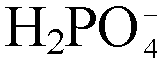Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Phosphate Transporters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
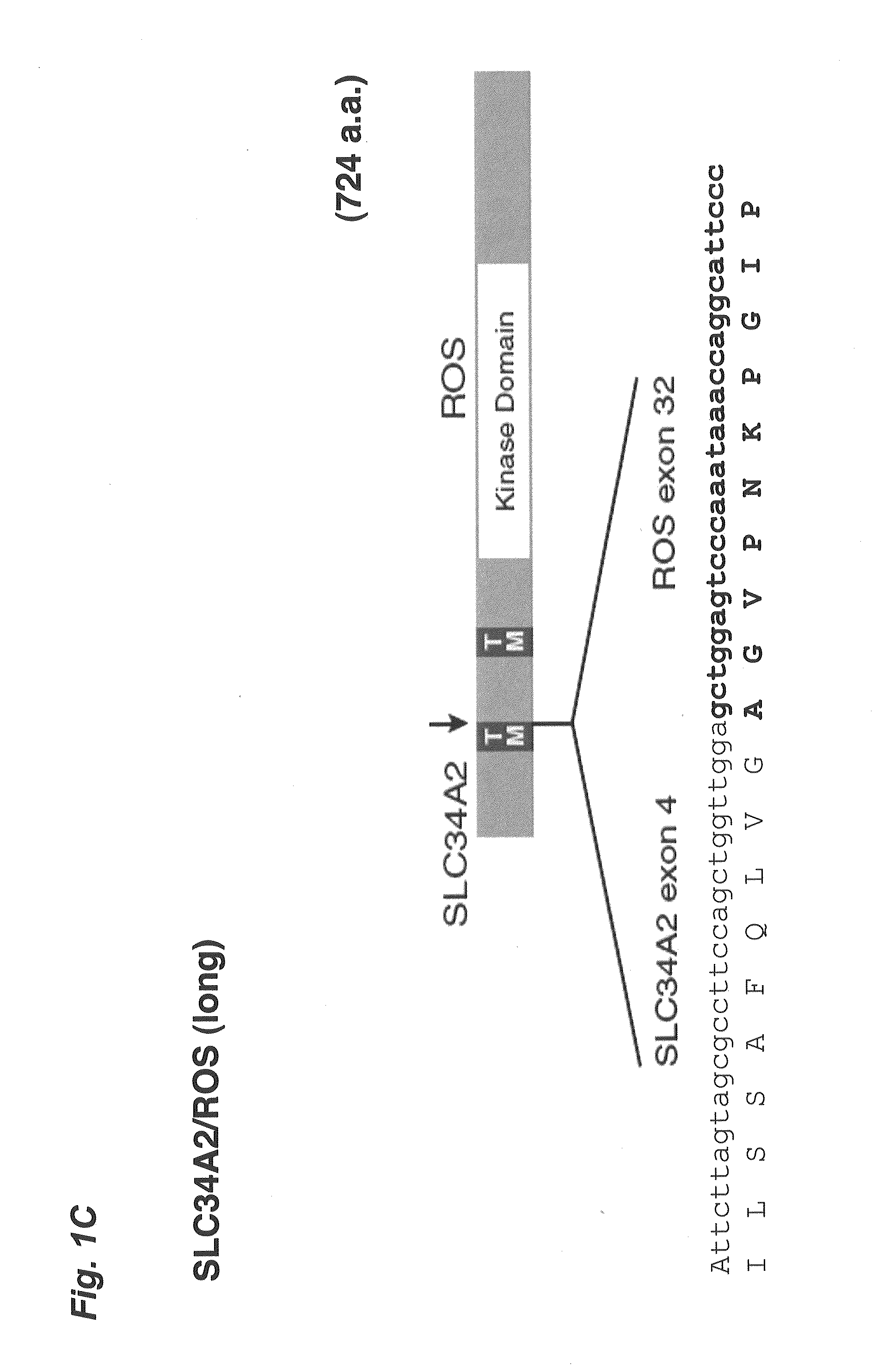
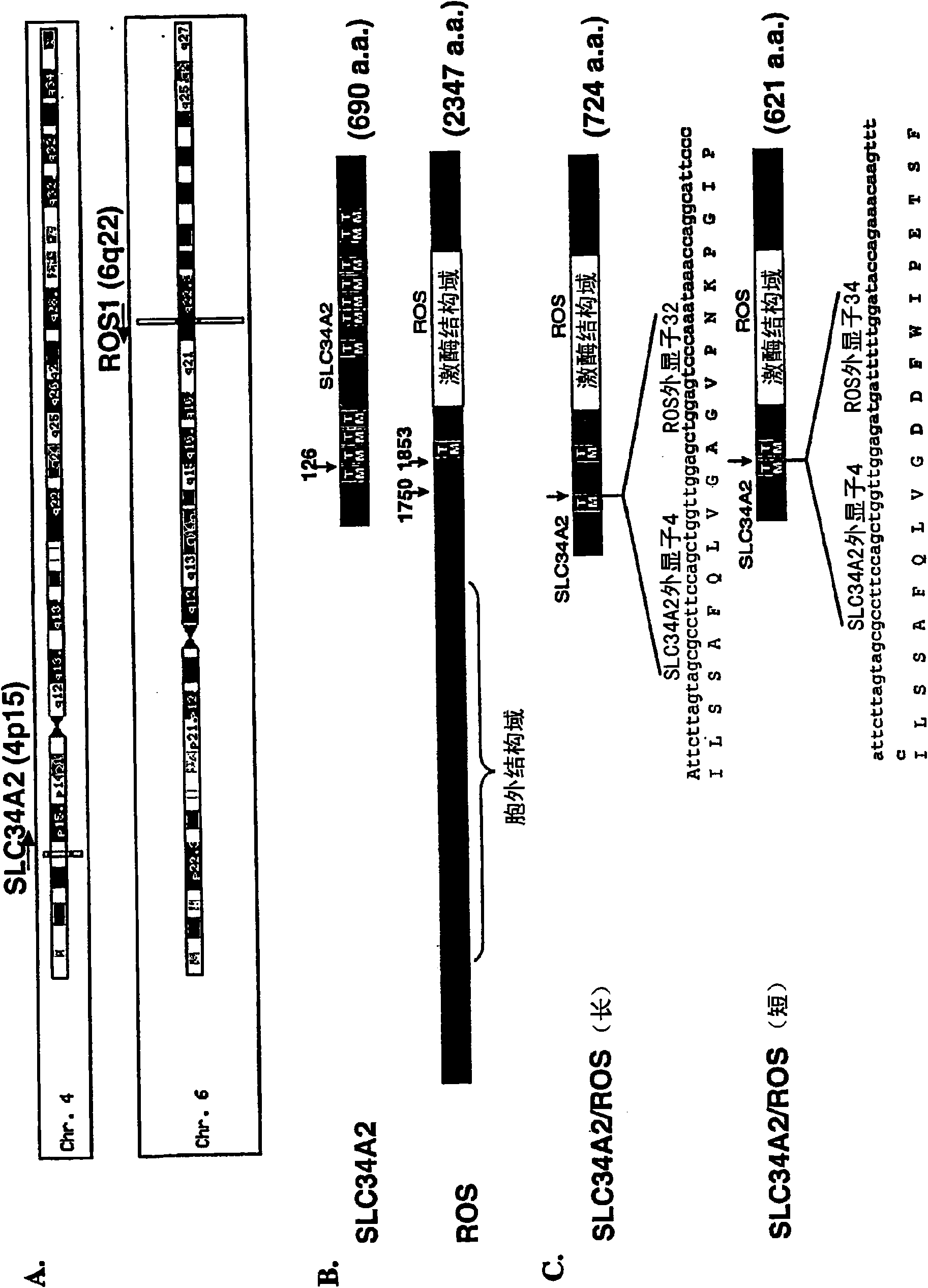
Translocation and mutant ros kinase in human non-small cell lung carcinoma
InactiveUS20100143918A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsProto-Oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase ROSCancer cell
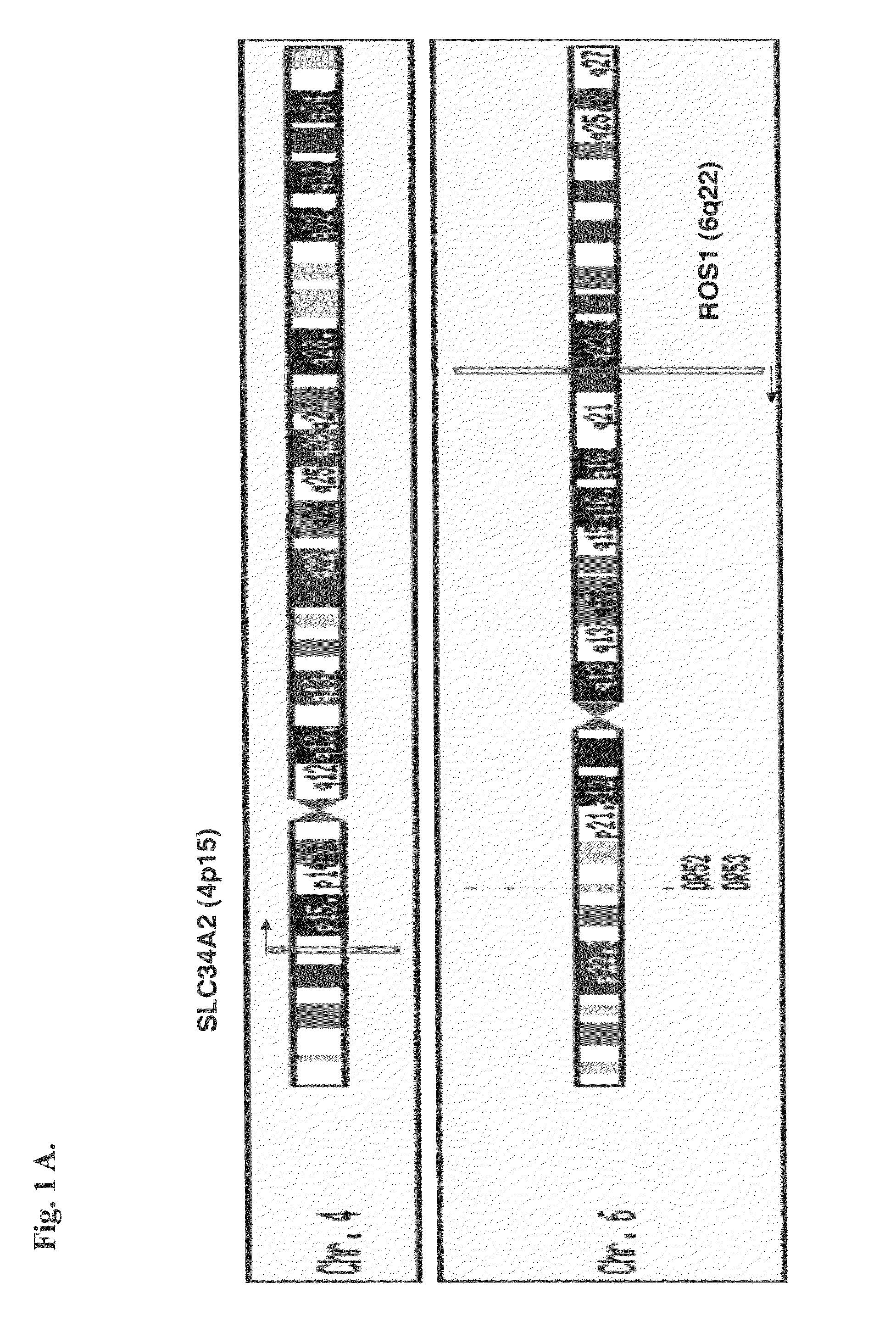
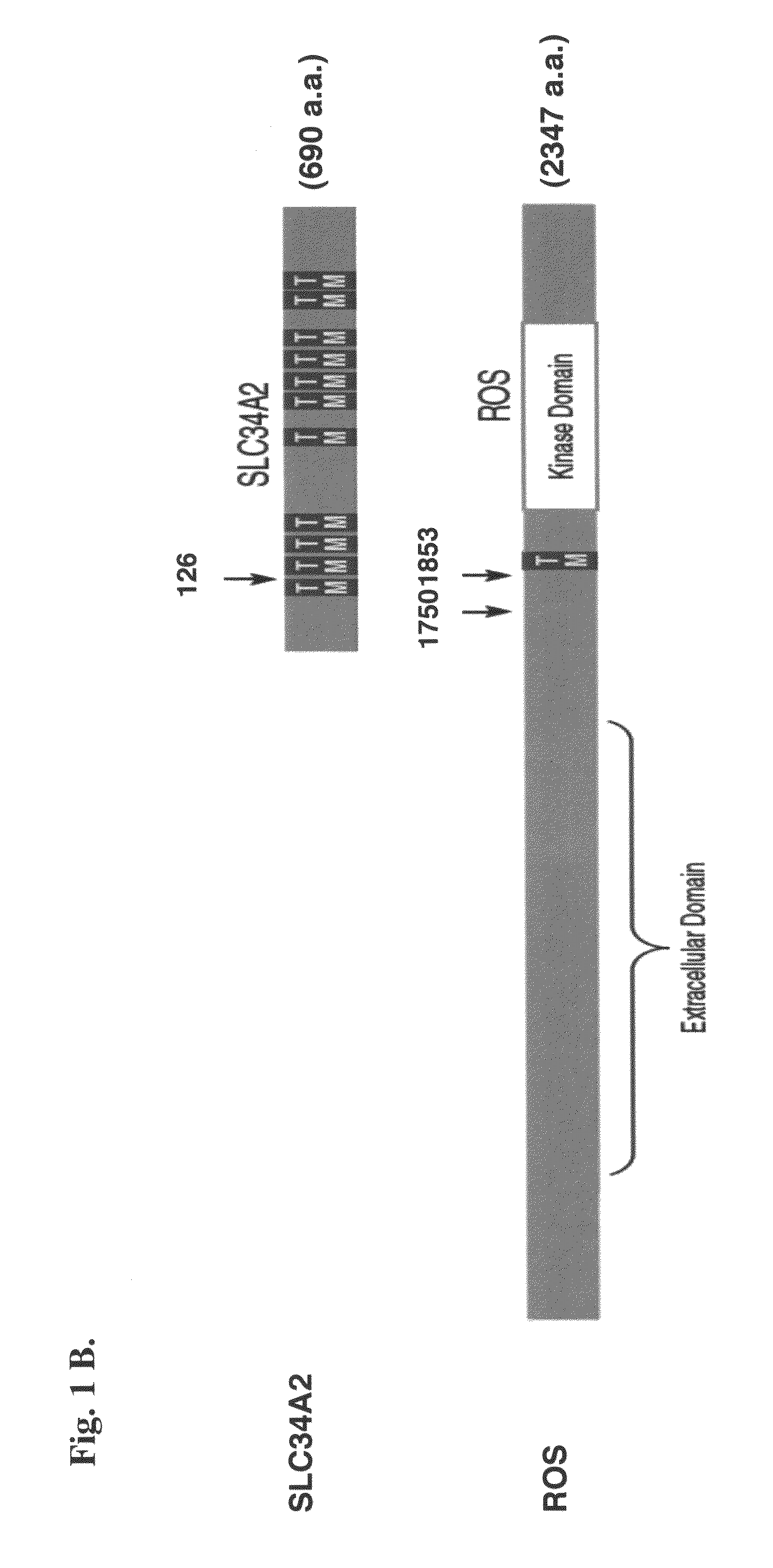
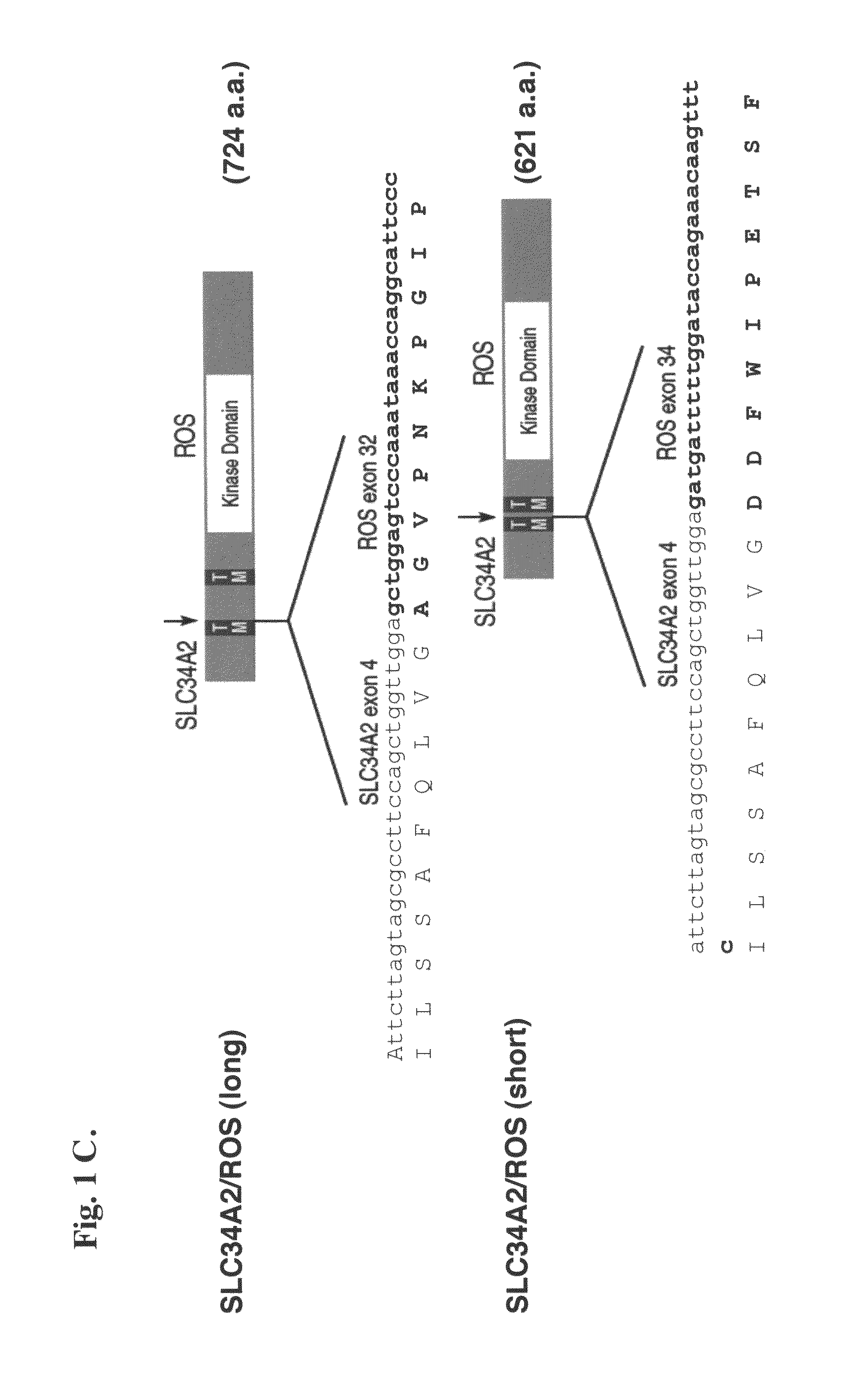
In accordance with the invention, a novel gene translocation, (4p15, 6q22), in human non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) that results in fusion proteins combining part of Sodium-dependent Phosphate Transporter Isoform NaPi-3b protein (SLC34A2) with Proto-oncogene Tyrosine Protein Kinase ROS Precursor (ROS) kinase has now been identified. The SLC34A2-ROS fusion proteins are anticipated to drive the proliferation and survival of cancer cells, and particularly drive the proliferation and survival of a subgroup of NSCLC tumor cells. The invention therefore provides, in part, isolated polynucleotides and vectors encoding the disclosed mutant ROS kinase polypeptides, probes for detecting it, isolated mutant polypeptides, recombinant polypeptides, and reagents for detecting the fusion and truncated polypeptides. The disclosed identification of the new fusion protein enables new methods for determining the presence of these mutant ROS kinase polypeptides in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer characterized by the mutant polynucleotides or polypeptides, which are also provided by the invention.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification pathogenic gene and detection method thereof
ActiveCN106834299AEfficient and comprehensive acquisitionAccurate acquisitionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringNervous systemInformation analysis
The invention relates to a human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification pathogenic gene and a detection method thereof. Human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification, namely IBGC is a neurodegenerative genetic disease. The invention provides seven mutation forms of four pathogenic genes including SLC20A2 (Sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 2), PDGFRB (Platelet-derived Growth Factor Receptor Beta), PDGFB (Platelet-derived Growth Factor Subunit B) and XPR1 (Xenotropic and Polytropic Retrovirus Receptor 1) and sequences of the seven mutation forms are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.7. The form of the pathogenic gene provided by the invention is not reported until now and can provide evidence and lay a foundation for analysis and medicine development of a pathogenic mechanism, pathogenic gene screening and detection, formulation of a therapeutic regimen and the like. Meanwhile, the invention constructs a pathogenic gene detection method; the pathogenic gene detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, capturing a pathogenic gene exon region by utilizing multi-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); carrying out next generation sequencing on the pathogenic gene exon region and carrying out information analysis to find out mutation; finally, identifying the mutation by utilizing Sanger sequencing, wherein a PCR captured primer group comprises amplification primer sequences SEQ ID NO.12 to SEQ ID NO.23, and amplification primer sequences of a Sanger sequencing segment are shown as SEQ ID NO.24 to SEQ ID NO.35. The detection method provided by the invention covers all exons of the four pathogenic genes and can be used for efficiently, comprehensively, rapidly and accurately acquiring mutation information.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
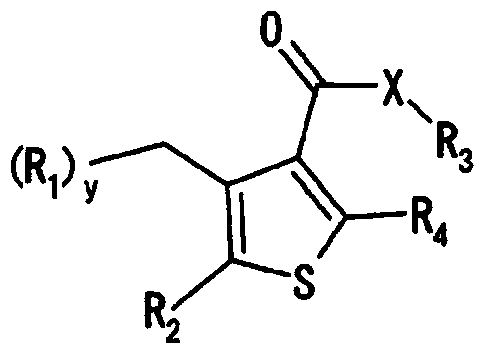
Tetrahydrobenzothiophene compound
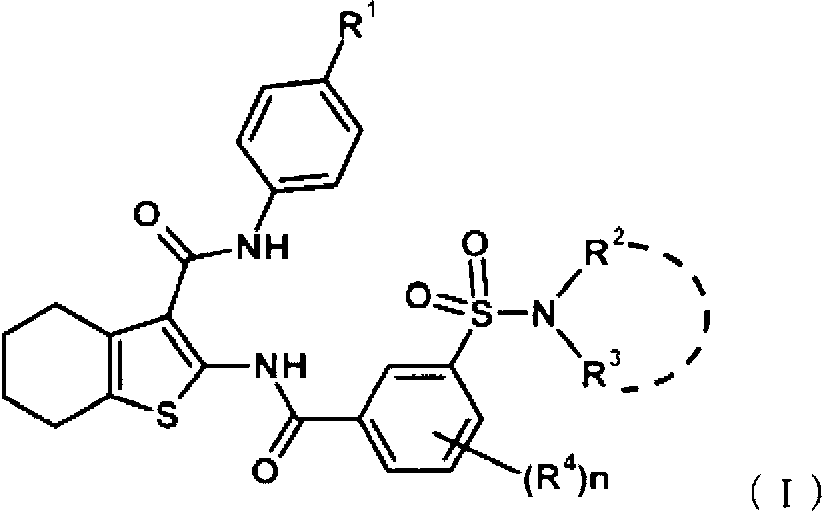
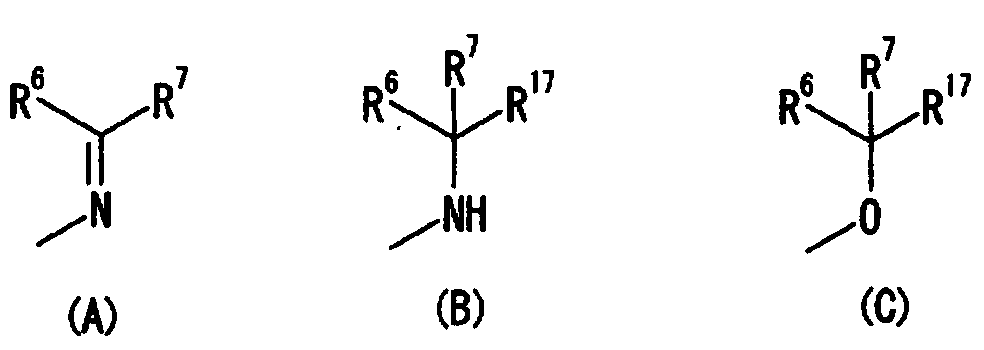
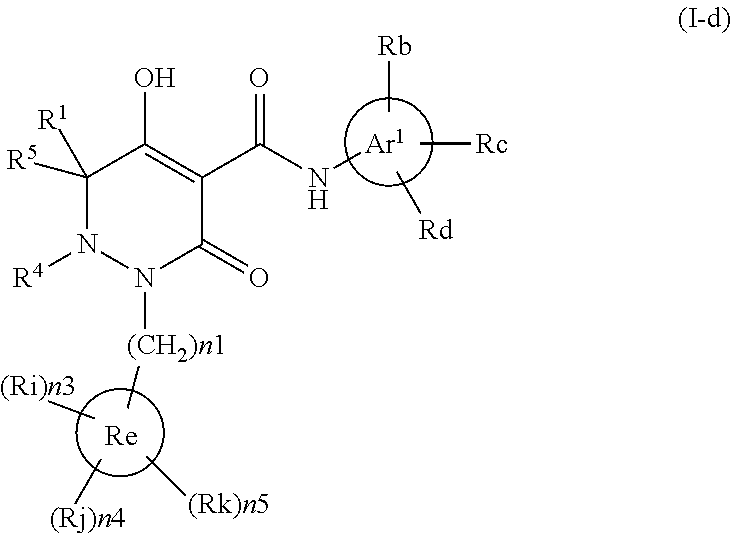
Disclosed is a compound which has an intestinal phosphate transporter (NPT-IIb) inhibition activity and is useful as an active ingredient for a therapeutic agent and / or a prophylactic agent for hyperphosphatemia. A tetrahydrobenzothiophene compound represented by formula (I) has an NPT-IIb inhibition activity and can be used as a prophylactic agent and / or a therapeutic agent for hyperphosphatemia. (In the formula, R1 represents -O-(lower alkyl), -(lower alkylene)-phenyl, or the like; R2 and R3 are same as or different from each other and independently represent H, a lower alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, an aryl group, a heteroaryl group, or the like, or R2, R3 and a nitrogen atom to which R2 and R3 are bound together may form a 5- to 7-membered saturated cyclic amino group; R4's are same as or different from each other and independently represent a halogen atom, a lower alkyl group, or the like; and n represents 0 to 2.)
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Aminoalkyl-substituted n-thienyl benzamide derivative
The objective of the present invention is to provide a compound having inhibitory activity against an intestinal phosphate transporter (NPT-IIb), and useful as an active ingredient in a hyperphosphatemia therapeutic agent and / or preventive. A thiophene compound represented by formula (I) may be used as a hyperphosphatemia therapeutic agent and / or preventive having NPT-IIb inhibitory activity. (In the formula, R1-6 each represent H or a lower alkyl or the like, L1-4 each represent a lower alkyl or the like, X1 represents CH2 or O, X2-3 each represent CH or N, k is 1-3, and n is 0-1.)
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Method for manufacturing L-amino acid
A method for producing an L-amino acid is provided. An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium having an L-amino acid-producing ability, which has been modified so that the activity of a phosphate transporter is increased, in a medium, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
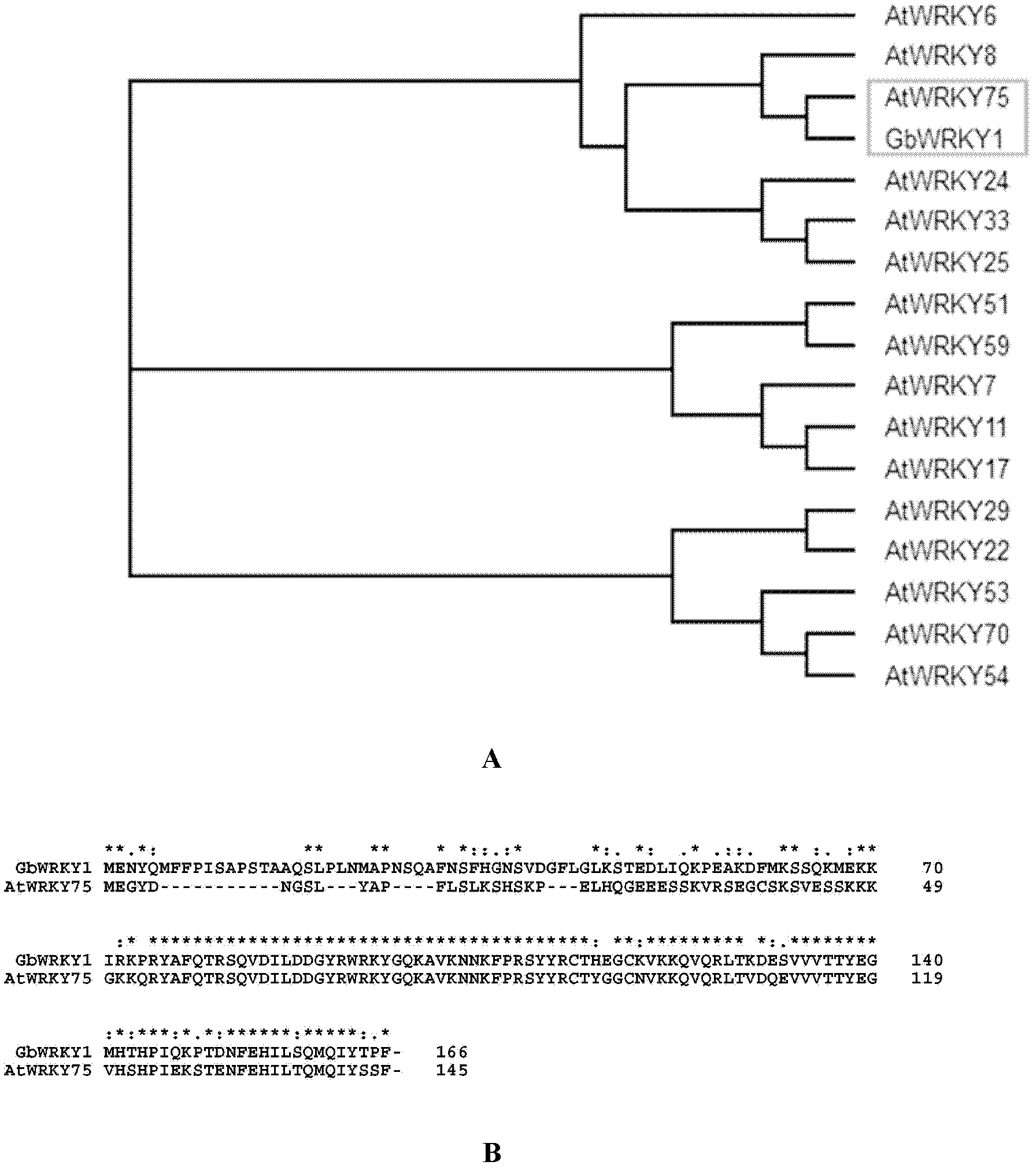
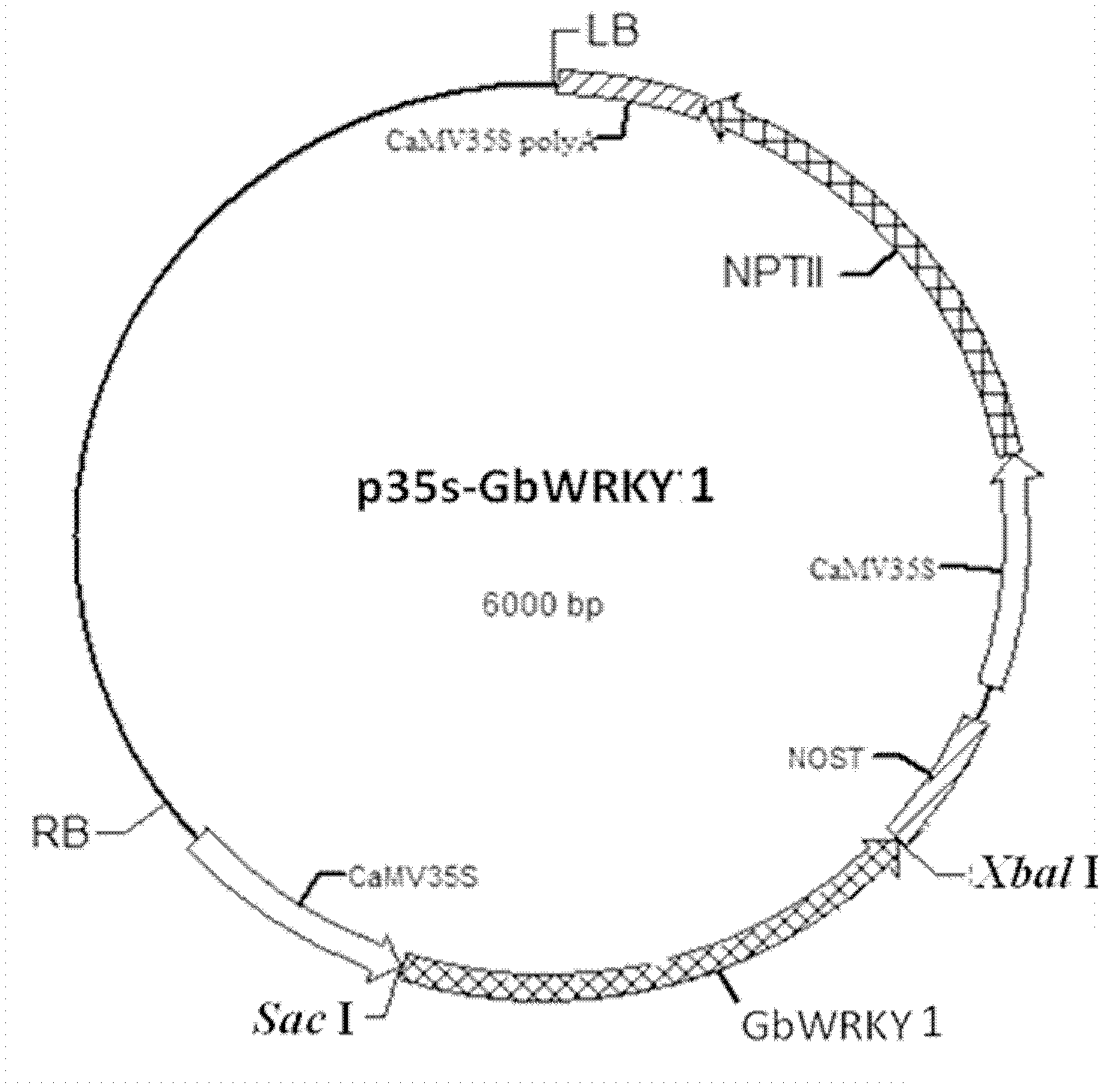
WRKY transcription factor of cotton and application of WRKY transcription factor
InactiveCN103173461AImprove stress resistanceAlleviate low phosphorus stress responsePlant peptidesFermentationPhosphate TransportersComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to isolation and cloning, functional verification and application of an identified Gb-based WRKY1 factor in Sea Island cotton. The cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of an encoding gene of the Gb-based WRKY1 factor is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; and the amino acid sequence of the encoding gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also discloses a function of the gene (Gb WRKY1) for promoting the expression of the phosphate transporter; and the gene has the function of promoting the efficient utilization of arabidopsis thaliana phosphorus nutrition.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Modified plants
Disclosed are improved plants that have increased yield. The plants show increased yield under low phosphate conditions and therefore require less fertilizer. The plants are characterised by expression of a mutant phosphate transporter gene.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Plants with Increased Yield
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 26S proteasome-subunit, 50S ribosomal protein L36, Autophagy-related protein, B0050-protein, Branched-chain amino acid permease, Calmodulin, carbon storage regulator, FK506-binding protein, gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate hydrolase, GM02LC38418-protein, Heat stress transcription factor, Mannan polymerase II complex subunit, mitochondrial precursor of Lon protease homolog, MutS protein homolog, phosphate transporter subunit, Protein EFR3, pyruvate kinase, tellurite resistance protein, Xanthine permease, and YAR047C-protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Soybean specific response low-phosphorous transcription factor GmPHRLP and application
InactiveCN108728451APromote absorptionIncrease biomassPlant peptidesFermentationBinding sitePhosphate Transporters
The invention provides a soybean specific response low-phosphorous transcription factor GmPHRLP and an application. A soybean variety 'BX10' serves as a material, a transcription factor is discoveredby RNA-seq, the expression level of the transcription factor is remarkably improved under the condition of phosphorus deficiency, a specific primer of a gene is designed by a sequencing joint sequence, cloned and subjected to homologous analysis, a result discovers that the transcription factor belongs to an MYB-CC family, the transcription factor and a phosphorous signal center regulating factorof model plant Arabidopsis and rice have high protein homology, P1BS (PHR1 Binding Sites) can be combined, expression of the transcription level of the transcription factor is affected by low-phosphorus specific induction, expression of a phosphate transporter protein can be induced, and absorption and transport of phosphorus are increased under low phosphorus. The gene is over-expressed in soybean hair roots, so that phosphorus absorption of soybeans can be improved, and biomass of the soybeans is remarkably improved under low-phosphorus culture conditions.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
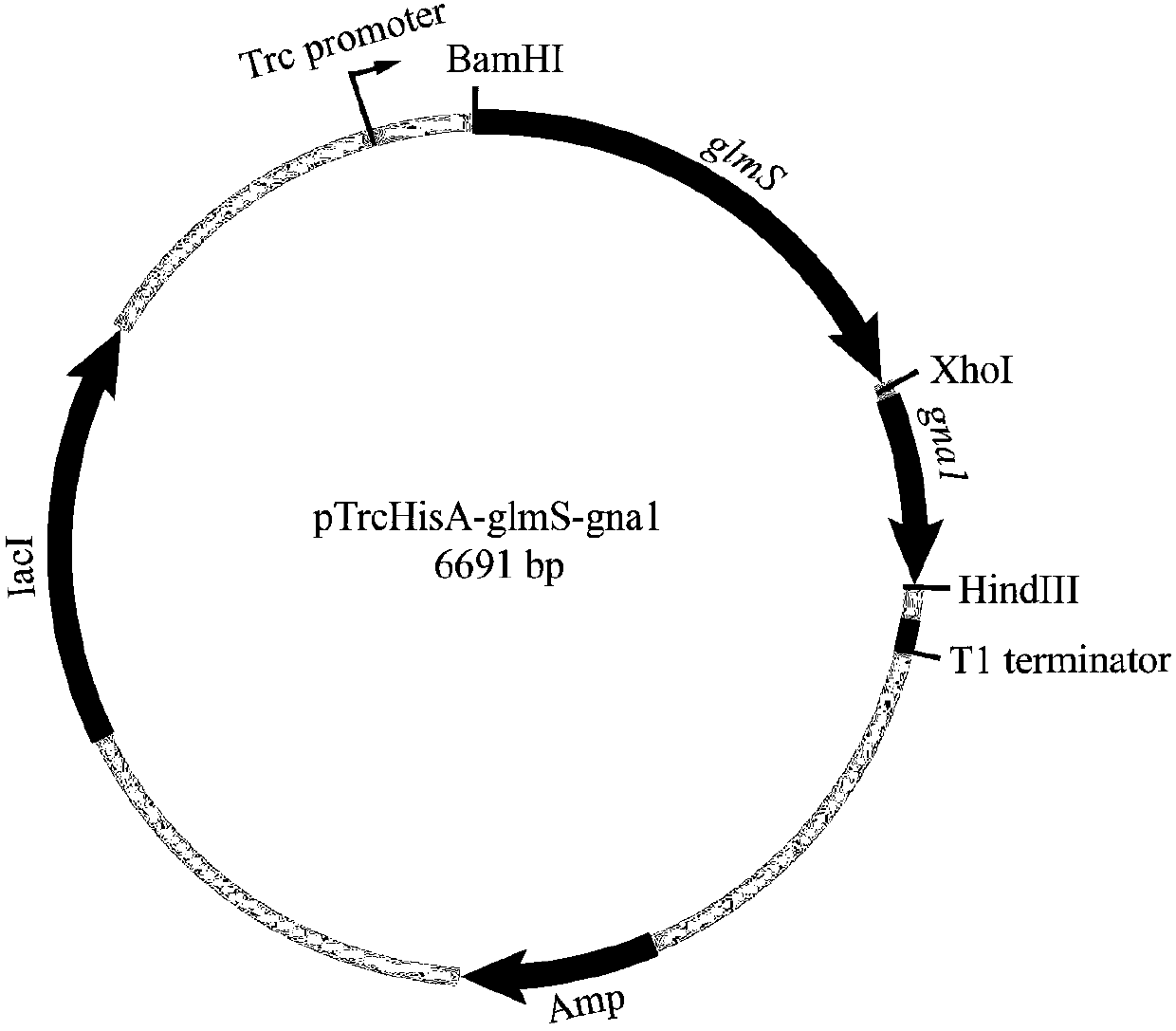
Recombinant escherichia coli capable of efficiently producing glucosamine and application thereof
InactiveCN107739728AIncrease productionLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli capable of efficiently producing glucosamine and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention successfully expresses an E.coli MG1655-sourced glucosamine synthase gene glmS and an S.cerevisiae BY4741-sourced glucosamine acetylase gene gna1 in a host E.coli MG1655, and on the basis, the expression intensities of an acetylglucosamine phosphate transporter gene nagE and a mannose phosphate transporter gene manX are weakened. Obtained genetically engineered strains are fermented in a 5L fermentation tank for 44 hours, the yield of the glucosamine reaches 131.5g / L, and the transformation rate reaches 35.1 percent; the obtained genetically engineered strains are fermented in a 1000L fermentation tank for 44 hours, the yield of the glucosamine reaches 137g / L, and the glucose transformation rate is 37.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Translocation and mutant ros kinase in human non-small cell lung carcinoma
ActiveCN101528921AOrganic active ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProto-Oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase ROSNucleotide
In accordance with the invention, a novel gene translocation, (4p15, 6q22), in human non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) that results in a fusion proteins combining part of Sodium-dependent Phosphate Transporter lsoform NaPi-3b protein (SLC34A2) with Proto- oncogene Tyrosine Protein Kinase ROS Precursor (ROS) kinase has now been identified. The SLC34A2-ROS fusion protein is anticipated to drive the proliferation and survival of a subgroup of NSCLC tumors. The invention therefore provides, in part, isolated polynucleotides and vectors encoding the disclosed mutant ROS kinase polypeptides, probes for detecting it, isolated mutant polypeptides, recombinant polypeptides, and reagents for detecting the fusion and truncated polypeptides. The disclosed identification of the new fusion protein enables new methods for determining the presence of these mutant ROS kinase polypeptides in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer characterized by the mutant polynucleotides or polypeptides, which are also provided by the invention.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
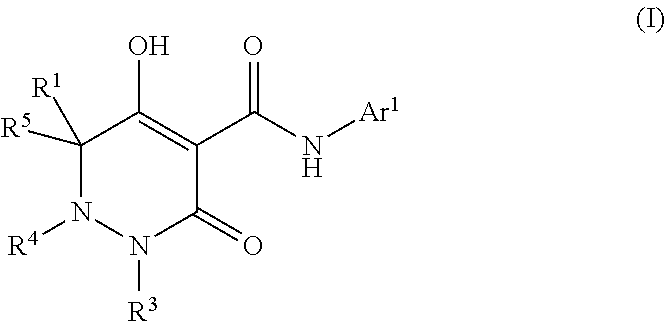
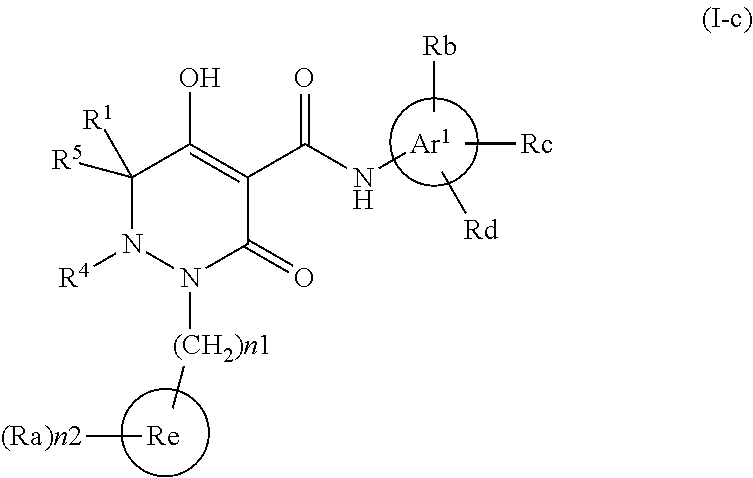
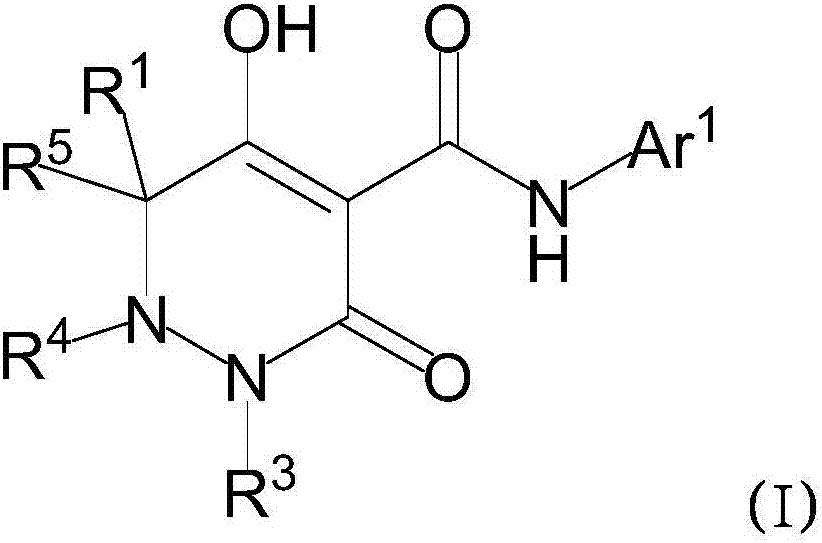
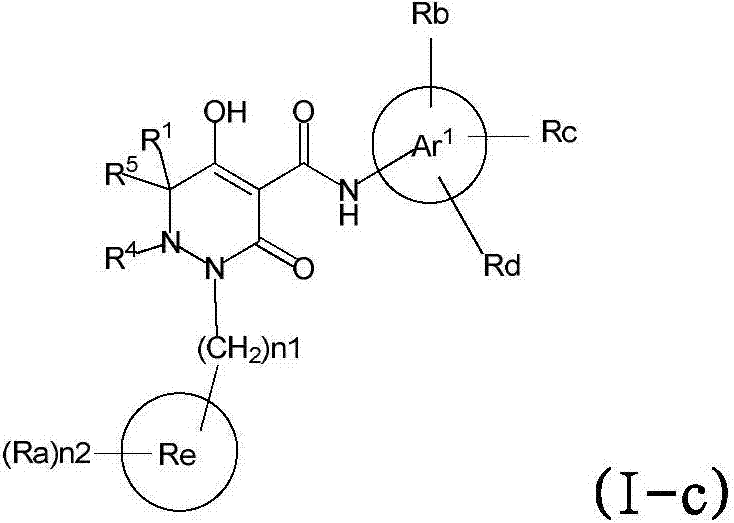
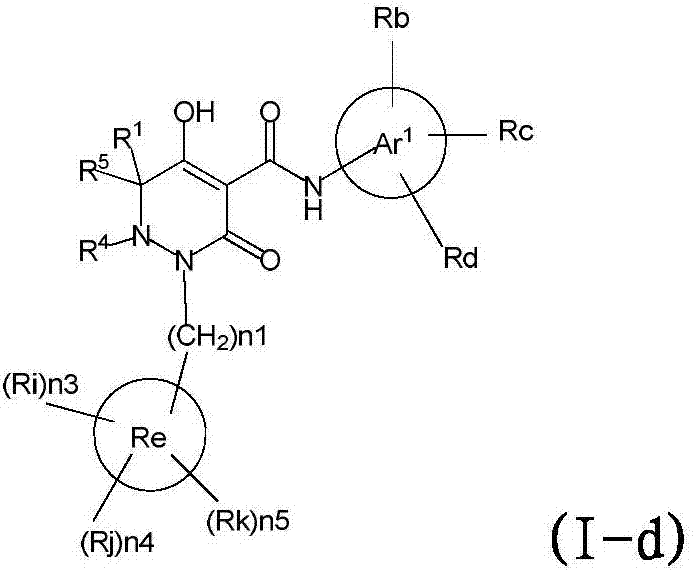
Dihydropyridazine-3,5-dione derivative and pharmaceuticals containing the same
ActiveUS20160002251A1Enhanced inhibitory effectHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChronic kidney failurePyridazine
The present invention provides a dihydropyridazine-3,5-dione derivative or a salt thereof, or a solvate of the compound or the salt, a pharmaceutical drug, a pharmaceutical composition, a sodium-dependent phosphate transporter inhibitor, and a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for hyperphosphatemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, chronic renal failure, chronic kidney disease, and arteriosclerosis associated with vascular calcification comprising the compound as an active ingredient, and a method for prevention and / or treatment.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Translocation and mutant ROS kinase in human non-small cell lung carcinoma
ActiveUS8383799B2Organic active ingredientsFungiAbnormal tissue growthProto-Oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase ROS
In accordance with the invention, a novel gene translocation, (4p15, 6q22), in human non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) that results in a fusion proteins combining part of Sodium-dependent Phosphate Transporter Isoform NaPi-3b protein (SLC34A2) with Proto-oncogene Tyrosine Protein Kinase ROS Precursor (ROS) kinase has now been identified. The SLC34A2-ROS fusion protein is anticipated to drive the proliferation and survival of a subgroup of NSCLC tumors. The invention therefore provides, in part, isolated polynucleotides and vectors encoding the disclosed mutant ROS kinase polypeptides, probes for detecting it, isolated mutant polypeptides, recombinant polypeptides, and reagents for detecting the fusion and truncated polypeptides. The disclosed identification of the new fusion protein enables new methods for determining the presence of these mutant ROS kinase polypeptides in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer characterized by the mutant polynucleotides or polypeptides, which are also provided by the invention.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Recombinant escherichia coli with glucosamine accumulation and application thereof
InactiveCN109929791AIncrease productionRealize accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExtracellularIntracellular
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli with glucosamine accumulation and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The escherichia coli is used as ahost, the recombinant escherichia coli is obtained by knocking out four genes of an acetylglucosamine transporter encoding gene nagE, a mannose phosphate transporter encoding gene manXYZ, a deacetylase gene nagA and a deaminase gene nagB gene in the glucosamine synthesis pathway of the escherichia coli, and the recombinant escherichia coli is applied to the production of the glucosamine to achieve the purpose of blocking the transport pathway of glucosamine from the extracellular to the intracellular. By means of overexpression of a glucosamine synthetase encoding gene and a glucosamine acetylase encoding gene, the synthesis pathway of the glucosamine is enhanced, and the yield of the glucosamine is increased accordingly.
Owner:YANGZHOU RIXING BIO TECH
Application of OsPTP1 in efficient plant phosphorus breeding
ActiveCN110923253AImprove phosphorus absorption efficiencyImprove absorption efficiencyHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyGenome editing
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a rice OsPTP1 (Phosphate Transporter Phosphatase 1) gene cloned by a reverse genetics approach, and the function of the gene is identified by an overexpression technology and a gene editing technology. The gene OsPTP1 is used for improving the absorption, transport or utilization of crops to phosphorus, sothat efficient phosphorus breeding is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Soybean root specific efficient phosphate transporter
InactiveCN102702336AIncrease profitImprove stress resistanceFungiPlant peptidesNucleotidePhosphorus utilization
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a soybean root specific efficient phosphate transporter GmPHT06 whose amino acid sequence is shown by SEQ ID No.2. The soybean root specific efficient phosphate transporter also has genes encoding the protein whose nucleotide sequence is shown by SEQ ID No.1. The soybean root specific efficient phosphate transporter GmPHT06 provided by the invention can be used to improve the phosphorus utilization of various plants and resistance ability of plants under phosphorus stress, so as to increase the yield of plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for changing phosphorylation site of rice phosphate transporter gene OsPT8 and application thereof
InactiveCN103614384APromote absorptionClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesGenetically modified ricePhosphorylation
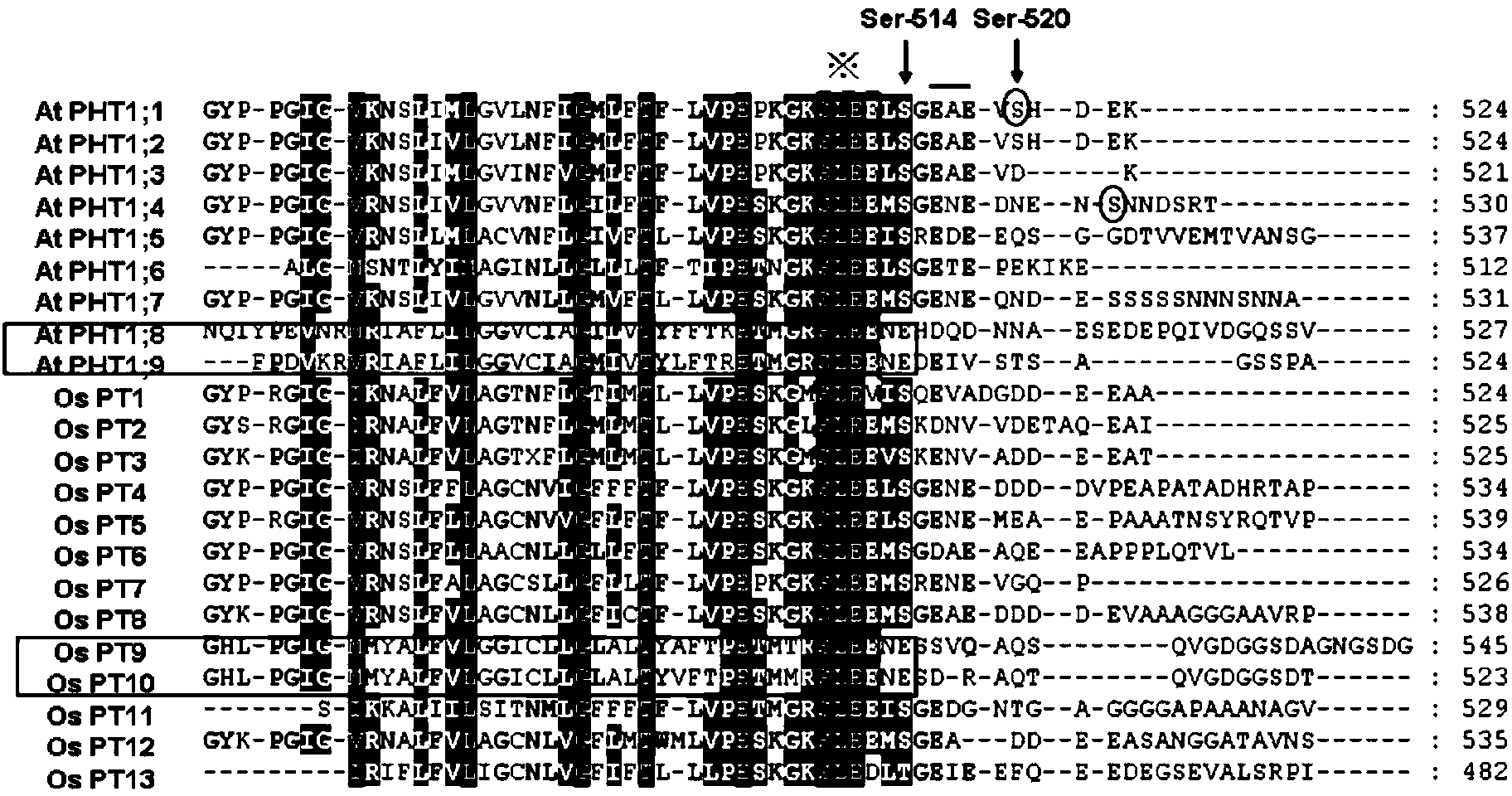
The invention discloses a method for changing phosphorylation sites of a rice phosphate transporter gene OsPT8. The method is as below: carrying out genetic engineering modification on possible phosphorylation sites of the OsPT8 protein sequence; mutating 517th amino acid residue serine (Ser) into alanine (Ala), so as to obtain the modified Ospt8 gene sequence. The invention also discloses a method for improving the ability of phosphorus absorption of rice. The modified Ospt8 gene sequence is transferred into rice, and the obtained transgenic rice gains enhanced ability of absorption on phosphorus. The method is specifically as below: the modified Ospt8 gene sequence is started by using its own promoters and transferred to rice through a transgenic approach.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae having attenuated expression of a phosphate transporter-encoding gene
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The bacterium can belong to the genus Escherichia, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a phosphate transporter-encoding gene, such as the pitA gene or pitB gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
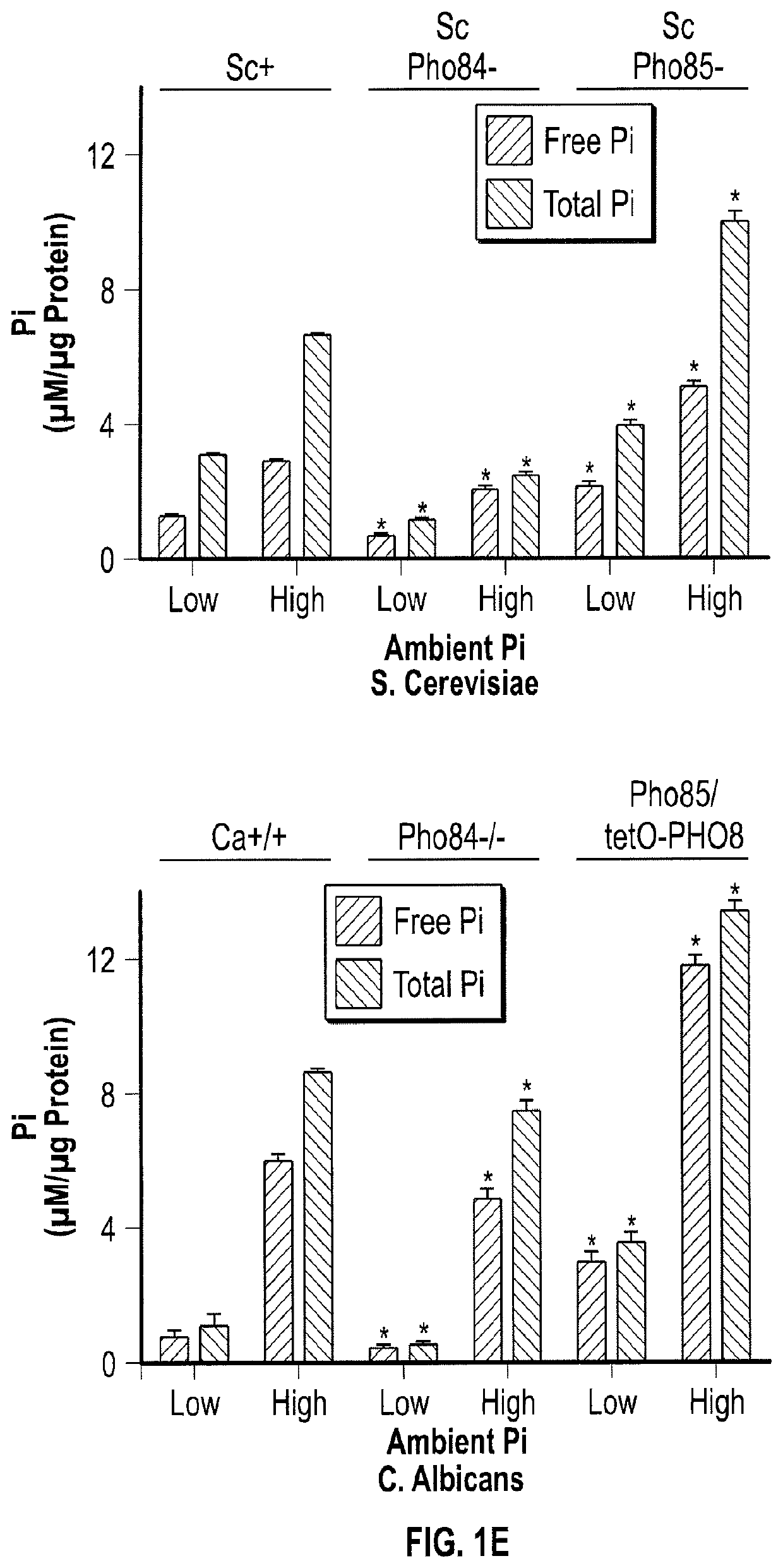
Inhibiting the Fungal Cell-Surface Phospate Transporter PHO84
InactiveUS20200061087A1Organic active ingredientsCompound screeningChemical compoundPhosphate Transporters
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Dihydropyridazine-3,5-dione derivative
ActiveCN105073715AExcellent NaPi-IIb inhibitionExcellent PiT-1 inhibitionOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderSodium dependentSecondary hyperparathyroidism
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
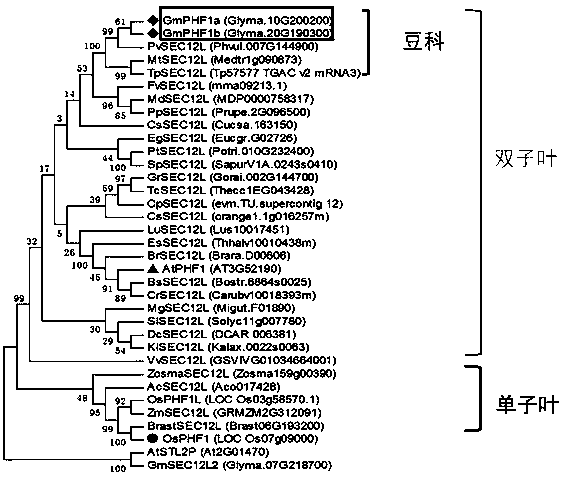
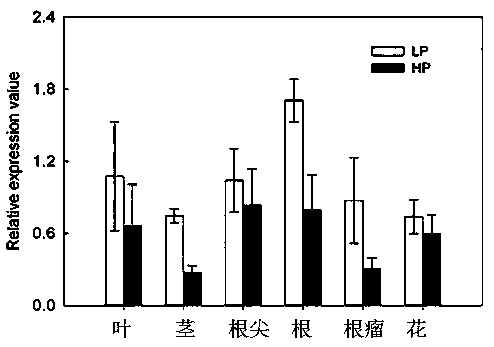
Application of transport assistance factor GmPHF1b of phosphate transporter
InactiveCN108841832AIncrease the number of nodulesWeight increasePlant peptidesFermentationPlant nodulePhosphate Transporters
The invention provides application of a transport assistance factor GmPHF1b of a phosphate transporter, and particularly relates to application of a GmPHF1b gene in promotion of obtaining of phosphorus by leguminous plants so as to promote nodulation and nitrogen fixation and in cooperation of nitrogen and phosphorus to achieve collaborative efficiency. Homologous comparison clones a gene GmPHF1bexpressed in a leaf, a stem, a root, a root nodule and a flower and verifies that a protein encoded by the gene GmPHF1b cooperates with a phosphate transporter GmPT5 / GmPT7 for controlling obtaining ofnodule phosphorus; overexpression of GmPHF1b obviously increases the number of root nodules of soybeans and the weight of the root nodules and improves the activity of the nitrogenase of the root nodules, so that the contents and the biomasses of nitrogen and phosphorus are increased, and the yield of the soybeans is finally increased.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for Producing an L-Amino Acid Using a Bacterium of the Family Enterobacteriaceae Having Attenuated Expression of a Phosphate Transporter-Encoding Gene
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The bacterium can belong to the genus Escherichia, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a phosphate transporter-encoding gene, such as the pitA gene or pitB gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
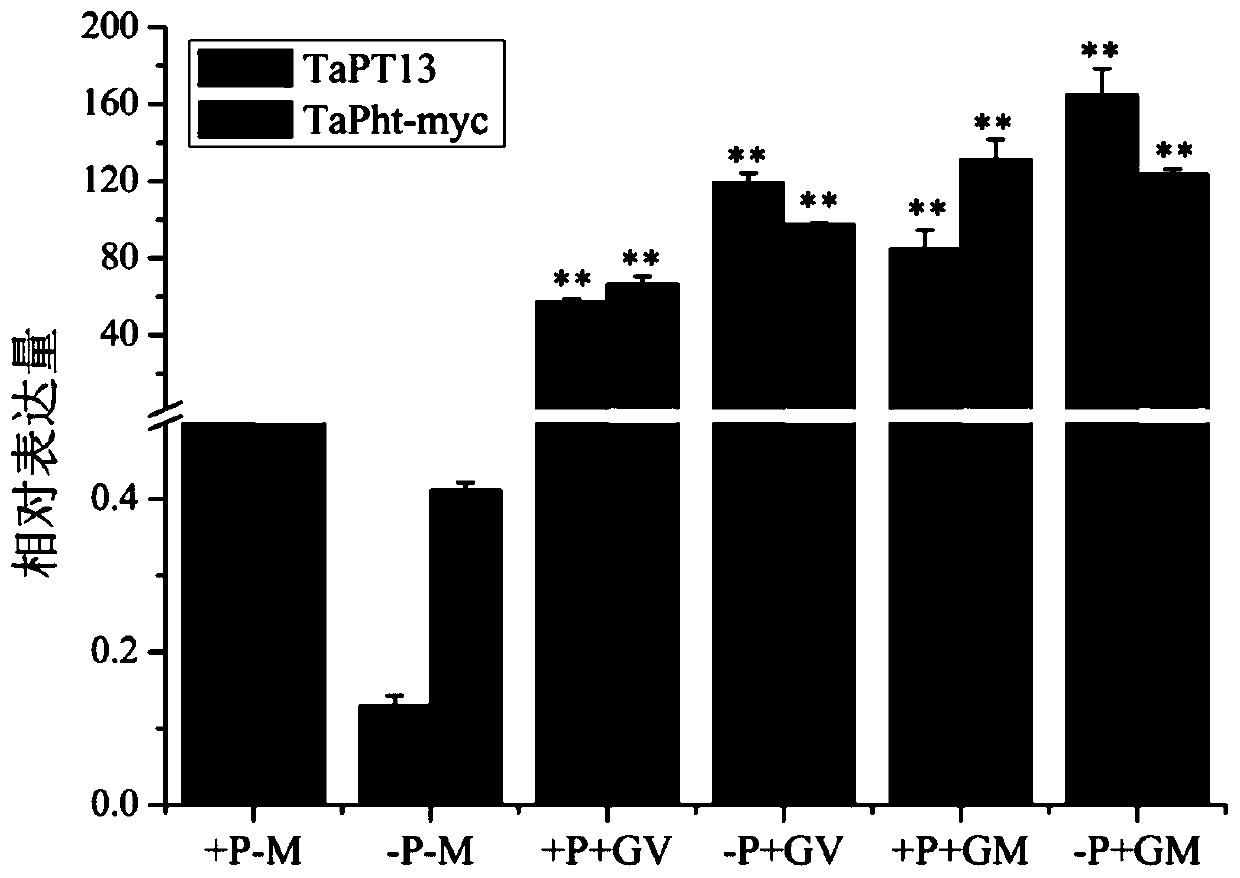
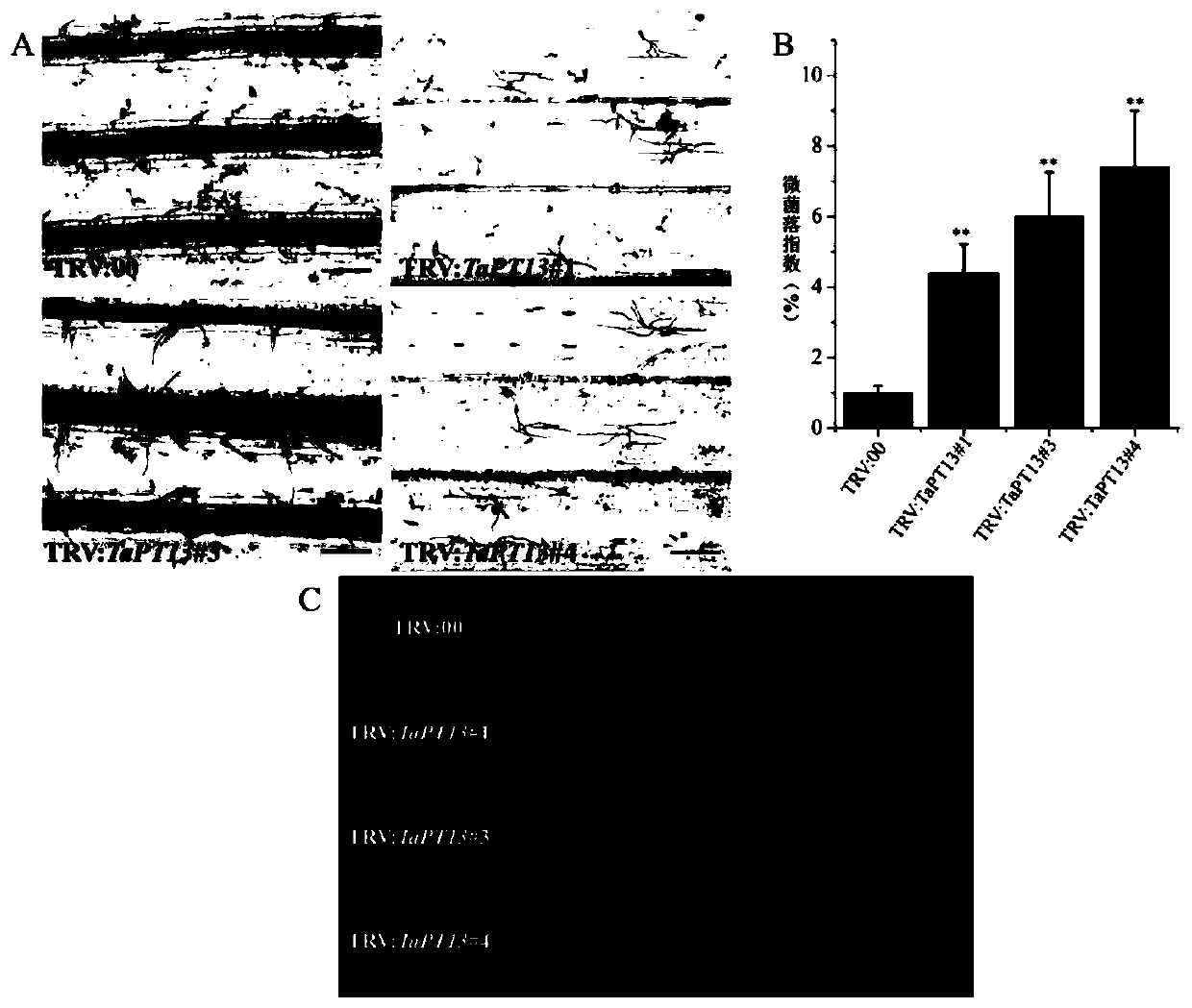
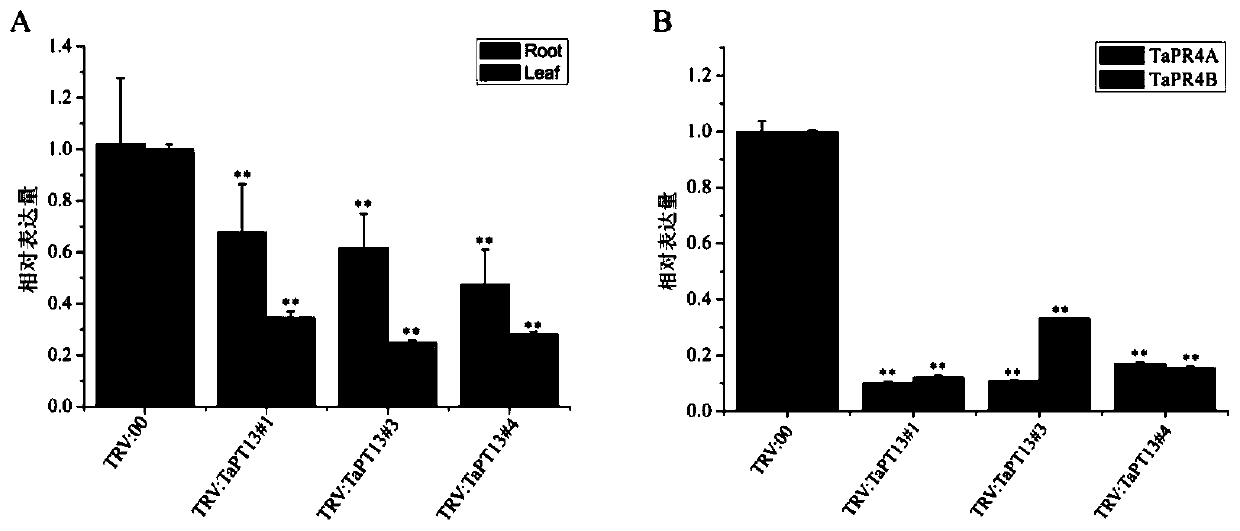
Application of gene TaPT13 in improving resistance of plants to powdery mildew
ActiveCN111424049AEffective absorptionImprove disease resistanceClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural biology, and particularly relates to an application of a gene TaPT13 in improving resistance of plants to powdery mildew. The specific phosphorus transporter gene TaPT13 of arbuscular mycorrhiza can be used for improving disease resistance of plants, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene TaPT13 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. According to the invention, the TaPT13 gene is determined to be a specific phosphate transporter gene of arbuscular mycorrhiza. After plants are inoculated with powdery mildew, the expression amount of the TaPT13 gene is obviously improved; and after the TaPT13 gene is silenced in the plants, susceptibility of the plants is increased, and the expression amount of a disease-resistant marker gene is reduced. Therefore, the TaPT13 gene can be used for improving resistance of wheat to powdery mildew, and has wide application space in plant breeding and cultivation.
Owner:HENAN INST OF SCI & TECH
Expression of a phosphate transporter for improving plant yield
InactiveCN110573623AMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyPhosphate Transporters
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Expression of a phosphate transporter for improving plant yield
InactiveUS20190367937A1Influence plant yieldIncrease nodulationClimate change adaptationStable introduction of DNAPhosphate TransportersTranslocator protein
The invention relates to a method of increasing yield in plants comprising increasing the expression of a nucleic acid encoding a phosphate transporter (PT7) polypeptide. The invention also relates to methods of making such plants and genetically altered plants that display an increased yield.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A phosphorous deficiency responsive phosphate transporter tapht1.6 and its coding gene and application
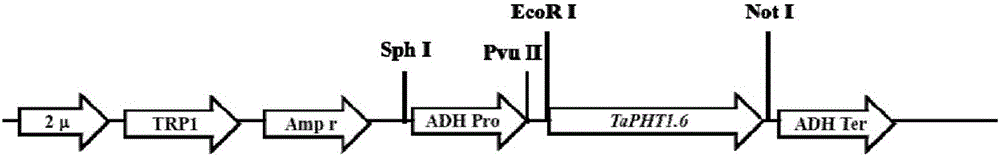
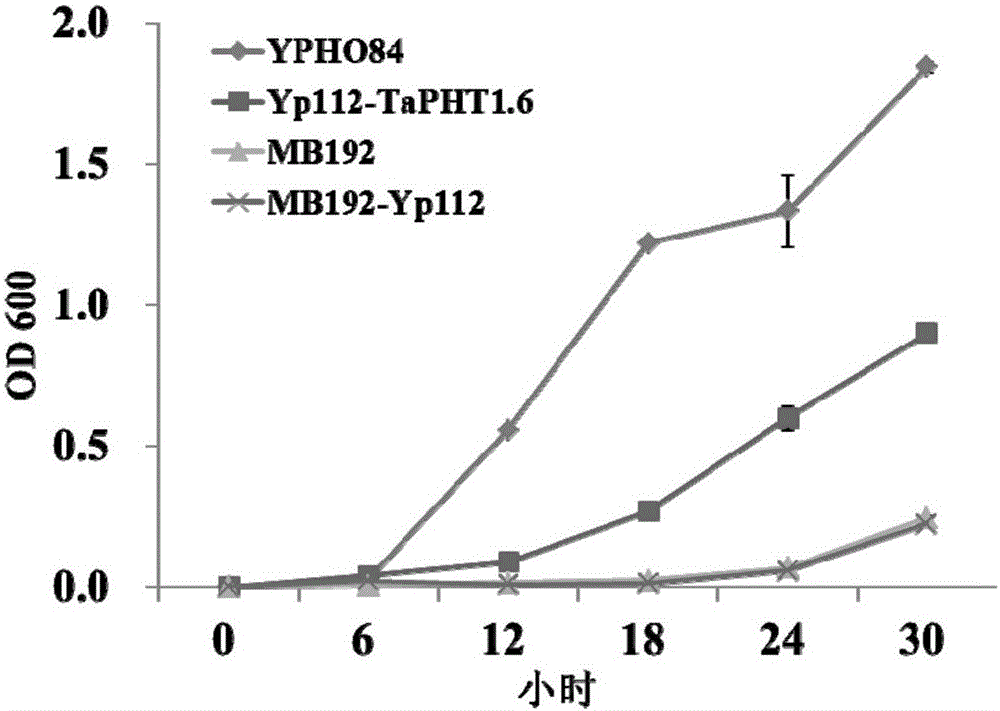
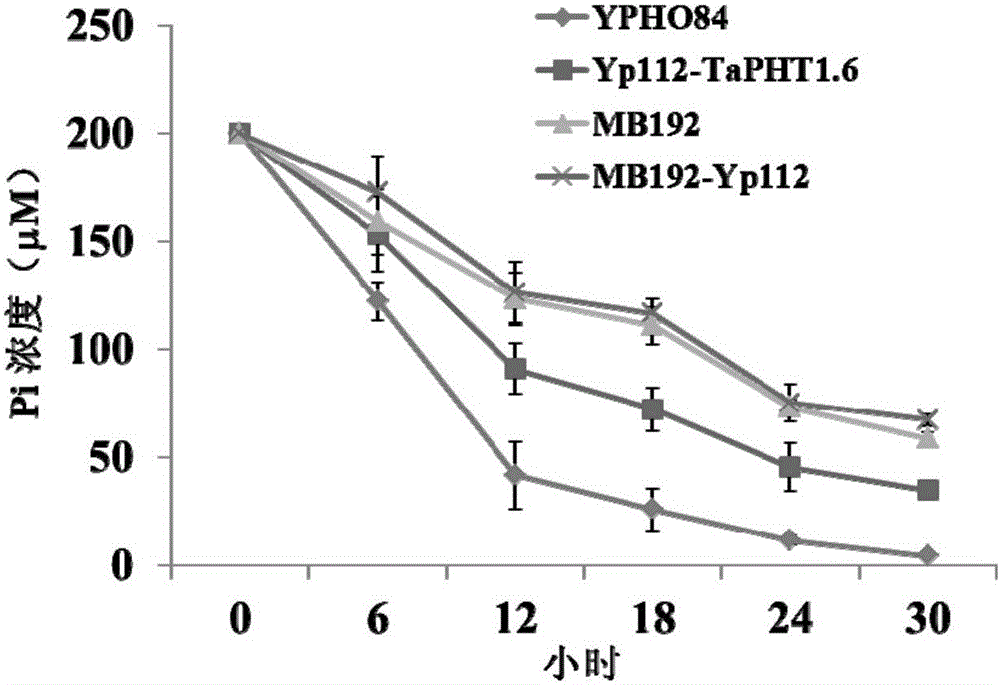
ActiveCN103864909BIncrease phosphorus uptake capacityPromote absorptionFungiPlant peptidesNutritional statusPhosphate Transporters
The invention discloses a phosphate radical transport protein TaPHT1.6 with phosphorus deficiency response as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is (a) or (b) as follows: (a), protein consisting of amino acid sequences as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and (b), protein obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2, having the same function as the protein a and derived from the sequence 2. Experiments prove that absorption of yeast to phosphor is increased and phosphor nutritional status of the protein is improved by inducing a coding gene of the protein into a yeast phosphor absorption mutant, so that growth velocity of the protein is obviously increased.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
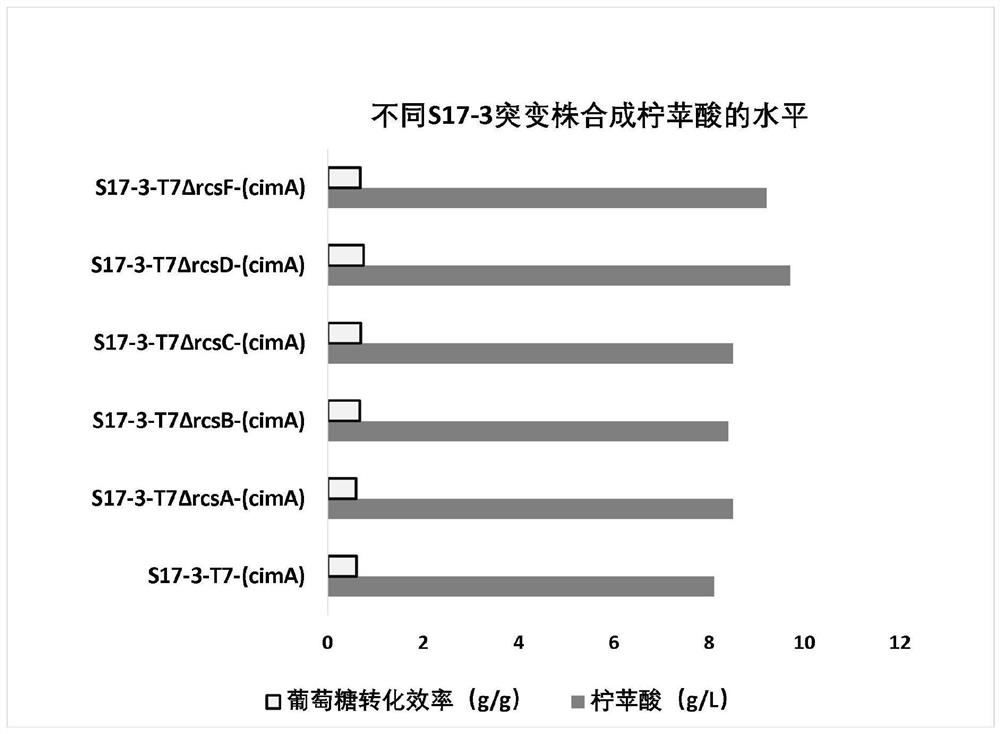
Modified Escherichia coli engineering bacterium and method for producing citramalic acid by using modified Escherichia coli engineering bacterium
ActiveCN114806987AHigh glucose conversion efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliEnterobacter species
The invention discloses a modified Escherichia coli engineering bacterium and a method for producing citramalic acid by using the modified Escherichia coli engineering bacterium. According to the method, Escherichia coli S17-3 is taken as an original strain, and a T7 RNA polymerase gene for identifying a T7 promoter is inserted into a genome of the original strain, so that the modified escherichia coli engineering strain is obtained. The modified escherichia coli engineering bacteria further highly express citramalic acid synthase genes and one or more functional proteins of an inactivation auxiliary response factor RcsA, a response regulation factor RcsB, transmembrane sensing kinase RcsC, phosphate transporter RcsD and outer membrane lipoprotein RcsF. The invention provides novel industrial escherichia coli and a fermentation culture method, the strain is easy to culture, citramalic acid can be efficiently biosynthesized by using a cheap carbon source, and the production efficiency is higher than that of the existing biosynthesis method.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Dihydropyridazine‑3,5‑dione derivatives
ActiveCN105073715BExcellent NaPi-IIb inhibitionExcellent PiT-1 inhibitionOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderSodium dependentSecondary hyperparathyroidism
The present invention provides a medicine, a pharmaceutical composition and a sodium-dependent phosphorus transporter inhibitor containing a dihydropyridazine-3,5-dione derivative or the salt or a solvate thereof, and the compound as an active ingredient , hyperphosphatemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, prophylactic and / or therapeutic agents for chronic renal failure, and methods of prevention and / or treatment.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Isolated polynucleotide encoding a novel phosphate transporter in plants and a method of modulating phosphate uptake in plants
InactiveUS20030207283A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePhosphate Transporters
An isolated polynucleotide encoding a novel plant phosphate transporter and, more particularly, to an essential phosphate transporter which, when inactivated, is associated with phosphate deficiency syndrome in plants, and to methods for using same to modulate, i.e., increase or decrease, phosphate uptake in plants.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Root-specific phosphate transporter promoters
InactiveUS20090113571A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPhosphate TransportersTransgene
The current invention provides plant promoter sequences. Compositions comprising the promoter sequence are described, as are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the promoters by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com