Modified Escherichia coli engineering bacterium and method for producing citramalic acid by using modified Escherichia coli engineering bacterium
A technology of Escherichia coli and engineering bacteria, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problem of low conversion rate of citric acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Escherichia coli engineering bacteria inserted with T7 RNA polymerase gene
[0036] The lactate dehydrogenase gene locus of Escherichia coli S17-3 was replaced and inserted into the T7 RNA polymerase gene by gene recombination, and then the kanamycin resistance gene as a selection marker was eliminated to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli Helicobacter sp. Escherichia coli S17-3-T7. The specific construction method includes the following steps:
[0037]The first step is to amplify the upstream and downstream long homology arm sequences, resistance fragments and T7 RNA polymerase fragments of the lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA). Homologous primers were designed to amplify the 300bp upstream and downstream DNA sequences of the Escherichia coli S17-3 ldhA gene by PCR respectively, and the pKD4 plasmid (commercial product) was used as a template for PCR amplification to obtain FRT sites at both ends. The gene fragment of kanamycin resistance is carried in th...
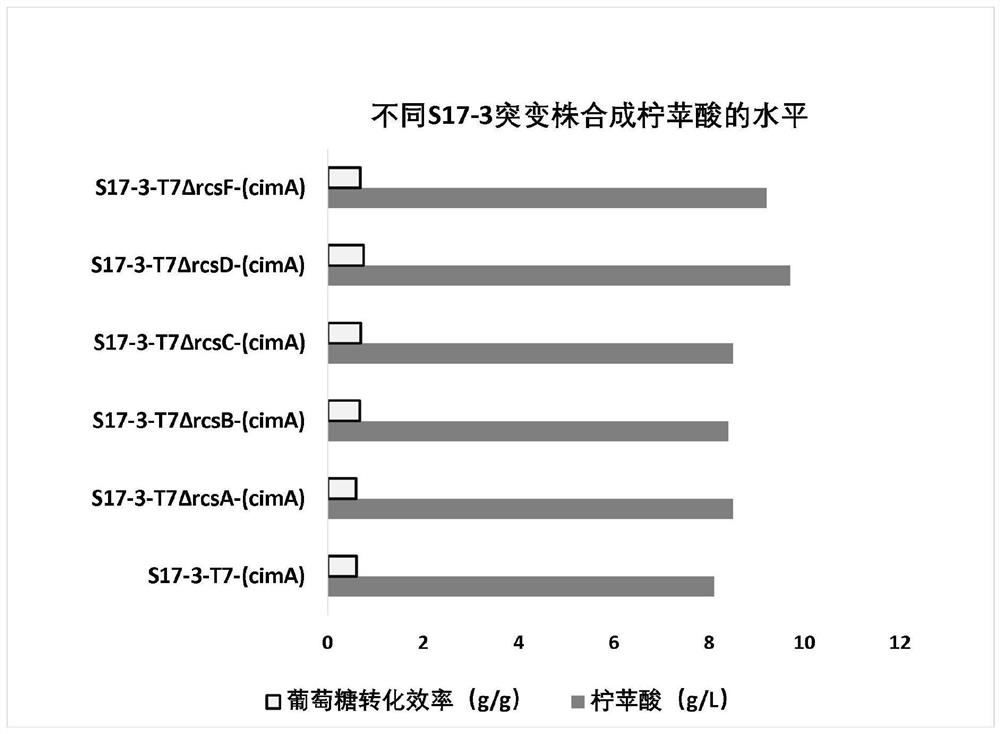
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Loss of function of the co-response factor RcsA
[0042] Using the method of gene recombination to replace and insert the resistance gene fragment at the auxiliary response factor gene locus of Escherichia coli S17-3-T7, and then eliminate the kanamycin resistance gene as a selection marker to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli Herba Escherichia coli S17-3-T7ΔrcsA, the construction process is as follows:
[0043] First, the upstream and downstream long homology arm sequences and the resistance gene fragments of the auxiliary response factor gene (rcsA) are amplified. The DNA sequences of 300bp upstream and downstream of the rcsA gene of Escherichia coli S17-3-T7 were amplified by PCR respectively. Then, PCR amplification was carried out using the pKD4 plasmid as a template to obtain a gene fragment with kanamycin resistance in the middle of the FRT site at both ends. Then use fusion PCR method to connect the above three fragments to form a recombinant gene ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Loss of function of the co-regulatory factor RcsB
[0045] Using the method of gene recombination to replace and insert the resistance gene fragment at the auxiliary response factor gene locus of Escherichia coli S17-3-T7, and then eliminate the kanamycin resistance gene as a selection marker to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli Helicobacter sp. Escherichia coli S17-3-T7ΔrcsB, the construction process is as follows:
[0046] First, the upstream and downstream long homology arm sequences and resistance gene fragments of the auxiliary response regulatory gene (rcsB) were amplified. The DNA sequences of 300bp upstream and downstream of the rcsB gene of Escherichia coli S17-3-T7 were amplified by PCR respectively. Then, PCR amplification was carried out using the pKD4 plasmid as a template to obtain a fragment containing the FRT site at both ends with a kanamycin resistance gene in the middle. Then use fusion PCR method to connect the above three fragments to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com