Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Processing enzymes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzymes are natural proteins that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions. Enzymes are processing aids: the enzyme itself is not functional in the final product.
Engineering intracellular sialylation pathways
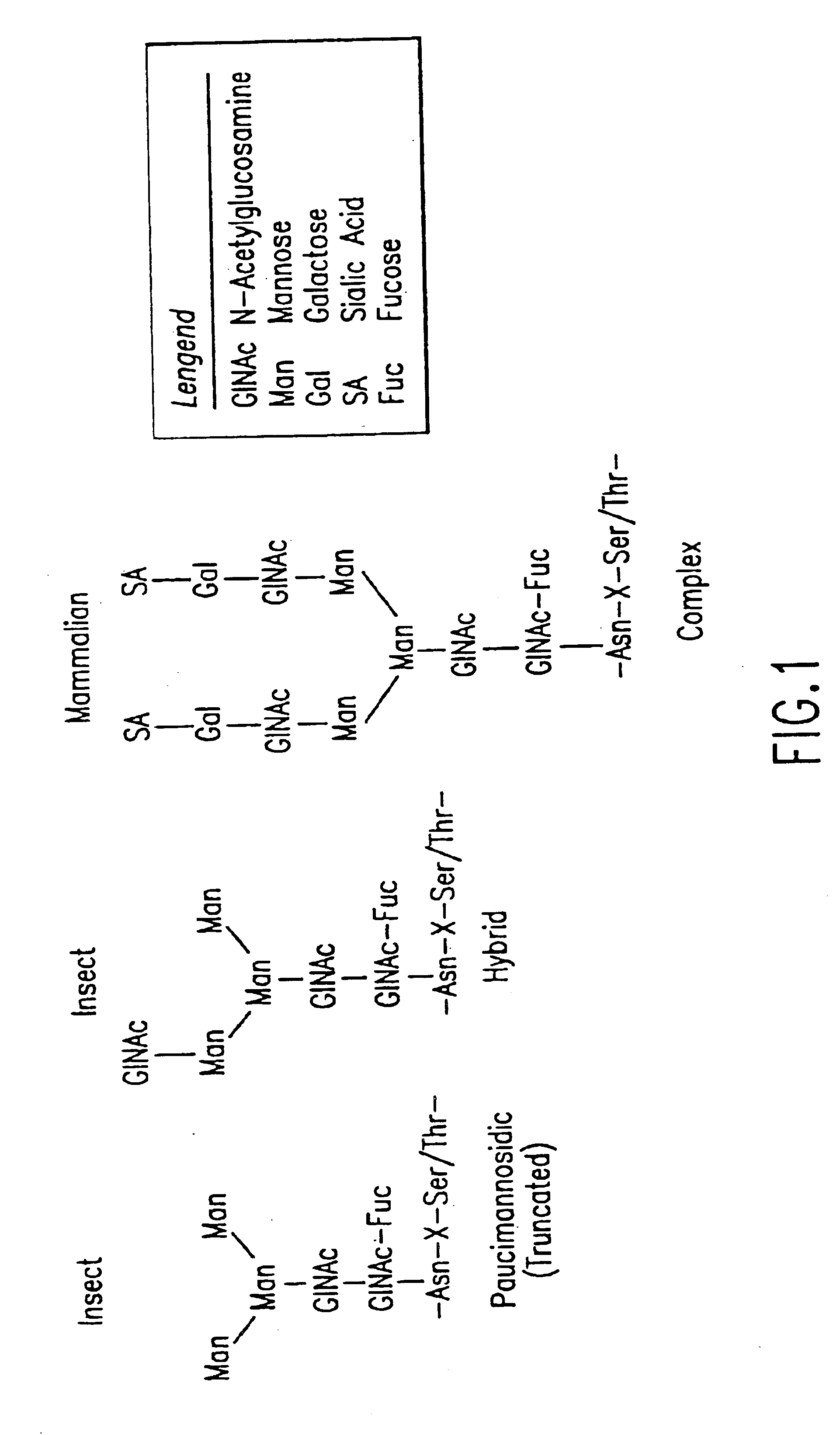
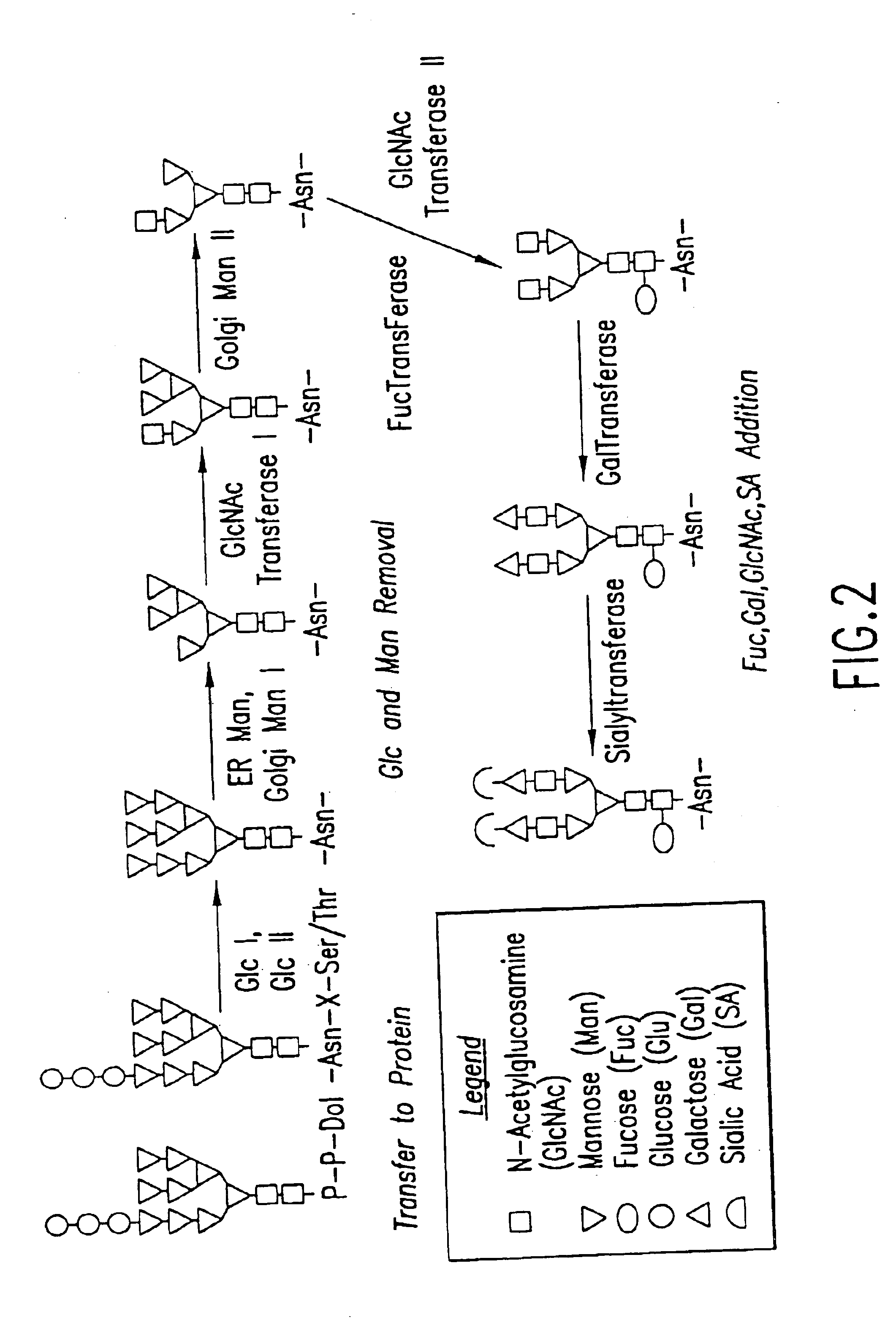
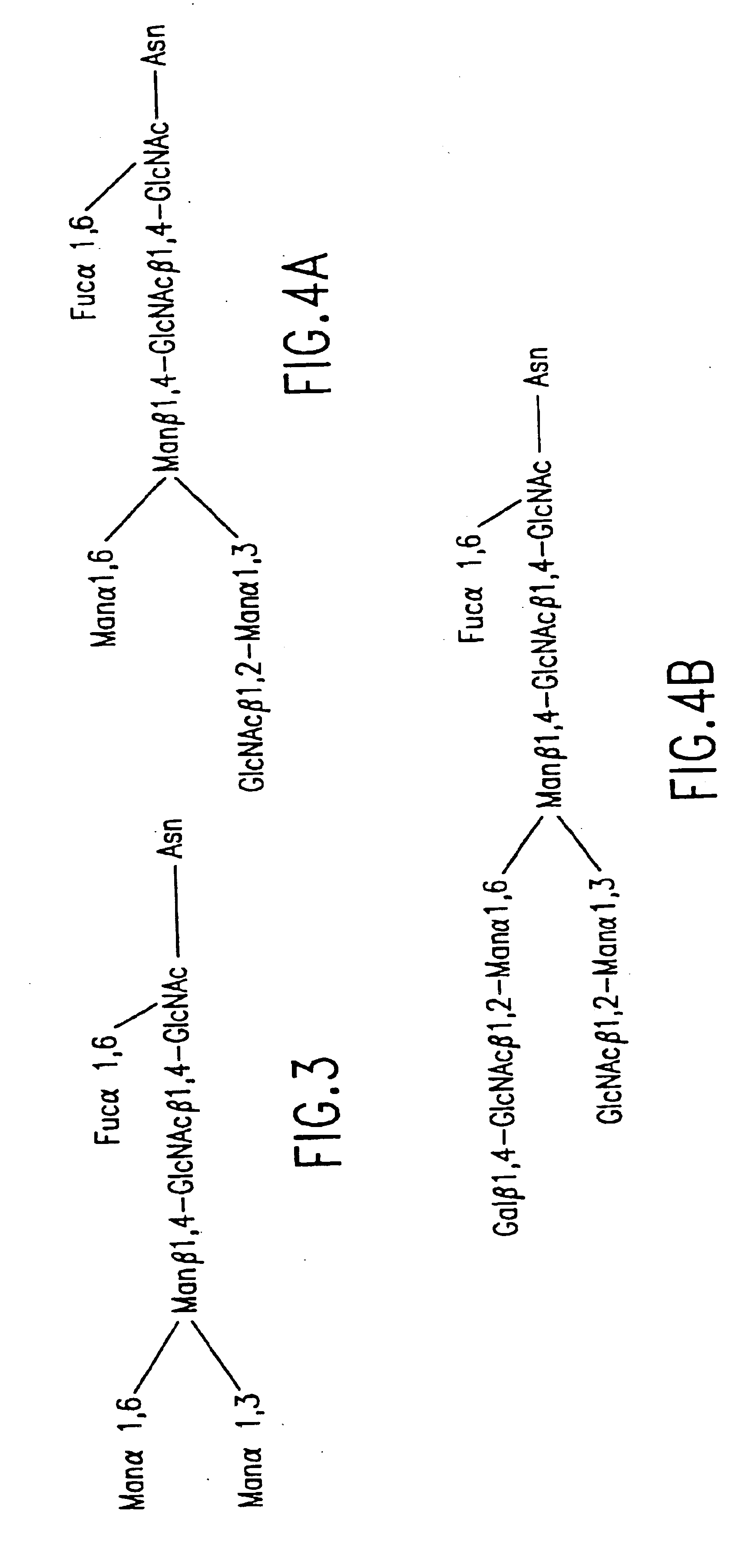
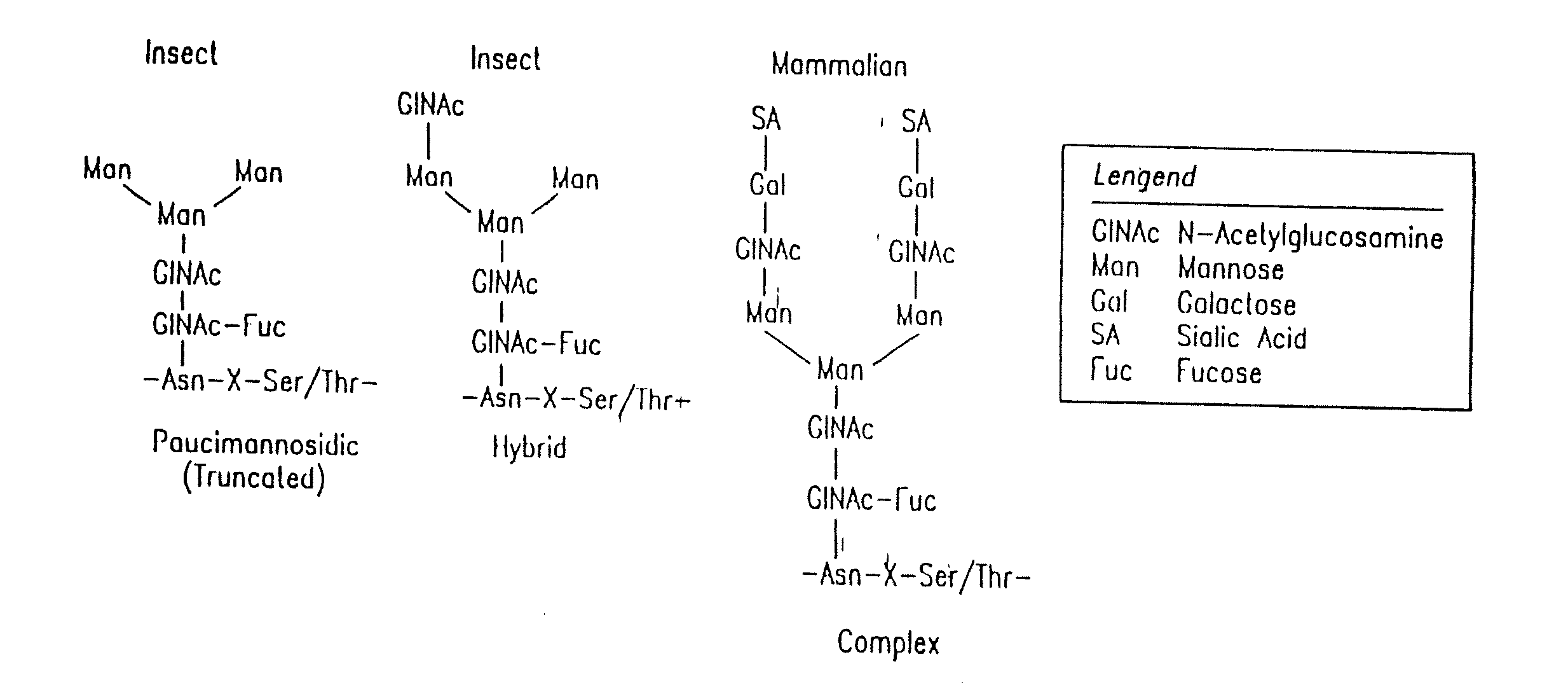
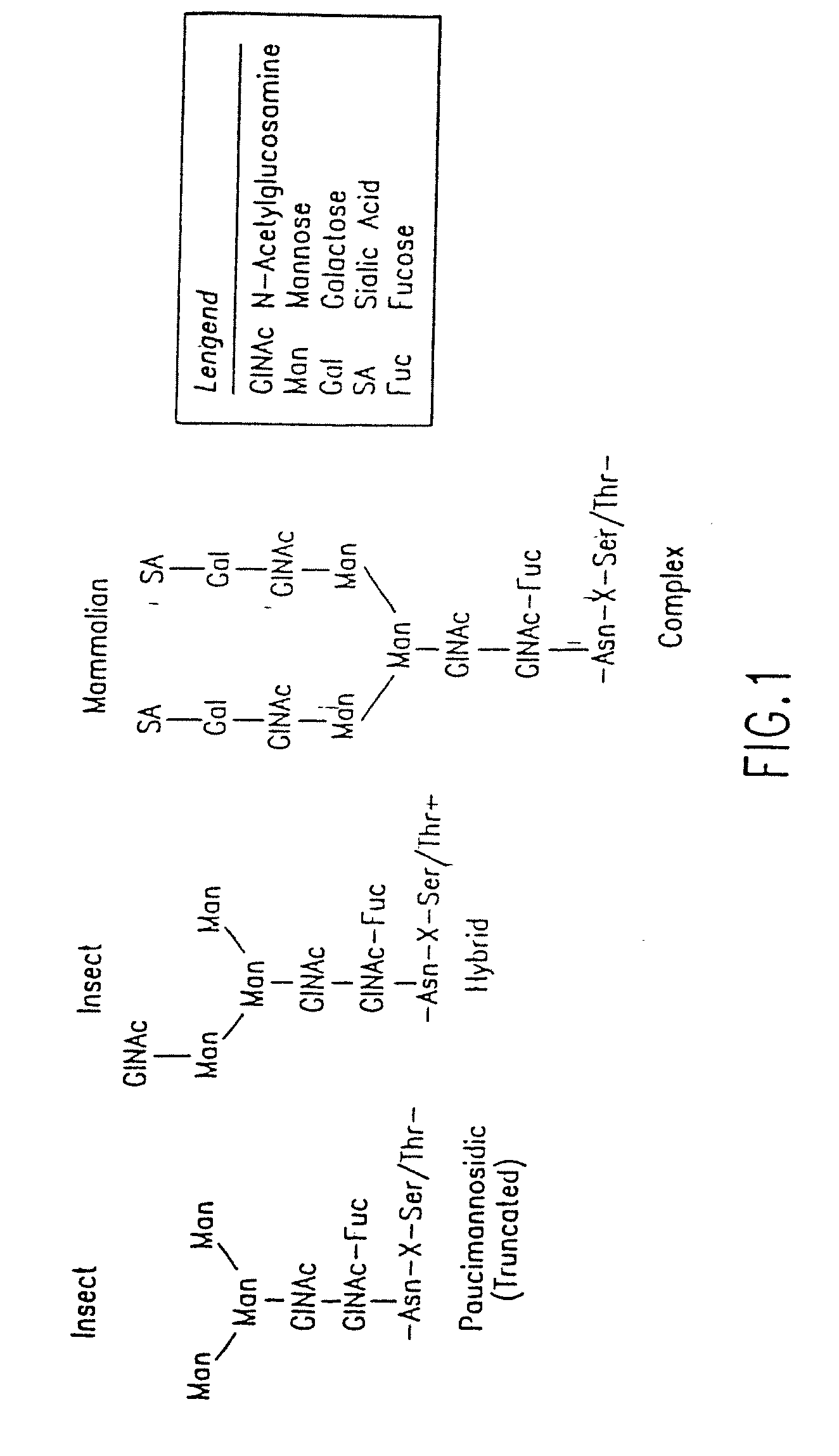
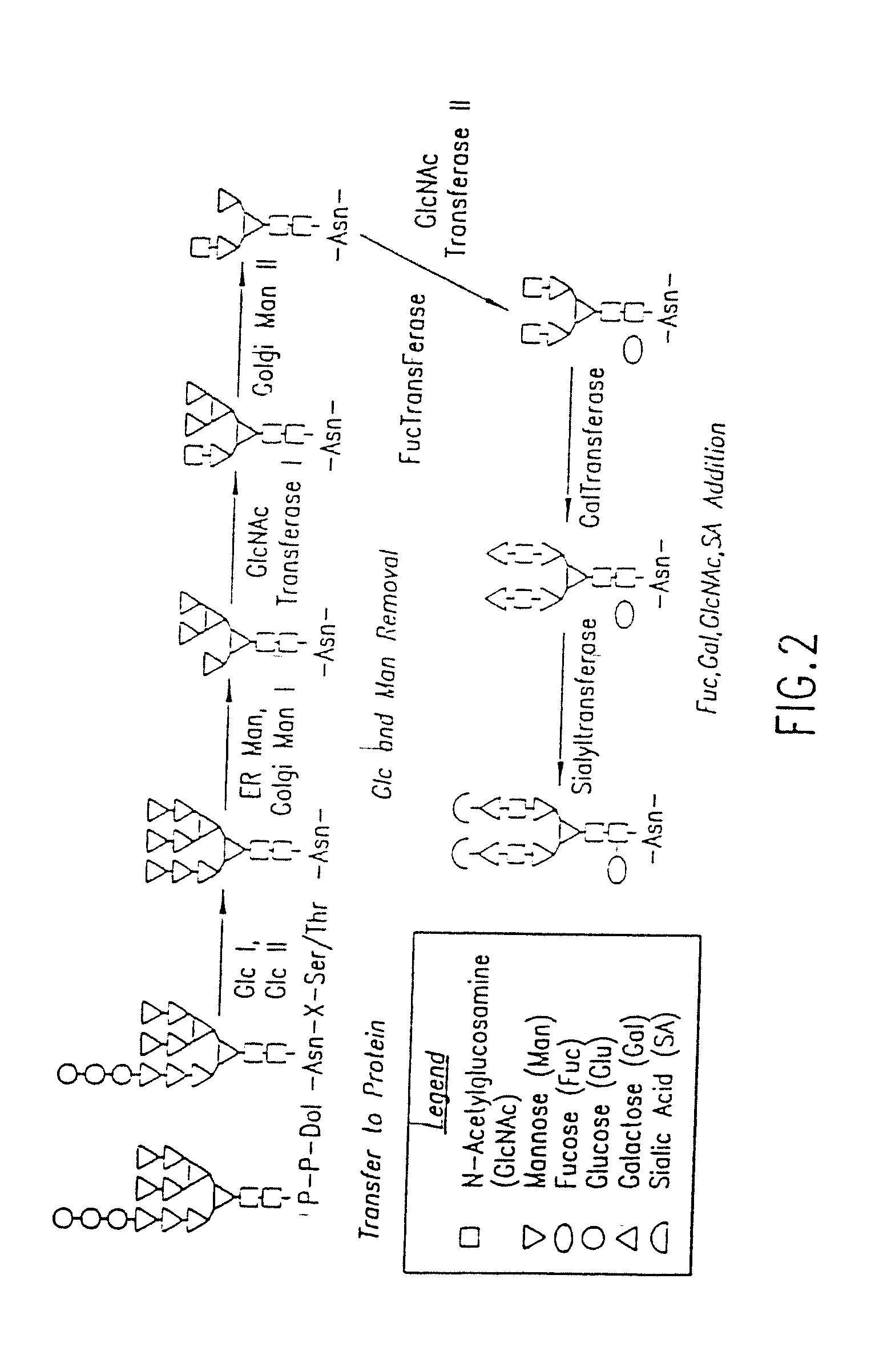
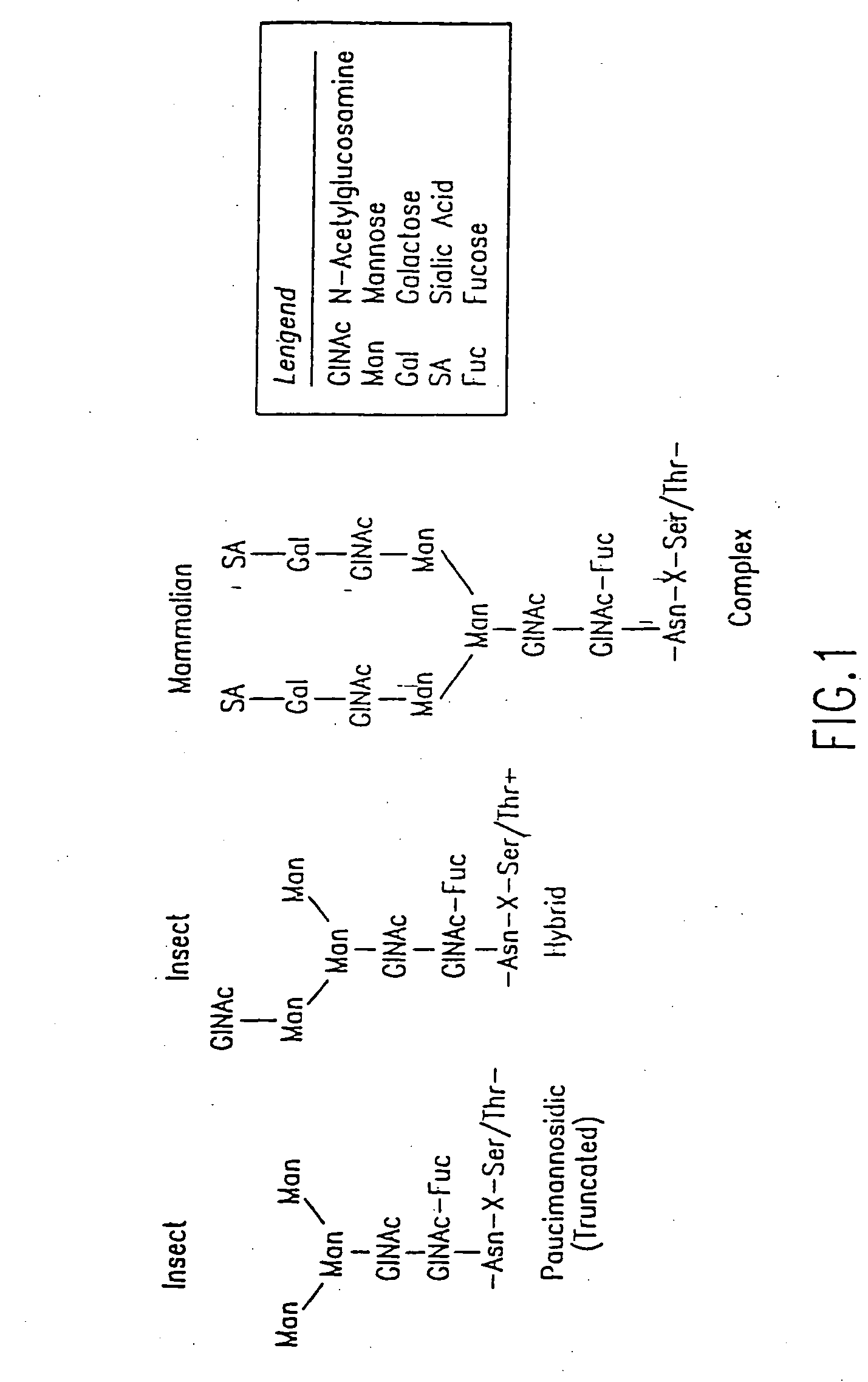
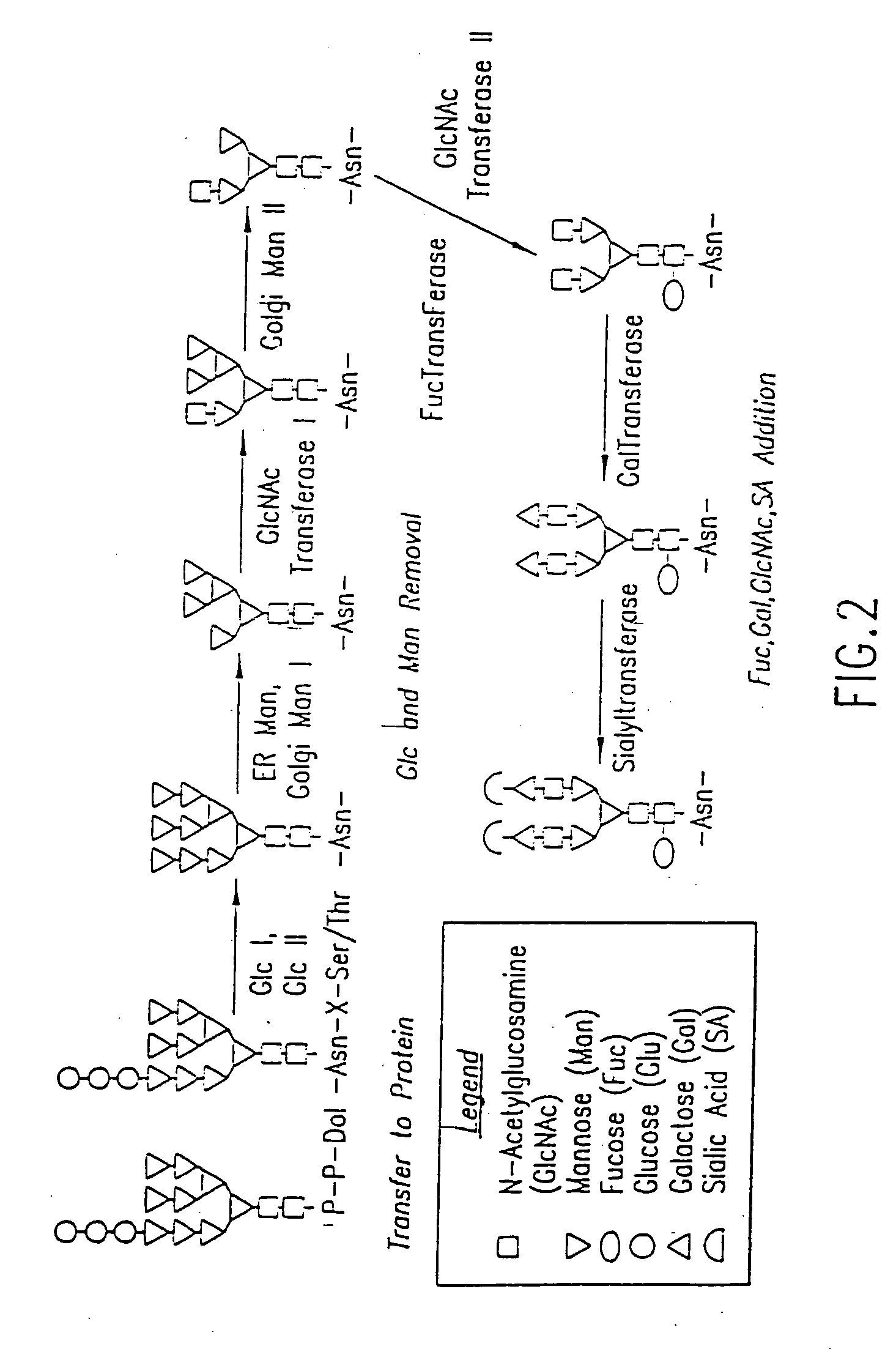
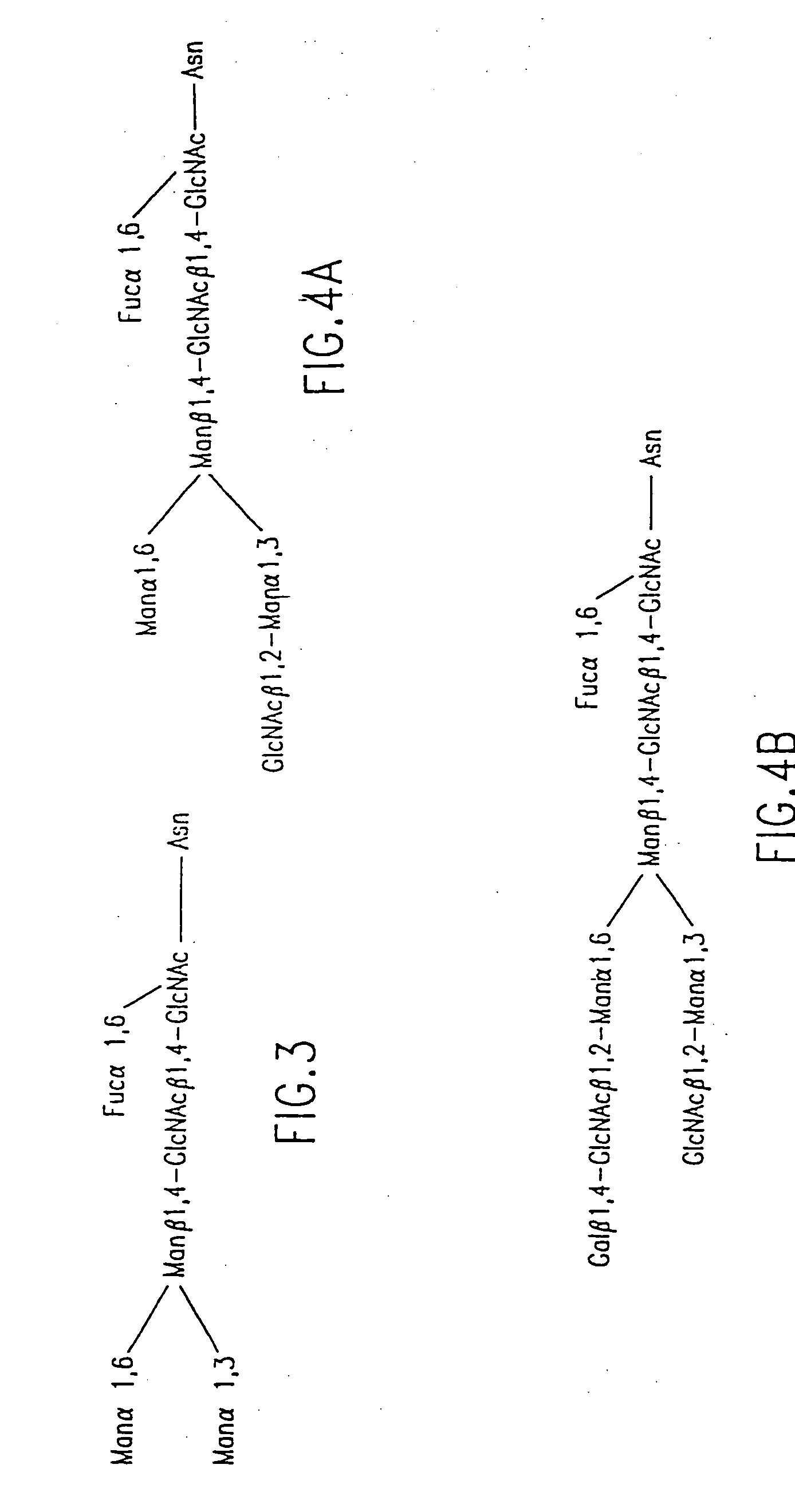
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
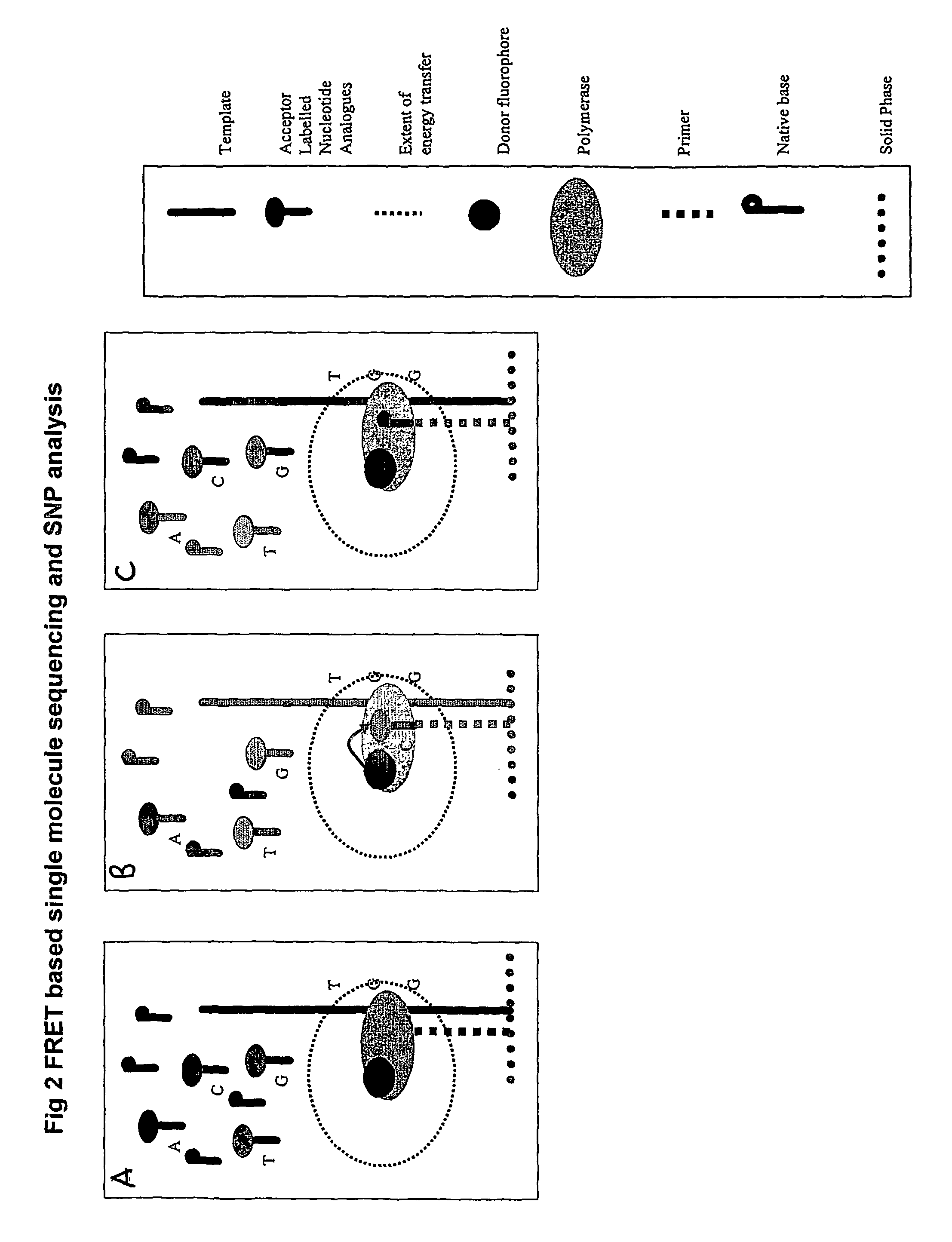
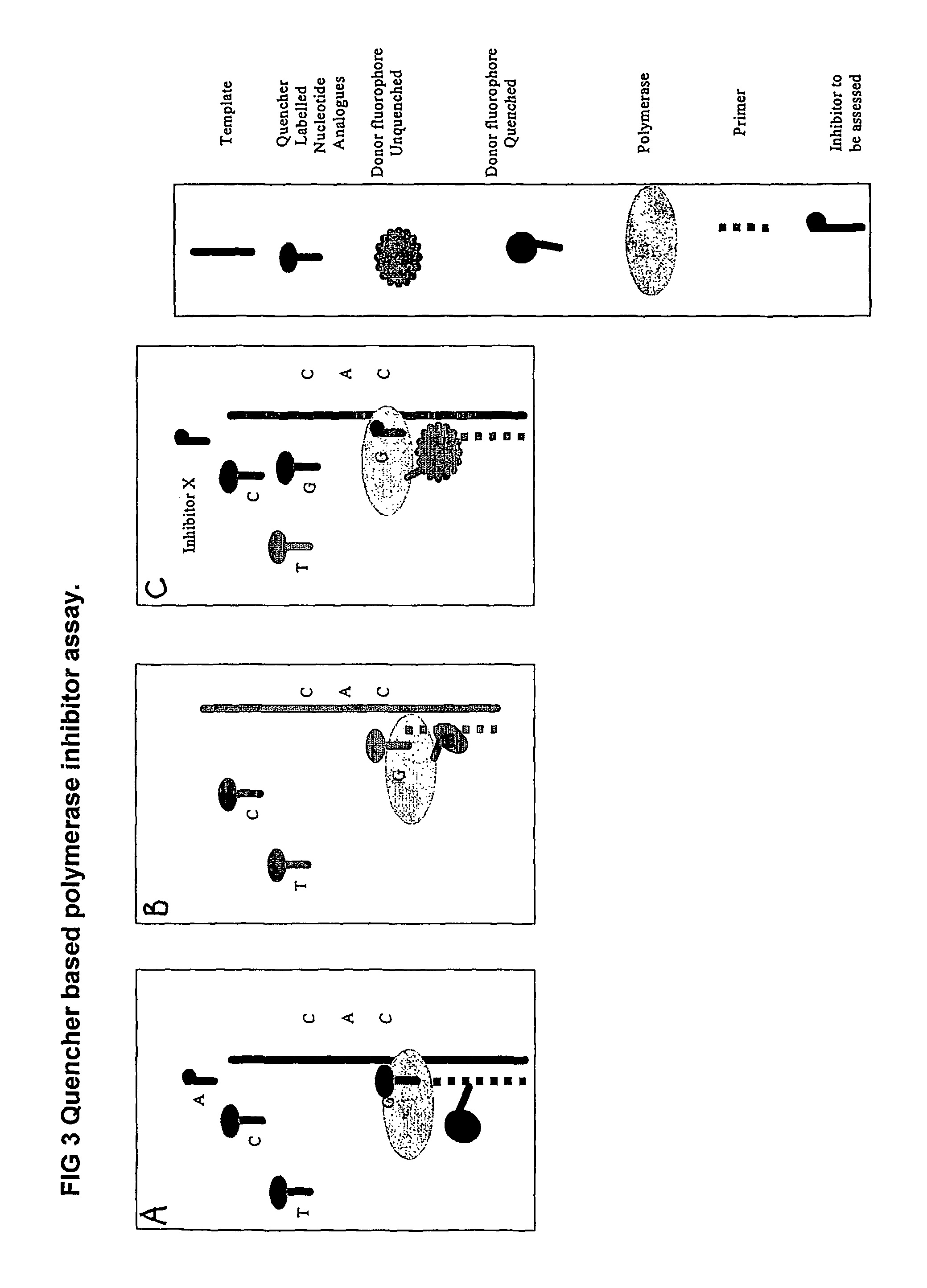
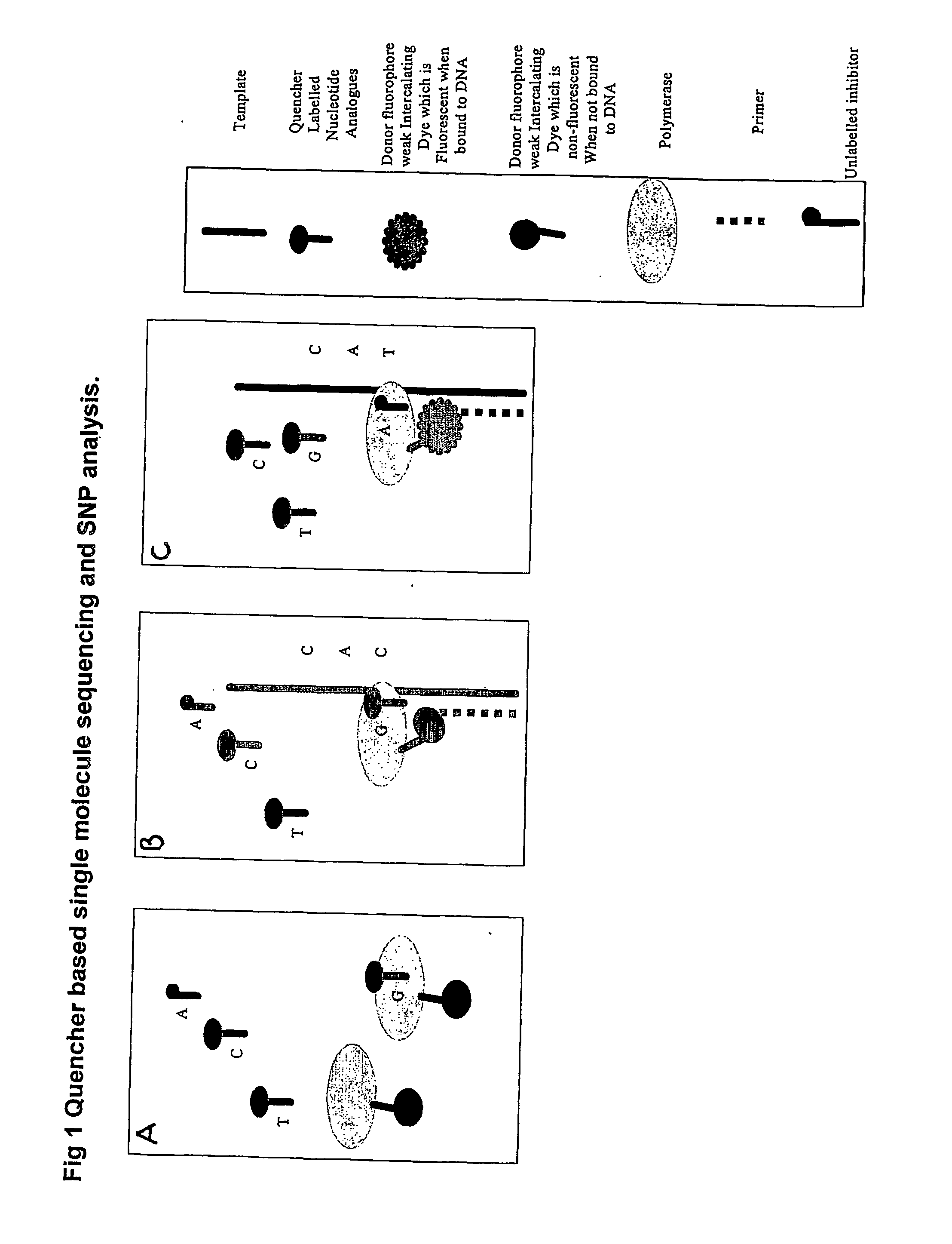
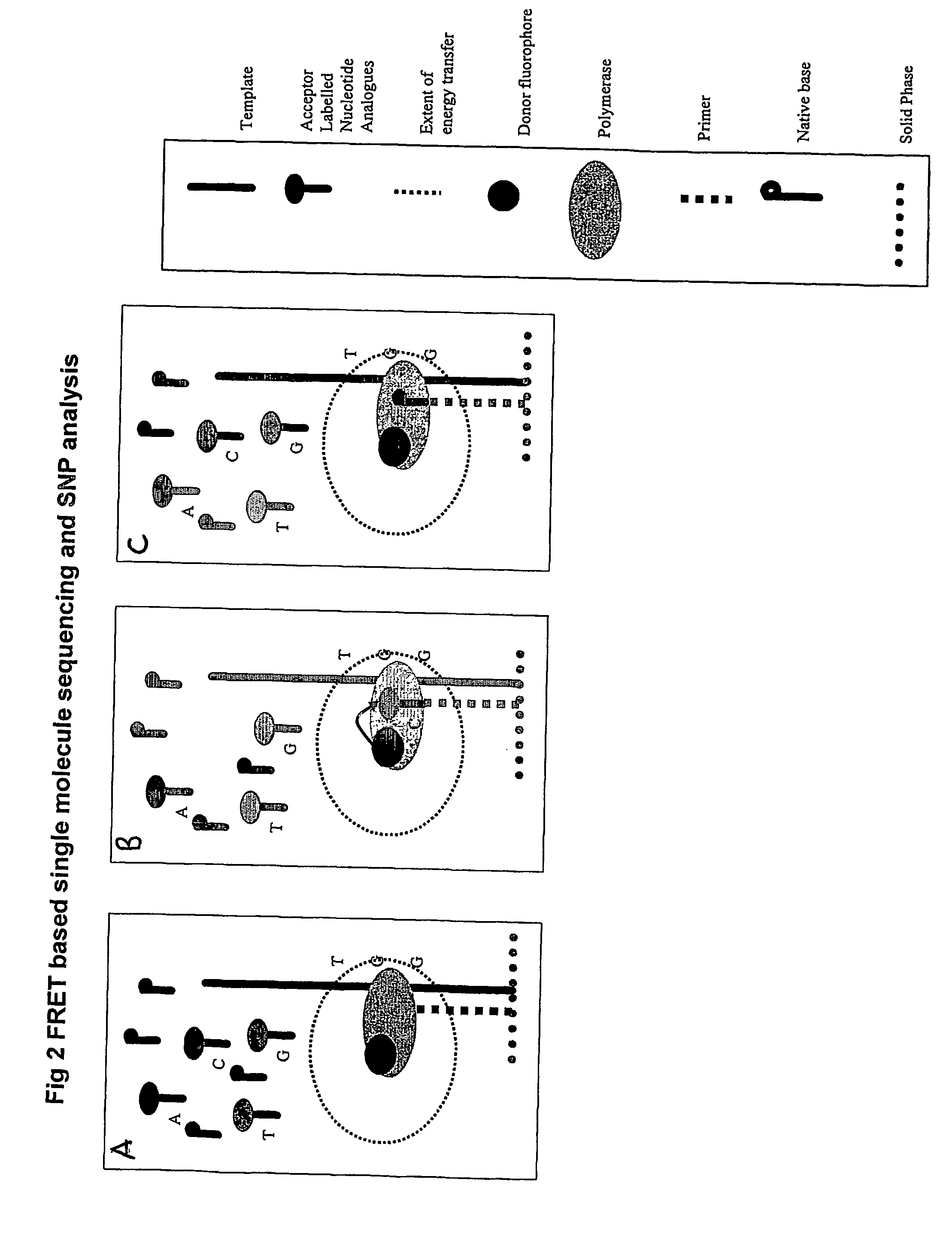
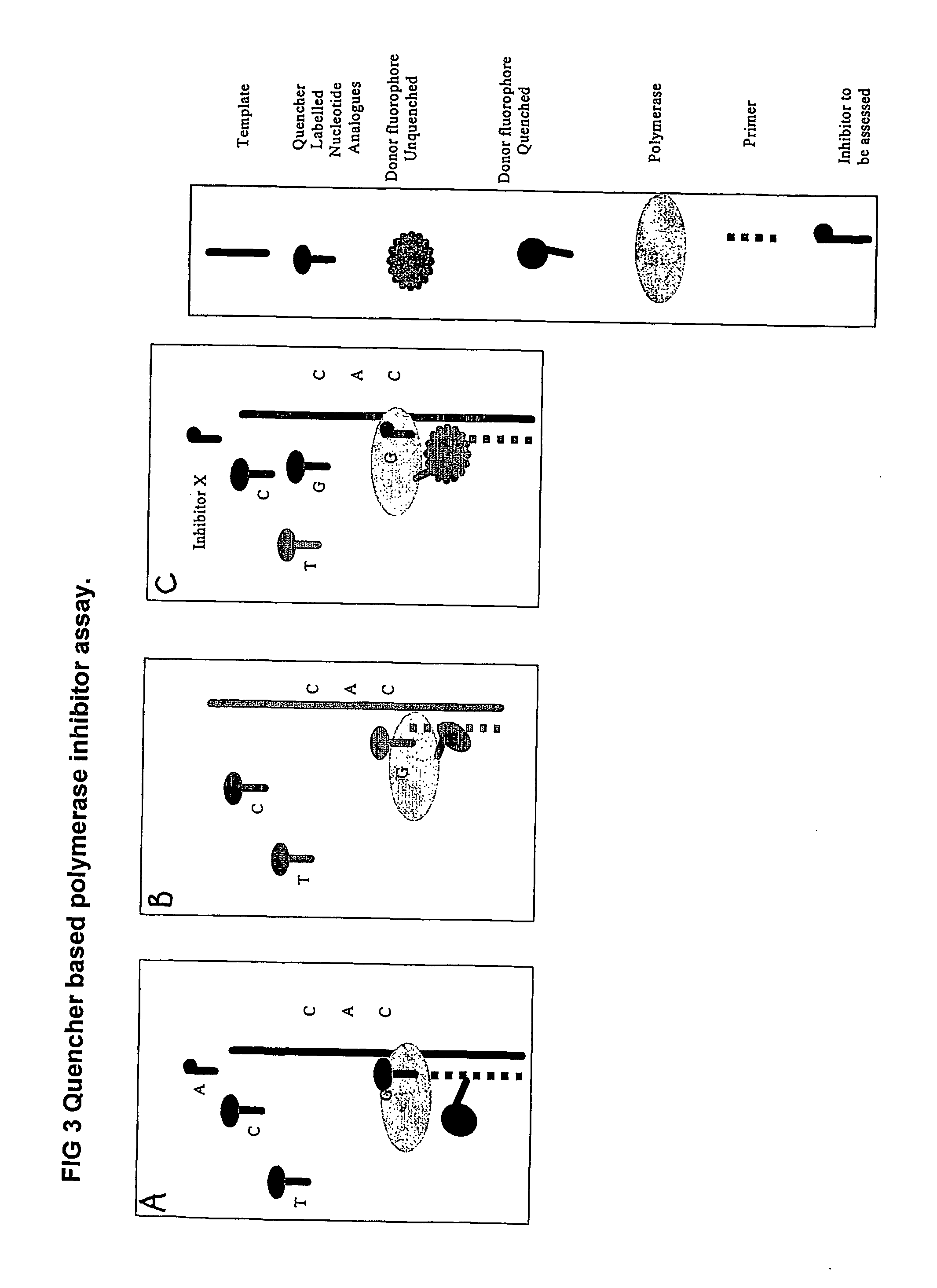
Nucleic acid sequencing methods, kits and reagents
ActiveUS8399196B2Highly controllable homogeneousOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingProcessing enzymes
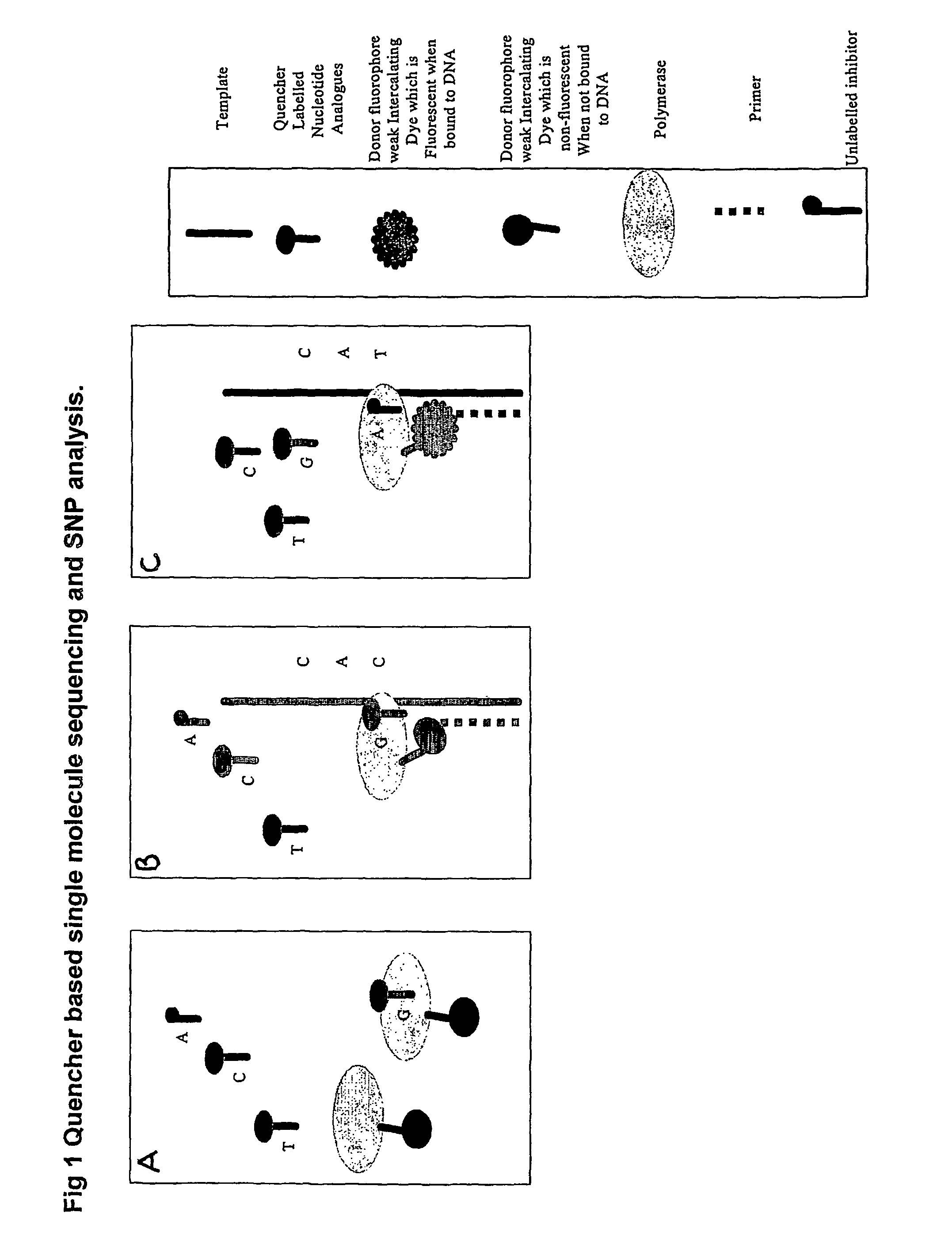
The present invention relates to nucleic acid sequencing methods, kits and reagents, and more particularly to methods of sequencing nucleic acid which employ a nucleic acid processing enzyme and one or more nucleotide analogues that are capable of binding to the active site of the enzyme and to complementary bases in the nucleic acid molecule being sequenced, but which are non-incorporable or inhibitors of the nucleic acid processing enzyme. In further aspects, the present invention relates to conjugates which comprise a deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (DNTPs) or an analogue thereof linked to an intercalating dye.
Owner:GENEFORM TECH LTD
Nucleic acid sequencing methods, kits and reagents
ActiveUS20070148645A1Conveniently preparedHighly controllable homogeneousSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReactive siteNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to nucleic acid sequencing methods, kits and reagents, and more particularly to methods of sequencing nucleic acid which employ a nucleic acid processing enzyme and one or more nucleotide analogues that are capable of binding to the active site of the enzyme and to complementary bases in the nucleic acid molecule being sequenced, but which are non-incorporable or inhibitors of the nucleic acid processing enzyme. In further aspects, the present invention relates to conjugates which comprise a deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (DNTPs) or an analogue thereof linked to an intercalating dye.
Owner:GENEFORM TECH LTD
Engineering Intracellular Sialylation Pathways
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method for detecting starch content in ash tree flower polysaccharide
InactiveCN1474183AEasy to operateThe measurement results are accurate and reliableChemical analysis using titrationProcessing enzymesRepeatability
The present invention is the method of detecting starch content in ash tree flower polysaccharide product. The detection includes the steps of eliminating liposoluble component, eliminating soluble saccharide as interference matter, enzyme decomposing starch, detecting starch, processing enzyme hydrolyzed starch liquid, Fehling's process of determining reducing sugar content, etc. The method ofthe present invention is suitable for operation, has stable and reliable determined result, small variation coefficient of determined result, less error, high repeatability and other advantages.
Owner:LAIYANG AGRI COLLEGE
Device, system and method for receiving, processing and dispersing cells
InactiveUS20050026275A1Easy to masterAvoid dissipationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWound dressingSprayer
The present invention relates to a system and method which includes a means for sterilely receiving and handling tissue, a means for mechanically handling and separating the tissue, a means for enzymatically disaggregating the tissue, a means for holding processing enzymes, a means for mechanically and thermally processing tissue, a means for storing processed tissue, and a multi-channel cell sprayer for delivering cells derived therefrom to a variety of surfaces, a means for storing components in a sterile manner, and a method for using such sprayer. More specifically, the present invention relates to a system for harvesting tissue, processing tissue and delivering cells derived therefrom to large areas such as wound surfaces or wound dressings.
Owner:TICELL BIOSERVICES
Self-Processing Plants and Plant Parts
The invention provides polynucleotides, preferably synthetic polynucleotides, which encode processing enzymes that are optimized for expression in plants. The polynucleotides encode mesophilic, thermophilic, or hyperthermophilic processing enzymes, which are activated under suitable activating conditions to act upon the desired substrate. Also provided are “self-processing” transgenic plants, and plant parts, e.g., grain, which express one or more of these enzymes and have an altered composition that facilitates plant and grain processing. Methods for making and using these plants, e.g., to produce food products having improved taste and to produce fermentable substrates for the production of ethanol and fermented beverages are also provided.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Self processing plants and plant parts
The invention provides polynucleotides, preferably synthetic polynucleotides, which encode processing enzymes that are optimized for expression in plants. The polynucleotides encode mesophilic, thermophilic, or hyperthermophilic processing enzymes, which are activated under suitable activating conditions to act upon the desired substrate. Also provided are “self-processing” transgenic plants, and plant parts, e.g., grain, which express one or more of these enzymes and have an altered composition that facilitates plant and grain processing. Methods for making and using these plants, e.g., to produce food products having improved taste and to produce fermentable substrates for the production of ethanol and fermented beverages are also provided.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Self processing plants and plant parts
The invention provides polynucleotides, preferably synthetic polynucleotides, which encode processing enzymes that are optimized for expression in plants. The polynucleotides encode mesophilic, thermophilic, or hyperthermophilic processing enzymes, which are activated under suitable activating conditions to act upon the desired substrate. Also provided are “self-processing” transgenic plants, and plant parts, e.g., grain, which express one or more of these enzymes and have an altered composition that facilitates plant and grain processing. Methods for making and using these plants, e.g., to produce food products having improved taste and to produce fermentable substrates for the production of ethanol and fermented beverages are also provided.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Engineering intracellular sialylation pathways
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:BETENBAUGH MICHAEL +3
Modified carbohydrate processing enzyme
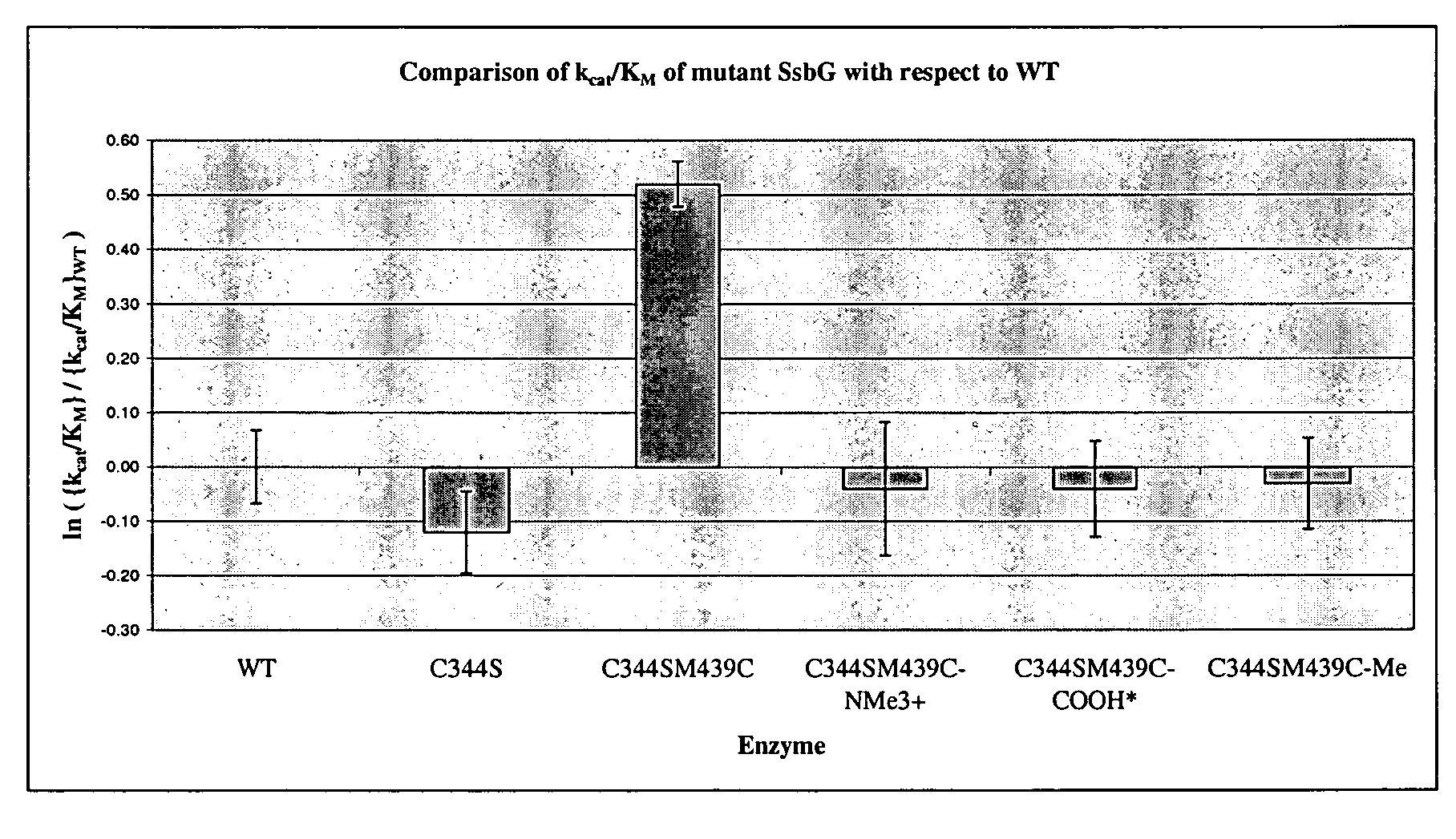
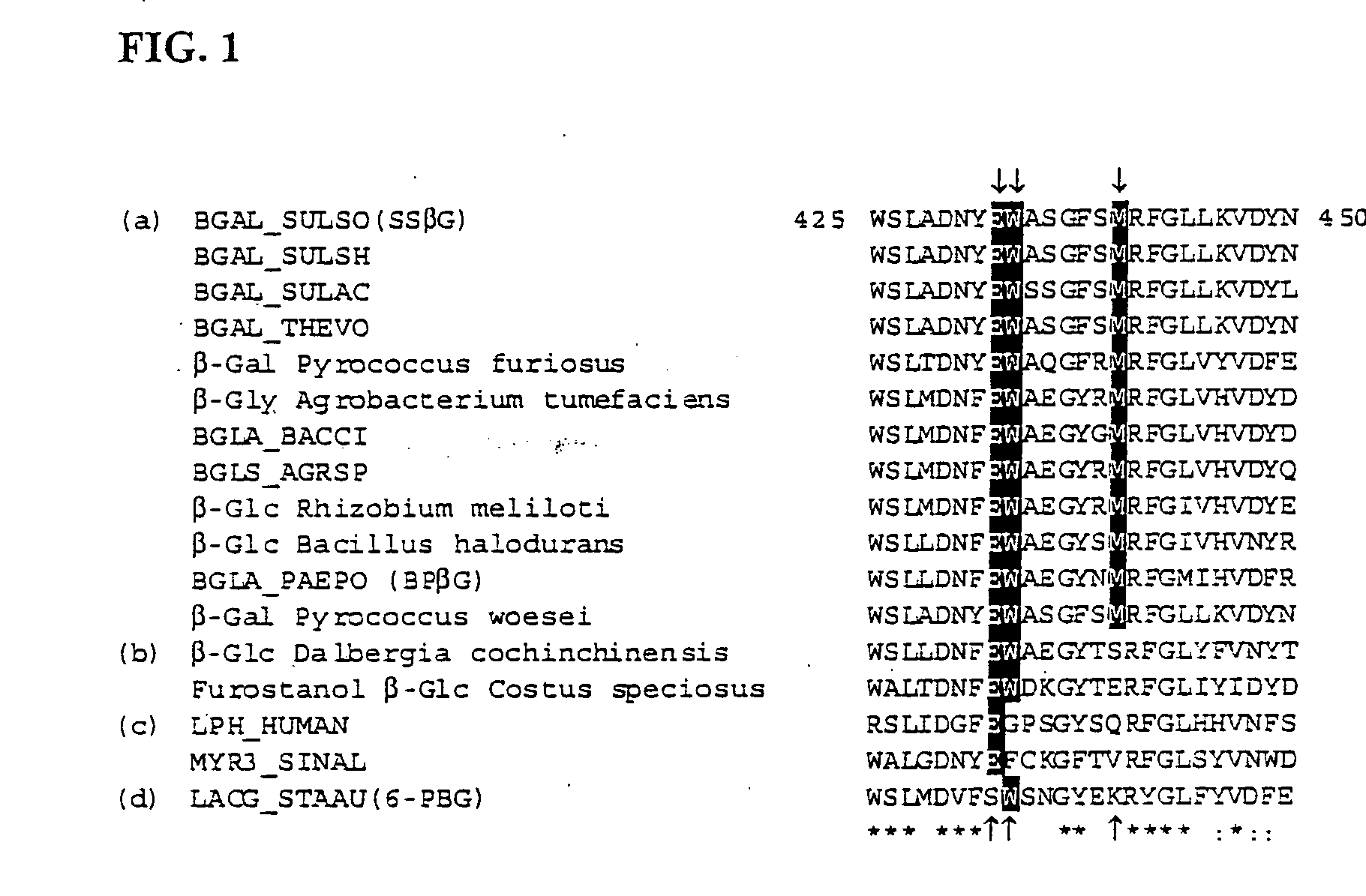
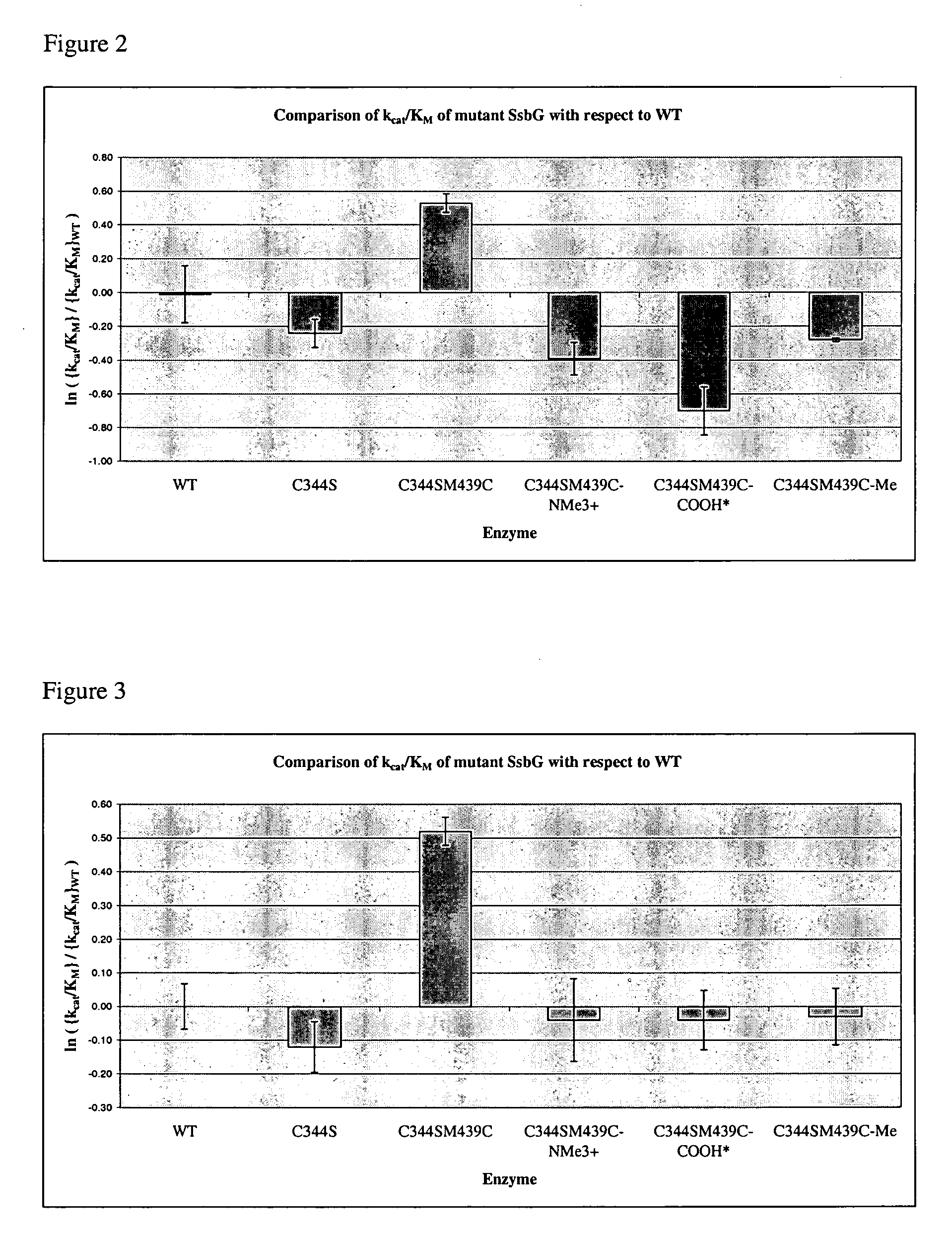
A modified polypeptide having carbohydrate processing enzymatic activity is provided, said polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence selected from: (a) the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 comprising a mutation in at least one of W433, E432 and M439; (b) the amino acid sequence of an enzyme of glycosyl hydrolase family 1, comprising at least one mutation at an amino acid residue equivalent to W433, E432 or M439 of SEQ ID NO:2; and (c) a variant of (a) or (b) having carbohydrate processing enzymatic activity and comprising at least one amino acid mutation at a position equivalent to W433, E432 or M439 of SEQ ID NO:2.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
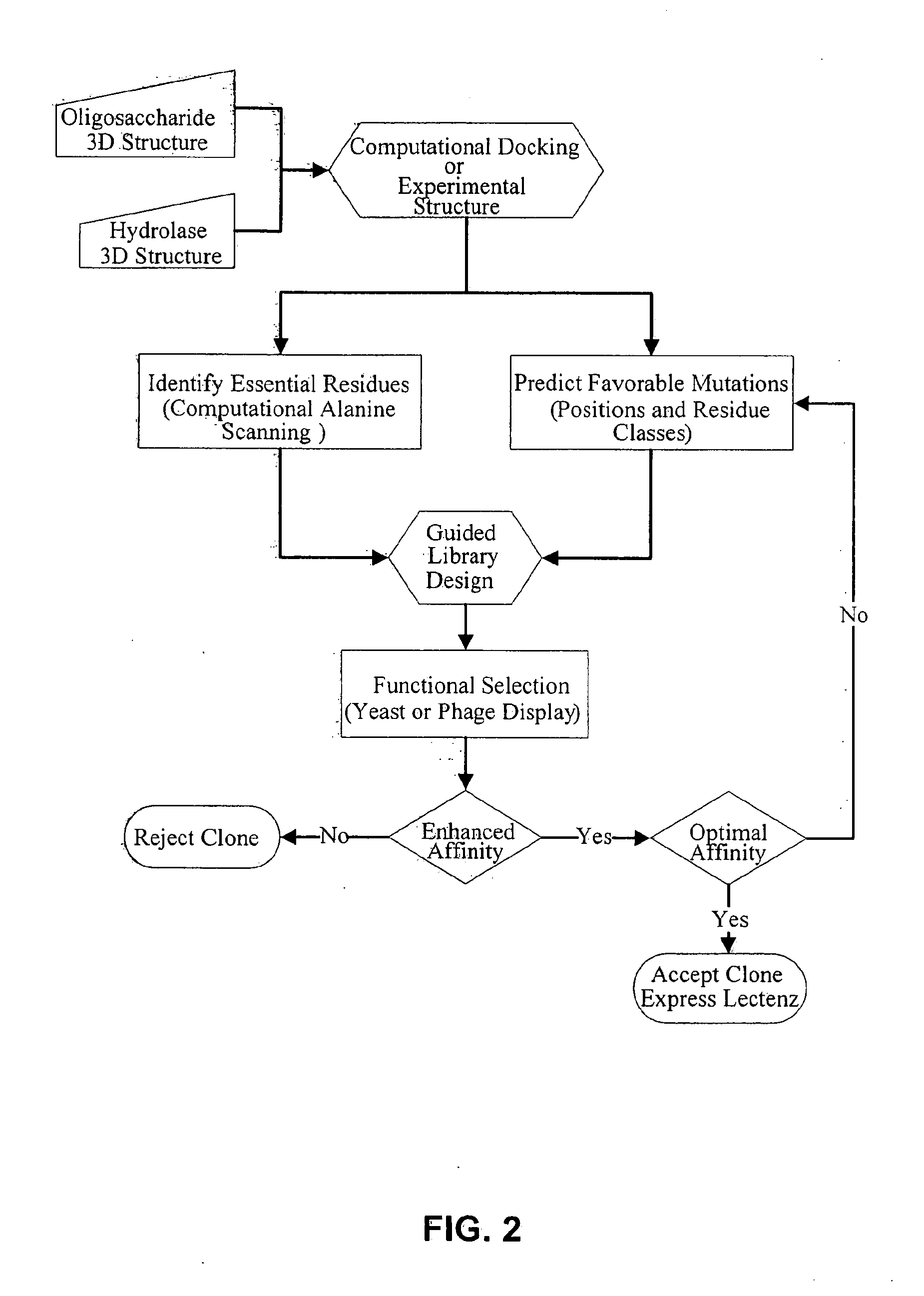
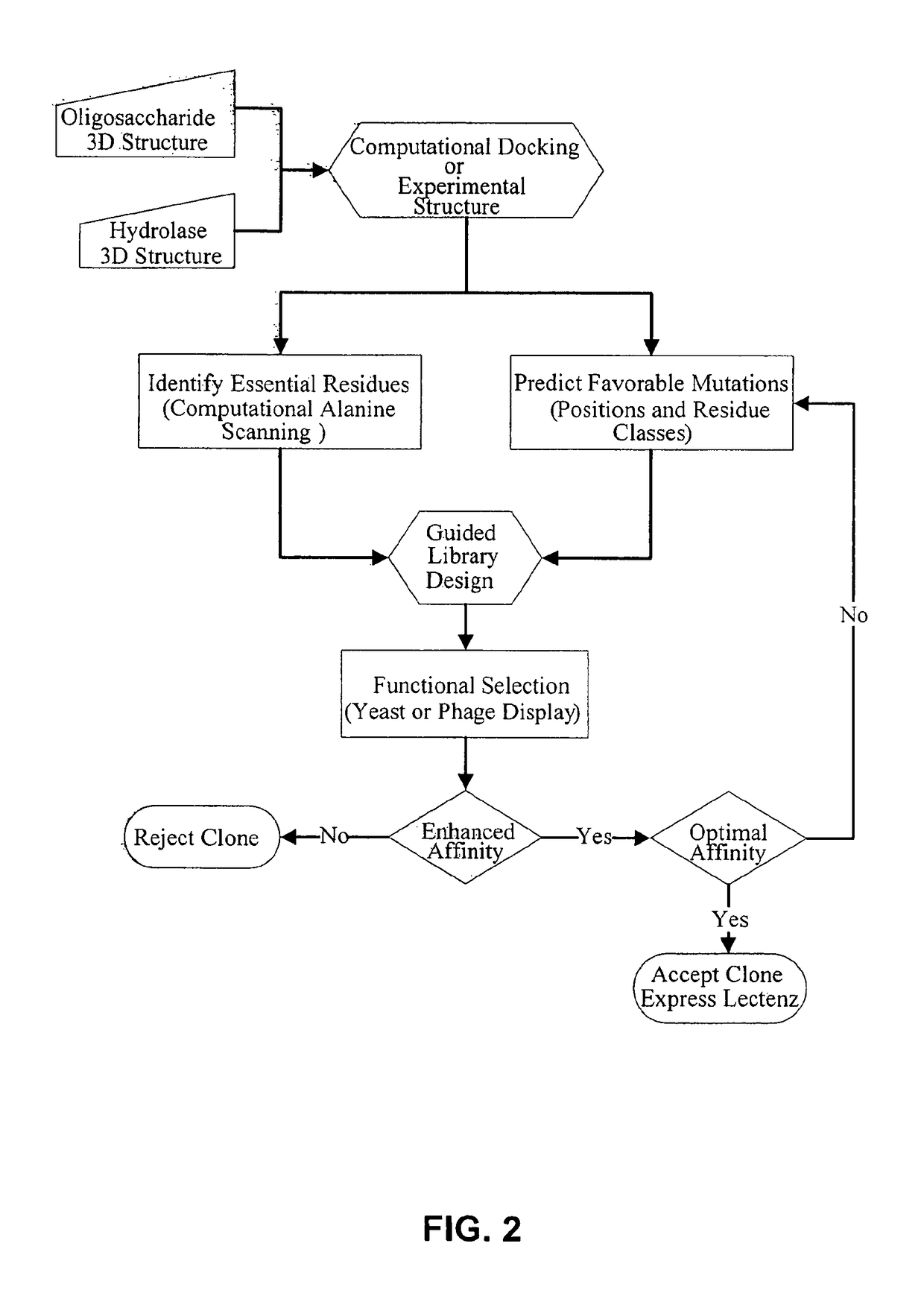
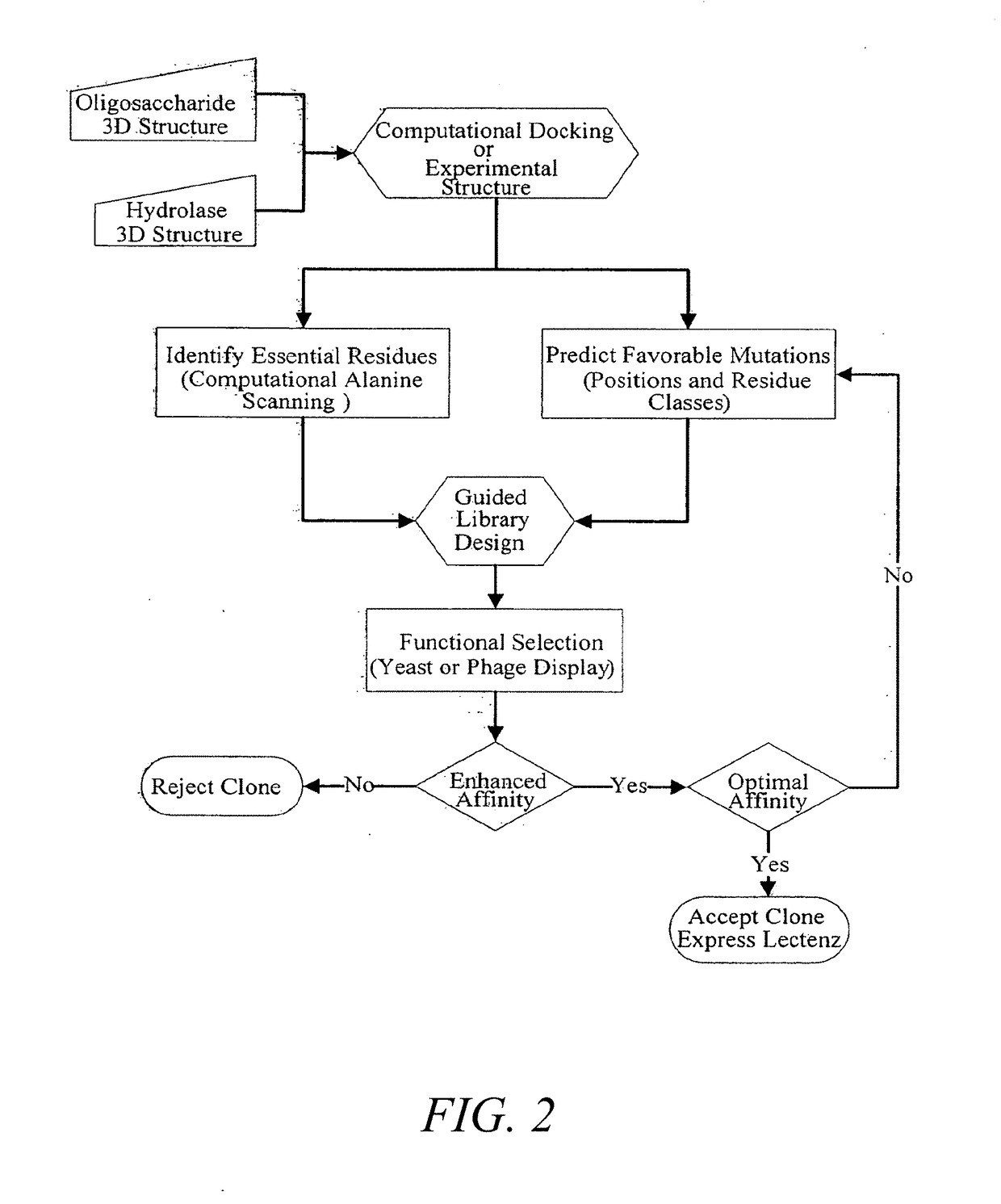
Glycan-Specific Analytical Tools
Provided are lectenz molecules, which are mutated carbohydrate processing enzyme enzymes that are catalytically inactive and that have had their substrate affinity increased by at least 1.2 fold. Further provided are methods for making and methods of using such lectenz. Additional mutated proteins following the lectenz approach are further provided.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
PC5 as a factor IX propeptide processing enzyme
ActiveUS20070259402A1Efficient processingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureFactor iiProcessing enzymes
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
Single molecule nucleic acid sequencing with molecular sensor complexes
InactiveUS20170159115A1High sensitivityAvoid insufficient lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNucleotideNucleic acid sequence
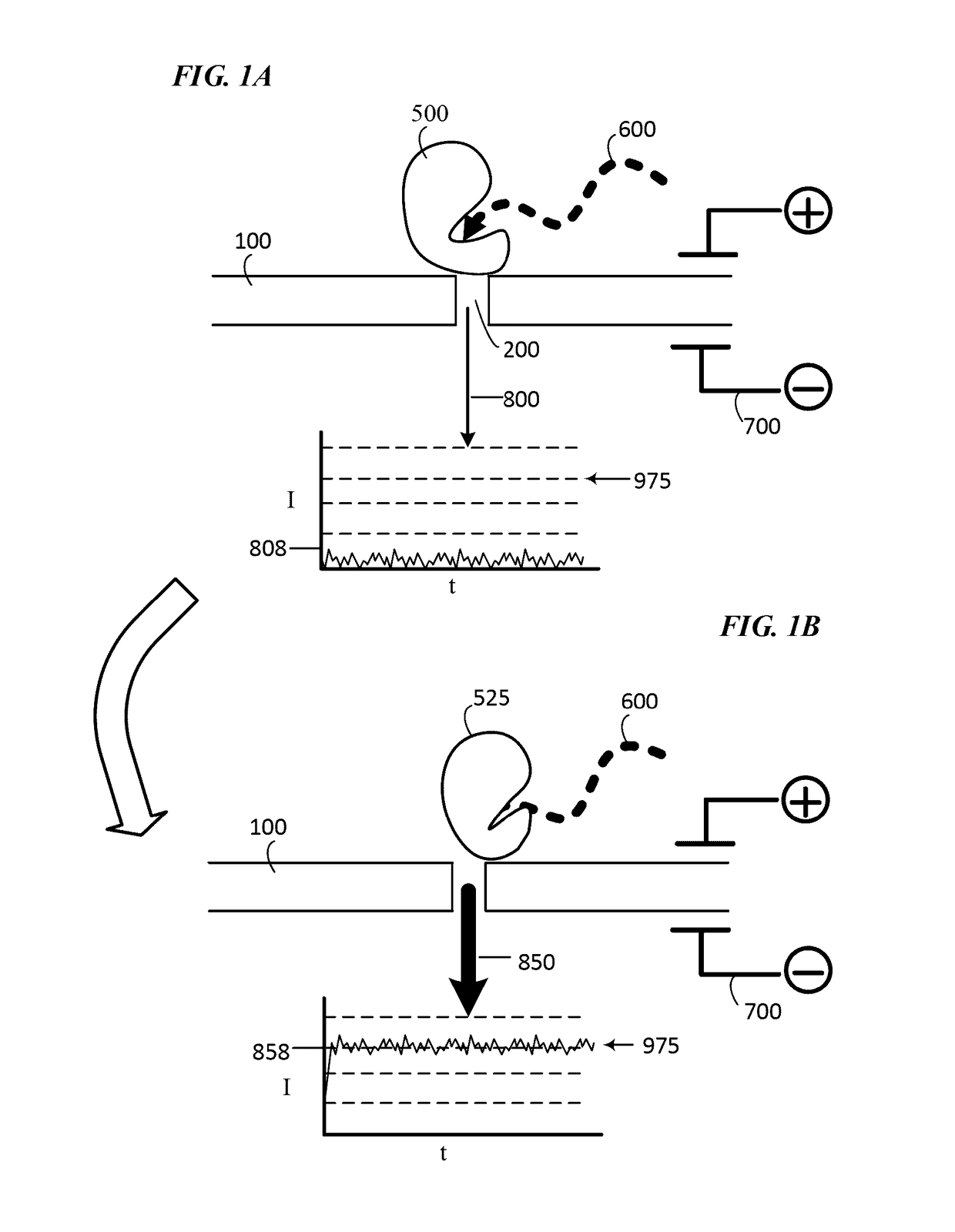
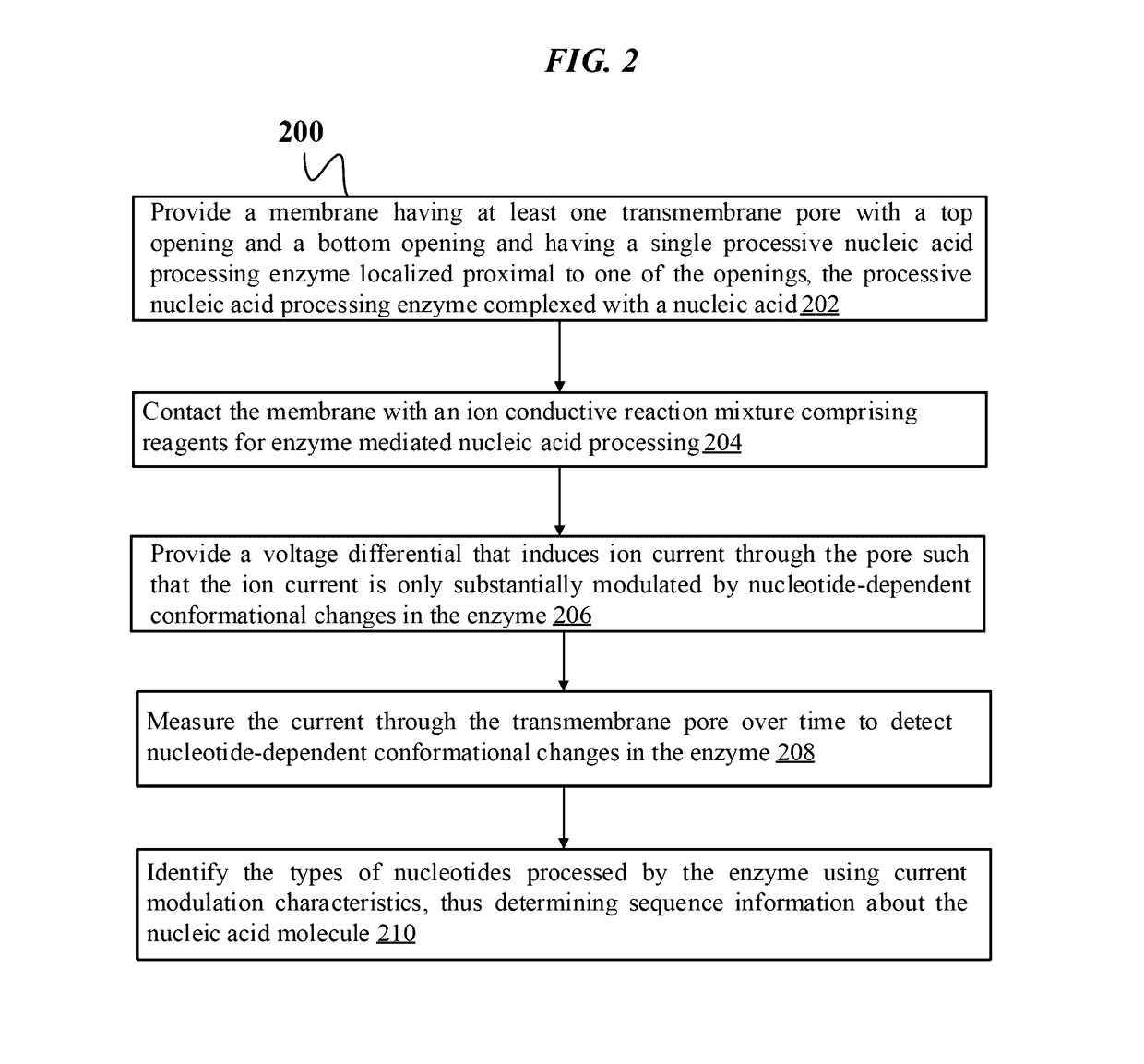
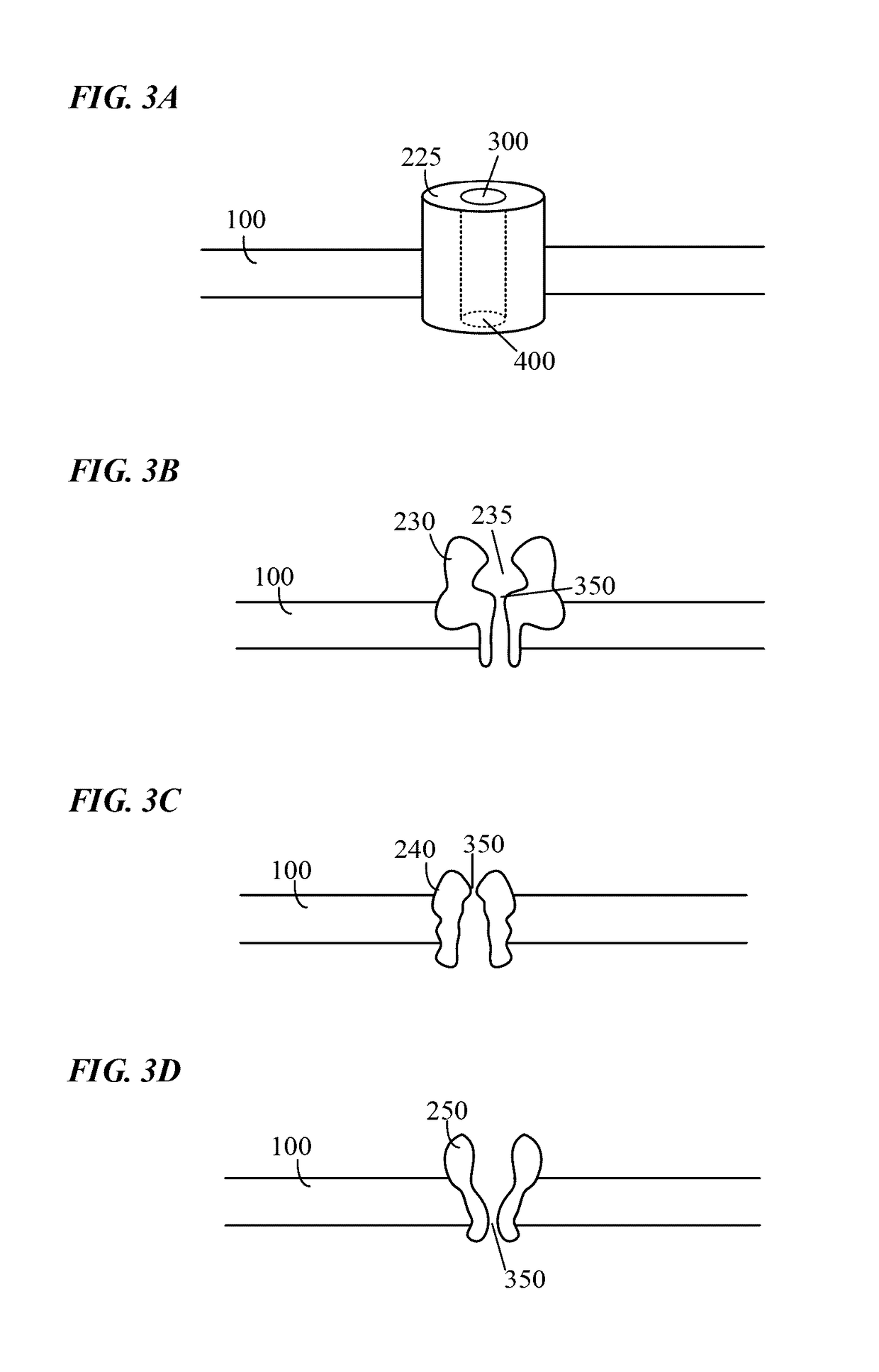
The present disclosure relates to methods and constructs for single molecule electronic sequencing of template nucleic acids. The constructs are molecular sensor complexes which comprise a processive nucleic acid processing enzyme localized to a nanopore. Conformational changes in the enzyme induced by single nucleic acid processing events are transduced into electric signals by the nanopore, which are used to identify individual nucleotides. The methods can include the steps of providing a membrane with the nanopore and the enzyme complexed with a template nucleic acid localized proximal to an opening in the pore, contacting the enzyme with an ion conductive reaction mixture including the reagents required for nucleic acid processing, providing a voltage drop across the pore that induces ion current through the pore that is modulated by conformational changes in the enzyme, measuring current through the pore over time to detect nucleotide-dependent conformational changes in the enzyme, and identifying the type of nucleotide processed by the enzyme using current modulation characteristics, thus determining sequencing information about the nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:STRATOS GENOMICS
Method, gene chip and detection reagent kit for detecting common cow pathogenic escherichia coli
InactiveCN101967509AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coli serotypeESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGEN
The invention provides a method, a gene chip and a detection reagent kit for detecting common cow pathogenic escherichia coli. The gene chip comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe comprises DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fragments selected from a glycosyl transferase gene and an oligose unit processing enzyme gene on a main escherichia coli serotype O-antigen gene cluster relative to cow septicemia and diarrhea. The gene chip and a designed primer are utilized for detecting and can be prepared into the reagent kit. The products and the method of the invention are utilized to reach the purpose for detecting the serotype of the common cow pathogenic escherichia coli and have the advantages of simple and convenient operation, high throughput, high accuracy, strong repeatability and important significance on the research and the diagnosis of epidemiology.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
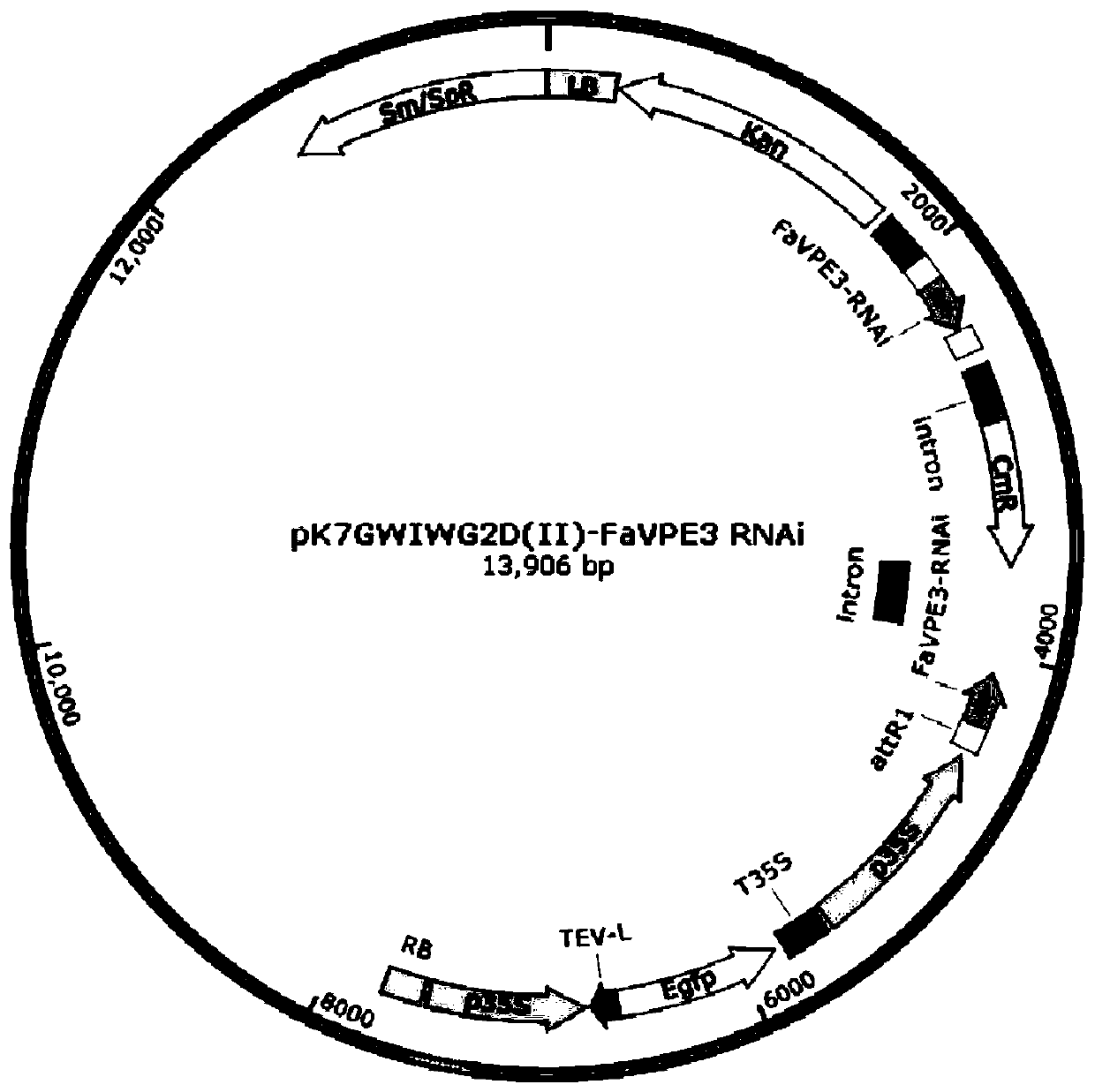
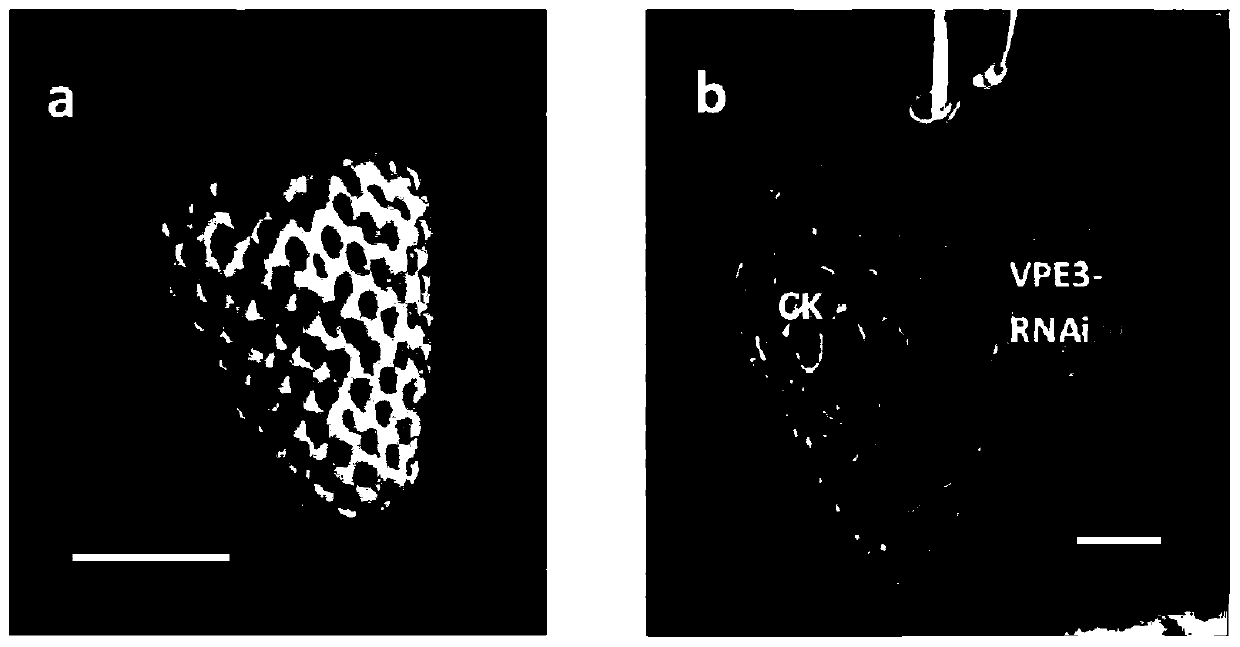
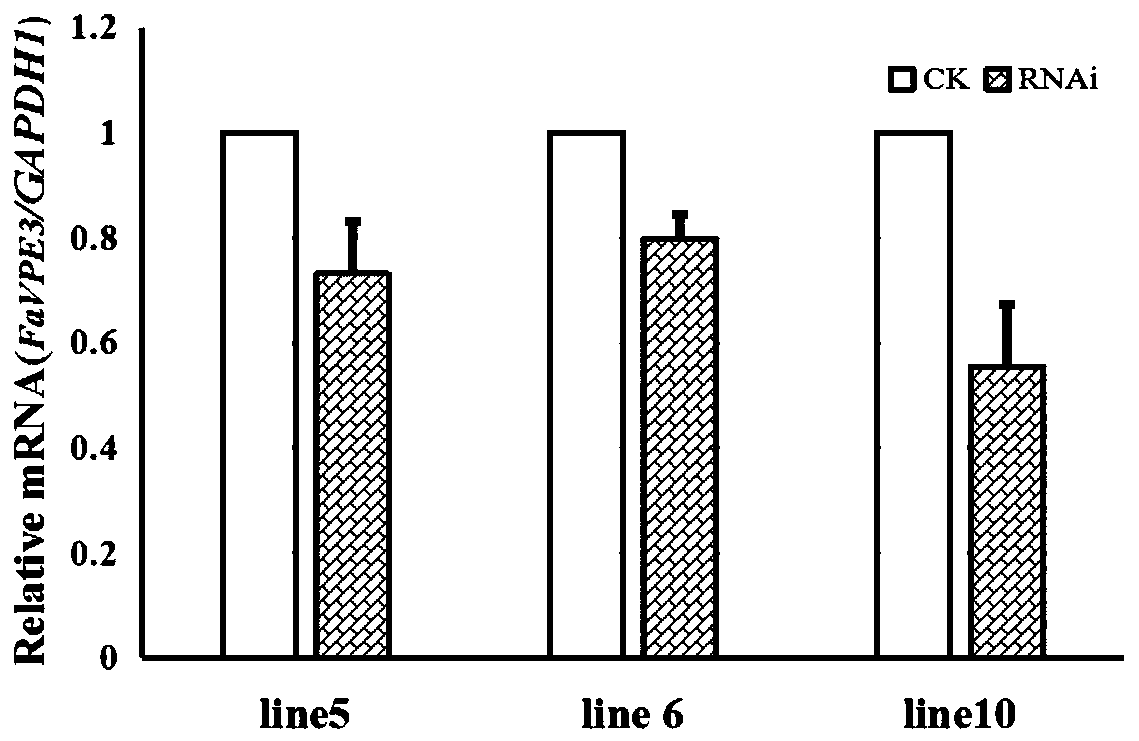
Fragaria ananassa vacuole processing enzyme coding gene FaVPE3 and application thereof
ActiveCN110511947ASucrose riseFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionFragariaMetabolite
The invention discloses a fragaria ananassa vacuole processing enzyme coding gene FaVPE3 and an application thereof. A nucleotide sequence and a protein sequence of the gene are provided, and furtheran RNA interference expression vector of the FaVPE3 gene is also constructed. An interference expression vector is transferred into agrobacterium tumefaciens, large fragaria ananassa green fruits areinfected by a microinjection method, and a transgenic fragaria ananassa strain of which the FaVPE3 gene expression is adjusted downwards is established. The gene has critical adjusting and controllingeffects on the accumulation of metabolism products of cane sugar, levulose, glucose, citric acid, malic acid and the like of fragaria ananassa fruits. A base is established for sugar acid quality adjusting and controlling mechanism of the fragaria ananassa fruits, genetic resources are provided for adjusting and controlling the sugar acid accumulation of the fragaria ananassa fruits through genetic engineering means, and important technique means are provided for development of functional SNP molecular markers and cultivation of superior fragaria ananassa.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Glycan-specific analytical tools
Provided are lectenz molecules, which are mutated carbohydrate processing enzymes that are catalytically inactive and that have had their substrate affinity increased by at least 1.2 fold. Further provided are methods for making and methods of using such lectenz. Additional mutated proteins following the lectenz approach are further provided.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
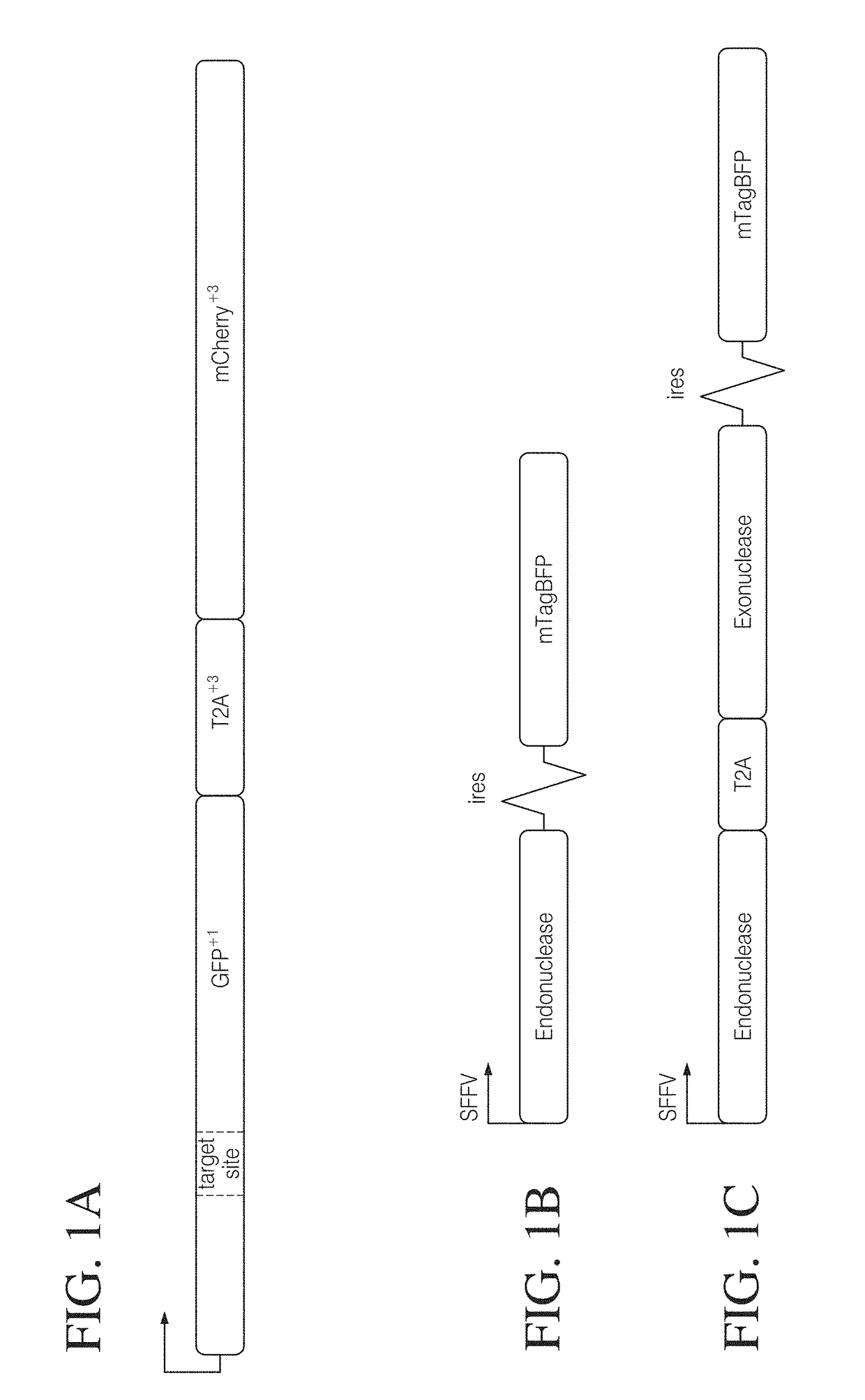
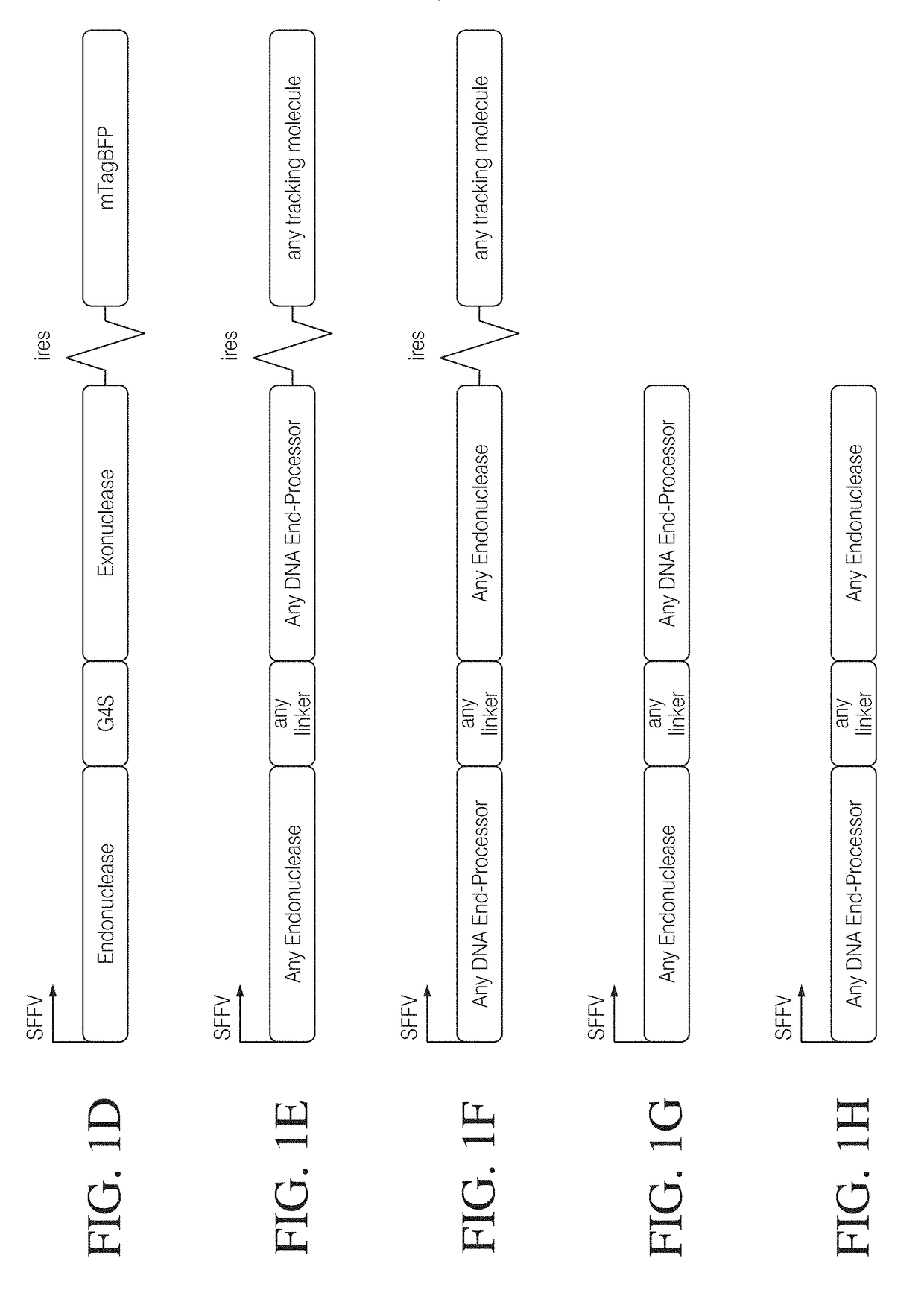
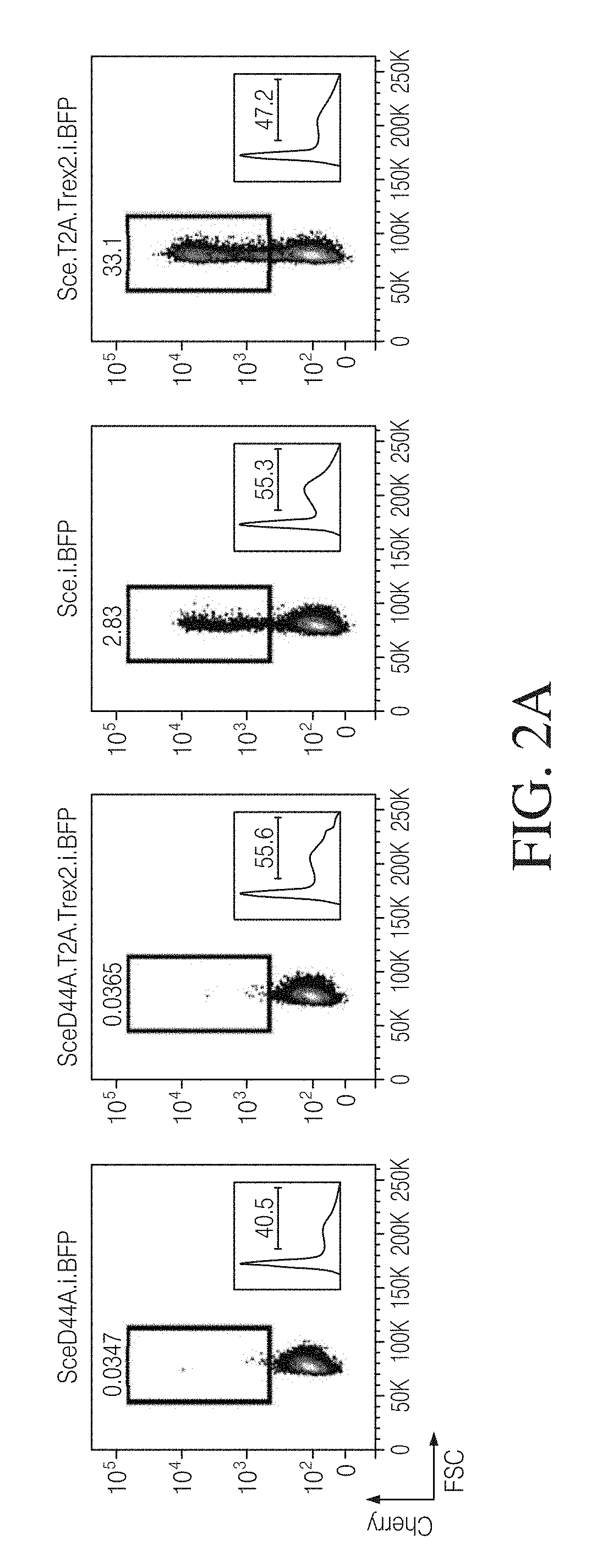
Coupling endonucleases with end-processing enzymes drives high efficiency gene disruption
ActiveUS20180320165A1Increase mutation frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesNucleotideProcessing enzymes
The present disclosure relates to the co-expression of an endonuclease with an end-processing enzyme for the purpose of enhanced processing of the polynucleotide ends generated by endonuclease cleavage.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL (DBA SEATTLE CHILDRENS RES INST)
Method for extracting crude fish oil from hairtail silvery fat
InactiveCN102888274ASimple processEasy to operateFatty-oils/fats productionHigh concentrationNeutral protease
The invention discloses a method for extracting crude fish oil from hairtail silvery fat, which comprises the following steps: 1) adding water to the hairtail silvery fat; adding neutral protease again; processing enzyme for 2.5-3.5 hours at 45-52 degrees centigrade; 2) processing inactivation treatment of the neutral protease to acquired enzyme solution, adding petroleum ether, processing extraction for 25-35 minutes in warm bath at 38-42 degrees centigrade; 3) rotating and evaporating the petroleum ether located on an upper layer obtained in the step 2) so as to ventilate the petroleum ether, and acquiring the crude fish oil containing impurity; and 4) centrifuging the crude fish oil containing the impurity, separating acquired supernatant, wherein the supernatant is the crude fish oil. By dint of the invention, the crush fish oil with relatively high concentration can be acquired.
Owner:NINGBO LANYANG AQUATIC FOOD
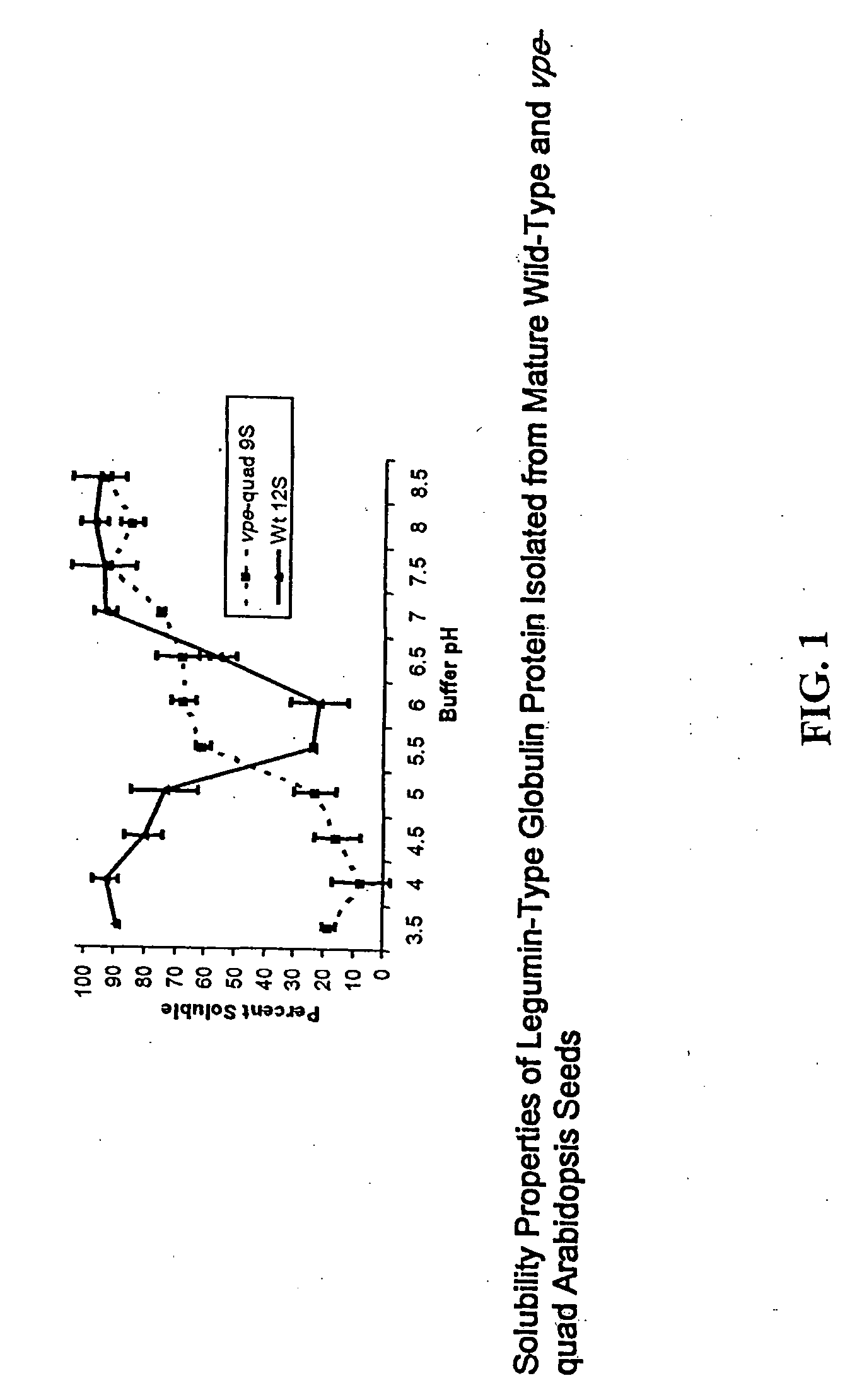
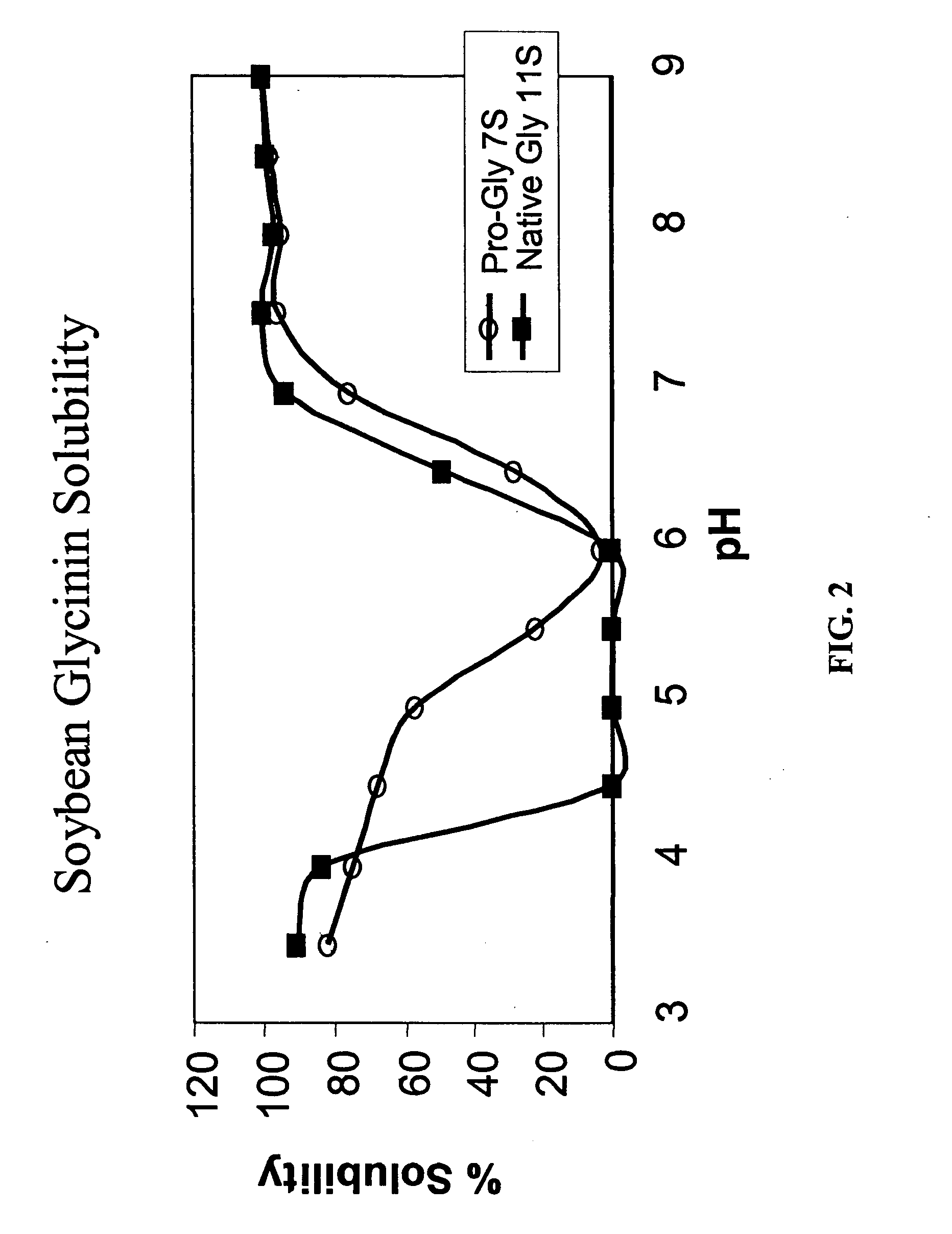
Methods and compositions for altering the functional properties of seed storage proteins in soybean
InactiveUS20050155102A1Altering functional propertyReducing and eliminating activityHydrolasesOther foreign material introduction processesVacuolar processing enzymeLowering plants
The present invention provides methods and compositions useful for altering the functional properties of soybean seed storage proteins. It is the novel finding of the present invention that the functional properties of seed storage proteins can be altered by reducing the expression of one or more vacuolar processing enzymes in plant seed. Accordingly, in one embodiment, the invention provides a method for altering the functional properties of one or more soybean seed storage proteins. The method comprises transforming a soybean plant cell with at least one expression cassette capable of expressing a polynucleotide that reduces the activity of a vacuolar processing enzyme in the seed of said soybean plant, regenerating a transformed plant from the transformed plant cell, and collecting seed from the regenerated transformed plant. Plants that are genetically modified or mutagenized to alter the functional properties of one or more seed storage proteins, and the transgenic seed of such plants are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
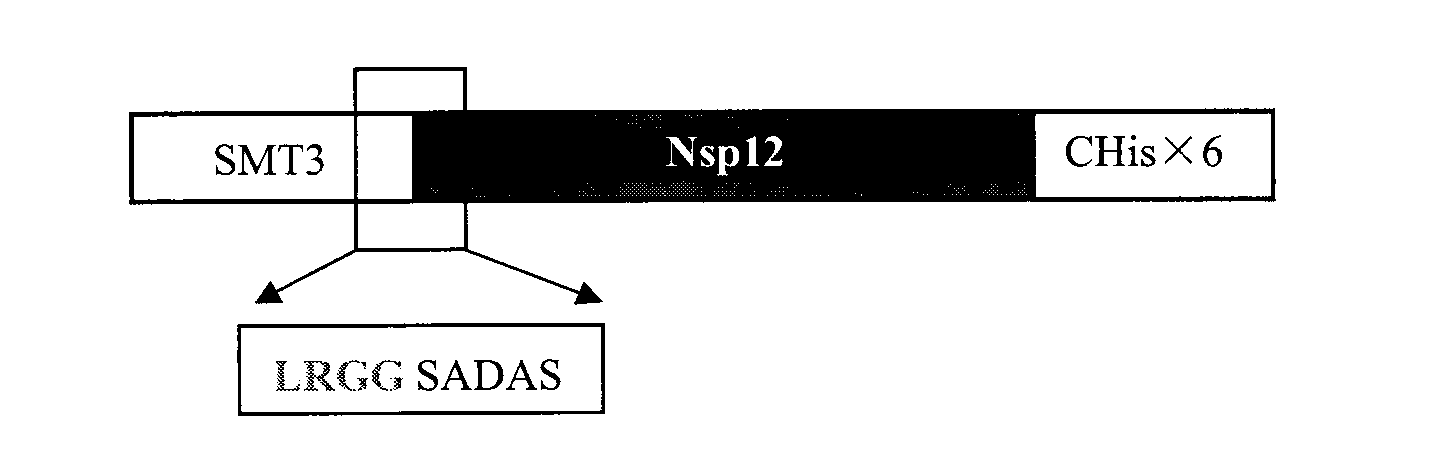
Exogenous recombinant expression and purification method for crystallizable mature SARS coronavirus non-structural protein 12 (sars-nsp12)
InactiveCN103184228AEnsure physical and chemical stabilityStable physicochemical stabilityBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPurification methods
According to the invention, a small ubiquitin-like modifier protein gene and a nsp12 gene are connected into a pET-26b vector to realize formation of a pET-26b-S-nsp12-CHis6 expression plasmid, a ubiquitin-like protein processing enzyme is linked into a pET11a vector to realize formation of a pET-11a-Ulp expression plasmid, and the aforementioned pET-26b-S-nsp12-CHis6 and the pET11a-Ulp expression plasmid are transformed into an escherichia coli BL21(DE3)pLysS to realize expression and purification of wild type protein of the nsp12. The obtained wild type protein of the nsp12 has normal RNA polymerase biological activity that should own by the wild-type protein, and can be used for crystallization experiments after necessary purification treatment, and can form a protein crystal. A method for exogenous recombinant expression and purification of crystallizable mature SARS coronavirus non-structural protein 12 (sars-nsp12) is provided by the invention.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
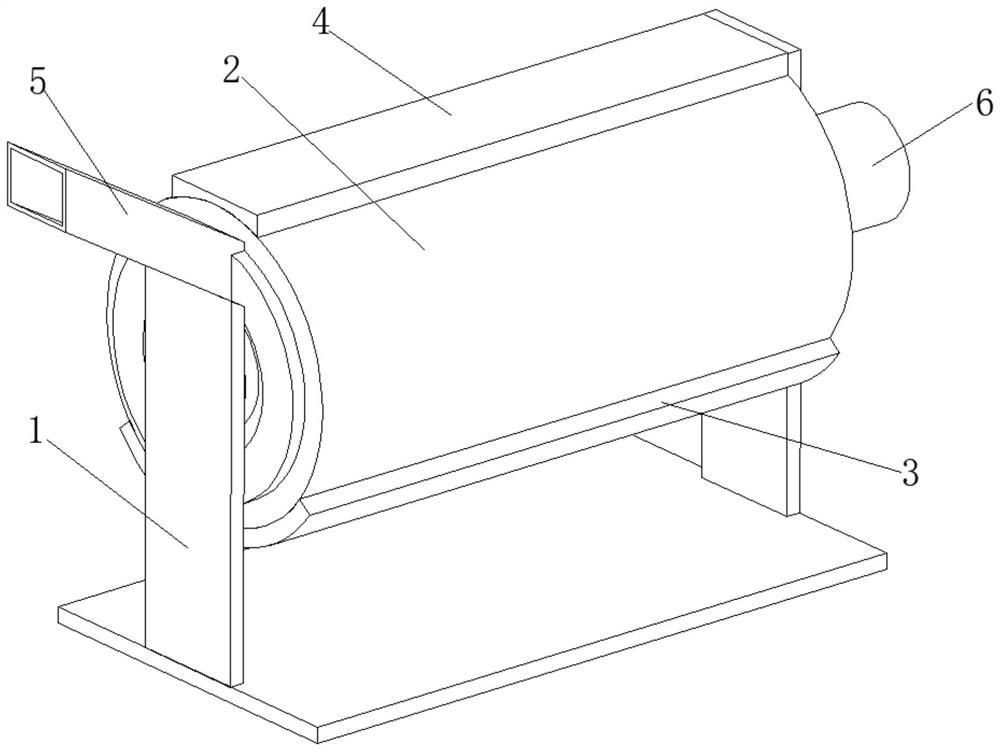
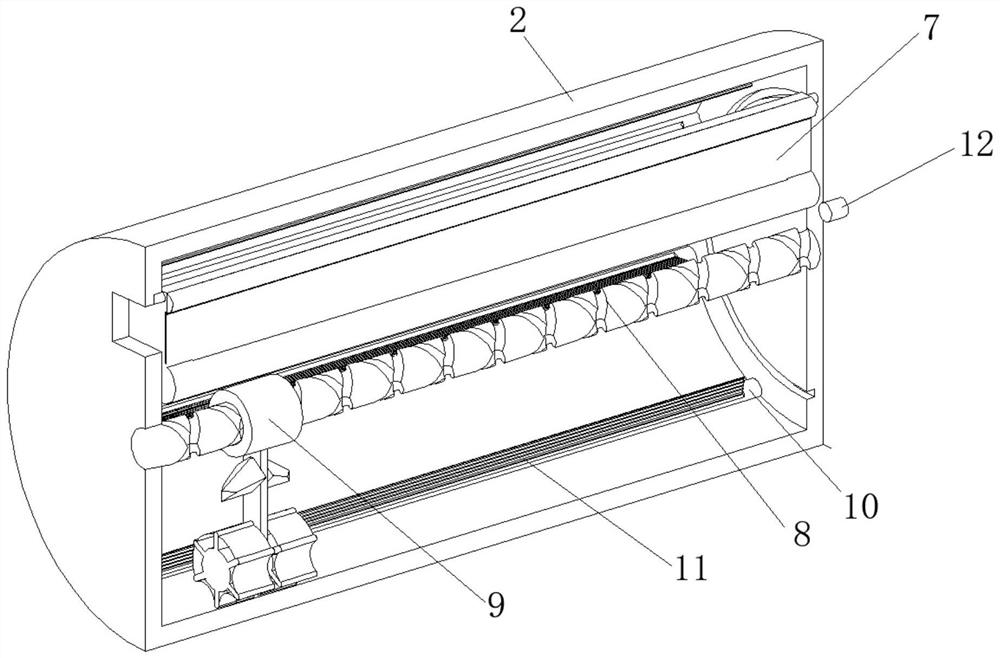
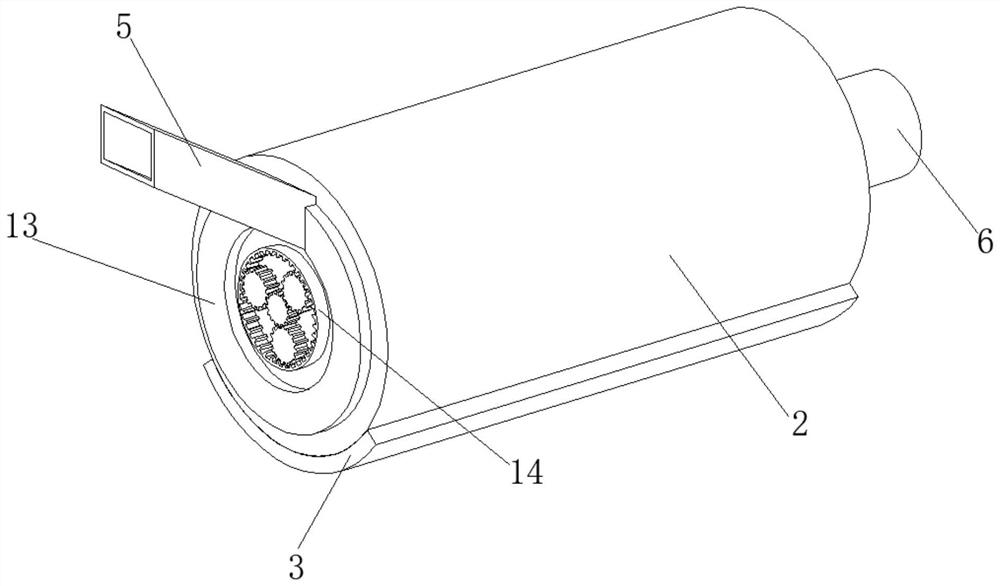
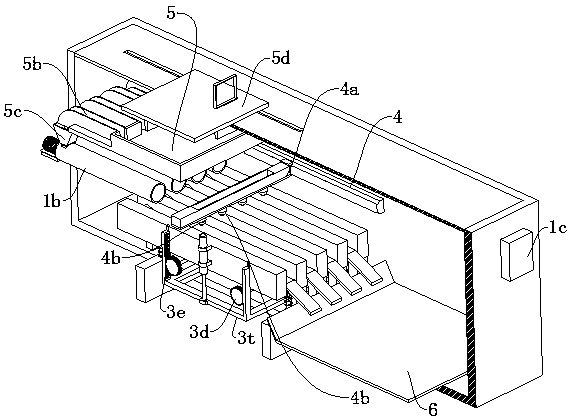
Tea leaf processing enzyme-deactivating device and processing method
InactiveCN113875834ARealize stir fryingImprove work efficiencyPre-extraction tea treatmentEngineeringProcessing enzymes
The invention relates to the technical field of tea leaf enzyme deactivating, and discloses a tea leaf processing enzyme-deactivating device. The tea leaf processing enzyme-deactivating device comprises a supporting plate; a roller is rotatably connected to the surface of the supporting plate; the lower surface of the roller is in contact with the upper surface of a heating plate; the upper surface of the roller is in contact with the lower surface of a magnetic plate; a feeding frame is fixedly connected to the top of the supporting plate; a motor is fixedly connected to the rear portion of the supporting plate; a collecting mechanism is arranged on the inner wall of the roller; a screw rod is rotatably connected to the inner wall of the roller; a pushing mechanism is arranged on the surface of the screw rod; a fixing block is fixedly connected to the inner wall of the roller; a pushing plate is rotatably connected to the inner wall of the fixing block through a torsional spring; and the surface of the feeding frame is fixedly connected with a circular ring. According to the tea leaf processing enzyme-deactivating device disclosed by the invention, the roller is driven by the motor to rotate, so that tea leaves can be automatically stir-fried, manual operation of workers is not needed, the working efficiency is improved, stir-frying enzyme deactivating of the tea leaves is realized, and the enzyme deactivating effect is improved.
Owner:卢名浩
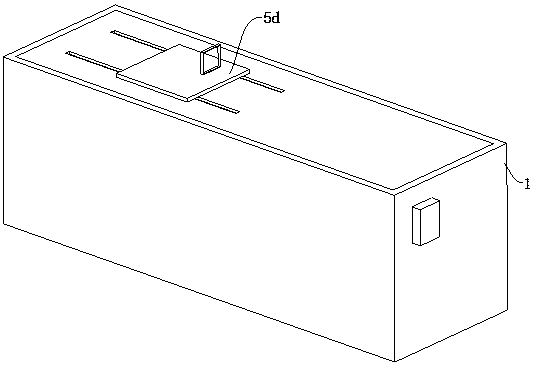
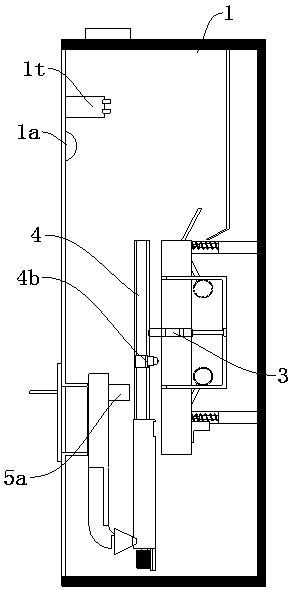
Rice processing enzyme liquid sprayer
The invention relates to the field of brown rice processing, in particular to a rice processing enzyme liquid sprayer which comprises a constant-temperature bin, a temperature detector, a jumping-typeconveying mechanism and a spraying mechanism, wherein three small-sized spiral feeders which are sequentially distributed at intervals in a straight line are arranged at the upper part of the interior of the constant-temperature bin; the jumping-type passing mechanism comprises a jumping power device and three conveying plates; each conveying plate is arranged below the discharging end of the corresponding small-sized spiral feeder; the jumping power device is arranged below all the conveying plates and in transmission connection with the bottoms of all the conveying plates; the temperature detector is mounted in the constant-temperature bin and used for detecting the internal temperature value of the constant-temperature bin in real time; a heater is arranged in the constant-temperaturebin; a controller is arranged outside the constant-temperature bin; the temperature detector and the controller are electrically connected; and the spraying mechanism is arranged above all the conveying plates. By the adoption of the rice processing enzyme liquid sprayer, an enzyme liquid can be automatically sprayed onto a large batch of brown rice, and the sufficient spraying onto each grain ofthe brown rice can be guaranteed.
Owner:黟县国有资产运营有限公司
Method for processing velvet antler enzyme
InactiveCN105105130APromote absorptionGood health effectFood ingredient functionsFood preparationLycium barbarum fruitBud
The invention discloses a method for processing velvet antler enzyme, which relates to a method for processing enzymes, and substantially solves the problem that existing enzymes lack animal enzymes and the like. The velvet antler enzymes comprise raw materials with parts by weight: antler powder 5 parts, Chinese wolfberry buds 10 parts, pineapples 10 parts, Chinese quinces 10 parts, mulberries 5 parts, carrots 5 parts, banana 5 parts, mangos 5 parts, rock candies 5 parts and grapes 40 parts. The method for processing the velvet antler enzyme comprises steps: the Chinese wolfberry buds are paved on a bottle bottom, carrot cubes and Chinese quince cubes are covered, the antler powder is scattered, and the banana, mango mixture and pineapple juice are poured to seal and stir, and are statically placed to ferment, enzyme stock solution which is centrifuged in a centrifugal machine is converted into a novel container, and residues are reserved. The rock candies is ground into candy powder, the grapes and the candy powder are commonly placed into enzyme residues after the grapes are broken, are added with saccharomycetes to ferment, seal and filter, and then residues are discharged. The enzyme stock solution which is fermented in a first segment and grape enzymes which are brewed in a second segment are mixed, and are filtered after maturing. The method for processing the velvet antler enzyme has the advantages that the enzymes contain the animal enzymes.
Owner:辽阳千山呈龙科技有限公司
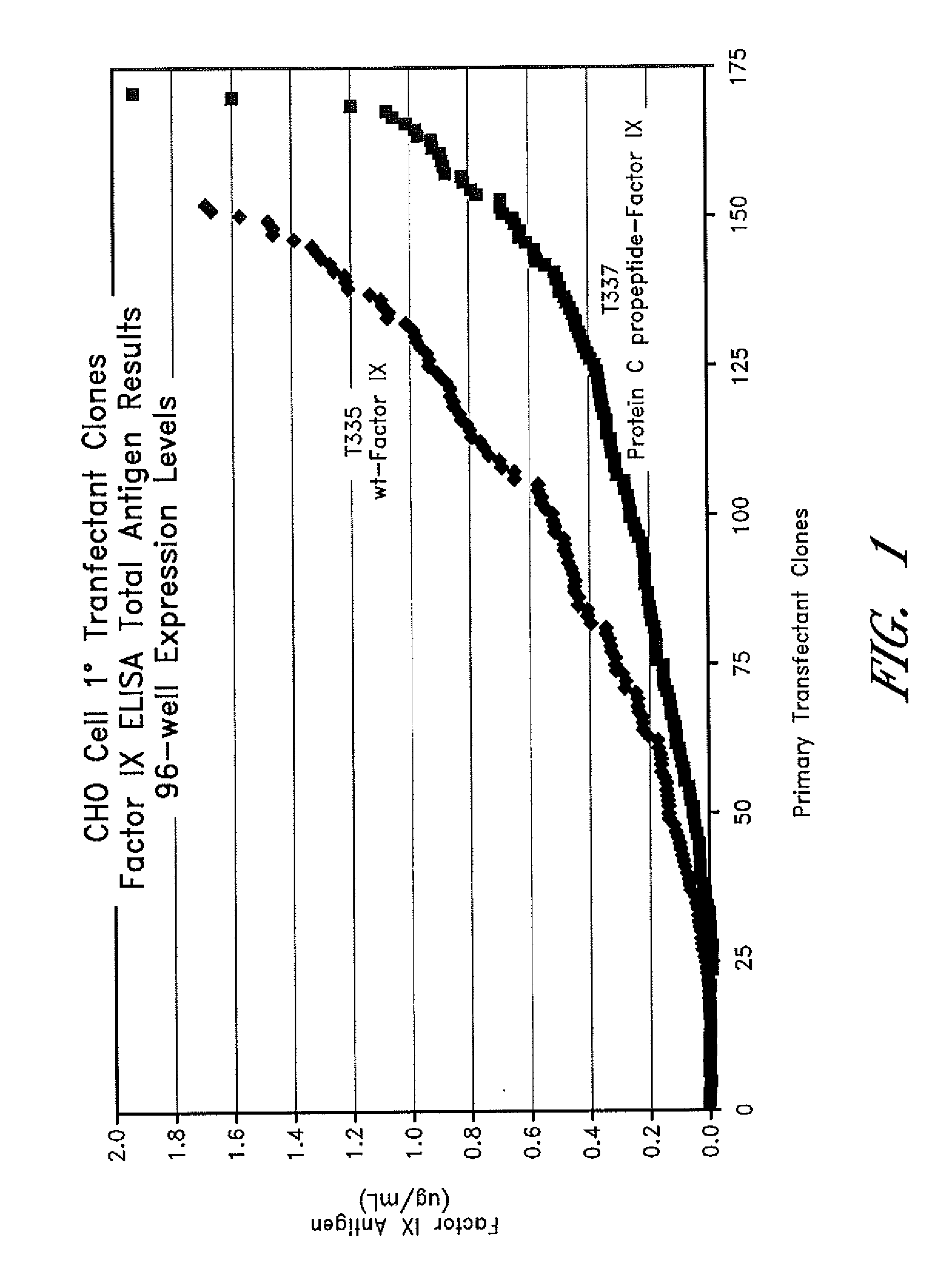
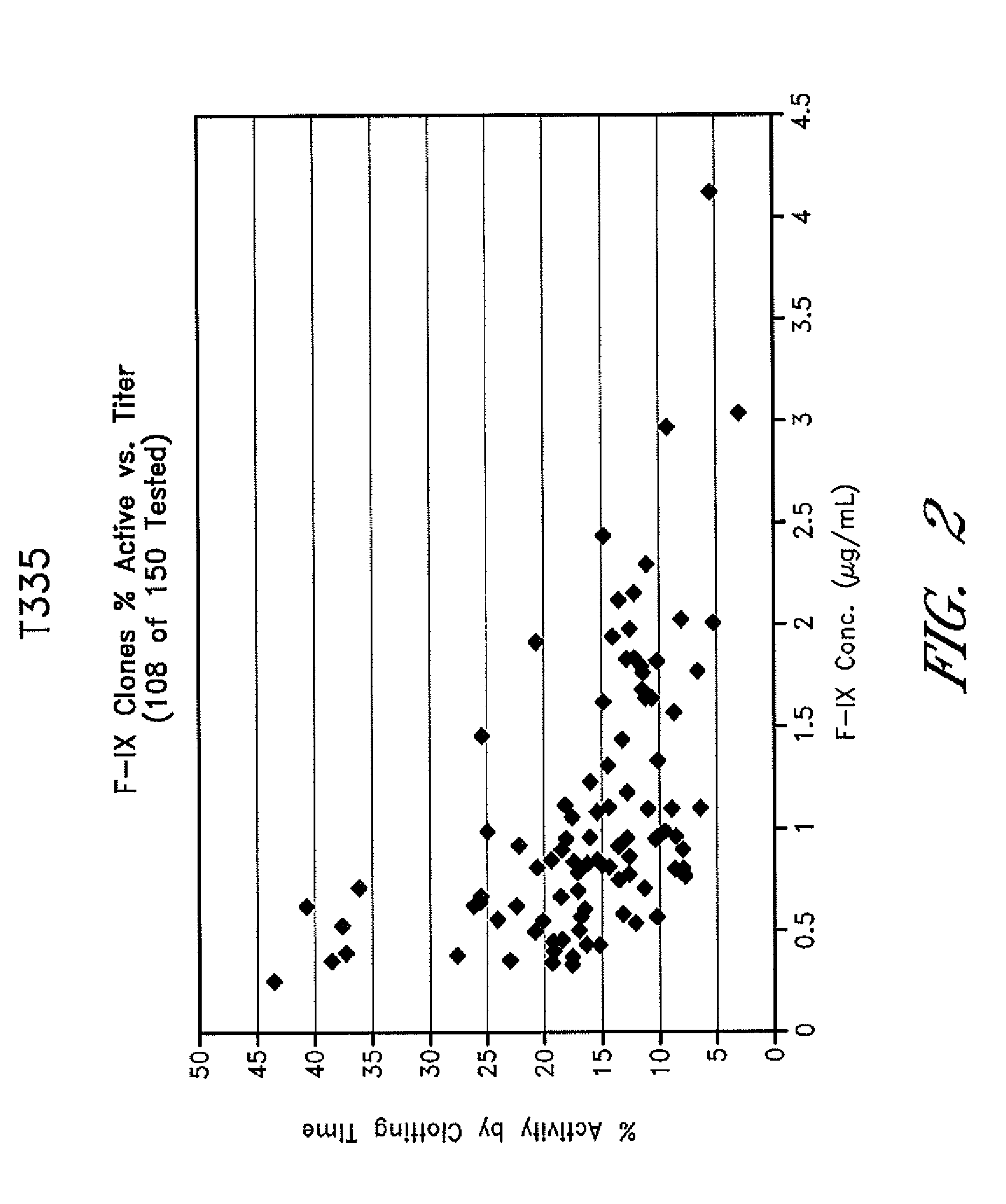
Method of producing recombinant vitamin k dependent proteins
Methods for producing cell lines with high levels of biologically active recombinant vitamin K dependent proteins are described. The transfected cell lines do not include heterologous genes for processing enzymes and are not subject to selection pressure such as methotrexate resistance. Cell lines producing Factor VII / VIIa and Factor IX are described. These cell lines can be used for isolation of Factor VII / VIIa and / or Factor IX for treatment of Hemophilia.
Owner:CNJ HLDG
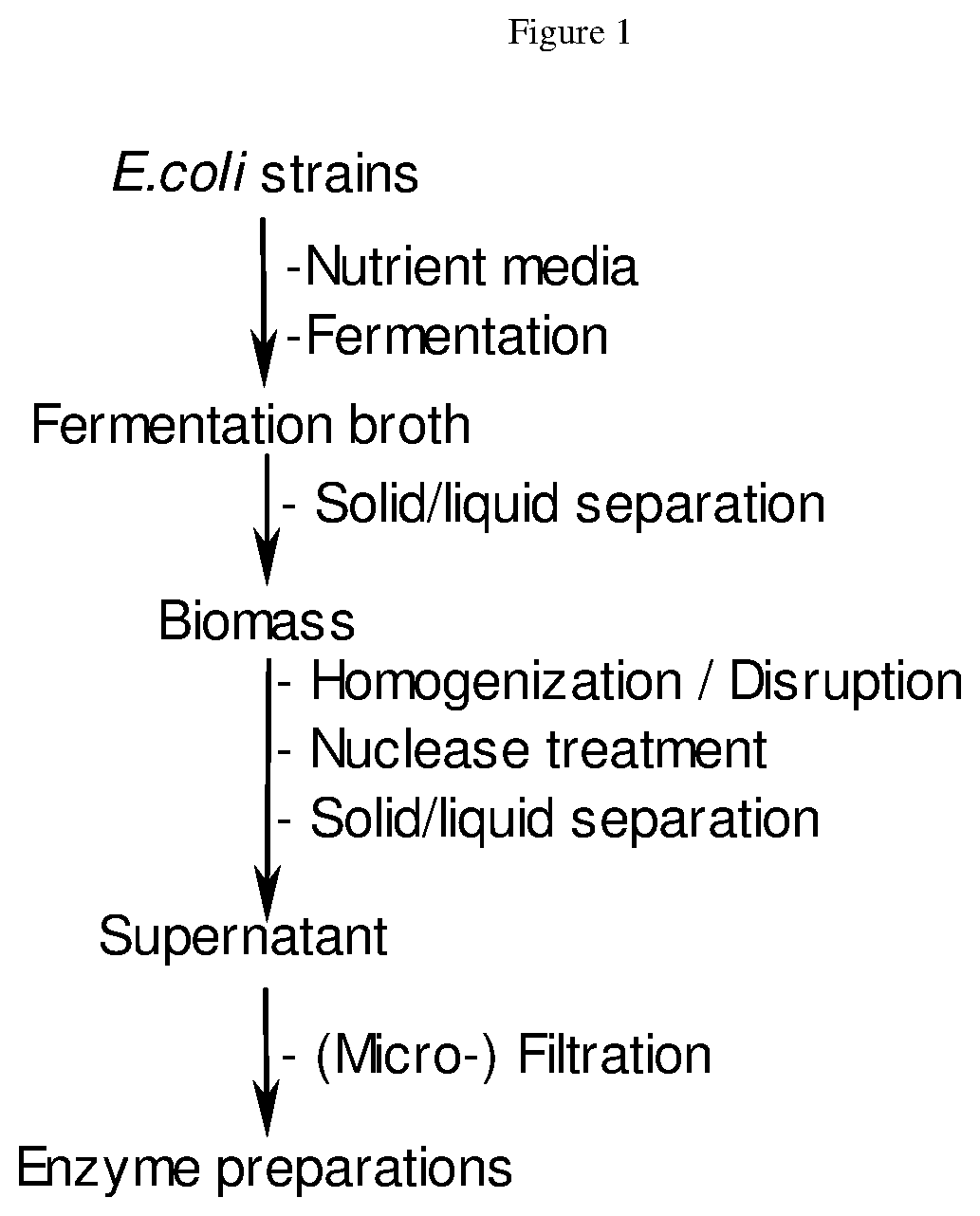
Enzyme products
ActiveUS20200140838A1Reduction is not desirableProcedure be improvedHydrolasesBiofuelsBiotechnologyProcessing enzymes
The invention relates to a process for the manufacturing and purification of recombinant enzyme products, in particular of food enzyme products and the use thereof. The invention particularly relates to a process for the processing of enzyme products from a microbial fermentation broth by methods of separation, enzymatic treatment and filtration procedures.
Owner:C LECTA GMBH
AFC1 and RCE1: isoprenylated CAAX processing enzymes
Two genes which encode polypeptides that mediate post-prenylation processing steps in CAAX polypeptides such as Ras are provided. The two genes (AFC1 and RCE1) encode polypeptides that mediate the removal of the AAX tripeptide from the CAAX polypeptide following prenylation. The genes and encoded polypeptides provide assays for testing compounds for an effect on post-prenylation processing steps. A heat shock assay for assessing Ras activity is also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Glycan-specific analytical tools
InactiveUS20180259508A1Not limitedBiological material analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansCrystallographyCarbohydrate structure
Provided are lectenz molecules, which are mutated carbohydrate processing enzyme enzymes that are catalytically inactive and that have had their substrate affinity increased by at least 1.2 fold. Further provided are methods for making and methods of using such lectenz. Further provided are compositions and methods directed to the multiplexed analysis of carbohydrates and carbohydrate containing compounds. The compositions and methods utilize suspension array technology (SAT) and an array of different carbohydrate binding molecules, each carbohydrate binding molecules with a known carbohydrate binding specificity, to obtain a glycoprofile of the carbohydrate structure(s) in a sample. Each carbohydrate binding molecule of a given specificity is linked to the external surface of a population of individually addressable particles.
Owner:GLYCOSENSORS & DIAGNOSTICS +1
A molecular marker method for predicting and identifying chicken belly fat mass and its application
ActiveCN108841932BSpeed up the breeding processEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme GeneProtein precursor
The invention discloses a molecular marker method and application for predicting and identifying chicken abdominal fat mass, belonging to the technical field of animal molecular genetics. The method provided by the present invention is to design primers according to the SNP site c.1880C>T upstream and downstream 190bp sequence of the egg white precursor processing enzyme 1 gene, and then carry out PCR amplification of chicken genomic DNA according to the obtained primers, and then use restriction endonuclease Enzyme digests the amplified product, then electrophoresis separates the digested product, and finally uses PCR‑RFLP technology to analyze gene polymorphisms to obtain chicken abdominal fat marker genotypes. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, low cost and high precision, can carry out automatic detection, is an effective molecular marker breeding method, and can greatly speed up the breeding process of chickens.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com