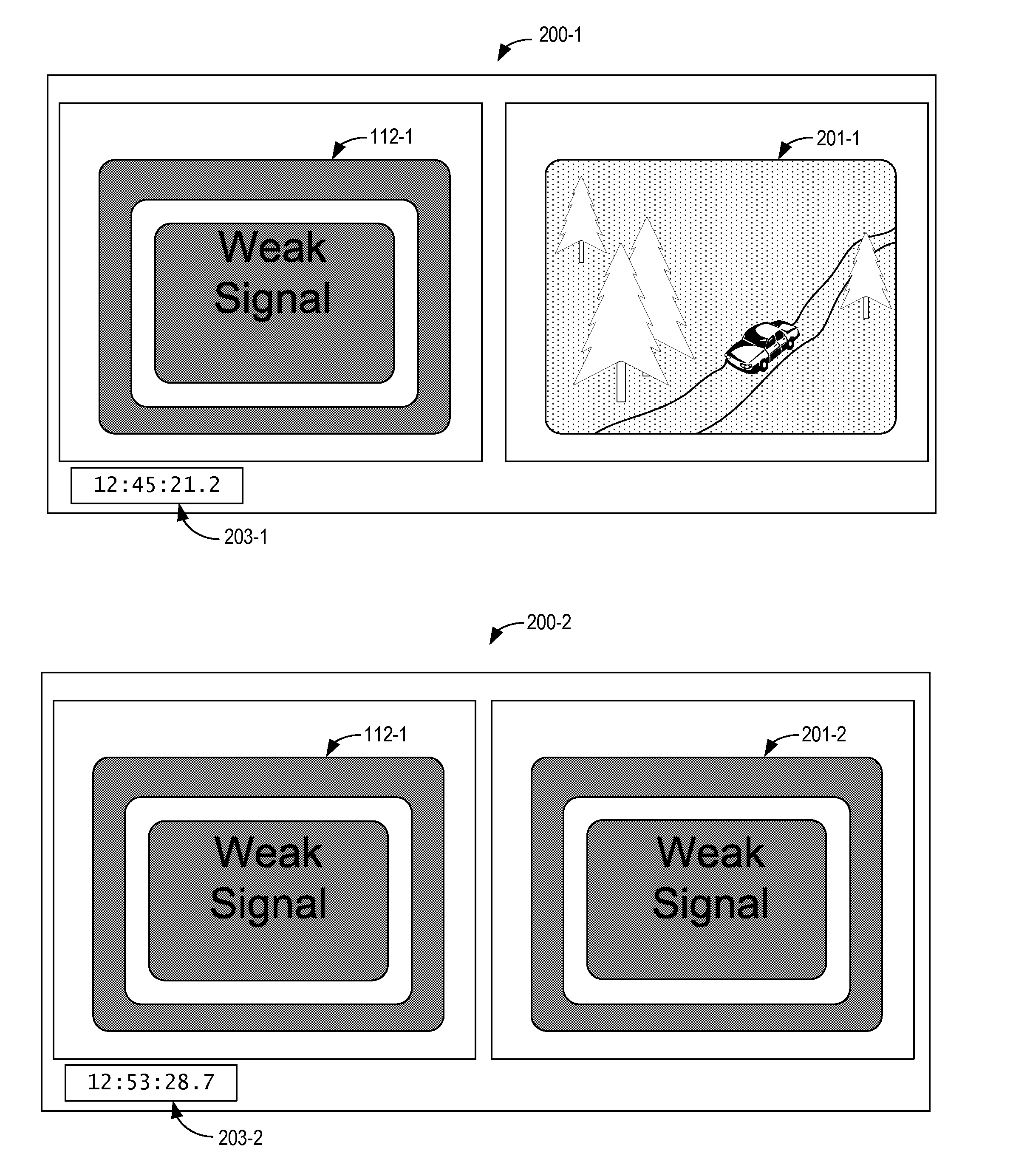
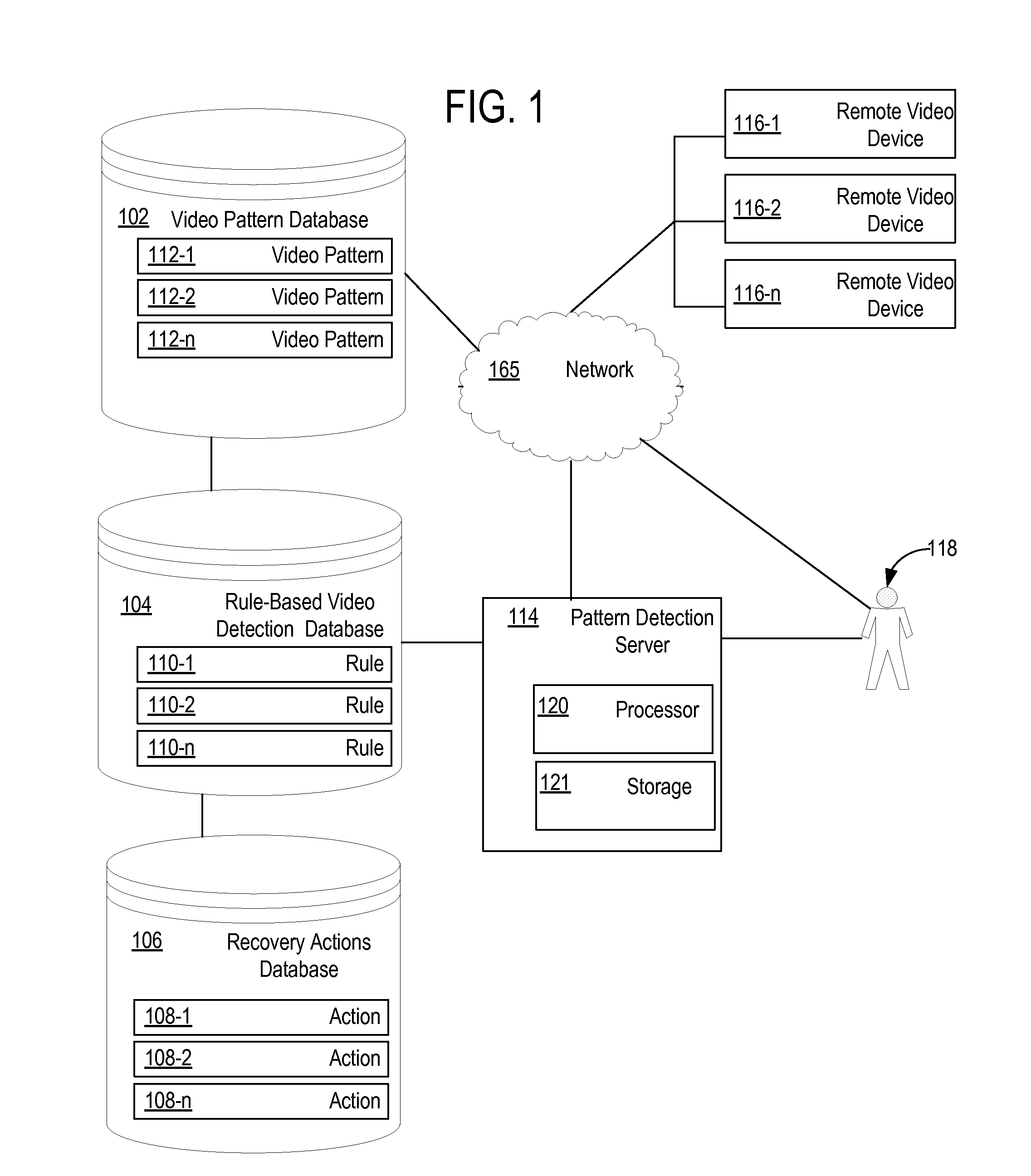
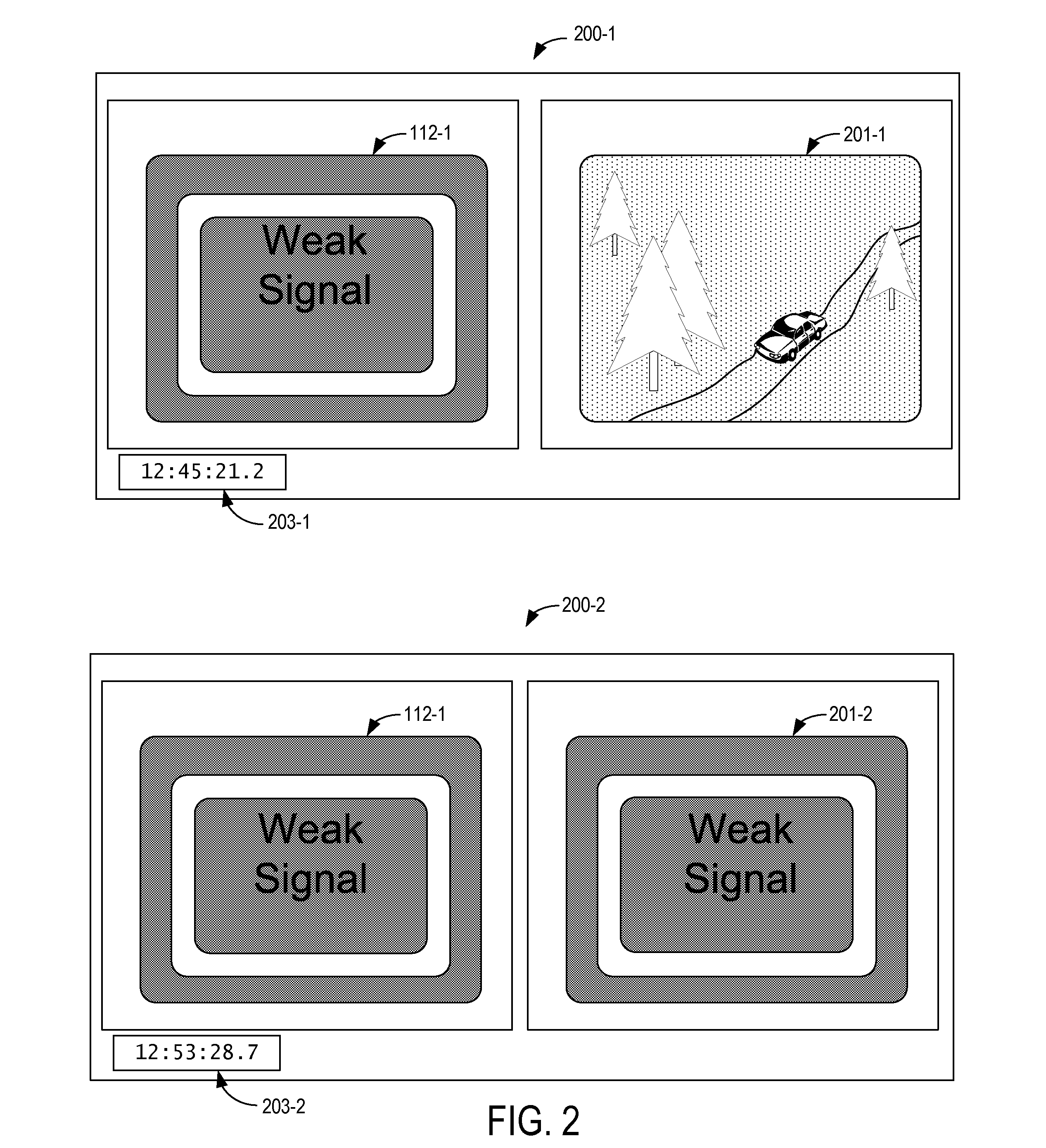
Remote video device monitoring
Remote video devices are monitored by receiving video pattern data from the remote video devices and comparing device video patterns represented by the video pattern data to predetermined video patterns. If device video patterns match the predetermined video patterns, a rule corresponding to the predetermined video pattern is accessed and execution of a recovery action is initiated.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
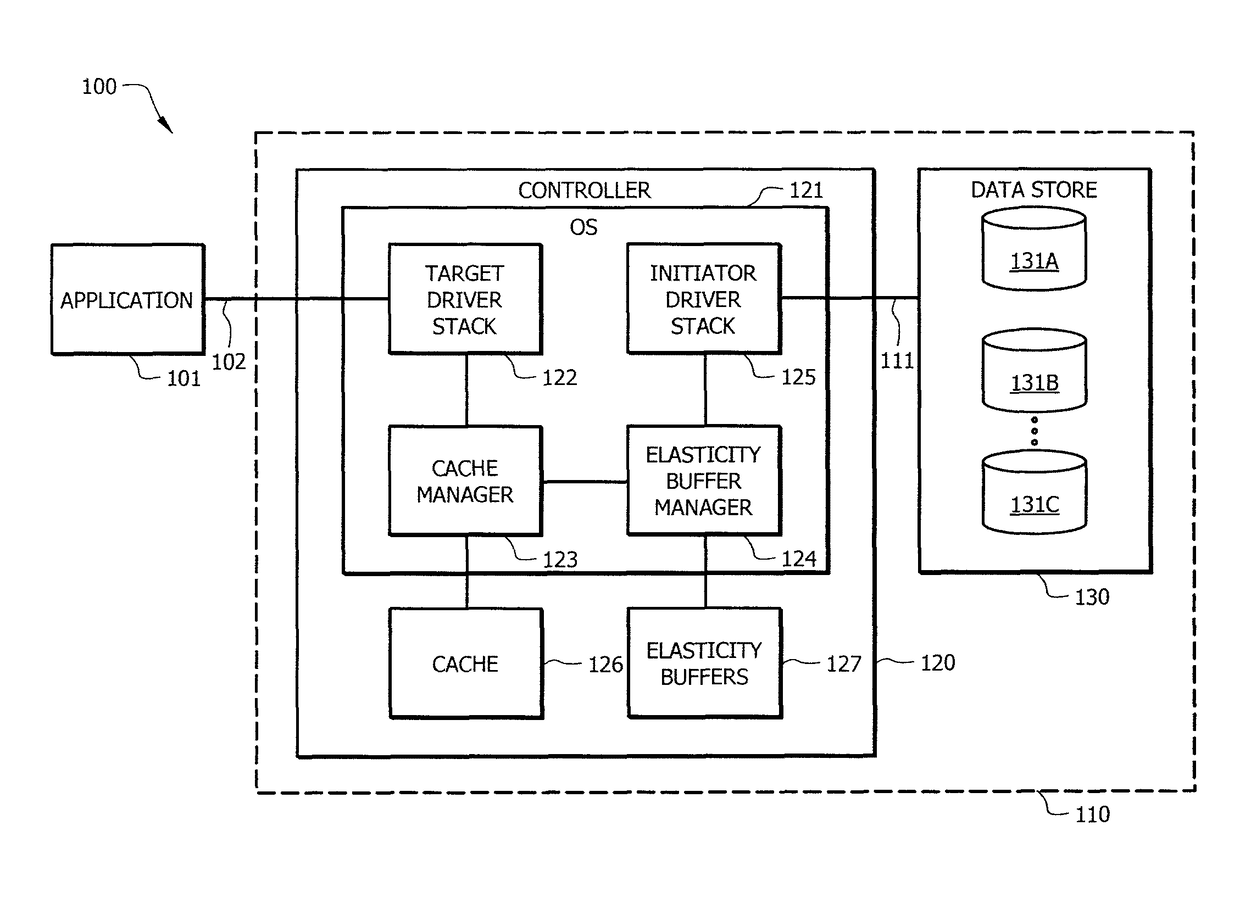
Systems and methods providing storage system write elasticity buffers
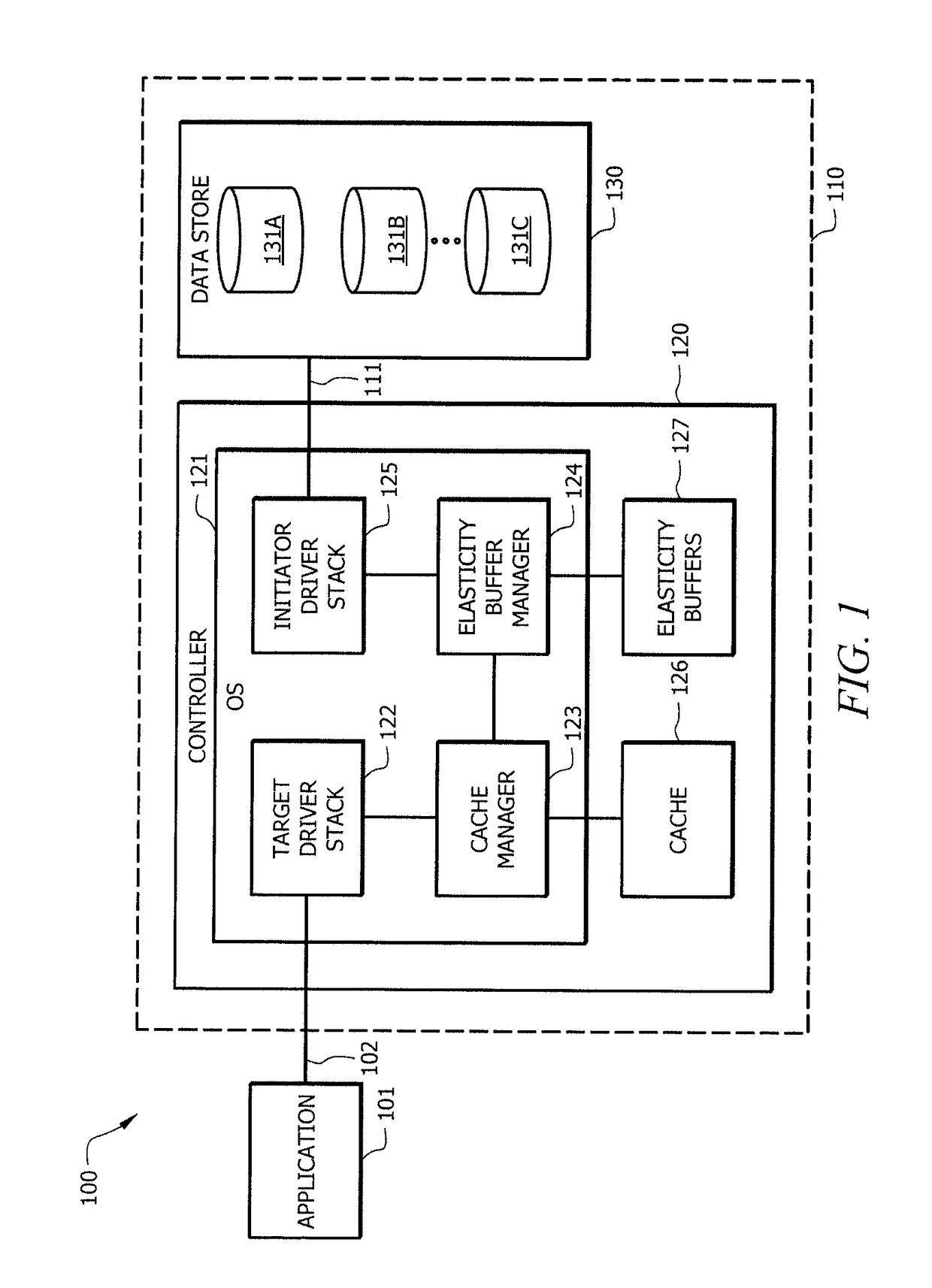
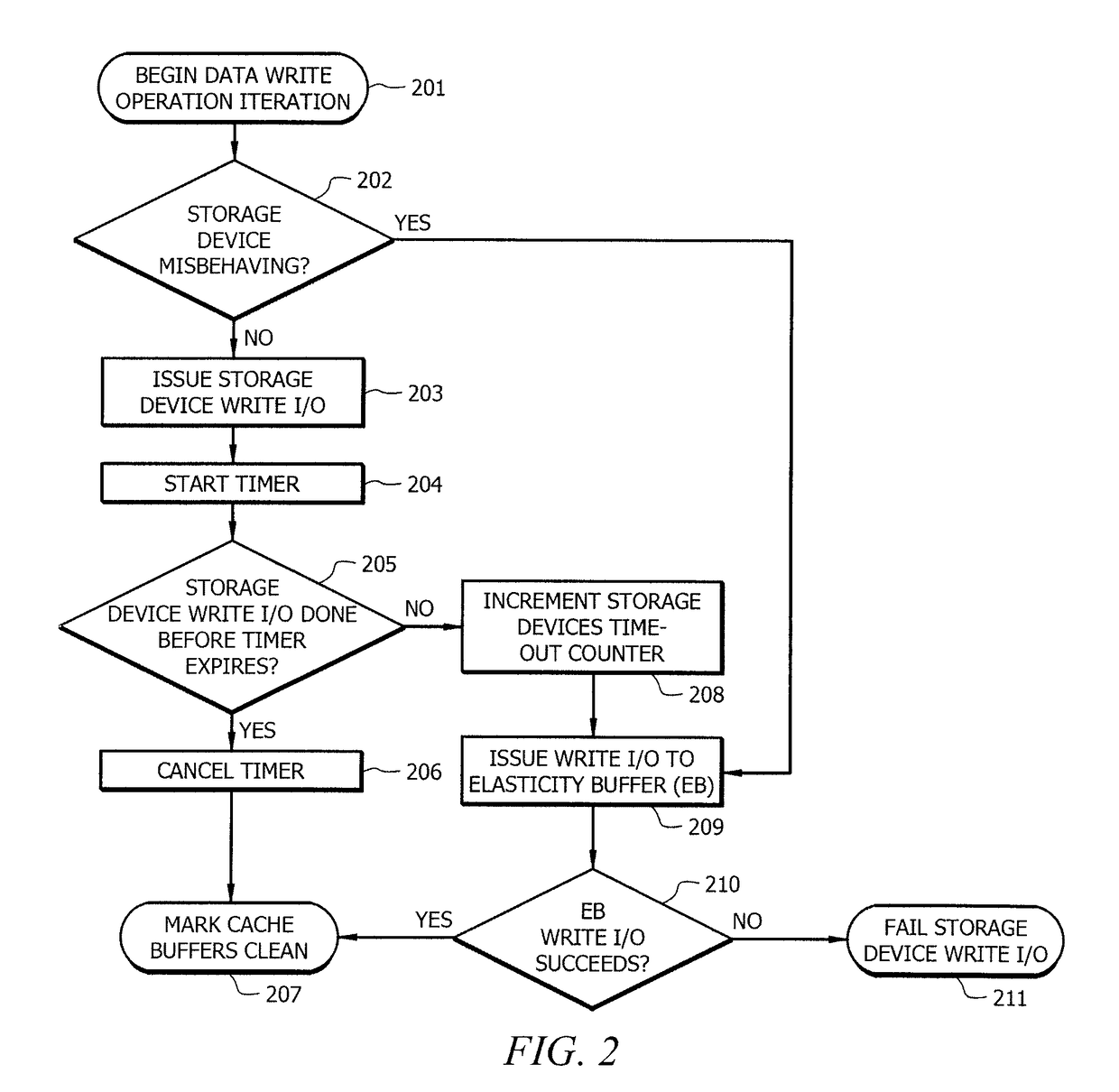
ActiveUS9690703B1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHybrid storage systemOperating system
Systems and methods which implement a buffer for storing data to be written to a storage device when a data write operation of the storage device is determined to be outside of an acceptable parameter are disclosed. An elasticity buffer of embodiments may provide buffering on an as needed basis with respect to storage device cache flushing operations to thereby persistently store dirty write data from a storage device cache when a storage device data write is experiencing aberrant operation, such as when the data write is taking too long. The resources of the storage device cache may thus be cleaned and made available for subsequent data caching. The data may subsequently be written from the elasticity buffer to the storage device, such as after recovery action is taken with respect to the storage device, when the storage device starts completing data write operations in a timely fashion, etc.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
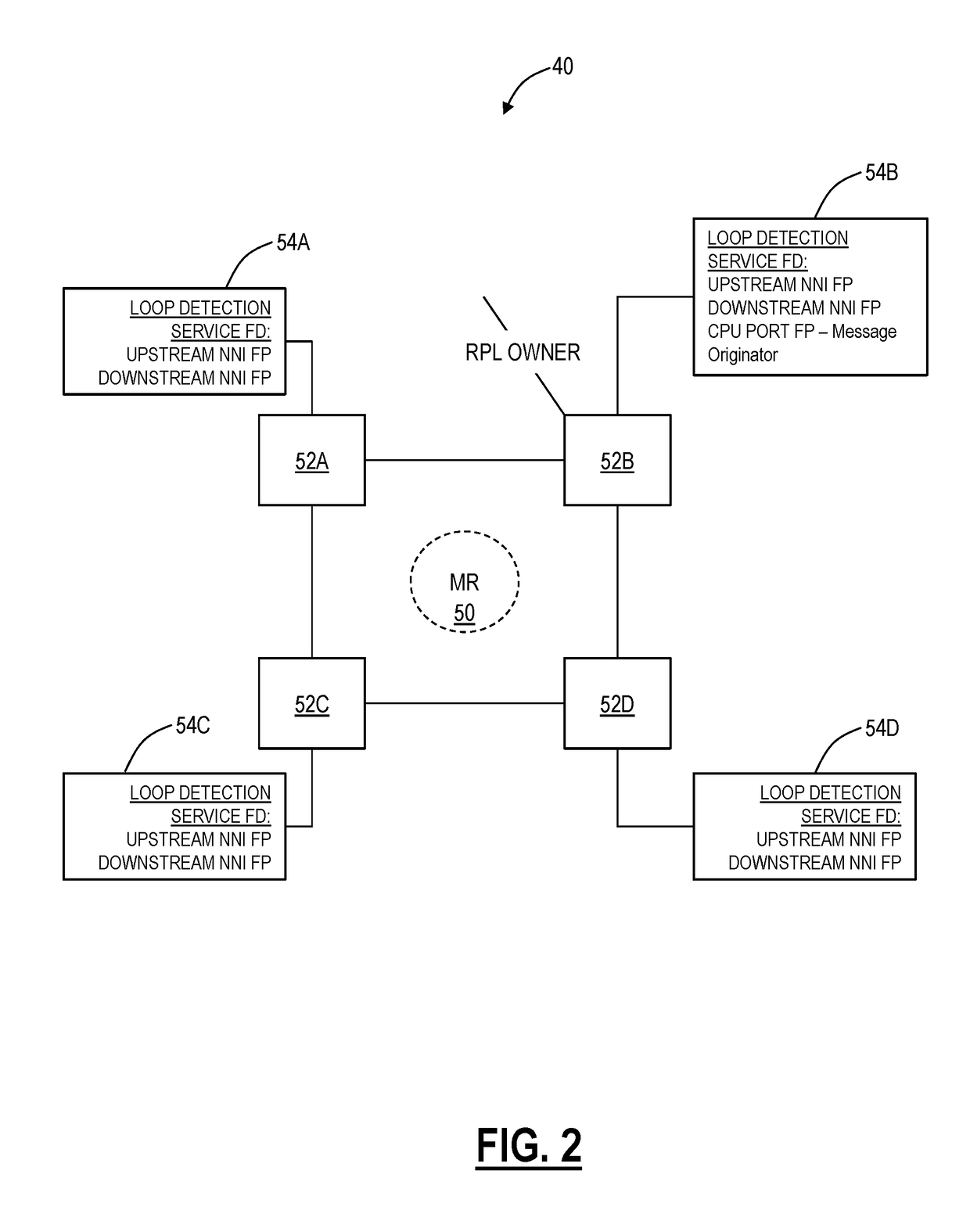
Systems and methods to detect and recover from a loop in an ethernet ring protected network
Loop detection systems and methods in an Ethernet Ring Protected network include, subsequent to creating a loop detection service on all nodes in the network, periodically transmitting a loop detection frame on both ports of the node; responsive to failing to receive the loop detection frame at the node, determining no loop exist in the ring; and, responsive to receiving the loop detection frame on a received port at the node, determining a loop exists in the ring and automatically implementing one or more recovery actions.
Owner:CIENA
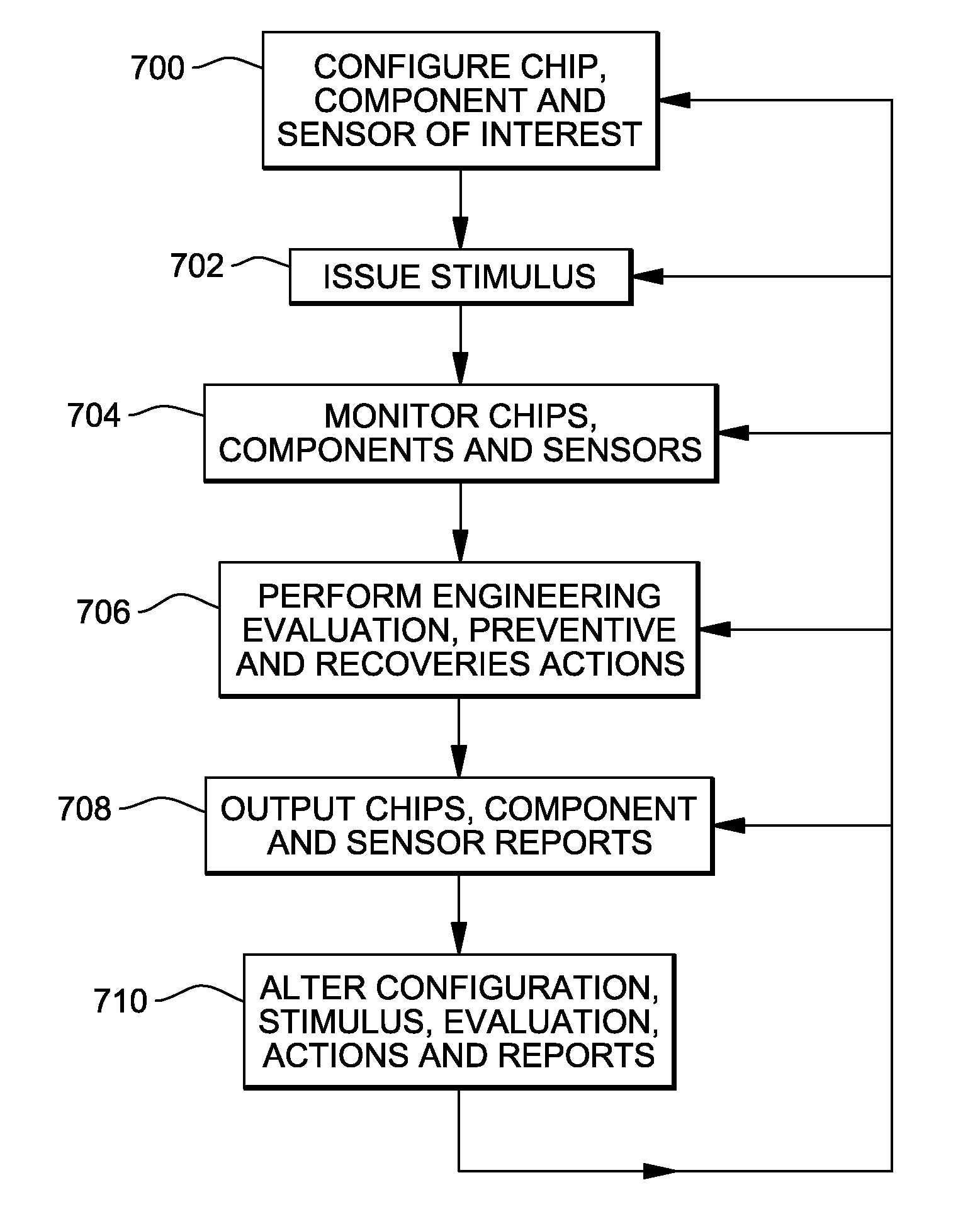
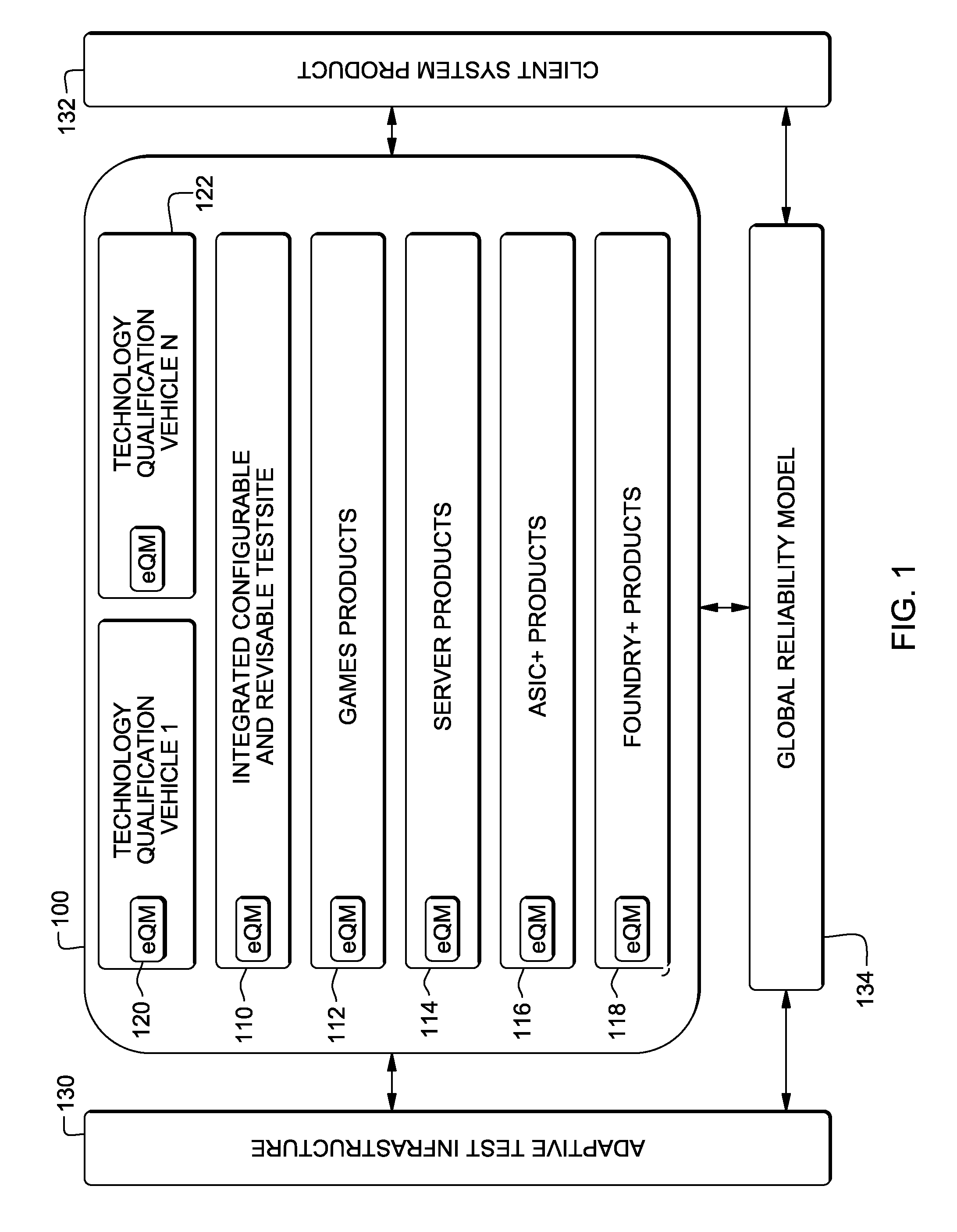
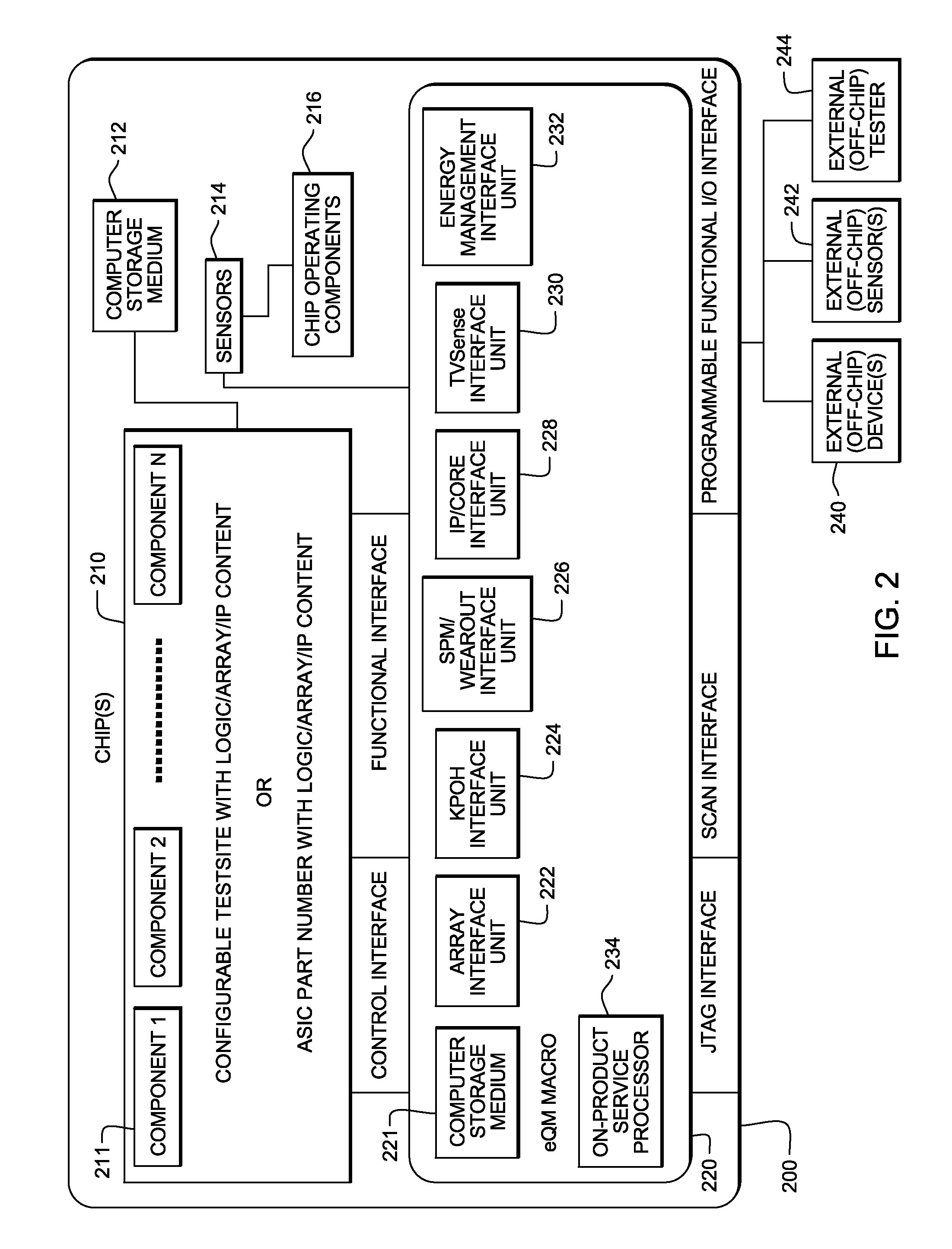
Integrating design for reliability technology into integrated circuits
InactiveUS8201038B2Electronic circuit testingReliability/availability analysisIntegrated circuit layoutSemiconductor
A method executes computerized instructions within an integrated and packaged semiconductor device using a centralized programming interface within the packaged semiconductor device to perform in-system preventive and recovery actions, configure and issue stimulus to chips, components and sensors within the semiconductor device. The method monitors chip, components and sensors within the packaged semiconductor device, using the centralized programming interface, to measure characteristics of the packaged semiconductor device in response to the stimulus. The structure including chips, components and sensors produce outputs representing the characteristics. The method performs an evaluation to determine whether the chip, component and sensor outputs are within predetermined limits, using the centralized programming interface; and reports occurrences of instances of the chip, component and sensor outputs being outside the predetermined limits, using the centralized programming interface, to an on-chip storage medium, external test equipment or computerized device outside of the packaged semiconductor device.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
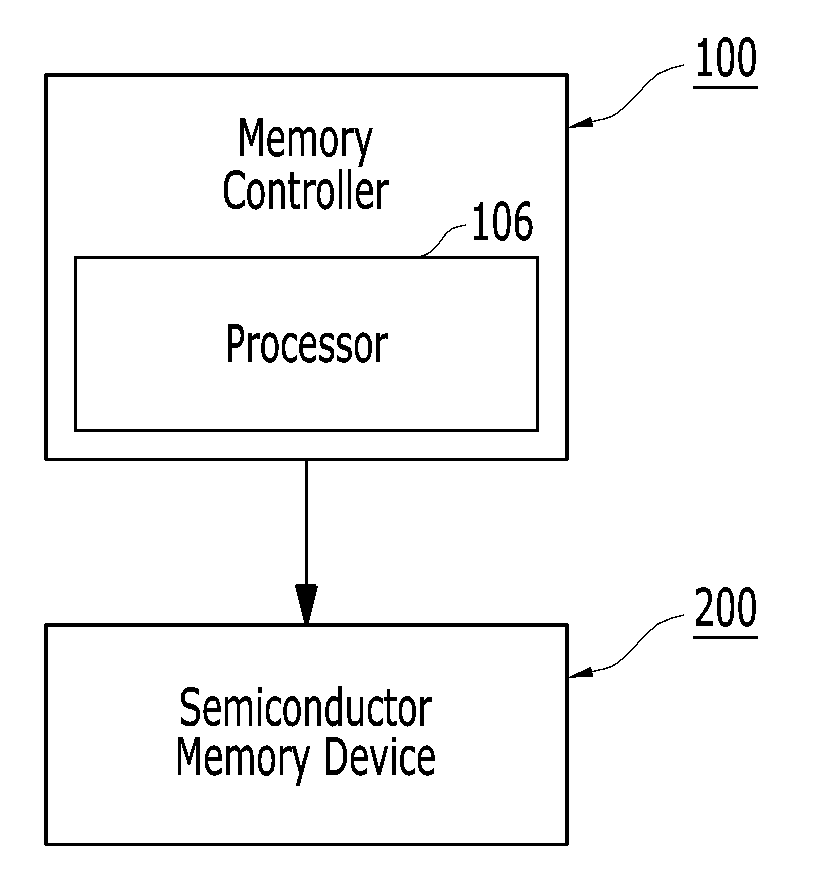
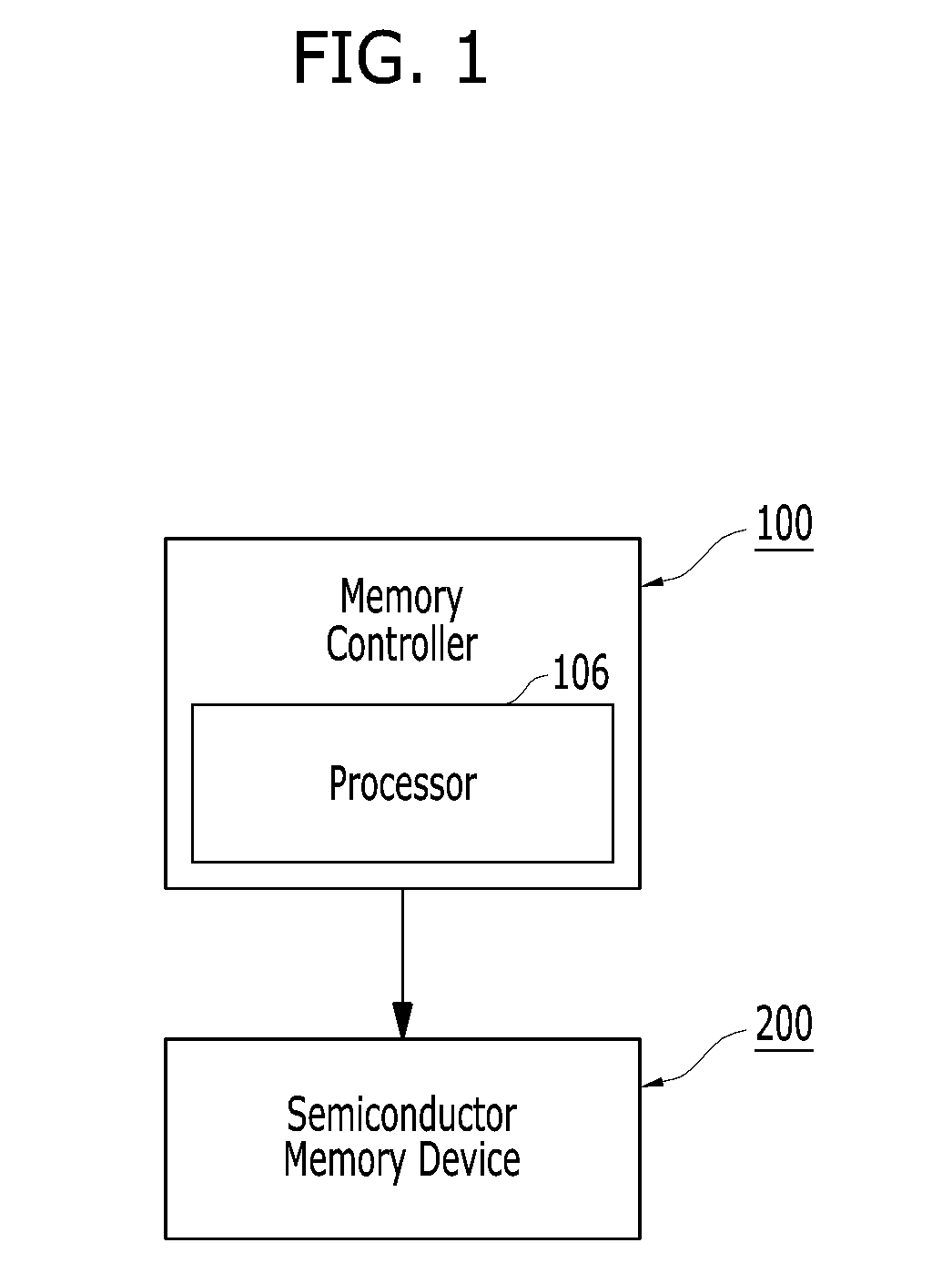
Media quality aware ecc decoding method selection to reduce data access latency
ActiveUS20180137003A1Improve reliability and performanceInput/output to record carriersNon-redundant fault processingDecoding methodsMethod selection
A memory system and operating method thereof includes a semiconductor memory device, and a memory controller controlling actions of the memory device. The memory controller contains a processor executing instruction and programs stored in the memory controller, a memory characterizer characterizing the memory system, and generating an index decision table, an in-flight assessor assessing read command, and predicting a proposed error recovery action in accordance with the index decision table, and a selective decoder executing the proposed error recovery action.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method and apparatus for handling transient memory errors
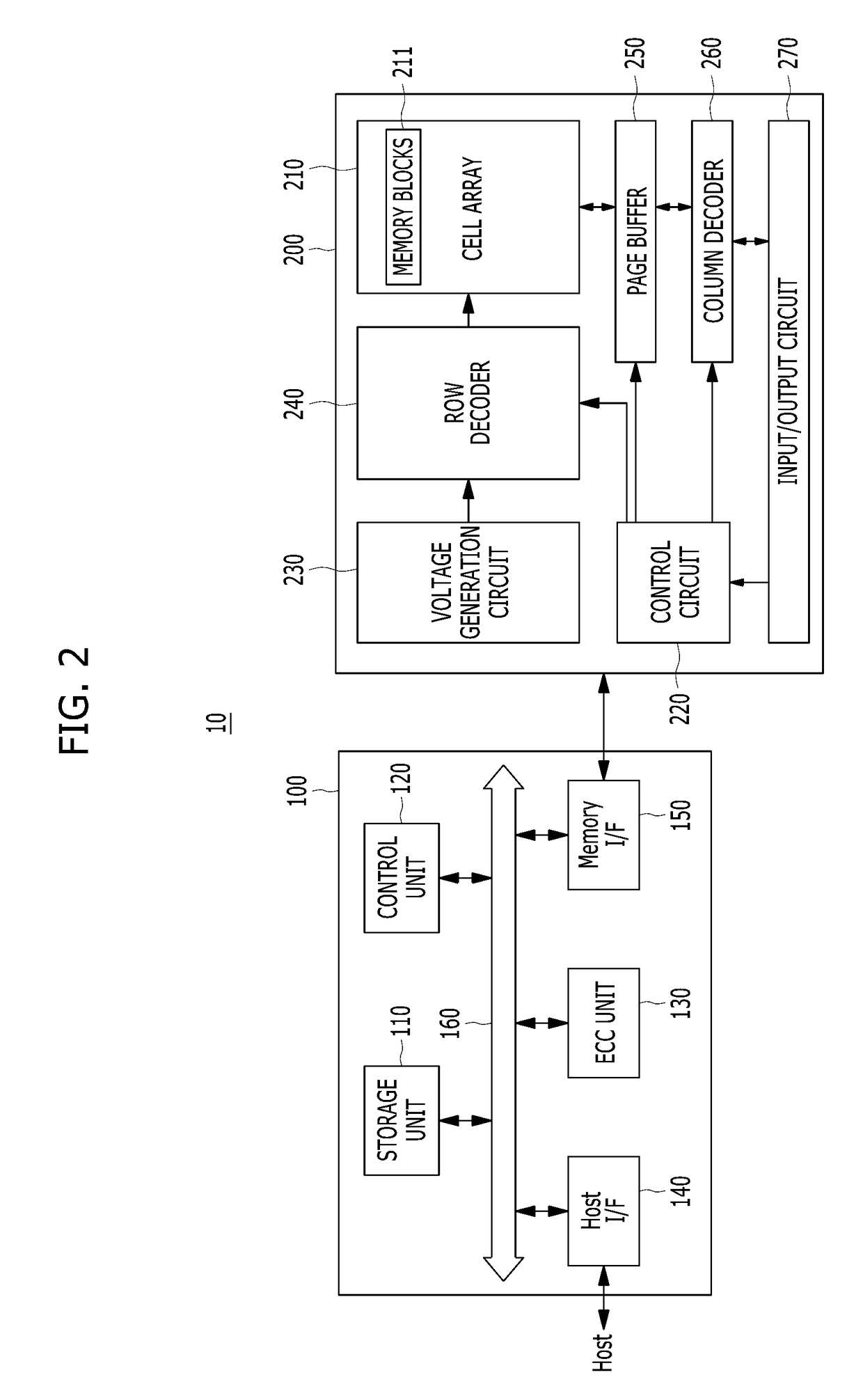
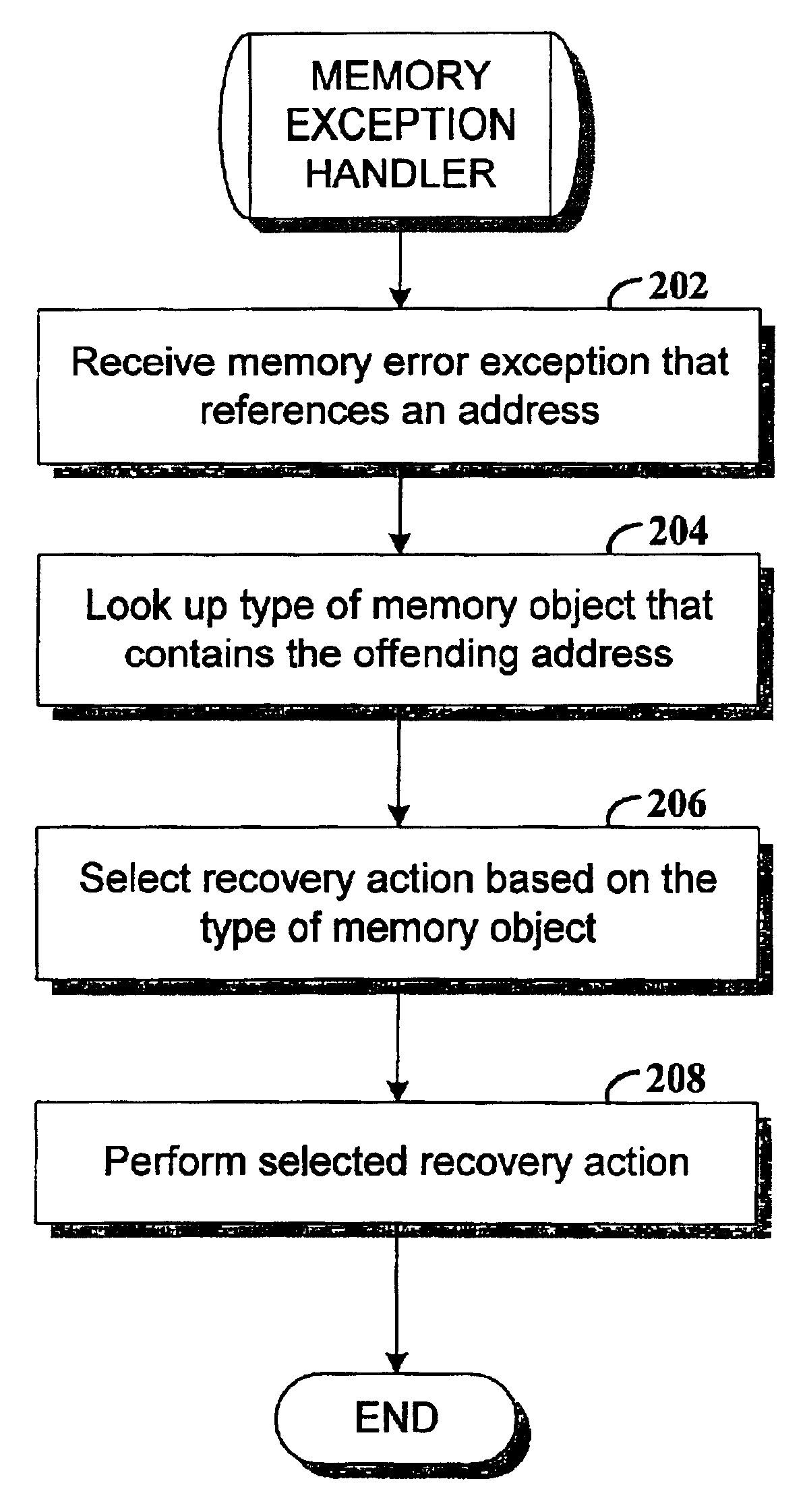
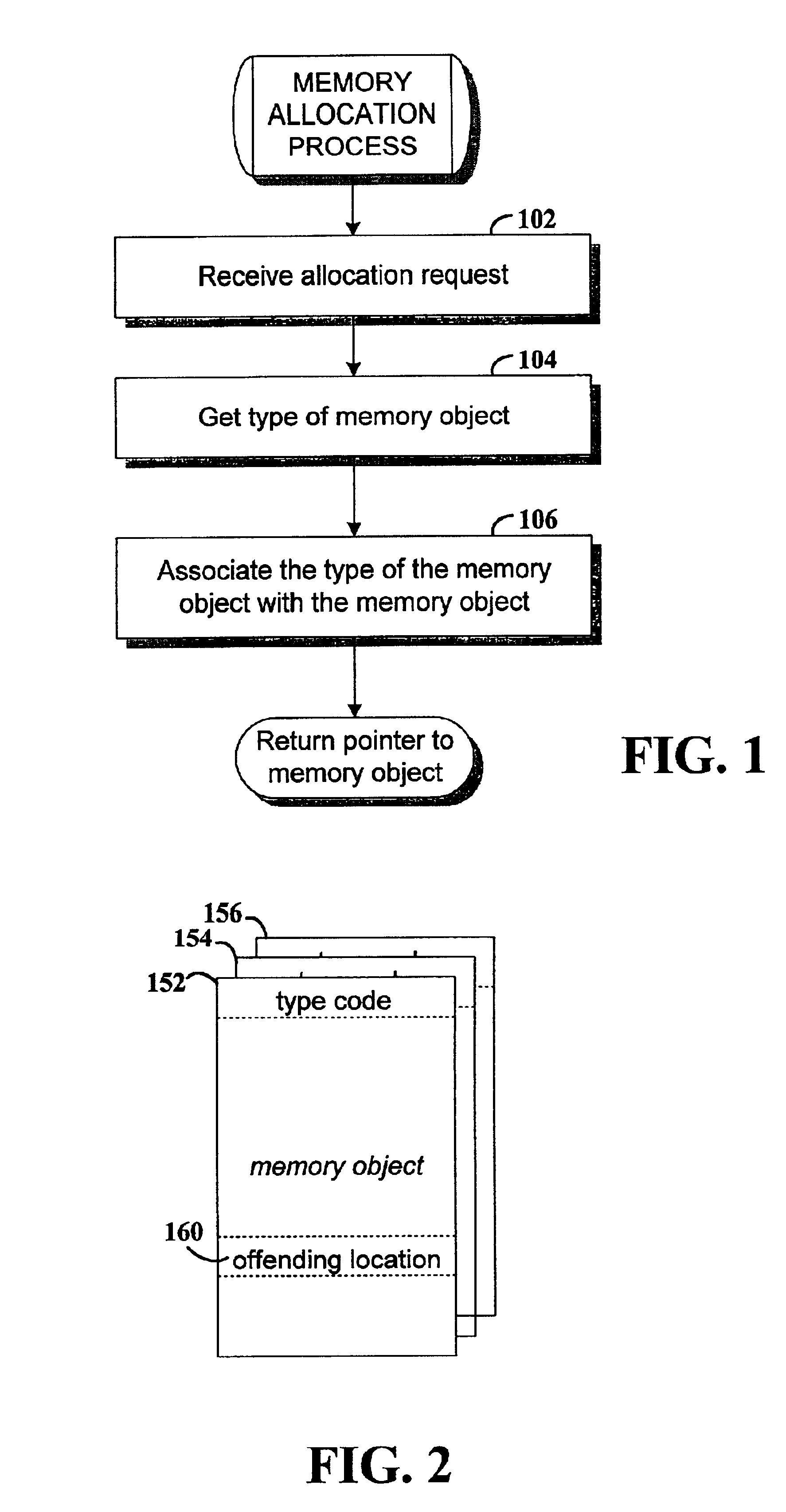
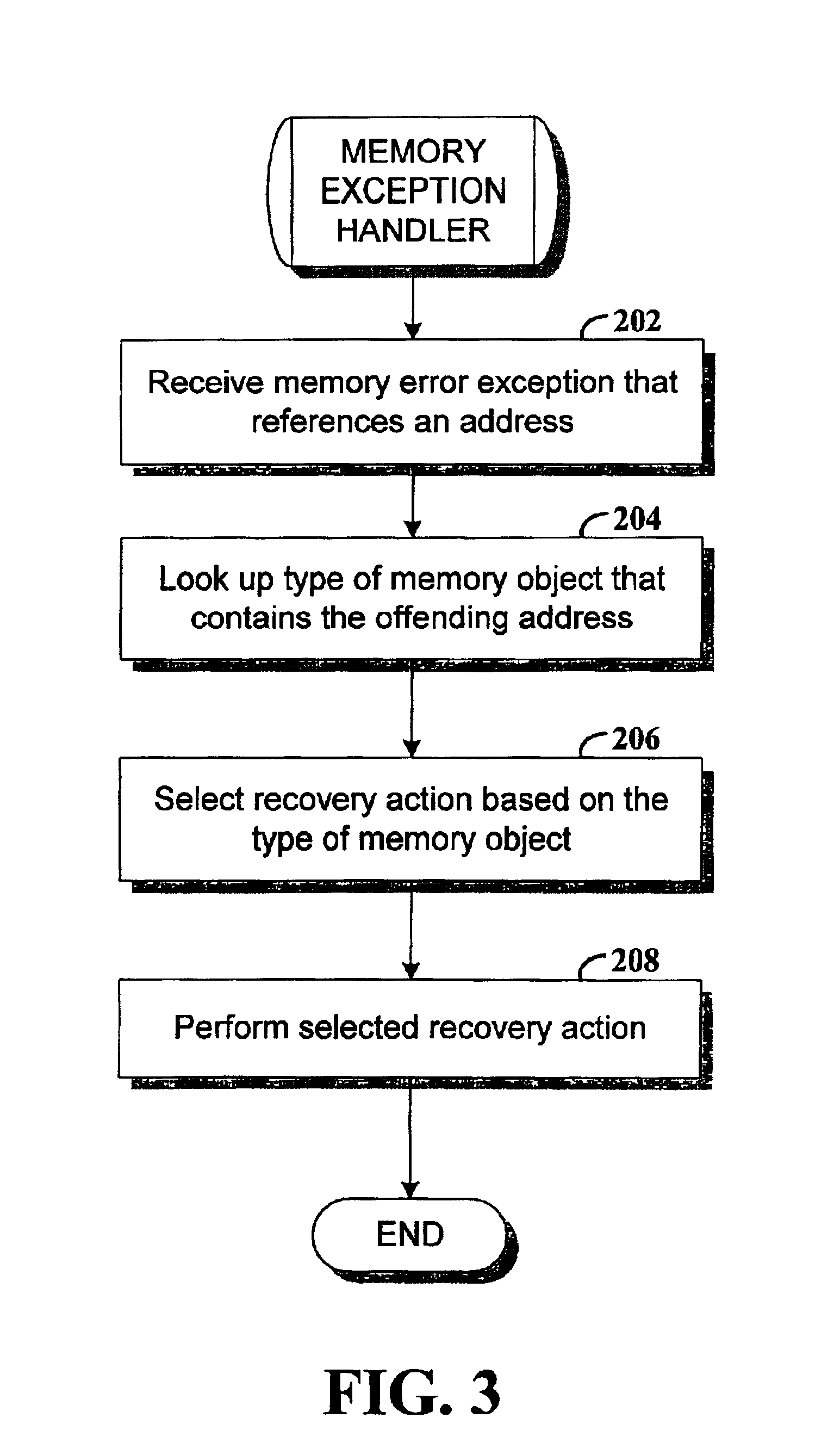
Method and apparatus for managing memory of a data processing system. In one embodiment, memory objects are allocated in response to memory allocation requests. Each object has an associated plurality of addresses. Type-identifier codes are respectively stored in association with the memory objects. Upon detection of a transient memory error at a memory address a recovery action is selected and performed based on the type-identifier code of the object that is associated with the erring memory address.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Apparatus and method for process recovery in an embedded processor system
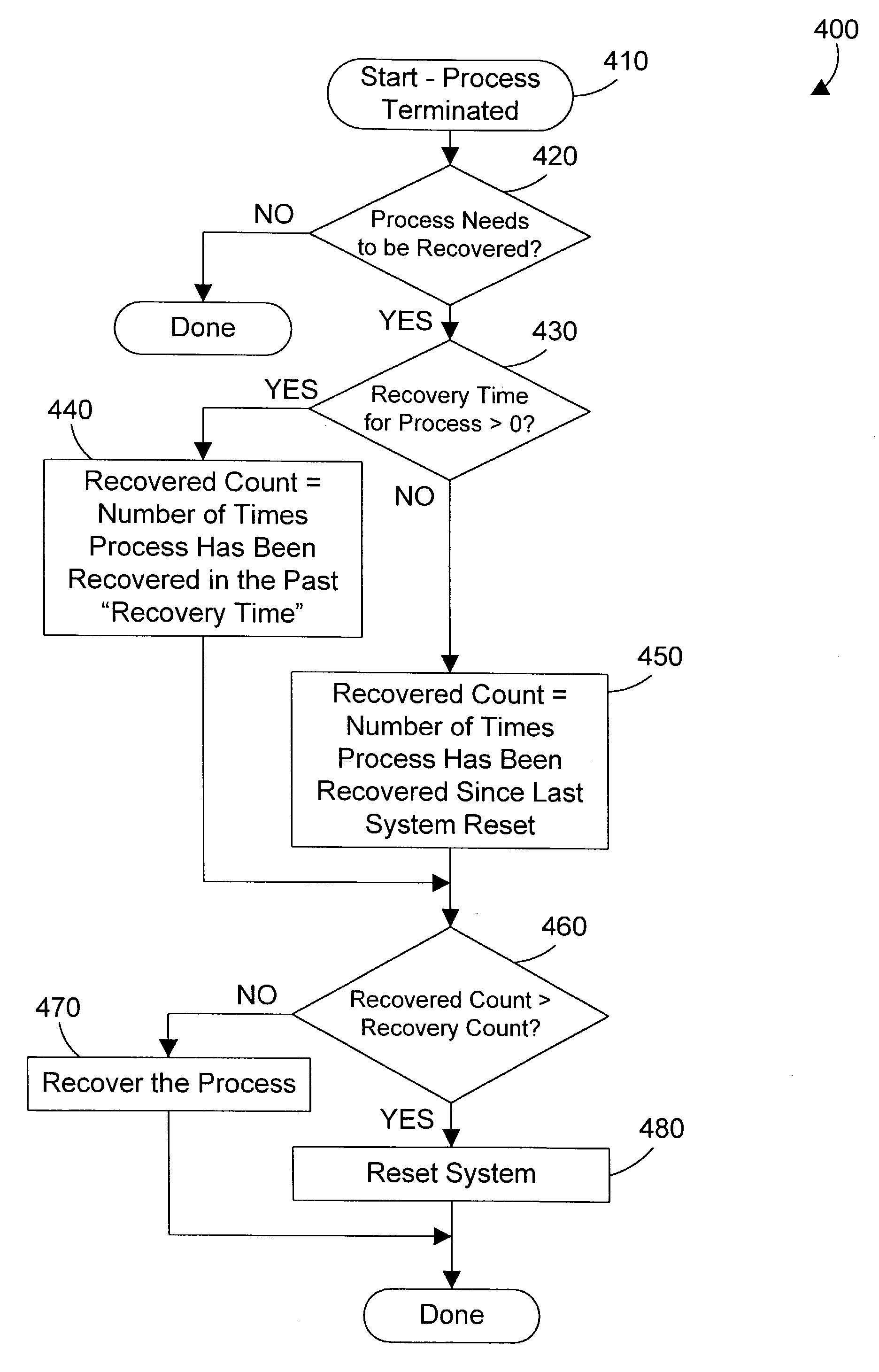
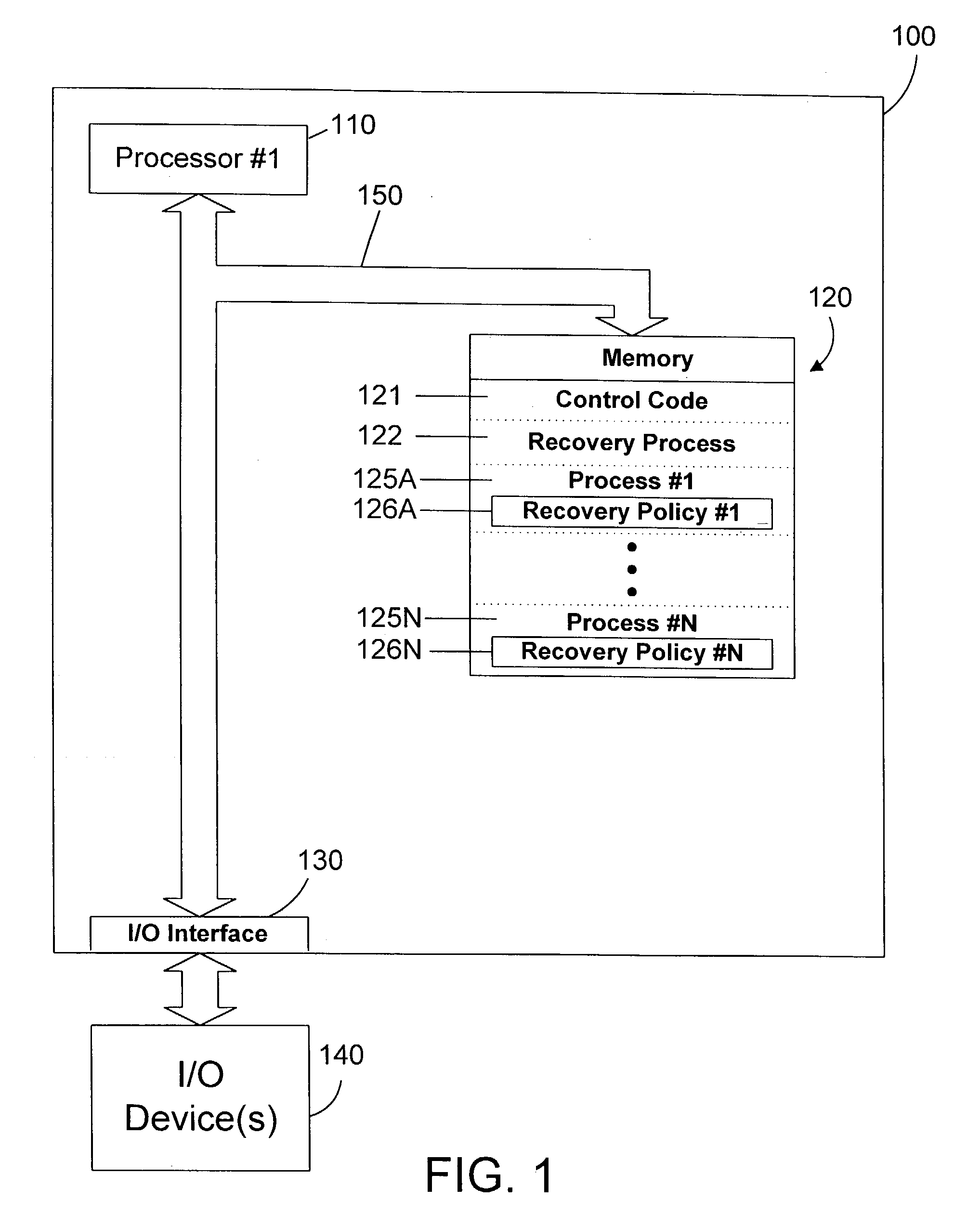
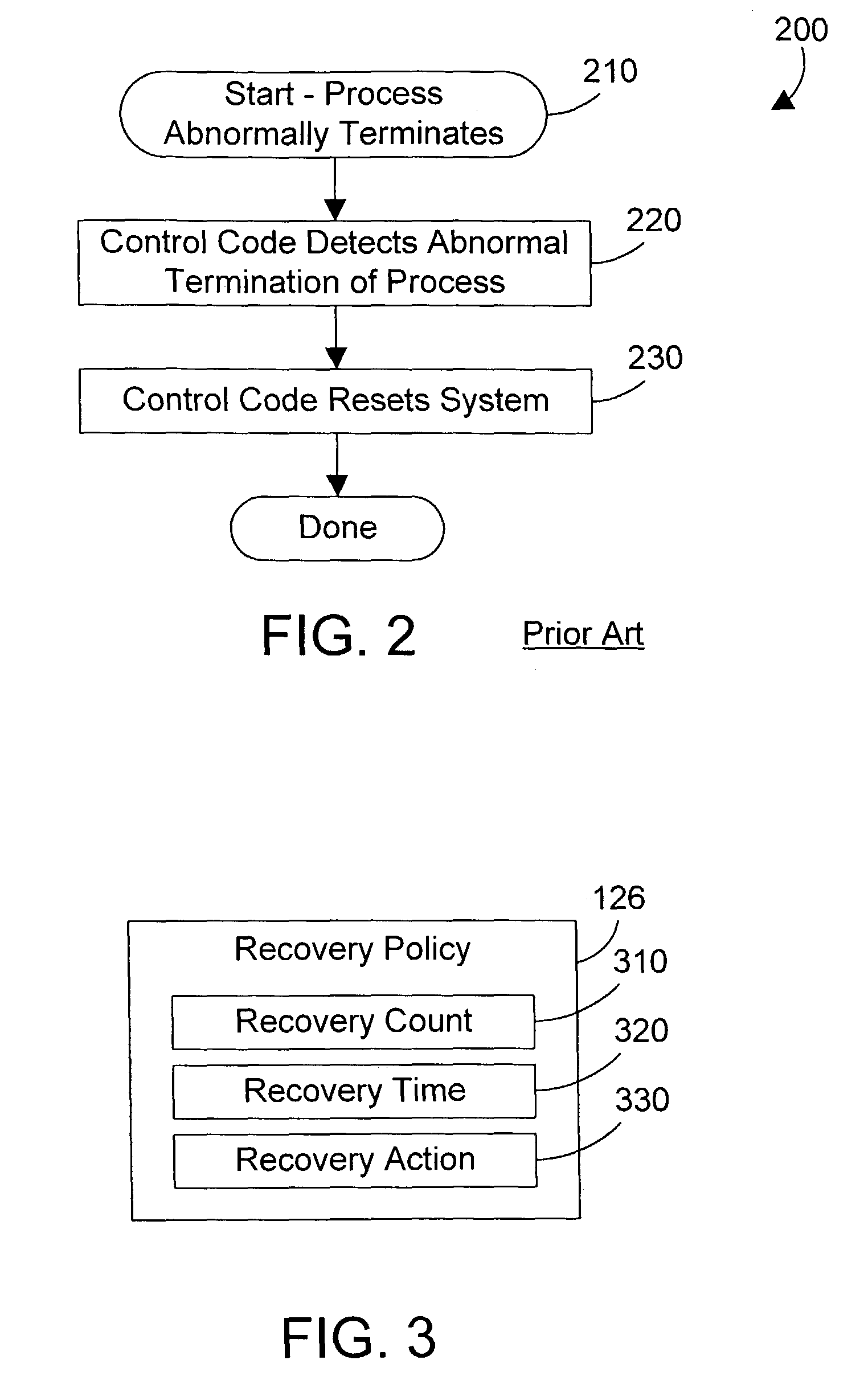
A recovery process for embedded processors monitors other processes in the system. Each process may specify a recovery policy residing in nonvolatile electronic memory that preferably includes a recovery count, a recovery time, and a recovery action. If a process terminates unexpectedly, the recovery process determines whether the process had a corresponding recovery policy. If not, the recovery process does not recover the process. If the process has a corresponding recovery policy, the recovery process determines whether it can recover the process by examining the recovery count and recovery time specified in the recovery policy. If the process can be recovered, the recovery process performs the recovery action specified in the corresponding recovery policy. If the process cannot be recovered, the recovery process resets the system. In this manner, a single process may be recovered by the recovery process without user intervention and without affecting other processes running on the system, and without performing a reset of the entire system.
Owner:IBM CORP
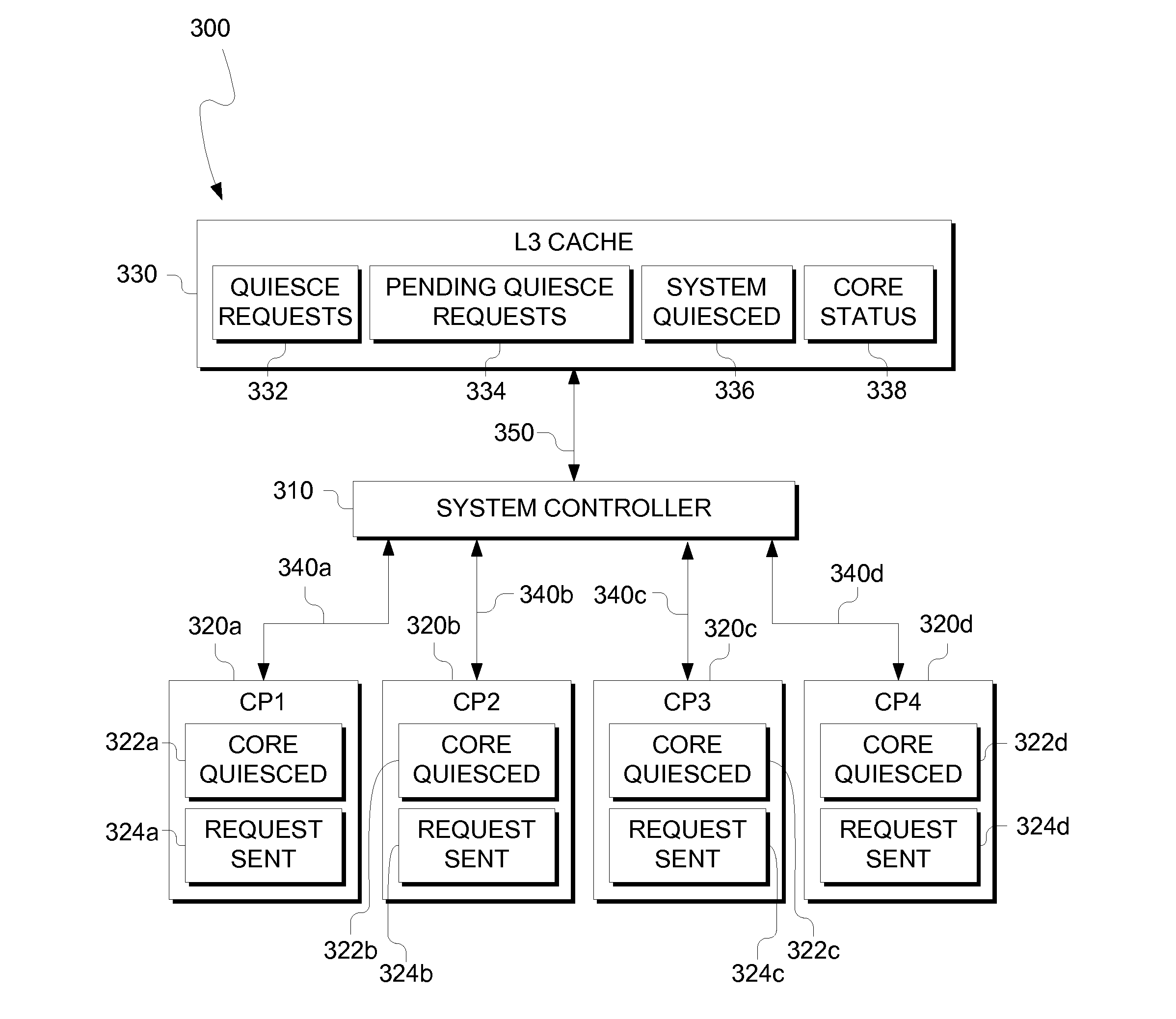
Recovery improvement for quiesced systems
InactiveUS20160140002A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingComputerized system
Methods and apparatuses for performing a quiesce operation during a processor recovery action is provided. A processor performs a processor recovery action. A processor retrieves a quiesce status of a computer system from a shared cache with a second processor. A processor determines a quiesce status of the first processor based, a least in part, on the retrieved quiesce status of the computer system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Resources monitoring and recovery
InactiveUS20120173713A1Digital computer detailsNon-redundant fault processingMonitoring systemRecovery techniques
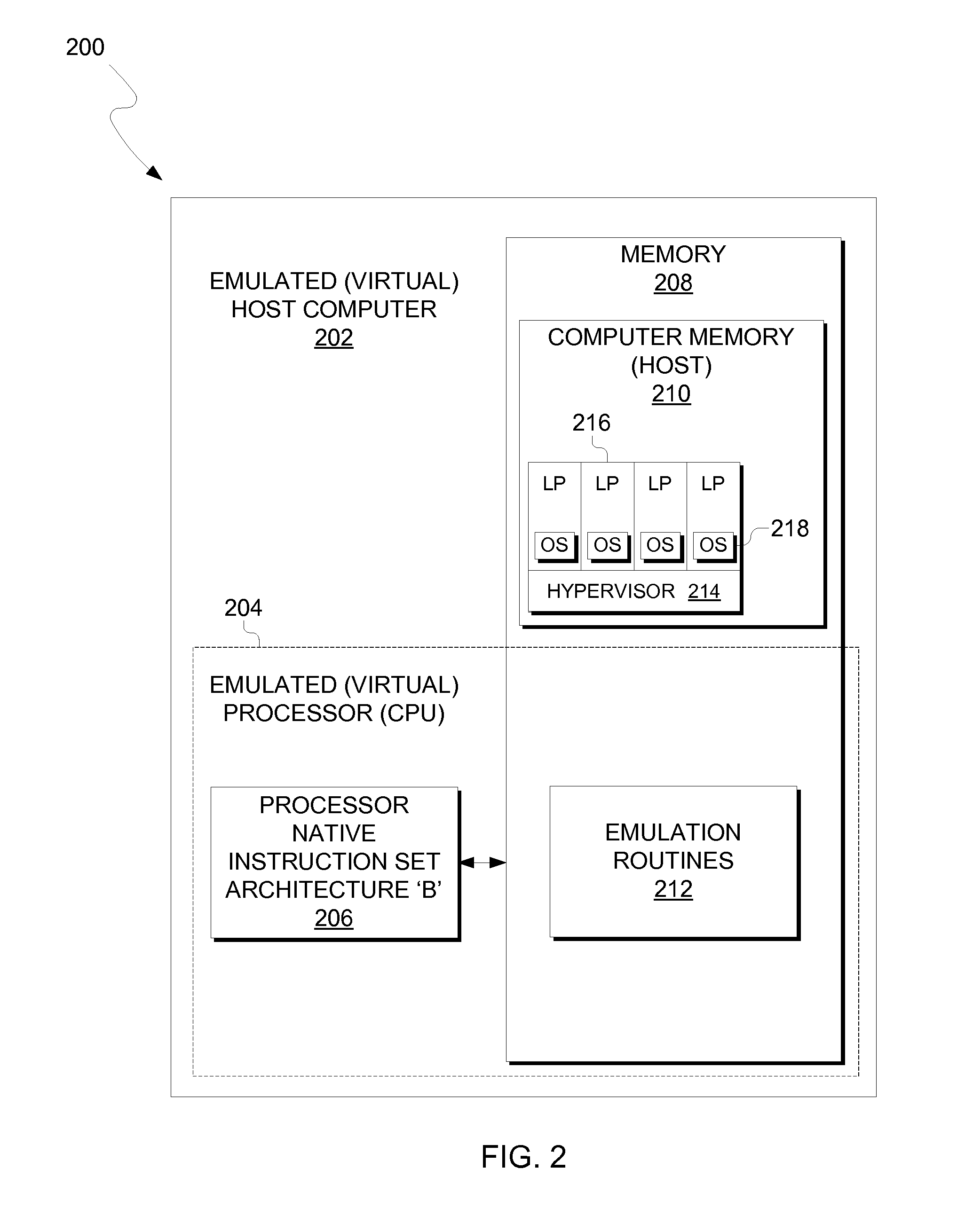
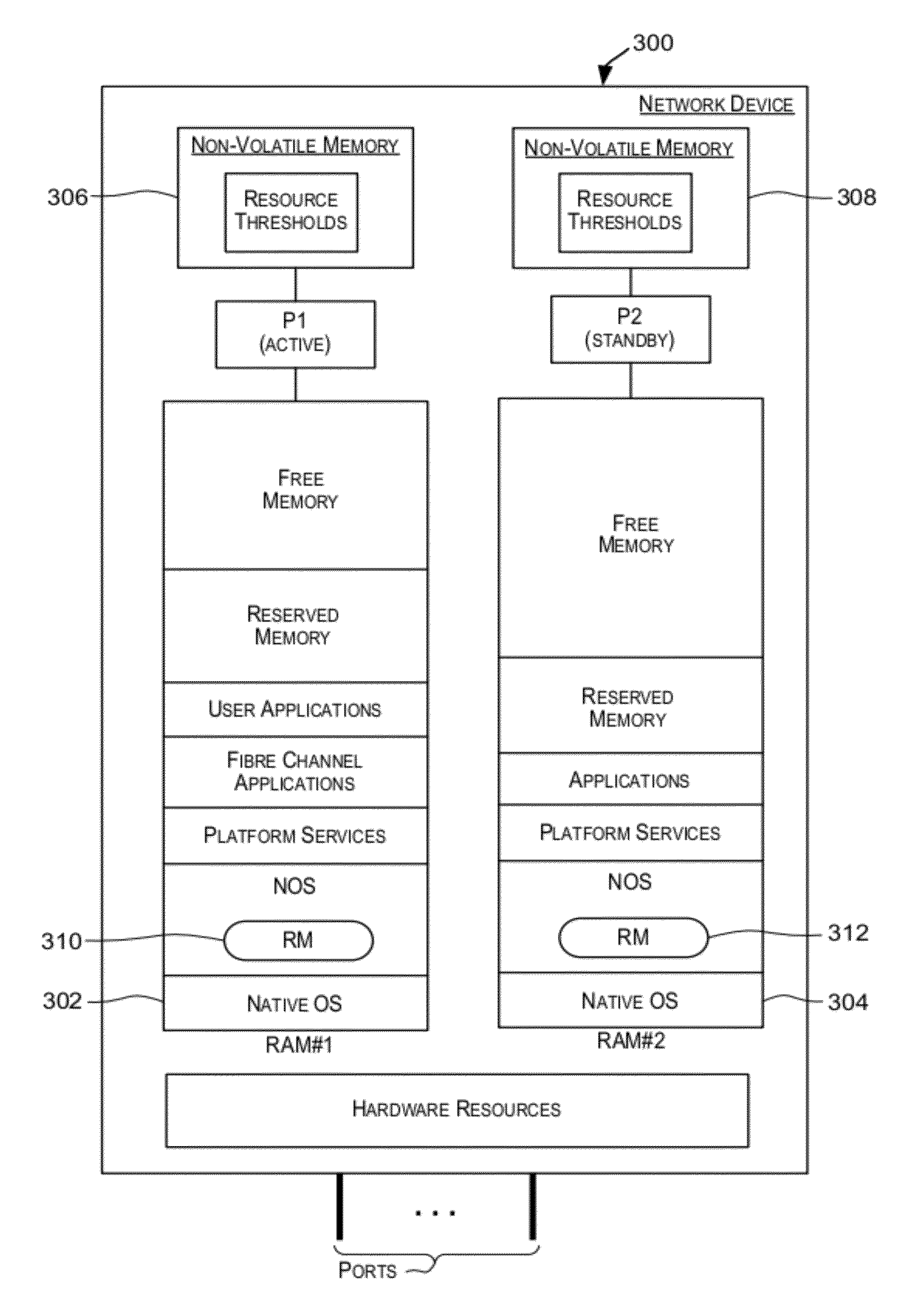
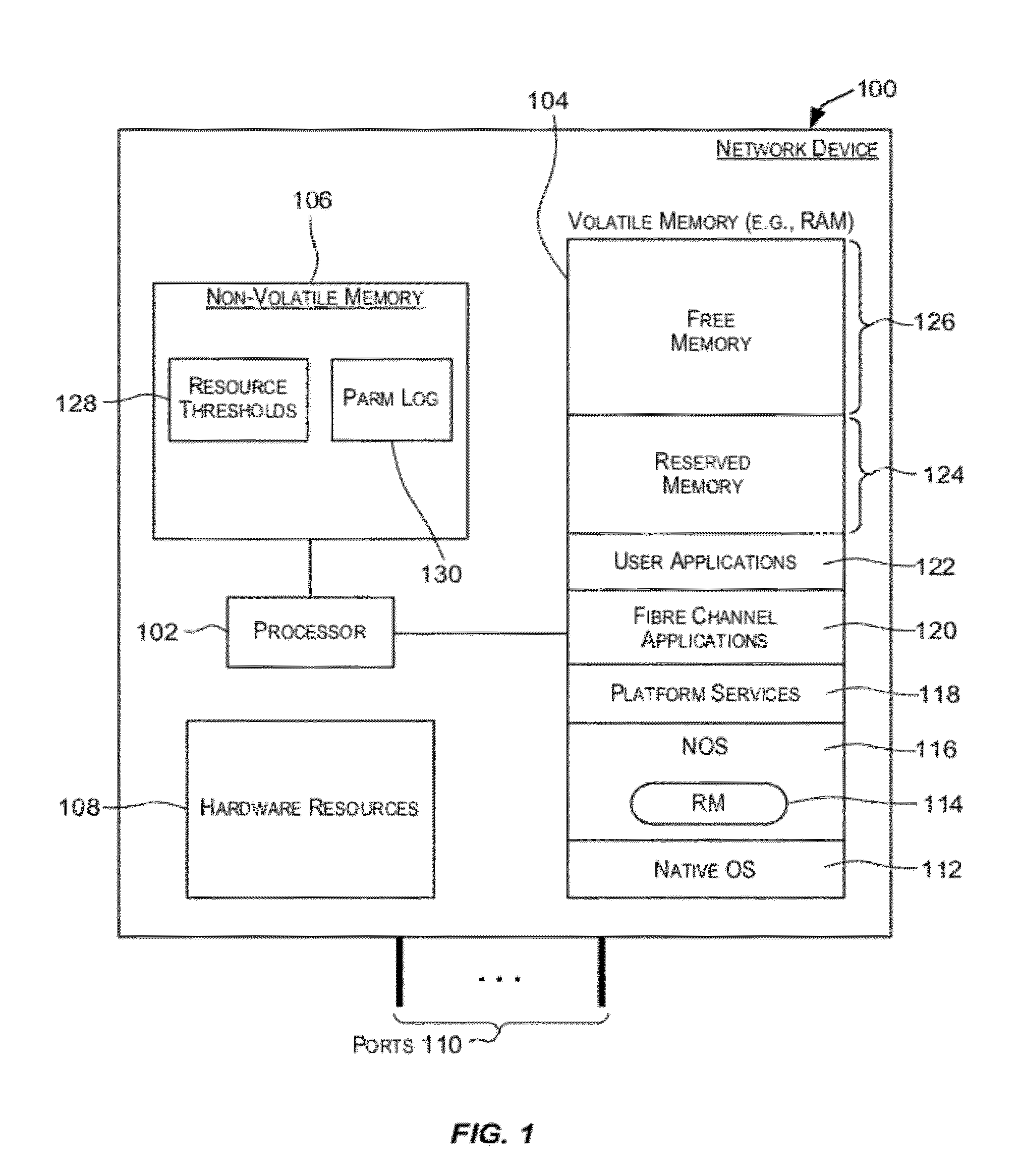
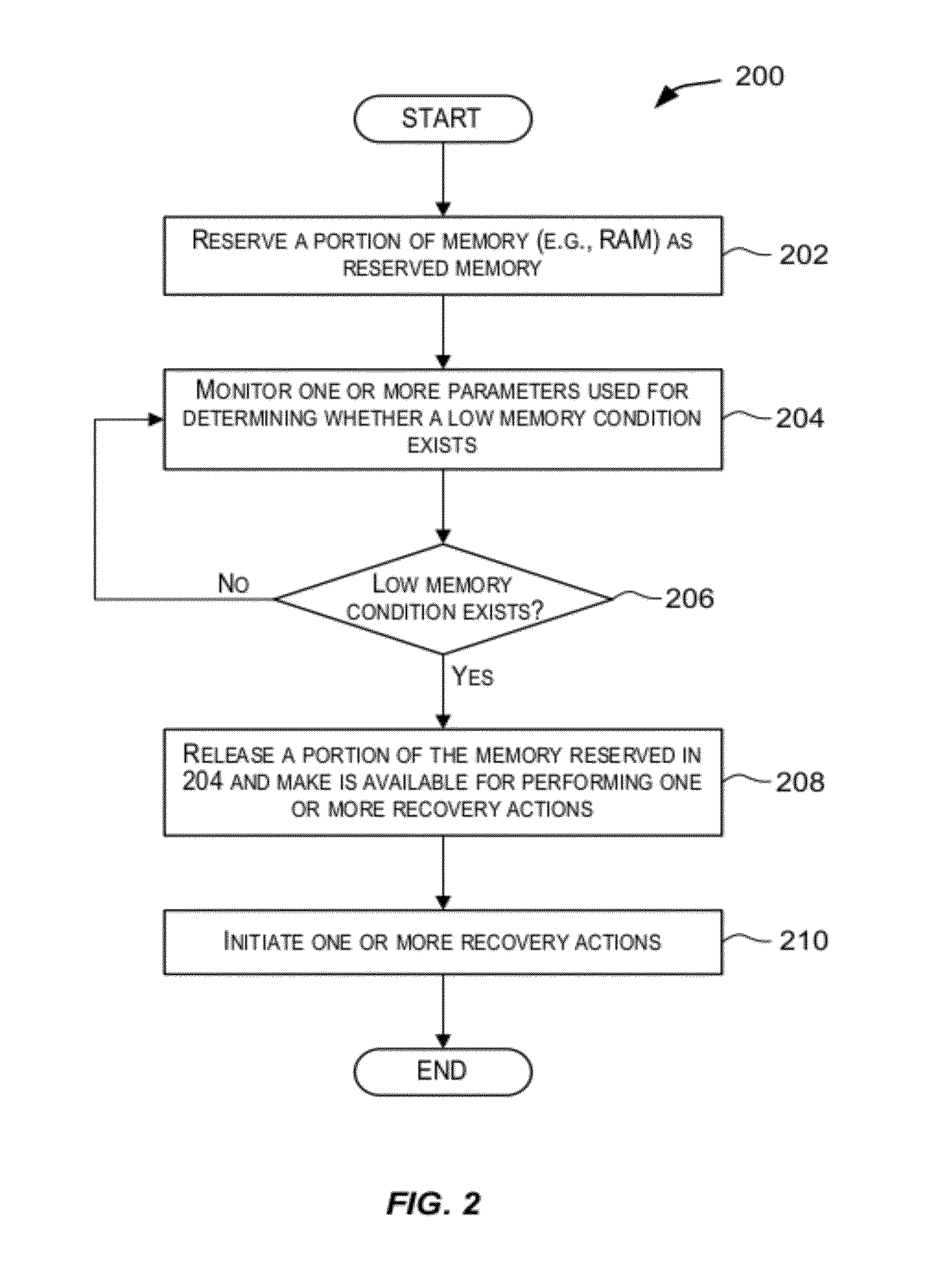
Techniques for monitoring system resources such that a resource-related problem can be identified at a point in time when it is still possible to initiate a set of recovery actions for remedying the problem without disrupting services provided by the system. Various system resources may be monitored including but not limited to system memory (e.g., RAM), one or more processors, non-volatile memory (e.g., Compact Flash usage), and the like.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for parity error recovery
InactiveUS6950978B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationCode conversionData processing systemError checking
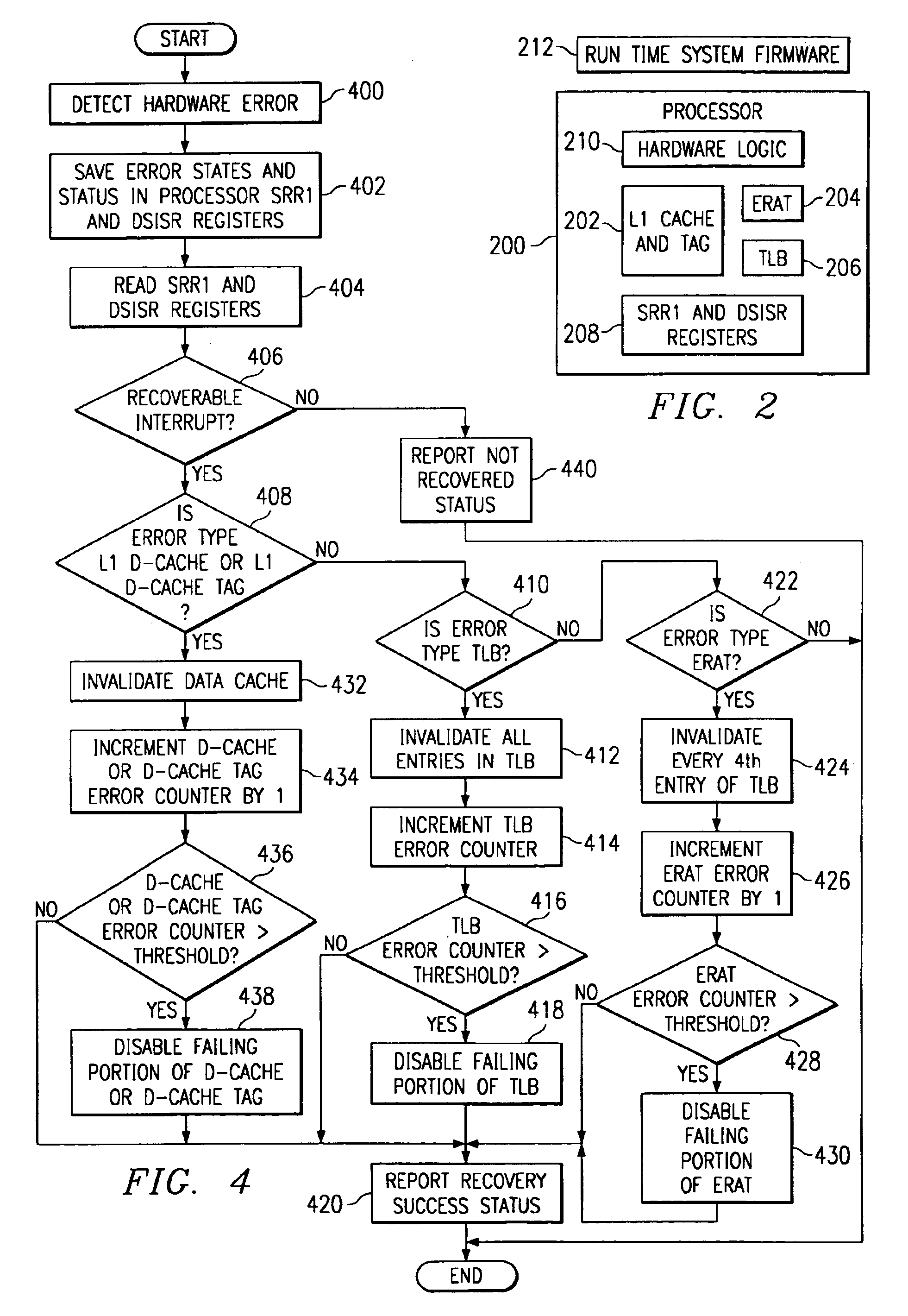
A method, apparatus, and computer implemented instructions for processing and recovering from soft errors in computer array with a parity error checking design in a data processing system. In response to an occurrence of a parity error, processor status information is stored to form stored processor information. A determination is made as to whether the parity error is a recoverable parity error using the stored processor information. In response to the parity error being a recoverable parity error, a recovery action is performed. The specific action taken varies depending on the type of error.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY INC
Suspicious node detection and recovery in mapreduce computing
Embodiments of the present invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to distributed computing for large data sets on clusters of computers and provide a novel and non-obvious method, system and computer program product for detecting and correcting malicious nodes in a cloud computing environment (e.g., MapReduce computing). In one embodiment of the invention, a computer-implemented method for detecting and correcting malicious nodes in a cloud computing environment can include selecting a task to dispatch to a first worker node, setting a suspicion index threshold for the selected task, determining a suspicion index for the selected task, comparing the suspicion index to the suspicion index threshold and receiving a result from a first worker node. The method further can include applying a recovery action when the suspicion index exceeds the selected suspicion index threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
Autonomic error recovery for a data breakout appliance at the edge of a mobile data network
InactiveUS20130157644A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic flowRecovery function
A mechanism provides autonomic recovery for a breakout appliance at the edge of a mobile data network from a variety of errors using a combination of hardware, software and network recovery actions. The recovery actions proceed upon a sliding scale depending on the severity of the problem to achieve the goals of minimizing disruption to traffic flowing through the NodeB while also maintaining an acceptable cost of ownership / maintenance of the system by automatically recovering from as many problems as possible. The error recovery functions within the breakout system hide the error recovery complexities from the management system upstream in the mobile data network. For critical, non-recoverable errors, the autonomic recovery mechanism works in conjunction with a fail-to-wire module to remove the breakout system in the event of a failure in such a way that the mobile data network functions as if the breakout system is no longer present.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com