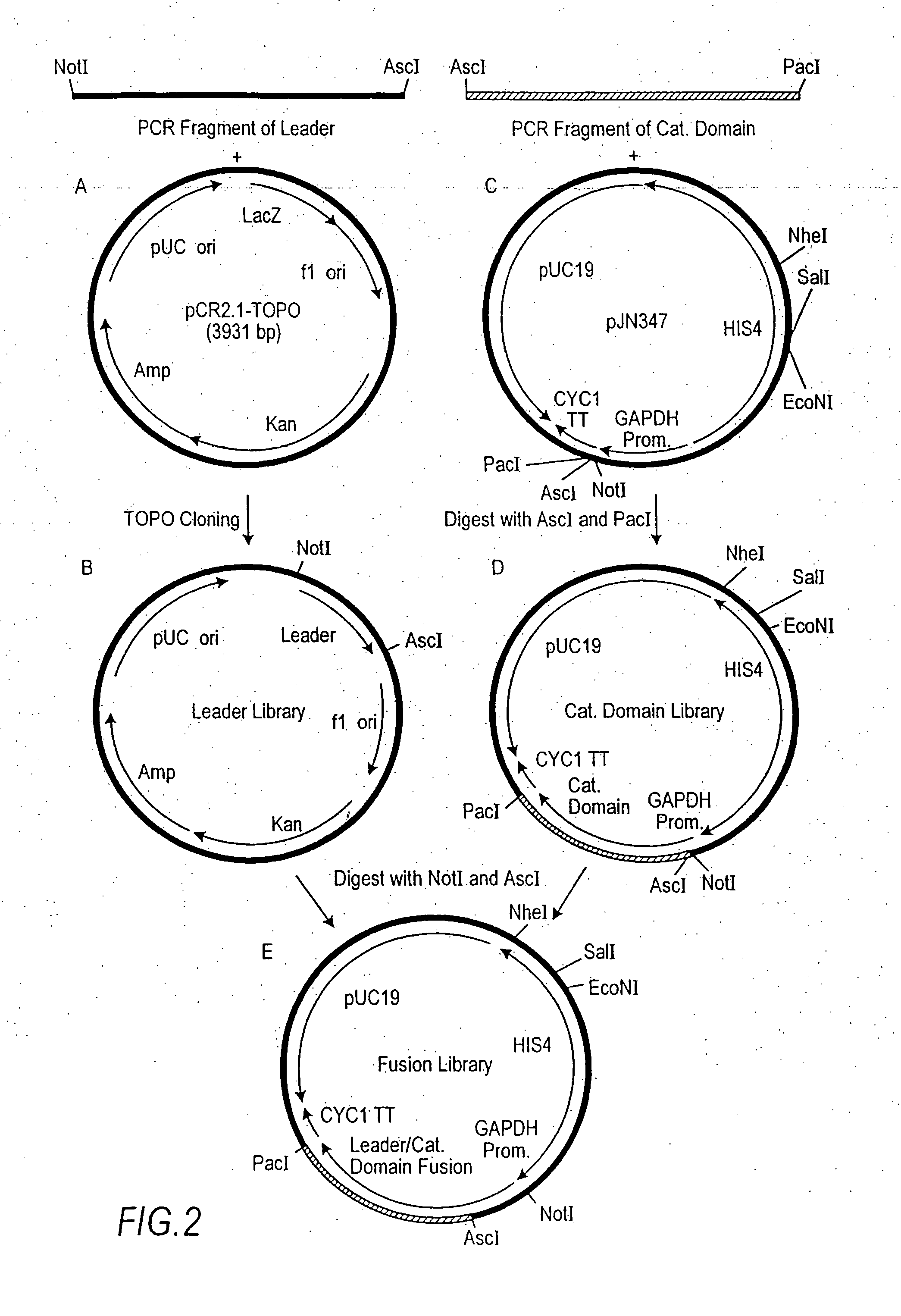
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1016 results about "Heterologous expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
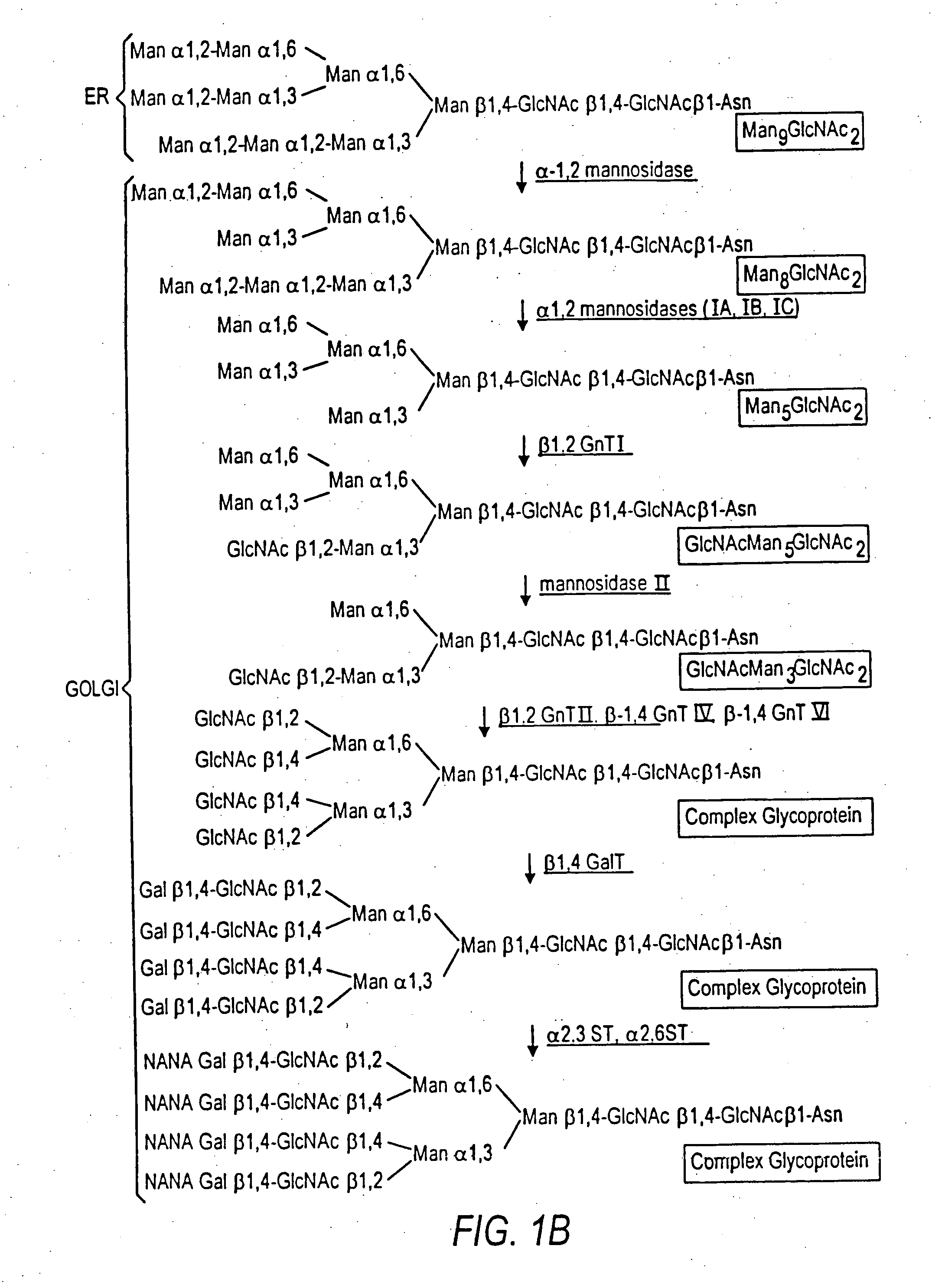
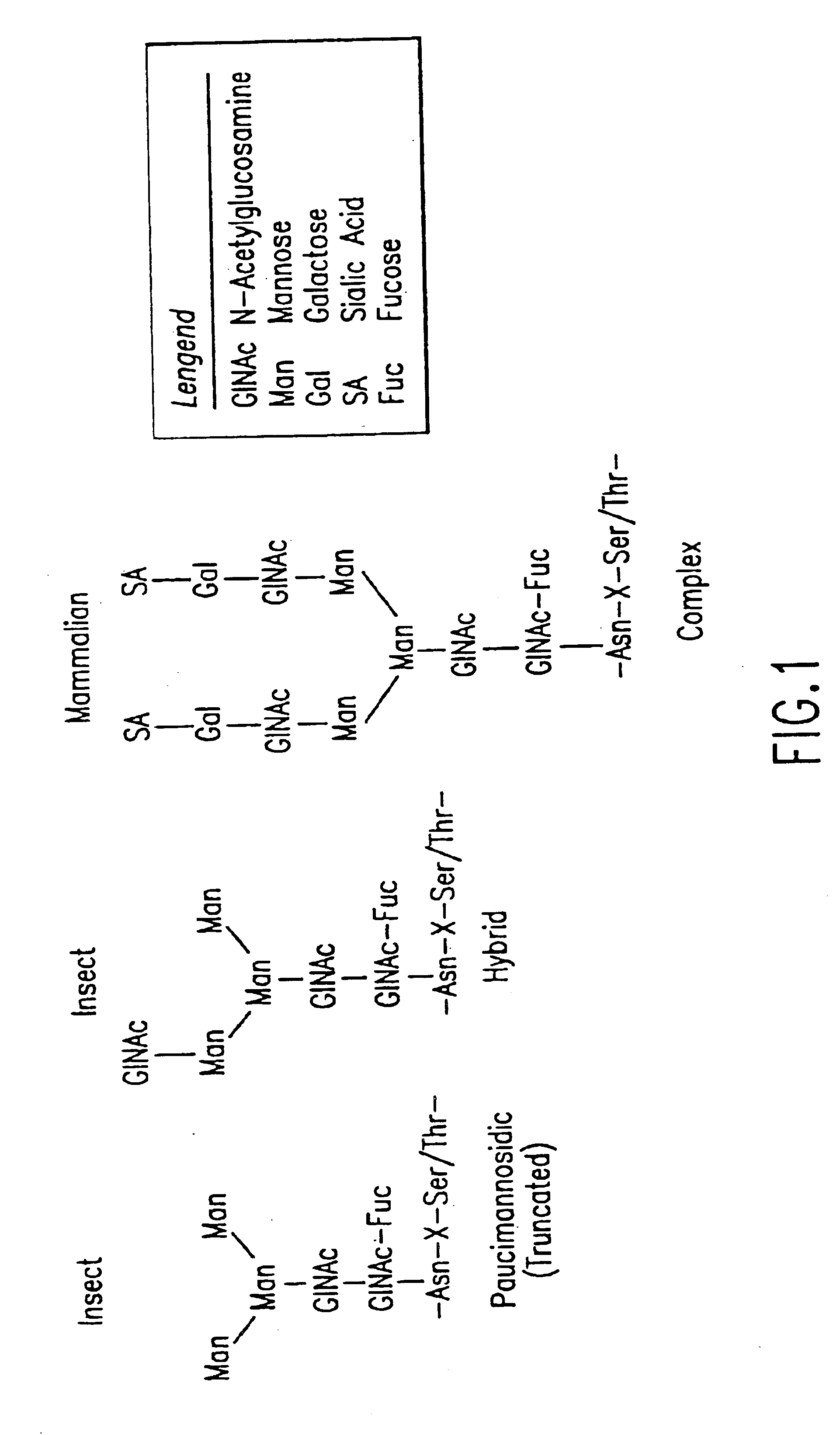
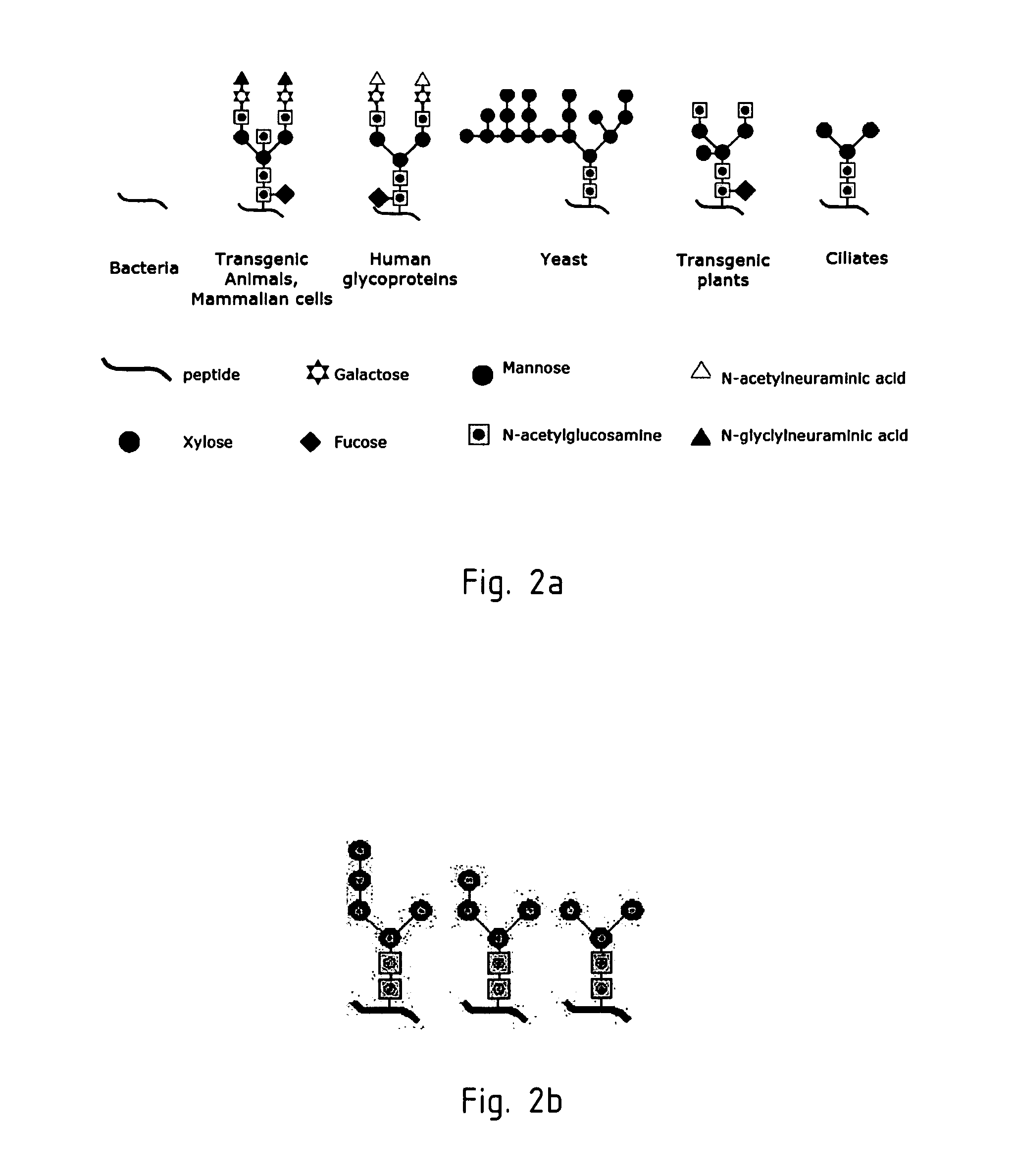
Heterologous expression refers to the expression of a gene or part of a gene in a host organism, which does not naturally have this gene or gene fragment. Insertion of the gene in the heterologous host is performed by recombinant DNA technology. After being inserted in the host, the gene may be integrated into the host DNA, causing permanent expression, or not integrated, causing transient expression. Heterologous expression can be done in many type of host organisms. The host organism can be a bacterium, yeast, mammalian cell, or plant cell. This host is called the "expression system". Homologous expression, on the other hand, refers to the overexpression of a gene in a system from where it originates.
Expression of heterologous proteins
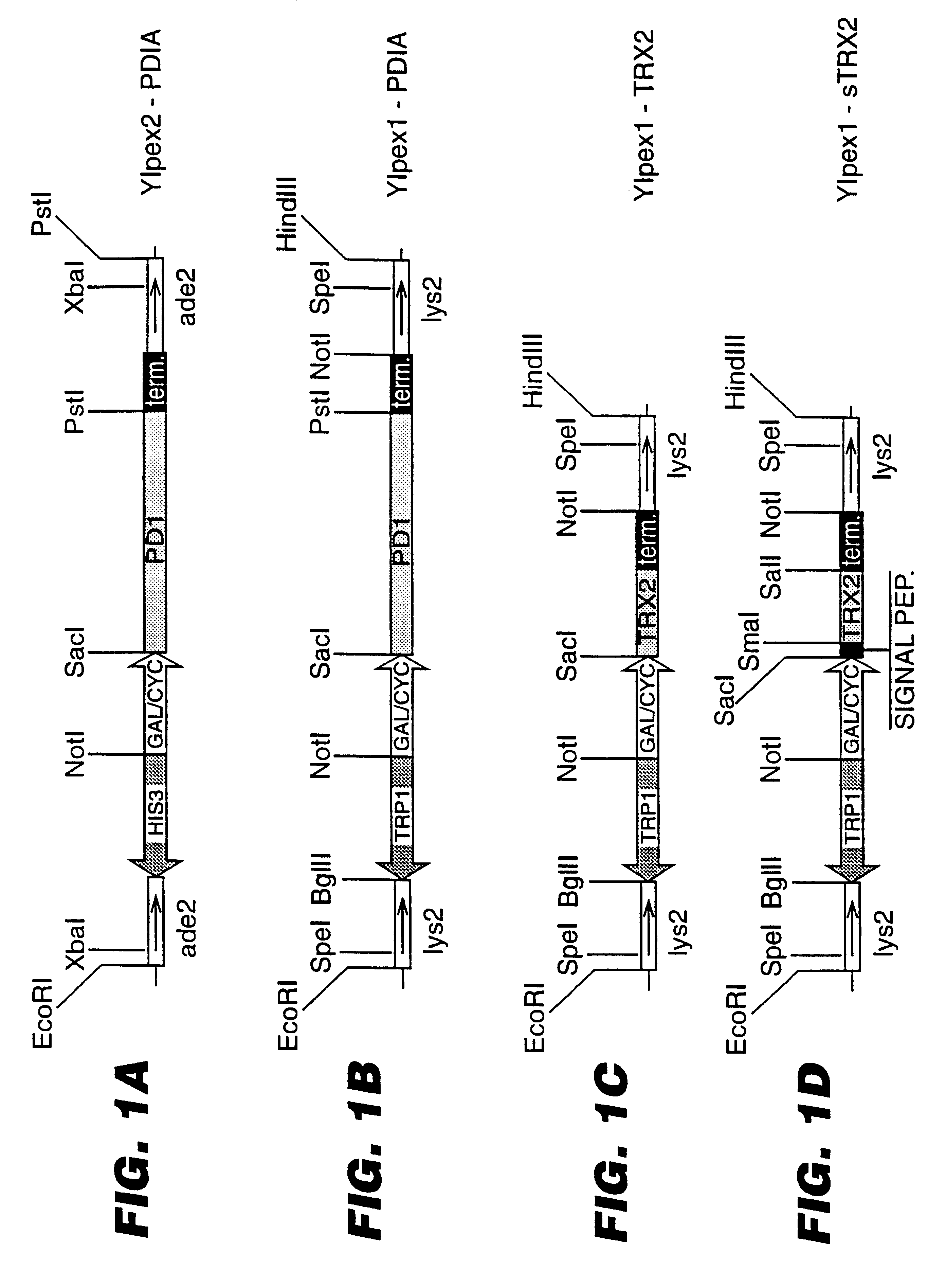
An expression system which provides heterologous proteins expressed by a non-native host organism but which have native-protein-like biological activity and / or structure. Disclosed are vectors, expression hosts and methods for expressing the heterologous proteins. The expression system involves co-expression of protein factor(s) which is / are capable of catalyzing disulphide bond formation and desired heterologous protein(s). The expression system is presented using yeast cells as the preferred host, protein disulphide isomerase (PDI) and thioredoxin (TRX) as the preferred examples of the protein factors and HCV-E2715 envelope glycoprotein and human FIGF as the preferred examples of the heterologous proteins.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
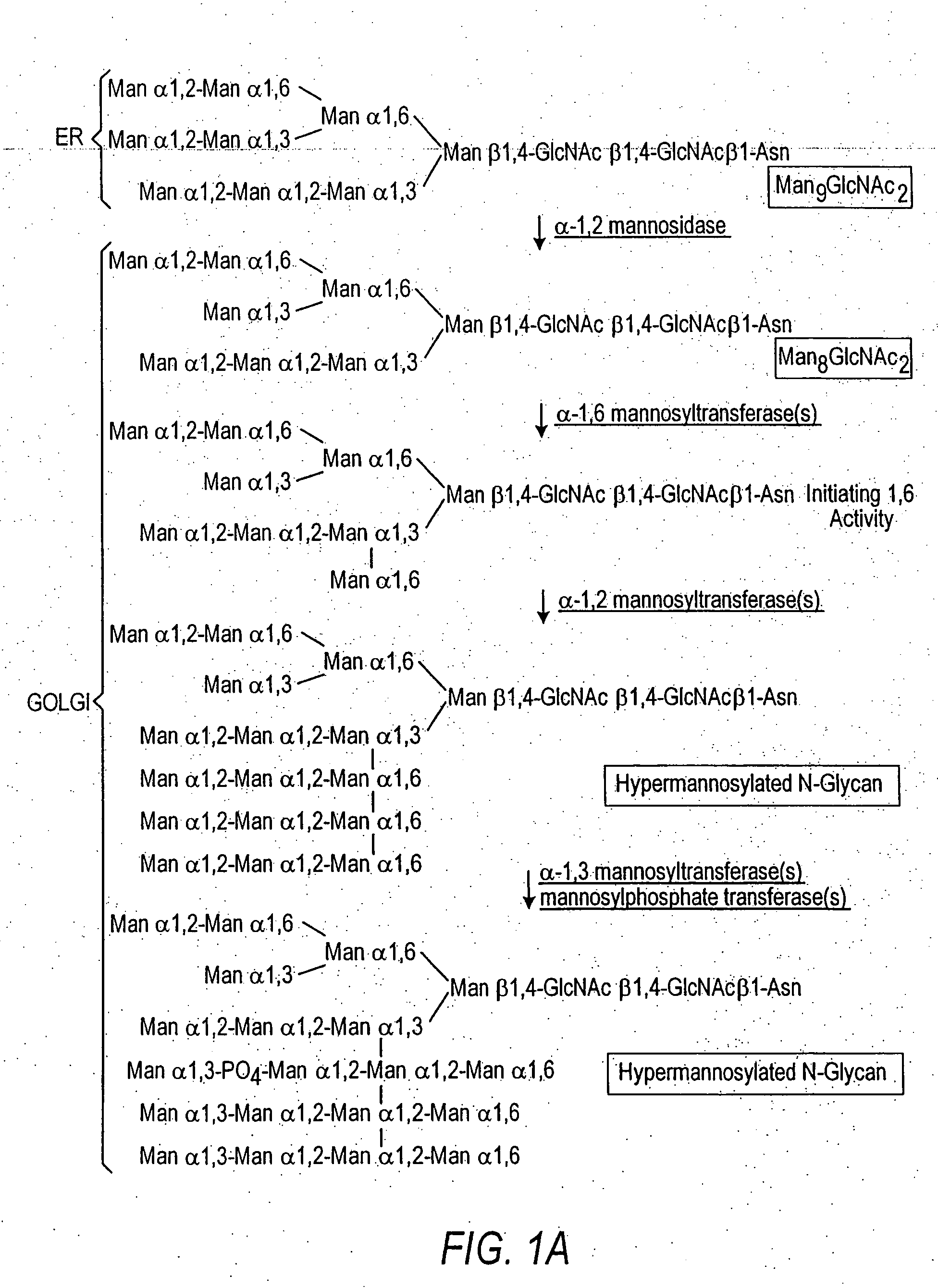
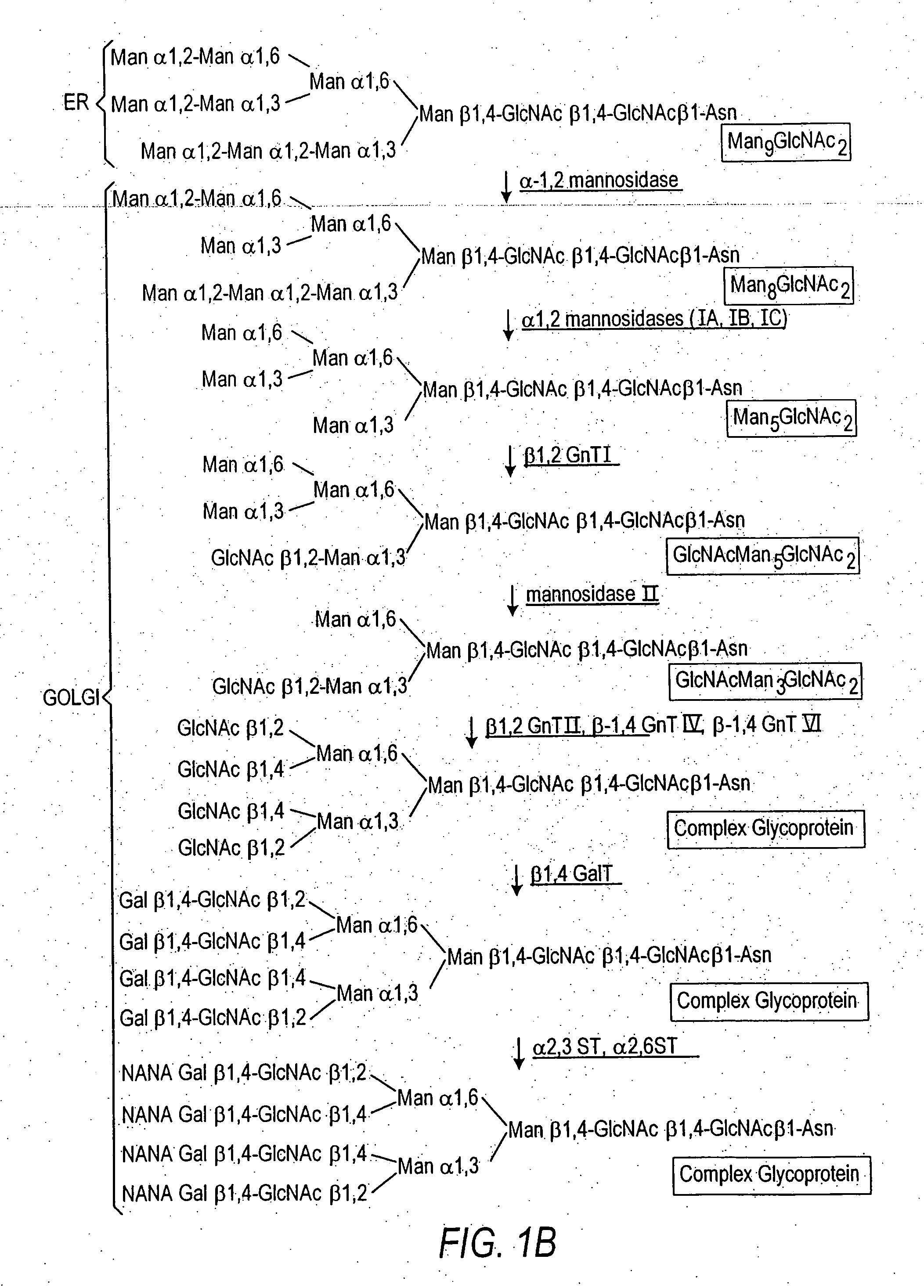
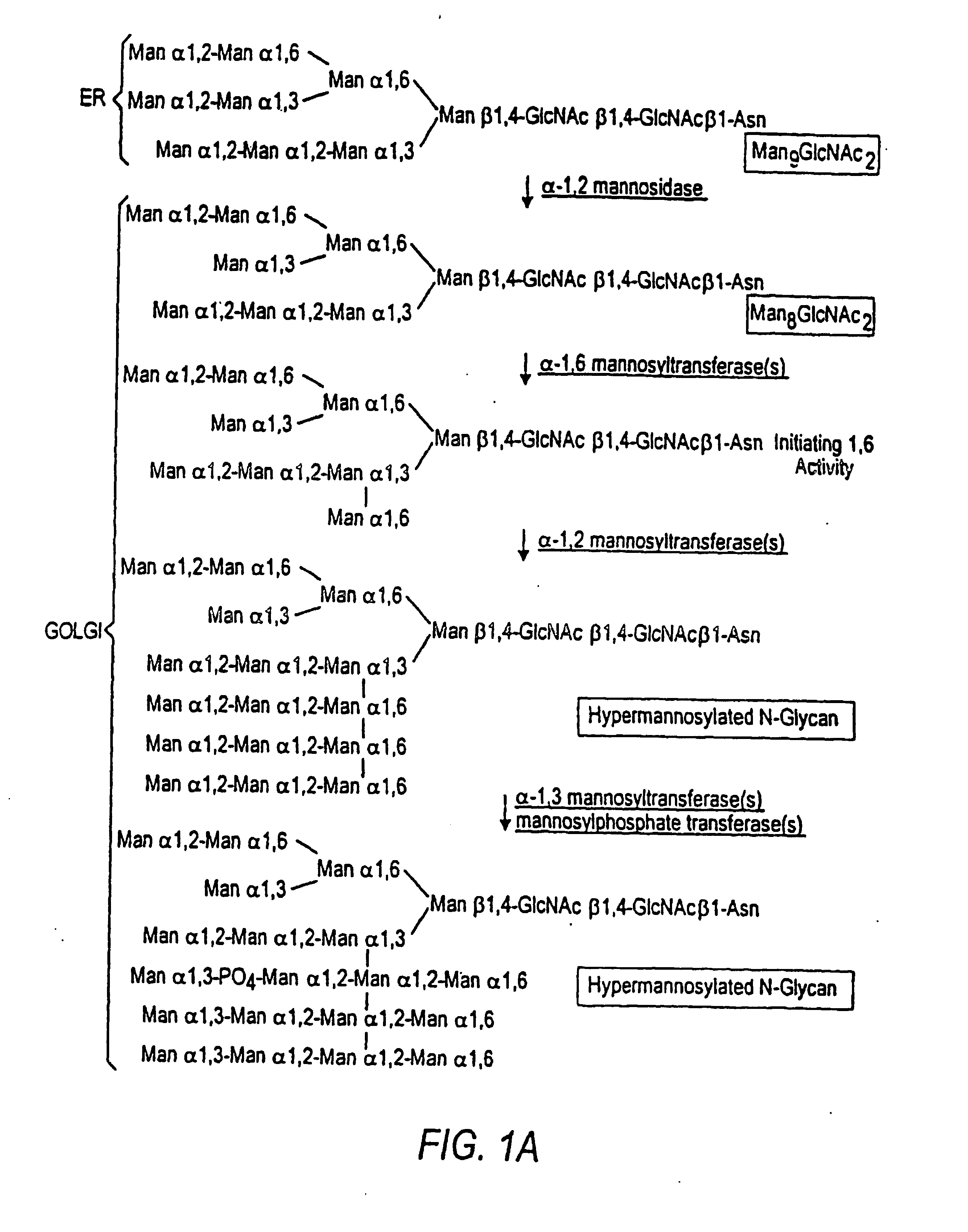
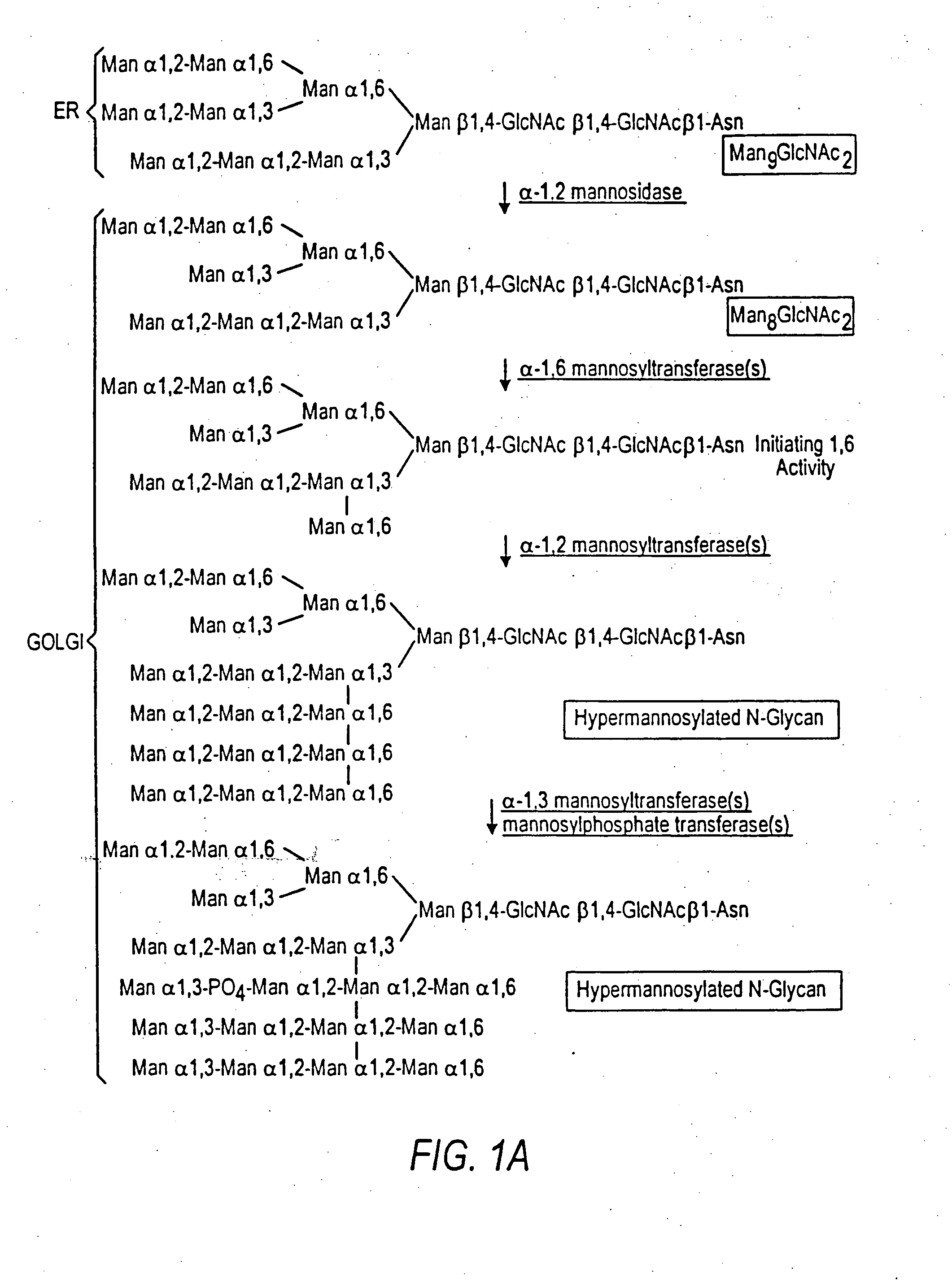
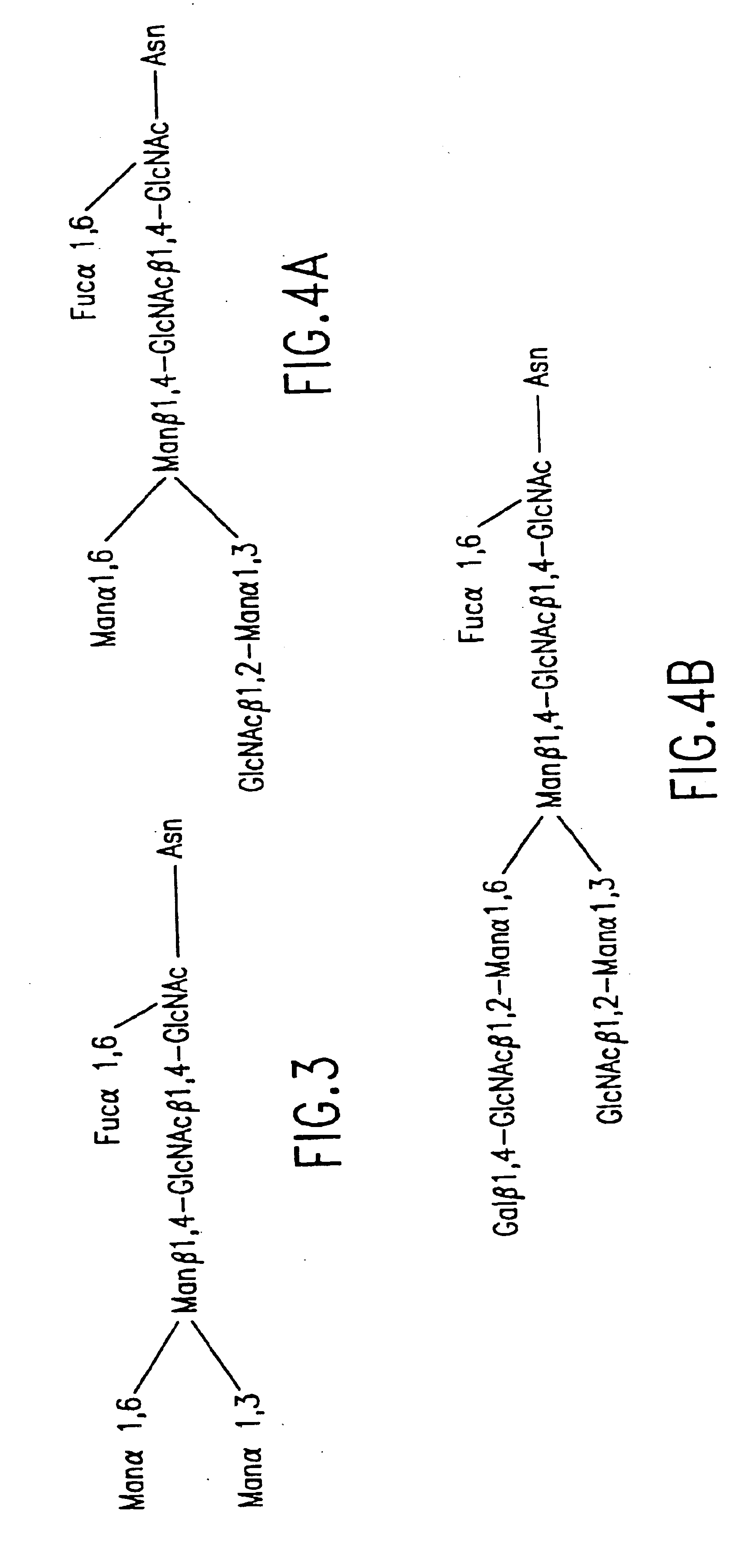
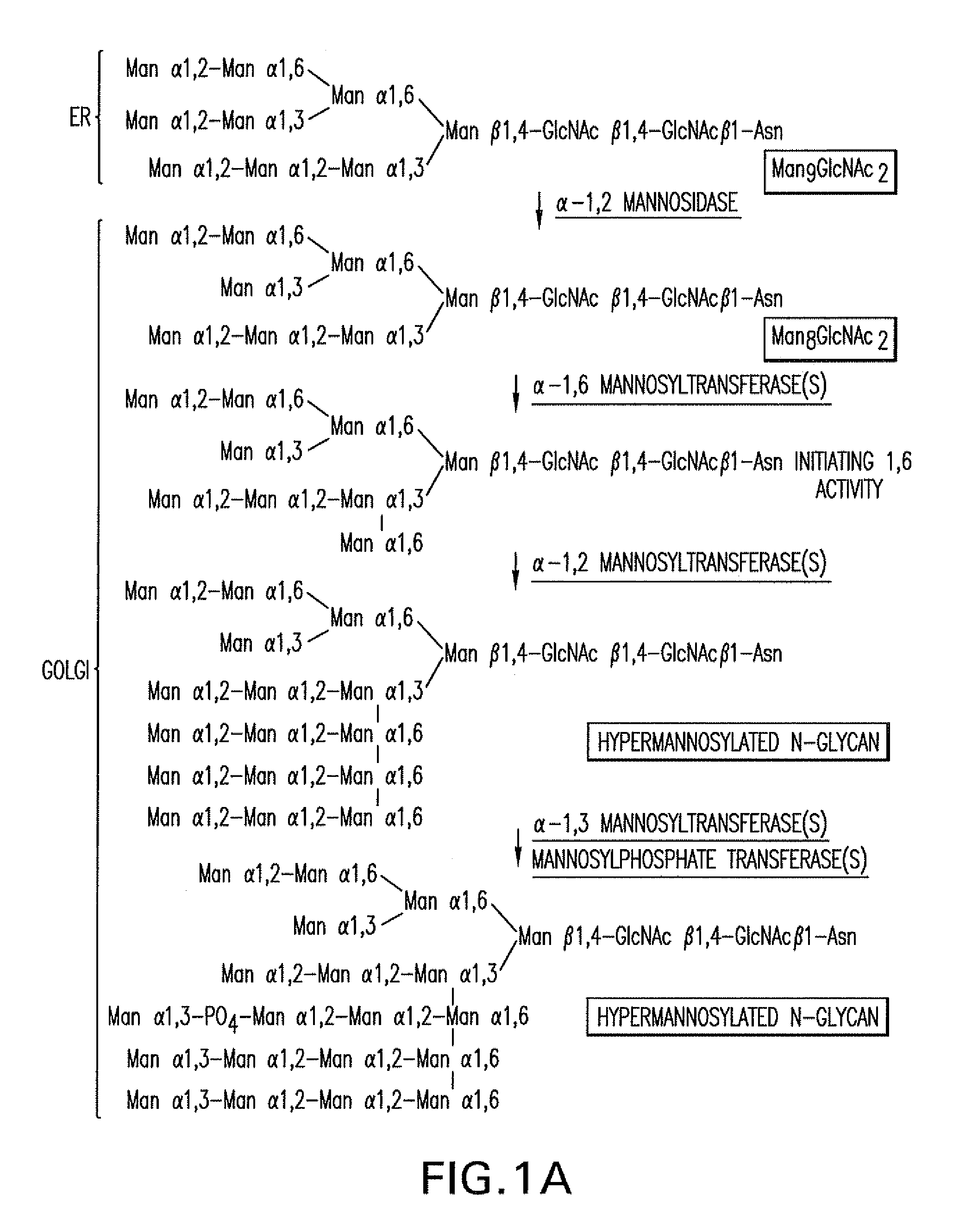
Combinatorial DNA library for producing modified N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS7449308B2The overall structure is closedHigh yieldSugar derivativesMicroorganismsHeterologousTherapeutic protein
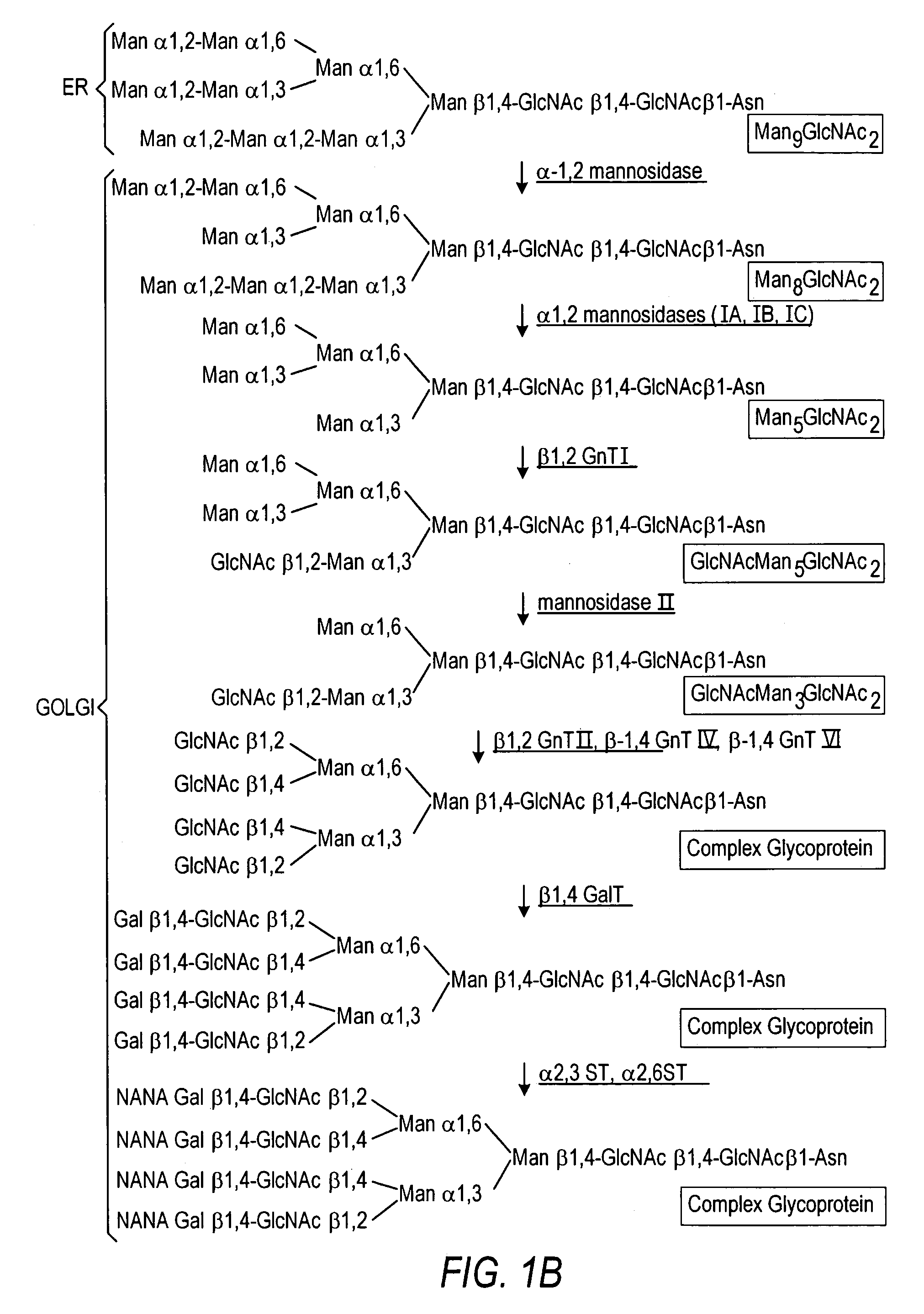
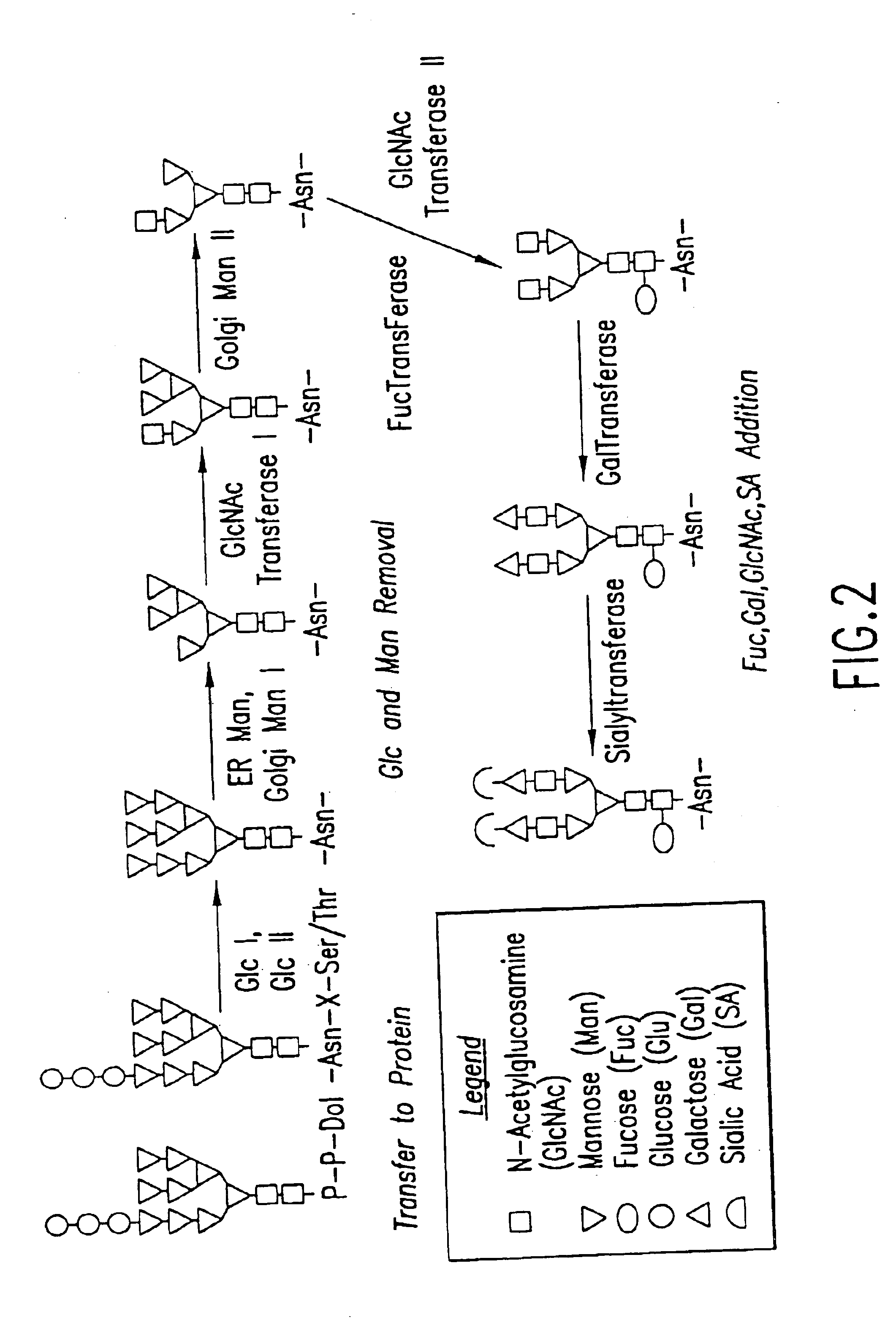
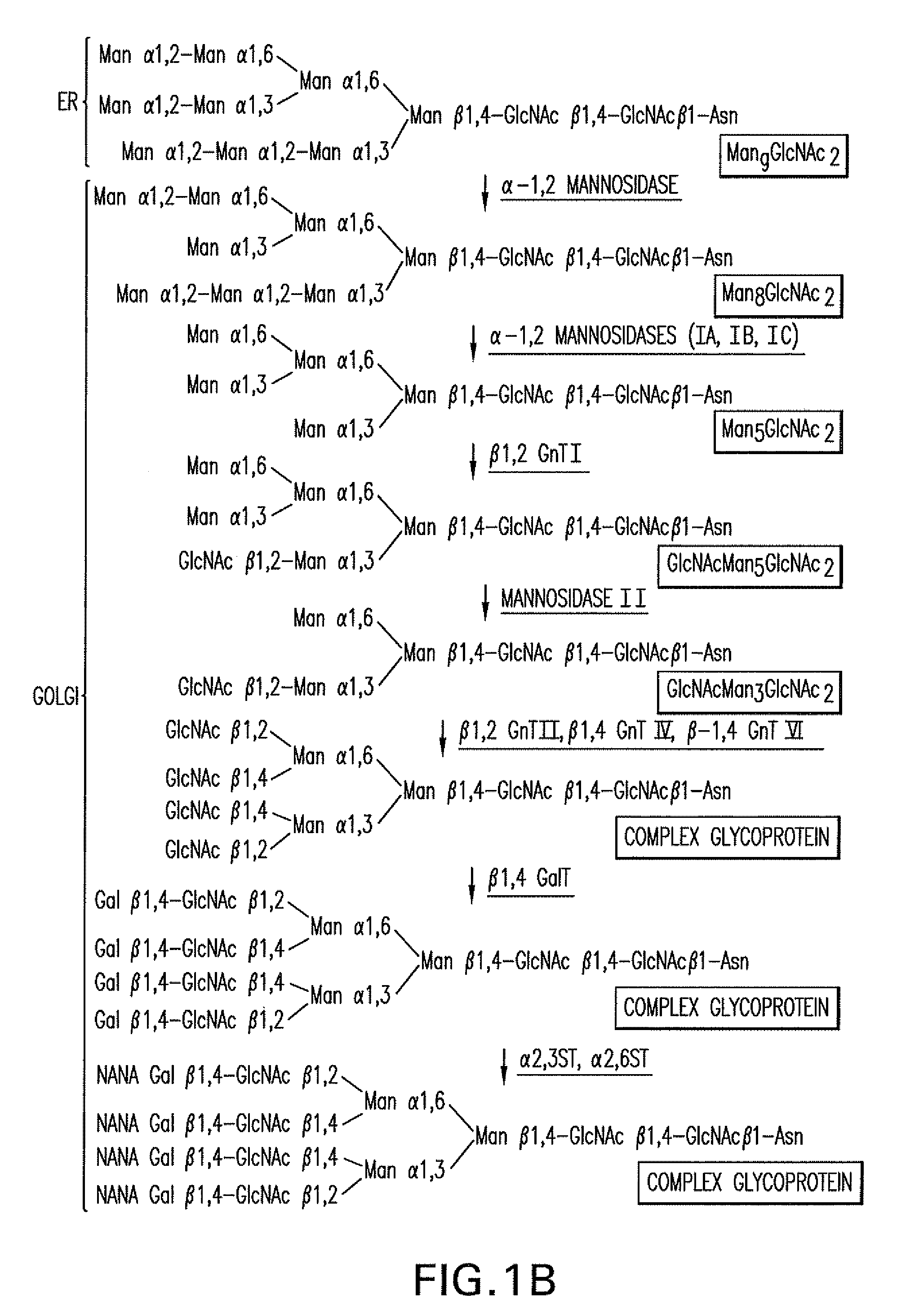
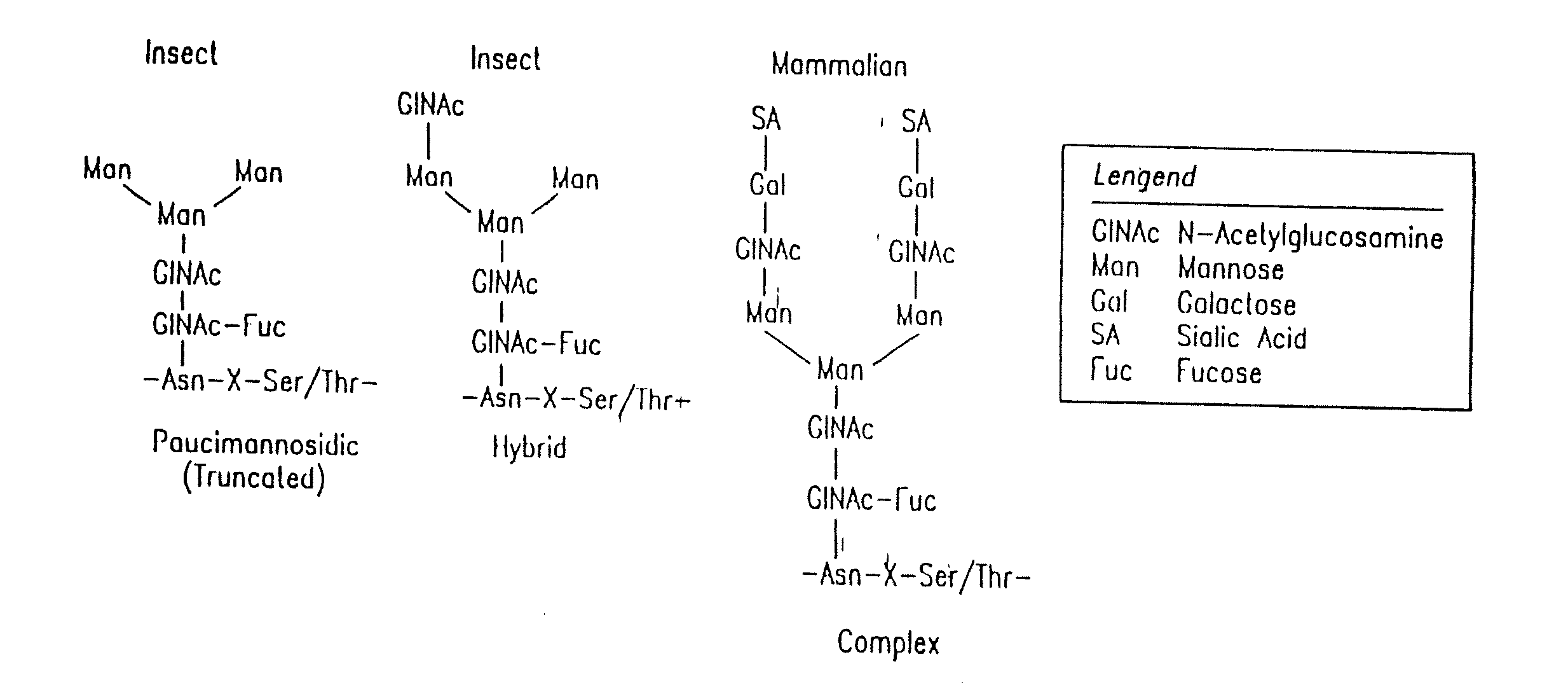
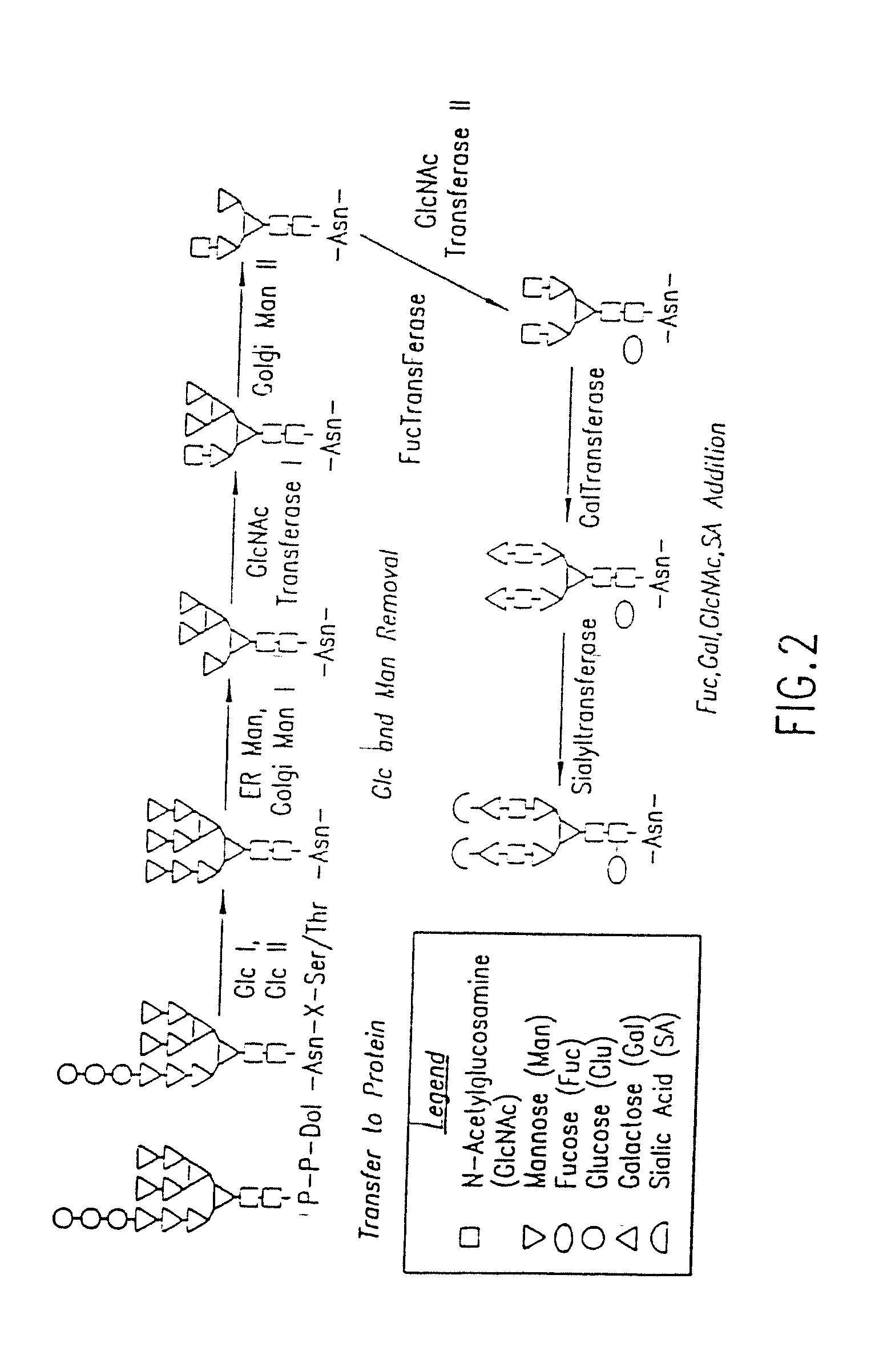
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities such as those involved in glycosylation to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells have a Man5GlcNAc2 core structure which may then be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Production of sialylated N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20060286637A1Improve efficiencyReducing competitive product inhibitionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesHeterologousSialic acid aldolase
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells which have been modified to produce sialylated glycoproteins by the heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferase and / or trans-sialidase, to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. Novel eukaryotic host cells expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities (such as those involved in sialylation) to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
rPA optimization
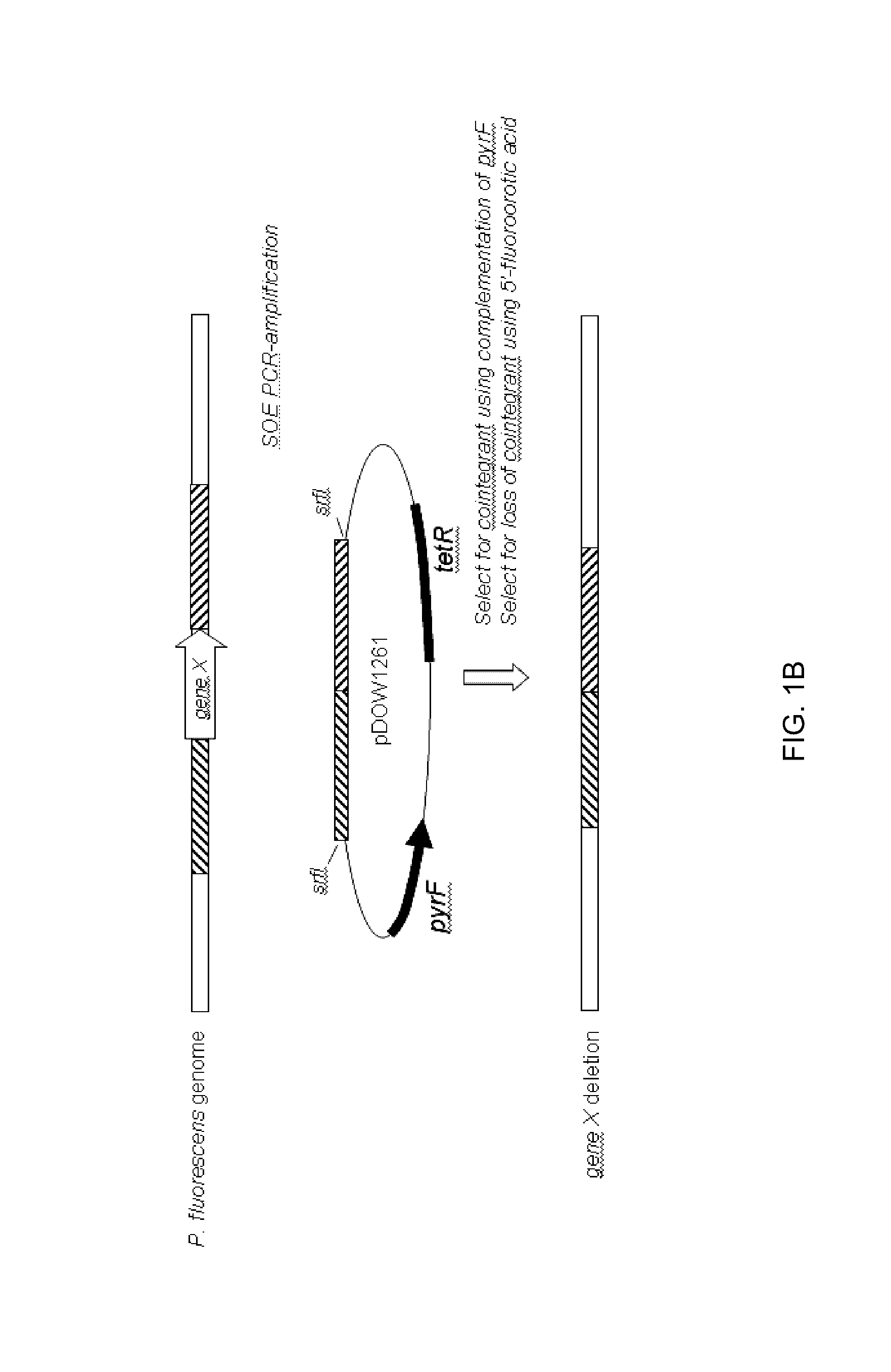
An optimized synthetic polynucleotide encoding a Bacillus anthracis protective antigen and an anthrax vaccine based on the encoded protective antigen. Furthermore, heterologous expression in a host Pseudomonas fluorescens bacteria of an optimized polynucleotide sequence encoding a Bacillus anthracis protective antigen.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
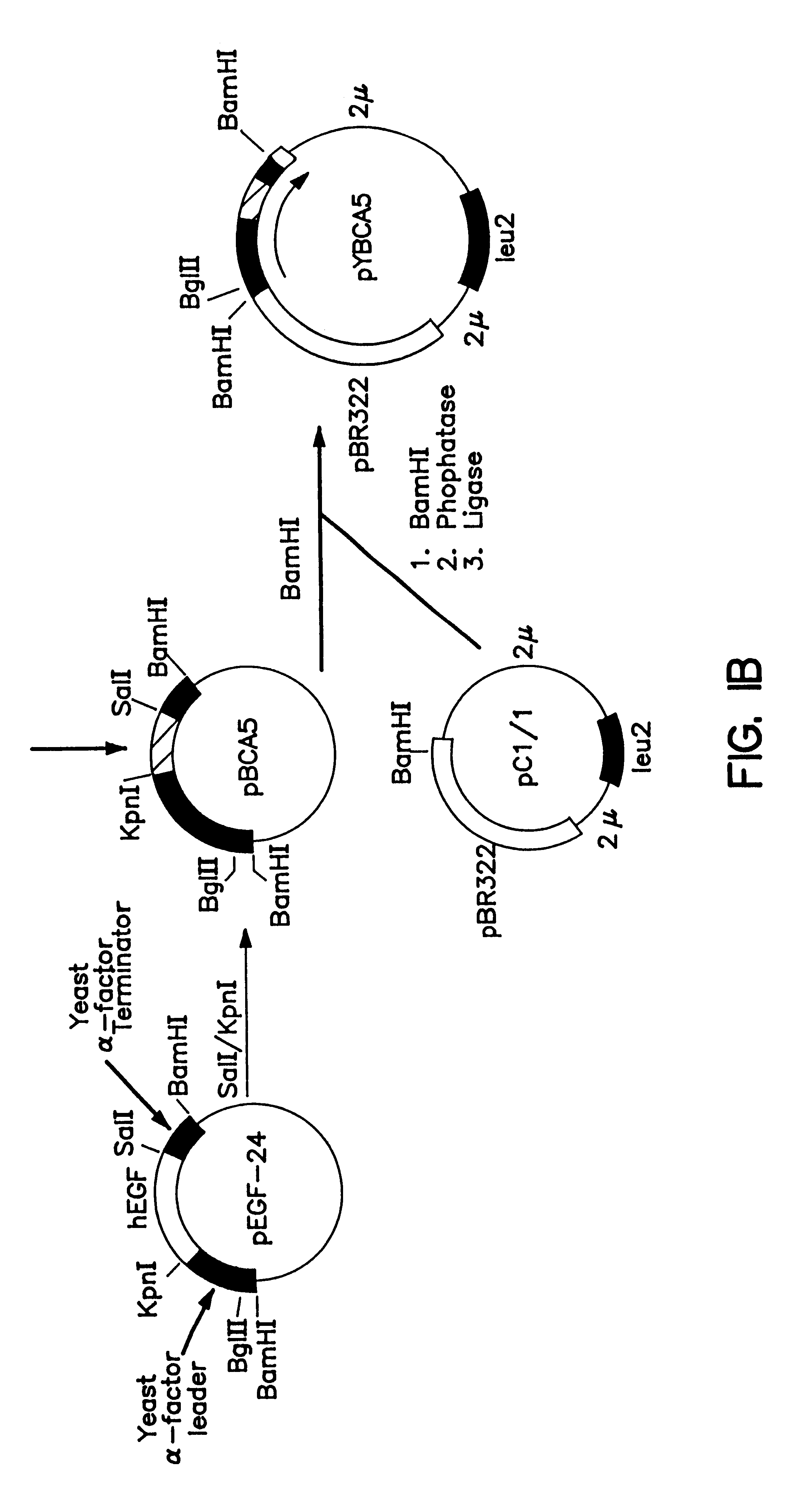
Expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in yeast employing truncated alpha-factor leader sequences
InactiveUSRE37343E1Efficiently direct expressionEfficient secretionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiHeterologousBiotechnology
A yeast alpha-factor expression system is provided comprised of a truncated leader sequence, containing the alpha-factor signal peptide and one glycosylation site, linked by a processing site to a non-yeast protein-encoding sequence.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Production of modified glycoproteins having multiple antennary structures
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells, especially lower eukaryotic host cells, having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar and sugar nucleotide transporters to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified lipid-linked oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells exhibit GnTIII, GnTIV, GnTV, GnT VI or GnTIX activity, which produce bisected and / or multiantennary N-glycan structures and may be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar, sugar nucleotide transporters, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
N-acetylglucosamintransferase III expression in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20050208617A1The overall structure is closedFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationHeterologous
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified lipid-linked oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells exhibit GnTIII activity, which produce bisected N-glycan structures and may be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
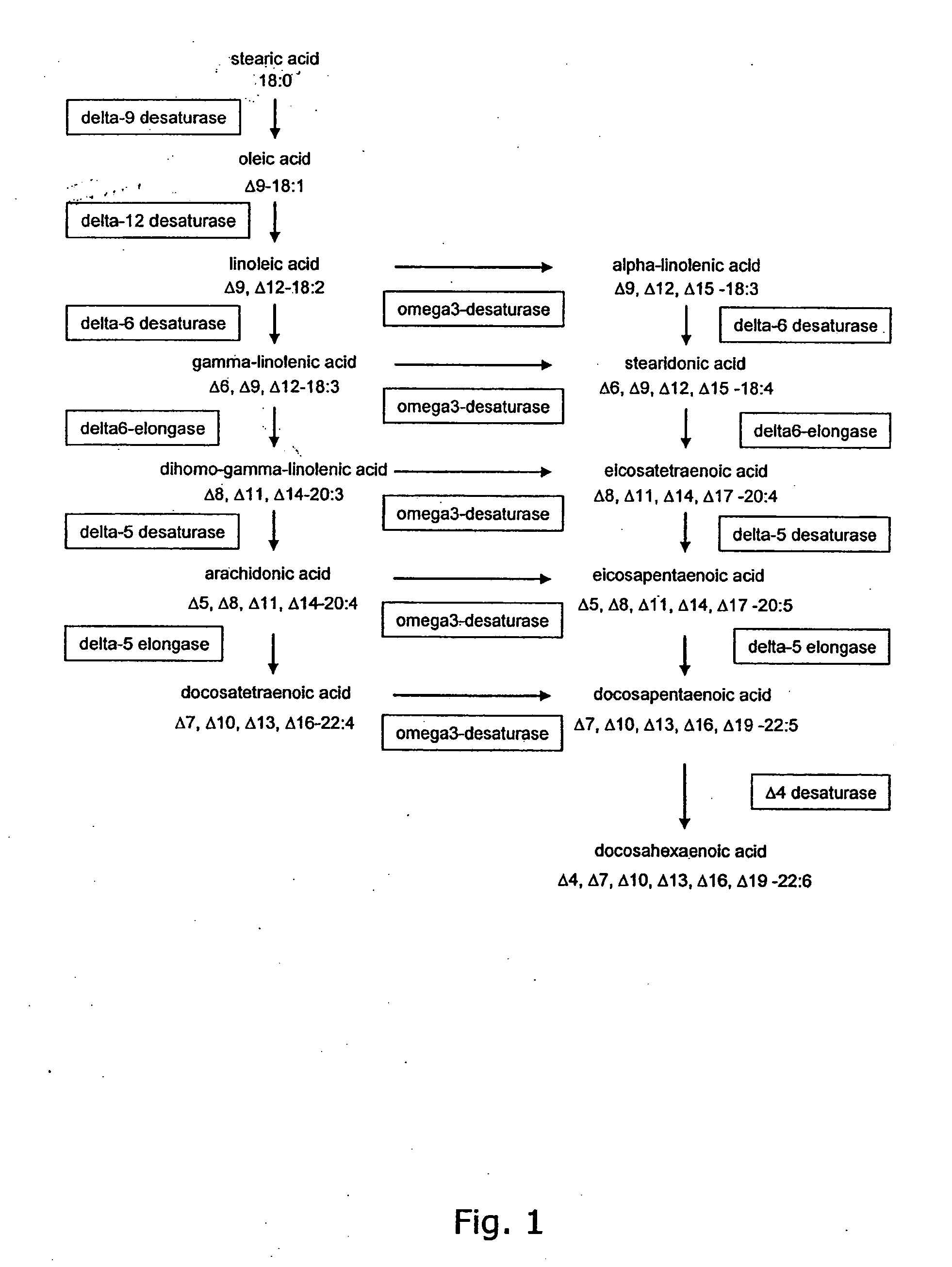
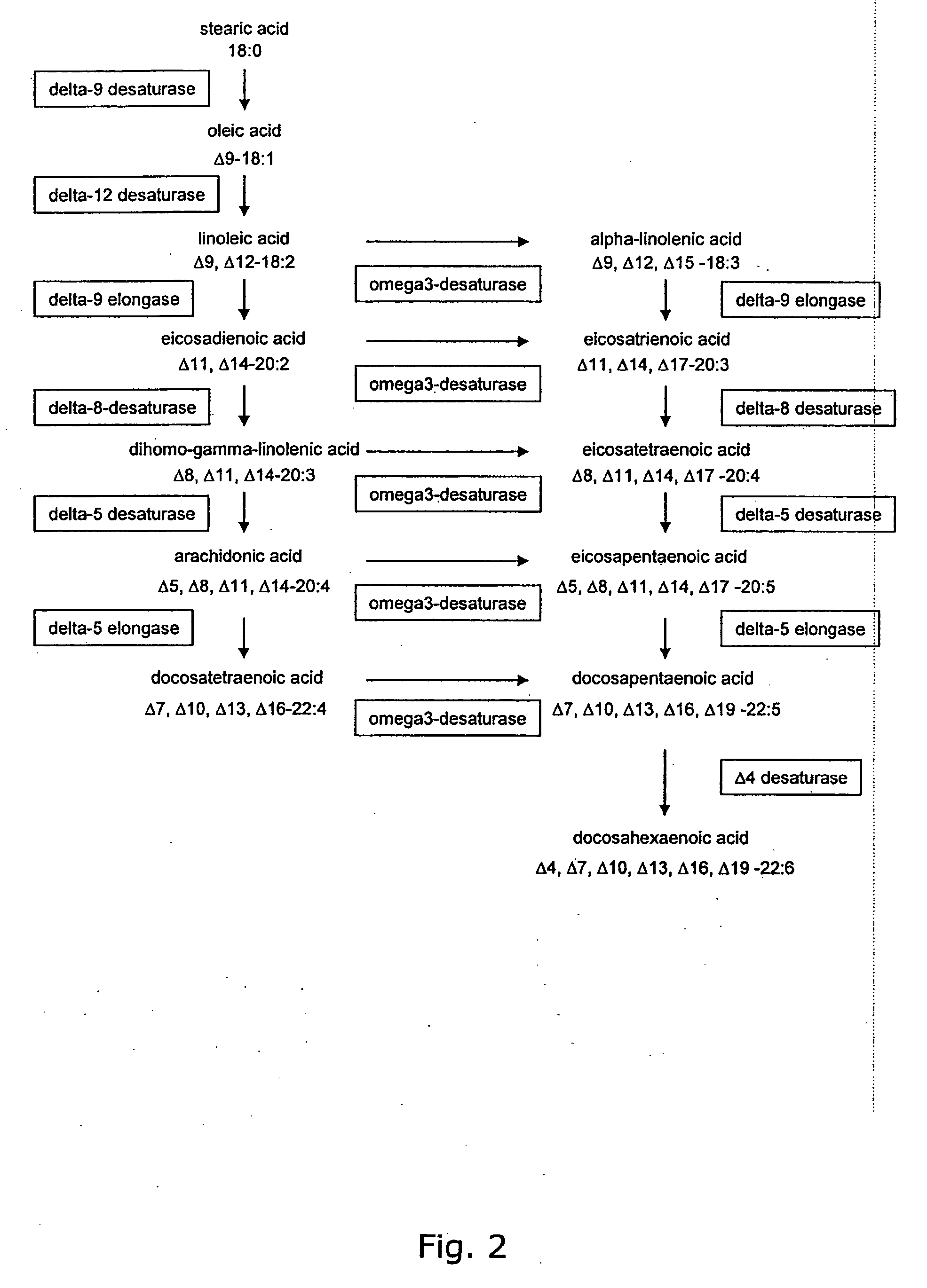
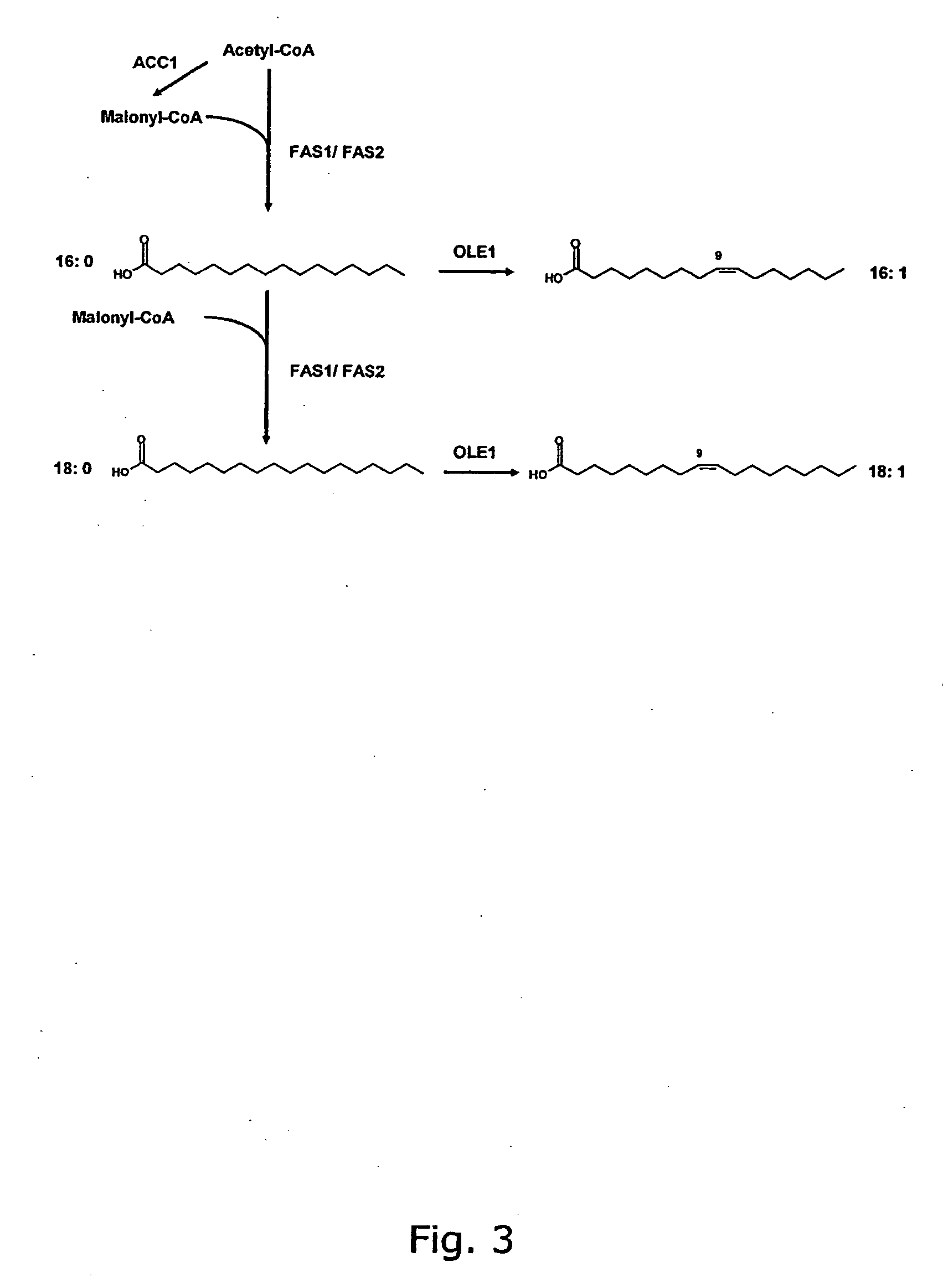
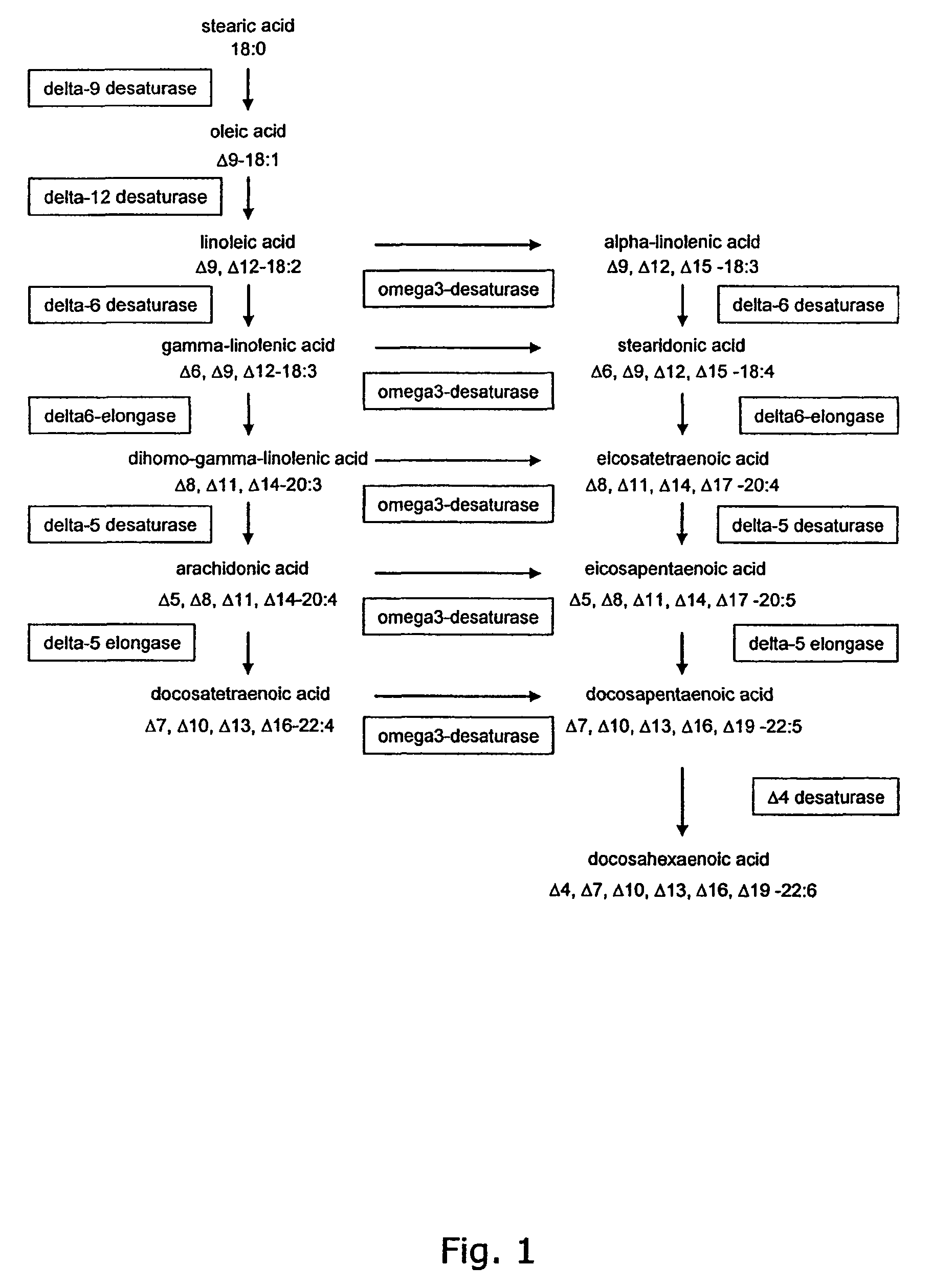
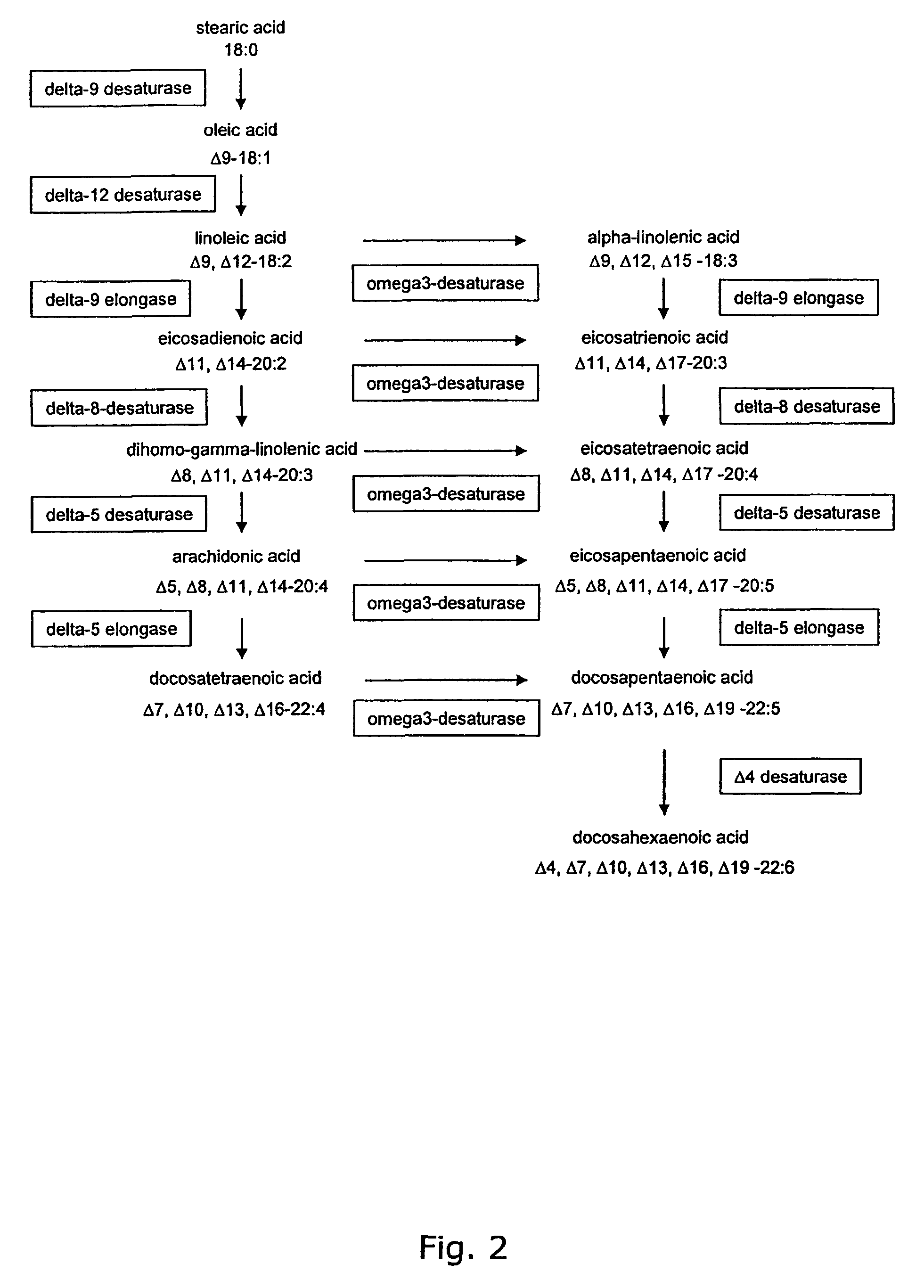
Metabolically engineered cells for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids
The present invention relates to the construction and engineering of cells, more particularly microorganisms for producing PUFAs with four or more double bonds from non-fatty acid substrates through heterologous expression of an oxygen requiring pathway. The invention especially involves improvement of the PUFA content in the host organism through fermentation optimization, e.g. decreasing the temperature and / or designing an optimal medium, or through improving the flux towards fatty acids by metabolic engineering, e.g. through over-expression of fatty acid synthases, over-expression of other enzymes involved in biosynthesis of the precursors for PUFAs, or codon optimization of the heterologous genes, or expression of heterologous enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of the precursor for PUFAs.
Owner:FLUXOME SCI AS
Method for rapidly screening microbial hosts to identify certain strains with improved yield and/or quality in the expression of heterologous proteins
ActiveUS20080269070A1High yieldQuality improvementBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment, or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest, including therapeutic proteins, hormones, a growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PFENEX
Codon optimization method
A heterologous expression in a host Pseudomonas bacteria of an optimized polynucleotide sequence encoding a protein.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Engineering intracellular sialylation pathways
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
Production of a transgenic avian by cytoplasmic injection
InactiveUS20030126629A1Promote absorptionImprove efficiencyVirusesNucleic acid vectorEmbryoTransgene
This invention provides methods for the stable introduction of heterologous coding sequences into the genome of a bird and expressing the coding sequences to produce desired proteins or to alter the phenotype of the bird. The present invention provides preferred methods for introducing a transgene into the cytoplasm of avian embryonic cells by cytoplasmic microinjection. The embryo then develops into a transgenic adult capable of expressing a heterologous protein and / or capable of generating a line of transgenic birds through breeding. Synthetic vectors and gene promoters useful in the methods are also provided by the present invention, as are transgenic birds that express heterologous protein and avian eggs containing heterologous protein.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
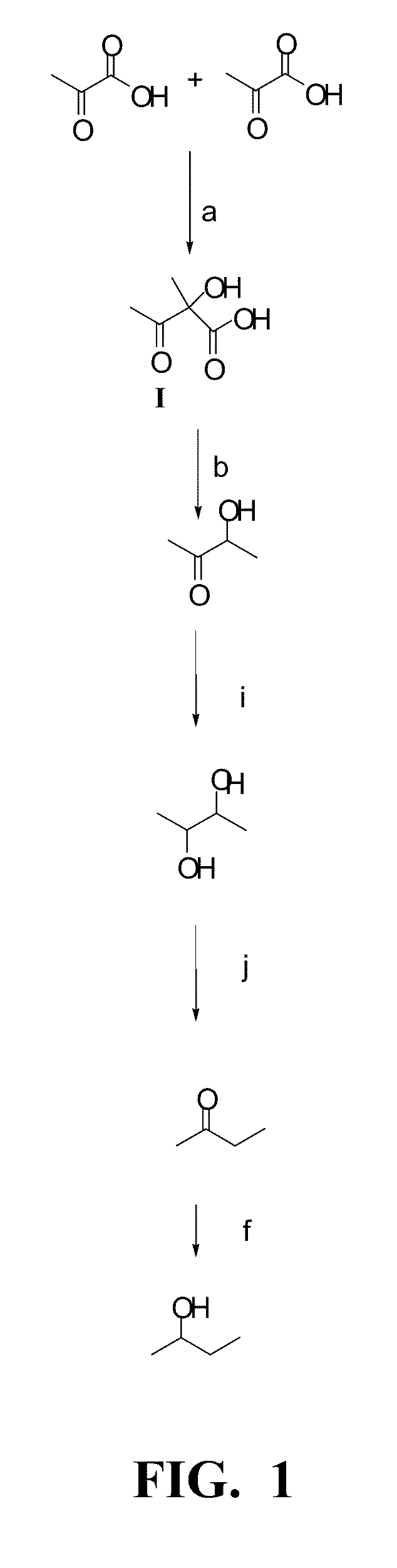
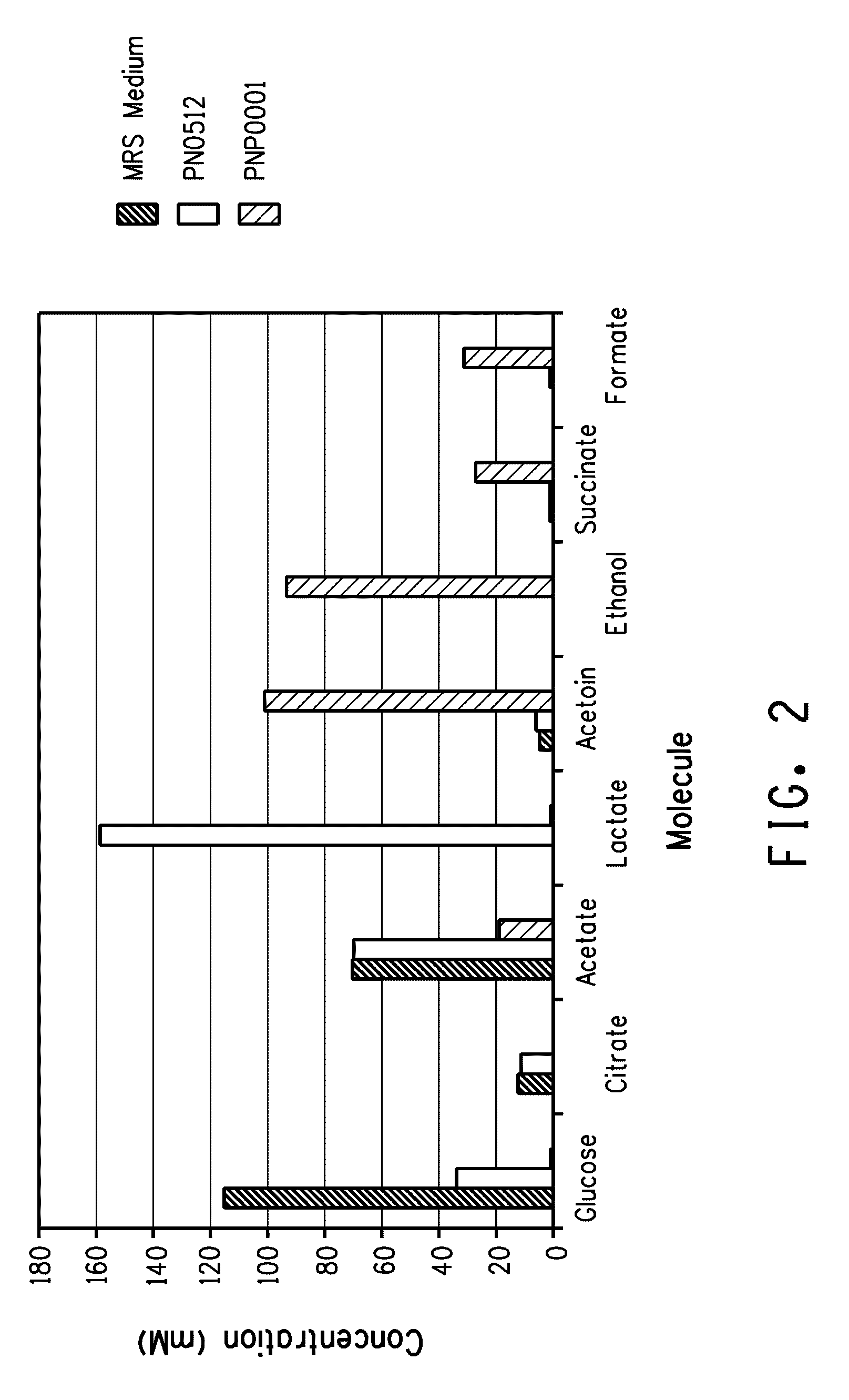
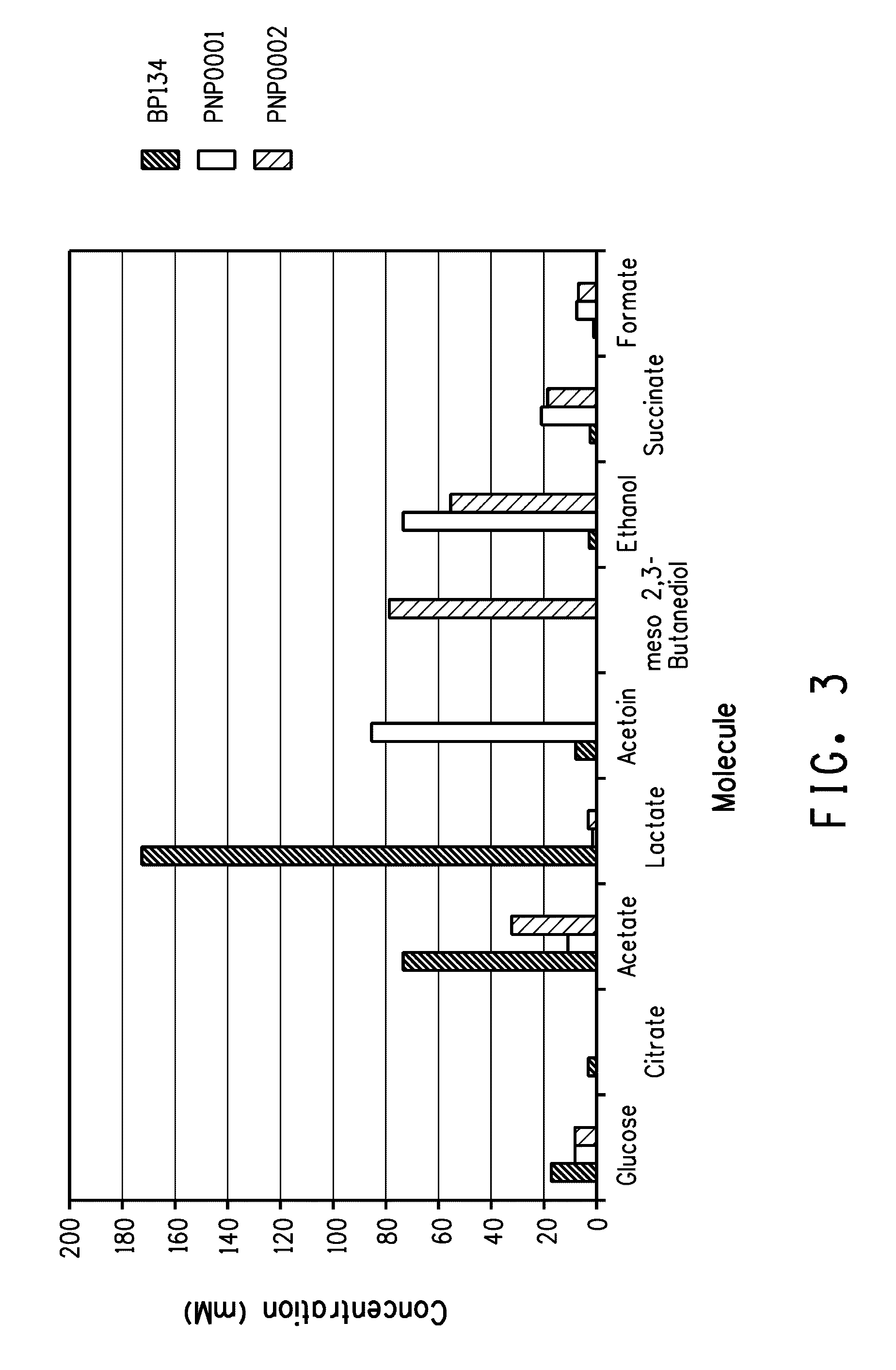
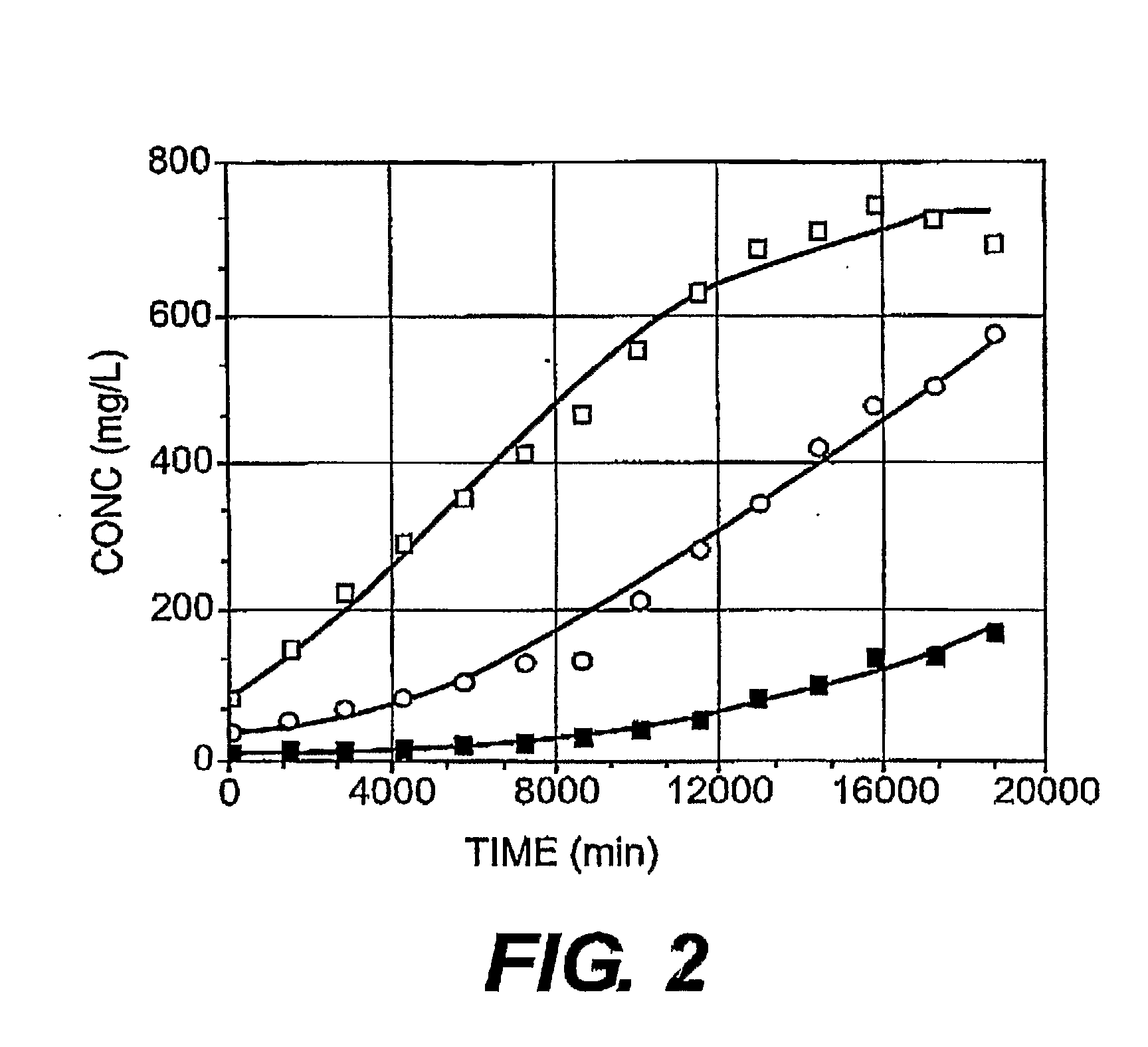
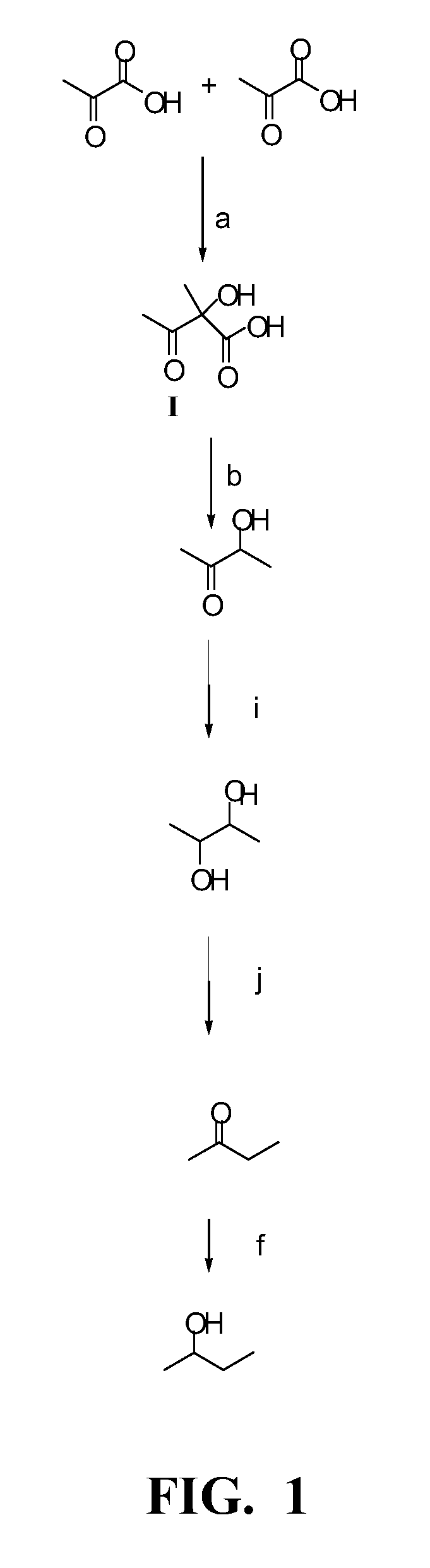
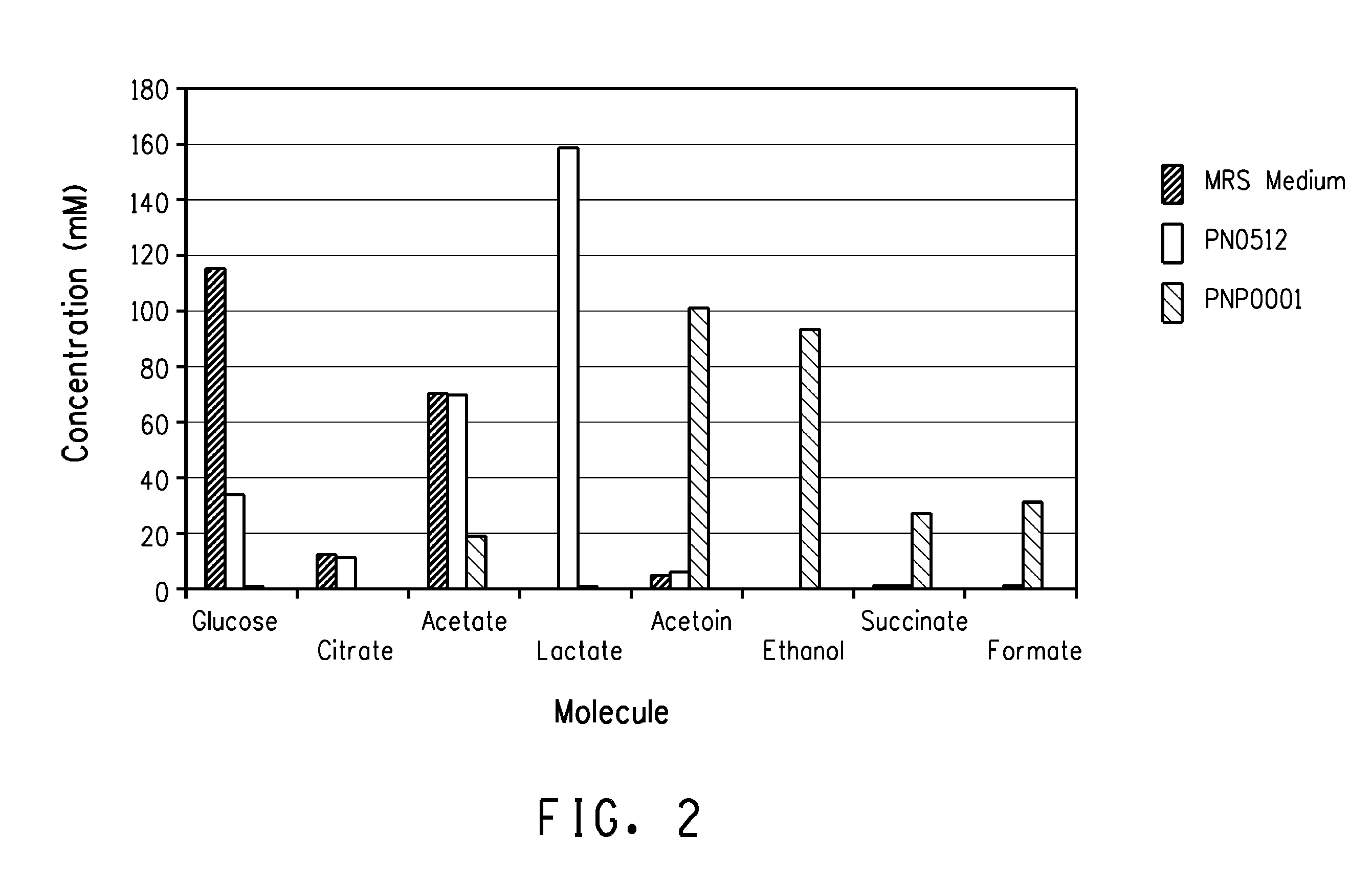
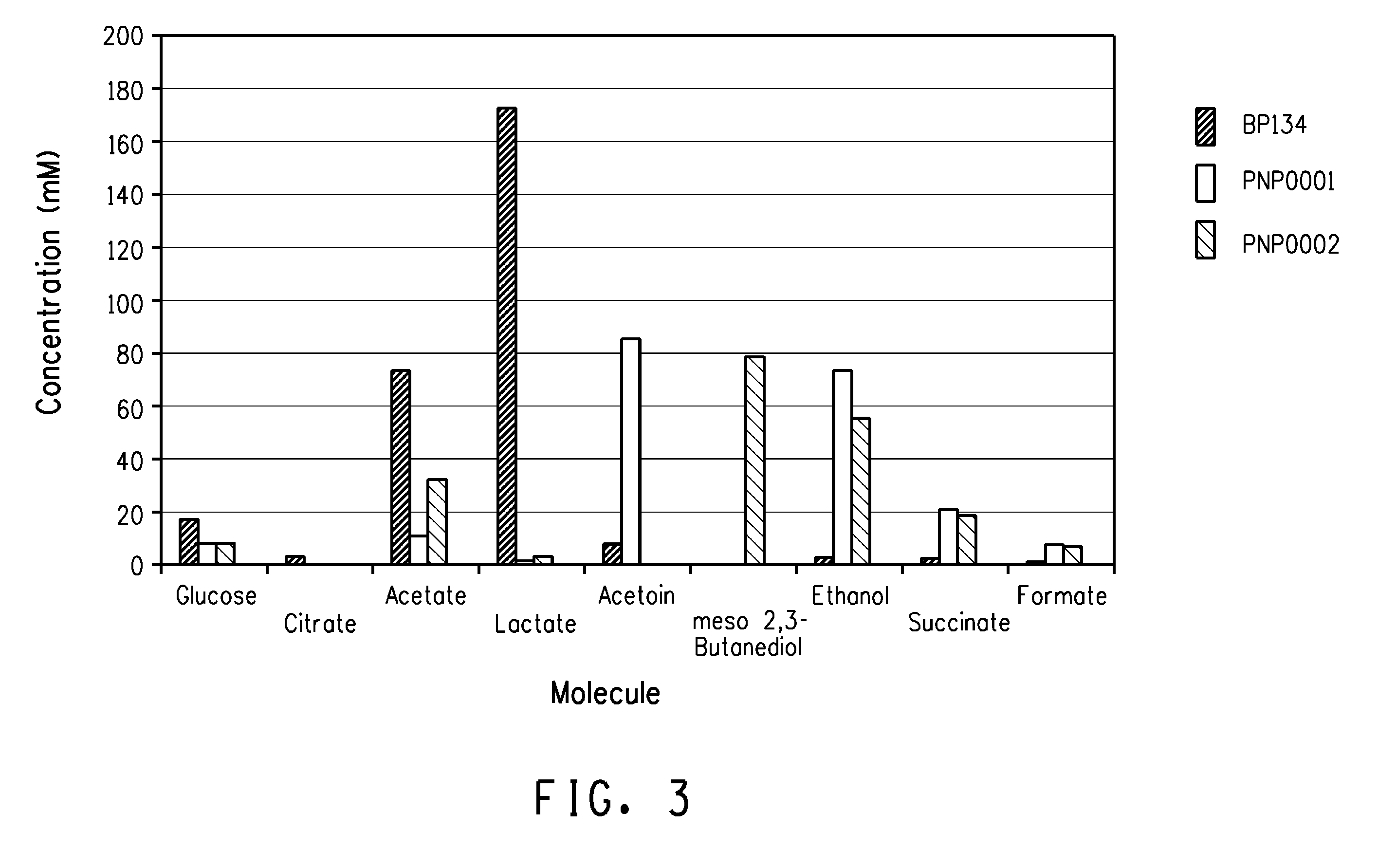
Enhanced pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol conversion in lactic acid bacteria
A high flux of metabolites from pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol in Lactobacillus plantarum was achieved through genetic engineering. Substantial elimination of lactate dehydrogenase activity in the presence of heterologously expressed butanediol dehydrogenase activity led to 2,3 butanediol production that was at least 49% of the total of major pyruvate-derived products.
Owner:GEVO INC
N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase III expression in lower eukaryotes
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified lipid-linked oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells exhibit GnTIII activity, which produce bisected N-glycan structures and may be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Identification of a novel bitter taste receptor, T2R76
Isolated nucleic acids encoding T2R76 polypeptides, recombinantly expressed T2R76 polypeptides, heterologous expression systems for recombinant expression of T2R76 polypeptides, assay methods employing the same, and methods for altering taste perception via administration of a T2R76 modulator. These T22R76 polypeptides can be expressed alone or co-expressed with another T2R polypeptide, preferably a different human T2R polypeptide.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
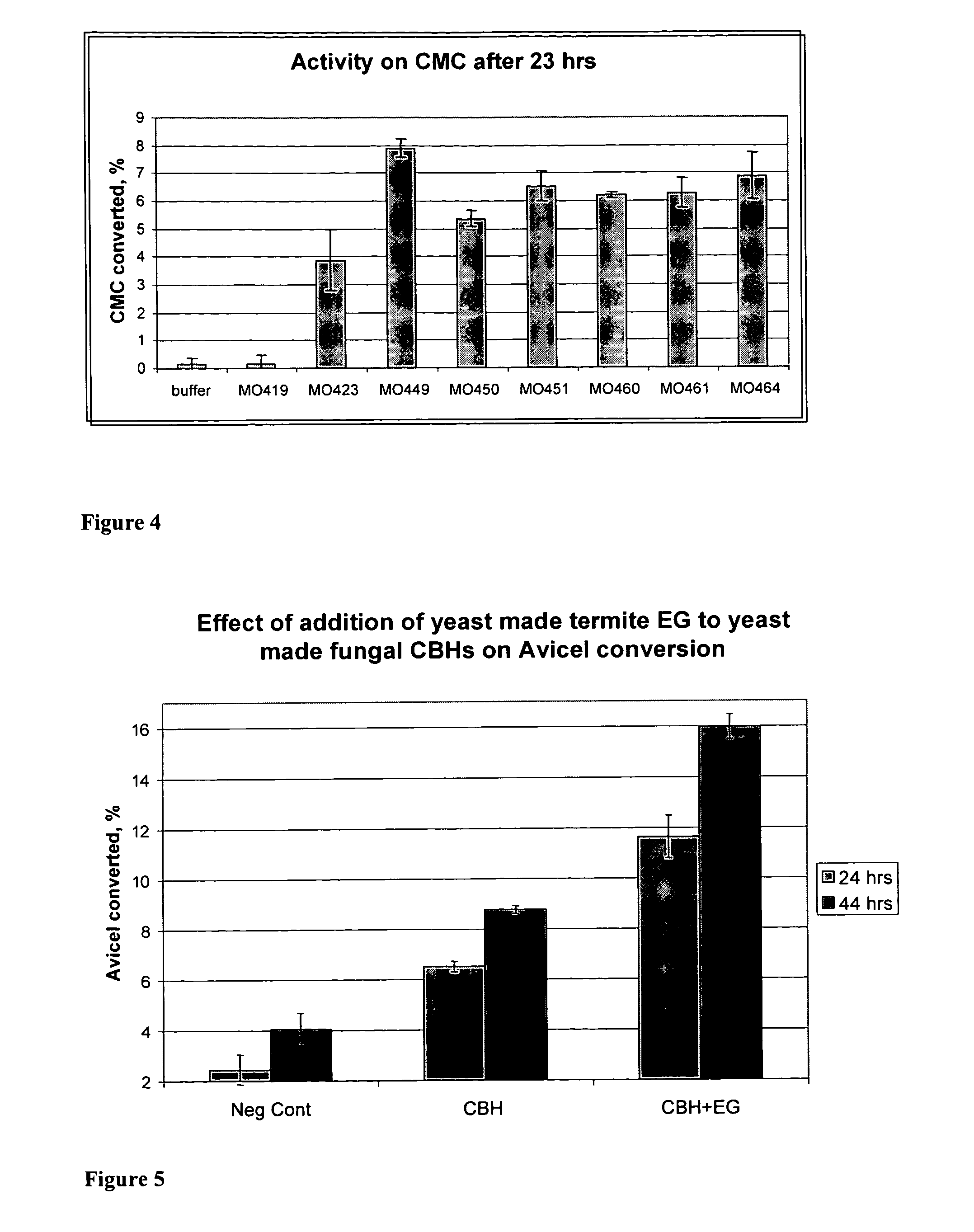
Heterologous Expression of Termite Cellulases Yeast
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of termite and termite-associated symbiont cellulases. The cellulases can, for example, be codon-optimized and expressed in yeast host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The cellulases can also be co-expressed in host cells with other cellulases. The expression in such host cells of the termite and termite-associated symbiont cellulases, and variants and combinations thereof, result in yeast with improved cellulosic activity. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Metabolically engineered Saccharomyces cells for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids
Owner:FLUXOME SCI AS
Optimization of Heterologous Polypeptide Expression
This invention relates to methods for controlling deamidation of at least one type of heterologously expressed polypeptide in cell culture.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
Enhanced pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol conversion in lactic acid bacteria
A high flux of metabolites from pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol in Lactobacillus plantarum was achieved through genetic engineering. Substantial elimination of lactate dehydrogenase activity in the presence of heterologously expressed butanediol dehydrogenase activity led to 2,3 butanediol production that was at least 49% of the total of major pyruvate-derived products.
Owner:GEVO INC
Protein synthesis efficiency enhancing RNA element
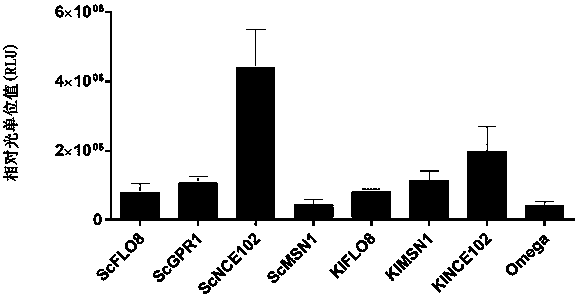
The invention provides a protein synthesis efficiency enhancing RNA element and particularly discloses a nucleic acid structure formed by coding sequences of optional promoters, yeast-derived IRES enhancers (such as ScGPR1, ScFLO8, ScNCE102, ScMSN1, KlFLO8, KlNCE102 and KlMSN1) and heterologous proteins. By application of the nucleic acid structure to a yeast in-vitro protein synthesis system, thesynthesized luciferase activity RLU (relative light unit) is extremely high.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Identification of a novel bitter taste receptor T2R76 that specifically responds to brucine and prop bitter ligands
Isolated nucleic acids encoding T2R76 polypeptides, recombinantly expressed T2R76 polypeptides, heterologous expression systems for recombinant expression of T2R76 polypeptides, assay methods employing the same, and methods for altering taste perception via administration of a T2R76 modulator. These T22R76 polypeptides can be expressed alone or co-expressed with another T2R polypeptide, preferably a different human T2R polypeptide. These T2R76 polypeptides specifcally respond to bitter ligands including brucine and propylthiouracil (PROP) and therefore can be used in assays that identify compounds that modulate, preferably block bitter taste.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Method for rapidly screening microbial hosts to identify certain strains with improved yield and/or quality in the expression of heterologous proteins
ActiveUS9580719B2High expressionReduce expressionLibrary screeningMicroorganism librariesHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing a heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest including therapeutic proteins, hormones, growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
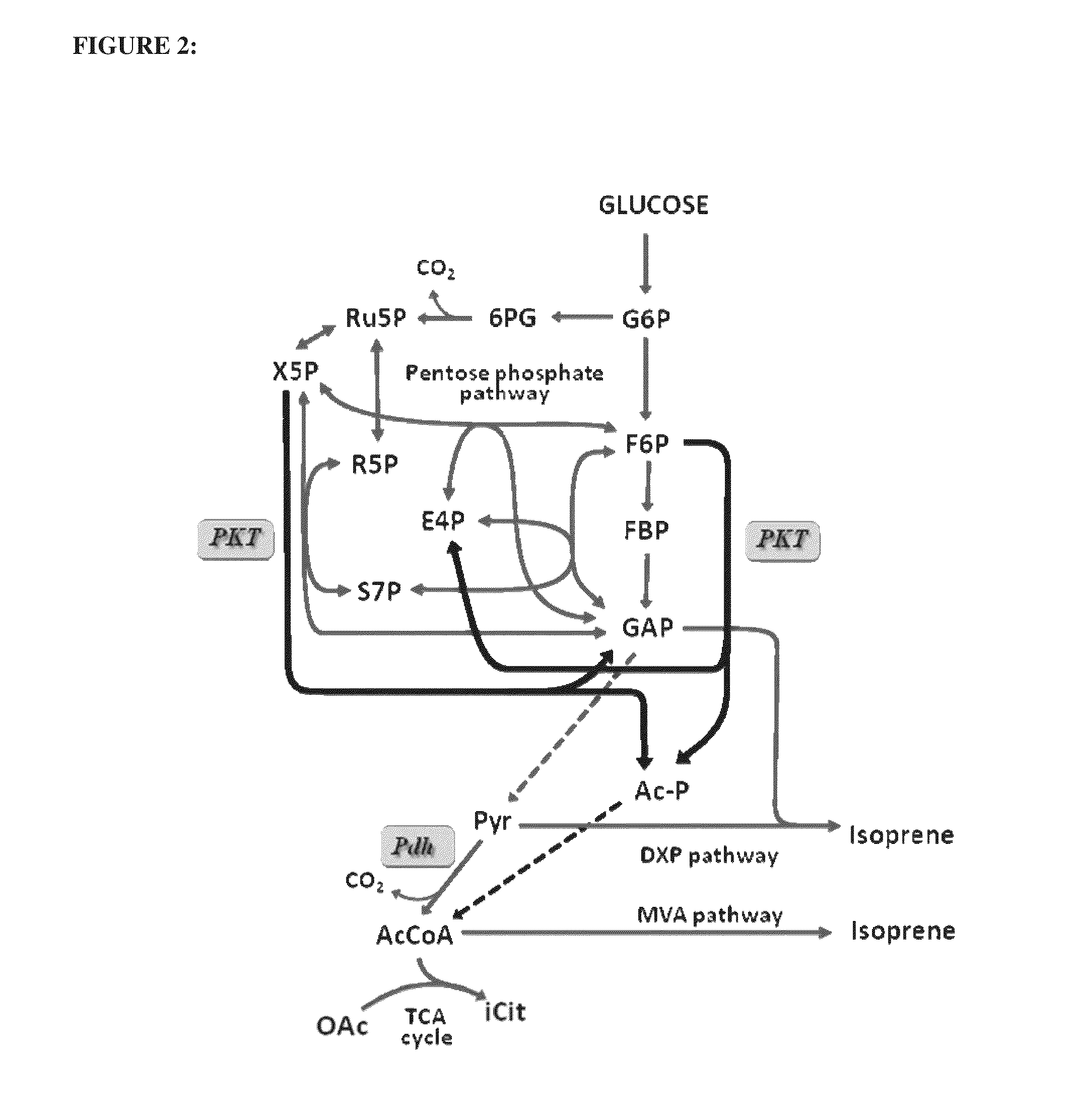
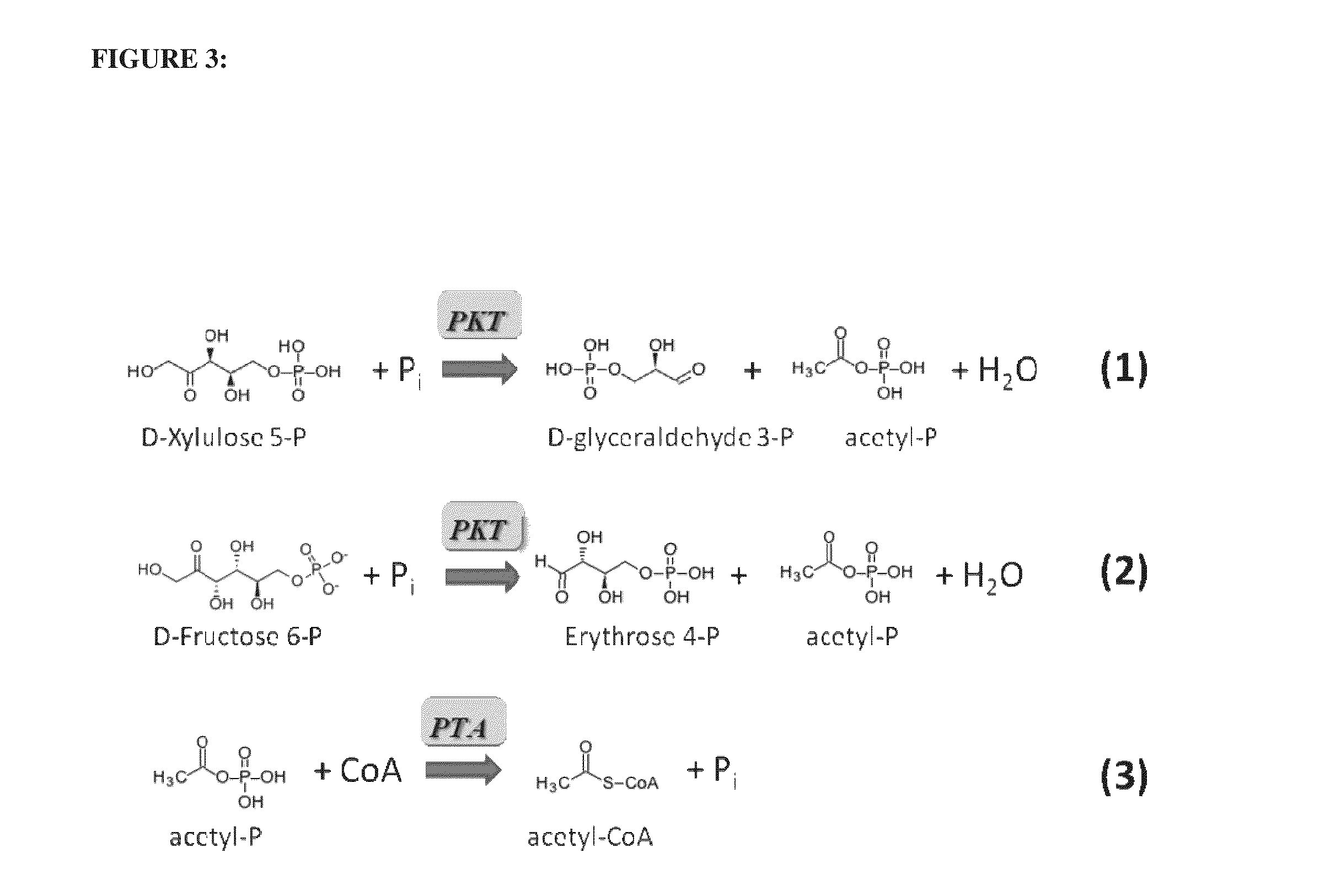
Utilization of phosphoketolase in the production of mevalonate, isoprenoid precursors, and isoprene
The invention provides for methods for the production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids in cells via the heterologous expression of phosphoketolase enzymes.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Vaccine composition
The present invention relates to the field of Gram-negative bacterial vaccine compositions, their manufacture, and the use of such compositions in medicine. More particularly it relates to the field of useful Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane vesicle (or bleb) compositions comprising heterologously expressed Chlamydia antigens, and advantageous methods of rendering these compositions more effective and safer as a vaccine.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
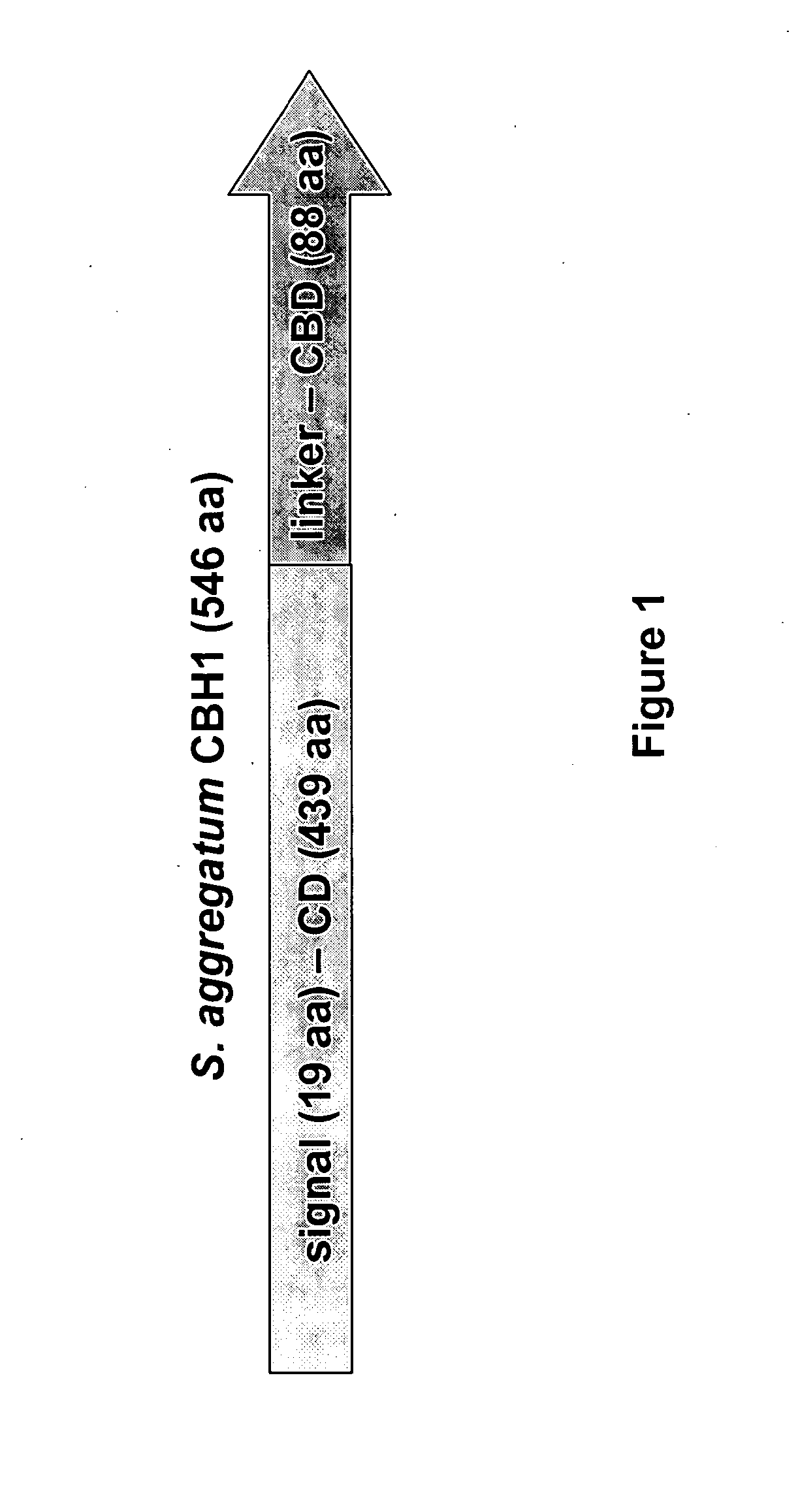
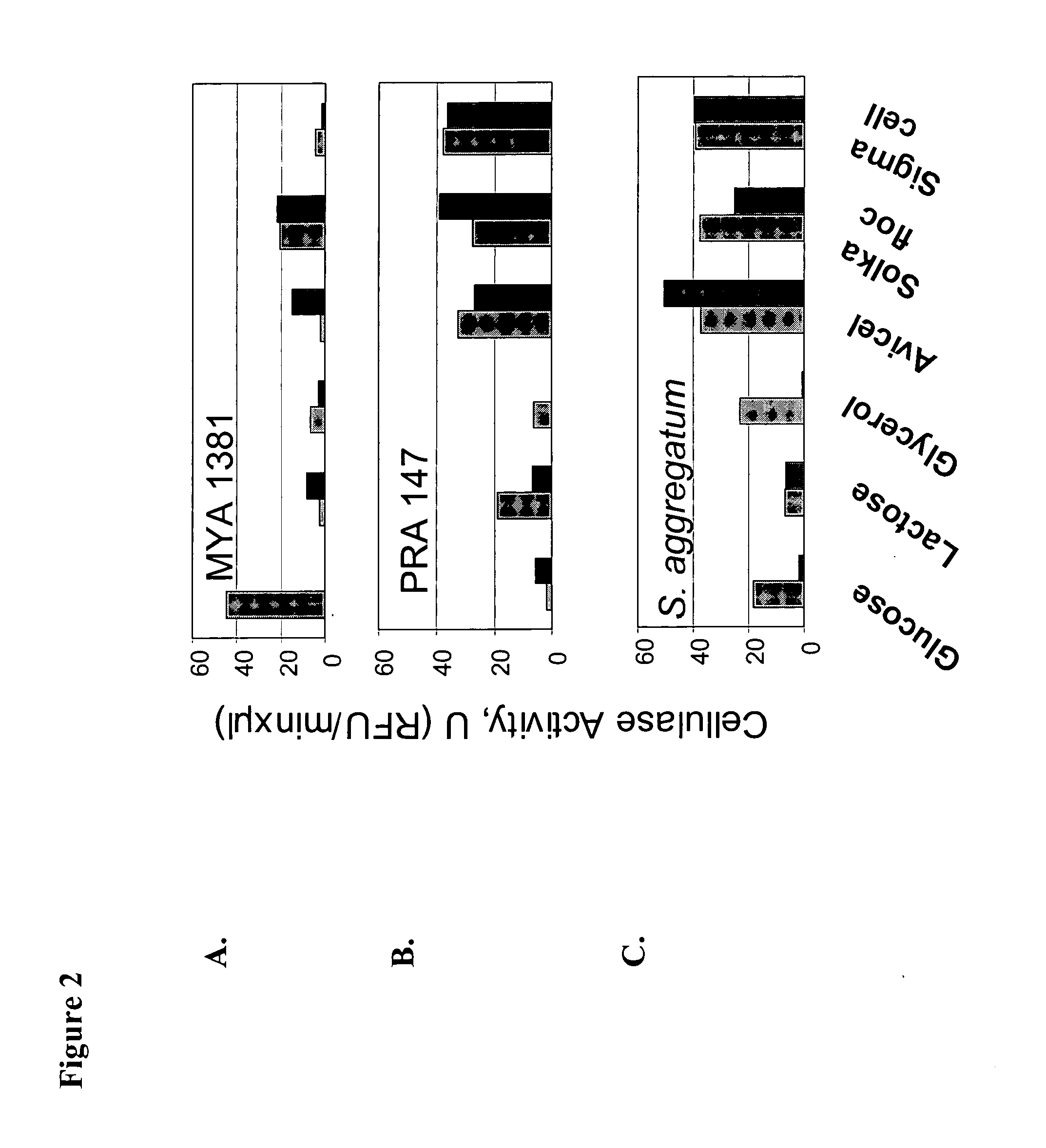
Isolation and Characterization of Schizochytrium Aggregatum Cellobiohydrolase I (CBH I)
ActiveUS20110312054A1Promote productionAugments cellulose digestionFungiBacteriaHeterologousCellulose
The present invention provides for the isolation and characterization of the cbh1 gene from Schizochytrium aggregatum. In particular, the present invention provides for the nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of Schizochytrium aggregatum cbh1, and domains, variants and derivatives thereof. The present invention further provides for the heterologous expression of Schizochytrium aggregatum Cbh1 in host cells, including yeast, e.g., Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Expression of Schizochytrium aggregatum Cbh1 in host cells will augment cellulose digestion and facilitate ethanol production by those host cells on cellulosic substrates. In certain embodiments, heterologous expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is in coordination with heterologous expression of other known, or newly identified saccharolytic enzymes. Therefore, the present invention also provides that the novel Schizochytrium aggregatum Cbh1 gene can utilized in a consolidated bioprocessing system.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Engineering Intracellular Sialylation Pathways
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Expression of monoclonal antibodies in ciliate host cells
The present invention is related to a system for the heterologous expression of a monoclonal Antibody (mAb) or a fragment or derivative thereof, said system comprising at least one ciliate host cell, and incorporated, into said ciliate host cell, at least one heterologous nucleic acid molecule encoding for said monoclonal Antibody, or a fragment or derivative thereof.
Owner:CILIAN
Incision alginate lyase Alg2B and coding gene, preparation and application thereof
The invention discloses a gene sequence of Incision alginate lyase Alg2B from Flavobacterium strain (Flavobacterium sp. S20). The invention also provides a method for preparing novel alginate lyase, which is characterized in that by using a gene engineering technical method, the gene of the alginate lyase is cloned to an escherichia coli expression vector, the escherichia coli recombinant strain capable of realizing heterogenous expression of enzyme can be obtained, the recombinant strain is used for heterogenous expression of the alginate lyase Alg2B, and thereby monosaccharide and oligosaccharides produced by sodium alginate can be degraded. The provided alginate lyase Alg2B can be widely used in the fields of agriculture, food, feed addictives, medicine and alga genetic engineering.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant alginate lyase and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN108285900AImprove thermal stabilityHigh level of activityHydrolasesGenetic engineeringHeterologousAlginate lyase
The invention discloses a recombinant alginate lyase and a construction method and an application thereof, which belong to the technical field of biology. The alginate lyase Aly-Cob is derived from anenvironment sample (a mixture of sea-tangle stacking place and factory production waste material). By using a gene engineering technology, a gene of the alginate lyase is cloned to an expression vector, and a recombinant bacterial strain for heterogenous expression of the alginate lyase is obtained. The alginate lyase Aly-Cob produced by the bacterial strain through fermentation has the functionfor degrading sodium alginate to prepare alginate oligosaccharide. The provided alginate lyase Aly-Cob can be widely used for the fields of agriculture, food, feed addition, medicine and alga processing.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com