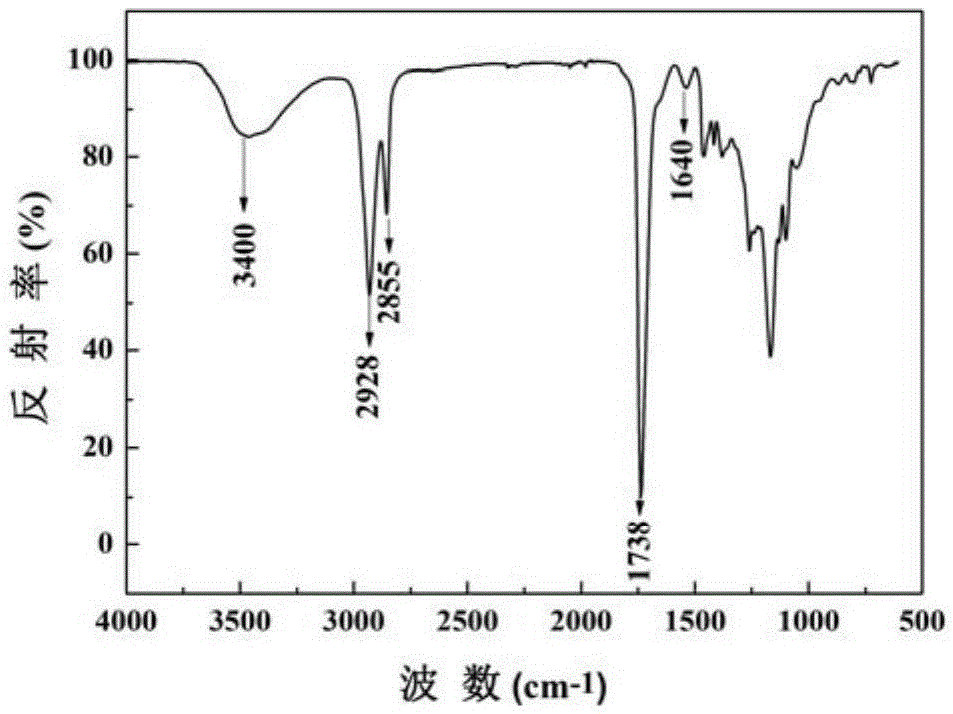
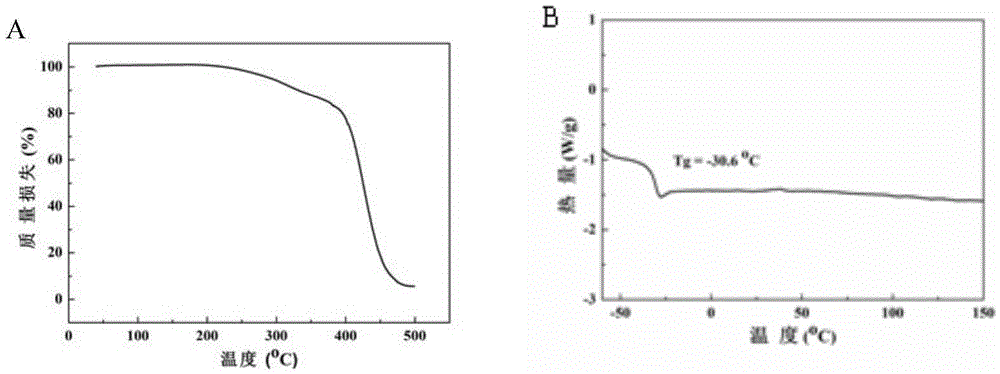
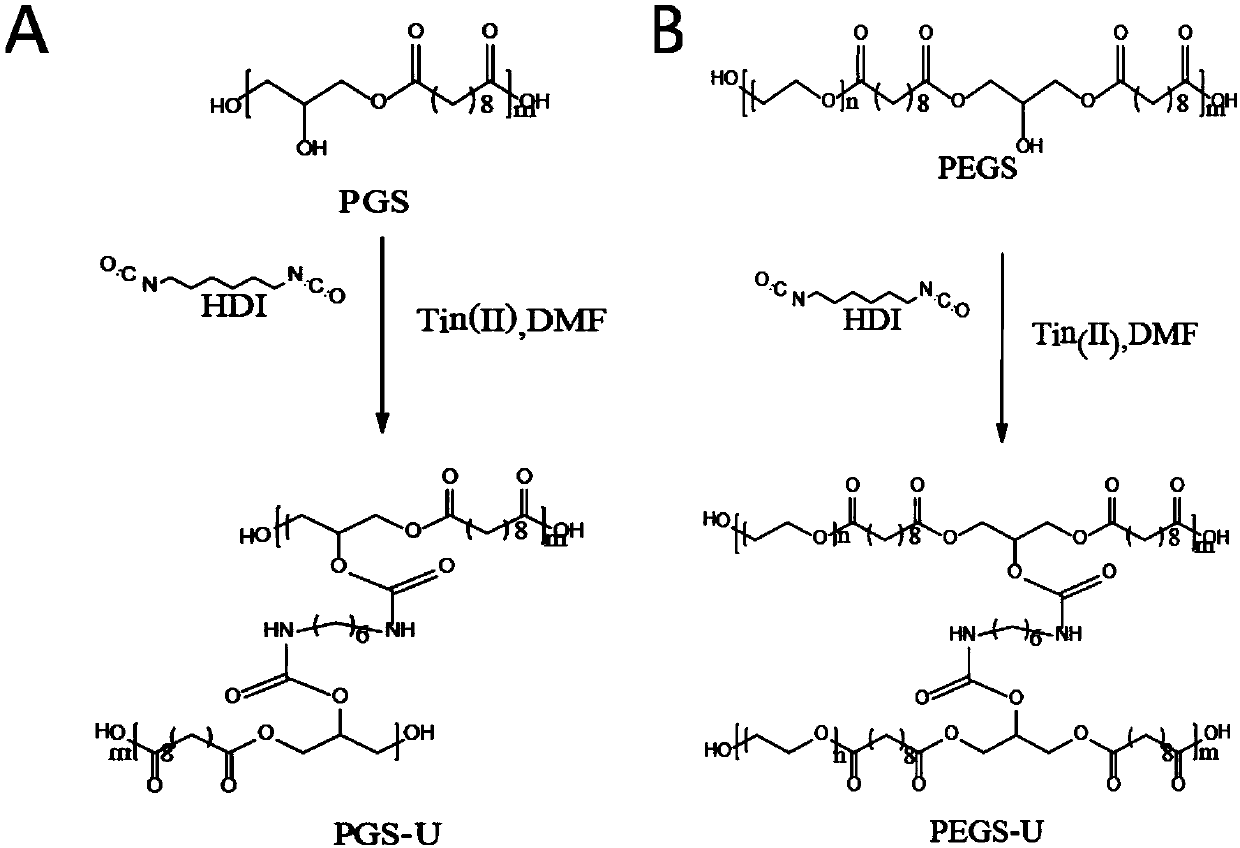
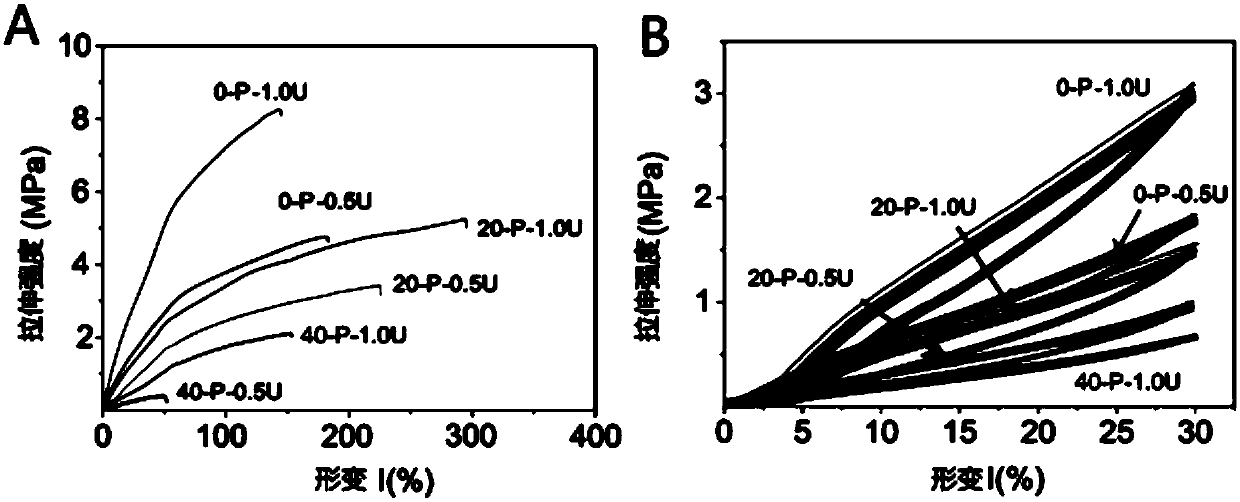
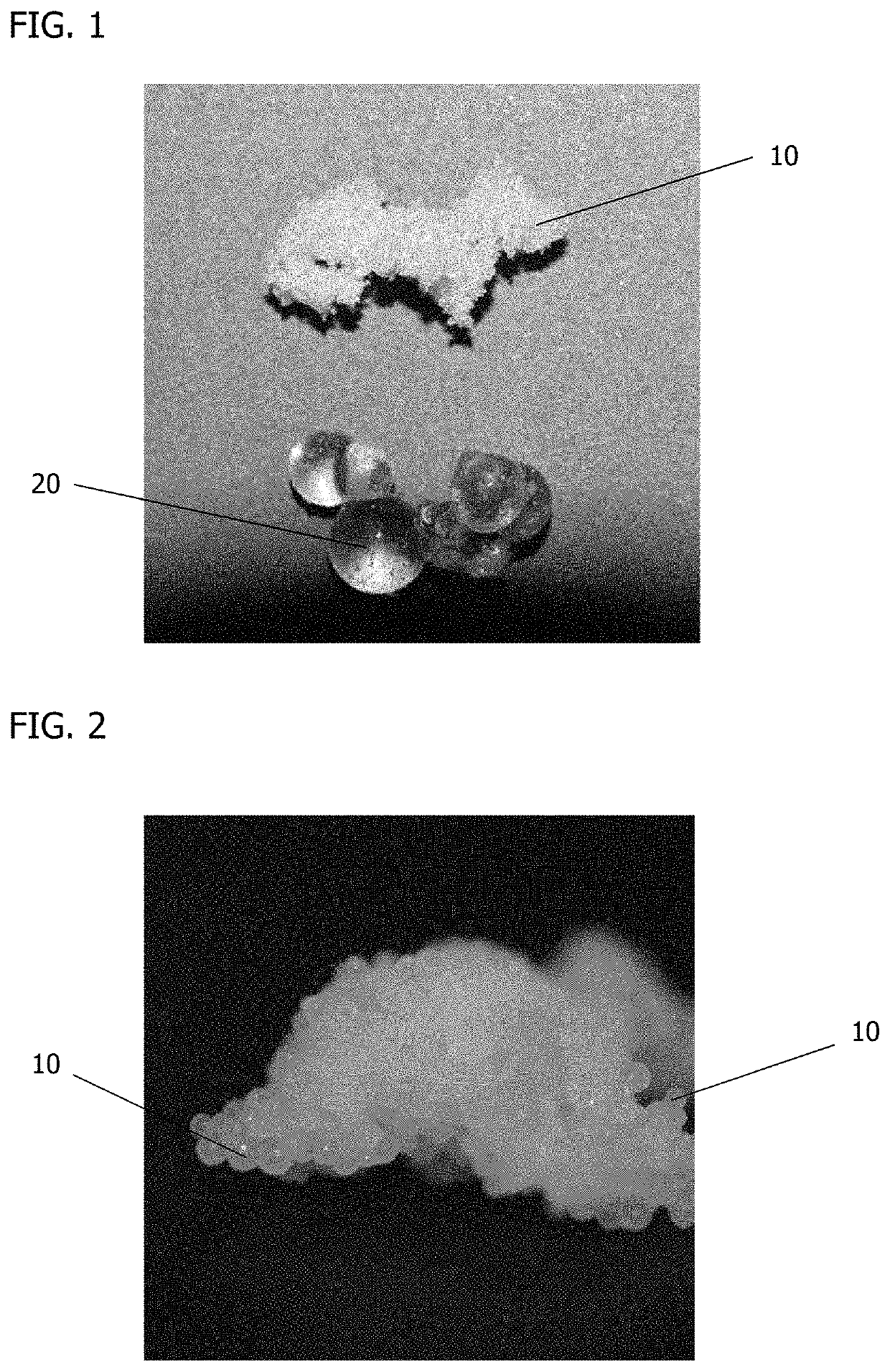
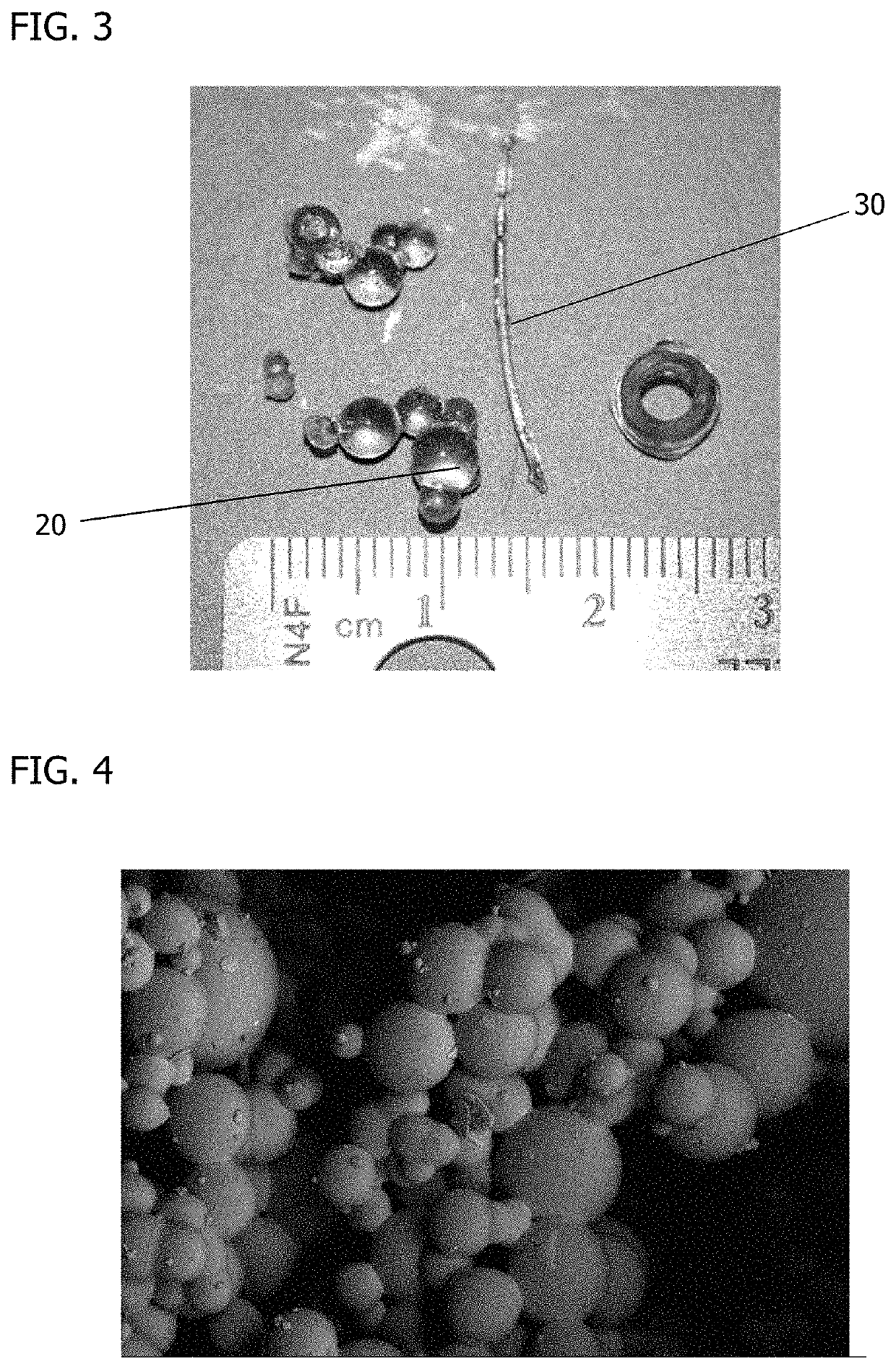
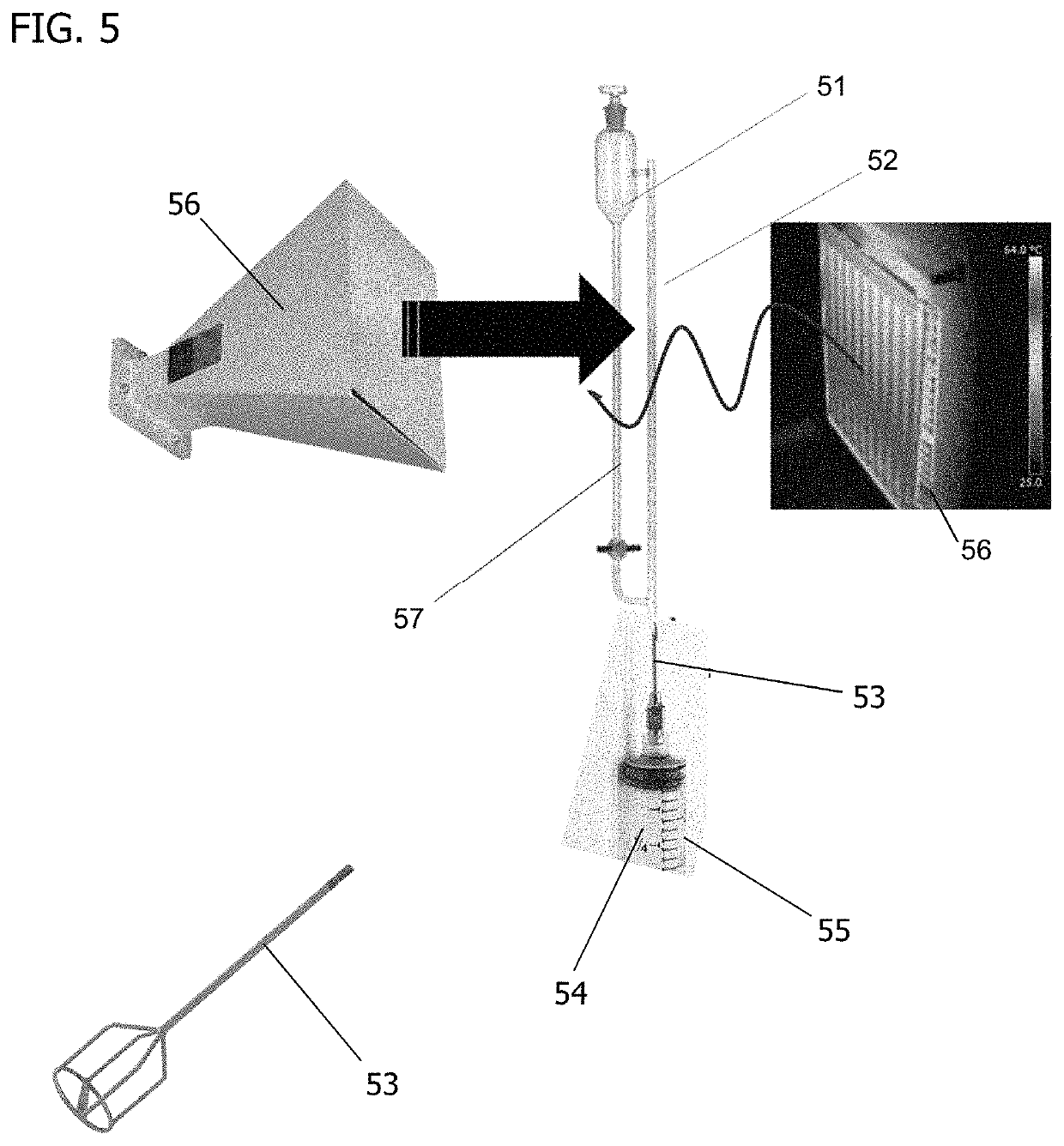
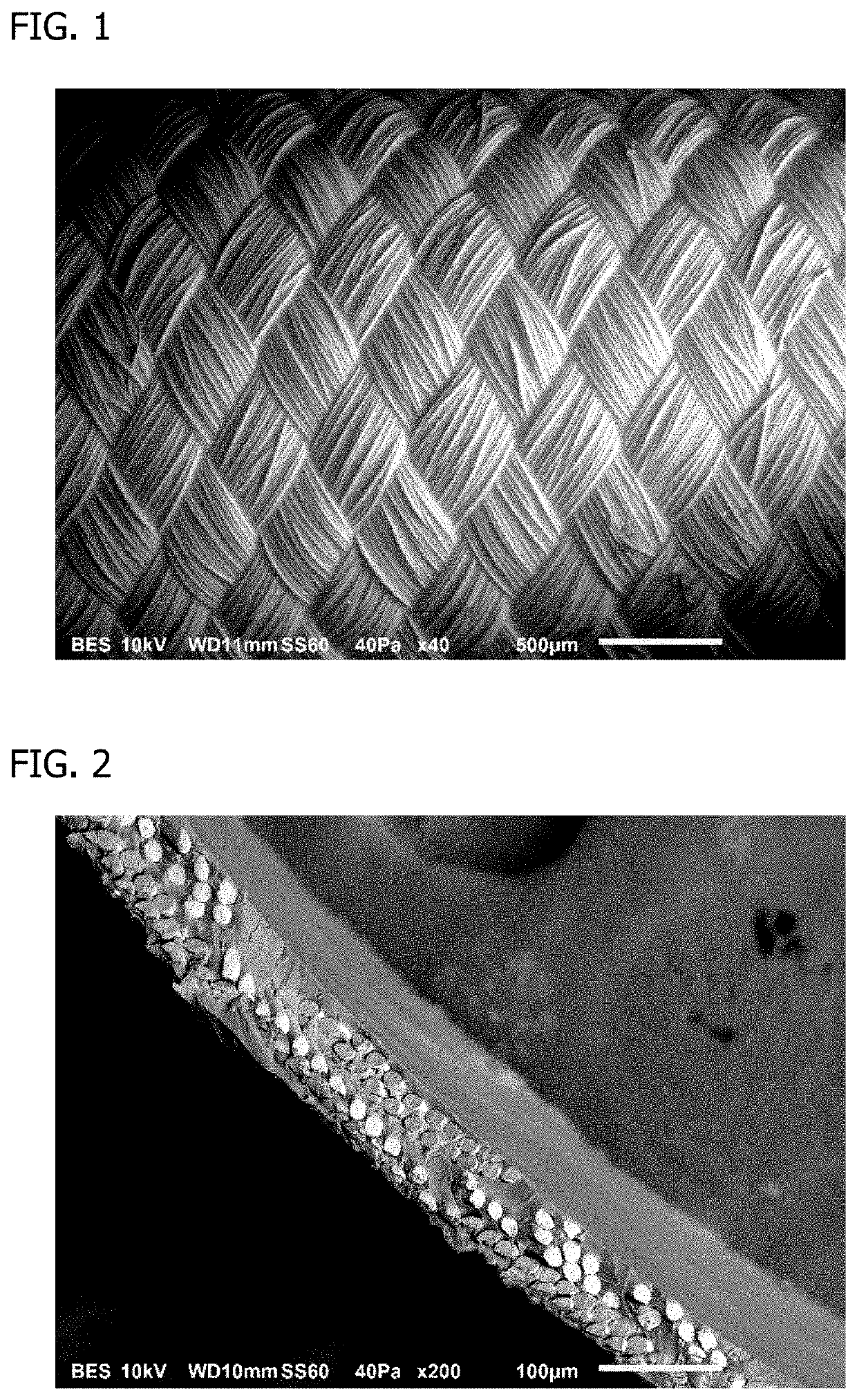
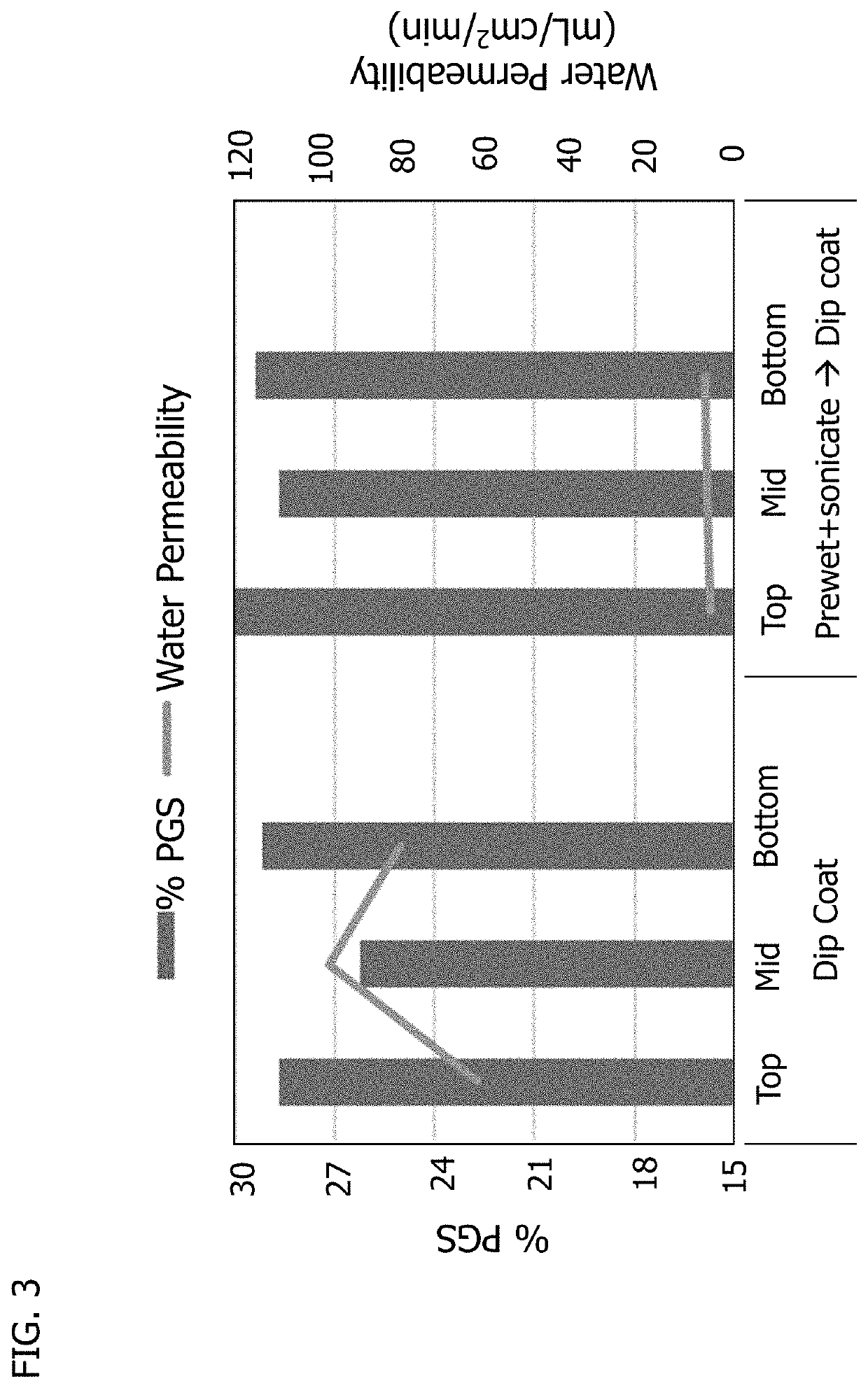
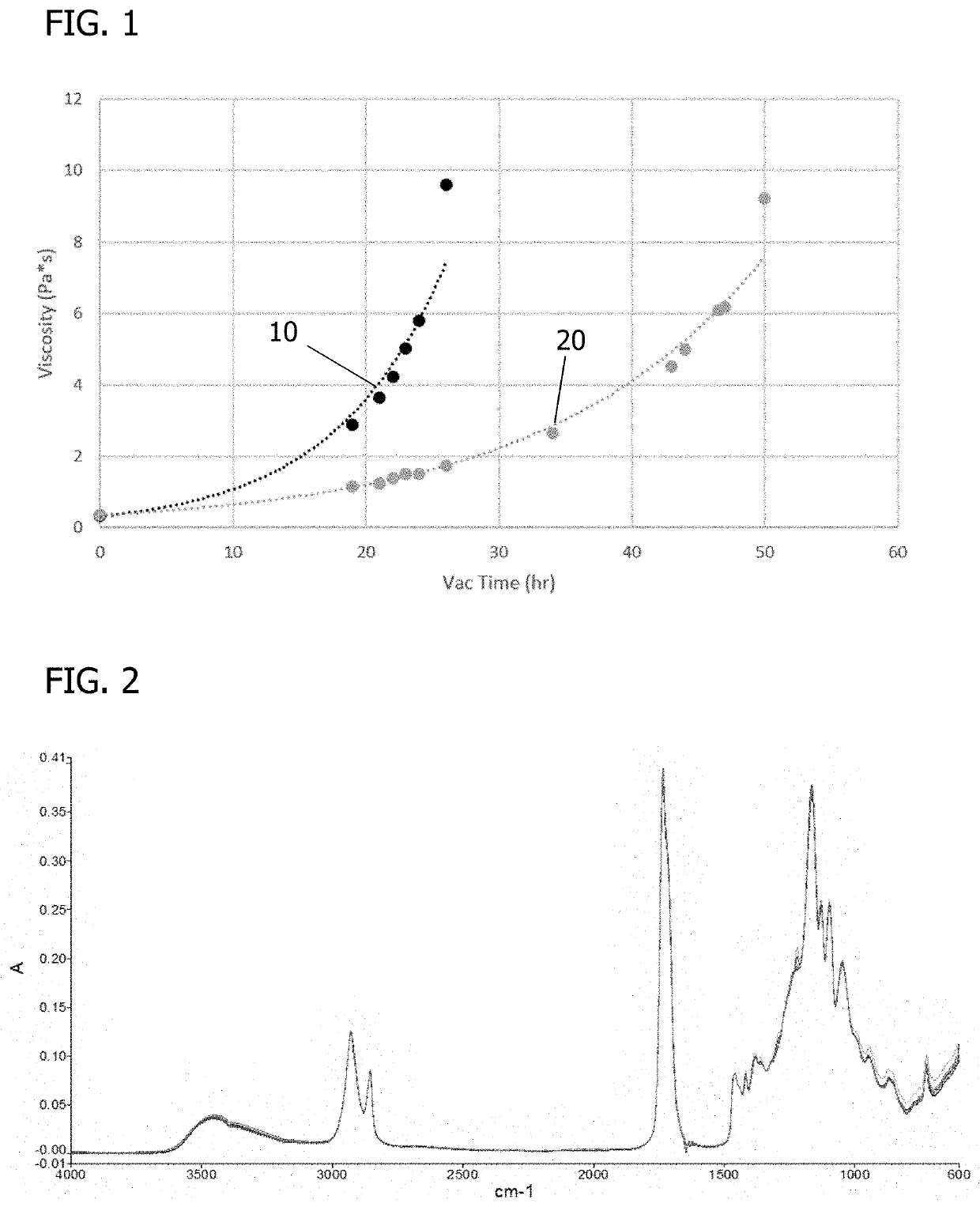
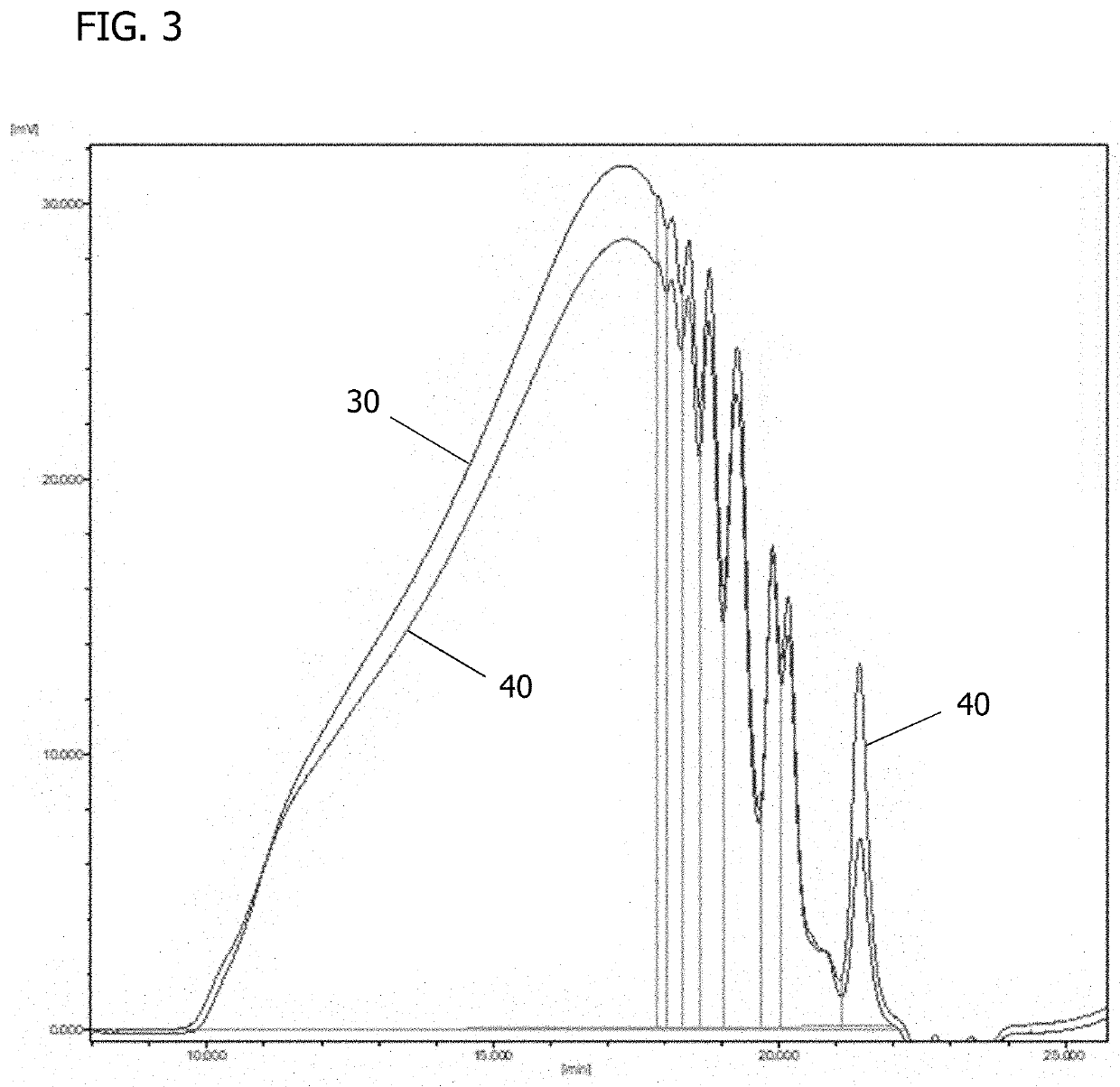
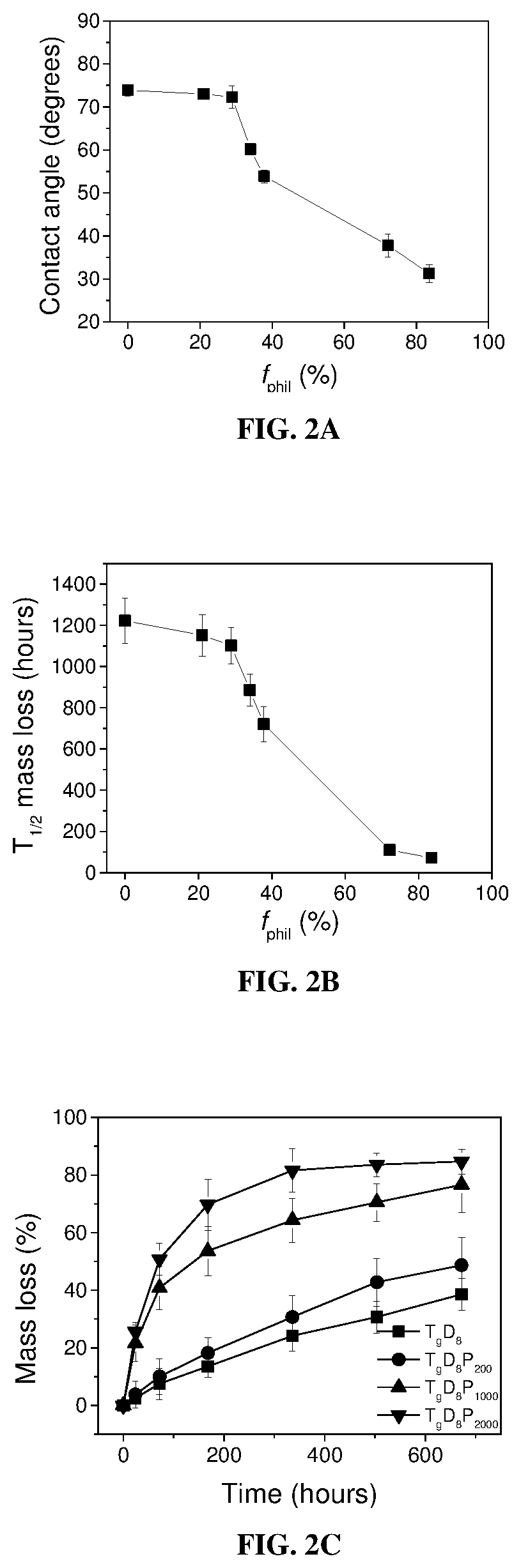
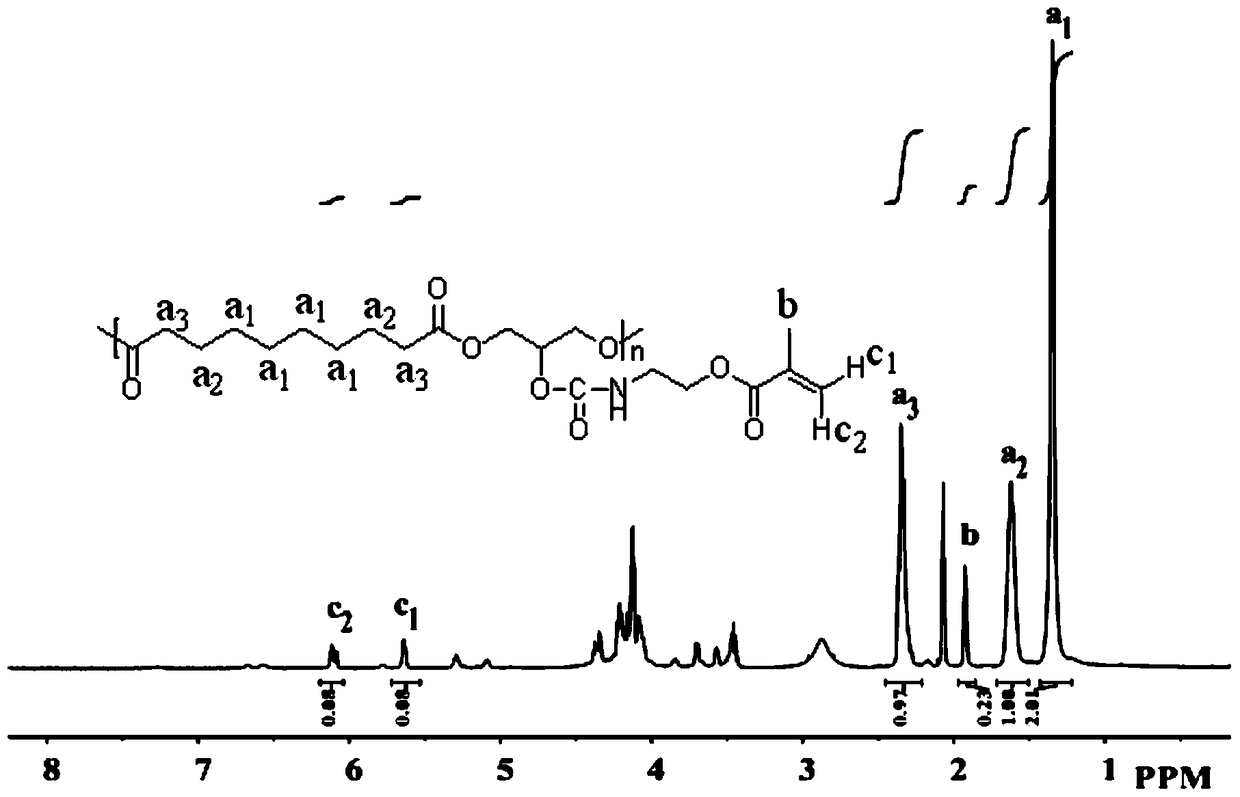
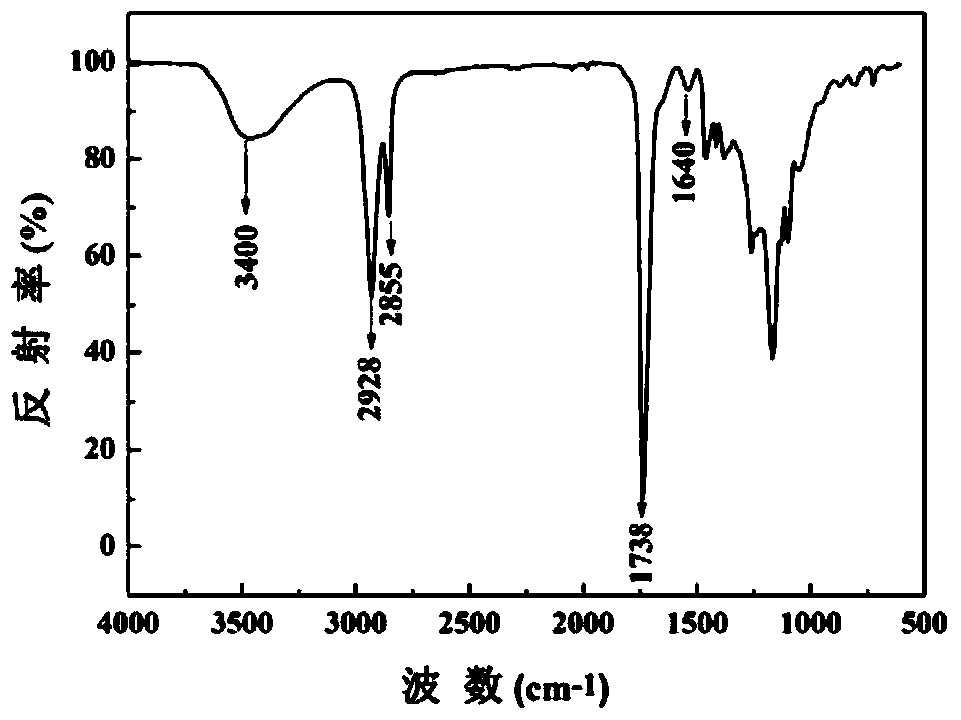
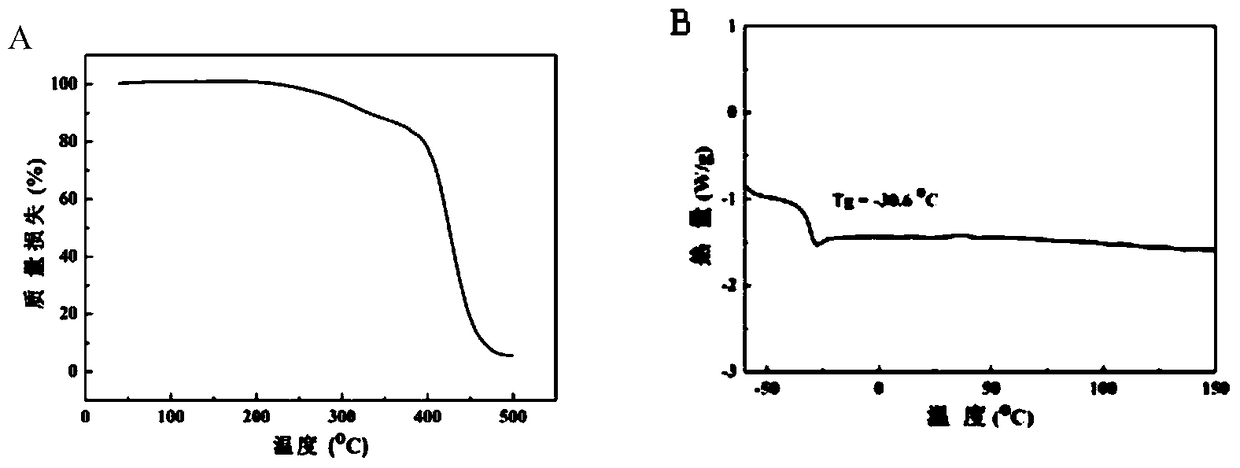
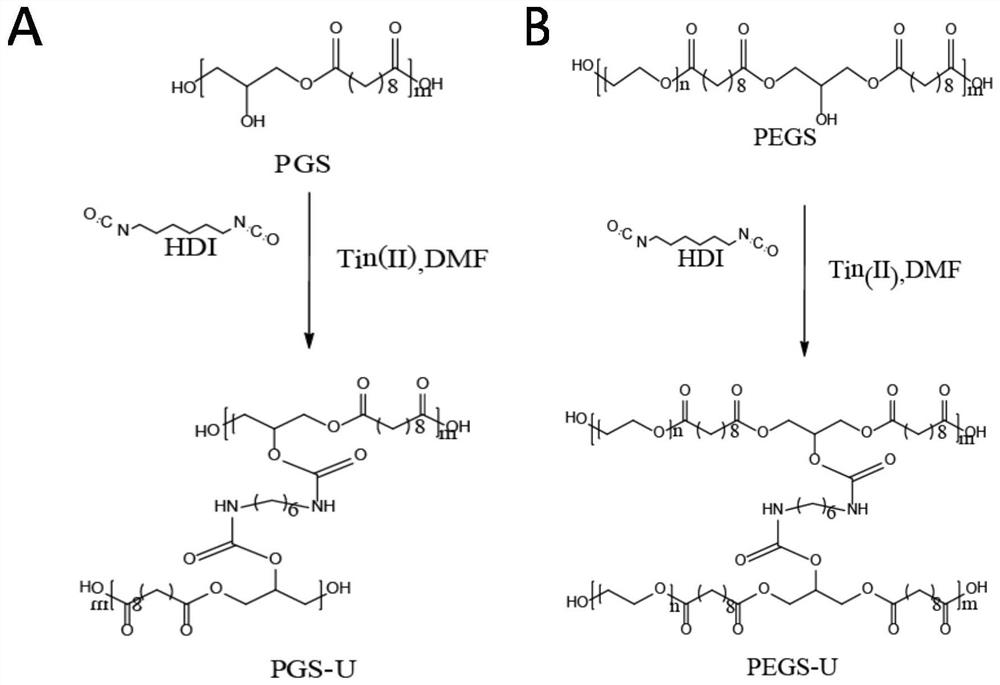
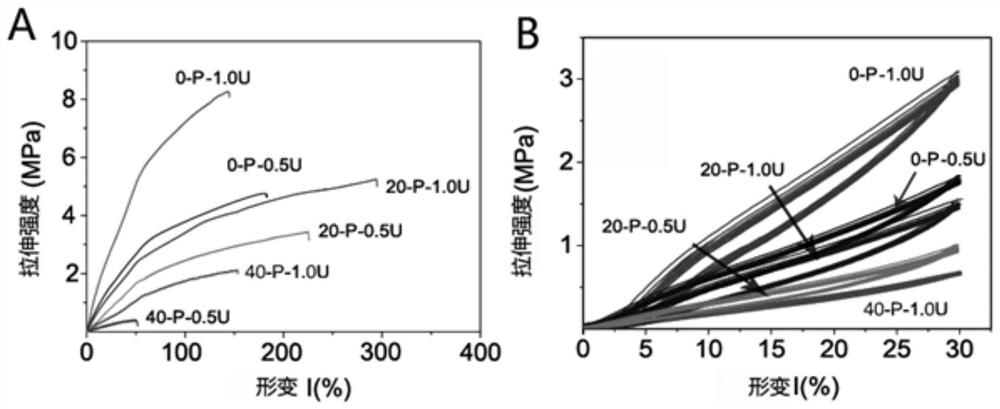
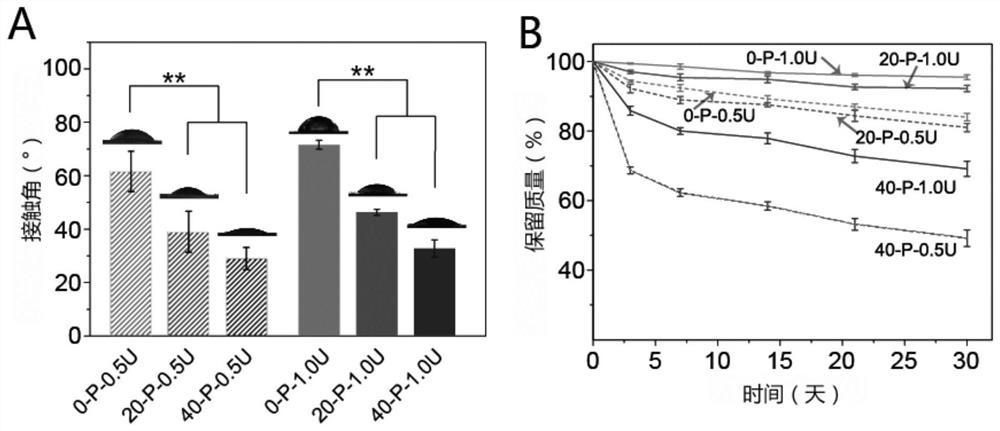
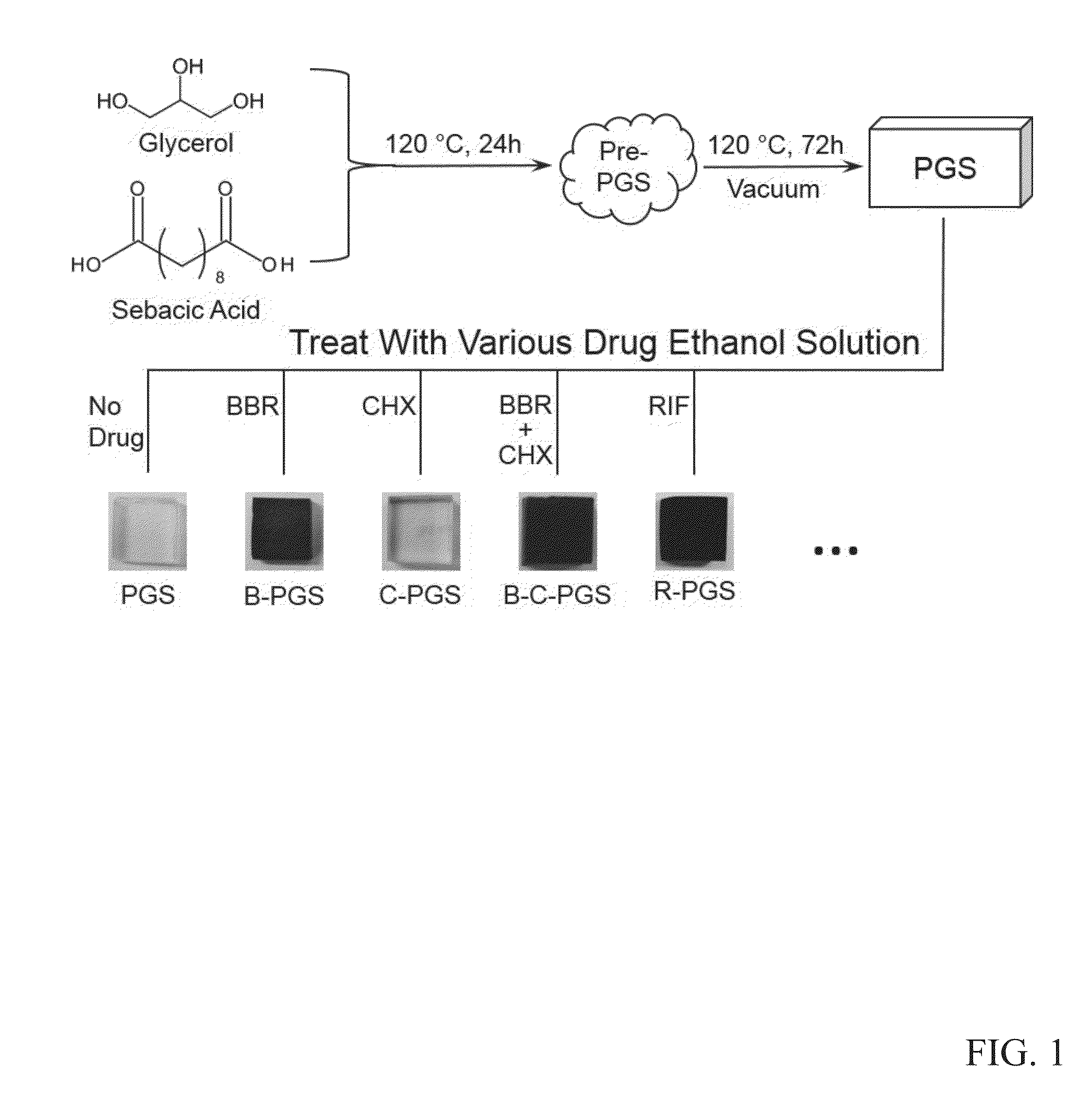
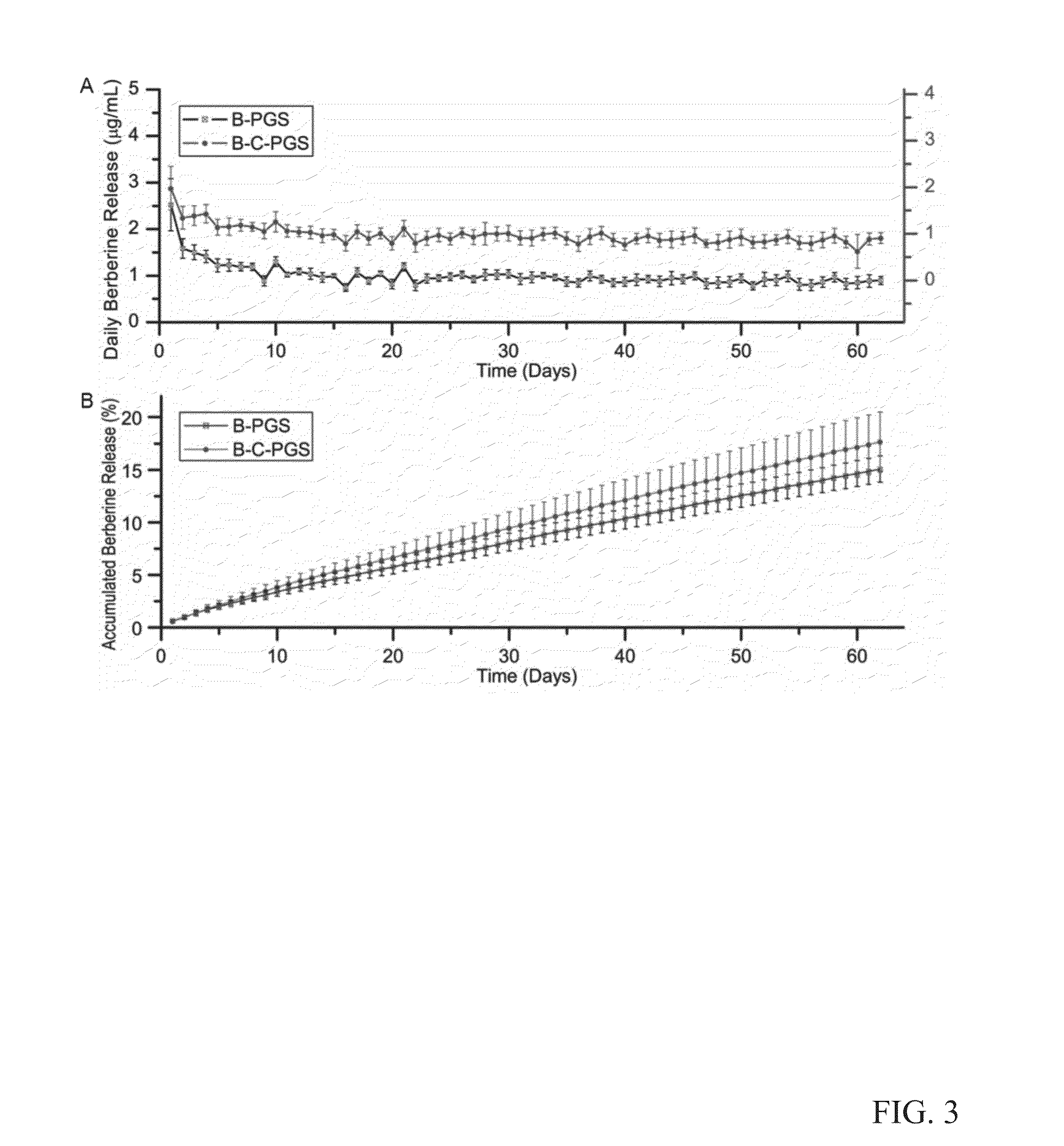
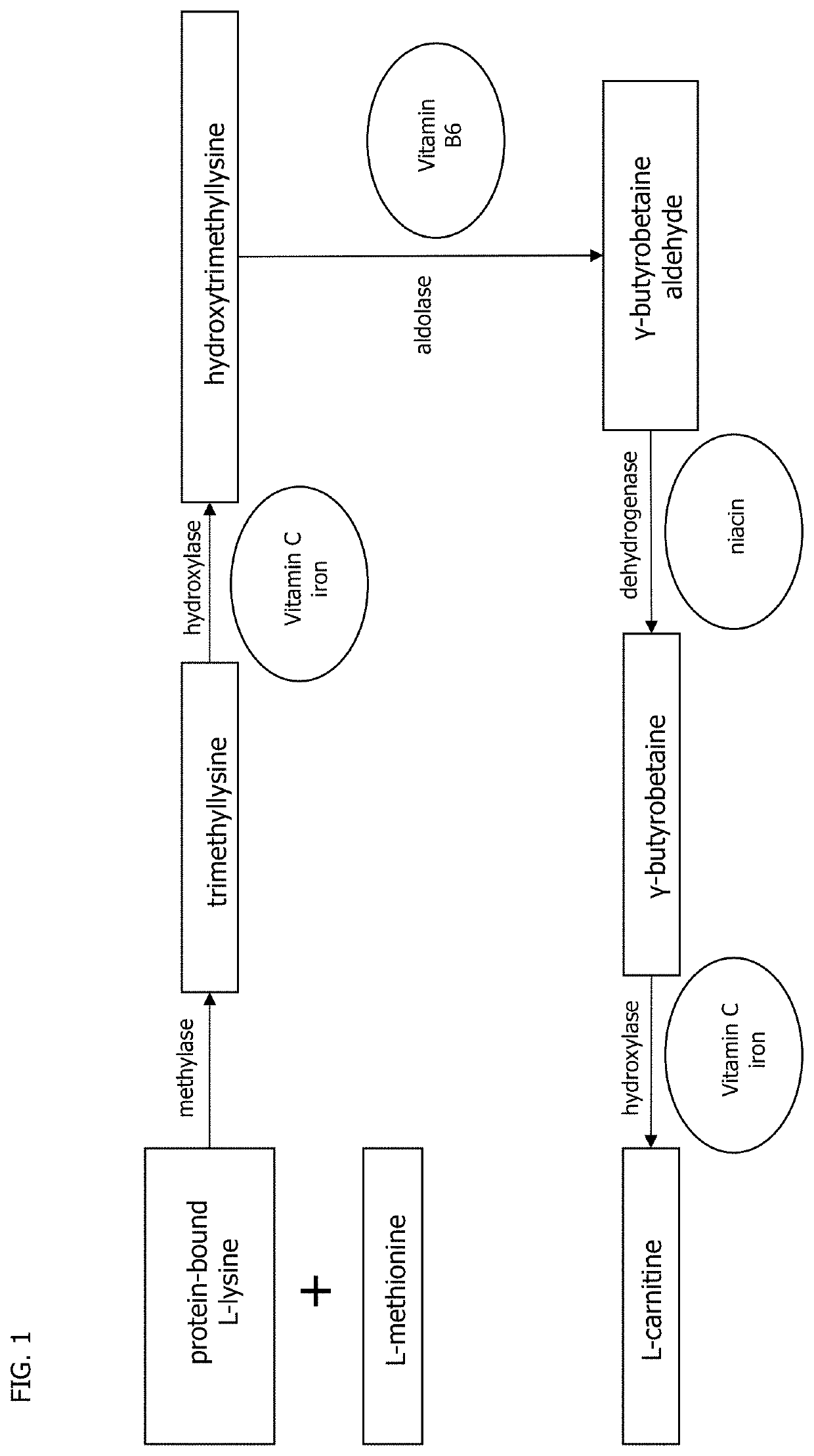
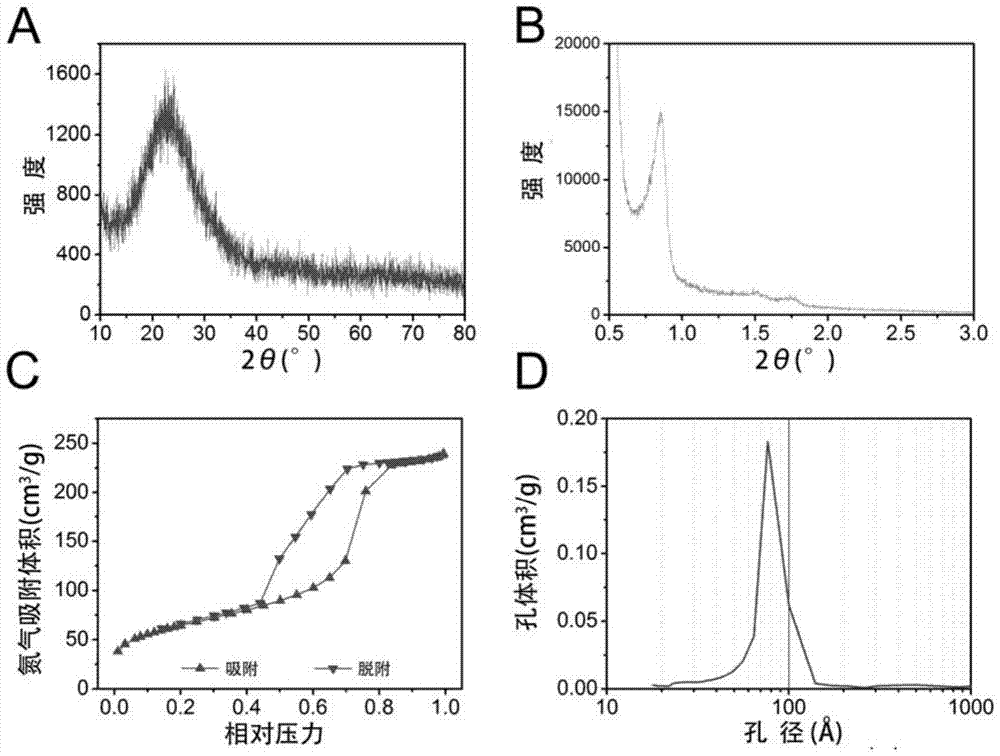
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Poly(glycerol-sebacate)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
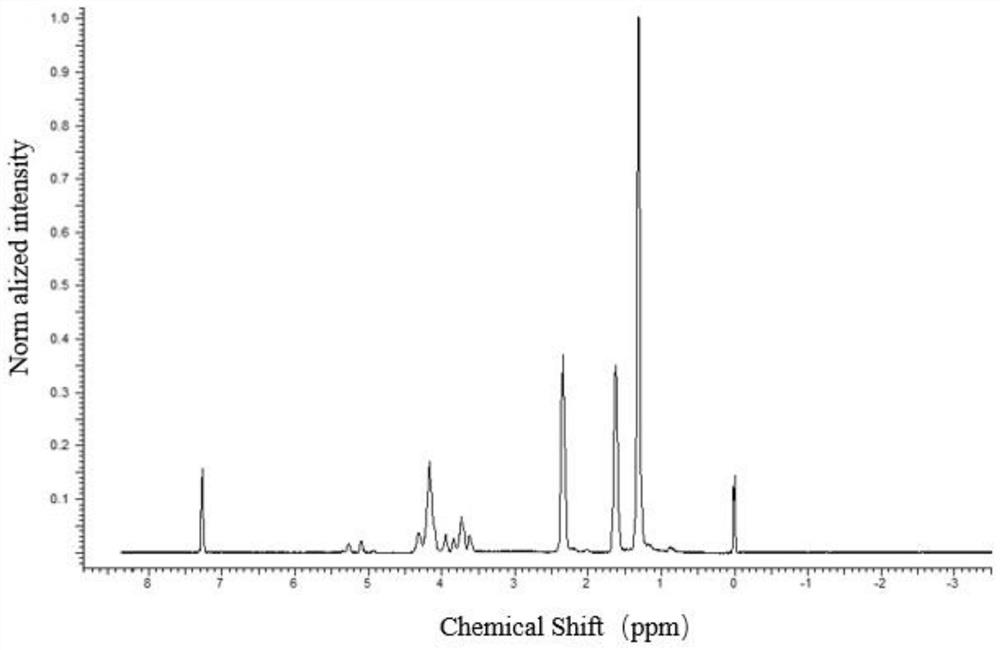
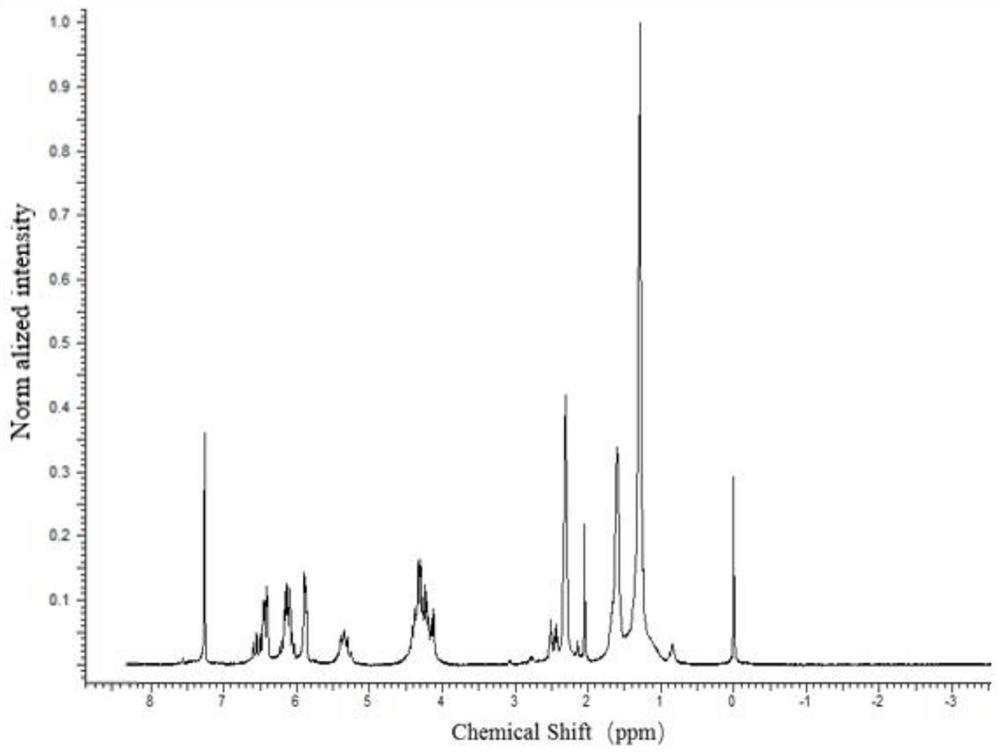
Poly(Glycerol Sebacate) in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine By: Yadong Wang, Steven Lu, Peter Gabriele, Jeremy J. Harris , Material Matters, 2016, 11.3 Yadong Wang, 1 Steven Lu, 2 Peter Gabriele, 2 Jeremy J. Harris 2 *
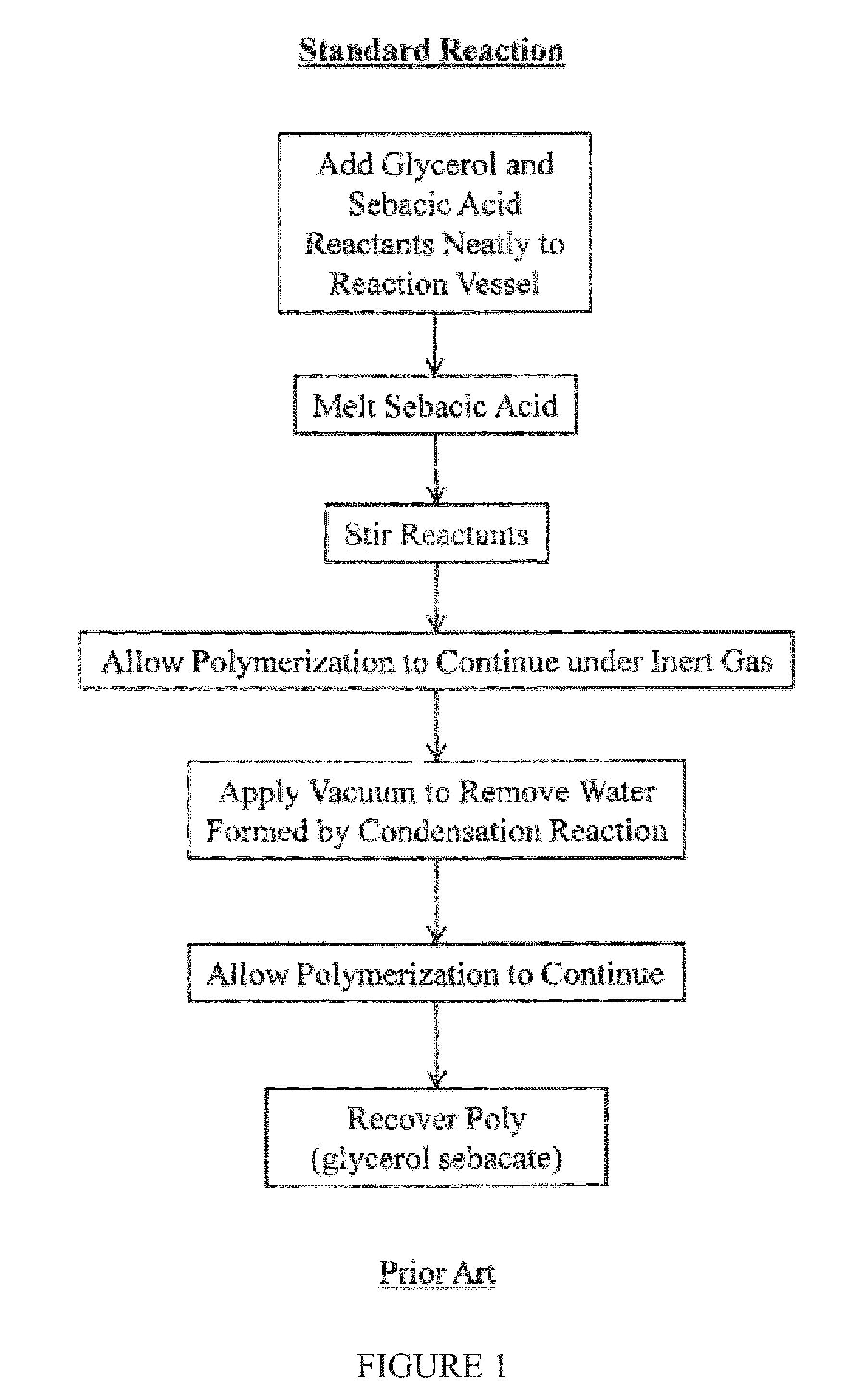
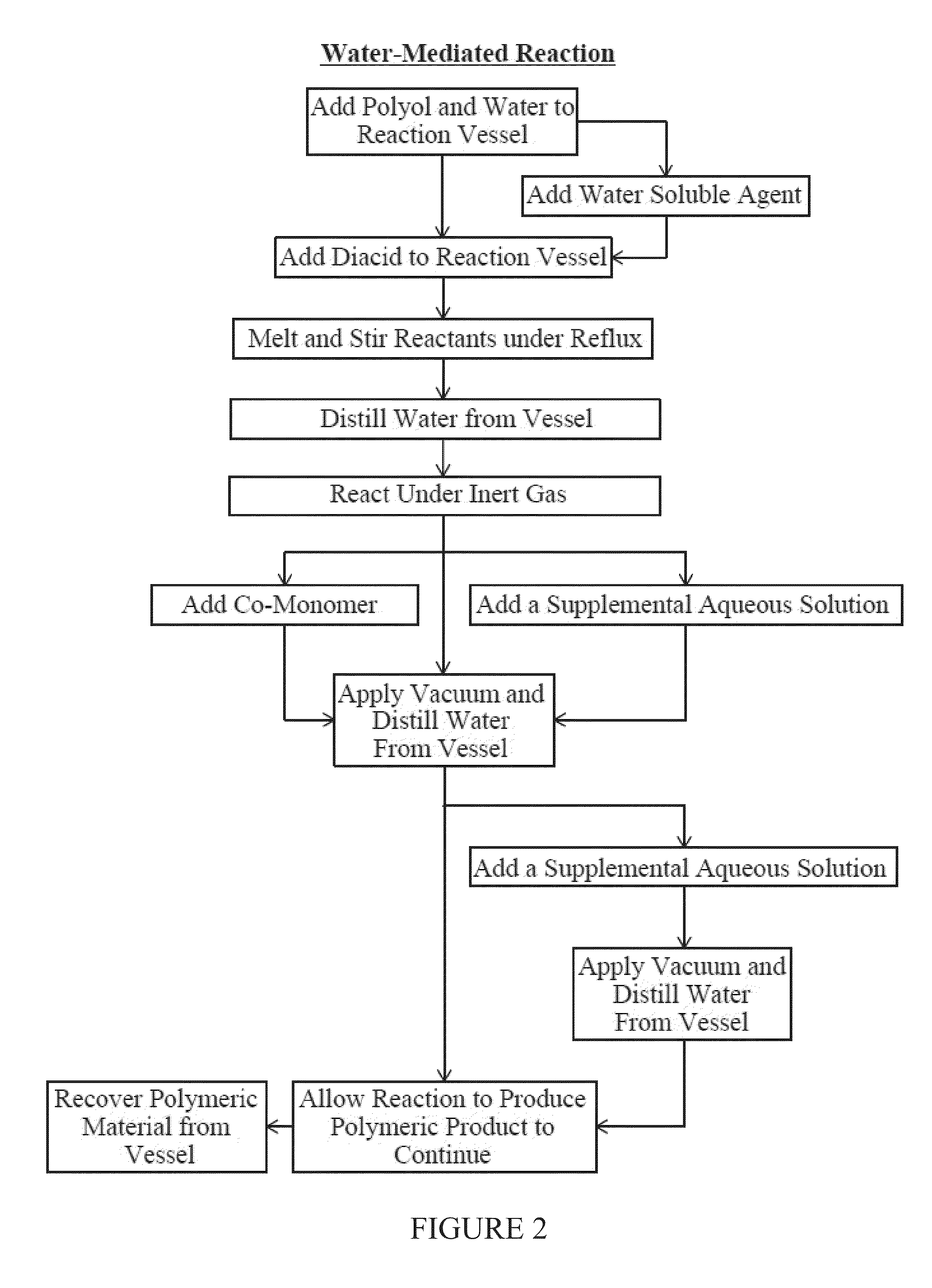
Water-mediated preparations of polymeric materials
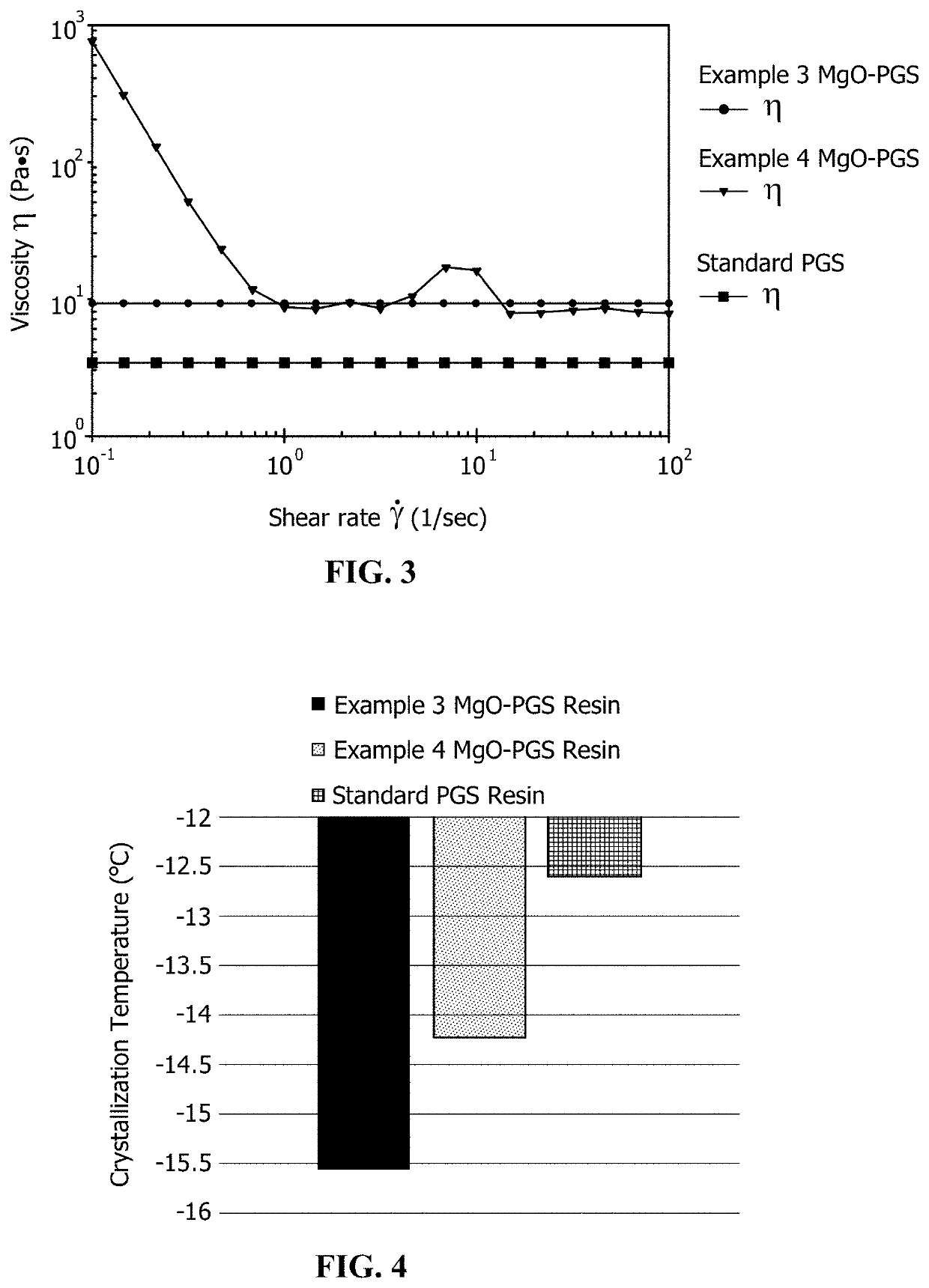
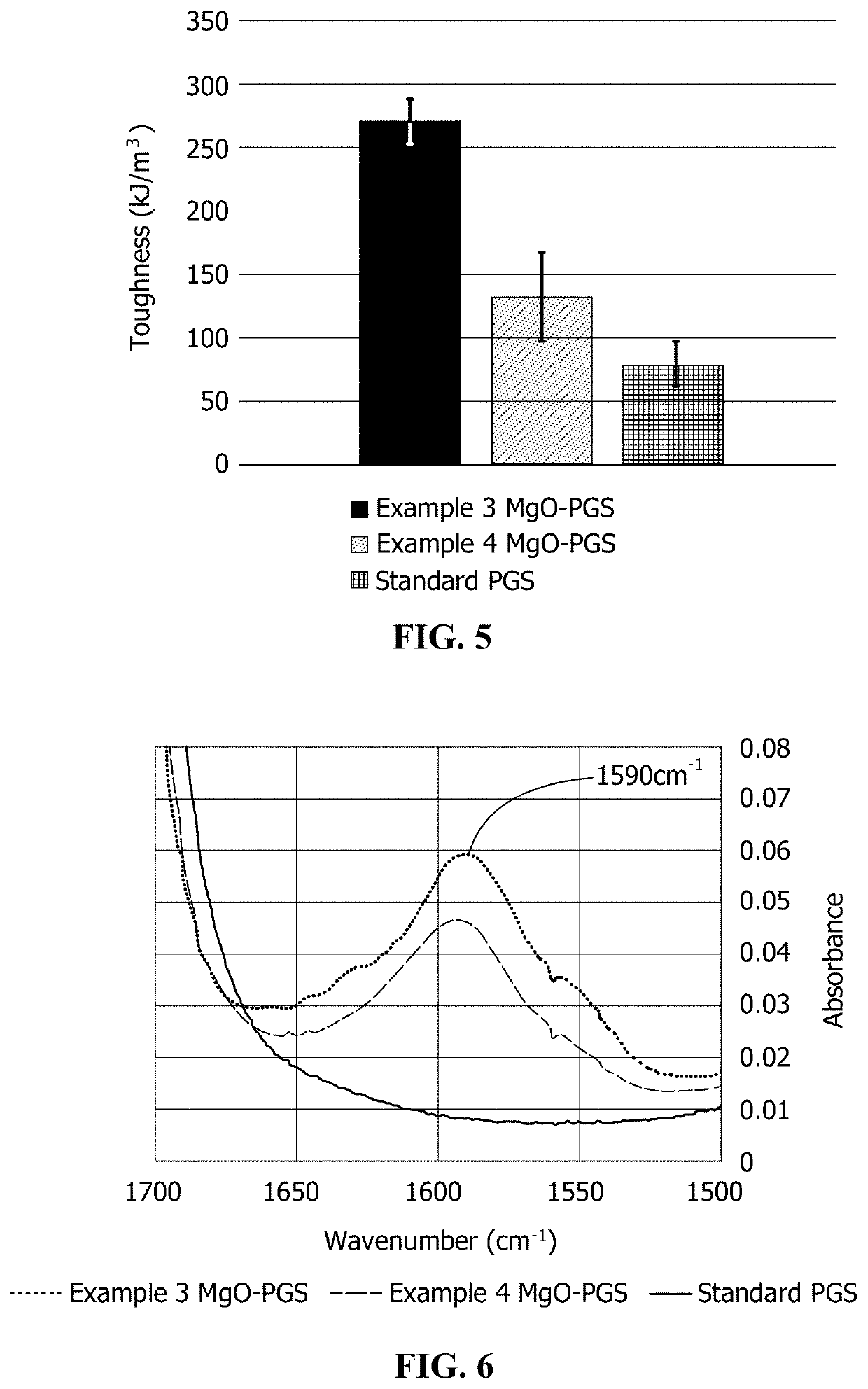
A process is provided for preparing a polymeric material through a water-mediated polymerization process that includes combining an alcohol monomer and an aqueous solution in a vessel, adding an acid monomer to the vessel, removing water from the vessel and producing the polymeric material from the vessel, wherein the polymeric material comprises a polyester of the alcohol monomer and the acid monomer. The methods described herein are particularly suitable for polymerization of poly(glycerol sebacate).
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
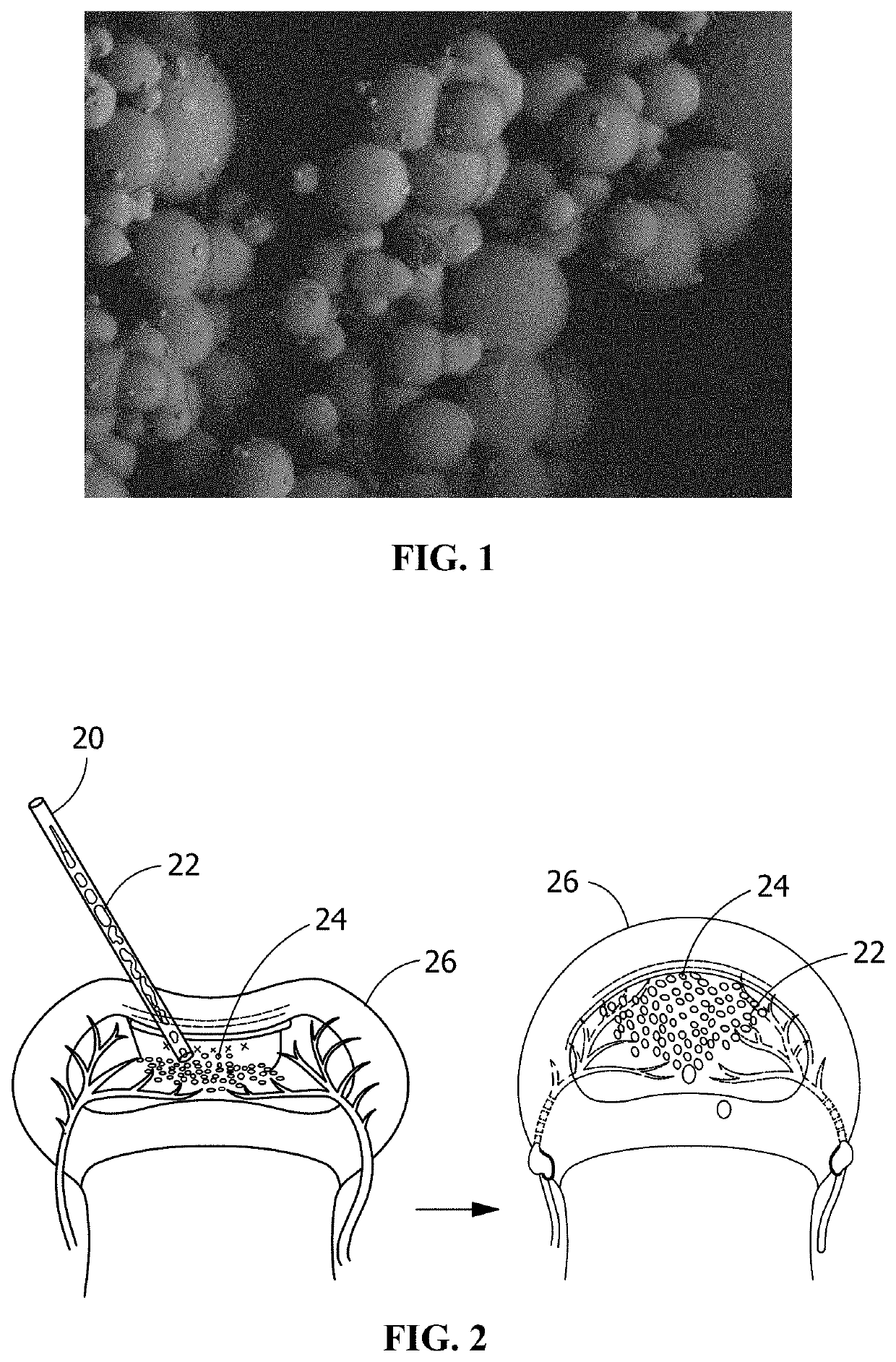
Preparation method of nanofiber scaffold for heart tissue engineering
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nanofiber scaffold for heart tissue engineering. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the nanofiber scaffold from poly(glyceroi sebacate) (PGS) / a gelatin nanofiber scaffold material with different components through electrostatic spinning, and crosslinking the nanofiber scaffold in a mixed solution of hydrochlorinated N,N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethyl-carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) to obtain the nanofiber scaffold. The nanofiber scaffold related by the invention can be used for promoting the formation of sarcomere and has wide prospects on the aspect of being used as a material for cardiac muscle cell regeneration and repair.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
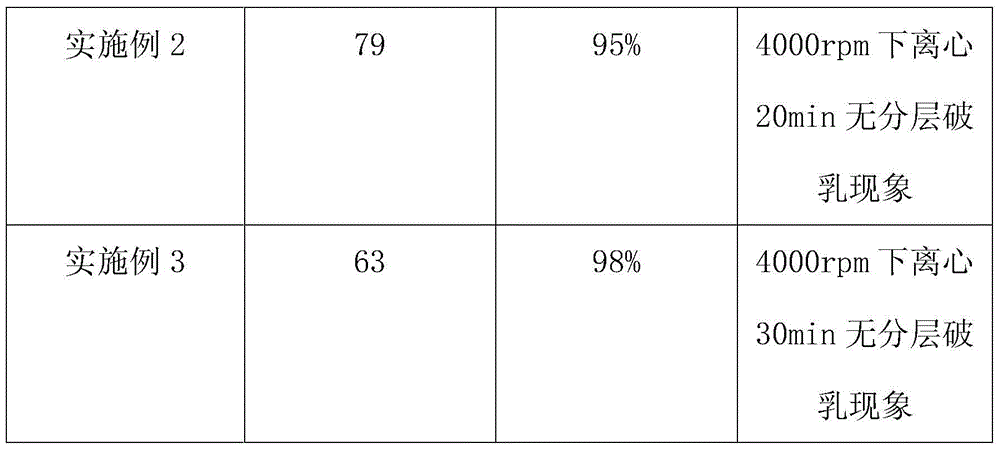
Glabridin micro-emulsion and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103976892AHigh content of glabridinNo delamination and demulsificationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEmulsionSulfite
The invention relates to glabridin micro-emulsion and a preparation method thereof. The glabridin micro-emulsion consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 10wt%-15wt% of glabridin, 10wt%-15wt% of stearic polyoxypropylene sulfite, 7wt%-11wt% of polydecyldiacid glyceride, 6wt%-9wt% of Twain 85, 12wt%-16wt% of propylene glycol and the balance of deionized water. The preparation method of the glabridin micro-emulsion comprises the steps of mixing and vortex oscillation, and the prepared glabridin micro-emulsion is high in encapsulation efficiency, good in stability and capable of being added into cosmetics as an ingredient for improving the stability of the glabridin.
Owner:WUJIANG YINGLIDA PLASTIC PACKAGING
Biodegradable photocurable medical adhesive and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN105561377ASimple preparation processMaterials are readily availableSurgical adhesivesPolymer scienceAdhesive
The present invention relates to a biodegradable photocurable medical adhesive and preparation and application thereof, the adhesive is poly-glycerol-sebacate-grafted methyl acrylate (2-isocyano ethyl) ester (PGS-IM); the molecular structure is shown in the specification, poly glycerol sebacate (PGS) is added into a solvent, under nitrogen protection, then placed in an oil bath and stirred until the PGS is dissolved, then methyl acrylate (2-isocyano ethyl) ester is added for reaction for 15-120min, and the biodegradable photocurable medical adhesive can be obtained after purifying and drying. PGS-IM is viscous semi-solid at room temperature, is convenient to apply, and is Blu-ray or UV curable, free of damage to a tissue and rapid in curing, and after curing, adhesion properties are good.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Isocyanate crosslinked polyethylene glycol-polyglycerol sebacate bio-elastomer as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110078880APromote regenerationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiocompatibility TestingPolyethylene glycol
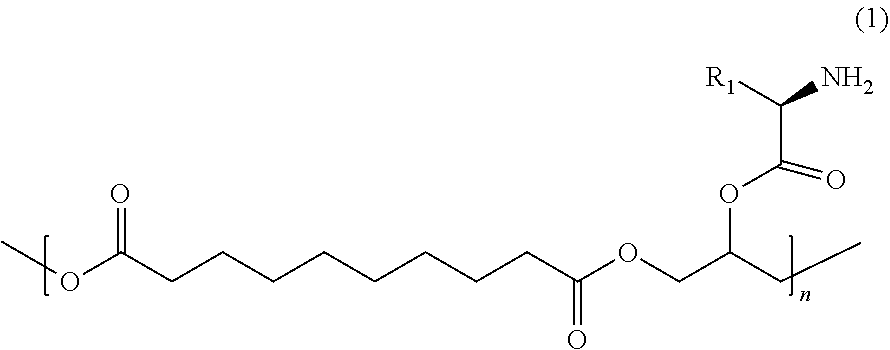
The invention discloses an isocyanate crosslinked polyethylene glycol-polyglycerol sebacate bio-elastomer as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The structure of the bio-elastomeris shown in formula I, wherein n is an integer of 10-80; m is an integer of 2-14. The bio-elastomer has the advantages that mechanical strength, hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity, degradation behavior, cell behavior and biocompatibility can be regulated and optimized through the content of isocyanate and polyethylene glycol, and is a soft tissue repair material with great clinical application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
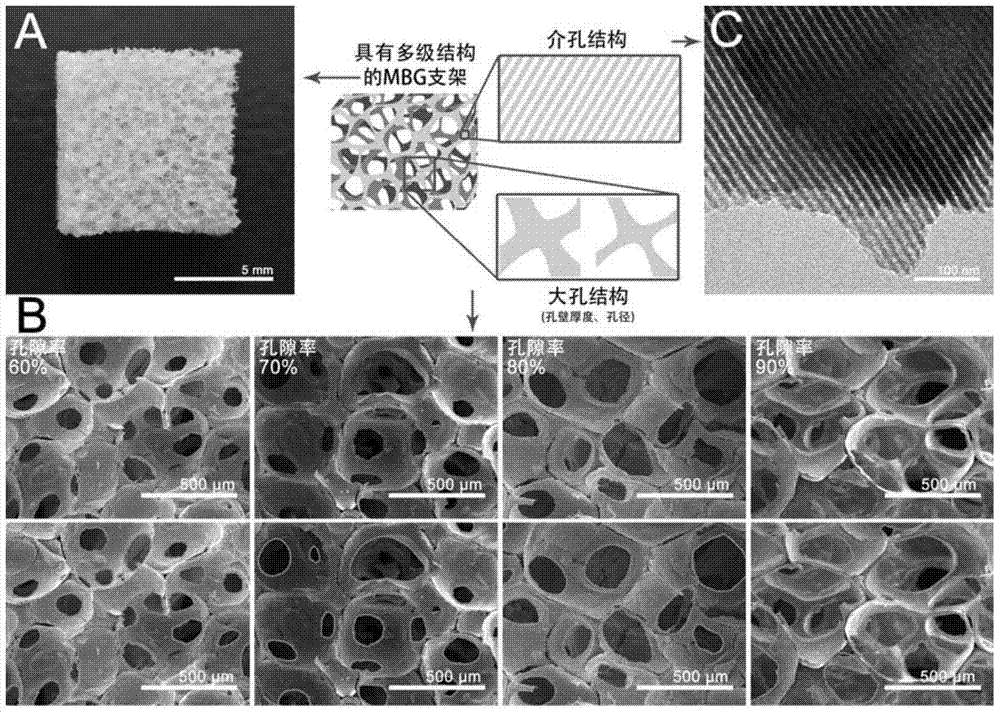
Mesoporous bioactive glass/poly-decyl diacid glyceride composite support as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104645417AMechanical Strength RegulationAdjustable mechanical strengthPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisDrug release rateCell adhesion
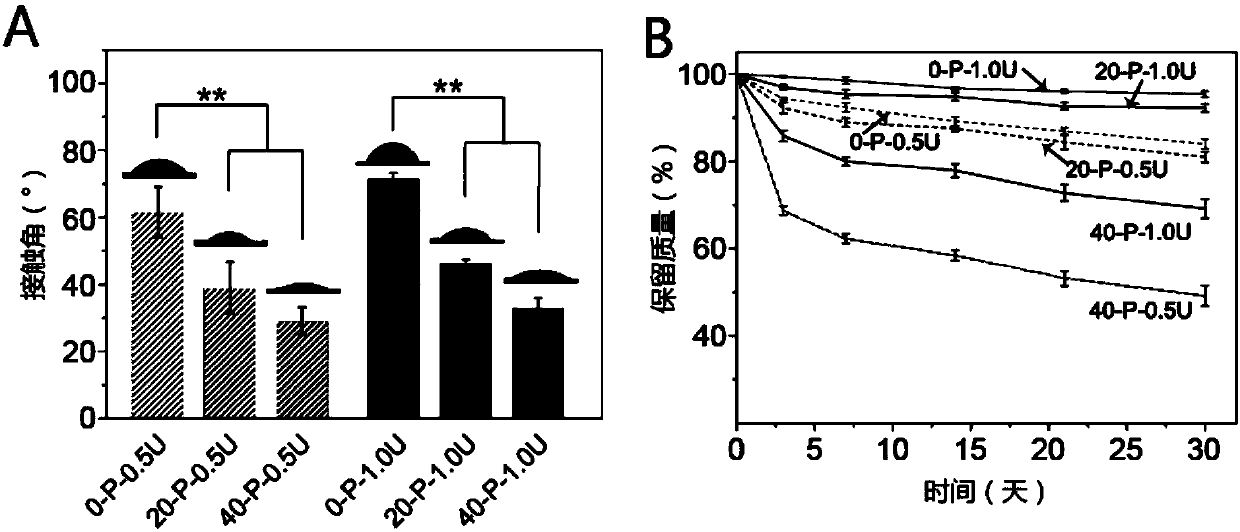
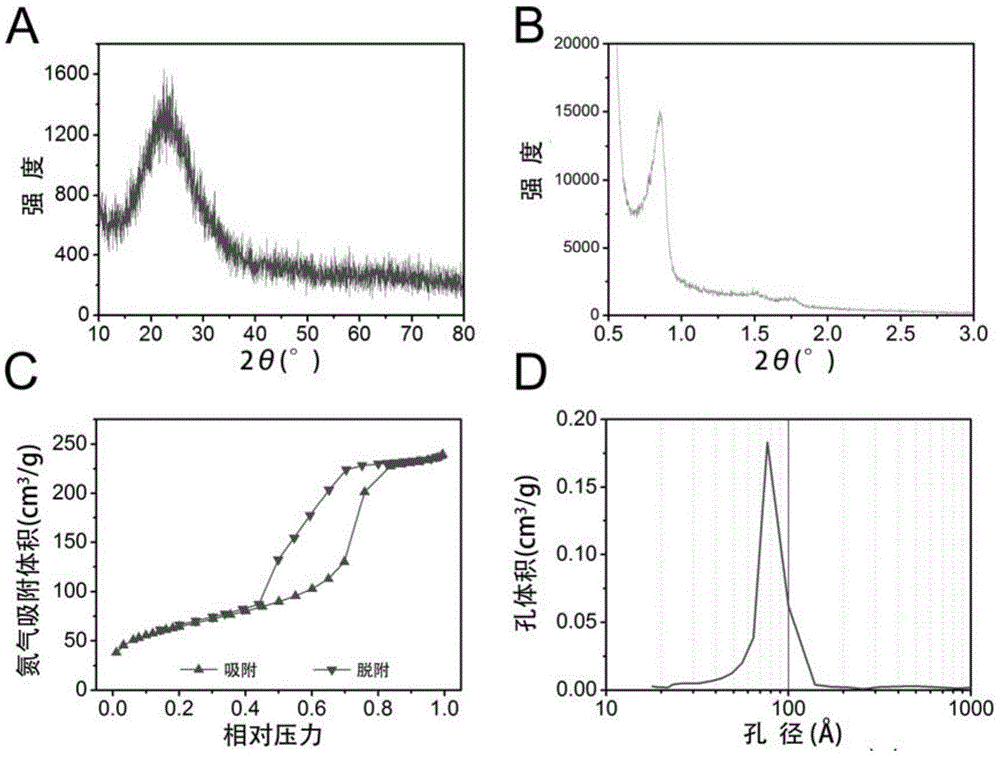
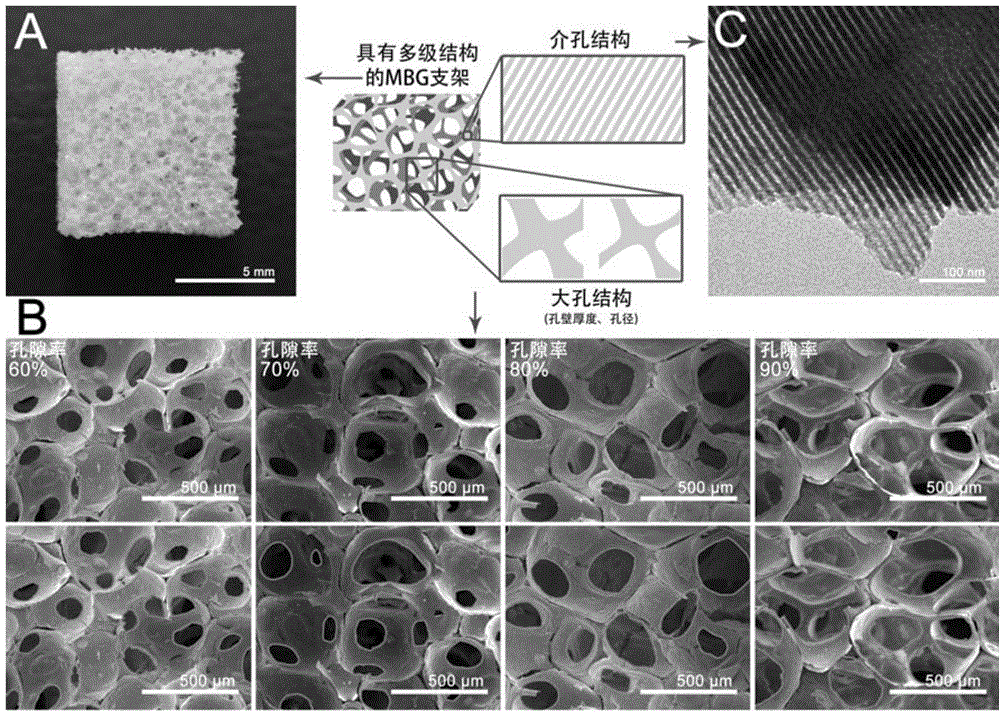
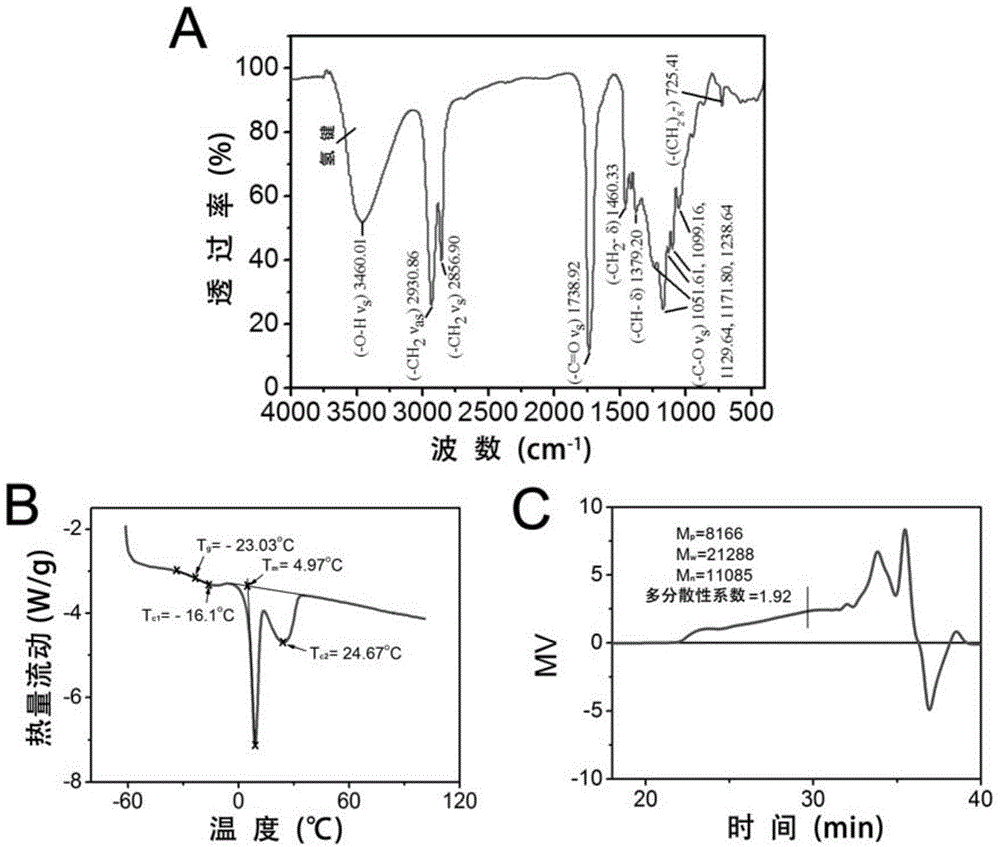
The invention discloses a mesoporous bioactive glass / poly-decyl diacid glyceride composite support as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The composite support of the invention uses a mesoporous bioactive glass porous support as a matrix and compounds poly-decyl diacid glyceride on the mesoporous bioactive glass porous support. Mechanical strength, degradation rate, drug release rate, cell behavior and the like of the composite support of the invention can be adjusted by pore wall thickness of the mesoporous bioactive glass matrix and thickness of the poly-decyl diacid glyceride coating. A PGS coating is utilized to successfully solve the problem of brittleness of an MBG support, so that mechanical strength of the composite support is adjustable in a load bearing range of a trabecular bone. According to the invention, adjustment to degradation rate and release rate of proteins immobilized in MBG mesopore can be realized and activities of the immobilized proteins free of influence from a moderate coating operation can be realized; and cell experiments prove that the PGS coating is capable of promoting cell adhesion and proliferation on surface of the support without affecting osteogenic activity of the MBG.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Modified polyethylene glycol-poly glyceride sebacate (PEGS) injectable biological elastomer as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a modified polyethylene glycol-poly glyceride sebacate (PEGS) injectable biological elastomer as well as preparation and application thereof, wherein the modified polyethyleneglycol-poly (sebacic acid) (PEGS) injectable biological elastomer can be in-situ cured at body temperature. The biological elastomer is obtained by taking polyethylene glycol-poly glyceride sebacate (PEGS) as a matrix, and respectively performing sulfhydrylation and acrylation reaction on hydroxyl groups of the main chain or the side chain of the matrix, two modified PEGS can be mixed and then injected into a body and cured at the body temperature. The mechanical strength, hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity, degradation behavior, cell behavior and biocompatibility of the biological elastomer can be regulated and optimized through the content of polyethylene glycol and the proportion of carboxyl hydroxyl. The biological elastomer can be successfully prepared into injectable hydrogel materials for bone repair and tissue regeneration. The research results show that the modified polyethylene glycol-poly glyceride sebacate (PEGS) injectable biological elastomer is a tissue repair material with a very wide clinical application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
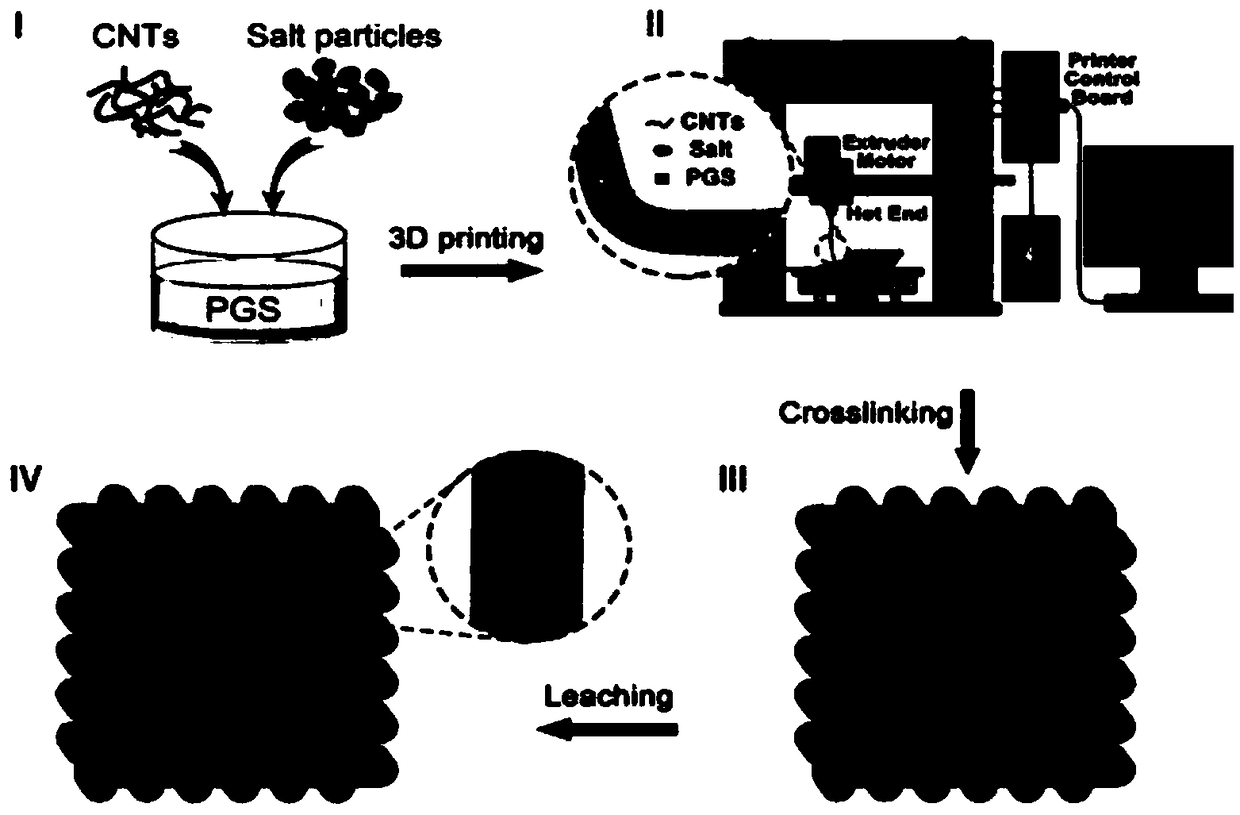
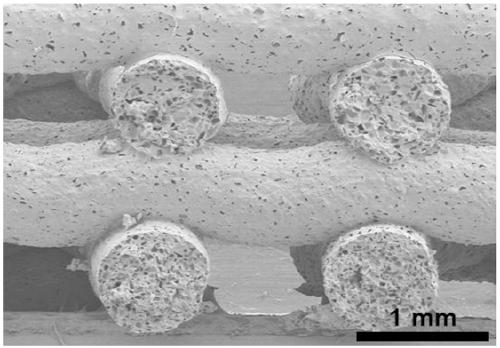
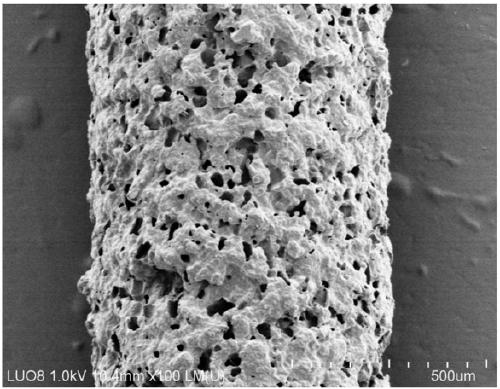
Poly(glycerolsebacate) 3D printing nano generator and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109233213ASimple preparation processIncrease elasticityAdditive manufacturing apparatusNanogeneratorCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a poly(glycerolsebacate) 3D printing nano generator and a preparation method and application thereof. The poly(glycerolsebacate) 3D printing nano generator is obtained by carrying out mixing, 3D printing, thermo-crosslinking and pore-forming agent dissolution on poly(glycerolsebacate) PGS, carbon nanotubes CNTs and a pore-forming agent in sequence. The poly(glycerolsebacate) 3D printing nano generator has high elasticity and electrical conductivity; and through the use of a 3D printing technology, the preparation process of most of the current flexible integrated TENGsis simplified, and the TENGs can be processed into complex and variable three-dimensional structures, so that the shape design has diversity and flexibility, thereby promoting the further developmentof flexible integrated 3DP-TENGs on wearable electronic devices.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Cured biodegradable microparticles and scaffolds and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS10556217B2Hard and rigid useSurgical adhesivesEster polymer adhesivesPolymer scienceCross linker
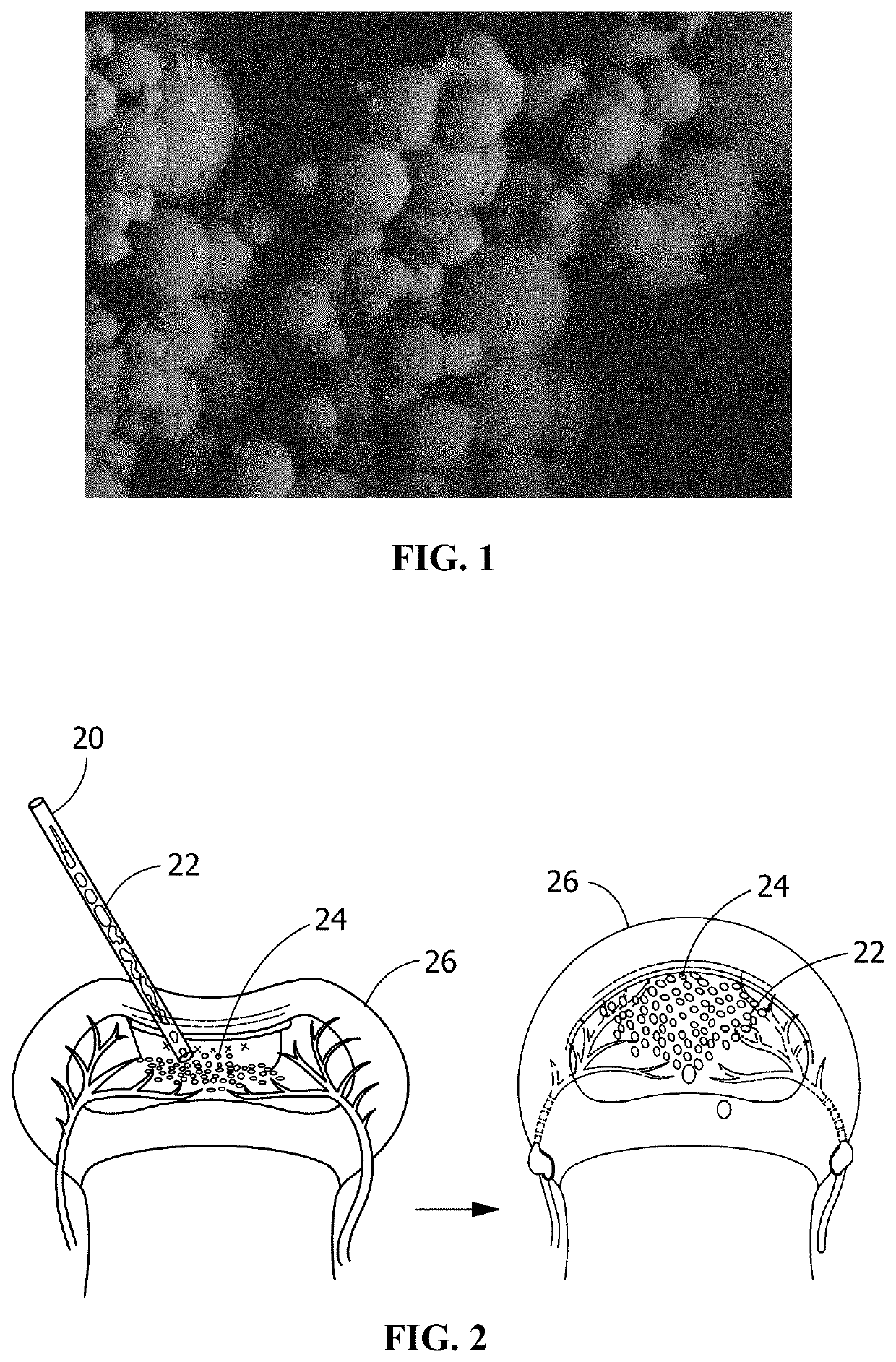
A method of forming cured microparticles includes providing a poly(glycerol sebacate) resin in an uncured state. The method also includes forming the composition into a plurality of uncured microparticles and curing the uncured microparticles to form the plurality of cured microparticles. The uncured microparticles are free of a photo-induced crosslinker. A method of forming a scaffold includes providing microparticles including poly(glycerol sebacate) in a three-dimensional arrangement. The method also includes stimulating the microparticles in the three-dimensional arrangement to sinter the microparticles, thereby forming the scaffold having a plurality of pores. A scaffold is formed of a plurality of microparticles including a poly(glycerol sebacate) thermoset resin in a three-dimensional arrangement. The scaffold has a plurality of pores.
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
Flexible hollow lumen composite
ActiveUS11065099B2Improve propertiesLife-saving and economicalStentsSurgeryPolymer scienceSebacic acid
A composite lumen includes an extruded tube of a composite including a poly(glycerol sebacate) (PGS) matrix mixed with a PGS thermoset filler. The composite lumen also includes an overbraid structure overlying an outer surface of the extruded tube. A method of forming a composite lumen includes extruding a PGS tube of a composite including a PGS matrix mixed with a PGS thermoset filler. The method also includes applying an overbraid structure over an outer surface of the extruded tube.
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
Tunable, controlled-release, urethane-containing elastomers and processes of forming the same
ActiveUS10918764B2Eliminate useAdditive manufacturing apparatusPill deliveryPolymer scienceCarbamate
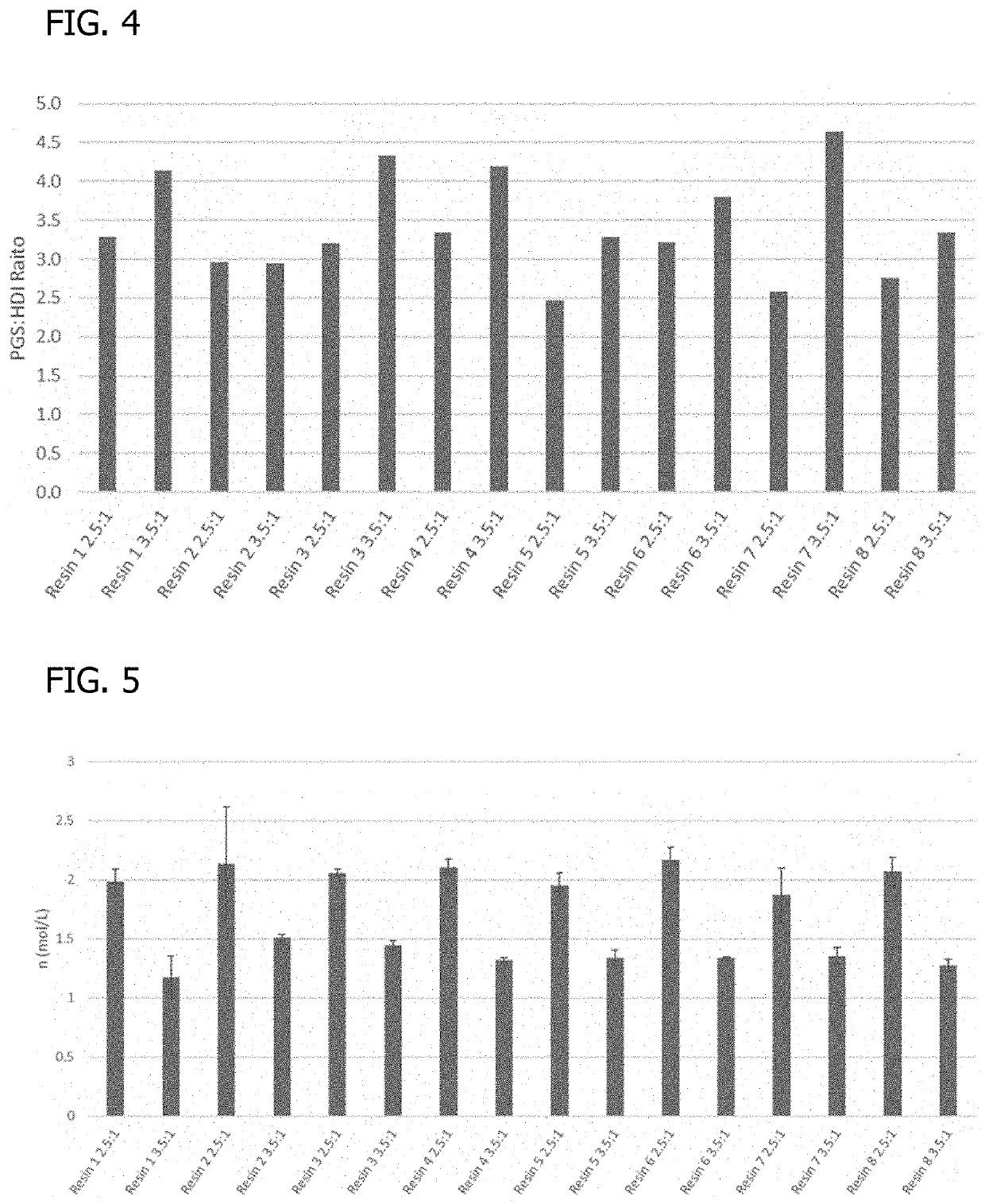
A process forms an implantable product including poly(glycerol sebacate) urethane (PGSU) loaded with an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). The process includes homogeneously mixing a flowable poly(glycerol sebacate) (PGS) resin with the API and a catalyst to form a resin blend. The process also includes homogeneously combining the resin blend with an isocyanate to form a reaction mixture and injecting the reaction mixture to form the PGSU loaded with the API. An implantable product includes a PGSU loaded with an API. In some embodiments, the implantable product includes at least 40% w / w of the API, and the implantable product releases the API by surface degradation of the PGSU at a predetermined release rate for at least three months under physiological conditions. In some embodiments, the PGSU is formed from a PGS reacted with an isocyanate at an isocyanate-to-hydroxyl stoichiometric (crosslinking) ratio in the range of 1:0.25 to 1:1.25.
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
pH-modulating biodegradable polymer and poly(glycerol sebacate)-augmented cell culture media
ActiveUS11124762B2Simple compositionEasy constructionCulture processCell culture mediaPolymer scienceCell culture media
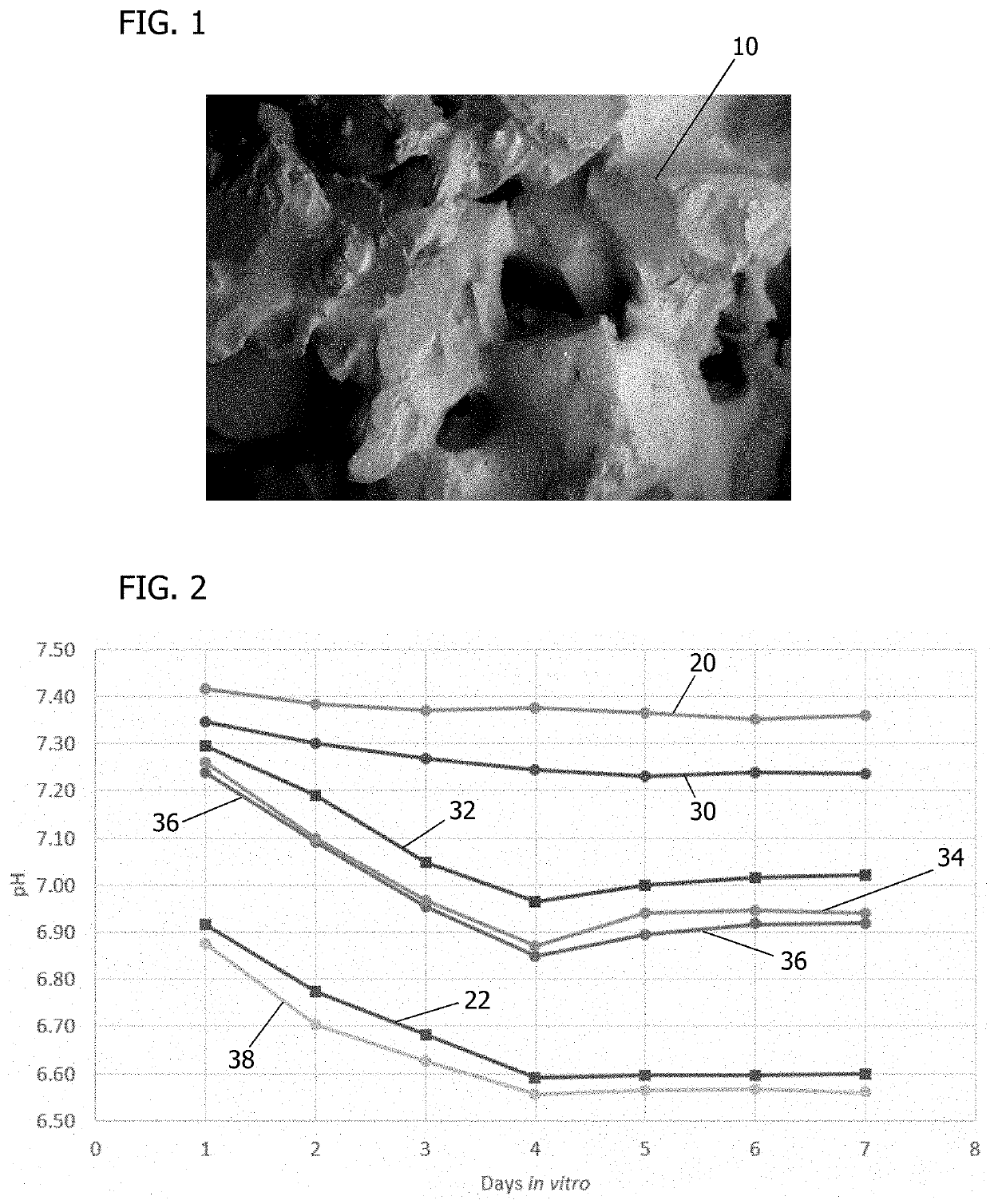
A pH-modulating poly(glycerol sebacate) composition includes poly(glycerol sebacate) and at least one pH-modulating agent associated with the poly(glycerol sebacate). A process of making a pH-modulating poly(glycerol sebacate) composition includes forming a poly(glycerol sebacate) by a water-mediated reaction from glycerol and sebacic acid and associating at least one pH-modulating agent with the poly(glycerol sebacate). A process of modulating a pH of a buffered aqueous solution includes placing a pH-modulating poly(glycerol sebacate) composition in a buffered aqueous solution. The pH-modulating agent is released into the buffered aqueous solution during degradation of the poly(glycerol sebacate) to reduce a decrease in pH of the buffered aqueous solution caused by degradation of the poly(glycerol sebacate).
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
Osteostimulating elastomeric bone filling compositions
A bone filling composition includes a bone filler. The bone filler includes microparticles of at least one elastomeric material. The at least one elastomeric material includes a poly(glycerol sebacate)-based thermoset. The poly(glycerol sebacate)-based thermoset may be porous thermoset poly(glycerol sebacate) flour, thermoset poly(glycerol sebacate) microspheres, or a combination thereof. In some embodiments, the bone filling composition is a bone filling composite that further includes a carrier material including a poly(glycerol sebacate) resin. A method of forming a bone filling composite includes selecting a bone filler and mixing the bone filler with a carrier material to form the bone filling composite. A method of treating a bony defect includes molding a bone filling composite and placing the bone filling composite in the bony defect. The bone filling composite includes a bone filler mixed with a carrier material.
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
Covalent anesthetic-polymer conjugates for prolonged local anesthesia
PendingUS20210275678A1Reduced local toxicityPrevent neuropathic painOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPoly(glycerol-sebacate)Poly ethylene
Anesthetics covalently conjugated onto biodegradable and biocompatible hydrophilic polymers via hydrolysable linkages provide controlled release of local anesthetics in vivo in an effective amount for nerve blockade with reduced toxicity relative to the unconjugated anesthetic agent. The rate of anesthetic release can be tuned by changing the hydrophilicity of the polymer. Exemplary formulations of Poly (glycerol sebacate) (PGS), optionally including Poly ethylene glycol (PEG) polymers conjugated to Tetrodotoxin (TTX) (PGS-PEG-TTX and PGS-TTX), and methods of use thereof are provided Nerve blockade from PGS-PEG-TTX and PGS-TTX was associated with minimal systemic and local toxicity to the muscle and the peripheral nerves. TDP-TTX conjugates homogeneously dispersed into PEG200 are also described. PEG200 not only worked as a medium, but also worked as a chemical permeation enhancer (CPE) to enhance the effectiveness of TTX.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
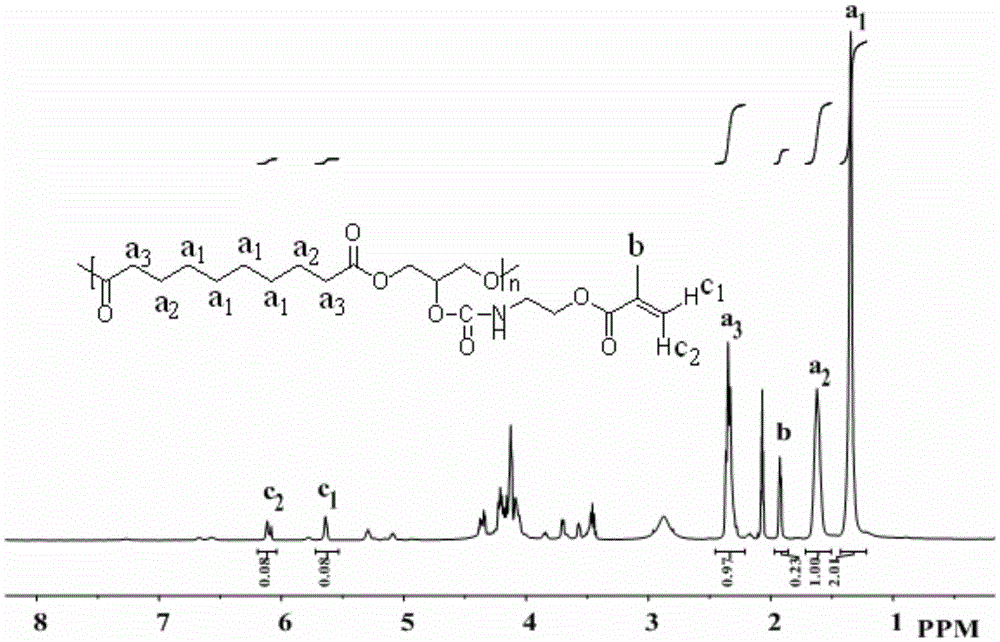
A degradable shape memory polymer and its preparation method and application, 4D printing degradable inferior vena cava filter
ActiveCN113501916BGood flexibilityEasy to processAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgery(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylateInferior vena cava filter
The invention provides a degradable shape memory polymer, its preparation method and application, and a 4D printed degradable inferior vena cava filter, belonging to the technical field of implantable medical devices. In the shape memory polymer provided by the present invention, the structural part of polyglycerol sebacate has an aliphatic long carbon chain structure, which can provide good biocompatibility, biodegradability and good cell binding performance; hydroxyethyl methacrylate The structural part provides the mechanical support required for the inferior vena cava filter; the acrylating group makes the composite material photocurable. The present invention uses the above-mentioned shape memory polymer and combines 3D printing technology to prepare a 4D printed degradable inferior vena cava filter, which is not only biodegradable, but also has good biocompatibility and ensures long-term patency of blood vessels; and has excellent mechanical properties and Deformability, can effectively intercept blood clots in a short period of time.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
A kind of degradable light curing medical adhesive and its preparation and application
ActiveCN105561377BSimple preparation processMaterials are readily availableSurgical adhesivesPolymer scienceAdhesive
The present invention relates to a biodegradable photocurable medical adhesive and preparation and application thereof, the adhesive is poly-glycerol-sebacate-grafted methyl acrylate (2-isocyano ethyl) ester (PGS-IM); the molecular structure is shown in the specification, poly glycerol sebacate (PGS) is added into a solvent, under nitrogen protection, then placed in an oil bath and stirred until the PGS is dissolved, then methyl acrylate (2-isocyano ethyl) ester is added for reaction for 15-120min, and the biodegradable photocurable medical adhesive can be obtained after purifying and drying. PGS-IM is viscous semi-solid at room temperature, is convenient to apply, and is Blu-ray or UV curable, free of damage to a tissue and rapid in curing, and after curing, adhesion properties are good.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Isocyanate-crosslinked polyethylene glycol-polyglycerol sebacate bioelastomer and its preparation method and application
The invention discloses an isocyanate-crosslinked polyethylene glycol-polyglyceryl sebacate bioelastomer, a preparation method and application thereof. The bioelastomer structure of the present invention is shown in formula I, wherein n is an integer of 10-80; m is an integer of 2-14. The bioelastomer of the present invention, whose mechanical strength, hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity, degradation behavior, cell behavior and biocompatibility can be regulated and optimized through the content of isocyanate and polyethylene glycol, is a soft tissue repair with great clinical application prospects Material.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biopolymer Drug Loading Method
ActiveUS20160263227A1Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMedicineBiopolymer
Owner:SOUTH DAKOTA BOARD OF REGENTS
Covalent anesthetic-polymer conjugates for prolonged local anesthesia
ActiveCN111867633ATreat or prevent neuropathic painPrevent neuropathic painOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticHydrophilic polymersPolyethylene glycol
Anesthetics covalently conjugated onto biodegradable and biocompatible hydrophilic polymers via hydrolysable linkages provide controlled release of local anesthetics in vivo in an effective amount fornerve blockade with reduced toxicity relative to the unconjugated anesthetic agent. The rate of anesthetic release can be tuned by changing the hydrophilicity of the polymer. Exemplary formulations of Poly (glycerol sebacate) (PGS), optionally including Poly ethylene glycol (PEG) polymers conjugated to Tetrodotoxin (TTX) (PGS-PEG-TTX and PGS-TTX), and methods of use thereof are provided Nerve blockade from PGS-PEG-TTX and PGS-TTX was associated with minimal systemic and local toxicity to the muscle and the peripheral nerves. TDP-TTX conjugates homogeneously dispersed into PEG200 are also described. PEG200 not only worked as a medium, but also worked as a chemical permeation enhancer (CPE) to enhance the effectiveness of TTX.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Augmented biocontainment materials and augmented biocontainment enclosures
ActiveUS11208627B2Improve survivabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCarbamateStructural composition
A biocontainment vessel includes a vessel structure including a structural composition and an enhancement composition associated with the structural composition. The enhancement composition includes a co-polymer. The co-polymer is a poly(glycerol sebacate) or a poly(glycerol sebacate urethane). The enhancement composition may also include an augmentation agent associated with the co-polymer. The enhancement composition is located with respect to the structural composition such that the enhancement composition benefits biological cells contained in the biocontainment vessel. A composition includes a co-polymer and an augmentation agent contained by the co-polymer. A method of containing biological cells includes placing the biological cells in an augmented biocontainment vessel and storing them in the augmented biocontainment vessel under predetermined conditions. An augmented substrate includes a substrate and an enhancement composition coating a surface of the substrate.
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
Cardiovascular Prostheses
Cardiovascular prostheses having particulate structures that are adapted to induce modulated healing of damaged or diseased cardiovascular tissue and, thereby, associated structures, when administered thereto. The particulate structures include a biological component and a polymer component. The biological component is in the form of a composition and includes decellularized amniotic membrane and placental tissue. The biological composition can also include a plurality of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells or embryonic stem cells. The polymer component includes poly(glycerol sebacate) (PGS).
Owner:CORMATRIX CARDIOVASCULAR INC
Human cell-deposited extracellular matrix coatings for textiles and fibers
A process of forming a coated textile includes culturing human cells on a fiber of a textile such that the human cells produce and deposit human extracellular matrix (hECM) on the textile. The process also includes removing the human cells from the hECM to provide the coated textile of the textile and a coating comprising a residual of the hECM produced and deposited by the human cells on the textile during the culturing. A coated textile includes a textile and a coating on the textile. The coating includes hECM in a cell-deposited state in the coating. A solid-state bioreactor composition includes a poly(glycerol sebacate) (PGS) adduct. The PGS adduct includes PGS and a promoting factor or a promoting factor precursor. Another method includes implanting a coated textile in a human. The coated textile is an autograft. The coating includes hECM deposited by human cells from the human.
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
A kind of mesoporous bioglass/polyglyceryl sebacate composite scaffold and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN104645417BMechanical Strength RegulationAdjustable mechanical strengthPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisDrug release rateCell adhesion
The invention discloses a mesoporous bioactive glass / poly-decyl diacid glyceride composite support as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The composite support of the invention uses a mesoporous bioactive glass porous support as a matrix and compounds poly-decyl diacid glyceride on the mesoporous bioactive glass porous support. Mechanical strength, degradation rate, drug release rate, cell behavior and the like of the composite support of the invention can be adjusted by pore wall thickness of the mesoporous bioactive glass matrix and thickness of the poly-decyl diacid glyceride coating. A PGS coating is utilized to successfully solve the problem of brittleness of an MBG support, so that mechanical strength of the composite support is adjustable in a load bearing range of a trabecular bone. According to the invention, adjustment to degradation rate and release rate of proteins immobilized in MBG mesopore can be realized and activities of the immobilized proteins free of influence from a moderate coating operation can be realized; and cell experiments prove that the PGS coating is capable of promoting cell adhesion and proliferation on surface of the support without affecting osteogenic activity of the MBG.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Degradable microparticle, degradable product comprising the same and application thereof
PendingUS20210261725A1High production costLow production costCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsChemical synthesisMalonic acid
Provided is a degradable microparticle with a grain size in a range of 2 micrometers to 1400 micrometers, and the degradable microparticle comprises poly(glycerol sebacate), poly(glycerol maleate), poly(glycerol succinate-co-maleate), poly(glycerol succinate), poly(glycerol malonate), poly(glycerol glutarate), poly(glycerol adipate), poly(glycerol pimelate), poly(glycerol suberate), poly(glycerol azelate), or any combination thereof. A degradable product produced from the degradable microparticles can obtain the desired degradation effect and can be produced by chemical synthesis to reduce the production cost. With these advantages, the applicability of the degradable microparticles is improved.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Degradable shape memory polymer, preparation method and application thereof, and 4D printing degradable inferior vena cava filter
ActiveCN113501916AGood flexibilityEasy to processAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgery(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylateInferior vena cava filter
The invention provides a degradable shape memory polymer, a preparation method and application thereof and a 4D printing degradable inferior vena cava filter, and belongs to the technical field of implantable medical instruments. In the shape memory polymer provided by the invention, a polysebacic acid glyceride structural part has an aliphatic long carbon chain structure, so that highd biocompatibility, biodegradability and high cell binding performance can be provided; a hydroxyethyl methylacrylate structure part provides mechanical support required by the inferior vena cava filter; and an acryloylated group enables the composite material to have photocuring performance. The shape memory polymer is used and combined with a 3D printing technology to prepare the 4D printing degradable inferior vena cava filter, and the 4D printing degradable inferior vena cava filter is biodegradable and has high biocompatibility, and the long-term patency rate of blood vessels is guaranteed; and the shape memory polymer has excellent mechanical properties and deformability, and can effectively intercept blood clots in a short period of time.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Osteostimulating elastomeric bone filling compositions
A bone filling composition includes a bone filler. The bone filler includes microparticles of at least one elastomeric material. The at least one elastomeric material includes a poly(glycerol sebacate)-based thermoset. The poly(glycerol sebacate)-based thermoset may be porous thermoset poly(glycerol sebacate) flour, thermoset poly(glycerol sebacate) microspheres, or a combination thereof. In some embodiments, the bone filling composition is a bone filling composite that further includes a carrier material including a poly(glycerol sebacate) resin. A method of forming a bone filling composite includes selecting a bone filler and mixing the bone filler with a carrier material to form the bone filling composite. A method of treating a bony defect includes molding a bone filling composite and placing the bone filling composite in the bony defect. The bone filling composite includes a bone filler mixed with a carrier material.
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
Preparation method and application of shock-proof modified engineering plastic
The invention discloses a preparation method of shock-proof modified engineering plastic and application of the shock-proof modified engineering plastic. According to the method, poly(glycerol sebacate), triallyl cyanurate, an acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrol copolymer, magnesium oxide, manganese carbonate and an ethanol solution are mixed to obtain a primary mixture, then the primary mixture is putinto a dispersion solution of kynar and acrylic resin, after an antioxidant is added for standing treatment, sediments are collected, washed and dried to obtain a modified mixture, then after the modified mixture and maleic anhydride are mixed, heating and stirring are conducted for reaction to obtain an intermediate mixture, then secondary modification is conducted to obtain a secondary modifiedmixture, then the secondary modified mixture, sepiolite fibers and deionized water are reacted in a high-pressure reaction kettle in a helium environment to obtain a high-temperature reaction material, and finally, through melt extrusion, the finished product engineering plastic is obtained. The shock-proof effect of the prepared engineering plastic is good, and thus the engineering plastic has good application prospects in the fields of household appliances, electronic engineering, automobiles and communication.
Owner:SUZHOU LUOTELAN NEW MATERIAL TECH
Sacroiliac Joint Stabilization Prostheses
Prostheses are described for stabilizing dysfunctional sacroiliac (SI) joints. The prostheses are sized and configured to be press-fit into surgically created pilot SI joint openings in dysfunctional SI joint structures. The prostheses include a polymer composition comprising poly (glycerol sebacate) (PGS). The polymer composition can also include selective biologically active agents, such as a bone morphogenic protein (BMP), and / or a pharmacological agent, such as an antibiotic.
Owner:TENON MEDICAL INC
A kind of glabridin microemulsion and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103976892BHigh content of glabridinNo delamination and demulsificationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEmulsionSulfite
The invention relates to glabridin micro-emulsion and a preparation method thereof. The glabridin micro-emulsion consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 10wt%-15wt% of glabridin, 10wt%-15wt% of stearic polyoxypropylene sulfite, 7wt%-11wt% of polydecyldiacid glyceride, 6wt%-9wt% of Twain 85, 12wt%-16wt% of propylene glycol and the balance of deionized water. The preparation method of the glabridin micro-emulsion comprises the steps of mixing and vortex oscillation, and the prepared glabridin micro-emulsion is high in encapsulation efficiency, good in stability and capable of being added into cosmetics as an ingredient for improving the stability of the glabridin.
Owner:WUJIANG YINGLIDA PLASTIC PACKAGING
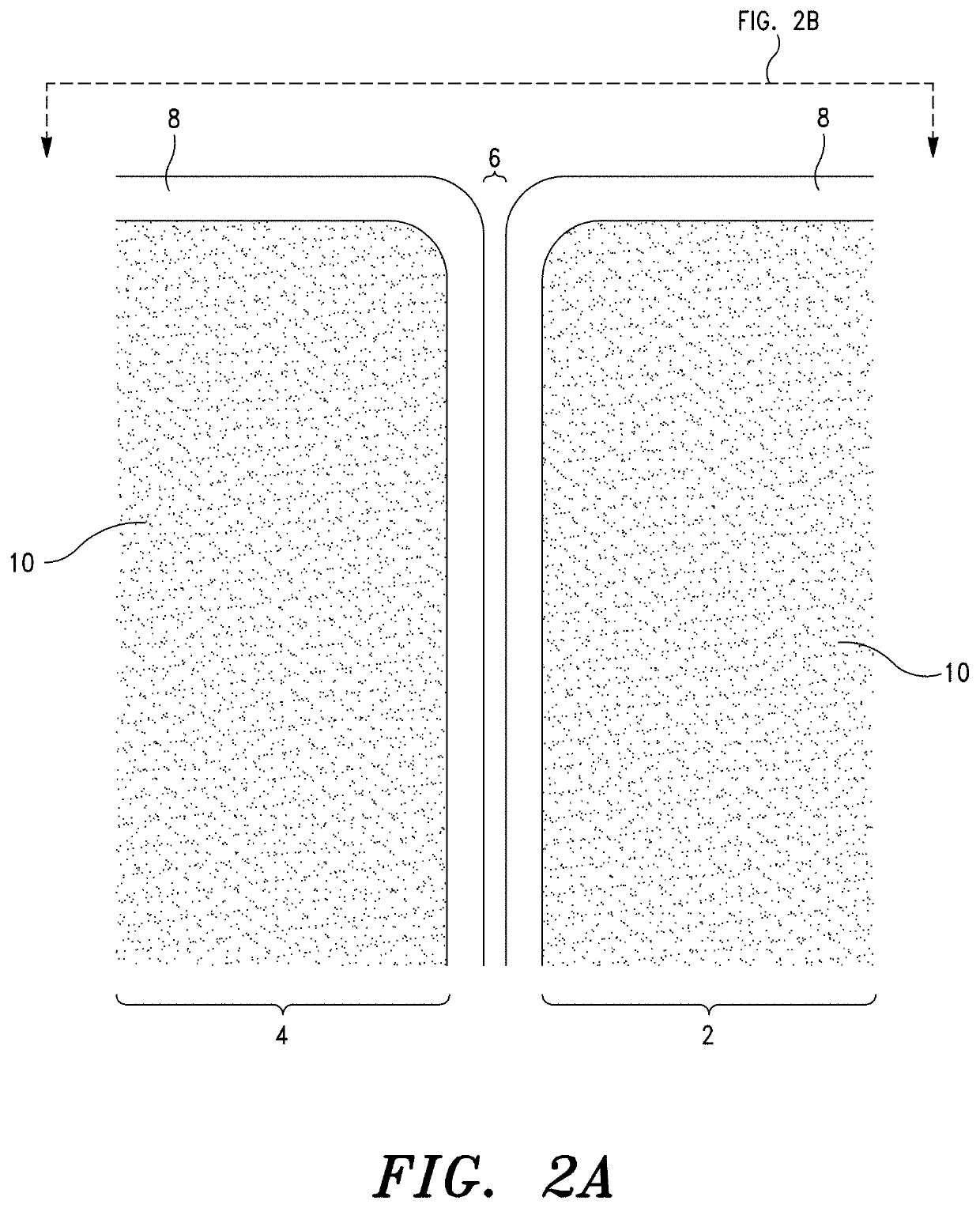
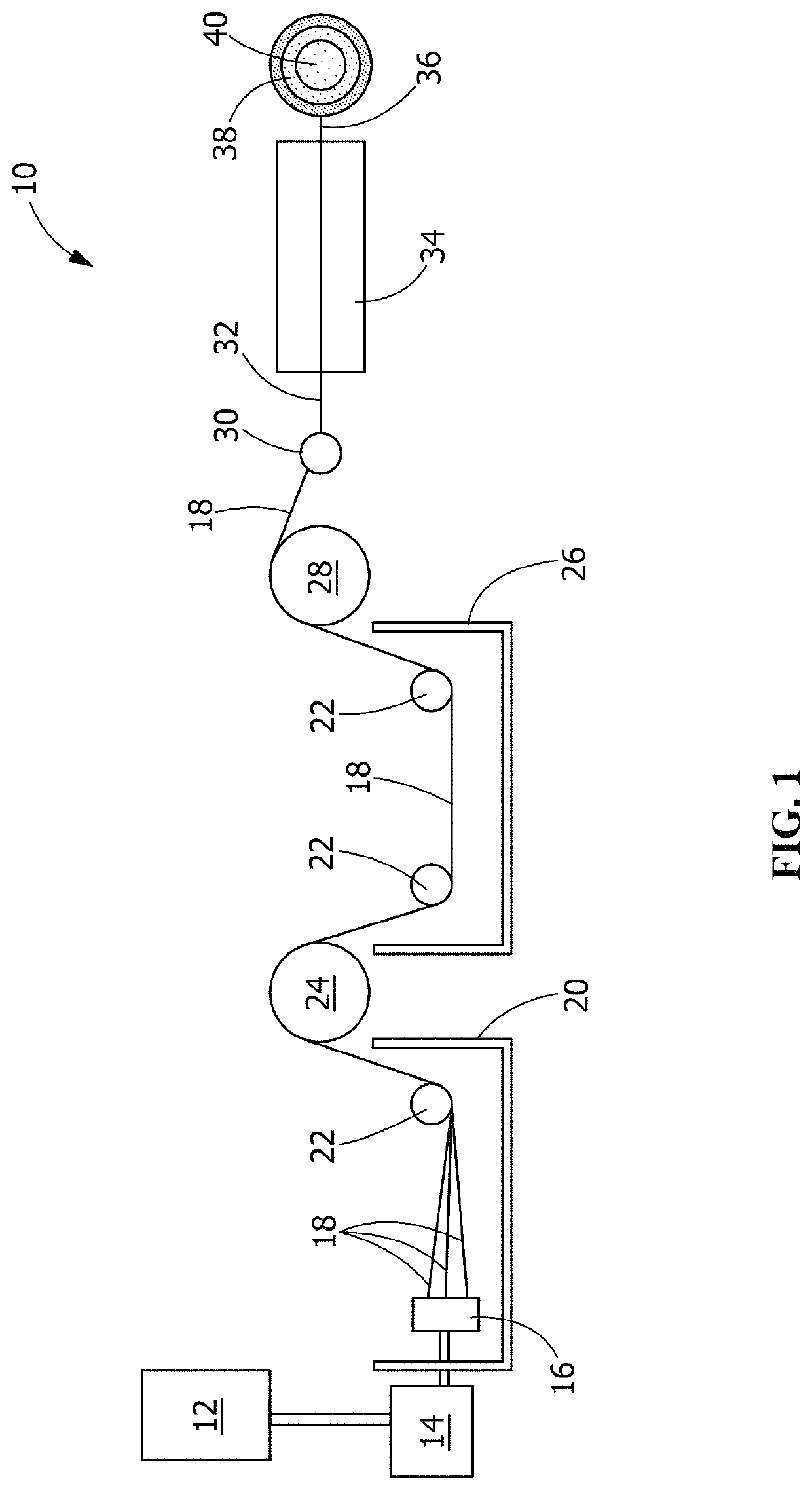
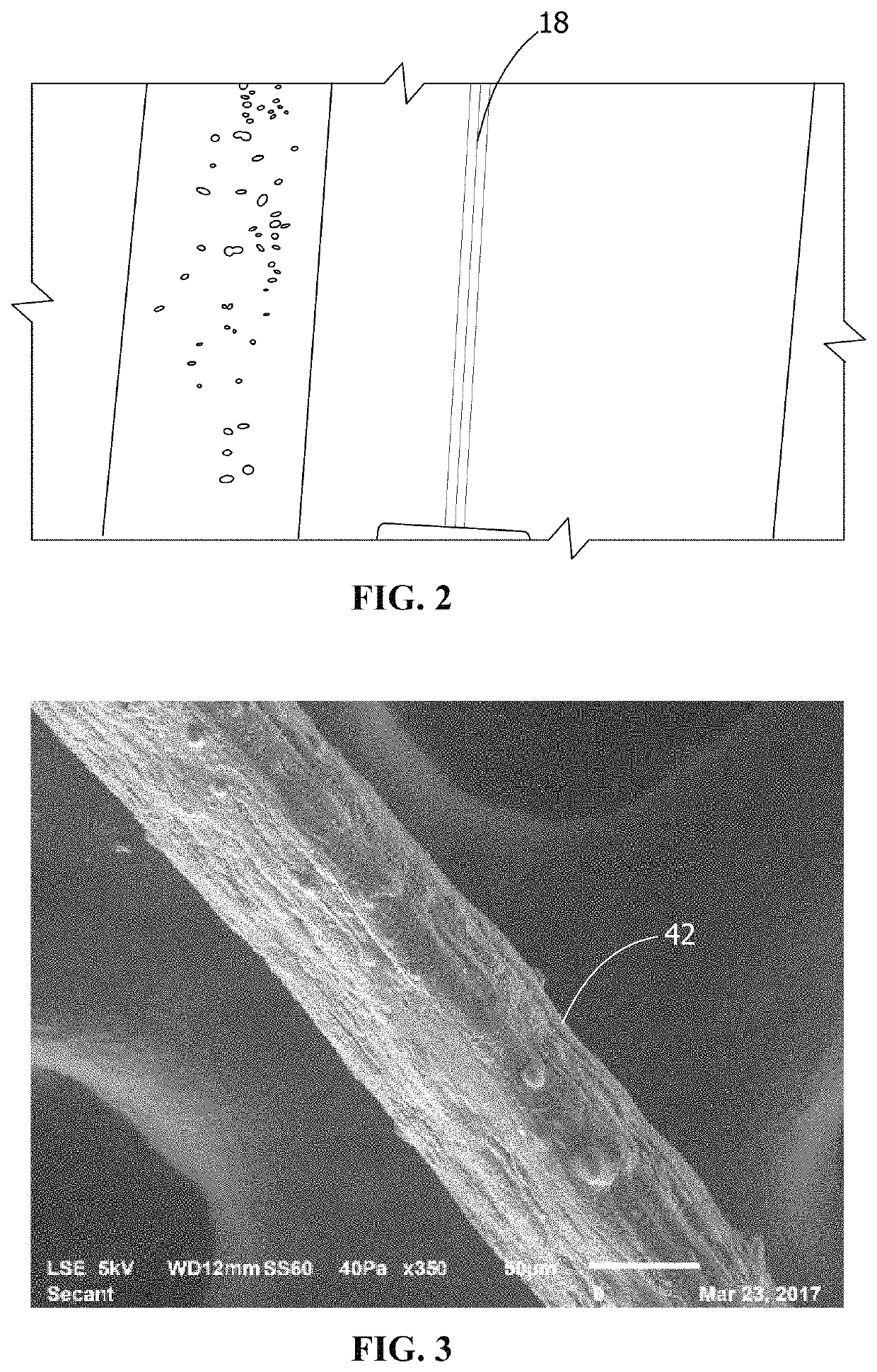
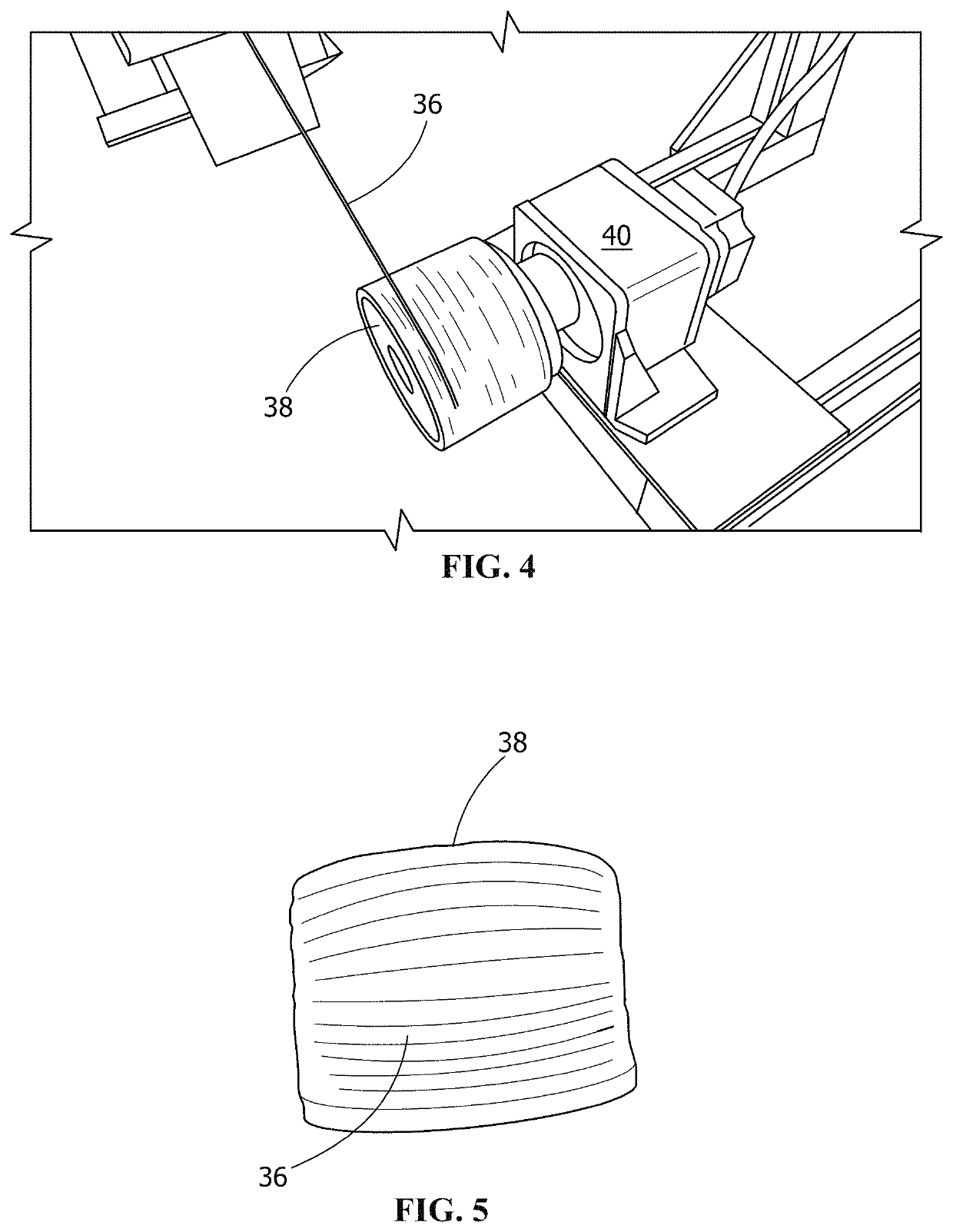
Poly(glycerol sebacate) fibers, fabrics formed therefrom, and methods of fiber manufacture
A manufacturing process includes spinning at least one continuous poly(glycerol sebacate) (PGS) / alginate fiber from a polymeric solution comprising PGS and alginate in water, drafting the at least one continuous PGS / alginate fiber in at least one coagulation bath, and drawing the at least one continuous PGS / alginate fiber from the at least one coagulation bath. A yarn includes at least one continuous PGS fiber. A continuous poly(glycerol sebacate) (PGS) / alginate fiber forming system includes a feeding tank holding a polymeric solution of alginate and PGS, a pump, a spinneret, a first coagulation bath, a first winder, a second coagulation bath, a second winder, and a bobbin winder, the system forming at least one continuous PGS / alginate fiber from the polymeric solution of alginate and PGS.
Owner:THE SECANT GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com